Page 1

For FANUC Series 30*-MODEL A
For FANUC Series 30*-MODEL A
For FANUC Series 30*-MODEL AFor FANUC Series 30*-MODEL A
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
B-66264EN/01
Page 2
• No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form.
• All specifications and designs are subject to change without notice.
The export of this product is subject to the authorization of the government of the country
from where the product is exported.
In this manual we have tried as much as possible to describe all the various matters.
However, we cannot describe all the matters which must not be done, or which cannot be
done, because there are so many possibilities.
Therefore, matters which are not especially described as possible in this manual should be
regarded as ”impossible”.
This manual contains the program names or device names of other companies, some of
which are registered trademarks of respective owners. However, these names are not
followed by or in the main body.
Page 3

B-66264EN/01 DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE
This manual includes safety precautions for protecting the user and
preventing damage to the machine. Precautions are classified into
Warning and Caution according to their bearing on safety. Also,
supplementary information is described as a Note. Read the Warning,
Caution, and Note thoroughly before attempting to use the machine.
WARNING
Applied when there is a danger of the user being
injured or when there is a danger of both the user
being injured and the equipment being damaged if
the approved procedure is not observed.
CAUTION
Applied when there is a danger of the equipment
being damaged, if the approved procedure is not
observed.
NOTE
The Note is used to indicate supplementary
information other than Warning and Caution.
• Read this manual carefully, and store it in a safe place.
s-1
Page 4

Page 5

B-66264EN/01 PREFACE
PREFACE
This manual describes the models indicated in the table below.
For descriptions about the FANUC Series 0, 15, 16, 18, 20, and 21,
refer to "FANUC MACRO COMPILER Programming Manual" (B66102E).
In the text, the abbreviations indicated below may be used.
Model name Abbreviation
FANUC Series 30i-MODEL A 30i -A Series 30i
FANUC Series 300i-MODEL A 300i-A Series 300i
FANUC Series 300is-MODEL A 300is-A Series 300is
This software can run on Microsoft Windows. This manual does
not describe the basic operation procedures for Windows. It does not
explain editors either.
Other companies' products mentioned in the manual
* Microsoft, Windows, and MS-DOS are the registered trademarks
of Microsoft Corp.
The other product names mentioned in the manual are the trademarks
or registered trademarks of the respective owners.
p-1
Page 6

Page 7

B-66264EN/01 TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE................................ s-1
PREFACE.................................................................................................. s-1
1 GENERAL ..............................................................................................1
1.1 FEATURES....................................................................................................2
1.2 OVERVIEW ...................................................................................................3
2 EQUIPMENT CONFIGURATION ...........................................................5
3 SYSTEM INSTALLATION (SETUP).......................................................6
3.1 INSTALLING THE FANUC MACRO COMPILER (FOR Series 30i)
SYSTEM ........................................................................................................7
3.2 INSTALLING THE FANUC MACRO LIBRARY (FOR Series 30i)..................9
3.3 PATH SETTING.............................................................................................9
3.4 COMPILER SERIES ....................................................................................10
4 FUNCTIONS.........................................................................................11
4.1 Macro Compiler (MCOMP30I)......................................................................12
4.2 MACRO LINKER (MLINK30I) ......................................................................16
4.3 CONVERSION TO A MEMORY CARD FORMAT (MCARD30I)..................20
5 SYMBOLIC MACRO PROGRAM.........................................................22
6 SYMBOL DEFINITION FILE ................................................................29
7 HOW TO VIEW REFERENCE LIST/ COMPILE LIST ..........................30
APPENDIX
A SYMBOL DEFINITION .........................................................................33
B COMPILE ERROR CODE TABLE .......................................................49
C COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE..................................................................52
D BOOT SYSTEM ...................................................................................78
D.1 OVERVIEW .................................................................................................79
D.1.1 Displaying the Power ON Sequence ..................................................................... 80
D.1.2 Starting the Boot System ....................................................................................... 81
D.1.3 System Files and User Files................................................................................... 81
D.2 SCREEN CONFIGURATION AND OPERATING PROCEDURE ................82
D.2.1 USER DATA LOADING/SYSTEM DATA LOADING Screen.......................... 83
c-1
Page 8

TABLE OF CONTENTS B-66264EN/01
D.2.2 SYSTEM DATA CHECK Screen......................................................................... 85
D.2.3 SYSTEM DATA DELETE Screen ....................................................................... 88
D.2.4 SYSTEM DATA SAVE Screen............................................................................ 90
D.2.5 SRAM DATA BACKUP Screen........................................................................... 92
D.2.6 MEMORY CARD FORMAT Screen.................................................................... 95
D.2.7 LOAD BASIC SYSTEM....................................................................................... 96
D.3 ERROR MESSAGES AND REQUIRED ACTIONS .....................................97
E PARAMETERS.....................................................................................99
E.1 COMPILE PARAMERTES .........................................................................100
E.2 EXECUTOR PARAMETERS .....................................................................116
c-2
Page 9

B-66264EN/01 1.GENERAL
1 GENERAL
The FANUC Macro Compiler/Executor function stores programs
created using custom macros (macro programs) in FLASH ROM
(called F-ROM in the following) so that machine tool builders can
implement their own conversational screens.
The FANUC Macro Compiler for
compiler utility to implement the Macro Compiler/Executor function
for Series
market.
This manual describes the procedures ranging to transferring macro
programs to Series
macro compiler utility.
For the syntax rule for creating macro programs, refer to the “FANUC
Series
PROGRAMMING MANUAL (B-63943EN-2).”
30i/300i/300is-A on personal computers available on the
30i/300i/300is-A via the memory card by using the
30i/300i/300is-A Macro Compiler / Macro Executor
FANUC Series 30i-A is a macro
- 1 -
Page 10

1.GENERAL B-66264EN/01
1.1 FEATURES
(1) The symbolic macro compiler function allows macro programs
to be coded in symbolic format, and also allows comments to be
coded.
(2) A program that references macro variables in array format can be
created.
(3) Compile list output makes macro program development,
debugging, and maintenance much easier.
(4) A linker (linkage editing) function is employed which allows
partial compilation and also facilitates the development and
maintenance of macro programs common to several models.
- 2 -
Page 11

B-66264EN/01 1.GENERAL
1.2 Overview
The Macro Compiler/Executor function of FANUC Series
3
30i/300i/300is-A allows Series 30i/300i/300is-A users to develop
their own macro program in a macro language, convert it into the
macro MEM file format with the macro compiler, and execute a
macro program developed by the macro executor function of Series
30i/300i/300is-A. (See the conceptual diagram on the next page.)
The Macro Compiler utility allows the users to develop and compile a
macro program and write it to the macro MEM file by using a
personal computer.
The macro compiler utility enables macro program development,
compilation, and writing to a macro MEM file on a personal
computer.
The macro compiler utility functions are listed below.
(1) Macro compiler
• Symbolic macro program analysis
• Macro program compilation
• Object program output
• Reference list/compile list output
(2) Macro linker
• Linkage editing of specified object programs and macro
executor/compile parameters
• ROM-format file output
• Link list output
(3) Memory card format conversion
• Converting macro programs to a format capable of
accepting write from a memory card
The macro compiler utility is distributed with a 3.5-inch (2HD) floppy
disk.
The utility does not provide functions such as those for editing macro
programs, and saving and restoring programs to and from floppy
disks.
- 3 -
Page 12

1.GENERAL B-66264EN/01
(Obj
)
LINK
Control
file
(xx.LNK)
MLINK30I
Text E d i t or
MACRO
Linker
Program
(Source file)
MCOMP30I
MACRO
Compiler
Program
Macro
(xx.REL)
Macro
file
(F30ia_xx.MEX)
* Create a macro program using an editor. (An editor is
not supplied.)
* The macro program (source file) must be in text format.
* The macro compiler generates an object file. It also
creates reference and compile lists at the same time as
the object file.
* The object file is linked based on a link control file to
generate a ROM-format file. The editor creates the link
control file.
* FANUC supplies a macro library.
Macro
Library
file
(xx.ROM)
ROM
format file
MCARD30I
Memory Card
(xx.MEM)
Memory Card
Reader
/Writer
Memory
Card
* The ROM-format file contains macros in binary form
output by the linker.
* The ROM-format file is converted into the memory card
format, sent to the CNC via the memory card, and
executed on the CNC.
Fig. 1.2 MACRO compiler utility function conceptual diagram
- 4 -
Page 13

B-66264EN/01 2.EQUIPMENT CONFIGURATION
2 EQUIPMENT CONFIGURATION
(1) Personal computer (IBM PC/AT series)
Main memory 640K bytes or more
OS Microsoft Windows95/98/NT/Me/2000/XP
Hard disk
Floppy disk drive 3.5"Floppy Drive. (2HD)
CAUTION
1 The macro compiler utility software is installed on
hard disk. This software occupies a hard disk space
of about 1M bytes. In addition, developed macro
programs and list files/object files generated at
compile time are output as files on hard disk. So the
size of hard disk depends on the macro programs
developed.
2 The macro compiler utility software and macro
executor are distributed with a 3.5-inch (2HD)
floppy disk. A 3.5-inch floppy disk drive is needed to
install the system and executor files.
3 Only IBM PC/AT compatible machines are
supported. NEC PC98 Series are not supported.
About 1M bytes is required for install the system
(Caution 1)
- 5 -
Page 14

3.SYSTEM INSTALLATION (SETUP) B-66264EN/01
3 SYSTEM INSTALLATION (SETUP)
The FANUC Macro Compiler software is distributed with the two
3.5-inch (2HD) floppy disks titled "FANUC Series 30i Macro
Compiler system floppy disk" and "FANUC Series 30i Macro Library
system floppy disk".
To use the software, load the software to the hard disk from the
system floppy disks.
- 6 -
Page 15
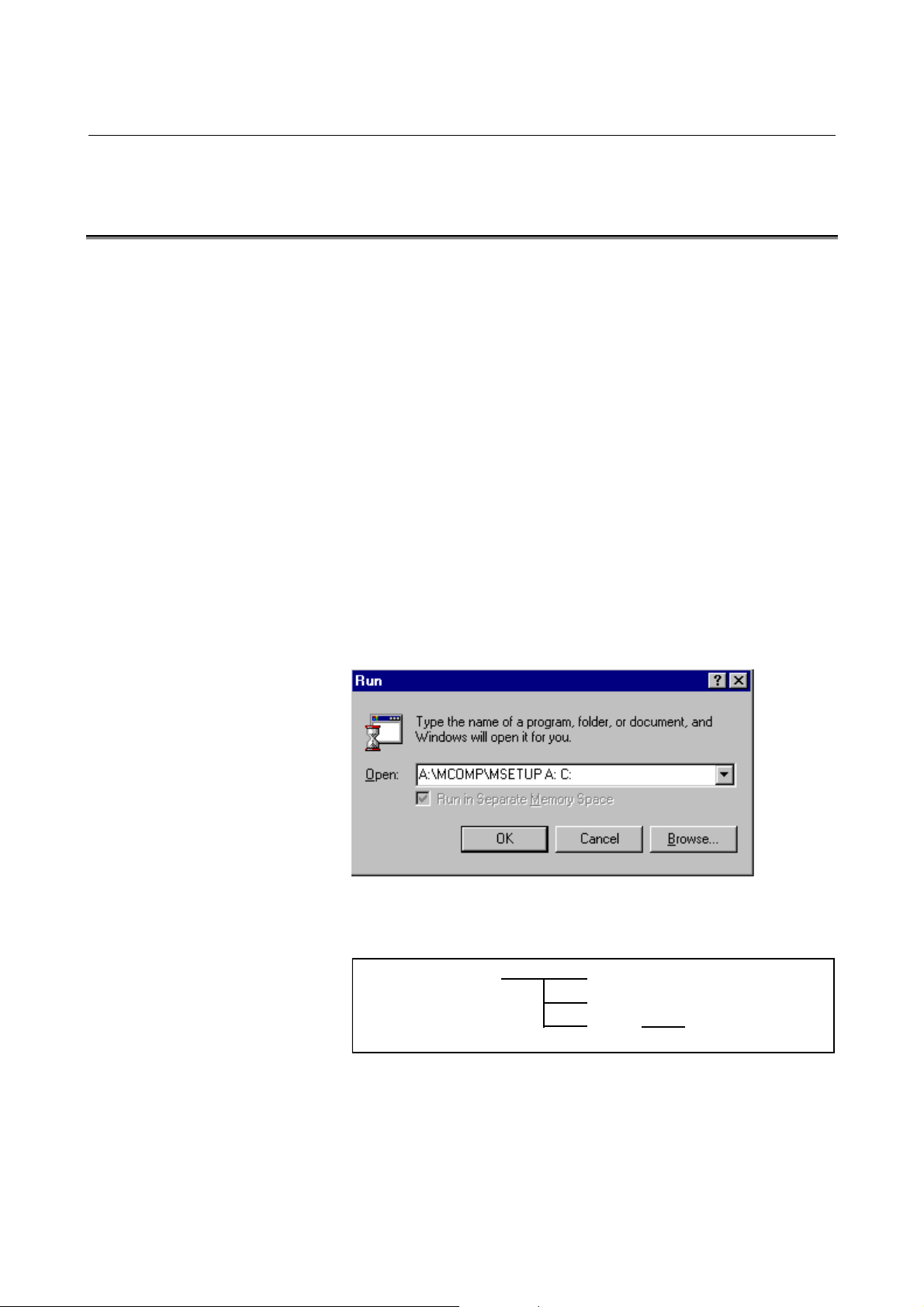
B-66264EN/01 3.SYSTEM INSTALLATION (SETUP)
3.1 INSTALLING THE FANUC MACRO COMPILER (FOR Series
30i) SYSTEM
This section describes how to install the FANUC Macro Compiler
(for
Series 30i) software on the hard disk.
Procedure
Insert the FANUC Series 30i Macro Compiler system floppy disk into
the floppy disk drive, click [Start], and then click [Run].
Enter the following command line in [Open] and then click <OK>.
?:\MCOMP\MSETUP <in> <out>
? : : Name of the drive containing the Macro Compiler system
floppy disk
("MSETUP.BAT" is in the "MCOMP" directory on the
system floppy disk.")
<in> : Specify the name of the drive containing the Macro Compiler
system floppy disk.
<out> : Specify the drive name of the hard disk to hold the system.
Example of installing the Macro Compiler
This example assumes that the system floppy disk is inserted into
drive A: and the system is to be installed on hard disk drive C:.
When the command line above is entered and then executed, the
following directories are created on drive C: and the system software
and sample programs are copied to them.
C:\MCOMP30I
\TOOL
\MEX
\USR
\SAMPL
- 7 -
Page 16
3.SYSTEM INSTALLATION (SETUP) B-66264EN/01
Explanation of the directories
(a) \MCOMP30I\TOOL
FANUC Macro Compiler system software, batch files, document
files, and so forth are stored under this directory.
MCOMP30I.EXE, MLINK30I.EXE, MCARD30I.EXE :
System software
ERROR.DOC : Compilation error code table
SYSTEM.DEF : Symbol definition file in English (for
$INCLUDE)
(b) \MCOMP30I\MEX
Library file is stored under this directory.
This is performed as described in Section 3.2, "INSTALLING
THE FANUC MACRO LIBRARY".
(c) \MCOMP30I\USR
Under this directory, create directories used to develop macro
programs.
C:\MCOMP30I
\ TOOL
\ MEX
\ USR
\ SAMPL
(d) \MCOMP30I\USR\SAMPL
Under this directory, the files including such a link control file,
compiler/link result files, and program files as described in
Appendix C are stored. Use these files as reference information
for development.
- 8 -
Page 17
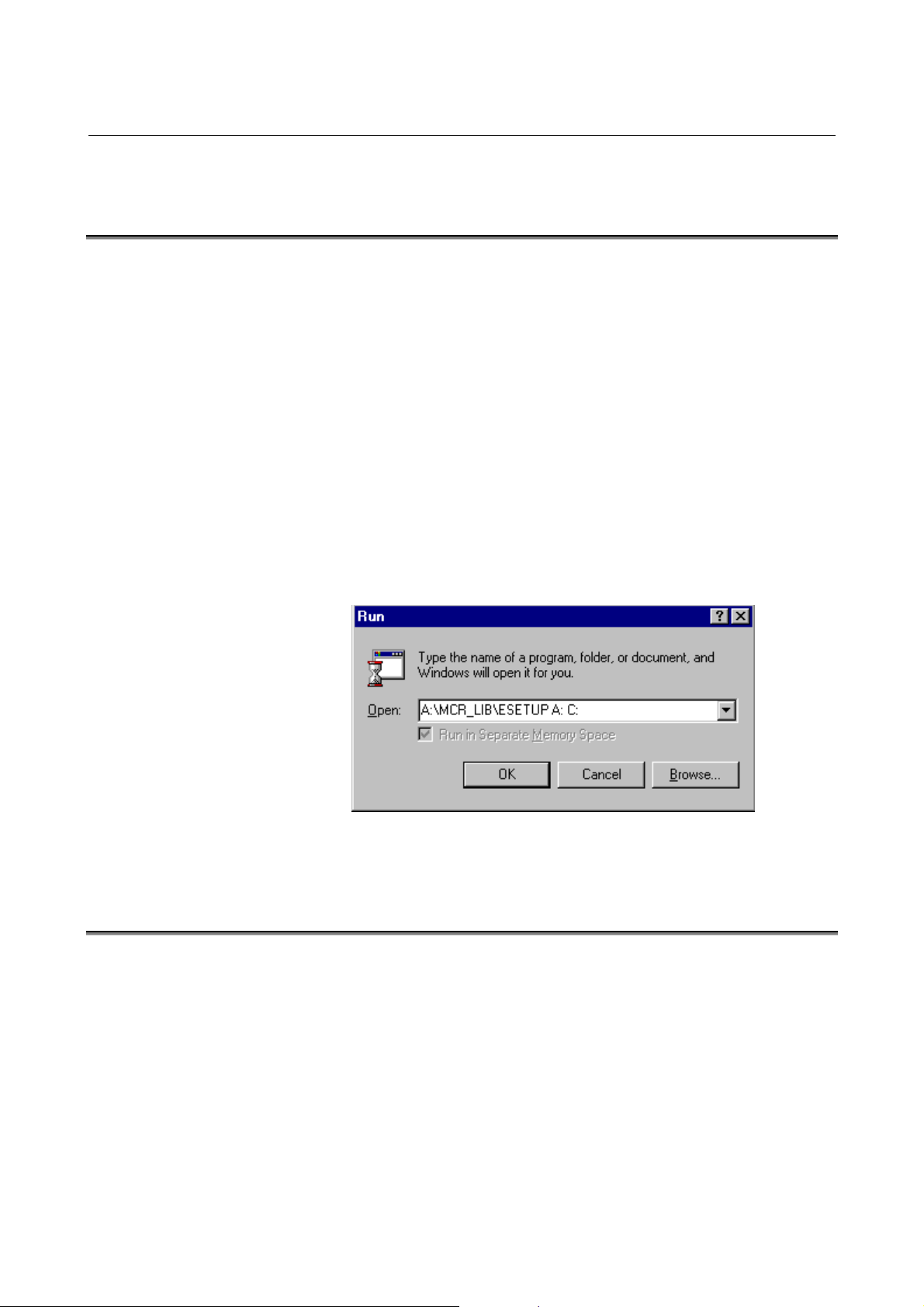
B-66264EN/01 3.SYSTEM INSTALLATION (SETUP)
3.2 INSTALLING THE FANUC MACRO LIBRARY (FOR Series
30i)
This operation loads the executor file under the library directory of
the FANUC Macro Compiler installed by the operation of Section
3.1.
Insert FANUC Macro Library system floppy disk for Series 30i into
the floppy disk drive, click [Start], and then click [Run].
Enter the following command line in [Open] and then click <OK>.
?:\MCR_LIB\ESETUP <in> <out>
? : : Name of the drive containing the Macro Library system
floppy disk.
("ESETUP.BAT" is in the "MCR_LIB" directory on the
system floppy disk.")
<in> : Specify the name of the drive containing the Macro Library
system floppy disk.
<out> : Specify the drive name of the hard disk holding the system.
Example of installing the Macro Library
Enter the command line above and then click <OK> to store the
library files in C:\Mcomp30I\Mex.
3.3 PATH SETTING
All system software is stored in the \MCOMP30I\TOOL directory.
So the PATH setting must be made from System in Control Panel.
- 9 -
Page 18
3.SYSTEM INSTALLATION (SETUP) B-66264EN/01
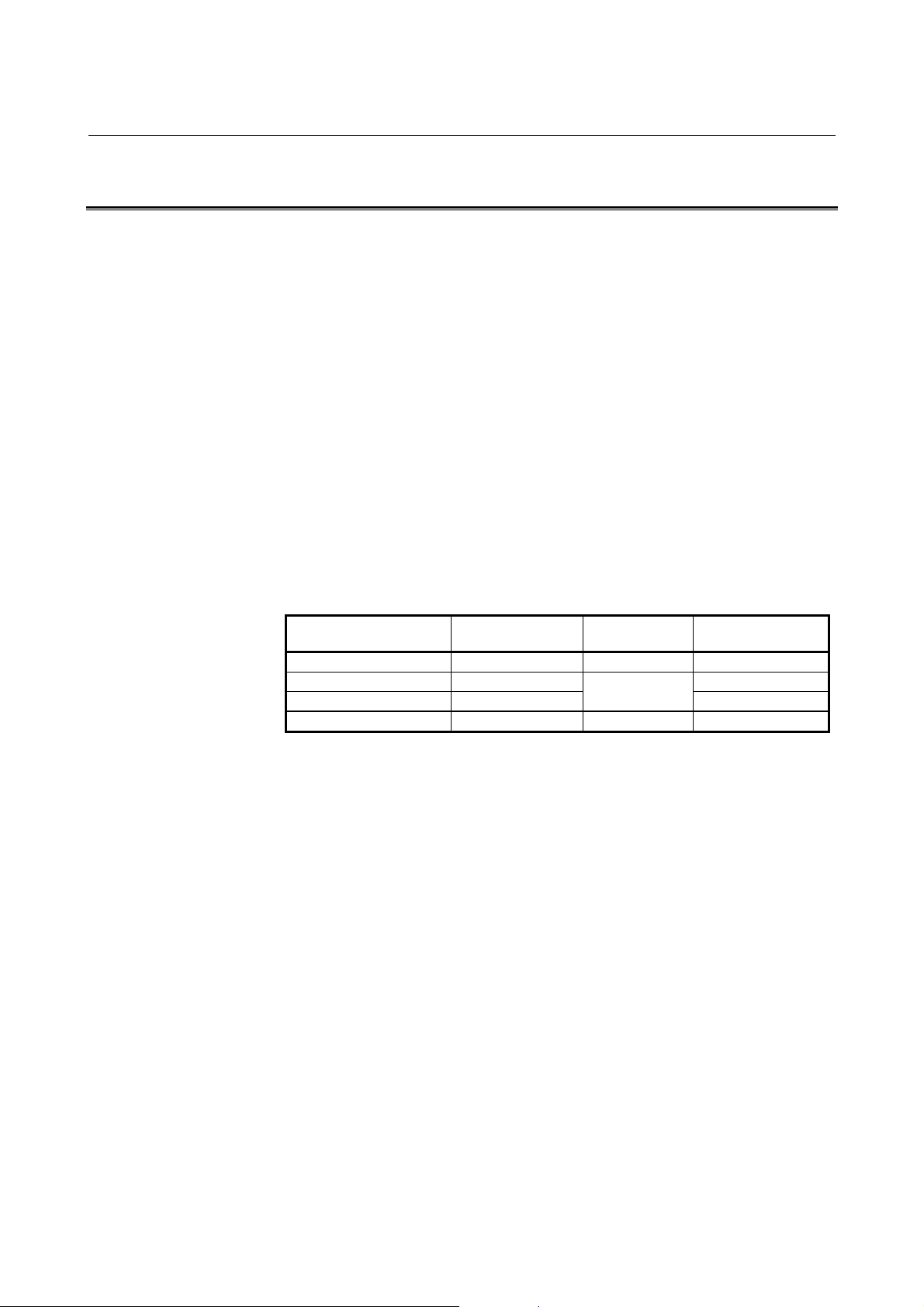
3.4 COMPILER SERIES
There are four types of FANUC Macro Compiler systems. One type is
for
FANUC Series 30i. The other three types are provided for the
systems shown below.
<1> For FANUC Series 0/Series 16/Series 18/Series 20/Series 21
<2> FANUC Series 15-A/15-B
<3> FANUC Series 15i-A
These Compiler systems are for the respective series only. Compiling
the same macro program using these compiler systems generates
different object codes. For this reason, be sure to use the execution
files (macro compiler/linker/memory card converter) and library files
suitable to the development model.
If multiple systems are to be installed on the same personal computer,
it is recommended that a separate directory be used for each CNC
series.
For the FANUC Macro Compiler system for FANUC Series
0/15/16/18/20/21, see the FANUC MACRO COMPILER
PROGRAMMING MANUAL (B-66102E).
CNC series Macro compiler Macro linker
30i
0/16/18/20/21
15-A/15-B
15i-A
MCOMP30I MLINK30I MCARD30I
MCOMP0 MMCARD
MCOMP15
MCOMP15I MLINK15I MCARD15I
* This manual provides information only on Series 30i.
MLINK
Memory card
format converter
MMCARD15
- 10 -
Page 19

