NEC UPD9611GT Datasheet

PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET
MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
µ
PD9611
FOUR-CHANNEL PCM CODEC
The µPD9611 incorporates 4-channel A-law/µ-law PCM CODECs compliant with ITU-T Recommendation G.711/
G.714 and is suitable for applications such as PBX analog subscriber line circuits.
Its gain setting circuit allows transmit/receive gain to be set for 4 channels independently by externally inputting
digital signals.
FEATURES
Single-chip CMOS monolithic LSI
•
ITU-T Recommendation G.711/G.714 compliant
•
Four-channel PCM CODECs integrated on a single chip
•
Compatible with A-law and µ-law
•
Digital gain setting for each channel
•
• Transmit : +7.5 to –8.0 dB (0.5 dB step)
• Receive : 0 to –15.5 dB (0.5 dB step)
Data transfer system: Transmit/receive synchronization
•
Data rate: 2048 kHz
•
+5 V single power supply
•
Power down function for each channel
•
Low power consumption
•
ORDERING INFORMATION
Part Number Package
µ
PD9611GT 48-pin shrink SOP (375 mil)
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Document No. S11018EJ2V0DS00 (2nd edition)
Date Published October 1996 P
Printed in Japan
©
1996
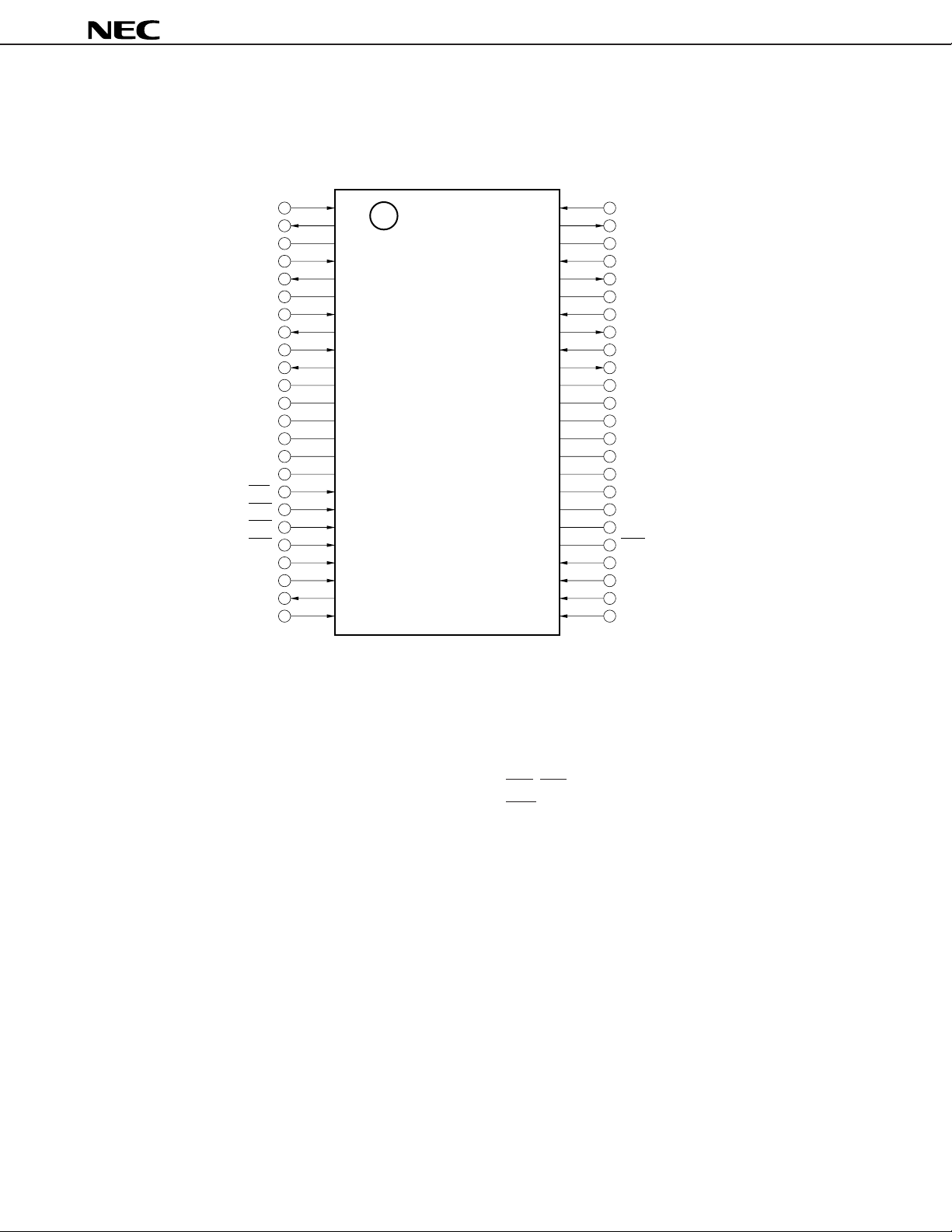
PIN CONFIGURATION (Top View)
48-pin shrink SOP (375 mil)
µ
PD9611
ACOM
ACOM
ACOM
ACOM
A
OUT
A
NC
AIN2
A
OUT
NC
