Page 1

SERVICE MANUAL
Color Inkjet Printer
EPSON Stylus Photo R800
SEIJ03012
Page 2

PRECAUTIONS
Precautionary notations throughout the text are categorized relative to 1)Personal injury and 2) damage to equipment.
DANGER Signals a precaution which, if ignored, could result in serious or fatal personal injury. Great caution should be exercised in performing
procedures preceded by DANGER Headings.
WARNING Signals a precaution which, if ignored, could result in damage to equipment.
The precautionary measures itemized below should always be observed when performing repair/maintenance procedures.
DANGER
1. ALWAYS DISCONNECT THE PRODUCT FROM THE POWER SOURCE AND PERIPHERAL DEVICES PERFORMING ANY MAINTENANCE OR REPAIR
PROCEDURES.
2. NO WORK SHOULD BE PERFORMED ON THE UNIT BY PERSONS UNFAMILIAR WITH BASIC SAFETY MEASURES AS DICTATED FOR ALL
ELECTRONICS TECHNICIANS IN THEIR LINE OF WORK.
3. WHEN PERFORMING TESTING AS DICTATED WITHIN THIS MANUAL, DO NOT CONNECT THE UNIT TO A POWER SOURCE UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO
DO SO. WHEN THE POWER SUPPLY CABLE MUST BE CONNECTED, USE EXTREME CAUTION IN WORKING ON POWER SUPPLY AND OTHER
ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS.
WARNING
1. REPAIRS ON EPSON PRODUCT SHOULD BE PERFORMED ONLY BY AN EPSON CERTIFIED REPAIR TECHNICIAN.
2. MAKE CERTAIN THAT THE SOURCE VOLTAGES IS THE SAME AS THE RATED VOLTAGE, LISTED ON THE SERIAL NUMBER/RATING PLATE. IF THE
EPSON PRODUCT HAS A PRIMARY AC RATING DIFFERENT FROM AVAILABLE POWER SOURCE, DO NOT CONNECT IT TO THE POWER SOURCE.
3. ALWAYS VERIFY THAT THE EPSON PRODUCT HAS BEEN DISCONNECTED FROM THE POWER SOURCE BEFORE REMOVING OR REPLACING
PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARDS AND/OR INDIVIDUAL CHIPS.
4. IN ORDER TO PROTECT SENSITIVE MICROPROCESSORS AND CIRCUITRY, USE STATIC DISCHARGE EQUIPMENT, SUCH AS ANTI-STATIC WRIST
STRAPS, WHEN ACCESSING INTERNAL COMPONENTS.
5. REPLACE MALFUNCTIONING COMPONENTS ONLY WITH THOSE COMPONENTS BY THE MANUFACTURE; INTRODUCTION OF SECOND-SOURCE
ICs OR OTHER NON-APPROVED COMPONENTS MAY DAMAGE THE PRODUCT AND VOID ANY APPLICABLE EPSON WARRANTY.
Page 3

About This Manual
This manual describes basic functions, theory of electrical and mechanical operations, maintenance and repair procedures of the printer. The instructions and
procedures included herein are intended for the experienced repair technicians, and attention should be given to the precautions on the preceding page.
Manual Configuration
This manual consists of six chapters and Appendix.
CHAPTER 1.PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS
Provides a general overview and specifications of the product.
CHAPTER 2.OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Describes the theory of electrical and mechanical operations of
the product.
CHAPTER 3.TROUBLESHOOTING
Describes the step-by-step procedures for the troubleshooting.
CHAPTER 4.DISASSEMBLY / ASSEMBLY
Describes the step-by-step procedures for disassembling and
assembling the product.
CHAPTER 5.ADJUSTMENT
Provides Epson-approved methods for adjustment.
CHAPTER 6.MAINTENANCE
Provides preventive maintenance procedures and the lists of
Epson-approved lubricants and adhesives required for servicing
the product.
APPENDIX Provides the following additional information for reference:
• Connector pin assignments
• Exploded diagram & Parts List
• Electric circuit boards components layout
• Electrical circuit boards schematics
Symbols Used in this Manual
Various symbols are used throughout this manual either to provide ad ditional
information on a specific topic or to warn of possible danger present during a
procedure or an action. Be aware of all symbols when they are used, and
always read NOTE, CAUTION, or WARNING messages.
Indicates an operating or maintenance procedure, practice or
condition that is necessary to keep the product’s quality.
Indicates an operating or maintenance procedure, practice, or
condition that, if not strictly observed, could result in damage to,
or destruction of, equipment.
May indicate an operating or maintenance procedure, prac tice or
condition that is necessary to accomplish a task efficiently. It may
also provide additional information that is related to a specific
subject, or comment on the results achieved through a previous
action.
Indicates an operating or maintenance procedure, practice or
condition that, if not strictly observed, could result in injury or loss
of life.
Indicates that a parti cu la r ta sk mu st be ca rr i ed o ut ac co rd ing to a
certain standard after disassembly and before re-assembly,
otherwise the quality of the components in question may be
adversely affected.
Page 4
Revision Status
Revision Date of Issue Description
A December 16, 2003 First Release
B May 27, 2004 Correction of the misspellings
Page 5

CONTENTS
Chapter 1 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
1.1 Overview.......................... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... ........... 9
1.2 PG Setting ....................................... .......................................... ... ......... 10
1.3 Functions ........ ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................... ... ... .... ... .. 11
1.3.1 Control Panel ............. ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................... .. 11
1.3.2 Switches ............................ ... ... ... .......................................... .... ..... 11
1.3.3 Indicators ........................................................... ... ......................... 11
1.3.4 Switch Functions ............................................................... ... .... ... .. 11
1.3.5 Indicator Display in Normal Mode ................................................. 12
1.3.6 Error Status ....... ... ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... .... ... .. 13
1.4 Casing Specifications .................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .. 14
1.5 Accessories .............. ............................................................................ 14
Chapter 2 OPERATING PRINCIPLES
2.1 Overview.......................... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... ......... 16
2.2 Printer Mechanism ............... .......................................... .... ... ............... 16
2.2.1 Carriage Mechanism .. ... .... ... ... ... .... .......................................... ... .. 17
2.2.2 Printhead Specifications ....................... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ......... 20
2.2.3 Paper Feeding Mechanism ........................................................... 20
2.2.4 Paper Loading Mechanism ........................................................... 24
2.2.5 Ink System Mechanism ................................................................. 26
2.2.6 Ink Sequence .......................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ............ 28
2.2.7 Paper Cutter Mechanism .............................................................. 30
2.2.8 Power-On Sequence ..................................................................... 32
2.3 Electrical Circuitry Operating Principles................................ ....... ... .. 33
2.3.1 Power Supply Circuit Operating Principle ..................................... 33
2.3.2 C550 MAIN Circuit Operating Principle .................................... ... .. 34
3.1 Overview ............................................................................................... 38
3.1.1 Troubleshooting according to panel messages ............................ 38
3.1.2 Superficial Phenomenon-Based Troubleshooting ......................... 62
Chapter 4 DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY
4.1 Overview ............................................................................................... 73
4.1.1 Precautions ................................................................................... 73
4.1.2 Tools to Be Used ............... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... . 74
4.1.3 Screw List ..................................................................................... 75
4.1.4 Pre-Shipment Checks ................................................................... 76
4.2 Disassembly ......................................................................................... 77
4.2.1 Removing the Housings ................................................................ 78
4.2.2 Stacker Assy. ................................................................................ 82
4.2.3 Waste Ink Pads ............................................................................. 84
4.2.4 ASF Assy. ..................................................................................... 86
4.2.5 Removing the Boards ................................................................... 90
4.2.6 Disassembling the Printer Mechanism .......................................... 96
4.2.7 Removing the Motors .................................................................. 130
4.2.8 Removing the Sensors ................................................................ 133
Chapter 5 ADJUSTMENT
5.1 Adjustment Items and Overview....................................................... 140
5.1.1 Servicing Adjustment Item List .................................................... 140
5.1.2 Replacement Part-Based Adjustment Priorities .......................... 143
5.1.3 Required Adjustment Jigs, Tools and Like .................................. 145
5.2 Adjustments........................................................................................ 145
5.2.1 PF Belt Tension Adjustment ....................................................... 145
5.2.2 PG Adjustment ............................................................................ 147
Chapter 3 TROUBLESHOOTING
Chapter 6 MAINTENANCE
Page 6

6.1 Overview.......................... ... ... .... ... .......................................... ... ... .... ... 153
6.1.1 ROM Replacement ..................... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... .......... 153
6.1.2 Cleaning .. ... ... .... .......................................... ... ... ... ... .................... 153
6.1.3 Service Maintenance ................................................................... 154
6.1.4 Lubrication ......................... ... ... .......................................... ... .... ... 155
Chapter 7 APPENDIX
7.1 Connector Summary .......................................................................... 162
7.1.1 Connectors and Pin Layouts ....................................................... 162
7.2 Exploded Diagram........................................................................... ... 163
7.3 Parts List for EPSON Stylus Photo R800 ......................................... 170
7.4 Component Layout............................................................................. 172
7.5 Circuit Diagram............................... .......................................... ... .... ... 174
Page 7
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
CHAPTER
1
Page 8
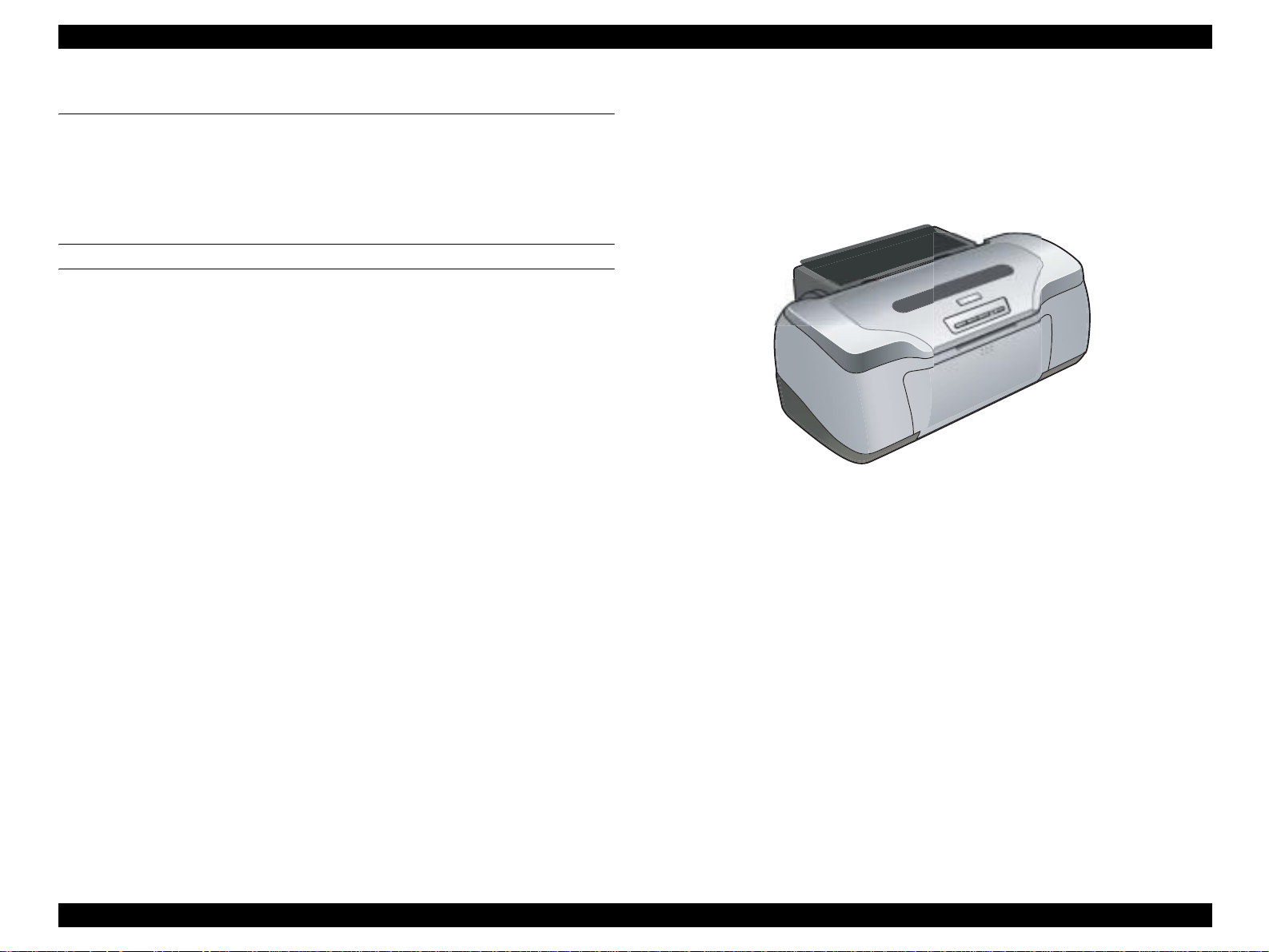
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
1.1 Overview
The Stylus Photo R800 is a photo printer designed for a wide range of users
from individual users to commercial users. As a successor to the Stylus Photo
950/960, this consumer middle high model is capable of CD-R/DVD-R printing
and roll paper cutter functions.
This product has the following features.
FEATURES
High Color Print Quality
High photo quality thanks to Photo Mach technology
Achievement of higher quality using microweaves and super
microweaves
High resolution printing of 5760 x 1440dpi, world's minimum dot 1.5pl
MSDT
High-speed printing
Two Different Interfaces Supported
USB 2.0 (HS compatibility)
IEEE-1394
Compact, space saving
Windows/Macintosh Exclusive
Multi-size Capable ASF
ASF equipped as standard supports forms ranging from business cards to
A4.
CSIC-compatible Independent Ink Cartridge
Roll paper compatibility
Note"*1": When user performs the "Auto nozzle check and cleaning", Prints
nozzle check pattern and automatically checks print head nozzles. If they are
clogged, performs head cleaning. If they are not recovered, and perfor ms head
cleaning and detection up to tree times.
Figure 1-1. Product Appearance
Fast, 4-side borderless printing compatibility
Two-sided printing compatibility
Prevention of platen printing by optical sensor
CD-R/DVD-R printing compatibility by front loading
Business card, card photo printing compatibility
Auto Nozzle Check and Cleaning*1
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Overview 9
Page 9
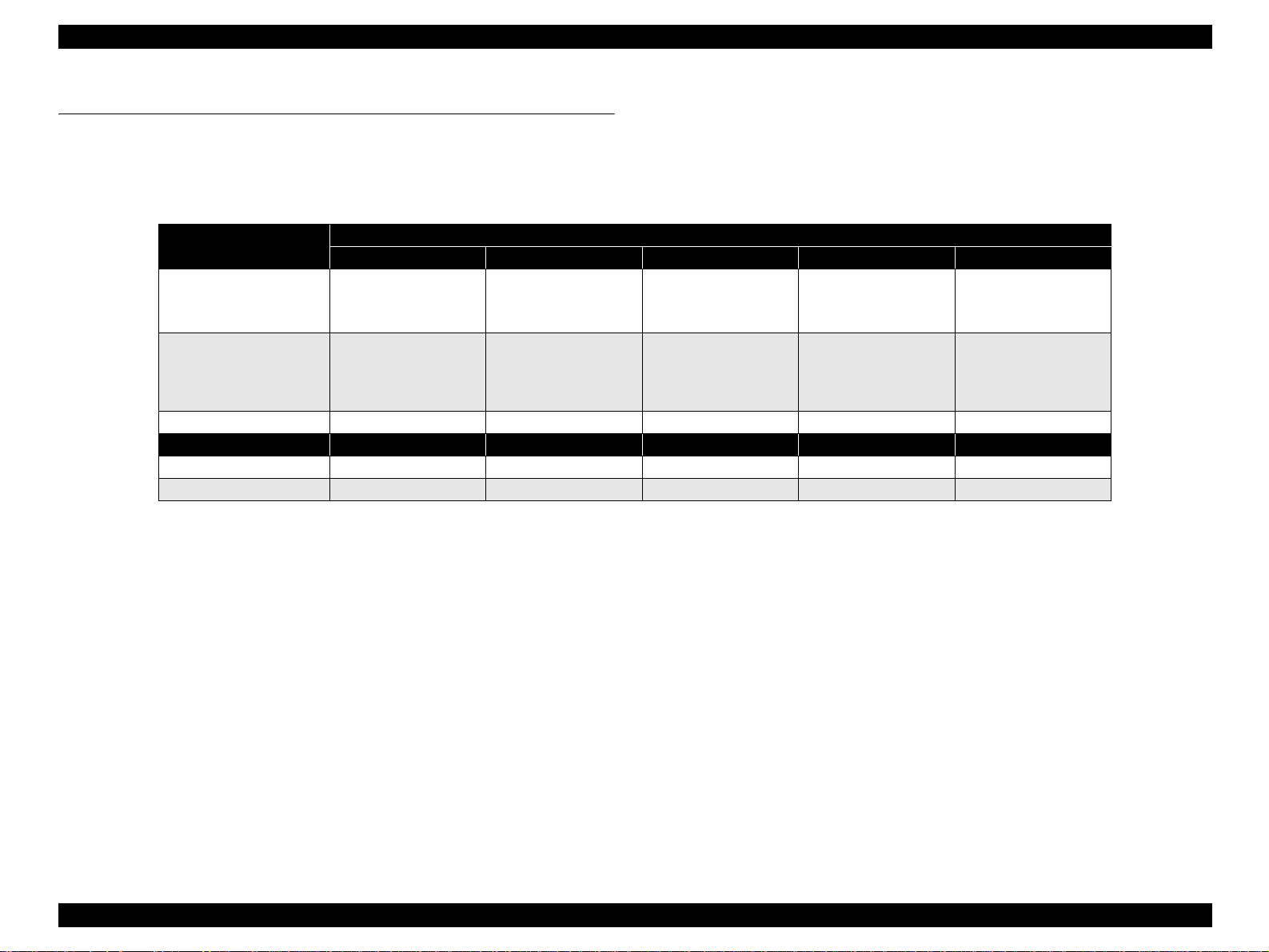
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
1.2 PG Setting
As this printer uses an Auto PG (APG), an appropriate PG position is set according to the used paper type.
The following table indicates the PG positions, the main applications of each position, and the relationships between the two sensors used with the APG.
Table 1-1.
Application
Printing • Special thick paper • Plain paper
Non-printing
PG value 1.2mm 1.7mm 2.1mm 4.5mm –
Sensor PG (-) PG (Typ.) PG (+) PG (++) Release
APG Sensor 1 OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
APG Sensor 2 ON ON ON OFF OFF
PG (-) PG (0) PG (+) PG (++) Release
• Special thin paper
• PG(-) rub avoidance
• Standby position
–
after power-on (For
bottom stacker)
PG Position
• Envelope
• PG(0) rub avoidance
–
• CD-R/Board paper
• Initialization at
power-on
• Cleaning (wiping)
–
• Waiting for CD-R/
Board paper to be
fed
• Paper jam removal
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION PG Setting 10
Page 10
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
1.3 Functions
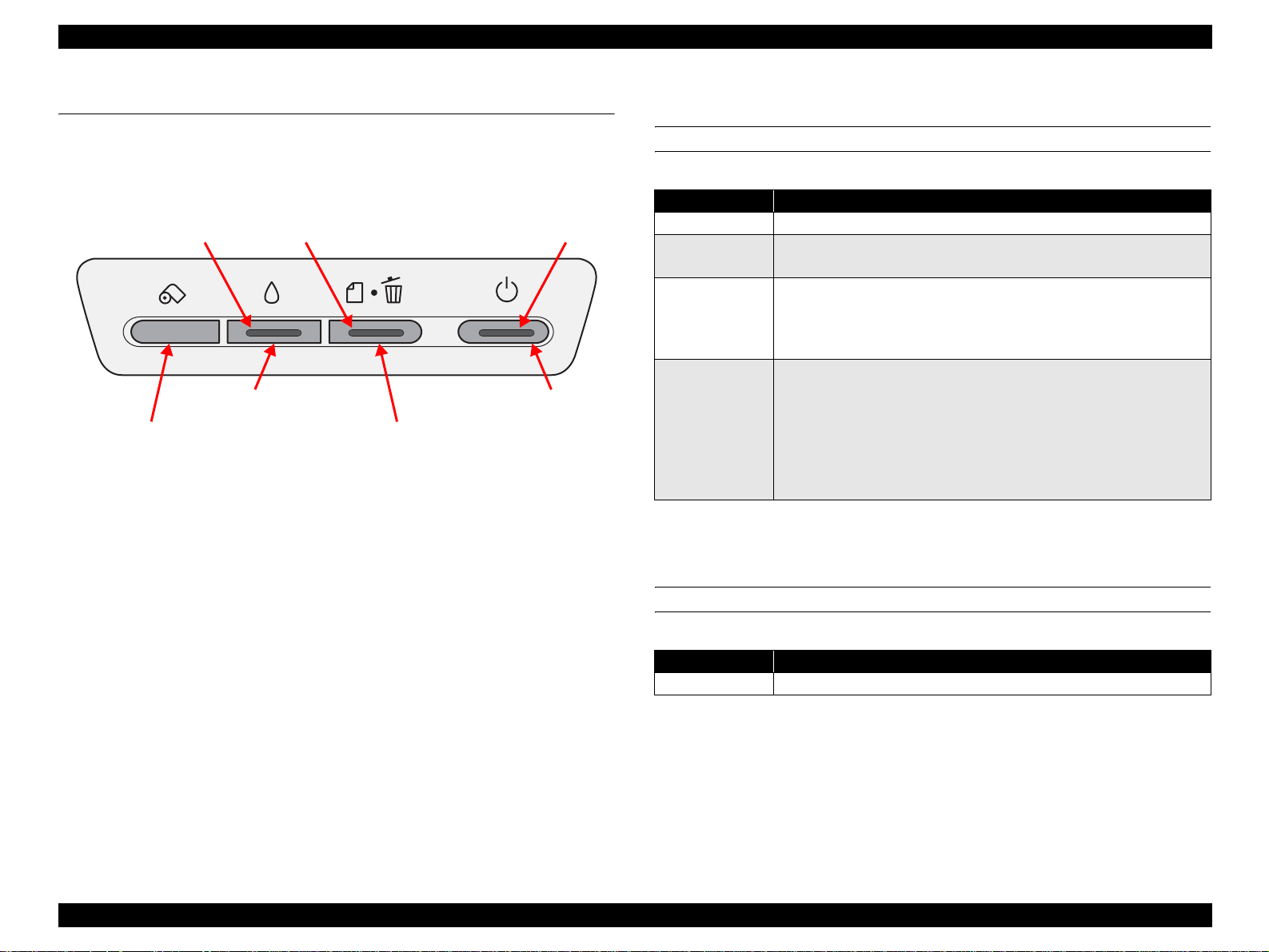
1.3.1 Control Panel
The appearance of the control panel is shown below.
Ink LED Paper LED
Ink switch
Roll paper switch
Figure 1-2. Control Panel Appearance
1.3.2 Switches
Paper switch
Power LED
Power switch
1.3.4 Switch Functions
FUNCTIONS IN NORMAL STATUS
Table 1-2. Normal-status Functions
Switch Function
Power switch • Power On/Off
Paper switch
Ink switch
Roll paper
switch
Note : When the prin ter has frozen, hold down the Power switch and Ink switch for 7
seconds to forcibly switch power off.
• Loads or Ejects the Paper.
• In the condition of printing, cancel the print job.
• Starts the Cleaning of head with 3 second pushing.
• Moves the Carriage to ink cartridge change position.
• When Carriage is on the ink cartridge change position, return
carriage from ink cartridge change position.
• Loads the Roll paper.
• Back out the roll paper with 3 second pushing.
• Move to tear off position / Return from tear off position.
• When the cutter is set, cuts the paper.
• When the photo album is used, ejects the paper forwards only.
(At this mode, the printer can't move the cutter and can't move
backwards.)
Power switch
Paper switch
FUNCTION AT POWER-ON
Ink switch
Roll paper switch
1.3.3 Indicators
Power LED : Green
Switch Function
Paper switch Starts status printings.*
Note "*1 ": Status printings prints firmware version, ink counter and nozzle check
patterns.
Table 1-3. Power-on Function
1
Paper LED : Red
Ink LED : Red
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Functions 11
Page 11
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
1.3.5 Indicator Display in Normal Mode
Table 1-4. Printer Condition and LED Status
Printer status Error status
Idle – On – – 20
Data Processing – Blink – – 19
Pause *
Ink Sequence Processing – Blink – – 17
Ink Cartridge Change Mode – Blink – – 16
PG Release Processing – Blink Blink Blink 15
Ink Low (warning) – – – Blink 14
Tear Off Status 11h – – – 13
Paper Mismatch Error 0Ch Fast Blink – 12
Paper Out 06h – On – 11
Ink Out 05h – – On 10
No Ink Cartridge or Ink Cartridge Error 05h – – On 9
Paper Jam Error 04h – Blink – 8
Card Loading Error 2Ah – Fast Blink – 7
Cutter Jam Error 1Dh –| Blink 2 – 6
Cover Open Error 02h – Blink 2 Fast Blink 5
Reset Input – On On On Å|
Fatal Error 00h Off Fast Blink Fast Blink 4
Cutter Position Error 1Ch Off Blink 2 Blink 2 3
Maintenance Request
Power Off – Fast Blink Off Off 1
1
Note: • "–" : Don't care
• Blink : 0.5sec on + 0.5sec off repetition
• Blink 2 : 0.2sec on + 0.2sec + 0.2sec on + 0.4sec off repetition
• Fast Blink : 0.1sec on + 0.1sec off repetition
• Blink alternately 1 : 0.5sec on + 0.5sec off repetition
• Blink alternately 2 : 0.5sec off + 0.5sec on repetition
Status 05h – – – 18
10h Off
Power Paper Ink Priority
Indicators
Blink
Alternately 1
Blink
Alternately 2
2
Note"*1": When the Photo album paper is end, the printer goes to this status.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Functions 12
Page 12

