Page 1

ACD 2000 AGENT/SUPERVISOR GUIDE
M I T E L N E T W O R K SM I T E L N E T W O R K S
Integrated
Communications Platform
3300
FOR THE MITEL NETWORKS™ 5020 IP PHONE
Page 2

DUE TO THE DYNAMIC NATURE OF THE PRODUCT DESIGN, THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN
THIS DOCUMENT IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. MITEL NETWORKS, ITS
AFFILIATES, AND/OR ITS SUBSIDIARIES ASSUME NO RESPONSIBILITY FOR ERRORS AND
OMISSIONS CONTAINED IN THIS INFORMATION.
™ Trademark of Mitel Networks Corporation.
© Copyright 2001, Mitel Networks Corporation.
All rights reserved.
Page 3

Contents
General Information About this Guide 5
What is Automatic Call Distributi o n (ACD) ? 6
About Your Mitel Networks 5020 IP Phone 7
Personal Keys 7
Line Select Keys/Line Appearances 7
Line Status Indicators 8
Feature Keys 8
Main Display 8
The SuperKey and Softkeys 9
Function Keys 9
Feature Access Codes 10
Features Not Available 10
ACD 2000 Agent Features and Capabilities 11
What are Agent Groups? 12
Logging In 14
Displaying Agent Log-In Information 16
Logging Out 17
Answering Calls 18
Using the Auto Answer Feature 19
Using a Headset 20
Using and Canceling the Work Timer 23
Taking a Break from Calls (Make Busy Feature) 24
Getting Help 25
Queue Threshold Alert 27
Queue Status 28
3
Page 4

ACD 2000 Supervisor Features and Capabilities 29
What is the Supervisory Position? 30
Queue Threshold Alert / Queue Status 31
Silent Agent and Group Monitoring 32
Conferencing 35
Responding to Help 36
System Reporting Capabilities 38
Personal Directory 40
4
Page 5

General Information About this Guide
This guide describes operation of the Automatic Call Distribut ion 2000 Feat ure
Package on a Mitel Networks 5020 IP phone. For further informat ion on ACD,
see ”What is Automatic Call Distribution“.
The displays shown throughout this guide are intended to be representative only.
Certain displays on the sets may differ from those shown, usually based on what
features or Class Of Service has been programmed into individual sets.
For operation of other features associated with the 5020 IP phone (som e of
which will work in conjunction with ACD), refer to the set guide.
IMPORTANT NOTE FOR HEADSET USERS: Mitel Networks Headsets with
Feature Control Switch (PN 9132-800-500-NA/9132-800-501-NA) must be
installed in the dedicated headset jack (t he jack nearest the front of the
set). Installation will disable your handset microphone. Disconnecting the
headset at the jack or at the quick-disconnect plug restores handset
operation.
5
Page 6