OUT
OUT
AV
DD
AV
DD
AV
DD
AV
DD
DV
NC
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
FSC
DCLK
IN
1
1
2
IN
1
1
IN
2
2
1
2
3
4
DD
D
X
D
R
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
µ
PD9611GT
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
AIN4
OUT
4
A
NC
IN
3
A
A
OUT
3
NC
ACOM
IN
ACOM
OUT
ACOM
IN
ACOM
OUT
AGND1
AGND2
AGND3
AGND4
SUBGND
DGND
NC
NC
NC
RST
LAW
SP
DATA
SP
SYNC
SP
CLK
3
3
4
4
IN1-ACOMIN4 : Analog common voltage in
ACOM
ACOMOUT1-ACOMOUT4: Analog common voltage out
AGND1-AGND4 : Analog ground
IN1-AIN4 : Analog signal in
A
AOUT1-AOUT4 : Analog signal out
DD1-AVDD4 : Analog power supply
AV
DCLK : Data clock in
DGND : Digital ground
R : Receive PCM data in
D
DVDD : Digital power supply
D
X : Transmit PCM data out
FSC : Frame synchronous clock in
LAW : A-law/µ-law control in
NC : No connection
PD1-PD4 : Power down control
RST : Reset in
CLK : Serial port data clock in
SP
SPDATA : Serial port data in
SPSYNC : Serial port synchronous clock in
SUBGND : Sub ground
2
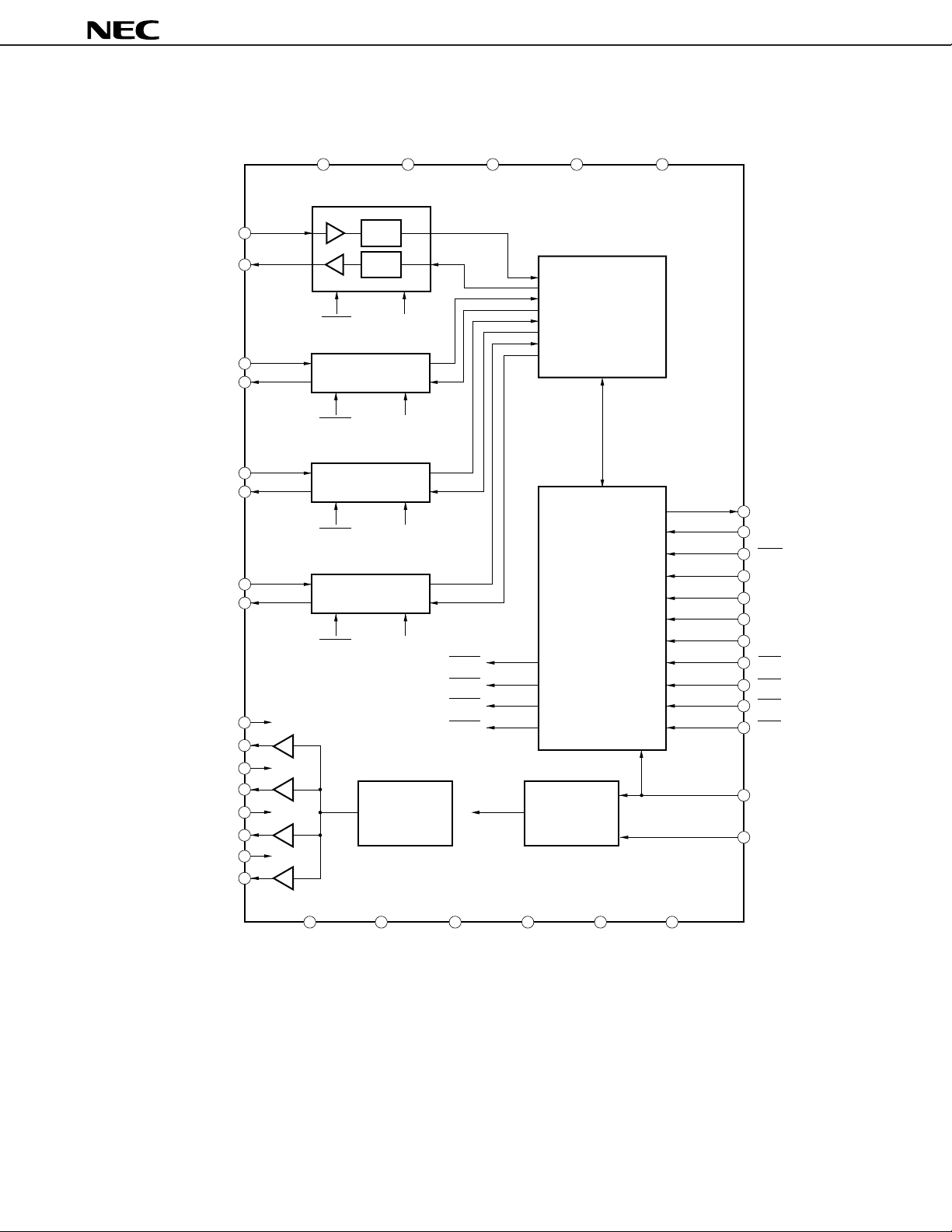
BLOCK DIAGRAM
µ
PD9611
A
A
A
A
ACOMIN1
ACOM
ACOM
ACOM
ACOM
ACOM
ACOM
ACOM
AIN1
OUT
IN
A
OUT
IN
A
OUT
IN
A
OUT
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
AVDD1AV
DD
2AV
DD
3AV
DD
4DV
DD
CH1
A/D
1
D/A
DSP
APD1
2
ACOM
CH2
IN
1
Channel FiIter
2
IN
APD2
3
ACOM
CH3
2
3
D
X
D
ACOMIN3APD3
