Page 1

HP Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager 7.2 Command Line Interface User Guide
Abstract
This user guide is intended for HP Virtual Connect administrators who are familiar with both Virtual Connect and the Virtual
Connect management suite, including HP Virtual Connect Manager, Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager and upper level
managers such as HP Matrix OE logical server management and HP Matrix Operating Environment.
HP Part Number: 656831-005a
Published: July 2013
Edition: 2
Page 2
© Copyright 2011, 2013 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial
Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under
vendor's standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Acknowledgments
Microsoft®, Windows®, Windows XP®, and Windows NT® are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Warranty
HP will replace defective delivery media for a period of 90 days from the date of purchase. This warranty applies to all Insight Management
products.
Revision history
Edition NotesPublication dateEdition numberSupported versionsManufacturing part
number
July 2013SecondVersion 7.2656831-005a
Removed “Registering for
software technical
support and update
service”
Initial publicationMarch 2013FirstVersion 7.2656831-005
June 2012FirstVersion 7.1656831-004
February 2012FirstVersion 7.0656831-003
August, 2011FirstVersion 6.3.1656831-002
Page 3

Contents
1 Getting started...........................................................................................6
VCEMCLI prerequisites..............................................................................................................6
Installing the VCEMCLI..............................................................................................................6
Removing the VCEMCLI.............................................................................................................6
Workflow tips...........................................................................................................................6
CLI use cases for administrators.............................................................................................6
Leveraging the VCEM web user interface................................................................................7
Gathering VC environment information...................................................................................7
Script development considerations..............................................................................................7
Choosing a location for the script files....................................................................................7
Initiating multiple commands.................................................................................................7
Security on the CMS............................................................................................................8
Authentication.....................................................................................................................8
Using delays in script commands...........................................................................................8
Profiles and powering off or powering on................................................................................8
Running scripts as Windows scheduled tasks...........................................................................8
Comparing VCMCLI scripts to VCEMCLI scripts........................................................................8
2 Using the VCEMCLI....................................................................................9
Executable...............................................................................................................................9
Environment Variable................................................................................................................9
Common options......................................................................................................................9
Using the VCEMCLI in a script .................................................................................................10
Authenticating by using VCEM.................................................................................................11
User-name and password logon................................................................................................11
Logging on without a password................................................................................................11
Session lifetime.......................................................................................................................12
Role-based access control (RBAC).............................................................................................12
RBAC Details.....................................................................................................................12
RBAC best practices...........................................................................................................14
Working with server profiles.....................................................................................................15
Creating a server profile.....................................................................................................15
Deleting a server profile......................................................................................................15
Modifying a server profile...................................................................................................15
Displaying job details.........................................................................................................18
Accessing the VCEMCLI help...................................................................................................19
Error reporting.......................................................................................................................20
3 Using VCEM commands............................................................................21
add profile............................................................................................................................21
set profile..............................................................................................................................23
assign profile.........................................................................................................................24
export profiles........................................................................................................................26
move profile...........................................................................................................................27
remove profile........................................................................................................................29
unassign profile......................................................................................................................30
add enet-connection...............................................................................................................31
set enet-connection.................................................................................................................34
remove enet-connection...........................................................................................................37
add fc-connection...................................................................................................................38
set fc-connection.....................................................................................................................40
remove fc-connection...............................................................................................................42
Contents 3
Page 4

add fcoe-connection...............................................................................................................43
set fcoe-connection.................................................................................................................46
remove fcoe-connection...........................................................................................................49
add iscsi-connection................................................................................................................50
set iscsi-connection..................................................................................................................53
remove iscsi-connection...........................................................................................................56
set iscsi-boot-param................................................................................................................57
remove iscsi-boot-param..........................................................................................................61
add server-port-map................................................................................................................62
set server-port-map..................................................................................................................64
remove server-port-map...........................................................................................................66
add server-port-map-range.......................................................................................................67
remove server-port-map-range...................................................................................................69
poweroff devicebay................................................................................................................70
poweron devicebay................................................................................................................72
show power-status...................................................................................................................73
show job...............................................................................................................................74
show version..........................................................................................................................75
show vcem-status....................................................................................................................76
startvcdfwupdate....................................................................................................................77
completevcdfwupdate.............................................................................................................78
startvcdmaint.........................................................................................................................79
cancelvcdmaint......................................................................................................................80
completevcdmaint...................................................................................................................81
4 Error messages.........................................................................................82
5 Troubleshooting the VCEMCLI..................................................................103
VCEMCLI calls result in access denied errors............................................................................103
VCEMCLI calls result in errors for invalid leading character or invalid characters...........................103
VCEMCLI calls result in 404 errors..........................................................................................103
API timeouts occur................................................................................................................103
High CPU usage on the CMS server while running a VCEMCLI client...........................................103
Job reports a failed status......................................................................................................103
Completed with a warning job status......................................................................................103
Unable to assign a profile to a domain group..........................................................................104
VC Domain reports configuration mismatch status.....................................................................104
VC Domain reports expired license status.................................................................................104
Error occurs on a database operation......................................................................................104
VCEM operation failed to execute because VC firmware is not supported.....................................104
Creating a server profile fails.................................................................................................105
Server profile edit operation fails when the target server is powered on.......................................105
Server profile job completed with success but changes have not occurred....................................105
After a server profile assignment, some connections defined in the server profile are not functional...106
Error message for the -add profile or -set profile command occurs...............................................106
Error message for the -add profile command............................................................................107
Unexpected results from non-blocked (-nb) commands................................................................107
Additional troubleshooting information and tools......................................................................107
6 Support and other resources....................................................................108
Information to collect before contacting HP...............................................................................108
How to contact HP................................................................................................................108
Security bulletin and alert policy for non-HP owned software components....................................108
Subscription service..........................................................................................................108
HP services..........................................................................................................................108
How to use your software technical support and update service.............................................109
4 Contents
Page 5

Warranty information.......................................................................................................109
HP authorized resellers.....................................................................................................109
Related information...............................................................................................................109
Documents......................................................................................................................109
Websites........................................................................................................................110
Typographic conventions.......................................................................................................110
7 Documentation feedback.........................................................................111
Index.......................................................................................................112
Contents 5
Page 6

1 Getting started
The HP Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager (VCEM) Command Line is a family of executables that
provide the facilities necessary for the most frequently used management operations for the VCEM
infrastructure.
The VCEM Command Line Interface (VCEMCLI) can be used as an alternative method for managing
common Virtual Connect operations. The VCEM.CMD executable provides failover management.
VCEMCLI.EXE is useful when scripting bulk operations on multiple Virtual Connect (VC) server
profiles.
VCEMCLI prerequisites
The VCEMCLI supports the same Windows operating environments as the corresponding release
of VCEM. For more information, see the latest version of the HP Insight Management Support
Matrix.
Installing the VCEMCLI
The VCEMCLI is automatically installed from the Insight Management 7.2 DVD when VCEM is
installed on the central management server (CMS) host.
Removing the VCEMCLI
The VCEMCLI is removed when VCEM is removed from the CMS host.
Workflow tips
This section helps you to use the VCEMCLI efficiently.
CLI use cases for administrators
The VCEMCLI can facilitate VC management tasks in a number of scenarios. The following are
some example use cases:
• Assemble a library of scripts to create different types of common profiles. If your environment
always assigns a particular set of network and storage connections for a class of servers such
as web servers or file servers, these settings can be captured in a script. When a new web
server profile is needed, run the script to create the new profile.
• Script VCMCLI and VCEMCLI operations:
Use the VCEMCLI to put the domain into maintenance.◦
◦ Use a secure shell (SSH) client to drive the VCMCLI.
◦ Use the VCEMCLI to cancel or complete maintenance on the domain.
• Script VCSU and VCEMCLI operations:
Use the VCEMCLI to put the domain into maintenance.◦
◦ Script VCSU commands.
◦ Use the VCEMCLI to cancel or complete maintenance on the domain.
• Manipulate networks or fabrics on groups of profiles.
• Script reassignment of profiles in response to changing workloads or environment.
6 Getting started
Page 7

• Run scripts in response to HP Systems Insight Manager events or from the Windows job
scheduler.
• Leverage the comma-separated values (CSV) export of profile data to answer questions such
as:
◦ Where is this MAC address or WWN used?
◦ Which profiles use this network?
◦ Which profiles use this fabric?
◦ What is different between these profiles?
Leveraging the VCEM web user interface
The VCEMCLI is designed to be used in addition to the VCEM web user interface. The web UI is
an easy way to gather information about your VC configuration and to examine the results of
scripted operations during the script development process.
Gathering VC environment information
Before you use the VCEMCLI, gather the following:
• Systems Insight Manager authentication information
• List of VC domains
• List of VC domain groups
• List of VC server profiles (can be done via the VCEMCLI -export profiles command)
• List of VC networks
• List of VC storage fabrics
• SAN-boot configuration details (if any)
• List of enclosures and a list of bays and servers contained in the enclosures
Script development considerations
The information in this section helps you with some key decisions on how your scripts are structured.
Choosing a location for the script files
Do not place the scripts you create in the VCEMCLI installation directory, because this approach
might prevent product upgrades from functioning. Instead, create your scripts in a separate directory
outside the HP installation directory tree.
Initiating multiple commands
Initiating several commands into the CMS quickly increases resource consumption on that system
for both CPU and memory. At some point, there is a risk of exceeding the system's ability to accept
and queue additional jobs.
To avoid this situation, HP recommends that you code script in such a way that it will be able to
cope with failed job submissions. Then, you must wait for a period of time and attempt to submit
the job again.
Do not use the -nb option when you are submitting multiple commands to operate on a single
profile, such as a series of commands to add multiple network connections. Doing so can cause
the commands to interfere with each other during processing.
Script development considerations 7
Page 8

Security on the CMS
The VCEMCLI is installed on the CMS. By installing on the CMS, you get the benefits of the security
measures already in place for the CMS. The trade-off is that the script execution imposes additional
load on the CMS.
HP recommends that you evaluate the amount of load that the script places on the CMS, and either
program in pauses or reduce the amount of work that each invocation of the script accomplishes.
Authentication
Decide whether user name and password authentication or certificate-based authentication is
appropriate for your environment. For more information about authentication, see “Authenticating
by using VCEM” (page 11).
Using delays in script commands
Do not poll for results in a tight loop. Insert delays in your scripts to allow the CMS time to manage
other tasks. Polling for results by using tight loops without delays might overload the CMS.
Profiles and powering off or powering on
Assigning a profile to a bay that contains a server requires that the bay be powered off in order
to complete the assignment. Graceful power-off operations allow time for the operating system on
the server to go through its normal shutdown processing. If an unresponsive process prevents the
normal shutdown from proceeding, you may need to resort to an ungraceful power-off. You should
use this method only as a last resort because it may result in data loss on the affected server. The
same power-off constraint applies to unassigning or updating a profile for a bay that contains a
server.
Running scripts as Windows scheduled tasks
By configuring the Windows Task Scheduler to run your VCEMCLI script, you can schedule
operations such as server reboots so they occur during nonworking hours. Configure the scheduled
task by using the credentials that correspond to the specific VCEMCLI script that the task will run.
Comparing VCMCLI scripts to VCEMCLI scripts
The VCEMCLI uses the same keyword names that the VCMCLI uses for items common to both CLIs.
VCEMCLI keywords are always preceded by a dash. In the VCMCLI whether a dash is required
depends on the specific keyword. Name/Value pairs in the VCEMCLI are separated by a space,
whereas they are separated by an equal sign (=) in the VCMCLI.
8 Getting started
Page 9
2 Using the VCEMCLI
The VCEMCLI can be executed from the Windows command-line or from scripts written in any
Windows-supported scripting language.
Executable
The vcemcli.exe executable is located in the HP VCEM Installation Root
Directory\Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager CLI directory.
During the VCEM installation process, the directory that contains vcemcli.exe is added to the
%PATH% environment variable (EV).
Environment Variable
You can control the behavior of the VCEMCLI and its common options by using the Windows EV
VCEMCLI. The format for the EV is exactly the same as the command-line. Any arguments contained
in this EV are appended to the list of arguments provided on the vcemcli.exe command-line.
Any arguments contained in the EV that are also provided on the command-line will be ignored.
Common options
VCEMCLI command-line options are not case sensitive. Options present on the command-line
override any corresponding values that the VCEMCLI environment variable (if set) contains.
Table 1 lists the common vcemcli.exe command-line options and their descriptions.
Table 1 Common options
-user username
-pw password
–port port
–loglevel level
–nb
DescriptionCLI options
Set as the user name for authentication with Systems Insight
Manager. If this command is not specified, the VCEMCLI
will use the Windows user name of the current user.
Used for authenticating with Systems Insight Manager when
the –user argument was also provided.
Used to contact the Systems Insight Manager server. If this
option is not provided, the default port is 50001. This
argument is required only if the Systems Insight Manager
environment is changed to require SOAP connections on
a different port.
File that contains VCEMCLI log messages.–logfile logfilename
Can be set to control the amount of information that
VCEMCLI logs. The available levels are: debug, info,
warn, error, and off.
The maximum size, in KB, of the VCEMCLI log file.–logsize size in kb
The default behavior is for commands to block and wait
for completion of the associated job or power operation
before they continue. The –nb (non-block) option causes
normally blocking commands to return immediately after
they are submitted. You must check the result of the
non-blocking job or power operation separately to
determine its success or failure.
Executable 9
Page 10
Table 1 Common options (continued)
DescriptionCLI options
NOTE: When you are using this option, sequential edits
queued for the same profile might conflict with the changes
being applied. HP recommends that you use blocking
operations when you are performing multiple changes to
a given profile. This approach ensures that the changes
for each edit are applied to the profile before the next
group of changes are initiated. Do not submit multiple
non-blocked commands for a single profile. Later
commands may overwrite the changes made by earlier
commands. For example, do not submit a series of
non-blocked commands to add network connections to a
given profile.
Suppresses output from the VCEMCLI.–silent
–timeout seconds
-pollinginterval seconds
Using the VCEMCLI in a script
The following example illustrates how the VCEMCLI can be used to automate common profile
management tasks. This example:
• Powers on the servers in the enclosure
• Creates server profiles
• Adds and edits network connections for the server profiles
• Assigns server profiles to the bays that contain servers
@echo off
set CLI=vcemcli.exe
set VCDG=OA-78-VCDG
set NEWNET=NET2
set MAXPROFILES=5
set MAXBAYS=16
set ENCLNAME=OA-78
set VCEMCLI=-logfile c:\demo.log
echo Turn on all servers in enclosure %ENCLNAME% -------------------------------------------for /L %%I in (1,1,%MAXBAYS%) DO (
%CLI% -show power-status -enclosureName %ENCLNAME% -bayname %%I
if ERRORLEVEL 240 (
echo There is no server in bay %%I
) else (
if ERRORLEVEL 1 (
echo Server in bay %%I is already on
) else (
echo Turning on server in bay %%I
%CLI% -poweron devicebay -enclosureName %ENCLNAME% -bayname %%I
if ERRORLEVEL 1 goto ERRORHANDLER
)
)
)
echo Creating %MAXPROFILES% profiles ------------------------------------------------------for /L %%I in (1,1,%MAXPROFILES%) DO (
echo Creating profile %%I of %MAXPROFILES%
%CLI% -add profile -vcdomaingroup %VCDG% -profilename PROFILE-%%I
if ERRORLEVEL 1 goto ERRORHANDLER
)
When set, instructs the VCEMCLI how long to wait for
blocking commands.
When set, instructs the VCEMCLI how often to poll VCEM
for job or power status.
echo Profile creation complete - adding network connections -------------------------------for /L %%I in (1,1,%MAXPROFILES%) DO (
echo Adding enet connection to PROFILE-%%I
%CLI% -add enet-connection -profilename PROFILE-%%I
if ERRORLEVEL 1 goto ERRORHANDLER
)
10 Using the VCEMCLI
Page 11