What is Automatic Call Distribution (ACD)?
The Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) 2000 Feature Package is offered by the
Mitel Networks 3300 Integrated Communications Platform (ICP). ACD is a
method of switching large volumes of similar calls directly to a selected group of
extensions (Agents). Up to 350 such Agents can be supported. All calls are
distributed equally among the Agents. The calls are all of a similar nature, and
the Agents are trained/equipped to provide the part icular information or service
the caller is requesting.
Typical examples of ACD applications include:
airline reservation offices
telephone order desks for department stores
customer service departments of telephone or cable T.V.
companies
When there are more incoming calls than available Agents, the calls may be
routed to recordings. The recordings may advise the callers that all Agents are
busy, and that an Agent will answer as soon as possible. Various recordings may
be provided to inform the caller as to call progress if an Agent is not accessed
immediately, or to advise the caller of information the Agent will require when
connection is established.
The Mitel Networks 3300 ICP also directs calls to the Agent so that all Agents
are given an equal workload. A Supervisor usually oversees the operation,
monitors the activity of the Agents, and handles unusual situations which may
arise.
6
Page 7
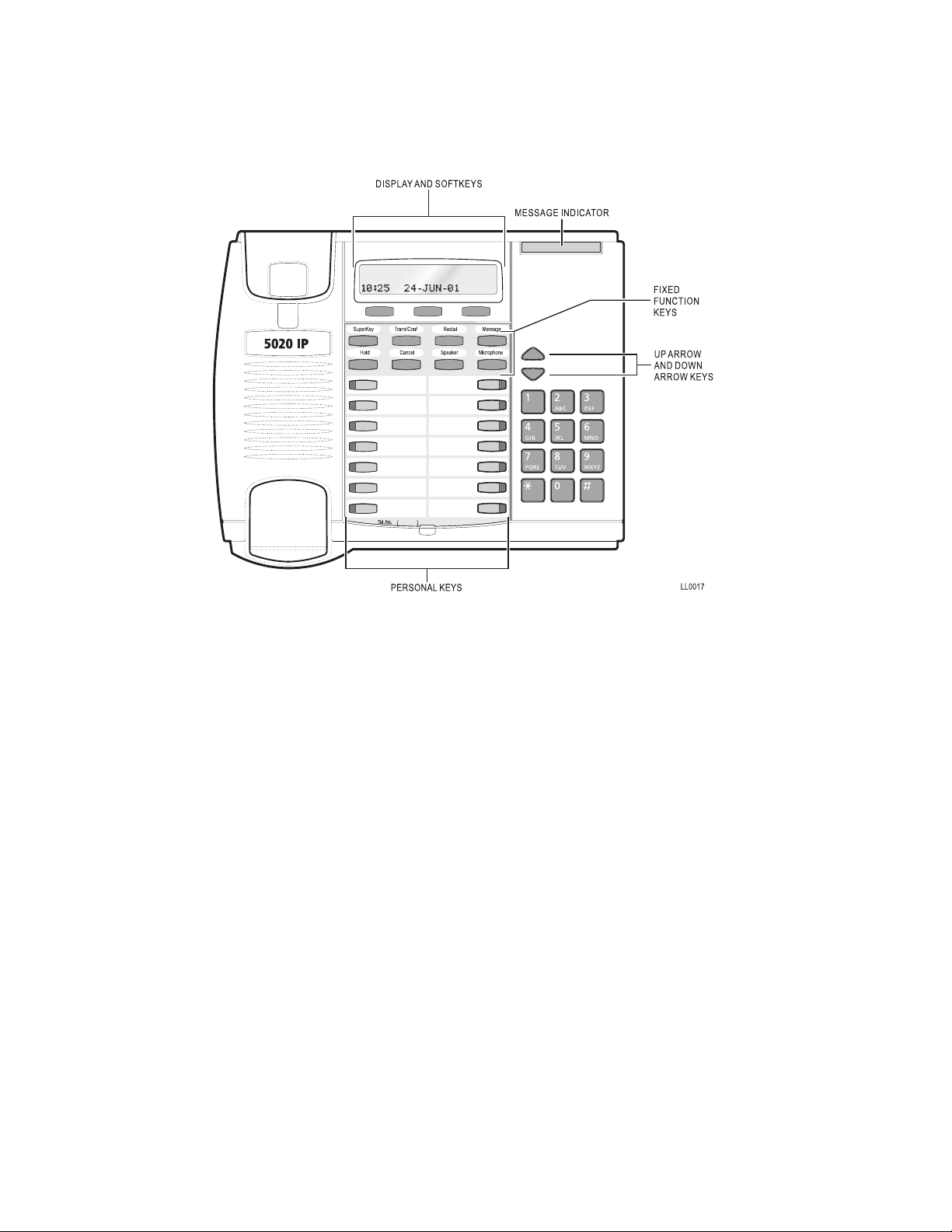
About Your 5020 IP Phone
Personal Keys
At the bottom of your 5020 IP phone there are two rows of Personal Keys. The
first Personal Key (the lower right-hand key) is your Prime Line, the telephone
line that you will usually use. Your extension number is the number of your Prime
Line. Other Personal Keys can be programmed as Speed Call Keys, Line Select
Keys or Feature Keys.
Line Select Keys/Line Appearances
Your 5020 IP phone can accommodate up to 14 lines, including your Prime Line
(your listed number). Your Prime Line always appears at the lower right-hand
Personal Key. A Personal Key can be programmed as a Line Select Key. Line
appearances on your set may be used as separate telephone lines or shared
with other extension users. However, you cannot intrude on any conversation
that they are having without their permission, and they cannot intrude on any
conversation you are having without your permission.
Contact your System Administrator to have Line Select Keys programmed for
your set.
7
Page 8

Line Status Indicators
The Line Status indicators are located on the outside edge of each Personal Key.
These LED indicators show you the status of the lines which you have
programmed on your set.
If a Personal Key has been programmed as a Feature Key, the status indicator
for that key will turn on when the feature is activated, and turn off when the
feature is disabled.
When a line is... the status indicator is...
Idle off
Busy solid on
Ringing flashing slowly
On Hold at your set flashing rapidly
On Hold at another set flashing in a slow on, fast off cycle on your
set’s Line appearance
Feature Keys
A Personal Key can also be programmed as a Feature Key by your System
Administrator for quick access to an often-used feature. When that key is
pressed to turn on the feature, the status indicator for that key will turn on.
Contact your System Administrator to have Feature Keys programmed for your
set.
Main Display
The main display, located at the top of your 5020 IP phone, shows the SuperKey
instructions and Softkey labels. The Redial number, the name of the feature
currently active, messaging information, and telephone system error messages
can also be shown.
When your telephone is idle, the current date and time of day are displayed
continuously. But as soon as you make or receive a call, the display shows
information about that call, such as which line or trunk is being used, and the
duration of the call. This is useful when you are charging the cost of a call to a
customer or an account number.
8
Page 9