R
RST
SYNC
4
4
CH4
I/O
Linear ↔ A,
µ
DGS
ACOMIN4APD4
MUX, DEMUX
APD1
APD2
APD3
APD4
SP
SP
SP
LAW
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
CLK
DATA
1
2
2
3
Voltage
Reference
Clock
Generator
3
FSC
DCLK
4
4
AGND1
AGND2 AGND3 AGND4 DGND SUBGND
3
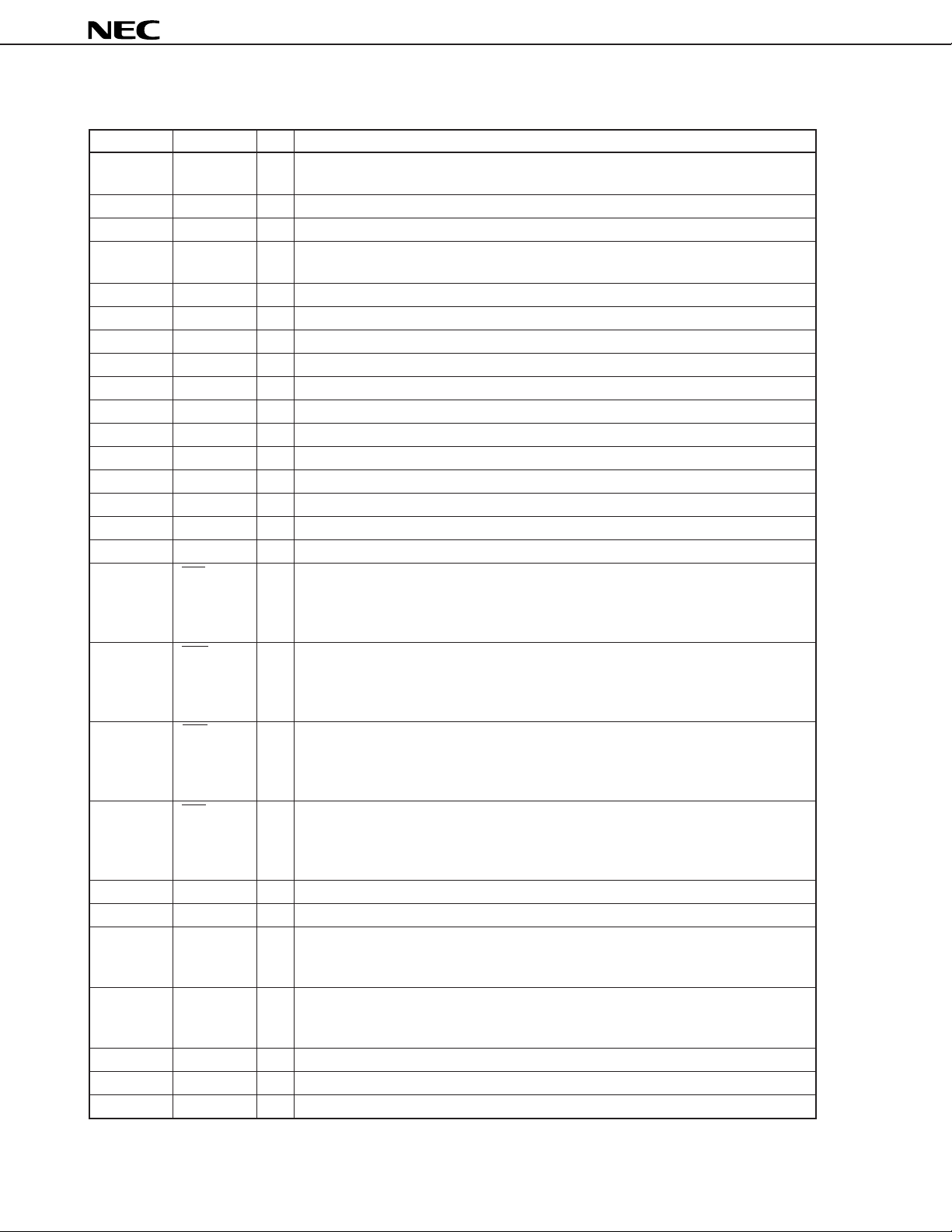
1. PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin No. Symbol I/O Name and Function
1AIN1 I Transmit analog input pin for channel 1
When not used, connect to ACOMOUT1 pin.
2AOUT1 O Receive analog output pin for channel 1
3 NC – Leave this pin open.
4AIN2 I Receive analog input pin for channel 2
When not used, connect to ACOMOUT1 pin.
5AOUT2 O Transmit analog output pin for channel 2
6 NC – Leave this pin open.
7 ACOMIN1 I Signal reference voltage input for channel 1
8 ACOMOUT1 O Signal reference voltage output for channel 1
9 ACOMIN2 I Signal reference voltage input for channel 2
10 ACOMOUT2 O Signal reference voltage output for channel 2
11 AVDD1 – Analog power supply pin for channel 1 +5 ± 0.25 V
12 AVDD2 – Analog power supply pin for channel 2 +5 ± 0.25 V
13 AVDD3 – Analog power supply pin for channel 3 +5 ± 0.25 V
14 AVDD4 – Analog power supply pin for channel 4 +5 ± 0.25 V
15 DVDD – Digital power supply pin +5 ± 0.25 V
16 NC – Leave this pin open.
17 PD1 I Power-down control input pin for channel 1
