Kenwood TK-7160H Service manual

VHF FM TRANSCEIVER
TK-7160H
SERVICE MANUAL
© 2004-12 PRINTED IN JAPAN
B51-8706-00 (N) 1120
Modular jack
(E08-0877-05)
RF coaxial receptacle (M)
(E04-0167-05)
Key top
(K29-9342-01)
CONTENTS
GENERAL .................................................. 2
SYSTEM SET-UP ...................................... 3
OPERATING FEATURES .......................... 4
REALIGNMENT ......................................... 5
INSTALLATION ......................................... 9
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR ................. 11
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION .......................... 12
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA ...................... 17
COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION .............. 18
PARTS LIST ............................................. 19
EXPLODED VIEW.................................... 26
DC cord
(E30-3448-05)
PACKING ................................................. 27
ADJUSTMENT ........................................ 28
TERMINAL FUNCTION ........................... 33
PC BOARD
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM.......................... 40
BLOCK DIAGRAM ................................... 44
LEVEL DIAGRAM .................................... 46
SPECIFICATION ................... BACK COVER
Panel assy
(A62-1107-13)
Badge
(B43-1179-04)
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3510-10) ............ 34
TX-RX UNIT (X57-7080-11) ................ 36

TK-7160H
GENERAL
INTRODUCTION
SCOPE OF THIS MANUAL
This manual is intended for use by experienced technicians familiar with similar types of commercial grade communications equipment. It contains all required service information for the equipment and is current as of this publication
date. Changes which may occur after publication are covered
by either Service Bulletins or Manual Revisions, which are
issued as required.
ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS
When ordering replacement parts or equipment information, the full part identification number should be included.
This applies to all parts : components, kits, and chassis. If the
part number is not known, include the chassis or kit number
of which it is a part and a sufficient description of the required
component for proper identification.
PERSONAL SAFETY
The following precautions are recommended for personal
safety :
•DONOT transmit if someone is within two feet (0.6
meter) of the antenna.
•DONOT transmit until all RF connectors are secure and
any open connectors are properly terminated.
• SHUT OFF this equipment when near electrical blasting
caps or while in an explosive atmosphere.
• All equipment should be properly grounded before power-
up for safe operation.
• This equipment should be serviced by only qualified tech-
nicians.
PRE-INSTALLATION CONSIDERATIONS
1. UNPACKING
Unpack the radio from its shipping container and check for
accessory items. If any item is missing, please contact
KENWOOD immediately.
2. LICENSING REQUIREMENTS
Federal regulations require a station license for each radio
installation (mobile or base) be obtained by the equipment
owner. The licensee is responsible for ensuring transmitter
power, frequency, and deviation are within the limits permitted by the station license.
Transmitter adjustments may be performed only by a licensed technician holding an FCC first, second or general
class commercial radiotelephone operator’s license. There is
no license required to install or operate the radio.
3. PRE-INSTALLATION CHECKOUT
3-1. Introduction
Each radio is adjusted and tested before shipment. However, it is recommended that receiver and transmitter operation be checked for proper operation before installation.
3-2. Testing
The radio should be tested complete with all cabling and
accessories as they will be connected in the final installation.
Transmitter frequency, deviation, and power output should
be checked, as should receiver sensitivity, squelch operation,
and audio output. Signalling equipment operation should be
verified.
4. PLANNING THE INSTALLATION
4-1. General
Inspect the vehicle and determine how and where the radio antenna and accessories will be mounted.
Plan cable runs for protection against pinching or crushing
wiring, and radio installation to prevent overheating.
4-2. Antenna
The favored location for an antenna is in the center of a
large, flat conductive area, usually at the roof center. The
trunk lid is preferred, bond the trunk lid and vehicle chassis
using ground straps to ensure the lid is at chassis ground.
4-3. Radio
The universal mount bracket allows the radio to be
mounted in a variety of ways. Be sure the mounting surface
is adequate to support the radio’s weight. Allow sufficient
space around the radio for air cooling. Position the radio close
enough to the vehicle operator to permit easy access to the
controls when driving.
4-4. DC Power and wiring
1. This radio may be installed in negative ground electrical
systems only. Reverse polarity will cause the cable fuse to
blow. Check the vehicle ground polarity before installation
to prevent wasted time and effort.
2. Connect the positive power lead directly to the vehicle
battery positive terminal. Connecting the Positive lead to
any other positive voltage source in the vehicle is not rec-
ommended.
3. Connect the ground lead directly to the battery negative
terminal.
4. The cable provided with the radio is sufficient to handle
the maximum radio current demand. If the cable must be
extended, be sure the additional wire is sufficient for the
current to be carried and length of the added lead.
2
GENERAL / SYSTEM SET-UP
TK-7160H
5. INSTALLATION PLANNING – CONTROL STATIONS
5-1. Antenna system
Control station. The antenna system selection depends on
many factors and is beyond the scope of this manual. Your
KENWOOD dealer can help you select an antenna system
that will best serve your particular needs.
5-2. Radio location
Select a convenient location for your control station radio
which is as close as practical to the antenna cable entry point.
Secondly, use your system’s power supply (which supplies
the voltage and current required for your system). Make sure
sufficient air can flow around the radio and power supply to
allow adequate cooling.
SERVICE
This radio is designed for easy servicing. Refer to the
schematic diagrams, printed circuit board views, and alignment procedures contained in this manual.
