Page 1

DATA SHEET
MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
8-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCONTROLLERS
The µPD178004A, 178006A, 178016A and 178018A are 8-bit single-chip CMOS microcontrollers that incorporate
hardware for digital tuning systems.
The CPU uses the 78K/0 architecture, which makes it easy to implement high-speed access to internal memory
and control of peripheral hardware. Also, the instructions used are the high-speed 78K/0 instructions, suitable for
system control.
The rich assortment of peripheral hardware includes an input/output port, 8-bit timer, A/D converter, serial interface,
power-ON clear circuits, as well as a pre-scaler for digital tuning, a PLL frequency synthesizer and a frequency counter.
The µPD178P018A, one-time PROM or EPROM versions which can be operated in the same supply voltage range
as for the mask ROM versions, and various development tools, are also available.
For more information on functions, refer to the following User’s Manuals. Be sure to read them when
designing.
µ
PD178018A Subseries User’s Manual: to be prepared
78K/0 Series User’s Manual Instruction: U12326E
FEATURES
• Internal high-capacity ROM and RAM
Items Program Memory Data Memory
Product Name ROM Internal High-Speed RAM Buffer RAM Internal Expanded RAM
µ
PD178004A 32 Kbytes 1 024 bytes 32 bytes Not provided
µ
PD178006A 48 Kbytes
µ
PD178016A 2 048 bytes
µ
PD178018A 60 Kbytes
• Instruction Cycle: 0.44 µs (4.5-MHz crystal oscillator used)
• Large array of on-chip peripheral hardware
General-purpose input/output port, A/D converter, serial interface, timer, frequency counter, power-ON clear
circuits.
• On-chip hardware for a PLL frequency synthesizer.
Dual modulus pre-scaler, programmable divider, phase comparator, charge pump.
• Vector interrupt sources: 17
• Supply Voltage: VDD = 4.5 to 5.5 V (during PLL operation)
VDD = 3.5 to 5.5 V (during CPU operation, when the system clock is fX/2 or lower)
VDD = 4.5 to 5.5 V (during CPU operation, when the system clock is fX)
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Document No. U12641EJ1V0DS00 (1st Edition)
Date Published July 1997 N
Printed in Japan
©
1997
Page 2

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
APPLICATIONS
Car stereo, home stereo systems.
ORDERING INFORMATION
Part Number Package
µ
PD178004AGC-×××-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 mm, 0.65-mm pitch)
µ
PD178006AGC-×××-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 mm, 0.65-mm pitch)
µ
PD178016AGC-×××-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 mm, 0.65-mm pitch)
µ
PD178018AGC-×××-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 mm, 0.65-mm pitch)
Remark ××× denotes the ROM code number. Also, the ROM code number becomes E×× when the I2C bus is used.
µ
PD178018A SUBSERIES AND µPD178003 SUBSERIES EXPANSION
µ
PD178018A Subseries
80 pins PROM : 60 KB RAM : 3 KBPD178P018A
80 pins ROM : 60 KB RAM : 3 KBPD178018A
80 pins ROM : 48 KB RAM : 3 KBPD178016A
80 pins ROM : 48 KB RAM : 1 KBPD178006A
80 pins ROM : 32 KB RAM : 1 KBPD178004A
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
Note
µ
PD178003 Subseries
Note Under development
2
80 pins ROM : 24 KB RAM : 0.5 KBPD178003
80 pins ROM : 16 KB RAM : 0.5 KBPD178002
µ
µ
Note
Note
Page 3

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
OUTLINE OF FUNCTION
Product name
Item
Internal ROM (ROM configuration) 32 Kbytes 48 Kbytes 60 Kbytes
memory (mask ROM) (mask ROM) (mask ROM)
High-speed RAM 1 024 bytes
Buffer RAM 32 bytes
Expansion RAM Not provided 2 048 bytes
General-purpose register 8 bits × 32 registers (8 bits × 8 registers × 4 banks)
Instruction cycle With variable instruction execution time function
Instruction set • 16-bit operation
I/O port Total : 62 pins
A/D converter 8-bit resolution × 6 channels
Serial interface • 3-wire/SBI/2-wire/I2C bus
Timer • Basic timer (timer carry FF (10 Hz)) : 1 channel
Buzzer (BEEP) output 1.5 kHz, 3 kHz, 6 kHz
Vectored Maskable Internal: 8, external: 7
interrupt
Source
Test input Internal: 1
Non-maskable Internal: 1
Software Internal: 1
µ
PD178004A
0.44 µs/0.88 µs/1.78 µs/3.56 µs/7.11 µs/14.22 µs (with 4.5-MHz crystal resonator)
• Multiplication/division (8 bits × 8 bits, 16 bits ÷ 8 bits)
• Bit manipulation (set, reset, test, Boolean operation)
• BCD adjustment, etc.
CMOS input : 1 pin
CMOS I/O : 54 pins
N-ch open-drain I/O : 4 pins
N-ch open-drain output : 3 pins
• 3-wire serial I/O mode
(with automatic transfer/receive function of up to 32 byte) : 1 channel
• 8-bit timer/event counter : 2 channels
• 8-bit timer (D/A converter: PWM output): 1 channel
• Watchdog timer : 1 channel
µ
PD178006A
Note
µ
PD178016A
mode selectable : 1 channel
µ
PD178018A
(1/2)
Note When using the I2C bus mode (including when this mode is implemented by program without using the
peripheral hardware), consult your local NEC sales representative when you place an order for mask.
3
Page 4

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
(2/2)
Product name
Item
PLL frequency Division mode Two types
synthesizer • Direct division mode (VCOL pin)
Reference frequency 7 types selectable by program (1, 3, 5, 9, 10, 25, 50 kHz)
Charge pump Error out output: 2 (EO0 and EO1 pins
Phase comparator Unlock detectable by program
Frequency counter • Frequency measurement
D/A converter (PWM output) 8-/9-bit resolution × 3 channels (shared by 8-bit timer)
Standby function • HALT mode
Reset • Reset by RESET pin
Power supply voltage • VDD = 4.5 to 5.5 V (with PLL operating)
Package • 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 mm, 0.65-mm pitch)
µ
PD178004A
• Pulse swallow mode (VCOH and VCOL pins)
• AMIFC pin: for 450-kHz count
• FMIFC pin: for 450-kHz/10.7-MHz count
• STOP mode
• Internal reset by watchdog timer
• Reset by power-ON clear circuit (3-value detection)
• Detection of less than 4.5 V
• Detection of less than 3.5 V
• Detection of less than 2.5 V
•VDD = 3.5 to 5.5 V (with CPU operating, CPU clock: fX/2 or less)
•VDD = 4.5 to 5.5 V (with CPU operating, CPU clock: fX)
µ
PD178006A
Note 2
µ
PD178016A
Note 1
)
Note 2
(CPU clock: fX)
(CPU clock: fX/2 or less and on power application)
Note 2
(in STOP mode)
µ
PD178018A
Notes 1. The EO1 pin can be set to high impedance for the µPD178016A and 178018A.
The following shows an application example.
µ
PD178016A
µ
PD178018A
EO0
EO1
VCOH
VCOL
LPF VCO
To Mixer
LPF : Low path filter
VCO : Voltage controlled oscillator
• To lock to a target frequency at high speed
Setting the EO0 and EO1 pins to error out output improves the output current potential and LPF
voltage control potential.
• Normal state
Setting only the EO0 pin to error out output maintains the LPF stable.
2. These voltage values are maximum values. Reset is actually executed at a voltage lower than these
values.
4
Page 5

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)................................................................................................ 6
2. BLOCK DIAGRAM ........................................................................................................................... 8
3. PIN FUNCTION LIST........................................................................................................................ 9
3.1 PORT PINS................................................................................................................................ 9
3.2 PINS OTHER THAN PORT PINS............................................................................................ 10
3.3 INPUT/OUTPUT CIRCUITS AND RECOMMENDED CONNECTION OF UNUSED PINS ..... 11
4. MEMORY SPACE .......................................................................................................................... 14
5. PERIPHERAL HARDWARE FUNCTION FEATURES .................................................................. 15
5.1 PORTS..................................................................................................................................... 15
5.2 CLOCK GENERATOR ............................................................................................................16
5.3 TIMER...................................................................................................................................... 16
5.4 BUZZER OUTPUT CONTROL CIRCUIT ................................................................................ 18
5.5 A/D CONVERTER ................................................................................................................... 19
5.6 SERIAL INTERFACES............................................................................................................ 19
5.7 PLL FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER ........................................................................................ 21
5.8 FREQUENCY COUNTER........................................................................................................ 22
6. INTERRUPT FUNCTIONS AND TEST FUNCTIONS .................................................................... 23
6.1 INTERRUPT FUNCTIONS ...................................................................................................... 23
6.2 TEST FUNCTION .................................................................................................................... 26
7. STANDBY FUNCTION ................................................................................................................... 27
8. RESET FUNCTION ........................................................................................................................ 27
9. INSTRUCTION SET ....................................................................................................................... 28
10. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS .................................................................................................. 30
11. PACKAGE DRAWINGS ................................................................................................................. 46
12. RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS ............................................................................. 47
APPENDIX A. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN µPD178018A AND µPD178018 SUBSERIES ............... 48
APPENDIX B. DEVELOPMENT TOOLS ............................................................................................ 49
APPENDIX C. RELATED DOCUMENTS ........................................................................................... 51
5
Page 6

µ
1. PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
• 80-PIN PLASTIC QFP (14 × 14 mm, 0.65 mm pitch)
µ
PD178004AGC-×××-3B9, 178006AGC-×××-3B9
µ
PD178016AGC-×××-3B9, 178018AGC-×××-3B9
RESET
VDDREGOSCX1X2
GND
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
REGCPU
P06/INTP6
P05/INTP5
P04/INTP4
P03/INTP3
P02/INTP2
P01/INTP1
P00/INTP0
P125
P124
P123
P122
P121
P120
P10/ANI0
P11/ANI1
P12/ANI2
P13/ANI3
P14/ANI4
P15/ANI5
P20/SI1
P21/SO1
P22/SCK1
P23/STB
P24/BUSY
P25/SI0/SB0/SDA0
P26/SO0/SB1/SDA1
P27/SCK0/SCL
P132/PWM0
P133/PWM1
P134/PWM2
P40
P41
P42
80 7978 77 76 75 7473 72 71 70 6968 67 66 65 6463 62 61
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 2223 24 25 26 2728 29 30 31 3233 34 35 36 3738 39 40
P43
P44
DDPORT
V
GNDPORT
P45
P46
P47
FMIFC
AMIFC
DDPLL
V
VCOL
VCOH
EO0
EO1
GNDPLL
IC
P50
P51
P52
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
P53
P37
P36/BEEP
P35
P34/TI2
P33/TI1
P32
P31
P30
P67
P66
P65
P64
P63
P62
P61
P60
P57
P56
P55
P54
Cautions 1. Connect the Internally Connected (IC) pin to GND directly.
2. Connect VDDPORT and VDDPLL pins to VDD.
3. Connect the GNDPORT and GNDPLL pins to GND.
4. Connect each of the REGOSC and REGCPU pins to GND via a 0.1-µF capacitor.
6
Page 7

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
AMIFC : AM Intermediate Frequency Counter Input
AN10 to AN15 : A/D Converter Input
BEEP : Buzzer Output
BUSY : Busy Output
EO0, EO1 : Error Out Output
FMIFC : FM Intermediate Frequency Counter Input
GND : Ground
GNDPLL : PLL Ground
GNDPORT : Port Ground
IC : Internally Connected
INTP0 to INTP6
P00 to P06 : Port 0
P10 to P15 : Port 1
P20 to P27 : Port 2
P30 to P37 : Port 3
P40 to P47 : Port 4
P50 to P57 : Port 5
P60 to P67 : Port 6
P120 to P125 : Port 12
: Interrupt Inputs
P132 to P134 : Port 13
PWM0 to PWM2
REGCPU : Regulator for CPU Power Supply
REGOSC : Regulator for Oscillator Circuit
RESET : Reset Input
SB0, SB1 : Serial Data Bus Input/Output
SCK0, SCK1 : Serial Clock Input/Output
SCL : Serial Clock Input/Output
SDA0, SDA1 : Serial Data Input/Output
SI0, SI1 : Serial Data Input
SO0, SO1 : Serial Data Output
STB : Strobe Output
TI1, TI2 : Timer Clock Input
VCOL, VCOH : Local Oscillator Input
VDD : Power Supply
VDDPLL : PLL Power Supply
VDDPORT : Port Power Supply
X1, X2 : Crystal Oscillator Connection
: PWM Output
7
Page 8

