Page 1

CH-9101 Herisau/Switzerland
E-Mail info@metrohm.com
Internet www.metrohm.com
tiamo User Manual
Program version 1.1
8.101.0013 09.2005/dö
Page 2

Teachware
Metrohm AG
Oberdorfstrasse 68
CH-9101 Herisau
teachware@metrohm.com
This tutorial is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
Although this tutorial has been prepared with the greatest care, errors cannot be completely excluded.
Should you notice any please contact the above address.
Page 3

Table of contents
Chapter 1 Introduction .................................. 1
1.1 Welcome to tiamo ................................................................1
1.2 User interface ......................................................................2
1.3 Integration of devices..........................................................3
1.4 Method editor .......................................................................4
1.5 Database ..............................................................................5
1.6 Communication ....................................................................6
1.7 Compliance ..........................................................................7
1.8 Versions................................................................................8
1.9 Online Help...........................................................................8
1.10 What's new in tiamo 1.1?.....................................................9
Chapter 2 General program functions ........ 11
2.1 Program parts ....................................................................11
2.2 Login/Password protection................................................12
2.2.1 General .....................................................................................12
2.2.2 Login .........................................................................................13
2.2.3 Manual logout........................................................................... 13
2.2.4 Automatic logout......................................................................13
2.2.5 Change password.....................................................................14
2.3 Electronic signatures.........................................................15
2.3.1 Rules .........................................................................................15
2.3.2 Procedure ................................................................................. 15
2.3.3 Signature Level 1 .....................................................................16
2.3.4 Signature Level 2 .....................................................................17
2.3.5 Delete Level 2 signatures ........................................................18
Table of contents iii
Page 4

2.4 Formula editor ................................................................... 19
2.4.1 Overview................................................................................... 19
2.4.2 Input field ................................................................................. 19
2.4.3 Arithmetic algorithms.............................................................. 20
2.4.4 Variables .................................................................................. 22
Overview.................................................................................................... 22
Method variables ...................................................................................... 22
Command variables.................................................................................. 23
Result variables ........................................................................................ 29
Determination variables ........................................................................... 29
System variables ...................................................................................... 30
Common variables.................................................................................... 30
2.4.5 Operators/Functions ................................................................ 31
Operators - Arithmetic.............................................................................. 32
Addition .............................................................................................. 32
Subtraction......................................................................................... 33
Multiplication ...................................................................................... 34
Division............................................................................................... 35
Potentiation ........................................................................................ 36
Operators - Logic...................................................................................... 37
AND .................................................................................................... 37
OR ...................................................................................................... 38
Operators - Compare................................................................................ 39
Equal .................................................................................................. 39
Larger than ......................................................................................... 40
Larger than or equal to....................................................................... 41
Smaller than ....................................................................................... 42
Smaller than or equal to..................................................................... 43
Unequal .............................................................................................. 44
Functions - Arithmetic .............................................................................. 45
Exponential function........................................................................... 45
Natural logarithm................................................................................ 45
Common logarithm ............................................................................ 46
Square root ........................................................................................ 46
Absolute value.................................................................................... 46
Fraction .............................................................................................. 47
Integer ................................................................................................ 47
Round integer..................................................................................... 48
Sign .................................................................................................... 48
Functions - Date/Time .............................................................................. 48
Time() ................................................................................................. 48
Time(Date).......................................................................................... 49
Time(Date + Time)............................................................................. 50
Functions - Type conversion.................................................................... 50
NumberToText ................................................................................... 50
NumberToTime .................................................................................. 51
TextToNumber.................................................................................... 51
TextToTime......................................................................................... 51
TimeToNumber .................................................................................. 52
TimeToText......................................................................................... 53
Functions - Text ........................................................................................ 54
TextPosition........................................................................................ 54
SubText .............................................................................................. 55
Trim .................................................................................................... 56
iv Table of contents
Page 5

Miscellaneous functions .......................................................................... 57
Case ....................................................................................................57
Error ....................................................................................................58
ASCII table ................................................................................................ 58
2.5 Edit......................................................................................60
2.5.1 Text editor ................................................................................60
2.5.2 Select date ...............................................................................61
2.6 Manual control ...................................................................62
2.6.1 General ..................................................................................... 62
2.6.2 Select device ............................................................................63
2.6.3 Functions .................................................................................. 63
2.6.4 Graphic display ........................................................................63
2.6.5 Dosing .......................................................................................63
General...................................................................................................... 64
Prepare...................................................................................................... 65
Fill .............................................................................................................. 66
Empty ........................................................................................................ 67
Add fixed volume...................................................................................... 68
Dosing ....................................................................................................... 70
2.6.6 Stirring ......................................................................................71
Switch on/off ............................................................................................. 72
Continuous operation............................................................................... 73
2.6.7 Remote functions ..................................................................... 74
2.6.8 Sample changer functions....................................................... 75
General...................................................................................................... 76
Move .......................................................................................................... 77
Assign position ......................................................................................... 79
Pump ......................................................................................................... 81
Heater/Gas ................................................................................................ 82
Table of contents v
Page 6

Chapter 3 Workplace....................................85
3.1 General .............................................................................. 85
3.1.1 General..................................................................................... 85
3.1.2 Desktop .................................................................................... 85
3.1.3 Menu bar .................................................................................. 85
Menu File................................................................................................... 86
Menu View................................................................................................. 86
Menu Tools................................................................................................ 86
Menu Help ................................................................................................. 87
3.1.4 Toolbar ..................................................................................... 87
3.1.5 Subwindows ............................................................................. 88
3.1.6 Functions.................................................................................. 88
3.1.7 Workplace views ...................................................................... 90
Change layout........................................................................................... 91
Save view .................................................................................................. 92
Load view .................................................................................................. 93
Rename view............................................................................................. 93
Delete view................................................................................................ 93
3.2 Workplaces ........................................................................ 94
3.2.1 Create new workplace ............................................................ 94
3.2.2 Edit workplace ......................................................................... 94
3.2.3 Show workplace ...................................................................... 95
Select workplace in workplace symbol................................................... 95
Show single workplace ............................................................................ 95
Show workplaces beside each other ...................................................... 95
Show workplaces one below the other ................................................... 95
3.2.4 Close workplace ...................................................................... 95
3.3 Sample tables.................................................................... 96
3.3.1 Edit ........................................................................................... 96
Create new sample table.......................................................................... 96
Open sample table.................................................................................... 96
Edit sample table ...................................................................................... 97
Edit sample data ....................................................................................... 98
Import sample data................................................................................. 100
Save sample table .................................................................................. 100
Print sample table (PDF) ........................................................................ 101
3.3.2 Properties............................................................................... 102
Display.............................................................................................. 102
Edit ................................................................................................... 103
Process............................................................................................. 104
Data import....................................................................................... 105
Comment.......................................................................................... 107
3.3.3 Manager ................................................................................. 107
Sample table manager ........................................................................... 107
Rename sample table............................................................................. 108
Copy sample table.................................................................................. 108
Delete sample table................................................................................ 108
vi Table of contents
Page 7

Export sample table................................................................................ 108
Import sample table................................................................................ 108
3.4 Tools .................................................................................109
3.4.1 Run test ..................................................................................109
3.4.2 Sample assignment table ......................................................109
General.................................................................................................... 109
Sample assignment table....................................................................... 110
Sample assignment ................................................................................ 110
Sample assignment request .................................................................. 111
3.4.3 Text templates .......................................................................111
3.5 Subwindow Run................................................................113
3.5.1 General ................................................................................... 113
3.5.2 Single determination..............................................................113
Overview ................................................................................................. 113
Operating tools ....................................................................................... 114
Status display ......................................................................................... 114
Determination parameters ..................................................................... 115
Modify remark ...................................................................................115
Sample data ............................................................................................ 116
Live modifications .................................................................................. 117
Modification comment for sample data................................................. 118
Determination run................................................................................... 118
Properties................................................................................................ 121
Display ..............................................................................................121
Process .............................................................................................122
Data import .......................................................................................123
3.5.3 Determination series .............................................................124
Overview ................................................................................................. 124
Operating tools ....................................................................................... 124
Status display ......................................................................................... 125
Determination parameters ..................................................................... 126
Modify remark ...................................................................................127
Modify autostart counter...................................................................127
Sample data ............................................................................................ 128
Determination run................................................................................... 128
Working sample table............................................................................. 132
Load new and empty sample table ..................................................132
Load sample table ............................................................................132
Edit working sample table ................................................................132
Edit sample data ...............................................................................135
Import sample data...........................................................................137
Save sample table.............................................................................137
Run test.............................................................................................138
Print sample table (PDF)...................................................................138
Properties................................................................................................ 139
Display ..............................................................................................139
Edit ....................................................................................................140
Process .............................................................................................142
Data import .......................................................................................143
Comment ..........................................................................................144
Table of contents vii
Page 8

3.6 Subwindow Method ......................................................... 145
3.6.1 General................................................................................... 145
3.6.2 Zoom for method window...................................................... 145
3.6.3 Live modifications.................................................................. 145
3.6.4 Quit command........................................................................ 146
3.7 Subwindow Live display.................................................. 147
3.7.1 General................................................................................... 147
3.7.2 Tracks..................................................................................... 147
3.7.3 Application note..................................................................... 148
3.7.4 Properties............................................................................... 148
3.8 Subwindow Report .......................................................... 151
3.8.1 General................................................................................... 151
3.8.2 Latest report .......................................................................... 151
3.8.3 Selected report ...................................................................... 151
3.8.4 Report overview ..................................................................... 151
viii Table of contents
Page 9

Chapter 4 Database ................................... 153
4.1 General .............................................................................153
4.1.1 General ................................................................................... 153
4.1.2 Desktop................................................................................... 153
4.1.3 Menu bar.................................................................................154
Menu File................................................................................................. 154
Menu Edit ................................................................................................ 154
Menu View............................................................................................... 154
Menu Determinations ............................................................................. 155
Menu Tools ............................................................................................. 156
Menu Help ............................................................................................... 156
4.1.4 Toolbar....................................................................................157
4.1.5 Subwindows ...........................................................................158
4.1.6 Functions ................................................................................ 159
4.1.7 Database views ......................................................................159
Change layout......................................................................................... 160
Save view ................................................................................................ 161
Load view ................................................................................................ 161
Rename view........................................................................................... 162
Delete view.............................................................................................. 162
4.2 Open/display database ....................................................163
4.2.1 Open database .......................................................................163
4.2.2 Select database in database symbol....................................164
4.2.3 Show single database............................................................ 164
4.2.4 Show databases beside each other ......................................164
4.2.5 Show databases one below the other...................................164
4.2.6 Close database.......................................................................165
4.3 Manage databases...........................................................166
4.3.1 Database manager................................................................. 166
4.3.2 Create new database............................................................. 167
4.3.3 Rename database ..................................................................167
4.3.4 Delete database ..................................................................... 168
4.3.5 Database properties ..............................................................168
General..............................................................................................168
Access rights.....................................................................................169
Backup..............................................................................................169
Monitoring .........................................................................................170
4.3.6 Manual database backup ......................................................171
4.3.7 Restore database ...................................................................171
4.4 Report templates .............................................................173
4.4.1 Create new report template ..................................................173
4.4.2 Open report template.............................................................173
Table of contents ix
Page 10

Edit report templates............................................................. 174
4.4.3
General.................................................................................................... 174
Desktop ............................................................................................ 175
Menu bar .......................................................................................... 175
Menu File.....................................................................................176
Menu Edit ....................................................................................176
Menu View...................................................................................176
Menu Insert .................................................................................177
Menu Tools..................................................................................177
Menu Help...................................................................................177
General toolbar ................................................................................ 177
Module-specific toolbar.................................................................... 178
Module bar ....................................................................................... 178
Functions................................................................................................. 179
Page setup ....................................................................................... 179
Define sections................................................................................. 180
Insert pages...................................................................................... 181
Insert modules.................................................................................. 181
Edit modules .................................................................................... 182
Zoom for report templates ............................................................... 183
Page preview.................................................................................... 183
Comment.......................................................................................... 184
Options............................................................................................. 185
Save report template........................................................................ 185
Modules................................................................................................... 187
Text field ........................................................................................... 187
Data field .......................................................................................... 188
Date field .......................................................................................... 189
Time field.......................................................................................... 190
Page number.................................................................................... 191
Number of pages ............................................................................. 192
Fixed report ...................................................................................... 193
Image ............................................................................................... 194
Line................................................................................................... 195
Rectangle ......................................................................................... 195
Curve field ........................................................................................ 196
Curve field - x axis.......................................................................197
Curve field - y1 axis.....................................................................198
Curve field - y2 axis.....................................................................200
Curve field - options....................................................................201
Calibration curve field....................................................................... 203
4.4.4 Manage report templates...................................................... 204
Manage report templates ....................................................................... 204
Rename report template .................................................................. 204
Copy report templates ..................................................................... 205
Delete report templates.................................................................... 205
Export report templates.................................................................... 205
Import report template ..................................................................... 205
4.5 Templates for control chart............................................ 206
4.5.1 Manage control chart templates .......................................... 206
4.5.2 Properties............................................................................... 206
Graphical settings ............................................................................ 207
Limits ................................................................................................ 208
Statistics ........................................................................................... 208
Comment.......................................................................................... 209
x Table of contents
Page 11

4.6 Templates for curve overlay ............................................210
4.6.1 Manage curve overlay templates ..........................................210
4.6.2 Properties ...............................................................................211
x Axis.................................................................................................211
y-axis .................................................................................................212
Options..............................................................................................213
Comment ..........................................................................................214
4.7 Export templates..............................................................215
4.7.1 Manage ...................................................................................215
4.7.2 Properties ...............................................................................216
Select fields.......................................................................................217
Options..............................................................................................218
4.8 Subwindow Determination overview...............................219
4.8.1 General ................................................................................... 219
Overview ................................................................................................. 219
Determination table ................................................................................ 219
Column display....................................................................................... 220
Filter selection ........................................................................................ 221
Navigation bar......................................................................................... 221
Table navigation ..................................................................................... 222
Data record selection ............................................................................. 222
4.8.2 Functions ................................................................................ 223
Overview ................................................................................................. 223
Update determination table.................................................................... 223
Determination comment......................................................................... 224
Search determinations ........................................................................... 224
Filter determinations .............................................................................. 226
Last filter............................................................................................226
Quick filter .........................................................................................226
Special filter.......................................................................................226
Edit filter criterion........................................................................ 228
Save filter .................................................................................... 229
All statistics records ..........................................................................229
Remove filter .....................................................................................229
Sign determinations ............................................................................... 230
Rules .................................................................................................230
Sign determinations at Level 1 .........................................................231
Sign determinations at Level 2 .........................................................232
Show determination signatures ........................................................233
Delete signatures 2 for determinations.............................................233
Export determinations ............................................................................ 234
Import determinations............................................................................ 234
Delete determinations ............................................................................ 234
Print determination overview................................................................. 235
Print determination report...................................................................... 236
Show determination method.................................................................. 236
Show determination history ................................................................... 238
Show calibration curve........................................................................... 238
Control chart ........................................................................................... 239
Overlay curves........................................................................................ 241
Table of contents xi
Page 12

Reprocess determinations .................................................... 242
4.8.3
General.................................................................................................... 242
Reprocessing window ............................................................................ 243
Reprocessing rules ................................................................................ 244
Modifications .......................................................................................... 245
Variables........................................................................................... 246
Method ............................................................................................. 247
Statistics ........................................................................................... 248
Curve evaluation............................................................................... 249
Edit curve ebvaluation............................................................................ 250
Properties ......................................................................................... 252
x axis............................................................................................252
y axis ...........................................................................................253
Options........................................................................................254
Result view.............................................................................................. 256
Modification comment for determinations............................................ 257
4.9 Subwindow Information.................................................. 258
4.9.1 Overview................................................................................. 258
4.9.2 Determination ........................................................................ 258
4.9.3 Method.................................................................................... 260
4.9.4 Sample.................................................................................... 262
4.9.5 Configuration ......................................................................... 263
4.9.6 Messages ............................................................................... 265
4.9.7 Determination comment........................................................ 265
4.10 Subwindow Results......................................................... 266
4.10.1 Overview................................................................................. 266
4.10.2 Results overview.................................................................... 266
4.10.3 Command name ..................................................................... 267
4.10.4 Properties............................................................................... 268
4.11 Subwindow Curves.......................................................... 269
4.11.1 General ................................................................................... 269
4.11.2 Measuring point list ............................................................... 270
4.11.3 Monitoring report ................................................................... 271
4.11.4 Properties............................................................................... 272
x Axis ....................................................................................................... 272
y1-axis ..................................................................................................... 273
y2 Axis ..................................................................................................... 275
Options.................................................................................................... 276
Measuring point list................................................................................ 277
xii Table of contents
Page 13

Chapter 5 Method....................................... 279
5.1 General .............................................................................279
5.1.1 General ................................................................................... 279
5.1.2 Desktop................................................................................... 280
5.1.3 Menu bar.................................................................................280
Menu File................................................................................................. 280
Menu Edit ................................................................................................ 281
Menu View............................................................................................... 281
Menu Insert ............................................................................................. 282
Menu Tools ............................................................................................. 282
Menu Help ............................................................................................... 282
5.1.4 Toolbar....................................................................................282
5.1.5 Functions ................................................................................ 284
5.2 Method editor ...................................................................285
5.2.1 Create new method................................................................ 285
5.2.2 Open method ..........................................................................285
5.2.3 Display method.......................................................................287
Selecting the method in the method symbol ........................................ 287
Display single method............................................................................ 287
Display methods beside each other...................................................... 287
Display methods one below the other .................................................. 287
Zoom for methods .................................................................................. 288
5.2.4 Edit method ............................................................................288
Edit tracks ............................................................................................... 288
Insert new track.................................................................................288
Select track .......................................................................................289
Move track.........................................................................................289
Copy track.........................................................................................289
Cut track............................................................................................290
Insert track ........................................................................................290
Delete track .......................................................................................290
Edit commands ....................................................................................... 290
Insert new command ........................................................................290
Select commands .............................................................................291
Move commands ..............................................................................291
Copy commands ..............................................................................291
Cut commands .................................................................................291
Insert commands ..............................................................................292
Delete commands.............................................................................292
Command properties........................................................................292
Command comment.........................................................................292
5.2.5 Check method ........................................................................293
5.2.6 Save method...........................................................................293
5.2.7 Comment on modification for method ..................................295
5.2.8 Close method..........................................................................295
Table of contents xiii
Page 14