NOTE
If you do not intend to use the 3.5-mm jack for the external
speaker, fit the supplied speaker-jack cap to stop dust and
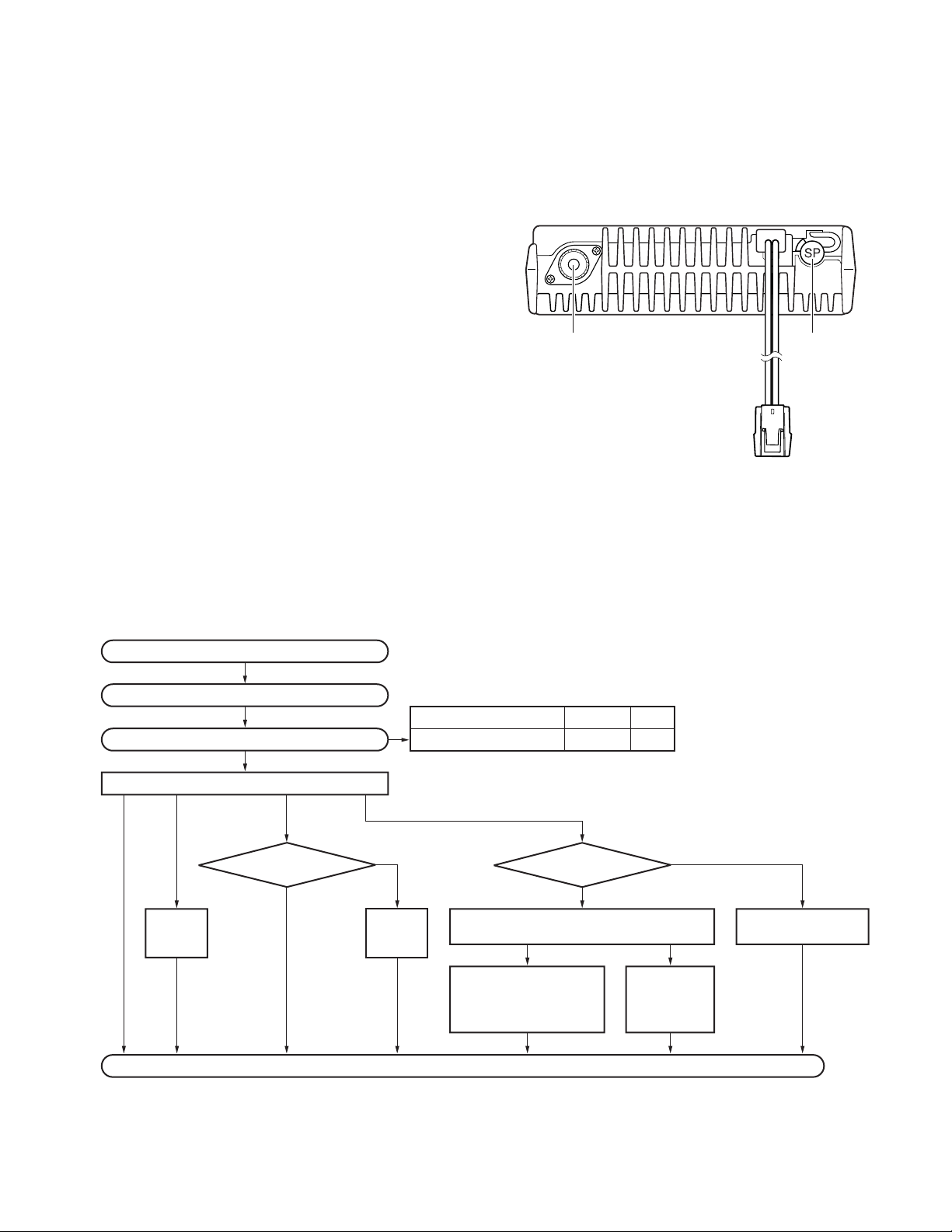
sand from getting in.
Antenna
connector
Power input
connector
External
speaker
jack
SYSTEM SET-UP
Merchandise received
License and frequency allocated by FCC
Choose the type of transceiver
Transceiver programming
KAP-2
Horn alert/P.A. relay
KES-3
External
speaker
(Option)
You can install either KAP-2 or KCT-39 to the transceiver.
unit
(Option)
External
speaker
(Option)
Frequency range (MHz) RF power
136~174 50W K,M
See page 5.
A personal computer (IBM PC or compatible), programming interface (KPG-46),
and programming software (KPG-99D) are required for programming.
KCT-39
Connection cable
(Option)
KES-5
KGP-2A
Modem GPS receiver or
KGP-2B
Modem GPS controller
Delivery
KCT-36
Extension cable
Type
or
Mobile data
(Option)
KDS-100
terminal
(Option)(Option)
KCT-18
Ignition sense cable
(Option)
3
TK-7160H
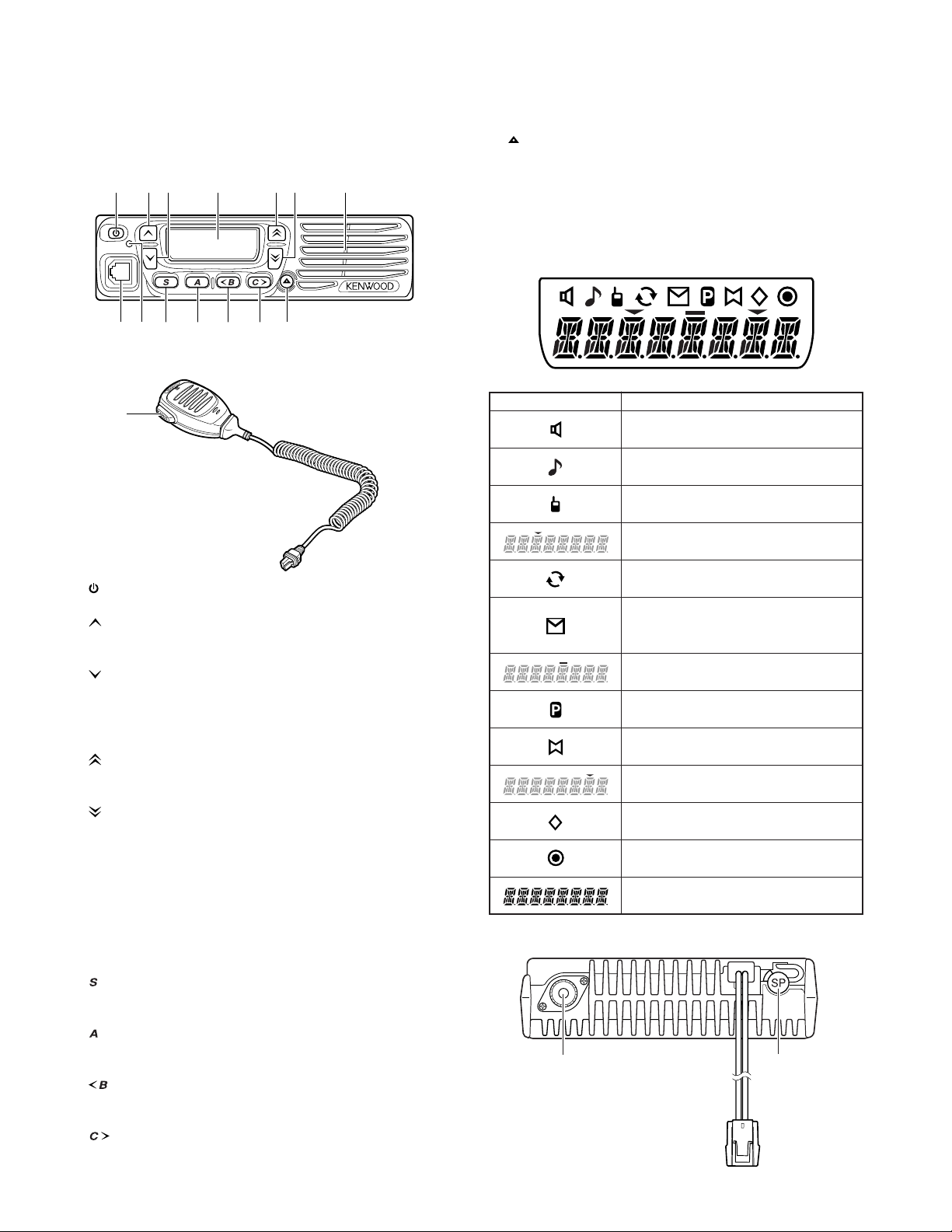
1. Controls and Functions
1-1. Front Panel
q
we r ty u
io !0 !1 !2 !3 !4
1-2. Microphone
OPERATING FEATURES
key
!4
Press to activate its programmable function. The default
setting is None (no function).
!5 PTT switch
Press this switch, then speak into the microphone to call a
station.