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
1.3.6 Error Status
If any of the following states is detected, this printer is put in an error status a nd
turns the interface signal -ERROR "Low" and BUSY "High" to inhibit data input.
At this time, the printer is automatically disabled from printing. However, when
communication is being made using the IEEE1284.4 protocol, communication
with the printer is enabled.
General error
After the cause of this type of error is removed, the printer can resume its
operation from where it stopped due to the error
Table 1-5. General error
Error Status Occurring Condition Resuming Condition
Paper Mismatch
Error
Paper Out When printer fails to load a sheet, it
Ink Out When the printer runs out the most
No Ink Cartridge/
CSIC Error
Paper Jam Error • Failure of ejecting a sheet
Card Loading
Error
If the paper path specified by the
print data is different from the
printer's real paper path, the printer
goes to this error.
goes Paper Out Error.
part of the ink of any one color, it
warns Ink Low and keeps printing.
When the printer runs out the whole
ink of any one color, it stops printing
and indicates Ink Out Error. User is
requested to install a new InkCartridge in this state.
When printer detects that Ink
Cartridge comes off, it goes this error
mode.
• Failure of loading a sheet to the
loading position
When the card was loaded to the
wrong position, the printer goes this
error.
Change the printer's
paper path to the one
specified by the data.
Set the paper to the ASF
and push the Paper
switch.
Install the new Ink
Cartridge.
Install the new Ink
Cartridge.
Remove the jammed
paper.
Set an A4 paper to the
ASF, and press the
Paper switch. If the card
couldn't eject at your first
try, repeat again the
same method.
Table 1-5. General error
Error Status Occurring Condition Resuming Condition
Cutter Jam Error When Cutter can't cut the paper, it
goes Cutter Jam Error.
Cover Open Error When the cover is opened at
Economy printing mode, the printer
goes this error.
Switch power off and
recheck the cutter state.
When a paper jam has
occurred, clear the
paper.
Close the cover.
Fatal error
After the cause of this type of error is removed, the printer cannot return to
normal unless it is powered off and then on again
Table 1-6. Fatal error
Error Status Occurring Condition Resuming Condition
Fatal Error When detecting a Fatal Error such as
a carriage control error, the printer is
placed in an error status.
Cutter Position
Error
Maintenance
Request
When Cutter can't return to cutter
home position, it goes Cutter Position
Error.
When the total quantity of ink wasted
through the cleaning and flushing is
reaches to the limit, printer indicates
this error and stops.
Turn off and turn on.
Switch power off and
recheck the cutter state.
When a paper jam has
occurred, clear the
paper.
Replace the Waste Ink
Pads in the printer
enclosure by a service
person.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Functions 13
Page 13
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
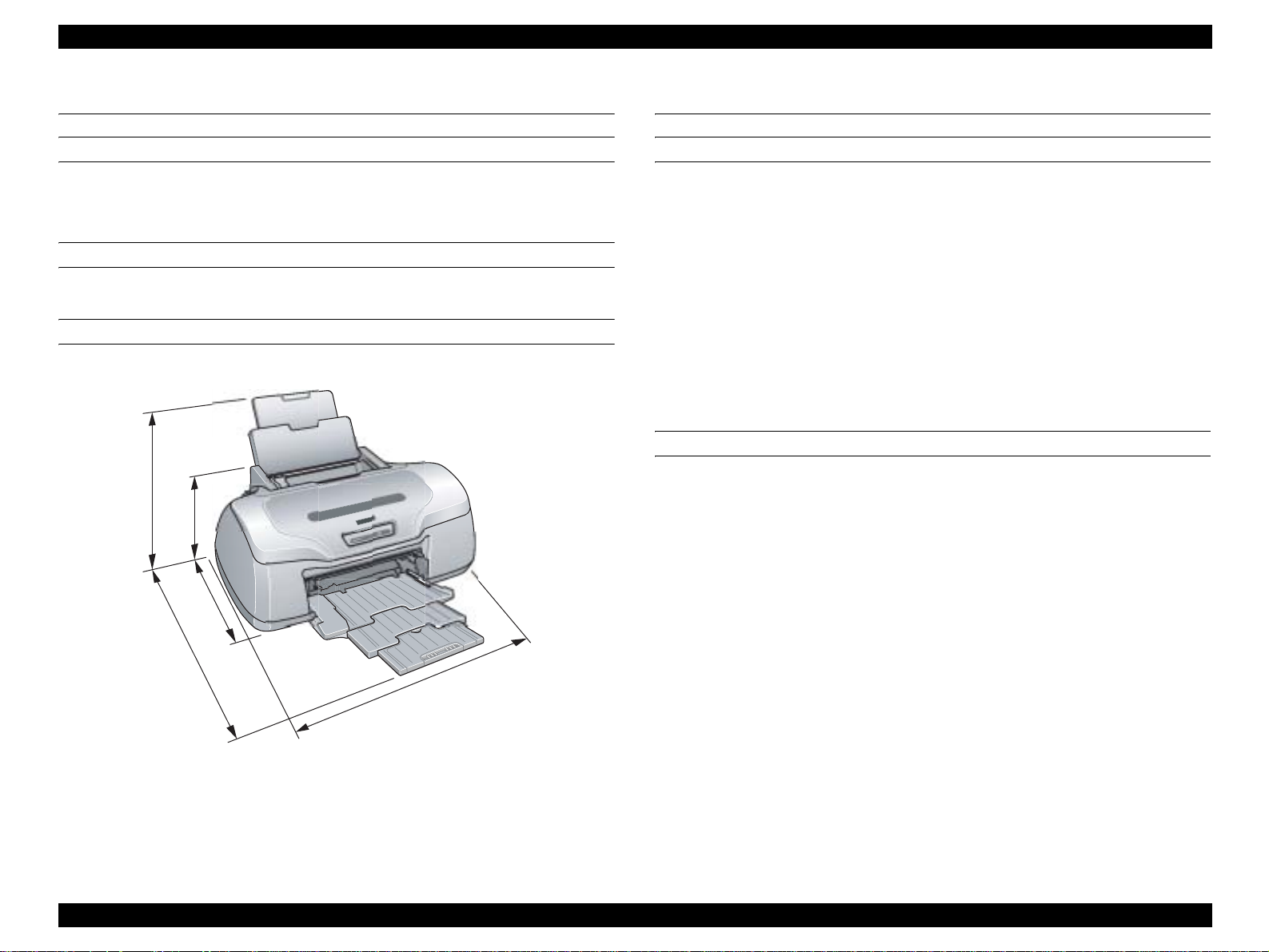
1.4 Casing Specifications
EXTERNAL DIMENSIONS
When tucked : 495 (width) x 305 (depth) x 193 mm (height)
When used : 495 (width) x 644 (depth) x 322 mm (height)
WEIGHT
7.0kg
EXTERNAL DIMENSION DIAGRAM
322
193
305
644
495
1.5 Accessories
STANDARD ACCESSORIES
Setup guide : 1 set
Ink Cartridge (one for each of 8 colors) : 1 set
CD-ROM (Printer driver utility) : 1 set
CD/DVD tray : 1 set
CD/DVD print position check sheet : 1 set
8cm CD/DVD attachment : 1 set
Roll paper holder : 1 set
Power cord : 1 set
CONSUMABLES AND OPTIONS
Ink cartridges
Gloss Optimizer: T0540
Black : T0541
Cy an : T0542
Magenta : T0543
Yellow : T0544
Red : T0547
Matte Black : T0548
Blue : T0549
Roll paper auto cutter
(Cutter, paper support basket, instruction manual) : PMA4RAC3
USB cable : USBCB2
Figure 1-3. External Dimension Diagram
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Casing Specifications 14
Page 14
OPERATING PRINCIPLES
CHAPTER
2
Page 15
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
2.1 Overview
This chapter explains the operating princ i ple s of th e mech an ica l sect ion s an d
electrical circuits in this product. The main components of this product are as
follows.
Control circuit board : C550 MAIN
Power supply circuit board : C550 PSB/PSE
Control panel board : C550 PNL
2.2 Printer Mechanism
Like the conventional model, this product uses DC motors as power sources.
The following table describes the motor types and their applications.
Table 2-1. Various Motors
Motor Name Type Applications/Functions
Used for carriage driving. Makes little noise
during driving. The CR linear scale and CR
encoder sensor are used to control the motor.
Power source to drive the Paper loading rollers
at the time of fixed-value paper loading or paper
feed/eject operation. To grasp the paper feed
pitch, the precision gear surface is fitted with the
PF scale and the PF encoder sensor is used to
control the motor.
Power source to drive the Carriage Unit at the
time of PG setting. The two APG Sensors and
Carriage Shaft are driven vertically to control the
motor.
Performs the paper feed operation of the ASF.
Because of a stepping motor, this motor does
not require a scale, photo sensor and like to be
fitted to grasp the driving conditions.
Drives the pump, wiper, etc. of the Ink System.
Because of a stepping motor, this motor does
not require a scale, photo sensor and like to be
fitted to grasp the driving conditions.
CR Motor
PF Motor
APG Motor
ASF Motor
Pump Motor
DC motor with
brushes
DC motor with
brushes
DC motor with
brushes
4-phase, 48-pole
PM type
stepping motor
4-phase, 48-pole
PM type
stepping motor
The basic structure of the mechanism has the following features.
The se nsor dedicated to Auto Bi-D adjustment and auto nozzle check is
installed.
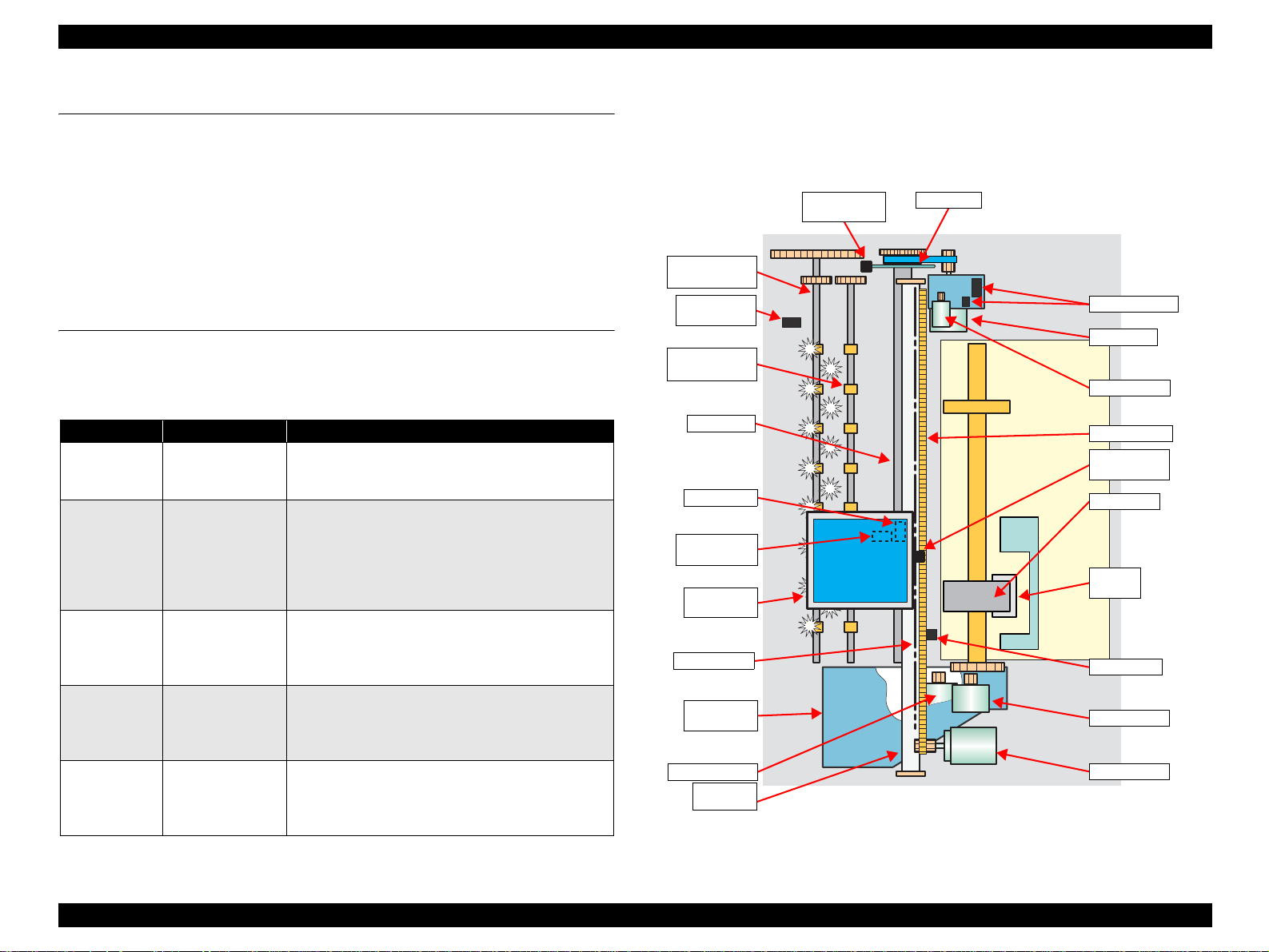
The following shows the outline of the printer mechanism.
PF Encoder
Sensor
Paper Eject
Roller (front)
PG Release
Sensor
Paper Eject
Roller (rear)
PF Roller
PW Sensor
Ink Mark
Sensor
Carriage
Unit
CR Scale
Ink System
Unit
Pump Motor
Carriage
Shaft
PF Scale
APG Sensors
PF Motor
APG Motor
Timing Belt
CR Encoder
Sensor
LD Roller
Retard
Roller
PE Sensor
ASF Motor
CR Motor
Figure 2-1. Printer Mechanism Outline
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Overview 16
Page 16
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
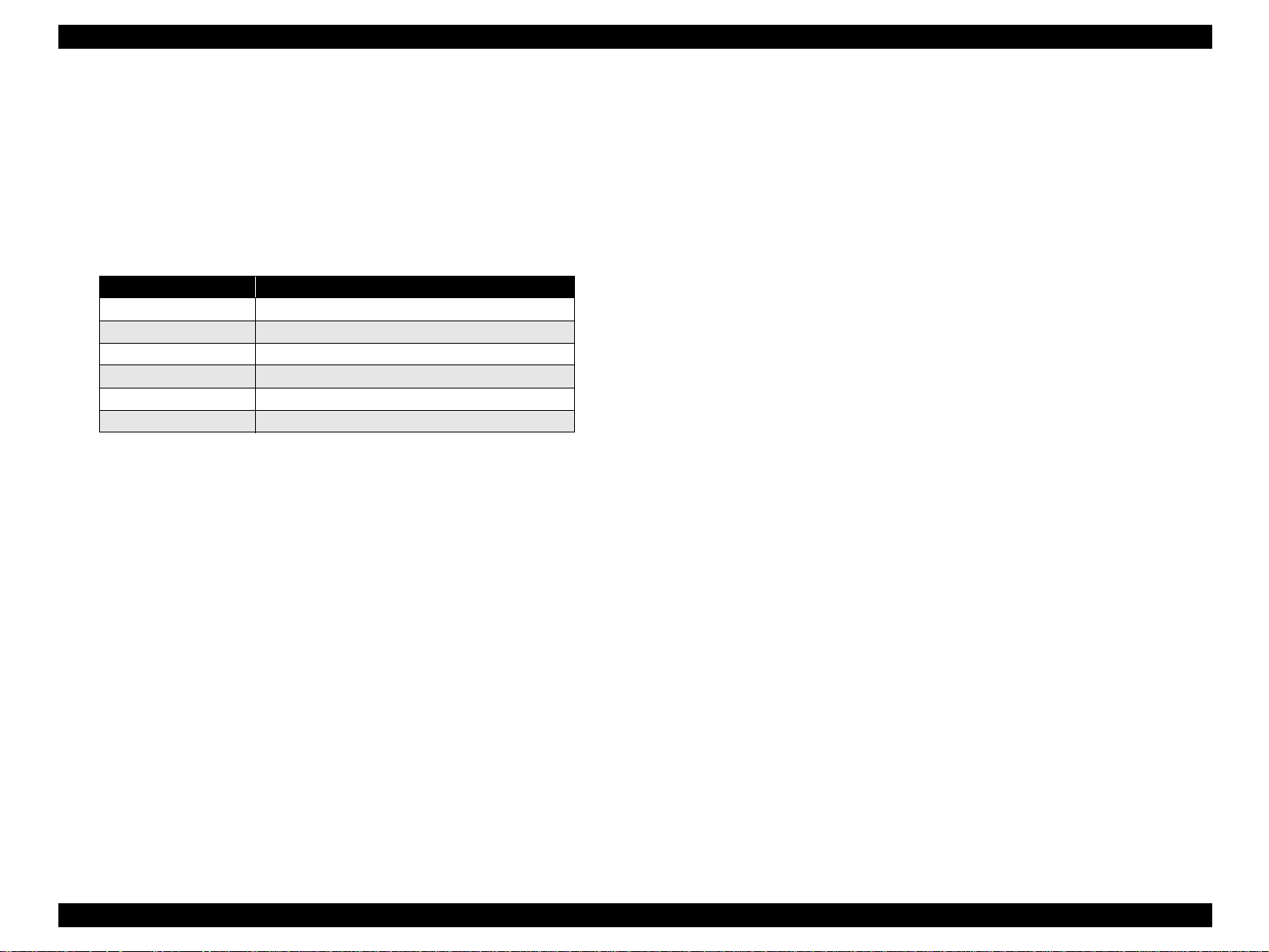
2.2.1 Carriage Mechanism
The Carriage mechanism consists of the Carriage Motor (CR Motor), Carriage
Shafts, Platen Gap Adjustment Mechanism, Carriage Lock Mechanism, and
others.
2.2.1.1 Carriage Mechanism
The following indicates the Carriage driving DC motor specifications.
Table 2-2. CR Motor Specifications
Item Specifications
Type DC motor with brushes
Drive voltage +42V ± 5% (voltage applied to driver)
Winding resistance 24.4Ω ± 15%
Inductance 17.5mH ± 25%
Drive method PWM, constant-current chopping
Drive IC A6615
Closed loop control based on the CR Motor (DC Motor) and CR Encoder
Sensor has advantages in stabilized print quality and silent operation.
Heat generation control
Using low-cost DC motors, this product grasps the variations of the torque
constants, coil resistances and power supply board output voltages of the
individual DC motors adequately to carry out heat generation control
according to individual differences.
CR variation measurement sequence
The variations of the torque constant, coil resistance and power supply
board output voltage of the motor are measured in a CR variation
measurement sequence when the CR mechanical load is in the initial
status and saved into the EEPROM (A6<H>). According to the variations
(individual differences) measured in this sequence, the voltage is corrected
to make the drive current value constant (without an individual difference)
according to the variations (individual differences) measured in this
sequence.
CR measurement sequence
To set the appropriate drive current value according to the variation of the
CR mechanical load, the mechanical load is measured in a CR
measurement sequence and saved into the EEPROM A4<H>, A5<H> in a
power-on or IC change sequence. However, if 46 is saved at the EEPROM
A4<H> and 05 at A5<H>, Fatal error will occur since too large load is
applied to the CR drive system.
The above control and sequences correct the drive current value of the CR
Motor according to not only the mechanical load but also the variations of the
motor and like. In addition, the resultant CR drive current value is used to
calculate a heating value, and when the specified heating value is reached,
wait time is provided per CR path for printing.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 17
Page 17

