Page 1

Intel® MAX® 10 JTAG Boundary-Scan
Testing User Guide
Subscribe
Send Feedback
UG-M10JTAG | 2019.05.10
Latest document on the web: PDF | HTML
Page 2

Contents
Contents
1. Intel® MAX® 10 JTAG BST Overview................................................................................3
2. JTAG BST Architecture.................................................................................................... 4
2.1. JTAG Pins............................................................................................................. 4
2.2. JTAG Circuitry Functional Model...............................................................................4
2.3. JTAG Boundary-Scan Register..................................................................................5
2.3.1. Boundary-Scan Cells in Intel MAX 10 I/O Pin................................................. 5
3. BST Operation Control.................................................................................................... 7
3.1. JTAG IDCODE .......................................................................................................7
3.2. JTAG Secure Mode................................................................................................. 8
3.3. JTAG Private Instruction......................................................................................... 8
3.4. JTAG Instructions.................................................................................................. 9
4. I/O Voltage Support in the JTAG Chain......................................................................... 10
5. Enabling and Disabling JTAG BST Circuitry....................................................................11
6. Guidelines for JTAG BST................................................................................................ 12
7. Boundary-Scan Description Language Support............................................................. 13
A. Document Revision History for the Intel MAX 10 JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing
User Guide............................................................................................................... 14
Intel® MAX® 10 JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing User Guide
2
Send Feedback
Page 3

UG-M10JTAG | 2019.05.10
Send Feedback
1. Intel® MAX® 10 JTAG BST Overview
Intel® MAX® 10 devices support the IEEE Std.1149.1 (JTAG) boundary-scan testing
(BST).
When you perform BST, you can test pin connections without using physical test
probes and capture functional data during normal operation. The boundary-scan cells
(BSCs) in a device can force signals onto pins, or capture data from pins or core logic
signals. Forced test data is serially shifted in from the TDI pin to the BSCs. Captured
data is serially shifted out to the TDO pin for external comparison with expected
results.
Note: You can perform BST on Intel MAX 10 devices before, after, and during configuration.
Related Information
• Intel MAX 10 FPGA Configuration User Guide
Provides more information about JTAG in-system programming.
• IEEE 1149.1 JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing in Altera Devices
Provides more information on IEEE 1149.1 JTAG boundary-scan testing.
• JTAG BST Architecture on page 4
• JTAG Boundary-Scan Register on page 5
• BST Operation Control on page 7
• I/O Voltage Support in the JTAG Chain on page 10
• Enabling and Disabling JTAG BST Circuitry on page 11
• Guidelines for JTAG BST on page 12
• Boundary-Scan Description Language Support on page 13
Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Agilex, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, Intel, the Intel logo, MAX, Nios,
Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or
other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in
accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services
at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any
information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel
customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published
information and before placing orders for products or services.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
ISO
9001:2015
Registered
Page 4

UG-M10JTAG | 2019.05.10
Send Feedback
2. JTAG BST Architecture
Intel MAX 10 JTAG interface uses four pins, TDI, TDO, TMS, and TCK.
2.1. JTAG Pins
Table 1. JTAG Pin Descriptions
Pin Function Description
TDI
TDO
TMS
TCK
Serial input pin for:
• Instructions
• Test data
• Programming data
Serial output pin for:
• Instructions
• Test data
• Programming data
Input pin that provides the control signal to
determine the transitions of the TAP
controller state machine.
The clock input to the BST circuitry. —
•
TDI is sampled on the rising edge of TCK
•
TDI pins have internal weak pull-up resistors.
•
TDO is sampled on the falling edge of TCK
• The pin is tri-stated if data is not being shifted out of the
device.
•
TMS is sampled on the rising edge of TCK
•
TMS pins have internal weak pull-up resistors.
All the JTAG pins are powered by the V
of I/O bank 1B. In JTAG mode, the I/O pins
CCIO
support the LVTTL/LVCMOS 3.3-1.5V standards.