B-66264EN/01 4.FUNCTIONS
4 FUNCTIONS
- 11 -
Page 20
4.FUNCTIONS B-66264EN/01
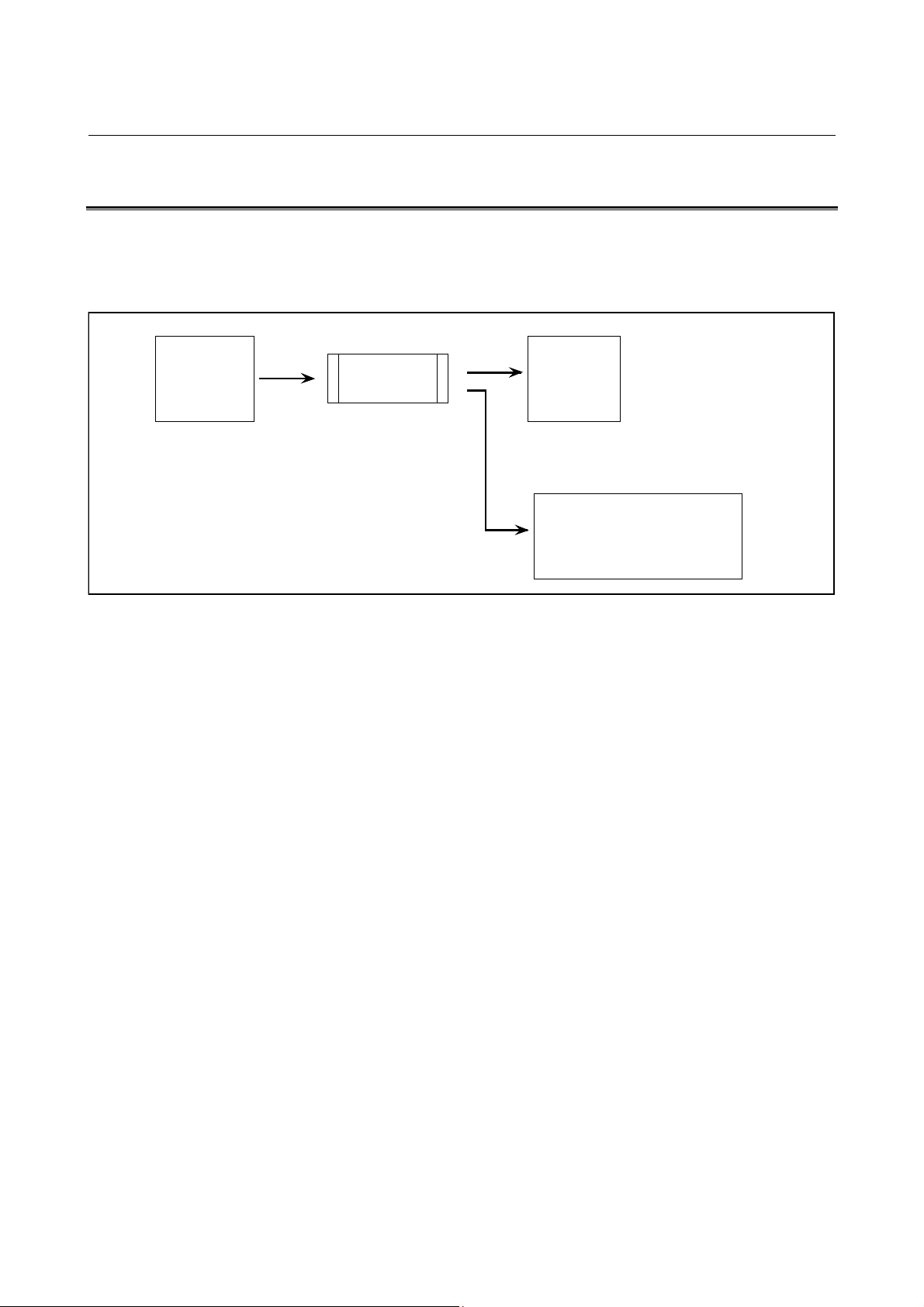
4.1 MACRO COMPILER (MCOMP30I)
The Macro Compiler can compile macro programs created in the text
file format. The Macro Compiler outputs an object file for the macro
linker, reference list file, and compile list file.
Source Fi le
Macro
(xx.SRC)
Procedure
Program
Ob ject Fi le
Object
MCOMP30I
Program
(xx.REL)
Reference List File(xx.REF)
Compile List File (xx.LST)
MACRO COMPILER
1 O0001;
2 #100=#101+10;
Any of the following methods can be selected, but this manual uses
method (2) for description.
(1) Click [Start] and then click [Run].
Enter the following command line in [Open] and then click
<OK>.
MCOMP30I file-spec [parameters]
(2) Click [Start], click [Programs], and then click [Command
Prompt]. Execute the command by entering it at the DOS
prompt.
Change the current directory to the folder in which the source
program is stored by using the CD command, and then execute
the following command line.
C:\xxxxx\xxxxx> MCOMP30I file-spec [parameters]
(xxxxx\xxxxx: Current directory)
* The following descriptions assume the source program to be
compiled is stored in C:\.
*1 file-spec
This specifies a macro program source file. The extension of a
source file name must be .SRC. Source files to be compiled can
be specified in three ways:
(1) Compilation of a single file
C:\> MCOMP30I ABC Þ Compiles ABC.SRC.
(2) Compilation of multiple cards by using a wild card
C:\> MCOMP30I ABC*
Þ Compiles all files whose names start
with ABC and have the
extension .SRC.
- 12 -
Page 21

B-66264EN/01 4.FUNCTIONS
r
(3) Selective compilation according to link control file
specification
C:\> MCOMP30I @ABC
Þ Compiles all files specified in the
link control file (file name:
ABC.LNK). (For details on the link
control file, see Section 4.2,
"MACRO LINKER".)
CAUTION
As described in Section 3.4, even if the same macro
program is compiled, the Macro Compiler for Series
30i creates an object file different from an object file
created by the Macro Compiler for Series
0/15/16/18/20/21. Select the compiler that matches a
development model.
*2 [parameters]
This specifies compile conditions.
-NR : Outputs no object file. If this parameter is omitted, an
object file with the extension .REL is output.
-L2 : Outputs no reference list file. If this parameter is omitted,
a reference list file with the extension .REF is output.
-L3 : Outputs a macro program file. If this parameter is omitted,
no macro program file is output. A macro program file is
output with the extension .PRG.
-PR : Makes no symbolic macro program analysis. Specify this
parameter when a program coded in standard macro
program format is to be compiled. No reference list file is
output. Even if this parameter is not specified, a macro
program can be compiled without trouble. However, this
parameter can save time required to make a symbolic
macro program analysis and can also save space for
reference list file output.
-Fo : Specifies a destination to which an
object file is output.
-Fr : Specifies a destination to which a
reference list file is output.
-Fl : Specifies a destination to which a
compile list file is output.
-Fp : Specifies a destination to which a
macro program file is output.
See "Specifying
the destinations to
which the compile
outputs files"
given later.
- 13 -
Page 22

4.FUNCTIONS B-66264EN/01
Macro program source file
A macro program source file must be created in text file.
The Macro Compiler can compile a macro program coded in symbolic
format.
For detailed information, see Chapter 5.
The Macro Compiler can also compile a program coded in standard
macro program format. In this case, specify the command parameter PR. This parameter can save time required to make a symbolic macro
program analysis and can also save space for reference list file output.
NOTE
Be sure to use .SRC as the extension of a file name.
Object file
An object file output by the compiler is subject to processing by the
macro linker. The name of an object file is the same as the source file
name, except that the extension .REL is assigned to the object file.
Reference list file
The reference list file is a list file output from macro program analysis
processing. A source program, errors, error codes, symbol name cross
reference information are listed. The name of a reference list file is
the same as the source file name, except that the extension .REF is
assigned to the reference list file.
Compile list file
A compile list file is output as a result of macro program compilation
after symbolic macro program analysis. A source program, errors,
error codes, variable cross reference information, object file size
information, and so forth are listed. The name of a compile list file is
the same as the source file name, except that the extension .LST is
assigned to the compile list file.
Macro program file
By specifying the command parameter -L3, a macro program after
symbolic macro program analysis processing can be preserved as a
file. The name of a macro program file is the same as the source file
name, except that the extension .PRG is assigned to the macro
program file.
Specifying the destinations to which the compiler outputs files
The directory of the destinations to which the compiler outputs files
can be specified as desired according to compiling conditions.
-Fo : Specifies a destination to which an object file is output.
-Fr : Specifies a destination to which a reference list file is
output.
-Fl : Specifies a destination to which a compile list file is
output.
-Fp : Specifies a destination to which a macro program file is
output.
- 14 -
Page 23

B-66264EN/01 4.FUNCTIONS
Execution example
C:\> CD MCOMP30I\USR\SAMPL
→ Change the current directory to the folder in which the source
program is stored.
C:\MCOMP30I\USR\SAMPL>MCOMP30I *.SRC
→ Compile all .SRC files.
Execution result
(The result is output to the current directory because no destination is
specified.)
When the following command line is executed, the object file is
output to C:\MCOMP30I\USR\OBJ and the compile list file to
C:\MCOMP30I\USR\LST.
MCOMP30I *.SRC -FoC:\MCOMP30I\USR\OBJ -FlC:\MCOMP30I\USR\LST
- 15 -
Page 24
4.FUNCTIONS B-66264EN/01
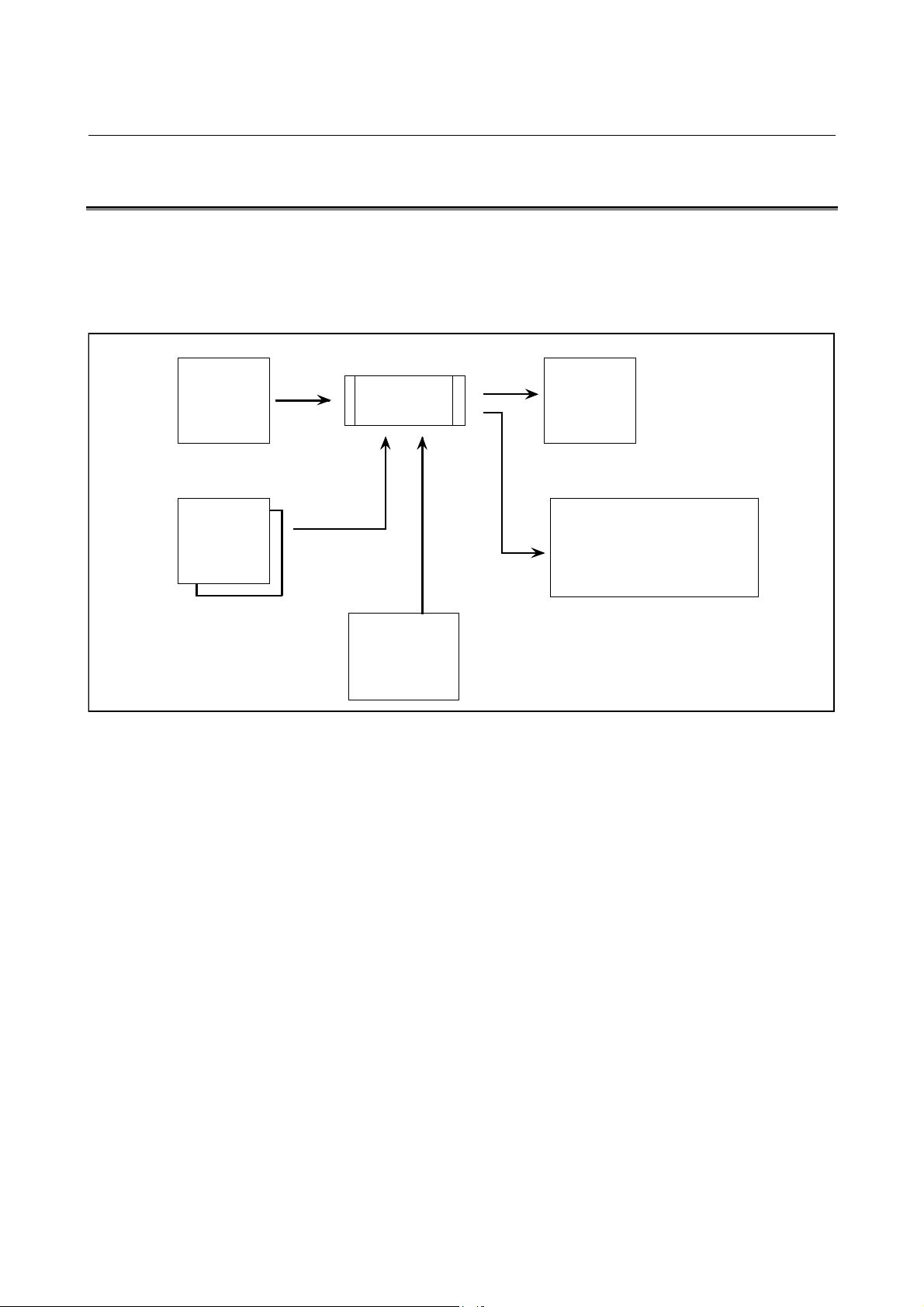
4.2 MACRO LINKER (MLINK30I)
According to the specification in the link control file created
beforehand, the macro linker links the object file and library file
compiled by the Macro Compiler and creates a ROM-format file and
link list file.
Link control File ROM Format File
Procedure
Link
Control
(xx.LNK)
Objec t File
Object
Program
(xx.REL)
ROM
MLINK30I
Macro
Library
file
(F30IA_XX.MEX)
File
(xx.ROM)
Link List File(xx.MAP)
MACRO LINKER
prog. Size.
1 O0001 00100H
2 O0002 00200H
Any of the following methods can be selected, but this manual uses
method (2) for description.
(1) Click [Start] and then click [Run].
Enter the following command line in [Open] and then click
<OK>.
MLINK30I file-spec [parameters]
(2) Click [Start], click [Programs], and then click [Command
Prompt]. Execute the command by entering it at the DOS
prompt.
Change the current directory to the folder in which the object file
is stored by using the CD command, and then execute the
following command line.
C:\xxxxx\xxxxx> MLINK30I file-spec [parameters]
(xxxxx\xxxxx: Current directory)
* The following descriptions assume the object file is stored in C:\.
*1 file-spec
This specifies a link control file created in a specified format
beforehand.
- 16 -
Page 25

