Page 1

Intel® Desktop Board
D865PCD
Technical Product Specification
April 2004
Order Number: C73314-001
The Intel® Desktop Board D865PCD may contain design defects or errors known as errata that may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current
characterized errata are documented in the Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Specification Update.
Page 2

Revision History
Revision Revision History Date
-001 First release of the Intel® Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product
Specification.
April 2004
This product specification applies to only standard Intel
®
Desktop Board D865PCD with BIOS
identifier RC86510A.86A.
Changes to this specification will be published in the Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Specification
Update before being incorporated into a revision of this document.
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED
BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN INTEL’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH
PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES
RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT,
COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. INTEL PRODUCTS ARE NOT INTENDED FOR USE IN
MEDICAL, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING APPLICATIONS.
Intel Corporation may have patents or pending patent applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property
rights that relate to the presented subject matter. The furnishing of documents and other materials and information does not
provide any license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any such patents, trademarks, copyrights, or other
intellectual property rights.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined.”
Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising
from future changes to them.
®
desktop boards may contain design defects or errors known as errata, which may cause the product to deviate from
Intel
published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an ordering number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be
obtained from:
Intel Corporation
P.O. Box 5937
Denver, CO 80217-9808
or call in North America 1-800-548-4725, Europe 44-0-1793-431-155, France 44-0-1793-421-777,
Germany 44-0-1793-421-333, other Countries 708-296-9333.
Intel, Pentium, and Celeron are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other
countries.
* Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright 2004, Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Page 3

Preface
This Technical Product Specification (TPS) specifies the board layout, components, connectors,
®
power and environmental requirements, and the BIOS for the Intel
describes the standard product and available manufacturing options.
Intended Audience
The TPS is intended to provide detailed, technical information about the Desktop Board D865PCD
and its components to the vendors, system integrators, and other engineers and technicians who
need this level of information. It is specifically not intended for general audiences.
What This Document Contains
Chapter Description
1 A description of the hardware used on the Desktop Board D865PCD
2 A map of the resources of the Desktop Board
3 The features supported by the BIOS Setup program
4 The contents of the BIOS Setup program’s menus and submenus
5 A description of the BIOS error messages, beep codes, and POST codes
Desktop Board D865PCD. It
Typographical Conventions
This section contains information about the conventions used in this specification. Not all of these
symbols and abbreviations appear in all specifications of this type.
Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE
✏
Notes call attention to important information.
INTEGRATOR’S NOTES
#
Integrator’s notes are used to call attention to information that may be useful to system
integrators.
CAUTION
Cautions are included to help you avoid damaging hardware or losing data.
iii
Page 4

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
WARNING
Warnings indicate conditions, which if not observed, can cause personal injury.
Other Common Notation
# Used after a signal name to identify an active-low signal (such as USBP0#)
(NxnX) When used in the description of a component, N indicates component type, xn are the relative
coordinates of its location on the Desktop Board D865PCD, and X is the instance of the
particular part at that general location. For example, J5J1 is a connector, located at 5J. It is
the first connector in the 5J area.
GB Gigabyte (1,073,741,824 bytes)
GB/sec Gigabytes per second
KB Kilobyte (1024 bytes)
Kbit Kilobit (1024 bits)
kbits/sec 1000 bits per second
MB Megabyte (1,048,576 bytes)
MB/sec Megabytes per second
Mbit Megabit (1,048,576 bits)
Mbit/sec Megabits per second
xxh An address or data value ending with a lowercase h indicates a hexadecimal value.
x.x V Volts. Voltages are DC unless otherwise specified.
* This symbol is used to indicate third-party brands and names that are the property of their
respective owners.
iv
Page 5

Contents
1 Product Description
1.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................12
1.1.1 Feature Summary ........................................................................................12
1.1.2 Board Layout................................................................................................13
1.1.3 Block Diagram..............................................................................................14
1.2 Online Support ...........................................................................................................15
1.3 Design Specifications .................................................................................................16
1.4 Processor ...................................................................................................................19
1.5 System Memory .........................................................................................................20
1.5.1 Memory Configurations ................................................................................22
1.6 Intel® 865P Chipset ....................................................................................................24
1.6.1 Universal 0.8 V / 1.5 V AGP 3.0 Connector..................................................24
1.6.2 USB..............................................................................................................25
1.6.3 IDE Support .................................................................................................26
1.6.4 Real-Time Clock, CMOS SRAM, and Battery...............................................26
1.7 I/O Controller..............................................................................................................27
1.7.1 Serial Port ....................................................................................................27
1.7.2 Parallel Port..................................................................................................27
1.7.3 Diskette Drive Controller ..............................................................................27
1.7.4 Keyboard and Mouse Interface ....................................................................28
1.8 Audio Subsystem........................................................................................................28
1.8.1 Realtek ALC202-based Audio Subsystem....................................................28
1.8.2 Audio Connectors.........................................................................................28
1.8.3 Audio Subsystem Software ..........................................................................29
1.9 LAN Subsystem..........................................................................................................29
1.9.1 Intel® 82562EZ Physical Layer Interface Device ..........................................29
1.9.2 RJ-45 LAN Connector with Integrated LEDs ................................................30
1.9.3 LAN Subsystem Software ............................................................................30
1.10 Chassis Intrusion and Detection .................................................................................30
1.11 Power Management ...................................................................................................30
1.11.1 ACPI.............................................................................................................31
1.11.2 Hardware Support ........................................................................................33
2 Technical Reference
2.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................37
2.2 Memory Map ..............................................................................................................37
2.3 DMA Channels ...........................................................................................................38
2.4 Fixed I/O Map.............................................................................................................38
2.5 PCI Configuration Space Map ....................................................................................39
2.6 Interrupts ....................................................................................................................40
2.7 PCI Interrupt Routing Map..........................................................................................41
2.8 Connectors.................................................................................................................43
2.8.1 Back Panel Connectors................................................................................44
v
Page 6

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
2.8.2 Internal I/O Connectors ................................................................................45
2.8.3 External I/O Connectors...............................................................................52
2.9 Jumper Blocks............................................................................................................56
2.9.1 Front Panel Audio Connector/Jumper Block.................................................56
2.9.2 BIOS Setup Configuration Jumper Block......................................................57
2.10 Mechanical Considerations.........................................................................................58
2.10.1 Form Factor .................................................................................................58
2.10.2 I/O Shield .....................................................................................................59
2.11 Electrical Considerations ............................................................................................60
2.11.1 DC Loading ..................................................................................................60
2.11.2 Add-in Board Considerations........................................................................60
2.11.3 Fan Connector Current Capability ................................................................60
2.11.4 Power Supply Considerations ......................................................................61
2.12 Thermal Considerations..............................................................................................61
2.13 Reliability ....................................................................................................................63
2.14 Environmental ............................................................................................................64
2.15 Regulatory Compliance ..............................................................................................65
2.15.1 Safety Regulations.......................................................................................65
2.15.2 EMC Regulations .........................................................................................65
2.15.3 European Union Declaration of Conformity Statement .................................66
2.15.4 Product Ecology Statements ........................................................................67
2.15.5 Product Certification Markings (Board Level) ...............................................67
3 Overview of BIOS Features
3.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................69
3.2 BIOS Flash Memory Organization ..............................................................................69
3.3 Resource Configuration..............................................................................................70
3.3.1 PCI Autoconfiguration ..................................................................................70
3.3.2 PCI IDE Support...........................................................................................70
3.4 System Management BIOS (SMBIOS).......................................................................71
3.5 Legacy USB Support ..................................................................................................71
3.6 BIOS Updates ............................................................................................................72
3.6.1 Language Support........................................................................................72
3.6.2 Custom Splash Screen.................................................................................73
3.7 Recovering BIOS Data ...............................................................................................73
3.8 Boot Options...............................................................................................................74
3.8.1 CD-ROM Boot..............................................................................................74
3.8.2 Network Boot................................................................................................74
3.8.3 Booting Without Attached Devices ...............................................................74
3.8.4 Changing the Default Boot Device During POST..........................................74
3.9 Fast Booting Systems with Intel® Rapid BIOS Boot....................................................75
3.9.1 Peripheral Selection and Configuration ........................................................75
3.9.2 Intel Rapid BIOS Boot ..................................................................................75
3.10 BIOS Security Features..............................................................................................76
vi
Page 7

4 BIOS Setup Program
4.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................77
4.2 Maintenance Menu.....................................................................................................78
4.3 Main Menu..................................................................................................................79
4.4 Advanced Menu..........................................................................................................80
4.4.1 PCI Configuration Submenu.........................................................................81
4.4.2 Boot Configuration Submenu .......................................................................82
4.4.3 Peripheral Configuration Submenu...............................................................83
4.4.4 Drive Configuration Submenu ......................................................................85
4.4.5 Floppy Configuration Submenu....................................................................88
4.4.6 Event Log Configuration Submenu...............................................................89
4.4.7 Video Configuration Submenu......................................................................90
4.4.8 USB Configuration Submenu .......................................................................91
4.4.9 Chipset Configuration Submenu...................................................................92
4.5 Security Menu ............................................................................................................94
4.6 Power Menu ...............................................................................................................95
4.6.1 ACPI Submenu ............................................................................................95
4.7 Boot Menu..................................................................................................................96
4.7.1 Boot Device Priority Submenu......................................................................97
4.7.2 Hard Disk Drives Submenu ..........................................................................98
4.7.3 Removable Devices Submenu .....................................................................98
4.7.4 ATAPI CD-ROM Drives Submenu................................................................99
4.8 Exit Menu ...................................................................................................................99
Contents
5 Error Messages and Beep Codes
5.1 BIOS Error Messages...............................................................................................101
5.2 Port 80h POST Codes..............................................................................................103
5.3 Bus Initialization Checkpoints ...................................................................................107
5.4 Speaker ...................................................................................................................108
5.5 BIOS Beep Codes ....................................................................................................108
vii
Page 8

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
Figures
1. Desktop Board D865PCD Components......................................................................13
2. Block Diagram ............................................................................................................14
3. Memory Channel Configuration ..................................................................................22
4. Example of Dual Channel Configuration with Dynamic Mode .....................................23
5. Example of Single Channel Configuration with Dynamic Mode...................................23
6. Example of Single Channel Configuration without Dynamic Mode.............................24
7. LAN Connector LED Locations...................................................................................30
8. Back Panel Connectors ..............................................................................................44
9. Audio Connectors .......................................................................................................46
10. Power and Hardware Control Connectors ..................................................................48
11. D865PCD Add-in Board and Peripheral Interface Connectors....................................51
12. External I/O Connectors .............................................................................................52
13. Connection Diagram for Front Panel Connector .........................................................53
14. Connection Diagram for Front Panel USB Connector.................................................55
15. Location of the Jumper Blocks....................................................................................56
16. Desktop Board D865PCD Dimensions .......................................................................58
17. I/O Shield Dimensions ................................................................................................59
18. Localized High Temperature Zones............................................................................62
Tables
1. Feature Summary.......................................................................................................12
2. Specifications .............................................................................................................16
3. Supported System Bus Frequency and Memory Speed Combinations.......................20
4. Supported Memory Configurations .............................................................................21
5. Characteristics of Dual/Single Channel Configuration with/without Dynamic Mode.....22
6. LAN Connector LED States........................................................................................30
7. Effects of Pressing the Power Switch .........................................................................31
8. Power States and Targeted System Power ................................................................32
9. Wake-up Devices and Events.....................................................................................32
10. System Memory Map..................................................................................................37
11. DMA Channels ...........................................................................................................38
12. I/O Map ......................................................................................................................38
13. PCI Configuration Space Map ....................................................................................39
14. Interrupts ....................................................................................................................40
15. PCI Interrupt Routing Map..........................................................................................42
16. ATAPI CD-ROM Connector ........................................................................................47
17. Front Panel Audio Connector .....................................................................................47
18. Rear Chassis Fan Connector .....................................................................................49
19. ATX12V Power Connector..........................................................................................49
20. Processor Fan Connector...........................................................................................49
21. Main Power Connector...............................................................................................49
22. Front Chassis Fan Connector.....................................................................................50
23. Chassis Intrusion Connector.......................................................................................50
24. Auxiliary Front Panel Power/Sleep/Message-Waiting LED Connector ........................53
25. Front Panel Connector ...............................................................................................53
viii
Page 9

Contents
26. States for a One-Color Power LED.............................................................................54
27. States for a Two-Color Power LED.............................................................................54
28. Front Panel Audio Connector/Jumper Block...............................................................57
29. BIOS Setup Configuration Jumper Settings................................................................57
30. DC Loading Characteristics........................................................................................60
31. Fan Connector Current Capability ..............................................................................60
32. Thermal Considerations for Components ...................................................................63
33. Desktop Board D865PCD Environmental Specifications ............................................64
34. Safety Regulations .....................................................................................................65
35. EMC Regulations........................................................................................................65
36. Product Certification Markings....................................................................................67
37. Boot Device Menu Options.........................................................................................74
38. Supervisor and User Password Functions..................................................................76
39. BIOS Setup Program Menu Bar .................................................................................77
40. BIOS Setup Program Function Keys ..........................................................................78
41. Maintenance Menu.....................................................................................................78
42. Main Menu..................................................................................................................79
43. Advanced Menu..........................................................................................................80
44. PCI Configuration Submenu.......................................................................................81
45. Boot Configuration Submenu......................................................................................82
46. Peripheral Configuration Submenu.............................................................................83
47. Drive Configuration Submenu.....................................................................................85
48. PATA Submenus........................................................................................................87
49. Floppy Configuration Submenu ..................................................................................88
50. Event Log Configuration Submenu.............................................................................89
51. Video Configuration Submenu....................................................................................90
52. USB Configuration Submenu......................................................................................91
53. Chipset Configuration Submenu.................................................................................92
54. Security Menu ............................................................................................................94
55. Power Menu ...............................................................................................................95
56. ACPI Submenu...........................................................................................................95
57. Boot Menu..................................................................................................................96
58. Boot Device Priority Submenu....................................................................................97
59. Hard Disk Drives Submenu ........................................................................................98
60. Removable Devices Submenu....................................................................................98
61. ATAPI CD-ROM Drives Submenu ..............................................................................99
62. Exit Menu ...................................................................................................................99
63. BIOS Error Messages...............................................................................................101
64. Uncompressed INIT Code Checkpoints....................................................................103
65. Boot Block Recovery Code Checkpoints ..................................................................103
66. Runtime Code Uncompressed in F000 Shadow RAM ..............................................104
67. Bus Initialization Checkpoints ...................................................................................107
68. Upper Nibble High Byte Functions............................................................................107
69. Lower Nibble High Byte Functions............................................................................108
70. Beep Codes..............................................................................................................109
ix
Page 10

