Page 1

Resona 7/Resona 7CV/Resona 7EXP/Resona 7S/Resona 7OB
Diagnostic Ultrasound System
Service Manual
Revision 11.0
Page 2

Page 3

i
Table of Content
Table of Content .....................................................................................................................i
Revision History .....................................................................................................................I
Intellectual Property Statement ............................................................................................II
Applicable for .........................................................................................................................II
Statement ...............................................................................................................................II
Responsibility on the Manufacturer Party .........................................................................III
Customer Service Department ............................................................................................III
1 Safety Precautions ..................................................................................................... 1-1
1.1 Meaning of Signal Words ..................................................................................................... 1-1
1.2 Symbols ................................................................................................................................ 1-1
1.2.1 Meaning of Safety Symbols .......................................................................................... 1-1
1.2.2 Warning Labels ............................................................................................................. 1-2
1.2.3 General Symbols .......................................................................................................... 1-2
1.3 Safety Precautions ............................................................................................................... 1-4
1.3.1 Electric safety ............................................................................................................... 1-4
1.3.2 Mechanical safety ......................................................................................................... 1-5
1.3.3 Personnel Safety .......................................................................................................... 1-5
1.3.4 Other ............................................................................................................................. 1-5
2 Specifications ............................................................................................................. 2-1
2.1 Overview .............................................................................................................................. 2-1
2.1.1 Intended Use ................................................................................................................ 2-1
2.1.2 Introduction of Each Unit .............................................................................................. 2-1
2.1.3 Peripherals Supported .................................................................................................. 2-9
2.2 Specifications ....................................................................................................................... 2-9
2.2.1 Dimensions & Weight ................................................................................................... 2-9
2.2.2 Electrical Specifications ................................................................................................ 2-9
2.2.3 Environmental Conditions ........................................................................................... 2-10
2.2.4 Monitor Specification .................................................................................................. 2-10
3 System Installation ..................................................................................................... 3-1
3.1 Preparations for Installation.................................................................................................. 3-1
3.1.1 Electrical Requirements ................................................................................................ 3-1
3.1.2 Installation Conditions ..................................................................................................... 3-2
3.1.3 Confirmation before Installation .................................................................................... 3-3
3.2 Unpacking ............................................................................................................................ 3-3
3.2.1 Unpacking Process ....................................................................................................... 3-3
3.2.2 Checking ....................................................................................................................... 3-6
3.3 Bare Machine Transport ....................................................................................................... 3-7
3.3.1 Tool ............................................................................................................................... 3-7
3.3.2 Device Transport ........................................................................................................... 3-8
3.3.3 Fixing Methods ............................................................................................................. 3-8
3.4 Installing Main Unit ............................................................................................................. 3-11
3.4.1 Opening up the Monitor .............................................................................................. 3-11
3.4.2 Connecting the Power Cord ....................................................................................... 3-11
3.4.3 Connecting ECG ......................................................................................................... 3-12
Page 4

ii
3.4.4 Installing Probe Holder ............................................................................................... 3-12
3.4.5 Installing Gel Holder ................................................................................................... 3-12
3.4.6 Connecting the Transducer ........................................................................................ 3-14
3.5 Installing Peripherals .......................................................................................................... 3-15
3.5.1 Connecting a Footswitch ............................................................................................ 3-15
3.5.2 Installing a Graph / Laser Printer ................................................................................ 3-16
3.5.3 Installing Video Printer ................................................................................................ 3-18
3.5.4 Installing a Wireless Printer ........................................................................................ 3-19
3.5.5 Installing a Barcode Scanner ...................................................................................... 3-20
3.6 Ascending/descending the Main Control Panel Manually .................................................. 3-21
3.7 System Configuration ......................................................................................................... 3-24
3.7.1 Running the System ................................................................................................... 3-24
3.7.2 Entering Doppler ......................................................................................................... 3-24
3.7.3 System Preset ............................................................................................................ 3-25
3.7.4 Printer Preset .............................................................................................................. 3-26
3.7.5 Network Preset ........................................................................................................... 3-27
3.7.6 DICOM/HL7 Preset ..................................................................................................... 3-28
3.7.7 Check System Information ......................................................................................... 3-29
4 Product Principle ........................................................................................................ 4-1
4.1 General Structure of Hardware System ............................................................................... 4-1
4.2 Ultrasound Front Unit ........................................................................................................... 4-2
4.2.1 Probe Board .................................................................................................................. 4-3
4.2.2 TR Board ...................................................................................................................... 4-4
4.2.3 Engine Board ................................................................................................................ 4-5
4.2.4 ECG Module ................................................................................................................. 4-6
4.2.5 4D-TEE Board .............................................................................................................. 4-7
4.3 Ultrasound Back-end Unit .................................................................................................... 4-7
4.3.1 COME (CPU) module ................................................................................................... 4-8
4.3.2 Independent GPU (GPU) .............................................................................................. 4-8
4.3.3 Memory device (SSD&SATA hard disk) ........................................................................ 4-8
4.3.4 PC carrier board ........................................................................................................... 4-8
4.3.5 User I/O Interface Board ............................................................................................. 4-16
4.3.6 WiFi Module ................................................................................................................ 4-17
4.4 Power Supply Unit .............................................................................................................. 4-17
4.4.1 AC Interface Module ................................................................................................... 4-17
4.4.2 Auxiliary Output Power Isolation Transformer ............................................................ 4-18
4.4.3 AC-DC module ............................................................................................................ 4-18
4.4.4 DC-DC board .............................................................................................................. 4-18
4.4.5 PHV module ................................................................................................................ 4-18
4.5 New Power Supply Unit ..................................................................................................... 4-19
4.5.1 AC-DC module ............................................................................................................ 4-20
4.5.2 12V to 24V Control Board ........................................................................................... 4-20
4.5.3 DC-DC board .............................................................................................................. 4-20
4.5.4 PHV module ................................................................................................................ 4-20
4.6 User Interaction Unit........................................................................................................... 4-21
4.6.1 Control Panel .............................................................................................................. 4-21
4.6.2 Primary Display Assembly .......................................................................................... 4-22
4.6.3 Secondary Display Assembly ..................................................................................... 4-22
4.6.4 Electrical Ascending/Descending and Electromagnet ................................................ 4-23
5 Function and Performance Checking Method ......................................................... 5-1
Page 5

iii
5.1 NOTE ................................................................................................................................... 5-1
5.2 Device Status Checking ....................................................................................................... 5-1
5.2.1 Running Status ............................................................................................................. 5-1
5.2.2 Working Condition ........................................................................................................ 5-1
5.3 General Exam ...................................................................................................................... 5-2
5.3.1 Check Flow ................................................................................................................... 5-2
5.3.2 Checking Content ......................................................................................................... 5-2
5.4 Function Checking ................................................................................................................. 5-4
5.4.1 Check Flow ................................................................................................................... 5-5
5.4.2 Content ......................................................................................................................... 5-5
5.5 Performance Test ............................................................................................................... 5-11
5.5.1 Test Process ............................................................................................................... 5-11
5.5.2 Test Content ................................................................................................................ 5-11
6 Software Installation &Maintenance ......................................................................... 6-1
6.1 Entering Maintenance .......................................................................................................... 6-1
6.2 Set Installment ...................................................................................................................... 6-1
6.3 Software Installation/Restoration ......................................................................................... 6-4
6.4 Enter Windows ..................................................................................................................... 6-4
6.5 Software Maintenance .......................................................................................................... 6-5
6.5.1 Export Log .................................................................................................................... 6-5
6.6 Data Backup and Storage .................................................................................................... 6-5
6.6.1 Preset Data Management ............................................................................................. 6-5
6.6.2 Patient Data Backup and Restoration .......................................................................... 6-6
6.7 Introduction on Hard Disk's Partitions .................................................................................. 6-7
7 Adjustments ................................................................................................................ 7-1
7.1 Adjusting Monitor .................................................................................................................. 7-1
7.1.1 Adjusting Position ......................................................................................................... 7-1
7.1.2 Adjusting Brightness and Contrast ............................................................................... 7-3
7.1.3 Monitor Test .................................................................................................................. 7-3
7.2 Touch Screen Adjustment .................................................................................................... 7-6
7.2.1 Touch Screen Brightness and Contrast Adjustment ..................................................... 7-6
7.2.2 Touch Screen Test ........................................................................................................ 7-6
7.3 Control Panel Adjustment ..................................................................................................... 7-7
7.4 Adjusting Caster ................................................................................................................... 7-7
8 Field Replaceable Unit ............................................................................................... 8-1
9 Structure and Assembly/Disassembly ...................................................................... 9-1
9.1 Structure of the Complete System ....................................................................................... 9-1
9.2 Preparation ........................................................................................................................... 9-2
9.2.1 Tools Required .............................................................................................................. 9-2
9.2.2 Engineers Required ...................................................................................................... 9-2
9.2.3 Requirements ............................................................................................................... 9-2
9.3 Assembly/Disassembly ........................................................................................................ 9-3
9.3.1 Large/Small Probe Holders, Left Bracket of Coupling Gel Heating cup, Intracavitary Probe
Holder 9-4
9.3.2 Cup Rack Assembly...................................................................................................... 9-5
9.3.3 Wire Pothook Assembly ................................................................................................ 9-6
9.3.4 Mesh of the Base .......................................................................................................... 9-6
9.3.5 Display (monitor) Assembly .......................................................................................... 9-7
9.3.6 Control Panel Assembly ............................................................................................... 9-9
Page 6

iv
9.3.7 Handle Panel Assembly ............................................................................................. 9-20
9.3.8 Touch Screen Assembly ............................................................................................. 9-20
9.3.9 Speaker Cover Assembly ........................................................................................... 9-22
9.3.10 Left/Right Speaker Assembly ...................................................................................... 9-23
9.3.11 Upper/Lower Support Arm Cover ............................................................................... 9-23
9.3.12 Support Arm Assembly ............................................................................................... 9-24
9.3.13 LCD Signal Connector PCBA assembly ..................................................................... 9-25
9.3.14 Support Arm Spanner/Bale of Wire for the Monitor/Side Control Panel Base/Base
Assembly ................................................................................................................................. 9-26
9.3.15 Control Panel Moving Mechanism Assembly ............................................................. 9-29
9.3.16 Main Unit Rear Cover Assembly ................................................................................. 9-34
9.3.17 Main Unit Left Cover Assembly .................................................................................. 9-34
9.3.18 Main Unit Right Cover Assembly ................................................................................ 9-35
9.3.19 Main Unit Front-top Cover Assembly .......................................................................... 9-36
9.3.20 Turbine Cover ............................................................................................................. 9-37
9.3.21 Turbine Protective Shell Assembly ............................................................................. 9-37
9.3.22 Main Unit Top Cover/Main Unit Top Cover Assembly ................................................. 9-38
9.3.23 Right/Left Brake Pedal ................................................................................................ 9-39
9.3.24 Machine Assembly...................................................................................................... 9-40
9.3.25 PC Main Board Assembly ........................................................................................... 9-47
9.3.26 Wireless Net Adapter .................................................................................................. 9-51
9.3.27 Antenna and Cable Assembly .................................................................................... 9-52
9.3.28 IO Assembly ................................................................................................................ 9-53
9.3.29 Probe Board Assembly ............................................................................................... 9-54
9.3.30 Electronics Assembly on the Base ............................................................................. 9-55
9.3.31 HDD Assembly ............................................................................................................ 9-63
9.3.32 DVD Assembly ............................................................................................................ 9-64
9.3.33 Front Output panel ...................................................................................................... 9-66
9.3.34 ECG Assembly ............................................................................................................ 9-68
9.3.35 Signal Cable of ECG Module ...................................................................................... 9-68
9.3.36 Mother Board Assembly ............................................................................................. 9-69
9.3.37 Housing Assembly of the Main Unit ............................................................................ 9-72
9.3.38 Magnetic Generator Trolley ........................................................................................ 9-88
9.3.39 Magnetic Navigator ..................................................................................................... 9-91
10 Installing Options ..................................................................................................... 10-1
10.1 Installing Optional Software ................................................................................................ 10-1
10.2 Installation of Hardware Optional Function ........................................................................ 10-3
10.2.1 Magnetic Transmitter Trolley Assembly ...................................................................... 10-4
10.2.2 Probe Adapter Installation .......................................................................................... 10-6
10.2.3 Pencil Probe Signal Cable Assembly ......................................................................... 10-7
11 System Diagnosis and Support ................................................................................11-1
11.1 General Status Indicator ..................................................................................................... 11-1
11.1.1 Indicators on Control Panel ........................................................................................ 11-1
11.1.2 The Status Indicator of the Batteries on IO Rear Board ............................................. 11-1
11.1.3 Display Status Indicator .............................................................................................. 11-2
11.1.4 Status of Entire Device ............................................................................................... 11-2
11.2 Starting Process of the Whole Machine ............................................................................. 11-3
11.3 Alarming and Errors ........................................................................................................... 11- 4
11.3.1 The voltage of system power is abnormal .................................................................. 11-4
11.3.2 Abnormal Temperature ............................................................................................... 11-4
Page 7

v
11.3.3 Fan Error ..................................................................................................................... 11 -5
11.3.4 PHV Error ................................................................................................................... 11-5
11.3.5 4D Board Error ............................................................................................................ 11-6
11.3.6 Other Errors ................................................................................................................ 11-6
11.3.7 Error Code List ............................................................................................................ 11-7
11.4 Self Test ............................................................................................................................ 11-12
11.4.1 Self Test Introduction ................................................................................................ 11-12
11.4.2 Operation Procedures of Maintenance Self Test ...................................................... 11-12
11.4.3 User Self Test ........................................................................................................... 11-17
11.4.4 Test Report ............................................................................................................... 11-19
12 Care and Maintenance .............................................................................................. 12-1
12.1 Overview ............................................................................................................................ 12-1
12.1.1 Tools, Measurement Devices and Consumables ....................................................... 12-1
12.1.2 Routine Maintenance Items ........................................................................................ 12-1
12.2 Cleaning ............................................................................................................................. 12-3
12.2.1 System Cleaning ......................................................................................................... 12-3
12.2.2 Peripherals Cleaning .................................................................................................. 12-7
12.3 Check ................................................................................................................................. 12-8
12.3.1 General Check ............................................................................................................ 12-8
12.3.2 System Performance Check ....................................................................................... 12-8
12.3.3 Check for Peripherals and Optional Functions ........................................................... 12-9
12.3.4 Mechanical Safety Inspection ................................................................................... 12-10
12.3.5 Electrical Safety Inspection ...................................................................................... 12-12
13 Troubleshooting of Regular Malfunctions .............................................................. 13-1
13.1 System Cannot Power On .................................................................................................. 13-1
13.1.1 Related Modules or Boards ........................................................................................ 13-1
13.1.2 Key Points Supporting Troubleshooting ..................................................................... 13-1
13.1.3 Troubleshooting---System Cannot Power up ............................................................. 13-2
13.2 System Cannot Start .......................................................................................................... 13-3
13.2.1 Related Modules or Boards ........................................................................................ 13-3
13.2.2 Key Points Supporting Troubleshooting ..................................................................... 13-3
13.2.3 Troubleshooting—The System Cannot Start .............................................................. 13-3
13.3 Image Problems ................................................................................................................. 13-4
13.3.1 Related Modules or Boards ........................................................................................ 13-4
13.3.2 Key Points Supporting Troubleshooting ..................................................................... 13-4
13.3.3 Troubleshooting-Imaging ............................................................................................ 13-5
13.4 Probe Socket System Malfunction ..................................................................................... 13-6
13.4.1 Related Modules or Boards ........................................................................................ 13-6
13.4.2 Key Points Supporting Troubleshooting ..................................................................... 13-6
13.4.3 Troubleshooting of Probe Socket System .................................................................. 13-6
13.5 IO Interface System Failure ............................................................................................... 13-6
13.5.1 Related Modules or Boards ........................................................................................ 13-6
13.5.2 Key Points Supporting Troubleshooting ..................................................................... 13-7
13.5.3 Troubleshooting of IO Interface System ..................................................................... 13-8
13.6 Control Panel Failure ......................................................................................................... 13-9
13.6.1 Related Modules or Boards ........................................................................................ 13-9
13.6.2 Key Points Supporting Troubleshooting ..................................................................... 13-9
13.6.3 Troubleshooting of Control Panel ............................................................................... 13-9
13.7 LCD Display Failure ......................................................................................................... 13-10
13.7.1 Related Modules or Boards ...................................................................................... 13-10
Page 8

vi
13.7.2 Key Points Supporting Troubleshooting ................................................................... 13-10
13.7.3 Troubleshooting of the Monitor ................................................................................. 13-11
13.8 ECG Module Failure ......................................................................................................... 13-11
13.8.1 Related Modules or Boards ...................................................................................... 13-11
13.8.2 Key Points Supporting Troubleshooting ................................................................... 13-12
13.8.3 Troubleshooting for ECG Module ............................................................................. 13-12
13.9 4D Troubleshooting .......................................................................................................... 13-12
13.9.1 Related Modules or Boards ...................................................................................... 13-12
13.9.2 Key Points Supporting Troubleshooting ................................................................... 13-12
13.9.3 4D Drive Troubleshooting ......................................................................................... 13-12
Appendix A Electrical Safety Inspection .................................................................. A-1
Appendix B Phantom Usage Illustration ................................................................... B-1
Appendix C Description of Self Test Items ............................................................... C-1
Page 9
I
Revision History
Mindray may revise this publication from time to time without written notice.
Revision Date Reason for Change
1.0 2015.10
Initial release
2.0 2015.12
Change FRU order number.
3.0 2016.4
Change the order number of wireless net adapter.
4.0 2016.5
Add the installation of the Gel holder.
5.0 2016.7
Add the installation of Magnetic Generator Trolley.
6.0 2016.8
Change the warning labels.
7.0 2016.12
Change the description of the gel warmer.
8.0 2017.03
Add the installation of probe adapter, change the description of
the CW assembly.
9.0 2017.06
Add the installation of protective board.
10.0 2017.09
Change FRU number of PC board.
11.0 2018.5
Add the installation of AC Power Assembly (UR POWER).
© 2015-2018 Shenzhen Mindray Bio-medical Electronics Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Page 10