2.2. JTAG Circuitry Functional Model
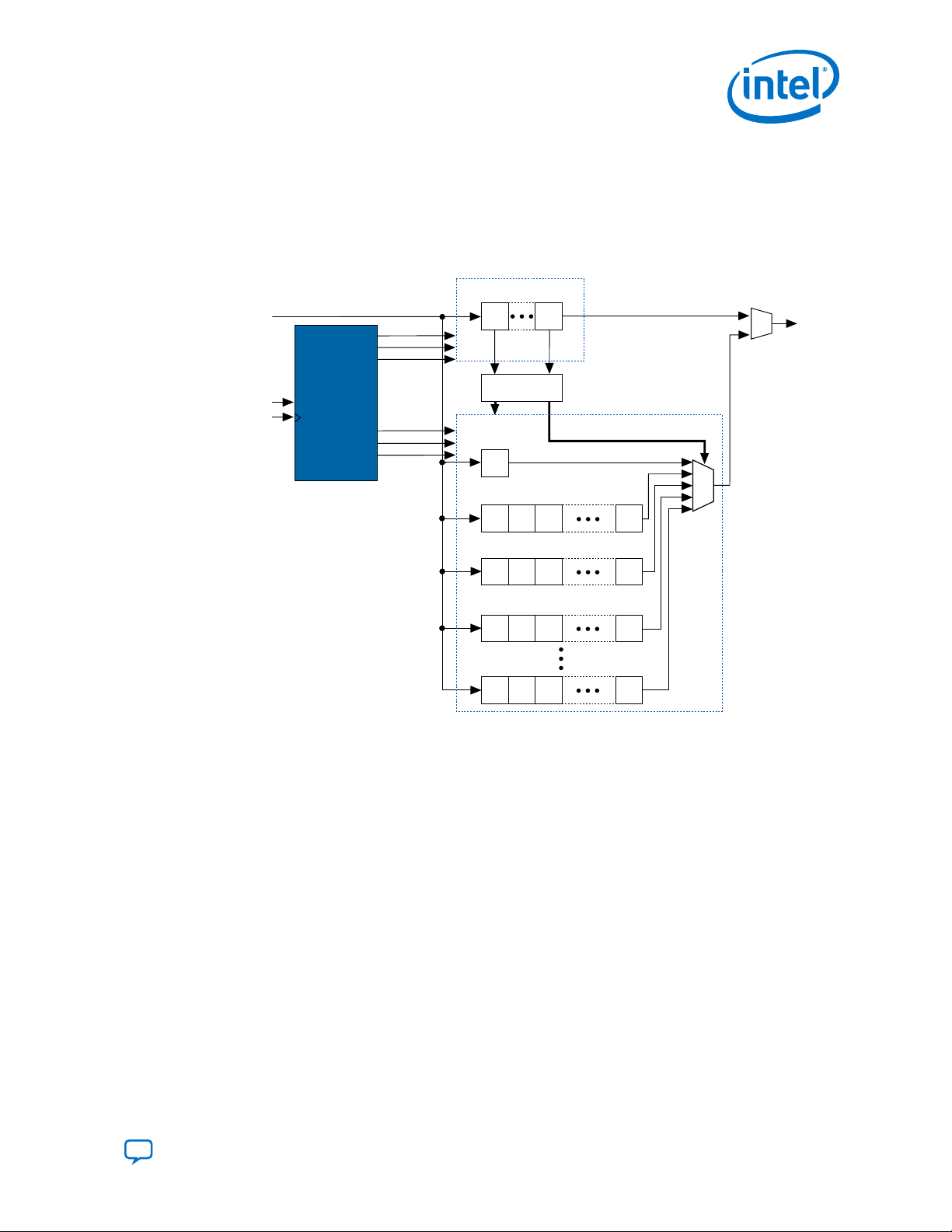
The JTAG BST circuitry requires the following registers:
• Instruction register—determines which action to perform and which data register
to access.
• Bypass register (1-bit long data register)—provides a minimum-length serial path
between the TDI and TDO pins.
• Boundary-scan register—shift register composed of all the BSCs of the device.
Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Agilex, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, Intel, the Intel logo, MAX, Nios,
Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or
other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in
accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services
at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any
information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel
customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published
information and before placing orders for products or services.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
ISO
9001:2015
Registered
Page 5
a
UPDATEIR
CLOCKIR
SHIFTIR
UPDATEDR
CLOCKDR
SHIFTDR
TDI
Instruction Register
Bypass Register
Boundary-Scan Register
Instruction Decode
TMS
TCK
TAP
Controller
ISP Registers
TDO
Data Registers
Device ID Register
2. JTAG BST Architecture
UG-M10JTAG | 2019.05.10
Figure 1. JTAG Circuitry Functional Model
• Test access port (TAP) controller—controls the JTAG BST.
•
TMS and TCK pins—operate the TAP controller.