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
x
Page 11

1 Product Description
What This Chapter Contains
1.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................12
1.2 Online Support ...........................................................................................................15
1.3 Design Specifications .................................................................................................16
1.4 Processor ...................................................................................................................19
1.5 System Memory .........................................................................................................20
1.6 Intel® 865P Chipset ....................................................................................................24
1.7 I/O Controller..............................................................................................................27
1.8 Audio Subsystem........................................................................................................28
1.9 LAN Subsystem..........................................................................................................29
1.10 Chassis Intrusion and Detection .................................................................................30
1.11 Power Management ...................................................................................................30
11
Page 12
Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
1.1 Overview
1.1.1 Feature Summary
Table 1 summarizes the major features of the Desktop Board D865PCD.
Table 1. Feature Summary
Form Factor
Processor
Memory
Chipset
Video
Audio
I/O Control
USB
Peripheral
Interfaces
LAN Support
BIOS
Instantly Available
PC Technology
Expansion
Capabilities
For information about
Available configurations for the Desktop Boards D865PCD Section 1.2, page 16
The board’s compliance level with ACPI, Plug and Play, and SMBIOS Section 1.3, page 16
microATX (9.60 inches by 9.60 inches [243.84 millimeters by 243.84 millimeters])
• Support for an Intel
400 or 533 MHz system bus
• Support for an Intel
400 MHz system bus
• Two 184-pin DDR SDRAM Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM) sockets
• Support for DDR 333 and DDR 266 DIMMs
• Support for up to 2 GB of system memory
®
Intel
865P Chipset, consisting of:
®
• Intel
• Intel
• 4 Mbit Firmware Hub (FWH)
Universal 0.8 V / 1.5 V AGP 3.0 connector (with integrated retention mechanism)
supporting 1x, 4x, and 8x AGP cards or an AGP Digital Display (ADD) card
Audio subsystem using the Realtek ALC202 codec
LPC Bus I/O controller
Support for USB 2.0 devices
• Six USB ports
• One serial port
• One parallel port
• Two Parallel ATA IDE interfaces with UDMA 33, ATA-66/100 support
• One diskette drive interface
• PS/2* keyboard and mouse ports
10/100 Mbits/sec LAN subsystem using the Intel
(PLC) device
• Intel/AMI BIOS (resident in the 4 Mbit FWH)
• Support for Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI), Plug and Play,
• Support for PCI Local Bus Specification Revision 2.2
• Suspend to RAM support
• Wake on PCI, RS-232, front panel, PS/2 devices, and USB ports
Three PCI bus add-in card connectors (SMBus routed to PCI bus connector 2)
82865P Memory Controller Hub (MCH)
®
82801EB I/O Controller Hub (ICH5)
and SMBIOS
®
Pentium® 4 processor in an mPGA478 socket with a
®
Celeron® processor in an mPGA478 socket with a
®
82562EZ Platform LAN Connect
Refer to
12
Page 13
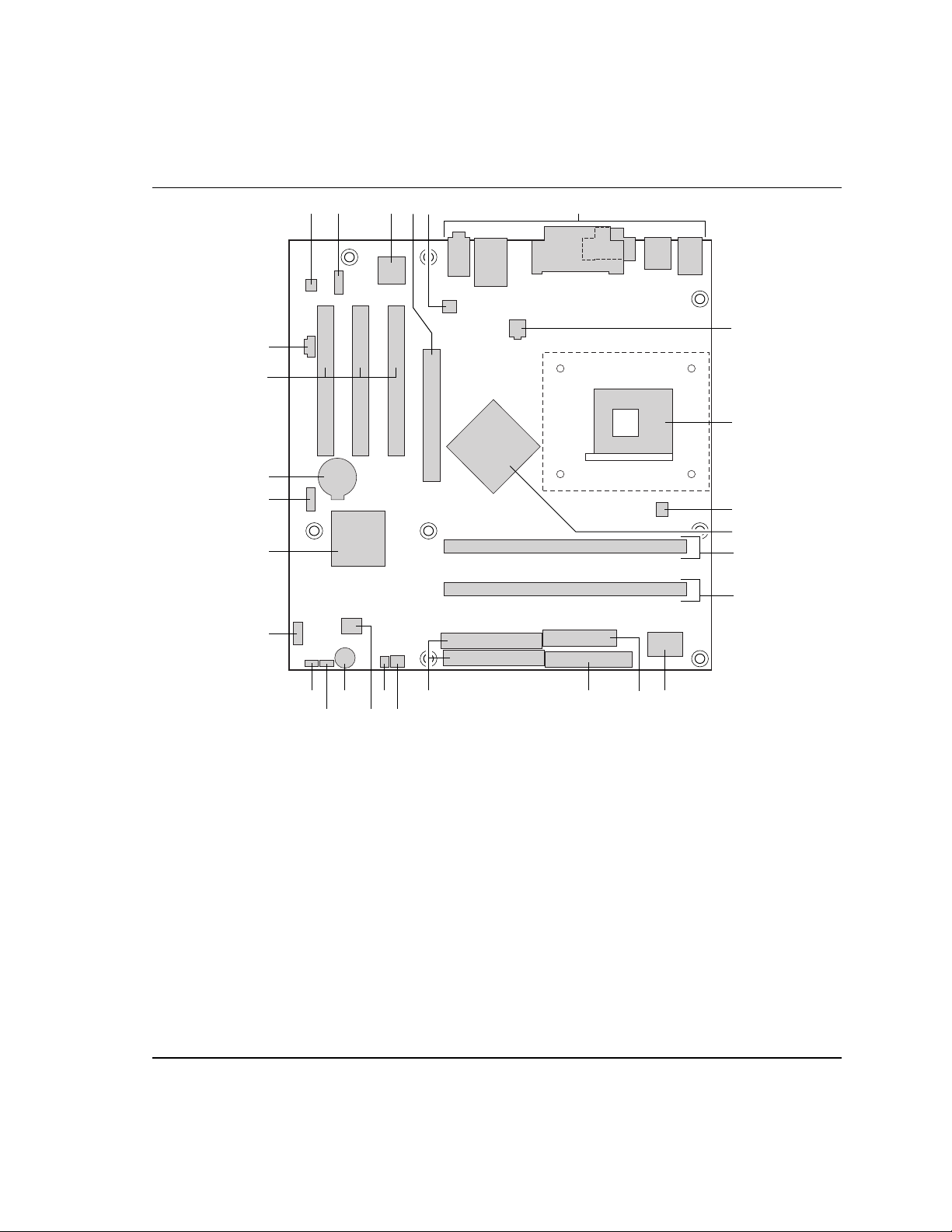
1.1.2 Board Layout
Figure 1 shows the location of the major components.
Product Description
BB
AA
W
B
A
C D
E
F
G
H
Z
Y
I
J
X
K
L
PRTV
U S
A Audio codec O Diskette drive connector
B Front panel audio connector P Parallel ATE IDE connectors
C Ethernet PLC device (optional) Q Front chassis fan connector
D AGP connector R Chassis intrusion connector
E Rear chassis fan connector S 4 Mbit Firmware Hub (FWH)
F Back panel connectors T Speaker
G +12V power connector (ATX12V) U BIOS Setup configuration jumper block
H mPGA478 processor socket V Auxiliary front panel power LED connector
I Processor fan connector W Front panel connector
J Intel 82865P MCH X Intel 82801EB I/O Controller Hub (ICH5)
K DIMM Channel A socket Y Front panel USB connector
L DIMM Channel B socket Z Battery
M I/O controller AA PCI bus add-in card connectors
N Power connector BB ATAPI CD-ROM connector
Q
ON
M
OM17040
Figure 1. Desktop Board D865PCD Components
13
Page 14
Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
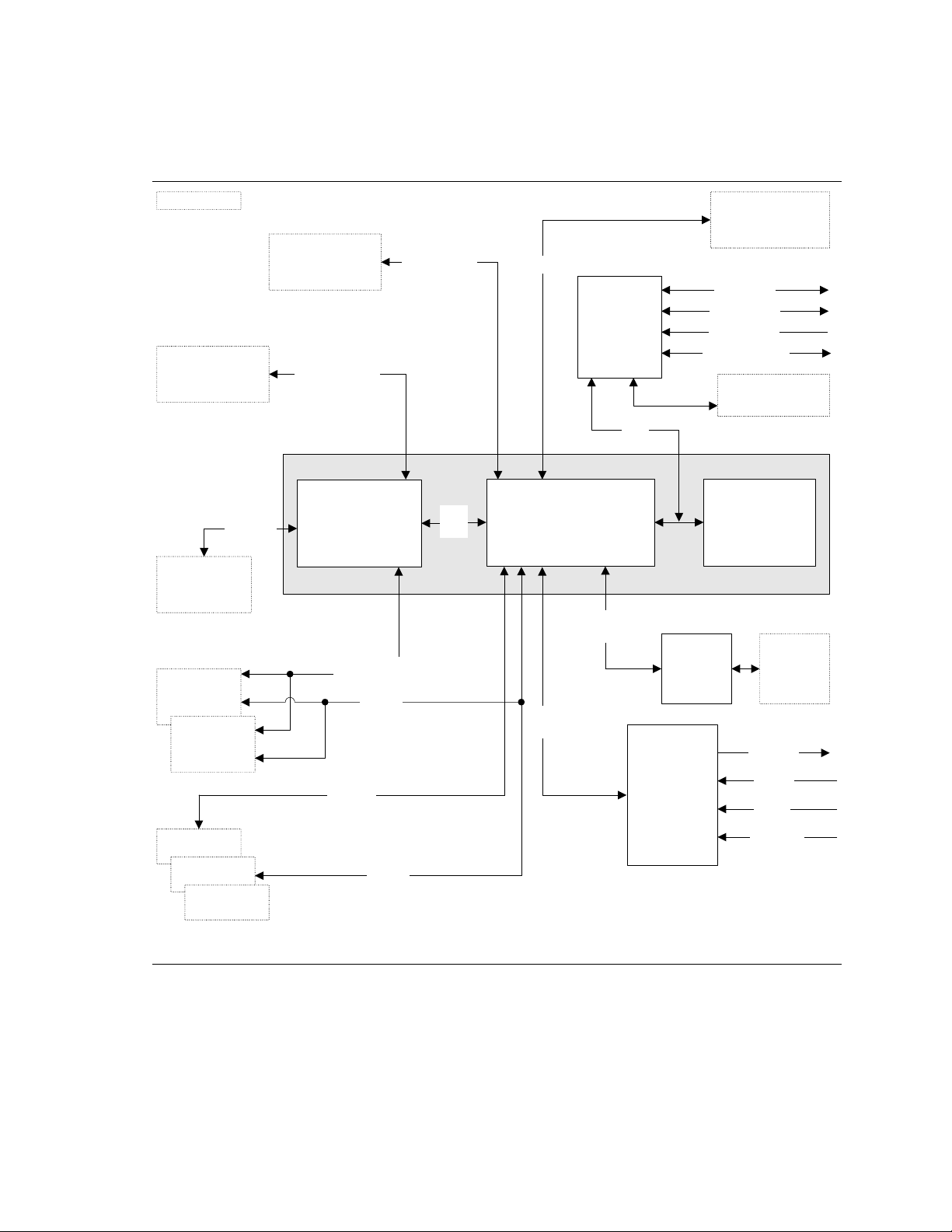
1.1.3 Block Diagram
Figure 2 is a block diagram of the major functional areas of the board.
mPGA478
Processor Socket
AGP
Interface
Universal 0.8/
1.5 V AGP 3.0
Connector
Channel A
DIMM
Channel B
DIMM
= connector or socket
Parallel ATA IDE
Connectors (2)
System Bus
(400/533 MHz)
Intel 82865P
Memory Controller
Hub (MCH)
Dual-Channel
Memory Bus
SMBus
Parallel ATA
IDE Interface
AHA
Bus
USB
LPC Bus
Controller
Intel 82801EB
I/O Controller Hub
(ICH5)
CSMA/CD
Unit Interface
AC
Link
I/O
LPC
Bus
Back Panel/
Front Panel
USB Ports
Serial Port
Parallel Port
PS/2 Mouse
PS/2 Keyboard
Diskette Drive
Connector
4 Mbit
Firmware Hub
(FWH)
Intel 865P Chipset
10/100
LAN PLC
Line Out
LAN
Connector
14
PCI Slot 1
PCI Slot 2
PCI Slot 3
PCI Bus
SMBus
Figure 2. Block Diagram
Realtek
ALC202
Audio Codec
Line In
Mic In
CD-ROM
OM17046
Page 15

1.2 Online Support
To find information about… Visit this World Wide Web site:
Intel Desktop Board D865PCD under
“Desktop Board Products” or “Desktop
Board Support”
Available configurations for the Desktop
Board D865PCD
Processor data sheets http://www.intel.com/design/litcentr
ICH5 addressing http://developer.intel.com/design/chipsets/datashts
Custom splash screens http://intel.com/design/motherbd/gen_indx.htm
Audio software and utilities http://www.intel.com/design/motherbd
LAN software and drivers http://www.intel.com/design/motherbd
Product Description
http://www.intel.com/design/motherbd
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop
http://developer.intel.com/design/motherbd/cd/cd_available.htm
15
Page 16
Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
1.3 Design Specifications
Table 2 lists the specifications applicable to the Desktop Board D865PCD.
Table 2. Specifications
Reference
Name
AC ’97 Audio Codec ’97 Revision 2.2,
ACPI Advanced Configuration and
AGP Accelerated Graphics Port
AMI BIOS AMIBIOS Desktop Core 8.0 AMIBIOS 8.0,
ASF Alert Standard Format (ASF)
ATA/
ATAPI-5
ATX ATX Specification Version 2.03,
ATX12V ATX/ATX12V Power Supply
BIS Boot Integrity Services (BIS)
Specification
Title
Power Interface
Specification
Interface Specification
Specification
Information Technology-AT
Attachment with Packet
Interface - 5 (ATA/ATAPI-5)
Design Guide
Application Programming
Interface (API)
Version, Revision Date,
and Ownership
September 2000,
Intel Corporation.
Version 2.0,
July 27, 2000,
Compaq Computer
Corporation,
Intel Corporation,
Microsoft Corporation,
Phoenix Technologies
Limited, and
Toshiba Corporation.
Revision 3.0,
September 2002,
Intel Corporation.
2001,
American Megatrends, Inc.
Version 1.03,
June 20, 2001,
DMTF,
Intel Corporation.
Revision 3,
February 29, 2000,
Contact: T13 Chair,
Seagate Technology.
December 1998,
Intel Corporation.
Version 1.2,
August 2000,
Intel Corporation.
Version 1.0,
August 4, 1999,
Intel Corporation.
The information is
available from…
ftp://download.intel.com/labs/
media/audio/download/ac97r
22.pdf
http://www.acpi.info/spec.htm
http://www.agpforum.org/spec
s_specs.htm
http://www.ami.com/support/d
oc/amibios8.pdf
http://www.dmtf.org/standards
/documents/ASF/DSP0114.p
df
http://www.t13.org
http://www.formfactors.org/de
veloper/specs/atx/atxspecs.ht
m
http://www.formfactors.org/de
veloper/specs/atx/atxspecs.ht
m
http://www.intel.com/labs/man
age/wfm/wfmspecs.htm
continued
16
Page 17
Table 2. Specifications (continued)
Reference
Name
DDR
SDRAM
EHCI
EPP IEEE Std 1284.1-1997
El Torito Bootable CD-ROM
LPC Low Pin Count Interface
MicroATX microATX Motherboard
PCI PCI Local Bus
PCI Bus Power
Plug and
Play
Specification
Title
Double Data Rate (DDR)
SDRAM Specification
Design Specification for
a 184 Pin DDR
Unbuffered DIMM
®
JEDEC DDR
Intel
200/266 Unbuffered
DIMM Specification
Addendum
Enhanced Host
Controller Interface
Specification for
Universal Serial Bus
(Enhanced Parallel Port)
Format Specification
Specification
Interface Specification
Specification
Management Interface
Specification
Plug and Play BIOS
Specification
Version, Revision Date and
Ownership
Version 1.0,
June 2000,
JEDEC Solid State Technology
Association.
Revision 1.0,
October 2001,
JEDEC Solid State Technology
Association.
Revision 0.9,
September 27, 2001,
Intel Corporation.
Revision 1.0,
March 12, 2002,
Intel Corporation.
Version 1.7,
1997,
Institute of Electrical and
Electronic Engineers.
Version 1.0,
January 25, 1995,
Phoenix Technologies Limited
and International Business
Machines Corporation.
Revision 1.0,
September 29, 1997,
Intel Corporation.
Version 1.0,
December 1997,
Intel Corporation.
Revision 2.2,
December 18, 1998,
PCI Special Interest Group.
Revision 1.1,
December 18, 1998,
PCI Special Interest Group.
Version 1.0a,
May 5, 1994,
Compaq Computer Corporation,
Phoenix Technologies Limited,
and Intel Corporation.
Product Description
The information is
available from…
http://www.jedec.org/
http://www.jedec.org/
http://developer.intel.com/t
echnology/memory/index.ht
m
http://developer.intel.com/t
echnology/usb/download/e
hci-r10.pdf
http://standards.ieee.org/re
ading/ieee/std_public/descr
iption/busarch/1284.11997_desc.html
http://www.phoenix.com/res
ources/specs-cdrom.pdf
http://www.intel.com/design
/chipsets/industry/lpc.htm
http://www.formfactors.org/
developer/specs/microatx/
microatxspecs.htm
http://www.pcisig.com/speci
fications
http://www.pcisig.com/speci
fications
http://www.microsoft.com/h
wdev/tech/PnP/default.asp
continued
17
Page 18
Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
Table 2. Specifications (continued)
Reference
Name
PXE Preboot Execution
SFX SFX/SFX12V Power
SMBIOS System Management
TFX12V TFX12V Power Supply
UHCI Universal Host Controller
USB Universal Serial Bus
WfM Wired for Management
Specification
Title
Environment
Supply Design Guide
BIOS
Design Guide
Interface Design Guide
Specification
Baseline
Version, Revision Date
and Ownership
Version 2.1,
September 20, 1999,
Intel Corporation.
Version 2.0,
May 2001,
Intel Corporation.
Version 2.3.1,
March 16, 1999,
American Megatrends
Incorporated,
Award Software International
Incorporated,
Compaq Computer Corporation,
Dell Computer Corporation,
Hewlett-Packard Company,
Intel Corporation,
International Business Machines
Corporation,
Phoenix Technologies Limited,
and SystemSoft Corporation.
Revision 1.01,
May 2002,
Intel Corporation.
Revision 1.1,
March 1996,
Intel Corporation.
Revision 2.0,
April 27, 2000,
Compaq Computer Corporation,
Hewlett-Packard Company,
Lucent Technologies Inc.,
Intel Corporation,
Microsoft Corporation,
NEC Corporation, and
Koninklijke Philips Electronics
N.V.
Version 2.0,
December 18, 1998,
Intel Corporation.
The information is
available from…
ftp://download.intel.com/lab
s/manage/wfm/download/p
xespec.pdf
http://www.formfactors.org/
developer/specs/sfx/sfx12v.
pdf
http://www.dmtf.org/downlo
ad/standards/DSP0119.pdf
http://www.formfactors.org/
developer/specs/tfx12v/tfx1
2v_psdg_101.pdf
http://developer.intel.com/d
esign/USB/UHCI11D.htm
http://www.usb.org/develop
ers/docs
http://www.intel.com/labs/m
anage/wfm/wfmspecs.htm
18
Page 19
Product Description
1.4 Processor
NOTE
✏
Refer to Thermal Considerations (Section 2.12, page 61) for important information when using an
®
Intel Pentium 4 processor operating above 2.80 GHz with this Intel
The board is designed to support the following:
• Intel Pentium
4 processors in an mPGA478 processor socket with a 400 or 533 MHz system
bus
• Intel Celeron processors in an mPGA478 processor socket with a 400 MHz system bus
See the Intel web site listed below for the most up-to-date list of supported processors.
For information about… Refer to:
Supported processors for the D865PCD board http://www.intel.com/design/motherbd/cd/cd_proc.htm
CAUTION
Use only the processors listed on web site above. Use of unsupported processors can damage the
board, the processor, and the power supply.
desktop board.
INTEGRATOR’S NOTES
#
• Use only ATX12V-, SFX12V-, or TFX12V-compliant power supplies. ATX12V, SFX12V, and
TFX12V power supplies have an additional power lead that provides required supplemental
power for the processor. Always connect the 20-pin and 4-pin leads of ATX12V, SFX12V, and
TFX12V power supplies to the corresponding connectors on the desktop board, otherwise the
board will not boot.
• Do not use a standard ATX power supply. The board will not boot with a standard ATX power
supply.
• Refer to Table 3 on page 20 for a list of supported system bus frequency and memory speed
combinations.
For information about Refer to
Power supply connectors Section 2.8.2.2, page 46
19
Page 20