1-3. Display
!5
q (Power) switch
Press to switch the transceiver ON or OFF.
w key
Press to activate its programmable function. The default
setting is Volume Up.
key
e
Press to activate its programmable function. The default
setting is Volume Down.
r Display
Refer to right.
key
t
Press to activate its programmable function. The default
setting is Zone Up.
key
y
Press to activate its programmable function. The default
setting is Zone Down.
u Speaker
Internal speaker.
i Microphone jack
Insert the microphone plug into this jack.
o TX/RX Indicator
Lights red while transmitting. Lights green while receiving a signal.
key
!0
Press to activate its programmable function. The default
setting is Squelch Off Momentary.
key
!1
Press to activate its programmable function. The default
setting is None (no function).
key
!2
Press to activate its programmable function. The default
setting is Channel Down.
key
!3
Press to activate its programmable function. The default
setting is Channel Up.
4
Indicator Description
Appears when the key programmed as
Monitor or Squelch Off is pressed.
Appears when the DTMF or 2-tone code of
a call matches the code in your transceiver.
Appears while using the Talk Around
function.
The selected zone is added to the
scanning sequence.
Appears while scanning.
Appears when a message is stored in the
transceiver stack memory. Appears and
blinks when a new message has arrived.
Appears when the AUX port has been
activated.
The selected channel is set as a Priority
channel.
Appears when the Horn Alert function
has been activated.
The selected channel is added to the
scanning sequence.
Appears when Scrambler function has
been selected.
Appears when the Public Address
function has been activated.
Displays the currently selected zone and
channel number, or the channel name.
1-4. Rear Panel
Antenna
connector
External
speaker
jack
Power input
connector

REALIGNMENT
TK-7160H
1. Modes
User mode PC mode PC programming mode
Clone mode
Self programming mode
Mode Function
User mode For normal use.
PC mode Used for communication between the
radio and PC (IBM compatible).
PC programming Used to read and write frequency data
mode and other features to and from the radio.
PC test mode Used to check the radio using the PC.
This feature is included in the FPU.
PC tuning mode Used to tune the radio using the PC.
Clone mode Used to transfer programming data from
one radio to another.
Self programming You can program the frequency, signalling
mode and other functions using only the radio.
PC test mode
PC tuning mode
2. How to Enter Each Mode
Mode Operation
User mode Power ON
PC mode Received commands from PC
Clone mode
Self programming mode [ ]+Power ON (Two seconds)
[ ]+Power ON (Two seconds)
3-2. Connection Procedure
1. Connect the TK-7160H to the personal computer with the
interface cable.
2. When the Power is switched on, user mode can be en-
tered immediately. When the PC sends a command, the
radio enters PC mode.
When data is transmitted from transceiver, the TX indica-
tor blink.
When data is received by the transceiver, the BUSY indi-
cator blink.
In the PC mode, “PROGRAM” is displayed on the LCD.
3-3. KPG-46 Description
(PC programming interface cable : Option)
The KPG-46 is required to interface the TK-7160H to the
computer. It has a circuit in its D-subconnector (25-pin) case
that converts the RS-232C logic level to the TTL level.
The KPG-46 connects the modular microphone jack of the
TK-7160H to the computers RS-232C serial port.
3-4. Programming Software Description
KPG-99D is the programming software for TK-7160H supplied on a CD-ROM. This software runs under Windows 98,
ME, Windows 2000 or XP on an IBM-PC or compatible machine.
The data can be input to or read from TK-7160H and edited
on the screen. The programmed or edited data can be
printed out. It is also possible to tune the transceiver.
4. Clone Mode
Programming data can be transferred from one radio to
another by connecting them via their modular microphone
jacks. The operation is as follows (the transmit radio is the
master and the receive radio is the slave).
3. PC Mode
3-1. Preface
The TK-7160H transceiver is programmed using a personal computer, a programming interface (KPG-46) and programming software (KPG-99D).
The programming software can be used with an IBM PC
or compatible. Figure 1 shows the setup of an IBM PC for
programming.
IBM-PC
KPG-46
KPG-99D
TK-7160H
Fig. 1
Note :
Clone mode should be enabled.
1. Turn the master TK-7160H power ON with the [
held down (2 seconds), “ CLONE ” is displayed on the
LCD.
2. Power on the slave TK-7160H.
3. Connect the cloning cable (No. E30-3382-05) to the modular microphone jacks on the master and slave.
4. Press the [
The data of the master is sent to the slave. While the
master is sending data, red LED blinked. While the slave is
receiving the data, “ PC ” is displayed and green LED
blinked. When cloning of data is completed, the master
displays “END”, and the master red LED turned off, and
the slave automatically operates in the User mode. The
slave can then be operated by the same program as the
master.
5. The other slave can be continuously cloned. Carry out the
operation in step 2 to 4.
] key on the master TK-7160H transceiver.
] key
5
TK-7160H
REALIGNMENT
4-1. Adding the data password.
If the data password is set in the optional feature menu,
you must enter the password (Master transceiver) to activate
a clone mode.
You can use 0~9 to configure the password. The maximum length of the password is 6 digits.
]+Power ON.
1. [
2. “CLN LOCK” is displayed on the LCD.
3. If the [ ] and [ ] keys is pressed while “CLN LOCK” is
displayed, numbers (0 to 9) are displayed flashing. When
you press the [
determined. If you press the [
password in this procedure, “CLONE” is displayed if the
entered password is correct. If the password is incorrect,
“CLN LOCK” is redisplayed.
Clone cable
(E30-3382-05)
] key, the currently selected number is
] key after entering the
Fig, 2
5. Self Programming Mode
Write mode for frequency data and signaling, etc. To be
used ONLY by the authorized service person maintaining the
user’s equipment. After programming, reset the FPU to the
“Self- Programming” disabled mode. Radios CANNOT be
delivered to the end-user in the self-programming mode.
5-1. Enter to the Self Programming Mode
Hold down the [ ] key 2 seconds and turn the power
switch on. When enter the self programming mode, “1- 1”
is displayed 2 seconds after “ SELF ” is displayed.
5-2. Adding the Data Password
If the data password is set in the optional feature menu,
you must enter the password to activate a self programming
mode.
You can use 0~9 to configure the password. The maximum length of the password is 6 digits.
1. [
]+Power ON.
2. “SLF.LOCK.R”* is displayed on the LCD.
3. If the [ ] and [ ] keys is pressed while “SELFLOCK” is
displayed, numbers (0 to 9) are displayed flashing. When
you press the [ ] key, the currently selected number is
determined. If you press the [
password in this procedure, “SELF” is displayed if the en-
tered password is correct. If the password is incorrect,
“SLF.LOCK.R”* is redisplayed.
* Read authorization password → “SLF.LOCL.R”
Overwrite password → “SLF.LOCK.W”
] key after entering the
■ Flow Chart (Master radio)
Press [ ] key+Power ON for 2 seconds
Is data
password
set?
No
Start the clone function
Ye s
Shows CLN LOCK
Input passward if
passward is correct
Clone mode
[ ]
Note :
This mode (self programming mode) cannot be set when
it has been disabled with the FPU.
5-3. Channel Setting Mode
Each channel can be setup in its action mode by using the
panel keys.