Channel 1 enters power-down mode when this signal is low level.
The output of DX pin for channel 1 becomes high-impedance and AOUT1 becomes
signal reference voltage in the power-down mode.
18 PD2 I Power-down control input pin for channel 2
Channel 2 enters power-down mode when this signal is low level.
The output of DX pin for channel 2 becomes high-impedance and AOUT2 becomes
signal reference voltage in the power-down mode.
19 PD3 I Power-down control input pin for channel 3
Channel 3 enters power-down mode when this signal is low level.
The output of DX pin for channel 3 becomes high-impedance and AOUT3 becomes
signal reference voltage in the power-down mode.
20 PD4 I Power-down control input pin for channel 4
Channel 4 enters power-down mode when this signal is low level.
The output of DX pin for channel 4 becomes high-impedance and AOUT4 becomes
signal reference voltage in the power-down mode.
21 FSC I Frame synchronous clock input pin (8 kHz)
22 DCLK I Data clock input pin (2048 kHz)
23 DX O Transmit PCM data output pin
This pin outputs PCM data for channel 1 to 4 in synchronization with rising edges
of DCLK after rising edges of FSC. It becomes high-impedance for other timings.
24 DR I Receive PCM data input pin
This pin inputs PCM data for channel 1 to 4 in synchronization with falling edges of
DCLK after rising edges of FSC.