II
Intellectual Property Statement
SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO-MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO., LTD. (hereinafter called Mindray)
owns the intellectual property rights to this Mindray product and this manual. This manual may
referring to information protected by copyright or patents and does not convey any license under
the patent rights or copyright of Mindray, or of others.
Mindray intends to maintain the contents of this manual as confidential information. Disclosure of
the information in this manual in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Mindray
is strictly forbidden.
Release, amendment, reproduction, distribution, rental, adaptation, translation or any other
derivative work of this manual in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Mindray
is strictly forbidden.
,
, , , , BeneView, WATO,
BeneHeart, are the trademarks, registered or otherwise, of Mindray in China and other
countries. All other trademarks that appear in this manual are used only for informational or
editorial purposes. They are the property of their respective owners.
Applicable for
This service manual is applicable for the service engineers, authorized service personnel and
service representatives of this ultrasound system.
Statement
This service manual describes the product according to the most complete configuration; some of
the content may not apply to the product you are responsible for. If you have any questions, please
contact Mindray Customer Service Department.
Do not attempt to service this equipment unless this service manual has been consulted and is
understood. Failure to do so may result in personnel injury or product damage.
Page 11

III
Responsibility on the Manufacturer
Party
Mindray is responsible for the effects on safety, reliability and performance of this product, only if:
z All installation operations, expansions, changes, modifications and repairs of this product are
conducted by Mindray authorized personnel;
z The electrical installation of the relevant room complies with the applicable national and local
requirements;
z The product is used in accordance with the instructions for use.
Mindray's obligation or liability under this warranty does not include any transportation or other
charges or liability for direct, indirect or consequential damages or delay resulting from the improper
use or application of the product or the use of parts or accessories not approved by Mindray or
repairs by people other than Mindray authorized personnel.
This warranty shall not extend to:
z Any Mindray product which has been subjected to misuse, negligence or accident;
z Any Mindray product from which Mindray's original serial number tag or product identification
markings have been altered or removed;
z Any products of any other manufacturers.
Customer Service Department
Manufacturer: Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd.
Address: Mindray Building, Keji 12th Road South, High-tech industrial park,
Nanshan, Shenzhen 518057,P.R.China
Website: www.mindray.com
E-mail Address: service@mindray.com
Tel:
+86 755 81888998
Fax:
+86 755 26582680
WARNING:
It is important for the hospital or organization that employs this
equipment to carry out a reasonable service/maintenance plan.
Neglect of this may result in machine breakdown or injury of human
health.
Page 12

Page 13
Safety precautions1-1
1 Safety Precautions
This chapter describes important issues related to safety precautions, as well as the labels and
icons on the ultrasound machine.
1.1 Meaning of Signal Words
In this operator’s manual, the signal words DANGER, WARNING, CAUTION and
NOTE are used regarding safety and other important instructions. The signal words and their
meanings are defined as follows.
Please understand their meanings clearly before reading this
manual.
Signal word Meaning
DANGER
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation that, if not avoided, will
result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not avoided,
could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not avoided, may
result in minor or moderate injury.
NOTE
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not avoided, may result
in property damage.
1.2 Symbols
The following tables provide location and information of the safety symbols and warning labels,
please read carefully.
1.2.1 Meaning of Safety Symbols
Symbol Meaning
Type-BF applied part
The ultrasound transducers connected to this system are type-BF applied parts.
The ECG module connected to this system is Type-BF applied part.
"Attention"
indicates the points that you should pay attention to. Before using the
system, be sure to carefully read the relevant contents of this operator’s manual.
Page 14
1-2 Safety precautions
1.2.2 Warning Labels
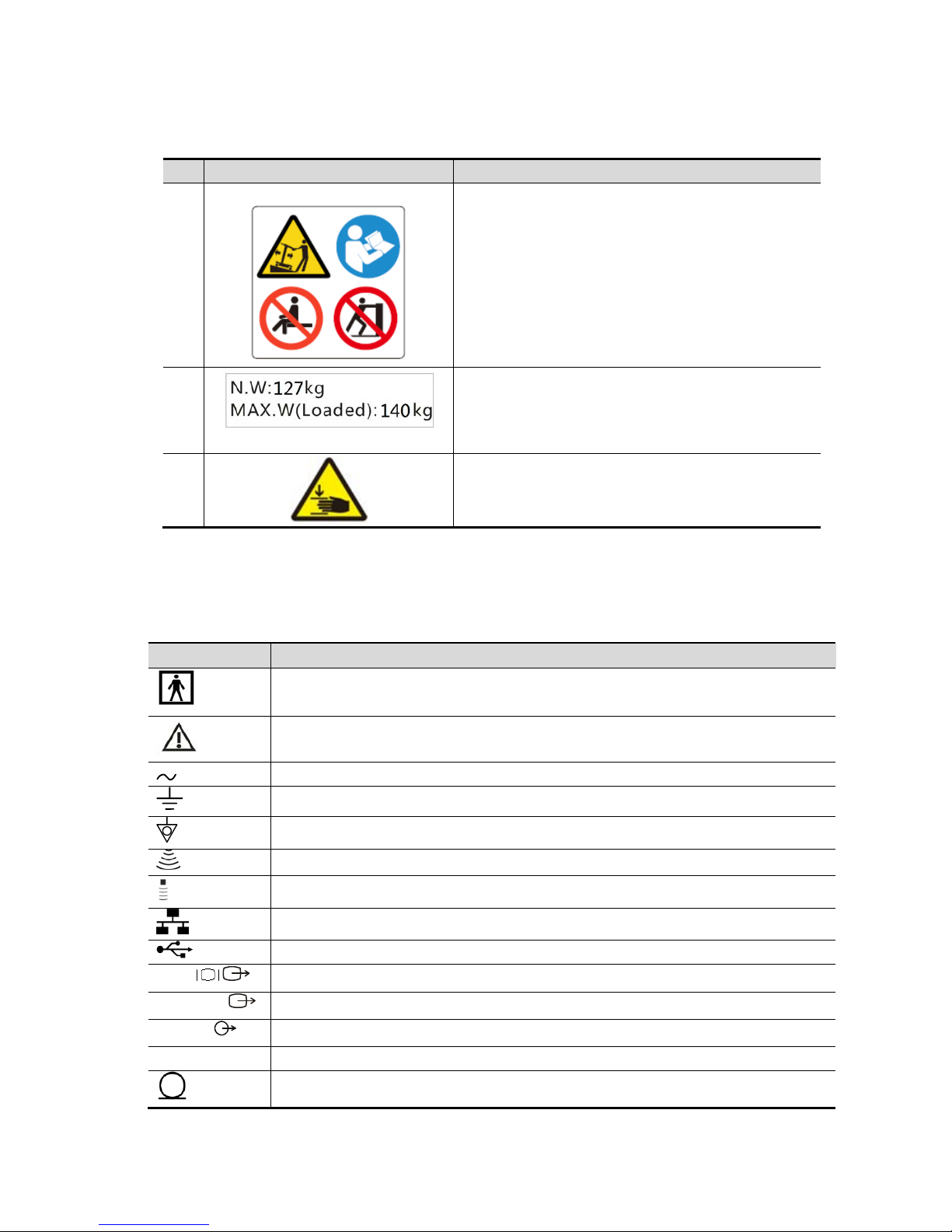
No. Warning Labels Meaning
1.
a. Do not place the device on a sloped surface.
Otherwise the device may slide, resulting in
personal injury or the device malfunction. Two
persons are required to move the device over a
sloped surface.
b. Do not sit on the device.
c. DO NOT push the device. When the casters are
locked.
2.
127kg:Main unit weight (not including the weight of
the probe)
140kg:The weight in total for main unit weight and
maximum load.
3.
Mind your hands.
1.2.3 General Symbols
This system uses the symbols listed in the following table, and their meanings are explained as
well.
Symbol Description
Type-BF applied part
Refer to the relevant content in the Operator’s Manual, to avoid safety incidents
AC (Alternating current)
Functional grounding
Equipotentiality
Transducer sockets
Pencil probe port
Network port
USB port
VGA
Used for VGA output.
S-VIDEO
Reserved, used for separate video output
AUDIO
Used for stereo audio output.
HDMI High definition multimedia interface.
Microphone input jack
a
b c
Page 15

Safety precautions1-3
Symbol Description
When the lever located at the bottom of the monitor supporting arm points to ,
you can move the monitor to the right and left.
When the lever located at the bottom of the monitor supporting arm points to
,
the supporting arm is fixed in the middle position.
Dangerous voltage
Product serial number
Manufacture date
Authorized representative in the European Community
This product is provided with a CE marking in accordance with the regulations stated
in Council Directive 93/42/EEC concerning Medical Devices. The number adjacent to
the CE marking (0123) is the number of the EU-notified body certified for meeting the
requirements of the Directive.
The radio device used in this product complies with the essential requirements
and other relevant provisions of Directive 1999/5/EC (Radio Equipment and
Telecommunications Terminal Equipment Directive). The product is in compliance
with ETSI EN 300 328 and ETSI EN 301 489.
Page 16
1-4 Safety precautions
1.3 Safety Precautions
Please read the following precautions carefully to ensure the safety of the patient and the operator
when using the probes.
DANGER
Do not operate this system in an atmosphere containing flammable
or explosive gases such as anesthetic gases, oxygen, and
hydrogen or explosive fluid such as ethanol because an explosion
may occur.
1.3.1 Electric safety
WARNING:
1.
Connect the power plug of this system and power plugs of the
peripherals to wall receptacles that meet the ratings indicated
on the rating nameplate. Using a multifunctional receptacle
may affect the system grounding performance, and cause the
leakage current to exceed safety requirements. Use the power
cord accompanied with the system provided by Mindray.
2.
Disconnect the AC power before you clean or uninstall the
ultrasound machine, otherwise, electric shock may result.
3.
When using peripherals not powered by the auxiliary output of
the ultrasound system, or using peripherals other than permitted
by Mindray, make sure the overall leakage current of peripherals
and the ultrasound system meets the requirement of the local
medical device electrical regulation (like enclosure leakage
current should be no more than 500uA of IEC 60601-1-1), and the
responsibility is held by the user.
4.
In maintenance or assembly/disassembly, make sure other
cables are connected well before the battery connecting cable
is connected, otherwise the system may be damaged due to
hot-plug.
5.
Do not use this system simultaneously with equipment such
as an electrosurgical unit, high-frequency therapy equipment,
or a defibrillator, etc.; otherwise electric shock may result.
6.
This system is not water-proof. If any water is sprayed on or
into the system, electric shock may result.
CAUTION:
1.
DO NOT connect or disconnect the system’s power cord or its
accessories (e.g., a printer or a recorder) without turning OFF
the power first. This may damage the system and its
accessories or cause electric shock.
2.
Avoid electromagnetic radiation when perform performance
test on the ultrasound system.
3.
In an electrostatic sensitive environment, don’t touch the
device directly. Please wear electrostatic protecting gloves if
necessary.
Page 17
Safety precautions1-5
4.
You should use the ECG leads provided with the ECG module.
Otherwise it may result in electric shock.
1.3.2 Mechanical safety
WARNING:
1.
Before moving the system, please hold the handle. If other parts
of the system are held, it may cause damage due to the
abnormal force. Do not push the system from the left/right side;
otherwise, it may be toppled over.
2.
Do not subject the transducers to knocks or drops. Use of a
defective probe may cause electric shock to the patient.
CAUTION:
1.
Fasten and fully secure any peripheral device before moving
the system, gently and carefully move the system to avoid
falling over.
2.
Do not expose the system to excessive vibration (during the
transportation) to avoid device dropping, collision, or
mechanical damage.
3.
Please install the system on a flat plane with the four casters
locked. Otherwise, damage may be resulted by accidental
moving.
4.
Pay extra attention when moving the system on a sloping
ground, do not move it on a more than 10°-sloped plane to avoid
system toppling.
5.
Move the system ONLY WHEN the system is shut down or in
standby status, otherwise the system hardware disk may be
damaged.
1.3.3 Personnel Safety
NOTE:
1.
The user is not allowed to open the covers and panel of the system, neither
device disassemble is allowed.
2.
To ensure the system performance and safety, only Mindray engineers or
engineers authorized by Mindray can perform maintenance.
3.
Only technical professionals from Mindray or engineers authorized by Mindray
after training can perform maintenance.
1.3.4 Other
NOTE:
For detailed operation and other information about the ultrasound system, please
refer to the operator’s manual.
Page 18