• Pressing [
setting mode.
• Select an item set using [ ] then change the selection
with the [
•The data displayed using [
• Pressing [
in the memory.
• Press [ ] to set the display to “ SELF ” and return to
reset (default) status.
] when “1- 1” is displayed, sets channel
] or [ ].
] is stored in the memory.
] proceeds to the next item without storing it
6

1. RX frequency
kHz setting
kHz step
MHz setting
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
Frequency clear
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] / [ ]
[ ]
[ ] / [ ]
[ ]
[ ] / [ ]
[ ]
: Cleared
13600000
136
*****
STPD500K
––––––––
––––––––
Display
Current
setting value
Value is not set
136
*****
2. RX signaling
Off
QT normal
Signaling setting
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
DQT normal
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
DQT inverse
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
[ ] / [ ]
[ ]
[ ] / [ ]
[ ]
[ ] / [ ]
[ ]
: Tone off
Display
TONEDOFF
QTDD
****
DQTD
***
N
DQTD
***
I
5. Channel name
1~8 digit
selection
Channel name
setting
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] / [ ]
[ ]
: Stored
Display
________
Character selection
If the [ ] key held down
(2 seconds), the blinking
character clears.
REALIGNMENT
■ Item Selection Mode ■ Item Setting Mode
TK-7160H
[ ] + Power on
Self programming mode
Zone / Channel selection
[ ] [ ]
Zone No. /
Channel No. selection
[ ]
[ ]
1. RX frequency
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
2. RX signaling
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
3. TX frequency
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
4. TX signaling
[ ] [ ]
5. Channel name
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
6. Wide / Narrow
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
7. RF power
[ ] [ ]
8. Scan Del/Add
[ ] [ ]
9. Beat shift on/off
[ ] [ ]
10. Compander on/off
Display
SEL F
[ ]
: Down
: Up
[ ]
[ ]
Refer to the
“Item setting mode”.
[ ]
Refer to the
“Item setting mode”.
[ ]
Same operation as the
“RX frequency”.
[ ]
Same operation as the
“RX signaling”.
[ ][ ]
Refer to the
“Item setting mode”.
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
→
[ ] / [ ]
[ ] / [ ]
[ ] / [ ]
[ ] / [ ]
[ ] / [ ]
1- 1
Zone Channel
[ ] : Stored
[ ] :
Not stored
[ ] : Stored
[ ] :
Not stored
[ ] : Stored
[ ] :
Not stored
[ ] : Stored
[ ] :
Not stored
[ ] : Stored
[ ] :
Not stored
7

TK-7160H
CN2
CN3
A
B
7
8
6
5
Chassis
Chassis
Cushion
KCT-39
sumi tube
PCB
Face down
Avoid forming the wiring towards
the shielding cover closure area.
Wire harness
band (Stopper)
End view of this area
9
10
13
15
1
3
REALIGNMENT
6. Accessory Connection Cable (KCT-39)
The KCT-39 is an accessory connection cable for connecting external equipment. The connector has 15 pins and the
necessary signal lines are selected for use.
6-1. Installing the KCT-39 in the Transceiver
1. Lift the DC cord bushing (1) from the chassis. Peel the
pad as shown in Figure 3 (
2
1
Fig. 3
).
2
3. Insert the KCT-39 cable (5) into the chassis (6). The
7
wire harness band (
) must be inside the chassis and
face down.
4. Connect the KCT-39 to the TX-RX unit as shown in Figure
8
).
5 (
2. Stick the pad to the DC cord (3) and chassis (4), both
of which are supplied with the KCT-39.
3
8
■ Accessory Port Function
No. Color Internal Name
1 Red CN2-1 SB
2 Pink CN3-1 IGN
3 Black CN2-3 GND
4 Brown CN3-3 DETO
5 Orange CN3-2 DATAI
6 Yellow CN2-8 FNC4
7 Green CN2-7 FNC3
8 Blue CN2-9 FNC5
connector
4
Fig. 4
No. Color Internal Name
9 Purple CN2-12 FNC8
10 Gray CN2-10 FNC6
11 White CN2-11 FNC7
12 NC NC
13 NC NC
14
15
Sky blue
Turquoise
connector
CN2-6 FNC2
CN2-5 FNC1
Fig. 5
5. Connect the KCT-39 to the external accessory by inserting
9
the crimp terminal (
) into the square plug (10), both of
which are supplied with the KCT-39.
Fig. 6
1471013
2581114
3691215

REALIGNMENT / INSTALLATION
TK-7160H
7. Ignition Sense Cable (KCT-18)
The KCT-18 is an optional cable for enabling the ignition
function. The ignition function lets you turn the power to the
transceiver on and off with the car ignition key.
7-2. Connecting the KCT-18 to the Transceiver
1. Install the KCT-39 in the transceiver. (See the KCT-39 sec-
tion)
2. Insert the KCT-18 lead terminal (
2
).
39 (
13
1
15
3
1
2
Fig. 7
1
) into pin 2 of the KCT-
1. PA/HA Unit (KAP-2 : Option)
1-1. Installing the KAP-2 in the Transceiver
The Horn Alert and Public Address functions are enabled
by inserting the KAP-2 relay unit.
■ Installation Procedure
The accessories of KAP-2 use “KIT A” for this transceiver.
1. Open the case and shield cover of the transceiver.
2. Remove the jumper lead from CN6 connector on the TXRX unit.
1
3. Lift the DC cord bushing (
move the pad as shown in the Figure 1 (
) from the chassis and re-
2
1
2
).
7-3. Modifying the Transceiver
Modify the transceiver as follows to turn the power on and
off with the ignition key.
1. Remove the jumper resistor (0Ω) R95 of the TX-RX unit.
■ Setting With the KPG-99D
Select “Function port” from the “Edit” menu and enable
the “Ignition Sense”.
TX-RX UNIT
Component side
CN2
R95
Fig. 1
4. Affix the new pads (supplied with the KAP-2) to the DC
3
cord (
) and chassis (4).
G13-2083-04
(9 x 3.5 x 4 mm)
3
G13-2084-04
(6 x 6 x 1.5 mm)
4
Fig. 2
Fig. 8
9

TK-7160H
INSTALLATION
5. Affix the 20 x 20 x 2.5 mm pad to the 40 x 33 mm transparent sheet, then attach it to the TX-RX unit printed area as
shown in Figure 3.
G11-4353-04
(40 x 33 mm)
q
IC281
G13-2065-04
(20 x 20 x 2.5 mm)
w
Fig. 3
6. Affix the 30 x 30 x 1 mm pad to the top of the KAP-2 relay
unit.
7. Affix the KAP-2 relay unit to the transparent sheet.
8. Attach the supplied cable to the CN3 connector of the
KAP-2 unit and the CN6 connector of the TX-RX unit.
9. Insert the extension cable connector into the CN2 connector of the KAP-2 unit.
Note : You must setup using the KPG-99D.
CN6
CN3
CN2
CN3
CN2
E37-1159-05
CN6
e
Fig. 4
G13-2063-04
(30 x 30 x 1 mm)
r
■ Cable (E37-1160-05)
6-pin Connector
Pin No.