25 SPCLK I Setting data clock input pin
26 SPSYNC I Setting synchronous clock input pin
27 SPDATA I Setting data input pin
µ
PD9611
4
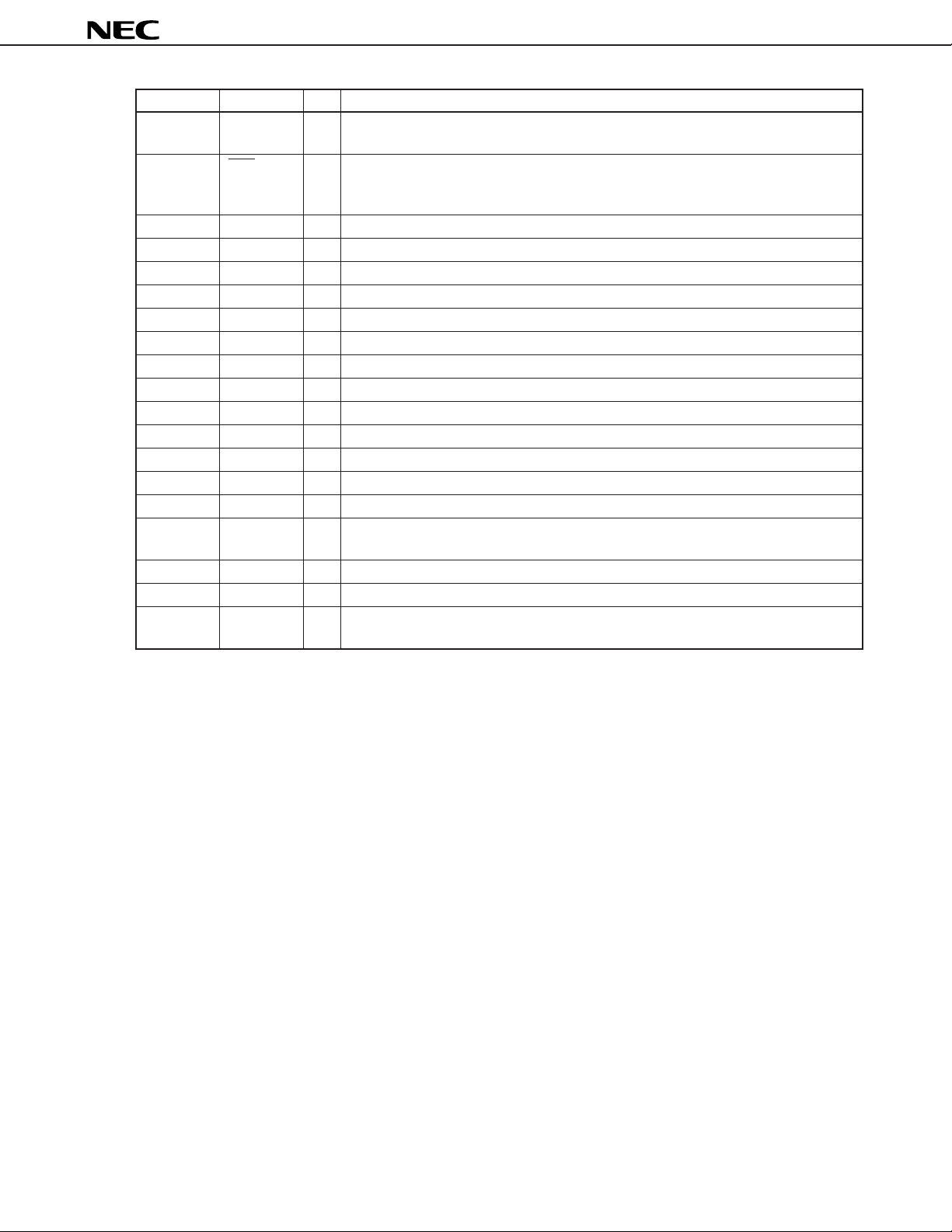
Pin No. Symbol I/O Name and Function
28 LAW I A-law/µ-law select pin in common to four channels
L: A-law, H: µ-law
29 RST – Reset input, power-on reset pin
H: normal operation
L: internal registers are in the default status.
30-32 NC – Leave this pin open.
33 DGND – Digital ground pin
34 SUBGND – Substrate ground pin
35 AGND4 – Analog ground pin for channel 4
36 AGND3 – Analog ground pin for channel 3
37 AGND2 – Analog ground pin for channel 2
38 AGND1 – Analog ground pin for channel 1
39 ACOMOUT4 O Signal reference voltage output for channel 4
40 ACOMIN4 I Signal reference voltage input for channel 4
41 ACOMOUT3 O Signal reference voltage output for channel 3
42 ACOMIN3 I Signal reference voltage input for channel 3
43 NC – Leave this pin open.
44 AOUT3 O Receive analog output pin for channel 3
45 AIN 3 I Transmit analog input pin for channel 3
When not used, connect to ACOMOUT1 pin.
