D-link DSR-500, DSR-1000N, DSR-250N, DSR-150N, DSR-250 User Manual
...
Building Networks for People
Unified Services Router
User Manual
DSR-150 / 150N / 250 / 250N / 500 / 500N /
1000 / 1000N
Ver. 1.05
Small Business Gateway Solution

User Manual
Unified Services Router
D-Link Corporation
Copyright © 2012.
http://www.dlink.com

Unified Services Router User Manual
User Manual
DSR-150 / 150N /250 / 250N / DSR-500 / 500N / 1000 / 1000N
Unified Services Router
Version 1.05
Copyright © 2012
Copyright Notice
This publication, including all photographs , illus trations and software, is protected under
international copyright laws, with all rights reserved. Neither this manual, nor any of the
material contained herein, may be reproduced without written cons ent of the author.
Disclaimer
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The manufacturer makes
no representations or warranties with respect to the contents hereof and specifically disclaim
any implied warranties of merchantability or fitnes s for any particular purpose. The
manufacturer reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to
time in the content hereof without obligation of the manufacturer to notify any pers on of s uch
revision or changes .
Limitations of Liability
UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES SHALL D-LINK OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR
DAMAGES OF ANY CHARACTER (E.G. DA MAGES FOR LOSS OF PROFIT, SOFTWARE
RESTORATION, WORK STOPPAGE, LOSS OF SAVED DATA OR ANY OTHER
COMMERCIAL DAMAGES OR LOSSES) RESULTING FROM THE A PPLICATION OR
IMPROPER USE OF THE D-LINK PRODUCT OR FAILURE OF THE PRODUCT, EVEN IF
D-LINK IS INFORMED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DA MAGES. FURTHERMORE, DLINK WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR THIRD-PA RTY CLAIMS AGAINST CUSTOMER FOR
LOSSES OR DAMAGES. D-LINK W ILL IN NO EVENT BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMA GES
IN EXCESS OF THE AMOUNT D-LINK RECEIVED FROM THE END-USER FOR THE
PRODUCT.
1

Unified Services Router User Manual
Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Introduction.......................................................................................................................................... 11
1.1 About this User Manual .................................................................................................... 12
1.2 Typographical Conventions............................................................................................. 12
Chapter 2. Configuring Your Network: LAN Setup ...................................................................................... 13
2.1 LAN Configuration .............................................................................................................. 13
2.1.1 LAN DHCP Reserved IPs ................................................................................................ 16
2.1.2 LAN DHCP Leased Clients.............................................................................................. 17
2.1.3 LAN Configuration in an IPv6 Network........................................................................ 18
2.1.4 Configuring IPv6 Router Advertisements ................................................................... 21
2.2 VLAN Configuration ........................................................................................................... 23
2.2.1 Associating VLANs to ports............................................................................................. 24
2.2.2 Multiple VLAN Subnets ..................................................................................................... 26
2.2.3 VLAN configuration ............................................................................................................ 27
2.3 Configurable Port: DMZ Setup ....................................................................................... 28
2.4 Universal Plug and Play (UPnP).................................................................................... 29
2.5 Captive Portal....................................................................................................................... 31
2.6 Captive portal setup ........................................................................................................... 32
Chapter 3. Connecting to the Internet: WAN Setup .................................................................................... 35
3.1 Internet Setup Wizard........................................................................................................ 35
3.2 WAN Configuration............................................................................................................. 36
3.2.1 WAN Port IP address ........................................................................................................ 37
3.2.2 WAN DNS Servers ............................................................................................................. 37
3.2.3 DHCP WAN .......................................................................................................................... 37
3.2.4 PPPoE .................................................................................................................................... 38
3.2.5 Russia L2TP and PPTP WAN ........................................................................................ 41
3.2.6 Russia Dual Access PPPoE............................................................................................ 42
3.2.7 WAN Configuration in an IPv6 Network ...................................................................... 43
3.2.8 Checking WAN Status....................................................................................................... 45
3.3 Bandwidth Controls ............................................................................................................ 47
3.4 Features with Multiple WAN Links ................................................................................ 49
3.4.1 Auto Failover ........................................................................................................................ 49
3.4.2 Load Balancing .................................................................................................................... 50
3.4.3 Protocol Bindings ................................................................................................................ 52
3.5 Routing Configuration........................................................................................................ 53
3.5.1 Routing Mode ....................................................................................................................... 53
3.5.2 Dynamic Routing (RIP) ..................................................................................................... 56
3.5.3 Static Routing ....................................................................................................................... 57
3.5.4 OSPFv2 .................................................................................................................................. 58
3.5.5 OSPFv3 .................................................................................................................................. 60
3.5.6 6to4 Tunneling ..................................................................................................................... 62
3.5.7 ISATAP Tunnels.................................................................................................................. 63
3.6 Configurable Port - WAN Option ................................................................................... 64
3.7 WAN 3 (3G) Configuration............................................................................................... 64
3.8 WAN Port Settings.............................................................................................................. 66
2