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
2.2.1.2 Carriage Home Position Detection
As in the conventional model, the Carriage Home Position is detected using the
drive current of the CR Motor and the speed/position signal of the CR Linear
Encoder.
The basic home position detection sequence is as described below.
1. The CR linear encoder pulse counter in the CPU is reset by the
initialization operation performed at power-on.
2. When the CR Motor rotates counterclockwise, the Carriage Unit moves
from left to right. When the following conditions are satisfied, the CPU
assumes that the Carriage Unit made contact with the right frame.
The ASIC detects 862/1500 counts or more in the PWM output under
CR Motor load positioning control.
P1 (number of output pulses from when power is switched on until the
Carriage Unit makes contact with the right frame) is 12 steps or less.
3. When the CR Motor rotates clockwise, the Carriage Unit moves from right
to left. When the following conditions are satisfied, the CPU assumes that
the Carriage Unit reached the CR lock confirmation position.
The ASIC detects 483/1500 counts or more in the PWM output under
CR Motor load positioning control.
A difference between P1 and P2 (number of output pulses from when
the Carriage Unit made contact with the right frame until it reaches the
Carriage lock confirmation position) is 12 steps or less.
4. When the CR Motor rotates counterclockwise to move the Carriage from
left to right and the CPU detects 862/1500 counts or more in the PWM
output under CR Motor load positioning control, the printer judges it as
contact with the frame.
5. When a difference between P1 and P3 (number of output pulses from
when the Carriage Unit reached the Carriage lock confirmation position
until it makes contact with the right frame) is 4 steps or less, the printer
judges that the Carriage Unit is in the home position.
The IC14 (ASIC) sets the drive current value adequate for the Carriage Unit
motion and outputs it to the motor driver.
Based on the signal output from the IC14 (ASIC), the IC5 (Motor Driver)
outputs the CR Motor drive current to the CR Motor.
2.2.1.3 Sequence Used for PW Detection
The PW (paper width detection) Sensor installed on the Carria ge Unit bottom is
used to control the printer according to various sequences.
The following briefly describes the PW Sensor operating principle.
A dark voltage is measured by the PW Sensor in three places on the right end
plane (area without the absorber) of the Front Paper Guide every time power is
switched on, and the measurement values are saved into the EEPROM as
threshold values.
Threshold value > detection voltage: Paper present
Threshold value < detection voltage: Paper absent
The following sequences are performed .
Off-paper printing prevention control
Before start of printing (immediately after the end of paper locating), or
during printing, whether paper is present or not is detected to prevent offpaper printing on the Paper Guide by borderless printing used in a wrong
way. (This applies to only the left or right end of the paper.)
This control applies to only the four-side borderless mode.
CD-R center detection control
When printing is not being performed, the PW detector is used to detect
the center of CD-R. Refer to "2.2.3.4 CD-R Printing Mechanism (p.23)" for
details.
Board paper/roll paper leading edge detection control
Control exercised to detect the user-preset board paper leading edge, or
control carried out to detect the roll paper edge. Therefore, the PW sensor
does not detect a paper leading edge at the time of ASF cut sheet feeding.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 18
Page 18
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Off-range restriction control
At the time of frameless printing, a paper leading edge is detected using
the PW Sensor to restrict the frameless off-range am o un t.
Complete frameless mode
Control is performed to print the print data 3mm larger at top, 5mm
larger at bottom, and 2.5mm lager at left and right than the detected
paper size.
Roll paper mode
In the left and right frameless mode, control is performed to print the
print data 2.5mm lager at left and right than the detected paper size.
PW sensor dark voltage (VH) measurement
PW sensor dark voltage (VH) measurement is performed at the following
timings and locations and used to calculate the threshold value of whether
paper is present or not.
Cut sheets, Roll paper
The dark voltage is measured and updated at every power-on, and th e
threshold value (VS) is calculated and saved in the EPROM area as a
PW detection level.
• Threshold value > detection voltage: Paper present
• Threshold value < detection voltage: Paper absent
CD-R Tray
When a CD-R is used, the dark voltage is measured on the CD-R tray,
and the threshold value (VS) is then calculated and saved in the
EPROM area as a PW detection level.
• Threshold value > detection voltage: CD-R present
(tray home position detected)
The measurement voltage in the presence of the CD-R is saved into
the EEPROM as a white level. The white level value is used to check
the sensor deterioration condition during servicing or like.
• If the measurement value of the white level is close to that of the PW
detection level, it means that the sensor is dirty or deteriorated.
2.2.1.4 APG (Auto PG) Mechanism
The following indicates the APG DC motor specifications.
Table 2-3. APG Motor Specifications
Item Specifications
Type DC motor with brushes
Drive voltage +42V ± 5% (voltage applied to driver)
Winding resistance 64.7Ω ± 15%
Inductance 37.6mH ± 25%
Drive method PWM, constant-current chopping
Drive IC A6615
The APG Motor (DC Motor) and two APG Sensors automatically adjust the PG
amount according to the paper.
APG Motor
PG Cam
Carriage Shaft
Figure 2-2. APG Mechanism
Carriage Unit
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 19
Page 19
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
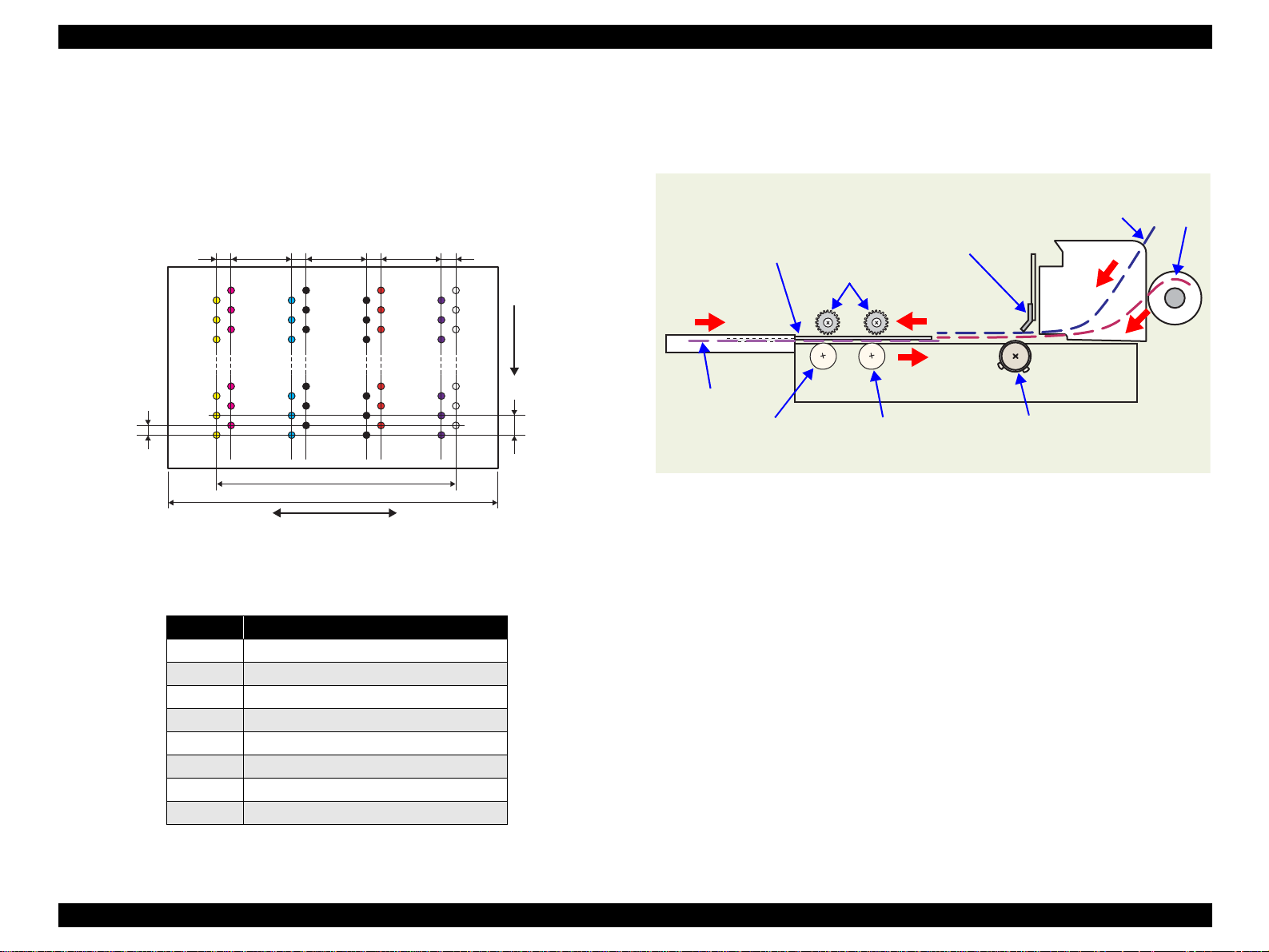
2.2.2 Printhead Specifications
The Printhead of this product is a F-Mach head.
The following shows the arrangement of the nozzles and the color
arrangement of each nozzle line when they are viewed from behind.
0.071mm
(1/360inch)
7.620mm
(216/720inch)
2.258mm
(64/720inch)
Line A
Figure 2-3. Nozzle Rear View
7.620mm
(216/720inch)
2.258mm
(64/720inch)
Line C
Line B
Carriage moving direction
(64/720inch)
Line E
Line D
31.89mm
41.66mm
(216/720inch)
2.258mm
Line F
7.620mm
2.258mm
(64/720inch)
Paper feeding
Line G
Line H
direction
0.141mm
(1/180inch)
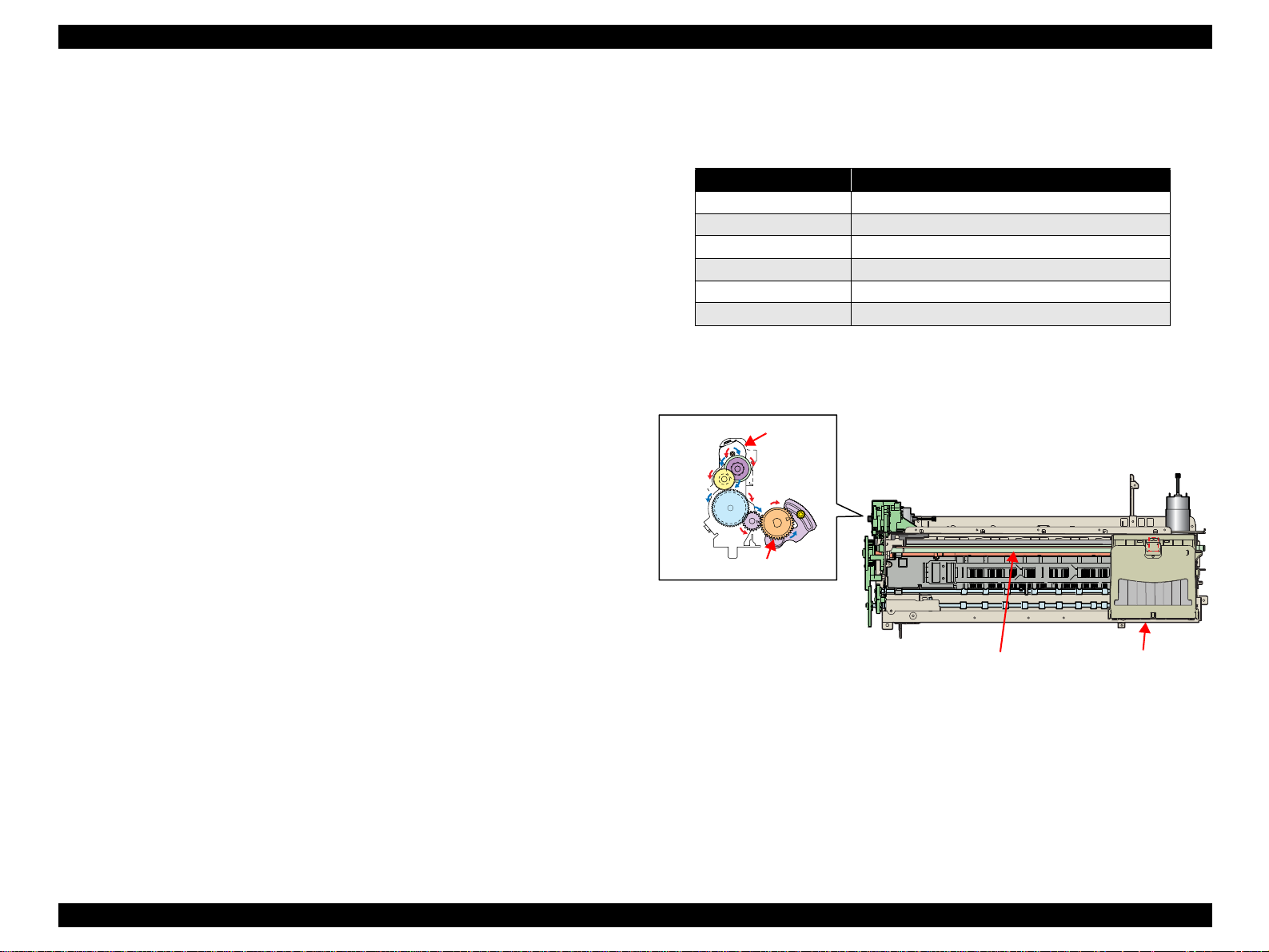
2.2.3 Paper Feeding Mechanism
The paper feeding mechanism indicates the me ch a nism tha t feed s pa pe r or
CD-R Tray to the PF Roller Shaft.
CD-R Tray
PE Sensor
Star Wheel Rollers
Board Paper
Paper eject roller (front) Paper eject roller (rear)
Figure 2-4. Paper Feeding Mechanism
Cut sheet
PF Roller
Roll paper
Table 2-4. Relationships between Nozzle Lines and Color Arrangement
Line Ink
AYellow
B Magenta
C Cyan
D Matte-black
EPhoto-black
F Red
GBlue
H
Gloss Optimizer
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 20
Page 20
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
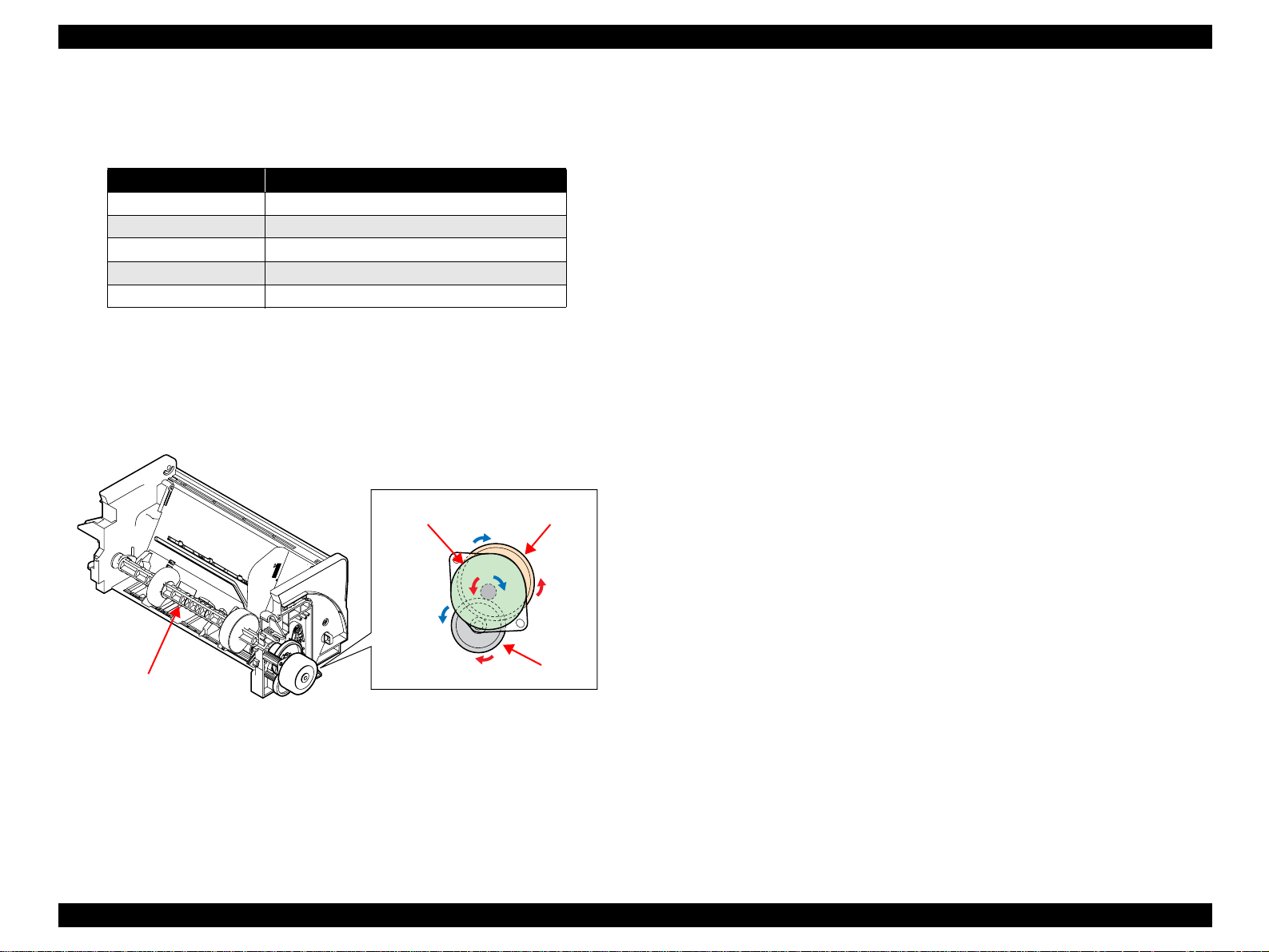
2.2.3.1 ASF Paper Feeding Mechanism
The following indicates the ASF Assy. driving stepping motor specifications.
Table 2-5. ASF Motor Specifications
Item Specifications
Type 4-phase, 48-pole PM type stepping motor
Drive voltage Bipolar drive/constant-current drive
Winding resistance +42 V ± 5% (voltage applied to driver)
Inductance 7.4Ω ± 10% (per phase at 25°C)
Drive method 12.0mH ± 20% (1kH, 1Vrms)
The drive of the ASF Motor is transmitted to the LD Roller in the following path.
LD Roller Drive Transmission Path
ASF Motor Pinion Gear
⇒ Combination Gear 29, 11 ⇒ Paper Back Cam
⇒ LD Roller
ASF Motor
Paper Back Cam
Driven by the ASF Motor, the ASF Assy. performs the following feeding
operation.
1. When a paper feeding command is issued from the PC or the Paper Switch
of the panel is pressed after power-on, the driving force of the ASF Motor
begins to be transmitted to the LD Roller.
2. The flag of the Paper Back Cam moves away from the home position of the
ASF Sensor and the LD Roller rotates.
3. When the LD Roller rotates one turn and the flag of the Paper Back Cam
returns to the home position of the ASF Sensor again, the LD Roller stop s
rotating.
2.2.3.2 Manual Paper Feeding Mechanism (Board Paper)
To enable direct printing onto thick paper and CD-R label, this product has the
mechanism to feed paper from the printer front manually.
1. When the Stacker is lifted, the close signal of the PG Release Sensor is
transmitted to the APG Assy. in the following order.
PG Release Sensor
⇒ Main Board ⇒ Relay Board ⇒ APG Motor
⇒ APG Assy.
2. Driven by the APG Motor, the APG Assy. sets the PG position to PG
release to release the Upper Paper Guide (Driven Roller).
3. Along the Paper Feed Guide of the Stacker, match the leading edge (front
side) of the board paper to the marking position of the Stacker.
After the above operation, press the Paper Switch. When the PE Sensor
detects that the paper is present, it detects the leading edge of the paper, and
LD Roller Shaft
Figure 2-5. LD Roller Drive Transmission Path
Combination Gear 29, 11
the printer performs paper locating and then enters the standby status.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 21
Page 21