echo Add network connection complete - Update network connections -------------------------for /L %%I in (1,1,%MAXPROFILES%) DO (
echo Assigning enet connection %NEWNET% to port 3 of PROFILE-%%I
%CLI% -set enet-connection -profilename PROFILE-%%I -network %NEWNET% -portnumber 3
if ERRORLEVEL 1 goto ERRORHANDLER
)
echo Assign the profiles to bays that have servers present --------------------------------for /L %%I in (1,1,%MAXPROFILES%) DO (
::Turn off the server in the target bay ONLY if a server is present
%CLI% -show power-status -enclosureName %ENCLNAME% -bayname %%I
if ERRORLEVEL 240 (
echo There is no server in bay %%I - skipping profile assignment
) else (
if ERRORLEVEL 1 (
echo ----------------------------------------- echo Turning off server in bay %%I
%CLI% -poweroff devicebay -enclosureName %ENCLNAME% -bayname %%I -forceOnTimeout
if ERRORLEVEL 1 goto ERRORHANDLER
)
echo ----------------------------------------- echo The server in bay %%I is off. Assigning profile PROFILE-%%I
%CLI% -assign profile -profilename PROFILE-%%I -enclosureName %ENCLNAME% -bayname %%I
if ERRORLEVEL 1 goto ERRORHANDLER
)
)
goto END
:ERRORHANDLER
echo Error processing last command. ERRORLEVEL = %ERRORLEVEL%
:END
exit /b %ERRORLEVEL%
Authenticating by using VCEM
The VCEMCLI allows two types of authentication:
• Systems Insight Manager certificate based (administrators only): If the VCEMCLI user is logged
on as the local administrator, no credentials are required for command execution. This is the
recommended authentication method.
• User-name and password credential pair: If you are not logged on as an administrator, a
user-name and password credential pair must be provided. If only the password argument is
provided, the VCEMCLI uses the user name of the current Windows user for authentication.
User-name and password logon
Logging on requires a user-name and password credential set, which is passed to the VCEM server
for authentication. In this case, a successful logon is occurs when Systems Insight Manager validates
the supplied credentials. If the logon attempt is unsuccessful, an error message that indicates the
failure is reported.
User-name and password authentication is simple to configure, easier for testing scripts, and more
suited for use with role-based access control (RBAC). User-name and password information must
be gathered at the time that the script is run, or you must define a sufficiently secure mechanism
in your environment to store the user-name and password so the information is available to the
script when it runs.
Logging on without a password
If you log on to the CMS as an administrator, it is possible to execute the VCEMCLI without providing
credentials. This method uses a pre-installed authentication certificate available only to the CMS
administrator . HP recommends this method for executing the VCEMCLI because no password is
required as an argument on the command-line.
Authenticating by using VCEM 11
Page 12
Session lifetime
VCEMCLI logon sessions remain active for a single command execution. The CLI automatically
logs out of the VCEM server after the execution finishes, whether the command succeeded or failed.
Role-based access control (RBAC)
You can use RBAC to designate which operations and resources can be manipulated.
RBAC Details
VCEM provides the following role-based user types. Individual VCEMCLI commands require different
access permissions based on the resource involved and the read or write operation being called.
Access is determined based on the credentials that the VCEMCLI uses.
• VCEM Administrator—Manages all VCEM resources. All operations are permitted to all
resources.
• VCEM Domain Group Administrator—Manages VC domains and server profiles in one or
more VC domain groups.
• VCEM Domain Group Operator—Manages server profiles in one or more VC domain groups.
• VCEM Domain Group Limited Operator—Manages the same tasks as the VCEM Domain Group
Operator except for creating, editing, and deleting a server profile.
• VCEM User (Read Only)—Has read-only access to all VCEM resources.
Table 2 lists command-line options and the role-based user access privileges that can use the
commands.
Table 2 RBAC privileges
VCEM
DomainVCEM
(page 21)
(page 23)
profile” (page 24)
profiles” (page 26)
(page 27)
profile” (page 29)
VCEM
AdministratorCommand-line option
Group
Administrator
xx-remove profile, see “remove
DomainVCEM Domain
Group
Operator
xxx-add profile, see “add profile”
xxx-set profile, see “set profile”
Group
Limited
Operator
xxxx-assign profile, see “assign
xxxx-move profile, see “move profile”
VCEM User
(Read Only)
xxxxx-export profiles, see “export
profile” (page 30)
enet-connection” (page 31)
enet-connection” (page 34)
“remove enet-connection” (page 37)
12 Using the VCEMCLI
xxxx-unassign profile, see “unassign
xxx-add enet-connection, see “add
xxx-set enet-connection, see “set
xxx-remove enet-connection, see
Page 13
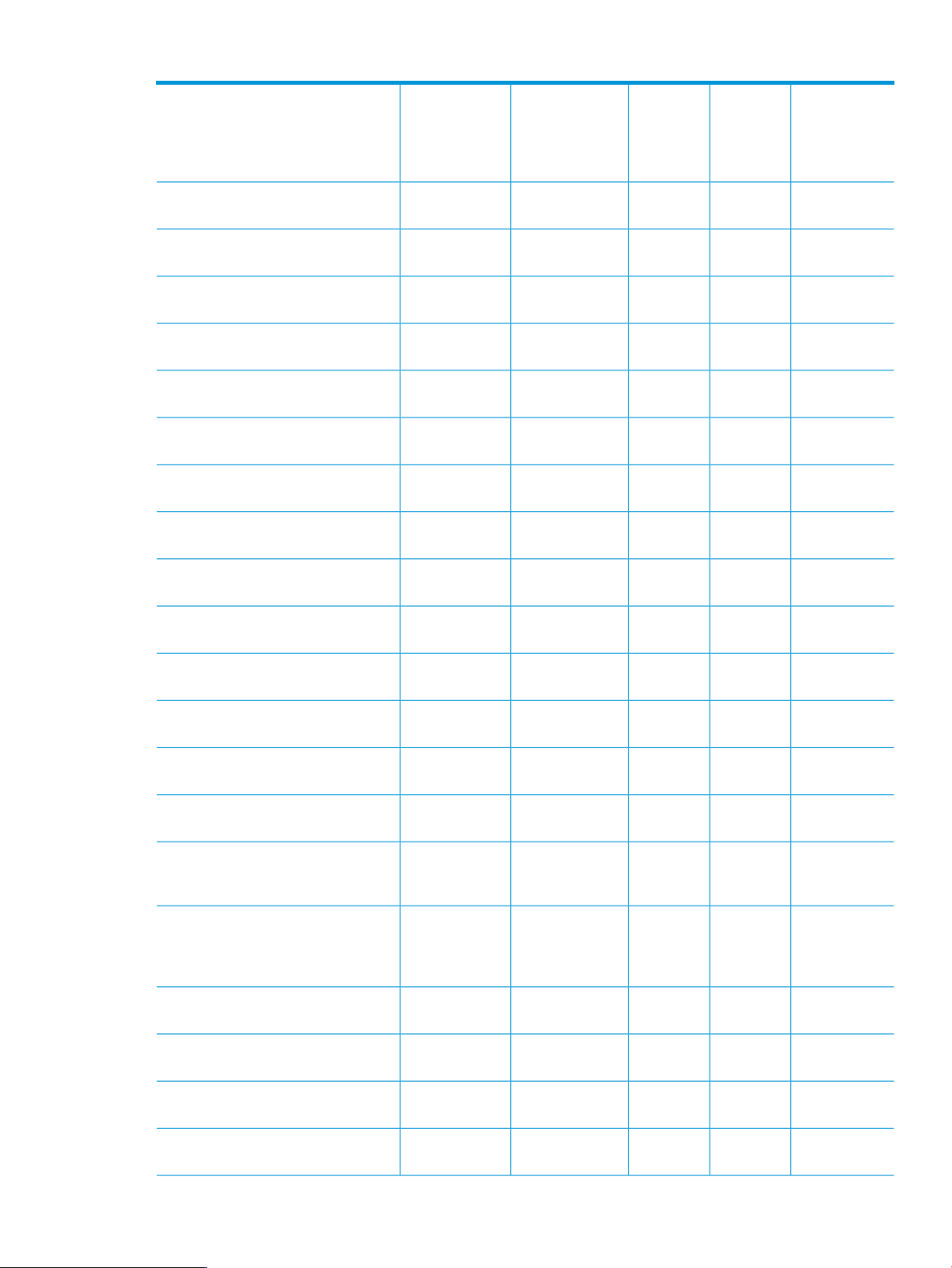
Table 2 RBAC privileges (continued)
VCEM
AdministratorCommand-line option
fc-connection” (page 38)
fc-connection” (page 40)
“remove fc-connection” (page 42)
fcoe-connection” (page 43)
fcoe-connection” (page 46)
“remove fcoe-connection” (page 49)
“add iscsi-connection” (page 50)
iscsi-connection” (page 53)
VCEM Domain
Group
Administrator
VCEM
Domain
Group
Operator
xxx-add fc-connection, see “add
xxx-set fc-connection, see “set
xxx-remove fc-connection, see
xxx-add fcoe-connection, see “add
xxx-set fcoe-connection, see “set
xxx-remove fcoe-connection, see
xxx-add iscsi-connection, see
xxx-set iscsi-connection, see “set
VCEM
Domain
Group
Limited
Operator
VCEM User
(Read Only)
“remove iscsi-connection” (page 56)
iscsi-boot-param” (page 57)
“remove iscsi-boot-param” (page 61)
server-port-map” (page 62)
server-port-map” (page 64)
“remove server-port-map” (page 66)
see “add server-port-map-range”
(page 67)
server-port-map-range, see
“remove server-port-map-range” (page
69)
“poweroff devicebay” (page 70)
xxx-remove iscsi-connection, see
xxx-set iscsi-boot-param, see “set
xxx-remove iscsi-boot-param, see
xxx-add server-port-map, see “add
xxx-set server-port-map, see “set
xxx-remove server-port-map, see
xxx-add server-port-map-range,
xxx-remove
xxxx-poweroff devicebay, see
“poweron devicebay” (page 72)
power-status” (page 73)
74)
xxxx-poweron devicebay, see
xxxxx-show power-status, see “show
xxxxx-show job, see “show job” (page
Role-based access control (RBAC) 13
Page 14
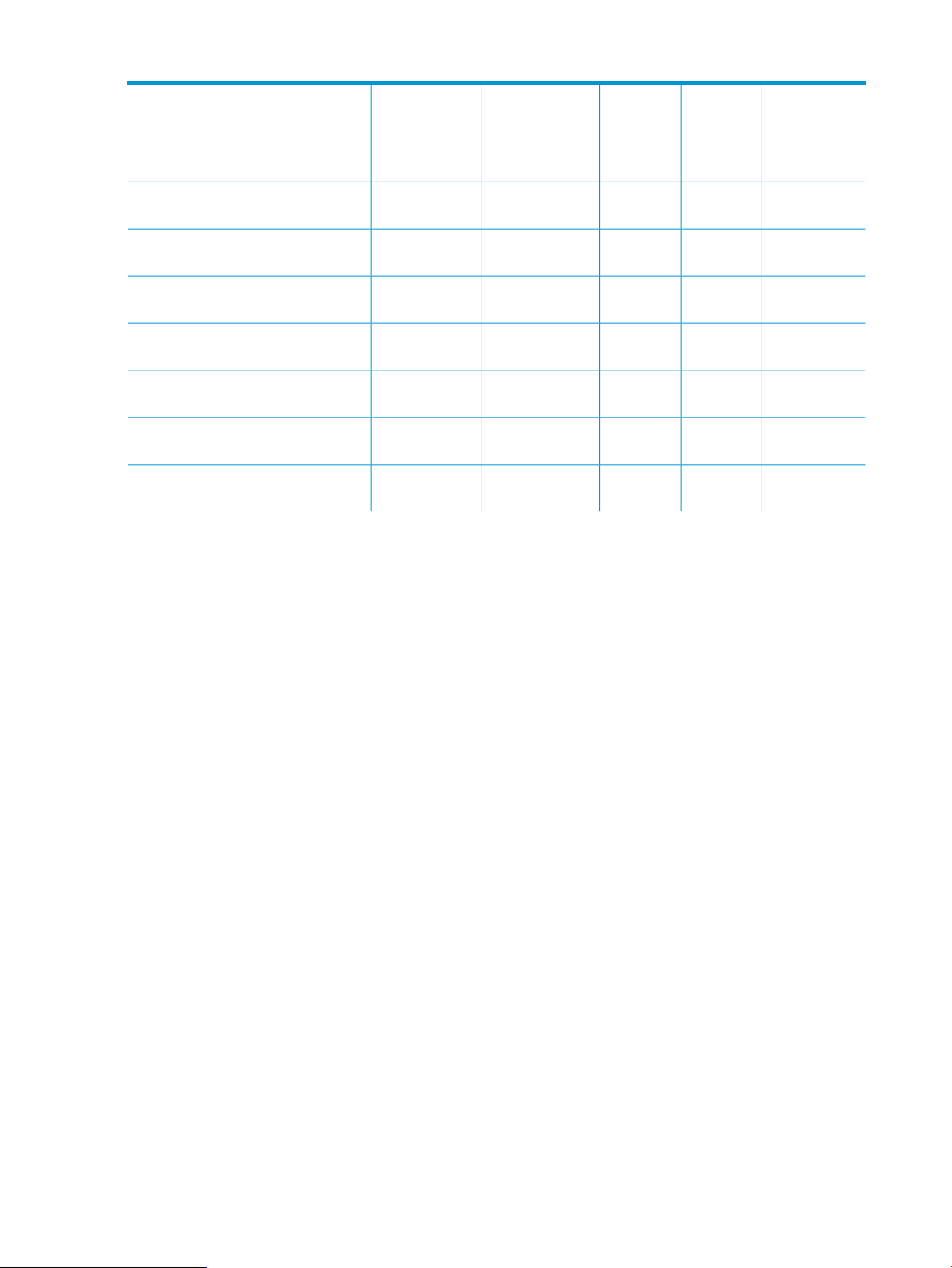
Table 2 RBAC privileges (continued)
VCEM
Domain
Group
Limited
Operator
VCEM User
(Read Only)
xxxxx-show version, see “show version”
xxxxx-show vcem-status, see “show
(page 75)
vcem-status” (page 76)
“startvcdfwupdate” (page 77)
“completevcdfwupdate” (page 78)
“startvcdmaint” (page 79)
“cancelvcdmaint” (page 80)
“completevcdmaint” (page 81)
VCEM
AdministratorCommand-line option
VCEM Domain
Group
Administrator
xx-startvcdfwupdate, see
xx-completevcdfwupdate, see
xx-startvcdmaint, see
xx-cancelvcdmaint, see
xx-completevcdmaint, see
VCEM
Domain
Group
Operator
VCEMCLI commands for read operations require minimum VCEM privilege, whereas write operations
require full privilege to the affected resource. You can set up the VCEM privilege from the Systems
Insight Manager: Options→Security→Users and Authorizations. If the minimum RBAC is not met,
the VCEMCLI reports an error. The error message contains a description of the reason for the
failure.
RBAC best practices
In configurations where VCEM is used in conjunction with an upper-level manager such as HP
Matrix Operating Environment or HP Matrix OE logical server management, make sure that
operations invoked through the VCEMCLI do not disrupt the functioning of the upper-level manager.
The VCEM user interface warns the administrator when it detects the risk of conflict, but the VCEMCLI
does not. For more information about which commands can cause disruption of upper-level
managers, see “Using VCEM commands” (page 21).
You can configure Systems Insight Manager by using RBAC to prevent conflicts between VCEM
and upper-level managers by not allowing changes to resources that would disrupt the upper-level
managers.
To prevent conflicts:
• Define specific Systems Insight Manager users for VCEM and the VCEMCLI.
• Define additional Systems Insight Manager users for upper-level managers.
• If needed, remove roles from the VCEM users to prevent conflict with upper-level managers.
• Set permissions on VC domain groups so that only specific Systems Insight Manager users
can access them.
• Confirm that the scripts specify the correct user-name and password credentials to ensure that
they are granted only the appropriate level of permissions.
• Ensure that NTFS permissions are set on the scripts on the CMS so that they are accessible
only to the CMS users who are authorized to run them.
14 Using the VCEMCLI
Page 15

Working with server profiles
The VCEMCLI provides the most commonly used server profile operations, including:
• Server profile creation or update
• Server profile assignment, unassignment, move or export to CSV
For more information on server profiles and the available server profile operations, see the HP
Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager User Guide available at: http://www.hp.com/go/vcem/.
Creating a server profile
Server profiles are defined in a multi-step process to reduce the number of arguments required in
a single VCEMCLI command. In the first step, the server profile is created as unassigned and with
default connections. Subsequent VCEMCLI operations on the same server profile define other
network and SAN connections.
Creation of a server profile requires only two attributes:
• Server profile name
• VC domain group to which the server profile will belong
The server profile name must be unique, be less than 64 characters in length, and contain only
alphanumeric characters, hyphens, and underscores. For more information, see “add profile”
(page 21).
After you create the server profile, you can add connections as required:
• For network connections, use the –add enet-connection command.
• For iSCSI connections, use the –add iscsi-connection command.
• For FC connections, use the –add fc-connection command.
• For FCoE connections, use the –add fcoe-connection command.
After you create the server profile and add the necessary connections, you can assign the server
profile. For more information see “assign profile” (page 24).
Deleting a server profile
Use the -remove profile command to remove server profiles.
Modifying a server profile
You can modify server profiles after you create them. You can choose from the following options
to modify a server profile:
• Rename the server profile by using the -set profile command.
• Select from the following network options:
Add networks by using the -add enet-connection command.◦
◦ Modify networks by using the -set enet-connection command.
◦ Remove networks by using the -remove enet-connection command.
◦ Add multiple networks by using the -add server-port-map command.
◦ Modify multiple networks by using the -set server-port-map command.
◦ Remove multiple networks by using the -remove server-port-map command.
Working with server profiles 15
Page 16

NOTE: The minimum number of network connections is two. You cannot remove these two
default connections. You cannot add more than the maximum allowed network connections.
The maximum allowed network connections is based on the VC firmware mode. For more
information see the HP Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager User Guide available at: http://
www.hp.com/go/vcem/.
• Select from the following Flex-10 iSCSI network connection options:
Add Flex-10 iSCSI network connections by using the -add iscsi-connection
◦
command.
◦ Modify Flex-10 iSCSI network connections by using the -set iscsi-connection
command.
◦ Remove Flex-10 iSCSI network connections by using the -remove iscsi-connection
command.
NOTE: You can remove all of the iSCSI connections. You cannot add more connections than
the maximum allowed. The maximum connections allowed is based on the VC firmware mode.
For more information, see the HP Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager User Guide available
at: http://www.hp.com/go/vcem/.
• Select from the following FC connection options:
Add FC SAN connections by using the -add fc-connection command.◦
◦ Modify FC SAN connections by using the -set fc-connection command.
◦ Remove FC SAN connections by using the -remove fc-connection command.
NOTE: You can remove all of the FC connections. You cannot add more connections than
the maximum allowed.
• Edit the FC boot parameters by using the -set fc-connection command.
• Select from the following FCoE connection options:
Add FCoE connections by using the -add FCoE-connection command.◦
◦ Modify FCoE connections by using the -set FCoE-connection command.
◦ Remove FCoE connections by using the -remove FCoE-connection command.
• Edit the FCoE boot parameters by using the -set FCoE-connection command.
• Select from the following iSCSI boot-parameter options:
Add iSCSI boot parameters by using the –set iscsi-boot-param command.◦
◦ Modify iSCSI boot parameters by using the –set iscsi-boot-param command.
◦ Remove iSCSI boot parameters by using the -remove iscsi-boot-param command.
You can’t add more than two boot parameters on the iSCSI connection.
NOTE: You cannot add more than two boot parameters on the iSCSI connection.
• Change the server profile’s bay assignment by using the –unassign profile command,
the –assign profile command, or the -move profile command.
Server profiles can be moved within as well as between VC domain groups. The assign and
unassign commands work within a domain group. The move command can work within as
16 Using the VCEMCLI
Page 17

well as between domain groups. Moving server profiles between domain groups offers new
options when upgrading hardware or firmware. As part of the move process, the source and
destination domain groups are checked for compatibility of network and storage connections.
Warnings or errors are reported, based on the severity of any mismatches that are detected.
The VCEMCLI move command can be executed from a script triggered from Systems Insight
Manager in response to designated events. The HP Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager User
Guide describes how the VCEM failover command-line utility can be invoked from Systems
Insight Manager. A similar approach can be used for Systems Insight Manager to execute the
VCEMCLI power and move commands to relocate server profiles in the event of a failure. The
VCEM failover command-line requires that compatible spare blades are designated through
the VCEM web UI, but the VCEMCLI power, move, assign and unassign commands can be
used to:
◦ Shut down a lower priority workload.
◦ Reassign a higher priority workload server profile to a vacated blade.
◦ Power up a high priority server profile in its new location.
Once the original blade has been repaired, the process can be reversed to restore the server
profiles to their normal assignments.
Working with server profiles 17
Page 18

