Page 1
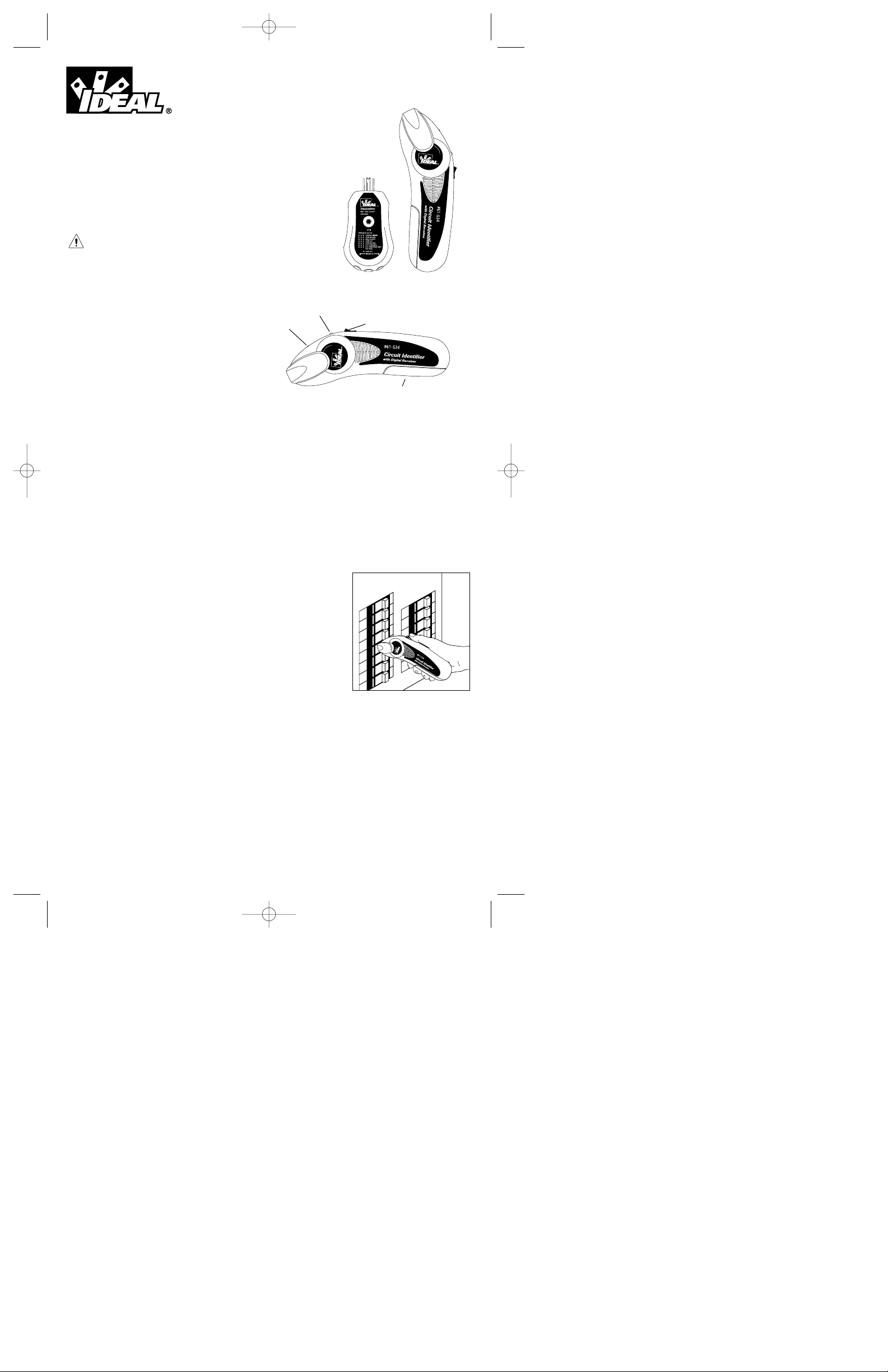
#61-534
Automatic Circuit Identifier
With Digital Receiver and
120/24 0V G F C I Receptacle Tester
The task of locating AC circuits is now made quick and easy. No more guessing
or trial and error when it comes to locating the correct circuit breaker supplying
power to an AC outlet or lighting fixture.
