Page 1
MIC-3358
6U CompactPCI Intel
Pentium® 4 Processor - M
Single Board Computer with
VGA / Dual Giga LAN / PMC
User’s Manual
®
Page 2

Copyright Notice
This document is copyrighted, 2003. All rights are reserved. The original
manufacturer reserves the right to make improvements to the products
described in this manual at any time without notice. No part of this manual may be reproduced, copied, translated or transmitted in any form or
by any means without the prior written permission of the original manufacturer. Information provided in this manual is intended to be accurate
and reliable. However, the original manufacturer assumes no responsibility for its use, nor for any infringements upon the rights of third parties
which may result from its use.
Acknowledgements
Award is a trademark of Award Software International, Inc.
IBM, PS/2, OS/2, and VGA are trademarks of International Business
Machines Corporation.
Intel® and Pentium® are trademarks of Intel Corporation.
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
NetWare is a trademark of Novell, Inc.
PICMG™, CompactPCI™ and the PICMG™, and CompactPCI™ logos
are trademarks of the PCI Industrial Computers Manufacturers Group.
All other product names or trademarks are properties of their respective
owners.
Technical Support and Sales Assistance
If you have any technical questions about the MIC-3358 or any other
Advantech products, please visit our support website at:
http://support.advantech.com.tw
For more information about Advantech's products and sales information,
please visit:
http://www.advantech.com.
Part No.2002335800 1st Edition
Printed in Taiwan June. 2003
MIC-3358 User’s Manual ii
Page 3

CE Notification
The MIC-3358, developed by Advantech CO., LTD., has passed the CE
test for environment specification when shielded cables are used for
external wiring. We recommend the use of shielded cables.
Product warranty
Advantech warrants to you, the original purchaser, that each of its products will be free from defects in materials and workmanship for one year
from the date of purchase. This warranty does not apply to any products
which have been repaired or altered by persons other than repair personnel authorized by Advantech, or which have been subject to misuse,
abuse, accident or improper installation. Advantech assumes no liability
under the terms of this warranty as a consequence of such events.
Because of Advantech's high quality-control standards and rigorous testing, most of our customers never need to use our repair service. If an
Advantech product is defective, it will be repaired or replaced at no
charge during the warranty period. For out-of-warranty repairs, you will
be billed according to the cost of replacement materials, service time and
freight. Please consult your dealer for more details.
If you think you have a defective product, follow these steps:
1. Collect all the information about the problem encountered. (For example, CPU speed, Advantech products used, other hardware and software
used, etc.) Note anything abnormal and list any on-screen messages you
get when the problem occurs.
2. Call your dealer and describe the problem. Please have your manual,
product, and any helpful information readily available.
3. If your product is diagnosed as defective, obtain an RMA (return merchandize authorization) number from your dealer. This allows us to process your return more quickly.
4. Carefully pack the defective product, a fully-completed Repair and
Replacement Order Card and a photocopy proof of purchase date (such as
your sales receipt) in a shippable container. A product returned without
proof of the purchase date is not eligible for warranty service.
5. Write the RMA number visibly on the outside of the package and ship
it prepaid to your dealer.
iii
Page 4

Packing List
Before installing your board, ensure that the following materials have
been received:
• 1 MIC-3358 all-in-one single board computer
• 1 Utility CD-ROM disc
• 1 CPU Heat sink (Assembled)
• 1 CPU thermal dissipation paste
• 1 Thermal pad (Assembled)
• 1 RJ-45 to RS-232 COM port adaptor
• 1 Hard drive isolation pad (Assembled)
• 1 Hard drive bracket (Assembled)
• 1 Solder-side cover (Assembled)
• Several screws
• 1 warranty certificate document
If any of these items are missing or damaged, contact your distributor or
sales representative immediately.
Warning! Any changes or modifications made to the
equipment which are not expressly approved by
the relevant standards authority could void your
authority to operate the equipment.
MIC-3358 User’s Manual iv
Page 5

Contents
Chapter 1 Hardware Configuration .................................2
1.1 Introduction ....................................................................... 2
1.2 Specifications .................................................................... 3
1.3 Functional Block Diagram ................................................ 6
Figure 1.1:MIC-3358 functional block diagram............. 6
1.4 Jumpers.............................................................................. 6
1.4.1 Jumper Locations ............................................................ 6
Table 1.1:MIC-3358 jumper descriptions....................... 6
Table 1.2:JP1 jumper definition (PMC Module Voltage
V(i/o))7
Table 1.3:JP2 jumper definitions (PMC Module Voltage
Vio)7
Table 1.4:JP7 jumper definitions (CompactFlash™ card)
7
1.4.2 Clear CMOS (JP4) .......................................................... 7
Table 1.5:Clear CMOS JP4 ............................................ 8
1.5 Connectors......................................................................... 8
Table 1.6:MIC-3358 connector descriptions .................. 8
Table 1.7:CN1 IDE Connector Definitions .................... 9
Table 1.8:CN2 CompactFlash™ Socket Definitions.... 10
Table 1.9:CN3 RJ-45 COM1 port Definitions.............. 11
Table 1.10:CN4 Handle Switch Definitions ................. 12
Figure 1.2:Handle Switch Definitions .......................... 12
Table 1.11:CN5 USB 1.1/2.0 port Definitions ............. 13
Table 1.12:CN6 USB 1.1/2.0 port Definitions ............. 13
Table 1.13:CN9 DB-15 VGA Connector Definitions .. 14
Table 1.14:PU1 Gigabit LAN Connector Definitions .. 14
Table 1.15:J11/J12/J14 PMC Connector Definitions .. 15
Table 1.16:D9 LED Definitions.................................... 18
Table 1.17:SW1 Vcore selection definitions ................ 18
Table 1.18:SW2 Drone mode definitions ..................... 19
Figure 1.3:MIC-3358 jumper and connector locations. 20
Figure 1.4:MIC-3358 front panel connector and indicator
locations21
1.6 Safety Precautions ........................................................... 21
1.7 Installing CPU and Heat Sink ........................................ 22
Figure 1.5:Complete assembly with heat sink and hard
disk 23
1.8 Software support ............................................................. 23
Chapter 2 Connecting Peripherals .................................26
2.1 IDE Device (CN1 and Rear I/O)..................................... 26
v
Page 6

2.2 VGA Display Connector (CN9 or Rear I/O)................... 26
2.3 PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Connector (Rear I/O)........... 26
2.4 Serial Ports (CN3 and Rear I/O) ..................................... 27
Table 2.1:MIC-3358 serial port default settings........... 27
2.5 Ethernet Configuration (PU1 , Rear I/O and J3)............. 27
2.6 USB Connector (CN5/6 and Rear I/O) ........................... 28
2.7 PMC Connector (J11, J12, J14) ...................................... 28
2.8 CompactFlash™ Socket (CN2)....................................... 28
2.9 Card Installation .............................................................. 28
Chapter 3 ..........................................................................32
3.1 Overview ......................................................................... 32
3.2 USB driver....................................................................... 32
3.3 CMM (Chassis Management Module) Driver ................ 33
3.3.1 Windows 2K Driver...................................................... 33
Figure 3.1:Right Click "My Computer" and click "Prop-
erties"33
Figure 3.2:Tab "Hardware" and click "Hardware Wizard"
33
Figure 3.3:click "Next" in Hardware Wizard ............... 34
Figure 3.4:click" Add/Troubleshoot a device" .............34
Figure 3.5:select " Add a new device" in Device windows
35
Figure 3.6:click "No, I want to select the hardware from a
list" 35
Figure 3.7:Select "Other devices" in Hardware types win-
dows36
Figure 3.8:Tab " Have Disk" in right bottom ............... 36
Figure 3.9:Browse proper driver in CD ROM device .. 37
Figure 3.10:click ok in the Wizard windows................ 37
Figure 3.11:click "ok" in Add New Hardware Wizard
Properties" windows38
Figure 3.12:click "yes" in Creating a Forced Configura-
tion windows38
Figure 3.13:click "Next" in Add/Remove Hardware Wiz-
ard windows39
Figure 3.14:Tab "Finish" in Add/Remove Hardware Wiz-
ard windows39
Figure 3.15:click "Yes" to restart your computer ......... 40
Figure 3.16:Go to Device Manager to see available A-
IPM drivers40
3.3.2 Windows XP Driver...................................................... 41
Figure 3.17:Right click My Computer to select "Proper-
ties"41
Figure 3.18:Tab "Hardware" and click "Add Hardware
MIC-3369 User’s Manual vi
Page 7

Wizard"41
Figure 3.19:Click "Next" in the windows..................... 42
Figure 3.20:Click "Yes , I have already connected the
hardware"42
Figure 3.21:Select "Add a new hardware device" in the
installed hardware window43
Figure 3.22:Click Install the hardware that I manually se-
lect from a list (Advanced)43
Figure 3.23:Select "Show all devices" in Common hard-
ware types windows44
Figure 3.24:tab "Have Disk"......................................... 44
Figure 3.25:Select proper driver in CD-ROM .............. 45
Figure 3.26:tab A-IPM driver and click "Have Disk" .. 45
Figure 3.27:Click " Next" ............................................. 46
Figure 3.28:Click "Finish" ............................................ 46
Figure 3.29:Go to My computer to see "A-IPM drivers" .
47
Chapter 4 Award BIOS Setup.........................................50
4.1 AWARD BIOS Setup...................................................... 50
Figure 4.1:Setup program initial screen........................ 50
4.1.1 Entering Setup............................................................... 50
4.1.2 Standard CMOS Setup.................................................. 51
Figure 4.2:Standard CMOS setup screen...................... 51
4.1.3 Advance BIOS Features Setup ..................................... 51
Figure 4.3:Advance BIOS features setup screen .......... 52
4.1.4 Advance Chipset Features Setup .................................. 55
Figure 4.4:Advance Chipset features setup screen....... 55
4.1.5 Integrated Peripherals ................................................... 57
Figure 4.5:Integrated Peripherals setup screen ............. 57
4.1.6 Power Management Setup ............................................ 60
Figure 4.6:Power management setup screen................. 60
4.1.7 PNP/PCI Configuration Setup ...................................... 61
Figure 4.7:PNP/PCI configuration screen .................... 61
4.1.8 PC Health Status ........................................................... 62
Figure 4.8:PC Health setup screen................................ 62
4.1.9 Load Optimized Defaults .............................................. 62
4.1.10 Set Password ................................................................. 63
4.1.11 Save & Exit Setup......................................................... 63
4.1.12 Exit Without Saving...................................................... 63
Appendix A ..........................................................................66
A.1 Programming the Watchdog Timer................................. 66
Appendix B Pin Assignments .............................................70
B.1 J1 Connector.................................................................... 70
Table B.1:J1 connector ................................................. 70
vii
Page 8