Unified Services Router User Manual
Chapter 4. Wireless Access Point Setup ........................................................................................................ 68
4.1 Wireless Settings Wizard ................................................................................................. 68
4.1.1 Wireless Network Setup Wizard .................................................................................... 69
4.1.2 Add Wireless Device with WPS ..................................................................................... 69
4.1.3 Manual Wireless Network Setup ................................................................................... 70
4.2 Wireless Profiles.................................................................................................................. 70
4.2.1 WEP Security ....................................................................................................................... 71
4.2.2 WPA or WPA2 with PSK .................................................................................................. 73
4.2.3 RADIUS Authentication .................................................................................................... 73
4.3 Creating and Using Access Points ............................................................................... 75
4.3.1 Primary benefits of Virtual APs: ..................................................................................... 77
4.4 Tuning Radio Specific Settings ...................................................................................... 78
4.5 WMM ....................................................................................................................................... 79
4.6 Wireless distribution system (WDS) ............................................................................. 80
4.7 Advanced Wireless Settings ........................................................................................... 81
4.8 Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) ......................................................................................... 82
Chapter 5. Securing the Private Network ....................................................................................................... 85
5.1 Firewall Rules....................................................................................................................... 85
5.2 Defining Rule Schedules .................................................................................................. 86
5.3 Configuring Firewall Rules............................................................................................... 87
5.4 Configuring IPv6 Firewall Rules..................................................................................... 92
5.4.1 Firewall Rule Configuration Examples......................................................................... 93
5.5 Security on Custom Services.......................................................................................... 97
5.6 ALG support.......................................................................................................................... 99
5.7 VPN Passthrough for Firewall ...................................................................................... 100
5.8 Application Rules .............................................................................................................. 101
5.9 Web Content Filtering...................................................................................................... 102
5.9.1 Content Filtering ................................................................................................................ 102
5.9.2 Approved URLs ................................................................................................................. 103
5.9.3 Blocked Keywords ............................................................................................................ 104
5.9.4 Export Web Filter .............................................................................................................. 105
5.10 IP/MAC Binding ................................................................................................................. 106
5.11 Intrusion Prevention (IPS).............................................................................................. 107
5.12 Protecting from Internet Attacks .................................................................................. 108
Chapter 6. IPsec / PPTP / L2TP VPN ............................................................................................................ 111
6.1 VPN Wizard ........................................................................................................................ 113
6.2 Configuring IPsec Policies ............................................................................................. 115
6.2.1 Extended Authentication (XAUTH) ............................................................................. 119
6.2.2 Internet over IPSec tunnel ............................................................................................. 120
6.3 Configuring VPN clients.................................................................................................. 120
6.4 PPTP / L2TP Tunnels...................................................................................................... 120
6.4.1 PPTP Tunnel Support ..................................................................................................... 120
6.4.2 L2TP Tunnel Support ...................................................................................................... 122
6.4.3 OpenVPN Support ............................................................................................................ 123
6.4.4 OpenVPN Remote Network .......................................................................................... 125
6.4.5 OpenVPN Authentication ............................................................................................... 126
3