Displaying job details
The –show job -jobid command displays details for the specified VCEM job. The command
returns a value that corresponds to the current state of the job.
The job state return codes are:
• COMPLETED (0)—The job is complete.
• PENDING (10)—The job is waiting to run.
• RUNNING (11)—The job is still running.
• WARNING (12)—The job succeeded with minor errors.
• FAILED (13)—The job failed.
Sample job details:
Y:\>vcemcli -show job -jobid 10
Listing details for specified VCEM job...
Job ID: 10
Job Name: Delete Server Profile [SmokeTestProf]
Job Description: Delete Server Profile
Job State: COMPLETED
Job Progress: 100%, [Mon Dec 20 11:13:47], Delete Server Profile finished.
Job User Name: VCEM-2K3-QA3\Administrator
Job Create Time: [Mon Dec 20 11:13:46]
Job Start Time: [Mon Dec 20 11:13:46]
Job End Time: [Mon Dec 20 11:13:47]
18 Using the VCEMCLI
Page 19

Accessing the VCEMCLI help
Obtain help by running the VCEMCLI without any arguments.
GETTING STARTED:
-help : displays a list of available commands and managed elements
-help <command | managed element>: displays help on the specified item
-----------------------------------------------------------------Control commands
------------------------------------------------------------------
-logfile : The path to a logfile for VCEMCLI diagnostic logging
-loglevel : Controls the level of diagnostic logging
-logsize : The maximum size in KB of the VCEMCLI logfile
-nb : Return immediately without waiting for command results
-pollinginterval : How frequently VCEMCLI checks for results
-pw : The password to authenticate with the CMS
-serverport : The port number to use when contacting the CMS
-silent : Suppress output from VCEMCLI
-timeout : Number of seconds VCEMCLI waits for results of blocking commands
-user : The username to authenticate with the CMS
-----------------------------------------------------------------Subcommands
------------------------------------------------------------------
-add : Add a new object to the domain or to another object
-assign : Assign a server profile to a device bay
-cancelvcdmaint : Cancel maintenance mode for the VC domain.
-completevcdmaint : Complete maintenance for the VC domain.
-completevcdfwupdate : Complete firmware update for the VC domain.
-export : Export VCEM information to a CSV file.
-fcoenetwork : Name of FCoE network associated with the connection
-help : Displays a list of available subcommands
-move : Move a server profile within the VC Domain Group or across VC Domain Groups
-poweroff : Power off a bay in an enclosure
-poweron : Power on a bay in an enclosure
-remove : Remove or delete an existing object (networks, etc.)
-set : Modify one or more configuration properties of an object
-show : Display information about a job, bay power, VCEM domain status or VCEMCLI version
-startvcdmaint : Enter maintenance mode for the VC domain.
-startvcdfwupdate : Enter firmware update mode for the VC domain.
-unassign : Unassign a server profile from a device bay
-----------------------------------------------------------------Subcommand options
------------------------------------------------------------------
-authentication : Authentication method used by the initiator to login to the target.
-bayname : The name or number of the bay containing the server
-bootlun : The logical unit number (LUN) to use for SAN boot
-bootorder : Enables or disables iSCSI boot.
-bootport : The target WWPN for the SAN target
-bootpriority : Controls whether the HBA port is enabled for SAN boot
-connectionbay : The bay containing the Ethernet or SAN interface
-customspeed : The custom speed for the FCoE connection
-dhcpvendorid : String used to match the Vendor Class Id field in the DHCP offer packet.
-domainname : Virtual Connect domain name
-efistate : Specifies the presence of EFI state information
-enclosurename : The name the administrator has assigned to the VC enclosure
-exportfile : The name of a file to receive the exported VCEM information.
-fabric : The name of an existing SAN fabric to associate with the profile
-force : Forces an abrupt power off operation
-forceontimeout : Force a shutdown if normal shutdown doesn't complete in the specified timeout period
-gateway : Default IP route used by the iSCSI initiator.
-initiatorip : IP address used by the iSCSI initiator.
-initiatorname : Name used for the iSCSI initiator on the booting system.
-iscsibootparamdhcp : Allows iSCSI option ROM to retrieve iSCSI boot parameters from DHCP or static configuration.
-jobid : The VCEM jobid to report status on
-lun : The Logical Unit Number (LUN) of the Target identifies the volume to be accessed.
-mactypeoverride : Override VCEM MAC address and instead use the factory default.
-mask : IP network mask used by the iSCSI initiator.
-matchuplinkset : Requires matching Vlans on uplinkset.
-mcastfilter : Name of an existing multicast filter associated with the connection.
-mcastfilterset : Name of an existing multicast filter set associated with the connection.
-mutualsecret : Mutual Secret password for CHAPM authentication.
-mutualusername : Mutual username for CHAPM authentication.
-nag : Network Access Group
-name : The new name to be set on the profile
-network : An existing network name to be associated with the profile
-networkparamdhcp : Allows iSCSI option ROM to retrieve TCP/IP parameters from DHCP or static configuration.
-portnumber : An integer uniquely identifying network connections in the server profile
-poweronbay : Power the bay on after assigning the profile.
-profilename : The name of the profile to be managed
-pxe : Specifies preboot execution environment setting for the connection
-restoreconfig : Restore previous domain configuration if needed
-secret : Secret password for CHAP and CHAPM authentication.
-sntypeoverride : Override the VCEM serial number and instead use the factory default
-speed : The speed for the connection
-speedtype : The speed setting for iSCSI, FCoE or Ethernet connections
-targetip : Primary IP address of the iSCSI target.
-targetip2 : Alternate target IP address for use if the primary port is unavailable.
-targetname : Name of the target from which to boot.
-targetport : The TCP port associated with the primary target IP address.
Accessing the VCEMCLI help 19
Page 20

-targetport2 : The TCP port associated with the alternate target IP address.
-tobayname : The name or number of the bay in the target enclosure
-tovcdg : The target Virtual Connect domain group name
-toenclosurename : The target Virtual Connect enclosure name
-untagged : Controls whether the network handles untagged packets
-uplinkset : The name of the shared uplinkset
-username : Username for CHAP and CHAPM authentication.
-validate : Validates certain preconditions
-vcdomaingroup : The name of the VCEM domain group for the profile
-vlanid : The vlanid to be used for the port mapping.
-vlanids : The vlanids to be used for the port mapping.
-wwntypeoverride : Override VCEM WWN and instead use the factory default
-----------------------------------------------------------------Managed Elements
-----------------------------------------------------------------devicebay : Bay which can contain a Virtual Connect server.
enet-connection : Ethernet Network Connection
fc-connection : Fibre Channel SAN Fabric Connections
fcoe-connection : Network and FCoE Fabric Connections
iscsi-boot-param : iSCSI Boot Parameter information
iscsi-connection : iSCSI Network Connections
job : VCEM jobs
power-status : Bay power status
profile : Virtual Connect Server Profile
profiles : VCEMCLI profile export information
server-port-map : Shared Server Downlink Port Mapping Configuration
server-port-map-range : Shared Server Downlink Port Mapping Range Configuration
vcem-status : The VCEM management status of the VC domain
version : VCEMCLI Version Information
Error reporting
All VCEMCLI commands can report errors. These error messages contain both a text description
of the exception and a numeric value in string form that represents the error code for the
corresponding exception.
The VCEMCLI sets the DOS ERRORLEVEL environment variable based on the success or failure of
the command. Success is indicated by a level of zero (0). Failure is indicated by levels of one (1)
or greater, where the specific value corresponds to an error described in the error message tables.
For the -show command, the ERRORLEVEL environment variable is set to indicate state, not an
error condition. This configuration allows for a script to execute -show for jobs or power states
and then, based on the value of ERRORLEVEL, change the control flow of a script. For example:
for /L %%I in (1,1,%MAXBAYS%) DO (
%CLI% -show power-status -enclosureName %ENCLNAME% -bayname %%I
if ERRORLEVEL 240 (
echo There is no server in bay %%I
) else (
if ERRORLEVEL 1 (
echo Server in bay %%I is already on
) else (
echo Turning on server in bay %%I
%CLI% -poweron devicebay -enclosureName %ENCLNAME% -bayname %%I
if ERRORLEVEL 1 goto ERRORHANDLER
)
)
)
For more information, see “Error Messages” (page 82) or the Systems Insight Manager
documentation.
20 Using the VCEMCLI
Page 21
3 Using VCEM commands
This chapter describes VCEMCLI commands.
add profile
The -add profile command creates a profile from the supplied description of a server profile.
Syntax
-add profile -profilename <profileName>
-vcdomaingroup <vcDomainGroupName>
[-mactypeoverride <true|false>]
[-wwntypeoverride <true|false>]
[-sntypeoverride <true|false>]
Parameters
Table 3 Parameter descriptions for -add profile
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
-vcdomaingroup
-mactypeoverride
-wwntypeoverride
-sntypeoverride
xSpecifies the unique name
of a newly created server
profile.
xSpecifies the name of the VC
domain group to which the
profile is added.
xUses factory-default MAC
addresses instead of
VCEM-provided settings for
Ethernet network connections
when creating the server
profile. Defaults to false.
xUses factory-default WWNs
instead of VCEM-provided
settings for FC SAN
connections when creating
the server profile. Defaults to
false.
xUses factory-default serial
numbers instead of
VCEM-provided settings
when creating the server
profile. Defaults to false.
Examples
• Create a new profile and add it to the domain, by using default connections and Virtual
Connect default serial numbers:
vcemcli -add profile -profilename MyNewProfile –vcdomaingroup Group1
• Create a new profile and use factory-default MACs for Ethernet connections:
vcemcli -add profile -profilename MyNewProfile2 –mactypeoverride true –vcdomaingroup Group1
Output
The function returns the result of the add operation or a jobid, if –nb is specified.
add profile 21
Page 22

Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Administrator
Remarks
This command creates a new unassigned server profile.
VCEM fills empty attributes with a default value. VCEM generates a profile based on the value
settings associated with the -vcDomainGroup argument (it fills all the minimum required attributes
to create a profile with default values), and it overwrites some of the default values with the values
specified on the VCEMCLI command-line.
You can obtain the job status of non-blocking operations by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show
job command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job”
(page 74).
Server profile prerequisites
The server profile must have:
• Unique name within all VCEM managed profiles
• Target VC domain group where the server profile will reside
22 Using VCEM commands
Page 23
set profile
The -set profile command modifies the properties on an existing server profile.
Syntax
-set profile -profilename <profileName>
[-name <NewName>] [-efistate absent]
Parameters
Table 4 Parameter descriptions for -set profile
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
profile you want to modify.
-name
the server profile.
-efistate
state information.
xSpecifies the name of the
xSpecifies the new name of
xSpecifies the presence of EFI
Output
The function returns the result of the set operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
Rename a profile from MyProfile to YourProfile:
vcemcli -set profile -profilename MyProfile –name YourProfile
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
CAUTION: If the VCEMCLI is used in environments where logical server managers or upper-level
managers are present, updating a server profile can make it inconsistent with the upper-level
managers. HP recommends using the upper-level managers to update server profiles.
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated jobid. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
set profile 23
Page 24
assign profile
The -assign profile command assigns the profile identified by the ProfileName to the bay
specified by the BayName.
Syntax
-assign profile –ProfileName <profileName>
-enclosurename <enclosureName> -bayname <bayName> [-poweronbay]
Parameters
Table 5 Parameter descriptions for -assign profile
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
of the server profile to be
assigned.
-enclosurename
contains the bay to assign
the profile to.
-bayname
the server profile is assigned
to.
NOTE: To assign a profile
to a multi-blade server, the
enclosure name and bay
name must match those for
the primary bay.
-poweronbay
the profile has been
assigned.
xSpecifies the unique name
xSpecifies the enclosure that
xSpecifies the device bay that
xPowers on the server after
Output
The function returns the result of the assign operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
• Assign a profile to device bay 1 of the enclosure:
vcemcli -assign profile -profilename MyProfile1 –enclosurename BigEnclosure –bayname 1
• Assign a profile to a multi-blade server in bays 5 to 8 of the enclosure:
NOTE: Note the use of bay 5 for a multi-blade server. A multi-blade server occupies more
than one slot in the enclosure. The operation fails if you specify any slot other than the slot
that the upper-left quadrant of the multi-blade server occupies.
vcemcli -assign profile –profilename MyProfile1 –enclosurename enc0 –bayname 5
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Limited Operator
CAUTION: If the VCEMCLI is used in environments where logical server managers or upper-level
managers are present, assigning a server profile can make it inconsistent with the upper-level
managers. HP recommends using the upper level managers to assign server profiles.
24 Using VCEM commands
Page 25
Remarks
You can obtain the job status of non-blocking operations by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show
job command and providing the associated jobid. For more information, see “show job”
(page 74).
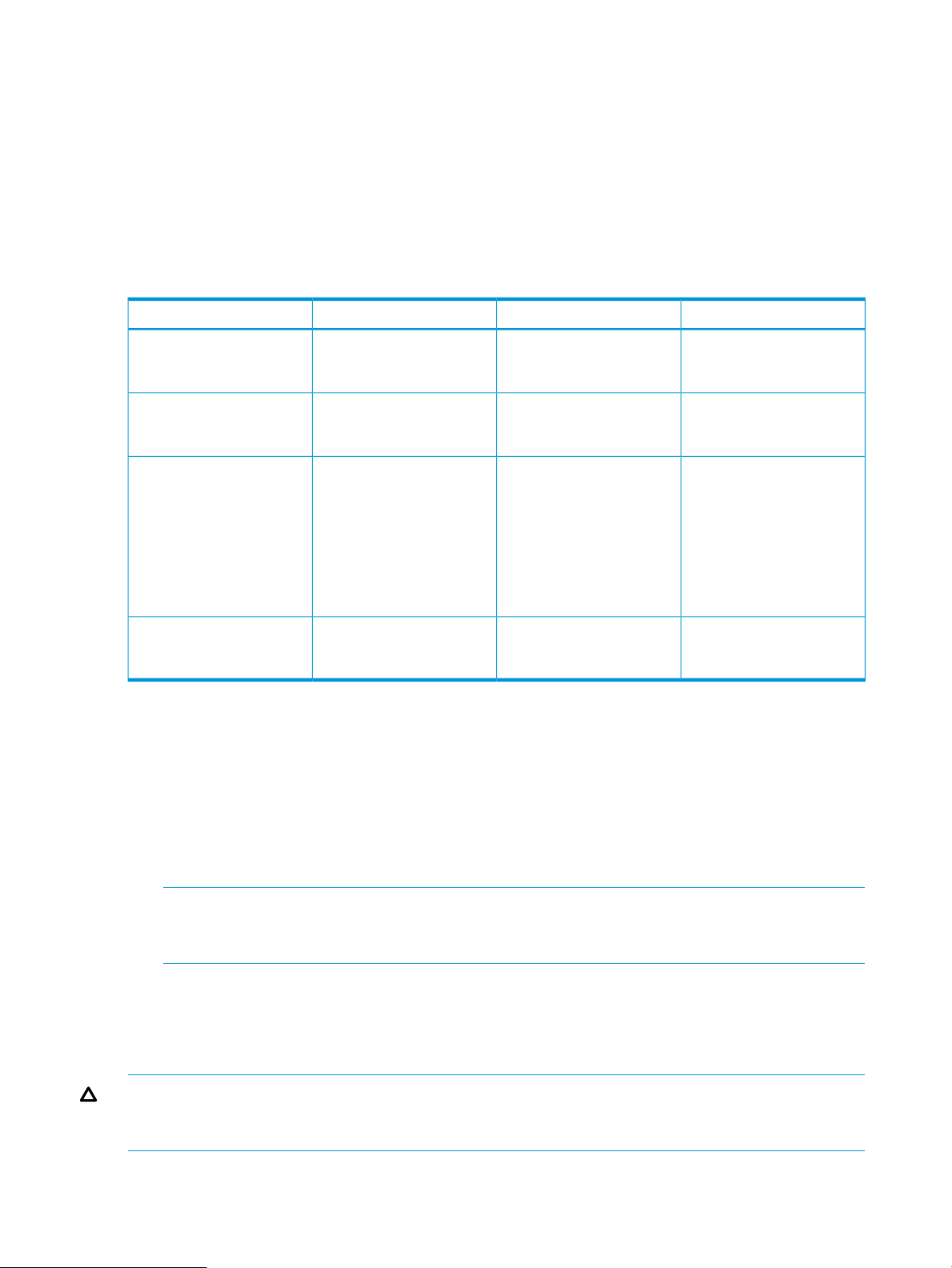
The system page in HP Systems Insight Manager provides the enclosure name, as shown circled
in red in Figure 1 (page 25).
Figure 1 Enclosure name
The bay name is a string representation of the bay number. The first bay is “1”; the second bay
is “2”. For a double-dense blade, the bay for the 1a blade has the name of “1a”, whereas the
bay for the 1b blade has the name of “1b”. If an invalid enclosure name and bay name are
supplied to the VCEMCLI, an error is reported.
Prerequisites
The bay that the server profile is assigned to must meet the following criteria:
• A profile can be preassigned to an empty bay. If the bay contains a server and the power
state is on, it must be powered off before you initiate the profile operation. This can be
accomplished with a vcemcli -poweroff command executed prior to this operation.
• The requested bay must be associated with an enclosure.
• The requested bay must not have a server profile.
• The bay must belong to the same VC domain group where the server profile belongs.
• The bay is not an auxiliary bay. VCEM currently does not provide a method to detect auxiliary
or covered bays. A server profile cannot be assigned to an auxiliary or covered bay. The
VCEMCLI reports an error if an attempt is made to assign a server profile to an auxiliary or
covered bay.
For more information about hardware and firmware, see the HP Virtual Connect for c-Class
BladeSystem User Guide.
assign profile 25
Page 26
export profiles
The -export profiles command exports server profiles to a CSV file for use with external
tools.
Syntax
-export profiles –exportfile <export filename>
Parameters
Table 6 Parameter descriptions for -export profiles
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-exportfile
to receive the exported
profile data in CSV format
xSpecifies the name of the file
Examples
vcemcli -export profiles -exportfile MyProfiles.csv
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM User
Remarks
None
26 Using VCEM commands
Page 27

move profile
The -move profile command moves a server profile across VC domain groups.
Syntax
-move profile —profilename <profile name> [-tovcdg <VCDGName>] [-toenclosurename <EnclosureName> —tobayname
<BayName> [-validate]
Parameters
Table 7 Parameter descriptions for -move profile
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
-tovcdg
-toenclosurename
-tobayname
-validate
profile to be moved
Specifies the name of the
target VC domain group
Specifies the name of the
target enclosure
Specifies the name of the
target bay
moving the profile
xSpecifies the name of the
Required for moving across
domain groups
Required for moving within
a domain group
Required for moving within
a domain group
Optional for moving within
a domain group
Optional for moving across
domain groups
Optional for moving across
domain groups
xVerify preconditions before
Output
The function returns the results of the move operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
• Move assigned profile profile_blue within VCD group:
vcemcli -move profile -profilename profile_blue -toenclosurename
hisenclosure -tobayname 3 -validate
• Move unassigned profile profile_blue to VCDG_blue (move across VCD groups):
vcemcli -move profile -profilename profile_blue -tovcdg VCGD_blue
• Move assigned profile profile_blue to VCDG_blue without specifying toenclosurename
and tobayname. The profile will be automatically unassigned (move across VCD groups):
vcemcli -move profile -profilename profile_blue -tovcdg VCGD_blue
• Move profile_blue to VCDG_red with -validate flag (move across VCD groups):
vcemcli -move profile -profilename profile_blue -tovcdg VCDG_red
-toenclosurename hisenclosure -tobayname 3 -validate
• Move profile_blue to VCDG_red (move across VCD groups):
vcemcli -move profile -profilename profile_blue -tovcdg VCDG_red
-toenclosurename hisenclosure -tobayname 3
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Limited Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
move profile 27
Page 28

