Page 1

HP Insight Control Server Migration 7.2 User Guide
Abstract
HP Insight Control server migration provides an automated, accurate, and affordable way to migrate existing servers to the
latest HP ProLiant server technologies or the latest virtualization platforms. This guide explains processes and procedures that
are not appropriate for the product's online help. The information in this guide is intended for users who have network
administrator–level access and knowledge.
HP Part Number: 461487-401a
Published: June 2013
Edition: 2
Page 2

© Copyright 2007, 2013 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Legal Notices
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial
Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under
vendor's standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Acknowledgements
Microsoft® and Windows® are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Java is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates.
Intel®, Itanium®, and Intel® Xeon® are registered trademarks of the Intel Corporation in the United States and other countries.
Warranty
HP will replace defective delivery media for a period of 90 days from the date of purchase. This warranty applies to all Insight Management
products.
Page 3

Contents
I Overview and concepts..............................................................................10
1 Server migration introduction..................................................................11
Overview..........................................................................................................................11
Installing and configuring server migration software...............................................................11
Installing or upgrading server migration software..............................................................11
Licensing server migration..............................................................................................11
Related products................................................................................................................11
2 Server migration concepts......................................................................13
Server migration components..............................................................................................13
Overview of migrating a server............................................................................................13
Migration checklist........................................................................................................13
HP Insight Control server migration software tabs...................................................................14
II Premigration tasks.....................................................................................16
3 Preparing hardware for migration...........................................................17
Verifying hardware and operating system support..................................................................17
Verifying system requirements for the application station..........................................................17
4 Planning the migration...........................................................................18
Planning a migration strategy..............................................................................................18
Preparing a schedule..........................................................................................................18
Considerations for multiboot systems.....................................................................................18
Migrating large NTFS partitions...........................................................................................18
Resizing file systems for migration........................................................................................18
Resizing Windows file systems........................................................................................18
Resizing Linux file systems...............................................................................................19
Manually disabling critical or hardware-dependent applications..............................................19
5 Preparing software for migration.............................................................20
Verifying licenses for software to be migrated........................................................................20
Migration security..............................................................................................................20
Disabling firewalls.........................................................................................................20
Disabling antivirus software............................................................................................21
Generating static or dynamic certificates..........................................................................21
Installing ProLiant Support Packs..........................................................................................21
Installing Service Pack for ProLiant........................................................................................21
III Migration................................................................................................23
6 Preparing the source server and deploying the Source Agent......................24
Verifying Windows source server requirements.......................................................................24
Preparing a Microsoft Hyper-V source server.....................................................................24
Verifying Linux source server requirements.............................................................................24
Removing guest tools..........................................................................................................25
Choosing server migration Agents........................................................................................25
Deploying server migration Agents.......................................................................................25
Deploying Agents..........................................................................................................25
Manually running server migration Source Agents on the source server.....................................26
Deploying a Windows server migration Source Agent locally on the source server.................26
Deploying a server migration Source Agent on domain controllers..................................28
Deploying the Linux server migration Source Agent locally on the source server.....................28
Detecting, stopping, or restarting a remotely deployed server migration Source Agent.................29
Contents 3
Page 4

7 Preparing the destination server and deploying the destination agent..........30
Prerequisites......................................................................................................................30
Physical destination servers.............................................................................................30
Virtual machine hosts.....................................................................................................30
Linux destination size requirement........................................................................................30
Booting the destination server..............................................................................................31
Booting a physical destination server manually by using the Insight Control server migration
ProLiant Boot CD ISO for X2P migrations..........................................................................31
Booting a physical destination server automatically by using the migration wizard.................32
iLO boot prerequisites...............................................................................................32
Manually creating and booting a virtual destination server.................................................32
Prerequisites for manually creating and booting a destination virtual machine..................32
Prerequisites for booting a virtual machine in Microsoft Hyper-V.................................32
Prerequisites for VMware ESX migration..................................................................33
Manually creating and booting a virtual machine destination server for X2V....................33
Automatically creating and booting a virtual destination server...........................................33
8 Migrating the servers............................................................................35
Prerequisites......................................................................................................................35
Minimum source server prerequisites for all migrations.......................................................35
Uploading drivers.....................................................................................................35
Preparing for a Windows server migration.......................................................................36
Windows source server prerequisites...........................................................................36
Source physical server prerequisites............................................................................36
Source virtual machine prerequisites...........................................................................37
Destination physical server prerequisites......................................................................37
Destination virtual machine host or virtual machine prerequisites.....................................37
Preparing for a Linux server migration..............................................................................37
Source physical server prerequisites............................................................................38
Source virtual machine prerequisites...........................................................................38
Destination physical server prerequisites......................................................................38
Destination virtual machine host or virtual machine prerequisites.....................................39
SAN migrations in Windows..........................................................................................39
Starting the migration wizard...............................................................................................40
Launching server migration by using the Deploy menu........................................................40
Launching server migration by using Quick Launch............................................................41
9 Postmigration tasks................................................................................44
Installing ProLiant Support Packs after migration.....................................................................44
Installing Service Pack for ProLiant after migration..................................................................44
X2P postmigration tasks (Windows)......................................................................................44
X2V postmigration tasks (Windows).....................................................................................45
Editing the Windows boot.ini file after migration (Windows Server 2003).................................45
X2P postmigration tasks (Linux)............................................................................................46
X2V postmigration tasks (Linux)............................................................................................46
Viewing migration logs.......................................................................................................47
Validating the migration.....................................................................................................47
Validating Linux migrations.............................................................................................47
Validating Windows migrations......................................................................................47
IV Troubleshooting and support.....................................................................48
10 Troubleshooting..................................................................................49
User interface....................................................................................................................49
Server migration wizard hangs........................................................................................49
Cause.....................................................................................................................49
Suggested action......................................................................................................49
4 Contents
Page 5

Browser displays an error after loading the server migration wizard from Systems Insight
Manager.....................................................................................................................49
Cause.....................................................................................................................49
Suggested action......................................................................................................49
Launching server migration from Systems Insight Manager throws an exception.....................49
Cause.....................................................................................................................49
Suggested action......................................................................................................49
The name of HP Ethernet 1Gb 4-port 331i-SPI Adapter is not displayed correctly...................49
Suggested action......................................................................................................50
Unable to launch server migration tools from Systems Insight Manager.................................50
Suggested Action.....................................................................................................50
Static IP configuration fails on Hyper-V VM when configured using Boot CD..........................50
Cause.....................................................................................................................50
Suggested action:................................................................................................50
Unable to migrate Windows 2008/2008 R2/2012 using Windows 2008 x64 CMS............50
Cause ....................................................................................................................50
Suggested Action ....................................................................................................50
Source preparation............................................................................................................51
Corrective action is required before this server can be migrated..........................................51
Cause.....................................................................................................................51
Suggested action......................................................................................................51
Source server identification fails......................................................................................51
Suggested action......................................................................................................51
Migration Agent deployment fails....................................................................................52
Suggested action......................................................................................................52
Linux Source Agent window does not appear on RHEL 64–bit.............................................52
Suggested action......................................................................................................53
Remote deployment of Linux Source Agent using nonroot credentials fails.............................53
Suggested action......................................................................................................53
Manual installation of Linux Source Agent using sudo user privileges fails........................53
Suggested action.................................................................................................53
Incorrect LUN size is detected in step 2 of the migration wizard...........................................53
Cause.....................................................................................................................53
Suggested action......................................................................................................53
Migrating a source server fails with the Microsoft Hyper-V role enabled................................53
Suggested action......................................................................................................53
Unable to boot Windows due to unsigned or corrupt drivers...............................................54
Suggested action......................................................................................................54
Destination preparation......................................................................................................54
Destination server identification fails................................................................................54
Suggested action......................................................................................................54
IP address configuration fails on a manually booted virtual machine in Microsoft Hyper-V for
a P2V or V2V migration.................................................................................................54
Suggested action......................................................................................................54
Kernel panic occurs in booting a virtual machine to the Insight Control server migration Virtual
Machine Boot CD ISO...................................................................................................54
Suggested action......................................................................................................55
Mouse does not work on a virtual machine booted with the Insight Control server migration
Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO.........................................................................................55
Cause.....................................................................................................................55
Suggested action......................................................................................................55
Primary array controller does not have logical drives defined..............................................55
Suggested action......................................................................................................55
Primary controller configured in the system does not have drives attached.............................55
Suggested action......................................................................................................55
Contents 5
Page 6

Primary controller in the system is not supported by this version of Insight Control server
migration.....................................................................................................................55
Suggested action......................................................................................................55
Destination server displays a blank screen when it boots to server migration Boot CD ISO......56
Suggested action......................................................................................................56
Some storage volumes on the destination server are not available for selection......................56
Suggested action......................................................................................................56
Static IP address cannot be assigned on the destination server while booting using the Boot
CD ISO........................................................................................................................56
Cause.....................................................................................................................56
Suggested action......................................................................................................57
Supported storage controllers display Unknown on the Boot CD ISO....................................57
Cause.....................................................................................................................57
Suggested action......................................................................................................57
Automatic booting of the destination physical server fails....................................................57
Suggested action......................................................................................................57
3 Insight Control server migration might not detect virtual machines on mapped network
drives..........................................................................................................................57
Cause.....................................................................................................................57
Suggested action......................................................................................................57
Destination server does not boot even though the automatic booting option was chosen during
X2P migrations.............................................................................................................57
Suggested action......................................................................................................57
Insight Control server migration stops responding during automatic booting of Microsoft Hyper-V
virtual machine.............................................................................................................58
Suggested action......................................................................................................58
Application station fails to connect to the destination server when the server is automatically
booted for an X2P migration...........................................................................................58
Cause.....................................................................................................................58
Suggested action......................................................................................................58
Warning message is not displayed for an unsupported server when the server is started using
the Insight Control server migration ProLiant Boot CD.........................................................58
Suggested action......................................................................................................58
Microsoft Windows 2008 OS migration results in a blue screen error on destination server
configured with NC551m FCoE card...............................................................................58
Suggested action......................................................................................................59
Migration process..............................................................................................................59
Drivers cannot be installed or injected onto a boot disk......................................................59
Suggested action......................................................................................................59
Large volumes fail with a server thread error.....................................................................59
Suggested action......................................................................................................59
Migrating a Linux source server that has large storage fails when the migration is initiated......59
Suggested action......................................................................................................59
Linux migration might fail when X Windows configuration is not properly formatted...............60
Suggested action......................................................................................................60
Partitions created with third-party partitioning tools do not show the proper file system type in
the server migration wizard............................................................................................60
Suggested action......................................................................................................60
Migration hangs if the source server is shut down..............................................................60
Suggested action......................................................................................................60
NTFS resize error message appears.................................................................................61
Cause.....................................................................................................................61
Suggested action......................................................................................................61
ReiserFS volumes are blocked for Linux migration...............................................................61
Cause.....................................................................................................................61
6 Contents
Page 7

Suggested action......................................................................................................61
Filesystem on source disk \\.\PhysicalDrive0, Partition 0 could not be resized during the
migration.....................................................................................................................61
Cause.....................................................................................................................61
Suggested action......................................................................................................62
Migration fails during the disk cloning phase....................................................................62
Cause.....................................................................................................................62
Suggested action......................................................................................................62
Failed: Drivers could Not Be Injected Into Boot Disk in the logs............................................62
Suggested action......................................................................................................62
Starting a new migration after a current migration is stopped..............................................62
Suggested action......................................................................................................62
Unrecoverable sector-read errors on the source server hard drive are not supported and fail
a Windows P2P or P2V migration...................................................................................62
Cause.....................................................................................................................63
Suggested action......................................................................................................63
Source Agent fails to launch when source server reboots in migration agent mode.................63
Suggested action......................................................................................................63
Error occurs during data copy of Linux migration...............................................................63
Cause.....................................................................................................................63
Suggested action......................................................................................................63
SAN-connected destination server displays a blue screen...................................................63
Suggested action......................................................................................................63
Out of memory error occurs on the application station during migration...............................64
Suggested action......................................................................................................64
Destination server boots with an invalid IP address............................................................64
Cause.....................................................................................................................64
Suggested action......................................................................................................64
Windows server migration Source Agent or PINT remote deployment is intermittent and
deployment fails with a General failure occurred error.......................................................64
Suggested action......................................................................................................64
Unable to detect HP FlexFabric 10Gb 2-port 554FLR-SFP+ Adapter configured as iSCSI disk
in step 5 of migration wizard..........................................................................................64
Suggested action......................................................................................................64
HP Smart Array B320i controller name is not displayed......................................................64
Suggested action......................................................................................................65
Unable to install Service Pack for ProLiant (SPP) on Windows 2008 SP2 operating system after
successful migration.......................................................................................................65
Suggested action......................................................................................................65
Linux migration to servers with iSCSI storage fails to boot ..................................................65
Suggested action: ....................................................................................................65
Postmigration ....................................................................................................................65
Migration does not start after confirmation. The event log continuously displays Operation
Migration waiting for connection to source.......................................................................65
Suggested action......................................................................................................65
Destination server mouse and keyboard do not work after a Windows migration...................65
Suggested action......................................................................................................65
USB mouse or keyboard drivers are not loaded after an X2P Windows migration..................66
Cause.....................................................................................................................66
Suggested action......................................................................................................66
Mouse does not work on the iLO of the destination server after a Linux X2P migration............67
Suggested action......................................................................................................67
Mouse does not work on the destination ESX virtual machine after a V2V migration...............67
Suggested action......................................................................................................67
Drive letters are not the same in the migrated virtual machine guest after migration................67
Contents 7
Page 8

Suggested action......................................................................................................67
Drives do not appear on the migrated operating system.....................................................68
Suggested action......................................................................................................68
Mouse and keyboard do not work after a Microsoft Hyper-V virtual machine is migrated to a
ProLiant server..............................................................................................................68
Suggested action......................................................................................................68
Static IP address cannot be assigned on the destination server after migration.......................68
Suggested action......................................................................................................68
Virtual machine hosts Integrated Components that are not installed on the destination virtual
machine after migration.................................................................................................68
Suggested action......................................................................................................68
Exclamation point (!) appears on the NIC adapter in Device Manager on the migrated virtual
machine......................................................................................................................69
Suggested action......................................................................................................69
Network adapter in the destination ESX virtual machine is not initialized after a V2V
migration.....................................................................................................................69
Suggested action......................................................................................................69
Destination virtual machine fails to boot after X2V migration...............................................69
Cause.....................................................................................................................69
Suggested action......................................................................................................69
During editing of the settings of guest VMs created by server migration, an invalid OS ID
warning appears..........................................................................................................69
Suggested action......................................................................................................69
Server is unresponsive during PSP installation....................................................................70
Suggested action......................................................................................................70
Destination server still shows server migration UI but server migration wizard shows migration
completed....................................................................................................................70
Suggested action......................................................................................................70
Operating system is not booting on a destination server that has SAN disks..........................70
Suggested action......................................................................................................70
Error is displayed for a missing file system while migrated Linux OS is booted on the destination
server..........................................................................................................................70
Suggested action......................................................................................................70
Logical drives of HP Smart Array B110i SATA RAID Controller are removed ..........................70
Suggested action......................................................................................................70
Unable to download the log files from the migration wizard when using IE 9........................71
Suggested action......................................................................................................71
Microsoft Windows 2008 R2 SP1 does not boot on ProLiant BL420c Gen8 with Emulex
LPe1205A FC storage controller. .....................................................................................71
Suggested action......................................................................................................71
Source server with SLES 11 SP2 x32 OS does not boot the operating system properly after
successful migration.......................................................................................................71
Suggested action......................................................................................................71
RHEL version 6.3 (x64) operating system does not boot after migrating to HP Dynamic Smart
Array B120i/B320i Controllers.......................................................................................71
Suggested action......................................................................................................71
RHEL version 6.3 (x64) operating system does not boot as destination after successful
migration.....................................................................................................................71
Suggested action......................................................................................................72
11 Support and other resources.................................................................73
Information to collect before contacting HP............................................................................73
How to contact HP.............................................................................................................73
Security bulletin and alert policy for non-HP owned software components .................................73
Subscription service ...........................................................................................................73
8 Contents
Page 9

Registering for software technical support and update service..................................................73
How to use your software technical support and update service..........................................74
HP authorized resellers.......................................................................................................74
Related information............................................................................................................74
Documents...................................................................................................................74
Websites......................................................................................................................74
Related documentation...................................................................................................75
Typographic conventions.....................................................................................................75
12 Documentation feedback......................................................................77
A Applying old server migration standalone licenses........................................78
B Performing migrations in a Microsoft Cluster server environment......................79
Premigration consideration steps for clusters...............................................................................79
Performing the migration..........................................................................................................80
Post migration considerations and steps.....................................................................................80
C Logging server migration application service Logs into Windows NT Events ....82
Glossary....................................................................................................83
Index.........................................................................................................84
Contents 9
Page 10