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
2.2.3.3 Roll Paper Feeding
Since panel operation in the roll paper mode differs from the above operation,
the differences of panel operation after roll paper feeding will be described.
1. When roll paper is fed, the PE Sensor detects the paper, and after 3
seconds have elapsed, the paper is fed.
2. The PW Sensor check for the leading edge of the paper, and if it detects
the paper, the printer operates in the Cutter Self-Cleaning Mode.
3. The printer back-feeds the paper to the paper print starting position.
At this time, panel Switch operation is invalid, and the definitions of the panel
operation and Paper Switch differ between cut sheets and roll paper.
The following describes a difference between Panel Switch operations
performed when roll paper is fed and performed when roll p aper printing data is
received from the PC.
When roll paper is fed
Pressing the Roll Paper Switch for more than 3 seconds back-feeds the
leading edge of the roll paper to the PE Sensor (the Paper LED blinks). In
this state, draw the roll paper and press the Paper Switch to return to the
panel operation that enables paper feeding from the ASF.
When roll paper printing data is received (when cutter is fitted)
When data is "No auto cut"
1. After end of printing, press the Roll Paper Switch. This feeds the
separation position in the print data to the roll paper cut position.
2. After the paper is cut, the leading edge of the paper retu rn s to th e
print starting position.
When data is "Standard 1 cut" or "Specific 2 cuts"
When roll paper printing data is received (when cutter is not fitted)
1. After end of printing, press the Roll Paper Switch.
2. A tear-off line is printed, and the roll paper is fed to the roll paper
cut position.
3. After cutting the roll paper with a pair of scissors or like, Press the
Roll Paper Switch. This returns the leading edge of the paper to
the print starting position.
1. The roll paper is cut automatically at every separation of the print
data.
2. After the paper is cut, the leading edge of the paper retu rn s to th e
print starting position.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 22
Page 22
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
2.2.3.4 CD-R Printing Mechanism
CD-R tray home position detection sequence
Lift the Stacker (PG Release Sensor: Close), insert the CD-R Tray into the
specified position, and press the Paper Switch. This starts the following
operation.
When the close signal of the PG Release Sensor is detected, no paper is
fed from the ASF if the Paper Switch is pressed. In this case, the Paper
Switch executes a CD-R Tray home position detection sequence.
1. When the APG Assy. is driven, the PG position is set to "++" and
the Driven Roller of the Upper Paper Guide presses the CD-R
Tray.
2. When the Carriage Unit moves leftward and the PW Sensor
detects the CD-R, the Carriage Unit returns to the carriage home
position (HP).
3. After waiting for about 5 seconds at the carriage HP, the Carriage
Unit moves to the CD-R Tray HP detectable position (right end of
the CD-R Tray).
4. The CD-R Tray is pulled in the ASF direction, the PW Sensor
detects the CD-R Tray HP, and then the Carriage Unit moves to
the center of the CD-R Tray.
5. When the PW Sensor detects the white marking in the center of
the CD-R Tray, the CD-R Tray is fed in the paper ejection
direction.
6. The Carriage Unit moves leftward, the PW Sensor detects the left
side white marking, then the Carriage Unit moves rightward, and
the PW Sensor detects the right side white marking.
7. The Carriage Unit moves to the center of the CD-R Tray, and the
PW Sensor starts detection in the back-and-forth direction of the
CD-R. After the leading edge of the CD-R is detected, the CD-R
Tray is fed in the paper ejection direction, and the trailing edge of
the CD-R is detected. After that, the CD-R Tray is fed to the center
of the CD-R in the paper ejection direction.
8. The Carriage Unit moves leftward, and the PW Sensor starts
detection in the horizontal direction of the CD-R. After the left end
of the CD-R is detected, the Carriage Unit moves rightward, and
the right end of the CD-R is detected.
9. The Carriage Unit moves to the CD-R Tray HP detectable position
and stops there, and then the CD-R Tray is fed in the ASF
direction.
10. When the CD-R Tray stops operating, the Carriage Unit moves to
the carriage HP and stands by.
If the CD-R Tray HP, white marking or CD-R cannot be detected in any
specified step operation in the CD-R Tray HP detection sequence, the CD-R
Tray is ejected and Paper Out Error is displayed.
PW Sensor
Carriage Unit
CD-R Tray
CD-R home position
Figure 2-6. CD-R Printing Mechanism
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 23
Page 23
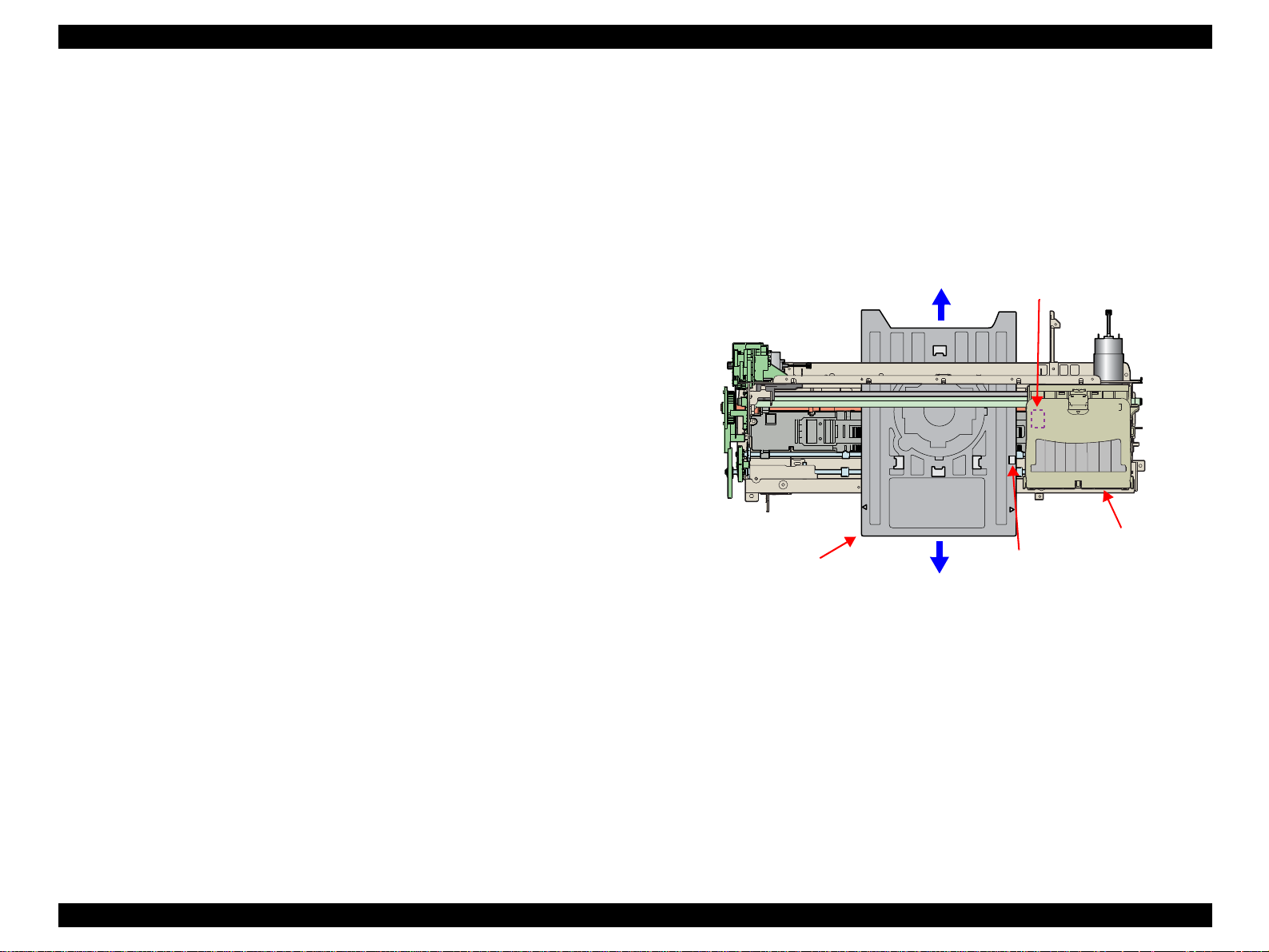
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
2.2.4 Paper Loading Mechanism
The Paper Loading Mechanism is designed to transfer the paper fed from the
ASF, Roll Paper Guide or Board Paper Guide or the CD-R fed from the CD-R
Tray according to the print data.
2.2.4.1 Paper Loading Mechanism
The following indicates the paper loading driving DC motor specifications.
Table 2-6. PF Motor Specifications
Item Specifications
Type DC motor with brushes
Drive voltage +42V ± 5% (voltage applied to driver)
Winding resistance 22.3Ω ± 25%
Inductance 17.3mH ± 25%
Drive method PWM
Drive IC A6615
Like the CR Motor, a DC motor is used as the PF Motor in this product.
Closed loop control based on the DC Motor and Rotary Encoder has the
following advantages.
Improved paper feed accuracy
Paper feed amount control
The driving force of the PF Motor is transmitted to the PF Roller and Paper
Eject Roller in the following path.
PF Roller Drive Transmission Path
PF Motor Pinion Gear
⇒ PF Timing Belt ⇒
Combination Gear 36.294, 45.5 ⇒ PF Roller Shaft
Paper Eject Roller (front) Drive Transmission Path
PF Motor Pinion Gear
⇒ PF Timing Belt ⇒
Combination Gear 36.294, 45.5 ⇒ Spur 31.5 ⇒ Spur 54 ⇒
Paper Eject Roller (front)
Paper Eject Roller (re ar) Drive Transmission Path
PF Motor Pinion Gear
⇒ PF Timing Belt ⇒
Combination Gear 36.294, 45.5 ⇒ Spur 31.5 ⇒ Spur 54 ⇒ Spur 18 ⇒
Spur 15.5
⇒ Spur 18 ⇒ Paper Eject Roller (rear)
The following shows the part names and outline of the drive transmission path.
Paper is transferred in the above driving force transmission path.
Combination Gear
36.294, 45.5
PF Timing Belt
Pinion Gear
Spur 18
Spur 31.5
PF Motor
Spur 15.5
Front Paper
Guide
Spur 54
Spur 18
PF Roller
Paper Eject
Roller (front)
Paper Eject
Roller (rear)
Figure 2-7. Paper Loading Mechanism 1
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 24
Page 24
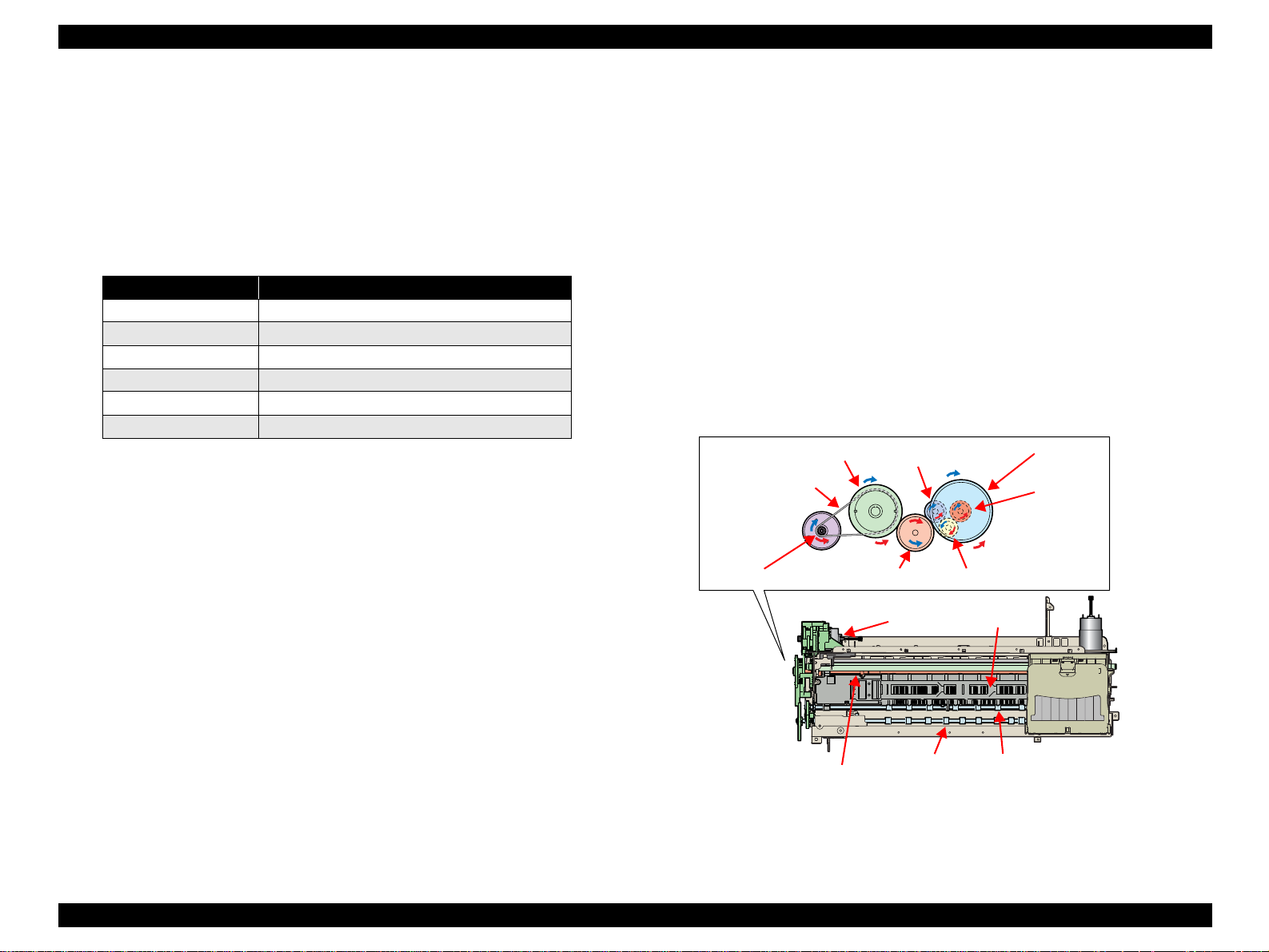
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
The fed paper is detected by the PE Sensor, and its leading edge is then
transferred to the front of the Front Paper Guide.
To eliminate the deflection of the paper, the paper is then returned toward the
ASF Assy. by the specified number of steps according to the paper feed mode.
The paper is transferred again to the specified paper locating position of the
Front Paper Guide.
Print Head
Paper
Paper eject roller (front) Paper eject roller (rear)
Star Wheel Rollers
Driven Roller
PF Roller
Figure 2-8. Paper Loading Mechanism 2
2.2.4.2 PF Measurement Sequence
The mechan ical load in the pap er loading path is measured in the following
cases to perform control so that an adequate current value is set according
to the mechanical load.
When power is switched on
When the Ink Cartridge is replaced
When the removal or fitting of the cutter is recognized in the paper feed
sequence
When the mech anical load in the paper loa ding p ath reaches the specified
value, Fatal Error is displayed. (When the cutter is not fitted)
When the cutter is fitted, the mechanical load when the cutter is fitted is
measured and reflected on the control since the mechanical load of the
cutter must be taken into consideration to set the adequate current value.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 25
Page 25
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
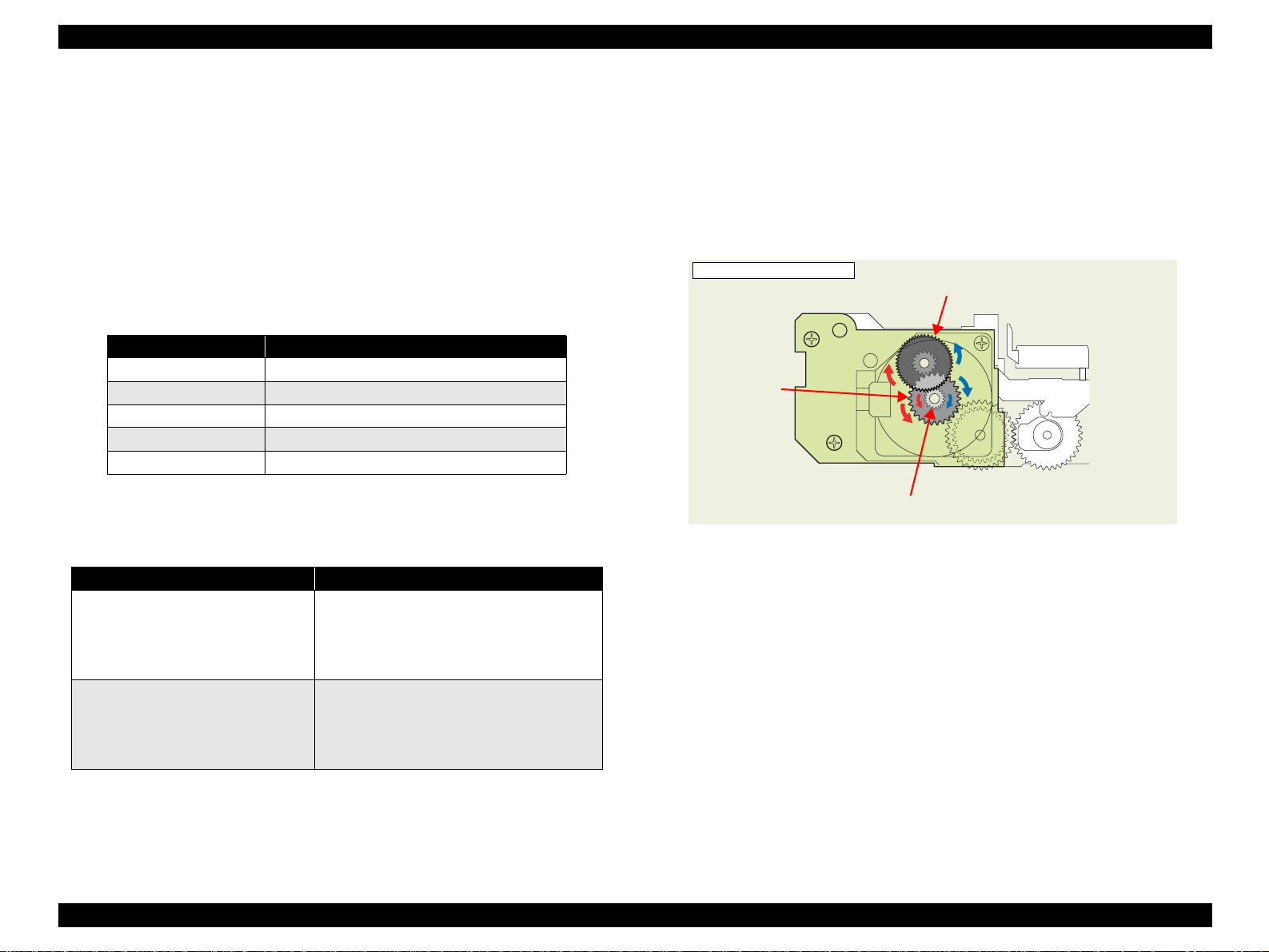
2.2.5 Ink System Mechanism
The Ink System Mechanism consists of the following mechanisms.
Pump Unit (including the CR Lock Lever)
Cap Unit
2.2.5.1 Pump Unit
The Pump Unit is designed to suck ink from the Print Head or Cap Unit. The
Cap Unit has a built-in Head Cleaning Wiper.
The following indicates the Pump Unit driving stepping motor specifications.
Table 2-7. Pump Motor Specifications
Item Specifications
Type 4-phase, 48-pole PM type stepping motor
Drive voltage Bipolar drive/constant-current drive
Winding resistance +42 V ± 5% (voltage applied to driver)
Inductance 10.3Ω ± 10% (per phase at 25°C)
Drive method 13.4mH ± 20% (1kH, 1Vrms)
The following operations are performed when the drive of the Pump Motor is
transmitted to the Pump Unit.
Table 2-8. Pump Motor Rotation Directions and Functions
Pump Motor Rotation Direction* Functions
• Cap closing
CW direction
CCW direction
• Ink suction
• Wiper resetting
• CR Lock setting
• Cap opening
• Pump release
• Wiper setting
• CR Lock resetting
2.2.5.2 Drive Transmission Path to Pump Unit
The drive of the Pump Motor is transmitted to the Pump Unit in the following
path.
Moto r Pinion Gear
⇒ Combination Gear 10.2, 21.2 IS
⇒ Spur Gear 20.4 IS ⇒ Pump Unit
The following shows the internal part names and operation outline of the Pump
Unit.
<Pump Unit inside>
Combination Gear 10.2, 21.2 IS
Spur Gear
20.4 IS
Motor Pinion Gear
Figure 2-9. Outline of Pump Unit Inside
Note: As the rotation directions of the motor, CW indicates a clockwise
direction, and CCW indicates a counterclockwise direction, as seen
from the output shaft side of the motor mounting plate.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 26
Page 26
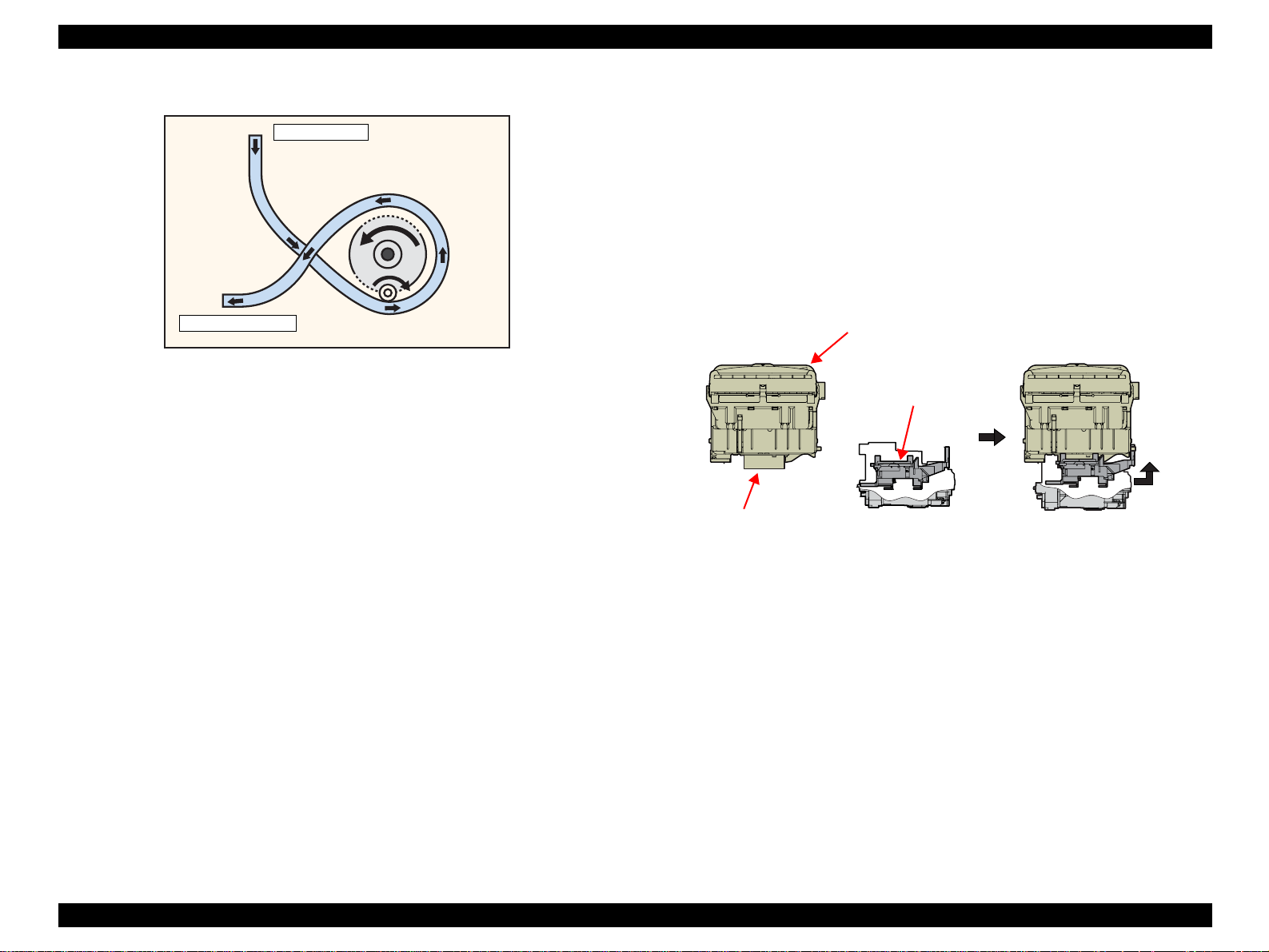
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
The following shows the Pump Unit operating principle.
Cap Unit Side
To Waste ink pad
Figure 2-10. Pump Unit Operating Principle
Ink suction
1. The Pinion Gear of the Pump Motor rotates in the CW direction.
2. The Roller turns and simultaneously presses the tube.
3. Ink is fed from the Cap Unit toward the Waste Ink Pad.
Pump release
1. The Pinion Gear of the Pump Motor rotates in the CCW direction.
2. The Roller moves away from the tube and releases the tube.
3. Ink is not sucked.
2.2.5.3 Cap Unit
The Cap Unit is designed to bring the Cap into close contact with the Print
Head surface and suck ink by the driving force of the Pump Unit to secure air
tightness in the Cap.
When the printer is in a standby status or its power is OFF, the Cap Unit
prevents the ink from thickening.
Ink is fed to the Waste Ink Pad in the following path.
Ink Cartridge
The following diagram shows the outline of Cap Unit operation.
Print Head
⇒ Head Cavity ⇒ Cap ⇒ Waste Ink Pad
Carriage Unit
Cap
Slider cap rises to perform
capping.
Figure 2-11. Capping Mechanism
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 27
Page 27