The SuperKey and Softkeys
Softkeys are the three keys located directly beneath the main display. You can
use the Softkeys to select the related prompt in the main display. These keys are
unlabeled because their functions can change as the prompts in the main display
change.
The SuperKey Function Key allows you to access the many features available
through the Softkeys. When you press the SuperKey the main display changes.
In particular, Softkey prompts on the screen change. Prompts appear only when
they can be used and if they are available to you.
To exit a SuperKey session, press the SuperKey once more.
Function Keys
The Function Keys are located just below the main display. A number of the 5020
IP phone features are accessed by using the Function Keys on your telephone.
1. Message Key: for sending and responding to messages.
2. Hold Key (red key): for placing calls on hold.
3. SuperKey (blue key): for programming Personal Keys as Speed Call
Keys, accessing most set features, and displaying set information.
4. Trans/Conf Key: for transferring calls and setting up conference calls.
5. Speaker Key: for answering and hanging up a call during hands free
mode.
6. Microphone Key: for turning the microphone on or off (a privacy
feature) during a handsfree call.
7. Redial Key: for redialling the last dialed number.
8. é
and ê Keys: for changing the volume of the handset receiver, the
volume and pitch of the ringer, and adjusting the contrast of the main
display.
9. Cancel Key: for canceling call features in progress.
9
Page 10

Feature Access Codes
Many features can be activated or disabled by Feature Access codes when no
Feature Keys are programmed for this purpose.
Contact your System Administrator for these and other Feature Access codes
available on your telephone system, or to have these features programmed into
your set’s Softkeys. Record your Feature Access codes in the Personal Directory
table at the end of this guide.
Features Not Available
There may be procedures in this guide which you cannot perform on your
telephone, and your display may not appear exactly as in the illustrations in this
guide. You may have additional functionality not described in this guide, or some
features described here may not be available to you. The reason for this is that
your company has specially selected your features and calling privileges. See
your System Administrator if you have any questions.
10
Page 11

ACD 2000 AGENT
FEATURES AND CAPABILITIES
11
Page 12

What are Agent Groups?
ACD Agents are normally grouped together to handle incoming telephone calls
that are associated with particular functions or departments in an organization;
for example, Sales or Engineering. Callers are then directed to the Group that
best serves their needs. The formation of ACD Agent Groups with two or more
Agents in each Group allows calls to be handled on a Group basis rather than on
an individual basis. An Agent can have multiple Agent ID’s, but Agents can only
have one Agent ID per group, and can only log in one Agent ID per telephone.
Agent Groups are assigned a unique 3-digit reporting number as well as an
Agent Group directory number. You will use both of these numbers as discussed
throughou t th is guide.
Agent Groups can be programmed to overflow between each other. This means
that if activated, calls that are directed to one Agent Group can be programmed
to overflow to other Agent Groups if the first Group was unavailable due to being
in an overload condition. This overflow capability allows ACD calls to be handled,
even though an Agent Group has been set in a Do Not Disturb mode.
You can have your set programmed to receive additional information concerning
Group activity. This information is called Queue Threshold Alert and Queue
Status.
The following Agent functionality is described in this section:
Logging In describes the procedure for logging in to a telephone programmed
for Automatic Call Distribution (ACD).
Displaying Agent Log-In Information describes the procedure for displaying
your Agent I.D. number for verification after logging in.
Logging Out describes the procedure for logging out from a telephone
programmed fo r AC D .
Answering Calls describes the procedure for answering ACD calls.
Using the Auto Answer Feature describes the feature which allows you to
answer calls automatically after one short ring.
Using a Headset describes the procedure for installing and programming a
headset for hands-free call answering.
Using and Canceling the Work Timer describes the purpose of the Work Timer
and the procedure for answering calls without waiting for the Timer to expire.
12
Page 13

Taking a Break from Calls (Make Busy Feature) describes the procedure for
placing your set in a pause mode when you need to be away from your set for
brief periods of time, without the need to log out and subsequently log in again.
Getting Help describes the procedure for requesting assistance from your
Supervisor during a call. The procedure for terminating a Help request is also
described.
Queue Threshold Alert / Queue Status describes alert indicators and means of
accessing queue information for regarding the status of the ACD Group (Queue)
into which you have logged.
13
Page 14

Logging In
Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) 2000 calls are directed to Logged In Agents
only. ACD calls are not directed to a telephone where there is no Agent Logged
In. You can log in by following the procedure described below.
An important concept in the ACD 2000 system for you to be aware of is agent
mobility. Since you as an Agent are assigned a 1- to 7-digit Identification (I.D.)
number to log in with, you can be called by this I.D. number, as well as by the
telephone extension number where you are working. This means that you can be
called by your I.D. number regardless of where you may be located. For this
reason it is also a good idea for your Agent I.D. number to be included in your
company’s telephone directory.
You can log in to only one Group at any one time. Check with your manager if
you do not know the ACD Log-In access code or do not have an I.D. number.
The Agent I.D. number is unique to each Agent, and allows the system to
distribute ACD calls to Logged In Agents. An Agent can stay logged in indefinitely
on the same telephone. You can also log in by using a special Feature Access
code not explained in this guide.
NOTE: If the I.D. is invalid, the display shows an INVALID error message
and the Log-In procedure is terminated.
If the I.D. is in use by another Agent, the display shows a USED BY error
message and your Log-In attempt is terminated.
If an Agent Log-In code is dialed, but no I.D. is entered within 60 seconds,
the Log-In procedure is not activated and your set is treated as a Logged
Out set.
After you have logged in, you can display your Log-In information. Refer to the
section ”Displaying Agent Log-In Information“ for further details.
14
Page 15