Unified Services Router User Manual
Chapter 7. SSL VPN ............................................................................................................................................ 129
7.1 Groups and Users............................................................................................................. 131
7.1.1 Users and Passwords ..................................................................................................... 137
7.2 Using SSL VPN Policies................................................................................................. 138
7.2.1 Using Network Resources ............................................................................................. 141
7.3 Application Port Forwarding .......................................................................................... 142
7.4 SSL VPN Client Configuration...................................................................................... 144
7.5 User Portal .......................................................................................................................... 147
7.5.1 Creating Portal Layouts .................................................................................................. 147
Chapter 8. Advanced Configuration Tools ................................................................................................... 150
8.1 USB Device Setup ............................................................................................................ 150
8.2 USB share port .................................................................................................................. 151
8.3 SMS service........................................................................................................................ 153
8.4 Authentication Certificates ............................................................................................. 154
8.5 Advanced Switch Configuration ................................................................................... 156
Chapter 9. Administration & Management ................................................................................................... 157
9.1 Configuration Access Control ....................................................................................... 157
9.1.1 Admin Settings................................................................................................................... 157
9.1.2 Remote Management ...................................................................................................... 158
9.1.3 CLI Access .......................................................................................................................... 159
9.2 SNMP Configuration ........................................................................................................ 159
9.3 Configuring Time Zone and NTP................................................................................. 161
9.4 Log Configuration.............................................................................................................. 162
9.4.1 Defining What to Log ....................................................................................................... 162
9.4.2 Sending Logs to E-mail or Syslog ............................................................................... 167
9.4.3 Event Log Viewer in GUI ................................................................................................ 169
9.5 Backing up and Restoring Configuration Settings................................................. 170
9.6 Upgrading Router Firmware.......................................................................................... 171
9.7 Upgrading Router Firmware via USB......................................................................... 172
9.8 Dynamic DNS Setup ........................................................................................................ 173
9.9 Using Diagnostic Tools ................................................................................................... 174
9.9.1 Ping........................................................................................................................................ 175
9.9.2 Trace Route ........................................................................................................................ 175
9.9.3 DNS Lookup ....................................................................................................................... 176
9.9.4 Router Options................................................................................................................... 176
9.10 Localization ......................................................................................................................... 177
Chapter 10. Router Status and Statistics ........................................................................................................ 178
10.1 System Overview .............................................................................................................. 178
10.1.1 Device Status ..................................................................................................................... 178
10.1.2 Resource Utilization ......................................................................................................... 180
10.2 Traffic Statistics ................................................................................................................. 183
10.2.1 Wired Port Statistics......................................................................................................... 183
10.2.2 Wireless Statistics............................................................................................................. 184
10.3 Active Connections........................................................................................................... 185
10.3.1 Sessions through the Router ........................................................................................ 185
4

Unified Services Router User Manual
10.3.2 Wireless Clients................................................................................................................. 187
10.3.3 LAN Clients ......................................................................................................................... 187
10.3.4 Active VPN Tunnels ......................................................................................................... 188
Chapter 11. Trouble Shooting ............................................................................................................................. 190
11.1 Internet connection ........................................................................................................... 190
11.2 Date and time ..................................................................................................................... 192
11.3 Pinging to Test LAN Connectivity................................................................................ 192
11.3.1 Testing the LAN path from your PC to your router................................................ 192
11.3.2 Testing the LAN path from your PC to a remote device...................................... 193
11.4 Restoring factory-default configuration settings ..................................................... 194
Chapter 12. Credits ................................................................................................................................................. 195
Appendix A. Glossary ............................................................................................................................................. 196
Appendix B. Factory Default Settings................................................................................................................ 199
Appendix C. Standard Services Available for Port Forwarding & Firewall Configuration................ 200
Appendix D. Log Output Reference ................................................................................................................... 201
Appendix E. RJ-45 Pin-outs.................................................................................................................................. 255
Appendix F. Product Statement .......................................................................................................................... 256
5

Unified Services Router User Manual
List of Figures
Figure 1: Setup page for LAN TCP/IP settings................................................................................................. 15
Figure 2: LAN DHCP Reserved IPs ..................................................................................................................... 17
Figure 3: LAN DHCP Leased Clients................................................................................................................... 18
Figure 4: IPv6 LAN and DHCPv6 configuration ............................................................................................... 19
Figure 5: Configuring the Router Advertisement Daemon ........................................................................... 22
Figure 6: IPv6 Advertisement Prefix settings .................................................................................................... 23
Figure 7: Adding VLAN memberships to the LAN ........................................................................................... 24
Figure 8: Port VLAN list ............................................................................................................................................ 25
Figure 9: Configuring VLAN membership for a port........................................................................................ 26
Figure 10: Multiple VLAN Subnets........................................................................................................................ 27
Figure 11: VLAN Configuration .............................................................................................................................. 28
Figure 12: DMZ configuration ................................................................................................................................. 29
Figure 13: UPnP Configuration .............................................................................................................................. 30
Figure 14: Active Runtime sessions ..................................................................................................................... 32
Figure 15: Captive Portal Setup............................................................................................................................. 33
Figure 16: Customized Captive Portal Setup .................................................................................................... 34
Figure 17: Internet Connection Setup Wizard................................................................................................... 35
Figure 18: Manual WAN configuration................................................................................................................. 38
Figure 19: PPPoE configuration for standard ISPs ......................................................................................... 39
Figure 20: WAN configuration for Japanese Multiple PPPoE (part 1)...................................................... 40
Figure 21: WAN configuration for Multiple PPPoE (part 2) .......................................................................... 41
Figure 22: Russia L2TP ISP configuration ......................................................................................................... 42
Figure 23: Russia Dual access PPPoE configuration .................................................................................... 43
Figure 24: IPv6 WAN Setup page ......................................................................................................................... 44
Figure 25: Connection Status information for both WAN ports................................................................... 46
Figure 26: List of Configured Bandwidth Profiles ............................................................................................ 47
Figure 27: Bandwidth Profile Configuration page ............................................................................................ 48
Figure 28: Traffic Selector Configuration............................................................................................................ 49
Figure 29: Load Balancing is available when multiple WAN ports are configured and Protocol
Bindings have been defined ............................................................................................................... 52
Figure 30: Protocol binding setup to associate a service and/or LAN source to a WAN and/or
destination network................................................................................................................................ 53
Figure 31: Routing Mode is used to configure traffic routing between WAN and LAN, as well as
Dynamic routing (RIP) .......................................................................................................................... 55
Figure 32: Static route configuration fields......................................................................................................... 58
6