B.2 J2 Connector.................................................................... 71
Table B.2:J2 connector ................................................. 71
B.3 J3 Connector.................................................................... 72
Table B.3:J3 connector ................................................. 72
B.4 J5 Connector.................................................................... 73
Table B.4:J5 connector ................................................. 73
B.5 System I/O Ports.............................................................. 74
Table B.5:System I/O ports .......................................... 74
B.6 Interrupt Assignments ..................................................... 75
Table B.6:Interrupt assignments ................................... 75
B.7 1st MB Memory Map...................................................... 75
Table B.7:1st MB memory map ................................... 75
MIC-3369 User’s Manual viii
Page 9
Hardware
Configuration
1
CHAPTER
Page 10

Chapter 1 Hardware Configuration
1.1 Introduction
The MIC-3358 is a CompactPCI® server blade with Intel® Pentium® 4
Processor-M on board to compliant with Compact Packet Switching
Backplane (cPSB) systems. Supporting the PICMG 2.16 specification,
the MIC-3358 delivers a cost performance platform for those applications
that demand high performance. It is an ideal platform for emerging application such as switch-fabric blade server, mission critical and computing
intensive applications.
The new MIC-3358 has been optimized for the Intel® Pentium® 4 Processor-M and Intel® 845E Chipset. It unveils as a high performance
cPCI platforms, delivering compelling system bus speed performance
across the 400 MHz with Intel NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture, Its innovated wider data paths and flexible memory refresh technology optimize
the DDR SDRAM performance in MIC-3358.
High Performance Intel® Pentium® 4 Processor -M
The MIC-3358 supports Intel® Pentium® 4 processor-M 1.7GHz and
2.2GHz , with u-FCPGA package. The Intel® Pentium®4 processor-M
has on-chip 512KB L2 cache providing high performance. With the support of a 400MHz front side bus, the MIC-3358 can fulfill customer’s
expectations of price-performance computing capability.
Compact Mechanical Design
The MIC-3358 has many functions on a single board with only one-slot
width. Advantech provides a CPU heat sink specially designed for the
Intel® Pentium®4 processor -M, enabling the MIC-3358 to operate without a cooling fan on the heat sink. It only needs external cooling air from
the chassis fans for ventilation. This enables the MIC-3358 to use Intel®
Pentium®4 processor - M within a mere 1-slot wide space.
Single P2P Bridge
The MIC-3358 with single PCI-to-PCI Bridge is applicable up to 8-slot
enclosure and drive up to seven bus master PCI slots in master mode. Furthermore, it supports master and drone modes. The MIC-3358 can also
operate in drone mode in a peripheral slot, whereby it functions as a
stand-alone computer and does not communicate on the CompactPCI®
bus.
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 2
Page 11

PMC (PCI Mezzanine Card) IEEE1386.1 Compliant
The MIC-3358 support one PMC site and compliant with PICMG 2.3
(PCI Mezzanine Card) specification. This 32-bit/33MHz PMC interface
provides front access capability by PMC modules for various function
demanding.
Complete I/O Functions
The MIC-3358 offers all the I/O functions of an industrial computer with
the rugged Eurocard form factor. The rest of I/O have fully connected to
the rear I/O module via user-define connector (J3 and J5) on the backplane. These I/O contain one Gigabit Ethernet port, one RJ-45 COM port,
two USB 2.0 ports, one VGA connector, and one PMC site. The front
panel also has a reset button and LEDs for hot swap indication, power status, HDD operation and Ethernet communication. The built-in high speed
IDE controller provides two separate IDE channels with Ultra DMA/33/
66/100 mode. The user-defined J3 connector is designed to support two
IDE devices, one floppy drives, one printer device, LAN 1/2 for PCIMG
2.16. These drives can simply be connected to the backplane or to the rear
transition board for easy service and maintenance.
Meets Switch Fabric, Mission Critical and Computing Intensive
Application requirements
Supporting the PICMG 2.16 specification, the MIC-3358 delivers a cost
performance platform for those applications that demand for low power
and high performance. It is an ideal platform for emerging application
such as switch-fabric blade server, mission critical and computing intensive applications like third-generation (3G) wireless, voice over Internet
protocol (VoIP), networking, image processing and the converged data
and voice communication applications.
The two-layer front panel design complies with IEEE 1101.10. Connectors are firmly screwed to the front panel, and the replaceable shielding
gasket is attached to the panel edge. This reduces emissions and gives
better protection against external interference. A watchdog timer can
automatically reset the system if the system stops abnormally.
1.2 Specifications
Standard SBC Functions
• CPU: Intel® Pentium® 4 processor-M u-FCPGA socket
• BIOS: Award 4Mb flash memory
3 Chapter 1
Page 12

• Chipset: Intel® 845E/ICH4 Chipset
• Front Side Bus: 400MHz (Intel® Pentium® 4 processor-M Processor)
• Bus Interface: PCI 32-bit/33 MHz
• 2nd level cache: Built-in 512KB on Intel® Pentium® 4 processor-M
die
• RAM: 512MB ECC DDR266 memory on board. Support up to 2GB
ECC DDR200/266.
• Enhanced IDE interface: Two channels handles one 2.5” IDE in SBC
and two IDEs in RIO module via J3 connector. Supports PIO mode 4
and ATA 33/66/100 mode. One IDE connector and space reserved for
embedded 2.5” HDD.
• Serial ports: One RJ-45 COM1 port (RS-232 interface) with 16C550
compatible UARTs
• USB port: Two USB ports with fuse protection comply with USB
specification 2.0/1.1
• CompactFlash socket: one CompactFlash socket on board.
• PMC expansion slot: One 32bit/33MHz PCI Mezzanine site on board
with +5V/+3.3V compliant.
• Watchdog timer: It provides system reset, interrupt and NMI support
via software control. Time interval is from 1 to 255 seconds.
PCI-to-PCI Bridge
• Controller chip: One PCI-to-PCI bridge controller chip provides master and drone mode
• (Master mode) Supports up to seven bus masters peripherals on each
bus segment
• (Drone mode) it could plug into a peripheral slot as a “drone mode” ,
whereby it functions as stand-alone computer.
10/100/1000Base-TX Ethernet Interface
• Controller chips: Two Intel® 82540EM Gigabit Ethernet controller
chips provides Dual Gigabit ports
• One front RJ-45 Gigabit LAN port
• 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps and 1000Mbps auto-switching
PCI VGA Interface
• Controller: AT I R a ge X L
• PCI 2.2 compliant, 32bit/33 MHz
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 4
Page 13

• Display memory: 8MB SDRAM VRAM
• Display Resolution Number of Colors:
:
2D Display Modes: Resolutions, Colors and Maximum Refresh Rates (Hz)
Resolution 640x 480 800x 600 1024x 768 1152x 864 1280x 1024 1600x 1200
256 colors 200 200 150 120 100 85
65K colors 200 200 150 120 100 85
16.7M colors 200 200 150 120 100 75
Maximum 3D Resolution(Hz)
8MB
65K colors 1600x1200
16.7M colors 1280x1024
Optional Rear I/O Boards
• RIO-3309C
NOTE: MIC-3358 does not support MIC-3960 storage carrier board
Mechanical and Environmental Specifications
• Operating temperature: 0 ~ 55° C (32 ~ 131° F)
• Storage Temperature: -20 ~ 80° C (-4 ~ 176° F)
• Humidity (Non-operating): 5~95%@60° C (non-condensing)
• Max Power Consumption: +5V / 4.19A, +3.3V / 4.5A, +12V / 35mA
• Board size: 233.35 x 160 mm (6U size), 1-slot (4 TE) wide
• Wei ght: 0.8 kg (1.76 lb)
• Shock: 20 G (operating); 50 G (Non-operating)
• Random vibration: 1.5 Grms (operating), 2.0 Grms (Non-Operating)
5 Chapter 1
Page 14
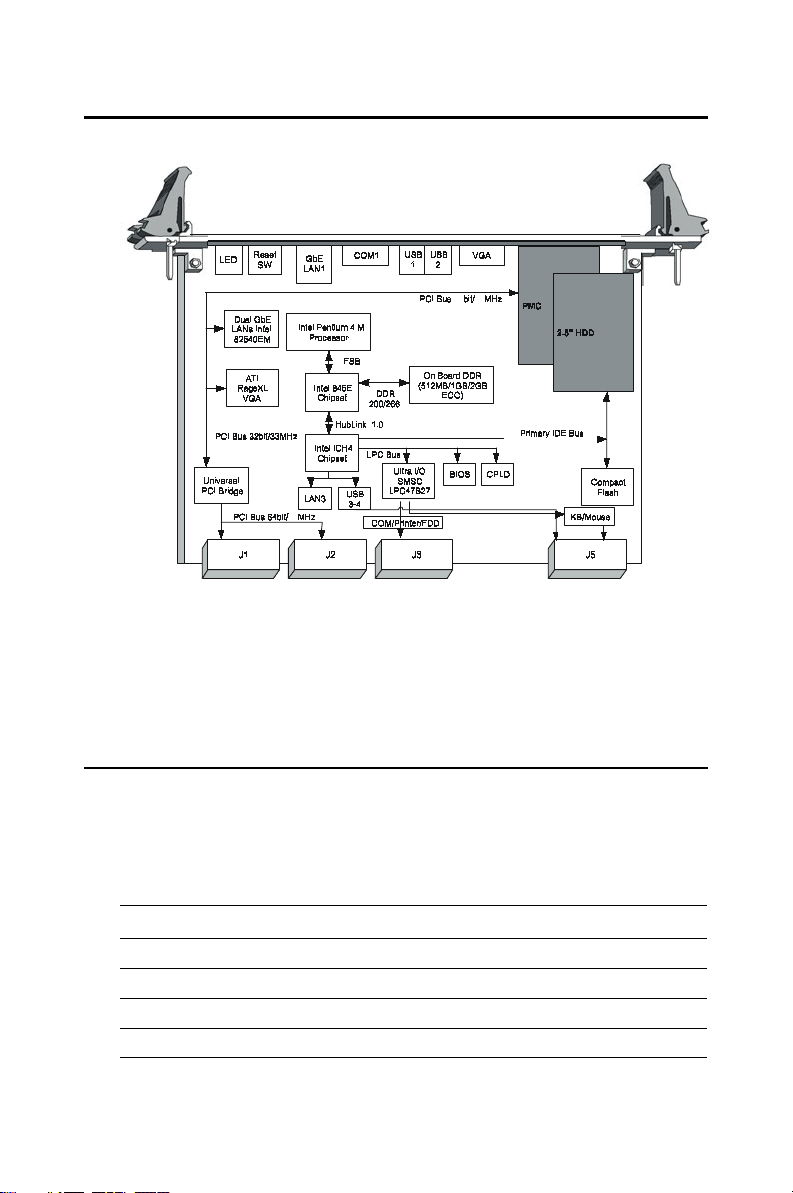
1.3 Functional Block Diagram
3332
33
Figure 1.1: MIC-3358 functional block diagram.
Note: MIC-3358 does not support shutdown function of ATX power supply.
1.4 Jumpers
1.4.1 Jumper Locations
Table 1-1 lists the jumper function. Figure 1-1 illustrates the jumper location. Read this section carefully before changing the jump setting on your
MIC-3358 card.
Table 1.1: MIC-3358 jumper descriptions
JP1 PMC module voltage V(i/o)
JP2 VGA output selector
JP4 Clear CMOS
JP7 CompactFlash™ card mode setting
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 6
Page 15
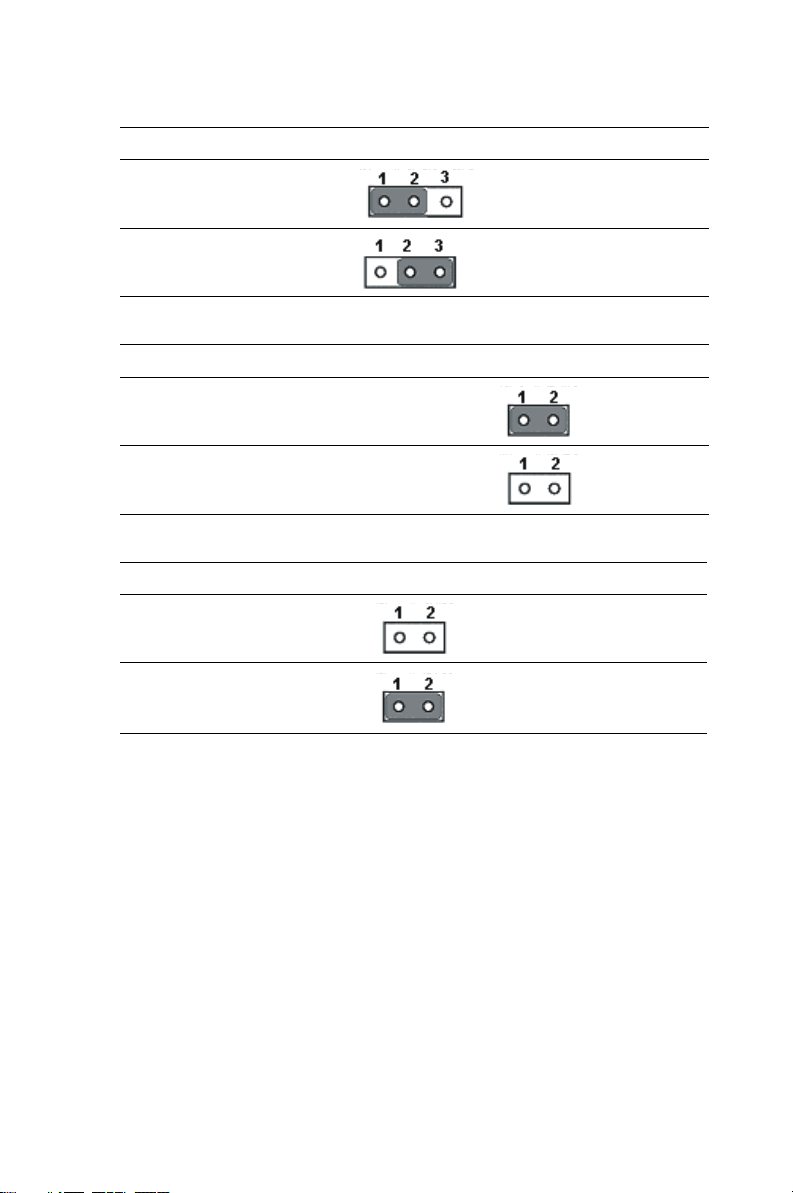
Table 1.2: JP1 jumper definition (PMC Module Voltage V(i/o))
5V
3.3V (Default)
Table 1.3: JP2 jumper definitions (PMC Module Voltage Vio)
VGA output in Rear IO
VGA output in front panel of MIC-3358
Table 1.4: JP7 jumper definitions (CompactFlash™ card)
Master
Slave (default)
1.4.2 Clear CMOS (JP4)
This jumper is used to erase CMOS data and reset system BIOS information. Follow the procedures below to clear the CMOS.
1. Turn off the system.
2. Close jumper JP4 (1-2) for about 3 seconds.
3. Set jumper JP4 (2-3) as normal.
4. Turn on the system. The BIOS is reset to its default setting.
7 Chapter 1
Page 16