2. BLOCK DIAGRAM
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
TI1/P33
TI2/P34
SI0/SB0/SDA0/P25
SO0/SB1/SDA1/P26
SCK0/SCL/P27
SI1/P20
SO1/P21
SCK1/P22
STB/P23
BUSY/P24
ANI0/P10 to
ANI5/P15
INTP0/P00 to
INTP6/P06
BEEP/P36
8-bit TIMER/
EVENT COUNTER 1
8-bit TIMER/
EVENT COUNTER 2
8-bit TIMER 3
WATCHDOG TIMER
BASIC TIMER
SERIAL
INTERFACE 0
SERIAL
INTERFACE 1
A/D CONVERTER
6
INTERRUPT
7
CONTROL
BUZZER OUTPUT
78K/0
CPU
CORE
RAM
ROM
PORT 0
PORT 1
PORT 2
PORT 3
PORT 4
PORT 5
PORT 6
PORT 12
PORT 13
D/A CONVERTER
(PWM)
FREQUENCY
COUNTER
P00
6
P01 to P06
6
P10 to P15
P20 to P27
8
8
P30 to P37
8
P40 to P47
8
P50 to P57
8
P60 to P67
6
P120 to P125
3
P132 to P134
PWM0/P132 to
3
PWM2/P134
AMIFC
FMIFC
RESET
X1
X2
V
DDPORT
GNDPORT
V
REGOSC
REGCPU
GND
SYSTEM
CONTROL
DD
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
RESET
CPU
PERIPHERAL
V
OSC
VCPU
Remark The internal ROM and RAM capacities depend on the version.
8
PLL
PLL
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
EO0
EO1
VCOL
VCOH
V
DDPLL
GNDPLL
IC
Page 9

3. PIN FUNCTION LIST
3.1 PORT PINS
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Pin Name I/O Function After Reset
P00 Input Port 0. Input only Input INTP0
P01 to P06 I/O
P10 to P15 I/O Port 1. Input ANI0 to ANI5
P20 I/O Port 2. Input SI1
P21
P22
P23 STB
P24 BUSY
P25 SI0/SB0/SDA0
P26
P27 SCK0/SCL
P30 to P32 I/O Port 3. Input —
P33
P34
P35 —
P36 BEEP
P37 —
P40 to P47 I/O Port 4. Input —
P50 to P57 I/O Port 5. Input —
P60 to P63 I/O Port 6. Middle voltage N-ch open drain Input —
P64 to P67 Input/output mode can be LEDs can be driven directly.
P120 to I/O Port 12. Input —
P125 6-bit input/output port.
P132 to Output Port 13. — PWM0 to
P134 3-bit output port. PWM2
7-bit input/output port.
6-bit input/output port.
Input/output mode can be specified bit-wise.
8-bit input/output port.
Input/output mode can be specified bit-wise.
8-bit input/output port.
Input/output mode can be specified bit-wise.
8-bit input/output port.
Input/output mode can be specified in 8-bit units.
Test input flag (KRIF) is set to 1 by falling edge detection.
8-bit input/output port.
Input/output mode can be specified bit-wise.
8-bit input/output port. input/output port.
specified bit-wise.
Input/output mode can be specified bit-wise.
N-ch open-drain output port.
Input/output mode can be specified bit-wise.
Input
Alternate Function
INTP1 to INTP6
SO1
SCK1
SO0/SB1/SDA1
TI1
TI2
9
Page 10

3.2 PINS OTHER THAN PORT PINS
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Pin Name I/O Function After Reset
INTP0 to Input External maskable interrupt inputs with specifiable valid edges (rising Input P00 to P06
INTP6 edge, falling edge, both rising and falling edges).
SI0 Input Serial interface serial data input Input
SI1 P20
SO0 Output Serial interface serial data output Input
SO1 P21
SB0 I/O Serial interface serial data input/output Input P25/SI0/SDA0
SB1
SDA0 P25/SI0/SB0
SDA1 P26/SO0/SB1
SCK0 I/O Serial interface serial clock input/output Input P27/SCL
SCK1 P22
SCL P27/SCK0
STB Output Serial interface automatic transmit/receive strobe output Input P23
BUSY Input Serial interface automatic transmit/receive busy input Input P24
TI1 Input External count clock input to 8-bit timer (TM1) Input P33
TI2 External count clock input to 8-bit timer (TM2) P34
BEEP Output Buzzer output Input P36
ANI0 to ANI5
PWM0 to PWM2
EO0, EO1 Output Error out output from charge pump of the PLL frequency synthesizer — —
VCOL Input Inputs PLL local band frequency (In HF, MF mode) — —
VCOH Input Inputs PLL local band frequency (In VHF mode) — —
AMIFC Input Inputs AM intermediate frequency counter — —
FMIFC Input Inputs FM intermediate frequency counter — —
RESET Input System reset input — —
X1 Input System clock oscillation resonator connection — —
X2 — ——
REGOSC — Oscillation regulator. Connected to GND via a 0.1-µF capacitor. — —
REGCPU — CPU power supply regulator. Connected to GND via a 0.1-µF capacitor. — —
VDD — Positive power supply — —
GND — Ground ——
VDDPORT — Positive power supply for port block — —
GNDPORT — Ground for port block — —
VDDPLL
GNDPLL
IC — Internally connected. Connected to GND or GNDPORT. — —
Input A/D converter analog input Input P10 to P15
Output PWM output — P132 to P134
Note
— Positive power supply for PLL — —
Note
— Ground for PLL — —
Alternate Function
P25/SB0/SDA0
P26/SB1/SDA1
P26/SO0/SDA1
Note Connect a capacitor of approximately 1 000 pF between the VDDPLL pin and GNDPLL pin.
10
Page 11

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
3.3 INPUT/OUTPUT CIRCUITS AND RECOMMENDED CONNECTION OF UNUSED PINS
Table 3-1 shows the input/output circuit types of pins and the recommended conditions for unused pins.
Refer to Figure 3-1 for the configuration of the input/output circuit of each type.
Table 3-1. I/O Circuit Type of Each Circuit
Pin Name I/O Circuit Type I/O Recommended Connections of Unused Pins
P00/INTP0 2 Input Connected to GND or GNDPORT
P01/INTP1 to P06/INTP6 8 I/O Set in general-purpose input port mode by software and
P10/ANI0 to P15/ANI5 11-A
P20/SI1 8
P21/SO1 5
P22/SCK1 8
P23/STB 5
P24/BUSY 8
P25/SI0/SB0/SDA0 10
P26/SO0/SB1/SDA1
P27/SCK0/SCL
P30 to P32 5
P33/TI1, P34/TI2 8
P35 5
P36/BEEP
P37
P40 to P47 5-G
P50 to P57 5
P60 to P63 13-D
P64 to P67 5
P120 to P125
P132/PWM0 to P134/PWM2 19 Output Set to low-level output by software and open
EO0 DTS-EO1 Open
EO1 DTS-EO3
VCOL, VCOH DTS-AMP Input Set to disabled status by software and open
AMIFC, FMIFC
IC — — Connected to GND or GNDPORT directly
Note
individually connected to VDD, VDDPORT, GND, or GNDPORT
via resistor.
Note For the µPD178004A and 178006A, the I/O circuit type is DTS-EO1.
11
Page 12

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Figure 3-1. Pin Input/Output Circuit of List (1/2)
Type 2
Type 5
data
output
disable
Type 8
VDD
IN
Schmitt-Triggered Input with
Hysteresis Characteristics
VDD
P-ch
IN/OUT
N-ch
data
output
disable
Type 10
data
open-drain
output disable
P-ch
IN/OUT
N-ch
VDD
P-ch
IN/OUT
N-ch
input
enable
Type 5-G Type 11-A
VDD
P-ch
IN/OUT
N-ch
data
output
disable
VDD
P-ch
N-ch
IN/OUT
data
output
disable
comparator
input
enable
P-ch
+
_
V
N-ch
REF (Threshold voltage)
Remark All VDD and GND in the above figures are the positive power supply and ground potential of the ports,
and should be read as VDDPORT and GNDPORT, respectively.
12
Page 13

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Figure 3-1. Pin Input/Output Circuit of List (2/2)
Type 13-D Type DTS-EO3
output disable
data
Type 19
N-ch
VDD
RD
Middle-Voltage Input Buffer
N-ch
P-ch
OUT
IN/OUT
Type DTS-AMP
IN
DW
UP
DDPLL
V
P-ch
N-ch
GNDPLL
DDPLL
V
OUT
Type DTS-EO1
DDPLL
V
DW
UP
P-ch
OUT
N-ch
GNDPLL
Remark All VDD and GND in the above figures are the positive power supply and ground potential of the ports,
and should be read as VDDPORT and GNDPORT, respectively.
13
Page 14

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
4. MEMORY SPACE
Figure 4-1 shows the µPD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, and 178018A memory map.
Figure 4-1. Memory Map
FFFFH
Special Function Registers
(SFR) 256 × 8 bits
FF00H
Data Memory
Space
Program Memory
Space
FEFFH
FEE0H
FEDFH
FB00H
FAFFH
FAE0H
FADFH
FAC0H
FABFH
nnnnH + 1
nnnnH
0000H
General-Purpose
Registers
32 × 8 bits
Internal High-Speed
RAM
1 024 × 8 bits
Use Prohibited
Buffer RAM 32 × 8 bits
Use Prohibited
Internal ROM
Note 3
FABFH
F800H
F7FFH
F000H
EFFFH
nnnnH + 1
nnnnH
1000H
0FFFH
0800H
07FFH
0080H
007FH
0040H
003FH
0000H
Use Prohibited
Internal Expanded RAM
2 048 × 8 bits
Use Prohibited
Program Area
CALLF Entry Area
Program Area
CALLT Table Area
Vectored Table Area
Note 2
Note 1
Notes 1. Available only for µPD178016A and 178018A
2. The µPD178018A does not contain this use prohibited area.
3. The internal ROM capacity depends on the version (see the table below).
Corresponding Product Internal ROM Last Address
Name nnnnH
µ
PD178004A 7FFFH
µ
PD178006A, 178016A BFFFH
µ
PD178018A EFFFH
14
Page 15

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
5. PERIPHERAL HARDWARE FUNCTION FEATURES
5.1 PORTS
The following 3 types of I/O ports are available.
• CMOS input (P00) : 1
• CMOS input/output (P01 to P06, port 1 to port 5, P64 to P67, port 12) : 54
• N-channel open-drain input/output (P60 to P63) : 4
• N-ch open drain output (Port 13) : 3
Total : 62
Table 5-1. Port Functions
Name
Port 0 P00
Port 1
Port 3 P30 to P37
Port 4 P40 to P47 Input/output port pins. Input/output specifiable in 8-bit units.
Port 5 P50 to P57
Port 6 P60 to P63
Port 12
Port 13 P132 to P134
Pin Name Function
Dedicated input port pins
P01 to P06
P10 to P15
P20 to P27
P64 to P67
P120 to P125 Input/output port pins. Input/output specifiable bit-wise.
Input/output port pins. Input/output specifiable bit-wise.
Input/output port pins. Input/output specifiable bit-wise.
Input/output port pins. Input/output specifiable bit-wise.Port 2
Input/output port pins. Input/output specifiable bit-wise.
Test flag (KRIF) is set to 1 by falling edge detection.
Input/output port pins. Input/output specifiable bit-wise.
N-channel open-drain input/output port pins. Input/output specifiable bit-wise.
LED direct drive capability.
Input/output port pins. Input/output specifiable bit-wise.
N-ch open drain output port.
15
Page 16