Color Name
1 Red HR2
2 Blue GND
3 Yellow OSP
4 Green ESP
5 Brown GND
6 Black HR1
Chassis
Cushion
Chassis
Face down
End view of this area
3
2
1
6
5
4
E37-1160-05
Fig. 5
Wire harness
band (Stopper)
PCB
Fig. 6
10

TK-7160H
INSTALLATION / DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR
2. External Speaker (Option)
2-1. KES-3
The KES-3 is an external speaker for the 3.5-mm-diameter
speaker jack.
■ Connection Procedure
1. Connect the KES-3 to the 3.5-mm-diameter speaker jack
on the rear of the transceiver.
2-2. KES-5
External speaker KES-5 can be installed for KAP-2. If KES-
5 is installed, it can be set by changing the CN1 short pin from
pins 4 and 5 to pins 5 and 6 on the KAP-2.
CN1 Connect Set Up
4-5 INT. SP or KES-3
5-6 KES-5
■ Connection Procedure
Insert the crimp terminal into the Square plug supplied
with the KAP-2.
1. When you remove the panel, turn the transceiver up side
down. Detach the panel by lifting the tabs as shown below.
Tabs
Fig. 1
2. To remove the cabinet, first turn the transceiver up side
down. Detach the cabinet by prying the tabs as shown
below.
Black/White
lead
F29-0481-05
4
5
Black lead
Tabs
E59-0419-05
Tabs
Fig. 2
Fig. 7
3. When mounting the front panel, match the 4 tabs of the
chassis with the panel, being sure they attach securely.
Tabs
Fig. 3
Tabs
11
TK-7160H
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
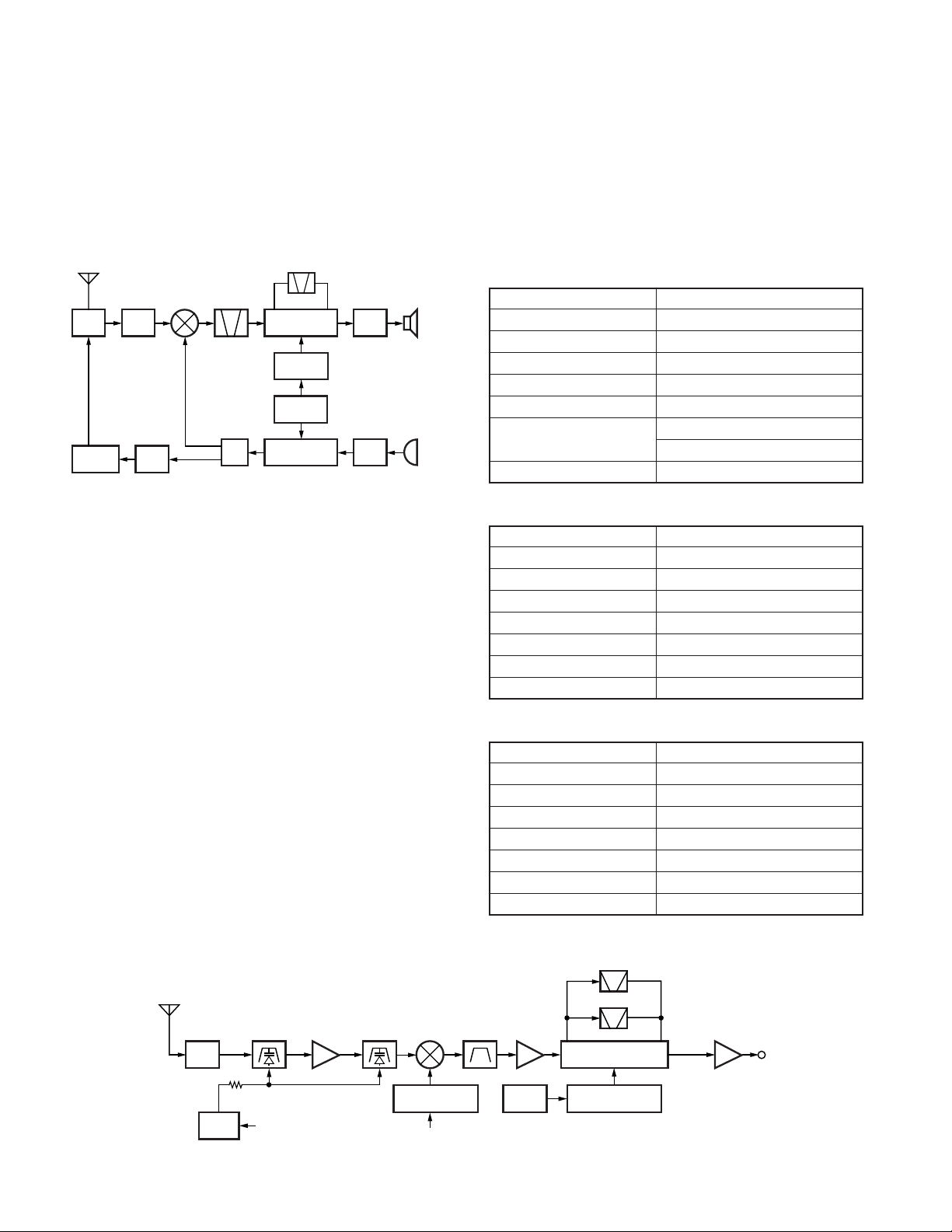
Frequency Configuration
The receiver utilizes double conversion. The first IF is
49.95MHz and the second IF is 450kHz. The first local oscillator signal is supplied from the PLL circuit.
The PLL circuit in the transmitter generates the necessary
frequencies. Figure 1 shows the frequencies.
1/2
CF 450kHz
IF SYSTEM
50.4MHz
X3
multiply
TCXO
PLL/VCO
AF
PA
16.8MHz
MIC
AMP
SP
MIC
ANT
ANTSWRF
POWER
AMP
AMP
RF
AMP
1st
MIX
MCF
49.95MHz
RX
TX
Fig. 1 Frequency configuration
Receiver System
The receiver is double conversion superheterodyne. The
frequency configuration is shown in Figure 1.
■ Front-end RF Amplifier
An incoming signal from the antenna is applied to an RF
amplifier (Q353) after passing through a transmit/receive
switch circuit (D603 and D605 are off) and a band pass filter
(L357, L356 and varactor diodes : D353, D354). After the
signal is amplified (Q353), the signal is filtered through a band
pass filter (L354, L355 and varactor diodes : D351, D352) to
eliminate unwanted signals before it is passed to the first
mixer.
The voltage of these diodes are controlled by tracking the
CPU (IC101) center frequency of the band pass filter. (See
Fig. 2)
■ First Mixer
The signal from the RF amplifier is heterodyned with the
first local oscillator signal from the PLL frequency synthesizer
circuit at the first mixer (Q352) to create a 49.95MHz first
intermediate frequency (1st IF) signal. The first IF signal is
then fed through one pair of monolithic crystal filter (MCF :
XF351) to further remove spurious signals.