B-66264EN/01 4.FUNCTIONS
*2 [parameters]
This specifies link conditions.
-NR : Outputs no ROM-format file. If this parameter is omitted,
a ROM-format file with the extension .ROM is output.
-NL : Outputs no link list file. If this parameter is omitted, a
link list file with the extension .MAP is output.
-Fm : Specifies the destination to which a link list file is output.
See the subsection describing specification of the
destination.
-Fr : Specifies the destination to which a ROM-format file is
output
Link control file
The link control file specifies a library file name, compile
parameters, and object file names subject to linkage. As with a source
file, a link control file must be created in text file.
In a link control file, a library file name, compile parameters, and
object file names subject to linkage are defined using keywords. A
comment line can be provided by using /*.
The link control file is also used as the control file for selective
compilation of the Macro Compiler. (See (3) "Selective compilation
according to link control file specification" in "Procedure" in Section
4.1, "Macro Compiler".) This function is useful when all programs to
be linked are compiled.
CNC = : CNC library file name. F30iA_??.MEX for Series
30i (??: version number)
P9999 = : Compile parameters (No.9000 to 9199)
FILE = : Object file name
(Multiple object files can be specified with each
name delimited by a comma.)
P-CODE_NUMBER=: P-CODE number (01 to system
maximum path number)
A P-CODE numbers is specified when
multiple P-CODEs are loaded.
NOTE
1 Be sure to use .LNK as the extension of the link
control file.
2 The number of P-CODEs that can be loaded in the
CNC must be equal to or less than the maximum
path number. A P-CODE number must be equal to or
less than the maximum path number.
3 When P-CODE_NUMBER is not specified, the
following error occurs.
“ERROR : Can not find SYSTEM define “
- 17 -
Page 26

4.FUNCTIONS B-66264EN/01
Sample link control file
/*
/* MACRO COMPILER UTILITY LINK FILE (SAMPLE)
/*
/* FOR F30I-A
CNC=\MCOMP30I\MEX\F30iA_01.MEX
P-CODE_NUMBER=01
/* Compile Parameter
P9000=00010000 /* P-CODE Size 1MB
P9010=100 /* M-Code Sub call O9001
P9038=8000 /* Conversational Macro program
/* Execution-Macro program
FILE=FRANGE_MAIN,FRANGE_SUB1,FRANGE_SUB2,FRANGE_SUB3
FILE=SHAFT1,SHAFT2
/* Conversational- Macro program
FILE=SCREEN
The example above is for P-CODE file 1. The compile parameters
(Nos. 9000, 9010, and 9038) are set and the object files
(FRANGE_MAIN.REL, FRANGE_SUB1.REL,
FRANGE_SUB2.REL, FRANGE_SUB3.REL, SHAFT1.REL,
SHAFT2.REL, and SCREEN.REL) are linked.
The specification of 0 is assumed for those compile parameters that
are not specified in the link control file.
Link list file
The link list file is output by the linker, and a library name, compile
parameters, compile program list and size information, erroneous
program numbers, error codes, ROM-format file size information and
so forth are listed.
The name of a link list file is the same as the link control file name,
except that the extension .MAP is assigned to the link list file name.
Specifying the destinations to which the macro linker outputs files
The directory of the destinations to which the macro linker outputs
files can be specified as desired according to linking conditions.
-Fm : Specifies a destination to which a link list file is output.
-Fr : Specifies a destination to which a ROM-format file is output.
Example
Assume that the object file is stored in C:\MCOMP30I\TEST.
Executing
C:\MCOMP30I\TEST >MLINK30I SAMPL –FmMAP –FrD:\MCOMP\LNK
generates SAMPL.MAP in C:\MCOMP30I\TEST \MAP and
SAMPL.ROM in D:\MCOMP\LNK.
- 18 -
Page 27

B-66264EN/01 4.FUNCTIONS
Checking the size of ROM format file at linking macro
A ROM format file that is created by linking is checked for its size
whether it is overflown or not. The size of ROM format file is set by
compile parameter Nos. 9000 and 9001.
If a prepared ROM format file may exceed the size that was set by
compile parameter Nos. 9000 and 9001 as a result of linking, an
following error is produced when the macro linker is executed.
ERROR : ROM size over
Bit No.
No. #7#6#5#4#3#2#1#0
Compile parameter
9000 M3MB M2MB M1MB M512 M256
Compile parameter
Execution example
9001 M4MB
M4MB M3MB M2MB M1MB M512 M256
4.0MB100000
3.0MB010000
2.0MB001000
1.0MB000100
512KB 0 0 0 0 1 0
256KB 0 0 0 0 0 1
C:\> CD MCOMP30I\USR\SAMPL
→ Change the current directory to the folder in which the object file
is stored.
C:\MCOMP30I\USR\SAMPL>MLINK30I SAMPL
Execution result
(The output file is output to the current directory because no
destination is specified.)
- 19 -
Page 28

4.FUNCTIONS B-66264EN/01
4.3 CONVERSION TO A MEMORY CARD FORMAT
(MCARD30I)
Convert a ROM-format file created by the macro linker (MLINK30I)
to the memory-card format file (MEM format file) which can be
loaded from the memory card using the boot function.
Source File
Object File
Macro
Program
(xxx.SRC)
Link Control File
Link
Control
(xxx.LNK)
Macro Library File
Macro
Library
(F30IA_XX.MEX)
MCOMP30I
Memory Card
Object
Program
(xxx.REL)
MLINK30I
To memory card
COPY C:xxx.MEM F:
(F: Memory card device number)
ROM File
(xxx.ROM)
MCARD30I
Memory Card File
Memory
Card File
(xxx.MEM)
Procedure
Any of the following methods can be selected, but this manual uses
method (2) for description.
(1) Click [Start] and then click [Run].
Enter the following command line in [Open] and then click
<OK>.
MCARD30I file-spec [parameters]
(2) Click [Start], click [Programs], and then click [Command
Prompt]. Execute the command by entering it at the DOS
prompt.
Change the current directory to the folder in which the source
program is stored by using the CD command, and then execute
the following command line.
C:\> MCARD30I file-spec
*1 file- spec
Specify the name of a ROM-format file to be converted without
using an extension. A MEM format file having the same name as
the ROM-format file and the extension .MEM is created.
- 20 -
Page 29

B-66264EN/01 4.FUNCTIONS
Execution example
C:\> CD MCOMP30I\USR\SAMPL
→ Change the current directory to the folder in which the object file
is stored.
C:\MCOMP30I\USR\SAMPL>MCARD30I SAMPL
Execution result
- 21 -
Page 30

5.SYMBOLIC MACRO PROGRAM B-66264EN/01
5 SYMBOLIC MACRO PROGRAM
Format
A macro program is to be created according the rule described below.
(1) A macro program must start with address O. Address % must be
specified at the end of the file. Multiple programs can be coded
in a single file. At this time, the start of each program can be
identified by address O. Data after address %, if any, is ignored.
When multiple programs are coded, address % must be coded at
the end.
O0001 #101=1;
G00 X#101;
:
O0002 G243 X0 Y0 (ABS);
#500=#501+#502;
:
%
(2) One line can contain only one block. The end of block (EOB) is
represented by a semicolon (;). All data after a semicolon on a
line is regarded as a comment.
#100=#101; COMMENT
G00 X123. Y234. ; G01; → "G01 ;" after ; is regarded as
comment.
(3) All data after /* is regarded as a comment. A line starting with /*
is regarded as a comment line; such a line is not compiled.
/* comment → Compiler ignores this line as comment line.
/* comment
/*
O0001 ;
/* comment → Compiler ignores this line as comment line.
G00 ...;
;/* comment → Blank block containing only ; is created.
M99;
%
- 22 -
Page 31

B-66264EN/01 5.SYMBOLIC MACRO PROGRAM
Programming using symbolic names
A symbolic name can be defined for a variable, expression, or
character string to allow programming using symbolic names. A
symbolic name can be defined as described below.
- Symbolic name definition
@xxxx yyyyyy
xxxx : Symbolic name
String of alphanumeric characters beginning with an
alphabetic character
Maximum 32 characters
yyyyyy : Definition character string
Maximum 80 characters
After a symbolic name is defined, the symbolic name used in a
program is replaced by the corresponding definition character string.
Example
/* SYMBOL DEFINE
@COUNT1 #100
@ON=1
@OFF =0
@CURSOR #8505
@RETURN M99
/*
Program
O0001 ;
CURSOR ON ;
COUNT1 = COUNT1+1 ;
RETURN ;
Meaning
#8505 =1 ;
→
#100 = #100+1 ;
- Symbolic name for sequence number
A symbolic name can be assigned to a sequence number as described
below. In above Item, a symbolic name is just used for a definition
character string. On the other hand, a symbolic name for a sequence
number is regarded as a sequence number when it is coded at the start
of a block, and is regarded as a jump (GOTO) destination number
when it is coded at a position other than the start of a block.
Definition of symbolic name for sequence number
>xxxx 9999
xxxx : Symbolic name for sequence number
String of alphanumeric characters beginning with an
alphabetic character
Maximum 32 characters
9999 : Number
After a symbolic name is defined, the symbolic name used in a
program is replaced by the corresponding sequence number.
- 23 -
Page 32

5.SYMBOLIC MACRO PROGRAM B-66264EN/01
Example
/* SYMBOL DEFINE
@COUNT1 #100
>JUMP1 100
>SKIP 200
/*
Program
Meaning
O0002 ;
GOTO JUMP1 ;
IF[COUNT1 LE 0]GOTO SKIP ;
SKIP ;
JUMP1 M99 ;
GOTO 100 ;
→
IF[#100 LE 0]GOTO 200 ;
N200 ;
N100 M99 ;
- Automatic conversion of hiragana and kanji codes
(Hiragana and kanji, when coded in quotation marks and parentheses
as ('
Compiler codes by coding.‘’)
(‘
Kanji and hiragana must be coded using full-size characters, and
alphanumeric characters, spaces, special symbols must be coded using
half-size characters.
'), can be auto-matically converted to internal Macro
’) % (*3929 3671 3872 3439 2437 245E 2439*)
- Reference to external file ($INCLUDE control statement)
By using the $INCLUDE control statement, a program, symbol
definition, and so forth contained in a separate file can be referenced.
With this function, definitions and processing common to multiple
programs can be specified in a separate file so that each program file
can reference those definitions and processing.
Example
- Program file
/*
INCLUDE \MCOMP30I\TOOL\SYSTEM.DEF
/*
Program
Meaning
O0003 ;
CMACRO1 =5 ;
RETURN ;
→
#8500 =5 ;
M99 ;
- Include file (\MCOMP30I\TOOL\SYSTEM.DEF)
@CMACRO1 #8500 /* Conversation MACRO - 1 MAIN
@RETURN M99 /* Return to main program.
- 24 -
Page 33
B-66264EN/01 5.SYMBOLIC MACRO PROGRAM
- Array variable coding
Variables can be used as a one-dimensional array by using a simple
coding method.
Coding method
#999 <expression>
999 : Number of first variable in array
By this coding method, variables can be referenced or written to as
array data with an index indicated by the expression and starting with
the variable specified in 999.
Example
#100<#101> is equivalent to #[100+#101].
- Reference list page eject control ($EJECT control statement)
By using the $EJECT control statement, reference list page eject
operation can be freely controlled.
Example
Program file
/*
$EJECT
/* → Advances reference list page.
O0003 ;
:
- Determination of an operation result
Only an operation expression can be specified as the condition of the
IF or WHILE statement. The execution of the IF or WHILE statement
is controlled depending on whether the operation result is equal to 0.
Format :
Example
The left macro instructions are equivalent to the right macro
instructions.
WHILE [#100] DO1 → WHILE [ #100 NE O ] DO1 ;
: :
END1 ; END1 ;
IF [#100+#101] GOTO123; → IF [[#100+#101] NE 0] GOTO123;
IF [SIN[#1]] THEN #1=0 ; → IF [SIN[#1] NE 0] THEN #1=0 ;
WHILE[operation-expression] DOx ;
ENDx ;
IF[operation-expression] GOTO xxx ;
IF[operation-expression] THEN <Macro statement> ;
- 25 -
Page 34

5.SYMBOLIC MACRO PROGRAM B-66264EN/01
- Logical operations, AND and OR
Multiple conditions can be specified in an IF statement. The
conditions ANDed or ORed control the execution of the IF statement.
Format :
IF[<condition> && <condition>] GOTO xxx ;
IF[<condition> || <condition>] THEN <MACRO statement> ;
An AND is represented with an && sign and OR with an || sign. Up to
three ANDs or ORs can be specified in a single IF statement.
However, an AND and OR must not be specified together in a single
IF statement.
IF[<condition>&&<condition>&&<condition>&&<condition>]THEN <MACRO stmnt>; → OK
IF[<condition> || <condition> || <condition> || <condition>] GOTO xxx; → OK
IF[<condition> && <condition> || <condition>] GOTO xxx; → NG
Example
IF[#100 EQ 1 && #101 GT 0] GOTO 100 ;
IF[#100 EQ 1 || #101 NE 1 || #102 GT 10] THEN #102=1 ;
- IF/THEN/ELSE/ENDIF
The syntax of an IF statement has been enhanced. Structured
programming is possible using IF/THEN/ELSE/ENDIF.
The following shows the formats of syntactically valid IF statements.
(1) IF [...] GOTO 999 ;
(2) IF [...] THEN Macro-st ;
(3) IF [...] THEN Macro-st ; * Macro-st
ELSE Macro-st ; Macro statement
(4) IF [...]THEN ; * Statement
Statement ; Macro or NC statement
:
ENDIF ;
(5) IF [...] THEN ;
Statement ;
:
ELSE ;
Statement ;
:
ENDIF ;
(a) When only a single macro statement is to be executed, the macro
statement can be specified immediately after THEN/ELSE as
shown in (2) and (3).
IF[#100 EQ 0] THEN #101 = 1;
ELSE #101 = 2;
- 26 -
Page 35
B-66264EN/01 5.SYMBOLIC MACRO PROGRAM
(b) When an instruction to be executed is an NC statement or
multiple instructions to be executed, the NC statement or
multiple instructions must be specified between the THEN/ELSE
line and ENDIF line as shown in (4) and (5).
IF[#100 EQ 0] THEN ;
G01 X100 Y200 ;
ENDIF ;
When instructions with THEN and ELSE must be executed as
shown in (5), the IF statement can be specified by combining the
formats in (a) and (b).
IF[#100 EQ 0]
THEN #101 = 1;
ELSE ;
#101 = 2 ;
G00 X#103 ;
ENDIF ;
- Up to ten levels of nesting of the IF statement are allowed.
Example
The following is an example of three levels of
nesting, but up to ten levels of nesting are
allowed.
IF[...] THEN ;
IF [...] THEN ;
Statement ;
:
ELSE ;
IF[...] THEN ;
Statement ;
ENDIF ;
ENDIF ;
Statement ;
:
ELSE ;
Statement ;
:
ENDIF ;
3rd
level
2nd
level
1st
level
- 27 -
Page 36
5.SYMBOLIC MACRO PROGRAM B-66264EN/01
CAUTION
When only a single macro statement is to be
executed, the macro statement can be specified
immediately after THEN/ELSE. In this case, no
ENDIF statement is usually required. However, an
ENDIF statement is required when IF [...] THEN
Macro-st ; is specified just before ELSE or ENDIF
of the previous nesting as shown below:
IF[...] THEN ;
IF [...] THEN Macro-st ;
IF [...] THEN Macro-st ;
ENDIF ; ← The ENDIF line is required
ELSE ; because is specified just
before ELSE or ENDIF of
the previous nesting.
IF [...] THEN Macro-st ;
IF [...] THEN Macro-st ;
ENDIF ; ← The ENDIF line is required
ENDIF ; because is specified just
before ELSE or ENDIF of
the previous nesting.
- 28 -
Page 37

B-66264EN/01 6.SYMBOL DEFINITION FILE
6 SYMBOL DEFINITION FILE
When the system is installed, a symbol definition file for Series 30i is
stored under the directory \MCOMP30I\TOOL. For macro program
creation, the user should make full use of the symbolic names defined
in the file for variables.
Symbol definition file for Series 30i
File name: \MCOMP30I\TOOL\SYSTEM.DEF
To use this file, use the external file reference function described in
Item in Chapter 5, “SYMBOLIC MACRO PROGRAM”.
Usage example
$INCLUDE \MCOMP30I\TOOL\SYSTEM.DEF
For details, see Appendix C, “COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE”.
For information about the defined symbols, see Appendix A,
“SYMBOL DEFINITION”.
- 29 -
Page 38