5.3 Manage methods............................................................. 296
5.3.1 Manage methods ................................................................... 296
5.3.2 Rename method..................................................................... 297
5.3.3 Copy method .......................................................................... 298
5.3.4 Move method.......................................................................... 298
5.3.5 Delete method........................................................................ 298
5.3.6 Export method........................................................................ 298
5.3.7 Import method ....................................................................... 299
5.3.8 Sign methods ......................................................................... 299
Rules........................................................................................................ 299
Sign method at level 1............................................................................ 300
Sign method at level 2............................................................................ 301
Show method signatures ....................................................................... 302
Delete signatures 2................................................................................. 302
5.3.9 Show method history ............................................................. 303
5.4 Manage method groups .................................................. 304
5.4.1 Manage method groups......................................................... 304
5.4.2 Method group properties ....................................................... 304
General.................................................................................................... 305
Access rights .......................................................................................... 305
5.5 Tracks .............................................................................. 306
5.5.1 General................................................................................... 306
5.5.2 Track types ............................................................................ 307
Main track................................................................................................ 307
Normal track............................................................................................ 307
Series start track..................................................................................... 308
Series end track...................................................................................... 308
Exit track.................................................................................................. 309
Error track ............................................................................................... 309
5.5.3 Edit tracks.............................................................................. 310
5.6 Commands....................................................................... 311
5.6.1 General................................................................................... 311
5.6.2 Edit commands ...................................................................... 312
5.6.3 Method command overview .................................................. 312
5.6.4 Track commands ................................................................... 314
START...................................................................................................... 315
General........................................................................................ 315
Application note ..........................................................................317
Method variables (table) .............................................................317
Method variables (properties).....................................................318
TRACK ..................................................................................................... 320
SERIES START........................................................................................ 321
SERIES END............................................................................................ 321
EXIT ......................................................................................................... 322
ERROR .................................................................................................... 322
END.......................................................................................................... 322
xiv Table of contents
Page 15

Titration commands ...............................................................323
5.6.5
DET .......................................................................................................... 323
DET pH..............................................................................................325
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 326
Start conditions .......................................................................... 328
Titration parameters ................................................................... 330
Stop conditions .......................................................................... 332
Potentiometric evaluation........................................................... 333
Additional evaluations ................................................................ 337
Additional measured values....................................................... 339
DET U................................................................................................341
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 342
Start conditions .......................................................................... 344
Titration parameters ................................................................... 346
Stop conditions .......................................................................... 346
Potentiometric evaluation........................................................... 347
Additional evaluations ................................................................ 349
Additional measured values....................................................... 351
DET Ipol ............................................................................................351
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 352
Start conditions .......................................................................... 354
Titration parameters ................................................................... 354
Stop conditions .......................................................................... 354
Potentiometric evaluation........................................................... 354
Additional evaluations ................................................................ 355
Additional measured values....................................................... 357
DET Upol...........................................................................................357
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 358
Start conditions .......................................................................... 360
Titration parameters ................................................................... 362
Stop conditions .......................................................................... 364
Potentiometric evaluation........................................................... 365
Additional evaluations ................................................................ 367
Additional measured values....................................................... 369
MET.......................................................................................................... 369
MET pH .............................................................................................370
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 371
Start conditions .......................................................................... 371
Titration parameters ................................................................... 371
Stop conditions .......................................................................... 373
Potentiometric evaluation........................................................... 373
Additional evaluations ................................................................ 373
Additional measured values....................................................... 373
MET U ...............................................................................................373
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 374
Start conditions .......................................................................... 374
Titration parameters ................................................................... 374
Stop conditions .......................................................................... 374
Potentiometric evaluation........................................................... 374
Additional evaluations ................................................................ 374
Additional measured values....................................................... 374
MET Ipol............................................................................................374
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 375
Start conditions .......................................................................... 375
Titration parameters ................................................................... 375
Stop conditions .......................................................................... 375
Potentiometric evaluation........................................................... 375
Table of contents xv
Page 16

Additional evaluations.................................................................375
Additional measured values .......................................................375
MET Upol.......................................................................................... 376
General/Hardware.......................................................................376
Start conditions ...........................................................................376
Titration parameters ....................................................................376
Stop conditions ...........................................................................377
Potentiometric evaluation............................................................377
Additional evaluations.................................................................377
Additional measured values .......................................................377
SET .......................................................................................................... 378
SET pH ............................................................................................. 379
General/Hardware.......................................................................380
Start conditions ...........................................................................380
Control parameters .....................................................................382
Titration parameters ....................................................................384
Stop conditions ...........................................................................385
Conditioning................................................................................386
Additional evaluations.................................................................387
Additional measured values .......................................................388
SET U ............................................................................................... 388
General/Hardware.......................................................................389
Start conditions ...........................................................................389
Control parameters .....................................................................390
Titration parameters ....................................................................392
Stop conditions ...........................................................................392
Conditioning................................................................................392
Additional evaluations.................................................................393
Additional measured values .......................................................394
SET Ipol............................................................................................ 394
General/Hardware.......................................................................395
Start conditions ...........................................................................395
Control parameters .....................................................................395
Titration parameters ....................................................................395
Stop conditions ...........................................................................395
Conditioning................................................................................395
Additional evaluations.................................................................395
Additional measured values .......................................................395
SET Upol .......................................................................................... 396
General/Hardware.......................................................................396
Start conditions ...........................................................................397
Control parameters .....................................................................398
Titration parameters ....................................................................400
Stop conditions ...........................................................................400
Conditioning................................................................................400
Additional evaluations.................................................................401
Additional measured values .......................................................402
KFT .......................................................................................................... 402
KFT Ipol ............................................................................................ 404
General/Hardware.......................................................................405
Start conditions ...........................................................................407
Control parameters .....................................................................407
Titration parameters ....................................................................409
Stop conditions ...........................................................................410
Conditioning................................................................................410
Additional evaluations.................................................................410
Additional measured values .......................................................410
xvi Table of contents
Page 17

KFT Upol ...........................................................................................410
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 411
Start conditions .......................................................................... 411
Control parameters .................................................................... 411
Titration parameters ................................................................... 411
Stop conditions .......................................................................... 411
Conditioning ............................................................................... 411
Additional evaluations ................................................................ 411
Additional measured values....................................................... 412
KFC.......................................................................................................... 412
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 413
Start conditions .......................................................................... 414
Control parameters .................................................................... 415
Titration parameters ................................................................... 416
Stop conditions .......................................................................... 417
Conditioning ............................................................................... 417
Additional evaluations ................................................................ 418
Additional measured values....................................................... 419
STAT ........................................................................................................ 420
STAT pH............................................................................................ 421
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 422
Start conditions .......................................................................... 425
Control parameters .................................................................... 426
Titration parameters ................................................................... 428
Stop conditions .......................................................................... 429
Monitoring................................................................................... 430
Evaluations ................................................................................. 434
Additional measured values....................................................... 436
STAT U ..............................................................................................436
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 437
Start conditions .......................................................................... 439
Control parameters .................................................................... 440
Titration parameters ................................................................... 441
Stop conditions .......................................................................... 442
Monitoring................................................................................... 443
Evaluations ................................................................................. 447
Additional measured values....................................................... 449
Evaluation ............................................................................................... 449
pK value and half neutralization potential.........................................449
Minimum and maximum evaluation..................................................450
Break point evaluation ......................................................................450
5.6.6 Measuring commands............................................................ 451
MEAS pH ................................................................................................. 451
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 452
Measuring parameters ............................................................... 454
Evaluations ................................................................................. 456
Additional measured values....................................................... 458
MEAS U ................................................................................................... 458
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 459
Measuring parameters ............................................................... 460
Evaluations ................................................................................. 462
Additional measured values....................................................... 464
MEAS Ipol................................................................................................ 464
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 465
Measuring parameters ............................................................... 466
Evaluations ................................................................................. 466
Additional measured values....................................................... 466
Table of contents xvii
Page 18

MEAS Upol .............................................................................................. 467
General/Hardware.......................................................................468
Measuring parameters................................................................ 469
Evaluations..................................................................................471
Additional measured values .......................................................473
MEAS T.................................................................................................... 473
General/Hardware.......................................................................474
Measuring parameters................................................................ 475
Evaluations..................................................................................477
Additional measured values .......................................................479
MEAS T/Flow........................................................................................... 479
General/Hardware.......................................................................479
Measuring parameters................................................................ 480
Evaluations..................................................................................480
Additional measured values .......................................................481
MEAS Conc ............................................................................................. 481
General/Hardware.......................................................................482
Measuring parameters................................................................ 483
Additional measured values .......................................................483
MEAS Cond............................................................................................. 483
General/Hardware.......................................................................484
Measuring parameters................................................................ 485
Evaluations..................................................................................486
Additional measured values .......................................................487
STDADD................................................................................................... 488
STDADD man ................................................................................... 488
General/Hardware.......................................................................489
Standard addition .......................................................................490
Measuring parameters................................................................ 491
STDADD dos .................................................................................... 492
General/Hardware.......................................................................493
Standard addition .......................................................................495
Measuring parameters................................................................ 496
STDADD auto ................................................................................... 496
General/Hardware.......................................................................496
Standard addition .......................................................................497
Measuring parameters................................................................ 497
5.6.7 Calibration commands .......................................................... 498
Calibrating with manual solution changing .......................................... 499
Calibrating with automatic solution changing ...................................... 500
CAL LOOP pH ......................................................................................... 501
CAL LOOP pH - properties .........................................................502
CAL MEAS pH ......................................................................................... 503
General/Hardware.......................................................................503
Measuring parameters................................................................ 505
CAL LOOP Conc ..................................................................................... 506
CAL LOOP Conc - properties .....................................................506
CAL MEAS Conc ..................................................................................... 507
General/Hardware.......................................................................507
Measuring parameters................................................................ 508
5.6.8 Dosing commands ................................................................. 509
ADD.......................................................................................................... 509
General/Hardware.......................................................................510
Dosing parameters .....................................................................512
xviii Table of contents
Page 19

DOS ......................................................................................................... 513
DOS pH.............................................................................................513
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 514
Dosing parameters..................................................................... 516
Stop conditions .......................................................................... 517
Monitoring................................................................................... 518
Additional measured values....................................................... 521
DOS U ...............................................................................................521
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 522
Dosing parameters..................................................................... 524
Stop conditions .......................................................................... 524
Monitoring................................................................................... 525
Additionan measured values ..................................................... 528
LQH.......................................................................................................... 528
General/Hardware ...................................................................... 528
Parameters ................................................................................. 529
PREP........................................................................................................ 531
PREP - properties....................................................................... 532
EMPTY ..................................................................................................... 533
EMPTY - properties .................................................................... 533
5.6.9 Automation commands..........................................................534
MOVE....................................................................................................... 534
MOVE - properties...................................................................... 535
SWING ..................................................................................................... 537
SWING - properties .................................................................... 537
LIFT.......................................................................................................... 539
LIFT - Properties ......................................................................... 539
PUMP....................................................................................................... 540
PUMP - properties...................................................................... 541
STIR ......................................................................................................... 542
STIR - properties ........................................................................ 542
RACK ....................................................................................................... 544
RACK - properties ...................................................................... 544
HEATER................................................................................................... 545
HEATER - properties .................................................................. 545
FLOW....................................................................................................... 547
FLOW - properties...................................................................... 547
5.6.10 Result commands...................................................................549
CALC ....................................................................................................... 549
CALC - result table............................................................................550
CALC result properties......................................................................552
Result - definition........................................................................ 552
Result - Monitoring ..................................................................... 553
Result - options .......................................................................... 555
Send e-mail ................................................................................ 556
Result templates ...............................................................................557
Manage result templates ........................................................... 557
Save result template................................................................... 557
Rename result template ............................................................. 558
DATABASE .............................................................................................. 558
DATABASE - properties ............................................................. 559
REPORT .................................................................................................. 560
REPORT - Properties.................................................................. 560
EXPORT................................................................................................... 561
EXPORT - properties.................................................................. 561
Table of contents xix
Page 20

5.6.11
5.6.12 Miscellaneous commands ..................................................... 575
Communication commands................................................... 562
CTRL........................................................................................................ 562
CTRL - Properties........................................................................563
SCAN ....................................................................................................... 564
SCAN - Properties.......................................................................564
SEND ....................................................................................................... 566
SEND - properties.......................................................................566
SEND - event messages.............................................................567
RECEIVE.................................................................................................. 568
RECEIVE - properties..................................................................568
RECEIVE - event/state ................................................................570
TRANSFER .............................................................................................. 571
TRANSFER - properties ..............................................................571
TRANSFER - transfer commands...............................................572
REQUEST ................................................................................................ 575
REQUEST - properties ................................................................575
REQUEST - sample data request...............................................577
CALL ........................................................................................................ 578
CALL - properties........................................................................578
CALL - call...................................................................................579
LOOP ....................................................................................................... 580
LOOP - properties.......................................................................581
WAIT ........................................................................................................ 582
WAIT - properties ........................................................................582
SEQUENCE ............................................................................................. 583
SEQUENCE - properties.............................................................584
5.7 Method reports ................................................................ 585
5.7.1 Select method reports ........................................................... 585
5.7.2 Method sequence report ....................................................... 585
5.7.3 Method parameters report .................................................... 586
5.7.4 Titration and measurement parameters report ................... 586
xx Table of contents
Page 21

Chapter 6 Configuration ............................ 587
6.1 General .............................................................................587
6.1.1 General ................................................................................... 587
6.1.2 Desktop................................................................................... 587
6.1.3 Menu bar.................................................................................588
Menu File................................................................................................. 588
Menu View............................................................................................... 588
Menu Tools ............................................................................................. 589
Menu Help ............................................................................................... 589
6.1.4 Toolbar....................................................................................590
6.1.5 Subwindows ...........................................................................590
6.1.6 Functions ................................................................................ 591
6.1.7 Configuration views ............................................................... 592
Change layout......................................................................................... 592
Save view ................................................................................................ 593
Load view ................................................................................................ 594
Rename view........................................................................................... 595
Delete view.............................................................................................. 595
6.2 Administration..................................................................596
6.2.1 Security settings ....................................................................596
Login/Password protection.................................................................... 597
Send e-mail .......................................................................................599
Audit Trail/Modifications ........................................................................ 600
Signatures............................................................................................... 601
Default reasons....................................................................................... 602
6.2.2 User administration ............................................................... 604
User groups ............................................................................................ 605
User group information.....................................................................605
Access rights.....................................................................................606
Signatures.........................................................................................607
Options..............................................................................................609
Add user group .................................................................................609
Copy user group...............................................................................610
Rename user group ..........................................................................610
Delete user group .............................................................................610
Add user............................................................................................610
Users ....................................................................................................... 611
User information................................................................................611
Add user............................................................................................612
Set start password ............................................................................612
6.2.3 Program administration......................................................... 613
Backup directories ................................................................................. 613
Create new backup directory............................................................614
Edit backup directory........................................................................614
Clients ..................................................................................................... 615
Licenses .................................................................................................. 615
Table of contents xxi
Page 22

6.3 Configuration data .......................................................... 617
6.3.1 Export/Import ......................................................................... 617
Export configuration data....................................................................... 617
Import configuration data....................................................................... 618
6.3.2 Backup/Restore...................................................................... 619
Backup configuration data automatically ............................................. 619
Backup configuration data manually..................................................... 620
Restore configuration data .................................................................... 621
6.3.3 Templates .............................................................................. 622
Custom calibration buffers .................................................................... 622
Templates for input lines........................................................................ 623
Templates for output lines ..................................................................... 624
6.3.4 Options ................................................................................... 626
General............................................................................................. 626
Save.................................................................................................. 627
PDF................................................................................................... 627
6.4 Audit Trail ........................................................................ 628
6.4.1 General................................................................................... 628
General.................................................................................................... 628
Desktop ................................................................................................... 628
Menu bar ................................................................................................. 628
Menu File.......................................................................................... 629
Menu View........................................................................................ 629
Menu Filter........................................................................................ 629
Menu Tools....................................................................................... 629
Menu Help........................................................................................ 629
Toolbar .................................................................................................... 630
Filter selection ........................................................................................ 630
Audit Trail - navigation bar..................................................................... 630
Functions................................................................................................. 631
6.4.2 Audit Trail table ..................................................................... 631
Column display....................................................................................... 633
Filter Audit Trail ...................................................................................... 633
Last filter ........................................................................................... 633
Quick filter ........................................................................................ 634
Special filter...................................................................................... 634
Edit filter condition ......................................................................635
Save filter.....................................................................................636
Remove filter .................................................................................... 636
Update Audit Trail................................................................................... 637
Export Audit Trail .................................................................................... 637
Archive Audit Trail .................................................................................. 637
Delete Audit Trail .................................................................................... 638
Print Audit Trail ....................................................................................... 639
Audit Trail monitoring............................................................................. 639
6.5 Subwindow Devices ........................................................ 640
6.5.1 General................................................................................... 640
6.5.2 Device table ........................................................................... 640
Column display....................................................................................... 642
Add new device....................................................................................... 643
Delete device .......................................................................................... 643
Print devices list ..................................................................................... 643
xxii Table of contents
Page 23

Device properties ...................................................................644
6.5.3
Overview ................................................................................................. 644
Titrando ................................................................................................... 644
General..............................................................................................645
Load new program version ........................................................ 645
Measuring inputs ..............................................................................646
MSB #...............................................................................................647
GLP ...................................................................................................648
Titrino ...................................................................................................... 649
General..............................................................................................649
Load new program version ........................................................ 650
Int. dosing device D0 ........................................................................651
Ext. dosing device D# ......................................................................651
RS 232...............................................................................................652
GLP ...................................................................................................653
Coulometer ............................................................................................. 654
General..............................................................................................654
Load new program version ........................................................ 655
RS 232...............................................................................................655
GLP ...................................................................................................656
Conductometer ....................................................................................... 657
General..............................................................................................657
Load new program version ........................................................ 658
RS 232...............................................................................................658
GLP ...................................................................................................659
Dosing Interface ..................................................................................... 660
General..............................................................................................660
Load new program version ........................................................ 661
MSB #...............................................................................................661
GLP ...................................................................................................662
814/815 USB Sample Processor............................................................ 663
General..............................................................................................664
Load new program version ........................................................ 664
Tower #.............................................................................................665
Robotic arm configuration.......................................................... 666
External position......................................................................... 667
Rack ..................................................................................................668
MSB #...............................................................................................669
GLP ...................................................................................................670
855 Robotic Titrosampler....................................................................... 671
General..............................................................................................671
Load new program version ........................................................ 672
Measuring inputs ..............................................................................672
Tower #.............................................................................................673
Robotic arm configuration.......................................................... 674
External position......................................................................... 675
Rack ..................................................................................................676
MSB #...............................................................................................677
GLP ...................................................................................................678
778/789 Sample Processor .................................................................... 679
General..............................................................................................679
Load new program version ........................................................ 680
Tower #.............................................................................................681
Robotic arm configuration.......................................................... 682
External position......................................................................... 683
Rack ..................................................................................................683
MSB #...............................................................................................684
Table of contents xxiii
Page 24