Part I Overview and concepts
This part focuses on conceptual information that will help to understand the product. It does not include
information on how to use server migration.
Page 11
1 Server migration introduction
Overview
HP Insight Control server migration provides an automated, accurate, and affordable way to
migrate existing servers running Microsoft Windows or Linux and their content to the latest HP
ProLiant server technologies or the latest virtualization platforms from VMware and Microsoft.
Insight Control server migration supports the following types of Microsoft Windows and Linux
migrations:
• Physical-to-ProLiant (P2P) migration—Migrates a physical machine to a ProLiant server.
• Physical-to-Virtual (P2V) migration—Migrates a physical machine to a virtual machine guest
in a virtual machine host.
• Virtual-to-ProLiant (V2P) migration—Migrates a virtual machine guest in a virtual machine host
to a ProLiant server.
• Virtual-to-Virtual (V2V) migration—Migrates a virtual machine guest between virtualization
layers.
Installing and configuring server migration software
Installing or upgrading server migration software
HP Insight Control server migration software is delivered on the HP Insight Management distribution
media and is installed through the Insight Management Integrated Installer. The server on which
you install Insight Management is designated to be the Central Management Server (CMS).
For installation and upgrade instructions and supported upgrade paths, see the HP Insight
Management Installation and Configuration Guide.
For a description of all software that is delivered on the Insight Management distribution media,
see the HP Insight Management Getting Started Guide.
Licensing server migration
The standard procedure for licensing Insight Control server migration is to purchase and apply
Insight Control licenses. So if your destination server is licensed by Insight Control version 6.0 or
later, you can perform unlimited migrations to the Insight Control licensed server.
For general licensing information, see the HP Insight Management Getting Started Guide, available
at the following website:
http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement
Related products
Table 1 (page 11) lists HP products that are available for extending deployment or customizing
the migrated server.
Table 1 Related products
HP Portable Images Network Tool (PINT) and HP Portable
Images Storage Assistant (PISA)
HP OpenView Change and Configuration Management
solutions
DescriptionProduct
Used to solve networking issues (specifically, NIC
configuration issues) in moving operating system images
between HP BladeSystem c-Class blades using VMware
ESX and Microsoft Hyper-V (for PINT only) virtual machines,
and HP Virtual Connect on HP BladeSystem c-Class blades.
Automates the management of software such as operating
systems, applications, patches, content, and configuration
Overview 11
Page 12
Table 1 Related products (continued)
DescriptionProduct
settings, so that each computing device is maintained in
the right configuration.
Insight Control server deployment
HP SmartStart CD
HP SmartStart Scripting Toolkit
Facilitates the installation, configuration, and deployment
of large server volumes through a GUI-based or a
web–based console, using scripting or imaging technology.
Server configuration time decreases so that you can quickly
scale server deployments to large volumes.
Provides step-by-step ProLiant server deployment assistance.
From configuring arrays and installing operating systems,
to updating optimized ProLiant server support software,
SmartStart ensures a stable and reliable configuration.
Included in the HP ProLiant Essentials Foundation Pack, the
SmartStart CD works with all HP ProLiant DL and ML 300,
500, and 700 series, and all ProLiant BL servers.
A server deployment product that delivers unattended
automated installation for high-volume ProLiant server
installations.
Available in Windows and Linux editions, the toolkit
supports ProLiant DL and ML 300, 500, and 700 series,
and all ProLiant BL servers.
The toolkit includes a modular set of tools and important
documentation that describes how to apply these tools to
automate server deployment.
12 Server migration introduction
Page 13

2 Server migration concepts
Server migration components
The Insight Control server migration environment consists of the following required components:
• Application station—The computer from which the migration is set up and performed. This
can be either a physical machine or a Windows guest on a supported hypervisor.
In earlier versions of HP Insight Management, the standalone installation of Insight Control
server migration software was enabled. The server on which the server migration software
was installed was then designated the application station. The installation of standalone server
migration software is no longer supported, and so the same server that hosts the installation
of Insight Management software and HP Systems Insight Manager now must host the Insight
Control server migration software. The terms “application station” and "CMS" now both refer
to the same server, which hosts both Insight Management and the server migration software.
• Source server—The physical source server or the virtual machine to be migrated.
• Destination server—The ProLiant server or the virtual machine to which the source server is
migrated.
Overview of migrating a server
Use the checklist in this section as a general guide to the tasks performed during a server migration.
For an explanation of the tabs in the server migration wizard, see “HP Insight Control server
migration software tabs” (page 14).
Migration checklist
The specific tasks required to complete a migration are listed in the server migration online help.
However, every migration can be condensed into the following general migration tasks:
1. Plan the migration.
2. Prepare the hardware and software for migration.
3. Prepare the source server or virtual machine for migration by installing the server migration
Source Agent on the source server or virtual machine:
a. Deploy the server migration Source Agent to the source server.
b. Select the source disks to migrate.
4. Prepare the destination server or virtual machine for migration:
a. Boot the destination server by using the Boot CD. For HP ProLiant Gen8 servers, only the
autoboot option is supported.
b. Create the destination disks.
5. Migrate the servers:
a. Test the network connectivity between the source and destination servers.
b. Map the source disks to the destination disks.
c. Choose destination server reboot, driver package, and network options.
d. Review choices and execute the migration.
6. Monitor the migration progress and view the logs when the migration is complete.
7. Log on to the new server and configure the drivers, communication settings, and boot options.
Server migration components 13
Page 14
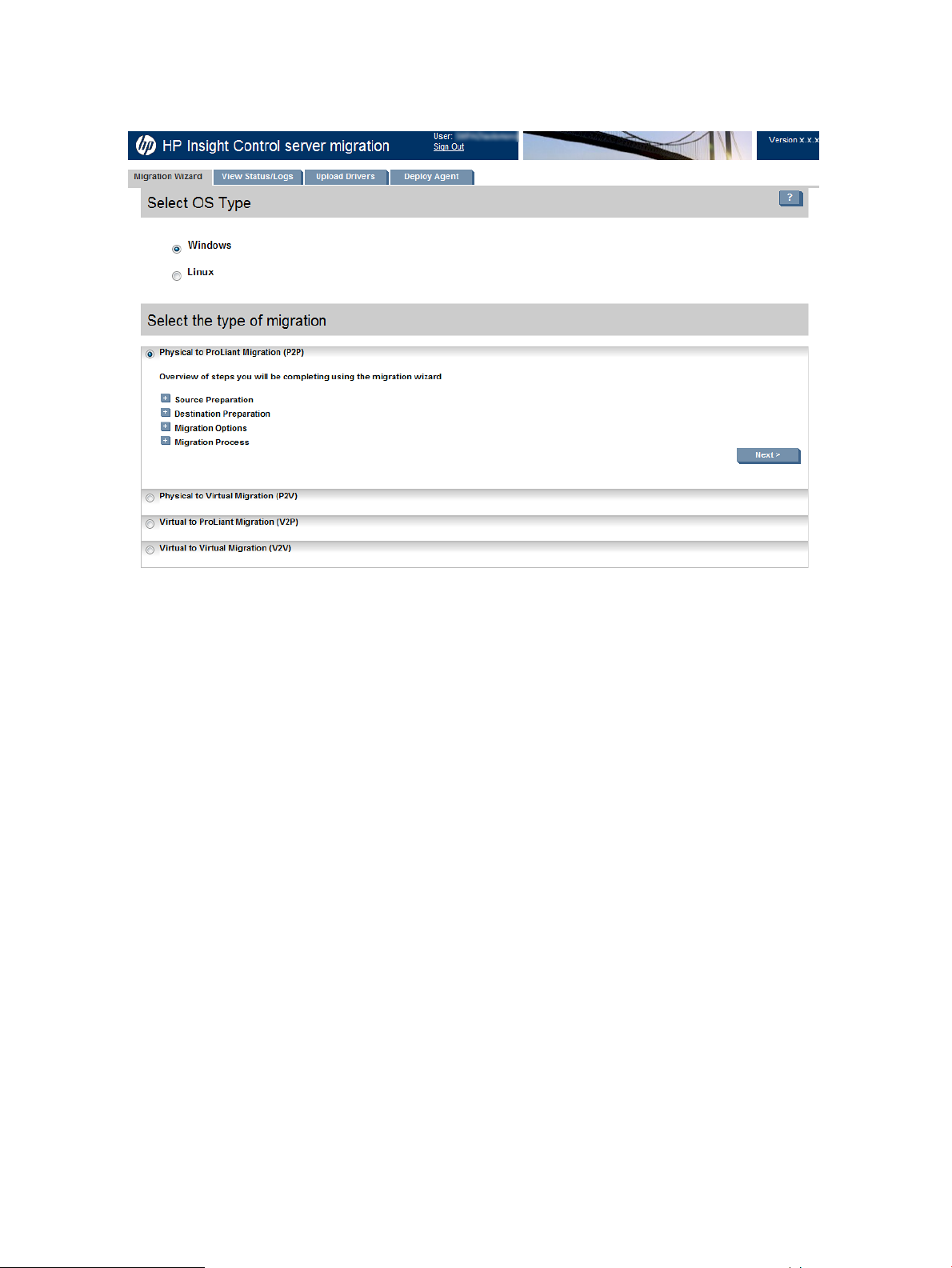
HP Insight Control server migration software tabs
Figure 1 Migration screen
The Insight Control server migration software screen has the following tabs:
• Migration Wizard
This tab enables you to perform the Insight Control server migration. In summary, the migration
wizard enables you to perform the following tasks:
◦ Identify the source server
◦ Select the volumes to migrate
◦ Identify the destination server
◦ Test the network connections
◦ Specify destination disks and resizing partitions
◦ Select additional migration options, as necessary
◦ Confirm and perform the migration
◦ Review migration progress
For more information about the migration wizard, see “Starting the migration wizard”
(page 40).
• View Status/Logs
This tab enables you to view the details and results of attempted migrations and to delete
migration results. For more information about viewing logs, see “Viewing migration logs”
(page 47).
14 Server migration concepts
Page 15

• Upload Drivers
This tab displays the status of iSCSI Initiator and DISM installed on the server and provides
the option to upload HP ProLiant Support Pack (PSP) executable files and HP Service Pack for
ProLiant (SPP) ISO images. This tab also displays the installation status of DevCon and provides
the option to upload the DevCon binary. For more information about this tab, see “Uploading
drivers” (page 35).
• Deploy Agent
This tab enables you to deploy the Insight Control server migration Source Agent and PINT
Agents.
HP Insight Control server migration software tabs 15
Page 16

Part II Premigration tasks
This part of the guide assists you in collecting information to prepare for a migration, and covers steps 1
and 2 of the checklist provided in “Migration checklist” (page 13).
Page 17
3 Preparing hardware for migration
Verifying hardware and operating system support
Before you start any X2P (P2P or V2P) migration, verify the following:
• The source server operating system is supported on the destination server. To verify OS support
on ProLiant destination servers, see the following website:
http://www.hp.com/go/ossupport
• For the supported hardware and software configurations of server migration, see HP Insight
Management Support Matrix available at:
http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs
Remove unsupported storage and NIC controllers from the destination server before you perform
a migration. Unsupported storage and NIC controllers can be added back on the destination
server, with proper manual configuration, after a migration.
Verifying system requirements for the application station
The application station has the following prerequisites:
• A supported Windows operating system running on physical hardware or as a Windows
guest on a supported hypervisor. For a list of supported operating systems, and CMS hardware
and software requirements and caveats, see HP Insight Management Support Matrix at the
following website:
http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs
• Microsoft iSCSI Initiator, which you can download and install from http://www.microsoft.com
if it is not already available with the operating system on your application station.
• Insight Control server migration installed on an NTFS partition.
• Availability of ports 51124 and 51125 (or ports specified during Insight Control installation
for agent communications and HP Integrated Lights-Out (iLO) booting).
• Availability of port 51127.
• User account credentials with administrative rights.
• Free disk space of at least 300 MB per iLO boot, while booting a destination server for P2P
and V2P.
• The initial installation of Insight Control server migration can take 1 GB of storage space, and
each automatically booted destination server will need at least 300 MB of storage space on
the application station for non-Gen8 servers.
Verifying hardware and operating system support 17
Page 18

4 Planning the migration
Planning a migration strategy
One challenge in migrating operating systems, applications, and data is modifying the migrated
operating system to boot on the destination server and to function properly on the hardware. Insight
Control server migration makes the required operating system changes for you.
To best prepare for a migration, consider developing a migration strategy before you run a
migration. Migration strategies vary depending on machine hardware, network landscape, and
applications. To develop a migration strategy, review the following before beginning your migration.
Preparing a schedule
Schedule preparation is an essential part of planning a migration strategy.
Be sure to include adequate time for copying data, because the source server will be offline until
the migration is complete. Large volumes take time to migrate. Under optimal conditions, 1 GB of
data requires 2 to 3 minutes to migrate. Using 2 minutes as a best-case scenario, migrating 500
GB of data might take more than 17 hours.
When a migration starts, the source server reboots to a minimal configuration so that no updates
occur on the source server during migration. Only those services required for the migration are
enabled.
Applications that normally run on the server are not available during migration. After the migration
is complete, the source server is restored to its premigration state.
Schedule the migration to occur at a time when the source server can be offline.
Considerations for multiboot systems
Although Insight Control server migration supports migrating multi-boot systems, consider the
following:
• A supported operating system must be set as the default operating system for the boot disk.
• The migration wizard enables the migration of all partitions with supported file systems.
Unsupported operating systems on those partitions are also enabled for migration, but Insight
Control server migration does not support them.
• If unsupported operating systems are migrated, they might be detected, but proper drivers
might not be installed. This issue can leave the unsupported operating system on the destination
server unable to be booted.
Migrating large NTFS partitions
Insight Control server migration cannot migrate NTFS partitions greater than 2 TB in size.
Resizing file systems for migration
During the migration progress, the partitions being migrated can be resized. There are some file
system caveats to be aware of that might affect the migration of your data.
Resizing Windows file systems
Insight Control server migration supports resizing and migration of NTFS volumes. However, some
conditions may prevent server migration from resizing NTFS partitions:
• Large NTFS partitions or NTFS partitions that have too many clusters, resulting in large volume
cluster bitmaps that cannot be resized. In some cases, the volume might be recognized as
18 Planning the migration
Page 19

RAW (partitions in which no file systems exist). Although server migration can perform
migrations on these volumes, it cannot resize the volumes.
• Volumes that have bad clusters. Server migration does not support the migration of volumes
that have bad clusters. You must manually migrate volumes that have bad clusters to the
destination server after a migration.
If an NTFS volume is detected but cannot be resized, you must run a disk check (for example,
CHKDSK.exe) to verify that the volume has no bad clusters before you begin the migration process.
NOTE: Before installing SPP on the destination server, as part of postmigration task, ensure that
the server has a minimum of 1 GB of available disk space.
Resizing Linux file systems
Insight Control server migration supports file systems in LVMs, and it supports resizing and migration
of the following Linux journaling file systems:
• ext2
• ext3
• ext4
• ReiserFS
• LVMs
However, Insight Control server migration does not support Linux file systems that have bad blocks.
Make sure that the Linux source file system does not have bad blocks by running file system–specific
disk maintenance tools to examine the disk and mark bad blocks, like the file system consistency
check (fsck).
Manually disabling critical or hardware-dependent applications
Some hardware applications are bound to the source server and might need reconfiguration to
function as expected after a server migration.
For added safety, manually disable critical and hardware-dependent applications before you
migrate a source server. You can then manually re-enable these applications after the migration
is complete.
Manually disabling applications prevents them from starting on the destination server before they
are reconfigured for the destination server.
Examples of applications that must be disabled during migration include:
• Applications that rely on unique hardware serial numbers, BIOS or chassis IDs, NICs, MAC
addresses, or devices that authenticate a piece of software.
• Applications that store data on a volume different from that of the operating system. Insight
Control server migration retains drive letters (for example, F:) during migration, but hardware
differences between the source and destination servers can force the drive letters to change.
• Applications that depend on physical disk identifiers instead of drive letters. Depending on
the disk enumeration order for the destination server and selections made in the migration
wizard, the contents of a physical disk might have a different sequential identifier on the
destination server. In these cases, the application must be reconfigured to use the new physical
disk identifiers.
Manually disabling critical or hardware-dependent applications 19
Page 20
5 Preparing software for migration
Verifying licenses for software to be migrated
Before you perform a migration, review all hardware, operating system, and application licenses
on the source server and acquire all valid licenses necessary for the destination server. Some
hardware, software, and OS license agreements might require you to purchase a new license for
the destination server.
IMPORTANT: Servers that have Windows OEM licenses are not supported for migration. For
licensing questions, contact HP support. For information about HP support, see “Support and other
resources” (page 73).
Migration security
Disabling firewalls
The source server Microsoft Windows firewall or Linux firewall and SELinux are disabled
automatically by server migration when a migration begins. The firewall and SELinux (if applicable)
are re-enabled after the migration is completed.
Before you perform the migration, you must manually disable, reconfigure, or remove other firewall
products. If you reconfigure a firewall product, you will be required to remove the product before
migration and reinstall it after migration.
If the firewall is not disabled or configured properly on the source server, application station, and
virtual machine hosts before a migration, the source server, application station, and virtual machine
hosts might not be able to communicate. Symptoms of this issue can include the following:
• The application station cannot detect the source server migration Agent for migrations.
• The source server hangs after booting into exclusive mode during migrations.
The following TCP ports are used for Insight Control server migration:
• Port 51124—For communication between the Insight Control server migration Web Service
and the Insight Control application service using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
• Port 51125—For communication between the Insight Control server migration Web Service
and iLO for autodestination boot
• Ports 51125 and 51126—For communication between the Insight Control server migration
Application Service and the migration agent on the source server
• Ports 51125 and 51126—For communication between the Insight Control server migration
Application Service and the migration agent on the destination server
• Port 51126—For communication between the migration agents on the source server and
destination server
• Port 51127—For use on the application station for Insight Control server migration Web
Service
• SSH port 22—For Linux migrations
20 Preparing software for migration
Page 21
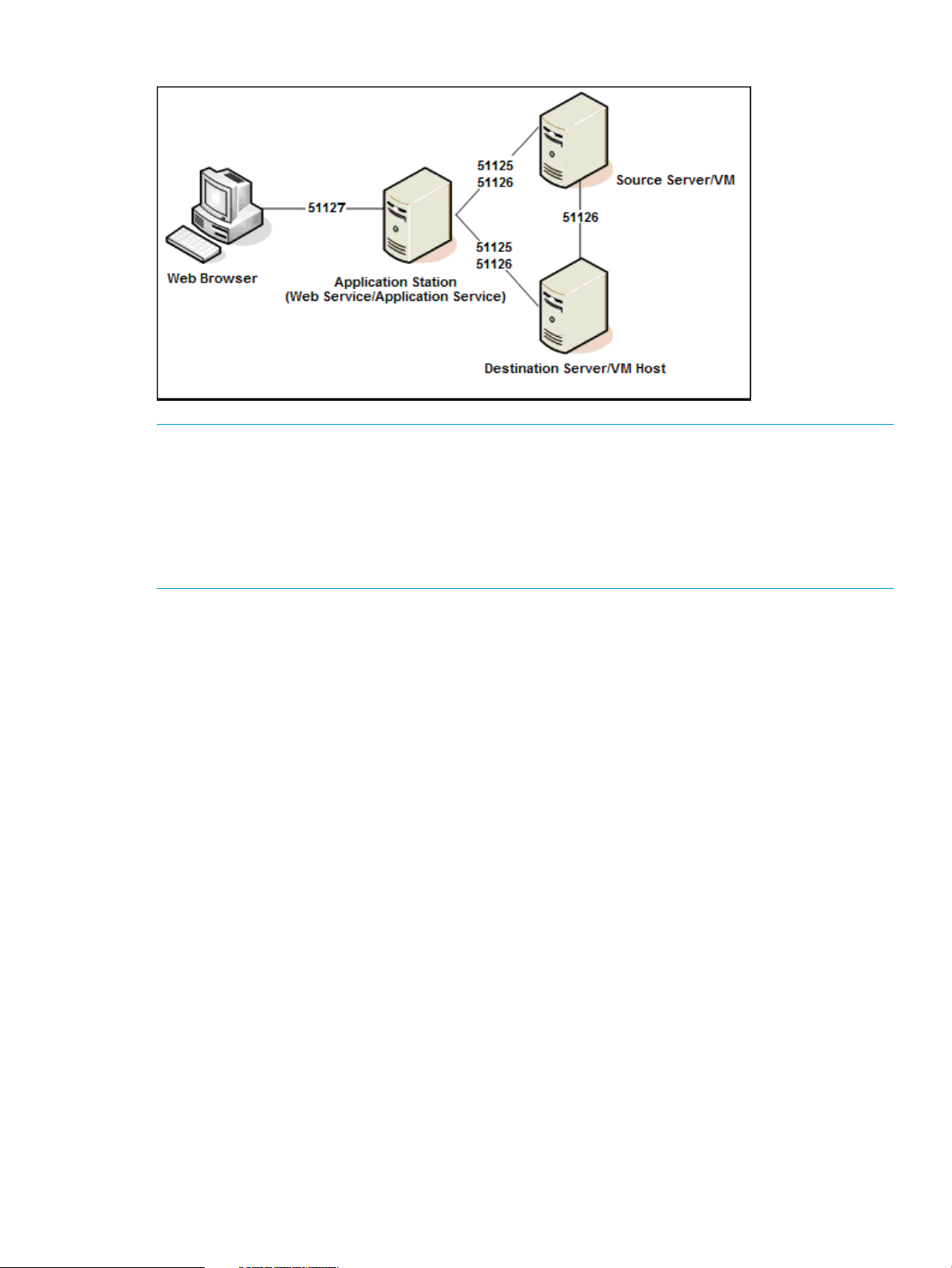
Figure 2 TCP ports in use during migration
NOTE: Insight Control uses the following encryption types:
• SSL RSA with RC4 128 MD5
• SSL RSA with RC4 128 SHA
• TLS RSA with AES 128 CBC SHA cipher suites. To enable the support of AES 256 and FIPS
140-2 cipher suites on server migration with strong cipher, use the utility: <Insight Control
server migration Installation Folder>/bin/cipherutil.cmd
Disabling antivirus software
For optimal performance during migration, verify that real-time scanning is temporarily disabled.
Also verify that no antivirus scans are running or are scheduled to run while the migration is
performed on the application station, source server, or virtual machine hosts.
Generating static or dynamic certificates
Static certificates are used when you run the server migration Source Agent manually on the source
server. However, dynamic certificates are generated and used when you use Insight Control server
migration to automatically deploy agents to the source and destination servers. HP recommends
that the agents be deployed automatically using Insight Control server migration.
Installing ProLiant Support Packs
PSPs contain sets of drivers to get a new ProLiant destination server running quickly after a migration.
Windows PSP executables can automatically be installed at the end of a Windows X2P migration.
• For Windows X2P migrations, upload the PSP you plan to use on the Upload Drivers tab of
the server migration UI. Also, Windows PSPs can be installed manually after migration.
• For Linux X2P migrations, you must manually apply the Linux PSP to the destination server after
the migration is complete.
Installing Service Pack for ProLiant
SPP contains sets of drivers and firmwares to get a new ProLiant Gen8 destination server running
quickly after a migration. SPP is installed automatically at the end of a Windows X2P migration.
• For Windows X2P migrations, upload the SPP you plan to use on the Upload Drivers tab of
the server migration UI. You can also manually install Windows SPP after server migration
Installing ProLiant Support Packs 21
Page 22