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
5.2 CLOCK GENERATOR
The instruction execution time can be changed as follows.
0.44 µs/0.88 µs/1.78 µs/3.56 µs/7.11 µs/14.22 µs (@ 4.5-MHz crystal oscillator with system clock.)
Figure 5-1. Clock Generator Block Diagram
Prescaler
Clock to the PLL
frequency synthesizer,
basic timer and buzzer
output control circuit.
X1
X2
System
Clock
Oscillator
STOP
fX
Scaler
fX
2
Selector
f
XX
f
XX
2
Prescaler
fXX
fXX
2
3
2
2
fXX
4
2
Selector
Standby
Control
Circuit
To INTP0
Sampling Clock
5.3 TIMER
The µPD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, and 178018A incorporate 5 channels of the timer.
• Basic timer : 1 channel
• 8-bit timer/event counter : 2 channels
• 8-bit timer (D/A converter)
• Watchdog timer : 1 channel
Note Used is shared with the 8/9-bit resolution × 3-channel D/A converter (PWM output).
Note
: 1 channel
Figure 5-2. Basic Timer Block Diagram
Clock to peripheral
hardware other than
the above.
Wait Control
Circuit
CPU Clock
(f
CPU)
16
4.5 MHz INTTMC
Divider
Page 17

xx/2 to fxx/2
f
fx/2
TI1/P33
fxx/2 to fxx/2
fx/2
TI2/P34
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Figure 5-3. 8-Bit Timer/Event Counter Block Diagram
Internal Bus
INTTM1
8-Bit Compare
Register (CR10)
Match
9
11
Selector
8-Bit Timer
Register 1 (TM1)
Selector
Clear
9
11
Selector
Selector
8-Bit Compare
Register (CR20)
Selector
Match
INTTM2
8-Bit Timer
Register 2 (TM2)
Clear
4.5 MHz
Clock
Generation
Block
f
PWM
Internal Bus
Figure 5-4. 8-Bit Timer (D/A Converter) Block Diagram
Internal Bus
INTPWM
PWM Data Register 2
(PWMR2)
Comparator Comparator Comparator
Clear
Circuit
PWM Duty Setting Block
Note
PWM Data Register 1
(PWMR1)
b8 b0
9-Bit Binary Counter
PWM Data Register 0
(PWMR0)
PWM
PWM
1SE
0SE
Output Select
Block
Output Select
Block
Output Select
Block
PWM Mode
Select Register
PWM
2SE
P132/PWM0
P133/PWM1
P134/PWM2
PWM
PWM
BIT
PWMMDPWMSTPWM
CK0
RES
PWM Control Register
Internal Bus
Note The PWM data register 2 (PWMR2) is multiplexed with the PWM timer register (PWMTMR).
17
Page 18

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Figure 5-5. Watchdog Timer Block Diagram
f
xx
3
2
f
f
xx
xx
4
2
5
2
f
2
xx
6
Prescaler
f
xx
7
2
f
f
xx
8
2
f
xx
xx
9
11
2
2
Selector
5.4 BUZZER OUTPUT CONTROL CIRCUIT
The clock with the following frequency can be output as a buzzer output.
• 1.5 kHz/3 kHz/6 kHz (@ 4.5-MHz crystal oscillator with system clock)
8-Bit Counter
Control
Circuit
INTWDT
Maskable
Interrupt Request
Reset
INTWDT
Non-Maskable
Interrupt Request
Figure 5-6. Buzzer Output Control Circuit Block Diagram
1.5 kHz
3 kHz
6 kHz
TCL27 TCL26 TCL25
Timer Clock Select Register 2
Selector
3
P36
Output Latch
Internal Bus
BEEP/P36
PM36
Port Mode Register 3
18
Page 19

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
5.5 A/D CONVERTER
An A/D converter of 8-bit resolution × 6 channels is incorporated.
The following two types of the A/D conversion operation start-up methods are available.
• Hardware start
• Software start
Figure 5-7. A/D Converter Block Diagram
Resistor String
ANI0/P10
ANI1/P11
ANI2/P12
ANI3/P13
ANI4/P14
ANI5/P15
Selector
Sample & Hold Circuit
Voltage Comparator
Tap
Selector
Succesive Approximation
Register (SAR)
DD
V
GND
INTP3/P03
Edge
Detection
Circuit
Control
Circuit
A/D Conversion
Result Register (ADCR)
Internal Bus
5.6 SERIAL INTERFACES
2 channels of the clocked serial interface are incorporated.
• Serial interface channel 0
• Serial interface channel 1
Table 5-2. Types and Functions of Serial Interface
Function
3-wire serial I/O mode
3-wire serial I/O mode with automatic
transmission/ reception function
SBI (serial bus interface) mode
2-wire serial I/O mode
I2C Bus Mode —
Serial Interface Channel 0
(MSB/LSB first switchable)
—
(MSB first)
(MSB first)
(MSB first)
Serial Interface Channel 1
(MSB/LSB first switchable)
(MSB/LSB first switchable)
INTAD
INTP3
—
—
19
Page 20

SI0/SB0/SDA0/P25
SO0/SB1/SDA1/P26
SCK0/SCL/P27
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Figure 5-8. Serial Interface Channel 0 Block Diagram
Internal Bus
Selector
Selector
Serial I/O Shift
Register 0 (SIO0)
Bus Release/Command/
Acknowledge Detection
Circuit
Serial Clock Counter
Output
Latch
Interrupt Request
Signal Generator
Busy/Acknowledge
Output Circuit
INTCSI0
Automatic Data Transmit/
Receive Address Pointer
SI1/P20
SO1/P21
(ADTP)
Serial Clock
Control Circuit
Figure 5-9. Serial Interface Channel 1 Block Diagram
Internal Bus
Buffer RAM
Interval Specification
Match
Serial I/O Shift Register 1 (SIO1)
Selector
Automatic Data
Transmit/Receive
Register (ADTI)
5-Bit Counter
fXX/2 to fXX/2
8
20
STB/P23
BUSY/P24
SCK1/P22
Handshake
Control
Circuit
Serial Counter
Serial Clock Control Circuit
Interrupt Request
Signal Generator
Selector
INTCSI1
f XX/2 to f XX/2
8
Page 21

5.7 PLL FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER
Figure 5-10. PLL Frequency Synthesizer Block Diagram
PLL Mode
Select Register
PLL
PLL
MD1
MD0
(PLLRL, PLLRH, PLLR0)
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Internal Bus
PWM
Data Transfer Register
PLL Data Register
PLL
NS0
Mixer
Voltage
Control
Generator
Low pass
VCOH
VCOL
Note
Note
Filter
Note External circuit
2
Input Select
Block
4.5 MHz
PLL Reference
Mode Register
2
Programmable
Divider
Reference
Frequency
Generator
PLL
PLL
RF3
RF2
4
PLL
RF1
Internal Bus
f
PLL
RF0
PLL Unlock
FF Judge
Register
N
fr
Phase
Comparator
φ
( -DET)
Unlock
FF
PLL
UL0
EO Select
Register
Charge
Pump
EOC
ON1
EO1
EO0
EOC
ON0
Cautions 1. Be sure to set EOCON0 to 0.
2. For the µPD178004A and 178006A, do not set EOCON1 to 1.
21
Page 22

5.8 FREQUENCY COUNTER
Figure 5-11. Frequency Counter Block Diagram
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
FMIFC
AMIFC
IFC
MD1
IF Counter
Mode Select
Register
Input Select
Block
2
IFC
IFC
MD0
CK1
IFC
CK0
2
IF Counter
Gate Judge
Register
Internal Bus
Gate Time
Control Block
Start/Stop
Control Block
IFC
JG0
IF Counter
Control
Register
IFC
ST
IF Counter
Register
(IFC)
Block
IFC
RES
22
Page 23

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
6. INTERRUPT FUNCTIONS AND TEST FUNCTIONS
6.1 INTERRUPT FUNCTIONS
Interrupt functions include three types and 17 sources, as shown below.
• Non-maskable: 1
• Maskable : 15
• Software : 1
Table 6-1. Interrupt Source List
Interrupt
Type
Nonmaskable
Maskable
Note 1
Default
Priority
—
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
10
11
12
13
14
—
Interrupt Source
Name
INTWDT
INTWDT
INTP0
INTP1
INTP2
INTP3
INTP4
INTP5
INTP6
INTCSI0
INTTMC
INTPWM Generation of match signal of 8-bit timer
INTTM1
INTTM2
INTAD
BRK
Watchdog timer overflow
(watchdog timer mode 1 selected)
Watchdog timer overflow
(interval timer mode selected)
Pin input edge detection
End of serial interface channel 0 transfer
End of serial interface channel 1 transfer
Generation of match signal of basic timer
Generation of match signal of 8-bit timer/
event counter 1
Generation of match signal of 8-bit timer/
event counter 2
End of conversion by A/D converter
BRK instruction execution
Trigger
Internal/
External
Internal
External
Internal
Vector Table
Address
0004H
0006H
0008H
000AH
000CH
000EH
0010H
0012H
0014HInternal
0016H9 INTCSI1
0018H
001AH
001CH
001EH
0020H
003EHSoftware
Basic
Configuration
Note 2
Type
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(B)
(E)
Notes 1. The default priority is a priority order when two or more maskable interrupts are generated
simultaneously. 0 is the highest order and 14, the lowest.
2. Basic configuration types (A) to (E) correspond to (A) to (E) in Figure 6-1, respectively.
23
Page 24

Figure 6-1. Interrupt Function Basic Configuration (1/2)
(A) Internal non-maskable interrupt
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Internal Bus
Interrupt
Request
(B) Internal maskable interrupt
Interrupt
Request
Priority Control
Circuit
Internal Bus
MK
IF
IE
PR ISP
Priority Control
Circuit
Vector Table
Address
Generator
Standby Release
Signal
Vector Table
Address
Generator
Standby Release
Signal
(C) External maskable interrupt (INTP0)
Interrupt
Request
Sampling Clock
Select Register
(SCS)
Sampling
Clock
External Interrupt
Mode Register
(INTM0)
Edge
Detection
Circuit
Internal Bus
MK IE
IF
PR ISP
Priority Control
Circuit
Vector Table
Address
Generator
Standby Release
Signal
24
Page 25

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Figure 6-1. Interrupt Function Basic Configuration (2/2)
(D) External maskable interrupt (except INTP0)
Internal Bus
Interrupt
Request
(E) Software interrupt
External Interrupt
Mode Register
(INTM0, INTM1)
Edge Detection
Circuit
Interrupt
Request
MK IE
IF
Priority Control
Internal Bus
Circuit
PR ISP
Priority Control
Circuit
Vector Table
Address
Generator
Vector Table
Address
Generator
Standby Release
Signal
IF : Interrupt request flag
IE : Interrupt enable flag
ISP : In-service priority flag
MK : Interrupt mask flag
PR : Priority specification flag
25
Page 26

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
6.2 TEST FUNCTION
A test function with a single source is provided, as shown in Table 6-2.
Table 6-2. Test Input Source List
Name Trigger
INTPT4 Port 4 falling edge detection External
IF : Test input flag
MK : Test mask flag
Test Input Source
Figure 6-2. Test Function Basic Configuration
Internal Bus
MK
Test Input
IF
Internal/External
Standby Release
Signal
26
Page 27