Page 19
Specifications 2-1
2 Specifications
2.1 Overview
2.1.1 Intended Use
The Resona 7/Resona 7CV/Resona 7EXP/Resona 7S/Resona 7OB series diagnostic ultrasound
system is intended for use in clinical ultrasonic diagnosis.
2.1.2 Introduction of Each Unit
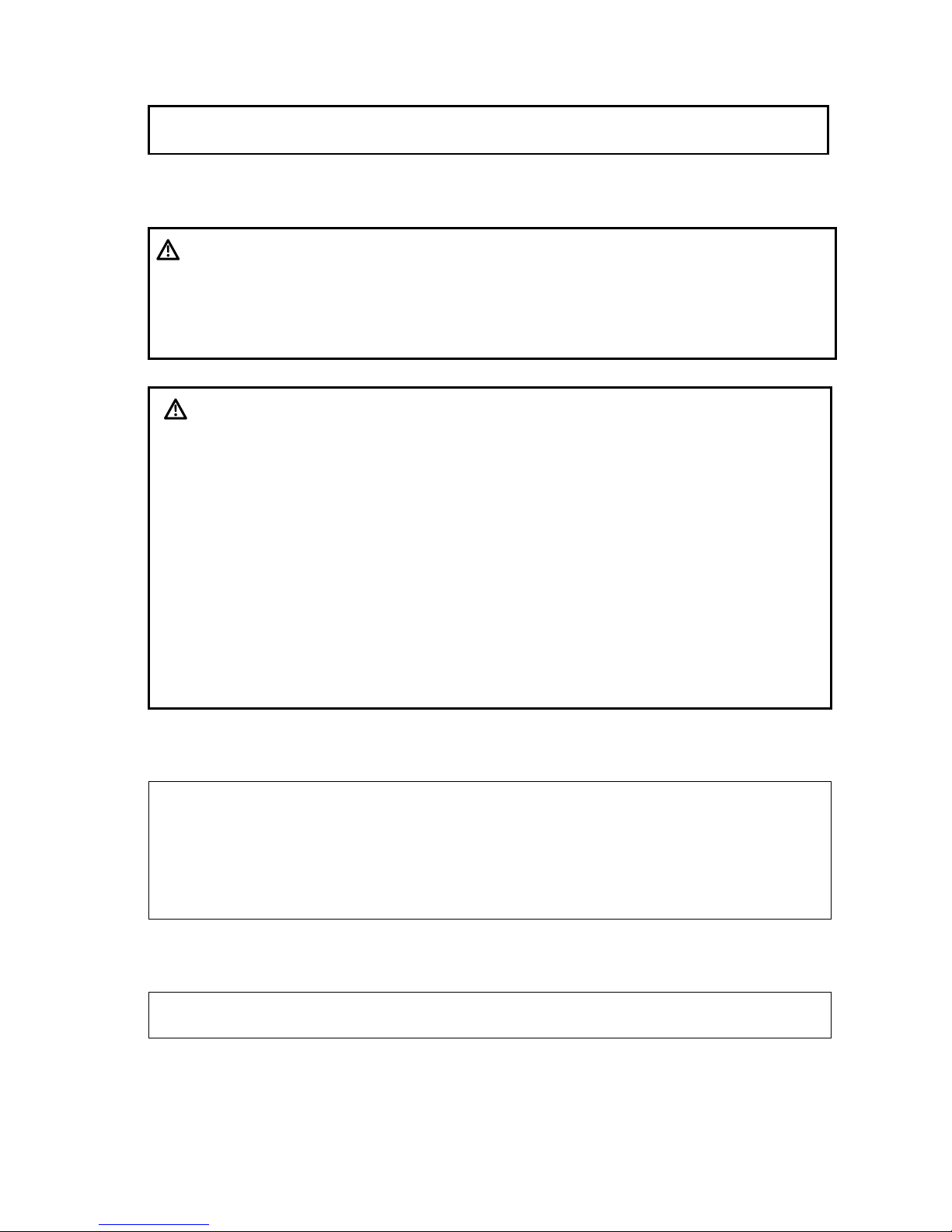
No. Name Function
<1> Monitor
Displays the images and parameters during scanning.
<2> Touch Screen
Screen-touching operator-system interface or accessible to
control.
<3> Speaker Outputs the audio.
<4> Power button Used for powering on/ off the power supply.
Page 20
2-2 Specifications
No. Name Function
<5> DVD driver DVD reading and writing
<6> Front-in panel Connected to ECG leads and USB drive, etc.
<7> Probe port Sockets connecting transducers and the main unit.
<8> Caster Used for moving the system.
<9> Central brake
Used for securing the system or moving the system straight
forward.
Step on the left brake pedal to lock the device from being
moved.
Step on the right walking pedal to move the device straight.
<10>
Intracavitary probe
holder
Used for placing the probe.
<11>
Rotatable knob on the
control panel
Lock or unlock the movement of the control panel
<12>
Ascending/descending
button
The button to ascending or descending the system.
<13> Control panel
Key- pressing operator-system interface or accessible to
control
<14> Transducer (gel) holder Used for placing transducers and gel temporarily.
<15> Monitor support arm
Supports the monitor, for adjusting the angle of LCD
monitor.
<16>
The control panel
stretch mechanism
Used for stretching or rotating the control panel.
Note: subject to the Control Panel Moving Mechanism
Assembly when the user purchases the product.
<17>
Motor-driven lift
mechanical assembly
Used for adjusting the height of the control panel
<18>
The back handle of
main unit
Used for winding the cables up and assisting for moving the
system.
<19> I/O Panel Port panel for input and output signals.
<20>
Power supply assembly
for the system
Provides the power to the system.
Page 21
Specifications 2-3
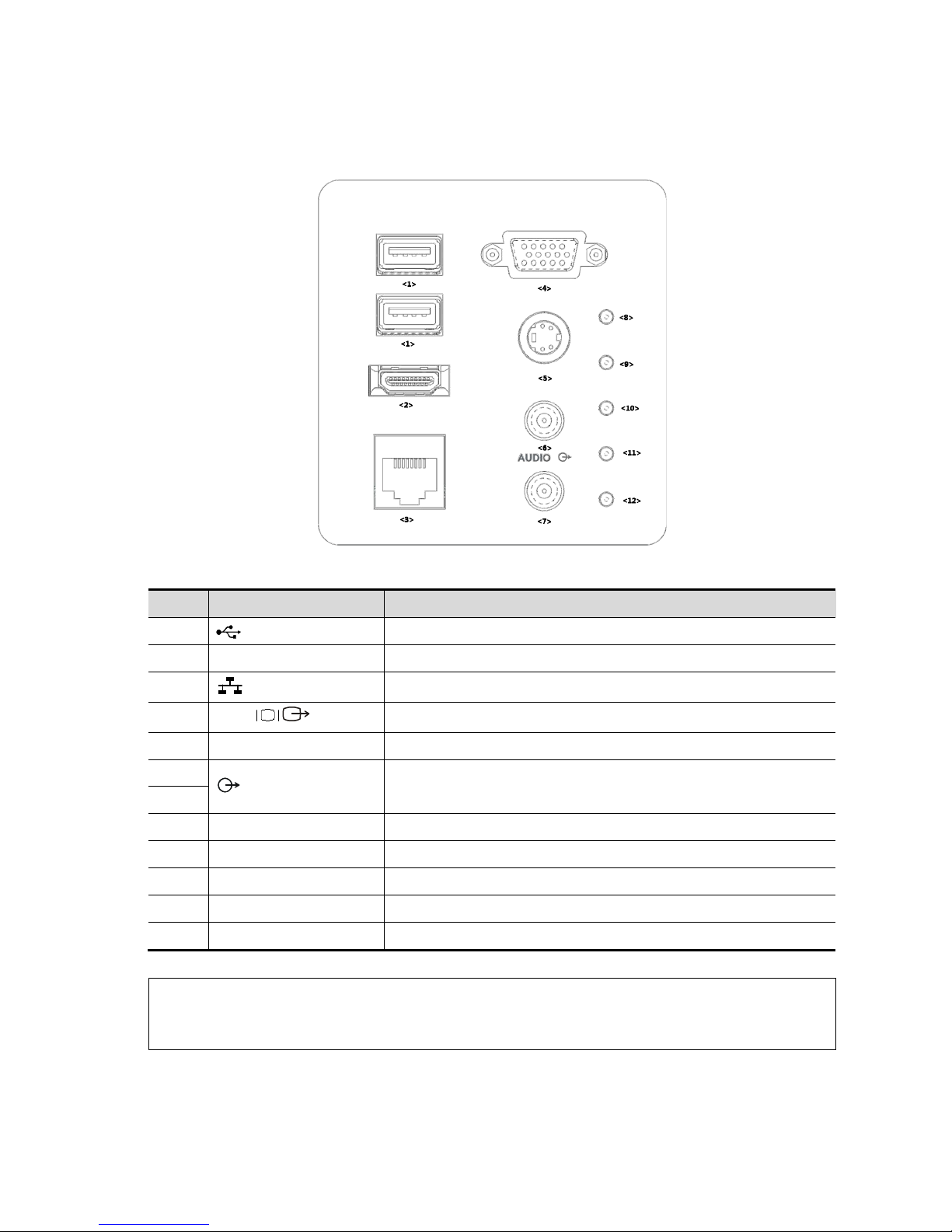
2.1.2.1 I/O panel
No. Symbol Function
<1>
USB ports.
<2> HDMI High definition multimedia interface.
<3>
Network port.
<4>
VGA
VGA signal output.
<5> S-Video Used for separate video output.
<6>
Audio signal output port, left channel.
Audio signal output port, right channel.
<7>
<8> / 12V power indicator
<9> / 5V power indicator
<10> / 3.3V power indicator
<11> / LVDS_OK indicator
<12> / PHV protection indicator (reserved)
NOTE: 1. The S-VIDEO port performs better with analog video printing.
2. When connecting an external video device (HDMI/VGA), make sure the display
resolution setting is 1920x1080, otherwise the image quality may be degraded.
Page 22
2-4 Specifications
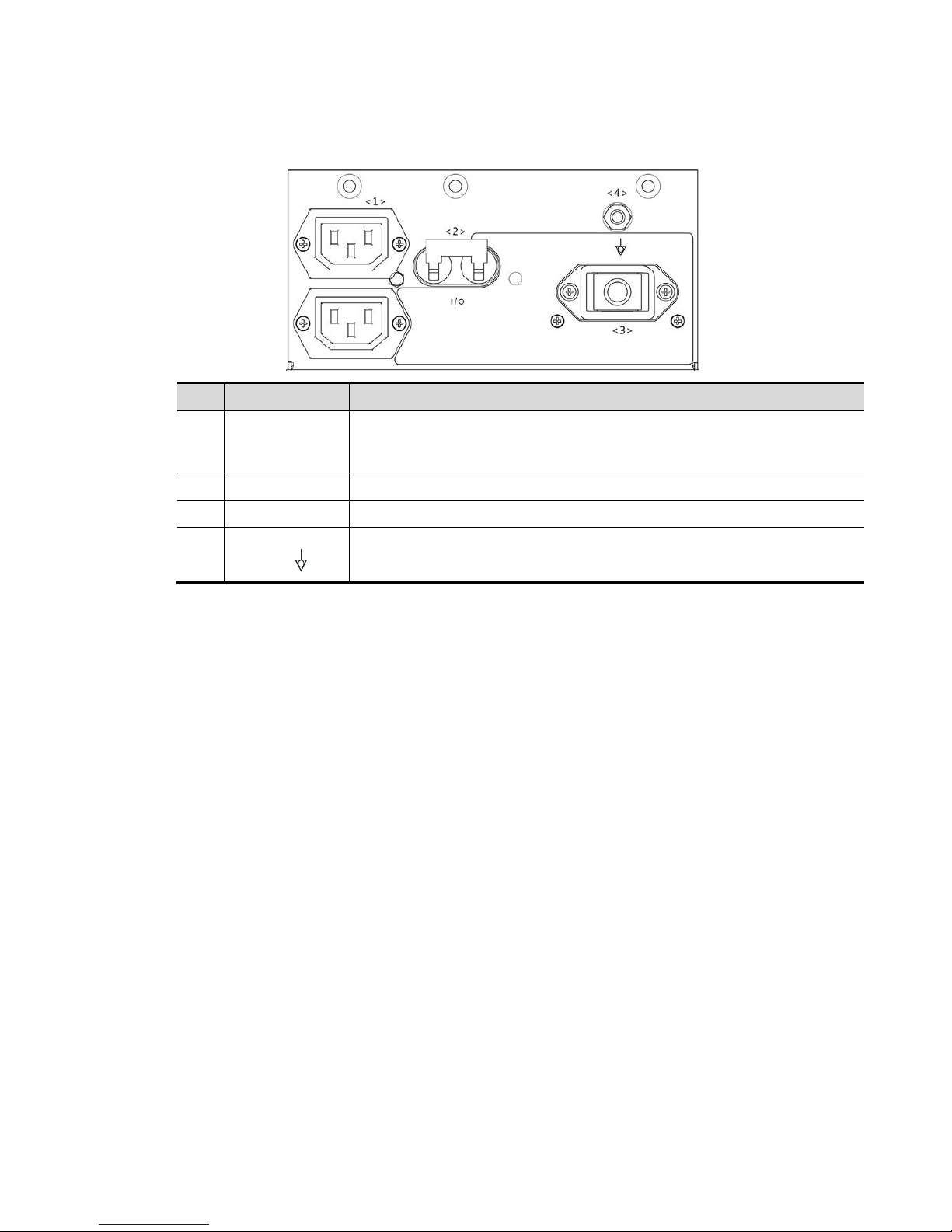
2.1.2.2 Power Supply Panel
No. Name Function
<1>
Alternative
current auxiliary
output
Supply power for optional peripheral devices.
<2> Circuit breaker Used for switching off/ on the power supply.
<3> Power inlet AC power inlet
<4>
Equipotential
terminal
Used for equipotential connection, that balances the protective earth
potentials between the system and other electrical equipment.
Page 23
Specifications 2-5
2.1.2.3 Physio Panel
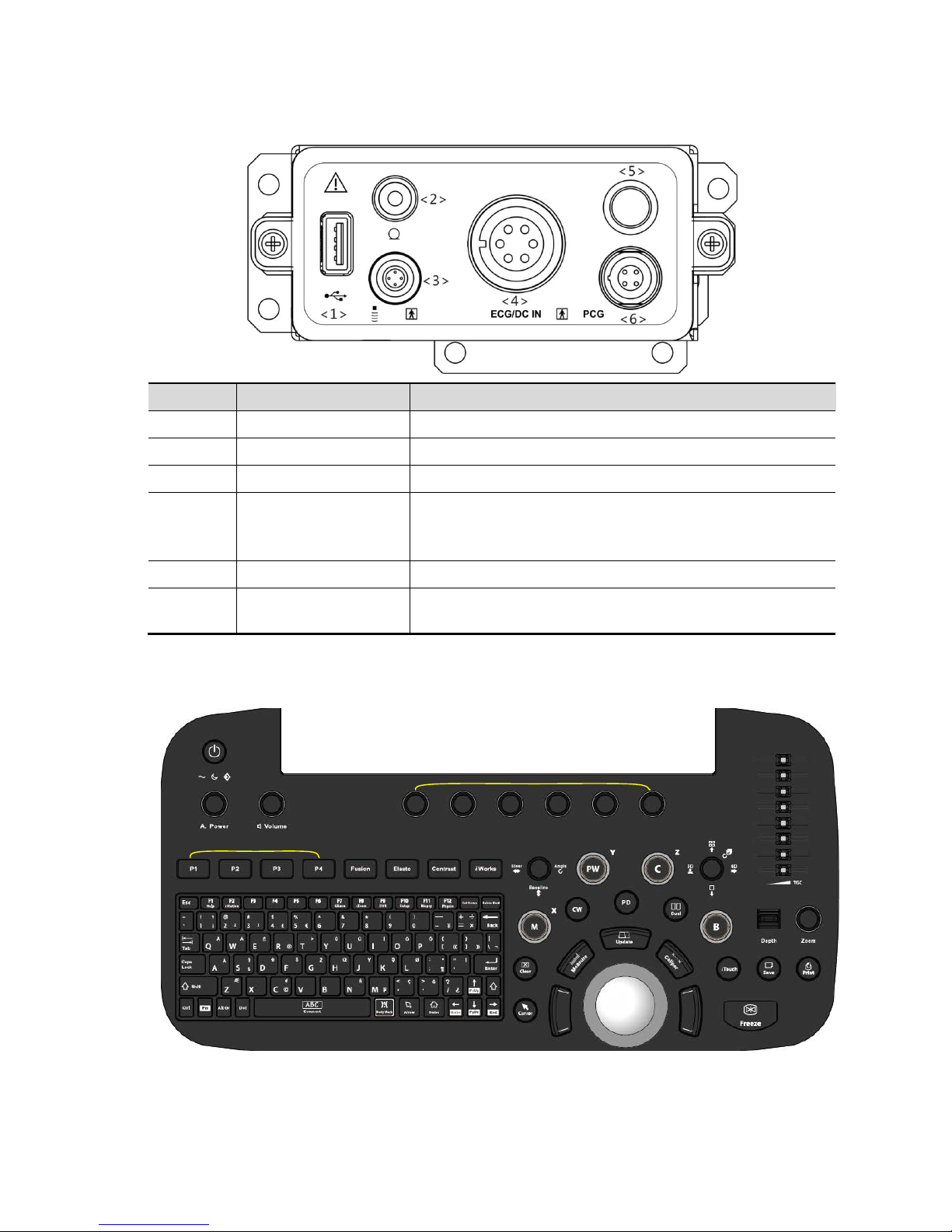
2.1.2.4 Control Panel
No. Name Function
<1> USB port Connects USB devices.
<2> MIC interface Microphone input
<3> Pencil probe port Used for connecting a pencil probe.
<4>
ECG lead signal input
port / external ECG
signal input port
Connects to ECG leads, to directly obtain the ECG signals of
the patient.
Connects the signal output port of ECG monitoring device.
<5> Reserved port Reserved feature.
<6> PCG signal input port
Connects to PCG transducer, to directly obtain the PCG
signals of the patient.
<1>
<2>
<3>
<4>
<8>
<9>
<6>
<7>
<5>
<10>
<11>
<12>
<13>
<14>
<15>
<16>
<17>
<18>
<19>
<20>
<21>
<22>
<23>
<24>
<25>
<26>
<27>
<28>
<29>
<30>
<31>
<32>
<33>
Page 24
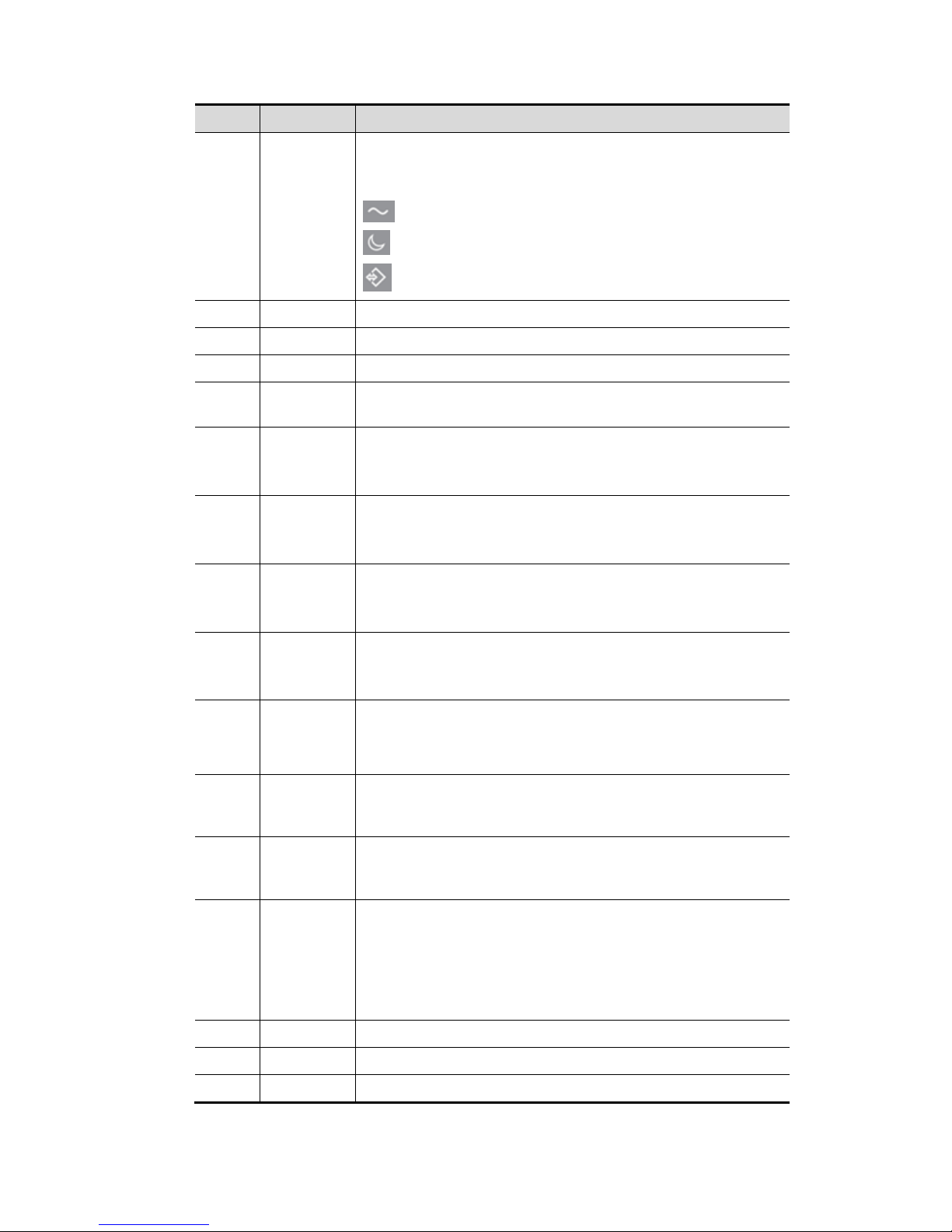
2-6 Specifications
No. Name Description
<1> /
Power button
Press the button to turn on the system, the system enters the
work status and the indicator becomes green.
AC (Alternating current). It turns on at AC supply.
Standby. It becomes orange in standby status.
Hard disk indicator. It blinks when reading/writing the disk.
<2> A.power Adjust the acoustic power.
<3> Volume /
<4> / Adjust the corresponding functions on the touch screen.
<5> P1-P4
Undefined Button, set by the user in the Preset. See the
operator’s manual [Basic Volume] for details.
<6> Fusion
Enter fusion. Or
Undefined Button, set by the user in the Preset. See the
operator’s manual [Basic Volume] for details.
<7> Elasto
Enter elastography. Or
Undefined Button, set by the user in the Preset. See the
operator’s manual [Basic Volume] for details.
<8> Contrast
Enter contrast imaging. Or
Undefined Button, set by the user in the Preset. See the
operator’s manual [Basic Volume] for details.
<9> iWorks
Enter iWorks. Or
Undefined Button, set by the user in the Preset. See the
operator’s manual [Basic Volume] for details
<10> /
Press: to set the Baseline
Rotate: to set the Scale
Slide: to set the Steer
<11> PW
Press to enter PW mode, and rotate to adjust PW gain (in PW
mode) or CW gain (in CW mode); while in 3D/4D mode, rotate
the knob to cycle the 3D image through Y axis.
<12> C
Press to enter Color mode, and rotate to adjust Color gain (in
color mode) or Power gain(in Power mode); while in 3D/4D
mode, rotate the knob to cycle the 3D image through Z axis.
<13> /
Press: to enter 3D
Slide right: to enter 4D
Slide upwards: to enter quad-split display
Slide downwards: to enter dual-split display
Rotate: to switch the view
<14> TGC Slide to adjust the depth gain.
<15> Cursor Display/hide the cursor.
<16> Clear Remove the comments or measurement caliper.
Page 25
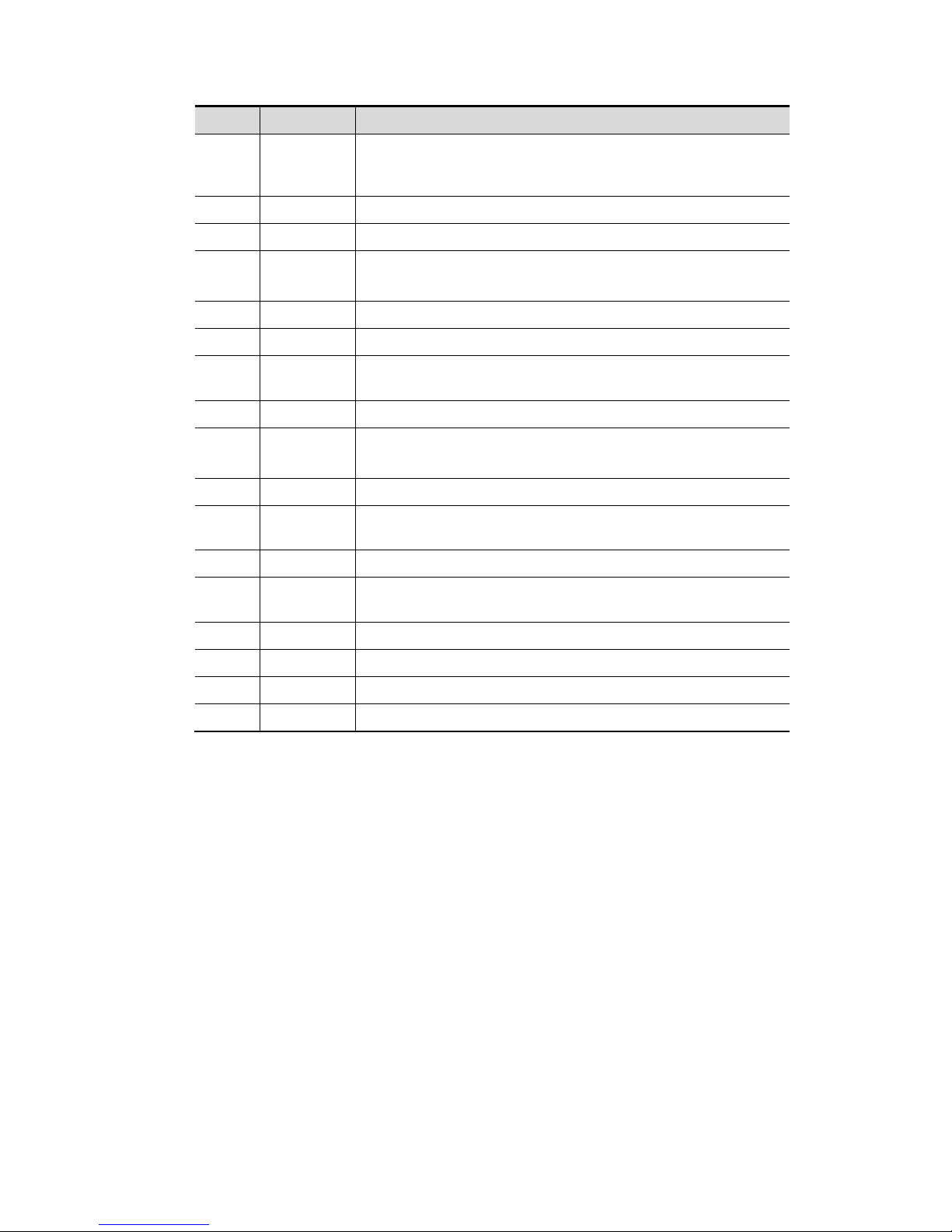
Specifications 2-7
No. Name Description
<17> M
Enter M mode, and rotate to adjust M mode gain. While in
3D/4D mode, rotate the knob to cycle the 3D image rotate
through X-axis.
<18> CW Enter CW mode.
<19> Power Enter Power mode.
<20> Dual
Enter Dual mode in Non-Dual mode.
Press to switch between the two interfaces in the Dual mode.
<21> B Press: to enter B mode; Rotate: to adjust B mode gain.
<22> Depth Adjust the depth in real-time imaging.
<23> Zoom
Rotate to enter the pan-zoom mode, and press to enter the
spot-zoom mode.
<24> Measure Enter/exit the application measurement mode.
<25> Update
Switching key: Press to change the currently active window.
Start/stop image acquisition in iScape or 3D/4D mode.
<26> Caliper Enter/exit the general measurement mode.
<27> /
Confirm an operation. The function is same with the
left-button of the mouse.
<28> / Move the trackball to change the cursor position.
<29> /
Confirm an operation. The function is same with the
left-button of the mouse.
<30> iTouch Press to optimize the images.
<31> Save Save the image; user-defined key.
<32> Print Print: user-defined key.
<33> Freeze Freeze/defreeze the image.
NOTE: “/” means the key is undefined or has no silk print. For the undefined keys, you can
customize them.
Page 26
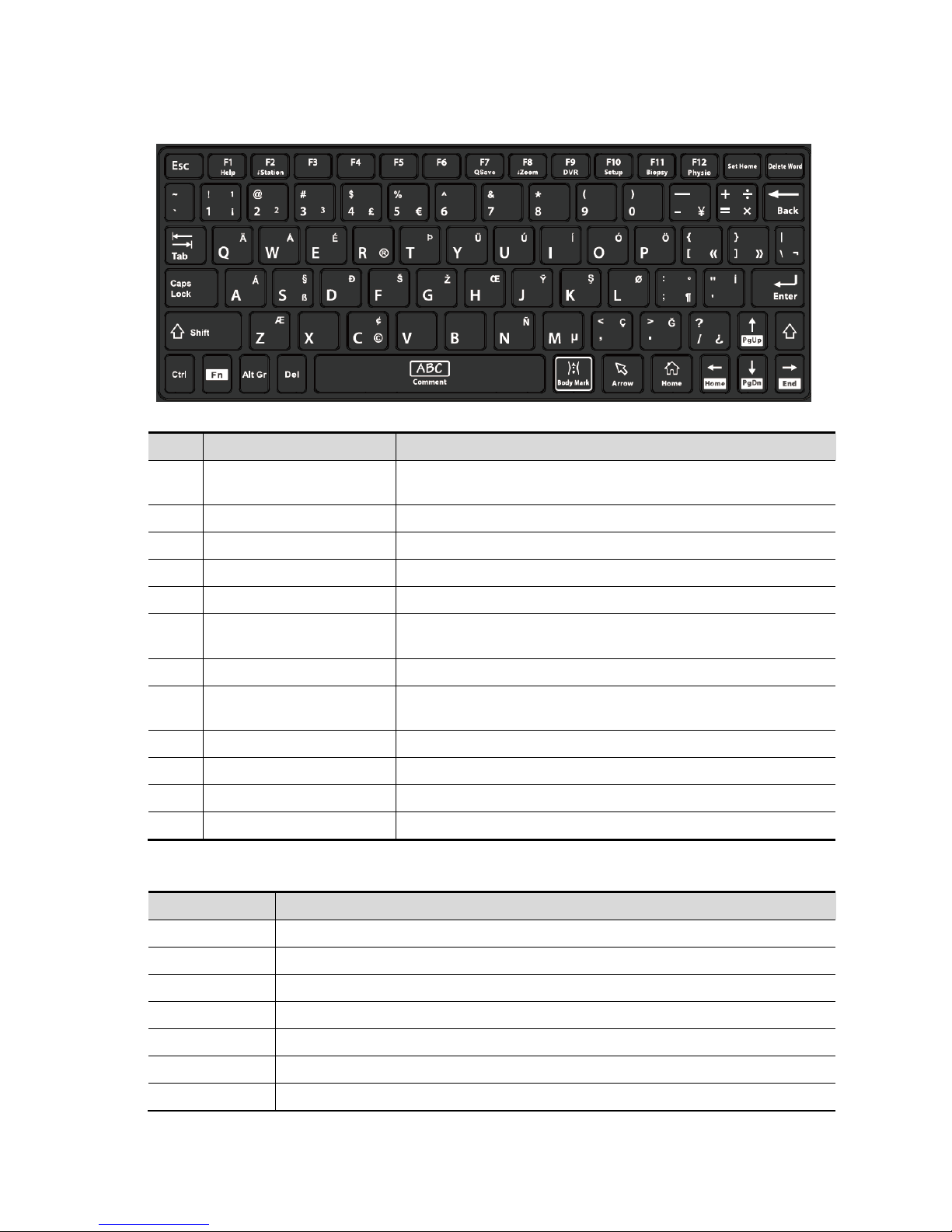
2-8 Specifications
Keyboard
Common functional keys
No. Key Description
1. Enter
Confirms the input data; or moves the cursor to the head of
next row of the text or the input field.
2. Esc Cancel or quit the operation.
3. Tab Go to the next operation item.
4. Space or comment Insert a space or input the comment
5. Caps Lock Switch the upper/ lower case.
6. Home
Activate the Home function: return to the start position of
comment.
7. Delete Text Delete all comments on the screen.
8. Direction keys
Move the cursor one letter each time; or, select the ambient
one in a selectable area.
9. Arrow Press the key to turn to the symbol of arrow.
10. Body Mark Press the key to enter the body mark.
11. Back Space Delete the character before the cursor
12. Del Delete the character after the cursor
Functions of the F1 to F12 keys
Key Function
F1 Help Open or close the accompanying help documents.
F2 iStation Enter or exit the Patient Info system.
F3~F6 User-defined keys, the functions of which can be preset.
F7 QSave Save the current image parameters quickly.
F8 iZoom Enter/exit full-screen zoom status.
F9 DVR Enter VCR/DVR mode.
F10 Setup Enter/exit Setup.
Page 27
Specifications 2-9
Key Function
F11 Biopsy Display/hide the guide line.
F12 Physio Enter Physio mode.
For user-defined keys, please refer to the operator’s manual [Basic Volume].
2.1.3 Peripherals Supported
Type Model
Graph/text printer HP Officejet 7000 wide format, HP Officejet Pro 8100
Black/white video
printer (digital)
MITSUBISHI P95D
SONY UP-D897
SONY UP-D898MD
Digital color video
printer
SONY UP-D25MD
Black/white video
printer (analog)
SONY UP-X898MD
Photo printer Cannon SELPHY CP800
Barcode reader SYMBOL LS2208 (1D), SYMBOL DS6707-SR
Footswitch
Wired: 971-SWNOM (2-pedal, 3-pedal)
Wireless: Steute (2-pedal, 3-pedal)
Note: the printer driver is preinstalled in the system. Please install other printer drivers for other
types of the printers.
2.2 Specifications
2.2.1 Dimensions & Weight
External dimension: depth: 945±10mm; width: 545±10 mm (main unit)/510±10mm (control panel);
height: 1360±10 mm (with the display vertical).
Weight: less than 135 Kg (not including the weight of the probe).
2.2.2 Electrical Specifications
2.2.2.1 AC Input
Voltage
220-240~ 100-127V~
Frequency 50/60Hz
Power consumption 1000VA
Page 28