•
TDI and TDO pins—provide the serial path for the data registers.
•
The TDI pin also provides data to the instruction register to generate the control logic for the data
registers.
2.3. JTAG Boundary-Scan Register
You can use the boundary-scan register to test external pin connections or to capture
internal data. The boundary-scan register is a large serial shift register that uses the
TDI pin as an input and the TDO pin as an output. The boundary-scan register consists
2.3.1. Boundary-Scan Cells in Intel MAX 10 I/O Pin
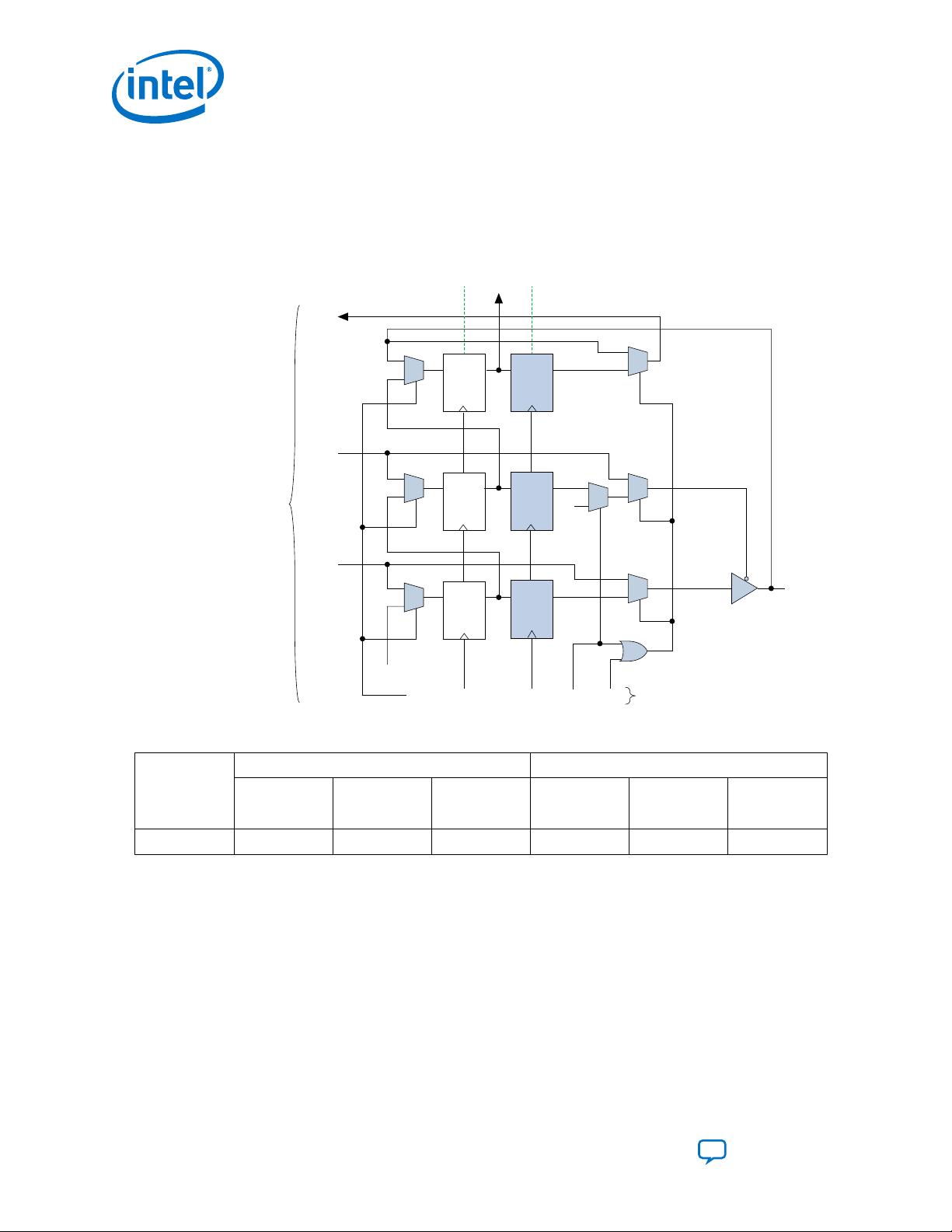
Send Feedback
of 3-bit peripheral elements that are associated with Intel MAX 10 I/O pins.
The Intel MAX 10 3-bit BSC contains the following registers:
•
Capture registers—connect to internal device data through OUTJ, OEJ, and
PIN_IN signals.