7.HOW TO VIEW REFERENCE LIST/ COMPILE LIST B-66264EN/01
7 HOW TO VIEW REFERENCE LIST/
COMPILE LIST
A source program coded using symbolic macro programs is converted
by the Macro Compiler to a program in custom macro format for
compile processing. The Macro Compiler outputs two types of list
files: one for a reference list, and the other for a compile list.
Since conversion processing is performed, the comment lines and
symbol definition lines in a source program are not listed. For this
reason, a reference list and compile list output two types of line
numbers to identify a compile error in a source program.
(1) Reference list
A source program coded using symbolic macro programs, cross
reference data of used symbols, error messages from conversion
processing, and so forth are output in a reference list.
Line number “S-Line” : Source program line number
“G-Line”: Line number after conversion
(2) Compile list
A program converted to a program in custom macro format, cross
reference data of used variables, compile error messages, and so
forth are output in a compile list.
Line number “G-Line” : Line number after conversion
“P-Line” : Line number for each program number
In the example below, the compile list has an error on G-Line
0002; the same G-Line 0002 in the reference list and the line 4 in
the source program have this error.
(Example)
*Reference list (xxx.REF)
--------------------------Program---------------------------------------------------S-Line G-Line
1 @ABC #100
2/*
3 0001 O1000 ;
4 0002 ABD = 0 ;
5 0003 M99 ;
6 0004 %
*Compile list (xxx.LST)
--------------------------program O1000------------------------------------------G-Line P-Line
0001 1 O1000;
0002 2 ABD=0;
error #140C -----------^
***** ERROR : 140C Illegal function code.
0003 3 M99;
0004 4 %
- 30 -
Page 39

APPENDIX
Page 40

Page 41

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX A.SYMBOL DEFINITION
A SYMBOL DEFINITION
•••• SYSTEM.DEF (ENGLISH) \MCOMP\TOOL\SYSTEM.DEF
$NOLIST
/*
/* ***************************************************
/* * symbol define *
/* * for series 30i (V01.00 2003.04.24) *
/* ***************************************************
/*
/*
/* No.01 Control instruction code.
/* ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
@CALL M98P /* Sub program call.
@RETURN M99 /* Return to main program.
@RETURNP M99P /* Return to main program with sequence No.
/*
@DISPLAY G243 /* Character display.
@FORM F /* Format.
@DATA D /* Data.
@NSUP Z0 /* No Zero suppress.
@ZSUP Z1 /* Zero suppress.
/*
@ELASE G202 /* CRT erase.
@ELASEGR G202P1 /* Graphic erase.
@ELASECH G202P2 /* Charactor erase.
@ELASEAL G202P3 /* Graphic & Character erase.
/*
@RECTNG G204 /* Rectangle display.
/*
@GRPNT G206 /* Graphic paint out.
/*
@COLOR G240 /* Display color select.
@BLACK G240P0 /* Black.
@RED G240P1 /* Red.
@GREEN G240P2 /* Green.
@YELLOW G240P3 /* Yellow.
@BLUE G240P4 /* Blue.
@PERPLE G240P5 /* Perple.
@SKYBL G240P6 /* Sky-blue.
@WHITE G240P7 /* White.
@REDR G240P-1 /* Reverse Red.
@GREENR G240P-2 /* Reverse Green.
@YELLOWR G240P-3 /* Reverse Yellow.
@BLUER G240P-4 /* Reverse Blue.
@PERPLER G240P-5 /* Reverse Perple.
- 33 -
Page 42

A.SYMBOL DEFINITION APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
@SKYBLR G240P-6 /* Reverse Sky-blue.
@WHITER G240P-7 /* Reverse White.
/*
@BON L1 /* Blink ON
@BOF L0 /* Blink OFF
/*
@DRLINEK G244 /* Graphic Line kind select.
@DRSTART G242 /* Draw start point.
@DRLINE G01 /* Linear line display.
@DRCW G02 /* Circle display(CW).
@DRCCW G03 /* Circle display(CCW).
/*
@GRCSR G249 /* Graphic cursor.
/*
@PMCDATA G310 /* PMC relay/data read and write.
@1BYTE L1 /* 1 BYTE
@2BYTE L2 /* 2 BYTE
@4BYTE L4 /* 4 BYTE
/*
@TRSVR G315 /* P-code variable transfer.
@TRSVRNML G315P001 /* normal transfer.
@TRSVRUPT G315P002 /* up transfer.
@TRSVRDWT G315P003 /* down transfer.
@TRSVRARG G315P101 /* transfer to arangement.
@TRSVRUPA G315P102 /* up transfer to arangement.
@TRSVRDWA G315P103 /* down transfer to arangement.
/*
@PAMAKE G320 /* CNC Prog. access. (Prog. make)
@PADELET G321 /* (Prog. delete)
@PACNDNS G322 /* (Prog. condense)
@PAREAD G325 /* (Block read)
@PAWRITE G326 /* (Block write)
@PABDELT G327 /* (Block delete)
@PACREAD G328 /* (Character block read)
@PACWRIT G329 /* (Character block write)
/*
@RSOPEN G330 /* RS232C open.
@RSCLOSE G331 /* close.
@RSRECV G335 /* receive 1ch.
@RSSEND G336 /* Data send.
@RSVARRD G337 /* Variable data read.
@RSVARWT G338 /* Variable data write.
@RSFUNC G339 /* FANUC cassettee control.
/*
@PMAFEED G340 /* PMC AXIS feed.
@PMACUT G341 /* cutting.
@PMADWLL G344 /* dwell.
@PMAREFC G345 /* reference position return.
@PMAMSCL G346 /* miscellaneous function.
@PMASNRD G348 /* signal read.
@PMASNWT G349 /* signal write.
- 34 -
Page 43

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX A.SYMBOL DEFINITION
/*
/*
/* No.02 Conversation MACRO (TAIWA MACRO) control Variable define.
/* ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
@CMACRO1 #8500 /* Conversation MACRO - 1 MAIN PROGRAM No.
@TAIWAP1 #8500
@CMACRO2 #8550 /* Conversation MACRO - 2 MAIN PROGRAM No.
@TAIWAP2 #8550
@CMACRO3 #8551 /* Conversation MACRO - 3 MAIN PROGRAM No.
@TAIWAP3 #8551
/*
@KEYCONT #8502 /* MDI-KEY IN CONTROL.
@NOREAD #8502=0 /* No Data read.
@NUMREAD #8502=1 /* Numeric Data read.
@ADRREAD #8502=2 /* Address+Numeric Data read.
@ASCREAD #8502=3 /* ASCII Data read.
/*
@KEYCODE #8501 /* MDI-KEY IN CODE.
@PAGEDW 1 /* "Page Down" KEY pushed.
@PAGEUP
2 /* "Page Up"
@CURDW 3 /* "Cursor Down"
@CURUP
4 /* "Cursor Up"
@ALTER 5 /* "Alter"
@INSRT
@DELET
6 /* "Insert"
7 /* "Delete"
@INPUT 8 /* "Input"
@START
9 /* "Start/Output"
@RESET 10 /* "Reset"
@CURRT
18 /* "Cursor Right"
@CURLF 19 /* "Cursor Left"
@PINPUT 28 /* "Input" add decimal point
/*
@SFTLF 11 /* "Soft key left" (9"CRT)
@SFT1 12 /* "Soft key 1" (9"CRT)
@SFT2 13 /* "Soft key 2" (9"CRT)
@SFT3 14 /* "Soft key 3" (9"CRT)
@SFT4 15 /* "Soft key 4" (9"CRT)
@SFT5 16 /* "Soft key 5" (9"CRT)
@SFTRT
17 /* "Soft key right" (9"CRT)
/*
@SFTFLF
20 /* "Soft key left" (14"CRT)
@SFTF1 21 /* "Soft key 1" (14"CRT)
@SFTF2 22 /* "Soft key 2" (14"CRT)
@SFTF3 23 /* "Soft key 3" (14"CRT)
@SFTF4 24 /* "Soft key 4" (14"CRT)
@SFTF5 25 /* "Soft key 5" (14"CRT)
@SFTF6 26 /* "Soft key 6" (14"CRT)
@SFTF7 27 /* "Soft key 7" (14"CRT)
@SFTF8 28 /* "Soft key 8" (14"CRT)
@SFTF9 29 /* "Soft key 9" (14"CRT)
@SFTF10 30 /* "Soft key 10" (14"CRT)
- 35 -
Page 44

A.SYMBOL DEFINITION APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
@SFTFRT 31 /* "Soft key right" (14"CRT)
@KEYDATA #8503 /* MDI-KEY IN DATA.
@KEYADRS
@KEYARRY #8552 /* MDI-KEY SPECIAL READ DATA VAR. No.
/*
@CURSOR #8505 /* CURSOR DISPLAY CONTROL.
@CURSORX #8506 /* CURSOR DISPLAY POSITION (X).
@CURSORY #8507 /* CURSOR DISPLAY POSITION (Y).
/*
@CHRPROG #8509 /* CHARACTER DEFINE PROGRAM No.
@CRTFUNC #8510 /* CRT FUNCTION CONTROL.
/*
@ARRY2BS #8512 /* Array CONTORL
@ARRY3BS #8513 /* Array CONTORL
@ARRY1CT #8516 /* Array CONTORL
@ARRY2CT #8517 /* Array CONTORL
@ARRYTOP #8519 /* Array CONTORL (Top variable No.)
/*
@TRNSDAT #8511 /* Transfer CONTORL
@TRNS2BS #8512 /* Transfer CONTORL
@TRNS3BS #8513 /* Transfer CONTORL
@TRNS2TO #8514 /* Transfer CONTORL
@TRNS3TO #8515 /* Transfer CONTORL
/*
@PAPROGN #8520 /* CNC PROG. ACCESS. (PROGRAM No.)
@PABLOKN #8521 /* CNC PROG. ACCESS. (BLOCK No.)
@PAVARNO #8522 /* CNC PROG. ACCESS. (DATA VAR. No.)
@PAPNTVN #8523 /* CNC PROG. ACCESS. (POINT DATA VAR. No.)
@PAERROR #8529 /* CNC PROG. ACCESS. (RETURN CODE)
/*
@PABGEDT #8526 /* BG-edit status.
@PAPGCNT #8527 /* Program count.
@PAFPMEM #8528 /* Free program memory.
/*
@RSERROR #8539 /* RS232C INTERFACE (RETURN CODE)
/*
@MDIKEYI #8549 /* MDI Key image
/*
@CUTTIME #8553 /* Cutting Time.
@CUTLENG #8554 /* Cutting length.
/*
@HELPPNM #8555 /* User's HELP screen Prog. Num.
@HELPRST #8556 /* User's HELP return status.
/*
@KEYLINX #8561 /* KEY in line X potion.
@KEYLINY #8562 /* KEY in line Y potion.
@KEYINUM #8563 /* KEY input number.
@KEYPRPT #8564 /* KEY in line prompt.
@KEYCLOR #8565 /* KEY in line color.
/*
#8504 /* MDI-KEY IN ADDRESS.
- 36 -
Page 45

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX A.SYMBOL DEFINITION
@ITLCNTL #8600 /* Inter Lock control.
@ITLSTTS #8601 /* Skip signal movement direction.
/*
@PMGSLCT #8602 /* PMC AXIS select. (G-code control)
/*
@PCDWKNO #8610 /* P-code Work No. search.
/*
@TRQLTO1 #8621 /* AXIS 1 limited torque override.
@TRQLTO2 #8622 /* AXIS 2
@TRQLTO3 #8623 /* AXIS 3
@TRQLTO4 #8624 /* AXIS 4
@TRQLTO5 #8625 /* AXIS 5
@TRQLTO6 #8626 /* AXIS 6
@TRQLTO7 #8627 /* AXIS 7
@TRQLTO8 #8628 /* AXIS 8
/*
@CNVTAD1 #8631 /* CHANNEL 1 A/D converter.
@CNVTAD2 #8632 /* CHANNEL 2
@CNVTAD3 #8633 /* CHANNEL 3
@CNVTAD4 #8634 /* CHANNEL 4
/*
@MSKCLAX #8690 /* AXIS Macro call mask.
@MSKCLTC #8691 /* T code call mask.
/*
@PMVSLCT #8700 /* PMC AXIS select. (VARIABLE control)
@PMVFLG1 #8710 /* PMC 1 control flag.
@PMVCMD1 #8711 /* command.
@PMVCSP1 #8712 /* cutting speed.
@PMVLNG1 #8713 /* length.
@PMVSTS1 #8715 /* status.
@PMVFLG2 #8720 /* PMC 2 control flag.
@PMVCMD2 #8721 /* command.
@PMVCSP2 #8722 /* cutting speed.
@PMVLNG2 #8723 /* length.
@PMVSTS2 #8725 /* status.
@PMVFLG3 #8730 /* PMC 3 control flag.
@PMVCMD3 #8731 /* command.
@PMVCSP3 #8732 /* cutting speed.
@PMVLNG3 #8733 /* length.
@PMVSTS3 #8735 /* status.
@PMVFLG4 #8740 /* PMC 4 control flag.
@PMVCMD4 #8741 /* command.
@PMVCSP4 #8742 /* cutting speed.
@PMVLNG4 #8743 /* length.
@PMVSTS4 #8745 /* status.
/*
@WINDIDX #8998 /* Window Index.
@WINDDAT #8999 /* Window Data.
/*
/*
/* No.03 System Variable.
- 37 -
Page 46

A.SYMBOL DEFINITION APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
/* ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
@EMPTY #0 /* "EMPTY".
@ENMTY #0 /* "EMPTY".
@[#_EMPTY] #0 /*
@[#_UI[0]] #1000 /* Interface input signals (bit) No.0
@[#_UI[1]] #1001
@[#_UI[2]] #1002
@[#_UI[3]] #1003
@[#_UI[4]] #1004
@[#_UI[5]] #1005
@[#_UI[6]] #1006
@[#_UI[7]] #1007
@[#_UI[8]] #1008
@[#_UI[9]] #1009
@[#_UI[10]] #1010
@[#_UI[11]] #1011
@[#_UI[12]] #1012
@[#_UI[13]] #1013
@[#_UI[14]] #1014
@[#_UI[15]] #1015
@[#_UI[16]] #1016
@[#_UI[17]] #1017
@[#_UI[18]] #1018
@[#_UI[19]] #1019
@[#_UI[20]] #1020
@[#_UI[21]] #1021
@[#_UI[22]] #1022
@[#_UI[23]] #1023
@[#_UI[24]] #1024
@[#_UI[25]] #1025
@[#_UI[26]] #1026
@[#_UI[27]] #1027
@[#_UI[28]] #1028
@[#_UI[29]] #1029
@[#_UI[30]] #1030
@[#_UI[31]] #1031
@[#_UIL[0]] #1032 /* Interface input signals (long) No.0
@[#_UIL[1]] #1033
@[#_UIL[2]] #1034
@[#_UIL[3]] #1035
@[#_UO[0]] #1100 /* Interface output signals (bit) No.0
@[#_UO[1]] #1101
@[#_UO[2]] #1102
@[#_UO[3]] #1103
@[#_UO[4]] #1104
@[#_UO[5]] #1105
@[#_UO[6]] #1106
@[#_UO[7]] #1107
@[#_UO[8]] #1108
@[#_UO[9]] #1109
@[#_UO[10]] #1110
- 38 -
Page 47

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX A.SYMBOL DEFINITION
@[#_UO[11]] #1111
@[#_UO[12]] #1112
@[#_UO[13]] #1113
@[#_UO[14]] #1114
@[#_UO[15]] #1115
@[#_UO[16]] #1116
@[#_UO[17]] #1117
@[#_UO[18]] #1118
@[#_UO[19]] #1119
@[#_UO[20]] #1120
@[#_UO[21]] #1121
@[#_UO[22]] #1122
@[#_UO[23]] #1123
@[#_UO[24]] #1124
@[#_UO[25]] #1125
@[#_UO[26]] #1126
@[#_UO[27]] #1127
@[#_UO[28]] #1128
@[#_UO[29]] #1129
@[#_UO[30]] #1130
@[#_UO[31]] #1131
@[#_UOL[0]] #1132 /* Interface output signals (long) No.0
@[#_UOL[1]] #1133
@[#_UOL[2]] #1134
@[#_UOL[3]] #1135
@[#_OFSX[1]] #2001 /* X Axis compensation value No.1(T System)
@[#_OFSX[2]] #2002
@[#_OFSX[3]] #2003
@[#_OFSX[4]] #2004
@[#_OFSX[5]] #2005
@[#_OFSX[6]] #2006
@[#_OFSX[7]] #2007
@[#_OFSX[8]] #2008
@[#_OFSX[9]] #2009
@[#_OFSX[10]] #2010
@[#_OFSX[11]] #2011
@[#_OFSX[12]] #2012
@[#_OFSX[13]] #2013
@[#_OFSX[14]] #2014
@[#_OFSX[15]] #2015
@[#_OFSX[16]] #2016
@[#_OFSZ[1]] #2101 /* Z Axis compensation value No.1 (T System)
@[#_OFSZ[2]] #2102
@[#_OFSZ[3]] #2103
@[#_OFSZ[4]] #2104
@[#_OFSZ[5]] #2105
@[#_OFSZ[6]] #2106
@[#_OFSZ[7]] #2107
@[#_OFSZ[8]] #2108
@[#_OFSZ[9]] #2109
@[#_OFSZ[10]] #2100
- 39 -
Page 48

A.SYMBOL DEFINITION APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
@[#_OFSZ[11]] #2111
@[#_OFSZ[12]] #2112
@[#_OFSZ[13]] #2113
@[#_OFSZ[14]] #2114
@[#_OFSZ[15]] #2115
@[#_OFSZ[16]] #2116
@[#_OFS[1]] #2001 /* Tool compensation value No.1(M System)
@[#_OFS[2]] #2002
@[#_OFS[3]] #2003
@[#_OFS[4]] #2004
@[#_OFS[5]] #2005
@[#_OFS[6]] #2006
@[#_OFS[7]] #2007
@[#_OFS[8]] #2008
@[#_OFS[9]] #2009
@[#_OFS[10]] #2010
@[#_OFS[11]] #2011
@[#_OFS[12]] #2012
@[#_OFS[13]] #2013
@[#_OFS[14]] #2014
@[#_OFS[15]] #2015
@[#_OFS[16]] #2016
@[#_WZ_SFTX] #2501 /* X Axis Work Shift(T)
@[#_WZ_SFTZ] #2601 /* Z Axis Work Shift(T)
@ALARM #3000 /* Alarm display.
@[#_ALM] #3000 /*
@TIMER1 #3001 /* Msec Timer.
@[#_CLOCK1] #3001 /*
@TIMER2 #3002 /* Hour Timer.
@[#_CLOCK2] #3002 /*
@SBKCNT #3003 /* Single blok/Auxilialy function control.
@[#_CNTL1] #3003 /*
@FLDCNT #3004 /* Feed hold/Over ride control.
@[#_CNTL2] #3004 /*
@SETTING
@[#_SETDT]
@[#_MSGSTP] #3006 /* Operation stopped with a message
@[#_MRIMG] #3007 /* Mirror image state (DI and setting)
@[#_PRSTR] #3008 /* Program not being restarted/program being restarted
@[#_BG_DSP]
@DATE #3011 /* System date.
@[#_DATE] #3011 /*
@TIME #3012 /* System Time.
@[#_TIME] #3012 /*
@[#_PI] #3101 /* Circle ratio(=3.1415926535)
@[#_E] #3102 /* Radian(=2.718281828459)
@PARTCNT #3901 /* Part count.
@[#_PRTSA] #3901 /*
@PARTRQT #3902 /* Part request.
@[#_PRTSN] #3902 /*
@[#_OFSMEM] #3980 /* Tool Offset Memory Type (M)
#3005 /* Setting data.
#3005 /*
#3010 /* Back Ground Draw.
- 40 -
Page 49