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
7. STANDBY FUNCTION
There are the following two standby functions to reduce the system power consumption.
• HALT mode : The CPU operating clock is stopped.
The average consumption current can be reduced by intermittent operation in combination with
the normal operating mode.
• STOP mode : The system clock oscillation is stopped. All operations by the system clock are stopped and
current consumption can be considerably reduced.
Figure 7-1. Stand-by Function
System Clock Operation
Interrupt
Request
STOP Mode
(System clock
oscillation stopped)
STOP
Instruction
Interrupt
Request
8. RESET FUNCTION
There are the following three reset methods.
• External reset input by RESET pin
• Internal reset by watchdog timer runaway time detection
• Internal reset by Power-On Clear (POC).
HALT
Instruction
HALT Mode
(Clock supply to CPU is
stopped, oscillation
continued)
27
Page 28
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
9. INSTRUCTION SET
(1) 8-bit instructions
MOV, XCH, ADD ADDC, SUB, SUBC, AND, OR, XOR, CMP, MULU, DIVUW, INC, DEC, ROR,
ROL, RORC, ROLC, ROR4, ROL4, PUSH, POP, DBNZ
Second
Operand
First
Operand
A
r
B,C
sfr MOV MOV
saddr
!addr16
PSW
[DE]
[HL] MOV
[HL + byte]
[HL + B]
[HL + C]
X
C
#byte A r
ADD
ADDC
SUB
SUBC
AND
OR
XOR
CMP
MOV MOV
MOV
ADD
ADDC
SUB
SUBC
AND
OR
XOR
CMP
Note Except r = A
[HL + byte]
MOV
XCH
ADD
ADDC
SUB
SUBC
AND
OR
XOR
CMP
[HL + B]
[HL + C]
MOV
XCH
ADD
ADDC
SUB
SUBC
AND
OR
XOR
CMP
$addr16 1
ROR
ROL
RORC
ROLC
DBNZ
None
INC
DEC
DEC
POP
ROR4
ROL4
MULU
DIVUW
Note
MOV
XCH
ADD
ADDC
SUB
SUBC
AND
OR
XOR
CMP
ADD
ADDC
SUB
SUBC
AND
OR
XOR
CMP
MOV DBNZ INC
MOV
MOVMOV PUSH
MOV
sfr saddr !addr16 PSW [DE] [HL]
MOV
XCH
MOV
XCH
ADD
ADDC
SUB
SUBC
AND
OR
XOR
CMP
MOV
XCH
ADD
ADDC
SUB
SUBC
AND
OR
XOR
CMP
MOV MOV
XCH
28
Page 29

µ
Second Operand
First Operand
AX
rp
sfrp
saddrp
!addr16
SP
#word
ADDW
SUBW
CMPW
MOVW
MOVW
MOVW
MOVW
AX
MOVW
Note
MOVW
MOVW
MOVW
MOVW
MOVW
XCHW
rp
Note
sfrp
MOVW
saddrp
MOVW
!addr16
MOVW
SP
MOVW
None
INCW
DECW
PUSH
POP
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
(2) 16-bit instructions
MOVW, XCHW, ADDW, SUBW, CMPW, PUSH, POP, INCW, DECW
Note Only when rp = BC, DE or HL
(3) Bit manipulation instructions
MOV1, AND1, OR1, XOR1, SET1, CLR1, NOT1, BT, BF, BTCLR
Second Operand
First Operand
A.bit
sfr.bit
saddr.bit
PSW.bit
[HL].bit
CY
A.bit sfr.bit saddr.bit PSW.bit [HL].bit CY $addr16 None
MOV1
AND1
OR1
XOR1
MOV1
AND1
OR1
XOR1
MOV1
AND1
OR1
XOR1
MOV1
AND1
OR1
XOR1
(4) Call instruction/branch instructions
CALL, CALLF, CALLT, BR, BC, BNC, BZ, BNZ, BT, BF, BTCLR, DBNZ
MOV1
AND1
OR1
XOR1
MOV1
MOV1
MOV1
MOV1
MOV1
BT
BF
BTCLR
BT
BF
BTCLR
BT
BF
BTCLR
BT
BF
BTCLR
BT
BF
BTCLR
SET1
CLR1
SET1
CLR1
SET1
CLR1
SET1
CLR1
SET1
CLR1
SET1
CLR1
NOT1
Second Operand
First Operand
Basic instruction
Compound
instruction
AX !addr16 !addr11 [addr5] $addr16
BR CALL
BR
CALLF CALLT BR, BC, BNC
(5) Other instructions
ADJBA, ADJBS, BRK, RET, RETI, RETB, SEL, NOP, EI, DI, HALT, STOP
BZ, BNZ
BT, BF
BTCLR
DBNZ
29
Page 30

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
10. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (TA = 25 °C)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Rating Unit
Power supply voltage VDD –0.3 to + 7.0 V
Input voltage VI1 Excluding P60 to P63 –0.3 to VDD + 0.3 V
VI2 P60 to P63 N-ch Open-drain –0.3 to +16 V
Output voltage VO –0.3 to VDD + 0.3 V
Output withstand V
voltage
Analog input voltage
Output current high IOH 1 pin –10 mA
Output current low IOL
Operating ambient TA –40 to +85 °C
temperature
Storage temperature Tstg –65 to +150 °C
BDS P132 to P134 N-ch Open-drain 16 V
VAN P10 to P15 Analog input pin –0.3 to VDD + 0.3 V
P01 to P06, P30 to P37, P56, P57, P60 to P67, –15 mA
P120 to P125 total
P10 to P15, P20 to P27, P40 to P47, P50 to P55, –15 mA
P132 to P134 total
Note
1 pin Peak value 15 mA
Effective value 7.5 mA
Note Effective value should be calculated as follows: [Effective value] = [Peak value] × √duty
Caution Product quality may suffer if the absolute maximum rating is exceeded for even a single
parameter even momentarily. That is, the absolute maximum ratings are rated values at which
the product is on the verge of suffering physical damage, and therefore the product must be
used under conditions which ensure that the absolute maximum ratings are not exceeded.
Remark The characteristics of alternate-function pins and port pins are the same unless specified otherwise.
RECOMMENDED SUPPLY VOLTAGE RANGES (TA = –40 to +85 °C)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Power supply voltage VDD1 During CPU operation and PLL operation. 4.5 5.5 V
VDD2 While the CPU is operating and the PLL is stopped. 3.5 5.5 V
Cycle Time: TCY ≥ 0.89 µs
VDD3 While the CPU is operating and the PLL is stopped. 4.5 5.5 V
Cycle Time: TCY = 0.44 µs
Remark T
CY: Cycle Time (Minimum instruction execution time)
30
Page 31

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
DC CHARACTERISTICS (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 3.5 to 5.5 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Input voltage high VIH1 P10 to P15, P21, P23, 0.7 VDD VDD V
P30 to P32, P35 to P37,
P40 to P47, P50 to P57,
P64 to P67, P120 to P125
VIH2 P00 to P06, P20, P22, 0.85 VDD VDD V
P24 to P27, P33, P34,
RESET
VIH3 P60 to P63 0.7 VDD 15 V
(N-ch Open-drain)
Input voltage low VIL1 P10 to P15, P21, P23, 0 0.3 VDD V
P30 to P32, P35 to P37,
P40 to P47, P50 to P57,
P64 to P67, P120 to P125
VIL2 P00 to P06, P20, P22, 0 0.15 VDD V
P24 to P27, P33, P34,
RESET
VIL3 P60 to P63 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 0 0.3 VDD V
(N-ch Open-drain) 3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 0 0.2 VDD V
Output voltage high VOH1 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V VDD – 1.0 V
IOH = –1 mA
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V VDD – 0.5 V
IOH = –100 µA
Output voltage low V OL1 P50 to P57, P60 to P63 VDD = 4.5 to 5.5 V, 0.4 2.0 V
IOH = 15 mA
P01 to P06, P10 to P15, V DD = 4.5 to 5.5 V, 0.4 V
P20 to P27, P30 to P37, IOL = 1.6 mA
P40 to P47, P64 to P67,
P120 to P125,
P132 to P134
V
OL2 SB0, SB1, SCK0 VDD = 4.5 to 5.5 V, 0.2 VDD V
open-drain pulled-up
(R = 1 KΩ)
(1/3)
Remark The characteristics of alternate-function pins and port pins are the same unless specified otherwise.
31
Page 32

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
DC CHARACTERISTICS (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 3.5 to 5.5 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Input leakage ILIH1 P00 to P06, P10 to P15, VIN = VDD 3
current high P20 to P27, P30 to P37,
P40 to P47, P50 to P57,
P64 to P67, P120 to P125,
RESET
ILIH2 P60 to P63 VIN = 15 V 80
Input leakage ILIL1 P00 to P06, P10 to P15, VIN = 0 V –3
current low P20 to P27, P30 to P37,
P40 to P47, P50 to P57,
P64 to P67, P120 to P125,
RESET
ILIL2 P60 to P63 –3
Output leakage ILOH P132 to P134 VOUT = 15 V 3
current high
Output leakage ILOL P132 to P134 VOUT = 0 V –3
current low
Output off leak ILOF EO0, EO1 VOUT = VDD, ±1
current VOUT = 0 V
Note
Note When an input instruction is executed, the low-level input leakage current for P60 to P63 becomes –200
µ
A (MAX.) only in one clock cycle (at no wait). It remains at –3 µA (MAX.) for other than an input instruction.
(2/3)
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
Remark The characteristics of alternate-function pins and port pins are the same unless specified otherwise.
REFERENCE CHARACTERISTICS (T
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Output current high IOH1 EO0 VOUT = VDD – 1 V –4 mA
EO1 (EOCON0 = 0) –1.8 mA
Output current low IOL1 EO0 VOUT = 1 V 6 mA
EO1 (EOCON0 = 0) 3.5 mA
A = 25 °C, VDD = 5 V)
(1/2)
32
Page 33

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
DC CHARACTERISTICS (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 3.5 to 5.5 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Power Supply
Note 1
IDD1 While the CPU is operating TCY = 0.89 µs
Note 2
2.5 15 mA
Current and the PLL is stopped
fX = 4.5 MHz operation
IDD2
TCY = 0.44 µs
Note 3
4.0 27 mA
VDD = 4.5 to 5.5 V
IDD3 While the CPU is operating TCY = 0.89 µs
Note 2
0.7 1.5 mA
and the PLL is stopped
HALT Mode
IDD4
Pin X1 sine wave
input VIN = VDD.
TCY = 0.44 µs
VDD = 4.5 to 5.5 V
Note 3
1.0 2.0 mA
fX = 4.5 MHz operation
Data Hold VDR1 When the crystal is oscillating TCY = 0.44 µs 4.5 5.5 V
Power Supply
Voltage
V
DR2 TCY = 0.89
V
DR3 When the crystal oscillator is stopped 2.6 5.5 V
µ
s 3.5 5.5 V
When power off by Power On Clear is detected
Data Hold
Power Supply Current
IDR1 While the crystal oscillator TA = 25 °C, VDD = 5V 2 4
is stopped
IDR2
230
Notes 1. The port current is not included.
2. When the Processor Clock Control register (PCC) is set at 00H, and the Oscillation Mode Select
register (OSMS) is set at 00H.
3. When PCC is set at 00H and OSMS is set at 01H.
(3/3)
µ
A
µ
A
Remarks 1. TCY: Cycle Time (Minimum instruction execution time)
2. fx: System clock oscillator frequency.
REFERENCE CHARACTERISTICS (T
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Power Supply I
Current and PLL operation.
DD5 During CPU operation TCY = 0.44
VCOH pin sine wave
input
fIN = 130 MHz,
VIN = 0.15 Vp-p
A = 25 °C, VDD = 5 V)
Note
µ
s
7mA
Note When the Processor Clock Control register (PCC) is set at 00H, and the Oscillation Mode Select register
(OSMS) is set at 01H.
Remark TCY: Cycle Time (Minimum instruction execution time)
(2/2)
33
Page 34