Table 1.5: Clear CMOS JP4
Clear
Normal (default)
1.5 Connectors
On-board connectors link to external devices such as hard disk drives,
keyboards, or floppy drives, etc. Table 1-6 lists the function of each connector and Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-2 illustrate each connector location.
Chapter 2 gives instructions for connecting external devices to your card.
Table 1.6: MIC-3358 connector descriptions
Number Function
CN1 2.5" IDE Connector
CN2 CompactFlash™ Socket
CN3 RJ-45 COM1 port
CN4 Handle Switch
CN5 USB 1.1/2.0 port
CN6 USB 1.1/2.0 port
CN8 Reset Switch
CN9 DB-15 VGA Connector
PU1 Gigabit RJ-45 LAN Connector
J11/J12/J14 PMC Connector
J1/J2 Primary CompactPCI™ bus
J3/J5 Rear I/O transition
D9 HDD LED and Power LED
LED1 Hot Swap LED
SW1 Vcore selection
SW2 Drone mode Selection
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 8
Page 17

Table 1.7: CN1 IDE Connector Definitions
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1PRST# 2GND
3PID7 4PID8
5PID6 6PID9
7PID5 8PID10
9PID4 10PID11
11 PID3 12 PID12
13 PID2 14 PID13
15 PID1 16 PID14
17 PID0 18 PID15
19 GND 20 N/C
21 PDRQ# 22 GND
23 PIOW# 24 GND
25 PIOR# 26 GND
27 PRDY 28 CSEL*
29 PACK# 30 GND
31 PIRQ 32 N/C
33 PDA1 34 PDIAG#**
35 PDA0 36 PDA2
37 PCS1# 38 PCS3#
39 HDD_LED 40 N/C
41 +5V 42 +5V
43 GND 44 N/C
#: active low
*: CSEL connected to GND
**: PDIAG# has 10K ohm pull-down to GND
9 Chapter 1
Page 18