■ IF Amplifier
The first IF signal is amplified by Q351, and the enters
IC321 (FM processing IC). The signal is heterodyned again
with a second local oscillator signal within IC321 to create a
450kHz second IF signal. The second IF signal is then fed
through a 450kHz ceramic filter (Wide : CF301, Narrow :
CF302) to further eliminate unwanted signals before it is amplified and FM detected in IC321.
Item Rating
Nominal center frequency 49.95MHz
Pass bandwidth ±5.0kHz or more at 3dB
35dB stop bandwidth ±20.0kHz or less
Ripple 1.0dB or less
Insertion loss 5.0dB or less
Guaranteed attenMuation 80dB or more at fo±1MHz
Spurious : 40dB or more within fo±1MHz
Terminal impedance 350Ω / 5.5pF
Table 1 Crystal filter (L71-0624-05) : XF351
Item Rating
Nominal center frequency 450kHz
6dB bandwidth ±6.0kHz or more
50dB bandwidth ±12.5kHz or less
Ripple 2.0dB or less
Insertion loss 6.0dB or less
Guaranteed attenuation 35.0dB or more within fo±100kHz
Terminal impedance 2.0kΩ
Table 2 Ceramic filter (L72-0993-05) : CF301
Item Rating
Nominal center frequency 450kHz
6dB bandwidth ±4.5kHz or more
50dB bandwidth ±10.0kHz or less
Ripple 2.0dB or less
Insertion loss 6.0dB or less
Guaranteed attenuation 60.0dB or more within fo±100kHz
Terminal impedance 2.0kΩ
Table 3 Ceramic filter (L72-0999-05) : CF302
CF301 (Wide)
12
ANT
D601
D602
D603
D605
ANT
SW
IC201
D/A
L357,356
D353,354
BPF
TV
CPU
Q353
RF AMP
L354,355
D351,352
Q352
BPF
MIX
IC402
1/2 divider
1st local
OSC (VCO/PLL)
XF351
MCF
Fig. 2 Receiver system
Q351
IF AMP
X401
TCXO
CF302 (Narrow)
IC321
IF system
Q341
X3 multiply
IC201
D/A CONVERTER
W/NO

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
TK-7160H
■ Wide/Narrow Switching Circuit
The Wide port (pin 23) and Narrow port (pin 22) of the CPU
is used to switch between ceramic filters. When the Wide
port is high, the ceramic filter SW diodes (D332, D331) cause
CF301 to turn on to receive a Wide signal.
When the Narrow port is high, the ceramic filter SW diodes (D332, D331) cause CF302 to turn on to receive a Narrow signal.
IC321
R334
IF System
R333
R332
Wide
IC101
23pin
Narrow
IC101 22pin
IF_IN MIX_O
CF301
(Wide)
CF302
D332 D331
(Narrow)
R335
Fig. 3 Wide/Narrow switching circuit
■ AF Signal System
The detection signal from IF IC (IC321) goes to D/A converter (IC201) to adjust the gain and is output to AQUA IC
(IC241) for characterizing the signal. The AF signal output
from IC241 and the DTMF/MSK signal, BEEP signal are
summed and the resulting signal goes to the D/A converter
(IC201). The AFO output level is adjusted by the D/A converter. The signal output from the D/A converter is input to
the audio power amplifier (IC281). The AF signal from IC281
switches between the internal speaker and speaker jack (J1)
output.
IC321
IF IC
IC201 IC241
W/NO
D/A
CONV.
AQUA
IC
IC201
D/A
CONV.
IC281 SP
AF PA
Fig. 4 AF signal system
■ Squelch Circuit
The detection output from the FM IF IC (IC321) passes
through a noise amplifier (Q301) to detect noise. A voltage is
applied to the CPU (IC101). The CPU controls squelch according to the voltage (SQIN) level. The signal from the RSSI
pin of IC321 is monitored. The electric field strength of the
receive signal can be known before the SQIN voltage is input
to the CPU, and the scan stop speed is improved.
IF
SYSTEM
Q301
NOISE AMP
AFO
RSSI
D301IC321 IC101
DET
SQIN
RSSI
CPU
Fig. 5 Squelch circuit
PLL Frequency Synthesizer
The PLL circuit generates the first local oscillator signal for
reception and the RF signal for transmission.
■ PLL
The frequency step of the PLL circuit is 5 or 6.25kHz. A
16.8MHz reference oscillator signal is divided at IC401 by a
fixed counter to produce the 5 or 6.25kHz reference frequency. The voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) output signal
is buffer amplified by Q446, then divided in IC401 by a dualmodule programmable counter. The divided signal is compared in phase with the 5 or 6.25kHz reference signal in the
phase comparator in IC401. The output signal from the
phase comparator is filtered through a low-pass filter and
passed to the VCO to control the oscillator frequency. (See
Fig. 6)
■ VCO
The operating frequency is generated by Q444 in transmit
mode and Q441 in receive mode. The oscillator frequency is
controlled by applying the VCO control voltage, obtained
from the phase comparator, to the varactor diodes (D443 and
D444 in transmit mode and D441 and D442 in receive mode).
The TX/RX pin is set low in receive mode causing Q443 and
Q442 to turn Q444 off, and turn Q441 on. The TX/RX pin is
set high in transmit mode. The outputs from Q441 and Q444
are amplified by Q446 and sent to the RF amplifiers.