NOTE: Before installing SPP on the destination server, ensure that the server has a minimum
disk space of 1 GB.
• For Linux X2P migrations, you must manually apply the Linux SPP to the destination server after
the migration is complete.
22 Preparing software for migration
Page 23

Part III Migration
This part of the guide contains information related to steps 3 through 5 of the checklist provided in “Migration
checklist” (page 13), and methods for manually completing some the steps of the migration wizard.
Remember, this guide does not describe each of the steps in specific detail. You can find specific information
in the online help.
Page 24

6 Preparing the source server and deploying the Source
Agent
Verifying Windows source server requirements
The physical or virtual Windows source server requires the following:
• Local system administrative credentials.
• A supported Windows operating system. For a list of operating systems, see HP Insight
Management Support Matrix at http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs.
• Available disk space of at least 180 MB.
• The availability of ports 51125 and 51126.
• Screen resolution of at least 800 x 600.
• All detachable media removed.
• If the source server is an application station, disable the HP Insight Control server migration
Application Service and the HP Insight Control server migration Web Service.
Preparing a Microsoft Hyper-V source server
If you are planning to migrate a source server that has the Microsoft Hyper-V role enabled, perform
one of the following on the source server:
• Turn off the hypervisor by using bcdedit /set hypervisorlaunchtype off at a
command line.
After the migration, you can re-enable the hypervisor at a command line by using bcdedit
/set hypervisorlaunchtype auto.
• Remove the Microsoft Hyper-V role from the source server by using the server configuration
tools.
Verifying Linux source server requirements
The physical Linux source server requires the following:
• User account credentials with administrative rights.
• SELinux running in passive mode.
• A supported Linux operating system. For a list of operating systems, see HP Insight Management
Support Matrix at http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs.
• Available disk space of at least 10 MB on /boot and 150 MB under the directory where the
Linux server migration Source Agent must be installed.
NOTE: When Linux Source Agent is launched remotely from the CMS, the default location
on the source server for agent installation is /root.
`
• The availability of ports 51125 and 51126.
• Verify that you have removed all unused boot entries from /boot/grub/menu.lst and the
corresponding initrd from /boot.
• Disable any scripts that might clean up the migration agent files on reboot or shutdown. For
instance, if the agent has been deployed manually to /root, make sure that no scripts will
clean up /root on restart or shutdown.
24 Preparing the source server and deploying the Source Agent
Page 25

• To enable the display of the Linux source server agent in 64–bit RHEL, installation of the X.Org
X11 libXtst runtime library libXtst-1.0.99.2-3.el6.i686.rpm.
• The 32-bit version of glibc to run the Linux server migration Source Agent. The library is
present by default on 32-bit Linux installations, but you might need to install it manually on
64-bit Linux systems. The 32-bit version of glibc is available on your Linux OS installation
CD/DVD.
• For SAN Linux migration, destination server–specific Fibre Channel HBA firmware files installed
on the source server. These firmware files are available on the installation media of the Linux
OS. For example, if you plan to migrate to a destination server with SAN storage by using a
QLogic HBA, you must install qlogic-firmware-<version>.noarch.rpm on SLES OS
or ql2xxx-firmware-<version>.noarch.rpm on RHEL OS. For information on the
firmware files required and the installation instructions, see the respective HBA documentation.
• If an IPv6 DHCP server running on the network and if the source is a SLES OS running DHCP
client for IPv6, then the source may not boot in the safe migration mode. To resolve this issue,
you must disable IPv6 DHCP on all the NIC interfaces in the source server prior to migration
and restart the server manually after the migration.
Removing guest tools
Before you start a migration, you must remove guest tools if you are migrating a source virtual
machine. Guest tools are not applicable on the destination server and might cause issues with the
normal functioning of the network adapters, keyboard, and mouse. After the migration is completed,
you can reinstall the guest tools on the source virtual machine.
Choosing server migration Agents
Deploy and run migration Agents on the source server and the destination server before you start
a server migration.
Table 2 Server and migration Agent types
Virtual machine destination
1
HP ProLiant Gen8 servers must be booted automatically from the server migration wizard. When HP ProLiant Gen8
servers are used as destination servers, the manual boot option of the Insight Control server migration ProLiant Boot CD
is not supported.
The Source Agent does not run as a service on the source server, and you must apply the agent
for each migration. The agent will no longer run on the source after migration.
Deploying server migration Agents
Migration AgentServer
Windows server migration Source AgentPhysical Windows source server or source virtual machine
Linux server migration Source AgentPhysical Linux source server or source virtual machine
Insight Control server migration ProLiant Boot CD ISO filePhysical destination server
1
Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD
ISO file
Deploying Agents
If you have administrative rights to connect to the source server, you can deploy a migration Agent.
NOTE: Shut down any running hypervisor or virtual machines on the source server before you
deploy the migration Agent. Failure to do so can result in improper IP address assignment and
can disrupt the migration.
Removing guest tools 25
Page 26
Use one of the following methods. For additional information on these procedures, see the server
migration online help.
• HP Systems Insight Manager
Click Deploy→Deploy Drivers, Firmware and Agents→Install server migration Agent.◦
◦ By using the Quick Launch feature, select a source server, hover your mouse over the
Quick Launch link, and then select Install server migration agent.
• Server migration wizard
From the Deploy Agent tab of the migration wizard or from the migration wizard during
◦
migration setup for source servers
◦ From the Identify Source Server step of the migration wizard
NOTE: When the deployment is performed through Systems Insight Manager and the server
migration wizard, the agent launched from the CMS will not be valid after 7 days, and will
need to be stopped and re-deployed on source before the migration can occur.
• Manually running server migration Source Agent on the source server
Manually running server migration Source Agents on the source server
Deploying a Windows server migration Source Agent locally on the source server
1. Access the server migration Source Agent in the following folder on the application station:
<Insight Control server migration Installation
Folder>\Agents\SMP\cp009582.exe
Figure 3 Navigate to server migration Source Agent
2. Copy the cp009582.exe file to the source server, and then run the file. If a security warning
window appears, click Run.
3. To launch the server migration Source Agent, click Install.
26 Preparing the source server and deploying the Source Agent
Page 27
Figure 4 Server migration agent install screen
When the server migration Source Agent is ready for migration, the following screen appears
on the source server.
Figure 5 Source Agent screen for Windows
Manually running server migration Source Agents on the source server 27
Page 28
4. Record the IP addresses listed for the source server entry when using Insight Control server
migration.
After the application station is connected to the migration Agent on these servers, the agent
is locked to the application station.
CAUTION: The agent deployment automatically opens the necessary ports in the firewall.
These ports will remain open unless you manually close them later by using your firewall
software.
5. To unlock the connection between the application station and the source server, or to stop the
server migration Source Agent, access the agent console on the source server, and then click
Abort and Exit.
Deploying a server migration Source Agent on domain controllers
Insight Control server migration supports migration of domain controllers.
To deploy a source migration agent on a source server domain controller:
1. Reboot the server.
2. During reboot, press F8 to boot to Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM).
3. Launch the migration agent in DSRM mode.
The migration runs in DSRM instead of booting in migration agent mode. As a result, CHKDSK
does not run before the migration of domain controllers.
Deploying the Linux server migration Source Agent locally on the source server
1. Access the server migration Source Agent in the following folder on the application station:
<Insight Control server migration Installation
Folder>\Agents\SMP\hpsmpagent.tar.gz
Figure 6 Navigate to server migration Source Agent
2. Copy the file in this folder to the source server, and then extract the file.
3. To launch the server migration Source Agent, go to the bin folder of the extracted directory,
and then execute the script startHPSMPCnt.sh. When the server migration Source Agent
is ready for migration, the following screen appears on the source server.
28 Preparing the source server and deploying the Source Agent
Page 29
Figure 7 Linux Source Agent screen
NOTE: The server migration Source Agent uses a 32–bit Java Runtime Environment. In 64–bit
RHEL, the Linux source migration agent window does not appear, although the agent is running.
4. Record the IP addresses listed for the source server.
CAUTION: The agent deployment automatically stops the firewall and disables SELinux.
5. After the application station is connected to the migration agent on these servers, the agent
is locked to the application station.
To unlock the connection between the application station and the source server, or to stop the
server migration Source Agent, access the Agent console on the source server, and then click
Abort and Exit.
NOTE: After a migration is complete, the server migration Source Agent no longer runs on the
source server.
Detecting, stopping, or restarting a remotely deployed server migration Source Agent
Because no indications appear on the source server when you launch an agent remotely from the
server migration wizard, do one of the following to detect or stop a server migration Source Agent:
• On a Windows source server, run the stopHPSMPAgent.cmd tool. This tool is installed on
the desktop when the agent is installed on the source server.
• On a Linux source server, run the stopSMPagent.sh tool. This tool is installed under the
/bin folder of the extracted directory when the agent is installed on the source server.
To restart locally deployed Windows or Linux Source Agents, click Abort and Exit on the agent
console, and then redeploy the agent.
Detecting, stopping, or restarting a remotely deployed server migration Source Agent 29
Page 30

7 Preparing the destination server and deploying the
destination agent
Prerequisites
Physical destination servers
A supported ProLiant destination server must be used for X2P migrations, and the destination server
disks must be configured to support migration of source servers.
For a list of supported ProLiant servers for X2P, see the list of supported servers in HP Insight
Management Support Matrix at the following website:
http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs
When you are performing a X2P migration, prepare your destination server disk sizes and
configuration to accommodate the partitions to be migrated. You can change the logical disk
numbers on the destination server. For example, data on \PhysicalDrive5 on the source server
during a Windows migration might be reordered to \PhysicalDrive2 on the destination server.
During a Linux migration, data on /dev/sda on the source server might be reordered to /dev/sdc
on the destination server.
Partitions on one disk on the source server can be migrated to only a single disk on the destination.
Insight Control server migration cannot migrate different partitions from the same disk on the source
server to different disks on the destination server. For example, if you have Partition P1 and Partition
P2 on Disk S1 on the source server, and disks D1 and D2 on the destination server, you cannot
migrate Source Partition P1 to Destination Disk D1 and Source Partition P2 to Destination Disk D2.
IMPORTANT: X2P migrations can be launched only for ProLiant servers that have been properly
discovered and licensed in Systems Insight Manager. For more information about discovery, see
HP Systems Insight Manager User Guide at the following website:
http://www.hp.com/go/insightsoftware/docs
Virtual machine hosts
The destination virtual machine hosts require the following:
• User account credentials with administrative rights
• Available memory of at least 1024 MB
• Available disk space of at least 750 MB
• The latest operating system updates installed
When you are performing an X2V migration, be sure your destination virtual machine host has
adequate memory, processor resources, and disk space to migrate the source server partitions.
For example, if Disk 1 on your source server has 10 GB of data to migrate, verify that the disk you
migrate to on the destination server has at least 10 GB of available disk space.
Linux destination size requirement
For migrating the /boot partition during Linux migration, Insight Control server migration needs
extra space for creating a new file for each of the valid initrd entries in
/boot/grub/menu.lst.
For each of the valid initrd entries in /boot/grub/menu.lst, a valid entry is created with a
corresponding file name followed by -smpue.
30 Preparing the destination server and deploying the destination agent
Page 31

Linux server migration can fail with the following error if the destination size chosen when you
specify destination disks in the migration wizard, does not have enough space to create the
<initrd name>-smpue files:
Server migration could not modify initrd on the destination server.
This could happen when there is not enough free space available on boot
partition. Increase free space on boot partition by deleting unused
files or make sure that boot partition has 10MB or more of free space
and retry migration process.
To resolve this issue, when you specify destination disks in the migration wizard, choose a
destination size that is large enough to create the /boot/<initrd name>-smpue files on the
corresponding disk partition on the destination server.
Booting the destination server
Boot the destination server by using the applicable Insight Control server migration Boot CD ISO.
To boot a destination physical server, you must be able to reboot the server and load through iLO.
For virtual machines, you must have access to the management console for the virtual machine
host. For information on choosing server migration agents, see “Choosing server migration Agents”
(page 25).
There are Boot CD ISO files available to boot destination servers manually. However, HP
recommends that you allow the server migration wizard to boot the destination server. You can
do this by selecting the Auto Boot - Let server migration Boot the destination server option in Step
3 of the wizard. For more information, see “Booting a physical destination server automatically
by using the migration wizard” (page 32) or check the Insight Control server migration online help.
• Insight Control server migration ProLiant Boot CD ISO file
You can use this ISO to manually boot a physical destination server for X2P migrations. This
ISO is available after you install Insight Control server migration. To access the ISO, see the
directory <Insight Control server migration Installation
Folder>\Agents\SMP\smpbootcd-p-[version #].iso.
• Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO file
You can use this ISO to manually boot the destination virtual machine guest for X2V migrations.
This ISO is available after you install Insight Control server migration. To access the ISO, see
the directory <Insight Control server migration Installation
Folder>\Agents\SMP\smpbootcd-v-[version #].iso.
The Insight Control server migration ProLiant or Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO can boot only
supported destination servers. For a list of supported servers, see HP Insight Management Support
Matrix at the following website:
http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs
To manually or automatically boot the destination server or virtual machine to the proper Insight
Control server migration Boot CD ISO, see the following procedures. After the destination system
is booted, you must configure it to launch the destination agent.
Booting a physical destination server manually by using the Insight Control server migration ProLiant Boot CD ISO for X2P migrations
NOTE: For Gen8 servers, the manual boot option is not supported.
1. Boot the server remotely by using the iLO virtual media feature.
2. After the destination server or virtual machine is booted to the proper Boot CD ISO file, use
the Boot CD ISO application to configure the destination server and launch the destination
Agent. From the Boot CD ISO application, click Help for instructions.
Booting the destination server 31
Page 32