RS 232.............................................................................................. 685
GLP................................................................................................... 685
730 Sample Changer .............................................................................. 687
General............................................................................................. 687
Load new program version.........................................................688
Towers.............................................................................................. 688
Rack ................................................................................................. 689
Dosing device................................................................................... 690
RS 232.............................................................................................. 690
GLP................................................................................................... 691
774 Oven Sample Processor ................................................................. 692
General............................................................................................. 692
Load new program version.........................................................693
Towers.............................................................................................. 694
Rack ................................................................................................. 694
Edit rack properties (774)................................................................. 695
Lift positions ................................................................................696
Special beakers ..........................................................................696
Dosing device................................................................................... 697
Oven ................................................................................................. 697
Gas ................................................................................................... 698
RS 232.............................................................................................. 698
GLP................................................................................................... 699
Balance.................................................................................................... 700
General............................................................................................. 700
RS 232.............................................................................................. 701
Test connection...........................................................................702
GLP................................................................................................... 703
Barcode reader ....................................................................................... 704
General............................................................................................. 705
Settings ............................................................................................ 706
Check connection .......................................................................706
GLP................................................................................................... 707
RS232 device .......................................................................................... 708
General............................................................................................. 708
RS 232.............................................................................................. 709
Test connection...........................................................................710
GLP................................................................................................... 711
6.6 Subwindow Titrants/Solutions........................................ 713
6.6.1 General................................................................................... 713
6.6.2 Solution table......................................................................... 713
Column display....................................................................................... 715
Add new solution .................................................................................... 715
Delete solution........................................................................................ 716
Print solution list..................................................................................... 716
6.6.3 Solution properties ................................................................ 716
Solution ............................................................................................ 717
Titer................................................................................................... 718
Titer history....................................................................................... 720
Titer history - Limits .....................................................................721
Exchange unit .................................................................................. 722
Dosing unit ....................................................................................... 725
GLP................................................................................................... 728
xxiv Table of contents
Page 25

6.7 Subwindow Sensors.........................................................730
6.7.1 General ................................................................................... 730
6.7.2 Sensor table ...........................................................................730
Column display....................................................................................... 732
Add new sensor...................................................................................... 732
Delete sensor.......................................................................................... 733
Print sensor list....................................................................................... 733
6.7.3 Sensor properties...................................................................734
Sensor...............................................................................................734
Calibration data.................................................................................736
Limits.................................................................................................738
History...............................................................................................739
Sensor history - Limits................................................................ 740
6.8 Subwindow Common Variables.......................................743
6.8.1 General ................................................................................... 743
6.8.2 Table of common variables ...................................................743
Column display....................................................................................... 745
Add new common variable..................................................................... 745
Delete common variable ........................................................................ 746
Print list of common variables ............................................................... 746
6.8.3 Common variables properties ...............................................746
Common variable..............................................................................747
History...............................................................................................749
History - limits............................................................................. 750
6.9 Subwindow Rack data .....................................................751
6.9.1 General ................................................................................... 751
6.9.2 Rack table ..............................................................................751
Add new rack .......................................................................................... 752
Delete rack .............................................................................................. 753
Print rack list........................................................................................... 753
6.9.3 Rack properties......................................................................753
Rack parameters...............................................................................754
Lift positions......................................................................................755
Special beakers ................................................................................756
Special beaker............................................................................ 757
Table of contents xxv
Page 26

Chapter 7 How to proceed ......................... 759
7.1 Audit Trail ........................................................................ 759
7.1.1 Open Audit Trail ..................................................................... 759
7.1.2 Filter Audit Trail ..................................................................... 759
7.1.3 Export Audit Trail ................................................................... 760
7.1.4 Archive Audit Trail ................................................................. 760
7.1.5 Delete Audit Trail ................................................................... 761
7.2 Backup............................................................................. 762
7.2.1 Backup database................................................................... 762
7.2.2 Restore database................................................................... 763
7.2.3 Backup configuration data.................................................... 763
7.2.4 Restore configuration data ................................................... 764
7.2.5 Backup methods .................................................................... 764
7.2.6 Archive Audit Trail ................................................................. 766
7.3 Determinations................................................................ 767
7.3.1 Start single determination .................................................... 767
7.3.2 Start determination series .................................................... 768
7.3.3 Search determinations .......................................................... 769
7.3.4 Filter determinations ............................................................. 769
7.3.5 Sign determination ................................................................ 770
7.3.6 Export determinations ........................................................... 771
7.3.7 Import determinations........................................................... 771
7.3.8 Delete determinations........................................................... 772
7.3.9 Make current previous determination version ..................... 772
7.3.10 Reprocess determinations .................................................... 772
7.3.11 Print determination report .................................................... 775
7.3.12 Print determination overview................................................ 775
7.4 Databases........................................................................ 776
7.4.1 Open database....................................................................... 776
7.4.2 Close database ...................................................................... 776
7.4.3 Create new database ............................................................ 776
7.4.4 Backup database................................................................... 777
7.4.5 Restore database................................................................... 778
7.4.6 Delete database..................................................................... 778
7.5 Configuration data .......................................................... 779
7.5.1 Export configuration data...................................................... 779
7.5.2 Import configuration data ..................................................... 779
xxvi Table of contents
Page 27

Backup configuration data .................................................... 779
7.5.3
7.5.4 Restore configuration data.................................................... 780
7.6 Methods ............................................................................781
7.6.1 Open method ..........................................................................781
7.6.2 Close method..........................................................................781
7.6.3 Create new method................................................................ 781
7.6.4 Save method...........................................................................782
7.6.5 Delete method ........................................................................ 782
7.6.6 Export method ........................................................................783
7.6.7 Import method........................................................................783
7.6.8 Sign method............................................................................783
7.6.9 Make current previous method version ................................ 784
7.6.10 Print method report................................................................785
7.7 Method groups .................................................................786
7.7.1 Create new method group .....................................................786
7.7.2 Delete method group..............................................................786
7.8 Sample tables ..................................................................787
7.8.1 Create new sample table.......................................................787
7.8.2 Edit sample table ................................................................... 787
7.8.3 Load working sample table ................................................... 788
7.8.4 Edit working sample table.....................................................788
7.9 Reports .............................................................................789
7.9.1 Create new report template ..................................................789
7.9.2 Edit report template...............................................................789
7.9.3 Print determination report..................................................... 790
7.9.4 Print method report................................................................791
7.9.5 Print determination overview ................................................ 791
Chapter 8 Index.......................................... 793
Table of contents xxvii
Page 28

xxviii Table of contents
Page 29

Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Welcome to tiamo
tiamo = titration and more
tiamo is a control and database software for titrators, dosing devices and sample
changers that allows complete laboratory automation, which is why the name
tiamo stands for «titration and more» – tiamo can do far more than just titrate.
tiamo is the successor of the TiNet and Workcell software. With it Metrohm now of-
fers worldwide a uniform software product for laboratory automation. This means
that an internationally operating concern can now use the same software platform
for processing all its samples and exchange data and methods without any loss.
The most important program features
• Easy to use and configurable user interface
• Easy integration of instruments and accessories
• Comfortable method editor
• Database program with client/server functionality
• Manifold import and export possibilities
• FDA compatibility according to 21 CFR Part 11
• Extensive online help
Welcome to tiamo 1
Page 30

1.2 User interface
The modern user interface makes it easy for users to familiarize themselves with
tiamo quickly. All command and control functions are located where users would
expect them. The tiamo bar on the left-hand side of the screen allows access to
the four basic tiamo components:
Whether these buttons are visible or concealed depends on the user’s rights of
access. The menu bar is located in the upper part of the screen. Again, each individual command can be concealed in accordance with the rights of access of the
user.
In the center of the screen are the information windows, in which settings, sample input templates, real-time curves or results are shown. This display can be adjusted individually for each user with the aid of the new Layout Manager. This
means that each user can only see the windows or buttons necessary for his or
her work. This shortens the familiarization time for users carrying out routine work
to a minimum; operating errors resulting from a cluttered screen are now a thing
of the past.
The methods and calculation templates successfully introduced with the Titrando system are also available with tiamo. Numerous tried and tested methods
allow users to draw up their own individual methods quickly and simply and to use
them immediately.
2 Introduction
Page 31

1.3 Integration of devices
tiamo brings together the world of Titrino devices with the new generation of the
Titrando system. In the software sector such compatibility with existing Metrohm
devices is not just a matter of course. The whole Titrino family, which was previously also controlled by TiNet, can continue to be operated under tiamo, and this
after more than 10 years on the market! In addition, sample changers, some of
which are no longer in our sales program, can also be operated under tiamo.
That's how Metrohm protects your investments!
Of course, all the models of the latest Titrando generation as well as the new
Sample Processors are compatible with tiamo. In this way all the advantages of
USB communication, such as plug and play or recognition of the intelligent dosing
systems, can be utilized to the full with tiamo. Even the mixed operation of older
RS 232-controlled and the new USB-controlled instruments is possible without any
problems.
Devices compatible with tiamo
• Titrando
808, 809, 835, 836, 841, 842, 855
• Titrino
702, 716, 718, 719, 720, 721, 736, 751, 758, 784, 785, 794, 795, 798,
799
• Conductometer
712
• KF Coulometer
756, 831
• Sample Changer
730, 774, 778, 789, 814, 815, 855
• Miscellaneous
846 Dosing Interface, balances, barcode readers ...
Integration of devices 3
Page 32

1.4 Method editor
The new graphical Method Editor makes more of your titration system. Methods
can be drawn up quickly and simply by using the numerous templates. Methods
that have been proved in practice are available for most routine and automation
tasks. A few clicks are all that is needed to adapt them and make them ready for
use.
It is now possible to program and link activities that take place in parallel. This
means that, together with the new Titrando system and the Robotic Sample Processors, a sample can now be titrated while the next sample is already being prepared. This saves time and increases sample throughput. The crowning achievement is the simultaneous processing of several samples – one Titrando can carry
out two titrations at the same time. This doubles sample throughput!
tiamo is flexible and adapts itself to the analytical sequence, not vice versa.
Overview of functions
• Graphical method editor
• Method manager
• Access rights management for each method group
• Templates for method development and calculations
• Method test
• Comments for methods
• Parallel track function
• Loop function
4 Introduction
Page 33

1.5 Database
tiamo is based on an industrially tested, object-oriented database. The configuration database contains all settings, the user administration, methods and
templates. The determination data are stored in determination databases defined by the user. These databases can be installed locally on the computer used
and represent a simple titration system. However, tiamo is also scaleable and
grows to meet the operating requirements. As soon as data security and central
data administration come to the fore, tiamo can be set up in a client-server con-
figuration, with the tiamo database installed on a server. All measuring and office
computers then act as clients. In this titration network all results are stored centrally and can be viewed and recalculated by all client PCs. In addition, all clients
can access the same pool of methods.
The new database provides all the necessary tools for managing results as well as
for searching for them and grouping them together. Quick Filters allow users to
search through thousands of determinations in a few seconds and present the
search results in a clear manner. Control charts provide a rapid overview of the
chronological sequence of the results.
All the possibilities for recalculation and re-evaluation are available to the users.
Overview of functions
• Object-oriented Client/Server database
• Quick filter and powerful search functions
• Access rights management for each database
• Automatic database backup function
• Layout manager for database view
• Reprocessing function for variables, methods, statistics, and curve
evaluation
• Control charts
Database 5
Page 34

1.6 Communication
Easy and inexpensive integration into existing laboratory information systems,
central databases and long-term archiving systems is crucial for the acceptance
of PC-controlled analytical systems.
tiamo is communicative. LIMS systems can easily import work lists into tiamo’s
own sample table and also control them remotely, without any additional modules.
Data generated in tiamo are now exported in XML format. This enables the simple
incorporation into all LIMS systems currently on the market. Export to long-term
archiving systems such as NuGenesis SDMS or Scientific Software CyberLABlab
is also supported.
With the new Report Designer the analysis reports can now be drawn up simply
and flexibly. The Report Designer allows report templates to be freely defined. In
this way reports of one or more determinations can be produced at any time with
a selectable layout in pdf format or as a paper printout.
A special feature of tiamo is that status messages, error messages or results can
be transmitted from the method sequence to the user by E-Mail.
Overview of functions
• Import of sample data
• Several data export formats,such as XML, CSV, SLK
• Direct export to NuGenesis SDMS, Scientific Software CyberLAB, etc.
• Report designer
• E-mail function for status messages, error messages, or results
• Import of external measured values
6 Introduction
Page 35

1.7 Compliance
tiamo also sets new standards with respect to compliance with GMP, GLP and
FDA requirements. The latest quality standards and validation procedures have
been used during the development and programming of the software. Right from
the very start tiamo has been designed to comply with the demands of FDA
Regulation 21 CFR Part 11 and its customer-specific interpretations. This is
confirmed by a compliance certificate. A central user administration determines
rights of access to program functions, methods and results. Any number of users
with freely definable user profiles are possible. The system administrator has comfortable access to the user administration from any tiamo client. Access to the
software is password-protected and either the tiamo or Windows login can be selected.
The use of digital signatures allows to sign methods and results. Two signatures
with different features are available. With the Level 1 Signature (Review) the user
confirms the he has correctly programmed the method or correctly performed the
analysis, whatever the case. The Level 2 Signature (Release) is used to release
the method or the result and protect it against further changes. This means that
company-specific workflows can be displayed in tiamo.
All data are managed by version control and protected against unauthorized
access, alteration or deletion in the database. The database itself controls access
to the data in network operation and offers archiving and recovery functions.
The Audit Trail protocols all user actions as well as important system events.
Compliance features of tiamo
• Designed and validated for compliance
• Central user administration
• Detailed access rights management
• tiamo or Windows password protection
• Digital signature with two levels
• Different signatures for methods and results
• Method and results history
• Detailed Audit Trail guarantees traceability
Compliance 7
Page 36

1.8 Versions
tiamo is available in three versions; these differ in the range of functions offered.
An upgrade is possible at any time.
tiamo 1.1 light tiamo 1.1 full tiamo 1.1 multi
Article 6.6056.111 6.6056.112 6.6056.113
Maximum number of instruments per PC 2 unlimited unlimited
Compliant with FDA 21 CFR Part 11
User administration
Security policies
Audit Trail
Client-server support
Number of licenses 1 1 3
Additional licenses (optional)
XML data export to LIMS
Parallel titrations
Upgrade available
z z z
z z
z z
z z
z z
z
z
z z
z z
1.9 Online Help
Help call
tiamo contains an extensive and detailed online help that can be called in two different ways:
• General call
With the menu item
opens with the subject Welcome. From there you can jump to desired
subject via
• Context-sensitive call
By pressing the key [F1] on the keypad the online help opens directly
with the subject showing information about the activated element (dialog window, tab).
Content, Index or Search.
Help, tiamo Help or the icon the online help
8 Introduction
Page 37

1.10 What's new in tiamo 1.1?
New devices
• 842 Titrando
• 855 Robotic Titrosampler
New commands
•
STAT pH
STAT Titration with pH electrodes (measuring quantity pH).
STAT U
•
STAT Titration with metal electrodes (measuring quantity U).
STDADD man
•
Standard addition with manual addition of the standard addition solution.
STDADD dos
•
Standard addition with addition of the standard addition solution from
a dosing device.
STDADD auto
•
Standard addition with automatic addition of the standard addition solution from a dosing device in such a way that a constant potential difference results.
DOS pH
•
Controlled dosing with measurement quantity pH.
DOS U
•
Controlled dosing with measurement quantity U.
New features in the Workplace program part
Sample size and/or Unit are entered or imported in an opened Sam-
• If
ple table on the
ble on the
Single determinations tab or in the working sample ta-
Determination series tab then in addition the time of data in-
put and the data source will be saved automatically. This data is
stored together with the determination and shown in the subwindow
Information under Sample/Sample data as Input date and Data source.
• If a command is canceled manually or the method is stopped manually then the data of the incompletely carried out command will be
newly saved in the database.
• In the Report window the name of the
to
Latest report.
• In Manual operation the filling of exchange and dosing units is now
also possible for Titrinos.
New features in the Database program part
• If sample data are altered live in the run window on the
tab or in the working sample table on the Determination series
nations
tab then these alterations will not only be recorded in the Audit Trail,
but also saved in the determination as messages.
• The appearance of the dialog window
tered.
• In methods containing the command
curves are shown in the
Calibration curve window.
Current report tab will be altered
Single determi-
Edit filter conditions has been al-
STDADD the standard addition
What's new in tiamo 1.1? 9
Page 38

New features in the Method program part
• The command
ADD can now also be carried out with a Tandem dosing
device.
• Introduction of new Command variables:
.RES, .VAR
.
.CYL, .RE, .MRT, .MRS, .MRC,
New features in the
• The
• The
Security settings can be printed out.
User administration data can be printed out.
• In the dialog window
tab has been replaced by the
client is additionally shown (active, inactive).
• Metrohm USB devices can now be initialized with the menu item
.
tialize
• For Metrohm RS232 devices the
• For 778, 789, 814, 815 and 855 Sample Changers the
tance between the rotary axis of the sample rack and rotary axis of the
robotic arm) is no longer entered in the dialog window
figuration
• For Sartorius balances you can now enter whether the balance has a
Data storage under legal control feature or not.
Configuration program part
Program administration the Computer identification
Clients tab, on which the status of the
Ini-
Baud rate can now be adjusted.
Axis offset (dis-
Robotic arm con-
, but on the Tower# tab.
10 Introduction
Page 39