•
Update registers—connect to external data through PIN_OUT and PIN_OE signals.
Intel® MAX® 10 JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing User Guide
5
Page 6
0
1
OUTPUT
OE
INPUTINPUT
OUTPUT
OE
From or
to Device
I/O Cell
Circuitry or
Logic Array
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
PIN_OUT
INJ
OEJ
OUTJ
VCC
SDO
Pin
SHIFT
SDI
CLOCK HIGHZ MODE
PIN_OE
PIN_IN
Output
Buffer
Capture
Registers
Update
Registers
Global
Signals
UPDATE
D Q
D Q
D Q D Q
D Q
D Q
2. JTAG BST Architecture
UG-M10JTAG | 2019.05.10
Figure 2. User I/O BSC with JTAG BST Circuitry for Intel MAX 10 Devices
The TAP controller generates the global control signals internally for the JTAG BST registers, shift, clock,
and update. The instruction register generates the MODE signal.
The data signal path for the boundary-scan register runs from the serial data in (SDI) signal to the serial data
out (SDO) signal. The scan register begins at the TDI pin and ends at the TDO pin of the device.
Table 2. BSC Capture and Update Register for Intel MAX 10 Devices
Pin Type Captures Drives
User I/O
Note:
All VCC and GND pin types do not have BSCs.
Intel® MAX® 10 JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing User Guide
6
Output
Capture
Register
OUTJ OEJ PIN_IN PIN_OUT PIN_OE INJ
OE Capture
Register
Input Capture
Register
Output Update
Register
OE Update
Register
Input Update
Register
Send Feedback
Page 7
UG-M10JTAG | 2019.05.10
Send Feedback
3. BST Operation Control
Table 3. Boundary-Scan Register Length for Intel MAX 10 Devices
Device Boundary-Scan Register Length
10M01 603
10M02 603
10M04 1080
10M08 732
10M16 1632
10M25 1164
10M40 1314
10M50 1620
Table 4. IDCODE Information for 32-Bit Intel MAX 10 Devices
The MSB is on the left. The IDCODE LSB is always 1.
Device
Version (4 Bits) Part Number (16 Bits) Manufacturer Identity (11
10M01 0000 0010 0000 1111 0001 000 0110 1110 1
10M02 0000 0010 0000 1111 0001 000 0110 1110 1
10M04 0000 0010 0000 1111 0010 000 0110 1110 1
10M08 0000 0010 0000 1111 0011 000 0110 1110 1
10M16 0000 0010 0000 1111 0100 000 0110 1110 1
10M25 0000 0010 0000 1111 0101 000 0110 1110 1
10M40 0000 0010 0000 1111 0110 000 0110 1110 1
10M50 0000 0010 0000 1111 0111 000 0110 1110 1
IDCODE (32 Bits)
Bits)
3.1. JTAG IDCODE
The IDCODE is unique for each Intel MAX 10 device. Use this code to identify the
devices in a JTAG chain.
LSB (1 Bit)
Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Agilex, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, Intel, the Intel logo, MAX, Nios,
Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or
other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in
accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services
at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any
information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel
customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published
information and before placing orders for products or services.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
ISO
9001:2015
Registered
Page 8

3. BST Operation Control
UG-M10JTAG | 2019.05.10
Table 5. IDCODE Information for Intel MAX 10 Devices
Device Device
Supply Option
Single-supply 10M02
(All except
U324)
10M02
(U324)
10M04 0000 0011 0001 1000 1010 000 0110 1110 1
10M08 0000 0011 0001 1000 0010 000 0110 1110 1
10M16 0000 0011 0001 1000 0011 000 0110 1110 1
10M25 0000 0011 0001 1000 0100 000 0110 1110 1
10M40 0000 0011 0001 1000 1101 000 0110 1110 1
10M50 0000 0011 0001 1000 0101 000 0110 1110 1
Dual-supply 10M02 0000 0011 0001 0000 0001 000 0110 1110 1
10M04 0000 0011 0001 0000 1010 000 0110 1110 1
10M08 0000 0011 0001 0000 0010 000 0110 1110 1
10M16 0000 0011 0001 0000 0011 000 0110 1110 1
10M25 0000 0011 0001 0000 0100 000 0110 1110 1
10M40 0000 0011 0001 0000 1101 000 0110 1110 1
10M50 0000 0011 0001 0000 0101 000 0110 1110 1
Version (4
Bits)
0000 0011 0001 1000 0001 000 0110 1110 1
0000 0011 0001 1001 1010 000 0110 1110 1
Part Number (16 Bits) Manufacturer Identity
(11 Bits)
LSB (1
Bit)
3.2. JTAG Secure Mode
In JTAG secure mode, the device only allows SAMPLE/PRELOAD, BYPASS, EXTEST,
and IDCODE JTAG instructions.