46 NC – Leave this pin open.
47 AOUT4 O Receive analog output pin for channel 4
48 AIN 4 I Transmit analog input pin for channel 4
When not used, connect to ACOMOUT1 pin.
µ
PD9611
5
2. CAUTIONS ON USE
(1) Absolute maximum ratings
Application of voltage or current in excess of the absolute maximum ratings to the µPD9611 may result
in damage due to latch up, etc. Be especially cautions about power supply noise, etc.
(2) Wiring pattern
µ
The design of the ground pattern is extremely important for operating the
Connect the analog ground pins (AGND1 to AGND4), digital ground pin (DGND) and substrate ground
pin (SUBGND) close to the IC pins, and connect to a wide analog ground line on the board.
(3) Addition of bypass capacitors for power supply pins
µ
Because the
PD9611 uses many internal high-frequency operational amplifiers, high power supply
impedance can cause instability (such as oscillation) in these internal operational amplifiers. To
suppress such instability and eliminate power supply noise, connect all power supply pins (AV
AVDD4, DVDD) close to the IC pins, and put bypass capacitors (CVDD = approximately 0.1 µF) having
superior high-frequency characteristics very close to the pins.
PD9611 with high precision.
µ
PD9611
DD1 to
(4) Addition of bypass capacitors for ACOM pins
µ
PD9611 incorporates references voltages for signal sources. Superposing of noise on these
The
reference voltages may have adverse effects on transmission characteristics, etc. Therefore, connect
the ACOM
OUT pin and ACOMIN pin close to the IC pins, and put bypass capacitors (CACOM = approximately
0.1 µF) having superior high-frequency characteristics very close to the pins.
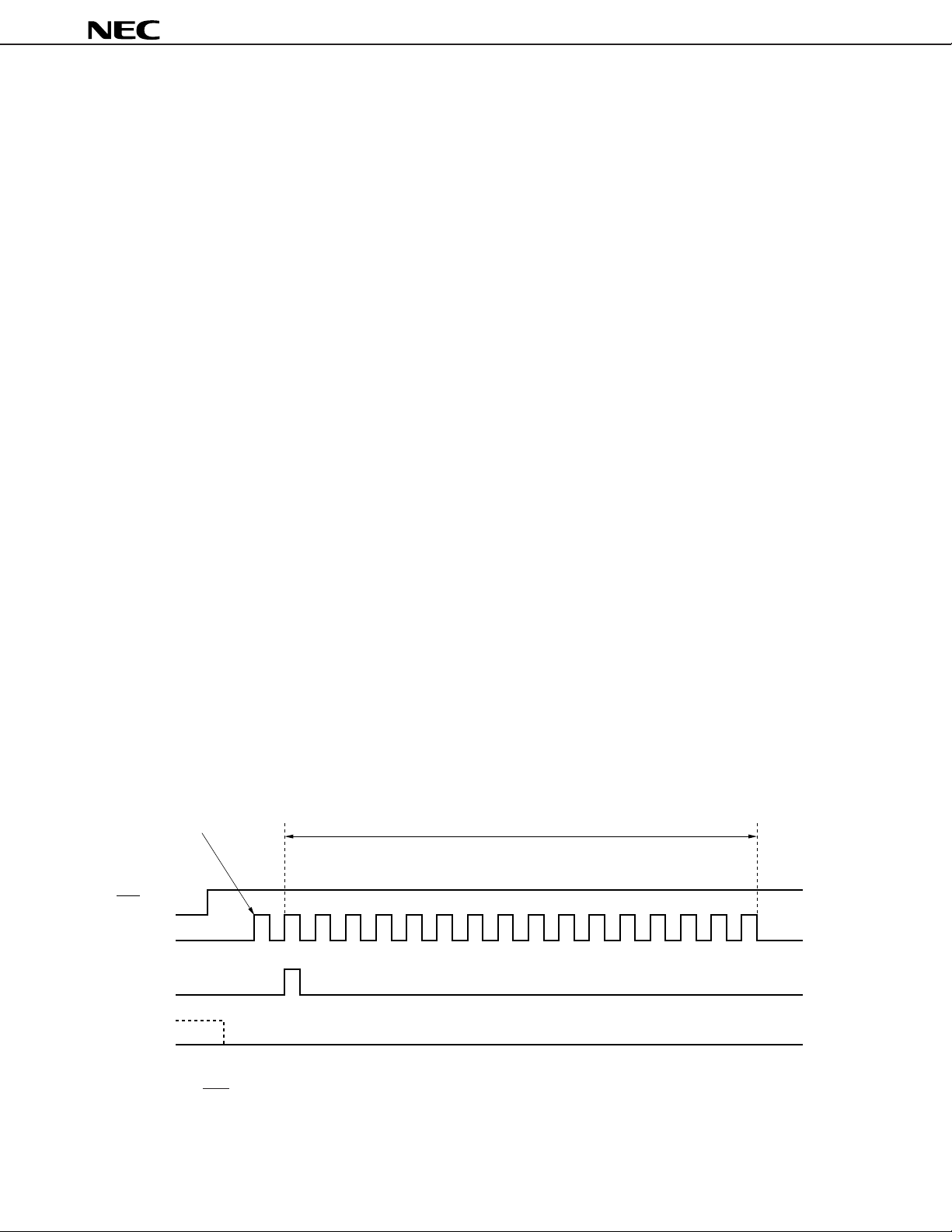
(5) Control or SP
DATA pin on reset
When inputting the setting data from the SPDATA pin after the µPD9611 is reset, first input the following
patterns to reset to 0 the couter used to fetch data from the SPDATA pin.