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
1.5 System Memory
The board has two DIMM sockets and supports the following memory features:
• 2.5 V (only) 184-pin DDR SDRAM DIMMs with gold-plated contacts
• Unbuffered, single-sided or double-sided DIMMs with the following restriction:
Double-sided DIMMS with x16 organization are not supported.
• 2 GB maximum total system memory
• Minimum total system memory: 64 MB
• Non-ECC DIMMs
• Serial Presence Detect
• DDR333 and DDR266 SDRAM DIMMs
Table 3 lists the supported system bus frequency and memory speed combinations.
Table 3. Supported System Bus Frequency and Memory Speed Combinations
To use this type of DIMM… The processor's system bus frequency must be…
DDR333 533 MHz
DDR266 533 or 400 MHz
✏ NOTES
• Remove the AGP video card before installing or upgrading memory to avoid interference with
the memory retention mechanism.
• To be fully compliant with all applicable DDR SDRAM memory specifications, the board
should be populated with DIMMs that support the Serial Presence Detect (SPD) data
structure. This allows the BIOS to read the SPD data and program the chipset to accurately
configure memory settings for optimum performance. If non-SPD memory is installed, the
BIOS will attempt to correctly configure the memory settings, but performance and reliability
may be impacted or the DIMMs may not function under the determined frequency.
For information about Refer to
Obtaining DDR SDRAM specifications Section 1.3, page 16
20
Page 21
Product Description
Table 4 lists the supported DIMM configurations.
Table 4. Supported Memory Configurations
DIMM
Capacity
64 MB SS 64 Mbit 8 M x 8/empty 8
64 MB SS 128 Mbit 8 M x 16/empty 4
128 MB DS 64 Mbit 8 M x 8/8 M x 8 16
128 MB SS 128 Mbit 16 M x 8/empty 8
128 MB SS 256 Mbit 16 M x 16/empty 4
256 MB DS 128 Mbit 16 M x 8/16 M x 8 16
256 MB SS 256 Mbit 32 M x 8/empty 8
256 MB SS 512 Mbit 32 M x 16/empty 4
512 MB DS 256 Mbit 32 M x 8/32 M x 8 16
512 MB SS 512 Mbit 64 M x 8/empty 8
1024 MB DS 512 Mbit 64 M x 8/64 M x 8 16
Note: In the second column, “DS” refers to double-sided memory modules (containing two rows of DDR SDRAM) and “SS”
refers to single-sided memory modules (containing one row of DDR SDRAM).
Configuration
DDR SDRAM
Density
DDR SDRAM Organization
Front-side/Back-side
Number of DDR
SDRAM Devices
21
Page 22
Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
1.5.1 Memory Configurations
The Intel 82865P MCH component provides two features for enhancing memory throughput:
• Dual Channel memory interface. The board has two memory channels, each with a single
DIMM socket, as shown in Figure 3
• Dynamic Addressing Mode. Dynamic mode minimizes overhead by reducing memory
accesses
Table 5 summarizes the characteristics of Dual and Single Channel configurations with and
without the use of Dynamic Mode.
Table 5. Characteristics of Dual/Single Channel Configuration with/without Dynamic Mode
Throughput
Level
Highest Dual Channel with Dynamic Mode DIMMs matched
Lowest
Configuration
Single Channel with Dynamic Mode Single DIMM
Single Channel without Dynamic Mode DIMMs not matched
Characteristics
(Example configuration shown in Figure 4)
(Example configuration shown in Figure 5)
(Example configuration shown in Figure 6)
22
Channel A DIMM
Channel B, DIMM
Figure 3. Memory Channel Configuration
OM17042
Page 23
Product Description
Single Channel Configuration without Dynamic Mode
(DIMMs not matched)
Channel A DIMM Channel B DIMM
Throughput
Level
Highest Dual Channel with Dynamic Mode DIMMs matched
Lowest
Configuration
Single Channel with Dynamic Mode Single DIMM
Single Channel without Dynamic Mode DIMMs not matched
Intel
82865P
MCH
Characteristics
Figure 4. Example of Dual Channel Configuration with Dynamic Mode
Single Channel Configuration with Dynamic Mode
(Single DIMM)
OM17043
Channel A DIMM Channel B DIMM
Throughput
Level
Highest Dual Channel with Dynamic Mode DIMMs matched
Lowest
Configuration
Single Channel with Dynamic Mode Single DIMM
Single Channel without Dynamic Mode DIMMs not matched
Intel
82865P
MCH
Characteristics
Figure 5. Example of Single Channel Configuration with Dynamic Mode
OM17044
23
Page 24
Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
Dual Channel Configuration with Dynamic Mode
(DIMMs matched)
Channel A DIMM Channel B DIMM
Throughput
Level
Highest Dual Channel with Dynamic Mode DIMMs matched
Lowest
Figure 6. Example of Single Channel Configuration without Dynamic Mode
Configuration
Single Channel with Dynamic Mode Single DIMM
Single Channel without Dynamic Mode DIMMs not matched
Intel
82865P
MCH
Characteristics
1.6 Intel® 865P Chipset
The Intel 865P chipset consists of the following devices:
• Intel 82865P Memory Controller Hub (MCH) with Accelerated Hub Architecture (AHA) bus
• Intel 82801EB I/O Controller Hub (ICH5) with AHA bus
• Firmware Hub (FWH)
OM17045
The MCH is a centralized controller for the system bus, the memory bus, the AGP bus, and the
Accelerated Hub Architecture interface. The ICH5 is a centralized controller for the board’s I/O
paths. The FWH provides the nonvolatile storage of the BIOS.
For information about Refer to
The Intel 865P chipset http://developer.intel.com/
Resources used by the chipset Chapter 2
1.6.1 Universal 0.8 V / 1.5 V AGP 3.0 Connector
The AGP connector supports the following:
• 4x, 8x AGP 3.0 add-in cards with 0.8 V I/O
• 1x, 4x AGP 2.0 add-in cards with 1.5 V I/O
• AGP Digital Display (ADD) cards
24
Page 25

Product Description
AGP is a high-performance interface for graphics-intensive applications, such as 3D applications.
While based on the PCI Local Bus Specification, Rev. 2.2, AGP is independent of the PCI bus and
is intended for exclusive use with graphical display devices. AGP overcomes certain limitations of
the PCI bus related to handling large amounts of graphics data with the following features:
• Pipelined memory read and write operations that hide memory access latency
• Demultiplexing of address and data on the bus for nearly 100 percent efficiency
INTEGRATOR’S NOTES
#
• AGP 2x operation is not supported.
• Install memory in the DIMM sockets prior to installing the AGP video card to avoid
interference with the memory retention mechanism.
• The AGP connector is keyed for Universal 0.8 V AGP 3.0 cards or 1.5 V AGP 2.0 cards only.
Do not attempt to install a legacy 3.3 V AGP card. The AGP connector is not mechanically
compatible with legacy 3.3 V AGP cards.
For information about Refer to
The location of the AGP connector Figure 1, page 13
Obtaining the Accelerated Graphics Port Interface Specification Section 1.3, page 16
1.6.2 USB
The board supports up to six USB 2.0 ports, supports UHCI and EHCI, and uses UHCI- and EHCIcompatible drivers.
The ICH5 provides the USB controller for all ports. The port arrangement is as follows:
• Two ports are implemented with stacked back panel connectors, adjacent to the PS/2
connectors
• Two ports are implemented with stacked back panel connectors, adjacent to the audio
connectors
• Two ports are routed to a front panel USB connector
NOTES
✏
• Computer systems that have an unshielded cable attached to a USB port may not meet FCC
Class B requirements, even if no device is attached to the cable. Use shielded cable that meets
the requirements for full-speed devices.
• Native USB 2.0 support has been tested with drivers for Windows* 2000 (with Service Pack 3)
and Windows XP (with Service Pack 1) and is not currently supported by any other operating
system. Check Intel’s Desktop Board website for possible driver updates for other operating
systems.
For information about Refer to
The location of the USB connectors on the back panel Figure 8, page 44
The location of the front panel USB connector Figure 12, page 52
The EHCI, front panel, UHCI, and USB specifications Section 1.3, page 16
25
Page 26

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
1.6.3 IDE Support
The board provides two Parallel ATA IDE connectors, which support a total of four devices (two
per connector). The ICH5’s Parallel ATA IDE controller has two independent bus-mastering
Parallel ATA IDE interfaces that can be independently enabled. The Parallel ATA IDE interfaces
support the following modes:
• Programmed I/O (PIO): processor controls data transfer.
• 8237-style DMA: DMA offloads the processor, supporting transfer rates of up to 16 MB/sec.
• Ultra DMA: DMA protocol on IDE bus supporting host and target throttling and transfer rates
of up to 33 MB/sec.
• ATA-66: DMA protocol on IDE bus supporting host and target throttling and transfer rates of
up to 66 MB/sec. ATA-66 protocol is similar to Ultra DMA and is device driver compatible.
• ATA-100: DMA protocol on IDE bus allows host and target throttling. The ICH5’s ATA-100
logic can achieve read transfer rates up to 100 MB/sec and write transfer rates up to 88 MB/sec.
✏ NOTE
ATA-66 and ATA-100 are faster timings and require a specialized cable to reduce reflections,
noise, and inductive coupling.
The Parallel ATA IDE interfaces also support ATAPI devices (such as CD-ROM drives) and ATA
devices using the transfer modes listed in Section 4.4.4.1 on page 86.
The BIOS supports Logical Block Addressing (LBA) and Extended Cylinder Head Sector (ECHS)
translation modes. The drive reports the transfer rate and translation mode to the BIOS.
The board supports Laser Servo (LS-120) diskette technology through the Parallel ATA IDE
interfaces. An LS-120 drive can be configured as a boot device by setting the BIOS Setup
program’s Boot menu to one of the following:
• ARMD-FDD (ATAPI removable media device – floppy disk drive)
• ARMD-HDD (ATAPI removable media device – hard disk drive)
For information about Refer to
The location of the Parallel ATA IDE connectors Figure 11, page 51
1.6.4 Real-Time Clock, CMOS SRAM, and Battery
A coin-cell battery (CR2032) powers the real-time clock and CMOS memory. When the computer
is not plugged into a wall socket, the battery has an estimated life of three years. When the
computer is plugged in, the standby current from the power supply extends the life of the battery.
The clock is accurate to ± 13 minutes/year at 25 ºC with 3.3 VSB applied.
✏ NOTE
If the battery and AC power fail, custom defaults, if previously saved, will be loaded into CMOS
RAM at power-on.
26
Page 27

1.7 I/O Controller
The I/O controller provides the following features:
• One serial port
• One parallel port with Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) and Enhanced Parallel Port
(EPP) support
• Serial IRQ interface compatible with serialized IRQ support for PCI systems
• PS/2-style mouse and keyboard interfaces
• Interface for one 1.44 MB or 2.88 MB diskette drive
• Intelligent power management, including a programmable wake-up event interface
• PCI power management support
The BIOS Setup program provides configuration options for the I/O controller.
For information about Refer to
SMSC LPC47M172 I/O controller http://www.smsc.com
National Semiconductor PC87372 I/O Controller http://www.national.com/
Product Description
1.7.1 Serial Port
The boards have one serial port connector located on the back panel. The serial port supports data
transfers at speeds up to 115.2 kbits/sec with BIOS support.
For information about Refer to
The location of the serial port A connector Figure 8, page 44
1.7.2 Parallel Port
The 25-pin D-Sub parallel port connector is located on the back panel. Use the BIOS Setup
program to set the parallel port mode.
For information about Refer to
The location of the parallel port connector Figure 8, page 44
Setting the parallel port’s mode Table 46, page 83
1.7.3 Diskette Drive Controller
The I/O controller supports one diskette drive. Use the BIOS Setup program to configure the
diskette drive interface.
For information about Refer to
The location of the diskette drive connector on the D865PCD board Figure 11, page 51
The supported diskette drive capacities and sizes Table 49, page 88
27
Page 28

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
1.7.4 Keyboard and Mouse Interface
PS/2 keyboard and mouse connectors are located on the back panel.
NOTE
✏
The keyboard is supported in the bottom PS/2 connector and the mouse is supported in the top
PS/2 connector. Power to the computer should be turned off before a keyboard or mouse is
connected or disconnected.
For information about Refer to
The location of the keyboard and mouse connectors Figure 8, page 44
1.8 Audio Subsystem
The board provides an audio subsystem based on the Realtek ALC202 codec.
1.8.1 Realtek ALC202-based Audio Subsystem
The Realtek ALC202-based audio subsystem consists of the following devices:
• Intel 82801EB I/O Controller Hub (ICH5)
• Realtek ALC202 audio codec
The audio subsystem includes these features:
• Signal-to-noise ratio ≥ 90 dB
• Supports wake events (driver dependent)
• Mic in pre-amp that supports dynamic, condenser, and electret microphones
The back panel audio connectors for this audio subsystem including the following:
• Line out
• Line in
• Mic in
1.8.2 Audio Connectors
1.8.2.1 Front Panel Audio Connector
A 2 x 5-pin connector provides mic in and line out signals for front panel audio connectors.
For information about Refer to
The location of the connector Figure 9, page 46
The signal names of the front panel audio connector Table 17, page 47
NOTE
✏
The front panel audio connector is alternately used as a jumper block for routing audio signals.
Refer to Section 2.9.1 on page 56 for more information.
28
Page 29

1.8.2.2 ATAPI CD-ROM Audio Connector
A 1 x 4-pin ATAPI-style connector connects an internal ATAPI CD-ROM drive to the audio
mixer.
For information about Refer to
The location of the ATAPI CD-ROM connector Figure 9, page 46
The signal names of the ATAPI CD-ROM connector Table 16, page 47
1.8.3 Audio Subsystem Software
Audio software and drivers are available from Intel’s World Wide Web site.
For information about Refer to
Obtaining audio software and drivers Section 1.2, page 15
1.9 LAN Subsystem
The 10/100 Mbits/sec LAN subsystem consists of the following:
®
• Intel
• Intel 82801EB ICH5 (with its CSMA/CD interface)
• RJ-45 LAN connector with integrated status LEDs
82562EZ Platform LAN Connect (PLC) device for 10/100 Mbits/sec Ethernet LAN
connectivity
Product Description
Additional features of the LAN subsystem include:
• PCI bus master interface
• CSMA/CD protocol engine
• PCI power management
Supports ACPI technology
Supports LAN wake capabilities
1.9.1 Intel® 82562EZ Physical Layer Interface Device
The Intel 82562EZ provides the following functions:
• Basic 10/100 Ethernet LAN connectivity
• Full device driver compatibility
• Programmable transit threshold
• Configuration EEPROM that contains the MAC address
29
Page 30
Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
1.9.2 RJ-45 LAN Connector with Integrated LEDs
Two LEDs are built into the RJ-45 LAN connector (shown in Figure 7 below).
Green LED
Figure 7. LAN Connector LED Locations
Yellow LED
OM15076
Table 6 describes the LED states when the board is powered up and the 10/100 Mbits/sec LAN
subsystem is operating.
Table 6. LAN Connector LED States
LED Color LED State Condition
Green
Off LAN link is not established
On LAN link is established
Blinking LAN activity is occurring
Off 10 Mbits/sec data rate is selected Yellow
On 100 Mbits/sec data rate is selected
1.9.3 LAN Subsystem Software
LAN software and drivers are available from Intel’s World Wide Web site.
For information about Refer to
Obtaining LAN software and drivers Section 1.2, page 15
1.10 Chassis Intrusion and Detection
The Desktop Board D865PCD supports a chassis security feature that detects if the chassis cover is
removed. The security feature uses a mechanical switch on the chassis that attaches to the chassis
intrusion connector. When the chassis cover is removed, the mechanical switch is in the closed
position.
1.11 Power Management
Power management is implemented at several levels, including:
• Software support through Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
• Hardware support:
Power connector
Fan connectors
LAN wake capabilities
Instantly Available PC technology
Resume on Ring
Wake from USB
Wake from PS/2 devices
30
Page 31