2-10 Specifications
2.2.3 Environmental Conditions
Operating conditions Storage and transportation conditions
Ambient temperature 0°C~40°C -20°C~55°C
Relative humidity 20%~85% (no condensation) 20%~95% (no condensation)
Atmospheric pressure 700hPa~1060hPa 700hPa~1060hPa
Warning:
Do not use this system in the conditions other than those
specified
2.2.4 Monitor Specification
2.2.4.1 Main Monitor
2.2.4.2 Touch Screen
Size 21.5 inches
Voltage 12 V
Resolution 1920×1080
Visible angle ≥170°
Size 12.1 inches
Voltage 12 V
Resolution 1280×800
Visible angle ≥140°
Page 29
System Installation 3-1
3 System Installation
3.1 Preparations for Installation
NOTE:
Do not install the machine in the following locations:
Locations near heat generators;
Locations of high humidity;
Locations with flammable gases.
3.1.1 Electrical Requirements
3.1.1.1 Requirement of Regulated Power Supply
Power specification is showing in chapter 2.2.2. Due to the difference of the power supply
stability of different districts, please advise the user to adopt a regulator of good quality
and performance such as an on-line UPS.
3.1.1.2 Grounding Requirements
The power cable of the system is a three-wire cable, the protective grounding terminal of
which is connected with the grounding phase of the power supply. Please ensure that the
grounding protection of the power supply works normally.
WARNING:
DO NOT connect this system to outlets with the same
fuses that control the current of devices such as
life-support systems. If this system malfunctions and
generates an over current, or when there is an
instantaneous current at power ON, fuses of the
building’s supply circuit may be tripped.
3.1.1.3 EMI Limitation
Ultrasound machines are susceptible to Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) by radio
frequencies, magnetic fields, and transient in the air wiring. They also generate a weak
electromagnetic radiation. Possible EMI sources should be identified before the unit is
installed. Electrical and electronic equipment may produce EMI unintentionally as the
result of defect.
These sources include: medical lasers, scanners, monitors, cauterizing guns and so on.
Besides, other devices that may result in high frequency electromagnetic interference
such as mobile phone, radio transceiver and wireless remote control toys are not allowed
to be presented or used in the room. Turn off those devices to make sure the ultrasound
system can work in a normal way.
Page 30

3-2 System Installation
3.1.2 Installation Conditions
3.1.2.1 Space Requirements
Place the system with necessary peripherals in a position that is convenient for operation:
1. Place the system in a room with good ventilation or an air conditioner.
2. The door is at least 0.8m wide. The ultrasound machines can move into the room
easily.
3. Leave at least 0.2m clearance around the system to ensure effective cooling.
4. An adjustable lighting system in the room (dim/bright) is recommended.
5. Except the receptacle dedicated for the ultrasound system, there should be at least
3-4 more receptacles on the wall for other medical devices and peripherals.
6. The distance between wall outlet and any peripherals should be less than 2m and
distance between ultrasound system and peripherals should be less than 1m, to
make it easy for cable connections.
3.1.2.2 Networking Pre-installation Requirements
Both wireless and wired LANs are supported by this ultrasound system.
Data transmission is allowed between different departments or areas without network
cable. Network can be automatically connected after disconnection in case that the device
is required to be moved, wireless transmission task can be recovered after the network
resumed to normal condition. Confirm the network devices and network conditions before
the installation.
1. General information: default gateway IP address, and the other routers relevant
information.
2. DICOM application information: DICOM server name, DICOM port, channels, and IP
address.
Page 31

System Installation 3-3
3.1.3 Confirmation before Installation
Perform the following confirmation before installing the system:
1. The video format used in the region or country where the system is installed.
2. The language used in the region or country where the system is installed.
3. The power voltage used in the region or country where the system is installed.
4. Obstetric formulae and other measurement formulae used in the region or country
where the system is installed.
5. Other settings to be used in the region or country where the system is installed but
different from the factory settings.
6. The doctor’s habits of using the system.
Perform the confirmation above before installing the system. And set up the system to
make it according with the usage of the region or country where the system is installed.
3.2 Unpacking
Unpacking tool: a pair of scissors
Installation duration: 1~2 people, 20 minutes.
3.2.1 Unpacking Process
1. Cut off 4 strips of the external package.
2. Remove the wooden cover and use it as the slope in the front of the device.
Page 32