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
2.2.6 Ink Sequence
The following ink sequence is executed according to various timer, counter,
flag and other information saved on the EEPROM.
CSIC-related sequence
The ink type code stored in the CSIC Memory Chip is identical regardless
of the Japanese domestic or overseas cartridges, and is saved at the Main
Board EEPROM.
At power-on, data is read from each color CSIC and the CSIC data status
is made valid. If the data read from each CSIC has any problem, Ink
cartridge error or Ink end error is displayed.
After CSIC operation is checked, the ink consumption of the I/C currently
installed per color is compared with the ink consumption saved in the
printer EEPROM, and control is performed under the following conditions.
When current I/C consumption differs (from ink consumption in
EEPROM)
1. On the assumption that the I/C has been changed at power-off, the
first I/C flag is reset.
2. The installation count in the printer EEPROM is updated for the
CSIC. In the CSIC information replacement sequence, the CSIC
side ink consumption data is updated to the ink consumption data
in the printer EEPROM.
3. The used model name data on the I/C side is rewritten.
Note: Reason why the used model name data is rewritten from the
printer to the I/C: To grasp which printer used the I/C removed.
4. The change flag 2 (flag that indicates change CL) is set and CL is
executed.
When current I/C consumption is the same (as ink consumption in
EEPROM)
1. When the initial filling flag is set and the CSIC side ink
consumption is 0, the printer judges that initial filling is not yet
performed.
(The printer before initial filling judges that the I/C is fitted in a
power-off status.)
2. Installation count updating, CSIC information replacement, and
initial filling are executed in this order.
3. If the initial filling flag is not set, the printer judges that I/C change
was not made at power-off and regards the CSIC data as valid.
Data is written to the CSIC at the following timings.
At powe r- of f
In the power saving mode
At the tim e of Ink C artr i dg e re pla ce m en t
At the time of cleaning
1. Data is read from the CSIC and developed in the RAM on the Main
Board.
2. The data is compared with the ink consumption in the printer
EEPROM. If the data are the same, the data is written to the CSIC.
If they are different, only the consumed difference is added and
written to the CSIC. When cleaning is performed, the CL count is
also written, and when the I/C is changed, the installation count is
also written.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 28
Page 28

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Initial ink filling
When the printer is powered on for the first time after the purchase of the
product, the printer executes the initial ink filling operation to fill the ink
cavities of the Head with ink. When the initial ink filling operation is
performed properly, the printer clears the flag in the EEPROM so that initi al
ink filling operation will not be performed when it is powered on next. The
Stylus Photo R800 requires about 150 seconds to perform the initial ink
filling operation and consumes about 1/ 7 of the new ink cartridge.
If the sequence does not end normally during initial filling, the initial filling
flag is not cleared and the CL operating flag is set. Because of these flags,
when powered on next time, the printer assumes that it was powered off for
some reason during initial filling and executes CL3 instead of the initial
filling sequence. (On the conventional mode, initial filling was executed
again. However, when this operation was performed, ink was wasted and
therefore CL3 is executed to cover the ink filling performance.)
When the initial filling flag is set and the CL operating flag is not set, the
printer assumes that the initial filling was not executed at all (power was
switched on but the cartridges were not set), and when the printer is
powered on next time, it executes initial filling.
Change cleaning
Change CL1 is executed when Ink Cartridge change is made.
Change CL1: 3.4g (0.425g per color)
Manual cleaning
This product provides three different manual cleanings to remove ink
coagulated by air bubbles, viscous material or foreign matter. Perform the
following manual CL operations by operating the panel or using the utility
included in the printer driver.
Independently of the printing path after the previous CL, perform manual
CL from CL1 to CL3 in order if the cumulative printing timer counter is less
than 7min. Only when the cumulative printing timer counter is more than
7min, execute only CL1.
CL1: 1.704g (0.213g per color)
CL2: 4.488g (0.561g per color)
CL3: 7.120g (0.890g per color)
Wiper operation
Clean the nozzle surface with the right-half rubber part of the wiper.
Flushing operation
Prevent color mixture. Stabilize the ink surface inside the nozzles.
If the remaining ink amount of the I/C is short or the I/C is in an Ink Low/Out
status, all manual cleanings are disabled and STM3 shows the condition.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 29
Page 29
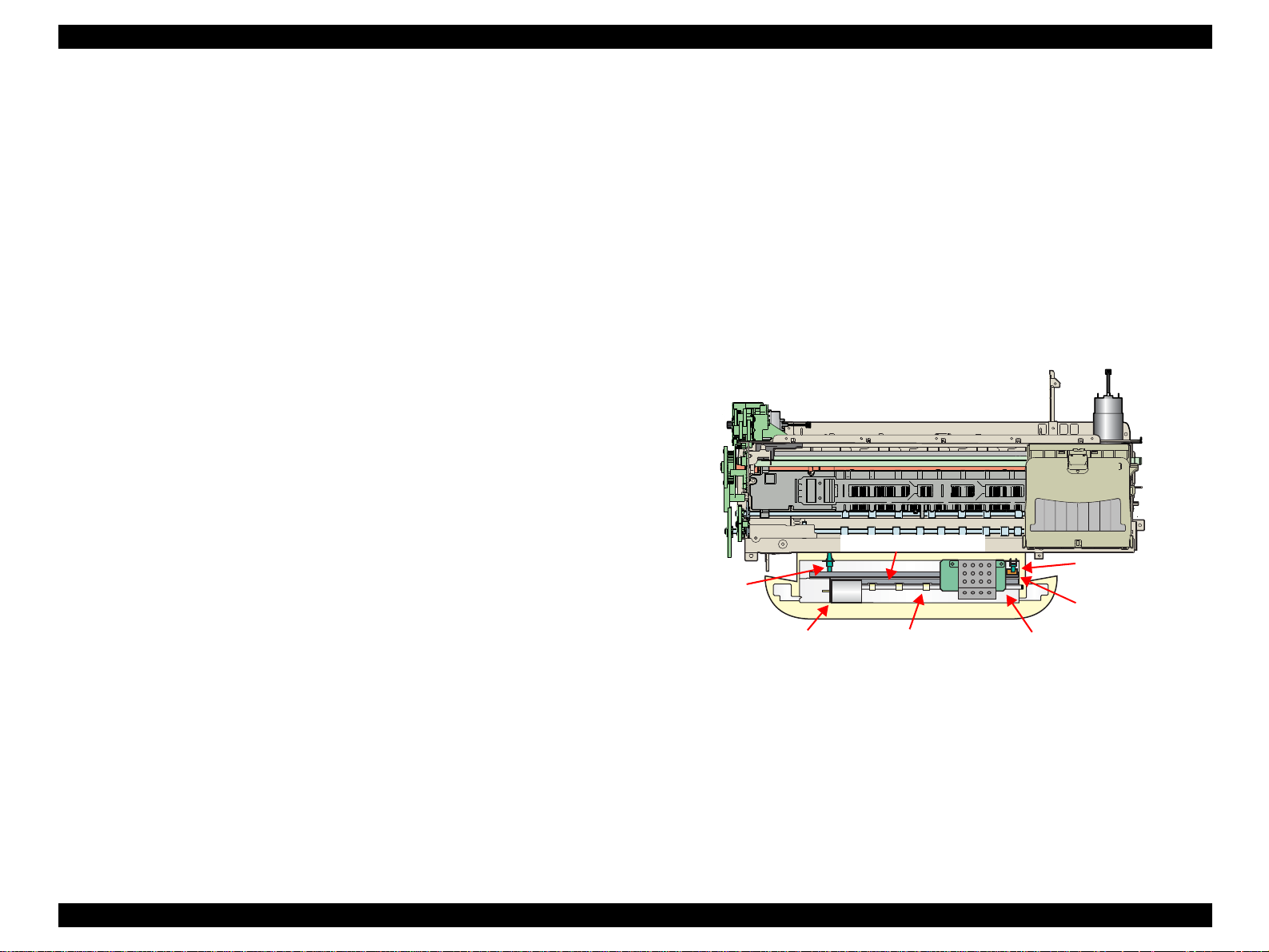
EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Timer cleaning
Ink is consumed depending on the combination of the cumulative printing
timer, cumulative cleaning count and cleaning timer.
Flushing
Two different flushing operations are executed for the following reasons.
Periodic flushing
This is done to prevent ink viscosity in the Print Head nozzles from
increasing during continuous printing. A specific small amount of ink is
discharged into the Cap according to the Periodic flushing timer.
Periodic large-amount flushing
This is done to prevent ink viscosity in the Print Head nozzles from
increasing during continuous printing. A large amount of ink is
discharged into the Cap according to the Periodic large-amount
flushing timer.
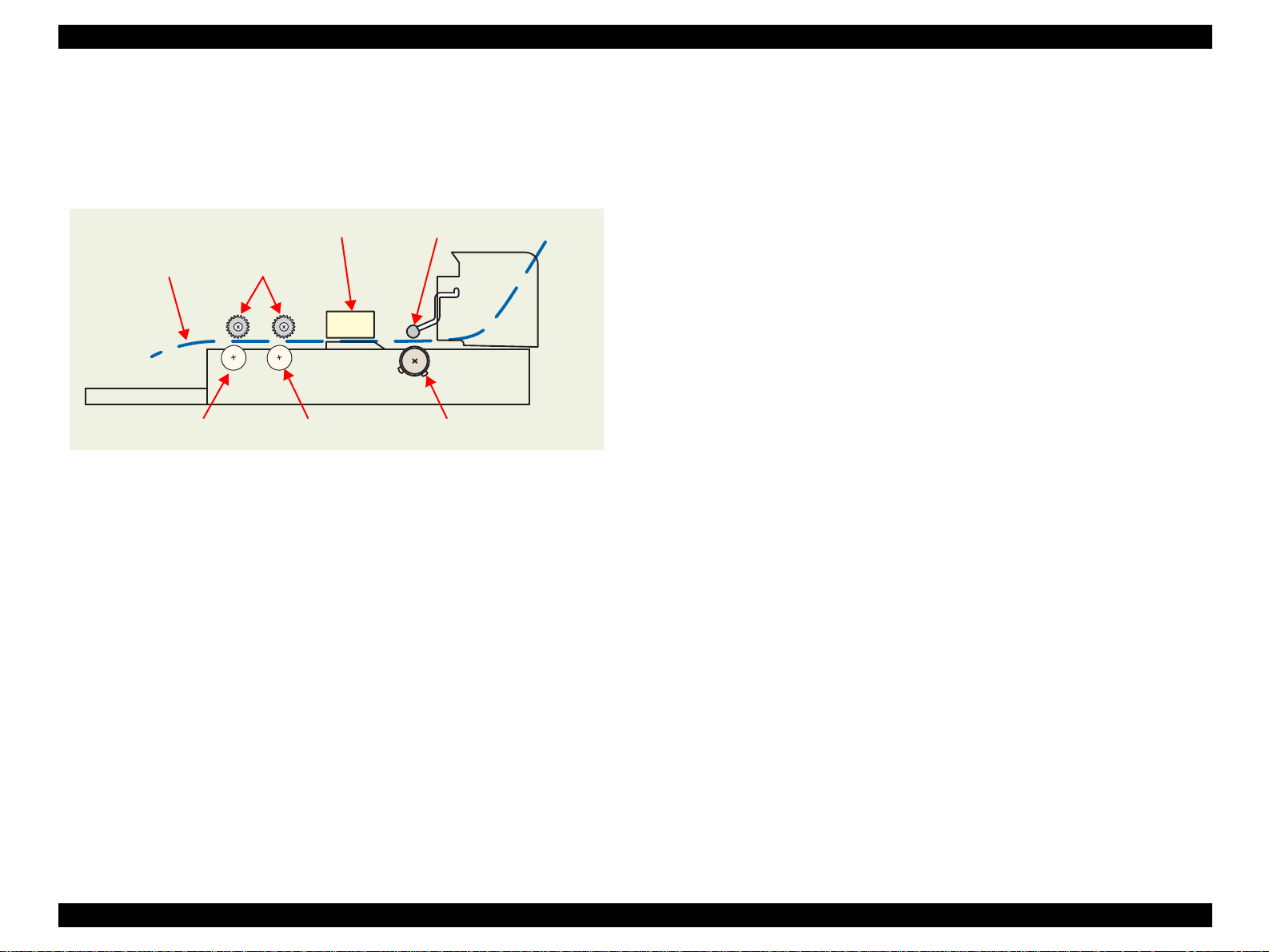
2.2.7 Paper Cutter Mechanism
The Paper cutter mechanism consists of such main parts as the Cutter Motor,
left and right HP Sensors (2 pcs. in all), Relay Board, Paper Eject Roller and
Paper Holddown Flap in the Cutter unit.
Operation during printing
When the Cutter Blade starts cutting, the Paper Hold-down Flap rises.
The paper is held and simultaneously cut.
The HP Sensors installed on both ends of the Cutter operating area
detect the Cutter Blade position.
The HP Sensors detect whether the Cutter Blade operates properly,
and Cutter Position Error or Cutter Jam Error is displayed according to
the operating condition.
Paper Holddown Flap
Left HP
Sensor
Right HP Sensor
Cutter Blade
Cutter Motor
Paper Eject Roller
Relay Board
Figure 2-12. Paper Cutter Mechanism
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 30
Page 30

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
2.2.7.1 Cutter Initialization Sequence
When the Cutter is fitted, the Cutter initialization sequence is executed if the
printer has confirmed that the Cutter has been fitted (the Power Switch blinks
about 5 seconds).
Cutter Initialization Sequence
The initialization sequence is performed to securely put the Cutter Blade in
a standby position detected by the right HP Sensor if the Cutter Blade is
not detected by the right HP Sensor.
The initialization operation is not performed if the Cutter Blade is in the
right HP Sensor position when the Cutter is fitted.
During Cutter operation, Cutter Position Erro r or Cutter Jam Erro r ma y oc cur .
These errors are explained below.
If the Cutter Blade cannot reach the left or right HP Sensor, the Cutter
Blade is returned to the HP Sensor located in the motion starting position
(right HP Sensor).
Cutte r Ja m Err or
Indicates that the Cutter Blade can return to the HP Sensor position in
the motion starting position within 3 seconds.
Cutter Position Error
Indicates that the Cutter Blade cannot return to the HP Sensor p osition
located in the motion starting position within 3 seconds.
Paper cutting by the Cutter consists of the basic cutting sequences 1 and 2.
Basic cutting sequences 1
Means movement from the right HP Sensor to the left HP Sensor. At this
time, as soon as the Cutter Blade starts moving from the right HP Sensor,
the Timer starts. If the left HP Sensor does not detect the Cutter Blade
within 3 seconds, the Cutter initialization sequence is executed and then
Cutter Jam Error or Cutter Position Error occurs.
Basic cutting sequences 2
Means movement from the left HP Sensor to the right HP Sensor. At this
time, if the Cutter Blade cannot move from the left HP Sensor to the right
HP Sensor within 3 seconds, Cutter Position Error occurs.
2.2.7.2 Cutter Self-cleaning
This sequence indicates the operation performed to hold down and remo ve the
ink, which may stick to the Plate above the Paper Hold-down Fl ap (Plate where
the paper print surface comes into contact), with the leading edge of the fed roll
paper.
The Cutter Blade must be operated left-to-right to operate the Paper Holddown Flap. At this time, the Cutter Blade generates operating noise during
Cutter self-cleaning when the roll paper is fed.
2.2.7.3 Cutter Cleaning (Driver Side)
This sequence is executed on the driver side. By cutting the roll paper three
times at intervals of 7cm, the ink that may stick to the Cutter Blade is removed
to clean the Cutter Blade.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 31
Page 31

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
2.2.8 Power-On Sequence
The following explains the operation to be performed when the Carriage Unit is
inside or outside the HP with the printer powered on.
CARRIAGE UNIT INSIDE HP (CR LOCKED)
1. After power-on, the drive of the APG Motor is transmitted to the Carriage
Shaft, and the PG position changes from PG Typ. to PG++.
2. The drive of the CR Motor is transmitted to the Carriage Unit, and the
Carriage Unit performs HP detection operation in the following path.
Home position ⇒ Right frame ⇒ CR Lock confirmation position
⇒ Right frame ⇒ Home position
3. The drive of the Pump Motor is transmitted to the Cap Unit, the Cap opens
(lowers), and the CR Lock is released.
4. After the Carriage Unit has moved leftward by the specified number of
steps, the Wiper is driven by the Pump Motor to perform the following
operation, and during that period, ink is sucked for about 4 seconds.
Wiper setting ⇒ Wiper resetting
5. The Carriage Unit returns to the home position, and the PG position
returns from PG++ to PG Typ.
6. The drive of the PF Motor is transmitted to the PF Roller and Paper Eject
Rollers (front and rear), which then rotate for about 2 seconds.
7. After moving between the left and right frames twice, the Carriage Unit
moves to the right end of the Front Paper Guide.
8. The PF Roller and Paper Eject Rollers (front and rear) rotate.
Rotation for about 4 seconds (slow speed) ⇒ Rotation for about 2
seconds
9. The Carriage Unit returns to the home position and is fixed by the CR Lock.
CARRIAGE UNIT OUTSIDE HP
1. When the PG position is other than PG++ after power-on, the drive of the
APG Motor is transmitted to the Carriage Shaft, and the PG position
changes to PG++.
2. The drive of the CR Motor is transmitted to the Carriage Unit, and the
Carriage Unit returns to the home position at slow speed.
3. The drive of the PF Motor is transmitted to the PF Roller and Paper Eject
Rollers (front and rear), which then rotate for about 2 seconds.
4. After the Carriage Unit has moved leftward by the specified number of
steps, the Wiper is set, driven by the Pump.
5. After the Carriage Unit has returned to the home position, it moves leftward
again by the specified number of steps. And, driven by the Pump Motor, ink
is sucked for about 4 seconds and then the Wiper is set, and the CR Lock
is placed.
6. The Carriage Unit performs HP detection operation in the following path.
Home position ⇒ Right frame ⇒ CR Lock confirmation position
⇒ Right frame ⇒ Home position
7. The drive of the Pump Motor is transmitted to the Cap Unit, the Cap o pens
(lowers), and the CR Lock is released.
8. The Carriage Unit returns to the home position, and the PG position
returns from PG++ to PG Type.
9. The drive of the PF Motor is transmitted to the PF Roller and Paper Eject
Rollers (front and rear), which then rotate and stop as described below.
Rotation for about 3 seconds ⇒ Stop for about 0.5 seconds ⇒
Rotation for about 2 seconds
10. As soon as the operation in step 9 starts, the drive of the ASF Motor is
transmitted to the LD Roller, and the LD Roller rotates one turn.
11. The operations in Steps 7 to 9 of "Carriage Unit inside HP (CR locked)
(p32)" are performed, and the Carriage Unit is locked.
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 32
Page 32

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
2.3 Electrical Circuitry Operating Principles
The electrical circuitry of Stylus Photo R800 consists of the following circuits.
Control circuit board : C550 MAIN
Power supply circuit board : C550 PSB/PSE
Control panel board : C550 PNL
The following shows how the three circuit boards are connected.
PNL Board
MAIN Board
CR Motor
PF Motor
APG Motor
ASF Motor
Pump Motor
Head drive circuit
Printer
Mechanism
2.3.1 Power Supply Circuit Operating Principle
The power supply circuit board of this product is the C550 PSB/PSE.
Basic circuit structure
RCC switching regulator system
+42VDC and +3.3VDC are supplied to the Printer Mechanism and
Control Board
The following indicates the applications of the voltages generated in this power
supply circuit.
Table 2-9. Supplied Power
Voltage Applications
+42VDC
Rated output current: 0.45A
+3.3VDC
Rated output current: 0.5A
• CR Motor
•PF Motor
•PG Motor
•ASF Motor
•Pump Motor
• Head drive voltage
• Logic sensor circuit
• Sensor circuit
• Nozzle selection circuit (above Print Head)
• Interface control circuit
Sensors
Power OFF +3.3VDC +42VDC
PSB/PSE
Power Supply
Board
Figure 2-13. Electrical Circuitry Block Diagram
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuitry Operating Principles 33
Page 33

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
The following is the block diagram of the power supply circuit.
2.3.2 C550 MAIN Circuit Operating Principle
The C550 MAIN Board consists of the following circuits and sensors.
Logic Circuits (CPU-ASIC 2 in 1, PROM, SDRAM)
Motor control/Drive circuits
(CR Motor, PF Motor, APG Motor, ASF Motor, Pump Motor)
Head control/Drive circuit
Interface Circuits
USB 2.0, IEEE1394
Sensor circuits
Reset circuits
EEPROM circuit
D/A converter circuit
Figure 2-14. Power Supply Circuit Block Diagram
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuitry Operating Principles 34
Page 34

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
The following indicates differences between the control circuits of this product
and conventional model.
Adoption of 1.5V drive logic circuit components
The 1.5V voltage is generated by the Regulator IC installed on the C550
MAIN Board that reduces +3.3VDC generated by the C550 PSB/PSE
Board, and is used to drive multiple components.
This is done to reduce the power of the logic circuit.
The following table indicates the 3.3V drive components and 1.5V drive
components.
Table 2-10. 3.3V and 1.5V Drive Components
3.3V 1.5V
• Nozzle selection circuit
(above Print Head)
• CR Encoder Sensor
• PE Sensor
• PG Release Sensor
•CSIC
• CPU-ASIC 2 in 1
•PROM
• SDRAM
• Motor circuit
• Panel LED
• Interface circuit
• USB 2.0
• Sensors
(other than CR Encoder Sensor, PE
Sensor, PG Release Sensor)
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuitry Operating Principles 35
Page 35

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
The following is the block diagram of the C550 MAIN control board.
CR Motor
IEEE 1394
CN3
IEEE 1394
(IC1)
PROM
(IC4, IC15)
SDRAM
(IC12)
USB
CN2
Reset
(IC13)
Data
Address
CPU-ASIC
2 in 1
(IC14)
CN5
DAC
(IC2)
Motor
Driver
(IC5)
Motor
Driver
(IC6)
Relay Board
CN4
PF Motor
APG Motor
ASF Motor
Pump Motor
PF Encoder Sensor
CR Encoder Sensor
Ink Mark Sensor
PW Sensor
C550 PSB/PSE Board
C550 Panel Board
CSIC Board
Cutter Unit
Reset
(IC16)
CN4
CN7
CN8
CN10
CN6
EEPROM
(IC3)
Head
Driver
(IC7)
CN11
CN12
Q13, Q14
CN13
CN14
PE Sensor
PG Release Sensor
ASF Sensor
APG Sensor 1
APG Sensor 2
Print Head
Figure 2-15. C550 MAIN Control Board Block Diagram
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Electrical Circuitry Operating Principles 36
Page 36