Chapter 2 General program
functions
2.1 Program parts
tiamo has four different program parts which can be opened by clicking on the
corresponding symbol in the vertical bar at the left-hand margin. The symbole for
the program part opened is shown in color, the symbols for the other program
parts in black and white. The menues, toolbars, and the content of the main window depend on the program part opened.
Program part Workplace
• Open/close workplaces
• Start single determinations and determination series
• Sample tables
• Manual operation of instruments
Program part Database
• Open/close databases
• Database manager
• Reprocessing
• Creation of report templates
Program part Method
• Open/close existing methods
• Create new methods
• Method manager
Program part Configuration
• Configuration of instruments, solutions, sensors, common variables, and rack data
• Security settings
• User administration
• Program administration
• Audit Trail
Note
The access to the different program parts can be switched off in the User administration. In this case, the corresponding symbols will be hidden.
Program parts 11
Page 40

2.2 Login/Password protection
2.2.1 General
Login in tiamo
tiamo can be configured so that all users must log in with User name and Password; these entries are then checked automatically. A requirement for this is that
a User administration has been set up and the corresponding Security settings
have been made. This data is stored in the configuration database. In client/server
systems this is found on the server and applies globally for all clients (central user
administration).
FDA-conform settings
If FDA-conform work is to be carried out then the settings on the tab
Login/Password protection in the dialog window
11 must be switched on with the button
observed:
• Each time that the program is started a Login with user name and
password is required.
• Password administration takes place in tiamo.
• User names must be unambiguous. Once users have been entered
they cannot be deleted.
• Passwords must be unambiguous for each user. No password that
has been used once by the user and has expired may be reused.
• Passwords must have a minimum number of characters.
• Passwords must have a defined Validity period after which they must
be changed.
• The number of incorrect attempts for entering the password is lim-
ited. If this number is exceeded then the user is automatically given
the status
inactive.
[Set]. The following conditions are then
Security settings as per 21 CFR
Actions
If login is switched on then the following actions can be carried out:
• Login at program start
• Manual logout
• Automatic logout
• Change password
12 General program functions
Page 41

2.2.2 Login
If the two options Enforce login with user name and Enforce login with password are
switched on in the Security settings then each time the program is started and
each time a user is logged out the dialog window
User
Entry of the short name of the user.
Password
Entry of the password.
Note
A user who is logging in for the first time or whose status has been reset from
active
or
ministrator. The window
word to be entered.
removed
to
Login will appear.
active
must log in with the Start password issued by the ad-
Change password
then opens automatically for the pass-
in-
Opens the window Change password in which the new password must be
entered and confirmed.
The login is cancelled, the program is closed.
2.2.3 Manual logout
A logged-in user can log out at any time with the menu item File, User, Logout. The
logout options defined in the Security settings apply. After the logout process has
finished the
Login window opens in which a new user can log in.
2.2.4 Automatic logout
If automatic logout is switched on in the Security settings then the user will be
logged out automatically if the mouse and keyboard are not used within the defined time. When this time has expired the
same user can log in again.
Login window opens in which only the
Note
Users with Administrator can always log in, an Emergency stop is also possible.
Login/Password protection 13
Page 42

2.2.5 Change password
This button in the dialog window Login opens the Change password window
in which the new password must be entered and confirmed.
Note
It is essential that the password is changed before the Validity period (see Security settings - Login/Password protection) of the password expires. This window
will open automatically for a user who is logging in for the first time or whose
status has been reset from
Start password. For
must be entered.
Old password
Entry of the previous password.
New password
24 characters
Entry of the new password. The Password options are defined in the security settings on the register card
Confirm password
24 characters
Confirms the new password.
Old password
inactive
or
removed
to
active
after logging in with the
the Start password issued by the Administrator
Login/Password protection.
14 General program functions
Page 43

2.3 Electronic signatures
2.3.1 Rules
In tiamo methods and determinations can be electronically signed at two levels.
The following rules apply:
• Signature levels
Methods and determinations can be signed at two levels (Signature
Level 1 and Signature Level 2) by entering the user name and password.
• Multiple signing
Methods and determinations can be signed several times at each
level. All the signatures are saved and documented in the Audit Trail.
• Sign at Level 1
If Level 2 has been signed then no more signatures are possible at
Level 1.
• Sign at Level 2
Level 2 can only be signed when signatures already exist at Level 1.
• Different users
The same user can only sign at either Level 1 or Level 2.
• Reason and note
Each signature must be accompanied by a reason selected from predefined default reasons. A further comment can be entered additionally.
• Saved data
The signature date, user name, full name, reason and note are saved
for each signature.
• Deleting Level 1 signatures
Signatures at Level 1 are automatically deleted when a new version is
generated.
• Deleting Level 2 signatures
Signatures at Level 2 can only be deleted by users who have the appropriate rights.
• Signing methods
Methods can always only be signed individually.
• Signature options
The options for electronic signatures are set on the tab Signatures in
the dialog window
Security settings.
2.3.2 Procedure
With respect to their signatures, methods and determinations can have one of the
following three statuses (see flow diagram):
• Not signed
Methods and determinations that have not been signed can be edited
and deleted; a new version is generated for each alteration.
• Signed (1)
When methods and determinations are signed at Level 1 no new versions are generated. If methods and determinations signed at Level 1
are edited then a new version is generated that contains no signatures. Methods and determinations signed at Level 1 can be deleted.
Electronic signatures 15
Page 44

• Signed (2)
When methods and determinations are signed at Level 2 no new versions are generated. Methods and determinations signed at Level 2
can neither be edited nor deleted. However, it is possible to delete
Level 2 signatures while retaining the Level 1 signatures.
2.3.3 Signature Level 1
In the Signature Level 1 window methods or determinations can be signed at Level
1.
Note
Methods or determinations that have been signed at Level 1 can be edited and
deleted. If the edited method or determination is saved as a new version then all
the existing signatures will be deleted automatically, i.e. the method or determination must be signed again.
Info
Information about signatures and the deletion of signatures is shown in this
field. The following messages are possible:
Signature possible
The selected method or determination can be signed.
Signature 1 not possible (signature 2 exists)
The selected method or determination cannot be signed at Level 1 as it has
already been signed at Level 2.
Signature not possible (accessed by other client)
The selected method or determination cannot be signed as it has already
been marked for signature by another client.
16 General program functions
Page 45

User
Entry of the user name (short name).
Password
Entry of the password.
Reason
Selection from standard reasons
Selection from the Default reasons defined in the dialog window
settings
Comment
1000 characters
for the category Signature Level 1.
Entry of remarks about the signature.
Signs for method or determination. The window remains open.
Note
Methods and determinations can only be signed at Level 1 when the user belongs to a user group that has the appropriate rights (see User administration/User group/Signatures).
2.3.4 Signature Level 2
Security
In the Signature Level 2 methods or determinations can be signed at Level 2.
Note
Methods or determinations that have been signed at Level 2 are blocked, i.e.
they can neither be edited nor deleted. In order to be able to edit such methods
or determinations again the signatures at Level 2 must first be deleted (see Delete Level 2 signatures).
Info
Information about signatures and the deletion of signatures is shown in this
field. The following messages are possible:
Signature possible
The selected method or determination can be signed.
Signature 2 not possible (signature 1 missing)
The selected method or determination cannot be signed at Level 2 as it has
not yet been signed at Level 1.
Signature not possible (accessed by other client)
The selected method or determination cannot be signed as it has already
been marked for signature by another client.
User
Entry of the user name (short name).
Password
Entry of the password.
Electronic signatures 17
Page 46

Reason
Selection from standard reasons
Selection from the Default reasons defined in the dialog window
settings
Comment
1000 characters
for the category Signature Level 2.
Entry of remarks about the signature.
Signs for method or determination. The window remains open.
Note
Methods and determinations can only be signed at Level 2 when the user belongs to a user group that has the appropriate rights (see User administration/User group/Signatures).
2.3.5 Delete Level 2 signatures
In the Delete Level 2 signatures window all the signatures at Level 2 for the selected
method or determination can be deleted.
Security
User
Entry of the user name (short name).
Password
Entry of the password.
Delete Level 2 signatures 2.
Note
Level 2 signatures can only be deleted when the user belongs to a user group
that has the appropriate rights (see User administration/User group/Signatures).
18 General program functions
Page 47

2.4 Formula editor
2.4.1 Overview
The Formula editor is used for support in entering formulas for calculating the result. It has an automatic Syntax check that is triggered when the formula is
adopted. The usual Rules of priority apply for computer operations (see Operator
functions - Overview).
The dialog window Formula editor contains the following items:
• Input field
Etry of the calculation formula.
• Function keys
Buttons for the quick input of operators and brackets.
• Variables
Selection from the variables available for the calculation formula.
• Operators/Functions
Selection from the operators and functions available for the calculation
formula.
• Description
Describes the selected variables, operators or functions.
2.4.2 Input field
In the Input field of the formula editor the Calculation formula is entered. The following possibilities exist for making entries:
Entry via keyboard
• Numbers
Numbers and mathematical functions can be entered directly via the
keyboard.
Formula editor 19
Page 48

• Text
Text must be introduced and terminated with inverted commas
"My text").
• Variables
Variables must be introduced and terminated with an inverted comma
' (e.g. 'MV.MyVariable').
• Time
Time information must always be entered by using the function
Time().
Entries using the function keys
Mathematical operators and brackets can be easily inserted in the formula
with the corresponding buttons. A space is inserted automatically before
and after the character.
" (e.g.
Addition
Subtraction
Multiplication
Division
Exponentiation
Equal to
Larger than
Smaller than
Unequal
Smaller than
or equal to
Larger than or
equal to
Input via selection
The item selected in the fields
formula with a double-click or
2.4.3 Arithmetic algorithms
Number format
The standard IEEE 754 (1985) for binary floating-point arithmetic has been
implemented in the software as "double precision" (64Bit).
Logical AND
Logical OR
Round brackets
Curly brackets e.g. for end point definition (e.g.
Undo last action
Restore last action
Variables or Operators can be entered in the
'DET pH 1.EP{1}.VOL')
.
Rounding method
Measured values and results are displayed rounded, depending on user
settings. For that purpose, arithmetic rounding is carried out according to a
method known as "Banker's rounding" (rounding towrds the nearest evan
number). With this method,
9
always rounded up. 5 is always rounded towards the even neighbor, so it
1, 2, 3, 4 are always rounded down and 6, 7, 8,
is rounded down if the neigbor is even (incl. 0) and rounded up if it is odd.
Examples
2.33 gets 2.3
2.35 gets 2.4
2.45 gets 2.4
20 General program functions
Page 49
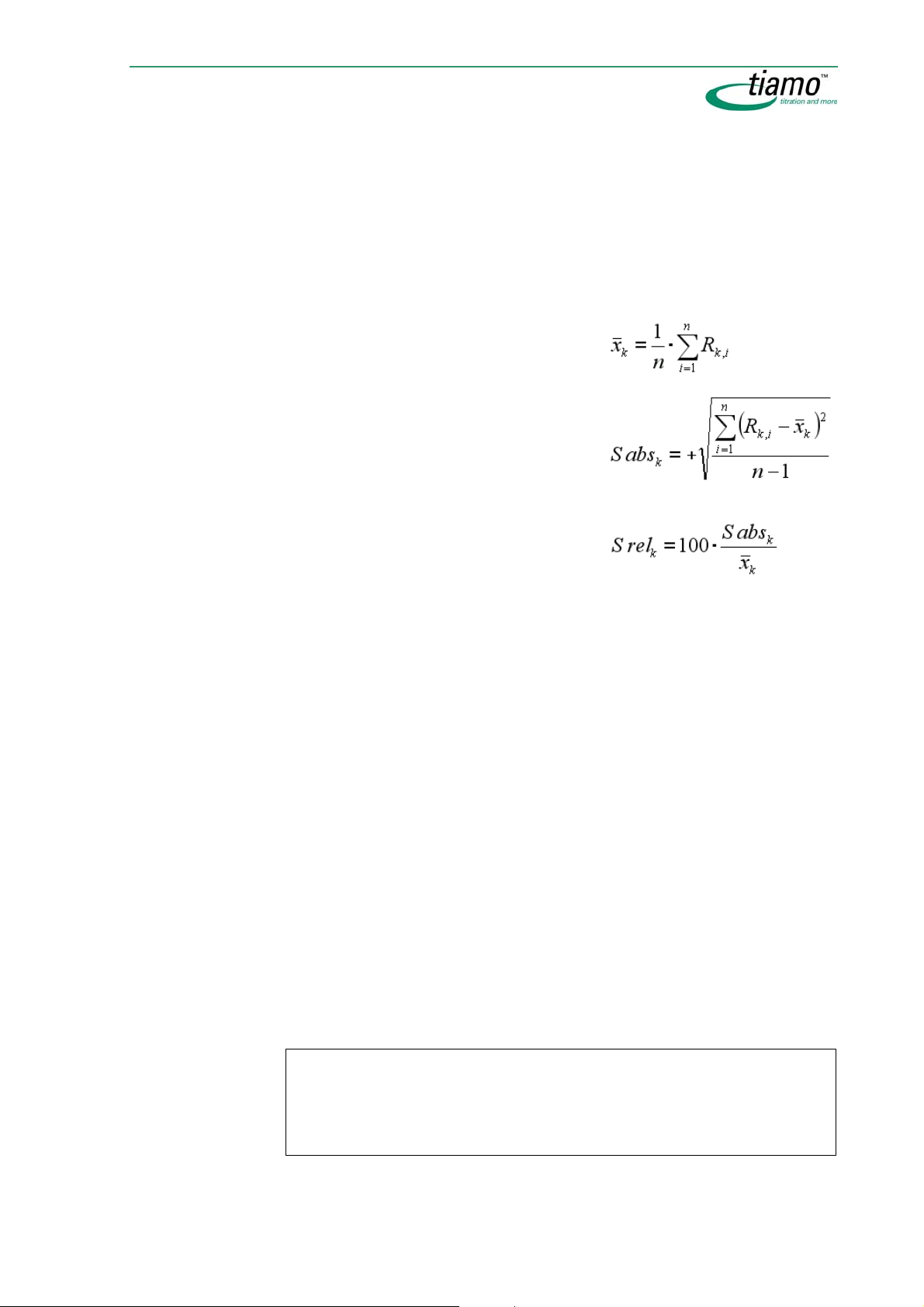
Statistics
2.47 gets 2.5
2.53 gets 2.5
2.55 gets 2.6
-2.35 gets -2.4
-2.45 gets -2.4
The following formulae are used for calculation of the arithmetic mean value
as well as the absolute and relative standard deviation for results R:
Mean value
Absolute standard addition
Relative standard addition (in %)
The statistical calculations in the software have been implemented in such
a way that they are as revisable as possible for the user. This is why the individual values used in the statistics are in full precision form.
It is not the number of decimal places which is decisive for the accuracy of
the calculations, but rather the number of significant digits of the decimal
numbers displayed. As a result of the binary 64-bit number format implemented on the basis of the IEEE 754 standard, the decimal numbers which
are produced have 15 reliable significant decimal digits.
You can influence the number of significant digits by selecting the unit and
the number of decimal places. As the results unit to be set sometimes contains both the prefix "milli" and the physical unit itself, the number of significant digits is altered accordingly in such a case by three digits.
Examples
The displayed result
1234.56789158763 mg/L has 15 reliable digits. It is to
be rounded to three decimal places according to the rounding method
given above:
1234.568 mg/L (7 significant digits, 3 of which are decimal places)
With the unit "
g/L" the same result 1.23456789158763 g/L is also rounded to
three decimal places:
1.235 g/L (4 significant digits, 3 of which are decimal places)
The number of significant digits has now been reduced by three to four digits by omitting the prefix "milli".
Note
The losses of accuracy by rounding described above in the range of the maximum reliable digits are only of theoretical relevance. Most of the time they are
lower by several orders of magnitude than – as an example – the uncertainties
resulting from weighing out the sample.
Formula editor 21
Page 50

2.4.4 Variables
Overview
Variable types
The following types of variable are differentiated:
Name/Syntax Description
Method variables
'MV.Variable name.Variable identifier'
Command variables
'Command name.Variable identifier'
Result variables
'RS.Result name.Variable identifier'
Determination variables
'DV.Variable identifier'
System variables
'SV.Variable identifier'
Common variables
'CV.Variable name.Variable identifiere'
Method variables are variables that are defined in the
command.
Command variables are variables that are generated by the
individual commands in the method sequence. The command variables are shown in the order in which the commands are carried out in the method sequence.
Result variables are special command variables that are
generated by
own name.
Determination variables are general variables and cannot be
assigned to individual commands.
System variables are general variables and cannot be assigned to individual commands or determinations.
Common variables are method-independent variables that
are accepted from the table in the configuration at the start
of the determination (see Configuration - common variables).
START
CALC commands and are available under their
Entering variables
Variables must always be entered enclosed by inverted commas
'MV.MyVariable').
Note
When using variables it is essential that their data type (
Date/Time
) is taken into account.
Number, Text
Method variables
Method variables are variables that are defined in the START command of methods. The data type (
there. These variables can be either sample data variables (
size unit
, Sample position, ID1...ID8, appear in the Run window of the Workplace) or
are assigned values. In the
available for the current method are listed according to their sorted com-
ables
mand name.
Syntax
'MV.Variable name.Variable identifier'
Examples:
In order to avoid syntax errors the method variables can be selected di-
rectly in the Formula editor under
Text, Number, Date/Time) of the variables can also be adapted
Sample size, Sample
Variables field of the Formula editor all the Method vari-
'MV.TestDate', 'MV.RestTime.VAL', 'MV.TestValue.OVF'
Variables/Method variables.
' (e.g.
or
22 General program functions
Page 51