AC CHARACTERISTICS
60
10
2.0
1.0
0.5
0.4
0
123456
Power Supply Voltage VDD [V]
Operation
Guaranteed
Range
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
(1) BASIC OPERATION (T
A = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 3.5 to 5.5 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
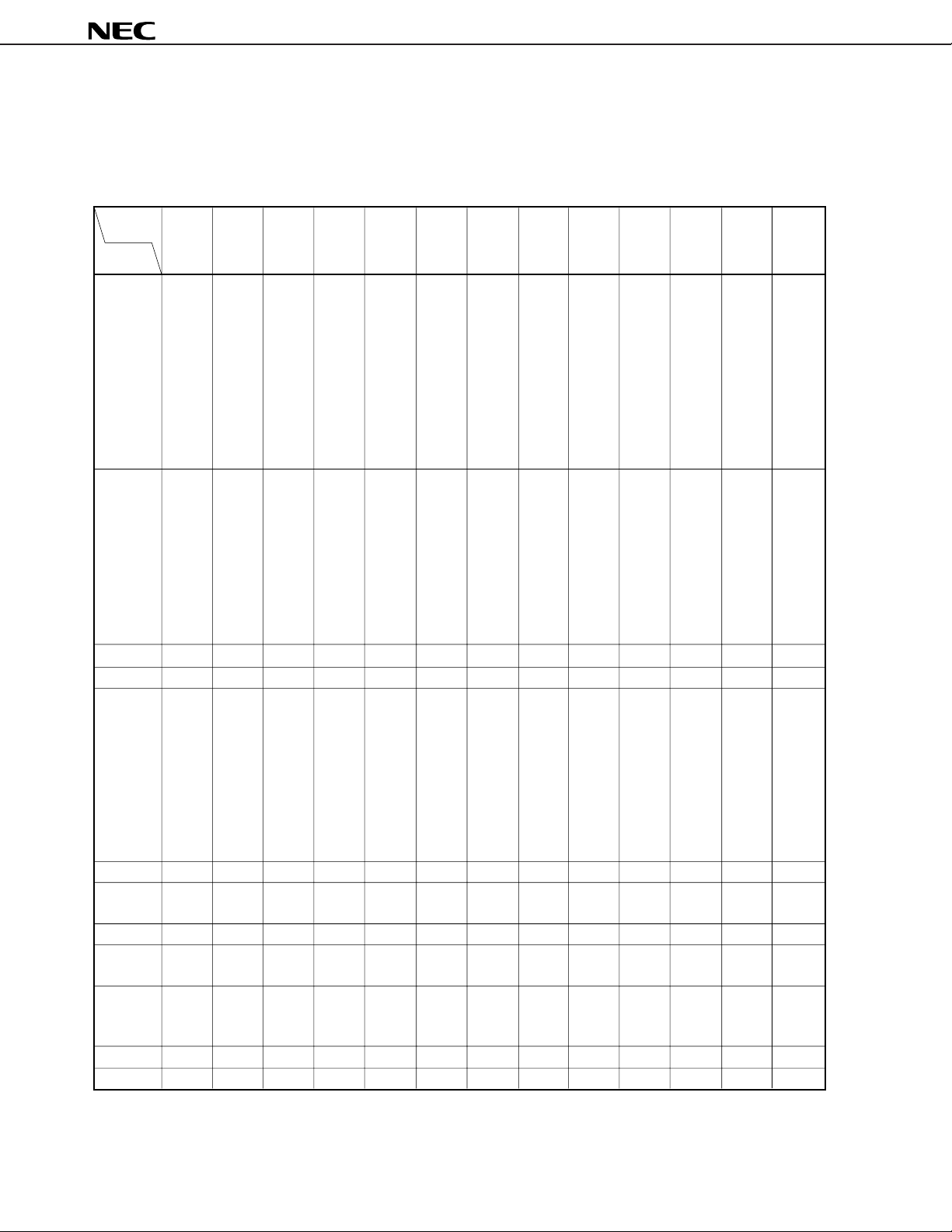
Cycle time TCY fXX = fX/2
(Minimum instruction
execution time)
fXX = fX
f
Note 1
, fX = 4.5 MHz operation 0.89 14.22
Note 2
, 4.5 ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 0.44 7.11
X = 4.5 MHz operation
3.5 ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 0.89 7.11
TI1, TI2 input fTI 4.5 ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 0 4.5 MHz
frequency
3.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 4.5 V 0 275 kHz
TI1, TI2 input high/ tTIH, 4.5 ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 111 ns
low-level width
Interrupt input high/ TINTH, INTP0
low-level width
t
TIL 3.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 4.5 V 1.8
8/fsam
T
INTL INTP1 to INTP6 10
Note 3
RESET low level tRSL 10
width
Notes 1. When oscillation mode selection (OSMS) register is set at 00H.
2. When OSMS is set at 01H.
3. In combination with bits 0 (SCS0) and 1 (SCS1) of sampling clock select register (SCS), selection
of fsam is possible between fXX/2N, fXX/32, fXX/64 and fXX/128 (when N = 0 to 4).
Remarks 1. f
XX: System clock frequency (fX or fX/2)
2. f X: System clock oscillation frequency
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
CY vs VDD (At FXX = FX/2
T
60
10
s]
µ
CY [
2.0
1.0
Cycle Time T
0.5
0.4
0
123456
Power Supply Voltage VDD [V]
system clock operation) TCY vs VDD (At FXX = FX system clock operation)
s]
Operation
Guaranteed
µ
CY [
Range
Cycle Time T
34
Page 35

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
(2) SERIAL INTERFACE (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 3.5 to 5.5 V)
(a) Serial interface channel 0
(i) 3-wire serial I/O mode (SCK0 ... internal clock output)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK0 cycle time tKCY1 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 800 ns
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 1 600 ns
SCK0 high-/low-level width tKH1, 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V
tKL1
SI0 setup time (to SCK0↑)tSIK1 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 100 ns
SI0 hold time (from SCK0↑)tKSI1 400 ns
SO0 output delay time from SCK0↓
tKSO1 C = 100 pF
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 150 ns
Note
tKCY1/2 – 50
tKCY1/2 – 100
300 ns
Note C is the load capacitance of SO0 output line.
ns
ns
(ii) 3-wire serial I/O mode (SCK0 ... external clock input)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK0 cycle time tKCY2 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 800 ns
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 1 600 ns
SCK0 high-/low-level width tKH2, 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 400 ns
tKL2
SI0 setup time (to SCK0↑)tSIK2 100 ns
SI0 hold time (from SCK0↑)tKSI2 400 ns
SO0 output delay time from SCK0↓
SCK0 at rising or falling edge time t R2, tF2 1 000 ns
tKSO2 C = 100 pF
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 800 ns
Note
300 ns
Note C is the load capacitance of SO0 output line.
35
Page 36

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
(iii) SBI mode (SCK0 ... internal clock output)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK0 cycle time tKCY3 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 800 ns
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 3 200 ns
SCK0 high-/low-level width t KH3, 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V
tKL3
SB0, SB1 setup time (to SCK0↑)tSIK3 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 100 ns
SB0, SB1 hold time (from SCK0↑)
SB0, SB1 output delay time from tKSO3 R = 1 kΩ 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 0 250 ns
SCK0↓
SB0, SB1↓ from SCK0
SCK0↓ from SB0, SB1↓ tSBK tKCY3 ns
SB0, SB1 high-level width tSBH tKCY3 ns
SB0, SB1 low-level width t
↑
tKSI3 tKCY3/2 ns
tKSB tKCY3 ns
SBL tKCY3 ns
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 300 ns
C = 100 pF
Note
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 0 1 000 ns
tKCY3/2 – 50
tKCY3/2 – 150
Note R and C are the load resistance and load capacitance of SB0 and SB1 output line.
(iv) SBI mode (SCK0 ... external clock input)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK0 cycle time tKCY4 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 800 ns
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 3 200 ns
SCK0 high-/low-level width t KH4, 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 400 ns
tKL4
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 1 600 ns
ns
ns
SB0, SB1 setup time (to SCK0↑)tSIK4 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 100 ns
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 300 ns
SB0, SB1 hold time (from SCK0↑)
SB0, SB1 output delay time from tKSO4 R = 1 kΩ 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 0 300 ns
SCK0↓
SB0, SB1↓ from SCK0
SCK0↓ from SB0, SB1↓ tSBK tKCY4 ns
SB0, SB1 high-level width tSBH tKCY4 ns
SB0, SB1 low-level width tSBL tKCY4 ns
SCK0 at rising or falling edge time tR4, tF4 1 000 ns
↑
tKSI4 tKCY4/2 ns
C = 100 pF
tKSB tKCY4 ns
Note
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 0 1 000 ns
Note R and C are the load resistance and load capacitance of SB0 and SB1 output line.
36
Page 37

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
(v) 2-wire serial I/O mode (SCK0 ... internal clock output)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK0 cycle time tKCY5 R = 1 kΩ 1 600 ns
SCK0 high-level width tKH5
SCK0 low-level width tKL5 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V
SB0, SB1 setup time (to SCK0↑)tSIK5 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 300 ns
SB0, SB1 hold time (from SCK0↑)
SB0, SB1 output delay time from tKSO5 0 300 ns
SCK0↓
tKSI5 600 ns
C = 100 pF
Note
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 350 ns
tKCY5/2 – 160
tKCY5/2 – 50
tKCY5/2 – 100
400 ns
ns
ns
ns
Note R and C are the load resistance and load capacitance of SCK0, SB0 and SB1 output line.
(vi) 2-wire serial I/O mode (SCK0 ... external clock input)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK0 cycle time tKCY6 1 600 ns
SCK0 high-level width tKH6 650 ns
SCK0 low-level width tKL6 800 ns
SB0, SB1 setup time (to SCK0↑)tSIK6 100 ns
SB0, SB1 hold time (from SCK0↑)
SB0, SB1 output delay time from tKSO6 R = 1 kΩ 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 0 300 ns
SCK0↓
SCK0 at rising or falling edge time t R6, tF6 1 000 ns
tKSI6 tKCY6/2 ns
C = 100 pF
Note
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 0 500 ns
Note R and C are the load resistance and load capacitance of SB0 and SB1 output line.
37
Page 38

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
(vii) I2C Bus mode (SCL ... internal clock output)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCL cycle time tKCY7 R = 1 kΩ 10
SCL high-level width t KH7
SCL low-level width tKL7 tKCY7 – 50 ns
SDA0, SDA1 setup time (to SCL↑)
tSIK7 200 ns
C = 100 pF
Note
tKCY7 – 160
µ
ns
s
SDA0, SDA1 hold time t
(from SCL↓)
SDA0, SDA1 output delay time tKSO7 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 0 300 ns
(from SCL↓)
SDA0, SDA1↓ from SCL↑ or tKSB 200 ns
SDA0, SDA1↑ from SCL
SCL↓ from SDA0, SDA1↓ tSBK 400 ns
SDA0, SDA1 high-level width t
↑
KSI7 0ns
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 0 500 ns
SBH 500 ns
Note R and C are the load resistance and load capacitance of SCL, SDA0 and SDA1 output line.
2
C Bus mode (SCL ... external clock input)
(viii) I
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCL cycle time tKCY8 1 000 ns
SCL high-/low-level width tKH8, tKL8 400 ns
SDA0, SDA1 setup time (to SCL↑)
SDA0, SDA1 hold time tKSI8 0ns
(from SCL↓)
SDA0, SDA1 output delay time tKSO8 R = 1 kΩ 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 0 300 ns
from SCL↓
SDA0, SDA1↓ from SCL↑ or tKSB 200 ns
SDA0, SDA1↑ from SCL↑
tSIK8 200 ns
C = 100 pF
Note
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 0 500 ns
SCL↓ from SDA0, SDA1↓ tSBK 400 ns
SDA0, SDA1 high-level width tSBH 500 ns
SCL at rising or falling edge time tR8, tF8 1 000 ns
Note R and C are the load resistance and load capacitance of SDA0 and SDA1 output line.
38
Page 39