TROUBLESHOOTING
CHAPTER
3
Page 37

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
3.1 Overview
This chapter describes unit-level troublesh oo tin g.
3.1.1 Troubleshooting according to panel messages
After checking the printer LED and EPW3 error indications, you can grasp the fault location using the check list in this section. When you have found the fault
location, refer to Chapter 4 "Disassembly and Reassembly" and change the corresponding part and/or unit. The following table indicates the check point reference
tables corresponding to the error states (LED and EPW3).
Table 3-1. Reference Tables of Error States
Error State Reference Table
Communication Error Refer to Table 3-2 "Phenomenon-Based Communication Error Check Points" on page 39
Model Difference Refer to Table 3-2 "Phenomenon-Based Communication Error Check Points" on page 39
Cover Open Error Refer to Table 3-3 "Phenomenon-Based Cover Open Error Check Points" on page 42
Paper Out Error Refer to Table 3-4 "Phenomenon-Based Pap er Out Error Check Points" on page 43
Paper Jam Error Refer to Table 3-5 "Phen omenon-Based Paper Jam Error Check Points" on page 48
Card Loading Error Refer to Table 3-6 "Phenomenon-Based Card Loading Error Check Points" on page 49
Paper Mismatch Error Refer to Table 3-7 "Phenomenon-Based Paper Mismatch Error Check Points" on page 50
Ink Low Refer to Table 3-8 "Phenomenon-Based Ink Low Check Points" on page 50
Ink Out Error Refer to Table 3-9 "Phenomenon-Based Ink Out Error Check Points" on page 50
No Ink Cartridge/CSIC Error Refer to Table 3-10 "Phenomenon-Based No Ink Cartridge/Ink Cartridge Error Check Points" on page 51
Cutter Jam Error Refer to Table 3-11 "Phenomenon-Based Cutter Jam Error Check Points" on page 53
Cutter Position Error Refer to Table 3-12 "Phenomenon-Based Cutter Position Error Check Points" on page 54
Maintenance Request Refer to Table 3-13 "Phenomenon-Based Maintenance Request Check Points" on page 55
Fatal Error Refer to Tabl e 3-14 "Phenomenon-Based Fatal Error Check Points" on page 56
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 38
Page 38

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-2. Phenomenon-Based Communication Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
Phenomenon Detail
At power-on The printer does not operate
at all.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Panel FFC 1. Check that the Panel FFC is securely connected to the
Panel Board connector and Main Board connector (CN8).
Panel FFC
Main Board
connector
Check Point Remedy
1. Connect the Panel FFC to the Panel
Board and Main Board connectors.
Panel FFC
Panel Board
connector
2. Check the Panel FFC for damage. 2. Change the Panel FFC for a new one.
Panel Board 1. Check the Panel Board for damage. 1. Change the Panel Board for a new one.
Power Supply
Board
1. Check that the Connector cable of the Power Supply
Board is securely connected to the Main Board (CN7).
Blue line
Connector cable
of the Power
Supply Board
1Pin side
1. Connect the Connector cable of the
Power Supply Board.
2. Check that the blue line side pin of the Power Supply
Board Connector cable is inserted into the 1 Pin. (Refer to
the above photo.)
2. Match and connect the blue line of the
Power Supply Board Connector cable
into the 1 Pin.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 39
Page 39

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-2. Phenomenon-Based Communication Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
At power-on The printer does not operate
Phenomenon Detail
at all.
After the power-on sequence
has started, the LED turns off
and the printer does not
operate.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Power Supply
Board
Main Board 1. Check that the Relay connector of the ASF Motor and the
3. Check that the Fuse (F1) on the Power Supply Board is not
blown.
4. Check the devices on the Power Supply Board for
damage.
Relay connector of the Pump Motor are not connected to
cause a short circuit.
Relay Connector
of the ASF Motor
Check Point Remedy
Fuse (F1)
3. Change the Power Supply Board for a
new one.
4. Change the Power Supply Board for a
new one.
1. Change the Main Board for a new one.
Relay Connector
of the Pump Motor
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 40
Page 40

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-2. Phenomenon-Based Communication Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
At operation Operation at power-on is
Phenomenon Detail
normal, but the error appears
when the print jog is sent to
the printer.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Interface cable 1. Check that the Interface cable is connected between the
PC and printer.
2. Check the Interface cable for wire break. 2. Change the Interface cable for a new
EPSON
USB driver
USB 1. Check that the PC and printer are connected via the USB
IEEE1394 1. Check that the same code as the IEEE1394 QR label code
Printer driver 1. Check that the Stylus Photo R800 printer driver has been
Main Board 1. Check that a wrong model name has not been input to the
1. When USB is used, check that the EPSON USB driver has
been installed in the PC.
hub.
is saved at BA<H> to BE<H> of the EEPROM.
installed.
2. Check that the connected printer is the Stylus Photo R800. 2. Connect the Stylus Photo R800 printer.
EEPROM address (E0<H>) on the Main Board.
Check Point Remedy
1. Connect the Interface cable to the PC
and printer.
one.
1. Install the EPSON USB driver.
1. Enter the USB serial No. indicated on the
product nameplate.
(Refer to Chapter 5 "ADJUSTMENT".)
1. Input the code given as the IEEE1394
QR label code.
(Refer to Chapter 5 "ADJUSTMENT".)
1. Install the Stylus Photo R800 printer
driver.
1. Using the Adjustment Program, enter the
correct model name (save 02 into
E0<H>).
(Refer to Chapter 5 "ADJUSTMENT".)
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 41
Page 41

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-3. Phenomenon-Based Cover Open Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
During printing Cover Open Error is
Phenomenon Detail
displayed during printing in
the "Economy" mode.
The Printer Cover is in a
closed state but Cover Open
Error is displayed.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Printer Cover 1. Che ck that the Printer Cover is not open. 1. Close the Printer Cover.
Cover Open
Sensor
1. Check that the Connector cable of the Cover Open Sensor
is securely connected to the connectors of the Cover Open
Sensor and Panel Board.
Panel Board
2. Check the Cover Open Sensor for damage. 2. Change the Cover Open Sensor for a
Check Point Remedy
1. Connect the Connector cable of the
Cover Open Sensor to the connectors of
the Cover Open Sensor and Panel
Board.
Cover Open Sensor
new one.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 42
Page 42

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-4. Phenomenon-Based Paper Out Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
Phenomenon Detail
At operation When the Paper Switch was
pressed, the LD Roller
attempt to feed paper but the
paper is not fed.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Check Point Remedy
ASF Assy. 1. Check the LD Roller or Retard Roller of the ASF Assy. for
paper dust and foreign matter.
1. Using a cleaning sheet, clean the LD
Roller and Retard Roller. The procedure
is as follows.
(1) Place the cleaning sheet upside
down and put it into the ASF Assy.
(2) Press the Paper Switch to start
paper feed.
(3) Repeat the above steps several
times.
* To remove persistent contamination,
staple an alcohol-dampened cloth to a
postcard and clean the rollers in the
following method.
Cleaning sheet Postcard used
Non-adhesive part
Adhesive part
This side down
as mount
Stapling
Cloth damped
with alcohol
(1) Place the alcohol-dampened cloth
toward the LD Roller surface of the
ASF Assy.
(2) Hold the mount top end securely
and press the Paper Switch.
(3) Repeat the paper feed sequence
several times to clean the LD Roller
surface of the ASF Assy.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 43
Page 43

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-4. Phenomenon-Based Paper Out Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
At operation Paper is not fed. ASF Motor 1. Check that the Connector cable of the ASF Motor is
Phenomenon Detail
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Check Point Remedy
connected to the Relay Connector.
ASF Motor
Relay Connector
2. Using a tester, check the resistance value of the ASF
Motor.
Resistance value: 7.4Ω ± 10%
3. Check the ASF Motor connector cable for damage. 3. Change the ASF Motor for a new one.
1. Connect the Connector cable of the ASF
Motor to the Relay Connector.
2. If the resistance value is abnormal,
change the ASF Motor for a new one.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 44
Page 44

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-4. Phenomenon-Based Paper Out Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
Phenomenon Detail
At operation Though paper is fed from the
ASF Assy., it stops near the
PE Sensor Lever.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Check Point Remedy
PE Sensor 1. Check that the Connector cable of the PE Sensor is
securely connected to the PE Sensor and Relay Board
Connector (CN3).
Relay Board Connector
PE Sensor
2. Check that the Sensor Holder is mounted to the
Mechanical frame correctly.
Sensor Holder
Detection Lever
Torsion Spring
1. Connect the Connector cable of the PE
Sensor to the PE Sensor and Relay
Board Connector.
2. Install the Sensor Holder correctly.
3. Move the Detection Lever actively by hand in the same
state as when the paper passes, and check that the
3. Change the PE Sensor Holder Unit for a
new one.
Detection Lever is returned to the original position
automatically by the Torsion Spring when released.
(Refer to the above photo.)
4. Using a tester, check that the PE Sensor is normal.
⋅ Paper present : 2.4V or more
4. Change the PE Sensor Holder Unit for a
new one.
⋅ Paper absent : 0.4V or less
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 45
Page 45

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-4. Phenomenon-Based Paper Out Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
The Paper Switch
was pressed at the
setting of the CD-R
Tray.
The Paper Switch
was pressed at the
setting of the CD-R
Tray or board paper
Phenomenon Detail
The CD-R Tray HP detection
sequence stops and the Tray
is ejected.
The CD-R Tray or board
paper is fed toward the ASF
Assy., but is ejected
immediately.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
CD-R Tray 1. Check the HP detection position or white markings of the
CD-R Tray for paper dust and foreign matter.
White Markings
2. Check the Driven Roller surface for contamination such as
paper dust and CD-R coating.
Check Point Remedy
1. Remove paper dust and/or foreign matter
from the detection portion.
HP detection
position
2. Pass plain paper of A4 width from the
ASF Assy. several times to remove
contamination.
3. Check that the HP detection position or white markings of
3. Change the CD-R Tray for a new one.
the CD-R Tray are not chipped.
PW Sensor 1. Check the PW Sensor for paper dust, ink, etc. 1. Clean the PW Sensor surface.
PW Sensor
Carriage Unit bottom
2. Compare the EEPROM values in two places (50<H> and
2. Change the PW Sensor for a new one.
51<H>) and check that they are not approximate to each
other.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 46
Page 46

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-4. Phenomenon-Based Paper Out Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
The Paper Switch
was pressed at the
setting of the CD-R
Tray or board paper
Phenomenon Detail
The trailing edge of the CD-R
Tray is fed toward the ASF
Assy. up to the Driven Roller
of the Upper Paper Guide,
and is then fed in an attempt
to move it farther, but the
Tray is ejected.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Check Point Remedy
PW Sensor 1. Check that the PW Sensor FFC is placed in the specified
routing positions and does not make contact with any
parts.
CR Encoder Board
Connector
FFC
PW Sensor
Connector
2. Check that the PW Sensor FFC is not disconnected from
the CR Encoder Board and PW Sensor Connectors. (Refer
to the above photo.)
3. Check the PW Sensor or PW Sensor FFC for damage. 3. Change the PW Sensor for a new one.
1. Place the PW Sensor FFC in the
specified routing positions.
2. Connect the FFC to the CR Encoder
Board and PW Sensor Connectors.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 47
Page 47

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-5. Phenomenon-Based Paper Jam Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
Phenomenon Detail
At operation At the time of paper ejection,
the PF Roller advances the
paper but cannot eject it
completely.
Paper is not ejected
completely and causes a jam
near the Paper Eject Frame.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
– 1. Check that the size of the fed paper is not larger than that
of the paper set on the driver side.
Check Point Remedy
1. Since the paper length is larger than the
specifications, notify the user.
ASF Assy. 1. Check that the paper is fed along the Right Edge Guide. 1. Feed the paper along the Right Edge
Guide.
Paper EJ Frame
Assy.
Spur Gear 54
and Spur Gear
18 (Paper EJ
Roller Assy.
(front/rear))
1. Check that the Star Wheel Units have not come off the
Paper EJ Frame Assy.
Paper EJ Frame Assy.
Star Wheel Units
2. Check the Paper EJ Frame Assy. for deformation or
damage.
1. Securely install the Star Wheel Units to
the Paper EJ Frame Assy.
2. Change the Paper EJ Frame Assy. for a
new one.
1. Check the Spur Gear 54 or Spur Gear 18 for damage. 1. Change the Front (or Rear) Paper EJ
Roller Assy. for a new one.
Spur Gear 18
Rear Paper EJ
Roller Assy.
Front Paper EJ
Roller Assy.
Spur Gear 54
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 48
Page 48

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-6. Phenomenon-Based Card Loading Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
Phenomenon Detail
During printing Printing starts but paper is
not fed.
The card size paper is loaded
correctly, but Card Loading
Error is displayed.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Check Point Remedy
– 1. Check that the card size paper is loaded in the portrait
orientation.
PW Sensor
1. Check that the PW Sensor FFC is not disconnected from
the CR Encoder Board or PW Sensor Connector.
CR Encoder Board
Connector
FFC
PW Sensor
Connector
2. Check the PW Sensor or PW Sensor FFC for damage. 2. Change the PW Sensor for a new one.
1. Load the cards of the same size correctly,
and press the Paper Switch to eject the
jammed paper.
1. Connect the FFC to the CR Encoder
Board or PW Sensor.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 49
Page 49

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-7. Phenomenon-Based Paper Mismatch Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
At operation When print data are sent, an
Occurrence
Timing
Phenomenon Detail
error is displayed on the LED
and EPW3.
Phenomenon Detail
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Stacker Assy. 1. Check that the Stacker Assy. setting position and paper
size set on the driver side are combined correctly.
PG Release
Sensor
1. Check that the Connector cable of the PG Release Sensor
is securely connected to the PG Release Sensor and
Relay Board Connector (CN7).
PG Release Sensor
2. Check the PG Release Sensor or Connector cable for
damage.
Check Point Remedy
Relay Board Connector
Table 3-8. Phenomenon-Based Ink Low Check Points
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Check Point Remedy
1. Correctly combine the Stacker Assy.
setting position and paper size.
1. Connect the Connector cable of the PG
Release Sensor to the PG Release
Sensor and Relay Board.
2. Change the PG Release Sensor for a
new one.
At operation or
during printing
A message is displayed on
the LED and EPW3 during
printing.
Ink Cartridge 1. Look at the remaining ink indication of the EPW3 to check
the amount of the ink remaining in the Ink Cartridge.
1. Prepare a new Ink Cartridge.
Table 3-9. Phenomenon-Based Ink Ou t Error Chec k Po ints
Occurrence
Timing
During printing After the Carriage has
Phenomenon Detail
detected the HP, an error is
displayed on the LED and
EPW3.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Ink Cartridge 1. Look at the remaining ink indication of the EPW3 to check
whether the ink remains in the Ink Cartridge.
Check Point Remedy
1. Change the Ink Cartridge for a new one.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 50
Page 50

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-10. Phenomenon-Based No Ink Cartridge/Ink Cartridge Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
At power-on After the Carriage has
Phenomenon Detail
detected the HP, an error is
displayed on the LED and
EPW3.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Ink Cartridge 1. Check that the Ink Cartridge is fitted properly. 1. Fit the Ink Cartridge properly.
2. Check that the Hook of the Ink Cartridge is not broken. 2. Change the Ink Cartridge for a new one.
3. Check that the Memory Chip is not disconnected or not
chipped.
Check Point Remedy
Hook
3. Change the Ink Cartridge for a new one.
Memory Chip
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 51
Page 51

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-10. Phenomenon-Based No Ink Cartridge/Ink Cartridge Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
Phenomenon Detail
At power-on After the Carriage has
detected the HP, an error is
displayed on the LED and
EPW3.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Check Point Remedy
Carriage Unit 1. Check that the Electrodes in the Carriage, which make
contact with the CSIC Board, are not bent.
Electrodes
CSIC FFC 1. Check that the CSIC FFC is connected to the CSIC Board
Connector and Main Board Connector (CN10).
CSIC FFC
CSIC Board Connector
Main Board
Connector
1. Change the Carriage Unit for a new one.
1. Connect the FFC to the CSIC Board and
Main Board Connectors.
2. Check the CSIC FFC for damage. 2. Change the CSIC FFC for a new one.
CSIC Board 1. Check the CSIC Board for damage. 1. Change the CSIC Board for a new one.
CSIC Board
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 52
Page 52

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-11. Phenomenon-Based Cutter Jam Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
At roll paper feeding When the paper roll is fed,
After end of printing The roll paper is not cut after
Phenomenon Detail
the Cutter produces
operating noise.
end of printing.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Cutter Unit 1. Check the rail groove of the Cutter for paper dust, foreign
matter, etc.
Cutter Motor 1. Check that the Connector cable of the Cutter Motor is
connected to the Relay Board Connector (CN2).
Check Point Remedy
Rail Groove
CN2
1. Remove the paper dust, foreign matter,
etc. from the rail groove of the Cutter.
1. Connect the Connector cable of the
Cutter Motor to the Relay Board
Connector.
Cutter Motor
2. Check the Cutter Motor or Connector cable for damage. 2. Change the Cutter Motor for a new one.
At roll paper
cutting
The roll paper is cut only
halfway.
Cutter Unit 1. Check that the paper used is not other than the EPSON
special media.
2. Check the Cutter for damage. 2. Change the Cutter Unit for a new one.
1. Use the EPSON special media.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 53
Page 53

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-12. Phenomenon-Based Cutter Position Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
Phenomenon Detail
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Check Point Remedy
At Cutter unit fitting
(At power-on)
At power-on, an error is
displayed on the Paper LED
and EPW3.
The Cutter produces
operating noise.
Cutter Motor 1. Check that the Connector cable of the Cutter Motor is
connected to the Relay Board Connector (CN2).
(When the Cutter position is other than the HP)
CN2
Cutter Motor
2. Check the Cutter Motor or Connector cable for damage.
(When the Cutter position is other than the HP)
Cutter HP
Sensor (right)
1. Check the Cutter HP Sensor (right) or the rail groove of the
Cutter for paper dust, foreign matter, etc.
Cutter HP Sensor (right)
CN4
1. Connect the Connector cable of the Cutter
Motor to the Relay Board Connector.
2. Change the Cutter Motor for a new one.
1. Remove the paper dust, foreign matter,
etc. from the Cutter HP Sensor (right) or
the rail groove of the Cutter.
2. Check that the Connector cable of the Cutter HP Sensor
(right) is connected to the Cuter HP Sensor (right) and
Relay Board Connector (CN4).
3. Check the Cutter HP Sensor (right) for damage. 3. Change the Cutter HP Sensor (right) for a
2. Connect the Connector cable of the Cutter
HP Sensor (right) to the Cuter HP Sensor
(right) and Relay Board Connector.
new one.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 54
Page 54

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-13. Phenomenon-Based Maintenance Request Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
At power-on At power-on, the printer does
Phenomenon Detail
not operate at all.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Waste Ink Pads 1. Using the Adjustment Program, check that the Protection
Counter A+B value is the following count or more.
Home side : 14787 count or more
Opposite-to-home side : 17115 count or more
Check Point Remedy
1. Change the Waste Ink Pads and reset
the Protection Counter A+B value with
the Adjustment Program.
Home side: 24<H>, 25<H>
Opposite-to-h ome side: 26<H>,
27<H>
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 55
Page 55

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-14. Phenomenon-Based Fatal Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
At power-on At power-on, the CR Motor
Phenomenon Detail
does not operate at all.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
CR Motor 1. Check that the CR Motor connector cable is connected to
the Relay Connector.
CR Motor
2. Using a tester, check the resistance value of the CR Motor.
Resistance value: 24.4Ω ± 15%
3. Check the CR Motor connector cable for damage. 3. Change the CR Motor for a new one.
Relay
Connector
Cable
1. Check that the Relay Connector Cable is connected to the
Main Board Connector (CN4).
Check Point Remedy
Relay Connector
1. Connect the CR Motor connector to the
Relay Connector.
2. If the resistance value is abnormal,
change the CR Motor for a new one.
1. Connect the Relay Connector Cable to
the Main Board.
Connector
2. Check the Relay Connector Cable for damage. 2. Change the Relay Connector Cable for a
new one.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 56
Page 56

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-14. Phenomenon-Based Fatal Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
At power-on The power-on sequence is
Phenomenon Detail
executed but Fatal error is
displayed.
At power-on, the PF Motor
does not operate at all.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
CR drive
system
PF Motor 1. Check that the PF Moto r connector cable is connected to
1. Check that the Carriage Shaft is lubricated with grease. 1. Wipe the surface of the Carriage Shaft
the Relay Connector.
Relay Connector
Check Point Remedy
Carriage Shaft
with a dry, soft cloth, and lubricate the
Carriage Shaft with grease G-70. (Refer
to Chapter 6 "MAINTENANCE".)
1. Connect the PF Motor connector cable to
the Relay Connector.
PF Motor
2. Using a tester, check the resistance value of the PF Motor.
Resistance value: 22.3Ω ± 25%
3. Check the PF Motor connector cable for damage. 3. Change the PF Motor Cable for a new
2. If the resistance value is abnormal,
change the PF Motor for a new one.
one.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 57
Page 57

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-14. Phenomenon-Based Fatal Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
At power-on At power-on, the APG Motor
Phenomenon Detail
does not operate at all.
At power-on, the Pump Motor
does not operate at all.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
APG Motor 1. Check that the APG Motor connector cable is connected to
the Relay Connector.
Relay Connector
2. Using a tester, check the resistance value of the APG
Motor.
Resistance value: 64.7Ω ± 15%
3. Check the APG Motor connector cable for damage. 3. Change the APG Motor Cable for a new
Pump Motor 1. Check that the Pump Motor connector cable is connected
to the Relay Connector.
Check Point Remedy
APG Motor
1. Connect the APG Motor connector cable
to the Relay Connector.
2. If the resistance value is abnormal,
change the APG Motor for a new one.
one.
1. Connect the Pump Motor connector cable
to the Relay Connector.
Relay Connector
2. Using a tester, check the resistance value of the Pump
Motor.
Resistance value: 10.3Ω ± 10%
3. Check the Pump Motor connector cable for damage. 3. Change the Ink System Unit Cable for a
2. If the resistance value is abnormal,
change the Ink System Unit for a new
one.
new one.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 58
Page 58

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-14. Phenomenon-Based Fatal Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
Phenomenon Detail
At power-on While the power-on
sequence is being executed,
Fatal error is displayed.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Check Point Remedy
APG Sensor 1. Check that the APG Sensor Connector cables are
connected to the APG Sensors and Relay Board
Connectors (CN5 and CN6).
APG Sensors
CN6
CN5
2. Check the APG Sensors for damage. 2. Change the APG Sensors for new ones.
Relay FFC 1. Check that the Relay FFC is connected to the Relay Board
Connector (CN1) and Main Board Connector (CN5).
1. Connect the APG Sensor Connector
cables to the APG Sensors and Relay
Board Connectors.
1. Connect the Relay FFC to the Relay
Board and Main Board Connectors.
Main Board Connector
Relay Connector
2. Check the Relay FFC for damage. 2. Change the Relay FFC Cable for a new
one.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 59
Page 59

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-14. Phenomenon-Based Fatal Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
Phenomenon Detail
At power-on At power-on, the Carriage
Unit moves away from the
home position and collides
with the left of the Frame.
At power-on, the PF Roller
rotates fast about a half turn.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Check Point Remedy
CR Scale 1. Check that the CR Scale is inserted in the slit of the CR
Encoder Sensor.
CR Scale
CR Encoder
Sensor
2. Check the CR Scale for damage and contamination. 2. Wipe contamination completely or
CR Encoder
1. Check the CR Encoder Sensor for paper dust, etc. 1. Remove the paper dust, etc. from the CR
Sensor
2. Check the CR Encoder Sensor for damage. 2. Change the CR Encoder Sensor Cable
PF Encoder
Sensor
1. Check that the PF Encoder Sensor is mounted correctly. 1. Install the PF Encoder Sensor correctly.
2. Check that the FFC of the PF Encoder Sensor is securely
connected to the PF Encoder Sensor Connector and Relay
Board Connector (CN9).
1. Insert the CR Scale into the slit of the CR
Encoder Sensor.
change the CR Scale for a new one.
Encoder Sensor.
for a new one.
2. Connect the PF Encoder Sensor FFC to
the PF Encoder Sensor and Relay Board
Connectors.
Relay Board Connector
PF Encoder Sensor
Connector
3. Check the PF Encoder Sensor for paper dust, etc. 3. Remove the paper dust, etc. from the PF
Encoder Sensor.
4. Check the PF Encoder Sensor for damage. 4. Change the PF Encoder Sensor Cable for
a new one.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 60
Page 60