Product Description
Power Management Event signal (PME#) wake-up support
1.11.1 ACPI
ACPI gives the operating system direct control over the power management and Plug and Play
functions of a computer. The use of ACPI with the Desktop Board D865PCD requires an
operating system that provides full ACPI support. ACPI features include:
• Plug and Play (including bus and device enumeration)
• Power management control of individual devices, add-in boards (some add-in boards may
require an ACPI-aware driver), video displays, and hard disk drives
• Methods for achieving less than 15-watt system operation in the power-on/standby
sleeping state
• A Soft-off feature that enables the operating system to power-off the computer
• Support for multiple wake-up events (see Table 9 on page 32)
• Support for a front panel power and sleep mode switch
Table 7 lists the system states based on how long the power switch is pressed, depending on how
ACPI is configured with an ACPI-aware operating system.
Table 7. Effects of Pressing the Power Switch
If the system is in this state…
Off
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
On
(ACPI G0 – working state)
On
(ACPI G0 – working state)
Sleep
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
Sleep
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
For information about Refer to
The Desktop Boards’ compliance level with ACPI Section 1.3, page 16
…and the power switch is
pressed for
Less than four seconds Power-on
Less than four seconds Soft-off/Standby
More than four seconds Fail safe power-off
Less than four seconds Wake-up
More than four seconds Power-off
…the system enters this state
(ACPI G0 – working state)
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
(ACPI G0 – working state)
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
1.11.1.1 System States and Power States
Under ACPI, the operating system directs all system and device power state transitions. The
operating system puts devices in and out of low-power states based on user preferences and
knowledge of how devices are being used by applications. Devices that are not being used can be
turned off. The operating system uses information from applications and user settings to put the
system as a whole into a low-power state.
Table 8 lists the power states supported by the Desktop Board D865PCD and along with the
associated system power targets. See the ACPI specification for a complete description of the
various system and power states.
31
Page 32

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
Table 8. Power States and Targeted System Power
Global States Sleeping States
G0 – working
S0 – working C0 – working D0 – working
state
G1 – sleeping
state
G1 – sleeping
state
S1 – Processor
stopped
S3 – Suspend to
RAM. Context
saved to RAM.
G1 – sleeping
state
S4 – Suspend to
disk. Context
saved to disk.
G2/S5 S5 – Soft off.
Context not saved.
Cold boot is
required.
G3 –
mechanical off
No power to the
system.
AC power is
disconnected
from the
computer.
Notes:
1. Total system power is dependent on the system configuration, including add-in boards and peripherals powered
by the system chassis’ power supply.
2. Dependent on the standby power consumption of wake-up devices used in the system.
Processor
States
Device States
state.
C1 – stop
grant
D1, D2, D3 –
device
specification
specific.
No power D3 – no power
except for
wake-up logic.
No power D3 – no power
except for
wake-up logic.
No power D3 – no power
except for
wake-up logic.
No power D3 – no power for
wake-up logic,
except when
provided by
battery or external
source.
Targeted System
Power
Full power > 30 W
5 W < power < 52.5 W
Power < 5 W
Power < 5 W
Power < 5 W
No power to the system.
Service can be performed
safely.
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
(Note 2)
(Note 2)
1.11.1.2 Wake-up Devices and Events
Table 9 lists the devices or specific events that can wake the computer from specific states.
Table 9. Wake-up Devices and Events
These devices/events can wake up the computer… …from this state
LAN S1, S3, S4, S5
Modem (back panel Serial Port A) S1, S3
PME# signal S1, S3, S4, S5
Power switch S1, S3, S4, S5
PS/2 devices S1, S3
RTC alarm S1, S3, S4, S5
USB S1, S3
Note: For LAN and PME# signal, S5 is disabled by default in the BIOS Setup program. Setting this option to Power On
will enable a wake-up event from LAN in the S5 state.
(Note)
(Note)
32
Page 33

Product Description
NOTE
✏
The use of these wake-up events from an ACPI state requires an operating system that provides full
ACPI support. In addition, software, drivers, and peripherals must fully support ACPI wake
events.
1.11.2 Hardware Support
CAUTION
Ensure that the power supply provides adequate +5 V standby current if LAN wake capabilities
and Instantly Available PC technology features are used. Failure to do so can damage the power
supply. The total amount of standby current required depends on the wake devices supported and
manufacturing options.
The Desktop Board D865PCD provides several power management hardware features, including:
• Power connector
• Fan connectors
• LAN wake capabilities
• Instantly Available PC technology
• Resume on Ring
• Wake from USB
• Wake from PS/2 keyboard
• PME# signal wake-up support
LAN wake capabilities and Instantly Available PC technology require power from the +5 V
standby line. The sections discussing these features describe the incremental standby power
requirements for each.
Resume on Ring enables telephony devices to access the computer when it is in a power-managed
state. The method used depends on the type of telephony device (external or internal).
NOTE
✏
The use of Resume on Ring and Wake from USB technologies from an ACPI state requires an
operating system that provides full ACPI support.
1.11.2.1 Power Connector
ATX12V-, SFX12V-, and TFX12V-compliant power supplies can turn off the system power
through system control. When an ACPI-enabled system receives the correct command, the power
supply removes all non-standby voltages.
When resuming from an AC power failure, the computer returns to the power state it was in before
power was interrupted (on or off). The computer’s response can be set using the Last Power State
feature in the BIOS Setup program’s Boot menu.
33
Page 34

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
For information about Refer to
The location of the power connector Figure 9, page 46
The signal names of the power connector Table 21, page 49
The BIOS Setup program’s Boot menu Table 57, page 96
The ATX12V, SFX12V, and TFX12V specifications Section 1.3, page 16
1.11.2.2 LAN Wake Capabilities
CAUTION
For LAN wake capabilities, the +5 V standby line for the power supply must be capable of
providing adequate +5 V standby current. Failure to provide adequate standby current when
implementing LAN wake capabilities can damage the power supply.
LAN wake capabilities enable remote wake-up of the computer through a network. The LAN
subsystem PCI bus network adapter monitors network traffic at the Media Independent Interface.
Upon detecting a Magic Packet* frame, the LAN subsystem asserts a wake-up signal that powers
up the computer. Depending on the LAN implementation, the Desktop Board D865PCD support
LAN wake capabilities with ACPI in the following ways:
• The PCI bus PME# signal for PCI 2.2 compliant LAN designs
• The onboard LAN subsystem
1.11.2.3 Instantly Available PC Technology
CAUTION
For Instantly Available PC technology, the +5 V standby line for the power supply must be
capable of providing adequate +5 V standby current. Failure to provide adequate standby current
when implementing Instantly Available PC technology can damage the power supply.
Instantly Available PC technology enables the Desktop Board D865PCD to enter the ACPI S3
(Suspend-to-RAM) sleep-state. While in the S3 sleep-state, the computer will appear to be off (the
power supply is off, and the front panel LED is amber if dual colored, or off if single colored.)
When signaled by a wake-up device or event, the system quickly returns to its last known wake
state. Table 9 on page 32 lists the devices and events that can wake the computer from the
S3 state.
The Desktop Board D865PCD supports the PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification.
For information on the version of this specification, see Section 1.3. Add-in boards that also
support this specification can participate in power management and can be used to wake the
computer.
The use of Instantly Available PC technology requires operating system support and PCI 2.2
compliant add-in cards and drivers.
34
Page 35

1.11.2.4 Resume on Ring
The operation of Resume on Ring can be summarized as follows:
• Resumes operation from ACPI S1 or S3 states
• Detects incoming call similarly for external and internal modems
• Requires modem interrupt be unmasked for correct operation
1.11.2.5 Wake from USB
USB bus activity wakes the computer from ACPI S1 or S3 states.
NOTE
✏
Wake from USB requires the use of a USB peripheral that supports Wake from USB.
1.11.2.6 Wake from PS/2 Devices
PS/2 device activity wakes the computer from an ACPI S1 or S3 state.
1.11.2.7 PME# Signal Wake-up Support
Product Description
When the PME# signal on the PCI bus is asserted, the computer wakes from an ACPI S1, S3, S4,
or S5 state (with Wake on PME enabled in BIOS).
35
Page 36

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
36
Page 37

2 Technical Reference
What This Chapter Contains
2.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................37
2.2 Memory Map ..............................................................................................................37
2.3 DMA Channels ...........................................................................................................38
2.4 Fixed I/O Map.............................................................................................................38
2.5 PCI Configuration Space Map ....................................................................................39
2.6 Interrupts ....................................................................................................................40
2.7 PCI Interrupt Routing Map..........................................................................................41
2.8 Connectors.................................................................................................................43
2.9 Jumper Blocks............................................................................................................56
2.10 Mechanical Considerations.........................................................................................58
2.11 Electrical Considerations ............................................................................................60
2.12 Thermal Considerations..............................................................................................61
2.13 Reliability ....................................................................................................................63
2.14 Environmental ............................................................................................................64
2.1 Introduction
Sections 2.2 - 2.6 contain several standalone tables. Table 10 describes the system memory map,
Table 11 lists the DMA channels, Table 12 shows the I/O map, Table 13 defines the PCI
configuration space map, and Table 14 describes the interrupts. The remaining sections in this
chapter are introduced by text found with their respective section headings.
2.2 Memory Map
Table 10 lists the system memory map.
Table 10. System Memory Map
Address Range (decimal) Address Range (hex) Size Description
1024 K - 2097152 K 100000 - 7FFFFFFF 2047 MB Extended memory
960 K - 1024 K F0000 - FFFFF 64 KB Runtime BIOS
896 K - 960 K E0000 - EFFFF 64 KB Reserved
800 K - 896 K C8000 - DFFFF 96 KB Potential available high DOS
memory (open to the PCI bus).
Dependent on video adapter used.
640 K - 800 K A0000 - C7FFF 160 KB Video memory and BIOS
639 K - 640 K 9FC00 - 9FFFF 1 KB Extended BIOS data (movable by
memory manager software)
512 K - 639 K 80000 - 9FBFF 127 KB Extended conventional memory
0 K - 512 K 00000 - 7FFFF 512 KB Conventional memory
37
Page 38

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
2.3 DMA Channels
Table 11. DMA Channels
DMA Channel Number Data Width System Resource
0 8 or 16 bits Open
1 8 or 16 bits Parallel port
2 8 or 16 bits Diskette drive
3 8 or 16 bits Parallel port (for ECP or EPP)
4 8 or 16 bits DMA controller
5 16 bits Open
6 16 bits Open
7 16 bits Open
2.4 Fixed I/O Map
Table 12. I/O Map
Address (hex) Size Description
0000 - 00FF 256 bytes Used by the Desktop Board D865PCD. Refer to the ICH5
data sheet for dynamic addressing information.
0170 - 0177 8 bytes Secondary Parallel ATA IDE channel command block
01F0 - 01F7 8 bytes Primary Parallel ATA IDE channel command block
0228 - 022F
0278 - 027F
02E8 - 02EF
02F8 - 02FF
0374 - 0377 4 bytes Secondary Parallel ATA IDE channel control block
0377, bits 6:0 7 bits Secondary IDE channel status port
0378 - 037F 8 bytes LPT1
03B0 - 03BB 12 bytes Intel 82865P MCH
03C0 - 03DF 32 bytes Intel 82865P MCH
03E8 - 03EF 8 bytes COM3
03F0 - 03F5 6 bytes Diskette channel
03F4 – 03F7 1 byte Primary Parallel ATA IDE channel control block
03F8 - 03FF 8 bytes COM1
04D0 - 04D1 2 bytes Edge/level triggered PIC
LPTn + 400 8 bytes ECP port, LPTn base address + 400h
0CF8 - 0CFB
0CF9
0CFC - 0CFF 4 bytes PCI configuration data register
FFA0 - FFA7 8 bytes Primary Parallel ATA IDE bus master registers
FFA8 - FFAF 8 bytes Secondary Parallel ATA IDE bus master registers
Notes:
1. Default, but can be changed to another address range
2. Dword access only
3. Byte access only
(Note 1)
8 bytes LPT3
(Note 1)
8 bytes LPT2
(Note 1)
8 bytes COM4
(Note 1)
8 bytes COM2
(Note 2)
4 bytes PCI configuration address register
(Note 3)
1 byte Reset control register
38
Page 39

Technical Reference
✏ NOTE
Some additional I/O addresses are not available due to ICH5 address aliasing. The ICH5 data
sheet provides more information on address aliasing.
For information about Refer to
Obtaining the ICH5 data sheet Section 1.2 on page 15
2.5 PCI Configuration Space Map
Table 13. PCI Configuration Space Map
Bus
Number (hex)
00 00 00 Memory controller of Intel 82865P component
00 01 00 Host to AGP bridge (virtual PCI-to-PCI)
00 03 00 PCI to CSA Bridge (virtual PCI-to-PCI)
00 1E 00 Hub link to PCI bridge
00 1F 00 Intel 82801EB ICH5 PCI to LPC bridge
00 1F 01 Parallel ATA IDE controller
00 1F 03 SMBus controller
00 1F 05 AC ’97 audio controller
00 1F 06 AC ’97 modem controller
00 1D 00 USB UHCI controller 1
00 1D 01 USB UHCI controller 2
00 1D 02 USB UHCI controller 3
00 1D 03 USB UHCI controller 4
00 1D 07 EHCI controller
01 00 00 AGP add-in card
(Note)
(Note)
(Note)
(Note)
(Note)
Note: Bus number = 03 when the Intel 82547EI Gigabit LAN controller is used. Otherwise, bus number = 02.
Device
Number (hex)
01 00 Intel 82547EI Gigabit LAN PLC (if present)
08 00 Intel 82562EZ 10/100 Mbits/sec LAN PLC (if present)
00 00 PCI bus connector 1
01 00 PCI bus connector 2
02 00 PCI bus connector 3
Function
Number (hex) Description
39
Page 40

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
2.6 Interrupts
The interrupts can be routed through either the Programmable Interrupt Controller (PIC) or the
Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) portion of the ICH5 component. The PIC is
supported in Windows 98 SE and Windows ME and uses the first 16 interrupts. The APIC is
supported in Windows 2000 and Windows XP and supports a total of 24 interrupts.
Table 14. Interrupts
IRQ System Resource
NMI I/O channel check
0 Reserved, interval timer
1 Reserved, keyboard buffer full
2 Reserved, cascade interrupt from slave PIC
3 COM2
4 COM1
5 LPT2 (Plug and Play option)/User available
6 Diskette drive
7 LPT1
8 Real-time clock
9 Reserved for ICH5 system management bus
10 User available
11 User available
12 Onboard mouse port (if present, else user available)
13 Reserved, math coprocessor
14 Primary IDE
15 Secondary IDE
(Note 2)
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Notes:
1. Default, but can be changed to another IRQ.
2. Available in APIC mode only.
USB UHCI controller 1 / USB UHCI controller 4 (through PIRQA)
(Note 2)
AC ‘97 audio/modem/User available (through PIRQB)
(Note 2)
ICH5 USB controller 3 (through PIRQC)
(Note 2)
ICH5 USB controller 2 (through PIRQD)
(Note 2)
ICH5 LAN (through PIRQE)
(Note 2)
User available (through PIRQF)
(Note 2)
User available (through PIRQG)
(Note 2)
ICH5 USB 2.0 EHCI controller/User available (through PIRQH)
(Note 1)
(Note 1)
(Note 1)
40
Page 41

Technical Reference
2.7 PCI Interrupt Routing Map
This section describes interrupt sharing and how the interrupt signals are connected between the
PCI bus connectors and onboard PCI devices. The PCI specification specifies how interrupts can
be shared between devices attached to the PCI bus. In most cases, the small amount of latency
added by interrupt sharing does not affect the operation or throughput of the devices. In some
special cases where maximum performance is needed from a device, a PCI device should not share
an interrupt with other PCI devices. Use the following information to avoid sharing an interrupt
with a PCI add-in card.
PCI devices are categorized as follows to specify their interrupt grouping:
• INTA: By default, all add-in cards that require only one interrupt are in this category. For
almost all cards that require more than one interrupt, the first interrupt on the card is also
classified as INTA.
• INTB: Generally, the second interrupt on add-in cards that require two or more interrupts is
classified as INTB. (This is not an absolute requirement.)
• INTC and INTD: Generally, a third interrupt on add-in cards is classified as INTC and a
fourth interrupt is classified as INTD.
The ICH5 has eight Programmable Interrupt Request (PIRQ) input signals. All PCI interrupt
sources either onboard or from a PCI add-in card connect to one of these PIRQ signals. Some PCI
interrupt sources are electrically tied together on the Desktop Boards D865PCD and therefore
share the same interrupt. Table 15 shows an example of how the PIRQ signals are routed.
For example, using Table 15 as a reference, assume an add-in card using INTA is plugged into PCI
bus connector 3. In PCI bus connector 3, INTA is connected to PIRQB, which is already
connected to the ICH5 audio controller. The add-in card in PCI bus connector 3 now shares an
interrupt with the onboard interrupt source.
41
Page 42

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
Table 15. PCI Interrupt Routing Map
PCI Interrupt Source
AGP connector INTA INTB
ICH5 USB UHCI controller 1 INTA
SMBus controller INTB
ICH5 USB UHCI controller 2 INTB
AC ’97 ICH5 Audio INTB
ICH5 LAN INTA
ICH5 USB UHCI controller 3 INTC
ICH5 USB UHCI controller 4 INTA
ICH5 USB 2.0 EHCI
controller
PCI bus connector 1 INTD INTA INTB INTC
PCI bus connector 2 INTC INTB INTA INTD
PCI bus connector 3 INTD INTA INTB INTC
PIRQA PIRQB PIRQC PIRQD PIRQE PIRQF PIRQG PIRQH
INTD
ICH5 PIRQ Signal Name
NOTE
✏
In PIC mode, the ICH5 can connect each PIRQ line internally to one of the IRQ signals (3, 4, 5, 6,
7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, and 15). Typically, a device that does not share a PIRQ line will have a
unique interrupt. However, in certain interrupt-constrained situations, it is possible for two or
more of the PIRQ lines to be connected to the same IRQ signal. Refer to Table 14 for the
allocation of PIRQ lines to IRQ signals in APIC mode.
42
Page 43