Table 1.8: CN2 CompactFlash™ Socket Definitions
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 GND 26 N/C
2ID3 27ID11
3 ID4 28 ID12
4 ID5 29 ID13
5 ID6 30 ID14
6 ID7 31 ID15
7 HCS1- 32 HCS3-
8 GND 33 N/C
9 GND 34 HIOR-
10 GND 35 HIOW-
11 GND 36 N/C
12 GND 37 HIRQ
13 +5V 38 +5V
14 GND 39 SANDISK
15 GND 40 N/C
16 GND 41 -HRST1
17 GND 42 HRDY
18 GDA2 43 N/C
19 HDA1 44 N/C
20 HDA0 45 SANLED
21 ID0 46 N/C
22 ID1 47 ID8
23 ID2 48 ID9
24 N/C 49 ID10
25 N/C 50 GND
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 10
Page 19
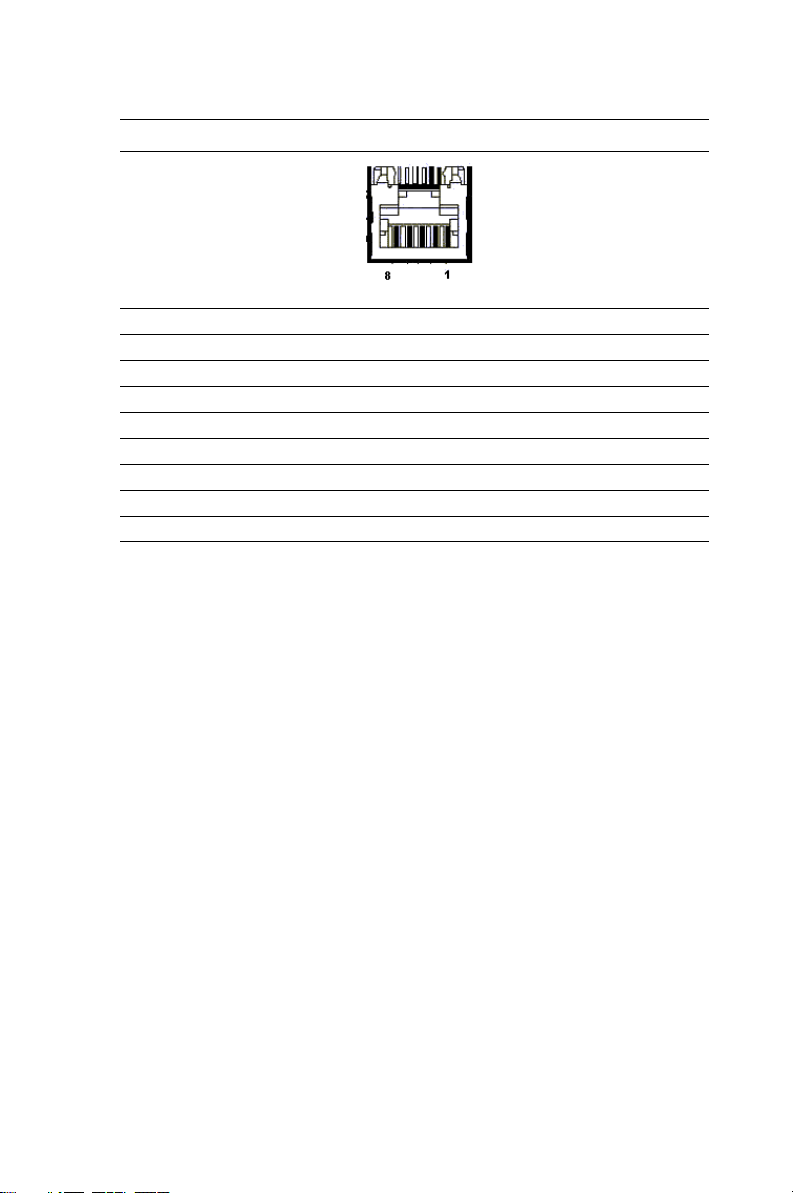
Table 1.9: CN3 RJ-45 COM1 port Definitions
Pin Signal
1 NRLSD1
2 NRX1
3NTX1
4 NDTR1
5GND
6 NDSR1
7NRTS1
8 NCTS1
11 Chapter 1
Page 20
Table 1.10: CN4 Handle Switch Definitions
Pin Signal
1 common
2 normal closed
3 normal open
Note: Pin 1-2 handle closed
Pin 1-3 handle open
CN2
15,10,5
CN9
11,6,1
JP4JP7
Battery
JP2
JP1
12
123
2121
JN1
63 646364
CN1
JN2
2
1
JN4
64
63
44 43
PU1
CN3
CN6
CN5
CN8
LED
SW2
2
ON
1
D9
CN4
1
ON
SW1
Intel
845E
CPU
6
1
Note: Handle closed is normal
Figure 1.2: Handle Switch Definitions
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 12
PCI-PCIX
Bridge
2 1
Page 21
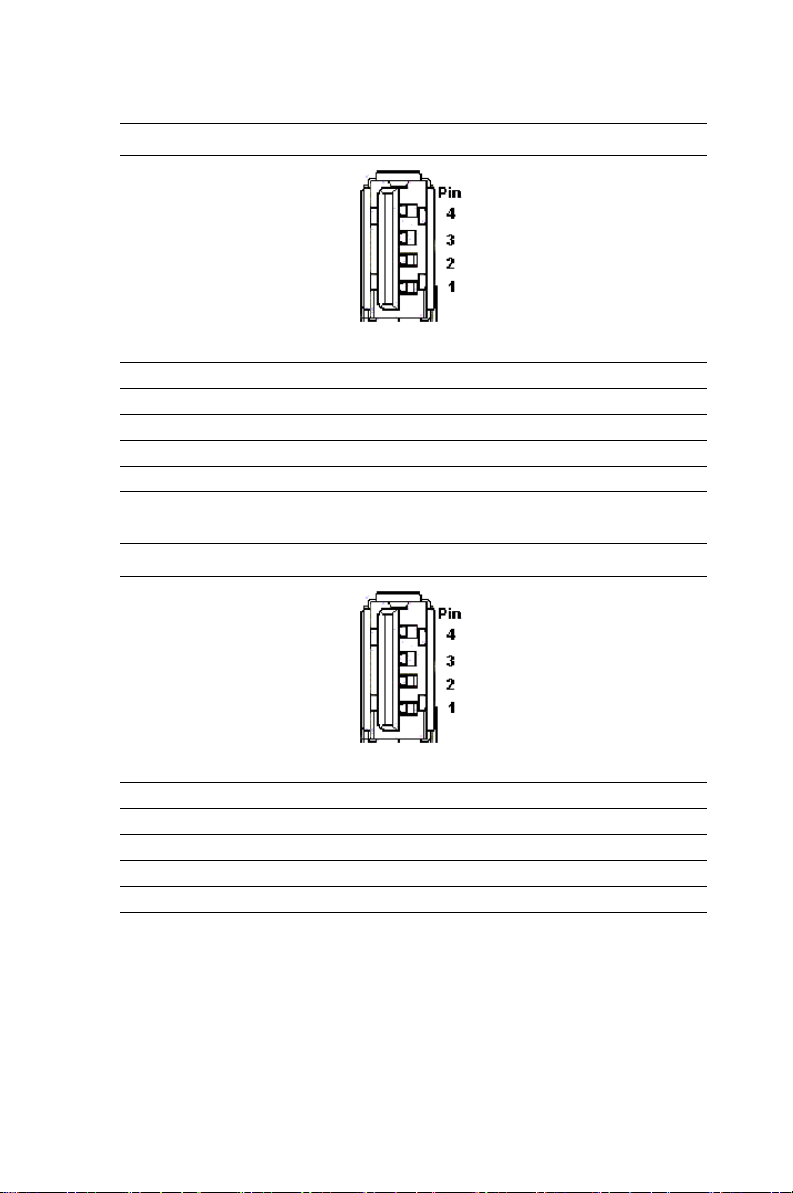
Table 1.11: CN5 USB 1.1/2.0 port Definitions
Pin Signal
1+5V
2 USB_P2-
3 USB_P2+
4GND
Table 1.12: CN6 USB 1.1/2.0 port Definitions
Pin Signal
1+5V
2 USB_P2-
3 USB_P2+
4GND
13 Chapter 1
Page 22
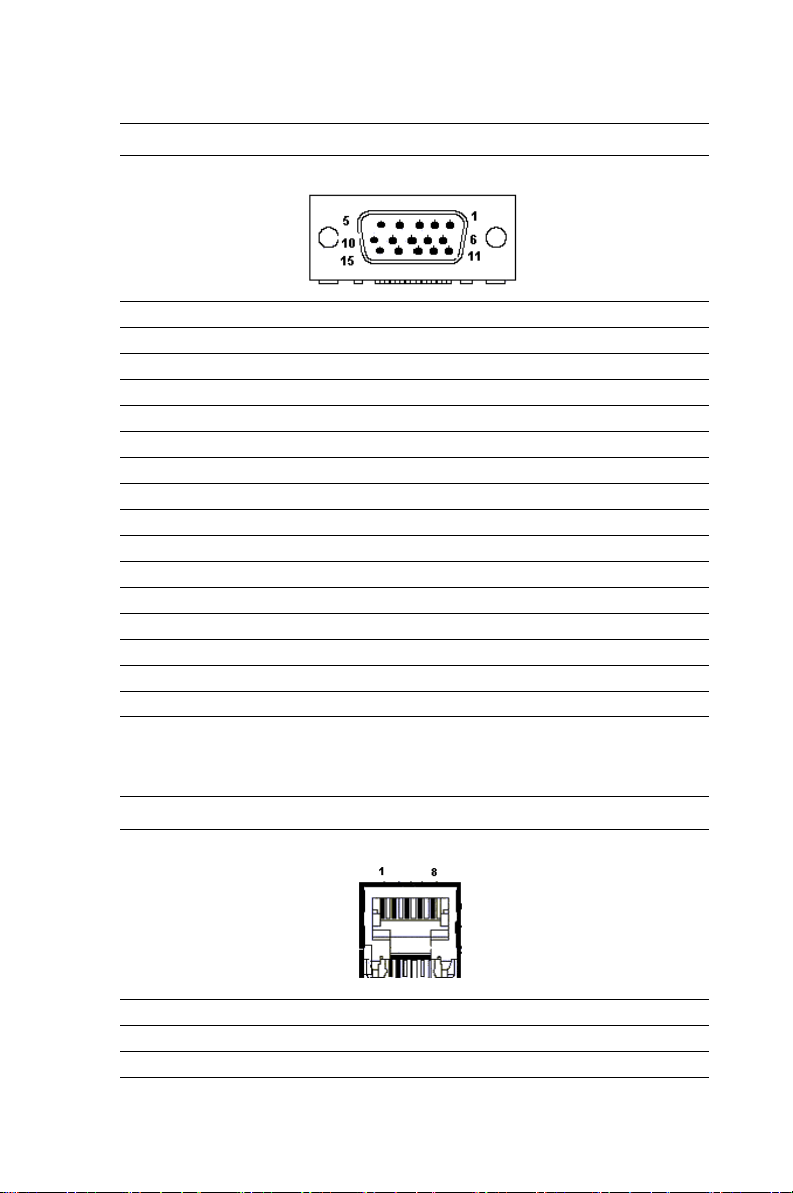
Table 1.13: CN9 DB-15 VGA Connector Definitions
Pin Signal
1RED
2GREEN
3BLUE
4N/C
5GND
6GND
7GND
8GND
9 N/C (VGAVCC)
10 GND
11 N/ C
12 VGA_SDA
13 HSYNC
14 VSYNC
15 VGA_SCL
Table 1.14: PU1 Gigabit LAN Connector Definitions
Pin Signal
1MDIAX1+
2MDIAX1-
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 14
Page 23

3MDIAX2+
4MDIAX3+
5MDIAX3-
6MDIAX2-
7MDIAX4+
8MDIAX4-
The LED indicator means
Left Right
10Mbps Off flick active/link mode
100Mbps Green
1000Mbps Orange
Table 1.15: J11/J12/J14 PMC Connector Definitions
J11 PIN SIGNAL
PIN# Single Name PIN# Single Name
1TCK2 -12V
3 GND 4 INTC#
5 INTD# 6 INTA#
7 BUSMODE1 8 +5V
9 INTB# 10 N/C
11 GND 12 N/C
13 CLK 14 GND
15 GND 16 GNT4#
17 REQ4# 18 +5V
19 V(I/O) 20 AD31
21 AD28 22 AD27
23 AD25 24 GND
25 GND 26 C/BE3#
27 AD22 28 AD21
29 AD19 30 +5V
31 V(I/O) 32 AD17
15 Chapter 1
Page 24

33 FRAME# 34 GND
35 GND 36 IRDY#
37 DEVSEL# 38 +5V
39 GND 40 LOCK#
41 SDONE# 42 SBO#
43 PAR 44 GND
45 V(I/O) 46 AD15
47 AD12 48 AD11
49 AD9 50 +5V
51 GND 52 C/BE0#
53 AD6 54 AD5
55 AD4 56 GND
57 V(I/O) 58 AD3
59 AD2 60 AD1
61 AD0 62 +5V
63 GND 64 REQ64#
J12 PIN SIGNAL
PIN# Single Name PIN# Single Name
1+12V2 TRST#
3TMS4 TDO
5 TDI 6 GND
7GND8 N/C
9N/C10N/C
11 BUSMODE2# 12 +3.3V
13 RST# 14 BUSMODE3#
15 +3.3V 16 BUSMODE4#
17 N/C 18 GND
19 AD30 20 AD29
21 GND 22 AD26
23 AD24 24 +3.3V
25 IDSEL(AD19) 26 AD23
27 +3.3V 28 AD20
29 AD18 30 GND
31 AD16 32 C/BE2#
33 GND 34 N/C
35 TRDY# 36 +3.3V
37 GND 38 STOP#
39 PERR# 40 GND
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 16
Page 25