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-14. Phenomenon-Based Fatal Error Check Points
Occurrence
Timing
Phenomenon Detail
At power-on At power-on, the PF Roller
rotates fast about a half turn.
During printing Before start of printing, Initial
Filling is executed and
printing is then started. Ink is
not delivered and paper stops
midway.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Check Point Remedy
PF Scale 1. Check that the PF Scale is inserted in the slit of the PF
Encoder Sensor.
PF Scale
Slit
2. Check the PF Scale for damage or contamination. 2. Change the PF Scale for a new one.
Head FFC 1. Check that the Head FFC is securely connected to the
Print Head Connectors and Main Board Connectors
(CN11, CN12, CN13, CN14).
Head FFC
1. Install the PF Scale in the slit of the PF
Encoder Sensor correctly.
1. Connect the Head FFC to the Print Head
and Main Board Connectors.
Main Board Connectors
Print Head
Connectors
2. Check the Head FFC for damage. 2. Change the Head FFC for a new one.
Ink is not delivered from most
Print Head 1. Check for occurrence of Head Hot. 1. Change the Print Head for a new one.
nozzles.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 61
Page 61

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
3.1.2 Superficial Phenomenon-Based Troubleshooting
This section applies to the fault locations of the error states (print quality fault and abnormal noise) other than the error states (LED and EPW3) in the previous
section.
Table 3-15. Print Quality Fault Check Points
Print Quality State Phenomenon Detail
Dot missing and
mixed colors
[Phenomenon 1]
• In the cleaning
sequence, the Ink
System Unit operates
properly but ink is not
ejected to the Waste
ink pads.
• Ink is not sucked from
the Print Head into the
Cap at all.
Hence, printing is not
executed if a print command
is given to the printer. (Dot
missing)
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Ink System Unit
(Cap Unit)
Check Point Remedy
1. Check for foreign matter around the Seal Rubber on the
Cap Unit.
Seal Rubbers
Extension Spring 1.19 IS
2. Check that the Ink Tube is connected to the Pump Tube. 2. Connect the Ink Tube to the Pump Tube
Ink Tube
Pump Tube
1. Remove the foreign matter around the
Seal Rubber securely.
securely.
Connection Portion
3. Check that the Extension Spring 1.19 IS is correctly
installed to the Cap Unit.
3. Change the Ink System Unit for a new
one.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 62
Page 62

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-15. Print Quality Fault Check Points
Print Quality State Phenomenon Detail
Dot missing and
mixed colors
(Continued)
[Phenomenon 2]
In the cleaning sequence, ink
is ejected to the Waste Ink
Pads. However, Dot missing/
displacement occurs in all
nozzles during printing and
this problem is not resolved
after several times of
cleaning. (Dot missing)
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Print Head 1. Check that each segment is printed correctly in the Nozzle
Check Pattern
2. Check that the Head FFC is securely connected to the
Print Head Connectors and Main Board Connectors
(CN11, CN12, CN13, CN14).
Main Board Connectors
3. Check the Head FFC for damage. 3. Change the Head FFC for a new one.
Main Board 1. Check the Main Board for damage. 1. Change the Main Board for a new one.
Check Point Remedy
1. Perform Head Cleaning and check the
Nozzle Check Pattern.
2. Connect the Head FFC to the Print Head
and Main Board Connectors.
Head FFC
Print Head
Connectors
If the problem still persists, also change
the Print Head.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 63
Page 63

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-15. Print Quality Fault Check Points
Print Quality State Phenomenon Detail
Dot missing and
mixed colors
(Continued)
[Phenomenon 3]
In the cleaning sequence, ink
is ejected to the Waste Ink
Pads. (This means that the
Pump Unit and Cap Unit
operate properly.) However,
Dot missing is not resolved in
indefinite nozzles after
cleaning has been executed
several times. (Dot missing/
mixed colors)
[Phenomenon 4]
In the cleaning sequence, ink
is ejected to the Waste Ink
Pads. However, drawing
operation is not performed
properly, resulting in mixture
of colors. (Mixed colors)
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Ink Cartridge 1. Look at the remaining ink indication of the EPW3 to check
for the ink remaining in the Ink Cartridge.
Ink System Unit
(Cap Unit)
1. Check that the Cleaner Blade is mounted on the Cleaning
Lever correctly.
Cleaner Blade
2. Check for foreign matter around the Seal Rubber on the
Cap Unit.
Check Point Remedy
Seal Rubbers
1. Change the Ink Cartridge for a new one.
1. Change the Cleaner Blade for a new one.
2. Change the Ink System Unit for a new
one.
Extension Spring 1.19 IS
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 64
Page 64

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-15. Print Quality Fault Check Points
Print Quality State Phenomenon Detail
White streak/color
unevenness
occurrence
Vertical stripes appear
relative to the CR moving
direction and printing is
uneven.
CR moving
direction
* If the problem is not solved,
change the CR Motor for a
new one.
Narrow stripes of the same
width appear horizontally
relative to the CR moving
direction.
CR moving
direction
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Adjustment 1. For printing in the Bi-D mode, check that the Bi-D
Adjustment has been performed properly.
Print Head 1. Check that each segment is printed correctly in the Nozzle
Check Pattern.
Carriage Shaft 1. Check the surfaces of the Carriage Shaft for foreign
matter.
2. Check that the Carriage Shaft is fully lubricated with
grease.
3. Check that the Carriage Shaft are mounted horizontally. 3. Reassemble the Carriage Shaft correctly.
4. Check the Carriage Shaft for damage. 4. Change the Carriage Shaft for a new one.
Printer Driver
and Exclusive
Paper
Print Head 1. Check that each segment is printed correctly in the Nozzle
PF Roller 1. Check the surface of the PF Roller for foreign matter. 1. Clean the PF Roller surface carefully.
1. Check that adequate paper is used according to the setting
of the Printer Driver.
Check Pattern.
Check Point Remedy
1. Perform Bi-D Adjustment to eliminate
displacements between the upper and
lower rules.
(Refer to Chapter 5 "ADJUSTMENT".)
1. Perform Head Cleaning and check the
Nozzle Check Pattern.
(Refer to Chapter 5 "ADJUSTMENT".)
If the problem is not solved, change the
Print Head for a new one.
1. Remove foreign matter from the Carriage
Shaft.
2. Wipe the grease applied to the Carriage
Shaft with a dry, soft cloth, and then
apply grease (G-70).
(Refer to Chapter 6 "MAINTENANCE".)
1. Use adequate paper according to the
setting of the Printer Driver.
1. Perform Head Cleaning and check the
Nozzle Check Pattern.
(Refer to Chapter 5 "ADJUSTMENT".)
If the problem is not solved, change the
Print Head for a new one.
2. Check the PF Roller for damage. 2. Change the PF Roller for a new one.
* If the problem is not solved,
change the PF Motor for a
new one.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 65
Page 65

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-15. Print Quality Fault Check Points
Print Quality State Phenomenon Detail
White streak/color
unevenness
occurrence
(Continued)
Occurrence of
Paper EJ Roller
traces
White streaks/color
unevenness occurs
horizontally in a fixed cycle
during 360dpi printing.
Star Wheel Rollers traces
appear relative to the CR
moving direction.
Printing is executed but blur
occurs.
Paper EJ Roller traces occur
during printing of print paper
or CD-R.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Adjustment 1. Check that PF Adjustment is executed properly. 1. Perform PF Adjustment properly. (Refer
2. Check for Dot missing. 2. Change the Ink System Unit for a new
Paper EJ Frame
Assy.
Printer Driver
and Exclusive
Paper
Print Head 1. Using the Adjustment Program, check that the correct Head
Printer Driver
and Exclusive
Paper
1. Check that the Star Wheel Units have not come off or the
Star Wheel Rollers turn.
1. Check that adequate paper is used according to the setting
of the Printer Driver.
ID has been written to the EEPROM.
1. Check that adequate paper is used according to the setting
of the Printer Driver.
Check Point Remedy
to Chapter 5 "ADJUSTMENT".)
one.
1. Install the Star Wheel Units to the Paper
EJ Frame Assy. correctly.
Star Wheel Units
Star Wheel Roller
1. Use adequate paper according to the
setting of the Printer Driver.
1. Using the Adjustment Program, enter the
31- digit code of the Head ID to the
EEPROM.
(Refer to Chapter 5 "ADJUSTMENT".)
1. Use adequate paper according to the
setting of the Printer Driver.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 66
Page 66

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-15. Print Quality Fault Check Points
Print Quality State Phenomenon Detail
Ink stain of paper Ink stain occurs at the back
or end of the print paper.
When the paper size in the
sent print data is larger than
the size of the fed paper, data
are printed on the Front
Paper Guide, extending off
the paper.
Ink sticks to other than the
print area of the paper,
resulting in contamination.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Front Paper
Guide Pad
PW Sensor 1. Check that the PW Sensor FFC is connected. 1. Connect the PW Sensor FFC.
Paper EJ Frame
Assy.
Front Paper
Guide
Front Paper
Guide Pad
1. Check that heaps of ink are not formed on the Front Paper
Guide Pad and that the Front Paper Guide Pad is installed
securely and evenly in the setting position.
Front Paper Guide Pad Front Paper Guide
2. Check that the PW Sensor is not faulty. 2. Change the PW Sensor for a new one.
1. Check the Star Wheel Rollers for ink stain. 1. Clean the Star Wheel Rollers with a soft
1. Check the Front Paper Guide for ink stain. 1. Clean the Front Paper Guide with a soft
1. Check that ink heaps are formed on the Front Paper Guide
Pad.
Check Point Remedy
1. If heaps of ink are formed, replace the
Front Paper Guide. If it has been
confirmed that the Ink pads have risen,
reinstall the Front Paper Guide Pad
correctly.
cloth.
cloth.
1. Change the Front Paper Guide for a new
one.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 67
Page 67

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-15. Print Quality Fault Check Points
Print Quality State Phenomenon Detail
Ink stain of paper
(Continued)
Ink sticks to other than the
print area of the paper,
resulting in contamination.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Lower Paper
Guide
Paper EJ Roller
Assy.
1. Check the Lower Paper Guide for ink stain. 1. Clean the Lower Paper Guide with a soft
Lower
Paper Guide
1. Check the Paper EJ Roller Assy. (front/rear) for ink stain. 1. Clean the Paper EJ Roller Assy. (front/
Check Point Remedy
cloth.
Rear Paper EJ Roller Assy.
Front Paper EJ Roller Assy.
rear) with a soft cloth.
(front/rear)
Driven Rollers 1. Check the Driven Rolle rs for ink stain. 1. Clean the Driven Rollers with a soft cloth.
Driven Rollers
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 68
Page 68

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-15. Print Quality Fault Check Points
Print Quality State Phenomenon Detail
Ink stain of paper
(Continued)
Ink sticks to other than the
print area of the paper,
resulting in contamination.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Ink System Unit 1. Check that wiping operation was performed properly. 1. Install the Cleaner blade correctly or
Cleaner Blade
PF Roller 1. Check the PF Roller for ink stain. 1. Clean the PF Roller with a soft cloth.
PF Roller
Check Point Remedy
change it for a new one.
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 69
Page 69

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-15. Print Quality Fault Check Points
Print Quality State Phenomenon Detail
Image graininess The image graininess is poor
in all print modes or the
image looks rough.
The image graininess is poor
only in the 2880dpi print
modes or the image looks
rough.
Color of image The whole image is reddish. Improper
Borderless Printing Bordered printing is executed
for borderless printing.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Improper
adjustment,
Main Board or
Print Head
Improper
adjustment,
Main Board or
Print Head
adjustment or
Print Head
PW Sensor 1. Check if the paper powder or scrap of the paper is on the
Check Point Remedy
1. Check that PG, Bi-D and Head Angular Adjustments have
been made properly.
2. Print the adjustment check patterns and check how rough
the image looks.
1. After making sure that PG, Bi-D and Head Angular
Adjustments have been made correctly, check whether
PW Sensor has been performed properly.
2. Print the adjustment check patterns and check how rough
the image looks.
1. Check that the PG Adjustment value is proper. 1. Make adjustments according to the
2. Check that Bi-D and Head Angular Adjustments have been
made properly.
3. Print the adjustment check patterns and check the image
color.
Front Paper Guide.
2. Check that the PW Sensor is operating normally.
Print the adjustment check patterns with the Adjustment
Program, and check that the clip function is executed
normally. (The clip function is executed normally if an
about 5mm margin is provided on the left of the first gray
band pattern in the patterns.)
1. Make adjustments according to the
specified adjustment priority. (Refer to
Chapter 5 "ADJUSTMENT".)
2. If the image graininess is not improved
after adjustment, change the Main Board
for a new one.
1. Make adjustments according to the
specified adjustment priority. (Refer to
Chapter 5 "ADJUSTMENT".)
2. If the image graininess is not improved
after adjustment, change the Print Head
and Main Board in this order, and check
the image graininess.
specified adjustment priority. (Refer to
Chapter 5 "ADJUSTMENT".)
2. Make adjustments according to the
specified adjustment priority. (Refer to
Chapter 5 "ADJUSTMENT".)
3. If the image color does not change after
adjustment, change the Print Head for a
new one.
1. Remove the paper powder or scrap of the
paper.
2. Change the PW Sensor for a new one if it
has been confirmed in the adjustment
check patterns of the Adjustment
Program that the clip function is not
executed. (Refer to Chapter 5
"ADJUSTMENT".)
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 70
Page 70

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Table 3-16. Phenomenon-Based Abnormal Noise Check Point
Print Quality State Phenomenon Detail
– Printing operati on is
performed normally but
abnormal noise is produced
at power-on or between
operations.
Faulty Part/
Part Name
Carriage Shaft 1. Check that the Carriage Shaft is fully lubricated with
grease.
Check Point Remedy
1. Wipe the grease applied to the Carriage
Shaft with a dry, soft cloth, and then
apply grease (G-70).
(Refer to Chapter 6 "MAINTENANCE".)
TROUBLESHOOTING Overview 71
Page 71

DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY
CHAPTER
4
Page 72

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4.1 Overview
This chapter describes procedures for disa sse mb lin g an d as se mb lin g this
product. Unless otherwise specified, the disassembled units or main
components can be reassembled by reversing the disassembling procedure.
WARNING
Procedures that could result in injury or loss of life, if cautions are not
taken, are described under the heading "WARNING".
CAUTION
Precautions for any disassembly or assembly procedures are described
under the heading "CAUTION".
CHECK POINT
Tips for disassembling procedures are described under the heading
"CHECK POINT".
REASSEMBLY
If the assembling procedure is different from the reverse procedure of
disassembling, it is described under the heading "REASSEMBLY".
ADJUSTMENT REQUIRED
Any adjustments required after disassembling or assembling ar e described
under the heading "ADJUSTMENT REQUIRED".
When you need to disassemble any units or parts that are not described in this
chapter, refer to the exploded diagrams in the Appendix.
4.1.1 Precautions
Before starting the disassembling/reassembling work of this product, always
read the descriptions under the following headings "WARNING" and
"CAUTION" carefully.
W A R N I N G
Before starting the disassembling/reassembling work of
this product, always disconnect the power cable.
However, if you cannot disconnect the power cable for
voltage measurement or like, be extremely careful not to
get an electric shock and follow the procedures in this
manual to do your work.
Always wear goggles to protect your eyes from ink. If ink
gets in your eyes, wash your eyes with clean water and
see the doctor.
To prevent injury from sharp metal edges, always wear
gloves for disassembly and reassembly.
If ink has adhered to your skin, wash it with soap and
water. If it has caused skin irritation, see the doctor.
To protect the microprocessors and circuitry, use static
discharge equipment, such as anti-static wrist straps,
and handle them carefully when accessing the internal
components.
Before starting your work, always read the precautions described in the next
section.
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Overview 73
Page 73

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
C A U T I O N
When the printer model uses the HAV Ink Cartridges,
transport it after removing the Ink Cartridges. Especially
for air transportation, always remove the Ink Cartridges
before transportation since ink will flow into the Cap Unit
via the Print Head with the reduction of the atmospheric
pressure, causing ink leakage.
Use only the recommended tools for disassembly,
reassembly and adjustment. (Refer to Table 4-1"Tool
List".)
Tighten screws to the specified torques.
Use the specified lubricants and adhesives.
Make the necessary adjustments under the instructions
given for disassembling.
(Refer to Chapter 5 "Adjustment".)
4.1.2 Tools to Be Used
The following table indicates the tools recommended for use for disassembly,
reassembly and adjustment.
Table 4-1. Tool List
Tool Name Supplier Code
Phillips Screw Driver (No.1) { 1080530
Phillips Screw Driver (No.2) { 1080532
Standard Screwdriver { 1080527
Tweezers { 1080561
Needle nose pliers { 1080564
Acetate Tape { 1003963
Sonic Tension Meter { 1231678
{: Available in the market
.
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Overview 74
Page 74

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4.1.3 Screw List
The following table lists the screws used in this product. When disassembling
and reassembling the printer, refer to the following table and use the specified
screws in the specified positions. The screw numbers given in this manual
correspond to the screw numbers in this table.
Table 4-2. Used Screw List
Appearance Specifications Appearance Specifications
1) C.B.S 3x10 2) C.B.S 3x6
3) C.B.P 3x6 4) C.B.S 3x8
5) C.B.P 3x12 6) C.B.P 3x8
Table 4-2. Used Screw List
Appearance Specifications Appearance Specifications
11) C.B.S (P4) 3x6 12) C.C 3x4
13) C.P.B (P1) 1.7x5 14) C.B.P 2.6x5
7) C.B.S (P4) 3x8 8) CR Mount Shaft
9) C.P 3x4 10) C.B.P 2.6x8
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Overview 75
Page 75

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4.1.4 Pre-Shipment Checks
When returning this product to the user after completion of printer repair, check that the work is complete using the following table.
Table 4-3. Servicing Completion Pre-Shipment Check List
Class Component Check Item Check Field
Main Unit Self-test Is the operation normal? Checked / Not necessary
On-line Test Is the printing successful? Checked / Not necessary
Print Head Is ink discharged normally from all the nozzles? Checked / Not necessary
Carriage Mechanism Does it move smoothly? Checked / Not necessary
Is there any abnormal noise during its operation? Checked / Not necessary
Is there any dirt or foreign objects on the CR Shaft? Checked / Not necessary
Is the CR Motor at the correct temperature? Checked / Not necessary
Paper Feeding Mechanism Is paper advanced smoothly? Checked / Not necessary
No paper jamming? Checked / Not necessary
No paper skew? Checked / Not necessary
No multiple feeding? Checked / Not necessary
No abnormal noise? Checked / Not necessary
Is the PF Motor at correct temperature? Checked / Not necessary
Is the paper path free of any obstructions? Checked / Not necessary
Adjustment Specified Adjustment Are all the adjustment done correctly? Checked / Not necessary
Lubrication Specifie d Lubrication Are all the lubrication made at the specifie d points? Checked / Not necessary
Is the amount of lubrication correct? Checked / Not necessary
Function ROM Version Version: Checked / Not necessary
Packing Ink Cartridge Have the ink cartridges been removed? Checked / Not necessary
Protective Materials Have all relevant protective materials been attached to the
printer?
Others CD-R Tray Is the operation normal? Checked / Not necessary
Cutter Unit Is the operation normal? Checked / Not necessary
Attachments, Accessories Have all the relevant items been included in the package? Checked / Not necessary
Checked / Not necessary
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Overview 76
Page 76

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4.2 Disassembly
A disassembling flowchart is shown below. When disassembling any unit, refer to the page number shown in the following flowchart.
START
"Rear Housing"
4.2.1.1 Page 78
"Upper Housing"
4.2.1.2 Page 78
"Lower Housing/
Printer Mechanism"
4.2.1.3 Page 80
"ASF Assy."
4.2.4 Page 86
"Ink System Unit"
4.2.6.7 Page 114
"Panel Board"
4.2.5.3 Page 94
"Waste Ink Pads"
4.2.3 Page 84
"CR Scale"
4.2.6.3 Page 99
"PG Release
Sensor"
4.2.8.2 Page 134
"CSIC Board"
4.2.6.6 Page 111
"Stacker Assy."
4.2.2 Page 82
"Cover Open
Sensor Holder"
4.2.8.1 Page 133
"PF Motor"
4.2.7.2 Page 131
"PF Encoder
Sensor Holder"
4.2.8.6 Page 138
"Main Board"
4.2.5.1 Page 90
"Paper EJ Frame
Assy."
4.2.6.8 Page 116
"PS Board"
4.2.5.2 Page 93
"CR Motor"
4.2.7.1 Page 130
"Carriage Shaft/
Carriage Unit"
4.2.6.5 Page 103
"Paper EJ Frame
Assy."
4.2.6.8 Page 116
"Front Paper
Guide"
4.2.6.11 Page 120
"PF Encoder
Sensor Holder"
4.2.8.6 Page 138
"Rear Paper EJ
Roller Assy."
4.2.6.12 Page 123
"Ink System Unit"
4.2.6.7 Page 114
"Stacker Assy."
4.2.2 Page 82
"Front Paper EJ
Roller Assy."
4.2.6.13 Page 124
"ASF Assy."
4.2.4 Page 86
"PE Sensor
Holder"
4.2.8.3 Page 135
"ASF Assy."
4.2.4 Page 86
"PF Roller"
4.2.6.14 Page 127
"Print Head"
4.2.6.2 Page 97
"CR Scale"
4.2.6.3 Page 99
"APG Assy."
4.2.6.4 Page 101
"Carriage Shaft/
Carriage Unit"
4.2.6.5 Page 103
"Ink Mark Sensor/
PW Sensor"
4.2.8.4 Page 136
"APG Assy."
4.2.6.4 Page 101
"ASF Assy."
4.2.4 Page 86
"FLAG Release
Assy."
4.2.6.9 Page 117
"Upper Paper
Guide Assys."
4.2.6.10 Page 119
"CR Encoder
Board"
4.2.8.5 Page 137
* The step for the unit or discrete part within
the broken line is not the shortest removal
step but is the step necessary for
removing the next unit or discrete part.
Figure 4-1. Disassembling Procedure Flowchart
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 77
Page 77