Booting a physical destination server automatically by using the migration wizard
1. Identify the source server and select volumes to migrate in steps 1 and 2 in the server migration
wizard.
2. In step 3 of the P2P or V2P migration wizard, select Auto Boot - Let server migration boot the
destination server.
3. Enter the iLO IP address and iLO credentials.
4. Enter the static IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway (Optional). If the network has
a gateway, enter it here to ensure connectivity. Optionally, you can also select the Duplex
Settings.
5. Click Next.
6. To view the boot progress, click Launch iLO, and then log on to the iLO remote console.
iLO boot prerequisites
You must meet the following requirements to use the feature of booting from iLO:
• The iLO user credentials provided must have Virtual Power and Reset and Virtual Media access
applied.
• The browser must be configured to support HTTP 1.1. To add this support:
On your web browser, open Internet Options, and then click the Advanced tab.1.
2. As appropriate, select Use HTTP 1.1 and Use HTTP 1.1 through proxy connections.
• An iLO Advanced license must be applied to the destination server iLO.
• At least 300 MB of free space must exist on the application station for each iLO boot. This
free space should exist on the partition on which Insight Control server migration is installed.
This space is recovered after the migration is complete or the boot job times out.
After the destination server is booted to the proper Boot CD ISO, use the Boot CD application to
configure the destination server and launch the destination agent. From the Boot CD application,
click Help for instructions.
If the migration is not started within 2 hours of the server being powered up through iLO, the server
migration will time out and power down the destination server.
Manually creating and booting a virtual destination server
Prerequisites for manually creating and booting a destination virtual machine
This section lists the prerequisites for manually creating a virtual machine for different migrations.
To manually create and boot a destination virtual machine, you must create the virtual machine
with the prerequisites specified, and then attach the Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine
Boot CD ISO to the virtual machine.
The following sections list the special steps required to prepare virtual machines for booting to the
Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO.
Prerequisites for booting a virtual machine in Microsoft Hyper-V
Make sure that the following parameters are met:
• The virtual machine does not have more than three disks attached.
• The virtual machine has at least 1024 MB of memory.
• The network adapter is a legacy network adapter.
• The network adapter is connected to a virtual network switch that is connected to an external
network.
• The virtual disks that you created are attached to an IDE controller.
32 Preparing the destination server and deploying the destination agent
Page 33

• The boot virtual disk is connected to the 0th channel of the first IDE controller.
• The Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO is attached to the destination
virtual machine.
Prerequisites for VMware ESX migration
Make sure that the following parameters are met:
• The virtual machine has at least 1024 MB of memory.
• You have created the virtual machine by selecting the correct operating system being migrated.
• You have created the virtual machine with at least one flexible network adapter.
• The network adapter is connected to a virtual network switch that is connected to an external
network.
• The Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO is attached to a virtual
CD-ROM device.
• You have discovered and configured VMware vCenter Server settings through Systems Insight
Manager. For more information, see HP Insight Management Installation and Configuration
Guide.
Manually creating and booting a virtual machine destination server for X2V
1. Access the management console for the virtual machine host, as provided by VMware ESX
or Microsoft Hyper-V.
2. Create a new virtual machine that has sufficient disk space for migration.
3. Boot the virtual machine to the Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO
file. You can find the Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO file at <Insight Control server
migration Installation Folder>\Agents\SMP\smpbootcd-v-[version #].iso.
4. After the destination server or virtual machine is booted to the proper Boot CD ISO file, use
the Boot CD ISO application to configure the destination server and launch the destination
agent. From the Boot CD ISO application, click Help for instructions.
Automatically creating and booting a virtual destination server
To automatically create and boot a destination virtual machine by using the migration wizard:
1. Run the migration wizard and complete steps 1 and 2 (select the source server and select the
volumes to migrate). In step 3 of the P2V and V2V migration wizard, identify the VM host and
then select the appropriate virtualization layer.
2. Select Auto Boot — Automatically have VM created through server migration wizard.
3. Enter the logon credentials for the virtual machine host (for Microsoft Hyper-V host only).
4. Configure the destination server networking by entering the static IP address, subnet mask,
and default gateway (optional). If the network has a gateway, enter it here to ensure
connectivity. When you are finished, click Next. Optionally, you can also select the Duplex
Settings.
5. Insight Control server migration verifies that the virtual machine host is licensed and then moves
to the next step, where you must enter the name of the virtual machine configuration and map
the source disks to the destination disks. When you are finished, click Next.
The Insight Control server migration application then connects to the virtual machine host,
creates the virtual machine, and boots the virtual machine by using the Insight Control server
migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO.
After the Boot CD agent is launched on the provided IP address, the application station connects
to the agent on the Boot CD, and the next page of the wizard appears.
Booting the destination server 33
Page 34

NOTE: If the application cannot connect to the destination virtual machine, return to step 3 of
the migration wizard. Then while leaving the migration wizard running, manually create a virtual
machine in the VM Host Management console outside of the migration wizard. Return to the
migration wizard and select Manual Boot — Manually create VM through VM Host's Infrastructure
Client, specify the IP address of the destination virtual machine, and then continue with the migration.
NOTE: If the VM boot is cancelled or not completed, server migration does not delete the virtual
machine. Use the VM Host Management console to delete the virtual machine manually.
34 Preparing the destination server and deploying the destination agent
Page 35

8 Migrating the servers
Prerequisites
CAUTION: If the Insight Control application station shuts down or fails during any migration, the
migration fails. The application station must be available during the complete migration cycle for
a successful migration.
Minimum source server prerequisites for all migrations
The prerequisites are the same for all migration types: P2P, P2V, V2P, or V2V. The subsequent
sections describe only the prerequisites specifically different for that particular type of migration.
Before you start any migration, verify that these minimum prerequisites are completed on the source
server:
• A valid network connection exists between the source server and destination server.
• The source server contains an active boot partition to be migrated.
• Any pending reboots and software installations on the source server are finished.
• Any antivirus software autoscans on the source server are temporarily disabled.
Re-enable the antivirus software after the migration.
• The disks are not corrupted. To verify, run CHKDSK (Windows) or File System Consistency
Check (Linux).
• All hard drives on the source (physical) server are correctly initialized (disk signature written).
• All partitions on the source server have a valid file system and are in a healthy state.
• All applications and background services on the source server are disabled.
After the migrated server has synchronized with the new hardware and is assigned a unique
network identity, appropriate applications can be manually re-enabled and configured for
the new environment.
• Insight Control server migration is not installed and the ports, 51126 and 51125, are not
used by any other service/application.
Uploading drivers
Use the Upload Drivers tab to upload binary files for the following:
• iSCSI Initiator
For Windows migrations, the Microsoft iSCSI Initiator software is required for proper connection
between the CMS and destination for mounting/injecting drivers.
• PSP (Windows only)
You can upload one or more PSPs when you select additional migration options from the
server migration wizard. When a PSP is selected during migration, it is copied to the destination
server and executed on first boot after migration.
For more information on loading PSP executables, see the server migration online help.
• SPP (Windows only)
You can upload one or more SPPs when you select additional migration options from the
server migration wizard. When a SPP is selected during migration, it will be automatically
applied to the destination server.
For more information on loading SPP ISO images, see the server migration online help.
Prerequisites 35
Page 36

NOTE: Before uploading the SPPs, ensure that the destination server has a minimum disk
space of 1 GB.
• DevCon binary
When the DevCon binary is uploaded here before migration, it will be available when selecting
additional migration options in the migration wizard. When DevCon is selected during
migration, it is automatically installed at the end of Windows migrations. HP recommends
that you use DevCon only if you face issues with mouse and keyboard devices on the destination
server after a migration. For more information about DevCon or to download the executable,
see http://support.microsoft.com/kb/311272 (or search for “DevCon” on the microsoft.com
website.) Do not extract the binary that you download from the Microsoft website before
uploading it here.
Preparing for a Windows server migration
The following sections list prerequisites for a Windows server migration.
If you use a firewall, see “Disabling firewalls” (page 20) .
Comply with all minimum prerequisites as listed in “Minimum source server prerequisites for all
migrations” (page 35).
Windows source server prerequisites
For Windows migrations, verify that the following source server prerequisites are completed:
• If Windows Server 2003 is installed, verify that the disks are initialized as MBR disks. Insight
Control server migration does not support GPT-based disks.
• During migration, the migration agent initiates an operating system reboot on the source
physical server. Verify that the operating system is on the first boot order. Insight Control server
migration supports migration of source servers that have operating systems installed on the
primary drive (Hard Disk 0) and the primary drive loaded first in the boot order.
• Record the drive letter or mount point to disk-partition mapping for dynamic disk partitions
before you perform the migration. Any simple (non-extended) dynamic disk partitions are
converted to basic disk partitions. You might have to manually reassign the mapped drive
letters after the migration.
• Before you migrate a source server with BitLocker Drive Encryption enabled and drives
encrypted using BitLocker, decrypt the drives on the source server and disable BitLocker.
• On the Windows source host, clear the Don’t allow exceptions check box under the General
tab of the Windows Firewall section.
• On the Windows source host, check the File and Printer Sharing check box under the Exceptions
tab of the Windows Firewall section.
Source physical server prerequisites
If you are migrating from a physical source server, verify that the following prerequisites are
completed:
36 Migrating the servers
Page 37

• Comply with all minimum prerequisites as listed in “Minimum source server prerequisites for
all migrations” (page 35).
• During migration, the migration Agent initiates an operating system reboot on the source
server. Verify that the operating system is on the first boot order. If not, manually change the
boot order:
◦ For Windows Server 2003, edit the [system drive]\boot.ini file or use the
bootcfg.exe tool.
◦ For Windows Server 2008 or later, use the bcdedit.exe tool.
Source virtual machine prerequisites
If you are migrating from a source virtual machine, verify that it complies with all minimum
prerequisites as listed in “Minimum source server prerequisites for all migrations” (page 35).
Destination physical server prerequisites
If you are migrating to a destination physical server, verify that the following prerequisites are
completed:
• Configure the primary storage controller with drives attached.
• Connect and configure the NIC cards.
• Manually boot the destination server with the Insight Control server migration ProLiant Boot
CD ISO and make sure that it is running the migration Agent.
• Select the Auto Boot option in step 3 of the migration wizard to automatically boot the
desalination server with Insight Control server migration ProLiant Boot CD ISO.
NOTE: For Gen8 servers, Manual Boot option is not supported.
Destination virtual machine host or virtual machine prerequisites
If you are migrating to a destination virtual machine, verify that the following prerequisites are
completed:
• Select one of the following:
Let Insight Control server migration create the virtual machine automatically, which will
◦
automatically create and boot the destination virtual machine by using the server migration
Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO.
◦ Create the virtual machine manually, and then boot the virtual machine manually by using
the server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO.
• Verify that the destination virtual machine host has sufficient system resources, including
processor, memory, and disk space to host the migrated virtual machine guest.
• Temporarily disable any antivirus software auto-scans on the destination virtual machine host
to prevent interrupting the migration process. Re-enable the antivirus software after the
migration.
Preparing for a Linux server migration
The following sections list prerequisites for a Linux server migration.
• If a firewall is running on the source server and Source Agent deployment is required, see
“Disabling firewalls” (page 20).
• Make sure that the SSH port is open when a firewall is in use, or the server migration Source
Agent might not be deployed successfully.
Prerequisites 37
Page 38

• Verify compliance with all minimum prerequisites. For more information, see “Minimum source
server prerequisites for all migrations” (page 35).
• Make sure that the 32–bit version of glibc is installed. The 32–bit version of glibc is
required to run the Linux server migration Source Agent. The library is present by default on
32–bit Linux installations, but you might need to install it manually on 64–bit Linux systems.
The 32–bit version of glibc is available on your Linux OS installation CD/DVD.
• If X–Windows is configured on the source server, make sure that the 32–bit version of the
libXtst runtime library is installed.
Source physical server prerequisites
If you are migrating from a source physical server, verify that the following prerequisites are
completed:
• Comply with all minimum prerequisites as listed in “Minimum source server prerequisites for
all migrations” (page 35).
• Make sure that PermitRootLogin and PasswordAuthentication are set to Yes in the
/etc/ssh/sshd_config file and that the sshd service is running.
• Make sure that GRUB Boot Loader is the primary boot loader on the source server.
Source virtual machine prerequisites
If you are migrating from a source virtual machine, verify that the following prerequisites are
completed:
• Comply with all minimum prerequisites as listed in “Minimum source server prerequisites for
all migrations” (page 35).
• Make sure that PermitRootLogin and PasswordAuthentication are set to Yes in the
/etc/ssh/sshd_config file and that the sshd service is running.
• Make sure that GRUB Boot Loader is the primary boot loader on the source server.
• Remove guest tools.
Destination physical server prerequisites
If you are migrating to a destination physical server, verify that the following prerequisites are
completed:
• Configure the primary storage controller with drives attached.
• Connect and configure the NIC cards.
• Manually boot the destination server with the Insight Control server migration ProLiant Boot
CD ISO and make sure that it is running the migration Agent.
• Select the Auto Boot option in step 3 of the migration wizard to automatically boot the
desalination server with Insight Control server migration ProLiant Boot CD ISO.
NOTE: For Gen8 servers, Manual Boot option is not supported.
38 Migrating the servers
Page 39

Destination virtual machine host or virtual machine prerequisites
If you are migrating to a destination virtual machine, verify that the following prerequisites are
completed:
• Select one of the following:
Let Insight Control server migration create the virtual machine automatically, and then
◦
boot it by using the Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO for
virtual machines.
◦ Create the virtual machine manually, and then boot the virtual machine manually by using
the Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO.
• Verify that the destination virtual machine host has sufficient system resources, including
processor, memory, and disk space to host the migrated virtual machine guest.
• Temporarily disable any antivirus software auto-scans on the destination virtual machine host
to prevent interrupting the migration process. Re-enable the antivirus software after the
migration.
SAN migrations in Windows
Insight Control server migration supports Windows or Linux migrations to destination physical
servers that have Fibre Channel SAN connectivity. To verify that your Fibre Channel HBA is
supported, see HP Insight Management Support Matrix at the following website:
http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs
The prerequisites for a migration to a server that has Fibre Channel SAN connectivity are the same
as the prerequisites for migration to a destination physical server—described in “Preparing for a
Windows server migration” (page 36), “Preparing for a Linux server migration” (page 37), and
“Destination physical server prerequisites” (page 37)—with the following additional preparatory
steps:
1. Manually set up the SAN environment by doing the following on the destination server:
• Create logical units on the storage.
• Configure SAN switches.
• Configure HBA.
2. After setting up the SAN environment, boot the destination server by using the Boot CD ISO.
3. Run the migration wizard.
4. Follow the relevant migration steps in “Preparing for a Windows server migration” (page 36).
5. In step 5 (specify destination disks) of the migration wizard, verify that you have selected the
boot LUN that you configured in the HBA BIOS of the destination server when you migrate
the boot partition on the source server.
NOTE: To migrate Windows 2003 to a SAN-connected destination server, you must first install
Service Pack 2 and the updated Storport storage driver (for more information, see http://
support.microsoft.com/kb/932755) on the source server.
You can perform a migration to a destination server with some source disks migrated to local disks
on the destination and some source disks migrated to SAN disks presented to the destination.
A local disk cannot be migrated to a SAN disk on the same server. That is, you cannot run a
DAS-to-SAN migration on the same server. For example, you cannot migrate a SAS disk on a
server to a SAN disk on the same server. The migration must be a migration from Server A to
Server B, where A and B are distinct servers.
Before you run any X2P migration to a SAN LUN, HP recommends that you disable any ports that
are not used for migrating to the destination HBA. Otherwise, if the operating system is migrated
to a SAN LUN connected to a Fibre Channel HBA in the destination server, the server migration
Prerequisites 39
Page 40

might not migrate to the primary LUN. Failing to disable unused ports might produce the error
message Error loading operating system when the destination server is booted.
Starting the migration wizard
After source and destination server agents are launched, you can start the migration from Systems
Insight Manager in two ways:
• Through the Deploy menu
• Through the Quick Launch feature
Launching server migration by using the Deploy menu
To launch Insight Control server migration from the Deploy menu, perform the following tasks:
1. In Systems Insight Manager, select the source server or source virtual machine. Make sure that
the source server is discovered properly and that the OS type and IP address are correctly
identified.
2. From the main wizard, select Deploy→Server Migration Tools, and then select the appropriate
migration option.
3. Systems Insight Manager verifies the source server or source virtual machine.
• If the selected server or virtual machine fails to satisfy the criteria to launch Insight Control
server migration, the Systems Insight Manager task wizard appears, the Next button is
disabled, and the migration cannot proceed.
Figure 8 Verify Source Physical server
• If the selected server or virtual machine meets the criteria, the Insight Control server
migration application opens in a new browser with the IP address of the selected host
added in step 1 of the migration wizard.
40 Migrating the servers
Page 41

Figure 9 Identify the source server
4. Click Show Server to view the server IP address, name, and OS details. If you manually
deployed the Source Agent, click Next now. Otherwise, select Deploy Insight Control server
migration Source Agent and then click Next.
5. For information about completing the rest of the steps in the server migration wizard, see the
server migration online help.
Launching server migration by using Quick Launch
To launch an Insight Control server migration from Systems Insight Manager by using the Quick
Launch option, perform the following tasks:
1. In Systems Insight Manager, select the source server or source virtual machine.
2. Access the Quick Launch button by using one of the following methods:
• From the All Systems page in the Systems Insight Manager console, click Quick Launch.
Quick Launch displays the available operations with the selected source virtual machine
or source server.
Starting the migration wizard 41
Page 42

Figure 10 Quick Launch
• From the All Systems page in the Systems Insight Manager console, select a source server,
and then scroll over Quick Launch. Quick Launch displays the available operations with
the selected source virtual machine or source server.
Figure 11 Available operations
42 Migrating the servers
Page 43

3. Systems Insight Manager verifies the source physical server or source virtual machine.
• If the selected server or virtual machine fails to satisfy the criteria to launch Insight Control
server migration, the Quick Launch list does not display the unsupported migration options.
• If the selected server or virtual machine meets the criteria and you select one of the options
displayed, the Insight Control server migration application opens to the first step of the
migration wizard in a new browser where the IP address of the selected source is entered
for you.
4. For information about completing the rest of the steps in the server migration wizard, see the
server migration online help.
IMPORTANT: Migrations can be launched only for source servers that have supported operating
systems and discoverable IP addresses that have been properly discovered in Systems Insight
Manager. For more information about discovery, see HP Systems Insight Manager User Guide at
the following website:
http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs
Starting the migration wizard 43
Page 44