41 +3.3V 42 SERR#
43 C/BE1# 44 GND
45 AD14 46 AD13
47 GND 48 AD10
49 AD8 50 +3.3V
51 AD7 52 N/C
53 +3.3V 54 N/C
55 N/C 56 GND
57 N/C 58 N/C
59 GND 60 N/C
61 ACK64# 62 +3.3V
63 GND 64 N/C
J14 Pin Signal
PIN# Single Name PIN# Single Name
1+5Vaux 2 +5V
3+5Vaux 4 +5V
5 GND 6 GND
7N/C 8 N/C
9N/C 10 N/C
11 N/ C 12 N /C
13 N/C 14 N/C
15 N/C 16 N/C
17 N/C 18 N/C
19 N/C 20 N/C
21 N/C 22 N/C
23 N/C 24 N/C
25 N/C 26 N/C
27 BMC_PWR_ON/OFF 28 N/C
29 BMC_PWROK 30 PMC_OS_SHUTDOWN
31 GA1 32 GA0
33 GA3 34 GA2
35 N/C 36 GA4
37 N/C 38 BMC_BD_SEL#
39 N/C 40 N/C
41 N/C 42 N/C
43 N/C 44 N/C
45 N/C 46 N/C
17 Chapter 1
Page 26
47 CMM1_SCL 48 CMM1_SDA
49 CMM2_SCL 50 CMM2_SDA
51 BMC_BD_SEL 52 N/C
53 N/C 54 N/C
55 BMC_LEDA 56 BMC_LEDL
57 GND 58 GND
59 BMC_TX+ 60 BMC_RX+
61 BMC_TX- 62 BMC_RX-
63 GND 64 GND
Table 1.16: D9 LED Definitions
Green Power Status
Yellow HDD Status
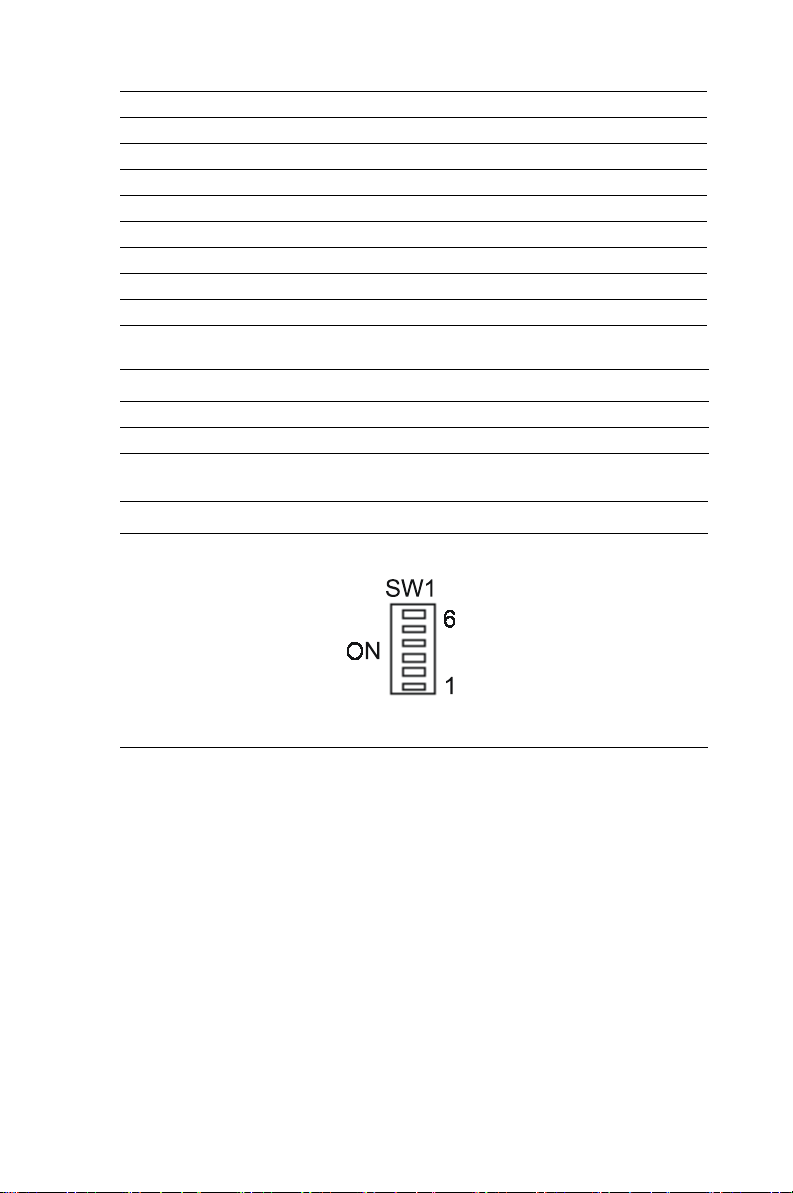
Table 1.17: SW1 Vcore selection definitions
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 18
Page 27

It's automatic selection when SW1-1~SW1-6 are all OFF.
SW1- 6 SW1- 5 SW1- 4 SW1- 3 SW1- 2 SW1- 1 VCORE
OFF X X X X X AUTO
ON ON ON ON ON ON 1.750V
ON ON ON ON ON OFF 1.700V
ON ON ON ON OFF ON 1.650V
ON ON ON ON OFF OFF 1.600V
ON ON ON OFF ON ON 1.550V
ON ON ON OFF ON OFF 1.500V
ON ON ON OFF OFF ON 1.450V
ON ON ON OFF OFF OFF 1.400V
ON ON OFF ON ON ON 1.350V
ON ON OFF ON ON OFF 1.300V
ON ON OFF ON OFF ON 1.250V
ON ON OFF ON OFF OFF 1.200V
ON ON OFF OFF ON ON 1.150V
ON ON OFF OFF ON OFF 1.100V
ON ON OFF OFF OFF ON 1.050V
ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF 1.000V
ON OFF ON ON ON ON 0.975V
ON OFF ON ON ON OFF 0.950V
ON OFF ON ON OFF ON 0.925V
ON OFF ON ON OFF OFF 0.900V
PS: X means either ON or OFF.
Table 1.18: SW2 Drone mode definitions
SW2
ON
2
1
19 Chapter 1
Page 28

When SW2 is ON, then the board is selected as drone mode. The rest of
the combination is reserved for other modes.
Please refer to Appendix B for J1/2/3/5 pin assignments.
12
JP2
123
JP1
2121
JN1
63 646364
CN1
JN2
2
1
JN4
64
63
44 43
15,10,5
CN9
11,6,1
CN2
JP4JP7
Battery
PU1
CN3
CN6
CN5
CN8
D9
LED
SW2
2
ON
1
SW1
CN4
1
ON
Intel
845E
6
1
Figure 1.3: MIC-3358 jumper and connector locations.
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 20
CPU
PCI-PCIX
Bridge
2 1
Page 29

Figure 1.4: MIC-3358 front panel connector and indicator locations
1.6 Safety Precautions
Follow these simple precautions to protect yourself from harm and the
products from damage.
21 Chapter 1
Page 30

1. To avoid electric shock, always disconnect the power from your PC
chassis before you work on it. Don't touch any components on the CPU
card or other cards while the PC is on.
2. Disconnect power before making any configuration changes. The sud-
den rush of power as you connect a jumper or install a card may damage
sensitive electronic components.
3. Always ground yourself to remove any static charge before you touch
your CPU card. Be particularly careful not to touch the chip connectors.
Modern integrated electronic devices, especially CPUs and memory
chips, are extremely sensitive to static electric discharges and fields. Keep
the card in its antistatic packaging when it is not installed in the PC, and
place it on a static dissipative mat when you are working with it. Wear a
grounding wrist strap for continuous protection.
1.7 Installing CPU and Heat Sink
The MIC-3358 supports Intel® Pentium® 4 processor - M . In order to
meet critical environmental conditions and the physical space of the
MIC-3358 at the same time, Advantech designed a heat sink to fulfill its
primary needs. Please refer to Figure 1-4 for an illustration of the heat
sink used for the MIC-3358.
The small aluminum plate is default fastened on the CPU in the factory.
When user doing the memory installation, the following steps should be
followed:
1. Remove the screws for the solder side cover. At this step, the front
panel will be also loose. Be careful about any improper disassemble procedure that could cause any damage of SBC.
2. Remove the rest four screws for heatsink standing, then the heat-
sink is loose for memory installation and relavant.
3. Follow the opposed procedure to assembly the heatsink and solder
side cover.
Note: The heat pad is sealed between heatsink and CPU is kind of frangible, please be
careful on the disassemble procedure. And be careful with any other damage of heat
pad will cause the thermal issue easily.
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 22
Page 31

Figure 1.5: Complete assembly with heat sink and hard disk
1.8 Software support
The MIC-3358 comes with a utility CD-ROM disc, which includes drivers and utility programs of Gigabit Ethernet, IAA and VGA interfaces.
The drivers support Windows 2000, XP and NT4.0 Operation systems.
Please visit Intel® website for detailed explanation.
23 Chapter 1
Page 32

MIC-3358 User’s Manual 24
Page 33

Connecting
Peripherals
CHAPTER
2
Page 34

Chapter 2 Connecting Peripherals
2.1 IDE Device (CN1 and Rear I/O)
The MIC-3358 provides two IDE (Integrated Device Electronics) channels via CN1 connector in MIC-3358 or via the J3 connector to the rear
transition board (RIO-3309C). CN1 connector support one 2.5" IDE
HDD in MIC-3358 and two IDE drives can be connected to Secondary
IDE connector (CN19) in the rear transition board. If two drives are
installed on one channel, remember to set one as the master and the other
one as the slave. You may do this by setting the jumpers on the drives.
Refer to the documentation that came with your drive for more information. A jumper diagram usually appears on the topside of a hard disk
drive.
Warning: Plug the other end of the cable into the drive with pin #1 on the
cable corresponding to pin #1 on the drive. Improper connection will
damage the drive.
2.2 VGA Display Connector (CN9 or Rear I/O)
The MIC-3358 provides a VGA chipset (ATI Rage XL) built-in display
for high performance application. The CN9 connector of MIC-3358 and
CN7 connector of rear I/O board are both DB-15 connector for VGA
monitor input. The system monitor display is able to be selected by
jumper JP2.
2.3 PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Connector (Rear I/O)
The MIC-3358 provides Keyboard/Mouse support via J5 connector to the
rear transition board which builds in one PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse connector (CN12). The package - one Y-type PS/2 keyboard/mouse cable - provides two transferred connectors. Since these two connectors are
identical, please, follow the icons on the cable to plug the keyboard and
the mouse into their correct connectors.
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 26
Page 35

2.4 Serial Ports (CN3 and Rear I/O)
The MIC-3358 offers one serial ports: COM1 in RS-232. With limited
front panel access, one COM1 (CN3) can be connected via a RJ-45 to RS232 adaptor and COM2 (CN9) interface has to be connected via rear I/O
module (RIO-3309C) for implement. These ports allow users to connect
to serial devices (a mouse, printers, etc.) or a communication network.
You can select the address for each port to disable it, using the BIOS
Advanced Setup program, covered in Chapter 5. Different devices implement the RS-232 standard in different ways. If you are having problems
with a serial device, be sure to check the pin assignments for the connector. The IRQ and address range for both ports are fixed. However, if you
wish to disable the port or change these parameters later, you can do this
in the system BIOS setup. The table below shows the settings for the
MIC-3358 board's ports:
Table 2.1: MIC-3358 serial port default settings
Port Address Default
COM1 3F8, 3E8 IRQ4
COM2 2F8, 2E8 IRQ3
2.5 Ethernet Configuration (PU1 , Rear I/O and J3)
The MIC-3358 is equipped with dual high performance 32-bit PCI-bus
Gigabit Ethernet interfaces which are fully compliant with IEEE 802.3u
10/100/1000Base-TX specifications. Users can select front GbE or rear
GbE or 2.16 by BIOS. Users can choice LAN1 connector either via front
RJ-45 jack (PU1) in MIC-3358 or rear RJ-45 (CN16) in rear module.
Another one Gigabit LAN connector (CN15) has to go through RIO module (RIO-3309C).
Moreover, the MIC-3358 supports PICMG 2.16 complaint with Packet
Switching Backplane Specification via J3 connector, it will installed in
PICMG 2.16 backplane as switch-fabric applications blade server
27 Chapter 2
Page 36