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX A.SYMBOL DEFINITION
@[#_MAINO] #4000 /* Main Program No.
@MDLG01 #4001 /* Modal G-code Group 1(Pre. Block)
@MDLG02 #4002
@MDLG03 #4003
@MDLG04 #4004
@MDLG05 #4005
@MDLG06 #4006
@MDLG07 #4007
@MDLG08 #4008
@MDLG09 #4009
@MDLG10 #4010
@MDLG11 #4011
@MDLG12 #4012
@MDLG13 #4013
@MDLG14 #4014
@MDLG15 #4015
@MDLG16 #4016
@MDLG17 #4017
@MDLG18 #4018
@MDLG19 #4019
@MDLG20 #4020
@MDLG21 #4021
@MDLG22 #4022
@[#_BUFG[1]] #4001
@[#_BUFG[2]] #4002
@[#_BUFG[3]] #4003
@[#_BUFG[4]] #4004
@[#_BUFG[5]] #4005
@[#_BUFG[6]] #4006
@[#_BUFG[7]] #4007
@[#_BUFG[8]] #4008
@[#_BUFG[9]] #4009
@[#_BUFG[10]] #4010
@[#_BUFG[11]] #4011
@[#_BUFG[12]] #4012
@[#_BUFG[13]] #4013
@[#_BUFG[14]] #4014
@[#_BUFG[15]] #4015
@[#_BUFG[16]] #4016
@[#_BUFG[17]] #4017
@[#_BUFG[18]] #4018
@[#_BUFG[19]] #4019
@[#_BUFG[20]] #4020
@[#_BUFG[21]] #4021
@[#_BUFG[22]] #4022
@[#_BUFG[23]] #4023
@[#_BUFG[24]] #4024
@[#_BUFG[25]] #4025
@[#_BUFG[26]] #4026
@[#_BUFG[27]] #4027
@[#_BUFG[28]] #4028
- 41 -
Page 50

A.SYMBOL DEFINITION APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
@[#_BUFG[29]] #4029
@[#_BUFG[30]] #4030
@[#_ACTG[1]] #4201 /* Modal G-code Group 1(Act. block)
@[#_ACTG[2]] #4202
@[#_ACTG[3]] #4203
@[#_ACTG[4]] #4204
@[#_ACTG[5]] #4205
@[#_ACTG[6]] #4206
@[#_ACTG[7]] #4207
@[#_ACTG[8]] #4208
@[#_ACTG[9]] #4209
@[#_ACTG[10]] #4210
@[#_ACTG[11]] #4211
@[#_ACTG[12]] #4212
@[#_ACTG[13]] #4213
@[#_ACTG[14]] #4214
@[#_ACTG[15]] #4215
@[#_ACTG[16]] #4216
@[#_ACTG[17]] #4217
@[#_ACTG[18]] #4218
@[#_ACTG[19]] #4219
@[#_ACTG[20]] #4220
@[#_ACTG[21]] #4221
@[#_ACTG[22]] #4222
@[#_ACTG[23]] #4223
@[#_ACTG[24]] #4224
@[#_ACTG[25]] #4225
@[#_ACTG[26]] #4226
@[#_ACTG[27]] #4227
@[#_ACTG[28]] #4228
@[#_ACTG[29]] #4229
@[#_ACTG[30]] #4230
@[#_INTG[1]] #4401 /* Modal G-code Group 1(Interrupted block)
@[#_INTG[2]] #4402
@[#_INTG[3]] #4403
@[#_INTG[4]] #4404
@[#_INTG[5]] #4405
@[#_INTG[6]] #4406
@[#_INTG[7]] #4407
@[#_INTG[8]] #4408
@[#_INTG[9]] #4409
@[#_INTG[10]] #4410
@[#_INTG[11]] #4411
@[#_INTG[12]] #4412
@[#_INTG[13]] #4413
@[#_INTG[14]] #4414
@[#_INTG[15]] #4415
@[#_INTG[16]] #4416
@[#_INTG[17]] #4417
@[#_INTG[18]] #4418
@[#_INTG[19]] #4419
- 42 -
Page 51

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX A.SYMBOL DEFINITION
@[#_INTG[20]] #4420
@[#_INTG[21]] #4421
@[#_INTG[22]] #4422
@[#_INTG[23]] #4423
@[#_INTG[24]] #4424
@[#_INTG[25]] #4425
@[#_INTG[26]] #4426
@[#_INTG[27]] #4427
@[#_INTG[28]] #4428
@[#_INTG[29]] #4429
@[#_INTG[30]] #4430
@[#_BUFE] #4108 /* E cord(Pre. Block)
@[#_ACTE] #4308 /* (Act. block)
@[#_INTE] #4508 /* (Interrupted block)
@CORDF #4109 /* F cord(Pre. Block)
@[#_BUFF] #4109 /*
@[#_ACTF] #4309 /* (Act. block)
@[#_INTF] #4509 /* (Interrupted block)
@CORDM #4113 /* M cord(Pre. Block)
@[#_BUFM] #4113 /*
@[#_ACTM] #4313 /* (Act. block)
@[#_INTM] #4513 /* (Interrupted block)
@SEQNUM #4114 /* Sequece number(Pre. Block)
@[#_BUFN] #4114 /*
@[#_ACTN] #4314 /* (Act. block)
@[#_INTN] #4514 /* (Interrupted block)
@PRGNUM #4115 /* Program number(Pre. Block)
@[#_BUFO] #4115 /*
@[#_ACTO] #4315 /* (Act. block)
@[#_INTO] #4515 /* (Interrupted block)
@CORDS #4119 /* S cord(Pre. Block)
@[#_BUFS] #4119 /*
@[#_ACTS] #4319 /* (Act. block)
@[#_INTS] #4519 /* (Interrupted block)
@CORDT #4120 /* T cord(Pre. Block)
@[#_BUFT] #4120 /*
@[#_ACTT] #4320 /* (Act. block)
@[#_INTT] #4520 /* (Interrupted block)
@[#_BUFWZP] #4130 /* add. workpiece coordinate system No.(Pre. Block)
@[#_ACTWZP] #4330 /* (Act. block)
@[#_INTWZP] #4530 /* (Interrupted block)
/*
@ABSIO1 #5001 /* Block end position. 1'st
@ABSIO2 #5002
@ABSIO3 #5003
@ABSIO4 #5004
@ABSIO5 #5005
@ABSIO6 #5006
@ABSIO7 #5007
@ABSIO8 #5008
@[#_ABSIO[1]] #5001
- 43 -
Page 52

A.SYMBOL DEFINITION APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
@[#_ABSIO[2]] #5002
@[#_ABSIO[3]] #5003
@[#_ABSIO[4]] #5004
@[#_ABSIO[5]] #5005
@[#_ABSIO[6]] #5006
@[#_ABSIO[7]] #5007
@[#_ABSIO[8]] #5008
@ABSMT1 #5021 /* Machine Position.
@ABSMT2 #5022
@ABSMT3 #5023
@ABSMT4 #5024
@ABSMT5 #5025
@ABSMT6 #5026
@ABSMT7 #5027
@ABSMT8 #5028
@[#_ABSMT[1]] #5021
@[#_ABSMT[2]] #5022
@[#_ABSMT[3]] #5023
@[#_ABSMT[4]] #5024
@[#_ABSMT[5]] #5025
@[#_ABSMT[6]] #5026
@[#_ABSMT[7]] #5027
@[#_ABSMT[8]] #5028
@ABSOT1 #5041 /* Current absolute position.
@ABSOT2 #5042
@ABSOT3 #5043
@ABSOT4 #5044
@ABSOT5 #5045
@ABSOT6 #5046
@ABSOT7 #5047
@ABSOT8 #5048
@[#_ABSOT[1]] #5041
@[#_ABSOT[2]] #5042
@[#_ABSOT[3]] #5043
@[#_ABSOT[4]] #5044
@[#_ABSOT[5]] #5045
@[#_ABSOT[6]] #5046
@[#_ABSOT[7]] #5047
@[#_ABSOT[8]] #5048
@ABSKP1 #5061 /* Skip cutting position.
@ABSKP2 #5062
@ABSKP3 #5063
@ABSKP4 #5064
@ABSKP5 #5065
@ABSKP6 #5066
@ABSKP7 #5067
@ABSKP8 #5068
@[#_ABSKP[1]] #5061
@[#_ABSKP[2]] #5062
@[#_ABSKP[3]] #5063
@[#_ABSKP[4]] #5064
- 44 -
Page 53

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX A.SYMBOL DEFINITION
@[#_ABSKP[5]] #5065
@[#_ABSKP[6]] #5066
@[#_ABSKP[7]] #5067
@[#_ABSKP[8]] #5068
@[#_TOFSWX] #5081 /* X AXIS Tool offset (T system)
@[#_TOFSWY] #5082 /* Y AXIS Tool offset (T system)
@[#_TOFSWZ] #5083 /* Z AXIS Tool offset (T system)
@[#_TOFS[1]] #5081 /* AXIS 1 Tool length offset (M system)
@[#_TOFS[2]] #5082
@[#_TOFS[3]] #5083
@[#_TOFS[4]] #5084
@[#_TOFS[5]] #5085
@[#_TOFS[6]] #5086
@[#_TOFS[7]] #5087
@[#_TOFS[8]] #5088
@[#_SVERR[1]] #5101 /* AXIS 1 Servo positional deviation value
@[#_SVERR[2]] #5102
@[#_SVERR[3]] #5103
@[#_SVERR[4]] #5104
@[#_SVERR[5]] #5105
@[#_SVERR[6]] #5106
@[#_SVERR[7]] #5107
@[#_SVERR[8]] #5108
@[#_MIRTP[1]] #5121 /* AXIS 1 Manual handle interrupt value
@[#_MIRTP[2]] #5122
@[#_MIRTP[3]] #5123
@[#_MIRTP[4]] #5124
@[#_MIRTP[5]] #5125
@[#_MIRTP[6]] #5126
@[#_MIRTP[7]] #5127
@[#_MIRTP[8]] #5128
@[#_DIST[1]] #5181 /* AXIS 1 Dist. to go value
@[#_DIST[2]] #5182
@[#_DIST[3]] #5183
@[#_DIST[4]] #5184
@[#_DIST[5]] #5185
@[#_DIST[6]] #5186
@[#_DIST[7]] #5187
@[#_DIST[8]] #5188
@OFSEXW1 #5201 /* AXIS 1 External workpiece reference offset.
@OFSEXW2 #5202
@OFSEXW3 #5203
@OFSEXW4 #5204
@OFSEXW5 #5205
@OFSEXW6 #5206
@OFSEXW7 #5207
@OFSEXW8 #5208
@[#_WZCMN[1]] #5201
@[#_WZCMN[2]] #5202
@[#_WZCMN[3]] #5203
@[#_WZCMN[4]] #5204
- 45 -
Page 54

A.SYMBOL DEFINITION APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
@[#_WZCMN[5]] #5205
@[#_WZCMN[6]] #5206
@[#_WZCMN[7]] #5207
@[#_WZCMN[8]] #5208
@OFS54W1 #5221 /* AXIS 1 G54 workpiece reference offset.
@OFS54W2 #5222
@OFS54W3 #5223
@OFS54W4 #5224
@OFS54W5 #5225
@OFS54W6 #5226
@OFS54W7 #5227
@OFS54W8 #5228
@[#_WZG54[1]] #5221
@[#_WZG54[2]] #5222
@[#_WZG54[3]] #5223
@[#_WZG54[4]] #5224
@[#_WZG54[5]] #5225
@[#_WZG54[6]] #5226
@[#_WZG54[7]] #5227
@[#_WZG54[8]] #5228
@OFS55W1 #5241 /* AXIS 1 G55 workpiece reference offset.
@OFS55W2 #5242
@OFS55W3 #5243
@OFS55W4 #5244
@OFS55W5 #5245
@OFS55W6 #5246
@OFS55W7 #5247
@OFS55W8 #5248
@[#_WZG55[1]] #5241
@[#_WZG55[2]] #5242
@[#_WZG55[3]] #5243
@[#_WZG55[4]] #5244
@[#_WZG55[5]] #5245
@[#_WZG55[6]] #5246
@[#_WZG55[7]] #5247
@[#_WZG55[8]] #5248
@OFS56W1 #5261 /* AXIS 1 G56 workpiece reference offset.
@OFS56W2 #5262
@OFS56W3 #5263
@OFS56W4 #5264
@OFS56W5 #5265
@OFS56W6 #5266
@OFS56W7 #5267
@OFS56W8 #5268
@[#_WZG56[1]] #5261
@[#_WZG56[2]] #5262
@[#_WZG56[3]] #5263
@[#_WZG56[4]] #5264
@[#_WZG56[5]] #5265
@[#_WZG56[6]] #5266
@[#_WZG56[7]] #5267
- 46 -
Page 55

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX A.SYMBOL DEFINITION
@[#_WZG56[8]] #5268
@OFS57W1 #5281 /* AXIS 1 G57 workpiece reference offset.
@OFS57W2 #5282
@OFS57W3 #5283
@OFS57W4 #5284
@OFS57W5 #5285
@OFS57W6 #5286
@OFS57W7 #5287
@OFS57W8 #5288
@[#_WZG57[1]] #5281
@[#_WZG57[2]] #5282
@[#_WZG57[3]] #5283
@[#_WZG57[4]] #5284
@[#_WZG57[5]] #5285
@[#_WZG57[6]] #5286
@[#_WZG57[7]] #5287
@[#_WZG57[8]] #5288
@OFS58W1 #5301 /* AXIS 1 G58 workpiece reference offset.
@OFS58W2 #5302
@OFS58W3 #5303
@OFS58W4 #5304
@OFS58W5 #5305
@OFS58W6 #5306
@OFS58W7 #5307
@OFS58W8 #5308
@[#_WZG58[1]] #5301
@[#_WZG58[2]] #5302
@[#_WZG58[3]] #5303
@[#_WZG58[4]] #5304
@[#_WZG58[5]] #5305
@[#_WZG58[6]] #5306
@[#_WZG58[7]] #5307
@[#_WZG58[8]] #5308
@OFS59W1 #5321 /* AXIS 1 G59 workpiece reference offset.
@OFS59W2 #5322
@OFS59W3 #5323
@OFS59W4 #5324
@OFS59W5 #5325
@OFS59W6 #5326
@OFS59W7 #5327
@OFS59W8 #5328
@[#_WZG59[1]] #5321
@[#_WZG59[2]] #5322
@[#_WZG59[3]] #5323
@[#_WZG59[4]] #5324
@[#_WZG59[5]] #5325
@[#_WZG59[6]] #5326
@[#_WZG59[7]] #5327
@[#_WZG59[8]] #5328
@[#_SKPDTC[1]] #5421 /* AXIS 1 skip point(DTC. unit) (M system)
@[#_SKPDTC[2]] #5422
- 47 -
Page 56

A.SYMBOL DEFINITION APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
@[#_SKPDTC[3]] #5423
@[#_SKPDTC[4]] #5424
@[#_SKPDTC[5]] #5425
@[#_SKPDTC[6]] #5426
@[#_SKPDTC[7]] #5427
@[#_SKPDTC[8]] #5428
@[#_FOFSP] #5500 /* Fixtur offset number (M system)
@[#_FOFSVAL[1]] #5501 /* AXIS 1 fixture offset value (M system)
@[#_FOFSVAL[2]] #5502
@[#_FOFSVAL[3]] #5503
@[#_FOFSVAL[4]] #5504
@[#_FOFSVAL[5]] #5505
@[#_FOFSVAL[6]] #5506
@[#_FOFSVAL[7]] #5507
@[#_FOFSVAL[8]] #5508
/*
/*
/* No.04 OTHER SYMBOL DEFINE.
/* ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
@ON =1
@OFF =0
/*
$LIST
- 48 -
Page 57

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX B.COMPILE ERROR CODE TABLE
B COMPILE ERROR CODE TABLE
The table below indicates the error codes that may occur in compile
processing.
Compile Error Codes
Error code Meaning
0000 Compiled OK.
0201 Too many program.
0202 No program.
1001 Find out period,on BLOCKDEL number.
1002 BLOCKDEL number not match 1-9.
1003 Find out program number,in unsuitable spot.
1004 Find out SEQ number,in unsuitable spot.
1005 NC statement default.
1006 Find out not EOB code,MACRO statement after.
1007 Not find '=',on MACRO statement.
1008 DO-END nest too deep.
1009 Not find Relational OP,on IF statement.
100a Not find GOTO,pair of IF statement.
100b Not find bracket,on IF statement.
100c Find out not EOB code,GOTOm after.
100d Find out not EOB code,DOm after.
100e Find out not EOB code,ENDm after.
100f Not agree END statement number to pair of DO.
1010 Not find END,pair of DO.
1011 Not find DO right of WHILE.
1012 Not find ']' ,on WHILE[•••].
1013 Illegal statement,NC or MACRO ?
1014 Not find DO, pair of END.
1015 Program NO. missmactch,directory to program.
1016 Not find program NO. on top of the program.
1017 Syntax ERR:THEN-END.
1018 Syntax ERR:SETVN.
1019 Syntax ERR:DEFADD.
101a Syntax ERR:POPEN.
101b Syntax ERR:PCLOS.
101c Syntax ERR:BPRNT.
101d Syntax ERR:DPRNT.
101e Syntax ERR:PGN.
101f Syntax ERR:FDEL.
1020 Syntax ERR:FOPEN.
1021 Syntax ERR:FCLOS.
1022 Syntax ERR:FREAD.
1023 Syntax ERR:FWRITE.
1024 Syntax ERR:FPSET.
- 49 -
Page 58