Technical Reference
2.8 Connectors
CAUTION
Only the following connectors have overcurrent protection: back panel USB, front panel USB,
and PS/2.
The other internal connectors are not overcurrent protected and should connect only to devices
inside the computer’s chassis, such as fans and internal peripherals. Do not use these connectors
to power devices external to the computer’s chassis. A fault in the load presented by the external
devices could cause damage to the computer, the power cable, and the external devices themselves.
This section describes the board’s connectors. The connectors can be divided into these groups:
• Back panel I/O connectors (see page 44)
PS/2 keyboard and mouse
USB (four ports)
Parallel port
Serial port A
LAN
Audio (line out, line in, and mic in)
• Internal I/O connectors (see page 45)
Audio (ATAPI CD-ROM and front panel audio)
Fans [three]
Power
Add-in boards (PCI and AGP)
Parallel ATA IDE
Diskette drive
Chassis intrusion
• External I/O connectors (see page 52)
Front panel USB (two connector for four ports)
Auxiliary front panel power/sleep/message-waiting LED
Front panel (power/sleep/message-waiting LED, power switch, hard drive activity LED,
reset switch, and auxiliary front panel power LED)
NOTE
✏
When installing the board in a microATX chassis, make sure that peripheral devices are installed
at least 1.5 inches above the main power connector, the diskette drive connector, the Parallel ATA
IDE connectors, and the DIMM sockets.
43
Page 44

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
2.8.1 Back Panel Connectors
Figure 8 shows the location of the back panel connectors. The back panel connectors are
color-coded in compliance with PC 99 recommendations. The figure legend below lists the
colors used.
F
C
A
B
G ID
Item Description Color Item Description Color
A PS/2 mouse port Green F LAN Black
B PS/2 keyboard port Purple G USB ports Black
C USB ports Black H Audio line in Light blue
D Serial port A Teal I Mic in Pink
E Parallel port Burgundy J Audio line out Lime green
Figure 8. Back Panel Connectors
NOTE
✏
HE
The back panel audio line out connector is designed to power headphones or amplified speakers
only. Poor audio quality occurs if passive (non-amplified) speakers are connected to this output.
J
OM17034
44
Page 45

2.8.2 Internal I/O Connectors
The internal I/O connectors are divided into the following functional groups:
• Audio (see page 46)
ATAPI CD-ROM
Front panel audio
• Power and hardware control (see page 48)
Fans [3]
ATX12V power
Main power
Chassis intrusion
• Add-in boards and peripheral interfaces (see page 51)
PCI bus
AGP
IDE
Diskette drive
Technical Reference
2.8.2.1 Expansion Slots
The board has the following expansion slots:
• AGP connector: The AGP connector is keyed for Universal 0.8 V AGP 3.0 cards or 1.5 V
AGP 2.0 cards only. Do not install a legacy 3.3 V AGP card. The AGP connector is not
mechanically compatible with legacy 3.3 V AGP cards.
• Three PCI rev 2.2 compliant local bus slots. The SMBus is routed to PCI bus connector 2 only
(ATX expansion slot 6). PCI add-in cards with SMBus support can access sensor data and
other information residing on the Desktop Board.
NOTE
✏
This document references back-panel slot numbering with respect to processor location on the
board. The AGP slot is not numbered. PCI slots are identified as PCI slot #x, starting with the
slot closest to the processor. Figure 11 (page 51) illustrates the board’s PCI slot numbering.
45
Page 46

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
2.8.2.2 Audio Connectors
Figure 9 shows the location of the audio connectors.
A
B
12
910
1
4
46
Item Description For more information see:
A ATAPI CD-ROM (black) Table 16
B
Front panel audio Table 17
Figure 9. Audio Connectors
OM17035
Page 47

Technical Reference
Table 16. ATAPI CD-ROM Connector
Pin Signal Name
1 Left audio input from CD-ROM
2 CD audio differential ground
3 CD audio differential ground
4 Right audio input from CD-ROM
Table 17. Front Panel Audio Connector
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 Mono Mic in (Stereo Mic 1) 2 Ground
3 Mono Mic Bias (Stereo Mic 2) 4 +5 V
5 RIGHT_OUT 6 Right channel return
7 Ground 8 Key
9 LEFT_OUT 10 Left channel return
INTEGRATOR’S NOTE
#
The front panel audio connector is alternately used as a jumper block for routing audio signals.
Refer to Section 2.9.1 on page 56 for more information.
47
Page 48

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
2.8.2.3 Power and Hardware Control Connectors
Figure 10 shows the location of the power and hardware control connectors.
A
1
3
B
4213
1
3
20
31
1
11
1
D CEF
Item Description For more information see:
A Rear chassis fan Table 18
B +12 V power connector (ATX12V) Table 19
C Processor fan Table 20
D Main power Table 21
E Front chassis fan Table 22
F Chassis intrusion Table 23
Figure 10. Power and Hardware Control Connectors
OM17036
48
Page 49

Technical Reference
Table 18. Rear Chassis Fan Connector
Pin Signal Name
1 Control
2 +12 V
3 REAR_TACH_OUT
INTEGRATOR’S NOTES
#
• Use only ATX12V-, SFX12V-, or TFX12V-compliant power supplies with the Desktop Board
D865PCD. ATX12V, SFX12V, and TFX12V power supplies have an additional power lead
that provides required supplemental power for the processor. Always connect the 20-pin and
4-pin leads of ATX12V, SFX12V, and TFX12V power supplies to the corresponding connectors
on the desktop board, otherwise the board will not boot.
• Do not use a standard ATX power supply. The board will not boot with a standard ATX power
supply.
Table 19. ATX12V Power Connector
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 Ground 2 Ground
3 +12 V 4 +12 V
Table 20. Processor Fan Connector
Pin Signal Name
1 Control
2 +12 V
3 CPU_FAN_TACH
Table 21. Main Power Connector
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 +3.3 V 11 +3.3 V
2 +3.3 V 12 -12 V
3 Ground 13 Ground
4 +5 V 14 PS-ON# (power supply remote on/off)
5 Ground 15 Ground
6 +5 V 16 Ground
7 Ground 17 Ground
8 PWRGD (Power Good) 18 No connect
9 +5 V (Standby) 19 +5 V
10 +12 V 20 +5 V
49
Page 50

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
Table 22. Front Chassis Fan Connector
Pin Signal Name
1 Control
2 +12 V
3 Tach
Table 23. Chassis Intrusion Connector
Pin Signal Name
1 Intruder
2 Ground
50
Page 51

Technical Reference
2.8.2.4 Add-in Board and Peripheral Interface Connectors
Figure 11 shows the location of the add-in board connector and peripheral connectors. Note the
following considerations for the PCI bus connectors:
• All of the PCI bus connectors are bus master capable.
• SMBus signals are routed to PCI bus connector 2. This enables PCI bus add-in boards with
SMBus support to access sensor data on the Desktop Board. The specific SMBus signals are
as follows:
The SMBus clock line is connected to pin A40.
The SMBus data line is connected to pin A41.
A B C D
2
1
2
1
40
2
39
1
39
34
33
GF E
Item Description Item Description
A PCI bus connector 3 E Diskette drive
B PCI bus connector 2 F Primary IDE [black]
C PCI bus connector 1 G Secondary IDE [white]
D AGP connector
Figure 11. D865PCD Add-in Board and Peripheral Interface Connectors
51
OM17037
Page 52

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
INTEGRATOR’S NOTES
#
• The AGP connector is keyed for Universal 0.8 V AGP 3.0 cards or 1.5 V AGP 2.0 cards only.
Do not attempt to install a legacy 3.3 V AGP card. The AGP connector is not mechanically
compatible with legacy 3.3 V AGP cards.
• Not all PCI video cards can be used in PCI bus connectors 1 and 2 (the PCI bus connectors
closest to the processor). To avoid clearance problems, install PCI video cards in PCI bus
connector 3.
2.8.3 External I/O Connectors
Figure 12 shows the locations of the external I/O connectors.
2
1
9
1
7
2
8
13
10
C
B
A
OM17038
Item Description Color For more information see:
A Auxiliary front panel power/sleep/message-waiting LED Black Table 24
B Front panel White Table 25
C Front panel USB Black Figure 14
Figure 12. External I/O Connectors
52
Page 53

Technical Reference
2.8.3.1 Auxiliary Front Panel Power/Sleep/Message-Waiting LED Connector
Pins 1 and 3 of this connector duplicate the signals on pins 2 and 4 of the front panel connector.
Table 24. Auxiliary Front Panel Power/Sleep/Message-Waiting LED Connector
Pin Signal Name In/Out Description
1 HDR_BLNK_GRN Out Front panel green LED
2 Not connected
3 HDR_BLNK_YEL Out Front panel yellow LED
2.8.3.2 Front Panel Connector
This section describes the functions of the front panel connector. Table 25 lists the signal names
of the front panel connector. Figure 13 is a connection diagram for the front panel connector.
Table 25. Front Panel Connector
Pin Signal In/Out Description Pin Signal In/Out Description
Hard Drive Activity LED Power LED
1 HD_PWR Out Hard disk LED pull-up
(750 Ω) to +5 V
3 HAD# Out Hard disk active LED 4 HDR_BLNK_
Reset Switch On/Off Switch
5 Ground Ground 6 FPBUT_IN In Power switch
7 FP_RESET# In Reset switch 8 Ground Ground
Power Not Connected
9 +5 V Power 10 N/C Not connected
2 HDR_BLNK_
GRN
YEL
Out Front panel green
LED
Out Front panel yellow
LED
Single-colored
Power LED
Hard Drive
Activity LED
Reset
Switch
+5 V DC
2
1
4
3
6
5
8
7
9
Power
Switch
N/C
Figure 13. Connection Diagram for Front Panel Connector
53
Dual-colored
Power LED
OM16110
Page 54

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
2.8.3.2.1 Hard Drive Activity LED Connector
Pins 1 and 3 can be connected to an LED to provide a visual indicator that data is being read from
or written to a hard drive. Proper LED function requires an IDE hard drive connected to an
onboard IDE connector.
2.8.3.2.2 Reset Switch Connector
Pins 5 and 7 can be connected to a momentary single pole, single throw (SPST) type switch that is
normally open. When the switch is closed, the board resets and runs the POST.
2.8.3.2.3 Power/Sleep/Message Waiting LED Connector
Pins 2 and 4 can be connected to a one- or two-color LED. Table 26 shows the possible states for
a one-color LED. Table 27 shows the possible states for a two-color LED.
Table 26. States for a One-Color Power LED
LED State Description
Off Power off/sleeping
Steady Green Running
Blinking Green Running/message waiting
Table 27. States for a Two-Color Power LED
LED State Description
Off Power off
Steady Green Running
Blinking Green Running/message waiting
Steady Yellow Sleeping
Blinking Yellow Sleeping/message waiting
✏ NOTE
To use the message waiting function, ACPI must be enabled in the operating system and a
message-capturing application must be invoked.
2.8.3.2.4 Power Switch Connector
Pins 6 and 8 can be connected to a front panel momentary-contact power switch. The switch must
pull the SW_ON# pin to ground for at least 50 ms to signal the power supply to switch on or off.
(The time requirement is due to internal debounce circuitry on the board.) At least two seconds
must pass before the power supply will recognize another on/off signal.
54
Page 55

Technical Reference
2.8.3.3 Front Panel USB Connectors
Figure 14 is a connection diagram for the front panel USB connector.
INTEGRATOR’S NOTES
#
• The +5 V DC power on the USB connector is fused.
• Pins 1, 3, 5, and 7 comprise one USB port.
• Pins 2, 4, 6, and 8 comprise one USB port.
• Use only a front panel USB connector that conforms to the USB 2.0 specification for high-
speed USB devices.
Power
(+5 V DC)
D−
D+
Ground
No Connect
One
USB
Port
OM15963
One
USB
Port
Power
(+5 V DC)
D−
D+
Ground
Key (no pin)
2
1
4
3
6
5
8
7
10
Figure 14. Connection Diagram for Front Panel USB Connector
55
Page 56

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
2.9 Jumper Blocks
CAUTION
Do not move any jumpers with the power on. Always turn off the power and unplug the power cord
from the computer before changing a jumper setting. Otherwise, the board could be damaged.
Figure 15 shows the location of the jumper blocks.
A
2
1
10
9
J9A2
B
31
J9J4
OM17039
Item Description Reference Designator
A Front panel audio connector/jumper block J9A2
B BIOS Setup configuration jumper block J9J4
Figure 15. Location of the Jumper Blocks
2.9.1 Front Panel Audio Connector/Jumper Block
This connector has two functions:
• With jumpers installed, the audio line out signals are routed to the back panel audio line out
connector.
• With jumpers removed, the connector provides audio line out and mic in signals for front panel
audio connectors.
56
Page 57

Technical Reference
Table 28 describes the two configurations of this connector/jumper block.
CAUTION
Do not place jumpers on this block in any configuration other than the one described in Table 28.
Other jumper configurations are not supported and could damage the Desktop Board.
Table 28. Front Panel Audio Connector/Jumper Block
Jumper Setting Configuration
1
34
5
7
9
2
6
10
1
34
5
7
9
2
6
10
1 and 2
3 and 4
5 and 6
9 and 10
No jumpers
installed
Audio line out signals are routed to the back panel audio line out
connector. The back panel audio line out connector is shown in Figure 8
on page 44.
Audio line out and mic in signals are available for front panel audio
connectors. Table 17 on page 47 lists the names of the signals available
on this connector when no jumpers are installed.
INTEGRATOR’S NOTE
#
When the jumpers are removed and this connector is used for front panel audio, the back panel
audio line out and mic in connectors are disabled.
2.9.2 BIOS Setup Configuration Jumper Block
The 3-pin jumper block determines the BIOS Setup program’s mode. Table 29 describes the
jumper settings for the three modes: normal, configure, and recovery. When the jumper is set to
configure mode and the computer is powered-up, the BIOS compares the processor version and the
microcode version in the BIOS and reports if the two match.
Table 29. BIOS Setup Configuration Jumper Settings
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
Normal
1-2
Configure
2-3
Recovery
None
1
13
13
The BIOS uses current configuration information and
3
passwords for booting.
After the POST runs, Setup runs automatically. The
maintenance menu is displayed.
The BIOS attempts to recover the BIOS configuration. A
recovery diskette is required.
57
Page 58

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
2.10 Mechanical Considerations
2.10.1 Form Factor
The Desktop Board D865PCD is designed to fit into either a microATX or an ATX-form-factor
chassis. Figure 16 illustrates the mechanical form factor for the Desktop Board D865PCD.
Dimensions are given in inches [millimeters]. The outer dimensions are 9.60 inches by
9.60 inches [243.84 millimeters by 243.84 millimeters]. Location of the I/O connectors and
mounting holes are in compliance with the ATX specification (see Section 1.3).
NOTE
✏
When installing the Desktop Board in a microATX chassis, make sure that peripheral devices are
installed at least 1.5 inches above the main power connector, the diskette drive connector, and the
IDE connector, and the DIMM sockets.
1.800
[45.72]
6.500
[165.10]
6.100
[154.94]
5.200
[132.08]
58
0.00
2.85
[72.39]
3.100
[78.74]
3.150
[80.01]
2.600
[66.04]
0.00
Figure 16. Desktop Board D865PCD Dimensions
6.200
[157.48]
6.450
[163.83]
OM17042
Page 59

Technical Reference
2.10.2 I/O Shield
The back panel I/O shield for the Desktop Board D865PCD must meet specific dimension and
material requirements. Systems based on this Desktop Board need the back panel I/O shield to
pass certification testing. Figure 17 shows the I/O shield. Dimensions are given in inches to a
tolerance of ±0.02 inches.
The figure also indicates the position of each cutout. Additional design considerations for I/O
shields relative to chassis requirements are described in the ATX specification. See Section 1.3 for
information about the ATX specification.
NOTE
✏
The I/O shield drawings in this document are for reference only. An I/O shield compliant with the
ATX chassis specification 2.03 is available from Intel.
6.390 Ref
[162.300]
0.063±0.005
[1.600±0.120]
0.884
[22.450]
0.276
[7.012]
0.00
0.465
[11.811]
0.567
[14.400]
0.039 Dia. [1.000]
0.00
0.447
[11.345]
0.787±0.010 TYP [20±0.254]
1.807
[45.892]
2.079
[52.804]
1.195
[30.360]
3x Dia 0.330 [8.380]
5.010
5.732
[127.250]
0.621
[15.770]
[145.584]
Pictorial
View
8X R0.5 MIN
0.519
[13.190]
0.027
[0.690]
1.89
0.465
[11.811]
0.567
[14.400]
Ref
Figure 17. I/O Shield Dimensions
59
OM12352
Page 60