When –validate is specified, the job is not triggered; only precondition validation is performed.
The CLI will return the results of the validation.
28 Using VCEM commands
Page 29

remove profile
The -remove profile command removes a server profile from VCEM.
Syntax
-remove profile —profilename <profile name>
Parameters
Table 8 Parameter descriptions for -remove profile
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
profile to be removed
xSpecifies the name of the
Output
The function returns the results of the remove operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
vcemcli -remove profile -profilename Server1Profile
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Domain Group Administrator
Remarks
None
remove profile 29
Page 30
unassign profile
The -unassign profile command unassigns the selected server profile.
Syntax
-unassign profile -profilename <profileName>
Parameters
Table 9 Parameter descriptions for -unassign profile
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
server profile that is currently
assigned to a device bay.
xSpecifies the name of a
Output
The function returns the result of the unassign operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
Unassign a server profile from a device bay:
vcemcli -unassign profile -profilename MyProfile1
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Limited Operator
CAUTION: If the VCEMCLI is used in environments where logical server managers or upper-level
managers are present, unassigning a server profile can make it inconsistent with the upper-level
managers. HP recommends using the upper-level managers to unassign server profiles.
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
You can unassign server profiles whether or not a server is in the specified bay. If a server is in
the bay, the bay must be powered off before the -unassign profile command is issued.
Unassigned profiles belong to the VC domain group.
Prerequisites
• The profile must exist and be associated with a bay.
• If the bay contains a server, the bay must be powered off before the server profile is unassigned.
30 Using VCEM commands
Page 31

add enet-connection
The -add enet-connection command adds a new Ethernet network connection to an existing
server profile in the VC domain.
NOTE: The maximum number of Ethernet connections that can be added to a server profile
depends on the Virtual Connect firmware version. For more information, see the HP Virtual Connect
Enterprise Manager User Guide available at: http://www.hp.com/go/vcem/.
Syntax
-add enet-connection –profilename <profileName>
[[-mcastfilter <mcastfiltername>]|
[-mcastfilterset <mcastfiltersetname>]]
[-network <NetworkName>]
[–pxe <enabled|disabled|usebios>]
[–speedtype <auto|preferred|custom|disabled>]
[–speed <speed>]
Parameters
Table 10 Parameter descriptions for -add enet-connection
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-mcastfilter
NOTE: The
-mcastfilter and
-mcastfilterset
parameters are optional.
You can omit them, or
specify one or the other. You
cannot specify both
-mcastfilter and
-mcastfilterset
together.
-mcastfilterset
-profilename
-network
xName of an existing
multicast filter associated
with the connection
xName of an existing
multicast filter set associated
with the connection
xSpecifies the name of an
existing profile to which the
connection is added.
xSpecifies the name of an
existing network to associate
with the connection. If the
network name is not
specified or is set to
unassigned, the network
will be left unassigned and
can be assigned later.
-pxe
xEnables or disables Preboot
Execution Environment (PXE)
on the network connection.
If this value is not specified,
the default will be usebios.
NOTE: Only one
connection can have PXE
enabled per profile.
add enet-connection 31
Page 32

Table 10 Parameter descriptions for -add enet-connection (continued)
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-speedtype
xSpecifies the requested
operational speed for the
server port. Valid values
include auto, preferred,
and custom. Default value
is preferred. The
following list describes the
speed type:
• auto—Allocates the
maximum port speed,
constrained by the
maximum configured
speed for the network.
• preferred—Ensures
that the speed of the
network matches the
preferred speed of the
network to which the
connection is associated.
NOTE: If no preferred
speed is configured, the
network speed defaults to
auto.
• custom—Configures
any speed from 100 Mb
to the maximum
configured speed for the
network in 100 Mb
increments.
• disabled— the server
port is disabled.
-speed
Specifies the user-defined
speed for the server port.
Valid values include 100
Mb to the maximum
configured speed for the
network in 100 Mb
increments. The value must
be an integer from 100 to
the maximum speed.
x
IMPORTANT: The -speed
parameter is required only
if the speed type is set to
custom.
Output
The function returns the result of the add operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
• Add a new Ethernet network connection and set a multicast filter:
vcemcli -add enet-connection -profilename MyNewProfile -Network
MyNetwork -MCastFilter MyMCastFilter
• Add a new Ethernet network connection and set a Multicast Filter Set:
vcemcli -add enet-connection -profilename MyNewProfile -Network MyNetwork -MCastFilterSet
MyMCastFilterSet
32 Using VCEM commands
Page 33

• Add a new Ethernet network connection to a profile:
vcemcli -add enet-connection –profilename MyNewProfile –network
SomeNetwork
• Add a new Ethernet network connection and enable PXE:
vcemcli -add enet-connection –profilename MyNewProfile –network
SomeNetwork2 –pxe enabled
• Add a new Ethernet network connection and leave the network unassigned for now:
vcemcli -add enet-connection –profilename MyNewProfile
• Add a new Ethernet network connection and set the speed to preferred:
vcemcli -add enet-connection –profilename MyProfile –network
MyNetwork –speedType preferred
• Add a new Ethernet network connection and set the speed to 2 Gb:
vcemcli -add enet-connection –profilename MyProfile –network
MyNetwork –speedtype custom –speed 2000
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
For more information about hardware and firmware, see the HP Virtual Connect for c-Class
BladeSystem User Guide.
add enet-connection 33
Page 34

set enet-connection
The -set enet-connection command modifies an Ethernet connection of a server profile.
Syntax
-set enet-connection –profilename <profileName> -portnumber <Port>
[[-mcastfilter <mcastfiltername>]|
[-mcastfilterset <mcastfiltersetname>]]
[-network <NetworkName>]
[–pxe <enabled|disabled|usebios>]
[–speedtype <auto|preferred|custom|disabled>]
[–speed <speed>]
Parameters
Table 11 Parameter descriptions for -set enet-connection
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-mcastfilter
NOTE: The
-mcastfilter and
-mcastfilterset
parameters are optional.
You can omit them, or
specify one or the other. You
cannot specify both
-mcastfilter and
-mcastfilterset
together.
-mcastfilterset
-profileName
-portnumber
-network
xName of an existing
multicast filter associated
with the connection
xName of an existing
Multicast Filter Set
associated with the
connection
xSpecifies the name of the
server profile that contains
the connection to modify.
xSpecifies the port number of
the connection being
modified.
xSpecifies the name of the
Ethernet network to associate
with the connection. Applies
to Ethernet network
connections only.
-pxe
34 Using VCEM commands
xEnables or disables PXE on
a connection. Valid values
are enabled, disabled,
and usebios.
NOTE: Only one
connection can have PXE
enabled per profile.
Page 35

Table 11 Parameter descriptions for -set enet-connection (continued)
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-speedtype
xSpecifies the requested
operational speed for the
server port. Valid values
include auto, preferred,
and custom. Default value
is preferred. The
following list describes the
speed type:
• auto—Allocates the
maximum port speed,
constrained by the
maximum configured
speed for the network.
• preferred—Ensures
that the speed of the
network matches the
preferred speed of the
network to which the
connection is associated.
NOTE: If no preferred
speed is configured, the
network speed defaults to
auto.
• custom—Configures
any speed from 100 Mb
to the maximum
configured speed for the
network in 100 Mb
increments.
• disabled— the server
port is disabled.
-speed
Specifies the user-defined
speed for the server port.
Valid values include 100
Mb to the maximum
configured speed for the
network in 100 Mb
increments. The value needs
to be an integer from 100
to the maximum speed.
x
IMPORTANT: The -speed
parameter is required only
if the speed type is set to
custom.
Output
The function returns the result of the set operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
• Change the associated multicast filter network of an Ethernet connection:
vcemcli -set enet-connection -profilename MyProfile2 -Network
NewNetworkName -MCastFilter MyMCastFilter
• Change the associated Multicast Filter Set network of an Ethernet connection:
vcemcli -set enet-connection -profilename MyProfile2 -Network
NewNetworkName -MCastFilterSet MyMCastFilterSet
set enet-connection 35
Page 36

• Change the associated network of an Ethernet connection:
vcemcli -set enet-connection –profilename MyProfile2 -portnumber 1
–network NewNetworkName
• Set an Ethernet network connection to unassigned:
vcemcli -set enet-connection –profilename -RedProfile1 -portnumber
1 –network ""
• Disable PXE on an Ethernet network connection:
vcemcli -set enet-connection –profilename GreenProfile3 -portnumber
1 –pxe disabled
• Modify an Ethernet network connection to set the speed to preferred:
vcemcli -set enet-connection –profilename MyProfile1 -portnumber 1
–speedtype preferred
• Modify an Ethernet network connection to set the speed to 2Gb:
vcemcli -set enet-connection –profilename MyProfile1 -portnumber 1
–speedtype custom –Speed 2000
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
36 Using VCEM commands
Page 37

remove enet-connection
The -remove enet-connection command removes the last Ethernet network connection from
an existing server profile.
Syntax
-remove enet-connection –profilename <profileName>
Parameters
Table 12 Parameter descriptions for -remove enet-connection
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
profile that is being
disconnected from the
Ethernet connection.
xSpecifies the name of the
Output
The function returns the result of the remove operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
Remove an Ethernet network connection from a profile:
vcemcli -remove enet-connection –profilename MyProfile
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information see “show job” (page 74).
remove enet-connection 37
Page 38

add fc-connection
The -add fc-connection command adds a new FC connection to a server profile.
Syntax
-add fc-connection –profilename <profileName>
-connectionbay <ConnectionBay>
[-fabric <FabricName>]
[-speed <auto|1Gb|2Gb|4Gb|8Gb|disabled>]
Parameters
Table 13 Parameter descriptions for -add fc-connection
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
-connectionbay
-fabric
-speed
xSpecifies the name of an
existing profile to add the
new connection to.
xSpecifies the bay for the
connection.
xSpecifies the name of an
existing fabric to associate
with the connection. If the
fabric name is not specified,
then the connection will be
marked as unassigned
but associated with a
specific bay.
xSpecifies the port speed of
the connection port. Valid
values include auto, 1Gb,
2Gb, 4Gb, 8Gb, and
disabled. The default port
speed is auto.
NOTE: For HP 4Gb VC-FC
Modules or HP Virtual
Connect 4Gb FC Modules,
supported speed values
include: auto, 1Gb, 2Gb,
4Gb, and disabled. If it is
set to 8Gb, VC
auto-negotiated the speed.
Output
The function returns the result of the add operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
38 Using VCEM commands
Page 39

Examples
• Add a new FC SAN fabric connection to a profile:
vcemcli -add fc-connection –profilename MyNewProfile –connectionbay
5 –fabric SAN_5
• Add a new FC SAN connection and configure the port speed:
vcemcli -add fc-connection –profilename MyNewProfile –connectionbay
6 –fabric SomeFabric –speed 4Gb
• Add a new FC SAN connection and use the next available fabric:
vcemcli -add fc-connection –profilename MyNewProfile –connectionbay
5
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
For more information about hardware and firmware, see the HP Virtual Connect for c-Class
BladeSystem User Guide.
add fc-connection 39
Page 40

set fc-connection
The -set fc-connection command modifies an existing FC connection to a server profile.
Syntax
-set fc-connection –profilename <profileName>
-portnumber <Port>
[-fabric <FabricName>]
[-speed <Auto|1Gb|2Gb|4Gb|8Gb|Disabled>]
[–bootpriority <priority>]
[–bootport <portName>]
[–bootlun <LUN>]
Parameters
Table 14 Parameter descriptions for -set fc-connection
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
-portnumber
-fabric
-speed
xSpecifies the name of the
server profile that contains
the connection to modify.
xSpecifies the port number of
the connection being
modified.
xSpecifies the name of an
existing fabric to associate
with the connection. If the
fabric name is not specified,
the connection will be
marked as unassigned
but associated with a
specific bay.
xSpecifies the port speed of
the connection port. Valid
values include auto, 1Gb,
2Gb, 4Gb, 8Gb, and
disabled. The default port
speed is auto.
NOTE: For HP 4Gb VC-FC
Modules or HP Virtual
Connect 4Gb FC Modules,
supported speed values
include: auto, 1Gb, 2Gb,
4Gb, and disabled. If it is
set to 8Gb, VC
auto-negotiates the speed.
-bootpriority
40 Using VCEM commands
xControls whether the FC
HBA port is enabled for
SAN boot and affects the
BIOS boot order. Valid
values include the following:
• usebios
• primary
• secondary
• disabled
Only one boot parameter is
allowed per FC connection.
Page 41

Table 14 Parameter descriptions for -set fc-connection (continued)
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-bootport
-bootlun
Specifies the target World
Wide Port Name (WWPN)
of the controller interface on
the Fibre Channel storage
target. The port name is a
64-bit identifier in the
following format:
NN:NN:NN:NN:NN:NN:NN:NN
The designation N stands for
a hexadecimal number.
Specifies the logical unit
number (LUN) of the volume
used for SAN boot. Valid
values include an integer
from 0 to 255 or 16
hexadecimal digits (HP-UX
only).
x
IMPORTANT: The
-bootport parameter is
required only when the
-bootpriority parameter
is set to either primary or
secondary.
IMPORTANT: The
-bootport parameter is
required only when the
-bootpriority parameter
is set to either primary or
secondary.
Output
The function returns the result of the set operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
• Change the fabric of a FC SAN fabric connection:
vcemcli -set fc-connection –profilename MyProfile1 -portnumber 2
–fabric SAN_5
• Set a FC SAN fabric connection to unassigned:
vcemcli -set fc-connection -profilename RedProfile2 -portnumber 2
–fabric ""
• Change the FC SAN fabric of an FC SAN connection:
vcemcli -set fc-connection -profilename BlueProfile1 -portnumber 2
–fabric SAN_7
• Change the port speed of an FC SAN connection:
vcemcli -set fc-connection -profilename BlueProfile1 -portnumber 2
–speed 4Gb
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
set fc-connection 41
Page 42

remove fc-connection
The -remove fc-connection command removes the last FC connection from a server profile.
Syntax
-remove fc-connection –profilename <profileName>
Parameters
Table 15 Parameter descriptions for -remove fc-connection
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
existing profile from which
the last FC connection is
removed.
xSpecifies the name of an
Output
The function returns the result of the remove operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
Remove an FC SAN connection from a profile:
vcemcli -remove fc-connection –profilename MyProfile
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by calling –show job.
42 Using VCEM commands
Page 43

add fcoe-connection
The -add fcoe-connection command adds a new FCoE connection to a server profile.
Syntax
-add fcoe-connection –profilename <profileName>
-connectionbay <ConnectionBay>
[[-fabric <FabricName>] | [-fcoenetwork <FCoENetworkName>]]
[-speedtype <1Gb|2Gb|4Gb|8Gb|custom|disabled>]
[-customspeed <100 — 10000>]
Parameters
Table 16 Parameter descriptions for -add fcoe-connection
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
-connectionbay
-fabric
fcoenetwork
xSpecifies the name of an
existing profile to add the
new connection to.
xSpecifies the bay for the
connection.
xSpecifies the name of an
existing fabric to associate
with the connection. If the
fabric name is not specified,
the connection will be
marked as unassigned
but associated with a
specific bay.
xName of an existing FCoE
network associated with the
connection.
NOTE: You cannot specify
both Fabric and
FcoeNetwork properties. If
neither property is specified,
the connection is marked as
Unassigned but associated
with a specific bay.
add fcoe-connection 43
Page 44

Table 16 Parameter descriptions for -add fcoe-connection (continued)
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-speedtype
-customspeed
the connection port. Valid
values include auto, 1Gb,
2Gb, 4Gb, 8Gb, custom,
disabled, and
preferred. The default
port speed is 4Gb.
The –customspeed
parameter is required if the
speed type is custom and is
the user-defined speed for
the server port. Valid values
include 100 Mb to 10 Gb
configured in 100 Mb
increments. The acceptable
value is 100 Mb/s to
10,000 Mb/s. The default
port speed is Preferred.
IMPORTANT: The speed
type Auto does not apply to
fabrics and 1 Gb to 8 Gb
does not apply to FCoE
networks.
Specifies the port speed of
the connection port. Valid
values include values
between 100 Mb and 10
Gb. The acceptable value is
between 100 Mb/s and
10,000 Mb/s.
xSpecifies the port speed of
x
NOTE: The parameter
-customspeed is required
if speed type is custom.
Output
The function returns the result of the add operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
• Add a new FCoE connection to a profile:
vcemcli -add fcoe-connection MyNewProfile -connectionbay 3 –fabric
SAN_5
• Add a new FCoE connection and configure the port speed:
vcemcli -add fcoe-connection MyNewProfile -connectionbay 3 –fabric
SomeFabric -speedtype 4Gb
• Add a new FCoE connection and leave it unassigned:
vcemcli -add fcoe-connection MyNewProfile -connectionbay 3
• Add a new FCoE connection and set the speed type to custom:
vcemcli -add fcoe-connection MyProfile -connectionbay 3 –fabric
MyFabric –speedtype custom –customspeed 5000
• Add a new FCoE network connection to a profile.
vcemcli -add fcoe-connection -profilename MyNewProfile -FCoENetwork
SomeFCoENetwork -connectionbay 3
44 Using VCEM commands
Page 45

Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
Creating FCoE connections requires a VC module that supports FCoE.
For more information about hardware and firmware, see the HP Virtual Connect for c-Class
BladeSystem User Guide.
add fcoe-connection 45
Page 46

set fcoe-connection
The -set fcoe-connection command modifies an existing FCoE connection.
Syntax
set fcoe-connection –profilename <profileName>
-portnumber <PortNumber>
[[-fabric <FabricName>] | [–fcoenetwork <FCoENetworkName> ]]
[-speedtype <1Gb|2Gb|4Gb|8Gb|Custom|Disabled>]
[–customspeed <100–10000>]
[–bootpriority <priority>]
[–bootport <portName>]
[–bootlun <LUN>]
Parameters
Table 17 Parameter descriptions for -set fcoe-connection
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
-portnumber
-fabric
-fcoenetwork
-speedtype
xSpecifies the name of the
profile to which the FcOE
connection will be assigned.
xSpecifies the port number of
the connection.
xSpecifies the name of the
FCoE SAN fabric to
associate with the
connection.
xName of an existing FCoE
network associated with the
connection.
NOTE: You cannot specify
both Fabric and
FcoeNetwork properties. If
neither property is specified,
the connection is marked as
Unassigned but associated
with a specific bay.
xSpecifies the requested
operational speed for the
server port. Valid values
include 1Gb, 2Gb, 4Gb,
8Gb, auto, custom,
disabled, and
preferred. If the speed
type is custom, you can
configure any speed from
100 Mb to 10 Gb in 100
Mb increments. The
-customspeed parameter
is required if the speed type
is custom and is the
user-defined speed for the
server port. Valid values
include 100 Mb to 10 Gb
configured in 100 Mb
increments. The acceptable
value is 100 Mb/s to
10,000 Mb/s.
46 Using VCEM commands
Page 47

Table 17 Parameter descriptions for -set fcoe-connection (continued)
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
The default port speed is
preferred.
IMPORTANT: The speed
type Auto does not apply to
fabrics and 1 Gb to 8 Gb
does not apply to FCoE
networks.
-customspeed
-bootpriority
-bootport
Specifies the user-defined
speed for the server port.
Valid values include 100
Mb to 10 Gb configured in
100 Mb increments. The
acceptable value is 100
Mb/s to 10,000 Mb/s.
HBA port is enabled for
SAN boot and affects the
BIOS boot order. Valid
values include the following:
• usebios
• primary
• secondary
• disabled
Only one boot parameter is
allowed per FCoE
connection.
Specifies the target World
Wide Port Name (WWPN)
of the controller interface on
the Fibre Channel storage
target. The port name is a
64-bit identifier in the
following format:
NN:NN:NN:NN:NN:NN:NN:NN
The designation N stands for
a hexadecimal number.
x
IMPORTANT: The
-customspeed parameter
is required if the speed type
is custom.
xControls whether the FC
x
IMPORTANT: The
-bootport parameter is
required only when the
bootpriority parameter
is set to either primary or
secondary.
-bootlun
Specifies the logical unit
number (LUN) of the volume
used for SAN boot. Valid
values include an integer
from 0 to 255 or 16
hexadecimal digits (HP-UX
only).
x
IMPORTANT: The
-bootlun parameter is
required only when the
bootpriority parameter
is set to either primary or
secondary.
Output
The function returns the result of the set operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
set fcoe-connection 47
Page 48

Examples
• Change the fabric of a FCoE SAN fabric connection:
vcemcli -set fcoe-connection –profilename MyProfile –portnumber 1
–fabric SAN_5
• Set a FCoE SAN fabric connection to unassigned:
vcemcli -set fcoe-connection –profilename RedProfile –portnumber 2
–fabric ""
• Modify the FCoE connection and set the speed to 5 Gb:
vcemcli -set fcoe-connection –profilename MyProfile –portnumber 1
–speedtype custom –customspeed 5000
• Change the SAN boot priority and set additional boot parameters:
vcemcli -set fcoe-connection –profilename BlueProfile –portnumber
1 -bootpriority primary –bootport 50:06:0B:00:00:C2:62:00 –bootlun
5
• Change the network of a FCoE network connection:
vcemcli -set fcoe-connection -profilename MyNewProfile -FCoENetwork
SomeFCoENetwork -connectionbay 3
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID.
For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
48 Using VCEM commands
Page 49

remove fcoe-connection
The -remove fcoe-connection command removes the last FCoE connection from an existing
server profile.
Syntax
-remove fcoe-connection –profilename <profileName>
Parameters
Table 18 Parameter descriptions for -remove fcoe-connection
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
existing profile from which
the last FCoE connection will
be removed.
xSpecifies the name of an
Output
The function returns the result of the remove operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
Remove an FCoE connection from a profile:
vcemcli -remove fcoe-connection –profilename MyProfile
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
remove fcoe-connection 49
Page 50

add iscsi-connection
The -add iscsi-connection command adds a new iSCSI connection to an existing VC server
profile.
NOTE: The -add iscsi-connection command can be executed only if the current VC
domain is managing one or more VC modules that support iSCSI connections.
Syntax
-add iscsi-connection –profilename <profileName>
[-network <NetworkName>]
[-speedtype <auto|preferred|custom|disabled>]
[-speed <speed>]
Parameters
Table 19 Parameter descriptions for -add iscsi-connection
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
-network
xSpecifies the name of an
existing profile to add the
new connection to.
xSpecifies the name of an
existing network to associate
with the connection. If the
network name is not
specified, the network is
unassigned and can be
assigned later.
50 Using VCEM commands
Page 51
Table 19 Parameter descriptions for -add iscsi-connection (continued)
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-speedtype
xSpecifies the requested
operational speed for the
server port. Valid values
include auto, preferred,
and custom. Default value
is preferred. The speed
types are:
• auto—Allocates the
maximum port speed,
constrained by the
maximum configured
speed for the network.
• preferred—Enables
the speed of the network
to match the preferred
speed of the network to
which the connection is
associated.
NOTE: If no preferred
speed is configured, the
network speed defaults to
auto.
• custom—Configures
any speed from 100 Mb
to the maximum
configured speed for the
network in 100 Mb
increments.
• disabled— The server
port is disabled.
-speed
Specifies the user-defined
speed for a server port.
Valid values include 100
Mb to the maximum
configured speed for the
network in 100 Mb
increments. The acceptable
value is 100 Mb to the
maximum.
x
NOTE: The parameter
-speed is required if
-speedtype is set to
custom.
Output
The function returns the result of the add operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
• Add a new iSCSI connection to the profile:
vcemcli -add iscsi-connection –profilename MyNewProfile –Network
SomeNetwork
• Add a new iSCSI connection and leave it unassigned:
vcemcli -add iscsi-connection –profilename MyNewProfile
add iscsi-connection 51
Page 52

• Add a new iSCSI network connection and set the speed to preferred:
vcemcli -add iscsi-connection –profilename MyProfile –network
MyNetwork –speedtype preferred
• Add a new iSCSI network connection and set the speed to 2 Gb:
vcemcli -add iscsi-connection –profilename MyProfile –network
MyNetwork –speedtype custom–speed 2000
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
To create an iSCSI connection, the VC domain must contain at least one VC module that supports
iSCSI in the interconnect bays.
For more information about hardware and firmware, see the HP Virtual Connect for c-Class
BladeSystem User Guide.
52 Using VCEM commands
Page 53

set iscsi-connection
The –set iscsi-connection command modifies the properties of a specified iSCSI connection.
Syntax
-set iscsi-connection –profilename <profileName>
-portnumber <PortNumber>
[-network <Network Name>]
[-speedtype <auto|preferred|custom>]
[–speed <speed>]
Parameters
Table 20 Parameter descriptions for –set iscsi-connection
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
-portnumber
-network
xSpecifies the profile for the
iSCSI connection.
xSpecifies the port number for
the iSCSI connection.
xSpecifies the name of an
existing network to associate
with the iSCSI connection. If
the network name is not
specified, the network is
unassigned and can be
assigned later.
set iscsi-connection 53
Page 54

Table 20 Parameter descriptions for –set iscsi-connection (continued)
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-speedtype
xSpecifies the requested
operational speed for the
server port. Valid values
include auto, preferred,
and custom. The default
value is preferred. The
speed types are:
• auto—Allocates the
maximum port speed,
constrained by the
maximum configured
speed for the network.
• preferred—Enables
the speed of the network
to match the preferred
speed of the network to
which the connection is
associated.
NOTE: If no preferred
speed is configured, the
network speed defaults to
auto.
• custom—Configures
any speed from 100 Mb
to the maximum
configured speed for the
network in 100 Mb
increments.
• Disabled— The server
port is disabled.
-speed
Specifies the user-defined
speed for a server port.
Valid values include 100
Mb to the maximum
configured speed for the
network in 100 Mb
increments. The acceptable
value is 100 Mb to the
maximum.
x
NOTE: The parameter
-speed is required if
speed type is set to
custom.
Output
The function returns the result of the set operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
• Change the network to a different one:
vcemcli -set iscsi-connection –profilename MyNewProfile –portnumber
1 –network SomeNetwork
• Unassign the network from the connection:
vcemcli -set iscsi-connection –profilename MyNewProfile –portnumber
1 –network ""
54 Using VCEM commands
Page 55

• Set the speed to preferred:
vcemcli -set iscsi-connection –profilename MyProfile –portnumber 1
–network MyNetwork –speedtype preferred
• Modify the iSCSI connection and set the speed to 2 Gb:
vcemcli -set iscsi-connection –profilename MyProfile –portnumber 1
–speedtype custom –speed 2000
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
set iscsi-connection 55
Page 56

remove iscsi-connection
The remove iscsi-connection command removes the highest-numbered iSCSI connection
from the server VC profile. If no connections exist, an error message appears.
Syntax
-remove iscsi-connection –profilename <profileName>
Parameters
Table 21 Parameter descriptions for –remove iscsi-connection
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
profile to remove the
connection from.
xThe name of an existing
Output
The function returns the result of the remove operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
Remove the last-added iSCSI connection from the profile:
vcemcli -remove iscsi-connection –profilename MyProfile
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
56 Using VCEM commands
Page 57

set iscsi-boot-param
The -set iscsi-boot-param command configures the basic iSCSI boot parameters on the
specified iSCSI connection.
Syntax
-set iscsi-boot-param
–profilename <profileName>
-portnumber <PortNumber>
-bootorder <Primary|Secondary|Disabled|USEBIOS>
[-lun <Logical Unit number>]
[-initiatorname <Initiator name>]
[-initiatorip <IP address>]
[-mask <Netmask>]
[-gateway <Gateway>]
[-vlanid <Vlan Id>]
[-targetname <Target Name>]
[-targetip <Primary Target IP>]
[-targetport <Primary Target Port>]
[-targetip2 <Alternate Target IP>]
[-targetport2 <Alternate Target Port>]
[-authentication <None|CHAP|CHAPM>]
[-username <username>]
[-secret <secret password>]
[-mutualusername <username>]
[-mutualsecret <Mutual secret password>]
[-iscsibootparamdhcp <enabled|disabled>]
[-networkparamdhcp <enabled|disabled>]
[-dhcpvendorid <VendorID>]
Parameters
Table 22 Parameter descriptions for -set iscsi-boot-param
-profilename
profile associated with the
iSCSI boot parameters.
-portnumber
port for this set of
parameters.
-bootorder
boot. Selecting primary,
secondary, or usebios
enable iSCSI boot. The
default selection for this
attribute is disabled.
-lun
target, which identifies the
volume to be accessed.
Valid values for standard
LUNs are 0 to 255 decimal.
Valid values for extended
LUNs are 13- to
16-character hexadecimal
values. The default value is
zero.
xSpecifies the name of the
xSpecifies the number of the
xEnables or disables iSCSI
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
xSpecifies the LUN of the
set iscsi-boot-param 57
Page 58

Table 22 Parameter descriptions for -set iscsi-boot-param (continued)
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-initiatorname
-initiatorip
-mask
-gateway
Specifies the name used for
the iSCSI initiator on the
booting system. The initiator
name length can be a
maximum of 223 characters.
If the initiator name string
contains non-alphanumeric
characters, it should be
enclosed in quotation marks.
Specifies the IP address that
the iSCSI initiator uses. This
value is in dotted decimal
format.
Specifies the IP network
mask that the iSCSI initiator
uses. This value is in dotted
decimal format.
that the iSCSI initiator uses.
This value is in dotted
decimal format.
x
NOTE: The
-initiatorname
parameter is required if the
-iscsibootparamdhcp
parameter is set to
disabled.
x
NOTE: The
-initiatorip parameter
is required if the
-networkparamdhcp
parameter is set to
disabled.
x
NOTE: The -mask
parameter is required if the
-networkparamdhcpparameter
is set to disabled.
xSpecifies the default IP route
-vlanid
-targetname
-targetip
-targetport
Specifies the VLAN number
that the iSCSI initiator uses
for all sent and received
packets. Valid values include
VLAN numbers between 1
and 4094.
Specifies the name of the
target from which to boot.
The target name length is a
maximum of 223 characters.
If the name string contains
non-alphanumeric
characters, it should be
enclosed in quotation marks.
Specifies the primary IP
address of the iSCSI target.
associated with the primary
target IP address. The default
value is 3260.
x
NOTE: The -vlanid
parameter is required if the
-networkparamdhcp
parameter is set to
disabled.
x
NOTE: The -targetname
parameter is required if the
-iscsibootparamdhcp
parameter is set to
disabled.
x
NOTE: The -targetip
parameter is required if the
-scsibootparamdhcpparameter
is set to disabled.
xSpecifies the TCP port
-targetip2
58 Using VCEM commands
xSpecifies the alternative
target IP address for use if
the primary port is
unavailable.
Page 59

Table 22 Parameter descriptions for -set iscsi-boot-param (continued)
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-targetport2
-authentication
-username
-secret
Specifies the TCP port
associated with the
alternative target IP address.
The default value is 3260.
method. The initiator and
target must agree on an
authentication method or the
iSCSI initiator cannot log on
to the target. Supported
authentication values include
none, chap, and chapm.
The default selection for this
attribute is none.
Specifies the user name for
authentication. The
user-name length is a
maximum of 223 characters.
If the name string contains
non-alphanumeric
characters, it should be
enclosed in quotation marks.
Specifies the secret
password for chap and
authentication. It is specified
as a string or a long hex
value (starting with 0x). This
value must be at least 96
bits (12 bytes, 24
hexadecimal digits) and at
most 16 bytes, 32
hexadecimal digits long.
x
NOTE: The
-targetport2 parameter
is required if the
-targetip2 parameter is
specified.
xSpecifies the authentication
x
NOTE: The -username
parameter is required if the
authentication type is chap
or chapm.
x
NOTE: The -secret
parameter is required if the
authentication type is chap
or chapm.
-mutualusername
-mutualsecret
-iscsibootparamdhcp
Specifies the user name for
authentication. The
user-name length is a
maximum of 223 characters.
If the name string contains
non-alphanumeric
characters, it should be
enclosed in quotation marks.
Specifies the password for
authentication. It should be
specified as a string or a
long hexadecimal value
(starting with 0x). This value
must be at least 96 bits (12
bytes, 24 hexadecimal
digits) and at most 16 bytes,
32 hexadecimal digits long.
ROM to retrieve the iSCSI
boot parameters from DHCP
or through static
configuration. Valid values
are enabled and
disabled. The default
x
NOTE: The
-mutualusername
parameter is required if the
authentication type is
chapm.
x
NOTE: The
-mutualsecret parameter
is required if the
authentication type is
chapm.
xAllows the iSCSI option
set iscsi-boot-param 59
Page 60

Table 22 Parameter descriptions for -set iscsi-boot-param (continued)
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
selection for this attribute is
disabled, which allows for
static configuration.
-networkparamdhcp
-dhcpvendorid
ROM to retrieve the TCP/IP
parameters from DHCP or
through static configuration.
Valid values are enabled
and disabled. The default
selection for this attribute is
disabled, which allows for
static configuration.
Specifies the string used to
match the value in the
Vendor Class Id field in the
DHCP offer packet when the
iSCSI boot parameters are
retrieved.
x
NOTE: The
-dhcpvendorid parameter
is required if the
-iscsibootparamdhcpparameter
is set to enabled.
xAllows the iSCSI option
Output
The function returns the result of the set operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
• Configure basic boot attributes on an iSCSI connection of the profile MyProfile1:
vcemcli -set iscsi-boot-param –profilename MyProfile1 –portnumber 1
–bootorder primary -Lun 100 -initiatorname "iqn.2009-
09.com.someorg.iSCSI-Initiator" –initiatorip 192.128.3.1
-mask 255.255.0.0 -targetname "iqn.2009-09.com.someorg.iSCSI-Target"
-targetip 192.128.3.2 –targetport 40000
-authentication CHAP –username SomeUserName
-secret SomePassword123
• Configure iSCSI boot attributes to be retrieved from DHCP:
vcemcli -set iscsi-boot-param –profilename MyProfile1 –portnumber 1
-bootorder primary –iscsibootparamdhcp enabled
-networkparamdhcp enabled –dhcpvendorid SomeVendorIDValue
• Configure CHAPM secret and secret values:
vcemcli -set iscsi-boot-param –profilename MyProfile1 –portnumber 1
-bootorder primary
-authentication CHAPM –username SomeUserName
-mutualusername SomeMutualUsername
-iscsibootparamdhcp enabled
-networkparamdhcp enabled
-dhcpvendorid SomeVendorIDValue
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
60 Using VCEM commands
Page 61

remove iscsi-boot-param
The –remove iscsi-boot-param command removes all the iSCSI boot parameters configured
on the specified iSCSI connection.
Syntax
-remove iscsi-boot-param –profilename <profileName> -port <port>
Parameters
Table 23 Parameter descriptions for –remove iscsi-boot-param
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
profile from which the boot
parameter is to be removed.
-port
from which the boot
parameter will be removed.
xSpecifies the name of the
xSpecifies the port number
Output
The function returns the result of the remove operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
Remove boot parameters configured on connection 1 of MyProfile1:
vcemcli -remove iscsi-boot-param –profilename MyProfile1 –port 1
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
remove iscsi-boot-param 61
Page 62

add server-port-map
The -add server-port-map command adds a new server port network mapping, and it allows
server ports to be shared among multiple VC Ethernet networks.
Syntax
-add server-port-map –profileName <profileName>
-portnumber <portNumber>
-network <NetworkName>
[-uplinkset <Uplink Set Name>]
[-vlanid <VLan Id>]
[-untagged <true|false>]
Parameters
Table 24 Parameter descriptions for -add server-port-map
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
-portnumber
-network
-uplinkset
-vlanid
existing profile to add the
server port map to.
port to add the server port
map to.
network to which the
mapping will be added.
Specifies the name of the
shared uplink set.
NOTE: If the uplink set
name is specified, the
vlanid property should not
be specified, since the server
VLAN ID will be forced to be
the same as the VLAN ID
used for adding the network
to the shared uplink set.
xSpecifies the name of an
xSpecifies the name of the
xSpecifies the name of a valid
NOTE: If the domain
setting
sharedservervlanid is
set to true, the
uplinkset is a required
value.
x
x
-untagged
62 Using VCEM commands
xEnables or disables the
network to handle untagged
packets. Only one network
in an Ethernet connection
can be made to handle
untagged packets. The
default value is false.
NOTE: If a shared uplink
set is being used, the
untagged network is the
same as a native network, if
present. However, any other
network can be configured
to handle untagged packets.
Page 63