9 Postmigration tasks
Installing ProLiant Support Packs after migration
If you perform a Windows X2P migration, without uploading the Windows PSP executable from
the Upload Drivers tab before migration, you must manually install the HP ProLiant Support Packs
(PSP) on the destination server after a migration.
You can configure Insight Control server migration to automatically install a PSP after the Windows
migration is completed in step 6 of the migration wizard, Additional Migration Options. To use
this feature, you must upload the Windows PSP executable from the Upload Drivers tab of the
migration wizard before you start a migration.
Installing Service Pack for ProLiant after migration
If you perform a Windows X2P migration, without uploading the Windows SPP ISO image from
the Upload Drivers tab before migration, you must manually install the HP Service Pack for ProLiant
(SPP) on the destination server after a migration.
You can configure Insight Control server migration to automatically install a SPP after completing
the Windows migration in step 6 of the migration wizard, Additional Migration Options. To use
this feature, upload the Windows SPP ISO images from the Upload Drivers tab of the migration
wizard before you start a migration.
X2P postmigration tasks (Windows)
NOTE: For migration of a domain controller source, postmigration steps will be disabled.
After you complete a X2P migration, perform the following steps on the destination server:
1. Log on with administrative rights.
2. At each of the Welcome to the Found New Hardware wizard screens, click Cancel.
3. When you are prompted to reboot the system at the System Settings Change Window, click
No.
4. Install the latest PSP (if you did not select this option during the X2P installation).
5. View the Windows event log on the destination server and disable any services or drivers that
might have failed.
6. If necessary, verify the network connections. If NIC teaming is required on the destination
server, NIC teaming must be re-established on the destination server after the migration and
installation of the PSP.
7. If the source and destination servers must be on the network at the same time:
a. Change the host name of either server or consider reconfiguring the applications.
b. If the IP addresses are static, reassign them.
8. (Optional) Reassign drive letters to former dynamic disk partitions.
9. (Optional) Convert basic disks to dynamic disks. During migration, all dynamic disks are
migrated to the destination server as basic disks. Therefore, if dynamic disks are preferred on
the destination server, basic disks can be manually converted back to dynamic disks.
10. Edit the boot.ini file. For more information about editing boot.ini, see “Editing the
Windows boot.ini file after migration (Windows Server 2003)” (page 45).
11. If the Windows license is not a volume license, reactivate it.
12. The mouse and keyboard might not be immediately active after the migration. Wait until the
guest operating system automatically installs all required drivers, and then reboot when you
are prompted.
44 Postmigration tasks
Page 45

X2V postmigration tasks (Windows)
After you complete a X2V migration, perform the following steps on the destination server:
1. If you manually booted the virtual machine by using the server migration Virtual Machine Boot
CD ISO, disconnect the ISO and then manually reboot or shut down the virtual machine.
2. Add necessary network configurations to the migrated virtual machine guest. To do so, access
the remote console for the destination virtual machine host to configure the network connections
for the migrated virtual machine guest.
3. (Optional) Add a CD-ROM component to the destination virtual machine. The CD-ROM might
be required to install additional Integrated Components.
After the virtual machine reboots, you must perform the following steps on the destination virtual
machine guest for hypervisors:
1. Modify the system host name.
2. Install the proper guest tools.
3. Check the network connections and re-establish network connectivity. If an IP address conflict
occurs when you are setting the static IP address, see the following website for more
information:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/269155/.
4. View the Windows event log on the destination server and disable any services or drivers that
might have failed.
5. If applicable, reassign drive letters of dynamic disk partitions by using the disk manager to
correspond with the original state. The virtual machine guest automatically detects new
hardware and installs the required drivers.
6. The mouse and keyboard might not be immediately active on the migrated virtual machine
guest. Wait until the guest operating system automatically installs all required drivers, and
then reboot the migrated virtual machine guest when you are prompted.
7. Edit the boot.ini file. For more information, see “Editing the Windows boot.ini file after
migration (Windows Server 2003)” (page 45).
Editing the Windows boot.ini file after migration (Windows Server
2003)
Edit the boot.ini file to activate a graphical boot process:
1. Remove the /bootlog and /sos options from the boot.ini file. These options are
automatically inserted during the migration process so that the boot process is logged in detail
for onscreen analysis. The active boot entry displayed during boot is highlighted, and the
original boot.ini entry appears as HP Insight Control Preserved: [name], where
[name] is the operating system.
2. To retain the original boot parameters, copy all valid flags from the original entry and other
appropriate boot flags as applicable, such as adding the /3GB flag (if the destination virtual
machine is configured with sufficient RAM).
X2V postmigration tasks (Windows) 45
Page 46

3. Delete the original (preserved) entry.
Example 1 Editing Boot.ini
[boot loader]
default=multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS
timeout=30
[operating systems]
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk0)partition(1)\WINDOWS=”Windows Server 2003, Enterprise” /sos 1 /bootlog
/noexecute=optout /fastdetect
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk0)partition(1)\WINDOWS=”HP Insight Control Preserved: Windows Server 2003,
Enterprise” /userva=3030 2 /3gb 2 /noexecute=optout2 /fastdetect
1
Delete this parameter.
2
Copy the parameter as needed to a new OS entry.
3
Delete this line.
X2P postmigration tasks (Linux)
After you complete an X2P migration, perform the following steps on the destination server:
1. Log in with administrative rights.
2. Install the latest LSP.
3. If necessary, verify the network connections. If NIC teaming is required on the destination
server, NIC teaming must be re-established on the destination server after the migration and
installation of the LSP.
4. If the source and destination servers must be on the network at the same time:
a. Change the host name of either server or consider reconfiguring the applications.
b. If the IP addresses are static, reassign them.
5. If the license is not a volume license, reactivate it.
6. The mouse and keyboard might not be immediately active after the migration. Wait until the
guest operating system automatically installs all required drivers.
2 3
1
3
X2V postmigration tasks (Linux)
After you complete an X2V migration, perform the following steps on the destination server:
1. If you manually booted the virtual machine by using the Insight Control server migration Virtual
Machine Boot CD ISO, you must disconnect the Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine
Boot CD ISO and then manually reboot or shut down the virtual machine.
2. Perform a network configuration for the migrated virtual machine guest. To do so, access the
remote console for the destination virtual machine host to configure the network connections
for the migrated virtual machine guest.
3. (Optional) Add a CD-ROM component to the destination virtual machine. The CD-ROM might
be required to install additional Integrated Components.
After the virtual machine reboots, you must perform the following steps on the destination virtual
machine guest for hypervisors:
1. Modify the system host name.
2. Install the proper guest tools.
3. If necessary, verify the network connections.
4. The mouse and keyboard might not be immediately active on the migrated virtual machine
guest. Wait until all the guest operating system automatically installs required drivers, and
then reboot the migrated virtual machine guest when you are prompted.
46 Postmigration tasks
Page 47

Viewing migration logs
From the View Status/Logs tab, you can:
• View currently running migrations.
• View a log of the migration results.
• Create support logs.
For more information, click the help icon on the server migration View Status/Logs page.
NOTE: When a job is complete, its link no longer appears in the View Status/Logs page, but
the job-specific log files are still available in the HP Insight Control server migration installation
path\logs directory.
Validating the migration
Validating Linux migrations
To verify that the Linux migration was successful, you can do the following:
1. Compare the md5 checksum of the files on the migrated filesystem with the checksum on the
source. The md5 checksum should match for all files except for the initrd and log files.
2. Make sure that the operating system on the destination server boots normally without critical
errors.
Validating Windows migrations
To verify that the Windows migrations was successful, you can do the following:
1. Make sure that the operating system on the destination server boots normally without critical
errors.
2. Compare the source server and the destination server to make sure that the partitions selected
on the source server are present on the destination server.
3. Compare random samples of files and directories between the source server and the destination
server to make sure that the data was migrated successfully.
Viewing migration logs 47
Page 48

Part IV Troubleshooting and support
Page 49

10 Troubleshooting
You can register to receive customer advisories via email. For more information, see HP Insight
Management Installation and Upgrade Release Notes at the following website:
http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs
User interface
Server migration wizard hangs
The wizard hangs if you press the Ctrl key while selecting tabs in Insight Control server migration.
Cause
Tabs in HP Insight Control server migration cannot be treated like hyperlinks. If you press the Ctrl
key while clicking the server migration tabs in your browser, Please wait while loading
the page appears and a new blank page opens up.
Suggested action
To avoid this issue, click the tab without pressing the Ctrl key.
Browser displays an error after loading the server migration wizard from Systems Insight Manager
Your browser might display the error message unable to connect when Insight Control server
migration is launched from Systems Insight Manager.
Cause
The HP Insight Control server migration Web Service is not running properly.
Suggested action
Open Windows Services and restart the HP Insight Control server migration Web Service, and
then retry launching server migration from Systems Insight Manager.
Launching server migration from Systems Insight Manager throws an exception
When you are launching server migration through Systems Insight Manager, an exception might
be thrown.
Cause
The source server is not discovered properly in Systems Insight Manager.
Suggested action
Make sure that the source server is discovered properly in Systems Insight Manager with the OS
type and IP address correctly identified. You can manually edit the source server node in Systems
Insight Manager to set correct values for these attributes. You can also try launching a server
migration by using a different, but properly discovered, source server and then changing the IP
address to your source server in the first step of the server migration wizard.
The name of HP Ethernet 1Gb 4-port 331i-SPI Adapter is not displayed correctly
When X2P migration is initiated to HP ProLiant DL 580 G7 configured with HP Ethernet 1Gb 4-port
331i-SPI Adapter and when you manually boot the destination server with HP Insight Control server
migration ProLiant Boot CD, the NIC name is not shown correctly under System Information and
User interface 49
Page 50

Network Configuration page. The name is displayed as Broadcom Corporation, Unknown
device instead of HP Ethernet 1Gb 4-port 331i-SPI Adapter.
Suggested action
No action required.
Unable to launch server migration tools from Systems Insight Manager
When you launch server migration tools from Systems Insight Manager, the system displays the
following error message:
An Exception occurred. SSO Validation Failed. Try launching again from
HP SIM.
VMwareDisconnectTimeout = 300000
Suggested Action
Perform the following steps:
1. In the hpvmm.conf file (<Insight Control server migration Installation Folder>\bin), add the
following:
VMwareDisconnectTimeout = 300000
2. Save the file and restart the server migration services.
NOTE: If this issue occurs again, change the VMwareDisconnectTimeout value from 300000
to 600000.
Static IP configuration fails on Hyper-V VM when configured using Boot CD
When you perform a Manual Boot operation using the Insight Control server migration Boot CD
for VMs on Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 with Hyper-V and Microsoft Windows Server
2012 with Hyper-V, and configure static IP on the Network configuration page, the following error
is displayed:
Selected Network Card doesn't have link - verify you have chosen the
correct device.
Cause
Static IP configuration fails on Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 with Hyper-V and Microsoft
Windows Server 2012 with Hyper-V.
Suggested action:
To resolve this issue, perform one of the following:
• Use the Auto boot option and enter the desired IP address in the step 3 of the Insight Control
server migration wizard.
• For Manual Boot option, select the required option on the Network configuration page to
configure dynamic IP using DHCP.
Unable to migrate Windows 2008/2008 R2/2012 using Windows 2008 x64 CMS
Cause
Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool is unavailable on the CMS.
Suggested Action
To resolve the issue, perform the following steps:
50 Troubleshooting
Page 51

1. Stop all running instances of Insight Control server deployment services.
2. Uninstall any previous installation instances of Windows Automated Installation Kit (WAIK)
versions 1.0 and 2.0.
3. Download and install WAIK version 3.0 for Windows 7 from the Microsoft Download Center
at: http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=5753.
4. To make DISM tool available for the App Server, perform one of the following:
• Update the hpmmsvc.conf file (<ICMigr Installation Path>\bin\windows\) to add
set.Path=<>;<WAIK Installation Path>\Tools\Servicing, and then restart
the server migration services.
• Add the windows PATH environmental variable with the - <WAIK Installation
Path>\Tools\Servicing parameter.
5. To verify and view that DISM version 6.1 is installed, go to the Upload Drivers tab of the server
migration wizard.
Source preparation
Corrective action is required before this server can be migrated
The following message appears when an affected system is detected during the launch of the
source server agent:
ATTENTION:Corrective action is required before this server can be
migrated.
Cause
Some versions of Windows Server 2003 that are preinstalled by HP cannot be migrated successfully
unless you perform corrective action before attempting the migration. The server migration Source
Agent detects affected systems during initialization. If the system is affected, instructions for
performing the corrective action are provided. If you attempt the migration without first performing
the corrective action, your destination server becomes nonbootable.
NOTE: The server migration Source Agent will not detect whether the corrective action has already
been performed. Subsequent attempts to execute this agent will indicate that corrective action is
still required. However, the corrective action must be applied only once.
Suggested action
Perform the following:
1. Cancel execution of the migration agent.
2. In the command prompt window, change to the root directory of the Windows disk.
3. Run the following command: SFC /SCANNOW. This command might take several minutes. For
more information about this command, see the following website:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/310747/en-us
Source server identification fails
The source server identification fails during the first step of the migration wizard.
Suggested action
1. Verify the identifier entered. If the name is entered for a source server that is in a domain, be
sure that the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) is entered.
2. Verify that the migration agent has been installed on the identified source server. For more
information about running the migration agent, see server migration online help.
Source preparation 51
Page 52

3. Verify that the source server can be reached from the application station. Communication on
network ports 51125 and 51126 must be enabled by any firewall between the application
station and the source server.
4. Verify that the agent status messages do not indicate that the source server is locked to another
server.
Migration Agent deployment fails
The migration Agent might fail deployment for several reasons, including:
• Incorrect password
• Reserved ports
• Insufficient disk space
• Network issues
• Special characters in the source password, like colon (:), quotation marks (“), or backslash
(\)
• A situation in which source server is inside a VPN and the CMS is outside the VPN
• Missing 32–bit libraries on a 64–bit Linux source server
Suggested action
Try the following:
• Verify that you have provided valid credentials with administrative rights for the source server
for the migration agent deployment.
• If the source server has Insight Control server migration installed, make sure that you have
disabled the server migration application and web services from the Windows Services console.
• Other processes might use the ports reserved for the migration agent (51124 through 51126).
Make sure that these ports are free on the source server. A reboot might resolve port locks by
other processes. If the issue persists, you must identify and disable other processes that are
using the ports.
• Sufficient disk space exists for the agent to be copied and installed properly.
• Make sure that the networks on both the source and the server migration application station
work properly.
• Make sure that the source server password does not contain special characters like colon (:),
quotation marks (“), or backslash (\).
• Make sure the source server and CMS are both either inside the same VPN or outside the
VPN.
• Make sure that 32-bit glibc is installed on 64-bit Linux source servers before Source Agent
deployment.
• In the source server, clear the Don’t allow exceptions check box under the General tab of the
Windows Firewall section.
• In the source server, select the File and Printer Sharing check box under the Exceptions tab of
the Windows Firewall section.
Linux Source Agent window does not appear on RHEL 64–bit
On 64–bit RHEL, the Linux Source Agent window does not appear after deployment, although it
is not impeding the migration.
52 Troubleshooting
Page 53

Suggested action
The server migration Source Agent uses a 32–bit Java Runtime Environment. In 64–bit RHEL, the
Linux source migration agent window does not appear, although the agent is running. To enable
the display of the agent, you must install the X.Org X11 libXtst runtime library,
libXtst-1.0.99.2-3.el6.i686.rpm.
Remote deployment of Linux Source Agent using nonroot credentials fails
Remote deployment of Linux Source Agent using nonroot credentials fails with the following error:
Failed to deploy server migration Source Agent. Error while installing
the server migration Source Agent on the given Server : exec tar -zxf
hpsmpagent.tar.gz -C /tmp on the remote host failed. The ports 51124,
51125 and 51126 required by the agent might be in use. : exec tar -zxf
hpsmpagent.tar.gz -C /tmp on the remote host failed. The ports 51124,
51125 and 51126 required by the agent might be in use.
Suggested action
Deploy the Linux Source Agent by using root privileges.
Manual installation of Linux Source Agent using sudo user privileges fails
Manual installation of Linux Source Agent using sudo user privileges fails.
Suggested action
Launch the server migration Linux Source Agent by using proper root user privileges.
Incorrect LUN size is detected in step 2 of the migration wizard
If the size of the source LUN detected during step 2 of the migration wizard is incorrect, you might
be attempting to initialize the LUN by using GPTs.
Cause
LUNs initialized with GPTs are not supported, even if they contain partitions with filesystems that
server migration supports. Those partitions appear as RAW partitions in the migration wizard, and
data might be incomplete after the migration.
Suggested action
Deselect LUNs initialized with GPTs in step 2 of the migration wizard, and manually copy data
on GPT disks after the migration.
Migrating a source server fails with the Microsoft Hyper-V role enabled
If you are trying to migrate a source server with the Microsoft Hyper-V role enabled, you must
make sure that certain preconditions are met.
Suggested action
Perform any one of the following on the source server:
• Turn off the hypervisor by using the following command:
bcdedit /set hypervisorlaunchtype off
After the migration, you can re-enable the hypervisor by using the following command:
bcdedit /set hypervisorlaunchtype auto
• Remove the Microsoft Hyper-V role from the source server.
Source preparation 53
Page 54

Unable to boot Windows due to unsigned or corrupt drivers
Windows operating system does not boot after successful migration to any ProLiant Server in case
of unsigned or corrupt drivers.
Suggested action
To resolve this issue, perform one of the following:
• Manually remove any unsigned or corrupt driver from Source Server or from the Device
Manager.
• During a Windows boot, press F8 to select Disable Driver Signature Enforcement
mode.
• Use Windows recovery and browse the directory system32\drivers to remove any
unsigned or corrupt drivers.
Destination preparation
Destination server identification fails
The destination server identification fails in step 3 of the wizard.
Suggested action
Try the following:
1. Verify that the network adapter on the destination server is configured with a valid IP address,
subnet, and gateway.
2. Verify that the destination server is booted from the Insight Control server migration Boot CD
ISO and ready for migration.
3. Verify that the destination server can be reached from the application station and source
server. Communication on network ports 51125 and 51126 must be enabled by any firewall
between the CMS, the source server, and the destination server.
4. Verify that another Insight Control application is not already communicating with the destination
server.
IP address configuration fails on a manually booted virtual machine in Microsoft Hyper-V for a P2V or V2V migration
You have manually created the virtual machine on Microsoft Hyper-V for a P2V or V2V migration
and booted the virtual machine manually with the Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine
Boot CD ISO. However, you cannot configure an IP address on the virtual machine.
Suggested action
Try the following:
• Ensure that the virtual machine that you have manually created has a legacy network adapter.
• Ensure that the legacy network adapter on the virtual machine is connected to the correct
virtual network switch on the host.
• Ensure that the Virtual network switch configuration on the Microsoft Hyper-V host is correct
and the virtual switch is connected to a physical network adapter with external network
connectivity.
Kernel panic occurs in booting a virtual machine to the Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO
Insight Control server migration requires that the destination virtual machine has at least 1024 MB
of RAM to boot to the Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO.
54 Troubleshooting
Page 55