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
2.11 Electrical Considerations
2.11.1 DC Loading
Table 30 lists the DC loading characteristics of the board. This data is based on a DC analysis of
all active components within the board that impact its power delivery subsystems. The analysis
does not include PCI add-in cards. Minimum values assume a light load placed on the board that
is similar to an environment with no applications running and no USB current draw. Maximum
values assume a load placed on the board that is similar to a heavy gaming environment with a
500 mA current draw per USB port. These calculations are not based on specific processor values
or memory configurations but are based on the minimum and maximum current draw possible
from the board’s power delivery subsystems to the processor, memory, and USB ports.
Use the datasheets for add-in cards, such as PCI, to determine the overall system power
requirements. The selection of a power supply at the system level is dependent on the system’s
usage model and not necessarily tied to a particular processor speed.
Table 30. DC Loading Characteristics
DC Current at:
Mode DC Power +3.3 V +5 V +12 V -12 V +5 VSB
Minimum loading 190.00 W 5.00 A 11.00 A 9.00 A 0.03 A 0.60 A
Maximum loading 286.00 W 11.00 A 15.00 A 13.00 A 0.10 A 1.38 A
2.11.2 Add-in Board Considerations
The boards are designed to provide 2 A (average) of +5 V current for each add-in board. The total
+5 V current draw for add-in boards for a fully loaded Desktop Board D865PCD (all three
expansion slots and the AGP slot filled) must not exceed 8 A.
2.11.3 Fan Connector Current Capability
CAUTION
The processor fan must be connected to the processor fan connector, not to a chassis fan
connector. Connecting the processor fan to a chassis fan connector may result in onboard
component damage that will halt fan operation.
Table 31 lists the current capability of the fan connectors.
Table 31. Fan Connector Current Capability
Fan Connector Maximum Available Current
Processor fan 1600 mA
Front chassis fan 600 mA
Rear chassis fan 600 mA
60
Page 61

Technical Reference
2.11.4 Power Supply Considerations
CAUTION
The +5 V standby line for the power supply must be capable of providing adequate +5 V standby
current. Failure to do so can damage the power supply. The total amount of standby current
required depends on the wake devices supported and manufacturing options.
System integrators should refer to the power usage values listed in Table 30 when selecting a
power supply for use with the board.
Additional power required will depend on configurations chosen by the integrator.
The power supply must comply with the following recommendations found in the indicated
sections of the ATX form factor specification.
• The potential relation between 3.3 VDC and +5 VDC power rails (Section 4.2)
• The current capability of the +5 VSB line (Section 4.2.1.2)
• All timing parameters (Section 4.2.1.3)
• All voltage tolerances (Section 4.2.2)
For information about Refer to
The ATX form factor specification
Section 1.3, page 16
2.12 Thermal Considerations
CAUTION
The use of an Intel Pentium 4 processor operating above 2.80 GHz with this Intel desktop board
requires the following:
• A chassis with appropriate airflow to ensure proper cooling of the components on the board
• A processor fan heatsink that meets the thermal performance targets for Pentium 4 processors
operating above 2.80 GHz
Failure to ensure appropriate airflow may result in reduced performance of both the processor
and/or voltage regulator or, in some instances, damage to the desktop board. For a list of chassis
that have been tested with Intel desktop boards please refer to the following website:
http://developer.intel.com/design/motherbd/cooling.htm
All responsibility for determining the adequacy of any thermal or system design remains solely
with the reader. Intel makes no warranties or representations that merely following the
instructions presented in this document will result in a system with adequate thermal performance.
61
Page 62

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
CAUTION
Ensure that the ambient temperature does not exceed the Desktop Board’s maximum operating
temperature. Failure to do so could cause components to exceed their maximum case temperature
and malfunction. For information about the maximum operating temperature, see the
environmental specifications in Section 2.14.
CAUTION
Ensure that proper airflow is maintained in the processor voltage regulator circuit. Failure to do
so may result in damage to the voltage regulator circuit. The processor voltage regulator area
(item A in Figure 18) can reach a temperature of up to 85
Figure 18 shows the locations of the localized high temperature zones.
o
C in an open chassis.
D
Item Description
A Processor voltage regulator area
B Processor
C Intel 82865P MCH
D Intel 82801EB ICH5
OM17041
A
B
C
62
Figure 18. Localized High Temperature Zones
Page 63

Technical Reference
Table 32 provides maximum case temperatures for the Desktop Board D865PCD components that
are sensitive to thermal changes. The operating temperature, current load, or operating frequency
could affect case temperatures. Maximum case temperatures are important when considering
proper airflow to cool the Desktop Board D865PCD.
Table 32. Thermal Considerations for Components
Component Maximum Case Temperature
Intel Pentium 4 processor For processor case temperature, see processor datasheets and
processor specification updates
Intel 82865P MCH 99 oC (under bias)
Intel 82801EB ICH5 115 oC (under bias)
For information about Refer to
Intel Pentium 4 processor datasheets and specification updates Section 1.2, page 15
2.13 Reliability
The Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) prediction is calculated using component and
subassembly random failure rates. The calculation is based on the Bellcore Reliability Prediction
Procedure, TR-NWT-000332, Issue 4, September 1991. The MTBF prediction is used to estimate
repair rates and spare parts requirements.
The MTBF data is calculated from predicted data at 55 ºC. The Desktop Board D865PCD MTBF
is 101,425 hours.
63
Page 64

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
2.14 Environmental
Table 33 lists the environmental specifications for the Desktop Board D865PCD.
Table 33. Desktop Board D865PCD Environmental Specifications
Parameter Specification
Temperature
Non-Operating -40 °C to +70 °C
Operating 0 °C to +55 °C
Shock
Unpackaged 50 g trapezoidal waveform
Velocity change of 170 inches/second
Packaged Half sine 2 millisecond
Product Weight (pounds) Free Fall (inches) Velocity Change (inches/sec)
<20 36 167
21-40 30 152
41-80 24 136
81-100 18 118
Vibration
Unpackaged 5 Hz to 20 Hz: 0.01 g² Hz sloping up to 0.02 g² Hz
20 Hz to 500 Hz: 0.02 g² Hz (flat)
Packaged 10 Hz to 40 Hz: 0.015 g² Hz (flat)
40 Hz to 500 Hz: 0.015 g² Hz sloping down to 0.00015 g² Hz
64
Page 65

Technical Reference
2.15 Regulatory Compliance
This section describes the Desktop Boards’ compliance with U.S. and international safety and
electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations.
2.15.1 Safety Regulations
Table 34 lists the safety regulations the Desktop Board D865PCD complies with when correctly
installed in a compatible host system.
Table 34. Safety Regulations
Regulation Title
UL 60950 3rd ed.,2000/CSA
C22.2 No. 60950-00
EN 60950:2000 The Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment including
IEC 60950, 3rd Edition, 1999 The Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment including
Bi-National Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment
including Electrical Business Equipment. (USA and Canada)
Electrical Business Equipment. (European Union)
Electrical Business Equipment. (International)
2.15.2 EMC Regulations
Table 35 lists the EMC regulations the Desktop Board D865PCD complies with when correctly
installed in a compatible host system.
Table 35. EMC Regulations
Regulation Title
FCC (Class B) Title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Parts 2 and 15, Subpart B,
Radio Frequency Devices. (USA)
ICES-003 (Class B) Interference-Causing Equipment Standard, Digital Apparatus. (Canada)
EN55022: 1998 (Class B) Limits and methods of measurement of Radio Interference
Characteristics of Information Technology Equipment.
(European Union)
EN55024: 1998 Information Technology Equipment – Immunity Characteristics Limits
and methods of measurement. (European Union)
AS/NZS 3548 (Class B) Australian Communications Authority, Standard for Electromagnetic
Compatibility. (Australia and New Zealand)
CISPR 22, 3rd Edition (Class B) Limits and methods of measurement of Radio Disturbance
Characteristics of Information Technology Equipment. (International)
CISPR 24: 1997 Information Technology Equipment – Immunity Characteristics – Limits
and Methods of Measurements. (International)
65
Page 66

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
2.15.2.1 FCC Compliance Statement (USA)
Product Type: D865PCD Desktop Board
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment to a different electrical branch circuit from that to which the receiver is
connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Any changes or modifications to the equipment not expressly approved by Intel Corporation could
void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
2.15.2.2 Canadian Compliance Statement
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appereil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
2.15.3 European Union Declaration of Conformity Statement
We, Intel Corporation, declare under our sole responsibility that the product: Intel
D865PCD is in conformity with all applicable essential requirements necessary for CE marking,
following the provisions of the European Council Directive 89/336/EEC (EMC Directive) and
Council Directive 73/23/EEC (Safety/Low Voltage Directive).
The product is properly CE marked demonstrating this conformity and is for distribution within all
member states of the EU with no restrictions.
This product follows the provisions of the European Directives 89/336/EEC and 73/23/EEC.
®
Desktop Board
66
Page 67

Technical Reference
2.15.4 Product Ecology Statements
The following information is provided to address worldwide product ecology concerns and
regulations.
2.15.4.1 Disposal Considerations
This product contains the following materials that may be regulated upon disposal: lead solder on
the printed wiring board assembly.
2.15.4.2 Recycling Considerations
Intel encourages its customers to recycle its products and their components (e.g., batteries, circuit
boards, plastic enclosures, etc.) whenever possible. In the U.S., a list of recyclers in your area can
be found at:
http://www.eiae.org/
In the absence of a viable recycling option, products and their components must be disposed of in
accordance with all applicable local environmental regulations.
2.15.5 Product Certification Markings (Board Level)
Table 36 lists the board’s product certification markings.
Table 36. Product Certification Markings
Description Marking
UL joint US/Canada Recognized Component mark. Includes adjacent
UL file number for Intel Desktop Boards: E210882 (component side).
FCC Declaration of Conformity logo mark for Class B equipment;
includes Intel name and D865PCD model designation (component
side).
CE mark. Declares compliance to European Union (EU) EMC directive
(89/336/EEC) and Low Voltage directive (73/23/EEC) (component side).
The CE mark should also be on the shipping container.
Australian Communications Authority (ACA) C-Tick mark. Includes
adjacent Intel supplier code number, N-232. The C-tick mark should
also be on the shipping container.
Printed wiring board manufacturer’s recognition mark: consists of a
unique UL recognized manufacturer’s logo, along with a flammability
rating (solder side).
94V-0
67
Page 68

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
68
Page 69

3 Overview of BIOS Features
What This Chapter Contains
3.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................69
3.2 BIOS Flash Memory Organization ..............................................................................69
3.3 Resource Configuration..............................................................................................70
3.4 System Management BIOS (SMBIOS).......................................................................71
3.5 Legacy USB Support ..................................................................................................71
3.6 BIOS Updates ............................................................................................................72
3.7 Recovering BIOS Data ...............................................................................................73
3.8 Boot Options...............................................................................................................74
3.9 Fast Booting Systems with Intel® Rapid BIOS Boot....................................................75
3.10 BIOS Security Features..............................................................................................76
3.1 Introduction
The Desktop Board D865PCD uses an Intel/AMI BIOS that is stored in the Firmware Hub (FWH)
and can be updated using a disk-based program. The FWH contains the BIOS Setup program,
POST, the PCI auto-configuration utility, and Plug and Play support.
The BIOS displays a message during POST identifying the type of BIOS and a revision code. The
initial production BIOSs are identified as RC86510A.86A.
When the BIOS Setup configuration jumper is set to configure mode and the computer is poweredup, the BIOS compares the CPU version and the microcode version in the BIOS and reports if the
two match.
For information about Refer to
The Desktop Boards’ compliance level with Plug and Play Section 1.3, page 16
3.2 BIOS Flash Memory Organization
The Firmware Hub (FWH) includes a 4 Mbit (512 KB) symmetrical flash memory device.
69
Page 70

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
3.3 Resource Configuration
3.3.1 PCI Autoconfiguration
The BIOS can automatically configure PCI devices. PCI devices may be onboard or add-in cards.
Autoconfiguration lets a user insert or remove PCI cards without having to configure the system.
When a user turns on the system after adding a PCI card, the BIOS automatically configures
interrupts, the I/O space, and other system resources. Any interrupts set to Available in Setup are
considered to be available for use by the add-in card.
For information about Refer to
The versions of PCI and Plug and Play supported by the BIOS Section 1.3, page 16
3.3.2 PCI IDE Support
If you select Auto in the BIOS Setup program, the BIOS automatically sets up the two
PCI IDE connectors with independent I/O channel support. The IDE interface supports hard drives
up to ATA-66/100 and recognizes any ATAPI compliant devices, including CD-ROM drives, tape
drives, and Ultra DMA drives (see Section 1.3 for the supported version of ATAPI). The BIOS
determines the capabilities of each drive and configures them to optimize capacity and
performance. To take advantage of the high capacities typically available today, hard drives are
automatically configured for Logical Block Addressing (LBA) and to PIO Mode 3 or 4, depending
on the capability of the drive. You can override the auto-configuration options by specifying
manual configuration in the BIOS Setup program.
To use ATA-66/100 features the following items are required:
• An ATA-66/100 peripheral device
• An ATA-66/100 compatible cable
• ATA-66/100 operating system device drivers
NOTE
✏
Do not connect an ATA device as a slave on the same IDE cable as an ATAPI master device. For
example, do not connect an ATA hard drive as a slave to an ATAPI CD-ROM drive.
70
Page 71

Overview of BIOS Features
3.4 System Management BIOS (SMBIOS)
SMBIOS is a Desktop Management Interface (DMI) compliant method for managing computers in
a managed network.
The main component of SMBIOS is the Management Information Format (MIF) database, which
contains information about the computing system and its components. Using SMBIOS, a system
administrator can obtain the system types, capabilities, operational status, and installation dates for
system components. The MIF database defines the data and provides the method for accessing this
information. The BIOS enables applications such as third-party management software to use
SMBIOS. The BIOS stores and reports the following SMBIOS information:
• BIOS data, such as the BIOS revision level
• Fixed-system data, such as peripherals, serial numbers, and asset tags
• Resource data, such as memory size, cache size, and processor speed
• Dynamic data, such as event detection and error logging
Non-Plug and Play operating systems, such as Windows NT*, require an additional interface for
obtaining the SMBIOS information. The BIOS supports an SMBIOS table interface for such
operating systems. Using this support, an SMBIOS service-level application running on a
non-Plug and Play operating system can obtain the SMBIOS information.
For information about Refer to
The Desktop Boards’ compliance level with SMBIOS Section 1.3, page 16
3.5 Legacy USB Support
Legacy USB support enables USB devices such as keyboards, mice, and hubs to be used even
when the operating system’s USB drivers are not yet available. Legacy USB support is used to
access the BIOS Setup program, and to install an operating system that supports USB. By default,
Legacy USB support is set to Enabled.
Legacy USB support operates as follows:
1. When you apply power to the computer, legacy support is disabled.
2. POST begins.
3. Legacy USB support is enabled by the BIOS allowing you to use a USB keyboard to enter and
configure the BIOS Setup program and the maintenance menu.
4. POST completes.
5. The operating system loads. While the operating system is loading, USB keyboards and mice
are recognized and may be used to configure the operating system. (Keyboards and mice are
not recognized during this period if Legacy USB support was set to Disabled in the BIOS
Setup program.)
6. After the operating system loads the USB drivers, all legacy and non-legacy USB devices are
recognized by the operating system, and Legacy USB support from the BIOS is no longer
used.
71
Page 72

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
To install an operating system that supports USB, verify that Legacy USB support in the BIOS
Setup program is set to Enabled and follow the operating system’s installation instructions.
NOTE
✏
Legacy USB support is for keyboards, mice, and hubs only. Other USB devices are not supported
in legacy mode.
3.6 BIOS Updates
The BIOS can be updated using either of the following utilities, which are available on the Intel
World Wide Web site:
®
• Intel
• Intel
Express BIOS Update utility, which enables automated updating while in the Windows
environment. Using this utility, the BIOS can be updated from a file on a hard disk, a 1.44 MB
diskette, or a CD-ROM, or from the file location on the Web.
®
Flash Memory Update Utility, which requires creation of a boot diskette and manual
rebooting of the system. Using this utility, the BIOS can be updated from a file on a 1.44 MB
diskette (from a legacy diskette drive or an LS-120 diskette drive) or a CD-ROM.
Both utilities support the following BIOS maintenance functions:
• Verifying that the updated BIOS matches the target system to prevent accidentally installing
an incompatible BIOS.
• Updating both the BIOS boot block and the main BIOS. This process is fault tolerant to
prevent boot block corruption.
• Updating the BIOS boot block separately.
• Changing the language section of the BIOS.
• Updating replaceable BIOS modules, such as the video BIOS module.
• Inserting a custom splash screen.
NOTE
✏
Review the instructions distributed with the upgrade utility before attempting a BIOS update.
For information about Refer to
The Intel World Wide Web site Section 1.2, page 15
3.6.1 Language Support
The BIOS Setup program and help messages are supported in five languages: US English,
German, Italian, French, and Spanish. The default language is US English, which is present unless
another language is selected in the BIOS Setup program.
72
Page 73

Overview of BIOS Features
3.6.2 Custom Splash Screen
During POST, an Intel® splash screen is displayed by default. This splash screen can be
augmented with a custom splash screen. A utility is available from Intel to assist with creating a
custom splash screen. The custom splash screen can be programmed into the flash memory using
the BIOS upgrade utility. Information about this capability is available on the Intel Support World
Wide Web site.
NOTE
✏
If you add a custom splash screen, it will share space with the Intel branded logo.
For information about Refer to
The Intel World Wide Web site Section 1.2, page 15
3.7 Recovering BIOS Data
Some types of failure can destroy the BIOS. For example, the data can be lost if a power outage
occurs while the BIOS is being updated in flash memory. The BIOS can be recovered from a
diskette using the BIOS recovery mode. When recovering the BIOS, be aware of the following:
• Because of the small amount of code available in the non-erasable boot block area, there is no
video support. You can only monitor this procedure by listening to the speaker or looking at
the diskette drive LED.
• The recovery process may take several minutes; larger BIOS flash memory devices require
more time.
• Two beeps and the end of activity in the diskette drive indicate successful BIOS recovery.
• A series of continuous beeps indicates a failed BIOS recovery.
To create a BIOS recovery diskette, a bootable diskette must be created and the BIOS update files
copied to it. BIOS upgrades and the Intel Flash Memory Update Utility are available from Intel
Customer Support through the Intel World Wide Web site.
NOTE
✏
Even if the computer is configured to boot from an LS-120 diskette (in the Setup program’s
Removable Devices submenu), the BIOS recovery diskette must be a standard 1.44 MB diskette not
a 120 MB diskette.
For information about Refer to
The BIOS recovery mode jumper settings Section 2.9.2, page 57
The Boot menu in the BIOS Setup program Section 4.7, page 96
Contacting Intel customer support Section 1.2, page 15
73
Page 74