2.6 USB Connector (CN5/6 and Rear I/O)
The MIC-3358 provides two USB (Universal Serial Bus) 2.0 channels
either via two front USB ports (CN5 and CN6) in MIC-3358 or via J5
connector to one USB connector (CN8) in real transition board. The USB
interface gives complete plug and play, hot attach/detach for up to 127
external devices. The MIC-3358 USB interface complies with USB specification rev. 2.0 and is polyswitch protected. The USB interface can be
disabled in the system BIOS setup. The USB controller default is
"Enabled" but the USB keyboard support default is "Disabled".
2.7 PMC Connector (J11, J12, J14)
The MIC-3358 supports one PMC (PMC Mezzanine Card) modules on
PCI bus. This 32-bit, 3.3/5 V(I/O) PCI bus is available at connectors J11
and J12. J14 is applied for user definitions. Front panel access is provided
for the PMC interface.
2.8 CompactFlash™ Socket (CN2)
CompactFlash™ is a standard form factor for mass storage and I/O cards.
Based on the PCMCIA Standard, CompactFlash™ cards are approximately 1/4 the volume of a PC Card. In order to achieve the small size,
the interface pin count is 50-pins compared to the PCMCIA's 68-pin.
The MIC-3358 supports one CompactFlash™ socket in CN2 connector. It
helps file and data storage in the CompactFlash™ card rather than the traditional hard drive.
2.9 Card Installation
The CompactPCI™ connectors are firm and rigid, and require careful
handling while plugging and unplugging. Improper installation of a card
can easily damage the backplane of the chassis. The inject/eject handles
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 28
Page 37

of MIC-3358 help you install and remove the card easily and safely. Follow the procedure below to install the
MIC-3358 into a chassis:
To install a card:
1. Hold the card vertically. Be sure that the card is pointing in the correct
direction. The components of the card should be pointing to the righthand side.
2. Pull out both handles to unlock it.
Caution: Keep your fingers away from the hinge to prevent your
fingers from getting pinched.
3. Insert the card into the chassis by sliding the upper and lower edges of
the card into the card guides.
4. Push the card into the slot gently by sliding the card along the card
guide until the handles meet the rectangular holes of the cross rails. Note:
If the card is correctly positioned and has been slid all the way into the
chassis, the handle should match the rectangular holes. If not, remove the
card from the card guide and repeat step 3 again. Do not try to install a
card by forcing it into the chassis.
5. Pull the upper handle down and lift the lower handle up to push the
card into place.
6. Secure the card by pushing in the red handle to lock it into place.
To remove a card:
1. Unscrew the screws on the front panel.
2. Lift the upper handle up and press the lower handle down to release the
card from the backplane.
3. Slide the card out.
29 Chapter 2
Page 38

MIC-3358 User’s Manual 30
Page 39

Driver Setup
CHAPTER
3
Page 40

Chapter 3
3.1 Overview
Advantech provides CD utility driver in the package. Please install
Chipset INF driver, VGA graphics driver, LAN driver and Intel® Application Accelerator (IAA) driver sequentially.
The Intel® Application Accelerator is a performance software package of
Intel® chipsets. It reduces the storage sub-system bottleneck, enabling
faster delivery of data from the hard drive to the processor and other system level hardware. Meanwhile, it enables a performance-enhancing data
pre-fetcher for Intel® Pentium® 4 and Pentium® M processor-based systems. In addition, it delivers faster overall system boot times by significantly accelerating the load time of the OS - enabling you to build
Pentium® 4 and Pentium® M processor-based systems with a better
overall end-user experience. IAA supports 48-bit Logical Block Addressing (48-bit LBA) for 137 GB and larger hard drives. Furthermore, IAA
enables Automatic Selection of Highest DMA Transfer Mode by the
ATA/ATAPI device/Intel chipset.
3.2 USB driver
If the manufacturer/vendor of a USB device recommends downloading
an Intel® USB driver update as part of troubleshooting your USB device,
please contact Microsoft® for USB driver support. Intel manufactures the
host controller but the driver is from Microsoft. While users installed
Intel INF driver, it will not install USB driver. Please go to "device manager" to update USB driver via Advantech CD utility or via Microsoft
website.
Note: There are no separate USB (version 1.1 and earlier) drivers
available for download for Intel® chipsets.
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 32
Page 41

3.3 CMM (Chassis Management Module) Driver
MIC-3358 supports MIC-3924B CMM. Please install driver as following
procedure.
3.3.1 Windows 2K Driver
Figure 3.1: Right Click "My Computer" and click "Properties"
Figure 3.2: Tab "Hardware" and click "Hardware Wizard"
33 Chapter 3
Page 42

Figure 3.3: click "Next" in Hardware Wizard
Figure 3.4: click" Add/Troubleshoot a device"
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 34
Page 43

Figure 3.5: select " Add a new device" in Device windows
Figure 3.6: click "No, I want to select the hardware from a list"
35 Chapter 3
Page 44

Figure 3.7: Select "Other devices" in Hardware types windows
Figure 3.8: Tab " Have Disk" in right bottom
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 36
Page 45

Figure 3.9: Browse proper driver in CD ROM device
Figure 3.10: click ok in the Wizard windows
37 Chapter 3
Page 46

Figure 3.11: click "ok" in Add New Hardware Wizard Properties" windows
Figure 3.12: click "yes" in Creating a Forced Configuration windows
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 38
Page 47

Figure 3.13: click "Next" in Add/Remove Hardware Wizard windows
Figure 3.14: Tab "Finish" in Add/Remove Hardware Wizard windows
39 Chapter 3
Page 48

Figure 3.15: click "Yes" to restart your computer
Figure 3.16: Go to Device Manager to see available A-IPM drivers
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 40
Page 49

3.3.2 Windows XP Driver
Figure 3.17: Right click My Computer to select "Properties"
Figure 3.18: Tab "Hardware" and click "Add Hardware Wizard"
41 Chapter 3
Page 50

Figure 3.19: Click "Next" in the windows
Figure 3.20: Click "Yes , I have already connected the hardware"
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 42
Page 51

Figure 3.21: Select "Add a new hardware device" in the installed hardware
window
Figure 3.22: Click Install the hardware that I manually select from a list
(Advanced)
43 Chapter 3
Page 52

Figure 3.23: Select "Show all devices" in Common hardware types windows
Figure 3.24: tab "Have Disk"
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 44
Page 53
Figure 3.25: Select proper driver in CD-ROM
Figure 3.26: tab A-IPM driver and click "Have Disk"
45 Chapter 3
Page 54

Figure 3.27: Click " Next"
Figure 3.28: Click "Finish"
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 46
Page 55

Figure 3.29: Go to My computer to see "A-IPM drivers"
47 Chapter 3
Page 56

MIC-3358 User’s Manual 48
Page 57

Award BIOS Setup
CHAPTER
4
Page 58

Chapter 4 Award BIOS Setup
4.1 AWARD BIOS Setup
Once you enter Award® BIOS CMOS Setup Utility, the Main Menu (Figure 4-1) will appear on the screen. The Main Menu allows you to select
from nine setup functions and two exit choices. Use arrow keys to select
among the items and press <Enter> to accept or enter the sub-menu.
Figure 4.1: Setup program initial screen
Award's BIOS ROM has a built-in Setup program that allows users to
modify the basic system configuration. This type of information is stored
in battery-backed CMOS so that it retains the Setup information when the
power is turned off.
4.1.1 Entering Setup
Turn on the computer and check for the "patch code". If there is a number
assigned to the patch code, it means that the BIOS support your CPU. If
there is no number assigned to the patch code, please contact Advantech's
application engineer to obtain an up-to-date patch code file. This will
ensure that your CPU's system status is valid. After ensuring that you
have a number assigned to the patch code, press <DEL> and you will
immediately be allowed to enter Setup.
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 50
Page 59

4.1.2 Standard CMOS Setup
The items in Standard CMOS Setup Menu are divided into 11 categories.
Each category includes no, one or more than one setup items. Use the
arrow keys to highlight the item and then use the <PgUp> or <PgDn>
keys to select the value you want in each item.
Figure 4.2: Standard CMOS setup screen.
Primary Master/Primary Slave/Secondary Master/Secondary Slave
Press PgUp/<+> or PgDn/<-> to select Manual, None, Auto type. Note
that the specifications of your drive must match with the drive table. The
hard disk will not work properly if you enter improper information for
this category. If your hard disk drive type is not matched or listed, you
can use Manual to define your own drive type manually. If you select
Manual, related information is asked to be entered to the following items.
Enter the information directly from the keyboard. This information
should be provided in the documentation from your hard disk vendor or
the system manufacturer.
4.1.3 Advance BIOS Features Setup
The "Advance BIOS FEATURES" screen will appear after the BIOS
FEATURES SETUP item from the CMOS SETUP UTILITY Menu was
chosen. This screen allows the user to configure the board according to
his particular requirements. Below are some major items that are provided in the BIOS FEATURES SETUP screen:
51 Chapter 4
Page 60

Figure 4.3: Advance BIOS features setup screen
Virus Warning
During and after the system boots up, any attempt to write to the boot sector or partition table of the hard disk drive will halt the system. If this
happens, a warning message will be displayed. You can run the anti-virus
program to locate the problem. If Virus Warning is disabled, no warning
message will appear if anything attempts to access the boot sector or hard
disk partition.
CPU L1 & L2 Cache
The default value is Enabled.
Enabled (default) Enable cache
Disabled Disable cache
Note: The internal cache is built in the processor.
Quick Power On Self Test
This category speeds up Power On Self Test (POST) after you power on
the computer. If this is set to Enabled, BIOS will shorten or skip some
check items during POST.
Enabled (default) Enable quick POST
Disabled Normal POST
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 52
Page 61

First/Second/Third Boot Device and Boot Other Device
The BIOS attempts to load the operating system from the devices in the
sequence selected in these items. The settings are Floppy, LS120, HDD0, SCSI, CDROM, HDD-1, HDD-2, HDD-3, ZIP100, USB-FDD, USBZIP, USB-CDROM, USB-HDD, LAN and Disabled.
Default
First boot device Floppy
Second boot device HDD-0
Third boot device CD-ROM
PS: When you boot by USB CD-ROM, please install Win XP with SP1 or
Win 2000 with SP3.
Swap Floppy Drive
Switches the floppy disk drives between being designated as A and B.
Default is Disabled.
Boot Up Floppy Seek
During POST, BIOS will determine if the floppy disk drive installed is 40
or 80 tracks. 360K type is 40 tracks while 760K, 1.2M and 1.44M are all
80 tracks. Default is Enabled.
Boot Up NumLock Status
The default value is On.
On (default) Keypad is numeric keys.
Off Keypad is arrow keys.
Gate A20 Option
Normal The A20 signal is controlled by keyboard controller or
chipset hardware.
Fast(default) The A20 signal is controlled by port 92 or chipset spe-
cific method.
53 Chapter 4
Page 62

Typematic Rate Setting
Key strokes repeat at a rate determined by the keyboard controller. When
enabled, the typematic rate and typematic delay can be selected. The settings are: Enabled/Disabled. Default is Disabled.
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec)
Set the number of times a second to repeat a key stroke when you hold the
key down. The settings are: 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 24, 30.
Typematic Delay (Msec)
Sets the delay time after the key is held down before it begins to repeat
the keystroke. The settings are: 250, 500, 750, 1000.
Security Option
This category allows you to limit access to the system and Setup, or just
to Setup.
System The system will not boot and access to Setup will be
denied if the correct password is not entered at the
prompt.
Setup(default) The system will boot, but access to Setup will be
denied if the correct password is not entered at the
prompt.
APIC Mode (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller)
Default is Enabled.
MPS Version Control for OS
The options includes 1.1 and 1.4. Default is 1.4
OS Select For DRAM > 64MB
Allows OS2® to be used with > 64 MB of DRAM. Settings are Non-OS/
2 (default) and OS2. Set to OS/2 if using more than 64MB and running
OS/2®.
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 54
Page 63