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
(b) Serial interface channel 1
(i) 3-wire serial I/O mode (SCK1 ... internal clock output)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK1 cycle time tKCY9 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 800 ns
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 1 600 ns
SCK1 high/low-level width tKH9, 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V
tKL9
SI1 setup time (to SCK1↑)tSIK9 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 100 ns
SI1 hold time (from SCK1↑)tKSI9 400 ns
SO1 output delay time (from SCK1↓)
tKSO9 C = 100 pF
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 150 ns
Note
tKCY9/2 – 50
tKCY9/2 – 100
ns
ns
300 ns
Note C is the load capacitance of SO1 output line.
(ii) 3-wire serial I/O mode (SCK1 ... external clock input)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK1 cycle time tKCY10 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 800 ns
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 1 600 ns
SCK1 high/low-level width t KH10, 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 400 ns
tKL10
SI1 setup time (to SCK1↑)tSIK10 100 ns
SI1 hold time (from SCK1↑)tKSI10 400 ns
SO1 output delay time (from SCK1↓
SCK1 at rising or falling edge time tR10, tF10 1 000 ns
)tKSO10 C = 100 pF
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 800 ns
Note
300 ns
Note C is the load capacitance of SO1 output line.
39
Page 40

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
(iii) 3-wire serial I/O mode with automatic transmit/receive function (SCK1 ... internal clock
output)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK1 cycle time tKCY11 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 800 ns
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 1 600 ns
SCK1 high/low-level width t KH11 , 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V
tKL11
SI1 setup time (to SCK1↑)tSIK11 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 100 ns
SI1 hold time (from SCK1↑)tKSI11 400 ns
SO1 output delay time (from SCK1↓
STB↑ from SCK1
Strobe signal high-level width tSBW
Busy signal setup time tBYS 100 ns
(to busy signal detection timing)
Busy signal hold time tBYH 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 100 ns
(from busy signal detection timing)
SCK1↓ from busy inactive tSPS 2tKCY11 ns
↑
)tKSO11 C = 100 pF
tSBD
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 150 ns
Note
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 150 ns
tKCY11/2 – 50
tKCY11/2 – 100
300 ns
tKCY11/2 – 100 tKCY11/2 + 100
tKCY11/ – 30 tKCY11 + 30
ns
ns
ns
ns
Note C is the load capacitance of SO1 output line.
(iv) 3-wire serial I/O mode with automatic transmit/receive function (SCK1 ... external clock
input)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK1 cycle time tKCY12 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 800 ns
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 1 600 ns
SCK1 high/low-level width t KH12 , 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 400 ns
tKL12
3.5 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V 800 ns
SI1 setup time (to SCK1↑)tSIK12 100 ns
SI1 hold time (from SCK1↑)tKSI12 400 ns
SO1 output delay time (from SCK1↓
SCK1 at rising or falling edge time tR12, tF12 1 000 ns
)tKSO12 C = 100 pF
Note
300 ns
Note C is the load capacitance of SO1 output line.
40
Page 41
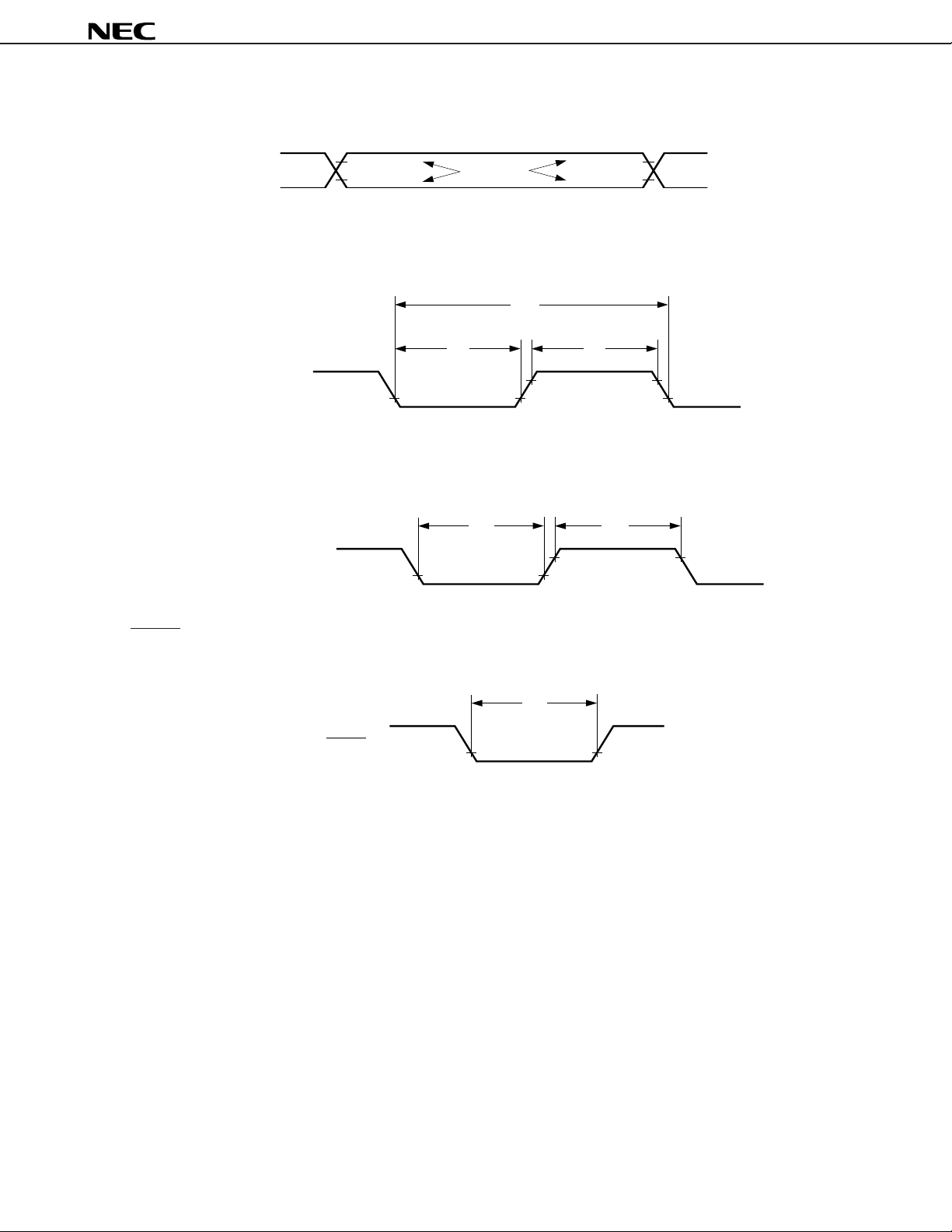
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
AC TIMING TEST POINT (EXCLUDING X1 INPUT)
TI Timing
TI1, TI2
Interrupt Input Timing
INTP0 to INTP6
0.8 VDD
0.2 VDD
Test Points
1/fTI
tTIL tTIH
tINTL tINTH
0.8 VDD
0.2 VDD
RESET Input Timing
tRSL
RESET
41
Page 42

SERIAL TRANSFER TIMING
3-Wire Serial I/O Mode:
SCK0, SCK1
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
tKCYm
tKLm tKHm
tRn
tSIKm tKSIm
tFn
SI0, SI1
tKSOm
SO0, SI1
Remark m = 1, 2, 9, 10
n = 2, 10
SBI Mode (Bus Release Signal Transfer):
SCK0
tKSB tSBK
tSBL
tSBH
Input Data
Output Data
tKL3, 4
tR4
tKCY3, 4
tKH3, 4
tF4
tSIK3, 4
tKSI3, 4
42
SB0, SB1
tKSO3, 4
Page 43
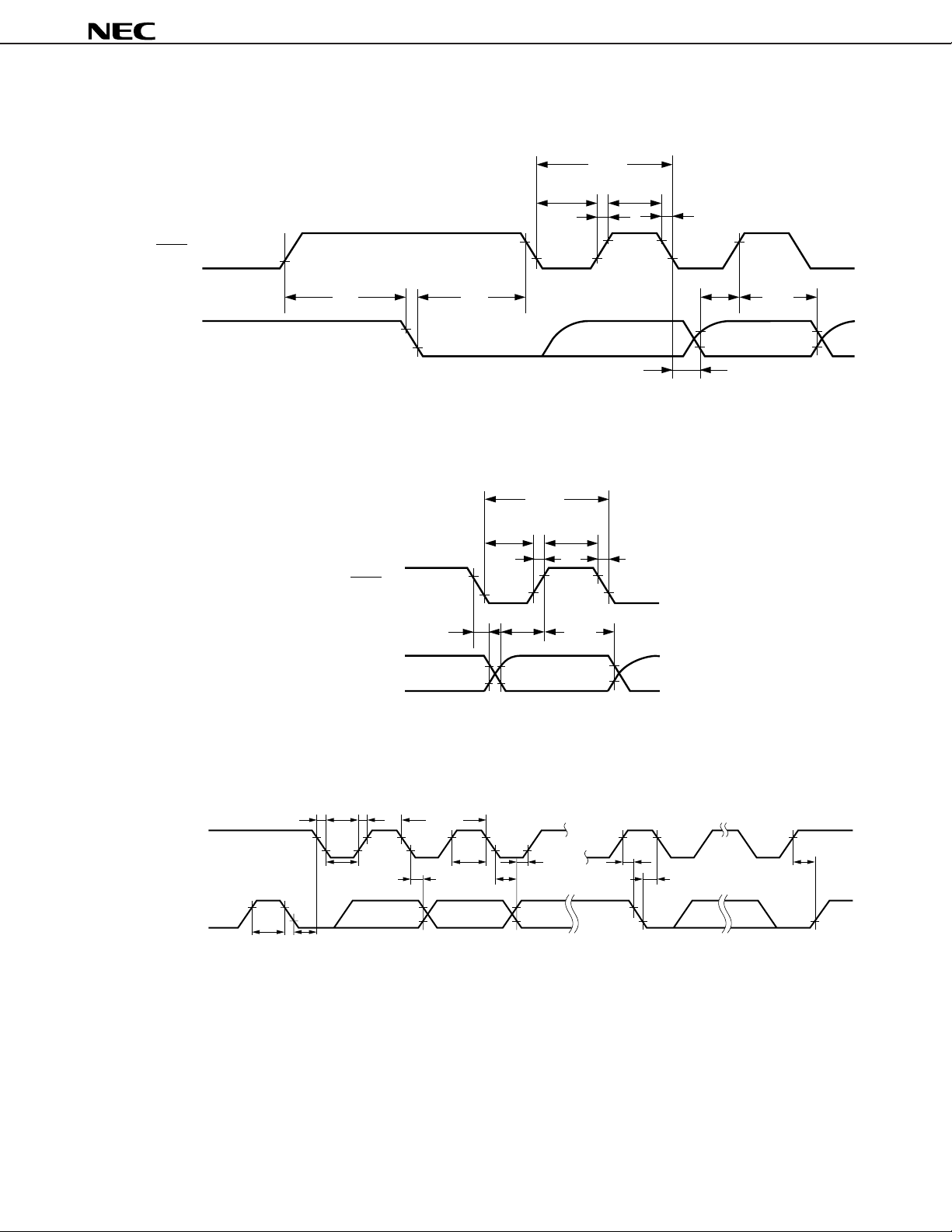
SBI Mode (Command Signal Transfer):
SCK0
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
tKCY3, 4
tKL3, 4
tR4
tKH3, 4
tF4
SB0, SB1
2-Wire Serial I/O Mode:
tKSB
SCK0
SB0, SB1
tKSO5, 6
tSBK
tKL5, 6
tSIK3, 4
tKSI3, 4
tKSO3, 4
tKCY5, 6
tKH5, 6
tF6tR6
tSIK5, 6
tKSI5, 6
I2C Bus Mode:
SCL
SDA0, SDA1
tF8 tR8
tKL7, 8
SBH
tSBK
t
tKCY7, 8
tKSI7, 8 tKH7, 8
tSIK7, 8
tKSO7, 8 tSBK
tKSB tKSB
43
Page 44