B.COMPILE ERROR CODE TABLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
Compile Error Codes
Error code Meaning
1025 Too many THEN statement.
1027 No EOB code after ccall_statement.
1028 IF statement, Nest too deep.
1029 Logical AND and OR, Mixed up on if statement.
1030 No ENDIF found on if then statement.
1031 Too MANY condition statement (Max = 4).
1033 Unsuitable ELSE found on if statement.
1034 Unsuitable ENDIF found on if statement.
1035 Unsuitable THEN found on if statement.
1201 Nest of bracket,over 5 hold.
1202 Not find ']',on #[•••].
1203 Not find ']',on [•••].
1204 Not find '[',on ATAN[•••]/[•••] of below the line.
1205 Not find '/',on ATAN[•••]/[•••].
1206 Not find ']',on ATAN[•••]/[•••] of above the line.
1207 Not find ']',on [•••].
1208 Illegal token function.
1209 Illegal token function,left of <•••>.
120a Illegal token func,on <ad>[f] or <ad>-[f] or GOTO [f].
120b Dimension Error.
1401 Too many number,Max 9 hold.
1402 Illegal period, after.
1403 Too many macro digit,Max 6 hold.
1404 Right of #,must have figure or '['.
1405 Too many program NO.,Max 8 hold.
1406 Too many sequence NO.,Max 8 hold.
1407 Not find '[',on func [•••].
1408 Not find '[',on IF[•••] or WHILE[•••].
1409 Too many 'm',on DOm or ENDm.
140a m of DOm•ENDm,not agree 1-3.
140b Find out non figure code on right of DO or END.
140c Illegal function code.
140d Too long func-code,Max 5 character.
140e Not find EOR on file.
140f Find out illegal code.
1410 Too many string length, Max 255.
1411 Too many hex code, max 4 hold.
1412 Illegal hex code.
1413 Find the undefind code.
1414 Not close by '*)',on (*•••*).
1415 Find the illegal string between '(' to ')'.
1416 Find the illegal string between ',' to ';'.
1417 Find the illegal string between '@' to '@'.
1418 Not close by '@',on @•••@.
1419 Too many hex code, max 2 hold.
1420 Illegal length or character in Hex Image String.
1421 Illegal 'O','N' number.
1601 STACK over flow.
1602 Location value size over flow.
- 50 -
Page 59

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX B.COMPILE ERROR CODE TABLE
Compile Error Codes
Error code Meaning
1603 Amount of address over 50.
1604 Too larg macro number,Max 6 hold.
1605 MACRO number not >=0.
1606 MACRO number period illegal.
1607 Too long GOTO number,Max 8 hold.
1608 GOTO number with period illegal.
1681 Too many GOTO statement.
1682 SEQ number not found.
1683 Too many WHILE statement.
1684 GOTO SEQ number duplicate.
1801 P-CODE size over the ROM size.
1900 '%' not find or illegal.
2000 Push on key \"RESET\".
2001 NC program Read ERR.
8000 program number ERR.
8001 ASCII to compiler code convert error.
9999 missmatch err_code !!
- 51 -
Page 60

C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
C COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
The compile/link example described below is created under the
directory
C:\MCOMP30I\USR\SAMPL
when the macro compiler utility system is installed.
Details of sample:
Times required for instruction execution by each of the
conversational macros are measured:
1. #100 = #101+#102 ;
2. #100 = #101 AND #102 ;
3. #100 = SIN [#101] ;
The number of test operations is set beforehand in the common
variable (#500). Time required for looping by the number of test
operations by the WHILE instruction is measured by the timer
variable (#3001). Then time required for the same number of loops by
the WHILE instruction containing an instruction subject to
measurement is measured. Thus the difference between two
measurement times is the execution time of the instruction subject to
measurement.
(1) Programs created
File name = MAIN.SRC Main source program file
File name = SUB1.SRC Subprogram source file
File name = MAIN.REF Main program reference list file
File name = MAIN.LST Main program compile list file
File name = MAIN.REL Main program object file
File name = SUB1.REF Subprogram reference list file
File name = SUB1.LST Subprogram compile list file
File name = SUB1.REL Subprogram object file
(2) Macro liner
File name = SAMPL.LNK Link control file
File name = SAMPL.MAP Link map list file
File name = SAMPL.ROM ROM-format file
- 52 -
Page 61

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
Main program source file File name : MAIN.SRC
/*
/* SAMPLE Program.
/*
/* Conversation MACRO Execution-Time Test Program.
/* (Vol 01.00 2003.04.10)
/*
/*
/* ( MAIN Program )
/*
/*
/* Symbol define.
/*
/* System common symbole FILE Include.
/*
$INCLUDE C:\MCOMP30I\TOOL\SYSTEM.DEF
/*
/*
@LOOPCT #500 /* TEST Loop count.
@TIMESAV #501 /* No-operatinon Time save.
@TSTTIME #502 /* Measured Time save.
/*
/*
@COUNT #100 /* Loop counter work.
@WORK #100 /* Work regster.
/*
/*
>LOOP 100 /* GOTO Sequense No. define.
>FIN 999
/*
/*
$EJECT
/*
/* No. O1000 : Main program.
/*
O1000 ;
NUMREAD ; Numeric data input.
CURSOR OFF ; Cursol OFF
DISPLAY X0 Y0 B0 ('EXECUTION TIME TEST') ; "MENU" display.
X2 Y2 ('1.#101=#102+#103') ;
X2 Y3 ('2.#101=#102 AND #103') ;
X2 Y4 ('3.#101=SIN[#102]') ;
;
LOOP DISPLAY X8 Y11 B1 (SELECT TEST NO.) ;
IF [KEYCODE NE INPUT]GOTO FIN ; "INPUT" key push ?
IF [KEYDATA LT 1]GOTO FIN ; 0 < DATA < 3 chk.
IF [KEYDATA GT 3]GOTO FIN ;
; No-ope. Time GET.
COUNT = LOOPCT ; Loop counter set.
TIMER1 = 0 ; Timer initialize.
WHILE[COUNT GT 0]DO1 ;
COUNT = COUNT –1 ; No-operation loop.
END1 ;
TIMESAV = TIMER1 ; Sample time save.
;
TAIWAP1 = KEYDATA*100+1000 ; Jump To TEST progra.
- 53 -
Page 62

C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
; O1x00:x=key in data.
;
FIN RETURNP LOOP ; END of conv. MACRO.
/*
/*
$EJECT
/*
/*
/* No. O1001 : Answer display sub program.
/*
/* LOOPCT : TEST Loop count.
/* TIMESAV : No-operatinon Time.
/* TSTTIME : Measured Time.
/*
O1001 ;
DISPLAY X5 Y4 B0 (SAMPLE COUNTER) ; Loop count display.
X20 Y4 FORM 6 ZSUP DATA LOOPCT ;
;
X5 Y6 (TOTAL TIME) ; Total measuer Time
X20 Y6 DATA [TSTTIME-TIMESAV] K1 (MSEC) ; display.
;
WORK = [TSTTIME-TIMESAV] / LOOPCT ; 1 operation Time
X5 Y8 (ONE OPERATION) ; display.
X20 Y8 FORM 5.2 DATA WORK K1 (MSEC) ;
;
RETURN ; Return to main.
/*
/*
%
- 54 -
Page 63

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
Main program reference list file File name : MAIN.REF
Fri Apr-25-2003 12:11:55 Page 1
(FS30i) Macro Compiler (Pre) V01.0 MAIN.SRC
---------- Compile Parameter -----------------------------------------
---------- Program ---------------------------------------------------
S-Line G-Line
1 /*
2 /* SAMPLE Program.
3 /*
4 /* Conversation MACRO Execution-Time Test Program.
5 /* (Vol 01.00 2003.04.10)
6 /*
7 /*
8 /* ( MAIN Program )
9 /*
10 /*
11 /* Symbol define.
12 /*
13 /* System common symbole FILE Include.
14 /*
15 $INCLUDE C:\MCOMP30I\TOOL\SYSTEM.DEF
16 $NOLIST
796 /*
797 /*
798 @LOOPCT #500 /* TEST Loop count.
799 @TIMESAV #501 /* No-operatinon Time save.
800 @TSTTIME #502 /* Measured Time save.
801 /*
802 /*
803 @COUNT #100 /* Loop counter work.
804 @WORK #100 /* Work regster.
805 /*
806 /*
807 >LOOP 100 /* GOTO Sequense No. define.
808 >FIN 999
809 /*
810 /*
811 $EJECT
- 55 -
Page 64

C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
Fri Apr-25-2003 12:11:55 Page 2
(FS30i) Macro Compiler (Pre) V01.0 MAIN.SRC
S-Line G-Line
812 /*
813 /* No. O1000 : Main program.
814 /*
815 0001 O1000 ;
816 0002 NUMREAD ; Numeric data input.
817 0003 CURSOR OFF ; Cursol OFF
818 0004 DISPLAY X0 Y0 B0 ('EXECUTION TIME TEST') ; "MENU" display.
819 0005 X2 Y2 ('1.#101=#102+#103') ;
820 0006 X2 Y3 ('2.#101=#102 AND #103') ;
821 0007 X2 Y4 ('3.#101=SIN[#102]') ;
822 0008 ;
823 0009 LOOP DISPLAY X8 Y11 B1 (SELECT TEST NO.) ;
824 0010 IF [KEYCODE NE INPUT]GOTO FIN ; "INPUT" key push ?
825 0011 IF [KEYDATA LT 1]GOTO FIN ; 0 < DATA < 3 chk.
826 0012 IF [KEYDATA GT 3]GOTO FIN ;
827 0013 ; No-ope. Time GET.
828 0014 COUNT = LOOPCT ; Loop counter set.
829 0015 TIMER1 = 0 ; Timer initialize.
830 0016 WHILE[COUNT GT 0]DO1 ;
831 0017 COUNT = COUNT –1 ; No-operation loop.
832 0018 END1 ;
833 0019 TIMESAV = TIMER1 ; Sample time save.
834 0020 ;
835 0021 TAIWAP1 = KEYDATA*100+1000 ; Jump To TEST progra.
836 0022 ; O1x00:x=key in data.
837 0023 ;
838 0024 FIN RETURNP LOOP ; END of conv. MACRO.
839 /*
840 /*
841 $EJECT
- 56 -
Page 65

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
Fri Apr-25-2003 12:11:55 Page 3
(FS30i) Macro Compiler (Pre) V01.0 MAIN.SRC
S-Line G-Line
842 /*
843 /*
844 /* No. O1001 : Answer display sub program.
845 /*
846 /* LOOPCT : TEST Loop count.
847 /* TIMESAV : No-operatinon Time.
848 /* TSTTIME : Measured Time.
849 /*
850 0025 O1001 ;
851 0026 DISPLAY X5 Y4 B0 (SAMPLE COUNTER) ; Loop count display.
852 0027 X20 Y4 FORM 6 ZSUP DATA LOOPCT ;
853 0028 ;
854 0029 X5 Y6 (TOTAL TIME) ; Total measuer Time
855 0030 X20 Y6 DATA [TSTTIME-TIMESAV] K1 (MSEC) ; display.
856 0031 ;
857 0032 WORK = [TSTTIME-TIMESAV] / LOOPCT ; 1 operation Time
858 0033 X5 Y8 (ONE OPERATION) ; display.
859 0034 X20 Y8 FORM 5.2 DATA WORK K1 (MSEC) ;
860 0035 ;
861 0036 RETURN ; Return to main.
862 /*
863 /*
864 0037 %
- 57 -
Page 66

C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
Fri Apr-25-2003 12:11:55 Page 4
(FS30i) Macro Compiler (Pre) V01.0 MAIN.SRC
---------- Cross Reference -------------------------------------------
Symbol Define Line No.
RETURN M99 861
RETURNP M99P 838
DISPLAY G243 818, 823, 851
FORM F 852, 859
DATA D 852, 855, 859
ZSUP Z1 852
TAIWAP1 #8500 835
NUMREAD #8502=1 816
KEYCODE #8501 824
INPUT 8 824
KEYDATA #8503 825, 826, 835
CURSOR #8505 817
TIMER1 #3001 829, 833
OFF =0 817
LOOPCT #500 828, 852, 857
TIMESAV #501 833, 855, 857
TSTTIME #502 855, 857
COUNT #100 828, 830, 831, 831
WORK #100 857, 859
LOOP 100 823, 838
FIN 999 824, 825, 826, 838
- 58 -
Page 67

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
Main program compile list file File name : MAIN.LST
------------------------------------------------------------------
25-Apr-2003 12:11:55 Page 1
(FS30i) Macro Compiler V01.0 MAIN.SRC
---------------------- Compile Parameter ------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------- program O1000 ----------------------------------------------------------------------
G-Line P-Line
0001 1 O1000;
0002 2 #8502=1;
0003 3 #8505=0;
0004 4 G243X0Y0B0 (*0045 0058 0045 0043 0055 0054 0049 004F004E 0020 0054 0049 004D 0045
0020 0054 0045 0053 0054*);
0005 5 X2Y2 (*0031 002E 0023 0031 0030 0031 003D 0023 0031 0030 0032 002B 0023 0031 0030
0033*);
0006 6 X2Y3 (*0032 002E 0023 0031 0030 0031 003D 0023 0031 0030 0032 0020 0041 004E 0044 0020
0023 0031 0030 0033*);
0007 7 X2Y4 (*0033 002E 0023 0031 0030 0031 003D 0053 0049 004E 005B 0023 0031 0030 0032
005D*);
0008 8 ;
0009 9 N100G243X8Y11B1 (SELECT TEST NO.);
0010 10 IF [#8501NE8] GOTO999;
0011 11 IF [#8503LT1] GOTO999;
0012 12 IF [#8503GT3] GOTO999;
0013 13 ;
0014 14 #100=#500;
0015 15 #3001=0;
0016 16 WHILE [#100GT0] DO1;
0017 17 #100=#100-1;
0018 18 END1;
0019 19 #501=#3001;
0020 20 ;
0021 21 #8500=#8503*100+1000;
0022 22 ;
0023 23 ;
0024 24 N999M99P100;
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0 errors, 24 blocks, 24 total lines
program size = 250 bytes
- 59 -
Page 68

C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
25-Apr-2003 12:11:55 Page 2
(FS30i) Macro Compiler V01.0 MAIN.SRC
--------------------- Cross Reference ---------------------------------------------------------------------#100 : 14, 16, 17, 17,
#500 : 14,
#501 : 19,
#3001 : 15, 19,
#8500 : 21,
#8501 : 10,
#8502 : 2,
#8503 : 11, 12, 21,
#8505 : 3,
25-Apr-2003 12:11:55 Page 3
(FS30i) Macro Compiler V01.0 MAIN.SRC
-------------------- program O1001 -----------------------------------------------------------------------G-Line P-Line
0025 1 O1001;
0026 2 G243X5Y4B0 (SANPLE COUNTER);
0027 3 X20Y4F6Z1D#500;
0028 4 ;
0029 5 X5Y6 (TOTAL TIME);
0030 6 X20Y6D [#502-#501] K1 (MSEC);
0031 7 ;
0032 8 #100= [#502-#501] /#500;
0033 9 X5Y8 (ONE OPERATION) ;
0034 10 X20Y8F5.2D#100K1 (MSEC);
0035 11 ;
0036 12 M99;
0037 13 %
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 errors, 13 blocks, 13 total lines
program size = 145 bytes
25-Apr-2003 12:11:55 Page 4
(FS30i) Macro Compiler V01.0 MAIN.SRC
-------------------- Cross Reference -----------------------------------------------------------------------
#100 : 8, 10,
#500 : 3, 8,
#501 : 6, 8,
#502 : 6, 8,
- 60 -
Page 69

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
Subprogram source file File name : SUB1.SRC
/*
/* SAMPLE Program.
/*
/* Conversation MACRO Execution-Time Test Program.
/* (Vol 01.00 2003.04.10)
/*
/*
/* ( SUB Program )
/*
/*
/* Symbol define.
/*
/* System common symbole FILE Include.
/*
$INCLUDE C:\\MCOMP30I\TOOL\SYSTEM.DEF
/*
/*
@LOOPCT #500 /* TEST Loop count.
@TIMESAV #501 /* No-operatinon Time save.
@TSTTIME #502 /* Measured Time save.
/*
/*
@COUNT #100 /* Loop counter work.
@MAINPR 1000 /* MAIN Program No.
@DISPSUB 1001 /* Answer display SUB Program.
/*
/*
>LOOP 100 /* GOTO Sequense No. define.
>FIN 999
/*
/*
$EJECT
- 61 -
Page 70

C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
/*
/*
/* (#101=#102+#103) Operation Time Test.
/*
/* No. O1100 : SUB program.
/*
/*
O1100 ;
NOREAD ; NO data read.
;
DISPLAY X2 Y2 B0 ('#101=#102+#103 TEST') ; Operation code disp.
;
COUNT = LOOPCT ; Loop counter set.
TIMER1 = 0 ; Timer initialize.
WHILE[COUNT GT 0]DO1 ;
#101 = #102 + #103 ; (Time Measure)
COUNT = COUNT –1 ;
END1 ;
;
TSTTIME = TIMER1 ; Measure Time save.
;
CALL DISPSUB ; Measure Time disp.
;
LOOP DISPLAY X8 Y11 B1 (PUSH RESET KEY) ;
IF[KEYCODE EQ RESET]GOTO FIN ; "RESET" key wait.
RETURNP LOOP ;
;
FIN TAIWAP1 = MAINPR ;
RETURN ;
/*
- 62 -
Page 71

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
$EJECT
/*
/*
/* (#101=#102 AND #103) Operation Time Test.
/*
/* No. O1200 : SUB program.
/*
/*
O1200 ;
NOREAD ; NO data read.
;
DISPLAY X2 Y2 B0 ('#101=#102 AND #103 TEST') ; Operation code disp.
;
COUNT = LOOPCT ; Loop counter set.
TIMER1 = 0 ; Timer initialize.
WHILE[COUNT GT 0]DO1 ;
#101 = #102 AND #103 ; (Time Measure)
COUNT = COUNT –1 ;
END1 ;
;
TSTTIME = TIMER1 ; Measure Time save.
;
CALL DISPSUB ; Measure Time disp.
;
LOOP DISPLAY X8 Y11 B1 (PUSH RESET KEY) ;
IF[KEYCODE EQ RESET]GOTO FIN ; "RESET" key wait.
RETURNP LOOP ;
;
FIN TAIWAP1 = MAINPR ;
RETURN ;
/*
- 63 -
Page 72

C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
$EJECT
/*
/*
/* (#101=SIN[#102]) Operation Time Test.
/*
/* No. O1300 : SUB program.
/*
/*
O1300 ;
NOREAD ; NO data read.
;
DISPLAY X2 Y2 B0 ('#101=SIN[#102]') ; Operation code disp.
;
COUNT = LOOPCT ; Loop counter set.
TIMER1 = 0 ; Timer initialize.
WHILE[COUNT GT 0]DO1 ;
#101 = SIN[#102] ; (Time Measure)
COUNT = COUNT –1 ;
END1 ;
;
TSTTIME = TIMER1 ; Measure Time save.
;
CALL DISPSUB ; Measure Time disp.
;
LOOP DISPLAY X8 Y11 B1 (PUSH RESET KEY) ;
IF[KEYCODE EQ RESET]GOTO FIN ; "RESET" key wait.
RETURNP LOOP ;
;
FIN TAIWAP1 = MAINPR ;
RETURN ;
- 64 -
Page 73