Suggested action
Try the following:
1. Power down the virtual machine.
2. Ensure that the virtual machine has at least 1024 MB of RAM.
3. Reboot to the Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO.
Mouse does not work on a virtual machine booted with the Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO
Cause
This issue occurs because virtual machine tools required for the mouse on certain virtualization
layers are not available on the Insight Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO.
Suggested action
Use the Tab and Enter/Return keys on the keyboard to navigate the user interface on the Insight
Control server migration Virtual Machine Boot CD ISO.
Primary array controller does not have logical drives defined
Suggested action
Confirm that your array controller has at least one logical drive defined.
You can confirm this by accessing the Configure Destination Server screen and then clicking Launch
Array Configuration Utility or by rebooting to Option ROM Configuration for many controllers
(ORCA).
Primary controller configured in the system does not have drives attached
Suggested action
Confirm that your hardware setup is correct and that the correct controller is set to primary in
ROM-Based Setup Utility (RBSU).
Primary controller in the system is not supported by this version of Insight Control server migration
When the destination server is manually booted using the Boot CD ISO, the error message The
primary controller in your system is not supported by this version of
Insight Control server migration Boot CD might appear on the destination server
console.
When the auto-boot option is chosen in step 3 of the migration wizard, the auto-boot of the
destination server fails, the destination server is powered off, and the error The Storage
controller is not supported with this version of Insight Control server
migration might appear.
Suggested action
Try the following:
1. Verify that the primary controller is supported for Insight Control server migration. For a
complete list of supported controllers, see HP Insight Management Support Matrix at the
following website:
http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs
2. Verify that the latest firmware is installed on the storage controller.
Destination preparation 55
Page 56

3. If the Insight Control server migration Boot CD ISO cannot detect the storage controller, you
might need to reconfigure the storage controller environment variable.
a. Reboot the destination server to Rom-Based Setup Utility (RBSU) by pressing the F9 key
during POST.
b. Select the Boot Controller Order option and verify the proper boot order for the storage
controllers.
c. Press Esc to exit RBSU, and then press F10 to confirm the exit and to save your changes.
d. Reboot the destination server by using the Insight Control server migration Boot CD ISO.
When the destination server boots, the Insight Control server migration Boot CD ISO will
detect the storage controller.
Destination server displays a blank screen when it boots to server migration Boot CD ISO
The destination server might display a blank screen when it boots to the server migration Boot CD
ISO if the server has more than 64 GB of RAM.
Suggested action
Try the following:
1. At the boot menu, press Esc to enter text mode.
2. At the text mode boot prompt, type sos mem=4G.
3. Press Enter.
Some storage volumes on the destination server are not available for selection
Some storage volumes configured on the destination server might not be available for selection in
step 5 (Specify Destination Disks and Resize NTFS Partitions) of the migration
wizard.
Suggested action
If expected volumes do not appear, try one of the following:
• Verify that Insight Control server migration supports the storage controller. Volumes configured
on an unsupported storage controller cannot be selected for migration. For more information
about supported controllers, see HP Insight Management Support Matrix at http://
www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs.
• Run the Array Configuration Utility (if your storage controller is supported), and verify the
status of the volumes on the Smart Array controller to be sure that the volumes are not in a
failed state. Also, verify that all volumes on the controller are numbered sequentially beginning
with Logical Drive 1, as required by the Insight Control server migration. If volumes are not
numbered sequentially, clear the configuration and re-create the necessary volumes.
Static IP address cannot be assigned on the destination server while booting using the Boot CD ISO
Assigning a static IP address on the destination server might result in an error similar to the following:
The IP address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx you have entered for this network adapter
is already assigned to another adapter.
Cause
This issue might occur if the IP address is assigned to another network adapter on the destination
server.
56 Troubleshooting
Page 57

Suggested action
Assign a different IP address to the network adaptor or reboot the server.
Supported storage controllers display Unknown on the Boot CD ISO
Cause
If the Insight Control server migration Boot CD ISO blocks the supported storage controllers for
P2P or V2P migrations, the controller might appear as Unknown.
Suggested action
To reset NVRAM on the destination server:
1. Reboot the destination server.
2. Press F9 during reboot to enter ROM-Based Setup Utility (RBSU).
3. Open Advanced Options, and then select Restore Settings/Erase Boot Disk or Clear NVRAM.
4. Reboot the system by using the Insight Control server migration Boot CD ISO. The proper
storage controller name is detected.
Automatic booting of the destination physical server fails
The destination server does not boot and no error message appears on the application station.
Suggested action
Reset the iLO network settings of the destination server and retry the automatic booting of the
destination server.
3 Insight Control server migration might not detect virtual machines on mapped network drives
Cause
Insight Control server migration cannot locate virtual machines stored on mapped network drives
if the service does not have access to the network shares.
Suggested action
Manually migrate these disks after a successful migration.
Destination server does not boot even though the automatic booting option was chosen during X2P migrations
During X2P migrations, if the automatic booting option was chosen during the Identify Destination
Server step of the migration wizard and if the destination server does not boot, either of the following
scenarios might occur:
• Automatic booting fails with the following error in the migration wizard: Could not get
timely response from remote management. Please try again or use
manual boot option.
• Automatic booting continues for more than 40 minutes without any error messages displayed
in the migration wizard.
Suggested action
Reset the iLO network settings on the destination server, and then retry the automatic booting or
manually boot the destination server. For more information on iLO, see the iLO user guide.
Destination preparation 57
Page 58

Insight Control server migration stops responding during automatic booting of Microsoft Hyper-V virtual machine
Insight Control server migration might stop responding during automatic booting of a Microsoft
Hyper-V virtual machine for an X2V migration.
Suggested action
Ensure the following:
• File sharing is enabled on the application station and the Microsoft Hyper-V host.
• The Server or Workstation service is started on the application station and the Microsoft
Hyper-V host.
• A "Client for Microsoft Networks" client is added to the network interface properties on the
application station and on the Microsoft Hyper-V host.
Application station fails to connect to the destination server when the server is automatically booted for an X2P migration
The application station can fail to connect to the destination server when the server is automatically
booted for a P2P or V2P migration, even though the destination server boots and the agent starts.
Cause
This issue might happen if the destination server has multiple NICs connected to different networks
and the IP address is configured to a NIC that is not on the same network as the application station
and the source server. Make sure that the duplex settings on the destination server match the duplex
settings on the network switch in your environment. You can also use the autonegotiate option at
either end to ensure proper communication between the destination server and the network switch.
The application station might also fail to connect if you have a gateway in your network and the
gateway value is not specified in the migration wizard when you are identifying the destination
server.
Suggested action
Manually boot the destination server, and then manually assign the IP address to the NIC that is
on the same network as the application station.
To resolve the gateway issue, make sure that you enter the gateway IP address in the migration
wizard when you are identifying the destination server.
Warning message is not displayed for an unsupported server when the server is started using the Insight Control server migration ProLiant Boot CD
HP Insight Control server migration does not support HP ProLiant Server versions G1 to G4. When
the unsupported server is started using the Insight Control server migration ProLiant Boot CD, the
migration wizard does not display the message that the server is not supported.
Suggested action
Before you start the migration, verify that the server is supported. For a list of supported servers,
see HP Insight Management Support Matrix at http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs.
Microsoft Windows 2008 OS migration results in a blue screen error on destination server configured with NC551m FCoE card
After a successful X2P migration with primary controller configured as NC551m FCoE Card, the
migration results in a blue screen error.
58 Troubleshooting
Page 59

Suggested action
Before you migrate, you must disable the AMD virtualization or Intel Hyper-Threading in the BIOS
of the destination server.
Migration process
Drivers cannot be installed or injected onto a boot disk
This error is reported if Insight Control fails to install or inject device drivers. In most cases, additional
information is reported on the destination server.
Suggested action
Possible causes and solutions for this error include:
• The boot partition was not migrated to the boot volume on the destination server. Verify that
the boot partition is selected for migration and placed on the boot volume of the destination
server.
• The network connection failed during driver installation.
• The destination server failed or was powered down during driver installation.
• The storage controller where the boot partition was placed is not supported. For a complete
list of supported controllers, see HP Insight Management Support Matrix at http://
www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs.
• The iSCSI initiator failed to mount the disk. To resolve this issue, perform the following steps:
1. Clear the stale iSCSI session.
2. Restart iSCSI services.
3. Restart the server migration service, if required.
Large volumes fail with a server thread error
Migrating extremely large volumes (larger than 1 TB) can result in a failed migration with the
following message:
Server Migration failed. Error occurred in server thread; nested
exception is: java.lang.OutOfMemoryError
Suggested action
Server migration does not support the migration of volumes larger than 1023 GB. Reduce the size
of any partition that exceeds this size limit before you attempt migration.
Migrating a Linux source server that has large storage fails when the migration is initiated
Migrating a Linux source server that has large storage might fail with the following error found in
the <Insight Control server migration Installation Folder>/log/
hpsmpsvc.log file:
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
Suggested action
Increase the heap size on the source server, by performing the following:
1. Ensure that the source agent is not running.
2. Change the current working directory on the source server to the smpagent folder (for example,
/root/smpagent if the agent was automatically deployed).
Migration process 59
Page 60

3. Increase the initial memory by changing the following parameters in /bin/hpvmmsmp.conf:
# Initial Java Heap Size (in MB)
wrapper.java.initmemory=512
# Maximum Java Heap Size (in MB)
wrapper.java.maxmemory=1024
4. Start the server migration Source Agent by doing one of the following at the command line:
• Type ./startHPSMPCnt.sh and then press Enter.
• Navigate to the smpagent/bin directory and then run the startHPSMPCnt.sh script.
Linux migration might fail when X Windows configuration is not properly formatted
Linux migrations might fail when the X Windows configuration file xorg.conf is not properly
formatted. The configuration file must have at least one ServerLayout section. The presence of log
items like the following examples in the hpsmpsvc.log file indicates that the xorg.conf file
does not have any ServerLayout sections:
2011/03/14 14:19:34 | - The job failed
2011/03/14 14:19:34 | com.hp.mx.smp.vmtools.grid.VmmRuntimeException:
java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Index: 0, Size: 0
2011/03/14 14:19:34 | at
com.hp.mx.smp.vmtools.grid.transport.LinuxMigrationJob.heteroInjectDrivers
(LinuxMigrationJob.java:1015)
2011/03/14 14:19:34 | at
com.hp.mx.smp.vmtools.grid.transport.LinuxMigrationJob.heterogenousCopy
(LinuxMigrationJob.java:258)
Suggested action
If the migration fails and the X Windows configuration file on the source server does not have at
least one ServerLayout section, do the following:
1. Rename /etc/X11/xorg.conf to /etc/X11/xorg.bak on the source server.
2. If required, boot the server in single user mode.
3. Re-run the migration.
4. After migration is complete, rename /etc/X11/xorg.bak back to /etc/X11/xorg.conf
on the source server.
Partitions created with third-party partitioning tools do not show the proper file system type in the server migration wizard
Partitions created with third-party partitioning tools such as Gnome might not show the proper file
system type in the server migration wizard. This does not affect migration.
Suggested action
Proceed with the migration.
Migration hangs if the source server is shut down
In some network, firewall, or router configuration scenarios, Insight Control might fail to recognize
that the source server is no longer available during a migration and remain in migration mode.
Suggested action
Perform the following procedure:
1. Close the server migration wizard.
60 Troubleshooting
Page 61

2. Open Windows Services Manager, and then restart the Insight Control application service
and the Insight Control server migration Web Service.
3. Retry the migration.
NTFS resize error message appears
The following message might appear during the migration of certain NTFS volumes:
The file system on source disk x, partition y could not be resized
during migration. The NTFS volume information could not be read. Retry
the migration without resizing this volume. Defragmenting the NTFS
volume or performing a "chkdsk /f" prior to the migration may resolve
this condition.
Cause
This message appears when Insight Control server migration cannot process the NTFS meta
information for this volume, and the volume cannot be resized during migration.
Suggested action
Do not resize the volume. Instead, perform a disk defragmentation or run CHKKDSK /F to resolve
the issue. However, performing a successful defragmentation and disk check does not guarantee
the ability to resize. In this case, the volume can only be migrated without resizing.
ReiserFS volumes are blocked for Linux migration
A ReiserFS might be blocked during migration.
Cause
Any Linux partitions that are not yet written to the disk will be detected by server migration as RAW
in step 2 of the migration wizard.
Suggested action
Reboot the source server to force the partitions to be written. Alternatively, perform the following
steps:
1. Execute the following command on the source server and note the output:
cat /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
2. Execute the following commands on the source server:
echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
echo <output of command in Step 1> > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
Filesystem on source disk \\.\PhysicalDrive0, Partition 0 could not be resized during the migration
The migration might fail with the following error: The file system on source disk
\\.\PhysicalDrive0, partition 0 could not be resized during the migration
in the logs.
Cause
One reason for the error could be that the migration wizard changes the Minimum Destination
Size and Destination Size fields to display 1 MB more than the Source Size field, even though a
disk resize was not selected in the migration wizard. This selection occurs during the "Specify
destination disks and Resize NTFS partitions" step of the migration wizard process.
Migration process 61
Page 62

Suggested action
Try the following:
1. During the Specify destination disks and Resize NTFS partitions step of the migration wizard
process, in the Assign Disks and Resize NTFS Volumes table, modify the disk size in the
Destination Size field to match the value shown in the Source Size field.
NOTE: After you modify the Destination Size field to match the Source Size field, the Minimum
Destination Size field will display 1 MB more than the Minimum Destination field.
2. Complete the rest of the steps to finish the migration process. The migration will successfully
finish.
Migration fails during the disk cloning phase
The following message might appear on the application station log (hpsmpsvc.log) if the
destination server disk has a Windows Logical Partition configured on it:
com.hp.mx.smp.vmdisk.api.APIException: Not enough space for partition!
Cause
An existing disk that already contains some Windows partitions is being used as the destination
for migration.
Suggested action
To resolve the issue, format the destination disk before you use it as a destination disk.
1. Reboot the destination server and press F9 to enter the BIOS settings of the destination server.
2. In the Advanced Options section, select Erase Boot Disk.
3. Rerun the migration process.
Failed: Drivers could Not Be Injected Into Boot Disk in the logs
Migration fails with the message Failed: Drivers could not be injected into boot
disk... and the iSCSI mounting error The target has already been logged in via
an iSCSI session appears in the log files.
Suggested action
Restart the application station and retry the migration.
Starting a new migration after a current migration is stopped
If a migration is stopped by means other than a cancellation or failure, the application station,
source server, and destination server might not recognize that the migration has stopped.
Suggested action
To start a new migration:
1. Restart the migration agent on the source and destination servers.
2. On the application station, close the migration wizard.
3. Restart the Insight Control application service and the Insight Control server migration Web
Service.
4. Reopen the migration wizard.
Unrecoverable sector-read errors on the source server hard drive are not supported and fail a Windows P2P or P2V migration
The following error message might appear if a volume that has unrecoverable sector-read errors
is migrated: Server Migration failed. ReadFile failed.
62 Troubleshooting
Page 63

Cause
Hard drives automatically take corrective action when they have difficulty reading a sector. These
sectors are marked as “bad sectors” and relocated to one of the sparse sectors in a reserved area
of the hard disk. In these cases, no read error is produced, and the drive continues to function
properly. The data is lost and a read error is propagated to the operating system only if the surface
error rate is too high and additional sparse sectors are not available, or when the sector is
completely unreadable from the beginning.
If file system tools are used to detect these failing sectors (for example, CHKDSK /p /r), the
clusters are marked as “bad.” However, the data usually cannot be recovered. In such cases, the
system is not consistent, and proper migration is not possible.
Suggested action
Insight Control server migration does not support the migration of volumes that have unrecoverable
bad sectors.
Source Agent fails to launch when source server reboots in migration agent mode
Suggested action
Try the following:
1. To return to the original configuration, reboot the source server to Profile 1 Hardware Profile.
2. Remove server migration Source Agent Mode manually.
a. Right-click My Computer, and then select Properties.
b. Click the Hardware tab, and then select Hardware profiles.
c. Select server migration Source Agent Mode, and then click Delete.
3. Before you start a new migration, verify that all antivirus and firewall software is properly
reconfigured or disabled.
Error occurs during data copy of Linux migration
An Error during data copy offset=offset srcPos=source sector
dstPos=destination sector amount=number of sectors message appears in the
source or destination log, followed by an I/O exception.
Cause
Bad blocks might exist on the source or destination disk.
Suggested action
Insight Control does not support migrations of disks that have bad blocks. If the bad block is on
the destination disk, change the destination disk.
SAN-connected destination server displays a blue screen
Suggested action
To migrate Windows Server 2003 to a SAN-connected destination server, install the following on
the source server:
• Service Pack 1
• Service Pack 2
• Updated Storport storage driver (for more information, see http://support.microsoft.com/kb/
932755)
Migration process 63
Page 64

Out of memory error occurs on the application station during migration
The Insight Control application station requires a minimum of 1024 MB of free memory for Insight
Control migrations.
Suggested action
Free memory or add memory to the application station, and then restart the migration.
Destination server boots with an invalid IP address
After a P2P migration, the destination server might boot with an invalid IP address (for example,
169.x.x.x), instead of using the IP address that was configured through the migration wizard.
Cause
This issue occurs if the destination IP address configuration fails or Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) is not enabled in the network. Whenever a NIC is added to the server, by default
the NIC is assigned an IP address using the DHCP configuration. If no DHCP server is configured
on the network, the server will boot with an invalid IP address.
Suggested action
After the P2P migration is complete, manually configure the IP address on the destination server.
For specific instructions on performing this task, see the help files for the specific OS documentation.
Windows server migration Source Agent or PINT remote deployment is intermittent and deployment fails with a General failure occurred error
When you remotely deploy the Windows server migration Source Agent or PINT from the Insight
Control server migration application station or from Systems Insight Manager, server migration
Source Agent deployment fails with the error General failure occurred. In addition, the
<Insight Control server migration Installation
Folder>\log\AgentLogs\hp\log\<source IP>\timestamp_smp_log.txt file displays
the following exception:
Received Target Exception: UnknownException : SoapSession::SoapSession : unknown exception!
No install was run, due to connection error
Suggested action
Manually install the server migration Source Agent or PINT on the source server.
Unable to detect HP FlexFabric 10Gb 2-port 554FLR-SFP+ Adapter configured as iSCSI disk in step 5 of migration wizard
When you start a P2P migration of any of the OS from any server to DL385p Gen8 with HP
FlexFabric 10Gb 2-port 554FLR-SFP+ Adapter configured as iSCSI disk and then start an auto
boot in step 3, you will observe that the adapter is not detected in step 5 of migration wizard and
the following error message is displayed:
"HP Insight Control could not find any disks on destination server"
Suggested action
You must disable IOMMU in RBSU (System Config > Processor Settings > AMD–Vi).
HP Smart Array B320i controller name is not displayed
When you perform X2P migration to Gen8 server having HP Smart Array B320i as primary
Controller, you will observe that the name of controller is not displayed in step 5 and 7 of the
migration wizard.
64 Troubleshooting
Page 65