When You Are Ready to Log In
To log in, perform the following tasks:
1. Press the SuperKey Function Key. The prompt AGENT LOGIN?
Appears.
2. Press the Yes Softkey.
3. Enter your Agent I.D. code on the keypad.
After entering your I.D. code, your display shows the number you enter
along with a ç Softkey to correct any digits you entered incorrectly.
4. Press the Enter Softkey. You are now logged in. The display
momentarily shows the name of the Agent logging in (if programmed)
and the Agent's I.D. number.
After a few seconds, the display returns to idle, with any programmed
Softkey features appearing on the display.
15
Page 16

Displaying Agent Log-In Information
It is possible to display and verify Log-In information when you are logged in to a
set. The information displayed is the Agent I.D. number logged in to that set. This
is accomplished by the following tasks:
1. Press the SuperKey Function Key.
2. Press the No Softkey until PERSONAL KEYS appears on the display.
3. Press the Yes Softkey. The Agent Identification (I.D.) number
currently logged in will be displayed for 3 seconds
4. The prompt SELECT A KEY appears. You may select another Line
Select Key for similar information if the set has more than one line
appearance.
If you press your Prime Line Key, your display shows your Agent I.D.
number and your name (if programmed).
4. To exit, press the Cancel Function Key.
.
16
Page 17

Logging Out
Logging out returns the set to Make Busy and it no longer receives Automatic
Call Distribution (ACD) calls, since ACD calls are directed to Logged In
telephones only. Your set operates normally for non-ACD use when logged out.
Logging Out can be activated during a call in progress, and takes effect only
when you terminate (hang up) the call. This allows you to activate this feature
before your set can ring again for another call.
When You Are Ready to Log Out
To log out, perform the following tasks:
1. Press the SuperKey Function Key
2. Press the No Softkey to scroll until AGENT LOG OUT? appears on
the display.
3. Press the Yes Softkey. You are now logged out. After a few seconds,
LOGGED OUT appears on the display.
17
Page 18

Answering Calls
Answering ACD calls is not unlike answering regular calls on 5020 IP phone.
When the telephone rings, the indicator beside your Line Select Key flashes.
To answer the call, pick up the handset and begin speaking.
A headset option can be programmed into your system, eliminating the need to
pick up the handset. This is helpful in high call traffic situations normally
encountered in an ACD environment. To use a headset, refer to ”Using A
Headset“. You should also refer to ”Using the Auto Answer Feature“ for high
telephone traffic situations.
18
Page 19

Using the Auto Answer Feature
You may prefer to answer your calls automatically using the Auto Answer
feature, for either handset or headset operation. Once programmed, when you
receive a call you hear one short ring before being automatically connected to
the caller.
Never leave your telephone unattended while the Auto Answer feature is turned
on.
How to Activate Auto Answer
To activate the Auto Answer feature, perform the following tasks:
1. Press the SuperKey Function Key. Press the No Softkey to scroll until
AUTO ANSWER? appears on the display.
2. Press the Turn On Softkey. Auto Answer is now activated and AUTO
ANSWER appears on the display.
How to Deactivate Auto Answer
To deactivate Auto Answer, perform the following tasks:
1. Press the SuperKey Function Key. Press the No Softkey to scroll until
AUTO ANSWER? appears on the display.
2. Press the Turn Off Softkey. Auto Answer is deactivated and AUTO
ANSWER disappears from the display.
19
Page 20

Using a Headset
Note: Your system administrator may have enabled full-t ime headset operation
on your telephone. Telephones with full-time headset operation enabled must be
operated only with headsets.
Telephones that are not programmed for full-time headset operation will provide
a HEADSET key to allow you to switch between handset and amplified headset
(no feature control switch) operation.
Switching between handset and headset mode when using a Headset wit h
Feature Control Switch can be accomplished by connecting or disconnecting the
headset at the quick-disconnect plug on the headset cord, but you should also
disable headset operation if the handset will be used for an extended period of
time.
A headset can be used either in regular answer mode or with the Auto Answer
feature programmed.
Most headsets are installed using the same jack that the handset plugs into.
Mitel Networks Headsets with Feature Control Switch (PN 9132-800- 500NA/9132-800-501-NA) plugs into the dedicated headset jack (the jack nearest
the front of the set).
To Install a Headset (no Feature Control Switch)
To install the headset for your use, perform the following tasks:
1.When the telephone is not in use, lift the handset from the cradle and
carefully turn the set upside down.
2.Unplug the handset cord where it connects to the t elephone.
3.Plug in the headset cord in the same place.
4.Set the telephone upright and return the handset to the cradle
5.Press the Headset Feature Key.
6.Store your handset in a safe place.
20
Page 21