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
3.8 Boot Options
In the BIOS Setup program, the user can choose to boot from a diskette drive, hard drives,
CD-ROM, or the network. The default setting is for the diskette drive to be the first boot device,
the hard drive second, and the ATAPI CD-ROM third. The fourth device is disabled.
3.8.1 CD-ROM Boot
Booting from CD-ROM is supported in compliance to the El Torito bootable CD-ROM format
specification. Under the Boot menu in the BIOS Setup program, ATAPI CD-ROM is listed as a
boot device. Boot devices are defined in priority order. Accordingly, if there is not a bootable CD
in the CD-ROM drive, the system will attempt to boot from the next defined drive.
For information about Refer to
The El Torito specification Section 1.3, page 16
3.8.2 Network Boot
The network can be selected as a boot device. This selection allows booting from the onboard
LAN or a network add-in card with a remote boot ROM installed.
Pressing the <F12> key during POST automatically forces booting from the LAN. To use this key
during POST, the User Access Level in the BIOS Setup program’s Security menu must be
set to Full.
For information about Refer to
The BIOS Setup program’s Security menu Table 54, page 94
3.8.3 Booting Without Attached Devices
For use in embedded applications, the BIOS has been designed so that after passing the POST, the
operating system loader is invoked even if the following devices are not present:
• Video adapter
• Keyboard
• Mouse
3.8.4 Changing the Default Boot Device During POST
Pressing the <F10> key during POST causes a boot device menu to be displayed. This menu
displays the list of available boot devices (as set in the BIOS setup program’s Boot Device Priority
Submenu). Table 37 lists the boot device menu options.
Table 37. Boot Device Menu Options
74
Boot Device Menu Function Keys Description
<↑> or <↓> Selects a default boot device
<Enter> Exits the menu, saves changes, and boots from the selected device
<Esc> Exits the menu without saving changes
Page 75

Overview of BIOS Features
3.9 Fast Booting Systems with Intel® Rapid BIOS Boot
These factors affect system boot speed:
• Selecting and configuring peripherals properly
®
• Using an optimized BIOS, such as the Intel
3.9.1 Peripheral Selection and Configuration
The following techniques help improve system boot speed:
• Choose a hard drive with parameters such as “power-up to data ready” less than eight seconds,
that minimize hard drive startup delays.
• Select a CD-ROM drive with a fast initialization rate. This rate can influence POST
execution time.
• Eliminate unnecessary add-in adapter features, such as logo displays, screen repaints, or mode
changes in POST. These features may add time to the boot process.
• Try different monitors. Some monitors initialize and communicate with the BIOS more
quickly, which enables the system to boot more quickly.
Rapid BIOS
3.9.2 Intel Rapid BIOS Boot
Use of the following BIOS Setup program settings reduces the POST execution time.
In the Boot Menu:
• Set the hard disk drive as the first boot device. As a result, the POST does not first seek a
diskette drive, which saves about one second from the POST execution time.
• Disable Quiet Boot, which eliminates display of the logo splash screen. This could save
several seconds of painting complex graphic images and changing video modes.
• Enable Intel Rapid BIOS Boot. This feature bypasses memory count and the search for a
diskette drive.
In the Peripheral Configuration submenu, disable the LAN device if it will not be used. This can
reduce up to four seconds of option ROM boot time.
NOTE
✏
It is possible to optimize the boot process to the point where the system boots so quickly that the
Intel logo screen (or a custom logo splash screen) will not be seen. Monitors and hard disk drives
with minimum initialization times can also contribute to a boot time that might be so fast that
necessary logo screens and POST messages cannot be seen.
This boot time may be so fast that some drives might be not be initialized at all. If this condition
should occur, it is possible to introduce a programmable delay ranging from three to 30 seconds
(using the Hard Disk Pre-Delay feature of the Advanced Menu in the Drive Configuration
Submenu of the BIOS Setup program).
For information about Refer to
Drive Configuration Submenu in the BIOS Setup program Section 4.4.4, page 85
75
Page 76

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
3.10 BIOS Security Features
The BIOS includes security features that restrict access to the BIOS Setup program and who can
boot the computer. A supervisor password and a user password can be set for the BIOS Setup
program and for booting the computer, with the following restrictions:
• The supervisor password gives unrestricted access to view and change all the Setup options in
the BIOS Setup program. This is the supervisor mode.
• The user password gives restricted access to view and change Setup options in the BIOS Setup
program. This is the user mode.
• If only the supervisor password is set, pressing the <Enter> key at the password prompt of the
BIOS Setup program allows the user restricted access to Setup.
• If both the supervisor and user passwords are set, users can enter either the supervisor
password or the user password to access Setup. Users have access to Setup respective to
which password is entered.
• Setting the user password restricts who can boot the computer. The password prompt will be
displayed before the computer is booted. If only the supervisor password is set, the computer
boots without asking for a password. If both passwords are set, the user can enter either
password to boot the computer.
Table 38 shows the effects of setting the supervisor password and user password. This table is for
reference only and is not displayed on the screen.
Table 38. Supervisor and User Password Functions
Password Set
Neither Can change all
Supervisor
only
User only N/A Can change all
Supervisor
and user set
Note: If no password is set, any user can change all Setup options.
For information about Refer to
Setting user and supervisor passwords Section 4.5, page 94
NOTES
✏
Supervisor
Mode
options
Can change all
options
Can change all
options
(Note)
User Mode Setup Options
Can change all
options
Can change a
limited number
of options
options
Can change a
limited number
of options
(Note)
None None None
Supervisor Password Supervisor None
Enter Password
Clear User Password
Supervisor Password
Enter Password
Password to
Enter Setup
User User
Supervisor or
user
• For enhanced security, use different passwords for the supervisor and user passwords.
• Valid password characters are A-Z, a-z, and 0-9.
Password
During Boot
Supervisor or
user
76
Page 77

4 BIOS Setup Program
What This Chapter Contains
4.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................77
4.2 Maintenance Menu.....................................................................................................78
4.3 Main Menu..................................................................................................................79
4.4 Advanced Menu..........................................................................................................80
4.5 Security Menu ............................................................................................................94
4.6 Power Menu ...............................................................................................................95
4.7 Boot Menu..................................................................................................................96
4.8 Exit Menu ...................................................................................................................99
4.1 Introduction
The BIOS Setup program can be used to view and change the BIOS settings for the computer. The
BIOS Setup program is accessed by pressing the <F2> key after the Power-On Self-Test (POST)
memory test begins and before the operating system boot begins. The menu bar is shown below.
Maintenance Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Table 39 lists the BIOS Setup program menu features.
Table 39. BIOS Setup Program Menu Bar
Maintenance Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Selects boot
options
✏
Clears
passwords and
displays
processor
information
NOTE
Displays
processor
and memory
configuration
Configures
advanced
features
available
through the
chipset
Sets
passwords
and security
features
Configures
power
management
features and
power supply
controls
In this chapter, all examples of the BIOS Setup program menu bar include the maintenance menu;
however, the maintenance menu is displayed only when the Desktop Board is in configure mode.
Section 2.9.2 on page 57 tells how to put the Desktop Board in configure mode.
Saves or
discards
changes to
Setup
program
options
77
Page 78

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
Table 40 lists the function keys available for menu screens.
Table 40. BIOS Setup Program Function Keys
BIOS Setup Program Function Key Description
<←> or <→> Selects a different menu screen (Moves the cursor left or right)
<↑> or <↓> Selects an item (Moves the cursor up or down)
<Tab> Selects a field (Not implemented)
<Enter> Executes command or selects the submenu
<F9> Load the default configuration values for the current menu
<F10> Save the current values and exits the BIOS Setup program
<Esc> Exits the menu
4.2 Maintenance Menu
To access this menu, select Maintenance on the menu bar at the top of the screen.
Maintenance
The menu shown in Table 41 is for clearing Setup passwords and displaying processor
information. Setup only displays this menu in configure mode. See Section 2.9.2 on page 57 for
configure mode setting information.
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Table 41. Maintenance Menu
Feature Options Description
Clear All Passwords • Ok (default)
• Cancel
CPU Stepping
Signature
CPU Microcode
Update Revision
No options Displays CPU’s Stepping Signature.
No options Displays CPU’s Microcode Update Revision.
Clears the user and supervisor passwords.
78
Page 79

BIOS Setup Program
4.3 Main Menu
To access this menu, select Main on the menu bar at the top of the screen.
Maintenance
Main
Table 42 describes the Main menu. This menu reports processor and memory information and is
for configuring the system date and system time.
Table 42. Main Menu
Feature Options Description
BIOS Version No options Displays the version of the BIOS.
Processor Type No options Displays processor type.
Hyper-Threading
Technology
Processor Speed No options Displays processor speed.
System Bus Speed No options Displays the system bus speed.
System Memory Speed No options Displays the system memory speed.
L2 Cache RAM No options Displays the size of second-level cache.
Total Memory No options Displays the total amount of RAM.
Memory Mode No options Displays the memory mode (Dual Channel or Single
Memory Channel A Slot 0
Memory Channel B Slot 0
Language • English (default)
System Time Hour, minute, and
System Date Day of week
Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
• Disabled
• Enabled (default)
No options Displays the amount and type of RAM in the DIMM
• Francais
second
Month/day/year
Disables/enables Hyper-Threading Technology. This
option is present only when a processor that supports
Hyper-Threading Technology is installed.
Channel).
sockets.
Selects the current default language used by the BIOS.
Specifies the current time.
Specifies the current date.
79
Page 80

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
4.4 Advanced Menu
To access this menu, select Advanced on the menu bar at the top of the screen.
Maintenance Main
Advanced
PCI Configuration
Boot Configuration
Peripheral Configuration
Drive Configuration
Floppy Configuration
Event Log Configuration
Video Configuration
USB Configuration
Chipset Configuration
Table 43 describes the Advanced Menu. This menu is used for setting advanced features that are
available through the chipset.
Security Power Boot Exit
Table 43. Advanced Menu
Feature Options Description
PCI Configuration Select to display
submenu
Boot Configuration Select to display
submenu
Peripheral Configuration Select to display
submenu
Drive Configuration Select to display
submenu
Floppy Configuration Select to display
submenu
Event Log Configuration Select to display
submenu
Video Configuration Select to display
submenu
USB Configuration Select to display
submenu
Chipset Configuration Select to display
submenu
Configures individual PCI slot’s IRQ priority.
Configures Plug and Play and the Numlock key, and resets
configuration data.
Configures peripheral ports and devices.
Specifies type of connected IDE devices.
Configures the diskette drive.
Configures Event Logging.
Configures video features.
Configures USB support.
Configures advanced chipset features.
80
Page 81

BIOS Setup Program
4.4.1 PCI Configuration Submenu
To access this submenu, select Advanced on the menu bar and then PCI Configuration.
Maintenance Main
Advanced
PCI Configuration
Boot Configuration
Peripheral Configuration
Drive Configuration
Floppy Configuration
Event Log Configuration
Video Configuration
USB Configuration
Chipset Configuration
The submenu shown in Table 44 is used to configure the IRQ priority of PCI slots individually.
Table 44. PCI Configuration Submenu
Security Power Boot Exit
Feature Options Description
PCI Slot1 IRQ Priority
(Note)
PCI Slot2 IRQ Priority
(Note)
PCI Slot3 IRQ Priority
(Note)
Note: Additional interrupts may be available if certain onboard devices (such as the serial and parallel ports) are disabled.
• Auto (default)
• 3
• 5
• 9
• 10
• 11
• Auto (default)
• 3
• 5
• 9
• 10
• 11
• Auto (default)
• 3
• 5
• 9
• 10
• 11
Allows selection of IRQ priority for PCI bus connector 1.
Allows selection of IRQ priority for PCI bus connector 2.
Allows selection of IRQ priority for PCI bus connector 3.
81
Page 82

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
4.4.2 Boot Configuration Submenu
To access this submenu, select Advanced on the menu bar and then Boot Configuration.
Maintenance Main
Advanced
PCI Configuration
Boot Configuration
Peripheral Configuration
Drive Configuration
Floppy Configuration
Event Log Configuration
Video Configuration
USB Configuration
Chipset Configuration
The submenu represented by Table 45 is for setting Plug and Play options and the power-on state
of the Numlock key.
Security Power Boot Exit
Table 45. Boot Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Plug & Play O/S • No (default)
• Yes
Numlock • Off
• On (default)
Specifies if manual configuration is desired.
No lets the BIOS configure all devices. This setting is
appropriate when using a Plug and Play operating system.
Yes lets the operating system configure Plug and Play
devices not required to boot the system. This option is
available for use during lab testing.
Specifies the power-on state of the Numlock feature on the
numeric keypad of the keyboard.
82
Page 83

BIOS Setup Program
4.4.3 Peripheral Configuration Submenu
To access this submenu, select Advanced on the menu bar and then Peripheral Configuration.
Maintenance Main
Advanced
PCI Configuration
Boot Configuration
Peripheral Configuration
Drive Configuration
Floppy Configuration
Event Log Configuration
Video Configuration
USB Configuration
Chipset Configuration
The submenu represented in Table 46 is used for configuring computer peripherals.
Table 46. Peripheral Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Serial Port A • Disabled
• Enabled
• Auto (default)
Base I/O address
(This feature is present
only when Serial Port A
is set to Enabled)
Interrupt
(This feature is present
only when Serial Port A
is set to Enabled)
• 3F8 (default)
• 2F8
• 3E8
• 2E8
• IRQ 3
• IRQ 4
(default)
Security Power Boot Exit
Configures serial port A.
Auto assigns the first free COM port, normally COM1, the
address 3F8h, and the interrupt IRQ4.
An * (asterisk) displayed next to an address indicates a
conflict with another device.
Specifies the base I/O address for serial port A, if serial port A
is set to Enabled.
Specifies the interrupt for serial port A, if serial port A is set to
Enabled.
continued
83
Page 84

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
Table 46. Peripheral Configuration Submenu (continued)
Feature Options Description
Parallel port • Disabled
• Enabled
• Auto (default)
Mode • Output Only
• Bi-directional
(default)
• EPP
• ECP
Base I/O address
(This feature is present
only when Parallel Port
is set to Enabled)
Interrupt
(This feature is present
only when Parallel Port
is set to Enabled)
DMA
(This feature is present
only when Parallel Port
Mode is set to ECP)
Audio • Enabled
Onboard LAN • Enabled
ASF Support • Disabled
• 378 (default)
• 278
• IRQ 5
• IRQ 7
(default)
• 1
• 3 (default)
(default)
• Disabled
(default)
• Disabled
• Enabled
(default)
Configures the parallel port.
Auto assigns LPT1 the address 378h and the interrupt IRQ7.
An * (asterisk) displayed next to an address indicates a
conflict with another device.
Selects the mode for the parallel port. Not available if the
parallel port is disabled.
Output Only operates in AT*-compatible mode.
Bi-directional operates in PS/2-compatible mode.
EPP is Extended Parallel Port mode, a high-speed
bi-directional mode.
ECP is Enhanced Capabilities Port mode, a high-speed
bi-directional mode.
Specifies the base I/O address for the parallel port.
Specifies the interrupt for the parallel port.
Specifies the DMA channel.
Enables or disables the onboard audio subsystem.
Enables or disables the onboard LAN device.
Enables or disables ASF (Alert Standard Format) support.
84
Page 85

4.4.4 Drive Configuration Submenu
To access this submenu, select Advanced on the menu bar and then Drive Configuration.
Maintenance Main
Advanced
PCI Configuration
Boot Configuration
Peripheral Configuration
Drive Configuration
Floppy Configuration
Event Log Configuration
Video Configuration
USB Configuration
Chipset Configuration
The menu represented in Table 47 is used to configure IDE device options.
Table 47. Drive Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
PCI IDE Bus Master • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
Hard Disk Pre-Delay • Disabled (default)
• 1 Second
• 2 Seconds
• 3 Seconds
• 4 Seconds
• 5 Seconds
• 6 Seconds
• 9 Seconds
• 12 Seconds
• 15 Seconds
• 21 Seconds
• 30 Seconds
SATA Port-0 None Not supported
SATA Port-1 None Not supported
PATA Primary Master Select to display
sub-menu
PATA Primary Slave Select to display
sub-menu
PATA Secondary Master Select to display
sub-menu
PATA Secondary Slave Select to display
sub-menu
Security Power Boot Exit
Enables/disables the use of DMA for hard drive BIOS
INT13 reads and writes.
Specifies the hard disk drive pre-delay.
Reports type of connected device on Parallel ATA
(PATA) IDE primary master interface.
Reports type of connected device on Parallel ATA
(PATA) IDE primary slave interface.
Reports type of connected device on Parallel ATA
(PATA) IDE secondary master interface.
Reports type of connected device on Parallel ATA
(PATA) IDE secondary slave interface.
BIOS Setup Program
continued
85
Page 86