Suggested action
No action required.
Unable to install Service Pack for ProLiant (SPP) on Windows 2008 SP2 operating system after successful migration
After successful server migration of Windows 2008 SP2 operating system, SPP fails to install as
part of postmigration task.
Suggested action
After the migration is complete, connect SPP ISO to the destination server and manually install SPP.
Linux migration to servers with iSCSI storage fails to boot
When you perform a X2P migration of Linux OS on any server with iSCSI storage as destination,
the kernel panic message appears.
Suggested action:
The iscsi-initiator-utils and dracut-network RPM packages are missing on the source
and must be installed on the source before migration.
Postmigration
Migration does not start after confirmation. The event log continuously displays
Operation Migration waiting for connection to source
When the migration starts, the source server reboots and runs the migration agent in exclusive
mode during migration.
Rebooting the source machine might take a few minutes. If this process takes a long time, verify
that the source machine is rebooted with the migration agent running in exclusive mode. The source
machine might be waiting for user input during the reboot. Another possibility is that the boot order
is incorrect.
If the migration agent is deployed on an operating system that is not first in the boot order, the
migration agent might fail to boot to the Insight Control mode.
Suggested action
Change the boot order by editing boot.ini, and verify that the operating system on which Insight
Control is deployed is first in the boot order.
Destination server mouse and keyboard do not work after a Windows migration
The mouse and keyboard might not be operational immediately on a destination server after a
migration.
Suggested action
To detect and activate the mouse and keyboard, reboot the destination server so that PnP correctly
detects and activates the mouse and keyboard.
If the mouse and keyboard still do not work, ensure that DevCon is installed and ready on the
Upload Drivers tab and then re-run the migration. Select Use DevCon in Step 6 of the P2P or V2P
migration wizard.
Postmigration 65
Page 66

NOTE: After successful use of DevCon during a migration, Windows Device Manager might
show yellow exclamation points (!) next to duplicate keyboard and mouse entries. Right–click the
device that has the yellow exclamation point and update the driver. The device should be
rediscovered and changed from an unknown device to an HID device. Devices that cannot be
rediscovered through this method are duplicates and can be removed using the right-click menu.
To attempt to solve the mouse and keyboard issues without restarting the migration, see “USB
mouse or keyboard drivers are not loaded after an X2P Windows migration” (page 66).
USB mouse or keyboard drivers are not loaded after an X2P Windows migration
After a successful Windows migration, the mouse and keyboard drivers might not be loaded. As
a result, the mouse and keyboard do not work on the destination server.
Cause
Insight Control does not inject any drivers for the USB keyboard or mouse on the target server.
Because these are plug–and–play devices, Windows automatically detects the devices and loads
the drivers. In some scenarios, the USB keyboard and mouse drivers might fail to load. Example
scenarios include a tampered source, a Microsoft Hyper-V VM source, or a migrated source that
used PS/2 drivers.
Suggested action
Try the following:
• Reboot the destination server a second time after the migration. During the reboot, verify that
Legacy USB is set to Enabled in the BIOS on the destination server. The PnP drivers should
load automatically through the Hardware Setup Wizard.
• If the second reboot did not solve the issue, log on to the destination server by using Windows
Remote Desktop to update the mouse and keyboard drivers.
NOTE: This solution will be successful only if Remote Desktop is enabled on the destination
server and an IP address was configured with the migration wizard.
To use the server migration wizard to configure an IP address on the destination server, perform
the following:
1. Upload the latest ProLiant Support Pack (PSP) supported by the source server to the Insight
Control server migration Upload Drivers tab.
2. Select the option to reboot the destination server in step 6 of the migration wizard.
3. Select to install the PSP after migration. Enter any static IP addresses that are required. If
a static IP address is not provided, DHCP will be assumed by default.
When you are logged on to Remote Desktop on the destination server, determine whether the
proper mouse and keyboard drivers are installed on the destination server. To do this, do one
of the following:
◦ Verify that the mouse and keyboard appear as Unknown in Device Manager and have
no drivers listed.
◦ Verify that the server has the following files:
66 Troubleshooting
Hidusb.sys–
– Hidkbd.sys
– Mouhid.sys
Page 67

Reinstall the mouse and keyboard drivers by using one of the following methods:
◦ Reinstall the PSP.
◦ Update the drivers in Device Manager.
• Confirm that all of the following criteria are met:
The source server has a PS/2 mouse and keyboard.◦
◦ The destination server has a USB mouse and keyboard.
◦ The destination mouse and keyboard do not work.
Then, use the following procedure:
1. Attach a USB mouse and keyboard (by using a USB or PS/2 dongle) to the source server.
2. On the source server, resolve any devices that display a yellow exclamation point (!) in
Device Manager (if any). Verify that the mouse and keyboard function on the source
server.
3. Attach a USB mouse and keyboard (by using a USB PS/2 dongle) to the destination
server.
4. Perform a P2P migration without using the PSP.
5. Install the latest Microsoft Service Pack on the destination server.
6. Install the latest PSP on the destination server.
7. Remove the (dongle-attached) USB mouse devices and keyboards from the source and
destination servers.
Mouse does not work on the iLO of the destination server after a Linux X2P migration
The mouse does not work on the iLO of the destination server after a Linux X2P migration.
Suggested action
Deselect high–performance mouse mode on the remote console of destination server iLO.
Mouse does not work on the destination ESX virtual machine after a V2V migration
The mouse might stop working on the destination ESX virtual machine after a V2V migration.
Suggested action
Use the following procedure:
1. Log on to the destination server by using the keyboard.
2. Press the Windows Key+Pause/Break to open System Properties.
3. Use the arrow keys or Tab key and the Enter key to open Device Manager.
4. In Device Manager, use the arrow keys or Tab key to move to VMware Pointing device, and
then press the Application key. Click Uninstall. The VMware Pointing Device entry disappears
from the list of devices.
5. Use the arrow keys to move to any selection of the Device Manager list, press the Application
key, and then select Scan for hardware changes. A PS/2 compatible–mouse appears in Device
Manager.
Drive letters are not the same in the migrated virtual machine guest after migration
The drive letters on the migrated virtual machine guest are not the same after migration.
Suggested action
Depending on the operating system, perform the following task:
Postmigration 67
Page 68

1. Open Windows Disk Management.
2. Correct the incorrect letter assignment in the migrated virtual machine guest by using the disk
administrator or manager.
Drives do not appear on the migrated operating system
After a successful migration, some migrated volumes do not appear in Windows Explorer.
Suggested action
Depending on the operating system, perform the following task to assign a driver letter to the
volume so it is visible in Windows Explorer:
1. For Windows Server 2003 systems: Select Control Panel→Administrative Tools→Computer
Management→Disk Management, and then verify that the disk manager has initialized all
disks.
2. Assign the driver letter in the migrated virtual machine guest by using the appropriate disk
administrator or manager.
Mouse and keyboard do not work after a Microsoft Hyper-V virtual machine is migrated to a ProLiant server
Suggested action
If the mouse and keyboard do not work after you migrate a Microsoft Hyper-V virtual machine to
a ProLiant server, reboot the destination server.
If rebooting does not solve the issue, try the following:
• Remove Microsoft Hyper-V Integration Tools on the source virtual machine before you perform
a migration.
• Rerun the migration, but select Automatic PSP installation in the migration wizard so that the
PSP is installed automatically on the destination server after a migration.
• Rerun the migration, but select Use DevCon in the migration wizard so that DevCon is installed
automatically on the ProLiant server at the end of the migration.
Static IP address cannot be assigned on the destination server after migration
Assigning a static IP address on the destination server might result in an error similar to the following:
The IP address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx you have entered for this network adapter
is already assigned to another adapter.
This scenario can occur if the IP address is assigned to a network adapter on the source server.
Suggested action
For more information, see the following website:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/269155/en-us
Virtual machine hosts Integrated Components that are not installed on the destination virtual machine after migration
Suggested action
Try the following:
1. Power down the destination virtual machine.
2. Add a CD-ROM drive to the virtual machine.
3. Power up the virtual machine, and then restart the installation of the Integrated Components.
68 Troubleshooting
Page 69

Exclamation point (!) appears on the NIC adapter in Device Manager on the migrated virtual machine
After a migration, the NIC adapter might not appear on the destination virtual machine. This might
happen during V2V migrations between VMware Server and VMware ESX servers. This might also
happen when a virtual machine is migrated from one Microsoft Hyper-V host to another Hyper-V
host.
You might be unable to assign the IP address to this device, which does not reappear on the
Network Connections page.
Suggested action
Manually remove the network adapter in Device Manager and trigger a Scan for Hardware
Changes. This action detects the NIC adapter and configures the drivers for it.
Network adapter in the destination ESX virtual machine is not initialized after a V2V migration
The network adapter in the destination ESX virtual machine might not be initialized after a V2V
migration.
Suggested action
1. Log on to the destination server by using the keyboard.
2. Navigate to Device Manager. To do so, right-click My Computer, and then select Manage.
3. Right-click VMware Accelerated AMD PCNet Adapter, and then select Uninstall. The VMware
Accelerated AMD PCNet Adapter entry disappears from the list of devices.
4. Select Scan for hardware changes. A valid virtual network adapter appears in Device Manager.
5. Reboot the virtual machine.
Destination virtual machine fails to boot after X2V migration
The destination virtual machine might fail to boot and display the following error: Attempting
to load a 64-bit application, however the CPU is not compatible with
64-bit mode or Status : 0xc0000225 The boot selection failed because a
required device is missing.
Cause
For a 64-bit OS to load on a virtual machine, Intel-VT must be enabled on the destination virtual
machine host.
Suggested action
Enable the Intel-VT option in the system BIOS of the destination virtual machine host and then reboot
the virtual machine.
During editing of the settings of guest VMs created by server migration, an invalid OS ID warning appears
After you perform an X2V migration to an ESX Host by using the Automatic Boot feature of the
server migration wizard and then change the settings of the migrated VM, the following warning
message might appear:
The guest OS ID <guest name> is not valid.
Suggested action
Follow the suggestion provided in the warning message to resolve the issue.
Postmigration 69
Page 70

After the issue is resolved, any disk can be added (which might involve upgrading the virtual
hardware on the virtual machine.)
Server is unresponsive during PSP installation
The server becomes unresponsive during PSP installation.
Suggested action
Reboot the server and then reinstall PSP manually.
Destination server still shows server migration UI but server migration wizard shows migration completed
After the migration, server migration loses connectivity to the Hyper-V host, which causes server
migration to fail to eject the boot CD and reboot the VM. If server migration cannot connect to the
Hyper-V host, reboot by using the destination agent. In this case, server migration will be unable
to eject the boot CD and as a result, after the reboot, the VM will boot back into the boot CD. This
issue is specific to Microsoft Hyper-V VMs.
Suggested action
Manually eject the virtual boot CD from the VM and reboot the VM.
Operating system is not booting on a destination server that has SAN disks
After you perform a successful P2P migration of the SLES 11 SP1 32-bit operating system on SAN
disks with Brocade or QLogic Fibre Channel HBA as the primary boot controller, the operating
system does not boot on the destination server.
Suggested action
Before you migrate any Linux distribution to a destination server that has SAN storage, make sure
that the RPM package containing firmware files (such as
brocade-firmware-<version>.noarch.rpm and
qlogic-firmware-<version>.noarch.rpm on SLES OS, and
ql2xxx-firmware-<version>.noarch.rpm on RHEL OS) for the target SAN Fibre Channel
HBA are installed on the source server from the OS installation media.
Error is displayed for a missing file system while migrated Linux OS is booted on the destination server
When you migrate a file system to the destination server multiple times, the multiple file systems
that contain the same UUID are created.
Suggested action
Make sure that multipath is configured on the source server. If multipath is not configured, make
sure that the file systems that are being migrated do not have the same UUID.
Logical drives of HP Smart Array B110i SATA RAID Controller are removed
After a successful X2P migration of the Windows Server 2008 OS, the logical drives of HP Smart
Array B110i SATA RAID Controller are removed.
Suggested action
When the logical drives are removed, you must re-create the exact logical drives by using ACU
or ORCA on the destination server after migration.
70 Troubleshooting
Page 71

Unable to download the log files from the migration wizard when using IE 9
While using IE 9, you are unable to download the log files from the migration wizard.
Suggested action
Perform the following steps:
1. From the IE 9 browser, click Tools→Internet Options.
2. Click Advanced and navigate to Security section under Settings.
3. Clear the Do not save encrypted pages on disk check box.
4. Click OK.
This will enable you to download the log files.
Microsoft Windows 2008 R2 SP1 does not boot on ProLiant BL420c Gen8 with Emulex LPe1205A FC storage controller.
After a successful migration of Windows 2008 R2 SP1 to ProLiant BL420c Gen8 configured with
Emulex LPe1205A FC storage controller, the OS does not boot up on the destination server.
Suggested action
Perform one of the following:
• During migration, make PSP installation as the default option.
• If a 'No Disk Error' is preventing the OS from booting after migration, reboot directly from
the iLO console and disable the secondary storage controller driver - Emulex LPe1205A from
the Windows Device Manager.
• Migrate the OS with PSP uploaded in Upload Drivers tab.
Source server with SLES 11 SP2 x32 OS does not boot the operating system properly after successful migration
Source server with SLES 11 SP2 x32 OS does not boot the operating system properly after successful
migration.
Suggested action
After the migration, restart the source server manually.
RHEL version 6.3 (x64) operating system does not boot after migrating to HP Dynamic Smart Array B120i/B320i Controllers
After performing a successful V2P migration of RHEL version 6.3 (x64), the operating system does
not boot up on destination with HP Dynamic Smart Array B120i/B320i Controllers.
Suggested action
Perform the following:
1. Disable VT-d in RBSU.
2. Uninstall virtualization package before migration.
3. Remove the parameter "intel_iommu=on" in grub menu.lst.
RHEL version 6.3 (x64) operating system does not boot as destination after successful migration
After a successful X2V migration, the RHEL version 6.3 (x64) OS does not boot up on Hyper-V/ESX
as destination and displays the following error message:
Multiboot kernel must be loaded before modules.
Postmigration 71
Page 72

Suggested action
You need to modify the following in the /boot/grub/grub.conf file from
root (hd0,0)
kernel /tboot.gz loggingvga,serial,memory
module /vmlinuz-2.6.32-269.el6.x86_64 ro root/dev/mapper/volGroup-lv_rot
intel_iommu=on rd_NO_LUKS LANG-en_US.UTF-8 rd_NO_MD
rd_LVM_LV=VolGroup/lv_swap SYSFONT=latarcyrheb-sun16
rd_LVM_LV=VolGroup/lv_root KEYBOARD=pc KEYTABLE=us crashkernel=auto
rhgb quiet rd_NO_DM ehgb quiet
module /initramfs-2.6.32-269.el6.x86_64.img
to
root (hd0,0)
kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.32-269.el6.x86_64 ro root/dev/mapper/volGroup-lv_rot
intel_iommu=on rd_NO_LUKS LANG-en_US.UTF-8 rd_NO_MD
rd_LVM_LV=VolGroup/lv_swap SYSFONT=latarcyrheb-sun16
rd_LVM_LV=VolGroup/lv_root KEYBOARD=pc KEYTABLE=us crashkernel=auto
rhgb quiet rd_NO_DM ehgb quiet
initrd /initramfs-2.6.32-269.el6.x86_64.img
72 Troubleshooting
Page 73

11 Support and other resources
Information to collect before contacting HP
Be sure to have the following information available before you contact HP:
• Software product name
• Hardware product model number
• Operating system type and version
• Applicable error message
• Third-party hardware or software
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
How to contact HP
Use the following methods to contact HP technical support:
• In the United States, see the Customer Service or Contact HP United States website for contact
options:
http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/contact_us.html
• In the United States, call 1-800-HP-INVENT (1-800-474-6836) to contact HP by telephone.
This service is available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. For continuous quality improvement,
conversations might be recorded or monitored.
• In other locations, see the Contact HP Worldwide website for contact options:
http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/wwcontact.html
Security bulletin and alert policy for non-HP owned software components
Open source software (such as OpenSSL) or third-party software (such as Java) are sometimes
included in HP products. HP discloses that the non-HP owned software components listed in the
Insight Management end user license agreement (EULA) are included with Insight Management.
The EULA is included with the Insight Management Installer on Insight Management DVD #1.
HP addresses security bulletins for the software components listed in the EULA with the same level
of support afforded HP products. HP is committed to reducing security defects and helping you
mitigate the risks associated with security defects when they do occur.
When a security defect is found, HP has a well defined process that culminates with the publication
of a security bulletin. The security bulletin provides you with a high level description of the problem
and explains how to mitigate the security defect.
Subscription service
HP recommends that you register your product at the Subscriber's Choice for Business website:
http://www.hp.com/country/us/en/contact_us.html
After registering, you will receive email notification of product enhancements, new driver versions,
firmware updates, and other product resources.
Registering for software technical support and update service
Insight Management includes one year of 24 x 7 HP Software Technical Support and Update
Service. This service provides access to HP technical resources for assistance in resolving software
implementation or operations problems.
Information to collect before contacting HP 73
Page 74