To return to handset operation, perform the following t asks:
1.When the telephone is not in use, lift the handset from the cradle and
carefully turn the set upside down.
2.Unplug the headset cord where it connects to the t elephone.
3.Plug in the handset cord in the same place.
4.Set the telephone upright and return the handset to the cradle.
5.Press the Headset Feature Key.
6.Store your headset in a safe place.
Handling Calls with a Headset (no Feature Control Switch):
To answer a call (when Auto Answer is disabled):
Press the flashing Line Select key.
To hang up:
Press the Cancel Function Key.
To Install a Headset with Feature Control Switch
IMPORTANT NOTE: Mitel Networks Headsets w ith Feature Control Switch
(PN 9132-800-500-NA/9132-800-501-N A) must be installed in the dedicated
headset jack (the jack nearest the front of the set). Installation will disabl e
your handset microphone. Disconnecting the headset at the jack or at the
quick-disconnect plug restores handset operation.
To install the headset for your use, perform the following tasks:
1.When the telephone is not in use, lift the handset from the cradle and
carefully turn the set upside down.
2.Plug the headset cord into the headset jack ( the jack nearest the front
of the set).
3. Set the telephone upright and return t he handset to the cradle.
4. Press the Headset Feature Key.
21
Page 22

To return to handset operation, perform the following tasks:
1. When the telephone is not in use, lift the handset from the cradle and
carefully turn the set upside down.
2. Unplug the headset cord where it connects to the telephone.
3. Set the telephone upright and return the handset to the cradle.
4. Press the Headset Feature Key.
5. Store your headset in a safe place.
Handling Calls with a Headset (with Feature Control Switch):
To answer a call (when Auto Answer is disabled):
Press the flashing Line Select key
-orQuickly press and release the Feature Control Switch.
To mute the headset microphone:
Press and hold the Feature Control Switch.
To hang up:
Press the Cancel Function Key
-orQuickly press and release the Feature Control Switch.
22
Page 23

Using and Canceling the W ork Timer
The Work Timer provides a delay after each ACD call, before the next call is
directed to you. This gives you a certain amount of time to compete any work
generated by the previous call.
The Work Timer is automatic and you are not required to perform any procedures
to activate it. The length of time provided by the timer varies from 0 to 600
seconds, and is programmed only by the System Administrator.
Work Timers apply to ACD Agents and ACD calls only. Other calls to and from
your set do not activate a Work Timer. If the Make Busy or Do Not Disturb
features are activated at your telephone, the Timer is cancelled for that call.
Once you terminate an ACD call, WORK TIMER appears on the display for the
duration of the Work Timer period.
When the Work Timer expires, WORK TIMER disappears from the display and
you are ready to take another call.
You have the option of canceling the Work Timer and accepting another call
before the Timer expires. Cancellation of the Timer affects only the next ACD
call.
To cancel the Work Timer, press the Cancel Function key. Your set displays the
normal screen and is now available for the next ACD call.
23
Page 24

Taking a Break from Calls
(Make Busy Feature)
The way to temporarily restrict your set from receiving calls is to activate the
Make Busy feature. The main purpose of Make Busy is to relieve you from your
Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) workload for relatively brief periods of time,
thereby avoiding the need to log out and subsequently log in again. Make Busy
ensures that an ACD set does not receive calls when you are unavailable. Make
Busy applies to only ACD sets and to only those stations that have logged in as
ACD Agents. Any set not logged in for ACD calls remains in the Make Busy state
until an Agent Log-In is performed.
Your 5020 IP phone operates as a normal telephone except for ACD use during
the Make Busy state. You can activate this feature during a call in progress. The
Make Busy state commences upon completion of that call. This allows you to
activate this feature before your set can ring again for another call.
How to Activate Make Busy
To activate the Make Busy feature, perform the following tasks:
1. Press the SuperKey Function Key. Press the No Softkey to scroll until
MAKE BUSY? appears on the display.
2. Press the Turn On Softkey. Your set displays MAKE BUSY until it is
deactivated.
How to Deactivate Make Busy
To deactivate the Make Busy feature, perform the following tasks:
1. Press the SuperKey Function Key. Press the No Softkey to scroll until
MAKE BUSY? appears on the display.
2. Press the Turn Off Softkey. Make Busy is now removed from your
set, and the display returns to idle.
24
Page 25

Getting Help
Whenever you are in a conversation on an Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) call,
you can request help from an ACD Supervisor. The type of help you receive
initially is to have the Supervisor silently monitor the conversation. The caller is
not aware that they are being monitored unless the Supervisor later decides to
initiate a three-way conference, which can be done at any time during the call.
If a Supervisor has not logged in with an Agent Identification (I.D.) code, the Supervisor’s
extension number must be dialed (when prompted to do so). If a Supervisor has logged in
with an Agent I.D. code, you can request help without having to know the location, by dialing
that Agent I.D. code (when prompted to do so).
A Supervisor’s I.D. code or extension number can be dialed by using either the
keypad or by having a Speed Call Key programmed for this purpose.
When You Need Help
To request help, perform the following tasks:
1. Press the SuperKey Function Key.
2. Press the No Softkey to scroll until HELP? appears on the display.
3. Press the Yes Softkey.
4. You will be prompted to enter the extension number of the Supervisor
you want.
Your help request is automatically cancelled if you do not enter digits
within 20 seconds. Digits dialed in error can be erased with the ç
Softkey.
The ç and Enter Softkey will appear after you start entering the digits.
3. Press the Enter Softkey. Your display shows the path name, then
updates to show originating party information, including the amount of
time that the caller has waited.
4. If the Supervisor is busy, the display shows BUSY (allowing you to
make another choice or to cancel your request for Help).
5. When the Supervisor answers, the display indicates HELP
accompanied by the Supervisor’s number or name.
If the Supervisor conferences into the call, a Split Softkey also appears.
6. When the Supervisor hangs up, the display returns to idle.
25
Page 26