PLL
DATA
16.8MHz
IC401 : PLL IC
1/N
REF
OSC
1/M
5kHz/6.25kHz
Phase
comparator
5kHz/6.25kHz
LPF
Charge
pump
Fig. 6 PLL circuit
D443,444
D441,442
Q444
TX VCO
Q441
RX VCO
Q431
AMP
Q446
BUFF
AMP
Q442,443
T/R SW
13
TK-7160H
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
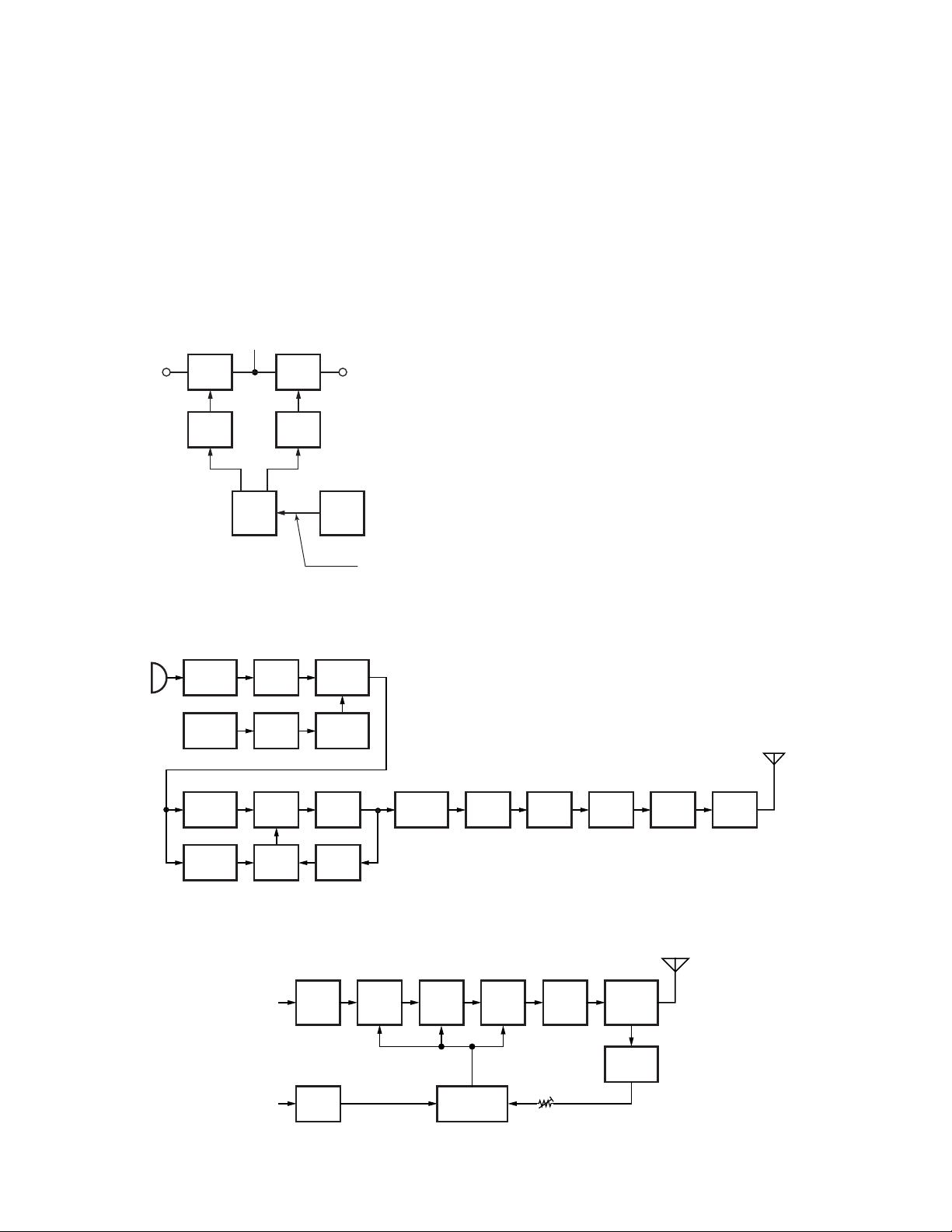
■ Unlock Circuit
During reception, the 8RC signal goes high, the 8TC signal
goes low, and Q44 turns on. Q43 turns on and a voltage is
applied to the collector (8R). During transmission, the 8RC
signal goes low, the 8TC signal goes high and Q46 turns on.
Q45 turns on and a voltage is applied to 8T.
The CPU in the control unit monitors the PLL (IC401) LD
signal directly. When the PLL is unlocked during transmission, the PLL LD signal goes low. The CPU detects this signal and makes the 8TC signal low. When the 8TC signal goes
low, no voltage is applied to 8T, and no signal is transmitted.
8C
8R 8T
Q43
SW
Q44
SW
8RC
IC101
CPU
Q45
SW
Q46
SW
LD
8TC
IC401
PLL
PLL lock
: LD “H”
Fig. 7 Unlock circuit
Transmitter System
■ Outline
The transmitter circuit produces and amplifies the desired
frequency directly. It FM-modulates the carrier signal by
means of a varicap diode.
■ Power Amplifier Circuit
The transmit output signal from the VCO passes through
the transmission/reception selection diode (D448) and amplified by Q501, Q502 and Q503. The amplified signal goes to
the final amplifier (Q504) through a low-pass filter. The lowpass filter removes unwanted high-frequency harmonic components, and the resulting signal is goes the antenna terminal.
■ APC Circuit
The automatic transmission power control (APC) circuit
detects part of a final amplifier output with a diode (D606,
D607 and D608) and applies a voltage to IC651. IC651 compares the APC control voltage (PC) generated by the D/A converter (IC201) and DC amplifier (IC214) with the detection
output voltage. IC651 generates the voltage to control Q502,
Q503 and Q504 and stabilizes transmission output.
The APC circuit is configured to protect over current of
Q502, Q503 and Q504 due to fluctuations of the load at the
antenna end and to stabilize transmission output at voltage
and temperature variations.
IC211MIC
MIC/
IDC
MIC KEY
INPUT
IC201
D/A
CONV.
TCXO
16.8MHz
X401
IC213
CPU
IC101
Q444
VCO
IC401
D448
PC
IC201
3pin
SW
TX
PLL
BUFF
Q431
Q501
RF
AMP
IC214
DC
AMP
IC241
AQUQ
IC
D/A
CONV.
IC201
Q446
RF
AMP
IC402
1/2
DIVIDER
Fig. 8 Transmitter system
Q502
PRE
DRIVE
AMP
Q503
DRIVE
AMP
IC651
APC
CONTROL
Q447
RF
AMP
Q504
FINAL
AMP
Q501
RF
AMP
D601,D602
D603,D605
ANT
SW
D606
D607
D608
VR1
Q502
PRE
DRIVE
AMP
POWER
LPF
DET
Q503
DRIVE
AMP
ANT
ANT
Q504
FINAL
AMP
14
Fig. 9 APC circuit
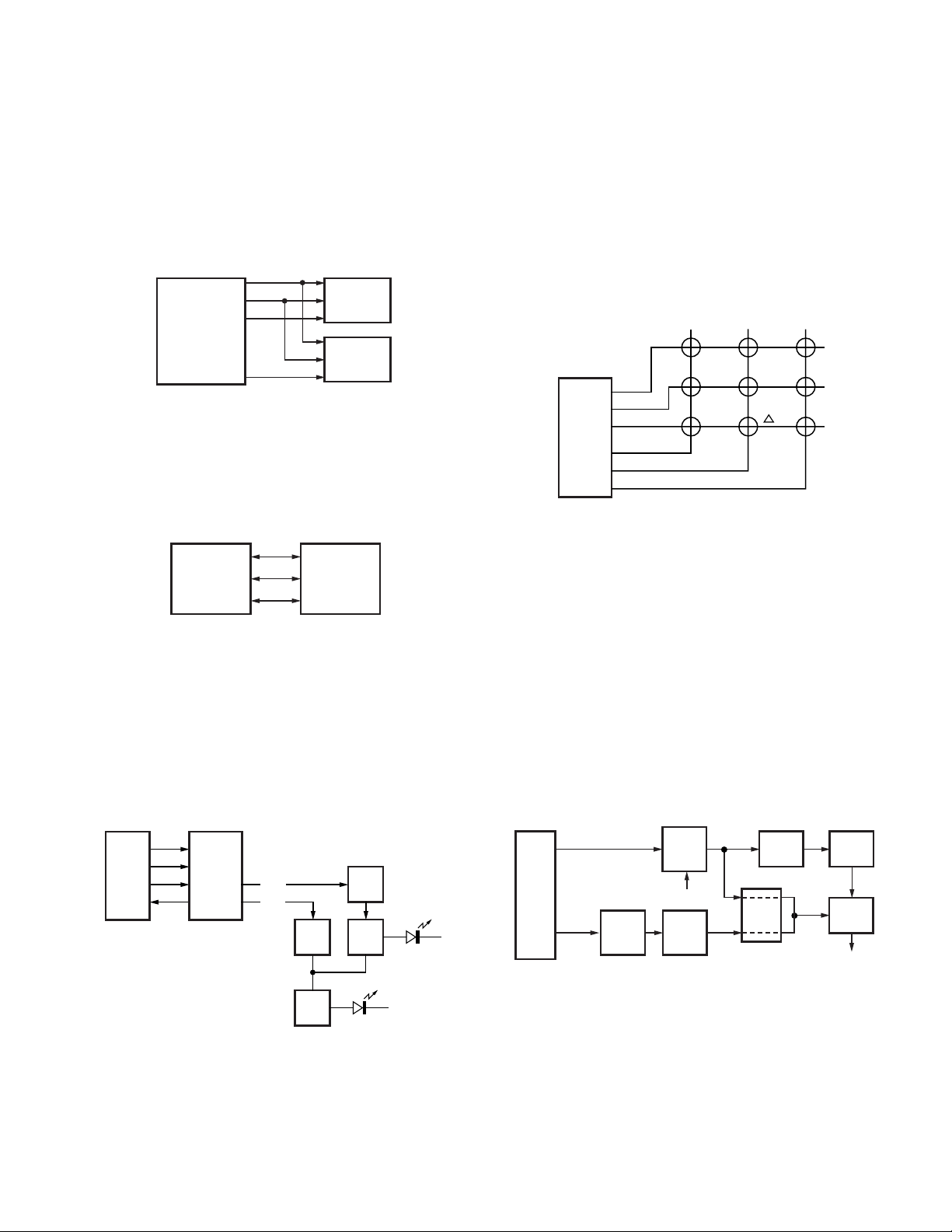
X401
TCXO
IC201
D/A
VCO
IC241
AQUA
IC
IC241
AQUA
IC
IC201
D/A
IC401
PLL
TCXO
MOD
VCO
MOD
HT
DI
QT/DQT
DTMF
IC101
CPU
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
TK-7160H
Control Circuit
The CPU carries out the following tasks:
1) Controls the WIDE, NARROW, TX/RX outputs.
2) Controls the AQUA IC (IC241).
3) Controls the PLL (IC401).
4) Controls the D/A converter (IC201) and adjusts the volume, modulation and transmission power.
CK
DT
IC101
CPU
LD
PLLE
Fig. 10 Control circuit
■ Memory Circuit
The transceiver has an 64k-bit EEPROM (IC81). The
EEPROM contains adjustment data. The CPU (IC101) controls the EEPROM through three serial data lines.
EEPCK
IC101
CPU
EEPDT
EEPWP
Fig. 11 Memory circuit
■ Display Circuit
The CPU (IC101) controls the display LCD and LEDs.
When power is on, the CPU will use the MBL line to control
the LCD illumination and key backlight LEDs.
The dimmer function is controlled by the switch Q1. The