Small logo (EPA) show
Default is Disabled.
4.1.4 Advance Chipset Features Setup
The Advanced Chipset Features Setup option is used to change the values
of the chipset registers. These registers control most of the system options
in the computer. Choose the "ADVANCED CHIPSET FEATURES" from
the Main Menu and the following screen will appear.
Figure 4.4: Advance Chipset features setup screen
DRAM Timing Configure
This field lets you select system memory timing data. Manual and BY
SPD are two options. Default is "BY SPD"
CAS Latency Time
When synchronous DRAM is installed, the number of clock cycles of
CAS latency depends on the DRAM timing. The settings are: 1.5, 2 and
2.5.
Active to Precharge Delay
This field let you select active to precharge delay. The settings are: 7, 6
and 5
DRAM RAS# to CAS# Delay
55 Chapter 4
Page 64

This field lets you insert a timing delay between the CAS and RAS strobe
signals, used when DRAM is written to, read from, or refreshed. Fast
gives faster performance; and Slow gives more stable performance. This
field applies only when synchronous DRAM is installed in the system.
The settings are: 2 and 3.
DRAM RAS# Precharge
If an insufficient number of cycles is allowed for the RAS to accumulate
its charge before DRAM refresh, the refresh may be incomplete and the
DRAM may fail to retain data. Fast gives faster performance; and Slow
gives more stable performance. This field applies only when synchronous
DRAM is installed in the system. The settings are: 2 and 3.
DRAM Data Integrity Mode
The settings are ECC (Default) and non-ECC.
Memory Frequency For
User can select 3 options: DDR200, DDR266, Auto (Default)
System BIOS Cacheable
Selecting Enabled allows caching of the system BIOS ROM at F0000hFFFFFh, resulting in better system performance. However, if any program writes to this memory area, a system error may result. The settings
are: Enabled (Default) and Disabled.
Video BIOS Cacheable
Select Enabled allows caching of the video BIOS, resulting in better system performance. However, if any program writes to this memory area, a
system error may result. The settings are: Enabled and Disabled
(Default).
Memory Hole At 15M-16M
You can reserve this area of system memory for ISA adapter ROM. When
this area is reserved, it cannot be cached. The user information of peripherals that need to use this area of system memory usually discusses their
memory requirements. The settings are: Enabled and Disabled (Default).
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 56
Page 65

Delayed Transaction
The chipset has an embedded 32-bit posted write buffer to support delay
transactions cycles. Select Enabled to support compliance with PCI specification version 2.1. The settings are: Enabled (Default) and Disabled.
4.1.5 Integrated Peripherals
Figure 4.5: Integrated Peripherals setup screen
57 Chapter 4
Page 66

On-Chip Primary/Secondary PCI IDE
The integrated peripheral controller contains an IDE interface with support for two IDE channels. Select Enabled to activate each channel separately. The settings are: Enabled (Default) and Disabled.
IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave PIO
The four IDE PIO (Programmed Input/Output) fields let you set a PIO
mode (0-4) for each of the four IDE devices that the onboard IDE interface supports. Modes 0 through 4 provide successively increased performance. In Auto mode, the system automatically determines the best mode
for each device. The settings are: Auto (Default), Mode 0, Mode 1, Mode
2, Mode 3, Mode 4.
IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave UDMA
Ultra DMA/33 implementation is possible only if your IDE hard drive
supports it and the operating environment includes a DMA driver (Windows 95 OSR2 or a third-party IDE bus master driver). If your hard drive
and your system software both support Ultra DMA/33 and Ultra DMA/66
and Ultra DMA/100, select Auto to enable BIOS support. The settings
are: Auto (Default), Disabled.
USB Controller
Select Enabled if your system contains a Universal Serial Bus (USB) 1.1
controller. The settings are: Enabled (Default), Disabled.
USB 2.0 Controller
Select Enabled if your system contains a Universal Serial Bus (USB) 1.1/
2.0 controller. The settings are: Enabled (Default), Disabled.
USB Keyboard/Mouse Support
Select Enabled if you use USB KB/Mouse in DOS mode.
Init Display First
User can choose display priority on either peripheral PCI slot or on board
VGA chip. There are 2 options: PCI slot (Default) and On board.
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 58
Page 67

SMBus Connector
Users can select IPMI source and application as below.
Source connected CMM
PCF8584T MIC-3924B
Hardware Monitor 83782D MIC-3924A
BMC (PMC type) (Reserved) CMM (Reserved)
There are 3 options: MIC-3924B (Default), MIC-3924A and CMM.
LAN 1 Connector
The item allows you to choice LAN1 connective way. There are 3
options: Front (Default), 2.16 and Rear
LAN 2 Connector
The item allows you to choice LAN2 connective way. There are 2
options: 2.16 and Rear (Default)
IDE HDD Block Mode
Block mode is also called block transfer, multiple commands, or multiple
sector read/write. If your IDE hard drive supports block mode (most new
drives do), select Enabled for automatic detection of the optimal number
of block read/writes per sector the drive can support. The settings are:
Enabled (Default), Disabled.
Onboard FDC Controller
Select Enabled if your system has a floppy disk controller (FDD)
installed on the system board and you wish to use it. If you install add-on
FDC or the system has no floppy drive, select Disabled in this field. The
settings are: Enabled (Default) and Disabled.
Onboard Serial Port 1/Port 2
Select an address and corresponding interrupt for the first and second
serial ports. The Serial Port 1 settings are: 3F8/IRQ4 (Default), 2E8/
IRQ3, 3E8/IRQ4, 2F8/ IRQ3, Disabled, Auto.
59 Chapter 4
Page 68

The Serial Port 2 settings are: 3F8/IRQ4, 2E8/IRQ3, 3E8/IRQ4, 2F8/
IRQ3 (Default), Disabled, Auto.
Onboard Parallel Port
There is a built-in parallel port on the on-board Super I/O chipset that
provides Standard, ECP, and EPP features. It has the following options:
Disabled, 3BCH/IRQ7 (Default), 278H/IRQ5 , 378H/IRQ7 and Disable
Parallel Port Mode
SPP (Default) Standard Parallel Port
EPP1.9+SPP Support both the SPP and EPP1.9 modes
ECP Extended Capability Port
EPP1.9+ECP Support both the ECP and EPP1.9 modes
Printer Support Printer modes
EPP1.7+SPP Support both the SPP and EPP1.7 modes
EPP1.7+ECP Support both the ECP and EPP1.7 modes
ECP Mode Use DMA
The options: 1 and 3 (Default)
4.1.6 Power Management Setup
The Power Management Setup allows you to configure you system to
most effectively save energy while operating in a manner consistent with
your own style of computer use.
Figure 4.6: Power management setup screen
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 60
Page 69

ACPI Function
This category allows you to select ACPI power management effective or
not. The options: Enabled (Default) and Disabled.
4.1.7 PNP/PCI Configuration Setup
This section describes configuring the PCI bus system. PCI, or Personal
Computer Interconnect, is a system which allows I/O devices to operate
at speeds nearing the speed the CPU itself uses when communicating
with its own special components. This section covers some very technical
items and it is strongly recommended that only experienced users should
make any changes to the default settings.
Figure 4.7: PNP/PCI configuration screen
Reset Configuration Data
Normally, you leave this field Disabled. Select Enabled to reset Extended
System Configuration Data (ESCD) when you exit Setup if you have
installed a new add-on and the system reconfiguration has caused such a
serious conflict that the operating system can not boot. The settings are:
Enabled and Disabled (Default).
Resource Controlled By
The Award Plug and Play BIOS has the capacity to automatically configure all of the boot and Plug and Play compatible devices. However, this
capability means absolutely nothing unless you are using a Plug and Play
61 Chapter 4
Page 70

operating system such as Windows® 95/98. If you set this field to "manual" choose specific resources by going into each of the sub menu that
follows this field (a sub menu is preceded by a "y"). The settings are:
Auto (ESCD) (Default), Manual.
IRQ Resources
When resources are controlled manually, assign each system interrupt a
type, depending on the type of device using the interrupt.
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
Leave this field at Disabled. The settings are Enabled, Disabled (Default).
4.1.8 PC Health Status
This section shows the Status of you CPU, Fan, Warning for overall system status. This is only available if there is Hardware Monitor onboard.
Figure 4.8: PC Health setup screen
Current CPU Temp./ Vcpu-core/Vtt/+3.3V/+5V/+12V/-12V/VBAT
(V)
This show system health status.
4.1.9 Load Optimized Defaults
When you press <Enter> on this item, you get a confirmation dialog box
with a message similar to:
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 62
Page 71

Load Optimized Defaults (Y/N) ? N
Pressing 'Y' loads the default values that are factory settings for optimal
performance system operations.
4.1.10 Set Password
To change, confirm, or disable the password, choose the "PASS-WORD
SETTING" option form the Setup main menu and press [Enter]. The
password can be at most 8 characters long. Remember, to enable this feature. You must first select the Security Option in the Advance BIOS FEATURES SETUP to be either "Setup" or "System." Pressing [Enter] again
without typing any characters can disable the password setting function.
4.1.11 Save & Exit Setup
If you select this and press the [Enter] key, the values entered in the setup
utilities will be recorded in the CMOS memory of the chipset. The microprocessor will check this every time you turn your system on and compare this to what it finds as it checks the system. This record is required
for the system to operate.
4.1.12 Exit Without Saving
Selecting this option and pressing the [Enter] key lets you exit the Setup
program without recording any new values or changing old ones.
63 Chapter 4
Page 72

MIC-3358 User’s Manual 64
Page 73
Programming the
Watchdog Timer
Appendix
A
Page 74

Appendix A
A.1 Programming the Watchdog Timer
To program the watchdog timer, you must write a program which writes a
value to I/O port address 443 (hex). This output value represents time
interval. The value range is from 01 (hex) to FF (hex), and the related
time interval is 1 sec. to 255 sec.
Data Time Interval
01 1 sec.
02 2 sec.
03 3 sec.
04 4 sec.
•
•
•
FF 255 sec.
After data entry, your program must refresh the watchdog timer by rewriting the I/O port 443. When you want to disable the watchdog timer, your
program should read I/O port 043 (hex). The following example shows
how you might program the watchdog timer in BASIC:
10 REM Watchdog timer example program
20 OUT &H443, data REM Start and restart the watchdog
30 GOSUB 1000 REM Your application task #1,
40 OUT &H443, data REM Reset the timer
50 GOSUB 2000 REM Your application task #2,
60 OUT &H443, data REM Reset the timer
70 X=INP (&H043) REM, Disable the watchdog timer
80 END
1000 REM Subroutine #1, your application task
•
•
•
MIC-3369 User’s Manual 66
Page 75