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
Subprogram reference list file File name : SUB1.REF
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Fri Apr-25-2003 12:11:55 Page 1
(FS30i) Macro Compiler (Pre) V01.0 SUB1.SRC
---------- Compile Parameter -----------------------------------------
---------- Program ---------------------------------------------------
S-Line G-Line
1 /*
2 /* SAMPLE Program.
3 /*
4 /* Conversation MACRO Execution-Time Test Program.
5 /* (Vol 01.00 2003.04.10)
6 /*
7 /*
8 /* ( SUB Program )
9 /*
10 /*
11 /* Symbol define.
12 /*
13 /* System common symbole FILE Include.
14 /*
15 $INCLUDE C:\\MCOMP30I\TOOL\SYSTEM.DEF
16 $NOLIST
796 /*
797 /*
798 @LOOPCT #500 /* TEST Loop count.
799 @TIMESAV #501 /* No-operatinon Time save.
800 @TSTTIME #502 /* Measured Time save.
801 /*
802 /*
803 @COUNT #100 /* Loop counter work.
804 @MAINPR 1000 /* MAIN Program No.
805 @DISPSUB 1001 /* Answer display SUB Program.
806 /*
807 /*
808 >LOOP 100 /* GOTO Sequense No. define.
809 >FIN 999
810 /*
811 /*
812 $EJECT
- 65 -
Page 74

C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
Fri Apr-25-2003 12:11:55 Page 2
(FS30i) Macro Compiler (Pre) V01.0 SUB1.SRC
S-Line G-Line
813 /*
814 /*
815 /* (#101=#102+#103) Operation Time Test.
816 /*
817 /* No. O1100 : SUB program.
818 /*
819 /*
820 0001 O1100 ;
821 0002 NOREAD ; NO data read.
822 0003 ;
823 0004 DISPLAY X2 Y2 B0 ('#101=#102+#103 TEST') ; Operation code disp.
824 0005 ;
825 0006 COUNT = LOOPCT ; Loop counter set.
826 0007 TIMER1 = 0 ; Timer initialize.
827 0008 WHILE[COUNT GT 0]DO1 ;
828 0009 #101 = #102 + #103 ; (Time Measure)
829 0010 COUNT = COUNT –1 ;
830 0011 END1 ;
831 0012 ;
832 0013 TSTTIME = TIMER1 ; Measure Time save.
833 0014 ;
834 0015 CALL DISPSUB ; Measure Time disp.
835 0016 ;
836 0017 LOOP DISPLAY X8 Y11 B1 (PUSH RESET KEY) ;
837 0018 IF[KEYCODE EQ RESET]GOTO FIN ; "RESET" key wait.
838 0019 RETURNP LOOP ;
839 0020 ;
840 0021 FIN TAIWAP1 = MAINPR ;
841 0022 RETURN ;
842 /*
843 /*
844 $EJECT
- 66 -
Page 75

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
Fri Apr-25-2003 12:11:55 Page 3
(FS30i) Macro Compiler (Pre) V01.0 SUB1.SRC
S-Line G-Line
845 /*
846 /*
847 /* (#101=#102 AND #103) Operation Time Test.
848 /*
849 /* No. O1200 : SUB program.
850 /*
851 /*
852 0023 O1200 ;
853 0024 NOREAD ; NO data read.
854 0025 ;
855 0026 DISPLAY X2 Y2 B0 ('#101=#102 AND #103 TEST') ; Operation code disp.
856 0027 ;
857 0028 COUNT = LOOPCT ; Loop counter set.
858 0029 TIMER1 = 0 ; Timer initialize.
859 0030 WHILE[COUNT GT 0]DO1 ;
860 0031 #101 = #102 AND #103 ; (Time Measure)
861 0032 COUNT = COUNT –1 ;
862 0033 END1 ;
863 0034 ;
864 0035 TSTTIME = TIMER1 ; Measure Time save.
865 0036 ;
866 0037 CALL DISPSUB ; Measure Time disp.
867 0038 ;
868 0039 LOOP DISPLAY X8 Y11 B1 (PUSH RESET KEY) ;
869 0040 IF[KEYCODE EQ RESET]GOTO FIN ; "RESET" key wait.
870 0041 RETURNP LOOP ;
871 0042 ;
872 0043 FIN TAIWAP1 = MAINPR ;
873 0044 RETURN ;
874 /*
875 /*
876 $EJECT
- 67 -
Page 76

C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
Fri Apr-25-2003 12:11:55 Page 4
(FS30i) Macro Compiler (Pre) V01.0 SUB1.SRC
S-Line G-Line
877 /*
878 /*
879 /* (#101=SIN[#102]) Operation Time Test.
880 /*
881 /* No. O1300 : SUB program.
882 /*
883 /*
884 0045 O1300 ;
885 0046 NOREAD ; NO data read.
886 0047 ;
887 0048 DISPLAY X2 Y2 B0 ('#101=SIN[#102]') ; Operation code disp.
888 0049 ;
889 0050 COUNT = LOOPCT ; Loop counter set.
890 0051 TIMER1 = 0 ; Timer initialize.
891 0052 WHILE[COUNT GT 0]DO1 ;
892 0053 #101 = SIN[#102] ; (Time Measure)
893 0054 COUNT = COUNT –1 ;
894 0055 END1 ;
895 0056 ;
896 0057 TSTTIME = TIMER1 ; Measure Time save.
897 0058 ;
898 0059 CALL DISPSUB ; Measure Time disp.
899 0060 ;
900 0061 LOOP DISPLAY X8 Y11 B1 (PUSH RESET KEY) ;
901 0062 IF[KEYCODE EQ RESET]GOTO FIN ; "RESET" key wait.
902 0063 RETURNP LOOP ;
903 0064 ;
904 0065 FIN TAIWAP1 = MAINPR ;
905 0066 RETURN ;
906 0067 %
- 68 -
Page 77

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
Fri Apr-25-2003 12:11:55 Page 5
(FS30i) Macro Compiler (Pre) V01.0 SUB1.SRC
---------- Cross Reference -------------------------------------------
Symbol Define Line No.
CALL M98P 834, 866, 898
RETURN M99 841, 873, 905
RETURNP M99P 838, 870, 902
DISPLAY G243 823, 836, 855, 868, 887,
900
TAIWAP1 #8500 840, 872, 904
NOREAD #8502=0 821, 853, 885
KEYCODE #8501 837, 869, 901
RESET 10 837, 869, 901
TIMER1 #3001 826, 832, 858, 864, 890,
896
LOOPCT #500 825, 857, 889
TSTTIME #502 832, 864, 896
COUNT #100 825, 827, 829, 829, 857,
859, 861, 861, 889, 891,
893, 893
MAINPR 1000 840, 872, 904
DISPSUB 1001 834, 866, 898
LOOP 100 836, 838, 868, 870, 900,
902
FIN 999 837, 840, 869, 872, 901,
904
- 69 -
Page 78

C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
Subprogram compile list file File name : SUB1.LST
25-Apr-2003 12:11:55 Page 1
(FS30i) Macro Compiler V01.0 SUB1.SRC
---------- Compile Parameter -----------------------------------------
---------- program O1100 ---------------------------------------------
G-Line P-Line
0001 1 O1100;
0002 2 #8502=0;
0003 3 ;
0004 4 G243X2Y2B0(*23 31 30 31 3D 23 31 30 32 2B 23 31 30 33 20 54 45 53 54*);
0005 5 ;
0006 6 #100=#500;
0007 7 #3001=0;
0008 8 WHILE[#100GT0]DO1;
0009 9 #101=#102+#103;
0010 10 #100=#100-1;
0011 11 END1;
0012 12 ;
0013 13 #502=#3001;
0014 14 ;
0015 15 M98P1001;
0016 16 ;
0017 17 N100G243X8Y11B1(PUSH RESET KEY);
0018 18 IF[#8501EQ10]GOTO999;
0019 19 M99P100;
0020 20 ;
0021 21 N999#8500=1000;
0022 22 M99;
----------------------------------------------------------------------
0 errors, 22 blocks, 22 total lines
program size = 163 bytes
- 70 -
Page 79

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
25-Apr-2003 12:11:55 Page 2
(FS30i) Macro Compiler V01.0 SUB1.SRC
---------- Cross Reference -------------------------------------------
#100 : 6, 8, 10, 10,
#101 : 9,
#102 : 9,
#103 : 9,
#500 : 6,
#502 : 13,
#3001 : 7, 13,
#8500 : 21,
#8501 : 18,
#8502 : 2,
- 71 -
Page 80

C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
25-Apr-2003 12:11:55 Page 3
(FS30i) Macro Compiler V01.0 SUB1.SRC
---------- program O1200 ---------------------------------------------
G-Line P-Line
0023 1 O1200;
0024 2 #8502=0;
0025 3 ;
0026 4 G243X2Y2B0(*23 31 30 31 3D 23 31 30 32 20 41 4E 44 20 23 31 30 33 20 54 45 53 54*);
0027 5 ;
0028 6 #100=#500;
0029 7 #3001=0;
0030 8 WHILE[#100GT0]DO1;
0031 9 #101=#102AND#103;
0032 10 #100=#100-1;
0033 11 END1;
0034 12 ;
0035 13 #502=#3001;
0036 14 ;
0037 15 M98P1001;
0038 16 ;
0039 17 N100G243X8Y11B1(PUSH RESET KEY);
0040 18 IF[#8501EQ10]GOTO999;
0041 19 M99P100;
0042 20 ;
0043 21 N999#8500=1000;
0044 22 M99;
----------------------------------------------------------------------
0 errors, 22 blocks, 22 total lines
program size = 167 bytes
- 72 -
Page 81

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
25-Apr-2003 12:11:55 Page 4
(FS30i) Macro Compiler V01.0 SUB1.SRC
---------- Cross Reference -------------------------------------------
#100 : 6, 8, 10, 10,
#101 : 9,
#102 : 9,
#103 : 9,
#500 : 6,
#502 : 13,
#3001 : 7, 13,
#8500 : 21,
#8501 : 18,
#8502 : 2,
- 73 -
Page 82

C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
25-Apr-2003 12:11:55 Page 5
(FS30i) Macro Compiler V01.0 SUB1.SRC
---------- program O1300 ---------------------------------------------
G-Line P-Line
0045 1 O1300;
0046 2 #8502=0;
0047 3 ;
0048 4 G243X2Y2B0(*23 31 30 31 3D 53 49 4E 5B 23 31 30 32 5D*);
0049 5 ;
0050 6 #100=#500;
0051 7 #3001=0;
0052 8 WHILE[#100GT0]DO1;
0053 9 #101=SIN[#102];
0054 10 #100=#100-1;
0055 11 END1;
0056 12 ;
0057 13 #502=#3001;
0058 14 ;
0059 15 M98P1001;
0060 16 ;
0061 17 N100G243X8Y11B1(PUSH RESET KEY);
0062 18 IF[#8501EQ10]GOTO999;
0063 19 M99P100;
0064 20 ;
0065 21 N999#8500=1000;
0066 22 M99;
0067 23 %
----------------------------------------------------------------------
0 errors, 23 blocks, 23 total lines
program size = 156 bytes
- 74 -
Page 83

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
25-Apr-2003 12:11:55 Page 6
(FS30i) Macro Compiler V01.0 SUB1.SRC
---------- Cross Reference -------------------------------------------
#100 : 6, 8, 10, 10,
#101 : 9,
#102 : 9,
#500 : 6,
#502 : 13,
#3001 : 7, 13,
#8500 : 21,
#8501 : 18,
#8502 : 2,
- 75 -
Page 84

C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
Link map list file File name : SAMPL.MAP
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Fri Apr-25-2003 12:12:0 Page 1
Macro Linker V01.0 SAMPL.MAP
---------- Macro Library List -----------------------------------------------
NO FILE NAME MACRO LIBRARY NAME
1 \MCOMP30I\MEX\F30iA_01.MEX FS30i MACRO LIBRARY FILE
---------- Compile Parameter ------------------------------------------------
P9000 = 00000100
P9001 = 00000000
P9002 = 00100000
P9003 = 00000001
P9004 = 00000000
P9005 = 00000000
P9006 = 00000000
P9007 = 00000000
P9008 = 00000000
P9009 = 00000000
P9010 = 0
P9011 = 0
P9012 = 0
P9013 = 0
P9014 = 0
P9015 = 0
P9016 = 0
P9017 = 0
P9018 = 0
P9019 = 0
P9020 = 0
P9021 = 0
P9022 = 0
P9023 = 0
P9024 = 0
P9025 = 0
P9026 = 0
P9027 = 0
P9028 = 0
P9029 = 0
P9030 = 0
P9031 = 0
P9032 = 0
P9033 = 0
P9038 = 1000
P9039 = 0
P9040 = 0
P9041 = 0
P9042 = 0
P9043 = 0
P9045 = 0
P9046 = 0
P9047 = 0
P9048 = 0
P9049 = 0
P9054 = 0
P9056 = 0
P9100 = 00000001
- 76 -
Page 85

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX C.COMPILE/LINK EXAMPLE
Fri Apr-25-2003 12:12:0 Page 2
Macro Linker V01.0 SAMPL.MAP
P9105 = 00000000
P9111 = 0
P9112 = 0
P9113 = 0
P9114 = 0
P9115 = 0
P9116 = 0
P9117 = 0
P9118 = 0
P9119 = 0
P9120 = 0
P9121 = 0
P9122 = 0
P9123 = 0
P9124 = 0
P9125 = 0
P9126 = 0
P9127 = 0
P9128 = 0
P9129 = 0
P9130 = 0
P9131 = 0
P9132 = 0
P9133 = 0
P9134 = 0
P9135 = 0
P9136 = 0
P9137 = 0
P9160 = 00000000
P9163 = 00000000
P9164 = 00000000
P9165 = 00000000
P9167 = 00000000
---------- Object List ------------------------------------------------------
FILE NAME PROG SIZE
MAIN.REL 00001000 0000FAH
00001001 000091H
SUB1.REL 00001100 0000A3H
00001200 0000A7H
00001300 00009CH
---------- ROM FILE SIZE ----------------------------------------------------
SIZE = 10000H ( 64KB )
Select type : 256K
Used size = 5771HB
Free size = 3A88FHB
- 77 -
Page 86

D.BOOT SYSTEM APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
D BOOT SYSTEM
- 78 -
Page 87

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX D.BOOT SYSTEM
D.1 OVERVIEW
The Boot System load the CNC system software (Flash RAM →
DRAM), then starts it so that software can be executed.
The Boot System provides the following maintenance functions for
the CNC:
(1) Registering a file in Flash ROM
Reads a file from a Memory card, in FAT format, into Flash
ROM.
(2) Checking a file (series and edition) in Flash ROM
(3) Checking a file (series and edition) in Memory card
(4) Deleting a file from Flash ROM
(5) Deleting a file from Memory card
(6) Saving a file in Flash ROM to a Memory card
(7) Batch saving and restoration of files of parameters and programs
backed up by battery (SRAM area), to and from a Memory card
(8) Formatting of a Memory card
This manual describes the activation of the Boot System, as well as
the screen displays and operation for the functions listed above.
CAUTION
1 This control unit supports the use of a Memory card as an input/output device. The
following Memory cards are available:
SRAM Memory card
Flash card
Flash ATA card
See the order list for details of the supported Memory card types.
2 On a Memory card, only those files that are in the root directory can be accessed for
display, reading, and writing. Those in subdirectories cannot be used.
3 The time required to read or write each data item varies depending on the Memory
card type, the status of use, and other factors.
4 For Flash cards, only those recommended by FANUC can be accessed for writing.
For reading, they can be usually be used in the same way as SRAM cards as long as
the FAT format is used.
When using a Flash card, note that the card capacity decreases by 128 KB.
A Flash memory card does not allow deletion of files one at a time. It is necessary to
delete all files on the card at a time.
5 For Flash ATA cards, only those recommended by FANUC are available.
6 When formatting a Flash ATA card, use the quick formatting method, which clears
the file allocation table and the directory information on the root directory. An
unformatted Flash ATA card cannot be used without being formatted with a personal
computer.
- 79 -
Page 88