Related Information
MAX 10 FPGA Configuration User Guide
Provides more information about the JTAG Secure Mode.
3.3. JTAG Private Instruction
Caution: Never invoke the following instruction codes. These instructions can damage the
device and render it unusable:
• 10 0100 0000
• 10 0011 0000
• 10 1110 0000
• 10 0011 0001
Intel® MAX® 10 JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing User Guide
8
Send Feedback
Page 9

3. BST Operation Control
UG-M10JTAG | 2019.05.10
3.4. JTAG Instructions
Instruction
Name
SAMPLE/
PRELOAD
EXTEST
(1)
BYPASS
USERCODE
IDCODE
(1)
HIGHZ
(1)
CLAMP
USER0
USER1
Instruction
Binary
00 0000 0101 • Permits an initial data pattern to be an output at the device pins.
• Allows you to capture and examine a snapshot of signals at the device pins if the
device is operating in normal mode.
00 0000 1111 • Forces test pattern at the output pins and capture the test results at the input pins.
• Allows you to test the external circuitry and board-level interconnects.
11 1111 1111 •
00 0000 0111 •
00 0000 0110 •
00 0000 1011 •
00 0000 1010 •
00 0000 1100 •
00 0000 1110 •
Places the 1-bit bypass register between the TDI and TDO pins.
• Allows the BST data to pass synchronously through target devices to adjacent
devices during normal device operation.
Places the 1-bit bypass register between the TDI and TDO pins.
•
Allows you to shift the USERCODE register out of the TDO pin serially.
Selects the IDCODE register and places it between the TDI and TDO pins.
•
Allows you to shift the IDCODE register out of the TDO pin serially.
Places the 1-bit bypass register between the TDI and TDO pins. The 1-bit bypass
register tri-states all the I/O pins.
• Allow the BST data to pass synchronously through target devices to adjacent
devices if device is operating in normal mode.
Places the 1-bit bypass register between the TDI and TDO pins. The 1-bit bypass
register holds I/O pins to a state defined by the data in the boundary-scan register.
• Allow the BST data to pass synchronously through target devices to adjacent
devices if device is operating in normal mode.
Allows you to define the scan chain between the TDI and TDO pins in the Intel MAX
10 logic array.
• Use this instruction for custom logic and JTAG interfaces.
Allows you to define the scan chain between the TDI and TDO pins in the Intel MAX
10 logic array.
• Use this instruction for custom logic and JTAG interfaces.
Description
(1)
HIGHZ, CLAMP, and EXTEST instructions do not disable weak pull-up resistors or bus hold
features.
Send Feedback
Intel® MAX® 10 JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing User Guide
9
Page 10

2.5-V
V
CCIO
1.8-V
V
CCIO
1.8-V
V
CCIO
TDI
TDO
Tester
Shift TDO to Level
Accepted by Tester
if Necessary
Must be 5.0-V
Tolerant
Must be 3.3-V
Tolerant
Must be 2.5-V
Tolerant
1.5-V
V
CCIO
Must be 1.8-V
Tolerant
Level
Shifter
3.3-V
V
CCIO
5.0-V
V
CCIO
UG-M10JTAG | 2019.05.10
Send Feedback
4. I/O Voltage Support in the JTAG Chain
A JTAG chain can contain several Intel FPGA and non-Intel FPGA devices.
The TDO pin of a device drives out at the voltage level according to the V
device. The devices can interface with each other although the devices may have
different V
For example, a device with 3.3-V V
CCIO
levels.
can drive to a device with 5.0-V V
CCIO
3.3 V meets the minimum VIH on transistor-to-transistor logic (TTL)-level input for the
5.0-V V
CCIO
device.
Intel MAX 10 devices can support 1.5-, 1.8-, 2.5-, or 3.3-V input levels, depending on
the V
voltage of I/O Bank 1B.