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4.2.1 Removing the Housings
4.2.1.1 Rear Housing
1. Remove the three screws 1) C.B.S 3x10 that secure the Rear Housing,
and remove the Rear Housing from the printer.
1) C.B.S 3x10
(6±1 kgf.cm)
2
1) C.B.S 3x10
(6±1 kgf.cm)
Rear Housing
1
Figure 4-2. Removing the Rear Hous ing
Tighten the screws in the order shown in Figure 4-2.
3
4.2.1.2 Upper Housing
1. Remove the Rear Housing. (p.78)
2. Open the Printer Cover, Stacker and Paper Support.
3. Remove the three screws 2) C.B.S 3x6 and two screws 3) C.B.P 3x6 that
secure the Upper Housing.
2) C.B.S 3x6
Upper Housing
(6±1 kgf.cm)
3
3) C.B.P 3x6
(6±1 kgf.cm)
5 4
2
Dowels
Left Rear Side
1
Right Rear Side
Figure 4-3. Screws That Secure the Upper Housing
Tighten the screws in the order shown in Figure 4-3.
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 78
Page 78

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4. Disconnect the Panel FFC from the Main Board Connector.
Panel FFC
Connector
Figure 4-4. Disconnecting the Panel FFC
5. Pull each Hook on the rear side of the Upper Housing toward the outside of
the printer, and insert a thickness gauge, etc. into the holes of the Lower
Housing to disengage the Hooks one by one.
6. Insert a Standard Screwdriver, etc. into each of the notches in the left and
right of the front bottom of the Lower Housing, and push it in the direction
of arrow to release the two Hooks that secure the Upper Housing.
7. Remove the Upper Housing upward.
Upper Housing
Notch
Notch
Notch
Notch
Figure 4-6. Removing the Upper Housing
Hole and HookHole and Hook
Figure 4-5. Hooks That Secure the Upper Housing
Match the Positioning Holes and Dowels of the Upper
Housing. (Refer to Figure 4-3)
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 79
Page 79

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4.2.1.3 Lower Housing/Printer Mechanism
1. Remove the Upper Housing. (p.78)
2. Hold both ends of the two fasteners with your fingers, and shift the
fasteners in the direction of arrow.
C H E C K
P O I N T
3. Pull the Waste Ink Tubes from the two Ink Tubes.
4. Remove the two screws 4) C.B.S 3x8, three screws 5) C.B.P 3x12, and
one screw 6) C.B.P 3x8 that secure the Printer Mechanism.
C A U T I O N
The 0 digit side (lower) Waste Ink Tube is marked red.
However, when ink flows in the tube, the marking becomes
difficult to identify. Refer to Figure 4-7 and mark the Waste
Ink Tube with a red magic marker before pulling it out of the
Ink Tube.
0 Digit Side Waste Ink Tube
5mm10mm
Figure 4-7. Marking the Waste Ink Tube
Always hold the grips when handling the Printer Mechanism.
Failure to do so can deform the Frame.
Grips
5. Hold the grips of the Printer Mechanism with both hands, and remove the
Printer Mechanism from the Lower Housing.
5) C.B.P 3x12
(6±1 kgf.cm)
4
3
5) C.B.P 3x12
(6±1 kgf.cm)
6) C.B.P 3x8
(6±1 kgf.cm)
1
2
5) C.B.P 3x12
(6±1 kgf.cm)
Ink Tubes
Fastener
Step 2
Waste Ink Tubes
4) C.B.S 3x8
(6±1 kgf.cm)
Figure 4-8. Handling the Printer Mechanism
5
6
Figure 4-9. Screws That Secure the Printer Mechanism
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 80
Page 80

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Align the Ink Tube lined green with the Waste Ink Tube
marked red.
Fit the Waste Ink Tube of longer tip to the 0 digit side Ink
Tube, and the one of shorter tip to the 80 digit side.
80 Digit Side Ink Tube
80 Digit Side Waste Ink Tube
0 Digit Side Ink Tube
0 Digit Side Waste Ink Tube
Figure 4-10. Installing the Ink Tubes
Afte r ins ert in g the tip of the Wa st e In k Tu be into th e Ink
Tube by about 10mm, refer to Figure 4-11 and secure th e
Waste Ink Tube with the fastener.
Fastener
1±0.5 mm 1±0.5 mm
Figure 4-11. Securing Position of Fastener
A D J U S T M E N T
R E Q U I R E D
Fit the 0 digit side Ink Tube, which comes out of the
Pump, to the lower side of the Hook.
Fit the 0 digit side Waste Ink Tube to the lower side of the
Hook.
0 Digit Side Ink Tube
80 Digit Side Ink Tube
Hook
Hook
Figure 4-12. Ink Tube Fitting Positions
Make sure that the Waste Ink Tubes are not caught in the
Printer Mechanism.
Tighten the screws in the order shown in Figure 4-9.
After replacing the Printer Mechanism, always make the
following adjustments.
1. PG Adjustment
2. Head Angular Adjustment
3. Ink Mark Sensor Adjustment
4. Auto Bi-D Adjustment
5. Ink Mark Sensor Check
6. First Dot Position
7. PW Sensor Adjustment
8. PF Deterioration Compensation Cou n ter Reset
9. PF Adjustment
10. PF Adjustment (Bottom Margin)
11. CR Motor Drive Dispersion
Refer to "CHAPTER 5 ADJUSTMENT" for details of the
adjustments.
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 81
Page 81

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4.2.2 Stacker Assy.
1. Remove the Printer Mechanism. (Refer to 4.2.1.3 Lower Housing/Printer
Mechanism (p.80))
2. Remove the Torsion Spring 105.84 from the Stacker Assy. Shaft with a
pair of long-nose pliers.
Torsion Spring 105.84
Figure 4-13. Removing the Torsion Spring 105.84
3. Disengage the Paper EJ Lock Lever from the Paper EJ Release Lever,
and remove the Paper EJ Lock Lever from the Stacker Assy. Shaft.
4. Remove the two screws 2) C.B.S 3x6 that secure the Stacker Shaft
Brackets (Left/Right).
5. Slide the Stacker Shaft Bracket (Left) upward to disengage the Hook and
Dowel.
6. Remove the Stacker Assy. to the front together with the Stacker Shaft
Brackets (Left/Right).
Dowel
Hook
2) C.B.S 3x6
(6±1 kgf.cm)
Paper EJ Lock Lever
Paper EJ Release Lever
Stacker Assy. Shaft
Stacker Shaft Bracket (Left)
Figure 4-15. Removing the Stacker Shaft Brackets (Left/Right)
Stacker Shaft Bracket (Right)
Figure 4-14. Removing the Paper EJ Lock Lever
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 82
Page 82

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
7. Remove the Stacker Shaft Brackets (Left/Right) from the Stacker Assy.
Shaft, and remove the Stacker Assy.
Stacker Assy. Shaft
Put the lever of the PG Release Sensor under the shaft
on the right of the Stacker Assy. (Refer to Figure 4-16)
Set the engagement positions of the Gears at both ends
of the Stacker Assy. to the same height.
Figure 4-17. Gear Engagement Positions
Engage the Shaft Support of the Paper EJ Release Link
with the Shaft of the Paper EJ Transmission Lock Lever.
Paper EJ Transmission Lock Lever
Paper EJ Release Link
Stacker Assy. Shaft
Figure 4-16. Removing the Stacker Assy.
Shaft Support
Figure 4-18. Installing the Stacker Shaft Bracket (Right).
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 83
Page 83

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
8. Disconnect the Connector from the PG Release Sensor, and remove the
Stacker Shaft Bracket (Left).
Connector
Figure 4-19. Removing the Stacker Shaft Bracket (Left).
4.2.3 Waste Ink Pads
1. Remove the Lower Housing. (Refer to 4.2.1.3 Lower Housing/Printer
Mechanism (p.80))
2. Remove the 11 Waste Ink Pads from the Lower Housing.
Waste Ink Pad
Figure 4-20. Removing the Waste In k Pads
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 84
Page 84

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Refer to Figure 4-21, and install the Waste Ink Pads
correctly.
4
3
Installation Order
2
1
4
3
Installation Order
2
1
Confirm that the Waste Ink Tubes are installed in the
correct top and bottom positions.
0 digit side : Bottom side
80 digit side : Top side
Match the markings at the tip of the Waste Ink Tubes with
the locators of the Lower Housing.
Waste Ink Tubes
7mm
80 Digit Side 0 Digit Side
Figure 4-22. Positions of Waste Ink Tubes
Refer to Figure 4-23, and make certain that the Protective
Sheet is applied in the correct position.
Protective Sheet
Figure 4-21. Installing the Waste Ink Pads
Figure 4-23. Position of Protective Sheet
A D J U S T M E N T
R E Q U I R E D
After replacing or removing the Waste Ink Pads, always
make the following adjustment.
Waste Ink Counter Reset
Refer to "CHAPTER 5 ADJUSTMENT" for details of the
adjustment.
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 85
Page 85

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4.2.4 ASF Assy.
1. Remove the Upper Housing. (p.78)
2. Remove the one screw 4) C.B.S 3x8 that secures the Earth Cables, and
remove the Earth Cables.
3. Disconnect the ASF Motor Connector from the Relay Connector.
4. Release the two Relay Connector Cables from the clamp of the ASF.
5. Peel off one Acetate Tape to release the ASF Motor Connector Cable.
4) C.B.S 3x8
(6±1 kgf.cm)
Earth Cables
Relay Connector Cables
Relay Connector
Clamp
Recess
Ferrite Core
A lw ay s sc rew th e tw o Eart h Ca bl es to ge th e r .
Place the Ferrite Core of the Relay Connector Cable in
the recess on the left side of the ASF Assy. as viewed
from the printer rear.
After placing the Ferrite Core of the Relay Connector
Cable in the recess of the Ink System Unit, secure it with
the Acetate Tape.
6. Disconnect all Connectors and FFCs from the Relay Board.
7. Disconnect the APG Motor Connector from the Relay Connector.
8. Release the Relay Connector Cable and PF Motor Connector Cable.
Relay Board
Relay Connector Cable
Relay Connector
Ferrite Core
ASF Motor Connector Cable
PF Motor Connector Cable
Figure 4-25. Releasing the Cables (2)
Refer to Figure 4-25, and route the Relay Connector Cable
Recess
Acetate Tape
and PF Motor Connector Cable correctly.
Figure 4-24. Releasing the Cables (1)
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 86
Page 86

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
9. Release the ASF Sensor Connector Cable from the three Hooks of the
Main Frame and the right side of the ASF Assy. as viewed from the printer
rear.
Hooks
Connector Cable
Figure 4-26. Releasing the Cables (3)
Refer to Figure 4-26, and route the ASF Sensor
Connector Cable correctly.
When the ASF Assy. is removed, the ASF Sensor
Connector Cable may have come off from the right side
of the ASF Assy. If it has come off, refer to Figure 4-27
and route it correctly.
Connector Cable
Figure 4-27. Routing the Cable
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 87
Page 87

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
10. Remove the one screw 2) C.B.S 3x6 that secure the LD Roller Guide.
11. Slide the LD Roller Guide to the right to disengage the two Dowels, and
while simultaneously moving away the Connector Cables, remove the LD
Roller Guide from the Printer Mechanism.
Front
LD Roller Guide
Dowels
2) C.B.S 3x6
(8±1 kgf.cm)
Figure 4-28. Removing the LD Roller Guide
12. Remove the two screws 7) C.B.S (P4) 3x8 and one screw 8) CR Mount
Shaft that secure the ASF Assy., and remove the ASF Assy. from the
Printer Mechanism.
8) CR Mount Shaft
(8±1 kgf.cm)
7) C.B.S (P4) 3x8
(8±1 kgf.cm)
ASF Assy.
ASF Assy.
Figure 4-29. Removing the ASF Assy.
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 88
Page 88

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Engage the one Dowel and four Hooks of the ASF Assy. with
the locators of the Main Frame to eliminate a clearance
between the ASF Assy. and Main Frame.
Hook
Hook
Dowel
Hook
A D J U S T M E N T
R E Q U I R E D
After replacing or removing the ASF Assy., always make the
following adjustment.
First Dot Position
Refer to "CHAPTER 5 ADJUSTMENT" for details of the
adjustments.
Hook
Figure 4-30. Installing the ASF Assy.
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 89
Page 89

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4.2.5 Removing the Boards
4.2.5.1 Main Board
1. Remove the Printer Mechanism. (Refer to 4.2.1.3 Lower Housing/Printer
Mechanism (p.80))
2. Peel the Acetate Tape from the Board Assy.
C A U T I O N
Once peeled, never stick the Acetate Tape again.
Acetate Tape
3. Remove the two screws 2) C.B.S 3x6 that secure the Board Assy.
2) C.B.S 3x6
(6±1 kgf.cm)
Screwed Frame
Screwed Frame
Board Assy.
Figure 4-32. Screws That Secure the Board Assy.
C A U T I O N
In the following step, be careful not to scratch the FFCs and
Connector Cables with the Screwed Frame.
4. Disconnect the FFCs and Connectors conne cte d to the Bo ar d Assy . in
order of front to rear, and avoiding the interference with the Mechanism
Frame and Power Cord, pull out the Board Assy. from the printer.
Figure 4-31. Peeling th e Ac et at e Ta p e
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 90
Page 90

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Point of Interference
Figure 4-33. Removing the Board Assy.
FFCs and Connectors
Paying attention to the burrs of the Shield Plate, insert
the FFCs and Connectors into the Main Board.
The Board Assy. should not ride on the PS Grounding
Plates (3 pcs.).
PS Grounding Plates
Figure 4-34. Installing the Board Assy.
5. In order of the numbers shown in Figure 4-35, unlock the Lock-type
Connector of the Main Board and disconnect the Connector Cable of the
PS Board.
Connector Cable
2
1
Lock-type Connector
Blue Line
1
1 Pin Side
Figure 4-35. Disconnecting the PS Board Connector Cable
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 91
Page 91

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Put the Blue Line on the 1 pin side, and connect the pins
one after another correctly into the corresponding ports
of the Lock-type Connector. (Refer to Figure 4-35)
After inserting the Connector Cable, securely lock the
Connector Lock Mechanism. (Refer to Figure 4-35)
6. Remove the four screws 2) C.B.S 3x6 and one screw 9) C.P 3x4 that
secure the Main Board.
9) C.P 3x4
(6±1 kgf.cm)
2) C.B.S 3x6
(6±1 kgf.cm)
2) C.B.S 3x6
(6±1 kgf.cm)
7. Remove the one screw 2) C.B.S 3x6 that secures the Grounding Plate,
and remove the Grounding Plate.
8. Remove the Main Board from the Board Assy.
2) C.B.S 3x6
(6±1 kgf.cm)
Grounding Plate
Figure 4-37. Removing the Main Board
Main Board
Figure 4-36. Screws That Secure the Main Board
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 92
Page 92

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
A D J U S T M E N T
R E Q U I R E D
After replacing the Main Board, always make the following
adjustments.
When data can be read from the old board.
1. Main Board Data Read/Write Function
When data cannot be read from the old board.
1. Main Board Data Read/Write Function
2. Initial Value Write
3. USB ID Input
4. IEEE-1394 ID Input
5. Head ID Input
6. Head Angular Adjustment
7. Ink Mark Sensor Adjustment
8. Auto Bi-D Adjustment
9. Ink Mark Sensor Check
10. First Dot Position
11. PW Sensor Adjustment
12. PF Deterioration Compensation Counter Reset
(Maximum value write)
13. PF Adjustment
14. PF Adjustment (Bottom Margin)
15. CR Motor Drive Dispersion
Refer to "CHAPTER 5 ADJUSTMENT" for details of the
adjustments.
4.2.5.2 PS Board
1. Remove the Board Assy. (Refer to 4.2.5.1 Main Board, Step 4 (p.90))
2. Remove the four screws 2) C.B.S 3x6 that secure the PS Board.
2) C.B.S 3x6
(6±1 kgf.cm)
PS Board
Figure 4-38. Screws That Secure the PS Board
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 93
Page 93

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
3. Disconnect the PS Board Connector. (Refer to 4.2.5.1 Main Board, Step 5
(p.91))
4. Remove the Power Cable from the notch of the Boar d F rame, an d r emo ve
the PS Board.
Notch
Power Cable
Figure 4-39. Removing the PS Board
A D J U S T M E N T
R E Q U I R E D
After replacing the PS Board, always make the following
adjustment.
CR Motor Drive Dispersion
Refer to "CHAPTER 5 ADJUSTMENT" for details of the
adjustment.
4.2.5.3 Panel Board
1. Remove the Upper Housing. (p.78)
2. Remove the two screws 6) C.B.P 3x8 that secure the Upper Housing
Support, and remove the Upper Housing Support from the Upper Housing.
Upper Housing Support
Figure 4-40. Removing the Upper Housing Support
3. Disconnect the Panel FFC and Cover Open Sensor Connector from the
Panel Board.
6) C.B.P 3x8
(6±1 kgf.cm)
Panel FFC
Cover Open Sensor Connector
Figure 4-41. Disconnecting the Panel FFC and Connector
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 94
Page 94

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4. Remove the two screws 2) C.B.S 3x6 that secure the Panel Assy., and
remove the Panel Assy. from the Upper Housing.
2) C.B.S 3x6
(6±1 kgf.cm)
5. Remove the two screws 6) C.B.P 3x8 and two screws 3) C.B.P 3x6 that
secure the Panel Board, and remove the Panel Board.
3) C.B.P 3x6
(6±1 kgf.cm)
Panel Board
6) C.B.P 3x8
(6±1 kgf.cm)
Figure 4-43. Removing the Panel Board
Panel Assy.
Figure 4-42. Removing the Panel Assy.
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 95
Page 95

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4.2.6 Disassembling the Printer Mechanism
4.2.6.1 Releasing the Carriage Lock
Two methods of releasing the Carriage Lock will be explained below.
RELEASING THE CARRIAGE LOCK 1
1. Remove the Printer Mechanism. (Refer to 4.2.1.3 Lower Housing/Printer
Mechanism (p.80))
2. Insert a Standard Screwdriver into the hole on the right side of the Frame,
and turn the white Shaft of the Ink System Unit 1.5 turns to release the
Carriage Lock.
RELEASING THE CARRIAGE LOCK 2
1. Power ON the printer.
2. Push the Ink SW. When the Carriage Unit has moved to the left,
disconnect the Power Cable from the receptacle.
C A U T I O N
Always disconnect the Power Cable before adjustments
made by the Adjustment Program.
White Shaft
Figure 4-44. Releasing th e Ca rri ag e Lo ck
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 96
Page 96

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4.2.6.2 Print Head
1. Remove the Upper Housing. (p.78)
2. Release the Carriage Lock, and move the Carr iage Unit to the center of the
printer. (Refer to 4.2.6.1 Releasing the Carriage Lock (p.96))
3. Open the Ink Cartridge Cover.
4. Disengage the three Hooks that secure the FFC Guide, and remove the
FFC Guide from the Carriage Unit.
FFC Guide
Hooks
Figure 4-45. Removing the FFC Guide
5. Remove the three screws 10) C.B.P 2.6x8 that secure th e Pr int Head , a nd
vertically lift and remove the Print Head.
Print Head
10) C.B.P 2.6x8
(3±0.5 kgf.cm)
Figure 4-46. Removing the Print Head
6. Disconnect the two FFCs from the Print Head.
FFCs
Figure 4-47. Disconnecting the FFCs
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 97
Page 97

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
Make sure that the Absorber is applied in the position
shown in Figure 4-48.
Absorber
Figure 4-48. Applying the Abso rb er
Install the Print Head after matching the Dowels of the
Carriage Unit with the Positioning Holes of the Print
Head.
Dowels
Positioning Holes
A D J U S T M E N T
R E Q U I R E D
Hold down the Print Head in the direction of arrow and
tighten the screws.
Figure 4-50. Installing the Print Head (2)
After replacing or removing the Print Head, always make the
following adjustments.
1. PG Adjustment
2. Head ID Input (for replacement only)
3. Head Angular Adjustment
4. Ink Mark Sensor Adjustment
5. Auto Bi-D Adjustment
6. First Dot Position
7. PW Sensor Adjustment
Refer to "CHAPTER 5 ADJUSTMENT" for details of the
adjustments.
Figure 4-49. Installing the Print Head (1)
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 98
Page 98

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4.2.6.3 CR Scale
1. Remove the Upper Housing. (p.78)
2. Release the Carriage Lock, and remove the Carriage Unit to the center of
the printer. (Refer to 4.2.6.1 Releasing the Carriage Lock (p.96))
C A U T I O N
3. Pull the right end of the CR Scale in the direction of arrow, and disengage
it from the Hook of the CR Shaft Mounting Plate (Right).
4. Pull the right end of the CR Scale to the left out of the rear side of the
Carriage Unit.
Step 4
In the following steps, be careful not to break both ends of
the CR Scale.
CR Shaft Mounting Plate (Right)
Step 3
5. With tweezers, disengage the coil part of the Torsion Spring 24.7 from the
Hook of the CR Shaft Mounting Plate (Left).
Hook
CR Shaft Mounting
Plate (Left)
Torsion Spring 24.7
Figure 4-52. Removing the Torsion Spring 24.7 (1)
6. Remove the Torsion Spring 24.7 from the CR Scale in the following
procedure.
6-1. Raise the coil part.
6-2. Push it down, and disengage the Foot 1 from the notch of the CR
Shaft Mounting Plate (Left).
6-3. Turn it counterclockwise.
6-4. Remove the Torsion Spring 24.7 from the hole of the CR Scale.
CR Scale
Hook
Step 6-3
Step 6-1
Foot 1
Figure 4-51. Pulling the CR Scale Out
Notch
Step 6-2
Figure 4-53. Removing the Torsion Spring 24.7 (2)
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 99
Page 99

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
7. Turn the CR Scale 90 degrees, and remove the CR Scale fr om the Hook of
the CR Shaft Mounting Plate (Left).
Hook
Figure 4-54. Removing the CR Scale
Pass the CR Scale into the slit of the CR Encoder Sensor.
CR Encoder
Sensor
CR Scale
Figure 4-55. Installing the CR Scale (1)
Install the left end of the CR Scale with the beveled
portion up.
Beveled Portion
CR Scale
Figure 4-56. Installing the CR Scale (2)
Install the right end of the CR Scale securely so that it is
not engaged with the hooked portion of the CR Shaft
Mounting Plate (Right).
CR Scale
OK
NG
Hooked Portion
Figure 4-57. Installing the CR Scale (3)
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 100
Page 100

EPSON Stylus Photo R800 Revision A
4.2.6.4 APG Assy.
1. Remove the Upper Housing. (p.78)
2. Disconnect the APG Motor Connector from the Relay Connector.
3. Disconnect the Connectors from the two APG Sensors.
Relay Connector
Connectors
APG Assy.
Figure 4-58. Disconnecting the connectors
4. Remove the three screws 2) C.B.S 3x6 that secure the APG Assy.
5. Peel off the Acetate Tape, and remove the APG Assy. from the Main
Frame.
2) C.B.S 3x6
(8±1 kgf.cm)
1
Ferrite Core
2
3
Acetate Tape
Figure 4-59. Removing the APG Assy.
DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY Disassembly 101
 Loading...
Loading...