3-4 System Installation
3. Remove the crate. Press the clasps down to release them.
4. Remove "front foam", "LCD protect foam", "back foam", "small accessory carton".
Page 33

System Installation 3-5
5. Remove "support arm foam", "big accessory carton", release the buckle, and remove
"front foam", "handle foam".
6. Pull the machine out along the slope.
Support arm
foam
Large accessory
carton
Front foam
Handle foam
Front foam
LCD protect foam
Small accessory carton
Back foam
Page 34

3-6 System Installation
Note: please follow up the procedures of reverse unpacking when transporting.
3.2.2 Checking
1. After unpacking, check the objects in the container with the package list to see if
anything is missing or is wrong.
2. Ensure there is no damage, indentation or cracks occurring to the machine. If any
happen, please contact Mindray Customer Service Department.
Page 35

System Installation 3-7
3.3 Bare Machine Transport
Refer to chapter 3.2.1 for machine transport.
If the machine is not packaged, it is only allowed for short-distance trasnport. Refer to the
following procedures to protect the machine during the transport.
3.3.1 Tool
Tool Specifications
Vehicle
Vehicle door size: larger than 700 mm (width) X 1280 mm (height)
The space for the ultrasound device: larger than 1050mm (length) X 700
mm (width) X 1280 mm (height).
LCD protection
foam
LCD protection foam for bare machine transport (1)
Note: Do not dispose of red protection foam after completing the
unpacking.
Rope Several
Page 36

3-8 System Installation
3.3.2 Device Transport
3.3.3 Fixing Methods
1. Press the button to lower the control panel to the minimum position when the
ultrasound device is powered on. Press the button
to push the moving mechanism
straight forward.
Protect the monitor with the red
foam, and use the rope to fasten it
around the device. Protect the
monitor from moving.
Lower the support arm
to the minimum
Fasten the moving
mechanism (from
moving). Tie the rope
around the back
handle. Do not press
the external cover of
the device hard.
Unlock the brake pedal
Four ends of the
ropes should be
fastened to four
directions of the
car. Keep the
device from
moving in the car
Page 37

System Installation 3-9
2. Toggle the control switch along the red arrow’s direction and press the upper support
arm down following the blue arrow’s direction. The support arm stays at the lowest
position.
3. Protect the monitor with the red foam, and use the rope to fasten it around the device.
Protect the monitor from moving.
4. Push the ultrasound device into the car against the slope (other methods also work).
5. Warp the device tight around the front handle and the back handle. Keep the device from
moving in the car.
Page 38

3-10 System Installation
6. Rotate the two switches anticlockwise. Keep the two switches and the brake pedal loosed
(marked with the red circle).
Page 39

System Installation 3-11
3.4 Installing Main Unit
NOTE:
To prevent the machine from damage, when you perform the following
operations, please lock the casters.
3.4.1 Opening up the Monitor
Adjust the monitor from the horizontal position to the vertical position.
NOTE: Take care of your hands when adjust the monitor up and down.
3.4.2 Connecting the Power Cord
1. Push the retaining clamp upward, and insert the power plug into the receptacle. Take
off two screws and the fixing board of the power plug from the accessory kits. Fix the
power plug board on electronics assembly on the base to press the power cable with
2 M3X8 sunk head screws.
2. Plug the other end of power plug into an appropriate outlet. The grounding terminal
should be connected with a power grounding cable to ensure that protective
grounding works normally.
The power plug board
Grounding terminal
Page 40

3-12 System Installation
NOTE: Make sure to allow sufficient slack in the cable so that the plug won't be pulled
out when the system is moved slightly.
3.4.3 Connecting ECG
Connect the ECG cable to the corresponding interface on the physio panel under the
control panel. See “2.1.2.3 Physio Panel” for details.
3.4.4 Installing Probe Holder
Insert the coupling gel heating cup, left bracket, 4D probe holder, larger probe holder,
small probe holder and plug the coupling gel heating cup to the control panel.
3.4.5 Installing Gel Holder
1. Slide the left/right support beneath the control panel along the gliding track according
to the marks (“L” refers to the left bracket and “R” refers to the right support) on the
support of the gel warmer.
4D probe
holder
Large probe
holder
Small probe
holder
Small probe
holder
Large
probe
holder
Gel warmer and
left support
Page 41

System Installation 3-13
2. Put the gel warmer into the left/right support, and plug the cable of the gel warmer
into the port of the control panel bottom.
“L” refers to the left support of the gel warme
r
“R” refers to the right support of the gel warme
r
For example:
Slide the left
support
beneath the
control panel
along the left
gliding track
Page 42

3-14 System Installation
Placing the gel bottle:
Fasten the gel bottle, and then place the bottle in the gel warmer. See the figure
below:
3.4.6 Connecting the Transducer
Four sockets (A, B, C, D) are configured on the system; every socket can be connected
with all types of supported transducers.
1. Keep the cable end of the transducer to the up side of the system, and insert the
connector into the socket of the system, and then press in fully. (Shown as the left
figure)
2. Turn the lock handle 90° clockwise to lock it securely. (Shown as the right figure)
Fasten the gel
bottle, and then
place the bottle
in the gel
warmer.
The indicator of the gel
warmer facing outside
Lock
Page 43

System Installation 3-15
3. Place the probe properly to avoid being treaded or wrapping with other devices (use
hanger or hook). DO NOT allow the probe head to hang free.
4. Turn the lock handle 90° anticlockwise to unlock it, and then pull out the connector.
3.5 Installing Peripherals
For the models of the supported peripherals, please refer to “2.1.3 Supported
Peripherals”.
3.5.1 Connecting a Footswitch
WARNING:
Do not connect two or more footswitches to the main unit;
otherwise, it may lead to the malfunction to the system.
The system supports the wired footswitch (two-pedal, and three-pedal) and wireless
footswitch (two-pedal, and three-pedal).
The setting for the wireless footswitch:
1. Connect the wireless footswitch to the main unit.
2. Press <F10 Setup> to open the page. Select [Maintenance]->[Setup]->[Paring
Wireless Footswitch] to set the footswitch.
3. Click [OK]. The dialog box appears.
4. The warning dialog box appears.
Page 44

3-16 System Installation
5. Press two footswitches. Click [OK].
6. Select [Key Config]->[Footswitch] to set for the footswitch. After completing the
configuration, each of the footswitch can be used according to its function. Step the
footswitch to complete the operation.
The setting for the wired footswitch:
1. Connection: directly insert the USB port of the footswitch to the system applicable
USB ports.
2. Function setting: for details, please refer to chapter 3.8.3.
3.5.2 Installing a Graph / Laser Printer
NOTE: Please restart the ultrasound system after printer installation.
Connecting a local printer
NOTE: Printers listed in “2.1.3 Peripherals Supported” Chapter have drivers installed
already.
As shown in the figure below, a graph / text printer has a power cord and data cable.
The power cord should be directly plugged into a well-grounded outlet.
1. Connect the data cable to the USB port on the ultrasound system.
Page 45

System Installation 3-17
2. Power the system and the printer on.
3. Put the installation optical disk of the printer driver into the DVD R/W drive.
4. Install the printer driver: Select [Setup]→[Print Preset]→[Add Printer].
NOTE: all the operations are finished with right <Set> key.
5. Select [Add a local printer] and click [Next] to enter the screen used for browsing driver.
NOTE: see the printer’s operation manual to select the port, or try to use the default port
of the system.
6. Click [Have Disk…] to find the driver path (the installation type should be WIN7 64), and
then click [Next] to install the driver.
Page 46

3-18 System Installation
7. Complete the operation according to the tips on the screen. Click [Finish] to end the
installation.
NOTE: 1. Before adding the local printer, make sure the printer is powered on, and the
printer has been well connected with the ultrasound device (a sound
feedback will be heard when connecting)
2. In case of installation failure under Doppler, try to install the printer in
Windows (click [Enter Windows] on the Maintenance menu). If the
installation can’t be performed neither in Doppler nor Windows, then the
printer can’t be supported by the ultrasound machine.
3. Use the original driver disk to perform the driver installation.
Add network printer
1. As the system is connected into a LAN, open [Setup]-> [Printer Preset] screen.
2. Click [Add Printer], select [Add a network, wireless or Bluetooth printer].
3. The system starts to search all available printers within the network. Select the target
printer and click [Next], the system tries to connect to this printer.
4. When the connection is successful, the system prompts the dialogue box, click [Next]
according to the screen tips and then click [Finish].The printer is installed successfully.
Tips: the system has combined many types/brands of printer drivers, if targeted printer
drive is not included in the system, you may need to install the driver for the network
printer. Please use the optical disk or USB disk with the driver to install according to the
system prompts.
NOTE: When you install the printer’s driver, you must specify the specific path for
installation. A vague path may result in longer searching times.
The network printer functions depending on the configured network environment
in the hospital, please consult the network configuration manager in case of
failure.
Before connecting a network printer, connect the ultrasound machine into the
same network with the printer and make sure the network works normally.
Once a network printer is found, an identification dialogue box will appear if the
server needs identity confirmation. Enter the user name and pass code; select
“Auto Connecting” and then click [OK].
The printer name typed should be valid, \\server\printer for example. Otherwise,
a connection failure notice may appear.
Print
Both report and image can be printed on a graph / text printer.
To set the default report printer and its attribute:
In "[Setup]→[Print Preset]" screen, select the "Report Print" column in the service list.
You can select printer from the driver list next to “Printer” in the lower screen and set the
items in the "Property" box. Click [Save] after you have finished setting.
Please refer to the accompanying manuals of the printers for more details.
3.5.3 Installing Video Printer
The system support both black/white video printers (digital) and color video printers
(digital).
Page 47

System Installation 3-19
CAUTION:
The auxiliary power outlet in the system is used to supply
power for approved peripheral devices. Do not connect
other/unapproved devices to this outlet; otherwise the rated
output power may be exceeded and the system failure may
result. Maximum output power of the outlet is 240VA.
Local printer installation
1. Position the printer in the proper place.
2. Plug the printer power cord into an appropriate outlet.
3. Use a USB cable to connect between the system's USB port and the printer's USB port.
4. Load a paper roll, and turn on the system and printer.
See section “3.5.2 Installing a Graph / Laser Printer” for the driver installation procedure
(printer drivers listed in chapter “2.1.3 Peripherals Supported” are installed already).
5. Add a print service:
(1) Open the “[Setup] → [Print Preset]” screen.
(2) Click [Add Service] to enter the page.
(3) Select the service type and enter the service name manually.
(4) Click [OK] to return to the page.
(5) Select the target printer from the drop-down list in the “Property” box and set other
printing properties.
(6) Click [Save] to complete.
3.5.4 Installing a Wireless Printer
The system supports the Officejet Pro 8100 wireless printer for report printing.
1. Plug the printer power cord into an appropriate outlet.
2. Power the system and the printer on.
3. Make sure the ultrasound machine and the printer are connected to the same LAN,
and turn the printer's W-LAN function on.
4. Add a wireless adapter, following the steps described in “Add network printer.” See
chapter “3.5.2 Installing a Graph / Laser Printer.”
5. Open the [Setup] → [Printer Preset] page, select “Report Print” from the printer list,
select the printer to be Officejet Pro 8100, and set properties.
6. Click [Save] to exit the preset and make the settings effective.
Page 48

3-20 System Installation
3.5.5 Installing a Barcode Scanner
The system supports barcode reader to read the patient information (ID).
1. For structure of the scanner, see the figure below. The important parts are: LED
indicator, scanning surface, and the switch.
2. Connect the cable to the port on the scanner.
3. Connect the other end of the cable to the USB port on the ultrasound system.
4. When the ultrasound system is working, information scanning can be performed by
pressing the switch on the scanner. For detailed operations, please refer to the
operator’s manual of the scanner.
Switch
Scanning surface
LED indicato
r
Page 49

System Installation 3-21
5. Fix the scanner on the bracket (see the figure below) to avoid accidental falling.
2D scanner 1D scanner
3.6 Ascending/descending the Main
Control Panel Manually
Ascending/descending the main control panel manually after the cut-off:
1. Turn the inner hexagon spanner on the device back left or right, and pull the spanner
straight forward.
2. Insert the shorter end of the inner hexagon spanner into the hole as shown in the
figure below.
Turn the inner hexagon spanner clockwise. The main control panel becomes lower;
Turn the inner hexagon spanner anti-clockwise. The main control panel becomes
higher;
Bracket
Bracket
Scanning surface
Page 50

3-22 System Installation
Note: z Re-insert the inner hexagon spanner into the hole when the spanner
reaches the horizontal level. Turn the spanner again to ascend or
descend the main control panel.
z Do not turn the inner hexagon spanner while the spanner becomes
tightened. It indicates the main control panel reaches the height
limits (lowest position or highest position).
Moving the main control panel horizontally after the cut-off:
1. Toggle the lever of support arm to Unlock. See the figure below.
2. Step the brake pedal down to lock the casters. See the figure below.
Unlocking
Page 51

System Installation 3-23
3. Stretch the main control panel out towards the arrow’s direction. See the figure below.
4. Move the main control panel left or right towards the arrow’s direction. See the figure below.
Brake pedal
Page 52

3-24 System Installation
3.7 System Configuration
3.7.1 Running the System
Connect the AC power; make sure the ultrasound system and other optional devices are correctly
connected.
When the AC power indicator on the control panel is on (indicator is in green), press the power
button
on the control panel to turn on the system.
3.7.2 Entering Doppler
After the system is activated and the initialization is completed (about 1 minute), it enters Doppler
interface, see the figure below:
Page 53

System Installation 3-25
3.7.3 System Preset
1. Press <F10> on the keyboard to open the Setup menu.
2. The system displays the System Preset screen.
Page 54

3-26 System Installation
The following settings can be performed on the System Preset screen.
Page Description
Region
To set the hospital name, language, time zone, system time format, system
date format and system date/time.
General
To set patient information, exam setup, patient management, storage, system
dormancy, operation log and so on.
Image To set some general parameters in imaging modes.
Application
To set the measure ruler, measure setting, follicle method, comment setting and
so on.
OB
To set the relevant information about fetal gestational age, fetal growth formula
and fetal weight.
Key Config To assign functions to footswitch and the user-defined keys.
Gesture Preset the gesture on the touch screen.
Audio Control Set audio function.
Output Set the output format, the range and the resolution for the image.
Admin To set the user account control relevant information.
Barcode To set relevant information of barcode.
3.7.4 Printer Preset
This screen is used to set up the printer and image printing.
Click [Print] in the preset menu to enter.
Printer setting
The printer settings include print service and print driver.
z
Print Service Setting
h Add Service: click to begin adding print services.
h Remove Service: click to delete the selected print service.
h Rename Service: click to rename the selected print service.
h Default print service: click to set the selected print service as the default one.
h Property: to preset print service properties.
Page 55

System Installation 3-27
Image Settings
Click [Image Setting] to enter the page, you can set the brightness, contrast and saturation of
image printing, or you can use the default values.
3.7.5 Network Preset
You can set the system as a hotspot. When other devices (with available wireless network function)
are connected to the system, DICOM, iStorage and network print function can be implemented this
way.
Turn on hosted network function:
1. Select [Wireless Network Connection] page in Network Preset screen.
2. Confirm the Wi-Fi is enabled: you see [Disable Wi-Fi] in the screen.
3. Enter the name and password for this hotspot in the Hosted Network box.
4. Click [Start] to enable the function.
5. Use other devices to search and connect to this network.
NOTE: Please do not switch [Disable Wi-Fi]/[Enable Wi-Fi] frequently. If [Start]/[Stop] button
become available after frequent switching or the system can no longer search any other
hotspots, please click [Disable Wi-Fi] again and then click [Enable Wi-Fi] to see if it works.
TCP/IP setting
Click the network icon in the bottom-right corner of the screen (including wireless connection icon
and wired connection icon ) to enter TCP/IP setting:
a) Select “DHCP”, and then click [OK].
b) Or, select "Static", input the IP address, subnet mask and gateway, then click [OK].
Note: the name of the device is saved under the service name by default. The system remembers
the service name of the ultrasound system when sending the image, the report to DICOM server.
Open the file (DCM Editor Tool、eZDicom.exe) to view the service name (iStation Name).
NOTE:
IP address of the system should be at the same network segment as that of the
server.
Page 56

3-28 System Installation
3.7.6 DICOM/HL7 Preset
NOTE:
Only if DICOM basic option is configured, [DICOM Preset] is available.
1. Click [DICOM/HL7] to open the DICOM Preset screen. Enter the AE Title of the ultrasound
system, port and PDU according to the actual situation.
2. DICOM Server Setting
1) Enter the device name and the IP address.
2) You can ping other machines to verify connection after entering the correct IP address by
clicking [Ping].
3) Click [Add] to add the server to the list if the connection works normally.
The following is an example:
NOTE:
1. AE Title should be the same with the SCU AE Title preset in the server
(PACS/RIS/HIS).
2. DICOM communication port should be the same with the one in the server.
3. If the currently entered name has already existed, the system will pop up: “The
server name exists!” Click [OK] to enter another name.
3. Click [Set DICOM Service].
Page 57