SP
SP
1 clocks or more
RST
CLK
SYNC
16 clocks or more
SP
DATA
After ther RST pin has been set to the high level, input 1 clock or more to the SPCLK pin, set the SPSYNC
pin to the high level and input 16 clocks more to the SPCLK pin.
During this operation, the SPDATA pin is held at the low level. Afterwards, input the setting data.
6

3. GENERAL OPERATION
(1) PCM data transfer
In the transmit section, if FSC pin is set to the high level in synchronization with the rising edge (↑) of
the data clock applied to the DCLK pin, the D
1 is output. The following data of 7 bits is clocked out in synchronization with the rising edge (↑) of each
data clock. Sign bit data (MSB) of channel 2 is output in synchronization with the rising edge (↑) of the
9th data clock. In the same manner, each data up to channel 4 is output and the rising edge (↑) of the
33rd data clock then sets the D
Similarly, in the receive section, if the FSC pin is set to the high level in synchronization with the rising
edge (↑) of the data clock applied to the DCLK pin, data of D
the data clock and consecutively clocked in.
(2) Power down control
µ
PD9611 has the following two methods for power down control and is able to control power-down
The
independently for each channel.
X pin becomes active and sign bit data (MSB) of channel
X pin to high-impedance state.
µ
PD9611
R pin is latched by the falling edges (↓) of
• Sets pins PD1 to PD4 to high or low level.
• Inputs 8-bit setting data from SP
DATA pin (see (5) Control of SPDATA pin).
Internal data is the logical sum of PD1 to PD4 pin state and 8-bit setting data input.
If the internal data is 0, the channel enters the power-down state. If the internal data is 1, the channel
enters the power-up state. In the power down state, PCM data in the channel goes to high-impedance
state and analog output becomes the signal reference voltage level.
8-Bit Setting Data PD1 Pin Internal Data
(Channel 1)
000
101
011
111
Remarks 1. 0: Power down, 1: Power up
2. The settings are the same for channel 2 to channel 4.
7

(3) A-law/µ-law control
µ
PD9611 has the following two methods for A-law/µ-law control.
The
• Sets LAW pin to high or low level.
• Inputs 8-bit setting data from SP
Internal data is the logical sum of LAW pin state and 8-bit setting data input.
If the internal data is 0, the
µ
-law mode.
8-Bit Setting Data LAW Pin Internal Data
000
101
011
111
Remark 0: A-law, 1: µ-law
µ
DATA pin (see (5) Control of SPDATA pin).
PD9611 enters A-law mode. If the internal data is 1, the µPD9611 enters
µ
PD9611
(4) Gain Setting control for transmit/receive
µ
PD9611 can control gain settings independently for the transmit/receive by inputting 8-bit setting
The
data (see (5) Control of SPDATA pin) from the SPDATA pin for four channels. Gain can be set from +7.5
to –8.0 dB for the transmit and +0.0 dB t o –15.5 dB for the receive in 0.5 dB steps.
8-bit setting data input from SP
of transmit/receive and gain setting in the second 8 bits.