CCIO
To interface the TDI and TDO lines of the JTAG pins of devices that have different
V
levels, insert a level shifter between the devices. If possible, construct the JTAG
CCIO
chain where device with a higher V
V
level. In this setup, you only require a level shifter for shifting the TDO level to a
CCIO
level drives to a device with an equal or lower
CCIO
level JTAG tester accept.
Figure 3. JTAG Chain of Mixed Voltages and Level Shifters
CCIO
CCIO
of the
because
Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Agilex, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, Intel, the Intel logo, MAX, Nios,
Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or
other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in
accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services
at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any
information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel
customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published
information and before placing orders for products or services.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
ISO
9001:2015
Registered
Page 11
UG-M10JTAG | 2019.05.10
Send Feedback
5. Enabling and Disabling JTAG BST Circuitry
The JTAG BST circuitry in Intel MAX 10 devices is automatically enabled after the
power-up.
To ensure that you do not inadvertently enable the JTAG BST circuitry when it is not
required, disable the circuitry permanently with pin connections as listed in the
following table.
Table 6. Pin Connections to Permanently Disable the JTAG BST Circuitry in Intel MAX
10 Devices
JTAG Pins Connection to Disable
V
TMS
TCK
TDI
TDO
supply of Bank 1B
CCIO
GND
V
supply of Bank 1B
CCIO
Leave open
You must enable this circuitry only if you use the BST or in-system programming (ISP)
features.
Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Agilex, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, Intel, the Intel logo, MAX, Nios,
Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or
other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in
accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services
at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any
information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel
customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published
information and before placing orders for products or services.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
ISO
9001:2015
Registered
Page 12

UG-M10JTAG | 2019.05.10
Send Feedback
6. Guidelines for JTAG BST
Consider the following guidelines when you perform BST with the device:
•
If the “10...” pattern does not shift out of the instruction register through the TDO
pin during the first clock cycle of the SHIFT_IR state, the TAP controller did not
reach the proper state. To solve this problem, try one of the following procedures:
—
Verify that the TAP controller has reached the SHIFT_IR state correctly. To
advance the TAP controller to the SHIFT_IR state, return TAP controller to the
RESET state and send the 01100 code to the TMS pin.
—
Check the connections to the VCC, GND, JTAG, and dedicated configuration
pins on the device.
•
Perform a SAMPLE/PRELOAD test cycle before the first EXTEST test cycle to
ensure that known data is present at the device pins when you enter EXTEST
mode. If the OEJ update register contains 0, the data in the OUTJ update register
is driven out. The state must be known and correct to avoid contention with other
devices in the system.
•
To perform testing before configuration, hold the nCONGFIG pin low.
Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Agilex, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, Intel, the Intel logo, MAX, Nios,
Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or
other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in
accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services
at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any
information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel
customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published
information and before placing orders for products or services.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
ISO
9001:2015
Registered
Page 13

UG-M10JTAG | 2019.05.10
Send Feedback
7. Boundary-Scan Description Language Support
The BSDL—a subset of VHDL—provides a syntax that allows you to describe the
features of an IEEE Std. 1149.1 BST-capable device that can be tested. Test software
development systems then use the BSDL files for test generation, analysis, failure
diagnostics, and in-system programming.
Related Information
IEEE 1149.1 BSDL Files
Provides more information about BSC group definitions.
Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Agilex, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, Intel, the Intel logo, MAX, Nios,
Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or
other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in
accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services
at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any
information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel
customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published
information and before placing orders for products or services.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
ISO
9001:2015
Registered
Page 14

UG-M10JTAG | 2019.05.10
Send Feedback
A. Document Revision History for the Intel MAX 10 JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing User Guide
Document
Version
2019.05.10 • Renamed the document as Intel MAX 10 JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing User Guide.
• Added single-supply device "10M02 (U324)" in IDCODE Information for Intel MAX 10 Devices table.
• Updated single-supply device "10M02" to "10M02 (All except U324)" in IDCODE Information for
Intel MAX 10 Devices table.
•
Added references to TDI and TDO pins for description of forced test data and captured data in Intel
MAX 10 JTAG BST Overview chapter.
Date Version Changes
February 2017 2017.02.21 Rebranded as Intel.
May 2015 2015.05.04 Added note on about performing the boundary-scan testing in 'Overview'.
September 2014 2014.09.22 Initial release.
Changes
Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Agilex, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, Intel, the Intel logo, MAX, Nios,
Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or
other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in
accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services
at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any
information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel
customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published
information and before placing orders for products or services.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
ISO
9001:2015
Registered
 Loading...
Loading...