System Installation 3-29
When the system is configured with DICOM basic function module, and installed DICOM Worklist,
MPPS, DICOM Structured Reporting and Query/ Retrieve modules, the corresponding preset
settings can be found in DICOM Service screen.
The DICOM Service Setting is used to set properties of DICOM services as Storage, Print, Worklist,
MPPS, Storage Commitment and Query/ Retrieve. The detailed information please refer to DICOM
chapter in the operator’s manual [Basic Volume].
NOTE:
Only if DICOM basic option is configured, Worklist page and other pages are
available.
3.7.7 Check System Information
In System Information screen, it displays the product configuration, the optional hardware
installation status, software version, hardware & boards, and driver related information. You can
check the product information here.
1. Press <F10 Setup>, and then click [About] to open the following screen.
2. On About Detail page, system hardware & board related information can be seen.
Page 58

3-30 System Installation
NOTE:
1. Be sure to confirm the system information before and after the software
maintenance.
2. If necessary, please remind the user of saving the current system
information.
Page 59

Product Principle 4-1
4 Product Principle
4.1 General Structure of Hardware System
Symbol Illustration
Figure
1 Schematic Diagram of System Hardware
The structure of Resona 7 series hardware system is shown in the figure above, the main unit
consisits of:
¾ Front unit (probe board, TR board, engine board, CW sub-board, 4D-TEE board, ECG
module);
¾ Back-end unit (PC carrier board, IO interface board);
¾ Power supply unit (AC input unit, AC-DC module (including 5V_STB, 12V, 24V module),
isolation transformer, DC-DC board, PHV board);
¾ User interaction unit (main monitor, touch screen (sub-monitor), speaker, control panel,
microphone, electronic ascending/descending, moving mechanism of the control panel);
Page 60

4-2 Product Principle
4.2 Ultrasound Front Unit
Fig
2 Schematic Diagram of Ultrasound System Front-end
Front-end unit mainly consists of:
¾ Probe board
¾ TR_A board, TR_B board, TR_C board
¾ Engine board
¾ CW sub-board (option configuration on the TR_A and TR_C board, standard configuration on
the TR_B board)
¾ 4D-TEE board
¾ ECG module
¾ Pencil probe board (optional)
Ultrasound front-end unit carries out the transmitting and receiving, the ultrasound image
signal will be sent to the CPU module on the digital board for post processing after amplification,
A/D conversion, beam forming and signal processing.
For details of the each board, see the following chapters:
Page 61

Product Principle 4-3
4.2.1 Probe Board
Moth
er
boar
d
CPLD
POUT
switch
array
(relay)
Prb Co n
A
Prb Con
B
Prb Con
C
Prb Con
D
POUT
x256
POUT
x256
POUT
x256
POUT
x256
ID_SPI
Probe control x4
Interrupt PRT_INT
TR board
xN
Control
JTAG
4D probe
control
selection
4D signal
Control
4D drive
module
4D signal
Control
192/TEE/DP special pro be cont rol
BTB connectionBTB connection
Probe
board
Power
supply
DSP
FPGA
Engine
board
EMIT[ 1-256]
Figure 3 Schematic Diagram of the Probe Board
The hardware structure of the probe board is shown in the figure above: The introduction of probe
board is described as follows:
¾ The probe board supports probe switching of four 408pin probe plug, every plug has 192-array
connecting with the main unit physical channels.
¾ 408-pin probe plug supports general probe (192-array at most), mechanical 4D, 1.25D/1.5D
probe, bi-plane, TEE (compatible with the interface) probe and probe containing high-voltage
switch.
¾ Probe board FPGA supports on-line upgrade.
¾ Support the detection of the probe’s hot swapping.
¾ Support activating the indicator of the probe.
¾ The probe board can be used for the burn-in without disassembling the JTAG of FPGA.
Page 62

4-4 Product Principle
4.2.2 TR Board
Figure
4 Principle Diagram of TR Board
The principle diagram of TR board is shown above, the main functions include:
¾ Transmitting: in accomplishing the transmitting focus of the entire unit, TR_FPGA controls 64
channels on a single board to send high-voltage ultrasound signal to the probe.
¾ Receiving: in accomplishing the receiving focus, TR_FPGA controls 64 channels on a single
board to receive ultrasound echo signal of the probe.
¾ Assemble CW function.
¾ It refers to the CW mini board on TRB board; it fulfills the filtering and sampling of adjustment of
CW, and accomplishes the reception of CW signal.
¾ Pencil probe supports: the switch between the receiving channel and general receiving
channel of pencil probe on TRB board
Page 63

Product Principle 4-5
4.2.3 Engine Board
Figure 5 Principle Diagram of Engine Board
The hardware circuit of engine board is shown in the figure above.
Function:
¾ Distribute the clock.
¾ Provides the control and management function of probe related.
a) Probe online, IDs, hot-plug.
b) Control of interior circuit of the probe, such as high-voltage switch, parallel turning, Cable
Driver, etc.
¾ Corresponding control signal of the probe board:
a) Control of the high-voltage (only applicable for the physical channel less than 128, Plato is
not equipped with the function).
b) Configuration of the CPLD on the probe.
c) SPI communicate with probe
¾ Responsible for the module resetting, online upgrade, the management of module information.
¾ Communication and control of the accessories related with image scan, the accessories
include:
a) 4D driving function module; it is an optional independent module, which belongs to the
engine board.
b) Physiological signals function module.
Page 64

4-6 Product Principle
4.2.4 ECG Module
Input
protection
LA_IN
RA_IN
LL_IN
MINDRAY ASIC
LA
RA
LL
SPI
RESET
Reset
(TPS3828)
JTAG
Upper
machine
UART
iso
lat
ion
DC_IN
UART
12V
POWER
ADC
tra
nsf
orm
er
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
ADC
Input Buffer Amplifier
High-pass
filter wave
Low-pass
filter
wave
MCU
(STM32F205
)
Clock
(12MHz)
Offset
adjustment
High-pass
filter wave
Amplitude
adjustment
Clock
(11.0592MH z)
High-pass
filter wave
Breathi
ng test
wave
Low-pass filter
wave
Carrier
circuit
Buffering
circuit
ECG
DC_IN
RESPIRATION
PWM
Simulati
on
switch
(CD4053)
Via simulation switch
RA-LA or RA-LL
PCG
High-pass
filter wave
Amplitude
adjustment
Offset
adjustment
ADC
PCG
Low-pass
filter
wave
Figure 6 Principle Diagram of ECG module
The ECG module is designed for monitoring of ECG signals and display of ECG waveforms, which
serve as the reference of ultrasound images. This module can synchronously trigger display of 2-D
images and color flow images. After the ECG signal is amplified, filtered and sampled, the signal is
sent to the DSC module through the serial port; at the same time the R-wave is detected, and the
detected ECG-triggering signal is sent to the system controllers through interrupt, to start the scan
transmission.
The detail specifications are:
¾ Support 3 lead: RA, LA and LL available.
¾ Do not support lead reorganization.
¾ Only support one channel.
¾ AC overloading protection, 50Hz/60Hz, 1Vp-p, duration 10s, module return to be normal after
overload signal disappear
¾ 3 lead provides drop check of all limbs lead and RL lead.
¾ QRS: 0.2mV.
¾ Input impedance is more than 5 MΩ (10Hz).
¾ The input range of ECG is ±8 mV.
Page 65

Product Principle 4-7
4.2.5 4D-TEE Board
FPGA
Drive
Filter
wave
Comp
DA
AD
Unit
Load
Digital
Simulation part
Current
monitoring
unit
overcurrent
Current monitoring
Overcurrent
TEE
AD
unit
ADC SPI
DAC SPI
4D Drive Board
Engine board
DSP
FPGA
Figure 7 Principle Diagram of 4D-TEE board
Function:
¾ Provides two channels H-bridge power amplified signal
¾ The gain of power amplified circuit can be adjusted.
¾ Provides the detection for the hot resistance in TEE probe.
¾ Provides the adjustment and switch for TEE probe's temperature signal.
¾ Provides self- diagnosis channel of 4D drive circuit.
¾ Overcurrent, overvoltage and over-temperature protection.
4.3 Ultrasound Back-end Unit
The back-end unit supports the platform of whole ultrasound system. It takes charge of back-end’s
central control. It also offers the calculation capacity for image post-processing, user information
storage, the display, etc. the modules include:
¾ COME (CPU) Module
¾ Independent GPU (GPU)
¾ Memory device (SSD&SATA hard disk)
¾ PC carrier board
¾ User I/O Interface Board
Page 66

4-8 Product Principle
¾ WIFI Module
To UI
Control/communi
cation/storage
Back end power
supply
Power supply
monitoring
Power on/off
control
PHV control
Reset and the
respond
Reserve
signal
JTAG
Front FPGA
cong status
PCIE bus
Printer
USB x1
Video
Digital
video
HDMI
VGA & I2C
WiFi
bluetoo
th
PCIE x1
USB x1
HDD
SATA 2.0x2
User
interfac
e
USB 2.0 x N
USB 3.0 x N
Video
output
Right channel
Speake
r mic
audio
Touch
screen
USB 2.0
Second
ary
displa y
video+ I2C
Primary
display
video + I2C
Control
panel
Electri c
al lift
USB 2.0
Simulat
ion
video
S-Video
MF
FPGA
IO
expansi
on
COME
&
GPU
EC
module
PC carrier
Back
end
monito
ring
DVR
Back unit
end
Ethernet
User IO
UI
Magnetic
navagator
USB x1
Figure 8 Diagram of Back-end Unit
4.3.1 COME (CPU) module
COME (CPU) module is integrated CPU (with integrated graphics), host bridge (IO extension),
memory bank, together with PC carrier board, hard disk and independent GPU, as the calculation
and control center of the entire unit, CPU module fulfills the comprehensive functions on the
computer system.
Key specification of Resona 7 COME (CPU) module is shown below:
¾ Select the industrial CPU module which meets the COME 2.0 Type 6.
¾ CPU: i7
¾ Memory: 8G
4.3.2 Independent GPU (GPU)
The independent GPU is used as the coprocessor of COME (CPU) module, it has stronger
calculation capacity. The key specification below:
¾ Module type under standard MAX 3.0 Type B. mechanical size: 82mm*105mm. Plug height:
5mm.
¾ Support CUDA, the processing ability is not less than GTX770M.
4.3.3 Memory device (SSD&SATA hard disk)
It is used for saving image data, user data and operating system. Together with COME (CPU)
module, PC carrier board and independent GPU, it fulfills the comprehensive functions on the
computer system.
Taking account of compatibility and capacity of , Resona 7 chooses a SSD with mSata interface
120G as the operating system disk and a 2.5 inches hard disk with 1T to save user data.
4.3.4 PC carrier board
Function
¾ Provide PC environment for ultrasound system
Page 67

Product Principle 4-9
¾ Provide interface of GPU processor.
¾ Responsible for interface output of the main screen and touch screen.
¾ Provide the interface of memory function, such as system hard disk, user memory hard disk,
drive, etc.
¾ Extend user IO interface, such as display interface, USB interface, and network interface.
¾ Provide the communication interface of engine board and PC system to fulfill data uploading
and control sending of front-end system.
¾ Fulfill power management function of ultrasound system.
¾ Provide interface of wireless module and Bluetooth.
¾ Provide ascending/descending management, high-voltage power management, system
monitoring, power monitoring.
¾ Provide printing control, JTAG interface of hardware system debug, ID management of
hardware board.
Figure 9 Schematic Diagram of PC carrier board
PC carrier board is used as the carrier of COME (CPU) module. The main functions include:
¾ as PC main board to support the following modules :
a) Support COME (CPU) module, provide the power, power management, on/off
management for COME (CPU) module.
b) Support GPU, provide power and power management for GPU, and provide the channel
(PEG×16) between GPU and COME (CPU) module.
Page 68

4-10 Product Principle
c) In order to decrease the distance between COME (CPU) module and SSD, the MSata is
on the carrier, and the carrier provides the power for SSD.
¾ Extend the interface of COME (CPU) module; it can be applied for user interface or
communicating with other module. The extend interface module include:
a) Video extension. Through mother board, PC carrier board provides Video extension to the
main monitor, touch screen, IO board.
b) Audio distribution. Through mother board, PC carrier board provides Audio distribution to
speaker and IO interface board.
c) USB extend module. Through mother board, PC carrier board provides USB extension to
other modules and IO interface board.
d) SATA extend module.
e) PCIE distribution. COME distribute PCIE interface to other modules by PC carrier board
and mother board, such as WIFI module, engine board, GPU, Ethernet port.
f) Network interface;
g) I2C distribution
¾ System monitoring function.
¾ System resetting function.
¾ System upgrade function.
Most of modules are coupled with user interaction unit, detail description is shown below.
4.3.4.1 Video Extension Function Specifications and Plans
Resona 7 product has following instantiated items on platform:
¾ Primary display interface Mini HDMI, resolution 1920*1080.
¾ Secondary display interface HDMI, resolution 1280*800.
The distribution image of Resona 7 is shown in figure 10, and the description is as follows:
¾ The primary display and secondary display use DVI signal, communicate with PC carrier board
through DDC, and adjust the display parameter.
¾ PC carrier board offers DDC channel. It communicates with VGA peripheral, HDMI peripheral.
Obtain peripheral resolution information, etc.
¾ The signal between primary display and secondary display is transmitted through the cables
(lifting column).
The primary display uses Mini HDMI.
The secondary display use HDMI cable to transport DVI signal
¾ The video signal of the peripheral is connected through board-to-board.
¾ The changes of the video signal and the resolution can be realized by the multifunctional logic
of PC carrier board.
Page 69

Product Principle 4-11
Pri_DP
Pri_AUX
Sec_DDC
PC carrier
Board
Pri_DVI
Pri_DDC
Sec_DP
Sec_AUX
HDMI
IO Board
VGA
Secondary Display
Primary Display
S-Video
DVR
VGA_DDC
HDMI_DDC
Sec_DVI
Fig 10 Plato Video Distribution
Page 70

4-12 Product Principle
4.3.4.2 USB Distribution Plan (including USB power distribution plan)
Figure 11 USB Distribution Plan
USB distribution plan is shown in figure 11, descriptions is as follows:
¾ The VBUS of USB comes from the DC-DC board; it is not distributed by PC carrier board. PC
carrier board only receives overcurrent indicating signal.
4.3.4.3 Network Port Requirements and Plan
Connect the network to ultrasound device to accomplish DICOM, remote control, remote print, etc.
The requirement of the system to network capability:
¾ Supports wired network: ten trillion Ethernet, hundred trillion Ethernet and gigabit Ethernet.
¾ Supports wireless network: Wi-Fi (802.11b/g/n). Bluetooth reserved.
Realization of network capability:
¾ Wired network: is realized based on CPU module (MAC+PHY) and isolation transformer of IO
board. The network capability is decided by CPU module. Isolation transformer and RJ45
network circuit have to meet the security requirements of creepage distance.
¾ Wireless network: uses built-in wireless module. The network capability is decided by wireless
module and cables.
Page 71

Product Principle 4-13
4.3.4.4 PCIE Interface Distribution plans
The data and controls of ultrasound devices are based on PCIE interface.
The structure of PCIE interface distribution of the system is shown in table 1
Table 1 PCIE distribution
PCIE interface on CPU
module
Device Transport speed
LANE [3:0]
Engine board on
front-end
PCIE Gen 2, 5Gbps,
Form x4
LANE [4]
Wireless module on
back-end
PCIE Gen 1, 2.5Gbps
LANE [6:5] Reserved /
4.3.4.5 SATA Interface Function Requirements and Plan
SATA interface is applied for connecting memory device; detail distribution is shown in table 2:
Table 2 SATA interface distribution
SATA interface on
CPU module
Device Description
Port 0 SSD for PC carrier
board
BTB connect, SATA 3.0
Port 3 Hard Disk WTB connect, SATA 2.0
Port 2 DVD driver WTB connect, SATA 1.0
4.3.4.6 Audio Interface Function Requirements and Plan
The audio interface is applied for connecting speaker, microphone, earphone and other devices, so
back-end must support speaker output, microphone input, general audio output (speaker and
earphone).
The load index of speaker: the speakers on the device support dual tracks of 10W/8Ω for
earphone and speaker, it supports dual output only.
Page 72

4-14 Product Principle
4.3.4.7 The Frame of System Monitor Function
Doppler
Driver
Operating System
CPU Module
MF FPGA
LPC
ATD7462
_A
ADD:0X58
ATD7462
_B
ADD:0X5C
Alert0
Alert1
Fan_OUT
GPU Fan
Fan_IN
Carrier
Board
Volt age
Carrier
Board
Temprature
SMBus0
ATD7462
ADD:0X5C
DC_DC
Board
Temprature
DC_DC
Board
Volt age
SMBus2
LPC1113
LiftCtr
Board 24V
Error Event
Alert2
Alert3
SMBus3
CPU Fan
DSP F PGA
Temperature
Core Voltage
RX1 FPGA
Temprature
Core Voltage
RX2 FPGA
Temprature
Core Voltage
RX3 FPGA
Temprature
Core Voltage
PCIE
Psoc3
Control
Panel
Key Stuck
GPU Temperature
USB
PHV Board
Volt age
Error Event
ADUC
7024
UART
4D FPGA
Error Event
CPU Temperature
Fig 12 Principle Diagram of System Monitor Function
Main monitoring content:
z CPU/GPU temperature
z GPU/GPU fan
z The voltage and temperature of PC carrier board, voltage and temperature of DCDC board
which are captured by 7462.
z The cooling fan captured by 7462
z PHV related voltage
z Electrical ascending/descending voltage, communication and key block monitor
z The key block of control panel
z DSP/RX1/RX2/RX3/4D FPGA voltage, temperature monitoring
Related monitor description:
Monitoring
items
Function description
Interface Description
CPU Fan
Monitor the rotation speed of
CPU fan and control the rotation
speed of CPU speed
Doppler software read the speed
via the port, and controls the
speed
GPU/CPU
Temperature
Monitor the temperature of
CPU/GPU
Doppler reads it directly by
interface.
Psoc3
Control panel, key block of
control panel
USB connects with main unit,
Doppler communicates with Psoc
by USB interface
Page 73