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
3-Wire Serial I/O Mode with Automatic Transmit/Receive Function:
SO1
SI1
SCK1
STB
D2 D1 D0 D7
tSIK11, 12
tKSO11, 12
tKL11, 12
tKCY11, 12
tKH11, 12
tR12
tKSI11, 12
tF12
tSBWtSBD
3-Wire Serial I/O Mode with Automatic Transmit/Receive Function (Busy Processing):
tBYS
10
Note
tBYH
10 + n
Note
tSPS
SCK1
789
Note
D7D2 D1 D0
1
BUSY
(Active high)
Note The signal is not actually driven low here; it is shown as such to indicate the timing.
44
Page 45
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
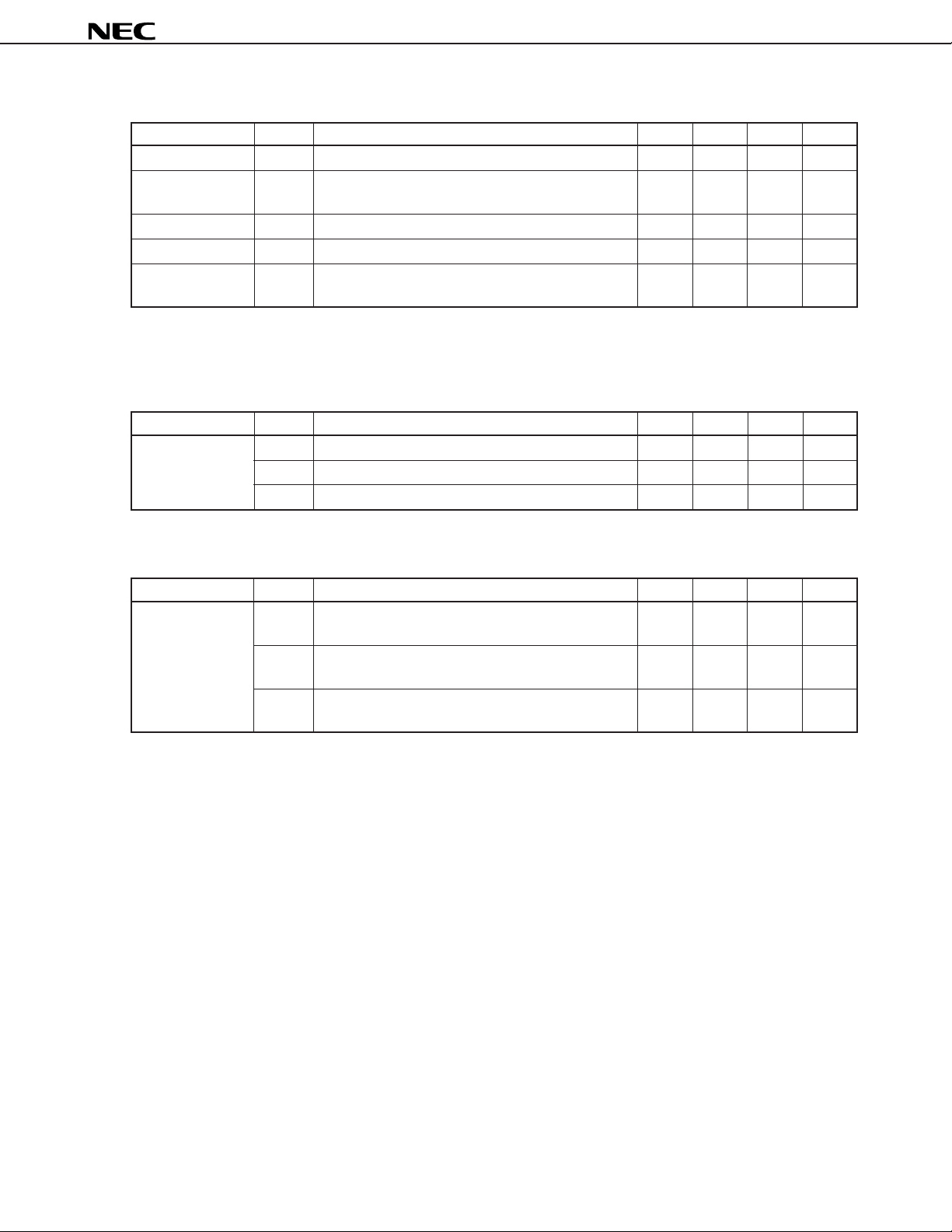
A/D CONVERTER CHARACTERISTICS (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 4.5 to 5.5 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Resolution 8 8 8 bit
Conversion total ±3.0 LSB
error
Conversion time tCONV 22.2 44.4
Sampling time tSAMP 15/fXX
Analog input VIAN 0VDD V
voltage
µ
s
µ
s
Remarks 1. f
XX: System clock frequency (fX/2)
2. fX: System clock oscillation frequency
PLL CHARACTERISTICS (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 4.5 to 5.5 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Operating fIN1 VCOL Pin MF Mode Sine wave input VIN = 0.1 Vp-p 0.5 3 MHz
Frequency
IFC CHARACTERISTICS (T
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Operating f
Frequency Sine wave input VIN = 0.1 Vp-p
Note The condition of a sine wave input of V
fIN2 VCOL Pin HF Mode Sine wave input VIN = 0.2 Vp-p 9 55 MHz
fIN3 VCOH Pin VHF Mode Sine wave input VIN = 0.15 Vp-p 60 160 MHz
A = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 4.5 to 5.5 V)
IN4 AMIFC Pin AMIF Count Mode 0.4 0.5 MHz
fIN5 FMIFC Pin FMIF Count Mode 10 11 MHz
Sine wave input VIN = 0.1 Vp-p
fIN6 FMIFC Pin AMIF Count Mode 0.4 0.5 MHz
Sine wave input VIN = 0.1 Vp-p
IN = 0.1 Vp-p is the standard value for operation of this device during
Note
Note
Note
stand-alone operation, so in consideration of the effect of noise, it is recommended that operation be at
an input amplitude condition of VIN = 0.15 Vp-p.
45
Page 46

11. PACKAGE DRAWINGS
80 PIN PLASTIC QFP (14×14)
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
A
B
61
60
41
40
CD
80
1
20
21
F
G
M
I
H
P
J
K
N
L
NOTE
Each lead centerline is located within 0.13 mm (0.005 inch) of
its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition.
detail of lead end
S
Q
R
M
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
A 17.2±0.4 0.677±0.016
B 14.0±0.2 0.551
C 14.0±0.2 0.551
D 17.2±0.4 0.677±0.016
F 0.825 0.032
G 0.825 0.032
H 0.30±0.10 0.012
I 0.13 0.005
J 0.65 (T.P.) 0.026 (T.P.)
K 1.6±0.2 0.063±0.008
L 0.8±0.2 0.031
M 0.15 0.006
N 0.10 0.004
P 2.7 0.106
Q 0.1±0.1 0.004±0.004
R5°±5° 5°±5°
S 3.0 MAX. 0.119 MAX.
+0.10
–0.05
+0.009
–0.008
+0.009
–0.008
+0.004
–0.005
+0.009
–0.008
+0.004
–0.003
S80GC-65-3B9-4
46
Page 47

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
12. RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS
This product should be soldered and mounted under the conditions recommended in the table below.
For detail of recommended soldering conditions, refer to the information document Semiconductor Device
Mounting Technology Manual (C10535E).
For soldering methods and conditions other than those recommended below, contact an NEC sales representative.
Table 12-1. Surface Mounting Type Soldering Conditions
µ
PD178004AGC-×××-3B9 : 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 mm, 0.65 mm pitch)
µ
PD178006AGC-×××-3B9 : 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 mm, 0.65 mm pitch)
µ
PD178016AGC-×××-3B9 : 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 mm, 0.65 mm pitch)
µ
PD178018AGC-×××-3B9 : 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 mm, 0.65 mm pitch)
Soldering ConditionsSoldering Method
Infrared reflow
VPS
Wave soldering
Partial heating
Package peak temperature: 235 °C, Duration: 30 sec. max. (at 210 °C or above),
Number of times: Three times max.
Package peak temperature: 215 °C, Duration: 40 sec. max. (at 200 °C or above),
Number of times: Three times max.
Solder bath temperature : 260 °C max., Duration : 10 sec. max., Number of times
: once, Preheating temperature : 120 °C max.
(package surface temperature)
Pin temperature: 300 °C max. Duration: 3 sec. max. (per pin row)
Caution Do not use different soldering method together (except for partial heating).
Recommended
Condition Symbol
IR35-00-3
VP15-00-3
WS60-00-1
—
47
Page 48

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
APPENDIX A. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN µPD178018A AND µPD178018 SUBSERIES
Product name
µ
PD178004AµPD178006AµPD178016AµPD178018AµPD178004µPD178006µPD178016µPD178018
Item
PLL Reference 7 types selectable by program 11 types selectable by program
frequency frequency (1, 3, 5, 9, 10, 25, 50 kHz)
synthesizer
EO0 pin output Buffer type
format
EO1 pin output Buffer type Constant-current power supply type
format
EO1 pin high- Not supported Supported Not supported
impedance function
µ
PD178018A Subseries
Note
µ
PD178P018A
µ
PD178018 Subseries
(1, 1.25, 2.5, 3, 5, 6.25, 9, 10, 12.5, 25, 50 kHz)
Note Under development
µ
Remark The mask ROM of mask versions (
PD178018A and µPD178018) is replaced with one-time PROM
or EPROM in the one-time PROM versions (µPD178P018A and µPD178P018).
µ
PD178P018
48
Page 49

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
APPENDIX B. DEVELOPMENT TOOLS
The following development tools are available for system development using the µPD178018A Subseries.
Language Processing Software
RA78K/0
CC78K/0
DF178018
CC78K/0-L
Notes 1, 2, 3, 4
Notes 1, 2, 3, 4
Notes 1, 2, 3, 4, 8
Notes 1, 2, 3, 4
78K/0 Series common assembler package
78K/0 Series common C compiler package
µ
PD178018A Subseries common device file
78K/0 Series common C compiler library source file
PROM Writing Tools
PG-1500 PROM programmer
PG-178P018GC Programmer adapters connected to a PG-1500
PA-178P018KK-T
PG-1500 controller
Notes 1, 2
PG-1500 control program
Debugging Tools
IE-78000-R In-circuit emulator common to 78K/0 Series
IE-78000-R-A In-circuit emulator common to 78K/0 Series (for the integration debugger)
IE-78000-R-BK Break board common to 78K/0 Series
IE-178018-R-EM Emulation board common to µPD178018A Subseries
IE-78000-R-SV3 Interface adapter and cable when using EWS as a host machine (for IE-78000-R-A)
IE-70000-98-IF-B Interface adapter when using the PC-9800 Series (except notebooks) as a host machine
(for IE-78000-R-A)
IE-70000-98N-IF Interface adapter and cable when using the PC-9800 Series notebook as a host machine
(for IE-78000-R-A)
IE-70000-PC-IF-B Interface adapter when using IBM PC/ATTM as a host machine (for IE-78000-R-A)
EP-78230GC-R Emulation probe common to µPD78234 Subseries
EV-9200GC-80 Socket for mounting on target system board created for 80-pin plastic QFP (GC-3B9 type)
EV-9900 Jig used when removing the µPD178P018AKK-T from the EV-9200GC-80.
SM78K0
ID78K0
SD78K/0
DF178018
Notes 5, 6, 7
Notes 4, 5, 6, 7
Notes 1, 2
Notes 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
78K/0 Series common system simulator
Integration debugger for IE-78000-R-A
IE-78000-R screen debugger
µ
PD178018A Subseries device file
49
Page 50