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
4.4.4.1 PATA Submenus
To access these submenus, select Advanced on the menu bar, then Drive Configuration, and then
the master or slave to be configured.
Maintenance Main
PCI Configuration
Boot Configuration
Advanced
Peripheral Configuration
Drive Configuration
SATA Port-0
SATA Port-1
PATA Primary Master
PATA Primary Slave
PATA Secondary Master
PATA Secondary Slave
Floppy Configuration
Event Log Configuration
Video Configuration
USB Configuration
Chipset Configuration
There are four available submenus in this screen:
• PATA primary master
• PATA primary slave
• PATA secondary master
• PATA secondary slave
Security Power Boot Exit
Table 48 on page 87 shows the format of the PATA IDE submenus. For brevity, only one example
is shown.
NOTE
✏
SATA support is not present on the Desktop Board D865PCD. The SATA submenus in this BIOS
screen are not accessible.
86
Page 87

BIOS Setup Program
Table 48. PATA Submenus
Feature Options Description
Drive Installed No options Displays the type of drive installed.
Type • Auto (default)
• User
Maximum Capacity No options Displays the drive capacity.
LBA/Large Mode • Disabled
• Auto (default)
Block Mode • Disabled
• Auto (default)
PIO Mode
Auto (default)
0
1
2
3
4
DMA Mode • Auto (default)
• SWDMA0
• SWDMA1
• SWDMA2
• MWDMA0
• MWDMA1
• MWDMA2
• UDMA0
• UDMA1
• UDMA2
S.M.A.R.T. • Auto (default)
• Disabled
• Enabled
Cable Detected No options Displays the type of cable connected to the IDE
Note: If an LS-120 drive is attached to the system, a row entitled ARMD Emulation Type will be displayed in the above
table. The BIOS will always recognize the drive as an ATAPI floppy drive. The ARMD Emulation Type should
always be set to Floppy.
Specifies the IDE configuration mode for IDE devices.
User allows capabilities to be changed.
Auto fills-in capabilities from ATA/ATAPI device.
Displays whether automatic translation mode is
enabled for the hard disk.
(This item is read-only unless Type is set to User.)
Displays whether automatic multiple sector data
transfers are enabled.
(This item is read-only unless Type is set to User.)
Sets the PIO mode.
(This item is read-only unless Type is set to User.)
Specifies the DMA mode for the drive.
Auto = Auto-detected
SWDMAn = Single Word DMAn
SWDMAn = Multi Word DMAn
UDMAn = Ultra DMAn
(This item is read-only unless Type is set to User.)
Enables/disables S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis,
and Reporting Technology).
(This item is read-only unless Type is set to User.)
interface: 40-conductor or 80-conductor (for ATA-100
peripherals).
87
Page 88

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
4.4.5 Floppy Configuration Submenu
To access this menu, select Advanced on the menu bar and then Floppy Configuration.
Maintenance Main
Advanced
PCI Configuration
Boot Configuration
Peripheral Configuration
Drive Configuration
Floppy Configuration
Event Log Configuration
Video Configuration
USB Configuration
Chipset Configuration
The submenu represented by Table 49 is used for configuring the diskette drive.
Table 49. Floppy Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Diskette Controller • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
Floppy A • Disabled
• 360 KB 5¼”
• 1.2 MB 5¼”
• 720 KB 3½”
• 1.44 MB 3½” (default)
• 2.88 MB 3½”
Diskette Write Protect • Disabled (default)
• Enabled
Security Power Boot Exit
Disables or enables the integrated diskette
controller.
Specifies the capacity and physical size of
diskette drive A.
Disables or enables write protection for the
diskette drive.
88
Page 89

4.4.6 Event Log Configuration Submenu
To access this menu, select Advanced on the menu bar and then Event Log Configuration.
Maintenance Main
Advanced
PCI Configuration
Boot Configuration
Peripheral Configuration
Drive Configuration
Floppy Configuration
Event Log Configuration
Video Configuration
USB Configuration
Chipset Configuration
The submenu represented by Table 50 is used to configure the event logging features.
Table 50. Event Log Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Event Log No options Indicates if there is space available in the event log.
View Event Log [Enter] Displays the event log.
Clear Event Log • Ok (default)
• Cancel
Event Logging • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
Mark Events As Read • Ok (default)
• Cancel
Security Power Boot Exit
Clears the event log after rebooting.
Enables/disables logging of DMI events.
Marks all events as read.
BIOS Setup Program
89
Page 90

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
4.4.7 Video Configuration Submenu
To access this menu, select Advanced on the menu bar and then Video Configuration.
Maintenance Main
Advanced
PCI Configuration
Boot Configuration
Peripheral Configuration
Drive Configuration
Floppy Configuration
Event Log Configuration
Video Configuration
USB Configuration
Chipset Configuration
The submenu represented in Table 51 is for configuring the video features.
Table 51. Video Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
AGP Aperture Size • 4 MB
• 8 MB
• 16 MB
• 32 MB
• 64 MB (default)
• 128 MB
• 256 MB
Primary Video Adapter • AGP (default)
• PCI
Security Power Boot Exit
Sets the aperture size for the video controller.
Selects primary video adapter to be used
during boot.
90
Page 91

4.4.8 USB Configuration Submenu
To access this menu, select Advanced on the menu bar and then USB Configuration.
Maintenance Main
Advanced
PCI Configuration
Boot Configuration
Peripheral Configuration
Drive Configuration
Floppy Configuration
Event Log Configuration
Video Configuration
USB Configuration
Chipset Configuration
The submenu represented in Table 52 is for configuring the USB features.
Table 52. USB Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
High-Speed USB • Enabled (default)
• Disabled
Legacy USB Support • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
USB 2.0 Legacy Support • Full-Speed (default)
• Hi-Speed
Security Power Boot Exit
Set to Disabled when a USB 2.0 driver is not
available.
Enables/disables legacy USB support.
Configures the USB 2.0 Legacy support to Hi-Speed
(480 Mbps) or Full-Speed (12 Mbps).
BIOS Setup Program
91
Page 92

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
4.4.9 Chipset Configuration Submenu
To access this menu, select Advanced on the menu bar and then Chipset Configuration.
Maintenance Main
Advanced
PCI Configuration
Boot Configuration
Peripheral Configuration
Drive Configuration
Floppy Configuration
Event Log Configuration
Video Configuration
USB Configuration
Chipset Configuration
The submenu represented in Table 53 is for configuring chipset options.
Table 53. Chipset Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
ISA Enable Bit • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
PCI Latency Timer • 32 (default)
• 64
• 96
• 128
• 160
• 192
• 224
• 248
Extended Configuration • Default (default)
• User Defined
SDRAM Frequency
(Note 1)
• Auto (default)
• 266 MHz
• 333 MHz
(Note 2)
Security Power Boot Exit
When set to Enable, a PCI-to-PCI bridge will only
recognize I/O addresses that do not alias to an ISA
range (within the bridge’s assigned I/O range).
Allows you to control the time (in PCI bus clock
cycles) that an agent on the PC bus can hold the bus
when another agent has requested the bus.
Allows the setting of extended configuration options.
Allows override of the detected memory frequency.
NOTE: If SDRAM Frequency is changed, you must
reboot for the change to take effect. After changing
this setting and rebooting, the System Memory
Speed parameter in the Main menu will reflect the
new value.
continued
92
Page 93

Table 53. Chipset Configuration Submenu (continued)
Feature Options Description
CPC Override • Auto (default)
• Enabled
• Disabled
SDRAM Timing Control
(Note 1)
• Auto (default)
• Manual – Aggressive
• Manual – User Defined
SDRAM RAS Active to
Precharge
(Note 3)
• 8
• 7
• 6 (default)
• 5
SDRAM CAS# Latency
(Note 3)
• 2.0
• 2.5 (default)
• 3.0
SDRAM RAS# to CAS#
(Note 3)
Delay
• 4
• 3 (default)
• 2
SDRAM RAS#
Precharge
(Note 3)
• 4
• 3 (default)
• 2
Notes:
1. This feature is displayed only if Extended Configuration is set to User Defined.
2. This option is displayed only if the installed processor has a 533 MHz system bus.
3. This feature is displayed only if SDRAM Timing Control is set to Manual – User Defined.
Controls the CPC/1n rule mode.
Enabled allows the DRAM controller to attempt chip
select assertions in two consecutive common clocks.
Auto = Timings will be programmed according to the
memory detected.
Manual – Aggressive = Selects most aggressive
user-defined timings.
Manual – User Defined = Allows manual override of
detected SDRAM settings.
Corresponds to tRAS.
Selects the number of clock cycles required to
address a column in memory.
Selects the number of clock cycles between
addressing a row and addressing a column.
Selects the length of time required before accessing
a new row.
BIOS Setup Program
93
Page 94

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
4.5 Security Menu
To access this menu, select Security from the menu bar at the top of the screen.
Maintenance Main Advanced
Security
The menu represented by Table 54 is for setting passwords and security features.
Table 54. Security Menu
If no password entered previously:
Feature Options Description
Supervisor Password No options Reports if there is a supervisor password set.
User Password No options Reports if there is a user password set.
Set Supervisor Password Password can be up to seven
alphanumeric characters.
(Note 1)
User Access Level
(Note 2)
Set User Password Password can be up to seven
Clear User Password
(Note 3)
Chassis Intrusion • Disabled (default)
Notes:
1. Valid password characters are A-Z, a-z, and 0-9.
2. This feature is displayed only if a supervisor password has been set.
3. This feature is displayed only if a user password has been set.
• No Access
• View Only
• Limited
• Full (default)
alphanumeric characters.
(Note 1)
• Ok (default)
• Cancel
• Log
• Log, notify once
• Log, notify until cleared
Power Boot Exit
Specifies the supervisor password.
Sets the user access rights to the BIOS Setup
Utility.
No Access prevents user access to the BIOS
Setup Utility.
View Only allows the user to view but not
change the BIOS Setup Utility fields.
Limited allows the user to changes some
fields.
Full allows the user to changes all fields
except the supervisor password.
Specifies the user password.
Clears the user password.
Disabled = Disables Chassis Intrusion
Log = Logs the intrusion in the event log
Log, notify once = Halts system during POST.
User must press <F4> to continue. Intrusion
flag is cleared and the event log is updated.
Log, notify til cleared = Halts system during
POST. User must enter BIOS setup Security
Menu and select “Clear Chassis Intrusion
Status” to clear the Chassis intrusion flag.
94
Page 95

4.6 Power Menu
To access this menu, select Power from the menu bar at the top of the screen.
Maintenance Main Advanced Security
ACPI
The menu represented in Table 55 is for setting the power management features.
Table 55. Power Menu
Feature Options Description
ACPI Select to display submenu Sets the ACPI power management options.
After Power Failure • Stay Off
• Last State (default)
• Power On
Wake on PCI PME • Stay Off (default)
• Power On
Specifies the mode of operation if an AC power loss
occurs.
Stay Off keeps the power off until the power button is
pressed.
Last State restores the previous power state before
power loss occurred.
Power On restores power to the computer.
Specifies how the computer responds to a PCI power
management event.
Power
BIOS Setup Program
Boot Exit
4.6.1 ACPI Submenu
To access this menu, select Power from the menu bar at the top of the screen and then ACPI.
Maintenance Main Advanced Security
Power
ACPI
The submenu represented in Table 56 is for setting the ACPI power options.
Table 56. ACPI Submenu
Feature Options Description
ACPI Suspend State • S1 State
• S3 State (default)
Wake on LAN* from S5 • Stay Off (default)
• Power On
S1 is the safest mode but consumes more power.
S3 consumes less power, but some drivers may not
support this state.
In ACPI soft-off mode only, determines how the
system responds to a LAN wake-up event.
Boot Exit
95
Page 96

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
4.7 Boot Menu
To access this menu, select Boot from the menu bar at the top of the screen.
Maintenance Main Advanced Security Power
Boot Device Priority
Hard Disk Drives
Removable Devices
ATAPI CD-ROM Drives
The menu represented in Table 57 is used to set the boot features and the boot sequence.
Table 57. Boot Menu
Feature Options Description
Silent Boot • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
Intel(R) Rapid BIOS Boot • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
Boot from Network • Disabled (default)
• Enabled
USB Boot • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
Boot Device Priority Select to display submenu Specifies the boot sequence from the available
Hard Disk Drives Select to display submenu Specifies the boot sequence from the available
Removable Devices Select to display submenu Specifies the boot sequence from the available
ATAPI CD-ROM Drives Select to display submenu Specifies the boot sequence from the available
Disabled displays normal POST messages.
Enabled displays OEM graphic instead of POST
messages.
Enables the computer to boot without running
certain POST tests.
Disables/enables PXE boot to LAN.
Note: When set to Enabled, you must reboot for
the Intel Boot Agent device to be available in the
Boot Device menu.
Disables/enables booting to USB boot devices.
types of boot devices.
hard disk drives.
removable devices.
ATAPI CD-ROM drives.
Boot
Exit
96
Page 97

4.7.1 Boot Device Priority Submenu
To access this menu, select Boot on the menu bar and then Boot Devices Priority.
Maintenance Main Advanced Security Power
Hard Disk Drives
Removable Devices
The submenu represented in Table 58 is for setting boot devices priority.
Table 58. Boot Device Priority Submenu
Feature Options Description
1st Boot Device
nd
2
Boot Device
rd
3
Boot Device
th
4
Boot Device
Note: The boot device identifier for Intel Boot Agent (IBA) may vary depending on the BIOS release.
• Removable Dev.
• Hard Drive
• ATAPI CD-ROM
®
• Intel
(Note)
Boot Agent
• Disabled
Specifies the boot sequence according to the device type.
The computer will attempt to boot from up to five devices
as specified here. Only one of the devices can be an IDE
hard disk drive. To specify boot sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <Enter> to set the selection as the intended
boot device.
The default settings for the first through fourth boot
devices are, respectively:
• Removable Dev.
• Hard Drive
• ATAPI CD-ROM
• Intel Boot Agent
BIOS Setup Program
Boot
Exit
Boot Device Priority
ATAPI CD-ROM Drives
97
Page 98

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
4.7.2 Hard Disk Drives Submenu
To access this menu, select Boot on the menu bar and then Hard Disk Drives.
Maintenance Main Advanced Security Power
Boot Device Priority
Removable Devices
The submenu represented in Table 59 is for setting hard disk drive priority.
Table 59. Hard Disk Drives Submenu
Feature Options Description
1st Hard Disk Drive
(Note)
Note: This boot device submenu appears only if at least one boot device of this type is installed. This list will display up
to twelve hard disk drives, the maximum number of hard disk drives supported by the BIOS.
Dependent on installed
hard drives
Specifies the boot sequence from the available hard
disk drives. To specify boot sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <Enter> to set the selection as the
intended boot device.
Boot
Hard Disk Drives
ATAPI CD-ROM Drives
Exit
4.7.3 Removable Devices Submenu
To access this menu, select Boot on the menu bar, then Removable Devices.
Maintenance Main Advanced Security Power
Boot Device Priority
Hard Disk Drives
The submenu represented in Table 60 is for setting removable device priority.
Table 60. Removable Devices Submenu
Feature Options Description
1st Removable Device
(Note)
Note: This boot device submenu appears only if at least one boot device of this type is installed. This list will display up
to four removable devices, the maximum number of removable devices supported by the BIOS.
Dependent on installed
removable devices
Specifies the boot sequence from the available
removable devices. To specify boot sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <Enter> to set the selection as the
intended boot device.
Boot
Removable Devices
ATAPI CD-ROM Drives
Exit
98
Page 99

BIOS Setup Program
4.7.4 ATAPI CD-ROM Drives Submenu
To access this menu, select Boot on the menu bar and then ATAPI CD-ROM Drives.
Maintenance Main Advanced Security Power
Boot Device Priority
Hard Disk Drives
Removable Devices
The submenu represented in Table 61 is for setting ATAPI CD-ROM drive priority.
Table 61. ATAPI CD-ROM Drives Submenu
Feature Options Description
1st ATAPI CDROM
(Note)
Note: This boot device submenu appears only if at least one boot device of this type is installed. This list will display up
to four ATAPI CD-ROM drives, the maximum number of ATAPI CD-ROM drives supported by the BIOS.
Dependent on installed
ATAPI CD-ROM drives
Specifies the boot sequence from the available
ATAPI CD-ROM drives. To specify boot sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <Enter> to set the selection as the
intended boot device.
Boot
ATAPI CD-ROM Drives
Exit
4.8 Exit Menu
To access this menu, select Exit from the menu bar at the top of the screen.
Maintenance Main Advanced Security Power Boot
The menu represented in Table 62 is for exiting the BIOS Setup program, saving changes, and
loading and saving defaults.
Table 62. Exit Menu
Feature Description
Exit Saving Changes Exits and saves the changes in CMOS SRAM.
Exit Discarding Changes Exits without saving any changes made in the BIOS Setup program.
Load Optimal Defaults Loads the optimal default values for all the Setup options.
Load Custom Defaults Loads the custom defaults for Setup options.
Save Custom Defaults Saves the current values as custom defaults. Normally, the BIOS reads the
Setup values from flash memory. If this memory is corrupted, the BIOS reads the
custom defaults. If no custom defaults are set, the BIOS reads the factory
defaults.
Discard Changes Discards changes without exiting Setup. The option values present when the
computer was turned on are used.
Exit
99
Page 100

Intel Desktop Board D865PCD Technical Product Specification
100
 Loading...
Loading...