Product Principle 4-15
ADUC 7024
PHV voltage monitoring
Communicate with multifunctional
FPGA by serial port
FPGA
DSP/RX1/RX2/RX3/4D FPGA
voltage, temperature monitoring
Communicate with PCIE and host
computer by DSP FPGA
ADT7462A/B/C
Monitor fan of machine, GPU fan
and PC carrier board, DCDC
related voltage, temperature.
Communicate with multifunctional
FPGA by Smbus
LPC1113
Electrical ascending/descending
voltage and warning monitor
Communicate with multifunctional
FPGA by Smbus
4.3.4.8 Extend Function of Other Interface
Except for the interfaces described above, the system uses modules to communicate with PC; the
main modules include:
1. System monitoring (power supply, temperature, fan): I2C interface.
2. VGA video I2C, HDMI video I2C.
3. The primary display/touch screen I2C (reserved for the display which is compatible but has
non-DP interface).
4. Battery management (serial port, platform reserved)
5. PHV module (serial port)
CPU module does not have any I2C interfaces, so the serial port and I2C interface must be
extended by MF_FPGA to connect with different devices. MF_FPGA communicates with CPU
module by LPC.
Page 74

4-16 Product Principle
4.3.5 User I/O Interface Board
Fig 13 Principle Diagram of I/O Box Board
Function:
IO interface board includes functions as follows:
¾ Provide user IO interface. IO interfaces are all from COME (CPU) module which is extended by
PC carrier board and connects to the IO interface. IO interface types include:
a) Video input and output interface
i. HDMI output
ii. VGA output
iii. SVIDEO output
b) Audio output port
i. Audio OUT
c) USB interface: 2, version 2.0 or above.
d) Ethernet port
¾ Debug interface
a) Test signal of output acoustic power.
b) JTAG port of machine debugging
¾ Standby status indicator
a) FPGA configuration status;
b) Power indicator.
¾ Wi-Fi module is on the IO interface board. Connect with COME (CPU) module through mother
board and PC carrier board by PCIE and USB interface.
Page 75

Product Principle 4-17
4.3.6 WiFi Module
TheWiFi module, as shown above, is on the IO interface board. Resona 7 uses wireless network
module and supports Bluetooth function. The functions are shown below:
¾ Built-in Wi-Fi module
¾ Mini PCIE interface
¾ Half-size card
¾ Meet 802.11 b/g/n
4.4 Power Supply Unit
AC-DC Module
AC Interface
Module
Assista nt Output
Module
DC-DC Module
AC input
Control S ystem & U ltrasound Functi ons
AC output
AC output
Printer
DC supply
AC Unit
control
PHV Module
Battery
Assembly
DC Unit
power
Power Unit
Devices
control control
AC input
AC input
AC output
Figure 14 Schematic Diagram of Power Supply Unit
The function of power supply unit is to provide power for each unit of machine, including: front-end
unit, back-end unit, user interaction unit, user peripherals (auxiliary output). Power supply is mainly
from net power, the system is compatible with the standby status when powering off; corresponding
battery and battery management do not have the function as the product does not define the
function. The power unit main include following modules:
¾ AC Interface Module
¾ Auxiliary Out Module
¾ AC-DC Module
¾ DC-DC Module
¾ PHV Module
4.4.1 AC Interface Module
The function of this module has the function of connection and net power processing. Main function
is to output the processed net power to AC-DC module and auxiliary output module, as follows:
¾ The function of connection board: support AC input connector, transport the processed AC
input power to user as auxiliary output and AC-DC as the input.
¾ The overcurrent protection of machine. When the current is overloaded, it can cut off the input
power.
¾ Provide the user with grounding equipotential terminal.
Page 76

4-18 Product Principle
¾ Select isolation transformer when switching between 220V and 110V. It is not necessary to
switch for AC-DC input It supports 110V or 220V generally.
¾ Auxiliary output switch control function; the default auxiliary output is off when the machine is
powered off.
4.4.2 Auxiliary Output Power Isolation Transformer
Auxiliary output provides AC power for the user peripherals. It needs to isolate the leakage current
of auxiliary output in order to meet the regulation. The platform uses the isolation transformer.
The key indices of the auxiliary output of Resona 7: 2 auxiliary output port, one for B/W printer,
another for color printer and other peripherals, Power consumption is totally 300VA (100~127 Vac or
220~240Vac@50/60Hz in total).The two interfaces of Resona 7 are on the AC interface module.
4.4.3 AC-DC module
AC-DC module changes the AC power to DC power to provide power for other assemblies by
DC-DC module. The module needs the indicating signal when AC power is off to control the circuit
of battery.
The specification of Resona 7 is as follows:
¾ AC-DC outputs 3 voltage, there are:
a) 12V: not less than 692W (DC-DC module 572W, PHV module 120W);
b) 24V: not less than 150W (electrical ascending/descending 50W, two electromagnets
each is 50W).
c) 5V_STB (Output from 5V board assembly): the peak current is 2A when powering on,
duration in 4ms; the average valve is in 500mA when working normally.
¾ Resona 7 does not define the function of standby status when battery in, so it is not
necessary to have AC power off indicator. Take the reservation into consideration by
platforms.
¾ The indicator when AC is in the place: reminds of the validity of AC input; it is used for
service personnel to decide the failure on the scene, available.
¾ I2C interface: main control system obtains the work status of module. Available.
4.4.4 DC-DC board
DC-DC board provides DC power for different functional boards and peripherals to fulfill the
requirement of current and voltage, special requirement as follows:
¾ Support PC system standby.
¾ Support ATX sequence.
The switch of DC-DC can interfere with the analog circuit of front-end easily. It should keep
away from the front-end board. Provide grounding shield when necessary.
Power-up and power-down sequence of functional board is realized in board.
4.4.5 PHV module
The PHV module provides the DC current for the following modules:
¾ Programmable voltage power of the general transmission circuit.
¾ Programmable power for CW transmission circuit.
¾ Power for high voltage switch.
¾ Programmable bias voltage for special probe.
The PHV board functional block diagram is shown in the figure below:
Page 77

Product Principle 4-19
High-voltage circuit
Flyback circuit
(programmable)
Figure 15 Schematic Diagram of PHV Board
4.5 New Power Supply Unit
Figure 16 Schematic Diagram of New Power Supply Unit
The function of new power supply unit is to provide power for each unit of machine, including:
front-end unit, back-end unit, user interaction unit, user peripherals (auxiliary output). Power supply
Page 78

4-20 Product Principle
is mainly from net power, the system is compatible with the standby status when powering off;
corresponding battery and battery management do not have the function as the product does not
define the function. The power unit main include following modules:
¾ 12V to 24V Control Board
¾ AC-DC Module
¾ DC-DC Module
¾ PHV Module
4.5.1 AC-DC module
AC-DC module changes the AC power to DC power to provide power for other assemblies by
DC-DC module. The module needs the indicating signal when AC power is off to control the circuit
of battery.
The specification of Resona 7/8 is as follows:
¾ AC-DC outputs 3 voltage, there are:
a) 12V: not less than 692W (DC-DC module 572W, PHV module 120W);
b) 5V_STB: the peak current is 2A when powering on, duration in 4ms; the average
valve is in 500mA when working normally.
c) Auxiliary Output :
¾ Resona 7/8 does not define the function of standby status when battery in, so it is not
necessary to have AC power off indicator. Take the reservation into consideration by
platforms.
¾ The indicator when AC is in the place: reminds of the validity of AC input; it is used for
service personnel to decide the failure on the scene, available.
¾ I2C interface: main control system obtains the work status of module. Available.
4.5.2 12V to 24V Control Board
4.5.3 DC-DC board
DC-DC board provides DC power for different functional boards and peripherals to fulfill the
requirement of current and voltage, special requirement as follows:
¾ Support PC system standby.
¾ Support ATX sequence.
The switch of DC-DC can interfere with the analog circuit of front-end easily. It should keep
away from the front-end board. Provide grounding shield when necessary.
Power-up and power-down sequence of functional board is realized in board.
4.5.4 PHV module
The PHV module provides the DC current for the following modules:
¾ Programmable voltage power of the general transmission circuit.
¾ Programmable power for CW transmission circuit.
Page 79

Product Principle 4-21
¾ Power for high voltage switch.
¾ Programmable bias voltage for special probe.
The PHV board functional block diagram is shown in the figure below:
High-voltage circuit
Flyback circuit
(programmable)
Figure 15 Schematic Diagram of PHV Board
4.6 User Interaction Unit
4.6.1 Control Panel
Control panel is the key assembly for user input; the basic functions is as follows:
¾ Key scan: scan the input action of user.
¾ Key backlights: according ID design requirement, lay the LED beneath the button; user knows
different key status and optimized function. Four adjustable levels for backlight’s brightness.
Four adjustable levels for sound volume.
¾ Signal processing about USB trackball input (including left/right key)
¾ USB extended function: extend 2 USB interface for user.
¾ USB communicates with main unit.
¾ Power on button
Page 80

4-22 Product Principle
¾ Status indicators: including working status, AC in-place, standby status, hard disk reading
status.
¾ Support outsourceuser-defined key, and support backlight function; the backlight’s brightness
can be adjusted.
¾ 8-segment TGC sliders.
¾ Provide the power supply to one gel heater: 12V@3A.
Figure 16 Schematic Diagram of Control Panel Assembly
4.6.2 Primary Display Assembly
Primary display shows the interface of ultrasound application program, including imaging area.
The specifications of Plato’s primary display are:
¾ 21.5 inches, resolution: 1920*1080 @ 60±1Hz.
¾ Visual angle: left/right angle is equal to or larger than 85°, up/down is equal to or larger
than 85°.
¾ Adjustable brightness and contrast can be adjusted via communication software.
¾ Display status indicator.
¾ Powering: 12V±5%.
¾ The signal is DVI; the connector is MiniHDMI.
4.6.3 Secondary Display Assembly
The secondary monitor shows auxiliary control interface of ultrasound application program and
completes touch control with touch screen.
The specifications of Plato’s primary display are:
¾ 12.1 inches, resolution: 1280*1080 @ 60±1Hz.
¾ Visual angle: left/right angle is equal to or larger than 85°, up/down is equal to or larger
than 85°.
¾ Adjustable brightness and contrast: can be adjusted via communication software.
¾ Powering: 12V±5%。
¾ The signal is DVI; the connector is HDMI.
¾ Power supply and the signal uses USB 1.1 standard. Used-definition of the connector.
Control
System
USB 1.1
USB 2.0
Status Indicators
PWR_BTN_N
Power
DC-DC
Module
POWER
ON/OF F
Button
Status
Indicator
LED
Character
Key Board
Function
Keys
Encoder Knob TGC Lever
TrackBall
Coupling
Solvent
Heater
Power
USB Ports
Touchscreen
USB 1.1
VBUS
Control Panel Assembly
USB 1.1
VBUS
Page 81

Product Principle 4-23
4.6.4 Electrical Ascending/Descending and Electromagnet
The diagram of electrical ascending/descending and moving system is shown below:
System
software
Operating
system
PC system
Power supply
Electrical lift
control
Electrical lift
drive
Machine
Turbine
mechanism
Control
panel
and the
display
assembly
Magnetic
control
Comm
Int
Ctrl&
Status
24V
24V
Quad-rod
mechanism
signal
Power
supply
Mechanis m
connection
Position
monitoring
Electrical lift
system
Lift button
control
Controle d Power
Support
Lock
3.3V
ShutDown
Figure 17 Schematic Diagram of Electrical Ascending/Descending and Moving System
There is only communication interface (defined as IIC), interruption interface, power interface
between electrical ascending/descending and main unit system. It supports the control panel, locks
the control panel.
Signal name Description Signal constraint
Comm
Communication interface (defined as IIC) of
electrical ascending/descending and main unit
system
3.3V level
Int
Interruption interface of electrical
ascending/descending and main unit system
Direction: electrical
ascending/descending
to main unit
3.3V
Control logical power of electrical
ascending/descending and moving system
/
24V Power supply /
ShutDown Switch control signal of 24V power Reserved design
Support
Four rods mechanism support the control
panel
/
Lock
Electromagnet locks/unlocks control panel to
move.
/
Page 82

Page 83

Function and Performance Checking Method 5-1
5 Function and Performance
Checking Method
5.1 NOTE
The chapter offers the detailed method for checking product main function and performance. It is
only for reference not a required task.
5.2 Device Status Checking
5.2.1 Running Status
1. Normal power on/off operation (duration time is normal), no abnormal sounds or phenomena
occur during normal operation.
2. After ultrasound system is turned on, the fan starts working and no abnormal sound when the
fan is working.
3. Check if configuration, software version are normal through the [About] in preset menu.
4. Check if contrast and brightness of the monitor are normal.
5. Check if time and date are valid and correct.
6. Check if all status indicators are normal.
7. Check all log records with user, to confirm if there is any abnormality.
5.2.2 Working Condition
Check the ambient temperature and humidity to see whether it meets the requirement. The
measurements related to safety features are particularly sensitive to humidity. If the insulation
feature of the system deteriorates due to the increase of system service time or system
malfunctions; the fluctuation range of measurement results are likely to increase with the increase
of humidity.
Page 84

5-2 Function and Performance Checking Method
5.3 General Exam
5.3.1 Check Flow
5.3.2 Checking Content
5.3.2.1 Check Control Panel
Procedure Checking Standard
Check all buttons, keys and knobs
Follow the direction: left to right, and up to down.
All keys and knobs are effective.
Function checking of the trackball:
Press the <Freeze> key to enter the Freeze status.
Press <Measure> to enter into measure status, do
vertical and horizontal measurement, or do other
trackball operations.
The trackball can be rotated easily; the
cursor responds sensitively, the rotation
direction is the same as the direction of
the cursor.
Page 85

Function and Performance Checking Method 5-3
5.3.2.2 Check the Monitor
Procedure Standard
z Monitor Brightness/Contrast
Adjustment
Press <F10>. Select
[System]→[General]. Click
[LCD] to adjust the brightness
and the contrast.
z Restore the factory default
settings
Press <F10>. Click
[System]→[General]. Click
[LCD] to adjust.
z Monitor maintenance
Log on as Service, click
[Maintenance]->[Test Main
Monitor] to check the monitor
functions
Press on the monitor to adjust the values, real-time
values will be displayed on the adjusting bar.
Brightness/Contrast load factory values
Click each functional button, the LCD responds
correctly, the standard is as follows:
1. Light-spot: 0; flash point: 0.
2. The adjoining dark spots are no more than 3 pairs, and
there is no adjoining dark spot in image area.
3. There is no adjoining dark spot of 3 or more than 3.
4. The dark spots are no more than 7 and those in the
image area are no more than 2
5. The distance between bad spots is no less than 5mm.
NOTE: image area refers to rectangle when the background
is black/right.
5.3.2.3 Check Touch Panel
Procedure Standard
z Check if keys on the touch screen of
each exam mode can respond normally.
z [Preset]→[System]→[General]. Click
[TouchPanel] to adjust the brightness
and the contrast.
z Press <F10>. Click
[System]→[General]. Click
[TouchPanel]→[Default] to adjust.
z Touch screen maintenance
Log on as Service, click
[Maintenance]->[Setup]->[Test Touch
Screen] to check the monitor functions
z All keys functions are effective.
z Press on the touch screen to adjust the values,
real-time values will be displayed on the
adjusting bar.
z Brightness/Contrast load factory values
z Click each functional button, the LCD responds
correctly, the standard is as follows:
1. Light-spot: 0; flash point: 0.
2. The adjoining dark spots are no more than
3 pairs, and there is no adjoining dark spot
in image area.
3. There is no adjoining dark spot of 3 or
more than 3.
4. The dark spots are no more than 7 and
those in the image area are no more than 2
5. The distance between bad spots is no less
than 5mm.
NOTE: image area refers to rectangle
when the background is black/right.
5.3.2.4 Check DVD-R/W
Procedure Standard
Press [Eject]
Use the optical disk drive to read and burning.
Disk can be normally ejected.
Normal, no abnormal sounds.
Page 86