Method variables
Identifier Description Commands
.VAL
.OVF
Result value (facultative, i.e.
'RS.RS01.VAL') (Text, Number or Date/Time)
Limit infringement for method variable
Number: 1 = limit infringed, 0 = limit
(
'RS.RS01' =
START
START
not infringed)
In the following lines you will find the method variables (sample data) that are available as standard,
appear in the Sequence window and which can be edited and deleted in the START command of the
corresponding method.
Sample size.VAL
Sample size.OVF
Sample size unit.VAL
Sample size unit.OVF
Sample position.VAL
Sample position.OVF
ID1 (...3).VAL
ID1 (...3).OVF
Value of 'Sample size' (
Limit infringement for 'Sample size' (
)
ber
Value of 'Sample size unit' (
Limit infringement for 'Sample size unit'
Number)
(
Value of 'Sample position' (
Limit infringement for 'Sample position'
Number)
(
Value of 'ID1...3' (
Limit infringement for 'ID...3' (
Number) START
Num-
Text) START
START
START
Number) START
START
Text) START
Number) START
Command variables
The availability of the command variables depends on the commands used in the
methods. Command variables also include solution and sensor variables, which
at the start of the determination are automatically adopted for the devicedependent commands from the corresponding tables in the Configuration and
assigned to the individual commands. In the
all the
Command variables that are available for the current method are listed ac-
cording to their sorted command name.
Syntax
'Command name.Variable identifier'
Examples:
'DET U 3.SME', 'Spur 6.BSY', 'Liquid Handling 4.CONC'
In order to avoid syntax errors the command variables can be selected directly in the Formula editor under
Command variables
Unless otherwise indicated, all the variables listed here in alphabetic order
are of the type
Number.
Note
For variables with index
.EP{3}.ERC
for the third end point).
{x}
the desired number
Without index specification, the last index is used automatically (e.g.
the last end point).
Variables field of the Formula editor
Variables/Command variables.
1...9
must be entered for x (e.g.
.EP.ERC
for
Formula editor 23
Page 52

Identifier Description Commands
.BLV
Blank value of the sensor used for the command (for
ISE sensors only) or the blank value calculated during
calibration (for CAL LOOP Conc)
DET U, MET U, SET U,
STAT U, MEAS U, MEAS
Conc, CAL LOOP Conc,
DOS U
.BP{#}.DME
.BP{#}.ERC
.BP{#}.MEA
.BP{#}.TEM
Difference in measured values for break point # (1...9) MET
ERC or 1st derivative for break point # (1...9) DET
Measured value for break point # (1...9) in the units of
the measured value
DET, MET, MEAS (without T/Flow)
Temperature for break point # (1...9) in °C DET, MET, MEAS (with-
out T/Flow)
.BP{#}.TIM
Time for break point # (1...9) in s DET, MET, MEAS (with-
out T/Flow)
.BP{#}.VOL
.BSY
Volume at break point # (1...9) in mL DET, MET
Command status; 1 = BUSY, HOLD or ERROR;
0 = READY; invalid (variable not present) = Com-
All except START and
END
mand has never been started
.CBY
Command status; 1 = conditioning active,
SET, KFT, KFC
0 = conditioning not active
.COK
Command status; 1 = conditioning criterion ful-
SET, KFT, KFC
filled, 0 = conditioning criterion not fulfilled
.CONC
Concentration of the solution used for the command DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, ADD, DOS, LQH,
STDADD
.CYL
Cylinder volume of the exchange or dosing unit used
for the command
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, STDADD dos,
STDADD auto, ADD,
DOS, LQH, PREP,
EMPTY
.DBL
Total duration for processing the command in s DET, MET, SET, KFT,
KFC, STAT, MEAS, CAL
MEAS, STDADD, DOS
.DRI
.DSC
Current or last drift for drift correction in µL/min SET, KFT, KFC
Duration for processing all start conditions in s DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT
.DTI
Time for the drift correction (time from start of titration
SET, KFT, KFC
until end of command) in s
.EGF
Last measured gas flow (measured value after proc-
MEAS T/FLow
essing the command) in mL/min
.EME
Final measured value (measured value after processing the command) in the units of the measured value
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
KFC, STAT, MEAS, CAL
MEAS, STDADD, DOS
.ENP
Electrode zero point of the sensor used for the command (dimensionless for pH sensor or in mV for ISE
sensor) or the electrode zero point calculated from the
calibration (for CAL LOOP)
DET pH, DET U, MET
pH, MET U, SET pH,
SET U, STAT, MEAS pH,
MEAS U, MEAS T, MEAS
Conc, STDADD, CAL
LOOP, DOS
.EP{#}.DME
Difference in measured values for end point # (1...9) MET
24 General program functions
Page 53

Identifier Description Commands
.EP.DVT
.EP{#}.ERC
.EP.MEA
.EP{#}.MEA
Drift for the end point in µg/min KFC
ERC for the end point # (1...9) DET
Measured value for the end point in mV KFC
Measured value for the end point # (1...9) in the units
DET, MET, SET, KFT
of the measured value
.EP{#}.MEP
Number of end points in the window # (1...9); 1 = 1
DET, MET, SET, KFT
end point, 2 = 2 or more end points, 3 = EP corrected with auto drift, 4 = EP corrected with manual drift
.EP.QTY
.EP{#}.TEM
.EP{#}.TIM
Measured value (water) for the end point in µg KFC
Temperature for end point # (1...9) in °C DET, MET. SET, KFT
Time for reaching end point # (1...9) in s DET, MET, SET, KFT,
KFC
.EP{#}.VOL
.ETE
Volume for end point # (1...9) in mL DET, MET, SET, KFT
Final temperature (temperature after processing the
command) in °C
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
KFC, STAT, MEAS (without T/Flow), CAL MEAS,
STDADD, DOS
.EVT
.FIN
Final volume (total volume added at the end of the
command) in mL
Command status; 1 = command has been finished
at least once, 0, invalid (variable not present) =
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, DOS
All except START and
END
command has never been finished
.FP{#}.DME
Difference in measured values for fixed end point #
MET
(1...9)
.FP{#}.DVT
.FP{#}.ERC
.FP{#}.MEA
Drift for fixed end point # (1...9) in µg/min KFC
ERC for fixed end point # (1...9) DET
Measured value for fixed end point # (1...9) in mV DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT
.FP{#}.MEA
.FP{#}.QTY
Measured value for fixed end point # (1...9) in the units
of the measured value
Measured value (water) for fixed end point # (1...9) in
KFC, MEAS (without
T/Flow)
KFC
µg
.FP{#}.TEM
Temperature for fixed end point # (1...9) in °C DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, MEAS (without
T/Flow)
.FP{#}.TIM
Time for reaching fixed end point # (1...9) in s DET, MET, SET, KFT,
KFC, STAT, MEAS (without T/Flow)
.FP{#}.VOL
Volume for fixed end point # (1...9) in mL DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT
.HP{#}.MEA
Measured value for HNP # (1...9) in mV (HNP = half-
DET, MET
neutralization potential)
.HP{#}.TEM
.HP{#}.TIM
.HP{#}.VOL
Temperature for HNP # (1...9) in °C DET, MET
Time for reaching HNP # (1...9) in s DET, MET
Volume for HNP # (1...9) in mL DET, MET
Formula editor 25
Page 54

Identifier Description Commands
.IGF
Initial gas flow (measured value at start of command)
MEAS T/Flow
in mL/min
.IME
.ITE
Initial measured value (measured value before processing the start condition) in the units of the measured
value
Initial temperature (temperature before processing the
start conditions) in °C
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, MEAS, CAL
MEAS, STDADD, DOS
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, MEAS (without
T/Flow), CAL MEAS,
STDADD, DOS
.LCO
Loop counter = current number of completed loops
LOOP, CAL LOOP
both for Repeat and While loops
.LP.CAx
Calculated value x (1...3) for the last measuring point DET, MET, SET, KFT,
KFC, STAT, MEAS, DOS
.LP.CHA
.LP.DME
.LP.DVT
.LP.ERC
.LP.EXx
Charge for last measuring point in mA·s KFC
Difference in measured values for last measuring point MET
dV/dt for the last measuring point (SET, KFT, STAT,
DOS) or drift for last measuring point in µg/min (KFC)
SET, KFT, KFC, STAT,
DOS
ERC for last measuring point DET
External value x (1...3) for last measuring point DET, MET, SET, KFT,
KFC, STAT, MEAS, DOS
.LP.GFL
.LP.IGE
.LP.MEA
Gas flow value for last measuring point in mL/min MEAS T/Flow
Current pulse current for last measuring point in mA KFC
Measured value for last measuring point in the units of
the measured value
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
KFC, STAT, MEAS, CAL
MEAS, DOS
.LP.QTY
.LP.TEM
Measured value (water) for last measuring point in µg KFC
Temperature for last measuring point in °C DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, MEAS, CAL
MEAS, DOS
.LP.TIM
Time for reaching last measuring point in s DET, MET, SET, KFT,
KFC, STAT, MEAS, CAL
MEAS, DOS
.LP.UGE
Potential at generator electrode for last measuring
KFC
point; 0 = not defined, 1 = <14 V, 2 = 14...28 V,
3 = >28 V
.LP.VOL
Volume for last measuring point in mL DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, DOS
.LPO
Current absolute lift position in mm (entry at end of
LIFT
command)
.LST
.MA.GFL
.MA.MEA
.MA.TEM
Start time of loop command (
Maximum gas flow in mL/min MEAS T/Flow
Maximum measured value in the units of the measured
value
Temperature for maximum measured value in °C DET, MET, SET, KFT,
Date/Time) LOOP, CAL LOOP
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, MEAS
STAT, MEAS
.MA.TIM
Time for reaching the maximum measured value in s DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, MEAS
26 General program functions
Page 55
Identifier Description Commands
.MA.VOL
Volume for maximum measured value in mL DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT
.MI.GFL
.MI.MEA
.MI.TEM
Minimum gas flow in mL/min MEAS T/Flow
Minimum measured value in the units of the measured
value
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, MEAS
Temperature for minimum measured value in °C DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, MEAS
.MI.TIM
Time for minimum measured value in s DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, MEAS
.MI.VOL
Volume for minimum measured value in mL DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT
.MR.MRC
Correlation coefficient for mean dosing rate for whole
STAT, DOS
range
.MR.MRS
Standard deviation für mean dosing rate for whole
STAT, DOS
range in mL/min
.MR.MRT
.MTE
Mean dosing rate for whole range in mL/min STAT, DOS
Temperature measurement with sensor; 1 = on,
0 = off)
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, MEAS (without
T/Flow), CAL MEAS,
STDADD, DOS
.NMP
Number of measuring points in list of measuring points DET, MET, SET, KFT,
KFC, STAT, MEAS, CAL
MEAS, DOS
.RAN
Current absolute shift angle of the rack in ° referred to
MOVE
the axis of the selected tower (entry at end of command)
.RE{x}.DRC
Correlation coefficient for mean dosing rate in window
STAT
x (1...9)
.RE{x}.DRS
Standard deviation for mean dosing rate in window x
STAT
(1...9) in mL/min
.RE{x}.DRT
.RE{x}.RWL
.RE{x}.RWH
.RES
.RPO
Mean dosing rate in window x (1...9) in mL/min STAT
Lower limit of evaluation window x (1...9) in s STAT
Upper limit of evaluation window x (1...9) in s STAT
Calculated result for standard addition in selected unit STDADD
Current rack position (entry at end of command);
MOVE
0 means 'not defined'
.SAN
Current absolute swing angle of the swing head in °
MOVE, SWING
(entry at end of command)
.SLO
Electrode slope of the sensor used for the command
(in % for pH sensor or mV for ISE sensor) or the electrode slope calculated from the calibration (for
STDADD and CAL LOOP)
DET pH, DET U, MET
pH, MET U, SET pH,
SET U, STAT, MEAS pH,
MEAS U, MEAS T, MEAS
Conc, STDADD, CAL
LOOP, DOS
.SME
Starting measured value (measured value after processing the start conditions) in the units of the meas-
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
KFC, STAT
ured value
Formula editor 27
Page 56

Identifier Description Commands
.SPO
Current external position (entry at end of command);
SWING
0 means invalid position
.STE
.STY
Start temperature (temperature after processing the
start conditions) in °C
Stop type with which the command has been stopped:
1 = normal;0 = manual or after error
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
KFC, STAT
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, MEAS, CAL
MEAS, STDADD, DOS
.SVA
.SVM
Start volume absolute (volume added in accordance
with the start condition "Start volume") in mL
Start volume measured value (volume added in accor-
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT
DET, MET
dance with the start condition "Start measured value")
in mL
.SVS
Start volume measured value (volume added in accor-
DET, MET
dance with the start condition "Start slope") in mL
.SVT
.TITER
Start volume total (volume added in accordance with
all three start conditions) in mL
DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT
Titer value for the solution used for the command DET, MET, SET, KFT,
STAT, STDADD dos,
STDADD auto, ADD,
DOS, LQH
.TOU
.VAR
Timeout status: 1 = max. delay period elapsed;
0 = max. delay period not elapsed
Variance of the calculated standard addition result in
RECEIVE, TRANSFER;
SCAN
STDADD
selected unit
.VOL
Added volume STDADD, ADD, DOS,
LQH
28 General program functions
Page 57

Result variables
Result variables are special command variables that are generated by CALC com-
. In the Variables field of the Formula editor all the Results that are available
mands
for the current method are listed according to their result name.
Syntax
'RS.Result name.Variable identifier'
Examples:
In order to avoid syntax errors the result variables can be selected directly
in the Formula editor under
Result variables
Unless otherwise indicated, all the variables listed here in alphabetic order are of
the type
Number.
Identifier Description Command
.VAL
.ASD
.MNV
.NSR
.NST
.OVF
Result value, facultative, i.e.
Absolute standard deviation for the result CALC
Mean value of the result CALC
Statistics current counter for the result CALC
Statistics set counter for the result CALC
Limit infringement for result; 1 = limit infringed, 0 = limit not in-
fringed
.RSD
.STS
.UNI
Relative standard deviation for result CALC
Statistics status for result; 1 = statistics on, 0 = statistics off CALC
Result unit (
Text) CALC
'RS.RS01.VAL' (='RS.RS01'), 'RS.TestTime.UNI'
Variables/Results.
'RS.RS01' = 'RS.RS01.VAL' CALC
CALC
Determination variables
Determination variables are variables which are assigned generally and not to individual commands that are generated in the method sequence. In the
field of the Formula editor all the
method are listed according to their sorted name.
Syntax
'DV.Variable identifier'
Examples:
In order to avoid syntax errors the determination variables can be selected
directly in the Formula editor under
Determination variables
Identifier Description
.DUR
.STT
Duration of the determination in s (
Time at which the determination was started (
Variables
Determination variables available for the current
'DV.DUR', 'DV.STT'
Variables/Determination variables.
Number)
Time/Date)
Formula editor 29
Page 58

System variables
System variables are general variables that are not assigned to individual commands or determinations that are accepted for the determination at the start of the
determination. In the
that are available for the current method are listed.
Syntax
'SV.Variable identifier'
Examples:
In order to avoid syntax errors the system variables can be selected directly
in the Formula editor under
System variables
Identifier Description
.ACC
.ACE
.FUN
.REM
.RUN
.SEN
.SIN
.SLI
.STA
.STC
.USN
.ORG
.STO
Autostart current counter (
Autostart set counter (
Full name of logged-in user (
Remarks (
Text)
Sample number (
Indicates whether the end of the sample table has been reached; 1 = yes, 0 =
Number)
no (
Indicates whether the determination was started as a single determination or within
a series; 1 = single determination, 0 = series determination (
Sample table current line (
Indicates whether statistics are switched on; 1 = yes, 0 = no (
Start counter (
Short name of logged-in user (
Method sequence: 1 = original determination, 0 = reprocessed (
Indicates whether the determination was stopped (manual stop, stop via a SEND
command, emergency stop); 1 = stopped, 0 = terminated normally (
Variables field of the Formula editor all the System variables
'SV.SIN', 'SV.SLI'
Variables/System variables.
Number)
Number)
Text)
Number)
Number)
Number)
Number)
Number)
Text)
Number)
Number)
Common variables
Common variables are global variables that are loaded from the corresponding
Table in the configuration at the start of the determination. In this table the common variables can be defined. In the
Common variables that are available are listed according to their sorted variable
Variables field of the Formula editor all the
name.
Syntax
'CV.Variable name.Variable identifier'
Examples:
'CV.TestDate', 'CV.TestTime.VAL', 'CV.MeanTemp.UNI'
In order to avoid syntax errors the common variables can be selected directly in the Formula editor under
Variables/Common Variables.
30 General program functions
Page 59

Common variables
Identifier Description
.VAL
.UNI
Value of the common variable (facultative, i.e.
or Date/Time)
ber
Unit of the common variable (
Text)
2.4.5 Operators/Functions
Overview of operators and functions
Operators Functions Miscellaneous
'CV.Test.VAL' = 'CV.Test') (Text, Num-
Arithmetic:
Addition (+)
Subtraction (-)
Multiplication (*)
Division (/)
Potentiation (^)
Logic:
AND
OR
Compare:
Equal (=)
Larger than (>)
Larger than/equal
to (>=)
Smaller than (<)
Smaller
than/equal to
(<=)
Unequal (<>)
Arithmetic:
Exponential function (Exp)
Natural logarithm (Ln)
Common logarithm (Log)
Square root (Sqrt)
Absolute value (Abs)
Fraction (Frac)
Integer (Int)
Round integer (Round)
Sign (sign)
Date/Time:
Time()
Time(Date)
Time(Date + Time)
Type conversion:
Number to text (NumberTo-
Text)
Number to time (NumberTo-
Time)
Text to number (TextToNum-
ber)
Text to time (TextToTime)
Time to number (TimeTo-
Number)
Time to text (TimeToText)
Text:
TextPosition
SubText
Trim
Error
Case
Formula editor 31
Page 60

Rules of priority for operators
The operators are processed in the sequence in which they are listed in the following table. It may be necessary to set operands in brackets to get the desired sequence.
Operators
Arithmetic
^
*, /
+, -
Compare <, <=, >, >=
Logic AND, OR
Operators - Arithmetic
Addition
Syntax
Operand1 + Operand2
The operands can either be entered directly or as a Variable and can be
of the type
Examples
Text, Number or Date/Time.
Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Both operands of the same type:
Number Number Number
Text Text Text
1.2 + 3 = 4.2
"Metrohm" + "AG" = "Metrohm
AG"
-
If the maximum permitted
length (65'536 characters) of
the character string is exceeded by the addition of the
operands then the excess
characters will be cut off by
nd
the 2
operand.
Time Time Time
Time(1998;04;06) +
Time(1964;02;03) = 59300.875
(for UTC+1)
Time(): see function
Time(Date)
Result: number of days calcu-
lated since December 1899,
dependent on the system time
Operands of different types: the operand that does not correspond to the type of result is converted
to the particular result type before the operation.
Number Text Text
Text Number Text
1.2 + "Metrohm" =
"1.2Metrohm"
"Metrohm" + 1.2 =
"Metrohm1.2"
-
-
32 General program functions
Page 61

Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Number Time Number
2.0 + Time(1999;11;7) =
36472.96
(for UTC+1)
Result: number of days calculated since December 1899,
dependent on the system time
Time Number Number
Time(1999;10;7) + 2.0 =
36441.92
(for UTC+2)
Result: number of days calculated since December 1899,
dependent on the system time
Text Time Text
Time Text Text
"Metrohm" + Time(1999;10;7) =
"Metrohm1999-10-07 00:00:00
UTC+2"
Time(1999;01;7) + "Metrohm" =
"1999-01-07 00:00:00
UTC+1Metrohm"
Before the operation an operand of type
verted to
Date/Time is con-
Text.
In this case the same rules
apply as for the previous operation.
Subtraction
Syntax
Operand1 - Operand2
The operands can either be entered directly or as a Variable and can be
of the type
Text, Number or Date/Time.
Examples
Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Both operands of the same type:
Number Number Number
Text Text Text
Time Time Number
1.2 - 3 = -1.8
"Metrohm" - "AG" = invalid
Time(1998;01;06) Time(1964;12;03) = 12'087.00
(for UTC+1)
-
This operation is not permitted.
Time(): see function
Time(Date)
Result: number of days calcu-
lated since December 1899,
dependent on the system time
Operands of different types: the operand that does not correspond to the type of result is converted
to the particular result type before the operation.
Number Text Text
Text Number Text
Number Time Number
1.2 - "Metrohm" = invalid
"Metrohm" - 1.2 = invalid
2.0 - Time(1999;10;7) = 36'437.917
(for UTC+2)
This operation is not permitted.
This operation is not permitted.
Result: number of days calculated since December 1899,
dependent on the system time
Time Number Number
Time(1999;10;7) - 2.5 =
36'437.917
(for UTC+2)
Result: number of days calculated since December 1899,
dependent on the system time
Text Time Text
Time Text Text
"Metrohm" - Time(1999;10;7) =
invalid
Time(1999;10;7) - "Metrohm" =
invalid
This operation is not permitted.
This operation is not permitted.
Formula editor 33
Page 62

Multiplication
Syntax
Operand1 * Operand2
The operands can either be entered directly or as a Variable and can be
of the type
Text, Number or Date/Time.
Examples
Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Operands of the same type:
Number Number Number
Text Text Text
Time Time Number
1.2 * 3 = 3.6
"Metrohm" * "AG" = invalid
Time(1998;05;06) *
Time(1902;02;03) =
27'478'004.545
(for UTC+1 or
+2 for Summer time)
-
This operation is not permitted.
Time(): see function
Time(Date)
Result: number of days calcu-
lated since December 1899,
dependent on the system time
Operands of different types: the operand that does not correspond to the type of result is converted
to the particular result type before the operation.
Number Text Text
Text Number Text
Number Time Number
2 * "Metrohm" = "MetrohmMetrohm"
"Metrohm" * 2 = "MetrohmMetrohm"
2.0 * Time(1999;10;7) =
72'879.833
(for UTC+2)
-
-
Result: number of days calculated since December 1899,
dependent on the system time
Time Number Number
Time(1999;10;7) * 2.0 =
72'879.833
(for UTC+2)
Result: number of days calculated since December 1899,
dependent on the system time
Text Time Text
Time Text Text
"Metrohm" * Time(1999;10;7) =
invalid
Time(1999;10;7) * "Metrohm" =
invalid
This operation is not permitted.
This operation is not permitted.
34 General program functions
Page 63

Division
Syntax
Operand1 / Operand2
The operands can either be entered directly or as a Variable and can be
of the type
Text, Number or Date/Time.
Examples
Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Operands of the same type:
Number Number Number
Text Text Text
Time Time Time
1.2 / 3 = 0.4
"Metrohm" / "AG" = invalid
Time(1998;04;06) /
Time(1964;02;03) = 1.533
UTC+1 or +2 for Summer
time)
(for
Operand2 must not be zero!
This operation is not permitted.
Time(): see function
Time(Date)
Result: number of days calcu-
lated since December 1899,
dependent on the system time
Operands of different types: the operand that does not correspond to the type of result is converted
to the particular result type before the operation.
Number Text Text
Text Number Text
Number Time Number
1.2 / "Metrohm" = invalid
"Metrohm" / 1.2 = ungültig
10'000 / Time(1999;10;7) =
0.274
(for UTC+2)
This operation is not permitted.
This operation is not permitted.
Result: number of days calculated since December 1899,
dependent on the system time
Time Number Number
Time(1999;02;17) / 10'000 =
3.621
(for UTC+1)
Result: number of days calculated since December 1899,
dependent on the system time
Text Time Text
Time Text Text
"Metrohm" / Time(1999;10;7) =
invalid
Time(1999;10;7) / "Metrohm" =
invalid
This operation is not permitted.
This operation is not permitted.
Formula editor 35
Page 64

Potentiation
Syntax
Operand1 ^ Operand2
The operands can either be entered directly or as a Variable and can be
of the type
Text, Number or Date/Time.
Examples
Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Operands of the same type:
Number Number Number
1.2 ^ 3 = 1.728
Complex results (of the type:
a+bi, i.e. made up from a real
and an imaginary component)
are shown as an error.
Text Text Text
Time Time Time
"Metrohm" ^ "AG" = invalid
Time(1900;01;05) ^
Time(1900;01;02) = 196.371
(for UTC+1)
This operation is not permitted.
Time(): see function Time(Date)
Result: number of days calculated since December 1899,
dependent on the system time
Operands of different types: the operand that does not correspond to the type of result is converted
to the particular result type before the operation.
Number Text Text
Text Number Text
Number Time Number
Time Number Number
Text Time Text
Time Text Text
1.2 ^ "Metrohm" = invalid
"Metrohm" ^ 1.2 = invalid
1.2 ^ Time(1900;02;03) =
586.198
Time(1999;10;7) ^ 2.5 =
253479847878.04
"Metrohm" ^ Time(1999;10;7)
= invalid
Time(1999;10;7) ^ "Metrohm"
= invalid
(for UTC+1)
(for UTC+2)
This operation is not permitted.
This operation is not permitted.
-
-
This operation is not permitted.
This operation is not permitted.
36 General program functions
Page 65

Operators - Logic
AND
Syntax
Operand1 AND Operand2
The operands can either be entered directly or as a Variable and can be
of the type
= true,
Operand1 Operand2 Result
Examples
Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Operands of the same type:
Number Number Number
Text Text Number
Time Time Number
Operands of different types:
Number Text Number
Text Number Number
Number Time Number
Time Number Number
Text, Number or Date/Time. The result type is always a number (1
0 = false). The following cases are possible:
1 1 1
0 1 0
1 0 0
0 0 0
5 AND 4 --> 1
4 AND 0 --> 0
"Metrohm" AND "AG" --> 1
"" AND "AG" --> 0
Numbers larger than 0 are interpreted as
1 (true).
An empty character string (
interpreted as
thing else as
0 (false), every-
1 (true). This
means that the first operation
Time(1999;10;07) AND
Time(1999;10;07) --> 1
1.2 AND "1.2" --> 1
0 AND "1" --> 1
0 AND "0" --> 1
0 AND "" --> 0
corresponds to
Time(): see function Time(Date)
Before the operation an operand
of the type
to the type
sion from
1 AND 1 --> 1.
Number is converted
Text, as the conver-
Text to Number makes
no sense. This means that in the
nd
2
operation the 0 is converted
to
"0", which corresponds to the
logical value
1 (true) as every
non-empty character string is
interpreted as 1.
"Metrohm" AND 1.2 --> 1
The same rules apply here as for
the previous operation.
2.0 AND Time(1999;10;7) -->
1
0 AND Time(1999;10;07) --> 0
Before the operation an operand
of the type
verted to the type
Date/Time is con-
Number; all
dates from 30 December 1899
Time(1999;10;7) AND 2.5 -->
1
are interpreted as
The same rules apply here as for
the previous operation.
1 (true).
"") is
Formula editor 37
Page 66

Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Text Time Number
"Metrohm" AND
Time(1999;10;7) --> 1
"" AND Time(1999;10;07) -->
0
Before the operation is carried
out an operand of the type
Date/Time is converted to the
type
Text and each non-empty
character string is interpreted as
1 (true).
Time Text Number
Time(1999;10;7) AND
"Metrohm" --> 1
The same rules apply here as for
the previous operation.
OR
Syntax
Operand1 OR Operand2
The operands can either be entered directly or as a Variable and can be
of the type
= true,
Text, Number or Date/Time. The result type is always a number (1
0 = false). The following cases are possible:
Operand1 Operand2 Result
1 1 1
0 1 1
1 0 1
0 0 0
Examples
Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Operands of the same type:
Number Number Number
5 OR 4 --> 1
4 OR 0 --> 0
Numbers larger than 1 are
automatically interpreted as 1
(true).
Text Text Number
"Metrohm" OR "AG" --> 1
"" OR "Metrohm" --> 1
"" OR "" --> 0
An empty character string (
is interpreted as
rything else as
0 (false), eve-
1 (true). This
"")
means that the first operation
corresponds to 1 OR 1 --> 1
Time Time Number
Time(1999;10;07) OR
Time(1964;02;03) --> 1
Time(): see function
Time(Date)
Operands of different types: the operand that does not correspond to the type of result is converted
to the particular result type before the operation.
Number Text Number
1.2 OR "1.2" --> 1
0 OR "" --> 1
Before the operation an operand of the type
verted to the type
conversion from
makes no sense. This
ber
means that in the 2
the 0 is converted to
Number is con-
Text, as the
Text to Num-
nd
operation
"0", which
corresponds to the logical
value
1 (true) as every non-
empty character string is interpreted as 1.
38 General program functions
Page 67

Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Text Number Number
"Metrohm" OR 1.2 --> 1
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Number Time Number
2.0 OR Time(1999;10;7) --> 1
0 OR Time(1964;02;03) --> 1
Before the operation an operand of the type
Date/Time is
converted to the type
all dates from 30 December
1899 are interpreted as
(true).
Time Number Number
Time(1999;10;7) OR 2.5 --> 1
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Text Time Number
"Metrohm" OR Time(1999;10;7)
--> 1
Before the operation an operand of the type Date/Time is
converted to the type
each non-empty character
string is interpreted as 1 (true).
Time Text Number
Time(1999;10;7) OR "Metrohm"
--> 1
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Number;
1
Text and
Operators - Compare
Equal
Syntax
Operand1 = Operand2
The operands can either be entered directly or as a Variable and can be
of the type
= true,
Examples
Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Operands of the same type:
Number Number Number
Text Text Number
Time Time Number
Operands of different types:
Number Text Number
Text, Number or Date/Time. The result type is always a number (1
0 = false).
5 = 5 --> 1
4 = 5 --> 0
"Metrohm" = "AG" --> 0
"aG" = "AG" --> 0
-
In a comparison between two
text the ASCII values (see ASCII
table) of the character strings
are compared. Note: upper
and lower case letters have
different values!
Time(1998;04;06) =
Time(1964;02;03) --> 0
1.2 = "1.2" --> 1
1.2 = "Metrohm" --> 0
Time(): see function Time(Date)
Before the comparative operation the Number is converted to
Text and then the texts are
compared according to the
ASCII table.
Formula editor 39
Page 68

Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Text Number Number
"Metrohm" = 1.2 --> 0
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Number Time Number
2.0 = Time(1999;10;07) --> 0
Before the comparative operation the
to
Date/Time is converted
Number. When the operation
is carried out the exact value
obtained after this conversion
is always used, even when only
a maximum of 5 decimal
places can be shown (for details please refer to Type conversion "TimeToNumber",
Note).
Time Number Number
Time(1999;10;7) = 2.0 --> 0
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Text Time Number
"Metrohm" = Time(1999;10;07)
--> 0
Before the operation an operand of type
verted to
00:00:00 UTC+2"
Date/Time is con-
Text (i.e.: "1999-10-07
), then the
texts are compared according
to the ASCII table.
Time Text Number
Time(1999;10;07) = "Metrohm"
--> 0
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Larger than
Syntax
Operand1 > Operand2
The operands can either be entered directly or as a Variable and can be
of the type
= true,
Text, Number or Date/Time. The result type is always a number (1
0 = false).
Examples
Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Operands of the same type:
Number Number Number
Text Text Number
5 > 4 --> 1
4 > 5 --> 0
"Metrohm" > "AG" --> 1
"Aarau" > "Zug" --> 0
-
In a comparison between two
texts the ASCII values (see
ASCII table) of the character
strings are compared. Note:
upper and lower case letters
have different values!
Time Time Number
Time(1998;04;06) >
Time(1964;02;03) --> 1
Time(): see function Time(Date)
40 General program functions
Page 69

Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Operands of different types:
Number Text Number
1.2 > "Metrohm" --> 0
1.23 > "1.2" --> 1
Before the comparative operation the
Text and then the texts are
Number is converted to
compared according to the
ASCII table.
Text Number Number
"Metrohm" > 1.2 --> 1
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Number Time Number
2.0 > Time(1999;10;07) --> 0
Before the comparison the
Date/Time is converted to a
Number (see Type conversion
"TimeToNumber").
Time Number Number
Time(1999;10;07) > 2.0 --> 1
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Text Time Number
"Metrohm" > Time(1999;10;07)
--> 1
Before the operation an operand of type
verted to
00:00:00 UTC+2"
Date/Time is con-
Text (i.e.: "1999-10-07
) and then the
texts are compared according
to the ASCII table.
Time Text Number
Time(1999;10;7) > "Metrohm" -
-> 0
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Larger than or equal to
Syntax
Operand1 >= Operand2
The operands can either be entered directly or as a Variable and can be
of the type
= true,
Text, Number or Date/Time. The result type is always a number (1
0 = false).
Examples
Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Operands of the same type:
Number Number Number
Text Text Number
5 >= 4 --> 1
4 >= 5 --> 0
"Metrohm" >= "AG" --> 1
-
In a comparison between two
texts the ASCII values (see
ASCII table) of the character
strings are compared. Note:
upper and lower case letters
have different values!
Time Time Number
Time(1998;04;06) >=
Time(1964;02;03) --> 1
Time(): see function Time(Date)
Formula editor 41
Page 70

Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Operands of different types:
Number Text Number
1.2 >= "1.2" --> 1
1.2 >= "Metrohm" --> 0
Before the comparative operation the
Text and then the texts are
Number is converted to
compared according to the
ASCII table.
Text Number Number
"Metrohm" >= 1.2 --> 1
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Number Time Number
2.0 >= Time(1999;10;07) --> 0
Before the comparison the
Date/Time is converted to a
Number (see Type conversion
"TimeToNumber").
Time Number Number
Time(1999;10;07) >= 2.0 --> 1
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Text Time Number
"Metrohm" >=
Time(1999;10;07) --> 1
Before the operation an operand of type
verted to
00:00:00 UTC+2"
Date/Time is con-
Text (i.e.: "1999-10-07
) and then the
texts are compared according
to the ASCII table.
Time Text Number
Time(1999;10;7) >= "Metrohm"
--> 0
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Smaller than
Syntax
Operand1 < Operand2
The operands can either be entered directly or as a Variable and can be
of the type
= true,
Text, Number or Date/Time. The result type is always a number (1
0 = false).
Examples
Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Operands of the same type:
Number Number Number
Text Text Number
5 < 4 --> 0
4 < 5 --> 1
"Metrohm" < "AG" --> 0
-
In a comparison between two
texts the ASCII values (see
ASCII table) of the character
strings are compared. Note:
upper and lower case letters
have different values!
Time Time Number
Time(1998;04;06) <
Time(1964;02;03) --> 0
Time(): see function Time(Date)
Operands of different types:
Number Text Number
1.2 < "Metrohm" --> 1
1.2 < "1" --> 0
Before the comparative operation the
Text and then the texts are
Number is converted to
compared according to the
42 General program functions
Page 71

Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
ASCII table.
Text Number Number
"Metrohm" < 1.2 --> 0
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Number Time Number
2.0 < Time(1999;10;07) --> 1
Before the comparison the
Date/Time is converted to a
Number (see Type conversion
"TimeToNumber").
Time Number Number
Time(1999;10;07) < 2.0 --> 0
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Text Time Number
"Metrohm" < Time(1999;10;07)
--> 0
Before the operation an operand of type
verted to
00:00:00 UTC+2"
Date/Time is con-
Text (i.e.: "1999-10-07
) and then the
texts are compared according
to the ASCII table.
Time Text Number
Time(1999;10;7) < "Metrohm" -
-> 1
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Smaller than or equal to
Syntax
Operand1 <= Operand2
The operands can either be entered directly or as a Variable and can be
of the type
= true,
Text, Number or Date/Time. The result type is always a number (1
0 = false).
Examples
Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Operands of the same type:
Number Number Number
Text Text Number
5 <= 4 --> 0
4 <= 5 --> 1
"Metrohm" <= "AG" --> 0
-
In a comparison between two
texts the ASCII values (see
ASCII table) of the character
strings are compared. Note:
upper and lower case letters
have different values!
Time Time Number
Time(1998;04;06) <=
Time(1964;02;03) --> 0
Time(): see function Time(Date)
Operands of different types:
Number Text Number
2 <= "1.2" --> 0
1.2 <= "Metrohm" --> 1
Before the comparative operation the
Text and then the texts are
Number is converted to
compared according to the
ASCII table.
Text Number Number
"Metrohm" <= 1.2 --> 0
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Formula editor 43
Page 72

Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Number Time Number
2.0 <= Time(1999;10;07) --> 1
Before the comparison the
Date/Time is converted to a
Number (see Type conversion
"TimeToNumber").
Time Number Number
Time(1999;10;07) <= 2.0 --> 0
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Text Time Number
"Metrohm" <=
Time(1999;10;07) --> 0
Before the operation an operand of type
verted to
00:00:00 UTC+2"
Date/Time is con-
Text (i.e.: "1999-10-07
) and then the
texts are compared according
to the ASCII table.
Time Text Number
Time(1999;10;7) <= "Metrohm"
--> 1
The same rules apply here as
for the previous operation.
Unequal
Syntax
Operand1 <> Operand2
The operands can either be entered directly or as a Variable and can be
of the type
= true,
Text, Number or Date/Time. The result type is always a number (1
0 = false).
Examples
Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
Operands of the same type:
Number Number Number
5 <> 4 --> 1
5 <> 5 --> 0
In a comparison between two
texts the ASCII values (see ASCII
table) of the character strings are
compared. Note: upper and lower
case letters have different values!
Text Text Number
Time Time Number
"Metrohm" <> "AG" --> 1
Time(1998;04;06) <>
Time(1964;02;03) --> 1
dfg
Time(): see function Time(Date)
Operands of different types:
Number Text Number
1.2 <> "1.2" --> 0
1.2 <> "Metrohm" --> 1
Before the comparative operation
the
Number is converted to Text
and then the texts are compared
according to the ASCII table.
Text Number Number
"Metrohm" <> 1.2 --> 1
The same rules apply here as for
the previous operation.
Number Time Number
2.0 <> Time(1999;10;07) --> 1
Before the comparison the
Date/Time is converted to a Num-
(see Type conversion "Time-
ber
ToNumber").
Time Number Number
Time(1999;10;07) <> 2.5 --> 1
The same rules apply here as for
44 General program functions
Page 73

Operand1 Operand2 Result Example Remarks
the previous operation.
Text Time Number
"Metrohm" <> Time(1999;10;07)
--> 1
Before the operation an operand
of type
Text (i.e.: "1999-10-07 00:00:00
UTC+2"
Date/Time is converted to
) and then the texts are
compared according to the ASCII
table.
Time Text Number
Time(1999;10;7) <> "Metrohm" -> 1
The same rules apply here as for
the previous operation.
Functions - Arithmetic
Exponential function
Syntax
y = exp(number)
Calculates e ^
Number. Another way of writing y = e
exponential (e = 2.71828...).
(number)
, where e is the
Parameter
Number Exponent
The parameter can either be entered directly as a number or as a Variable
of the type
type then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion
"TextToNumber"). If this is not possible then "
result of this operation.
Examples
Exp(1.5) = 4.48169
Exp('CV.MeanTemp') = potential of the exponent (Common variable) based
on e
Natural logarithm
Syntax
y = ln(number)
Returns the logarithm of the entered number based on e. Another way of
writing y = log
Parameter
Number >0
The parameter can either be entered directly as a number or as a Variable
of the type
type then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion
"TextToNumber"). If this is not possible then "
result of this operation.
Number. If the parameter does not correspond to the selected
invalid" will be returned as the
(Number), where e is the exponential (e = 2.71828...).
e
Number. If the parameter does not correspond to the selected
invalid" will be returned as the
Formula editor 45
Page 74

Examples
Ln(3) = 1.09861
Ln('CV.MeanTemp') = natural logarithm of the value of the Common variable
based on e
Common logarithm
Syntax
y = log(number)
Gives the logarithm of the entered number to the base 10. Another way of
writing y = log
(number).
10
Parameter
Number > 0
The parameter can either be entered directly as a number or as a Variable
of the type
type then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion
"TextToNumber"). If this is not possible then "
result of this operation.
Examples
Log(10) = 1
Log('CV.MeanTemp') = common logarithm of the value of the Common vari-
able
Square root
Syntax
y = sqrt(Number)
Returns the square root of the entered number. Another way of writing y =
√
Parameter
Number >=0
The parameter can either be entered directly as a number or as a Variable
of the type
type then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion
"TextToNumber"). If this is not possible then "
result of this operation.
Number. If the parameter does not correspond to the selected
Number or y =
Number. If the parameter does not correspond to the selected
2
√Number.
invalid" will be returned as the
invalid" will be returned as the
Examples
Sqrt(33) = 5.745
Sqrt('CV.MeanTemp') = square root of the value of the Common variable
Absolute value
Syntax
y = Abs(number)
Returns the absolute value of the entered number, i.e. the value of the
number irrespective of its sign.
Parameter
Number
46 General program functions
Page 75

Examples
Fraction
Syntax
Note
In the Result properties under Definition it is essential that the number of
places
shown.
Parameter
The parameter can either be entered directly as a number or as a Variable
of type
Number. If the parameter does not correspond to the selected type
then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion "TextToNumber"). If this is not possible then "
invalid" will be returned as the result of
this operation.
Abs(-55.3) = 55.3
Abs('CV.MeanTemp') = value of the Common variable without sign
y = Frac(number)
Returns the fractional part of the entered number.
Decimal
of the result is entered, as otherwise the decimal fraction cannot be
Number
The parameter can either be entered directly as a number or as a Variable
of the type
Number. If the parameter does not correspond to the selected
type then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion
"TextToNumber"). If this is not possible then "
invalid" will be returned as the
result of this operation.
Examples
Integer
Syntax
Parameter
Examples
Frac(-55.325) =0.325
Frac('CV.MeanTemp') = value of the Common variable without sign
y = Int(Number)
Returns the integer of the entered number.
Number
The parameter can either be entered directly as a number or as a Variable
of the type
Number. If the parameter does not correspond to the selected
type then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion
"TextToNumber"). If this is not possible then "
invalid" will be returned as the
result of this operation.
Int(-55.325) = -55
Int('CV.MeanTemp') = integer part of the value of the Common variable
Formula editor 47
Page 76

Round integer
Syntax
y = Round(Number)
Returns the rounded value of the entered number as a whole number.
Note
If the value to be rounded lies exactly between two whole numbers then it will be
rounded to the next whole even number: 1.5 -> 2, 4.5 -> 4, 0.5 -> 0
Parameter
Number
The parameter can either be entered directly as a number or as a Variable
of the type
type then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion
"TextToNumber"). If this is not possible then "
result of this operation.
Examples
Round(-55.5259) = -56
Round('CV.MeanTemp') = rounded value of the Common variable
Number. If the parameter does not correspond to the selected
invalid" will be returned as the
Sign
Syntax
Parameter
Examples
y = Sign(Number)
Returns the sign of the entered number:
1 for a positive number, -1 for a
negative number.
Number
The parameter can either be entered directly as a number or as a Variable
of the type
Number. If the parameter does not correspond to the selected
type then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion
"TextToNumber"). If this is not possible then "
invalid" will be returned as the
result of this operation.
Sign(-55.3) = -1
Sign(26.115) = 1
Sign('CV.MeanTemp') = sign of the value of the Common variable
Functions - Date/Time
Time()
Syntax
y = Time()
Returns the current date and current time.
48 General program functions
Page 77

Parameter
Return value
Note
UTC = Universal Time Coordinated: reference time for the different time zones
on the earth. MET (Mean European Time) equals UTC plus 1 hour, in the summer time UTC plus 2 hours.
Time(Date)
Syntax
none
Current date and current time in the format
y = Time(year; month; day)
Returns the entered numbers in the format
yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss UTC ±xx
Date/Time.
Parameter
Note
Only the whole number part will be used for all parameters.
A variable of the type
In both the automatic and the explicit conversion of a Time into the type Num-
ber the number of days since 30 December 1899 at 01 a.m. will be counted.
Note: 30 December 1899 01 a.m. = 0.00000 days, this number is rounded to 5
decimal places; however, e.g. a comparative operation will be carried out with
the exact value!
Return value
year
month
day
00...99 or 1000...9999
1...12
1...31
The parameter can either be entered directly as a number or as a Variable
of the type
Number. If the parameter does not correspond to the selected
type then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion
"TextToNumber"). If this is not possible then "
invalid" will be returned as the
result of this operation.
Date/Time
Date/Time in the format
cannot be transferred as a parameter here.
yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss UTC ±xx
Note
UTC = Universal Time Coordinated: reference time for the different time zones
on the earth. MET (Mean European Time) equals UTC plus 1 hour, in the summer time UTC plus 2 hours.
Examples
Time(2004;02;02) = 2004-02-02 00:00:00 UTC +1 (depends on the system
time)
Time('CV.Testyear';'CV.Testmonth';'CV.Testday') = date complied from the
Common variables
Formula editor 49
Page 78

Time(Date + Time)
Syntax
y = Time(year; month; day; hour; minute; second)
Returns the entered numbers in the format
Date/Time.
Parameter
Note
Only the whole number part will be used for all parameters.
A variable of the type
In both the automatic and the explicit conversion of a Time into the type Num-
ber the number of days since 30 December 1899 at 01 a.m. will be counted.
Note: 30 December 1899 01 a.m. = 0.00000 days, this number is rounded to 5
decimal places; however, in e.g. a comparative operation it will be carried out
with the exact value!
year
month
day
hour
minute
second
00...99 or 1000...9999
1...12
1...31
0...23
0...59
0...59
The parameter can either be entered directly as a number or as a Variable
of the type
Number. If the parameter does not correspond to the selected
type then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion
"TextToNumber"). If this is not possible then "
invalid" will be returned as the
result of this operation.
Date/Time
cannot be transferred as a parameter here.
Return value
Date/Time in the format
yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss UTC ±xx
Note
UTC = Universal Time Coordinated: reference time for the different time zones
on the earth. MET (Mean European Time) equals UTC plus 1 hour, in the summer time UTC plus 2 hours.
Examples
Time(2004;06;02;10;30;25) = 2004-06-02 10:30:25 UTC +2 (depends on the
system time)
Time('CV.Testyear';'CV.Testmonth';'CV.Testday';'CV.TestHour';'CV.TestMin';'CV.T
estSec')
= date complied from the Common variables
Functions - Type conversion
NumberToText
Syntax
y = NumberToText(Number)
Returns the entered number as
Text.
50 General program functions
Page 79

Parameter
Number
The parameter can either be entered directly as a number or as a Variable
of the type
Examples
NumberToText(-55.3) = -55.3
NumberToText('CV.MeanTemp') = value of the Common variable as Text
NumberToTime
Syntax
y = NumberToTime(Number)
Returns the entered number as
preted as the number of days since 30 December 1899 at 01 a.m.
Number.
Date/Time, with the number being inter-
Parameter
Number
The parameter can either be entered directly as a number or as a Variable
of the type
Examples
NumberToTime(35545.526) = 1997-05-25 14:37:26 UTC+2 (depends on the
system time)
NumberToTime(35780.55) = 1997-12-16 14:12:00 UTC+1 (depends on the
system time)
NumberToTime('CV.TestDate') = value of the Common variable as Date/Time
TextToNumber
Syntax
y = TextToNumber(Text)
Returns the entered text as
Parameter
Text
The parameter must only contain numerical characters or Variables of the
type
conversion or calculation would be "
by Inverted commas.
Number.
Number.
Text as otherwise type conversion is not possible. The result of this
invalid". The text must also be enclosed
Examples
TextToNumber("-55.3") = -55.3
TextToNumber('CV.MeanTemp') = value of the Common variable as a Num-
ber
TextToNumber('MV.ID1') = entered text of ID 1 as a Number
TextToTime
Syntax
y = TextToTime(Text;Format)
Returns the entered text as
Date/Time.
Formula editor 51
Page 80

Parameter
Text
The parameter must only contain numerical characters or Variables of the
Text as otherwise type conversion is not possible (result = "invalid").
type
You can use the following characters as Separators between year, month,
etc.: slash (
/), full stop (.), minus (-), semicolon (;), colon (:), empty space
and comma. You can determine the Sequence of the individual entries
yourself, but these must be entered in the parameter
Format
Format.
Defines in which format or sequence the text must be entered. This parameter must be enclosed with Inverted commas and can be composed
of the following code characters:
Character Meaning
y
M
d
H
h
m
s
a
Year
Month
Day
Hour 0...23
Stunde AM/PM
Minute
Second
AM/PM marking
Note
If you enter the time in the format AM/PM then in addition to the formatting char-
acter h you must us the AM/PM marking a (see first example below).
Examples
TextToTime("2004-12-3 5:22:01 PM";"yMdhmsa") = 2004-12-03 17:22:01
UTC+1
TextToTime("12-15-01 2001:3:5";"HmsyMd") = 2001-03-05 12:15:01 UTC+1
(depends on the system time)
TextToTime('CV.TestDate';'CV.TestFormat') = values of the Common vari-
ables in the entered time format
TextToTime('MV.ID1';'CV.TestFormat') = entered text of ID1 in the given time
format
TimeToNumber
Syntax
y = TimeToNumber(Time)
Returns the entered time as
Note
In both the automatic and the explicit conversion of a Time into the type Num-
ber the number of days since 30 December 1899 at 01 a.m. will be counted.
Note: 30 December 1899 01 a.m. = 0.00000 days, this number is rounded to 5
decimal places; however, e.g. a comparative operation will be carried out with
the exact value.
(depends on the system time)
Number.
52 General program functions
Page 81

Parameter
Time
This parameter can be entered in either the form of a Time function or as a
Variable of the type
Examples
TimeToNumber(Time()) = current date and current time shown as a Number
(in days since December 1899)
TimeToNumber(Time(1999;12;31;23;59;59)) = 36525.95832
TimeToNumber(Time('TestYear';'TestMonth';'TestDay')) = value of the Com-
mon variables as number of days as
TimeToText
Syntax
y = TimeToText(Time)
Returns the entered time as
y = TimeToText(Time;Format)
Returns the entered time as
Time.
Number
Text.
Text in the required format.
Parameter
Time
This parameter can be entered in either the form of a Time function or as a
Variable of the type
Date/Time.
Format
Defines in which format or sequence the text must be entered. This parameter must be enclosed with Inverted commas and can be composed
of the following code characters:
Character Meaning Example
y
yyyy
M
MM
MMM
MMMM
d
dd
h
hh
H
HH
m
mm
s
2-place date in years
4-place date in years
1- or 2-place date in months
2-place date in months
Abbreviated name of month
Month name
1- or 2-place date in days
2-place date in days
1- or 2-place time in hours (1...12 AM/PM)
2-place time in hours (1...12 AM/PM)
1- or 2-place time in hours (0...23)
2-place time in hours (0...23)
1- or 2-place time in minutes
2-place time in minutes
1- or 2-place time in seconds
03
1999
4, 12
04, 12
Jul, Aug
July, August
2, 25
02, 25
5, 11
05, 11
8, 17
08, 17
2, 25
02, 25
3, 55
Formula editor 53
Page 82

Character Meaning Example
ss
E
EEEE
D
DD
DDD
F
w
ww
W
a
'
''
2-place time in seconds
Abbreviated day of week
Day of week
1- , 2- or 3-place number of day in year
2- or 3-place number of day in year
3-place number of day in year
1-place number of day in month, e.g. the 2nd Monday in May
1- or 2-place number of week in year
2-place number of week in year
1-place number of week in month
Format AM/PM
Introductory and terminating characters for entering any text
Enters '
03, 55
Mo, Tu, We
Monday, Tuesday
2, 35, 142
02, 35, 142
002, 035, 142
2
5, 25
05, 25
3
AM, PM
'
Note
If you want to return the time in the format AM/PM then in addition to the formatting character h you must use the AM/PM marking a.
Examples
TimeToText(Time()) = current date and current time (system) as Text
TimeToText(Time(2004;05;04)) = 2004-05-04 00:00:00 UTC+2 (depends on
the system time)
TimeToText('CV.TestTime') = value of the Common variable (type Time) as
Text
TimeToText(Time(2000;12;31);"EEEE', 'dd'.'MMMM' 'yyyy") = Sunday, 31 December 2000
TimeToText(Time(1997;05;22);"M'/'d'/'yyyy', 'ha") = 5/22/1997, 12PM
Functions - Text
TextPosition
Syntax
y = TextPosition(Text ; Sample text)
Returns the Index that indicates at which position the
curs in the
Sample text first oc-
Text. The numbering of the index starts at 1!
Parameter
Text
The parameter can either be entered directly or as a Variable of the type
Text, Number or Date/Time.
54 General program functions
Page 83

Note
Entries of the type
Example:
verted to 3.0 and this is not contained in the text.
Examples
Sample text
The parameter can either be entered directly or as a Variable of the type
Text, Number or Date/Time. If the types of the two parameters are not identi-
cal then the type
tions - type conversion). If the
"
invalid" will be returned.
Sample text will always be converted to Text (see Func-
Sample text is not contained in the Text then
Number
TextPosition("12345";3) = invalid
TextPosition("Citric acid";"acidic") = 9, from the index number 9 the word
"
acidic" occurs in the text
TextPosition("Citric acid";"Acidic") = invalid, the word "Acidic" (with a capital
are always given with one decimal place.
, as before the operation the 3 is con-
letter) does not occur in the text
TextPosition("Citric acid";"salt") = invalid, the word "salt" does not occur in
the text
TextPosition(Time(2004;05;05);"5") = 7
TextPosition(3362.14;"6") = 3
TextPosition('MV.ID2';"Carbonate") = index, in which the word part "Carbon-
" first starts in ID2
ate
SubText
Syntax
Parameter
y = SubText(Text ; Position ; Length)
Returns that text part from
length
Length.
Text
Text that starts at the index Position and has the
The parameter can either be entered directly as text or as a Variable of
the type
Text. If the parameter does not correspond to the expected type
then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion "NumberToText" or "TimeToText"). If this type conversion is not possible then the result of this operation will be returned as "
invalid".
Position
The numbering of the
tered directly as a number or as a Variable of the type
Position starts at 1. The parameter can either be en-
Number . If the pa-
rameter does not correspond to the expected type then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion "TextToNumber"). If the type conversion is not possible or if the position does not exist then the result of this
operation will be returned as "
invalid".
Length
The parameter can either be entered directly as number or as a Variable
of the type
Number. If the parameter does not correspond to the expected
type then it will be automatically converted to it (see Type conversion
"TextToNumber"). If the type conversion is not possible or if the length given
here is longer than the length of the subtext then "
invalid" will be returned
Formula editor 55
Page 84

Examples
Trim
Syntax
Parameter
SubText("Citric acid";9;5) = acidic
SubText("Citric acid";9;6) = invalid, from the position 9 only five characters
are present
SubText('MV.ID2';1;3) = the first three characters of the identification 2
y = Trim(Text)
Returns the
Text without any empty spaces in front of it or behind it.
y = Trim(Text ; Sample text)
Returns the
Text
Text without Sample text.
The parameter can either be entered directly or as a Variable of the type
Text, Number or Date/Time.
Sample text
The parameter can either be entered directly or as a Variable of the type
Text, Number or Date/Time. If the types of the two parameters are not identi-
cal then the type
Sample text will always be converted to the type Text (see
Functions - Type conversion).
Note
Entries of the type
Example:
verted to 3.0 and this is not contained in the text.
Examples
Number
TextPosition("12345";3) = invalid
Trim(" Citric acid ") = "Citric acid"
Trim("Citric acid";"acid") = lemons
Trim("Citric acid";"salt") = Citric acid
are always given with one decimal place.
, as before the operation the 3 is con-
56 General program functions
Page 85