Real-Time OS
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
RX78K/0
MX78K0
Notes 1, 2, 3, 4
Notes 1, 2, 3, 4
78K/0 Series real-time OS
78K/0 Series OS
Notes 1. PC-9800 Series (MS-DOSTM) based
2. IBM PC/AT and compatible (PC DOS
3. HP9000 Series 300
4. HP9000 Series 700
TM
based
TM
(HP-UXTM) based, SPARCstationTM (SunOSTM) based, EWS4800 Series
(EWS-UX/V) based
5. PC-9800 Series (MS-DOS + Windows
6. IBM PC/AT and compatible (PC DOS/IBM DOS/MS-DOS + Windows) based
7. NEWS
TM
(NEWS-OSTM) based
8. Under development
Fuzzy Inference Development Support System
FE9000
FT9080
FI78K0
FD78K0
Note 1
Note 1
Notes 1, 3
Notes 1, 3
/FE9200
/FT9085
Note 2
Note 3
Fuzzy knowledge data creation tool
Translator
Fuzzy inference module
Fuzzy inference debugger
Notes 1. PC-9800 Series (MS-DOS) based
2. IBM PC/AT and its compatibles (PC DOS/IBM DOS/MS-DOS + Windows) based
3. IBM PC/AT and its compatibles (PC DOS/IBM DOS/MS-DOS) based
TM
/IBM-DOSTM/MS-DOS) based
TM
) based
Remarks 1. Please refer to the 78K/0 Series Selection Guide (U11126E) for information on third party
development tools.
2. The RA78K/0, CC78K/0, SD78K/0, ID78K/0, SM78K/0 and RX78K/0 are used in combination with
the DF178018.
50
Page 51

APPENDIX C. RELATED DOCUMENTS
Device Documents
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Title
µ
PD178018A Subseries User’s Manual
78K/0 Series User’s Manual—Instruction U12326J U12326E
78K/0 Series Instruction Set U10904J —
78K/0 Series Instruction Table U10903J —
µ
PD178018A Subseries Special Function Register Table
78K/0 Series Application Note Basics (II) U10121J U10121E
Document No. Document No.
(Japanese) (English)
To be prepared To be prepared
To be prepared
—
Development Tool Documents (User’s Manual)
Title
RA78K Series Assembler Package Operation EEU-809 EEU-1399
Language EEU-815 EEU-1404
RA78K Series Structured Assembler Preprocessor EEU-817 EEU-1402
RA78K0 Assembler Package Operation U11802J U11802E
Assembly Language U11801J U11801E
Structured Assembly U11789J U11789E
Language
CC78K Series C Compiler Operation EEU-656 EEU-1280
Language EEU-655 EEU-1284
CC78K/0 C Compiler Operation U11517J U11517E
Language U11518J U11518E
CC78K/0 C Compiler Application Notes
CC78K Series Library Source File U12322J —
PG-1500 PROM Programmer U11940J EEU-1335
PG-1500 Controller PC-9800 Series (MS-DOS) Based EEU-704 EEU-1291
PG-1500 Controller IBM PC Series (PC DOS) Based EEU-5008 U10540E
IE-78000-R U11376J U11376E
IE-78000-R-A U10057J U10057E
IE-78000-R-BK EEU-867 EEU-1427
IE-178018-R-EM U10668J U10668E
EP-78230 EEU-985 EEU-1515
SM78K0 System Simulator Windows Based Reference U10181J U10181E
SM78K Series System Simulator U10092J U10092E
ID78K0 Integrated Debugger EWS Based Reference U11151J U11151E
ID78K0 Integrated Debugger PC Based Reference U11539J U11539E
ID78K0 Integrated Debugger Windows Based Guide U11649J U11649E
SD78K/0 Screen Debugger PC-9800 Series (MS-DOS) Based
SD78K/0 Screen Debugger IBM PC/AT (PC DOS) Based Introduction EEU-5024 EEU-1414
Programming Know-how
External Parts User
open Interface
Specifications
Introduction EEU-852 U10539E
Reference U10952J —
Reference U11279J U11279E
Document No. Document No.
(Japanese) (English)
EEA-618 EEA-1208
Caution The contents of the above documents are subject to change without notice. Please ensure that
the latest versions are used in design work, etc.
51
Page 52

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Related Documents for Embedded Software (User’s Manual)
Title
78K/0 Series Realtime OS Basics U11537J —
Installation U11536J —
78K/0 Series OS MX78K0 Basics U12257J —
Fuzzy Knowledge Data Creation Tool EEU-829 EEU-1438
78K/0, 78K/II, 87AD Series EEU-862 EEU-1444
Fuzzy Inference Development Support System—Translator
78K/0 Series Fuzzy Inference Development Support System—
78K/0 Series Fuzzy Inference Development Support System EEU-921 EEU-1458
—Fuzzy Inference Debugger
Fuzzy Inference Module
Document No. Document No.
(Japanese) (English)
EEU-858 EEU-1441
Other Documents
Title
IC Package Manual C10943X
Semiconductor Device Mounting Technology Manual C10535J C10535E
Quality Guides on NEC Semiconductor Devices C11531J C11531E
NEC Semiconductor Device Reliability and Quality Control C10983J C10983E
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Test MEM-539 —
Semiconductor Device Quality Assurance Guide C11893J MEI-1202
Microcomputer-related Product Guide (Products by other Manufacturers) U11416J —
Document No. Document No.
(Japanese) (English)
Caution The contents of the above documents are subject to change without notice. Ensure that the
latest versions are used in design work, etc.
52
Page 53

[MEMO]
µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
53
Page 54

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
NOTES FOR CMOS DEVICES
1 PRECAUTION AGAINST ESD FOR SEMICONDUCTORS
Note: Strong electric field, when exposed to a MOS device, can cause destruction of
the gate oxide and ultimately degrade the device operation. Steps must be
taken to stop generation of static electricity as much as possible, and quickly
dissipate it once, when it has occurred. Environmental control must be
adequate. When it is dry, humidifier should be used. It is recommended to avoid
using insulators that easily build static electricity. Semiconductor devices
must be stored and transported in an anti-static container, static shielding bag
or conductive material. All test and measurement tools including work bench
and floor should be grounded. The operator should be grounded using wrist
strap. Semiconductor devices must not be touched with bare hands. Similar
precautions need to be taken for PW boards with semiconductor devices on it.
2 HANDLING OF UNUSED INPUT PINS FOR CMOS
Note: No connection for CMOS device inputs can be cause of malfunction. If no
connection is provided to the input pins, it is possible that an internal input level
may be generated due to noise, etc., hence causing malfunction. CMOS device
behave differently than Bipolar or NMOS devices. Input levels of CMOS devices
must be fixed high or low by using a pull-up or pull-down circuitry. Each unused
pin should be connected to VDD or GND with a resistor, if it is considered to have
a possibility of being an output pin. All handling related to the unused pins must
be judged device by device and related specifications governing the devices.
3 STATUS BEFORE INITIALIZATION OF MOS DEVICES
Note: Power-on does not necessarily define initial status of MOS device. Production
process of MOS does not define the initial operation status of the device.
Immediately after the power source is turned ON, the devices with reset function
have not yet been initialized. Hence, power-on does not guarantee out-pin
levels, I/O settings or contents of registers. Device is not initialized until the
reset signal is received. Reset operation must be executed immediately after
power-on for devices having reset function.
54
Page 55

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Regional Information
Some information contained in this document may vary from country to country. Before using any NEC
product in your application, please contact the NEC office in your country to obtain a list of authorized
representatives and distributors. They will verify:
• Device availability
• Ordering information
• Product release schedule
• Availability of related technical literature
• Development environment specifications (for example, specifications for third-party tools and
components, host computers, power plugs, AC supply voltages, and so forth)
• Network requirements
In addition, trademarks, registered trademarks, export restrictions, and other legal issues may also vary
from country to country.
NEC Electronics Inc. (U.S.)
Santa Clara, California
Tel: 800-366-9782
Fax: 800-729-9288
NEC Electronics (Germany) GmbH
Duesseldorf, Germany
Tel: 0211-65 03 02
Fax: 0211-65 03 490
NEC Electronics (Germany) GmbH
Benelux Office
Eindhoven, The Netherlands
Tel:040-2445845
Fax: 040-2444580
NEC Electronics (France) S.A.
Velizy-Villacoublay, France
Tel:01-30-67 58 00
Fax: 01-30-67 58 99
NEC Electronics Hong Kong Ltd.
Hong Kong
Tel:2886-9318
Fax: 2886-9022/9044
NEC Electronics Hong Kong Ltd.
Seoul Branch
Seoul, Korea
Tel: 02-528-0303
Fax: 02-528-4411
NEC Electronics (UK) Ltd.
Milton Keynes, UK
Tel: 01908-691-133
Fax: 01908-670-290
NEC Electronics Italiana s.r.1.
Milano, Italy
Tel: 02-66 75 41
Fax: 02-66 75 42 99
NEC Electronics (France) S.A.
Spain Office
Madrid, Spain
Tel: 01-504-2787
Fax: 01-504-2860
NEC Electronics (Germany) GmbH
Scandinavia Office
Taeby, Sweden
Tel: 08-63 80 820
Fax: 08-63 80 388
NEC Electronics Singapore Pte. Ltd.
United Square, Singapore 1130
Tel:253-8311
Fax: 250-3583
NEC Electronics Taiwan Ltd.
Taipei, Taiwan
Tel: 02-719-2377
Fax: 02-719-5951
NEC do Brasil S.A.
Sao Paulo-SP, Brasil
Tel: 011-889-1680
Fax: 011-889-1689
J96. 8
55
Page 56

µ
PD178004A, 178006A, 178016A, 178018A
Purchase of NEC I2C components conveys a license under the Philips I2C Patent Rights to use these components in an I2C
system, provided that the system conforms to the I2C Standard Specification as defined by Philips.
MS-DOS and Windows are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United
States and/or other countries.
IBM DOS, PC/AT, and PC DOS are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation.
HP9000 Series 300, HP9000 series 700, and HP-UX are trademarks of Hewlett-Packard Company.
SPARCstation is a trademark of SPARC International, Inc.
SunOS is a trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
NEWS and NEWS-OS are trademarks of Sony Corporation.
The related documents indicated in this publication may include preliminary versions.
However, preliminary versions are not marked as such.
The export of this product from Japan is regulated by the Japanese government. To export this product may be
prohibited without governmental license, the need for which must be judged by the customer. The export or reexport of this product from a country other than Japan may also be prohibited without a license from that country.
Please call an NEC sales representative.
No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without the prior written
consent of NEC Corporation. NEC Corporation assumes no responsibility for any errors which may appear in
this document.
NEC Corporation does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights or other intellectual property
rights of third parties by or arising from use of a device described herein or any other liability arising from use
of such device. No license, either express, implied or otherwise, is granted under any patents, copyrights or other
intellectual property rights of NEC Corporation or others.
While NEC Corporation has been making continuous effort to enhance the reliability of its semiconductor devices,
the possibility of defects cannot be eliminated entirely. To minimize risks of damage or injury to persons or
property arising from a defect in an NEC semiconductor device, customers must incorporate sufficient safety
measures in its design, such as redundancy, fire-containment, and anti-failure features.
NEC devices are classified into the following three quality grades:
"Standard", "Special", and "Specific". The Specific quality grade applies only to devices developed based on a
customer designated "quality assurance program" for a specific application. The recommended applications of
a device depend on its quality grade, as indicated below. Customers must check the quality grade of each device
before using it in a particular application.
Standard: Computers, office equipment, communications equipment, test and measurement equipment,
audio and visual equipment, home electronic appliances, machine tools, personal electronic
equipment and industrial robots
Special: Transportation equipment (automobiles, trains, ships, etc.), traffic control systems, anti-disaster
systems, anti-crime systems, safety equipment and medical equipment (not specifically designed
for life support)
Specific: Aircrafts, aerospace equipment, submersible repeaters, nuclear reactor control systems, life
support systems or medical equipment for life support, etc.
The quality grade of NEC devices is "Standard" unless otherwise specified in NEC's Data Sheets or Data Books.
If customers intend to use NEC devices for applications other than those specified for Standard quality grade,
they should contact an NEC sales representative in advance.
Anti-radioactive design is not implemented in this product.
56
M4 96.5
 Loading...
Loading...