Output
The function returns the result of the add operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
• Add a new server port to a dedicated network mapping:
vcemcli -add server-port-map –profilename MyProfile –portnumber 1
–network Network1 –vlanid 100
• Add a new server port to a shared network mapping:
vcemcli -add server-port-map –profilename MyProfile –portnumber 2
–network RedNetwork –uplinkset MyUplinkSet1
• Add a new server port to a shared network and label it as untagged:
vcemcli -add server-port-map –profilename MyProfile –portnumber 3
–network GreenNetwork –uplinkset MyUplinkset1 –untagged true
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status of the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the -show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
For more information about hardware and firmware, see the HP Virtual Connect for c-Class
BladeSystem User Guide.
add server-port-map 63
Page 64

set server-port-map
The -set server-port-map command modifies the properties of a server port network mapping.
Syntax
-set server-port-map –profilename <profilename>
-portnumber <PortNumber>
-network <Network Name>
[-vlanid <VLan Id>]
[–untagged <true|false>]
Parameters
Table 25 Parameter descriptions for -set server-port-map
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
-portnumber
-network
-Vlanid
-untagged
xSpecifies the name of an
existing profile to associate
with the server port map to
be modified.
xSpecifies the number of the
port to modify the server port
map for.
xSpecifies the name of a valid
Ethernet network to associate
with the mapping.
xSpecifies the new VLAN ID
used for mapping the server
port to the network. Valid
VLAN ID values are 1 to
4094.
xEnables or disables the
network to handle untagged
packets. Only one network
in an Ethernet connection
can be made to handle
untagged packets.
NOTE: If a shared uplink
set is being used, an
untagged network is the
same as a native network, if
present. However, any
network can be configured
to handle untagged packets.
Output
The function returns the result of the set operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
• Modify the VLAN ID of an existing server port network mapping:
vcemcli -set server-port-map –profilename MyProfile –portnumber 1
–network Network1 –vlanid 100
• Modify the existing server port network mapping to handle untagged packets:
vcemcli -set server-port-map –profilename MyProfile –portnumber 1
–network Network1 –untagged true
64 Using VCEM commands
Page 65

NOTE: When VCEM sets a VLAN ID in an untagged VLAN, it sets the VLAN ID to zero and
does not return an error. This is because zero is the correct value to use for an untagged
VLAN.
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
set server-port-map 65
Page 66

remove server-port-map
The –remove server-port-map command removes a server port network mapping.
NOTE: The –remove server-port-map command cannot be used if the domain setting
vlantagcontrol is set to tunnel. This restriction is lifted for VC domain groups running VC
3.30 and later firmware mode.
Syntax
-remove server-port-map –profilename <ProfileName>
-portnumber <portnumber>
[-network <Network Name>]
Parameters
Table 26 Parameter descriptions for –remove iscsi-boot-param
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
profile from which the server
port mapping is to be
removed.
-portnumber
the server port mapping
targeted for removal.
-network
Ethernet network on which
the mapping exists.
xSpecifies the name of the
xSpecifies the port number of
xSpecifies the name of an
Output
The function returns the result of the remove operation or a jobid if –nb is specified.
Examples
• Remove a server port network mapping that has the name Rednetwork:
vcemcli -remove server-port-map –profilename MyProfile –portnumber
1 –network RedNetwork
• Remove all the server port network mappings from an Ethernet connection:
vcemcli -remove server-port-map –profilename MyProfile –portnumber
1
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
66 Using VCEM commands
Page 67

add server-port-map-range
The -add server-port-map-range command adds multiple network port mappings to a
server profile.
Syntax
-add server-port-map—range –profilename <Profile Name>
-portnumber <Port Number>
[-uplinkset <Uplink Set Name>]
[-vlanids <VLan ID range list>]
[-matchUplinkSet]
Parameters
Table 27 Parameter descriptions for -add server-port-map-range
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
-portnumber
-uplinkset
-vlanids
xSpecifies the name of the
profile where the server port
map will be added.
xSpecifies the name of the
port where the server port
map range will be added.
xSpecifies the name of the
shared uplink set. The uplink
set should be defined in the
VC domain group
containing the server profile.
xSpecifies the list of VLAN IDs
to be used for the port
mapping.
The Vland IDs are defined
within the VC domain group
containing the server profile.
The format is a comma
separated list of VLAN ID
ranges where a range is
either a single VLAN ID, or
a hyphen-separated pair of
VLAN IDs that identify a
range of VLAN IDs.
Valid VLAN ID values are 1
to 4094.
-matchUplinkSet
xRequires that the VLANs
used for mappings match the
VLAN IDs specified on the
identified uplink set.
If this parameter is not set,
the command will not set the
profile force same VLAN
mapping attribute (but it will
use the uplink set VLAN IDs
from the shared uplink set).
If there are already server
port map entries for the
specified profile network
connection, then either the
uplink set must match, or the
port map entries must not
add server-port-map-range 67
Page 68

Table 27 Parameter descriptions for -add server-port-map-range (continued)
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
have the force same
VLAN mapping attribute
specified.
Output
The function returns the result of the add operation or a jobid if –nb is specified, or error code
265 if the profile is not found.
Examples
• Add multiple networks to a server port map:
vcemcli -add server-port-map-range –profilename MyProfile -portnumber
2 –uplinkset MyUplinkSet1 -vlanids 201-224,115
• Add multiple networks to a server port map and force VLANs to a shared uplink set:
vcemcli -add server-port-map-range –profilename MyProfile -portnumber
2 –uplinkset MyUplinkSet1 -vlanids 10-20 –matchuplinkset
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
68 Using VCEM commands
Page 69

remove server-port-map-range
The -remove server-port-map-range command removes multiple network port mappings
from a server profile.
Syntax
-remove server-port-map—range –profilename <Profile Name>
-portnumber <Port Number>
[-vlanids <VLan ID range list>]
Parameters
Table 28 Parameter descriptions for -remove server-port-map-range
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-profilename
profile where the server port
map will be removed.
-portnumber
port where the server port
map range will be removed.
-vlanids
to be removed from the port
mapping.
The VLAN IDs are defined
within the VC domain group
containing the server profile.
The format is a comma
separated list of VLAN ID
ranges where a range is
either a single VLAN ID or a
hyphen-separated pair of
VLAN IDs that identify a
range of VLAN IDs.
Valid VLAN ID values are 1
to 4094.
xSpecifies the name of the
xSpecifies the name of the
xSpecifies the list of VLAN IDs
Output
The function returns the result of the remove operation or a jobid if –nb is specified, or error
code 265 if the profile is not found.
Examples
Remove multiple server port network mappings:
vcemcli -remove server-port-map-range –profilename MyProfile -portnumber
2 -vlanids 201-224,115
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Operator
Remarks
You can obtain the job status for the jobid by executing the VCEMCLI with the –show job
command and providing the associated job ID. For more information, see “show job” (page 74).
remove server-port-map-range 69
Page 70

poweroff devicebay
The -poweroff devicebay command sends a power-off request to Virtual Connect Manager
for a given bay.
Syntax
-poweroff devicebay –enclosurename <enclosurename> —bayname <bayname>
[-force|-forceontimeout]
Parameters
Table 29 Parameter descriptions for -poweroff devicebay
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-enclosurename
-bayname
-force
-forceontimeout
Output
xSpecifies the name of the
enclosure that contains the
bay to be powered off.
xSpecifies the name of the
bay to be powered off.
NOTE: For a multiblade
server, the bay name must
be the name of the primary
bay.
xForces a power-off operation
without waiting for the OS
to shut down normally. This
option should be used only
as a last resort because it
can cause data loss on the
server.
xAttempts a normal power off
operation, but if the server
does not power off within
the timeout period (default
is 3600 seconds), it is
forced to power off.
The result of the power-off operation. If –nb is in effect for the command, nothing is returned, and
you can verify the results of the command by polling -show power-status for the enclosure
bay.
Examples
• Conduct a normal power-off operation on device bay 2 of an enclosure that has the ID enc0:
vcemcli -poweroff -enclosurename enc0 –bayname 2
• Conduct a forced power-off operation on device bay 2 of an enclosure that has the ID enc0:
vcemcli -poweroff –enclosurename enc0 –bayname 2 –force –timeout
300
70 Using VCEM commands
Page 71

• Conduct a normal power-off operation on device bay 2 of an enclosure that has the ID enc0.
If the timeout occurs, the system is forced to power off.
vcemcli -poweroff –enclosurename enc0 –bayname 2 –forceontimeout
–timeout 300
• Conduct a normal power-off operation on a specific multiblade server that occupies bays 1
to 4 of enclosure enc0:
vcemcli -poweroff –enclosurename enc0 –bayname 1
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Limited Operator
Remarks
Most profile operations require bays that contain servers to be powered off, before the operation
begins.
When –nb is specified, this command does not indicate that the power has actually been turned
off. It is only an indication that the request has been successfully passed to Virtual Connect Manager.
When you are using the –nb option, the –show power-status command must be polled to
determine when the bay has successfully been powered off. An error is reported if the bay or
enclosure name is invalid.
Before you initiate the power-off operation, evaluate the current status of the bay. The power status
values are:
• ON—Server is present and is powered on (DOS ERRORLEVEL EV = 1).
• OFF—Server is present and is powered off (DOS ERRORLEVEL EV = 0).
• UNKNOWN—No server is present in the bay (DOS ERRORLEVEL EV = 240).
NOTE: The -poweroff devicebay command does not generate a job and might take a
significant time to finish. In particular, normal power-off operations wait for the host operating
system to shut down. This requires additional time while processes are shut down before the
operating system can shut down.
When a timeout is specified, this command will block and poll the power status on an interval
defined by pollingInterval until the timeout is reached. A return of success means the
power is successfully turned off. The VCEMCLI waits for a maximum of 3600 seconds (1 hour) by
default when no timeout has been specified for the command.
Prerequisites
The bay must contain a server.
poweroff devicebay 71
Page 72

poweron devicebay
The -poweron devicebay command sends a power-on request to Virtual Connect Manager for
a given bay.
Syntax
-poweron devicebay -enclosurename <enclosurename> -bayname <bayname>
Parameters
Table 30 Parameter descriptions for -poweron devicebay
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-enclosurename
enclosure that contains the
bay to be powered on.
-bayname
bay to be powered on.
NOTE: For a multiblade
server, the bay name must
be the name of the primary
bay.
xSpecifies the name of the
xSpecifies the name of the
Output
The result of the power-on operation. If –nb is in effect for the command, nothing is returned, and
you can verify the results of the command by polling -show power-status for the enclosure
bay.
Examples
• Power on a specific server in bay 2 of the enclosure enc0:
vcemcli -poweron devicebay –enclosurename enc0 –bayname 2
• Power on a specific multi-blade server that occupies bays 1 to 4 of the enclosure enc0:
vcemcli -poweron devicebay –enclosurename enc0 –bayname 1
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Group Limited Operator
Remarks
When –nb is specified, this command does not indicate that the power has actually been turned
on. It is only an indication that the request has been successfully passed to Virtual Connect Manager.
The –show power-status command must be polled to determine whether the bay has been
successfully powered on. An error is reported if the bay or enclosure name is invalid.
NOTE: When a timeout is specified, this command will block and poll the power status on an
interval defined by pollinginterval until the timeout is reached. A return of success means
the power is successfully turned on. The VCEMCLI will wait for a maximum of 3600 seconds (1
hour) by default when no timeout has been specified for the command.
Prerequisites
The bay must contain a server.
72 Using VCEM commands
Page 73

show power-status
The -show power-status command displays the power status of the indicated bay.
Syntax
-show power-status -enclosurename <enclosurename> -bayname <bayname>
Parameters
Table 31 Parameter descriptions for -show power-status
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-enclosurename
enclosure in the domain.
-bayname
bay in the enclosure.
NOTE: For a multiblade
server, the bay name must
be the name of the primary
bay.
xSpecifies the name of an
xSpecifies the name of the
Output
The command reports the status of the indicated bay by using one of the following strings and sets
the DOS ERRORLEVEL environment variable to the value shown in parentheses:
• ON—Server is present and powered on (1).
• OFF—Server is present and powered off (0).
• UNKNOWN—No server is present in the bay (240).
Examples
Power on the server in bay 2 of the enclosure enc0 if it is currently powered off:
vcemcli –show power-status –enclosurename enc0 –bayname 2
if ERRORLEVEL 240 (
echo There is no server in bay 2
) else (
if ERRORLEVEL 1 (
echo Server in bay 2 is already on
) else (
echo Turning on server in bay 2
vcemcli -poweron devicebay -enclosureName enc0 -bayname 2
if ERRORLEVEL 1 goto ERRORHANDLER
)
)
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM User
Remarks
An error is reported if the bay or enclosure name is invalid.
show power-status 73
Page 74

show job
The -show job command reports the status of the indicated job.
Syntax
-show job –jobid <jobNumber>
Parameters
Table 32 Parameter descriptions for -show job
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-jobid
existing job.
xSpecifies the ID of an
Output
The -show job command displays the status of the indicated job.
VCEM jobs can have the status values as listed in Table 33.
Table 33 Job status values
Return codeJob status
0Completed
221Pending
222Running
223Warning
224Failed
225Get status failed
226Job does not exist
Examples
Report the status of job number 5002 from the VCEM server:
vcemcli –show job -jobid 5002
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM User
74 Using VCEM commands
Page 75

show version
The -show version command displays version information for the VCEM server.
Syntax
-show version
Parameters
None
Output
The -show version command reports version information for the VCEM server.
Examples
Display version information for the VCEM server:
vcemcli –show version
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM User
show version 75
Page 76

show vcem-status
The -show vcem-status command displays the VCEM management status for the specified VC
domain.
Syntax
-show vcem-status -domainname<DomainName>
Parameters
Table 34 Parameter descriptions for -show vcem-status
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-domainname
domain for which VCEM
status will be displayed.
xSpecifies the name of
Output
The -show vcem-status command displays the VCEM management status of the indicated
domain. VCEM status codes are shown in Table 35 (page 76).
Table 35 VCEM status codes
CLI return codeVCEM status
320Not licensed
321Expired license
322Licensed
323Connectivity failure
324Missing external manager lock
325Under maintenance
326Configuration mismatch
327Pending
NOTE: “Pending” status means an operation such as adding a VC domain to a VC domain
group is in progress but has not yet finished.
Examples
Report the VCEM status of GreenDomain managed by VCEM:
vcemcli -show vcem-status -domainname GreenDomain
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM User
76 Using VCEM commands
328Incompatible firmware
329Unknown status
0Managed by VCEM
330In firmware update
Page 77

startvcdfwupdate
The -startvcdfwupdate command starts VC firmware updates on VC 3.50 or later domains
when used in combination with VCSU 1.7.0 or later.
Syntax
-startvcdfwupdate <Domain Name>
Parameters
Table 36 Parameter descriptions for -startvcdfwupdate
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-startvcdfwupdate
domain to be enabled for
firmware update.
xSpecifies the name of the
Output
This function returns the results of the start firmware update operation or a jobid, if –nb is specified.
Examples
vcemcli -startvcdfwupdate GreenDomain
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Domain Group Administrator
Remarks
This CLI starts the Enable Firmware Update Mode process and updates the VC domain status to
FIRMWARE_UPDATE.
This command returns the result of the start firmware update operation by enabling VCSU 1.7.0
or later to update the VC firmware in the domain. The VCEMCLI command does not carry out the
actual firmware update. The firmware update is performed by VCSU.
If any domain in the domain group is already in maintenance mode, no domain in that domain
group can be put into firmware update mode. Similarly, while a domain in the domain group is
in firmware update mode, no domain in the domain group can be put into maintenance mode.
startvcdfwupdate 77
Page 78

completevcdfwupdate
The -completevcdfwupdate command finishes a VC firmware update that was started using
the startvcdfwupdate command on a VC 3.50 or later domain when used in combination
with VCSU 1.7.0 or later.
Syntax
-completevcdfwupdate <Domain Name>
Parameters
Table 37 Parameter descriptions for -completevcdfwupdate
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-completevcdfwupdate
domain that was enabled for
firmware update.
xSpecifies the name of the
Output
This function returns the results of the complete firmware update operation or a jobid, if –nb is
specified.
Examples
vcemcli -completevcdfwupdate GreenDomain
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Domain Group Administrator
Remarks
This CLI completes the Firmware Update Mode process and updates the VC domain status to
MANAGED.
78 Using VCEM commands
Page 79

startvcdmaint
The -startvcdmaint command starts the VC domain maintenance operation on the specified
VC domain. For more information on the VCM operations that are allowed in VC domain
maintenance mode, see the HP Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager User Guide available at:
http://www.hp.com/go/vcem/.
Syntax
-startvcdmaint <DomainName>
Parameters
Table 38 Parameter descriptions for -startvcdmaint
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-startvcdmaint
domain to be placed in
maintenance mode.
xSpecifies the name of the
Output
The -startvcdmaint command returns the result of the start VC domain maintenance mode
operation, reporting success or indicating the reason for failure.
Examples
Start maintenance on BlueDomain:
vcemcli -startvcdmaint BlueDomain
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Domain Group Administrator or VCEM Administrator
startvcdmaint 79
Page 80

cancelvcdmaint
The -cancelvcdmaint command cancels the VC domain maintenance operation on the specified
VC domain.
Syntax
-cancelvcdmaint <DomainName>
Parameters
Table 39 Parameter descriptions for -cancelvcdmaint
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-cancelvcdmaint
domain where maintenance
mode will be canceled.
xSpecifies the name of the
Output
The -cancelvcdmaint command returns the result of the cancel VC domain maintenance
operation, reporting success or indicating the reason for failure.
Examples
Cancel maintenance on OrangeDomain:
vcemcli -cancelvcdmaint OrangeDomain
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Domain Group Administrator or VCEM Administrator
80 Using VCEM commands
Page 81
completevcdmaint
The -completevcdmaint command completes the VC domain maintenance operation on the
specified VC domain and propagates changes across all domain group members.
Syntax
-completevcdmaint <DomainName> [-restoreConfig]
Parameters
Table 40 Parameter descriptions for -completevcdmaint
OptionalRequiredDescriptionParameter
-completevcdmaint
domain where maintenance
will be completed.
-restoreConfig
configuration, if the new
configuration is incompatible
with the configuration of the
current domain.
xSpecifies the name of the
xRestores the original VC
Output
The -completevcdmaint command returns the result of the complete VC domain maintenance
operation, reporting success or indicating the reason for failure.
Examples
Complete maintenance on RedDomain:
vcemcli -completevcdmaint RedDomain
Minimum required role-based security
VCEM Domain Group Administrator or VCEM Administrator
completevcdmaint 81
Page 82