WARNING:
Use extreme care when working around AC circuits, severe shock hazards exist.
If used on a circuit controlled by a dimmer, turn the dimmer to the highest on
position. Do not use in cardiac care areas.
Features:
• Automatically and quicklly finds correct breaker
• Non-contact voltage sensor for 80-300VAC
• Transmitter works 120/240VAC circuits
• Verifies wiring configuration
• Low battery detection
OPERATION:
Self-Test
Turn the receiver's power switch forward to the ON position.
The unit will perform a self-test to ensure proper operation.
Low Battery Detection
After performing the self-test the receiver will verify the voltage of the 9Vdc battery. If the battery voltage is below 7.3 volts, the
receiver will beep three times and turn itself off. Remove the old battery, and replace it with a standard 9Vdc battery.
Idle Mode
Provided the battery is good, the receiver will enter the idle mode. Both the receiver’s LEDs will remain on and the receiver will
continually check for any active signals.
Non-Contact Voltage Test
Point the receiver’s nose towards a live AC receptacle or power cord. Once an AC Voltage field of > 50V is sensed, the receiver
will switch to Voltage Sensor mode. The red LED remains lit and the receiver will audibly beep. The beeping speed will increase
when the receiver is moved closer to the AC power source, and slows when the receiver is moved further away. Once the receiver
senses a signal from the transmitter, it will switch to the circuit identifier mode. The circuit identifier mode is indicated by a
steady green LED. To leave this mode and use the receiver for AC Voltage detection, turn the power switch off, then on again.
Locating A Circuit Breaker or Fuse:
1. Plug the transmitter into the receptacle.
2. Go to the circuit breaker panel box.
3. Turn the receiver on, and allow it to complete its self-test away from power.
4. Place the flat surface of the tapered end of the receiver directly onto the circuit
breaker or fuse as shown in Fig A. If the receiver is held at any other angle
inaccurate readings may occur.
5. Move the receiver down each side of the panel passing over each breaker
or fuse. This will calibrate the receiver to the signal from the transmitter.
6. Move the receiver down each side once more. On the second pass, the receiver
will continually beep and the green LED will flash while at circuit breaker powering
the transmitter. Some signals will be detected on the first pass.
7. Trip the breaker off and check that the LED's of the transmitter in the outlet are off
to confirm you have selected the correct breaker or fuse to turn off.
Locating a Circuit Breaker or Fuse Controlling an Incandescent Light Fixture
1. If the incandescent light fixture is controlled by a wall switch, make sure the wall switch is OFF.
2. Remove light bulb.
3. Install a Screw-in socket adapter (not included).
4. Plug the transmitter into the adapter.
5. Turn on the wall switch and follow the procedure described in Locating a Circuit Breaker or Fuse steps 3 through 8.
Receiver Auto Power Off:
If the receiver is left on and not utilized for 10 minutes (no energized AC circuit or transmitter signals are detected), it will
automatically shut down to conserve its battery life.
BATTERY REPLACEMENT:
Remove battery cover. Insert new 9V battery into battery compartment and re-install battery cover.
Power Switch
Battery Compartment
Green LED
Red LED
FIG A
ND 5416-1 61-534 Instructions 7/19/05 11:58 AM Page 1
Page 2

Verifying Receptacles for Correct Wiring:
Plug the transmitter into a standard 120 Vac receptacle. The three LED lamps on the transmitter will indicate the wiring configuration, the label on the transmitter indicates each sequence.
Testing GFCI Receptacles:
1. Consult the GFCI manufacturer’s installation instructions to determine that the GFCI is installed in accordance with the manufacturer’s specifications.
2. Check for correct wiring of receptacle and all remotely connected receptacles on the branch circuit.
3. Operate the test button on the GFCI. The GFCI must trip. If it does not – do not use the circuit – consult an electrician. If
the GFCI does trip, reset the GFCI. Then, insert the GFCI tester into the receptacle to be tested.
4. Activate the test button on the GFCI tester for a minimum of 6 seconds when testing the GFCI condition. Visible indication
on the GFCI tester must cease when tripped.