Canceling Help
While waiting for the Supervisor to respond to your Help request, you can cancel
the Help request before it is answered by pressing the Cancel Function Key. This
cancels the request and you are prompted to enter a second help number, if
desired. Your Help request is automatically cancelled if you do not enter digits.
26
Page 27

Queue Threshold Alert
Thresholds are programmed into the ACD system to provide a basis for alerting
Agents and Supervisors that calls have waited longer than acceptable limits
(thresholds) to be answered.
If your set is programmed with a Generic Group Queue Status Feature Key, it
can provide a visual indication of the current workload conditions of the
Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) Group into which you are logged (Supervisors
may have two or more Specific Group Queue Status Feature Keys and
threshold alerts, allowing them to monitor activity in more than one Group). Your
set may also be programmed to provide an audible alert that Queue Status has
changed.
NOTE: Agents in the Logged Out, Do Not Disturb, or Make Busy states are not
considered active Agents for the purpose of Queue Threshold Alert.
Visual Indications
If your set is programmed to provide a visual alert, the indicator beside the
Queue Status Feature Key indicates the three levels of alert as follows:
a solid indicator beside the Line Select Key on your set indicates that
the workload is below the first threshold limit programmed
a slowly flashing indicator indicates that the workload is above the first
but below the second threshold limit programmed
a quickly flashing indicator indicates that the workload is above the
second threshold limit programmed.
Audible Indications
For sets programmed for audible indications, the system provides the following
different ringing patterns, depending on the threshold alert status:
a single ring occurs when the longest waiting caller exceeds the
programmed fir s t threshold time interval
a double ring occurs when the longest waiting caller exceeds the
programmed second threshold time interval
a single or double ring occurs when a previous threshold time interval
is reverted to (i.e., when the longest waiting call is answered and the
next longest waiting caller is in a different threshold level).
27
Page 28

Queue Status
Agents may access the following queue-status information about their Group
(Supervisors may query more than one Group):
the number of active Agents in the Group
the number of calls waiting for the Group (queue)
the length of time that the longest call has been waiting for the Group.
NOTE: Agents in the Logged Out, Do Not Disturb, or Make Busy states are not
considered active Agents for the purpose of Queue Status.
When You Need To Know A Group's Queue Status
If your set is programmed with a Generic Group Queue Status
Feature Key, press the key (for Supervisors, press the appropriate
Specific Group Queue Status Feature Key).
28
Page 29

ACD 2000 SUPERVISOR
FEATURES AND CAPABILITIES
29
Page 30

What is the Supervisory Position?
The Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) Supervisor position is for individuals who
are responsible for the supervision of one or more Agent Groups. All Supervisorrelated functions are programmed into the system by the System Administrator.
While Supervisors can log in as Agents to perform similar activities, they have
additional capabilities in order to support and monitor ACD Group activities. A
Supervisor need only log in if they are performing Agent activities to answer ACD
calls.
Several management and reporting statistics and information can be produced
by the 3300 ICP, but are beyond the scope of this guide. Supervisors should
consult with the System Administrator concerning the availability of other
management tools.
The following Supervisor functionality is described in this section:
Queue Threshold Alert / Queue Status describes the meaning of threshold
alert indicators and the means of accessing queue information for specific
groups.
Silent Agent and Group Monitoring describes the procedure for silently
listening to Agents’ calls, and lists the benefits of and restrictions to this feature.
Conferencing describes the procedure for joining into a three-way conversation
with an Agent and a caller under Silent Monitor.
Responding to Help describes the procedure for answering a Help request
made by an Agent.
System Reporting Capabilities briefly describes the two types of reports that
can be produced by the feature package. These reports can be used by
management to study the effectiveness of the ACD operation:
Real Time Events Records
Station Message Detail Recordings.
30
Page 31

Queue Threshold Alert / Queue Status
Supervisors may need to be alerted when any of two or more Agent Groups have
exceeded programmed limits. For this reason, Supervisors may have two or
more Specific Group Queue Status Feature Keys programmed on their set, each
dedicated to a different Group's activities. Their operation and the alerts
associated with them are the same as Generic Group Queue Status Feature
Keys, which are detailed in "Queue Threshold Alert" and "Queue Status" in the
Agent Features and Capabilities section of this guide.
31
Page 32