4 Error messages
To help you troubleshoot symptoms, Table 41 (page 82), Table 42 (page 82) and Table 43 (page
85) list error message numbers and descriptions.
Table 41 ERROR_LEVEL values
ERROR_LEVELStatus
0JOB_COMPLETED
224JOB_FAILED
265PROFILE_NOT_FOUND
267PROFILE_PORTNUMBER_UNAVAILABLE
268PROFILE_INVALID_PORTNUMBER
270PROFILE_NO_MORE_CONN_FOR_REMOVE
350MOVE_PROFILE_CONFIG_STATUS
351MOVE_PROFILE_WARNING_STATUS
352MOVE_PROFILE_ERROR_STATUS
360ENCLOSURE_BAY_EMPTY
362ENCLOSURE_INVALID
Table 42 VCEMCLI error messages and descriptions
Error message descriptionError message number
0
0
Start VC Domain FW Update operation on VC Domain %s
succeeded.
Complete VC Domain FW Update operation on VC Domain
%s succeeded.
363BAY_INVALID
364PROFILE_NOT_ASSIGNED_TO_BAY
380VLANID_OUT_OF_RANGE
381VLANID_RANGE_INVALID_FORMAT
382VLANID_RANGE_INVALID_CHAR
383VLANID_RANGE_TOO_LONG
384VLANID_RANGE_OUT_OF_SEQUENCE
385UPLINKSET_DOES_NOT_EXIST
386SERVER_PORT_MAP_VLANS_NOT_FOUND
387NO_SERVER_PORT_MAP_VLAN_FOUND_UNDER_UPLINKSET
10
82 Error messages
Unable to expand environment variable because the
expanded string is too large.
Unable to expand environment string.11
Failed to convert argument to a boolean representation.12
Failed to convert argument to a numeric representation.13
Argument is invalid.20
Page 83

Table 42 VCEMCLI error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message descriptionError message number
Multiple subcommands found.21
Missing subcommand.22
Password argument not found.23
Unsupported managed element for subcommand.24
Subcommand not implemented.25
Unsupported managed element for subcommand.27
Corresponding value for argument was not found.28
Corresponding value for argument was not found.30
Invalid result from getArgPair.31
Index out of range.32
Unsupported managed element for subcommand.33
Command line value found without an identifying keyword.47
48
49
105
120
Cannot use Systems Insight Manager certificate
authentication with a non-local host.
Argument contains invalid value. Passwords must contain
12 to 16 ASCII characters.
Argument contains invalid value.50
Invalid log level.100
Failed to create log file.103
Invalid path specified for file.104
Log file name is too long. Maximum length is 260
characters.
Logging system internal error.106
Help file not found.107
Warning: Failed to get current system time. Command
execution will not timeout.
Failed to get username from system.121
Failed to initialize the XML parser.123
Failed to initialize XML parser.124
Failed to create the export file.140
142
144
145
Invalid path specified for the export file.141
Export file name is too long. Maximum length is 260
characters.
Failed to find server profile data structure key. Column
alignment may be affected.
Duplicate key found while mapping server profile. Column
alignment may be affected.
Invalid speed for FC connection.160
Invalid speed for FCOE connection.170
83
Page 84

Table 42 VCEMCLI error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message descriptionError message number
No help information available.200
JOB_FAILED224
Unable to get job.225
VCEM job ID does not exist.226
Operation timed out.242
VC domain group does not exist.260
Failed to assign profile to bay in enclosure.261
Failed to unassign profile.262
No managed element defined for the profile operation.264
Server profile does not exist.265
Port is not available in server profile.267
268
269
270
301
310
311
312
313
Port number is invalid for profile. The port number must be
greater than zero.
Internal error: Invalid connection type in profile object
m_size call.
There are no more connections in profile available for
removal.
Cannot find the server port network mapping for network.280
There are no network connections available for removal.281
VC Domain does not exist in VCEM.300
VC Domain names cannot exceed 64 characters.302
VC Domain names can only consist of alphanumeric
characters, hyphens (-), underscore (_).
Start VC Domain Maintenance operation on VC Domain
%s failed.
Cancel VC Domain Maintenance operation on VC Domain
%s failed.
Complete VC Domain Maintenance operation on VC
Domain %s failed.
Start VC Domain Firmware Update operation on VC
Domain failed.
314
360
362
363
364
84 Error messages
Complete VC Domain FW Update operation on VC Domain
failed.
Cannot move server profile because the target enclosure
name and bay name cannot be empty.
Cannot move server profile because the target enclosure
does not exist.
Cannot move server profile because the target bay %s does
not exist.
Cannot move server profile because it is not associated
with a server bay.
Page 85

Table 42 VCEMCLI error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message descriptionError message number
380
382
384
387
VlanId range list is invalid because %s is smaller than
Minimum of 1.
VlanId range list contains invalid format.381
VlanId range list contains invalid character %s. VlanId
range can only consist of numeric characters, hyphens (-),
and comma (,).
VlanId range length too long, the maximum length is 9.383
VlanId range starting value cannot be bigger than ending
value.
Uplinkset does not exist in the VC domain group385
Cannot find these vlanIds %s in the VC domain group.386
Cannot find any network with vlanIds range under the
uplinkset in the VC domain group.
Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
1999
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
VCEM received an unexpected error from VC Manager.
Verify that VC Manager is working properly and perform
the operation again. The exception received from VC API:
[x].
2006
2015
2016
2035
2037
2038
The VC domain group cannot be created because unique
configuration of the VC Domain could not be retrieved for
VC Domain [x]. Possible causes are: a failure to connect
to the VC Domain or VCEM has no lock on the VC Domain.
Verify that the VCEM can communicate with the VC Domain
and that the VC Domain is locked for the VCEM and then
perform the operation again.
The operation could not be performed because a VC
Domain with name [x] is already being managed by
VCEM. Enter a unique name for the VC Domain name and
perform this operation again.
The enabled VC feature(s) [x] are not supported by Virtual
Connect Enterprise Manager (VCEM). Verify how to disable
VC features according to VC domain group firmware mode
in the VCEM User Guide.
The operation could not be performed because the VC
Domain with ID [x] was not found in the VCEM database.
Verify the entered VC Domain ID is valid and then perform
the operation again.
The operation could not be performed because the VC
domain group with id was not found in the VCEM
database. Verify the specified VC domain group id is valid
and perform the operation again.
The operation could not be performed because the VC
Domain was not found. Provide a valid VC Domain and
then perform the operation again.
2040
The operation cannot be performed because VC firmware
version is not supported by VCEM. Refer to the VCEM User
85
Page 86

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
Guide to verify the VC firmware versions supported by
each VC domain group firmware mode.
2041
2045
2055
2057
The new VC Domain configuration is using uplink ports
from a VC Ethernet module of an cabinet [x] that is not
configured in all VC Domains from a VC domain group
[x]. To use uplink ports present in a remote enclosure, verify
that all VC Domains that belong to the VC domain group
have a corresponding remote enclosure configured, and
then perform the operation again.
The operation could not be performed because VCEM was
not able to obtain the necessary permissions to manage
the VC Domain [x]. Possible causes are:
1) Another user is enabled as the External Manager at VC
Domain and the VCEM cannot manage this VC Domain.
2) VCEM lost the External Manager lock at the VC Domain.
To resolve this issue:
1) Verify if there is no other user as the External Manager.
2) Remove this VC Domain from the VC domain group and
add it back to the same VC domain group.
The operation cannot be performed because VCEM could
not push the VC Domain base configuration to VC Domain
[x]. Verify VCEM can communicate with VC Manager and
perform the operation again.
The operation cannot be performed because the entered
MAC addresses range is invalid. Verify it is well formed
(NN-NN-NN-NN-NN-NN, where N is a hexadecimal digit
(0-F)) and then perform the operation again.
2096
2097
2099
2100
2101
2102
2106
VCEM cannot perform the requested operation because
the VC Domain [x] is not under maintenance.
VCEM cannot perform the requested operation because
the VC Domain [x] is already under maintenance.
VCEM detected some server profiles from VC Domain [x]
have changed and do not match the existing server profiles
in the VCEM database: [x]
To continue managing this VC Domain with VCEM,
resynchronize the VC Domain configuration and server
profiles by clicking on the VC Domain Maintenance
operation via UI or by completing the VC Domain
Maintenance operation via CLI/SDK.
The following server profiles were not found in VC Domain:
[x]
The following server profiles were not found in VCEM
database: [x]
The following server profiles were changed in VC Domain:
[x]
The operation cannot be performed because VCEM could
not get the VC Domain SNMP configuration to VC Domain
[x]. Verify that VCEM can communicate with VC Manager
and perform the operation again.
86 Error messages
Page 87

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
2108
2139
2142
2145
2146
2148
2150
VCEM cannot perform the requested operation because
the VC Domain [x] firmware version [x] is not supported.
Verify that the VC Domain has a supported firmware
version and perform the operation again.
VCEM could not verify the license for cabinet [x] in the
specified VC Domain because it failed to communicate
with HP Systems Insight Manager . Verify Systems Insight
Manager is correctly functioning and perform the operation
again.
VCEM could not verify the license because the specified
enclosures list is empty.
VCEM could not retrieve the product version. Verify VCEM
was correctly installed and is running over a supported
platform.
VCEM cannot perform the requested power operation
because of the current power state of the server.
VCEM cannot perform the requested power operation
because the VC Domain status is not Managed. Verify the
VC Domain belongs to a VC domain group.
VCEM could not update the VC domain group
configuration because the Master VC Domain is
unreachable. Check if the corresponding VC Manager can
be accessed from your CMS environment and is locked to
this VCEM then perform the operation again.
2151
2152
2153
2154
2156
VCEM could not update the VC domain group
configuration because there is at least one unlicensed VC
Domain inside the specified VC domain group.
The operation cannot be performed because the new VC
domain group configuration is not compatible with server
profiles already existing in the VC domain group. Some
networks or FC SAN fabrics in use by server profiles might
have been deleted. Verify there are no server profiles using
the networks or FC SAN fabrics that should be removed
and perform the operation again.
VCEM did not update the VC domain group configuration
because the master VC Domain was not being updated
when the operation was confirmed or canceled.
VCEM could not update the VC domain group [x]
configuration because there are server profiles [x] still using
the following resources that were removed during VC
Domain Maintenance: [x]
Verify all these resources exist and then perform the
operation again.
Cannot put VC Domain [x] into maintenance because its
VC domain group [x] already has another VC Domain in
maintenance. Perform operation again when the VC
domain group does not have any VC Domain in
maintenance.
2167
VCEM could not perform the requested operation due to
concurrent database access trying to save out of date
information. Verify that there is no other user or process
87
Page 88

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
using the resources involved in this operation and then
perform the operation again.
2170
2176
2182
The operation could not be completed because the VC
Domain is under maintenance.
VCEM cannot perform the operation because the hardware
disposition was changed during VC Domain maintenance
in the VC Domain [x].
Verify the following:
- The enclosure model matches the model of the other
enclosures that belong to the VC domain group.
- The VC modules in the enclosure match the model,
disposition, and power status of the other VC Domains that
belong to the VC domain group.
- The VC Domain support for double-density blades matches
the support for double-density blades of other VC Domains
that belong to the VC domain group.
- Remote enclosures were imported in the same order as
remote enclosures from other VC Domains already
managed in the VC domain group, and they have the same
VC Ethernet and FC module disposition. (For example,
Remote enclosure 1 from a VC Domain must match the VC
module disposition of Remote enclosure 1 from other VC
Domains in the VC domain group.)
The operation cannot be performed because the VC
Domain [x] has one or more VC FC modules with invalid
status. Possible causes are:
- The VC FC modules in the VC Domain were replaced by
VC FC modules from a different model and are not
compatible with the current VC Domain configuration.
- The VC Domain firmware version was downgraded to a
version that does not support the VC FC modules in the VC
Domain.
- The VC Domain has remote enclosure(s) with VC FC
modules disposition different than the primary enclosure
VC FC modules disposition. The adjacent VC FC modules
are not compatible with each other.
Verify the following:
- All VC FC modules have valid status and are compatible
with the VC Domain configuration.
- The VC FC modules disposition is the same among all
enclosures from the VC Domain.
- Adjacent VC FC modules are compatible with each other.
Verify that all VC FC modules have valid status and are
compatible with the VC Domain configuration, and then
perform the operation again.
2186
88 Error messages
VCEM cannot perform this operation because the VC
Domain [x] has one or more VC Ethernet modules with
invalid status. Possible causes are:
- The VC Ethernet modules in the VC Domain were replaced
by VC Ethernet modules from a different model and are
not compatible with the current VC Domain configuration.
Page 89

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
- The VC Domain firmware version was downgraded to a
version that does not support the VC Ethernet modules in
the VC Domain.
- The VC Domain has remote enclosure(s) with VC Ethernet
modules disposition different than the primary enclosure
VC Ethernet modules disposition. The adjacent VC Ethernet
modules are not compatible with each other. Verify the
following:
- All VC Ethernet modules have valid status and are
compatible with the VC Domain configuration.
- The VC Ethernet modules disposition is the same among
all enclosures from the VC Domain.
- Adjacent VC Ethernet modules are compatible with each
other. Verify that all VC Ethernet modules have valid status
and are compatible with the VC Domain configuration,
and then perform the operation again.
2187
2189
VCEM cannot perform this operation because the VC
domain group {0 } firmware mode is not supported. Verify
that the VC domain group has a supported firmware mode
and perform the operation again.
To upgrade the VC domain group firmware mode, perform
the following steps in the VCEM GUI, and then perform
the operation again:
1. For each VC Domain marked with an incompatible
status:
a. Enable the VC Domain maintenance operation.
b. Upgrade the managed VC Domains to (at least) the
minimum VCEM-supported VC firmware version.
c. Complete the VC Domain maintenance operation.
2. Upgrade the VC domain group firmware mode to (at
least) the minimum supported by VCEM. To update the
VC Domain firmware version, check the HP Insight
Management Support Matrix for VCEM-supported VC
firmware versions.
The cabinet [x] or VC modules installed in the enclosure
[x] interconnect bays of VC Domain [x] do not match the
counterpart enclosure of VC domain group [x].
Verify the following:
- The enclosure model matches the counterpart enclosure
model of VC Domains that belong to the VC domain group.
- The VC Ethernet/FC modules in each enclosure match the
model, disposition, and power status of the counterpart
enclosures of VC Domains that belong to the VC domain
group.
- The VC Domain configuration for supporting
double-density blades matches the configuration for all
other VC Domains that belong to the VC domain group.
2192
The operation cannot be performed because the VC
Manager has lost communication with the enclosure's [x]
Onboard Administrator (OA). This communication issue
could be intermittent. Go to VC Manager to check the status
of all the enclosures associated with that VC Domain. See
89
Page 90

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
the Virtual Connect user guide for more information if there
is a lost communication.
2200
2201
2401
2403
2414
2420
There was an error getting the VC Domain by the primary
enclosure name from HP Systems Insight Manager
There was an error getting the VC Domain by the primary
enclosure name from HP Systems Insight Manager The
enclosure name is not valid.
Database operation error. Check that VCEM is installed
correctly and that the database service is running.
VCEM could not retrieve the product version. Verify VCEM
was correctly installed and is running over a supported
platform.
The operation cannot be performed because the
configuration of VC Domain [x] has changed and does
not match the VC domain group configuration in the VCEM
database. To continue managing this VC Domain with
VCEM, resynchronize the VC Domain configuration and
server profiles by clicking on the VC Domain Maintenance
operation via UI or by completing the VC Domain
Maintenance operation via CLI/SDK.
The operation cannot be performed because VC Domain
firmware version [x] is incompatible with VC domain group
firmware mode [x]. Refer to the VCEM User Guide to verify
the VC firmware versions supported by each VC domain
group firmware mode.
2421
2425
2426
2430
2551
The enabled VC feature(s) [x] are blocking the addition of
VC Domain [x] to the VC domain group. Verify how to
disable VC features according to VC domain group
firmware mode in the VCEM User Guide.
The operation cannot be performed because the Server
Profiles [x] are using an invalid untagged VLAN. Refer to
the VCEM User Guide troubleshooting section for
information on how to use untagged VLANs in Server
Profiles.
The operation cannot be performed because the VC
Domain [x] is no longer configured. To continue managing
this VC Domain with VCEM, remove the VC Domain from
the VC domain group, and then add it back to the VC
domain group.
The operation cannot be performed because the VC
Domain [x] was upgraded a firmware version that does
not provide backward compatibility with the VC domain
group firmware mode [x]. To continue managing this VC
Domain with VCEM, use the complete VC Domain
maintenance operation and after that, upgrade all the
remaining VC Domains inside the VC domain group to a
firmware version that is compatible among them.
Server profile name is empty or invalid. Names can only
have alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-) or underbars
(_) and are limited to 64 characters.
90 Error messages
Page 91

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
2552
2553
2554
2555
2556
2557
2559
2560
Server profile name is duplicate. Another server profile
with the same name already exists in VCEM.
There are more than one network interfaces (NIC)
configured with PXE enabled. Only one NIC in the profile
can be PXE enabled.
Cannot remove network connection. Verify: 1- The provided
connection exists. 2- The provided port number is different
from 1 or 2. 3- The provided connection is the last one in
the network connections list.
Cannot find network connection for the specified port
because the port number is invalid. Verify there is a
connection for the provided port number.
Cannot create network connection because the specified
network does not exist. Enter a valid network name.
In the FC SAN connection for interconnect bay , the
selected FC SAN fabric does not exist. The provided FC
SAN fabric must exist in the VC Domain group the Server
profile belongs.
Cannot create a network connection for the entered port.
Ethernet network connections require a valid network. Verify
all port connections are correctly pointing to a valid
network and then perform the operation again.
In the FC SAN connection for interconnect bay , the
selected FC SAN fabric does not have a physical
connection to this port.
2561
2562
2563
2564
2601
2602
2603
The server bay cannot be changed when updating an
assigned server profile.
The entered MAC addresses is invalid. Verify it is well
formed (NN-NN-NN-NN-NN-NN, where N is a
hexadecimal digit (0-F)).
The entered WWN addresses is invalid. Verify it is well
formed (NN:NN:NN:NN:NN:NN:NN:NN,
NN-NN-NN-NN-NN-NN-NN-NN or
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN, where N is a hexadecimal
digit (0-F)).
The entered Logical Serial Number is invalid. Verify it is
well formed (VCX00NNNNN, VCX01NNNNN or
VCYNNNNNNN, where N is a alpha-numeric digit (0-9
or A-Z)).
Cannot configure FC SAN connection because the specified
the interconnect bay number is invalid.
Cannot configure FC SAN connection because the specified
FC SAN fabric does not exist or it cannot be assigned to
the provided port. Each FC SAN fabric can only be
assigned to its corresponding port. Verify the provided FC
SAN fabric exists and can be assigned to the provided
port.
In the FC SAN connection for interconnect bay , the
selected port speed is invalid.
91
Page 92