1070 RETURN
2000 REM Subroutine #2, your application task
•
•
•
2090 RETURN.
67 Chapter A
Page 76

MIC-3369 User’s Manual 68
Page 77

Pin Assignments
Appendix
B
Page 78

Appendix B Pin Assignments
B.1 J1 Connector
Table B.1: J1 connector
Pin Z A B C D E F
25 GND +5V REQ64# ENUM# +3.3V +5V GND
24 GND AD[1] +5V V(I/O) AD[0] ACK64# GND
23 GND +3.3V AD[4] AD[3] +5V AD[2] GND
22 GND AD[7] GND +3.3V AD[6] AD[5] GND
21 GND +3.3V AD[9] AD[8] M66EN C/BE[0]# GND
20 GND AD[12] GND V(I/O) AD[11] AD[10] GND
19 GND +3.3V AD[15] AD[14] GND AD[13] GND
18 GND SERR# GND +3.3V PAR C/BE[1]# GND
17 GND +3.3V IPMB_SCL IPMB_SDA GND PERR# GND
16 GND DEVSEL# GND V(I/O) STOP# LOCK# GND
15 GND +3.3V FRAME# IRDY# BD/SEL# TRDY# GND
12-14 Key Area
11 GND AD[18] AD[17] AD[16] GND C/BE[2]# GND
10 GND AD[21] GND +3.3V AD[20] AD[19] GND
9 GND C/BE[3]# N/C AD[23] GND AD[22] GND
8 GND AD[26] GND V(I/O) AD[25] AD[24] GND
7 GND AD[30] AD[29] AD[28] GND AD[27] GND
6 GND REQ0# GND +3.3V CLK0 AD[31] GND
5 GND N/C N/C RST# GND GNT0# GND
4 GND IPMB_PWR Healthy# V(I/O) INTP INTS GND
3 GND INTA# INTB# INTC# +5V INTD# GND
2 GND TCK +5V TMS N/C TDI GND
1 GND +5V -12V TRST# +12V +5V GND
#: Low active
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 70
Page 79

B.2 J2 Connector
Table B.2: J2 connector
Pin Z A B C D E F
22 GND GA4 GA3 GA2 GA1 GA0 GND
21 GND CLK6 GND RSV RSV RSV GND
20 GND CLK5 RSV RSV GND RSV GND
19 GND RSV GND RSV (SMBB_SDA) RSV (SMBB_SCL) RSV GND
18 GND RSV RSV RSV GND RSV GND
17 GND RSV GND PRST# REQ6# GNT6# GND
16 GND RSV RSV RSV GND RSV GND
15 GND RSV GND RSV REQ5# GNT5# GND
14 GND AD[35] AD[34] AD[33] GND AD[32] GND
13 GND AD[38] GND V(I/O) AD[37] AD[36] GND
12 GND AD[42] AD[41] AD[40] GND AD[39] GND
11 GND AD[45] GND V(I/O) AD[44] AD[43] GND
10 GND AD[49] AD[48] AD[47] GND AD[46] GND
9 GND AD[52] GND V(I/O) AD[51] AD[50] GND
8 GND AD[56] AD[55] AD[54] GND AD[53] GND
7 GND AD[59] GND V(I/O) AD[58] AD[57] GND
6 GND AD[63] AD[62] AD[61] GND AD[60] GND
5 GND C/BE[5]# 64EN# V(I/O) C/BE[4]# PAR64# GND
4 GND V(I/O) RSV C/BE[7]# GND C/BE[6]# GND
3 GND CLK4 GND GNT3# REQ4# GNT4# GND
2 GND CLK2 CLK3 SYSEN# GNT2# REQ3# GND
1 GND CLK1 GND REQ1# GNT1# REQ2# GND
#: Low active
Note: GA[4...0] shall be used for geographic addressing on the backplane
71 Chapter B
Page 80

B.3 J3 Connector
Table B.3: J3 connector
Pin Z A B C D E F
19 GND NC NC NC NC NC GND
18 GND MDIA0+ MDIA0- GND MDIA2+ MDIA2- GND
17 GND MDIA1+ MDIA1- GND MDIA3+ MDIA3- GND
16 GND MDIB0+ MDIB0- GND MDIB2+ MDIB2- GND
15 GND MDIB1+ MDIB1- GND MDIB3+ MDIB3- GND
14 GND NC NC NC NC NC GND
13 GND SDD0 SDD2 NC NC NC GND
12 GND SDD1 SDD3 SDD12 SDD4 SDD7 GND
11 GND SDD5 SDD9 SDD13 SDD6 SDD8 GND
10 GND SDD15 SDD14 SDIOR# SDD10 SDD11 GND
9 GND IDE_SDLED CLK7 SDIOW# SDREQ# SDCS3# GND
8 GND IRQ15 SD_CBL_DET SDA0 SDA1 SDA2 GND
7 GND FD_DIR# SDACK# IDE_RST# SIORDY SDCS1# GND
6 GND SLIN- INIT- FD_WGATE# FD_HDSEL# FD_DS0# GND
5 GND PE SLCT FD_STEP# FD_MTR0# FD_WDATA# GND
4 GND ERR- ACK- FD_RDATA# FD_WRTPRT# FD_TRK0# GND
3 GND STB- AFD- FD_DRVEN0 FD_INDEX# FD_DSKCHG# GND
2 GND LPTD5 LPTD6 LPTD7 BUSY FD_DRVEN1 GND
1 GND LPTD0 LPTD1 LPTD2 LPTD3 LPTD4 GND
#: Low active
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 72
Page 81

B.4 J5 Connector
Table B.4: J5 connector
Pin Z A B C D E F
22 GND ICH_RX+ ICH_RX- GND ICH_TX+ ICH_TX- GND
21 GND BMC_RX+ BMC_RX- GND BMC_TX+ BMC_TX- GND
20 GND GND GND USBD1- GND GND GND
19 GND USBD0- GND USBD1+ GND VGA_RED GND
18 GND USBD0+ GND GND VGA-H GND GND
17 GND GND RIO_REQ7# NC GND VGA_GREENGND
16 GND USB_OC0# RIO_GNT7# GND VGA-V GND GND
15 GND USB_OC1# RIOINSTALL# RIO_HW_SW GND VGA_BLUE GND
14 GND NRLSD1 NRI1 RIO_HW_LED ICH_LEDSPD GND GND
13 GND NRTS1 NDTR1 BMC_LEDACT ICH_LEDLINK VGA_SCL GND
12 GND NTX1 NDSR1 BMC_LEDLINK ICH_LEDACT VGA_SDA GND
11 GND NRX1 NCTS1 NC NC MCLK GND
10 GND NDCD2 TX2 NRI2 NDRS2 MDAT GND
9 GND 2RXD232 RX2 NDTR2 NCTS2 KBCLK GND
8 GND NRXD2 RTS2# NTXD2 NRTS2 KBDAT GND
7 GND LINKA1G# PORTA_LINK# LINKB100# PORTB_LINK# +5V GND
6 GND LINKA100# PORTA_ACT# LINKB1G# PORTB_ACT# +5V GND
5 GND GND GND +3.3V GND GND GND
4 GND MDIB2- MDIB2+ GND MDIB3+ MDIB3- GND
3 GND MDIB0- MDIB0+ GND MDIB1+ MDIB1- GND
2 GND MDIA2- MDIA2+ GND MDIA3+ MDIA3- GND
1 GND MDIA0- MDIA0+ GND MDIA1+ MDIA1- GND
73 Chapter B
Page 82

B.5 System I/O Ports
Table B.5: System I/O ports
Address range (Hex) Device
000-00F Direct memory access controller
000-CF7 PCI bus
010-01F Motherboard resources
020-021 Programmable interrupt controller
022-03F Motherboard resources
040-043 System timer
044-05F Motherboard resources
060-060 Standard 101/102-Key or Microsoft natural PS/2 keyboard
061-061 System speaker
062-063 Motherboard resources
064-064 Standard 101/102-Key or Microsoft natural PS/2 keyboard
065-06F Motherboard resources
070-073 System CMOS / real time clock
074-07F Motherboard resources
080-090 Direct memory access controller
091-093 Motherboard resources
094-09F Direct memory access controller
0A0-0A1 Programmable interrupt controller
0A2-0BF Motherboard resources
0C0-0DF Direct memory access controller
0E0-0EF Motherboard resources
0F0-0FF Numeric data processor
170-177 Secondary IDE channel
1F0-1F7 Primary IDE channel
274-277 ISAPNP read data port
279-279 ISAPNP read data port
294-297 Motherboard resources
2F8-2FF Communication port (COM2)
376-376 Secondary IDE channel
378-37F Printer port (LPT1)
3B0-3BB ATI Technologies Inc. Rage XL PCI
3C0-3DF ATI Technologies Inc. Rage XL PCI
3F0-3F5 Standard floppy disk controller
3F6-3F6 Primary IDE channel
3F7-3F7 Standard floppy disk controller
3F8-3FF Communication port (COM1)
447-44A A-IPM driver
4D0-4D1 Motherboard resources
800-87F Motherboard resources
A79-A79 ISAPNP read data port
0D00-FFFF PCI bus
MIC-3358 User’s Manual 74
Page 83

4000-40BF Motherboard resources
5000-501F Intel® 82801DB/DBM SMBus controller -24C3
C000-C0FF ATI Technologies Inc. Rage XL PCI
C400-C43F Intel® 82540EM based network connection #2
C800-C83F Intel® 82540EM based network connection
CC00-CC3F Intel® PRO/100 VE network connection
D000-D01F Intel® 82801DB/DBM USB universal host controller - 24C4
D400-D41F Intel® 82801DB/DBM USB universal host controller - 24C2
F000-F00F Intel® 82801DB Ultra ATA Storage controller - 24CB
B.6 Interrupt Assignments
Table B.6: Interrupt assignments
Interrupt# Interrupt source
IRQ 0 (ISA) System timer
IRQ 1 (ISA) Standard 101/102-Key or Microsoft natural PS/2 keyboard
IRQ 3 (ISA) Communications port (COM2)
IRQ 4 (ISA) Communications port (COM1)
IRQ 5 (ISA) A-IPM driver
IRQ 8 (ISA) System CMOS / real time clock
IRQ 9 (ISA) Microsoft ACPI-Compliant system
IRQ 12 (ISA) PS/2 compatible mouse
IRQ 13 (ISA) Numeric data processor
IRQ 14 (ISA) Primary IDE channel
IRQ 15 (ISA) Secondary IDE channel
B.7 1st MB Memory Map
Table B.7: 1st MB memory map
Address range (Hex) Device
F000h - FFFFh System ROM
CC00h - EFFFh Unused
CA00h - CBFFh Used
C000h - C9FFh Expansion ROM
B800h - BFFFh CGA/EGA/VGA text
B000h - B7FFh Unused
A000h - AFFFh EGA/VGA graphics
0000h - 9FFFh Base memory.
75 Chapter B
Page 84

MIC-3358 User’s Manual 76
 Loading...
Loading...