Silent Agent and Group Monitoring
Silent monitoring allows you to listen to conversations between Agents and ACD
callers, or between Agents and ACD callers in conference with a third party, in
one or more Agent Groups.
Benefits of Silent Monitoring
Silent monitoring can be done either with or without an Agent’s knowledge,
depending on how this feature was set up by your System Administrator. If Agent
notification has been programmed, the Agent you are monitoring will receive a
Conference tone at the start of the monitoring period. Agents can only be
monitored by one Supervisor at a time. When you are monitoring an Agent,
neither the Agent or the ACD caller can hear you. During Agent monitoring, you
can join into the conversation by initiating a ”Conference“ as described later in
this guide.
Restrictions to Silent Monitoring
While monitoring, you cannot be interrupted by previously-activated
features such as Camp On or Callback.
During monitoring, you temporarily lose Hard Hold, Soft Hold, and
Phonebook features.
A call cannot be transferred to you while you are monitoring.
An Agent who has a call on Soft Hold cannot be monitored.
You cannot commence Agent monitoring if you have a call on hold.
You cannot monitor calls that are directed to a recorded
announcement until the ACD caller has been answered by an Agent.
If you establish a conference during Silent Monitoring, you will not be
placed automatically in Silent Monitor mode once the conference has
ended. You must start over and re-establish Silent Monitoring
follow ing termi nation of th e Conferenc e.
If you are responsible for monitoring more than one Agent Group, you
must exit the Silent Monitor feature for the Group you are presently
monitoring and then re-establish it for the next Group you want to
monitor.
32
Page 33

Using Silent Monitoring for Individual Agents
Silent Monitoring can be performed on- or off-hook.
To establish this type of Silent Monitor, perform the following tasks:
1. Lift the handset and listen for dial tone, if off-hook operation is
desired. Otherwise, skip this step.
2. Press the Monitor Softkey.
3. Enter the Agent Identification (I.D.) Number or Extension number of
the Agent you want to monitor. When you start to enter the number, a
ç arrow appears. Use the ç Softkey to change incorrect entries.
If no conversation is taking place, you will hear silence, and the display
will show the Extension number followed by WAITING.
If a conversation is in progress, or begins, you will hear a conference tone
prior to the conversation, and the display will show the Extension number
and the Agent’s name.
When the conversation ends you receive Conference tone followed by
silence until the next conversation begins. To join the conversation being
monitored, refer to ”Conferencing“ later in this guide.
4. To exit Silent Monitoring, hang up your handset or press the Cancel
Function Key.
Using Silent Monitoring for Agent Groups
Silent Monitoring can be performed on- or off-hook.
To establish this type of Silent Monitor, perform the following tasks:
1. Lift the handset and listen for dial tone, if on-hook operation is
desired. Otherwise, skip this step.
2. Press the Monitor Softkey.
3. Enter the Agent Group Number you want to monitor. If no
conversations are taking place in the Group, you will hear silence and
the display will show the Group number, followed by WAITING.
33
Page 34

If a conversation is in progress or begins, you will hear Conference tone
prior to the conversation, and the display will show the Group number and
the name of the Agent.
When the conversation ends you will receive Conference tone followed by
silence until the next conversation begins. To join the conversation being
monitored, refer to ”Conferencing“ later in this guide.
You may monitor a different Agent in the Group by pressing the ç
Softkey. There is a brief period of silence between the removal of the first
monitor and the creation of the second. When the ç Softkey is pressed,
and there are no other conversations in the Group, you are returned to
the original conversation.
4. To exit Silent Agent Group Monitoring, hang up your telephone or
press the Cancel Function Key.
34
Page 35

Conferencing
This feature allows you to join into a conversation that is being monitored. You,
the Agent, and the ACD caller are joined in conversation. All parties hear the
Conference tone when you start the Conference.
Starting a Conference
1. Establish a Silent Agent or Group Monitor as explained in "Silent
Agent and Group Monitoring".
2. Press the Trans/Conf Function Key to join the conversation. Silent
Monitoring ends when the Conference begins.
3. To exit the Conference, hang up your telephone or press the Cancel
Function Key. Following termination of a Conference you must start
over and re-establish Silent Monitoring as described in "Silent Agent
and Group Monitoring".
35
Page 36

Responding to Help
As a Supervisor, Help requests are made to you by Agents under your
supervision. These Help requests are initially for you to silently monitor a
conversation in progress. Once you are monitoring your Agent and a caller they
are in conversation with, you have the ability to remove your Silent Monitor and
actively join the conversation in progress. You also have the option of
discontinuing the Silent Monitor mode that was established when you responded
to the Help request.
Help requests override any Call Forwarding, Do Not Disturb, or Re-routing that
may have been established on your set. A Help request does not respond to Call
Pickup from other sets.
If you are currently monitoring an Agent who requests Help from you, a delay of 5
seconds takes place at the Agent’s set prior to the Agent’s indication that Help is
in progress. This is done so that the Agent doesn’t necessarily know that
monitoring was in progress.
If you are monitoring an Agent that requests Help from a Supervisor other than
yourself, you receive a Conference tone, are temporarily removed from your
monitor status, and return to the WAITING display on your set. This Conference
tone indicates that this is not the normal completion of a call. When this Help
session is completed, the original monitor is re-created and you receive
Conference tone again to indicate that the active monitor condition has resumed.
If you have logged in as an Agent in addition to your supervisory role, Agents are
able to request Help from you without knowing your location by using your Log-In
I.D. number. This allows you to move freely from station to station. If you decide
to log out during a Help or Silent Monitor session, the Log Out does not affect the
session in any way until you hang up.
36
Page 37