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
2604
2605
2606
2607
2608
2609
The target server bay is already in use by another server
profile.
The target server bay does not exist or does not belong to
the same VC domain group that the server profile belongs.
In the FC SAN connection for interconnect bay , the entered
boot target WWPN is not well formed. Valid format is
xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx or xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx or
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx where each x represents a hexadecimal
digit.
In the FC SAN connection for interconnect bay , the
specified boot target LUN is invalid. Valid values are either
a 3-digit decimal between 0 and 255, or a 13- to 16-digit
hexadecimal between 0 and FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF.
Cannot set SAN boot settings because the specified boot
priority is not valid.
Cannot create server profile because the specified server
profile does not contain the minimal required information.
Verify the server profile has: - A unique name - A VC
domain group - At least two Ethernet network connection
physical ports defined - One FC SAN connection physical
port defined for each available FC SAN fabric module SAN boot settings for each FC SAN connection physical
port.
2610
2611
2612
2613
2614
2615
2616
2617
There are missing or duplicate Ethernet network
connections. A continuous sequence finishing on the last
valid Ethernet network connection port is required.
The specified VC domain group does not exist. A server
profile must be assigned to an existent VC domain group.
Cannot perform server profile assignment because the
specified VC Domain has an expired license. Apply a
permanent license and then perform the operation again.
Cannot perform server profile assignment because the
target Server Bay is already in use by another server
profile.
Cannot perform the Server Profile operation because there
is a server bay with a server powered up. Verify that all
servers involved in the operation are powered down, and
then perform the operation again.
Cannot perform server profile assignment because the
specified target Server Bay is not valid. Verify the specified
target Server Bay belongs to a managed VC Domain.
Cannot perform server profile assignment because the
server profile is already assigned to another Server Bay.
The assignment was triggered explicitly, or this profile was
either (a) failed over, (b) moved, or (c) edited.
Cannot perform server profile assignment because an
exception occurred. Here is the exception: {0}
2618
92 Error messages
Cannot perform server profile unassignment because an
exception occurred. Here is the exception: {0}
Page 93

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
2619
2620
2623
2624
2626
Cannot perform server profile unassignment because the
specified server profile is not currently assigned to a server
bay.
Cannot perform the {0} operation because the VC Domain
maintenance is not completed. Perform these steps:
1. Go to the VCEM - VC Domains tab and select the VC
Domain that is under maintenance.
2. Click VC Domain Maintenance.
3. Click Complete VC Domain Maintenance to apply the
configuration changes to the entire VC domain group,
or click Cancel to not apply changes and restore the
current VC domain group configuration to the VC
Domain. Verify that the VC Domain maintenance
operation was completed or canceled with success, and
then perform the operation again.
Cannot perform rollback on a server profile move operation
because the server profile could not be assigned back to
its original Server Bay. The profile is saved as unassigned.
Cannot move the server profile because the specified server
profile is not currently assigned to a Server Bay.
The number of FC SAN connections is incorrect.2625
In the FC SAN connection for interconnect bay , the range
type is not compatible with the addresses inside the
connection.
2627
2628
2629
2630
2631
2632
2633
2636
A server profile cannot have less than two Ethernet network
connections. At least two Ethernet network connection
physical ports are required.
In the FC SAN connection for interconnect bay , the
connection was replaced by a new one. To replace a
connection by a new one, first edit the profile and delete
the connection, then edit the server profile again and add
a new connection.
It was not possible to remove the provided vNet mapping
from the server profile.
The target server bay does not support server profiles.
Verify the device in the server bay is supported by VC
Manager.
Server Profile identifier cannot be found. Verify that a server
profile is informed, the associated VC Domain is managed
by VCEM and the server profile exists in VCEM.
Specified Server Bay ID does not correspond to a managed
server profile in VCEM.
Cannot perform server profile move because the specified
server profile was already moved from Server Bay on VC
Domain .
Cannot perform the server profile operation because it is
not possible to have connections with different address
types in the same server profile.
93
Page 94

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
2638
2639
2640
2641
2643
2644
2645
2646
Cannot move the server profile because the specified target
Server Bay does not belong to the same VC domain group
that the server profile belongs.
The target server is powered up. The operation requires
the server to be powered down.
In the ethernet connection for port , the range type is not
compatible with the addresses inside the connection.
In the ethernet connection for port , the connection was
replaced by a new one. To replace a connection by a new
one, first edit the profile and delete the connection, then
edit the server profile again and add a new connection.
There are more than one FC SAN connections configured
as secondary SAN boot. Only one FC SAN connection
can be configured as secondary SAN boot.
There is one FC SAN connection configured as secondary
SAN boot, but no one configured as primary SAN boot.
There are missing or duplicate FC SAN connections. A
continuous sequence finishing on the last valid FC SAN
connection port is required.
In the ethernet connection for port {0}, the selected Network
does not exist. The provided Network must exist in the VC
Domain group the Server profile belongs to.
2647
2648
2650
2651
2652
2655
2657
2658
2659
A server profile cannot have more than x Ethernet network
connections where x represents a number.
Cannot perform the server profile operation because the
VC Domain {0} does not have a valid status.
Cannot find FC connection for the specified interconnect
bay because the interconnect bay number is invalid.
Cannot perform server profile operation because the target
server bay is not specified. Select a target server bay and
perform the operation again.
Cannot move the server profile to the same target server
bay it is assigned. Select a different target server bay and
perform the operation again.
The server profile is configured to use Factory Defaults for
Serial Numbers. Verify no Serial Number and no UUID
are entered when using the Factory Defaults Serial
Numbers.
The port speed information could not be retrieved for the
specified connection. Verify the provided network id
corresponds to an existing network.
In the FC SAN connection for interconnect bay , the base
boot configuration is not set.
In the FC SAN connection for interconnect bay , the
maximum number of boot configurations was exceeded.
94 Error messages
Page 95

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
2660
2661
2662
2663
2674
2675
2676
In the ethernet connection for port , the port speed is
incorrect. Unassigned ethernet connections must have port
speed set to Preferred.
In the Ethernet connection for port , the port speed is
incorrect. The minimum and maximum port speeds cannot
be empty. The minimum must be lower than or equal to the
maximum, and the values must be a multiple of 100 Mb.
In the ethernet connection for port , the port speed exceeds
the maximum allowed port speed for the selected network
(Gb).
In the ethernet connection for port , the port speed is below
the minimum allowed port speed for the selected network
(Gb).
The provided port speed value is not a valid number.2664
In the FC SAN connection for port number and interconnect
bay , the maximum number of boot configurations was
exceeded.
In the FC SAN connection for port number and interconnect
bay , the specified boot target LUN is invalid. Valid value
is a 3-digit decimal between 0 and 255.
In the FC SAN connection for port number and interconnect
bay , the selected FC SAN fabric does not exist. The FC
SAN fabric must exist in the VC domain group the Server
Profile belongs.
2677
2678
2679
2680
2681
2682
2683
2684
In the FC SAN connection for port number and interconnect
bay , the selected port speed is invalid.
In the FC SAN connection for port number and interconnect
bay , the specified boot target WWPN is not well-formed.
Valid formats are xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx.
xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx, or xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx, where each
x is a hexadecimal digit.
In the FC SAN connection for port number and interconnect
bay , the specified boot target LUN is invalid. Valid values
are either a 3-digit decimal between 0 and 255, or a 13
to 16-digit hexadecimal between 0 and FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF.
In the FC SAN connection for port number and interconnect
bay , the selected FC SAN fabric does not have a physical
connection to this port.
Invalid number of WWN addresses in the FC SAN
connection for interconnect bay . VCEM does not support
multiple WWPN addresses per physical port when using
Factory-Default WWN addresses.
Missing base initiator configuration in FC SAN connection
for interconnect bay .
Cannot perform server profile assignment because bay {0}
is an auxiliary server blade.
Cannot assign server profile because the selected bay is
covered.
95
Page 96

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
2685
2709
2710
2717
2718
2719
2720
2721
2722
Cannot perform server profile assignment because the
specified VC Domain was not licensed. Apply a license
and then perform the operation again.
The slot number associated with node is not valid for a
server blade. Valid numbers are 1 - 16.
Systems Insight Manager did not find an cabinet associated
with node .
Cannot create FC SAN connection because the maximum
number of FC SAN connections was reached.
The operation could not be performed because Server
Profile already contains the maximum number of network
connections.
Cannot remove FC SAN connection because the Server
Profile does not have a FC SAN connection.
Cannot remove Multiple Network because the Server Profile
does not have more available Multiple Networks to be
removed.
Could not remove the connection because the port number
was not found.
Could not set the Multiple Network because the given port
was not found.
2724
2726
2728
2729
2731
2732
2733
Only one VNet can be Untagged.2723
The provided configuration for multiple networks exceeds
the maximum allowed number of VNet mappings. The
maximum number of VNet mappings is {0}.
There are duplicated VNet Names. Choose a different one.2725
The entered VLAN id is not valid. Please enter a valid value
(1-4094) for Server VLan Id.
No networks under selected object. Choose other object.2727
The vNet name cannot be Unassigned. Select one vNet
name for each mapping.
There are duplicated server VLAN Ids. Type a different
VLAN Id for each mapping.
The provided configuration for multiple networks does not
have the minimal number of VNet mappings. At least one
VNet mapping is required.
There is no VNet selected. Only mappings with a VNet
selected can be marked as untagged.
In the FC SAN connection for interconnect bay , the
selected port speed is invalid. Verify that the FC module
of interconnect bay supports the 8Gb downlink speed
value.
2734
96 Error messages
The provided network does not exist in the specified VC
domain group. The network must exist in the VC domain
group to which the Server Profile belongs.
Page 97

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
2735
2736
2737
2739
Cannot create Server Profile because an address is already
in use by Server Profile. To resolve this: 1. Access VCEM
and delete the Server Profile with the address reported as
in use, or choose another valid address. 2. Perform the
Create Profile operation again.
There was a problem allocating the address . Possible
causes are: 1. The address is being requested by an
upper-level manager application but it was not reserved.
2. The address is part of an exclusion range. 3. The
address does not belong to any range known to VCEM.
To resolve this, respectively: 1. Verify that the address is
reserved by an upper-level manager application by
checking the owner field of this address. 2. Remove or
adjust the exclusion range to exclude this address. 3.
Create a User-Defined address range that contains all
addresses in use by the Server Profiles. Perform the Create
Profile operation again.
Cannot find iSCSI connection for the specified port because
the port number is invalid. Verify that there is a connection
for the specified port number.
Server Profile has too many iSCSI connections.2738
There is more than one iSCSI connection configured as a
primary Boot Setting. Only one iSCSI connection can be
configured as a primary Boot Setting.
2740
2741
2742
2743
2744
2745
2746
2747
There is more than one iSCSI connection configured as a
secondary Boot Setting. Only one iSCSI connection can
be configured as a secondary Boot Setting.
There is an iSCSI connection configured as a secondary
Boot Setting, but not one configured as a primary Boot
Setting. To have a secondary Boot Setting configured, a
primary Boot Setting must also be configured.
The iSCSI Boot Settings cannot be empty when the iSCSI
connection is configured as primary or secondary.
In the iSCSI connection for port , the port speed is incorrect.
The minimum and maximum port speeds cannot be empty.
They must have the same value, and the value must be a
multiple of 100 Mb.
In the iSCSI connection for port , the port speed exceeds
the maximum allowed port speed for the selected network
(Gb).
In the iSCSI connection for port , the port speed is lower
than the minimum allowed port speed for the selected
network (Gb).
There are missing or duplicate FCoE connections. A
continuous sequence that finishes on the last valid FCoE
connection port is required.
There are more than one FCoE connection configured as
primary boot. Only one FCoE connection can be configured
as primary boot.
97
Page 98

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
2748
2749
2750
2751
2752
2753
2754
2755
There are more than one FCoE connection configured as
secondary boot. Only one FCoE connection can be
configured as secondary boot.
In the Ethernet Connection in port {0}, the number of
networks {1} defined in multiple networks exceeds the
maximum number allowed {2} in the target VC domain
group.
In the FCoE connection for interconnect bay , the selected
FC SAN fabric does not have a physical connection to this
port.
In the FCoE connection for interconnect bay , the selected
FC SAN fabric does not exist. The FC SAN fabric must
exist in the VC domain group to which the Server Profile
belongs.
Cannot configure FCoE connection because the specified
interconnect bay is invalid. A valid interconnect bay must
have a VC module that supports FCoE connections.
In the FCoE connection for interconnect bay , the selected
port speed type is invalid. The valid values are {2}.
In the FCoE connection for interconnect bay , the selected
port speed is invalid. The valid values are {2}.
In the FCoE connection for interconnect bay , the custom
port speed is incorrect. The minimum and maximum port
speeds cannot be empty. They must have the same value,
and the value must be a multiple of 100 Mb.
2756
2757
2758
2759
2760
2761
2762
In the FCoE connection for interconnect bay , the custom
port speed is lower than the minimum allowed port speed
(Gb).
In the FCoE connection for interconnect bay , the MAC
range type is not compatible with the addresses inside the
connection.
In the FCoE connection for interconnect bay , the number
of MAC addresses is not correct. Each connection must
have only one MAC address.
In the FCoE connection for interconnect bay , the
connection was replaced by a new one. To replace a
connection, edit the Server Profile and delete the
connection, and then edit the Server Profile again and add
the new connection.
In the FCoE connection for interconnect bay , the WWN
range type is not compatible with the addresses inside the
connection.
Invalid number of WWN addresses in the FCoE connection
for interconnect bay . VC Domains with multiple logical
HBA ports per physical HBA port support up to 17
WWNN/WWPN pairs per physical port; otherwise, only
one WWNN/WWPN pair is supported per physical port.
In the FCoE connection for port number and interconnect
bay , the specified boot target WWPN is missing or not
well-formed. Valid formats are xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx,
98 Error messages
Page 99

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx, or xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx, where each
x is a hexadecimal digit.
2763
2764
2765
2766
2767
2768
2769
2770
In the FCoE connection for port number and interconnect
bay , the specified boot target LUN is missing or invalid.
Valid values are either a 3-digit decimal between 0 and
255, or a 13- to 16-digit hexadecimal between 0 and
FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF.
Cannot create FCoE connection because the maximum
number of FCoE connections was reached.
Cannot remove FCoE connection because the Server Profile
does not have a FCoE connection.
Cannot find FCoE connection for the specified interconnect
bay because the interconnect bay number is invalid or
there is not a FCoE connection for this interconnect bay.
In the FCoE connection for port number and interconnect
bay , the custom port speed exceeds the maximum allowed
port speed ({2}Gb).
In the Ethernet connection for port , the port speed is
incorrect. The minimum and maximum must be the same
when connection speed type is Custom.
VCEM cannot update server profile . The connection bay
was changed.
VCEM cannot update server profile . The connection port
number is duplicated.
2773
2774
2775
2776
2778
2779
2781
2782
There are conflicting boot configuration types defined in
this profile (FC and FCoE). A Server Profile can have only
one boot configuration type specified.
There are conflicting boot configuration types defined in
this profile (FC and iSCSI). A Server Profile can have only
one boot configuration type specified.
There are conflicting boot configuration types defined in
this profile (FCoE and iSCSI). A Server Profile can have
only one boot configuration type specified.
A Server Profile does not support more than two configured
Boot Setting parameters in Flex-10 iSCSI connections. The
additional Flex-10 iSCSI connections 'Boot Settings'
parameters must be set to 'Disabled' value.
Cannot perform Server Profile operation because the VC
domain group does not support adding iSCSI connections.
Cannot perform Server Profile operation because the VC
domain group does not support adding FCoE connections.
VCEM cannot update Server Profile. The connection port
number is not arranged in order.
VCEM cannot update Server Profile. The connection port
number is out of supported port range.
99
Page 100

Table 43 VCEM server error messages and descriptions (continued)
Error message description
NOTE: The error message descriptions in this table use
Error message number
[x] to represent variables in the error message output.
2783
2784
2785
2786
2787
2788
2789
There was a problem allocating the address because it is
already in use by another connection port number in Server
Profile.
VCEM cannot add connection because a Virtual Connect
interconnect module was added. To correct this situation
remove the existing connections, save the Server Profile
then edit this Server Profile again.
The iSCSI connections port numbering is incorrect. A
continuous sequence finishing on the last valid iSCSI
connection port number is required.
In the iSCSI connection for port , the selected Network
does not exist. The provided Network must exist in the VC
Domain group the Server profile belongs.
In the iSCSI connection for port, the range type is not
compatible with the addresses inside the connection.
In the iSCSI connection for port, the number of MAC
addresses is not correct. Each port must have only one
MAC address.
The address type or the MAC address was changed in the
existing iSCSI connection for port . To change the address
type or the MAC address, first edit the profile and delete
the connection, then edit the server profile again and add
a new connection.
2790
2791
2792
2793
2795
2802
2804
2805
2806
Cannot create FCoE connection because the maximum
number of FCoE connections was reached.
Cannot create FC connection because there are
connections with duplicated WWN Addresses.
Cannot create FCoE connection because there are
connections with duplicated WWN Addresses.
The provided Shared Uplink Set does not exist in the
specified VC domain group. The Shared Uplink Set must
exist in the VC domain group to which the Server Profile
belongs.
There are VNet mappings that are not associated with the
specified Shared Uplink Set.
This action cannot be performed because the current user
does not have the required privileges.
Error logging in. Incorrect username or password.2803
Access denied. The entered logon token is invalid. Obtain
a new token and perform the operation again.
Error logging in: The user is not a user in HP Systems Insight
Manager Repeat the operation with an existing user, or
add the user to HP Systems Insight Manager.
This user does not have authorization to use or view HP
Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager.
2807
100 Error messages
The entered logon token is invalid. Obtain a new token
and perform the operation again.
 Loading...
Loading...