D.BOOT SYSTEM APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
D.1.1 Displaying the Power ON Sequence
(1)
RAM TEST :END
(2)
ROM TEST :END [60W1A]
(3)
DRAM ID :xxxxxxxx
(4)
SRAM ID :xxxxxxxx
(5)
FROM ID :xxxxxxxx
*** MESSAGE ***
(7)
LOADING CNC DATA-1 xxxxxx/xxxxxx
END
RAM TEST :END
(2)
ROM TEST :ERROR
*** MESSAGE ***
ROM PARITY ERROR:NC BASIC. HIT SELECT.
(6)
Processing is stopped in the event of an
error
SELECT key → SYSTEM MONITOR
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
Details of display items
(1) WORK RAM test results are displayed. In the event of an error,
however, the sequence is not displayable, and LED indication is
conducted without error display.
(2) BOOT ROM parity test results are displayed. During normal
operation, the series and edition are displayed. In the event of an
error, processing is stopped.
(3) The ID of the DRAM MODULE installed in the CNC is
displayed.
(4) The ID of the SRAM MODULE installed in the CNC is
displayed.
(5) The ID of the FROM MODULE installed in the CNC is
displayed.
(6) The CNC BASIC software in Flash memory is checked for
validity and, in the event of an error, an error is displayed. In the
event of an error, clicking the [SELECT] soft key allows you to
select the SYSTEM MONITOR screen.
(7) This message indicates that the CNC BASIC software is being
transferred to Flash memory to DRAM.
- 80 -
Page 89
B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX D.BOOT SYSTEM
D.1.2 Starting the Boot System
In ordinary system activation, the Boot System automatically transfers
files from Flash ROM to DRAM in the background.
The user is not aware of this operation. However, the Boot System
must be operated manually, from menu screen, when maintenance is
to be carried out or when the Flash ROM does not contain a required
file.
(1) In system maintenance, for example, to replace a file in Flash
ROM
Operation : Turn the power on by simultaneously pressing the
two soft keys at the right end. If no soft keys are provided as
with a touch panel, use MDI numeric keys 6 and 7.
1234567
After an FROM ID and other items are displayed on the CNC
screen, releasing the key brings you to the SYSTEM MONITOR
screen.
(2) When the Flash ROM does not contain a file required to start the
CNC
Immediately after the CNC is turned on, the Boot System starts
transferring files from Flash ROM to DRAM. If, for some reason,
a file required to start the CNC (NC BASIC) is not in Flash
ROM or has been destroyed, the Boot System is automatically
started.
D.1.3 System Files and User Files
The Boot System organizes files in Flash ROM into two main
groups : system files and user files. These two file types have the
following characteristics :
System files
CNC and servo control software provided by FANUC
User files
PMC sequence program (ladder), P-CODE macro program, and other
user-created files
- 81 -
Page 90
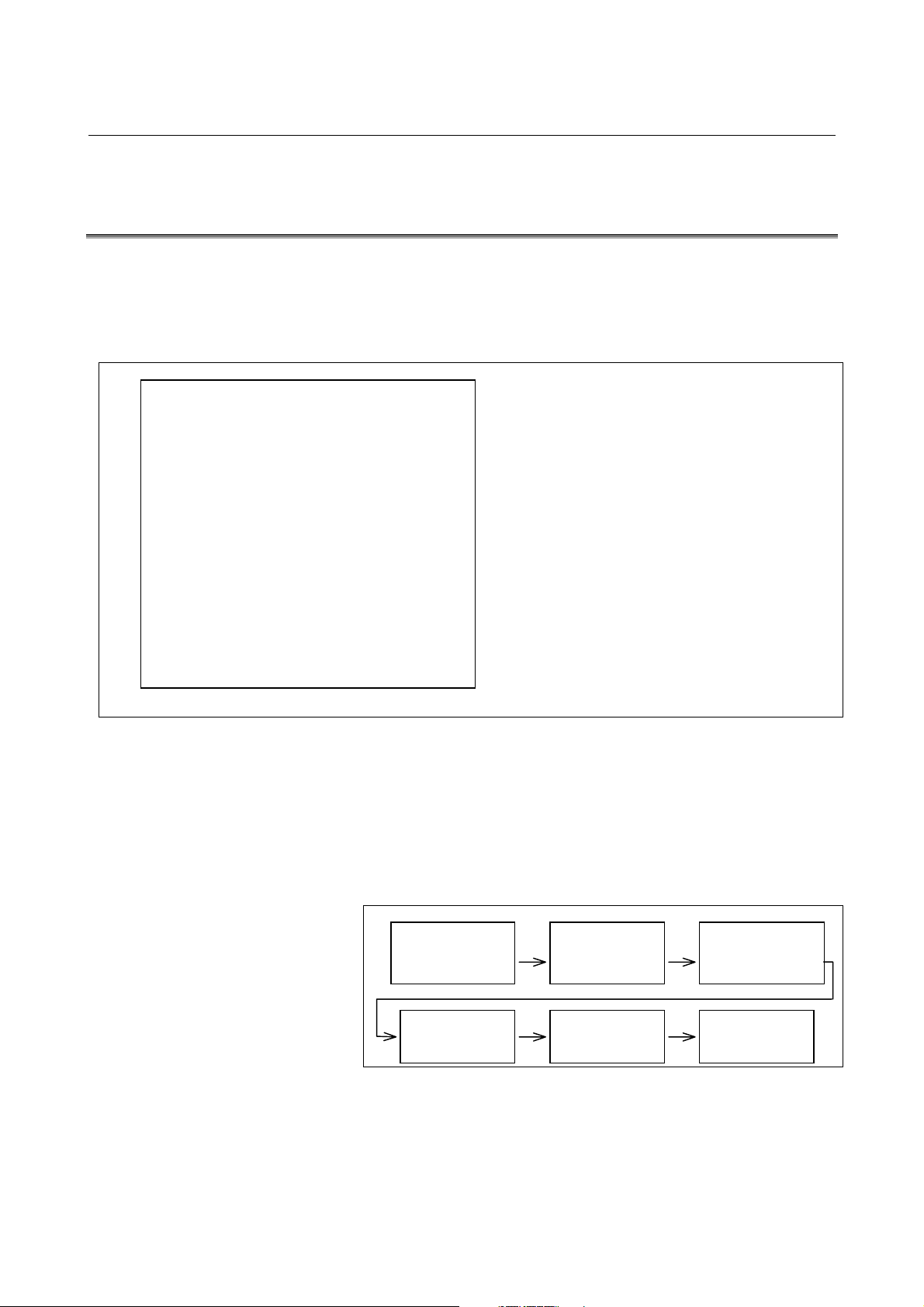
D.BOOT SYSTEM APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
D.2 SCREEN CONFIGURATION AND OPERATING
PROCEDURE
When the Boot System is first started, the MAIN MENU screen is
displayed. This screen is described below :
MAIN MENU screen
SYSTEM MONITOR MAIN MENU 60W1 - 01
(1)
1.END
(2)
2.USER DATA LOADING
(3)
3.SYSTEM DATA LOADING
(4)
4.SYSTEM DATA CHECK
(5)
5.SYSTEM DATA DELETE
(6)
6.SYSTEM DATA SAVE
(7)
7.SRAM DATA BACKUP
(8)
8.MEMORY CARD FORMAT
(9)
*** MESSAGE ***
SELECT MENU AND HIT SELECT KEY.
(10)
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
(1) Screen title. The series and edition of
the BOOT SYSTEM are displayed at
the right end.
(2) Function for terminating the Boot
System and starting the CNC.
(3) Function for writing data to Flash ROM.
(4) Function for writing data to Flash ROM.
(5) Function for checking the edition of a
file in ROM.
(6) Function for deleting a file from Flash
ROM or Memory card.
(7) Function for making a backup copy of
the data stored on the Memory card.
(8) Function for backing up and restoring
the SRAM area
(9) Function for formatting a Memory card.
(10) Simple operating instructions and error
messages are displayed.
Operating procedure
Basic operation
Press the [UP] or [DOWN] soft key to select the desired function.
After positioning the cursor to the desired function, press the
[SELECT] soft key. Before executing a function, the system my
request confirmation from the operator by having him/her press the
[YES] or [NO] soft key.
Position the cursor.
[ UP ]
[ DOWN ]
Execute the
function
Select a function
[SELECT]
Select END
Check the selection
[ YES ]
[ NO ]
Return to original
state
- 82 -
Page 91
B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX D.BOOT SYSTEM
D.2.1 USER DATA LOADING/SYSTEM DATA LOADING Screen
Description
This screen is used to read a system or user file from a Memory card
into Flash ROM.
The USER DATA LOADING screen is used to load ROM data from
a Memory card to Flash memory.
The SYSTEM DATA LOADING screen is used to check the contents
of the ROM card installed in a Memory card and then load ROM data
from the Memory card to Flash memory.
Screen configuration
SYSTEM DATA LOADING
(1)
MEMORY CARD DIRECTORY (FREE[KB]: 5123)
(2)
1 G001A_B1.MEM 1048704 2003-01-01 12:00
(3)
2 G001A_B2.MEM 1048704 2003-01-01 12:00
3 END
(4)
(1) Screen title.
(2) The size of the free space of the
Memory card is displayed.
(3) A list of files in the Memory card is
displayed.
*** MESSAGE ***
SELECT MENU AND HIT SELECT KEY.
(5)
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
Operating procedure
(4) Returning to the MAIN MENU.
(5) Message
(1) Position the cursor to the file to be read from the Memory card
and written to Flash ROM. Then, press the [SELECT] soft key.
- A single page can list up to ten file names.
- If the Memory card contains ten or more files, the
remaining files are displayed on another page.
To display the next page, press the
To display the previous page, press the
soft key.
soft key. The
END option is displayed on the last page.
The END option is displayed on the last page.
(2) When you select a file from the USER DATA LOADING screen,
you are prompted for confirmation.
SYSTEM DATA LOADING
MEMORY CARD DIRECTORY (FREE[KB]: 5123)
1 G001A_B1.MEM 1048704 2003-01-01 12:00
2 G001A_B2.MEM 1048704 2003-01-01 12:00
3 END
*** MESSAGE ***
LOADING OK ? HIT YES OR NO.
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
- 83 -
Page 92

D.BOOT SYSTEM APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
(3) When you select a file from the SYSTEM DATA LOADING
screen, a ROM data confirmation screen is displayed for
confirmation.
SYSTEM DATA CHECK & DATA LOADING
G001A_B1.MEM
1 G001 001A
2 G001 021A
3 G001 041A
4 G001 061A
5 G001 081A
6 G001 0A1A
7 G001 0C1A
8 G001 0E1A
*** MESSAGE ***
LOADING OK ? HIT YES OR NO.
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
(4) To start loading, press the [YES] soft key. To cancel, press the
[NO] key.
*** MESSAGE ***
LOADING FROM MEMORY CARD xxxxxx/xxxxxx
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
(5) When loading terminates normally, the system displays the
following message. Press the [SELECT] soft key. If an error
occurs, see C.3
*** MESSAGE ***
LOADING COMPLETE.
HIT SELECT KEY.
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
- 84 -
Page 93
B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX D.BOOT SYSTEM
D.2.2 SYSTEM DATA CHECK Screen
Description
This screen is used to list files in Flash ROM or Memory card,
together with the corresponding numbers of management units in each
file and the series and edition of the software.
Screen configuration
SYSTEM DATA CHECK
(1)
1.FROM SYSTEM
(2)
2.MEMORY CARD SYSTEM
(3)
3.END
(4)
*** MESSAGE ***
SELECT MENU AND HIT SELECT KEY.
(5)
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
(1) Screen title.
(2) Select the FROM SYSTEM screen.
(3) Select the MEMORY CARD SYSTEM
screen.
(4) Returning to the MAIN MENU.
(5) Message
Screen configuration (FROM SYSTEM screen)
SYSTEM DATA CHECK
(1)
FROM DIRECTORY
1 NC BAS-1(0008)
(2)
2 NC BAS-2(0008)
3 NC BAS-3(0008)
4 NC BAS-4(0008)
5 DGD0SRVO(0003)
6 PS0B (0006)
7 END
(3)
*** MESSAGE ***
SELECT FILE AND HIT SELECT KEY.
(4)
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
(1) Screen title.
(2) Names of files in Flash ROM The
number of management units
constituting each file appears in
parentheses to the right of the filename.
(3) Returning to the MAIN MENU.
(4) Message
- 85 -
Page 94

D.BOOT SYSTEM APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
Screen configuration (MEMORY CARD SYSTEM screen)
SYSTEM DATA CHECK
(1)
MEMORY CARD DIRECTORY (FREE[KB]: 5123)
(2)
1 G001A_B1.MEM 1048704 2003-01-01 12:00
(3)
2 G001A_B2.MEM 1048704 2003-01-01 12:00
3 END
(4)
(1) Screen title.
(2) The size of the free space of the
Memory card is displayed.
(3) A list of files in the Memory card is
displayed.
(4) Returning to the MAIN MENU.
*** MESSAGE ***
SELECT FILE AND HIT SELECT KEY.
(5)
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
(5) Message
Operating procedure
(1) Select either the FROM SYSTEM or MEMORY CARD
SYSTEM screen.
(2) Select the file that you want to confirm (for example, "NC BAS-
1 (0008)").
(3) For the selected file, the management unit numbers are listed,
together with the series and editions of the management units.
After checking the listed data, select the [SELECT] soft key to
return to the file selection screen.
SYSTEM DATA CHECK
(1)
NC BAS-1(0008)
1 G001 001A 0000
(2)
2 G001 021A 0001
3 G001 041A 0002
4 G001 061A 0003
5 G001 081A 0004
6 G001 0A1A 0005
7 G001 0C1A 0006
8 G001 0E1A 0007
*** MESSAGE ***
HIT SELECT KEY.
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
(1) Screen title.
(2) The following items are displayed for
each management unit:
- Series
- ROM number and edition
- Internal management-unit number
If a check result cannot be displayed, a
"@" is displayed.
- 86 -
Page 95

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX D.BOOT SYSTEM
Others (Parity information for the system file and user file)
The NC BAS-1, DGD0SRVO, and other system files in Flash ROM
contain parity information in each management unit. If the file name
field or parity field on the check screen contains a non-ASC II
character or an "@", the Flash ROM may have been destroyed or a
damaged file may have been read. Re-read the data from the Memory
card.
The PMC1, and other user files do not contain parity information in
each management unit. A non-ASCII character or an "-" may appear
in the series/edition information. In this case, it does not indicate that
the file has been damaged.
- 87 -
Page 96
D.BOOT SYSTEM APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
D.2.3 SYSTEM DATA DELETE Screen
Description
This screen is used to delete a user file from Flash ROM or Memory
card.
Screen configuration
SYSTEM DATA DELETE
(1)
1.FROM SYSTEM
(2)
2.MEMORY CARD SYSTEM
(3)
3.END
(4)
*** MESSAGE ***
SELECT MENU AND HIT SELECT KEY.
(5)
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
(1) Screen title.
(2) Select the FROM SYSTEM screen.
(3) Select the MEMORY CARD SYSTEM
screen.
(4) Returning to the MAIN MENU.
(5) Message
Screen configuration (FROM SYSTEM screen)
SYSTEM DATA DELETE
(1)
FROM DIRECTORY
1 NC BAS-1(0008)
(2)
2 NC BAS-2(0008)
3 NC BAS-3(0008)
4 NC BAS-4(0008)
5 DGD0SRVO(0003)
6 PS0B (0006)
7 PMC1 (0001)
8 END
(3)
*** MESSAGE ***
SELECT FILE AND HIT SELECT KEY.
(4)
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
(1) Screen title.
(2) Names of files in Flash ROM
The number of management units
constituting each file appears in
parentheses to the right of the filename.
(3) Returning to the MAIN MENU.
(4) Message
- 88 -
Page 97

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX D.BOOT SYSTEM
Screen configuration (MEMORY CARD SYSTEM screen)
SYSTEM DATA DELETE
(1)
MEMORY CARD DIRECTORY (FREE[KB]: 5123)
(2)
1 G001A_B1.MEM 1048704 2003-01-01 12:00
(3)
2 G001A_B2.MEM 1048704 2003-01-01 12:00
3 END
(4)
(1) Screen title.
(2) The size of the free space of the
Memory card is displayed.
(3) A list of files in the Memory card is
displayed.
(4) Returning to the MAIN MENU.
*** MESSAGE ***
SELECT FILE AND HIT SELECT KEY.
(5)
(5) Message
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
Operating procedure
(1) Select either the FROM SYSTEM or MEMORY CARD
SYSTEM screen.
(2) Select the file you want to delete.
(3) The following message is displayed for confirmation.
*** MESSAGE ***
DELETE OK ? HIT YES OR NO.
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
(4) Click the [YES] soft key to start reading. Click [NO] to cancel
reading.
*** MESSAGE ***
EXECUTING
ADDRESS xxxx:
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
(5) Upon normal termination, a message such as that shown below is
displayed. Click the [SELECT] soft key. In the event of an error,
see the list of error messages and corrective actions, given later.
*** MESSAGE ***
DELETE COMPLETE. HIT SELECT KEY.
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
Others (System files and user files on SYSTEM DATA DELETE screen)
The system files are protected from accidental deletion. User files,
however, are not protected. Protected system files can be overwritten
from the USER DATA LOADING / SYSTEM DATA LOADING
screen.
- 89 -
Page 98

D.BOOT SYSTEM APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
D.2.4 SYSTEM DATA SAVE Screen
Description
This screen is used to write a user file in Flash ROM to a Memory
card. Only user files can be saved from Flash ROM to a Memory card.
System files cannot be saved.
Screen configuration
SYSTEM DATA SAVE
(1)
FROM DIRECTORY
1 NC BAS-1(0008)
(2)
2 NC BAS-2(0008)
3 NC BAS-3(0008)
4 NC BAS-4(0008)
5 DGD0SRVO(0003)
6 PS0B (0006)
7 PMC1 (0001)
8 END
(3)
(1) Screen title.
(2) Names of files in Flash ROM
The number of management units
constituting each file appears in
parentheses to the right of the filename.
(3) Returning to the MAIN MENU.
*** MESSAGE ***
SELECT FILE AND HIT SELECT KEY.
(4)
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
Operating procedure
(4) Message
(1) Select the file you want to save.
(2) The system displays the following confirmation message :
*** MESSAGE ***
SYSTEM DATA SAVE OK ? HIT YES OR NO.
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
(3) To start saving, press the [YES] key. To cancel, press [NO].
*** MESSAGE ***
STORE TO MEMORY CARD
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
- 90 -
Page 99

B-66264EN/01 APPENDIX D.BOOT SYSTEM
(4) When saving terminates normally, the system displays the
following message. Press the [SELECT] key. The names of files
written to the Memory card are listed. Check the file names by,
for example, making a note of the list.
*** MESSAGE ***
FILE SAVE COMPLETE. HIT SELECT KEY.
SAVE FILE NAME : PMC1.000
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
Others (System files and user files on SYSTEM DATA SAVE screen)
The SYSTEM DATA SAVE function provides a safeguard against
free copying of the system files.
User files, however, are not protected.
Files saved from Flash ROM to a Memory card have the following
names :
Header ID in Flash ROM File name in Memory card
PMC1.xxx
PMC1
PD010.5M
PD011.0M
→
PD010_5M.xxx
→
PD011_0M.xxx
→
"xxx" is replaced by one of 32 numbers "000", "001", ,,, and "031".
For example, if you attempt to save the file "PMC1 " from Flash
ROM to a Memory card, it will be saved with a name of "PMC1.000"
if no file with a name of "PMC1.000" is found on the Memory card. If,
however, that file is saved to a Memory card that already contains a
file named PMC1.000, the saved file is named PMC1.001. As files are
added, the extension is incremented up to a maximum of PMC1.031.
Any no-longer used numbers in the sequence of the extension
numbers are used in as cending order. If two or more files having
identical names but different extension numbers are normally saved to
the Memory card, check the file names displayed subsequently.
- 91 -
Page 100
D.BOOT SYSTEM APPENDIX B-66264EN/01
D.2.5 SRAM DATA BACKUP Screen
Description
This screen is used to collectively save and restore parameters,
programs, and other data, retained after the CNC power in SRAM is
turned off, to and from a Memory card.
Screen configuration
SRAM DATA BACKUP
(1)
1.SRAM BACKUP ( CNC -> MEMORY CARD )
(2)
2.RESTORE SRAM ( MEMORY CARD -> CNC )
3.END
(3)
(1) Screen title.
(2) Menu
(3) Returning to the MAIN MENU.
(4)
(5)
(6)
SRAM FILE SIZE : 1MBYTE
SRAMBAK.001
*** MESSAGE ***
SET MEMORY CARD NO.001
ARE YOU SURE ? HIT YES OR NO.
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
*** MESSAGE ***
SELECT MENU AND HIT SELECT KEY.
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
Operating procedure (Backing up data)
(1) Select "1.SRAM BACKUP" The following confirmation
message is displayed. Click [YES] to start backup.
(2) If the data cannot be saved entirely onto a single Memory card, a
message such as that shown below is displayed. With the power
still on, insert the second Memory card and click the [YES] key.
Press the [NO] key to cancel saving.
(4) The SRAM file size is displayed.
(Displayed after a processing option is
selected.)
(5) The name of the file currently being
saved or loaded is displayed. (Displayed
after a processing option is selected.)
(6) Message
*** MESSAGE ***
SET MEMORY CARD NO.002
ARE YOU SURE ? HIT YES OR NO.
[SELECT][ YES ][ NO ][ UP ][ DOWN ]
(3) In this way, you can divide SRAM data onto a maximum of 999
Memory card for backup.
- 92 -
 Loading...
Loading...