Miscellaneous functions
Case
Syntax
y = Case(condition ; Value_true ; Value_false)
y = Case(condition ; Value_true ; Value_false ; Value_error)
Returns
turned. If an error occurs in the condition (Result "
will be returned.
Parameters
Condition Number
Any Variable (type
eration can be carried out whose operators are either adopted directly or
transferred as a Variable. This could be of the type
Date/Time (Time()).
Value_true
If the Condition <> 0 then this parameter will be saved as the result of the
function.
This parameter can either be transferred directly or as a Variable and can
be of the type
can also be transferred here.
Value_false
If the Condition = 0 then this parameter will be saved as the result of the
function.
This parameter can either be transferred directly or as a Variable and can
be of the type
can also be transferred here.
Value_error
If the Condition = invalid then this parameter will be saved as the result of
the function.
This parameter can either be transferred directly or as a Variable and can
be of the type
can also be transferred here.
Value_true if the condition is true. Otherwise Value_false will be re-
number) can be entered here, or a Compare or logic op-
Text, Number or Date/Time (Time()). Complete Operations
Text, Number or Date/Time (Time()). Complete Operations
Text, Number or Date/Time (Time()). Complete Operations
invalid") then Value_error
Text, Number or
Examples
Case('MV.ID1' = "";"ID1 empty";"ID1 not empty") = if in the Run window no
entry has been made for ID1 then in the result the text "
pear, otherwise "
ID1 not empty" will be saved.
ID1 empty" will ap-
Case( 'DET pH 1.EP{1}.VOL';'DET pH 1.EP{1}.VOL';0;0) = if in the titration DET
an endpoint has been found for which the volume is not 0 (Value_true)
pH 1
then this will be saved as the result. If EP1 is at 0 exactly then
turned. If no endpoint has been found then
0 will also be saved as the result
0 will be re-
of this function.
Case('RS.InterRes' > 5.5;"Intermediate result too high";'RS.InterRes' *
26.5;"error occurred")
text "
Intermediate result too high " will be written in the result, otherwise the
= if the the result "InterRes" is larger than 5.5 then the
intermediate result will be multiplied by 26.5. If in the comparison
(
'RS.InterRes' > 5.5) an error occurs then "Error occurred" will be saved as the
result of this operation.
Formula editor 57
Page 86

Error
Syntax
Parameters
Examples
y = Error(value)
Returns
+1 if Value invalid (error) or 0 if Value valid. This function can be
used, for example, to check whether variables exist or if they are valid.
Value
The variable to be tested.
Error('RS.InterRes') = 0: the intermediate result could be calculated.
Error('RS.InterRes') = 1: the intermediate result is invalid.
Error('DET pH 6.EP{1}.MEA') = 0: the variable for the measured value at
Endpoint 1 exists.
Error('DET pH 6.EP{1}.MEA') = 1, no variable exists for the measured value or
no EP is present.
ASCII table
Only characters that can be printed out are shown in the following table:
ASCII
value
(dec)
Character ASCII
value
(dec)
Character ASCII
value
(dec)
Character
32 Blank character 64 'At' sign (@) 96 Accent grave (`)
33 Exclamation mark
65 A 97 a
(!)
34 Inverted commas (") 66 B 98 b
35 Lozenge (#) 67 C 99 c
36 Dollar ($) 68 D 100 d
37 Percent (%) 69 E 101 e
38 Ampersand "and"
70 F 102 f
(&)
39 Inverted comma (') 71 G 103 g
40 Open round brack-
72 H 104 h
ets (()
41 Close round brack-
73 I 105 i
ets ())
42 Multiplication sign
74 J 106 j
(*)
43 Addition sign (+) 75 K 107 k
44 Apostrophe (´) 76 L 108 l
45 Subtraction sign (-) 77 M 109 m
46 Full stop (.) 78 N 110 n
47 Slash (/) 79 O 111 o
48 0 80 P 112 p
49 1 81 Q 113 q
58 General program functions
Page 87

ASCII
value
(dec)
Character ASCII
value
(dec)
Character ASCII
value
(dec)
Character
50 2 82 R 114 r
51 3 83 S 115 s
52 4 84 T 116 t
53 5 85 U 117 u
54 6 86 V 118 v
55 7 87 W 119 w
56 8 88 X 120 x
57 9 89 Y 121 y
58 Colon (:) 90 Z 122 z
59 Semicolon (;) 91 Open square
bracket ([)
123 Open curly
bracket ({)
60 Smaller than (<) 92 Backslash (\) 124 Vertical line (¦)
61 Equals (=) 93 Close square
bracket (])
125 Close curly
bracket (})
62 Larger than (>) 94 Circumflex (^) 126 Tilde (~)
63 Question mark (?) 95 Underscore (_)
Formula editor 59
Page 88

2.5 Edit
2.5.1 Text editor
The text editor is used for entering formatted text in text fields and is opened with
the button
.
The symbol bar of the text editor contains the following functions:
Cuts selected text and copies it to the clipboard.
Copies selected text to the clipboard.
Pastes text from clipboard.
Opens the Formula editor for entering calculation formulas.
Note
In order that the results of formulas of the type
must be converted to
Text
in the text window with the function TimeToText().
Date
are shown correctly they
Font size in pt.
Selects the text color.
Bold.
Italic.
Underlined.
60 General program functions
Page 89

Justified left.
Centered.
Justified right.
2.5.2 Select date
In order to be able to enter a date in a field the dialog window Select date must be
used; this is opened with the button
.
Selects the month
Selects the year
Selects the day
Selected date
Edit 61
Page 90

2.6 Manual control
2.6.1 General
Open
Manual control of devices is carried out in the independent dialog window
control
determination is running) with
of the window contains the usual Windows buttons for closing, diminishing, maximizing and minimizing.
Close
The dialog window
ton for closing.
Subwindows
The dialog window
can be enlarged and diminished by dragging the separating bar between the windows:
which can be called up from all program parts at any time (even while a
Tools, Manual control or the symbol . The title line
Manual control can be closed with [Close] or the Windows but-
Note
Manual control can only be closed when no manually triggered actions are being carried out (exception: stirrer switched on).
Manual control contains the following three subwindows which
Manual
• Select device
• Functions/Parameters
• Graphic function display
62 General program functions
Page 91

2.6.2 Select device
In the subwindow for device selection the devices (or functional units of the devices) can be selected whose functions are to be triggered manually. These are
shown in a tree structure. All the devices configured in the device table with the
status "
device type. The currently selected device is shown with a blue background. Devices that are still carrying out manually triggered actions are shown in red.
ok" are shown with the device name and (in brackets) the number of the
2.6.3 Functions
In the subwindow for functions/parameters both the functions for manual control
of the selected device as well as their associated parameters can be selected. In
addition the measured values for running actions and messages are shown here.
Depending on the device the following functions are possible:
• Dosing
• Stirring
• Remote functions
• Sample changer functions
2.6.4 Graphic display
In the subwindow for graphic display the manually triggered functions that are
running are shown graphically.
2.6.5 Dosing
If in the Select device subwindow the group Dosing devices or a single Dosing de-
is selected then in the subwindow for Functions/Parameters the functions and
vice
parameters that are possible with these dosing devices will appear.
Dosing functions
Dosing functions for exchange and dosing units are shown on the following register cards:
• General
• Prepare
• Fill
• Empty
• Add fixed volume
• Dosing
Devices
The dosing functions can be carried out with dosing devices that are built into or
connected to the following instruments :
Titrino: 702, 716, 718, 719, 720, 721, 736, 751, 758, 785, 784, 785, 794, 795, 798,
799
Titrando: 808, 809, 835, 836, 841, 842, 855
Dosing Interface: 846
Sample changer: 814, 815, 855
Manual control 63
Page 92

General
Information about the selected dosing device, the attached exchange/dosing unit
and the solution it contains is shown here. This tab only appears when a single
dosing device is selected.
Exchange/Dosing unit
Name
Shows the entered name of the Exchange unit or Dosing unit defined under
Configuration. This field always appears for intelligent exchange/dosing
units. With non-intelligent exchange/dosing units it only appears if a solution
has been selected under
Type
Shows the type of exchange/dosing unit attached to the dosing device (EU,
IEU, DU, IDU).
Cylinder volume
Shows the cylinder volume of the exchange/dosing unit attached to the
dosing device.
Solution
Solution
Titrant/Solution, [ not defined ]
Selection from the titrants and solutions listed in the Solution table for nonintelligent exchange/dosing units. For intelligent exchange/dosing units only
the name is shown.
Titer
Shows the titer of the solution in the exchange/dosing unit. This field only
appears for intelligent exchange/dosing units, or if a solution has been selected for non-intelligent exchange/dosing units.
Solution.
64 General program functions
Page 93

Prepare
The preparation of exchange/dosing units can be started and stopped here. This
tab appears for the selection of a single dosing device as well as for all dosing
devices.
Note
This tab will not be displayed for the internal dosing devices on Titrinos 702,
716, 718, 719, 720, 721, 784, 785, 794, 795, 798.
Start preparing the selected dosing device(s). The parameters defined for
the Exchange unit or Dosing unit will be used.
Stop preparing the selected dosing device(s).
Manual control 65
Page 94

Fill
Filling exchange/dosing units can be started and stopped here. This tab appears
for the selection of a single dosing device as well as for all dosing devices.
Note
Before filling dosing devices connected to Titrinos, make sure that the exchange
or dosing devices are mounted. If the filiing process is started nevertheless, it
may be that the Titrino does not respond any more and must be switched off
and on again.
Start filling the selected dosing device(s).
Stop filling the selected dosing device(s).
66 General program functions
Page 95

Empty
Emptying dosing units can be started and stopped here. This tab appears for the
selection of a single dosing device as well as for all dosing devices.
Note
This tab will not be displayed for external dosing devices on Titrinos 736, 751,
756, 799.
Start emptying the selected dosing device(s). The parameters defined for
the Dosing unit will be used.
Stop emptying the selected dosing device(s).
Manual control 67
Page 96

Add fixed volume
Adding a predefined volume can be started and stopped here. This tab only appears when a single dosing device has been selected.
Volume
[ 0.100 ] ... 99999.9 mL
Fixed volume to be added.
Dosing rate
[ maximum ]
0.01 ... 166.00 mL/min
0.01 ... 160.00 mL/min
0.01 ... 150.00 mL/min
(Titrando, 814, 815, 855)
(730, 774, 778, 789)
(Titrino)
The volume is added at this speed. The maximum dosing speed depends
on the cylinder volume of the Exchange unit or Dosing unit used. If the entered dosing rate is too high for the selected dosing device then during
dosing it will automatically be reduced to the largest possible value.
Note
The dosing rate should be reduced for viscous liquids.
Filling rate
[ maximum ]
0.01 ... 166.00 mL/min
0.01 ... 160.00 mL/min
0.01 ... 150.00 mL/min
(Titrando, 814, 815, 855)
(730, 774, 778, 789)
(Titrino)
After dosing the buret will be refilled at this speed. The maximum filling
speed depends on the cylinder volume of the Exchange unit or Dosing unit
used. If the entered filling rate is too high for the selected dosing device
then during filling it will automatically be reduced to the largest possible
value.
68 General program functions
Page 97

Note
The filling rate should be reduced for viscous liquids.
Fill automatically
This parameter is only visible for Titrandos, Dosing Interface and the USB
Sample Processor.
[ on ], off
If this option is switched on then the buret will be refilled automatically after
dosing. During the filling procedure the volume display is reset to
mL
. If this option is switched off then the added volume will be displayed
0.0000
cumulatively.
Start adding the fixed volume for the selected dosing device. The added
volume is shown live.
Note
Parameters that are altered after dosing has started only apply to the next dosing
procedure.
Start filling the buret for the selected dosing device. This button is only present when
volume display is reset to
Fill automatically is switched off. During the filling procedure the
0.0000 mL.
Stop adding the fixed volume for the selected dosing device. Once dosing
has been stopped it can no longer be restarted.
Manual control 69
Page 98

Dosing
Manual dosing can be started and stopped here. This tab only appears if a single
dosing device has been selected; it does not appear for
vices.
Titrino-type dosing de-
Dosing rate
[ maximum ]
0.01 ... 166.00 mL/min
0.01 ... 160.00 mL/min
(Titrando, 814, 815, 855)
(778, 789)
Speed at which dosing is to be carried out. The maximum dosing speed
depends on the cylinder volume of the Exchange unit or Dosing unit used.
If the entered dosing rate is too high for the selected dosing device then
during dosing it will automatically be reduced to the largest possible value.
Note
The dosing rate should be reduced for viscous liquids.
Filling rate
[ maximum ]
0.01 ... 166.00 mL/min
0.01 ... 160.00 mL/min
(Titrando, 814, 815, 855)
(778, 789)
After dosing the buret will be refilled at this speed. The maximum filling
speed depends on the cylinder volume of the Exchange unit or Dosing unit
used. If the entered filling rate is too high for the selected dosing device
then during filling it will automatically be reduced to the largest possible
value.
Note
The filling rate should be reduced for viscous liquids.
70 General program functions
Page 99
Start manual dosing for the selected dosing device. Dosing will continue for
as long as the button is pressed down. The added volume is shown live.
Note
Parameters that are altered after dosing has started only apply to the next dosing
procedure.
Start filling the buret for the selected dosing device. During the filling procedure the volume display is reset to
0.0000 mL.
2.6.6 Stirring
If a stirrer connected via MSB or a stirrer connection is selected in the Select device subwindow then all the possible functions and parameters for the stirrers will
appear in the Functions/Parameters subwindow.
Stirrer functions
The stirrer functions are shown on the following tabs:
• Switch on/off
• Continuous operation
Devices
The stirrer functions can be carried out with stirrers that are connected to the following instruments:
Titrino: 702, 716, 718, 719, 720, 721, 736, 751, 758, 785, 784, 785, 794, 795, 798,
799
Titrando: 808, 809, 835, 836, 841, 842, 855
Dosing Interface: 846
Sample Changer: 730, 774, 778, 789, 814, 815, 855
Manual control 71
Page 100
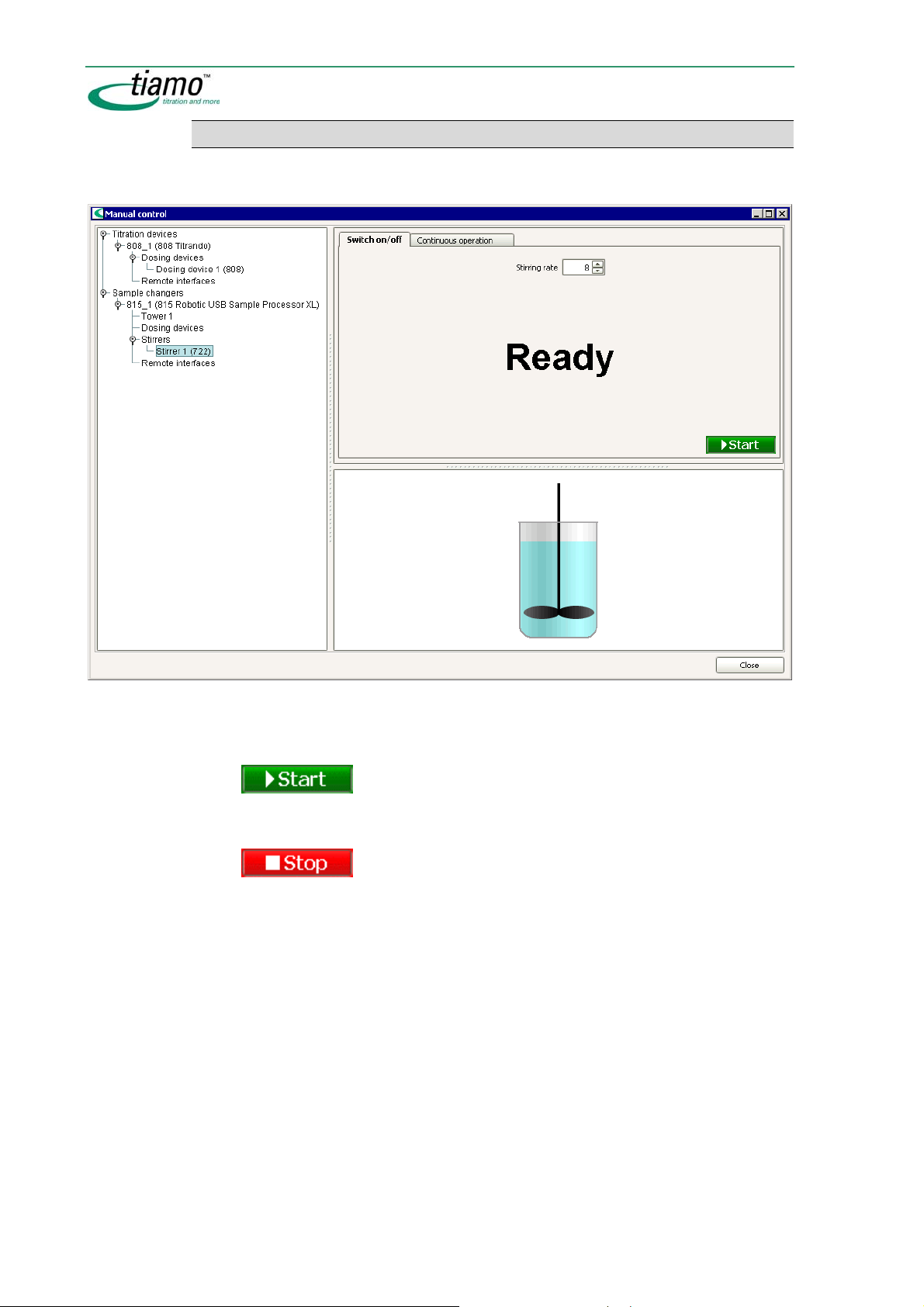
Switch on/off
Stirrers can be switched on and off here. This tab appears for the selection of a
single stirrer as well as for all stirrers.
Stirring rate
-15 ... -1, 1 ... [ 8 ] ... 15
Selects the stirring speed. This parameter can also be altered live.
Start stirring for the selected stirrer(s).
Stop stirring for the selected stirrer(s).
72 General program functions
 Loading...
Loading...