5-4 Function and Performance Checking Method
5.3.2.5 Check Peripherals
Procedure Standard
Footswitch:
Connect the footswitch; check the
functions of footswitch according to the
functions listed in Key Config. (e.g. right
key- image frozen, middle keyProspectivet, left key- Retrospective)
Press the freeze key (the right key), image is
frozen, the freeze menu is displayed; press the
key again, image is unfrozen.
Press the print key (middle key), color printing
starts.
Press the print key (left key), B/W printing starts.
Video printer:
Check if the video printer and ultrasound
system are correctly connected. Then
check the function of each key.
Press <Print> key, the printer begins to work, no
image print deficiency or degradation.
Switch video output port or USB port; repeat the step.
Text/graph printer:
Check if the printer and ultrasound system
are correctly connected.
Then check the function of each key.
Press <Print> key, the printer begins to work, no print
deficiency or degradation.
Barcode reader:
Perform code bar scanning when the
ultrasound system is running normally.
The bar code is correctly displayed on the screen.
5.3.2.6 Check ECG Module
Procedure Standard
Confirm if the ECG module is
configured, then:
Set [ECG] as “On”.
ECG trace is displayed; the heart icon is displayed
at the upper right corner of the screen.
The parameters [Speed], [ECG Gain], [ECG Pos],
[Rotate] can be adjusted.
ECG signal can be reviewed correctly.
5.3.2.7 Check I/O Ports
Procedure Standard
Checking the main I/O ports:
Besides the video/audio ports, USB ports, the
other ports required to be checked including:
VGA port;
Connect external VGA/LCD monitor (with
resolution supporting 1280*1024)
Other USB ports.
The contents displayed on the display are
the same as those displayed on the
ultrasound system displayer, no character
and image loss, no color difference, no
fluttering and flicking.
Smooth communication.
USB port data storage/accessing are
normal.
5.4 Function Checking
NOTE: A complete function inspection is described here, do the checking according to the actual
system configuration.
Page 87

Function and Performance Checking Method 5-5
5.4.1 Check Flow
5.4.2 Content
5.4.2.1 Imaging Modes
¾ B mode
In B Mode scanning, the image parameter area in the upper left corner of the screen will
display the real-time parameter values as follows:
Parameter F D G FR DR iClear iBeam iTouch Zoom
Meaning Frequency Depth Gain Frame Rate Dynamic Range Display when the function is turned on.
Parameters that can be adjusted to optimize the B Mode image are indicated in the following.
Adjustment Parameter
Control panel Gain, depth, TGC, iTouch, Zoom, Focus Position, Steer
Touch screen / menu
Tint map, line density, flip, persistence, image quality, focus, FOV, iClear,
dynamic range, TSI, iBeam, H Scale, dual live, LGC, echo boost, gray
map
Page 88

5-6 Function and Performance Checking Method
Procedure Checking criteria
Press <B> button. Enter B mode image. B mode interface appears.
Gain adjustment G
Rotate <B> button
Gain increases with rotating the knob clockwise;
Gain decreases with rotating the knob anticlockwise;
Depth adjustment D
Poke <Depth> rod.
The depth of the image changes accordingly. Depth range varies
depending upon the probe types.
TGC adjustment
Adjust 8 sliders on the control
panel
Push the slider right to increase the gain. The brightness of the
area becomes brighter.
Push the slider right to decrease the gain. The brightness of the
area becomes darker.
About 1.5s after the adjustment is finished, the TGC curve
disappears.
iTouch
Press <iTouch> button
Press <iTouch> on the control panel to enter the iTouch status, the
symbol of which will be displayed in the image parameter area of
the screen.
Click [iTouch] on the image menu to adjust the gain in iTouch
status among -12 through 12dB.
Long press <iTouch> to exit iTouch mode.
Zoom
Rotate <Zoom> button
Rotate clockwise to zoom in the image and vice versa.
Roll the trackball to change the image position.
Press <Zoom> to exit magnification status.
Acoustic power adjustment
B image touch
screen-[Acoustic power].
The system offers 34 values to adjust the acoustic power.
Acoustic power (AP) is displayed in real time in the upper part of
the screen.
Focus
B image touch screen-[Focus
number]
Use <Focus> deflector rod to
adjust focus position.
Focus position/number adjustment
The focus position icon
is displayed on the right side of the
image.
Scan range and FOV position
B image touch screen-[FOV].
Image display adjustment
[FOV] is on and move the trackball to adjust the scan range.
Frequency adjustment
B image touch screen-[Image
quality]
The real-time value of frequency is displayed in the image
parameter area in the upper screen (fundamental wave-F,
Harmonic frequency-H). Values of frequency vary depending upon
the probe types.
Steer
Use <Steer> deflector rod.
To steer the beam the probe transmits.
ExFov
B image touch screen-[ExFov]
Click [ExFov] on the touch screen to enable/disable the function.
Line Density
B image touch screen-[Line
Density].
The function determines the quality and information of the image.
Levels of line density: UH/ H/ M/ L.
Page 89

Function and Performance Checking Method 5-7
Dynamic Range
B image touch
screen-[Dynamic Range].
The adjusting range of parameter is 30-180 dB in increments of 5
dB.
iClear
B image touch screen-[iClear].
The system provides 7 levels of iClear effects adjustment, Off
represents iClear is disabled, and the bigger the value is the
stronger the effect becomes.
Persistence
B image touch
screen-[Persistence].
The system provides 7 level of persistence. The bigger the value
is the stronger the effect becomes.
Rotation/Invert
B image touch screen-[L/R
Flip]/[U/D Flip].
To invert the image horizontally or vertically.
Image can be rotated by the angle of 0°, 90°, 180° and 270°.
When the image is rotated in the angle of 90° or 270°, the depth
scale is displayed on the upper part of the screen.
The “M” mark indicates the direction of the image; the M mark is
located on the top of the imaging area by default.
iBeam
B image touch screen-[iBeam].
The system provides 4 values of iBeam in B mode. iBeam is
disabled when it is off.
Auto Merge
B image touch screen-[Auto
Merge].
In the Dual-split mode, when the images of the two windows have
the same probe type, depth, invert status, rotation status and
magnification factor, the system will merge the two images so as
to extend the field of vision.
Turn on or off the function through the [Auto Merge] item in the
touch screen;
Gray Map
B image touch screen-[Gray
Map]
Adjust the gray from [Gray Map] on the touch screen;
There are 8 different maps available.
Tint Map
B image touch screen-[Tint
Map]
Select the tint map from [Tint Map] on the touch screen.
Turn on or off the tint map from [Tint Map] on the touch screen.
TSI
B image touch screen-[TSI].
Select TSI from [TSI] on the touch screen.
The system provided 4 ways of optimization for specific tissues:
general, muscle, fluid and fat.
HScale
B image touch
screen-[HScale]
Click [HScale] on the menu to display or hide the scale (HScale).
Dual live
B image touch screen-[Dual
live].
Enable [Dual Live] on touch screen, and dual-split window of
images are displayed on the screen.
Two pages of adjustable parameters are displayed on the touch
screen as well; where, shared parameters and left window
parameters are displayed on the B(L) page, while right window
parameters are displayed on the B(R) page.
LGC
B image touch screen-[LGC].
Images corresponding to four groups of parameters are displayed
on the touch screen (from left to right).
Click [LGC1-5] to adjust the parameters.
Page 90

5-8 Function and Performance Checking Method
¾ M mode
In M mode scanning, the image parameter area in the upper left corner of the screen displays
the real-time parameter values as follows:
Parameter F D G V DR
Meaning Frequency Depth M Gain M speed M Dynamic Range
Parameters that can be adjusted to optimize the M Mode image are indicated in the following.
Control Panel Gain, Depth, TGC, Focus position
Touch Screen
Speed, Display Format, Gray Map, Dynamic Range, Tint Map, M Soften, Edge
Enhance
¾ Color mode
In Color mode scanning, the image parameter area in the upper left corner of the screen
displays the real-time parameter values as follows:
Parameter F G PRF WF
Meaning Frequency Color Gain Pulse Repetition Frequency (PRF) Color Wall Filter
Parameters that can be adjusted to optimize the Color Mode image are indicated in the
following.
Control Panel Gain, Depth, iTouch, Scale
Touch Screen
Invert, Baseline, B/C Wide, Dual Live, Image quality, Flow State, Priority, Packet
Size, Map, Wall Filter, Line Density, Smooth, Persistence, Velocity Tag, steer
¾ Power mode
In Power mode scanning, the image parameter area in the upper left corner of the screen
displays the real-time parameter values as follows:
Display F G WF PRF
Parameter Frequency Power
Gain
Power Wall
Filter
Pulse
Repetition
Frequency
¾ PW/CW mode
The parameters will be displayed in the image parameter area on the left part of the screen as
follows:
Display F G PRF WF SVD SV Angle
Parameters
Frequency Gain Pulse
Repetition
Frequency
WF
(Wall
Filter)
SV
Position
SV Size
(only CW )
Angle
Echo Boost
B image touch screen-[Echo
Boost].
[Echo Boost] is enabled when it is on in B mode. (Highlighted) the
system is in “Echo Boost” status.
Page 91

Function and Performance Checking Method 5-9
Parameters that can be adjusted to optimize the PW/CW Mode image are indicated in the
following.
Control Panel Gain, iTouch, Baseline, PW Steer, Scale, Angle
Menu
Display Format, Invert, Duplex/ Triplex, Quick Angle, Wall Filter, Image Quality,
Tint Map, Dynamic Range, Trace Area, Speed, SV,
Gray Map, T/F Res, Auto Calc, Auto Calc Para, HPRF, Auto Calc cycle, Volume,
A. power
5.4.2.2 Basic Measurements
Procedure Standard
In B image mode:
Press <Measure>:
Press <Caliper> key
The system enters application measurements
The system enters general measurement mode.
Perform any 1-2 measurements (e.g., length, area), the
results will display at the lower part of the image.
Press the same key again or press
<Esc>.
Exits measurement.
Do the same operation in other image
modes.
Application measurements are classified into different
application packages, do the application measurements
selectively.
5.4.2.3 Cine Review
Procedure Standard
Press [Freeze] key to freeze an image, and the
[Cine] key indicator lights on. The system
automatically enters the manual cine status.(It has
been set that when system enters into freeze mode,
the default status is cine review.)
Press <iStation> key, then click [Review]; or press
<Review> key to open a cine file.
The system enters into cine review status
The system enters into auto cine review
status.
Roll the trackball Manual cine review
Click [Auto Play] on the menu or soft menu.
Auto play function is turned on, adjust the
soft menu button.
The greater the value is, the quicker the
speed is.
When the value is 0, the system exits auto
play mode.
Move the cursor onto the desired start point of the
cine loop, click [Set First Frame] in the menu or soft
menu to set the start point.
Set the start point of cine loop.
Move the cursor onto the desired end point of the
cine loop, click [Set Last Frame] in the menu or soft
menu to set the start point.
Set the end point of cine loop.
Click [Auto Play] again Review region is confined to the set start
point and end point.
Page 92

5-10 Function and Performance Checking Method
Then press the [Cine] key again. Cine review stops.
Press the <Freeze> key to unfreeze the image.
Press <Cine> or <Esc> key.
Freeze indicator light is off; the system will
return to image scanning and exit cine
review.
The images are still frozen but the system
exits cine review.
5.4.2.4 Probe Recongizing/Switching
Procedure Standard
Press <Freeze> key→ connect the probe to the
system→ press <Freeze> key→ press <Probe>
key to select the probe.
Connect a convex probe to probe socket A, and
then connect a linear probe to probe socket B,
the operator can select probe A or probe B as the
active probe.
Press <Freeze> key→ disconnect the probe→
connect another probe to the port
The system can recognize the newly connected
probe in no time.
5.4.2.5 Patient Information Management
Procedure Standard
Press <Save> (the function already set) during
image scanning
Image will be saved to the patient database, and
a thumbnail will be displayed at the right part of
the screen.
Open [Setup] →[System Preset]→”General”,
then check “Send/Print Image after End Exam”
in the Patient Management area.
Click [End] during image scanning
The system automatically sends the images of
the exam to the default DICOM storage server or
print server.
z Click [Review].
z Click [Exit] on the Review screen; or, Click
[Review] again, or, press <Esc> key
z The system enters into image review mode.
z The system exits image review mode.
z Select the contents to be demonstrated,
and select the demo mode in the iVision
screen. Then select an item already added
to the list and click [Start]
z When the demonstration is finished, click
[Exit] or press <Esc>.
z Demonstration begins.
z Image files are played according to file
names one by one (including the image of
system-relevant and PC-compatible format).
z The system exits the demonstration.
A
uto Review Region
Start mark
End mark
Playback mark
Current
frame
Total frames
Page 93

Function and Performance Checking Method 5-11
Press <iStation> key to enter patient information
management (iStation page)
The saved patient information (images) can be
found, and the patient information can be:
z Backed up/ Restored
z Sent (To DICOM or USB disk etc. )
5.5 Performance Test
5.5.1 Test Process
5.5.2 Test Content
NOTE:
The image used here is only for reference, stick to the image effect in the real
situation.
Requirements:
1. Display: set the contrast and brightness at the clinical application value (or the default status)
2. Operation environment: dark room, simulating the clinical application environment.
3. Scanning techniques: contact the probe with the acoustic window of the phantom, no spacing
nor pressing.
Tips:
For the testing phantoms, please refer to Appendix B.
KS107BD is low frequency phantom and used when Probe focus frequency is less than 4MHZ;
KS107BG is high frequency phantom and used when Probe focus frequency is more than
5MHZ;
Page 94

5-12 Function and Performance Checking Method
5.5.2.1 Resolution
transverse resolution
Test Step:
1. Cover the scan surface of the phantom with water or couple gel, gently contact the probe with
the scan surface, making the transverse resolution testing targets to be displayed around the
midline of the image.
2. Scan the position where the transverse resolution testing targets are displayed.
3. Adjust parameters like gain, dynamic range, TGC, making the background tissue unseen, just
displaying the target image clearly.
4. In condition that the transverse resolution testing targets are horizontally displayed, record the
minimal distance of two targets that can be clearly recognized.
5. Repeat the operation above for the transverse resolution testing targets at other depths.
As shown in figure below.
Axial resolution
Test Step:
1. Cover the scan surface of the phantom with water or couple gel, gently contact the probe with
the scan surface, making the longitudinal resolution testing targets to be displayed around the
midline of the image.
2. Adjust the focus point focuses at the position where the longitudinal resolution testing targets
are displayed.
3. Adjust parameters like gain, dynamic range, TGC, making the background tissue unseen, just
displaying the target image clearly.
4. Record the minimal distance of two longitudinal resolution testing targets that can be clearly
recognized.
Page 95

Function and Performance Checking Method 5-13
5. Repeat the operation above for the longitudinal resolution testing targets at other depths.
NOTE:
1.
When using the convex probe, keep the transverse resolution testing targets
displaying near the midline.
2.
When using a linear probe with steer function, do not turn on the steer function
when performing the transverse resolution test.
3.
Zoom in the region where the targets located if necessary.
4.
The diameter of the target point at a certain depth is equal to the transverse
resolution at the depth.
5.5.2.2 Maximum Depth
Test Step:
1. Cover the scan surface of the phantom with water or couple gel, gently contact the probe with
the scan surface
2. Set the system display depth according to the expected maximum available depth of the probe
in use.
3. Adjust the focus point to the deepest, and AP at the maximum value.
4. Set gain, contrast, TGC at a greater value, but no halation nor defocus is allowed.
5. Record the depth of the furthest target (the target can be seen clearly).
NOTE:
1.
Increasing the gain will also increase the noise, and echo may be covered.
2.
When using a linear probe, please completely contact the probe with the scan
surface, no side clearance is allowed.
3.
When using a convex or phased-array probe, make the axis targets to be
displayed at the middle of the scanning image.
4.
When system is not frozen, the fast field target information may be similar to that
of the noise, do not use this target.
Page 96

5-14 Function and Performance Checking Method
As shown in figure below.
Page 97

Function and Performance Checking Method 5-15
5.5.2.3 Geometric positioning accuracy
Longitudinal geometric positioning accuracy
Test Step:
1. Do adjustments as the way in testing the maximum depth.
2. Record the distance by 20mm each segment on the longitudinal targets line using the
measurement caliper;
3. Select the value with the greatest error (to 20mm), calculate the accuracy using the formula
below
NOTE:
1.
The measurement caliper should be positioned at the upper edge of the
target, not the middle nor the lower edge.
2.
The scanning plane should be vertical to the target line, that means the
scanning plane is parallel with the cross-section of the phantom
As shown in figure below.
Transverse geometric positioning accuracy
Test Step:
1. Cover the scan surface of the phantom with water or couple gel, gently contact the probe with
the scan surface
2. Adjust the depth, making the transverse targets to be displayed in the image.
3. Adjust the focus point to be positioned beside the transverse targets (the standard is not clear)
4. Adjust parameters like gain, TGC, making each transverse targets to be clearly displayed.
Page 98

5-16 Function and Performance Checking Method
5. Record the distance by 20mm each segment on the transverse targets line by using the
measurement caliper
6. Select the value with the greatest error (to 20mm), calculate the accuracy by using the formula
below
NOTE:
1.
When using a linear probe, record the transverse distance by segment.
2.
When using a convex probe, all transverse targets should be displayed
integrally in an image.
3.
The measure caliper should be posited at the upper side or lower side of
the target center.
As shown in figure below.
Page 99

Function and Performance Checking Method 5-17
5.5.2.4 Blackout Area
Test Step:
1. Cover the scan surface of the phantom with water or couple gel, gently contact the probe with
the scan surface
2. Adjust the depth at a lower value, and set the focus at the nearest place to the scan surface.
3. Decrease the value of parameters like AP, Gain until the background noise just can be seen.
4. Record the smallest depth of the target that can be seen clearly, that value is the blackout area
value.
NOTE:
1.
When using a linear probe, please completely contact the probe with the
scan surface, no side clearance is allowed.
2.
For convex probe, the targets in the blackout area should be positioned on
the midline of the scanning plane.
As shown in figure below.
Page 100

 Loading...
Loading...