What Happens in a Help Request
When you receive a Help request from an Agent, your set emits a triple ring.
HELP is displayed, followed by the Extension number and name (if programmed)
of the Agent requesting Help.
To respond to the Help request:
1. Pick up your handset. Your set automatically goes into Silent Monitor
mode and you hear the conversation in progress. HELP disappears
from your display, but the Extension number and name (if
programmed) rema i n s displayed.
At any time during monitoring, you can either initiate a Conference or exit
from the Help mode.
To initiate a Conference, press the Trans/Conf Function Key on your set.
The display shows CONFERENCE and Conference tone is sent to the
Agent only. You are now in Conference with the Agent and any other
callers they are speaking to.
NOTE: Split allows you to break the conference and redirect the call to another
party.
2. To exit from Help or Conference modes, hang up your telephone.
37
Page 38

System Reporting Capabilities
The 3300 ICP is capable of producing many reports that can be used as
management tools to study the effectiveness of the ACD operation. These
reports may be presented in a variety of ways based on the software package
used to generate them.
The categories of reports that pertain to ACD are Real Time Events Records and
Station Message Detail Recordings (SMDR). It is beyond the scope of this guide
to discuss these reports in detail, but a brief description of them is included to
summarize their intended use.
Time Events Records
Real Time Events Records are used to record the activity of the entire ACD
operation, and are available from the System Administrator. These records are
divided into two groups: Call Events and Group and Path Statistics Events. Call
Events report on individual ACD Agent activity, while Group and Path Statistics
Events provide a cumulative report on Group and Path status.
Call Events
As ACD Agent activities occur, a report is generated to show the following:
Work Timer Start Event: Indicates the start of the timer, for an agent’s
set with Work Timer programmed. Work timers are given only for
answering ACD 2000 calls.
Work Timer End Event: Signifies the end of the Agent’s Work Timer,
for both normal timer expiration, and timer cancelled by Agent.
Answer Personal Call: Signifies the Agent answering a personal call,
i.e., a non-ACD 2000 call.
Originate Call Event: Signifies the Agent entering a conversation.
Agent Idle Event: Signifies the Agent completing a personal call or, if
no Work Timer is programmed on the Agent’s set, any call.
Call Hold Event: Occurs when an Agent puts a call on Hard Hold.
Call Hold Retrieve Event: Occurs when an agent retrieves a call from
Hard Hold.
Call Hold Abandon Event: Occurs when an Agent’s held party clears
down (i.e., is answered) while on hold.
38
Page 39

Agent Log-In: Records each time an Agent successfully logs in.
Agent Log Out: Records each time an Agent successfully logs out.
Set Do Not Disturb (DND): Records each time a set is placed in the
DND state.
Remove DND: Records each time a set is removed from DND state.
Set Make Busy: Records each time a set is placed in Make Busy
state.
Remove Make Busy: Records each time a set is removed from the
Make Busy state.
Answering Incoming ACD Calls: Records each time an Agent answers
an ACD call that was directed to a Path, and includes the Agent I.D.
number, extension number and Path Reporting number
Agent Idle: Records the time when the Agent Work Timer expires or
was cancelled. If the Work Timer is not in effect, the end of each call
or the start of the Work Timer is recorded.
Path and Group Statistics Events
The Group and Path Statistics Events provide a cumulative report on Group and
Path status. The events are generated once every 15 seconds (less frequently
under high-traffic environments) for those Paths and Groups programmed to
report statistics events. One additional event, a Refresh Reports event, is
generated to signify the start of each new cycle of Path and Group Statistics
events.
Station Message Detail Recording (SMDR)
SMDR contains additional details about call re-routing and call transfer. The
following descriptions pertain to ACD-related SMDR reports:
Time to Answer: Records the total time to answer a call
Transferred Call s: Records each time a call was transferred
Digits Dialed Field: Records the ACD Path which was called, each
Group the call was presented to and the Group which answered the
call. Paths and Groups are identified by their reporting numbers within
the Digits Dialed field.
Called Party Field: Records the Agent ID of the Agent which
answered the ACD Path call.
39
Page 40

Personal Directory
Your Extension Number:____________________
Your Agent I.D. Number:____________________
Your Supervisor I.D. Number:________________
Your Group Name/Number:___________________
Use this table to record your frequently used numbers.
Name Number
Use this table to record the feature access codes you are most likely to need on
your telephone.
Feature Access Code
Auto Answer
Do Not Disturb
Headset Operation
Make Busy
40
Page 41

Notes
41
 Loading...
Loading...