LCD controller (IC1) controls the functions of the LCD
through the DO, CE, CL, DI lines from the CPU.
IC201
D/A
converter
IC401
PLL
IC81
EEPROM
■ Key Matrix Circuit
The TK-7160H front panel has function keys. Each of
them is connected to a cross point of a matrix of the KMI1 to
KMO3 ports of the IC1 LCD driver. The KMO1 to KMO3
ports are always high, while the KMI1 to KMI3 ports are always low.
The microprocessor monitors the status of the KMI1 to
KMO3 ports. If the state of one of the ports changes, the
microprocessor assumes that the key at the matrix point corresponding to that port has been pressed.
CH
UP
CH
DN
A
<B
C>
IC1
LCD
driver
KMI1
KMI2
KMI3
KMO3
KMO2
KMO1
VOL
UP
VOL
DN
S
Fig. 13 Key matrix circuit
■ Encode
The QT and DQT signals are output from QT/DQT of the
CPU (IC101) and summed with the external pin DI line by the
AQUA IC (IC241) and the resulting signal goes to the D/A converter (IC201). The DTMF signal is output from DTMF of the
CPU and goes to the D/A converter (IC201). The signal is
summed with a MIC signal by the AQUA IC (IC241), and the
resulting signal goes to the D/A converter (IC201).
The D/A converter (IC201) adjusts the MO level and the
balance between the MO and QT/DQT levels. Part of a QT/
DQT signal is summed with MO and the resulting signal goes
to the VCOMOD pin of the VCO. This signal is applied to a
varicap diode in the VCO for direct FM modulation.
IC101
CPU
CE
CL
DO
IC1
DI
LCD
driver
BRI
BL
Fig. 12 Display circuit
Q4
SW
Q3
SW
Q1
SW
Q2
SW
D1~D6
Key backlit
D7~D18
LCD
illumination
Fig. 14 Encode
15

TK-7160H
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
■ Decode
The signal goes to EXTLIMIN (pin 5) of AQUA IC (IC241).
The QT/DQT signal will pass through the low-pass filters in
the AQUA IC (IC241) and be decoded within the AQUA IC
(IC241). The DTMF signal will be decoded within the AQUA
IC (IC241).
IC241
AQUA IC
EXTLIMIN
5
Fig. 15 Decode
■ D/A Converter
The D/A converter (IC201) is used to adjust MO modulation, AF volume, TV voltage, FC reference voltage, and PC
POWER CONTROL voltage level.
Adjustment values are sent from the CPU as serial data.
The D/A converter has a resolution of 256 and the following
relationship is valid:
D/A output = (Vin – VDAref) / 256 x n + VDAref
Vin: Analog input
VDAref: D/A reference voltage
n: Serial data value from the microprocessor (CPU)
Power Supply Circuit
When the power switch on the display unit is pressed, the
power port on the display unit which is connected port 17
(POWER), goes low, then port 78 (SBC) goes high, Q42 turns
on, SB SW (Q41) turns on and power (SB) is supplied to the
radio.
When the DC power supplied to the radio, the voltage
regulator IC (IC43) supply into the CPU VDD and reset voltage
detect IC (IC44). IC44 will generate signal (RESET) in to the
reset terminal on the CPU (IC101) to carry out a power ON
reset. Also, CPU (IC101) is checking on port 91 (BATT). If DC
power is less than about 9.5V, the radio is unable to power
on.
When the DC power voltage deceases from normal voltage, the INT voltage detector IC (IC45) will set to high on CPU
port 18 (INT) if B line will became less than about 9.5V. Then
CPU send to EEPROM (IC81) the backup data and go into
STOP mode.
This circuit has an overvoltage protection circuit. If a DC
voltage of 16V or higher is applied to the base of Q81, this
voltage turns Q81 on and sets port 18 (INT) to low. As a
result port 78 (SBC) is low, and turns Q42 and Q41 (SB) off.
SB
IGN
R93R92
POWER
SW
Q41
SW
Q84
SW
BATT
INT
IGN
IC101
CPU
POWER
RESET
SBC
5M
Q42
SW
5M
IC44
RST
Fig. 16 Power supply circuit
Q81
SW
IC43
AVR
IC45
AVR
B
D81
R49R50
16
 Loading...
Loading...