5. If the tester fails to trip the GFCI, it suggests: A wiring problem with a totally operable GFCI, or b) proper wiring with a
faulty GCFI. Consult with an electrician to check the condition of the wiring and GFCI.
Caution: When testing GFCIs installed in 2-wire systems (no ground wire available), the tester may give a false indication that
the GFCI is not functioning properly. If this occurs, recheck the operation of the GFCI using the test and reset buttons. The
GFCI button test function will demonstrate proper operations.
NOTE:
• All appliances or equipment on the circuit being tested should be unplugged to help avoid erroneous readings.
• Not a comprehensive diagnostic instrument but a simple instrument to detect nearly all probable common improper wiring
conditions.
• Refer all indicated problems to a qualified electrician.
• Will not indicate quality of ground.
• Will not detect 2 hot wires in circuit.
• Will not detect a combination of defects.
• Will not indicate reversal of grounded and grounding conductors.
SPECIFICATIONS:
Operating Range: 100-250VAC
Operating Frequency: 47-63Hz
Maximum Load: 18A (4ms) at 120VAC, 200mW max, at 120VAC
Duty Cycle: Max: 4mS every 16.6mS (continuous), (.24%)
Weight (excluding battery): Transmitter approx 50gr., Receiver approx. 85 gr.
Power Supply: 9VDC battery
Operating Temperature: 0 to 50ºC
Identificador automático de circuitos de ID EAL con
probador de receptáculos equipado con interruptor
accionado por pérdidas a tierra E-Z Check® Plus
La tarea de ubicar circuitos de CA se hace ahora más rápida y sencilla. Ya no hay necesidad de tratar de adivinar o tantear
cuando haya que localizar el disyuntor correcto que suministra corriente a una toma o lámpara de CA.
PRECAUCIÓN:
Tenga mucho cuidado al trabajar en las proximidades de circuitos de CA, ya que existe la posibilidad de electrocución. Su
identificador automático de circuitos IDEAL no tiene como finalidad sustituir las buenas prácticas eléctricas, sino ayudar a
saber cómo está conectada su casa o lugar de trabajo. Todos los trabajos de corrección deben ser realizados por un electricista
capacitado. Respete los códigos eléctricos correspondientes. Si se usa en un circuito controlado por un reductor de intensidad
luminosa, gire el reductor a la posición más alta. No use en áreas de cuidados para enfermos del corazón. Cerciórese siempre
con un probador/medidor de voltaje que se haya desconectado el disyuntor o fusible correcto antes de realizar un trabajo.
INSTALACIÓN DE LA PILA:
Quite la tapa de la pila. Conecte la pila según se muestra en la Fig. A. Introduzca la pila nueva en el compartimiento correspondiente y vuelva a instalar la tapa.
OPERACIÓN:
Autocomprobación
Ponga el interruptor de corriente del receptor en la posición de encendido. La unidad realizará una autocomprobación para asegurar la operación apropiada.
Detección de pila descargada
Después de realizar la autocomprobación, el receptor verificará el voltaje de la pila de 9 VCC. Si el voltaje de la pila es menor
que 7,3 voltios, el receptor emitirá un pitido tres veces y se apagará por sí solo. Saque la pila vieja, y reemplácela por una pila
normal de 9 VCC.
Modalidad inactiva
Siempre que la pila esté en buenas condiciones, el receptor pasará a la modalidad inactiva. El LED del receptor brillará con
una luz amarilla y el receptor comprobará continuamente si hay señales activas.
Prueba de voltaje sin contacto
Apunte el extremo del receptor hacia un receptáculo o cordón de alimentación de CA. Una vez que se detecte un campo de
voltaje de CA > 50V, el receptor pasará a la modalidad del sensor de voltaje. Se encenderá el LED rojo del receptor, y emitirá un
sonido de forma alternativa. La velocidad de los pitidos aumentará cuando el receptor se acerque a la fuente de alimentación de
CA, y disminuirá cuando se aleje. Una vez que el receptor detecte una señal del transmisor, permanecerá en la modalidad del
identificador del circuito. Para salir de esta modalidad y usar el receptor para la detección de voltaje de CA, ponga el interruptor
en la posición de apagado y después en encendido.
#61-534
ND 5416-1 61-534 Instructions 7/19/05 11:58 AM Page 2
 Loading...
Loading...