DATA pin specifies the channel set in the first 8 bits, and performs selection
8
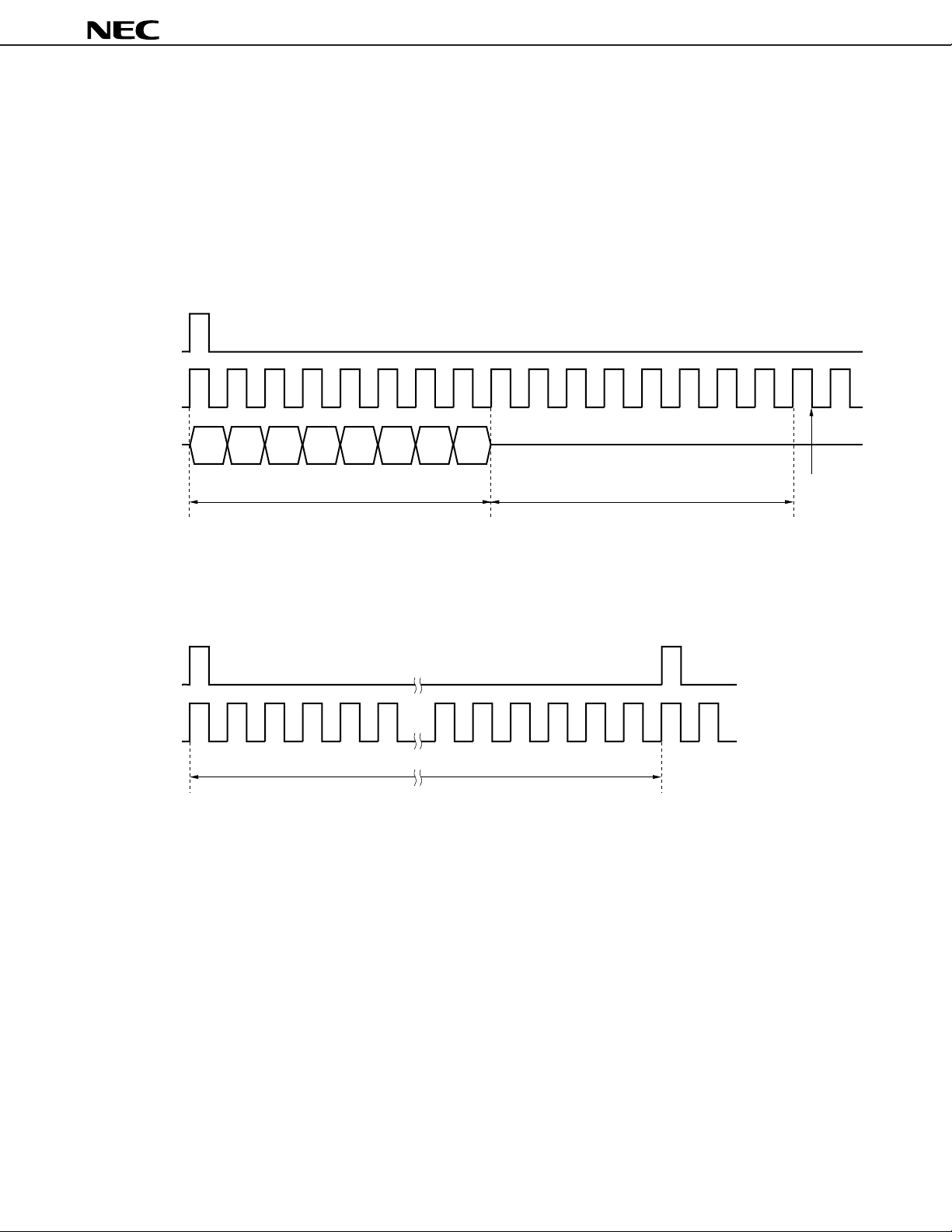
(5) Control of SPDATA pin
SYNC pin is set to the high level in synchronization with the rising edge (↑) of the data clock applied
If SP
to the SPCLK pin, data of the SPDATA pin is latched by the falling edge (↓) of the data clock and
consecutively fetched in.
After the 8-bit data has been fetched, the setting operation is performed according to the data.
This setting operation is performed during the 8 clocks after fetching the data and the next data is valid
at the 17th clock.
Therefore, when setting 1 word (8 bits) of data, input 17 clocks or more to the SP
SP
SYNC
CLK pin.
µ
PD9611
SP
SP
SP
123456789101112131415161718
CLK
DATA
Ensure that 17 clocks or more are input to the SP
SYNC.
17 clocks or more
SP
SYNC
CLK
the next SP
Don’t care
Setting operationData fetch
CLK pin between the rising of SPSYNC and the rising of
Setting
completed
(The next
data is valid.)
9
 Loading...
Loading...