The service also provides access to software updates and reference manuals in electronic form as
they are made available from HP.
With this service, Insight Management customers benefit from expedited problem resolution as
well as proactive notification and delivery of software updates. For more information about this
service, see the following website:
http://www.hp.com/services/insight
Registration for this service takes place following online redemption of the license certificate.
How to use your software technical support and update service
As HP releases updates to software, the latest versions of the software and documentation are
made available to you. The Software Updates and Licensing portal gives you access to software,
documentation and license updates for products on your HP software support agreement.
You can access this portal from the HP Support Center:
http://www.hp.com/go/hpsc
After creating your profile and linking your support agreements to your profile, see the Software
Updates and Licensing portal at http://www.hp.com/go/hpsoftwareupdatesupport to obtain
software, documentation, and license updates.
HP authorized resellers
For the name of the nearest HP authorized reseller, see the following sources:
• In the United States, see the HP U.S. service locator website:
http://www.hp.com/service_locator
• In other locations, see the Contact HP worldwide website:
http://www.hp.com/go/assistance
Related information
Documents
• HP Systems Insight Manager
The Systems Insight Manager information library is available at the Systems Insight Manager
product website:
http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/sim/docs
• HP Insight Control
Documentation for Insight Control, including documentation for Insight Control virtual machine
management and Insight Control power management, is available from the HP Insight Control
website:
http://www.hp.com/go/insightcontrol/docs
Websites
HP ProLiant Support Pack (PSP)
To find and download the HP ProLiant Support Pack (PSP) (ProLiant Support Pack (PSP)) that is
appropriate for your ProLiant server and Linux OS, follow these steps:
1. Open a browser to the following web address:
http://www.hp.com
2. Select the Support & Drivers tab.
74 Support and other resources
Page 75

3. Select the Download drivers and software (and firmware) option.
4. Enter your server model (for example, BL460c G5) in the For product text box, and select
Go>> to search for that server.
NOTE: If more than one server model matches the value you entered in the For product text
box, select the appropriate server model from the search results.
5. Select the appropriate Linux OS and version from the list of available operating systems.
6. Scroll down the page until you see the table labeled Software - Support Pack.
7. Select the PSP or SPP link in the Description column.
8. To download the PSP or SPP, select the Download>> button associated with the *.tar.gz
(gzipped) file.
To view or download the associated User Guide, select the Release Notes tab.
Related documentation
Related documentation
• HP Insight Management Preinstallation Worksheet
• HP Insight Management Quick Installation Guide
• HP Insight Management Installation and Configuration Guide
• HP Insight Control Getting Started Guide
• HP Insight Control Release Notes
• Portable Images Network Tool (PINT) README (Linux and Windows)
• HP Insight Control server migration Online Help
• For a list of supported platforms for Insight Control, see the HP Insight Management Support
Matrix at: http://www.hp.com/go/insightmanagement/docs
Typographic conventions
This document uses the following typographical conventions:
Book title The title of a book. On the web, this can be a hyperlink to the
Command A command name or command phrase, for example ls -a.
Computer output Information displayed by the computer.
Ctrl+x or Ctrl-x A key sequence that indicates you must hold down the keyboard
ENVIRONMENT VARIABLE The name of an environment variable, for example, PATH.
Key The name of a keyboard key. Return and Enter both refer to the
Term A term or phrase that is defined in the body text of the document,
User input Indicates commands and text that you type exactly as shown.
book itself.
key labeled Ctrl while you press the letter x.
same key.
not in a glossary.
Replaceable The name of a placeholder that you replace with an actual value.
[ ] In command syntax statements, these characters enclose optional
content.
{ } In command syntax statements, these characters enclose required
content.
| The character that separates items in a linear list of choices.
Typographic conventions 75
Page 76

... Indicates that the preceding element can be repeated one or more
times.
WARNING An alert that calls attention to important information that, if not
understood or followed, results in personal injury.
CAUTION An alert that calls attention to important information that, if not
understood or followed, results in data loss, data corruption, or
damage to hardware or software.
IMPORTANT An alert that calls attention to essential information.
NOTE An alert that contains additional or supplementary information.
TIP An alert that provides helpful information.
76 Support and other resources
Page 77

12 Documentation feedback
HP is committed to providing documentation that meets your needs. To help us improve the
documentation, send any errors, suggestions, or comments to Documentation Feedback
(docsfeedback@hp.com). Include the document title and part number, version number, or the URL
when submitting your feedback.
77
Page 78

A Applying old server migration standalone licenses
Starting with Insight Control 6.0, HP Insight Control server migration is no longer available as a
standalone and is available exclusively through Insight Control. The addition of server migration
functionality into HP Insight Control is a function of the Insight Control software, not of the license
key or the part number. There are no new part numbers needed for the addition of server migration
functionality. So if your destination server is licensed by Insight Control 6.0 or above, you can
perform unlimited migrations to the Insight Control licensed server.
The standard procedure for licensing Insight Control server migration is to purchase Insight Control
licenses and apply them through the Deploy→License Manager menu item from the CMS
management console.
Older licenses for versions of HP Insight Control server migration earlier than 6.0 are not supported.
78 Applying old server migration standalone licenses
Page 79
B Performing migrations in a Microsoft Cluster server
environment
Migrations in a Microsoft Cluster server environment often require you to move an operating system,
appropriate applications, and data to new server hardware. In a cluster, various applications such
as Microsoft Exchange, Microsoft SQL Server, or a file share can be installed. Cluster migration
includes moving these additional resources.
This appendix discusses a scenario where a file share with both nodes and the cluster resources
must be migrated. Basic components in a Microsoft Cluster server environment include:
• Shared disk, where the quorum and log reside
• Cluster IP address
• Cluster network name
• Application resources (such as Microsoft Exchange, SQL Server, or file share)
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 x64-based failover clusters support up to 16 nodes in a single
cluster. Microsoft Windows 2003 Server Enterprise Edition and Windows Server 2003 Data Center
Edition support up to eight nodes in a cluster. These nodes are connected to a Fibre Channel switch
that is connected to a storage array where the quorum and resources are stored. If multipathing
is used, multiple Fibre Channel switches connect the nodes to the server so that if one path fails,
the other path takes over the connection from the nodes to SAN array.
Figure 12 The basic hardware design of a three-node duster.
Premigration consideration steps for clusters
1. Note the IP address and network names of the nodes to which the clusters are attached.
Premigration consideration steps for clusters 79
Page 80

2. Review the event logs and cluster logs to verify that there are no critical issues that might affect
the migration. If an Exchange or SQL Server is installed on the cluster, the premigration steps
are similar to those of a standalone Exchange or SQL Server. The only deviation from this
procedure is that you would not need to set services to Manual. (By default, all the Exchange
and SQL Server services are set to Manual.)
3. (Optional) If a file share is present on the cluster, remove sharing access on the file share.
Re-enable sharing access after the migration is finished.
4. Take all the cluster resource groups offline.
5. Verify that the target server has enough disk space both for capacity and performance for the
applications to be migrated.
6. Verify that the application station, source server, and destination server are on the same
network subnet.
7. Shut down all nodes except the one to be migrated.
8. Stop the cluster service on that node.
9. Start the P2P migration - see “Performing the migration” (page 80).
Performing the migration
Perform the migration steps in the migration wizard as in a typical migration. As an example, if
your migration involved two nodes, you must perform P2P migration for two servers.
You must ensure that the Host Bus Adaptors (HBAs) are properly migrated to the new servers and
verify that any established Fibre Channel zones are updated as necessary. Fibre Channel zones
can be based either on the unique World Wide Name (WWN) of the HBA (software-based zoning),
on the switch port (hardware-based zoning), or both. In the software-based zoning case, you must
either transfer the same physical HBAs from the source machine to the destination machine, or
update the Fibre Channel zones with the new World Wide Names of the destination HBAs.
Post migration considerations and steps
After the migration completes:
1. Power down the source server nodes.
2. Boot the destination server nodes.
3. Update the entire destination server using the ProLiant Support Pack (PSP). For more information,
see http://www.hp.com/servers/psp.
4. All source configuration settings will also be transferred to the destination server hence it is
same as the source (like static IPs, node name, domain membership).
5. Present the Quorum disk & shared disks to the destination sever.
6. If required edit the network configuration. By default, the migration process configures the
network cards to use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). To implement static IP
addressing, apply the static network settings and ensure that the target nodes have the same
the IP address as the previous nodes.
7. Update the boot.ini file with the desired switches as necessary. A copy of the source server
boot.ini entries are within the file and the SMP – P2P application entry can be removed. Set
all memory switches, such as /3gb and /PAE, for use on the desired target server.
8. Verify that the Exchange or SQL databases and log volumes use the same letters as were used
on the source server.
9. Start the cluster service on the migrated node.
10. Start the cluster resources groups.
11. Now power on all the other nodes in the cluster and verify that the nodes can connect to the
cluster.
12. Cluster will run the same as before with our new destination server replacing the old source
server.
13. These steps can be repeated for each node to successfully migrate the full cluster.
14. Perform the Exchange or SQL postmigration steps on the cluster, as described later in this
white paper.
80 Performing migrations in a Microsoft Cluster server environment
Page 81

15. Review the event logs and cluster logs to see if there are any issues occurring with the newly
migrated cluster.
Post migration considerations and steps 81
Page 82

C Logging server migration application service Logs into
Windows NT Events
To log the server migration application service logs into Windows NT Events, perform the following
steps:
1. In the file <Insight Control server migration Installation
Folder>\bin\windows\hpmmsvc.conf make the following changes:
a. Change the statement wrapper.syslog.loglevel=NONE to
wrapper.syslog.loglevel=INFO
b. Add another statement wrapper.syslog.format=TM
2. Restart the HP Insight control server migration application service.
This should start logging the HP Insight Control server migration application service logs into
Windows NT events.
NOTE: Enabling Windows Events for HP Insight Control server migration application service can
generate too many events.
82 Logging server migration application service Logs into Windows NT Events
Page 83

Glossary
ESX VMware ESX, a virtualization product produced by VMware, Inc.
EVA Enterprise Virtual Array
MSA Modular Smart Array
TCP Transmission Control Protocol
X2P P2P or V2P migrations
X2V P2V or V2V migrations
83
Page 84

Index
A
antivirus software, 21
application station
description, 13
fails to connect to the destination server for X2P, 58
auto booting destination server fails, 57
B
blue screen error
X2P migration, 58
boot disk cannot be installed or injected with drivers, 59
boot disk cannot be installed or injected with drivers in
log file, 62
booting the destination server, 31
manually creating and booting a virtual machine, 32
migration wizard for a virtual destination, 33
prerequisites for Microsoft Hyper-V, 32
prerequisites for virtual machine host, 24
prerequisites for VMware ESX, 33
using BOOT CD ISO for X2P, 31
using the migration wizard, 32
virtual machine destination server for P2V, 33
virtual machine destination server for V2V, 33
C
certificates
dynamic, 21
static, 21
controllers appears as unknown, 57
corrective action is required before this server can be
migrated, 51
critical or hardware-dependent application preparation,
19
D
Deploy Agent
overview, 14
deploying
Linux server migration Source Agent, 28
server migration Source Agent on domain controller,
28
Source Agents, 25
Windows server migration Source Agent, 26
destination preparation
troubleshooting, 54
destination server
auto booting fails, 57
booting, 31
description, 13
does not boot when auto boot was chosen during
X2P migration, 57
identification fails, 54
invalid IP address, 64
IP address configuration fails in Microsoft Hyper-V, 54
Linux, 30
mouse does not work, 67
mouse or keyboard does not work, 65, 68
prerequisites, 30
SAN-connected server displays blue screen, 63
static IP address cannot be assigned, 56, 68
storage volumes not available for selection, 56
USB mouse or keyboard does not work, 66
virtual machine hosts, 30
destination server boots with invalid IP address, 64
destination server does not boot, 57
detecting a migration agent, 29
disk cloning
troubleshooting, 62
documentation
HP Insight Control, 74
licenses, 78
PSP User Guide, 74
related documentation, 75
SIM, 74
drivers
cannot be installed or injected into boot disk, 59
cannot be installed or injected into boot disk in log file,
62
letters appear differently, 67
drives
do not appear on migrated operating system, 68
E
editing the Windows Boot.ini file, 45
error during data copy of Linux migration, 63
errors
credentials, 49
NTFS, 61
out of memory, 64
troubleshooting, 49
F
FAQs, 49
file system could not be resized, 61
file systems
with the same UUID, 70
firewalls, 20
H
HP Insight Control
documentation, 74
HP Smart Array B320i controller name is not displayed,
64
I
incorrect LUN size detected in step 2 of the migration
wizard, 53
Insight Control does not detect virtual machines on mapped
network drives, 57
Integrated Components
84 Index
Page 85

do not install on destination virtual machine after
migration, 68
IP address cannot be assigned on destination server, 56
K
kernel panic when booting to the Insight Control CD ISO,
54
keyboard
does not work when booting to the Insight Control CD
ISO, 55
troubleshooting, 65, 66, 68
L
launching
migration wizard, 40
migrations through Quick Launch, 41
migrations through Systems Insight Manager, 40
licenses
overview, 11, 14
standalone documentation, 78
verifying, 20
Linux
data copy error, 63
deploying Source Agent, 28
destination physical server prerequisites, 38
destination size requirement, 30
destination virtual machine prerequisites, 39
installing PSP before migration, 21
installing SPP before migration, 21
mouse does not work, 67
P2V postmigration tasks, 46
preparing for a server migration, 37
resizing file systems, 19
Source Agent using nonroot credentials fails, 53
source physical server prerequisites, 38
source server requirements, 24
source virtual machine prerequisites, 38
X2P postmigration tasks, 46
logical drives
removed or deleted, 70
M
manually creating a virtual destination server
virtual machine, 32
menus missing, 49
Microsoft Cluster
migration overview, 79
postmigration, 80
preforming the migration, 80
premigration, 79
migration
different drive letters after migration, 67
fails with the Microsoft Hyper-V role enabled, 53
hangs if source server is shut down, 60
hangs or incomplete, 70
Microsoft Cluster server environment, 79
starting a new one after current one is stopped, 62
stops responding during auto-booting of Microsoft
Hyper-V, 58
troubleshooting, 59
migration agent
deployment fails, 52
migration checklist, 13
migration does not start after confirmation, 65
migration wizard, 14
hangs, 49
launching, 40
using to boot a virtual destination server, 33
mouse
does not work, 67
does not work when booting to the Insight Control CD
ISO, 55
troubleshooting, 65, 66, 67, 68
N
Nagios
documentation, 74
network adapter
in destination ESX virtual machine is not initialized, 69
NTFS partitions
error message, 61
resizing, 18
O
out of memory error, 64
overview
Deploy Agent, 14
license, 14
migration wizard, 14
server migration, 13
status / logs, 14
types of migration, 11
upload drivers, 14
P
P2P, 11
postmigration tasks, 44
source server prerequisites, 35
P2V, 11
booting a virtual destination server, 33
source server prerequisites, 35
using the migration wizard, 33
physical destination servers prerequisites, 30
Physical-to-ProLiant migration see P2P
Physical-to-Virtual migration see P2V
planning
migration strategy, 18
preparing a schedule, 18
ports
used, 20
postmigration
troubleshooting, 65
postmigration tasks
editing the Windows Boot.ini file, 45
installing ProLiant Support Packs for Windows, 44
installing Service Pack for ProLiant for Windows, 44
Linux , 46
Linux P2V, 46
85
Page 86

validating the migration, 47
Windows P2P, 44
Windows X2V, 45
premigration tasks
installing ProLiant Support Packs for Windows, 21
Installing Service Pack for ProLiant, 21
preparing
application station requirements, 17
application station system requirements, 17
choosing server migration Agents, 25
critical or hardware-dependent applications , 19
Linux server migration, 37
migration checklist, 13
source server operating system support, 17
uninstalling guest tools, 25
Windows server migration, 36
primary controller
does not have drives attached, 55
does not have logical drives defined, 55
not supported, 55
ProLiant Support Pack see PSP
PSP
documentation, 74
downloading, 74
installing Windows after migration, 44
installing Windows before migration, 21
Q
Quick Launch
launching server migrations, 41
R
related products
HP OpenView, 11
HP SmartStart CD, 11
HP SmartStart Scripting Toolkit, 11
Insight Control server deployment, 11
PINT and PISA, 11
requirements
Linux source server, 24
Windows source server, 24
resizing Linux file systems, 19
restarting a migration agent, 29
source server
deploying Windows Source Agent, 26
description, 13
dual-boot, 18
fails with the Microsoft Hyper-V role enabled, 53
identification fails, 51
Linux requirements, 24
migration hangs, 60
NTFS partitions, 18
prerequisites, 35
Source Agent fails to launch when rebooting in
migration agent mode, 63
unrecoverable sector-read errors on hard drive not
supported and fail a P2P migration, 62
unrecoverable sector-read errors on hard drive not
supported and fail a P2V migration, 62
Windows requirements, 24
source server operating system support, 17
SPP
installing Windows after migration, 44
installing Windows before migration, 21
status / logs
overview, 14
viewing migration logs, 47
stopping a migration agent, 29
storage controllers display as unknown, 57
support
how to contact HP, 73
warranty information, 73
system requirements
application station, 17
Systems Insight Manager
launching server migrations, 40
T
troubleshooting, 49
destination preparation, 54
migration process, 59
postmigration, 65
source preparation, 51
user interface, 49
types of migration, 11
typographic conventions, 73, 75
S
SAN migration, 39
schedule preparation, 18
server
unresponsive during PSP installation, 70
server thread error, 59
SIM
documentation, 74
Source Agent
detecting, stopping, or restarting, 29
Source Agents
choosing, 25
deploying, 25
source preparation
troubleshooting, 51
86 Index
U
Unable to detect HP FlexFabric 10Gb 2-port 554FLR-SFP+
Adapter configured as iSCSI disk in step 5 of migration
wizard, 64
unable to download the log files
when using IE 9, 71
uninstalling guest tools, 25
unsupported servers
warning message is not displayed, 58
upgrading server migration software, 11
user interface
troubleshooting, 49
V
V2P, 11
Page 87

source server prerequisites, 35
V2V, 11
booting a virtual destination server, 33
source server prerequisites, 35
using the migration wizard, 33
validating the migration, 47
verifying licenses, 20
virtual machine
kernel panic when booting, 54
mouse does not work, 55
Virtual-to-ProLiant migration see V2P
Virtual-to-Virtual migration see V2V
W
websites
HP documentation, 74
ProLiant Support Pack (PSP), 74
Windows
destination physical server prerequisites, 37
destination virtual machine prerequisites, 37
installing PSP after migration, 44
installing PSP before migration, 21
installing SPP after migration, 44
installing SPP before migration, 21
P2P postmigration tasks, 44
preparing for a server migration, 36
SAN migration, 39
source physical server prerequisites, 36
source virtual machine prerequisites, 37
unrecoverable sector-read errors, 62
USB mouse or keyboard do not work, 66
X2V postmigration tasks, 45
Windows server migration PINT fails with General failure
occurred error, 64
X
X2V
postmigration tasks, 45
Y
yellow bang (!) appears on NIC adapter, 69
87
 Loading...
Loading...