Unified Services Router User Manual
Figure 33: OSPFv2 configured parameters ....................................................................................................... 59
Figure 34: OSPFv2 configuration .......................................................................................................................... 60
Figure 35: OSPFv3 configured parameters ....................................................................................................... 61
Figure 36: OSPFv3 configuration .......................................................................................................................... 62
Figure 37: 6 to 4 tunneling ....................................................................................................................................... 63
Figure 38: ISATAP Tunnels Configuration ......................................................................................................... 64
Figure 39: WAN3 configuration for 3G internet ................................................................................................ 66
Figure 40: Physical WAN port settings................................................................................................................ 67
Figure 41: Wireless Network Setup Wizards..................................................................................................... 69
Figure 42: List of Available Profiles shows the options available to secure the wireless link .......... 71
Figure 43: Profile configuration to set network security................................................................................. 73
Figure 44: RADIUS server (External Authentication) configuration .......................................................... 75
Figure 45: Virtual AP configuration ....................................................................................................................... 76
Figure 46: List of configured access points (Virtual APs) shows one enabled access point on the
radio, broadcasting its SSID ............................................................................................................... 77
Figure 47: Radio card configuration options...................................................................................................... 78
Figure 48: Wi-Fi Multimedia .................................................................................................................................... 79
Figure 49: Wireless Distribution System............................................................................................................. 80
Figure 50: Advanced Wireless communication settings................................................................................ 82
Figure 51: WPS configuration for an AP with WPA/WPA2 profile ............................................................. 83
Figure 52: List of Available Firewall Rules ......................................................................................................... 86
Figure 53: List of Available Schedules to bind to a firewall rule ................................................................. 87
Figure 54: Example where an outbound SNAT rule is used to map an external IP address
(209.156.200.225) to a private DMZ IP address (10.30.30.30) ............................................. 90
Figure 55: The firewall rule configuration page allows you to define the To/From zone, service,
action, schedules, and specify source/destination IP addresses as needed. ................... 91
Figure 56: The IPv6 firewall rule configuration page allows you to define the To/From zone,
service, action, schedules, and specify source/destination IP addresses as needed. .. 92
Figure 57: List of Available IPv6 Firewall Rules ............................................................................................... 93
Figure 58: Schedule configuration for the above example........................................................................... 96
Figure 59: List of user defined services. ............................................................................................................. 98
Figure 60: Custom Services configuration ......................................................................................................... 98
Figure 61: Available ALG support on the router. ........................................................................................... 100
Figure 62: Passthrough options for VPN tunnels .......................................................................................... 101
Figure 63: List of Available Application Rules showing 4 unique rules .................................................. 102
Figure 64: Content Filtering used to block access to proxy servers and prevent ActiveX controls
from being downloaded...................................................................................................................... 103
7

Unified Services Router User Manual
Figure 65: Two trusted domains added to the Approved URLs List ....................................................... 104
Figure 66: One keyword added to the block list ............................................................................................. 105
Figure 67: Export Approved URL list ................................................................................................................. 106
Figure 68: The following example binds a LAN host’s MAC Address to an IP address served by
DSR. If there is an IP/MAC Binding violation, the violating packet will be dropped and
logs will be captured............................................................................................................................ 107
Figure 69: Intrusion Prevention features on the router ................................................................................ 108
Figure 70: Protecting the router and LAN from internet attacks ............................................................... 109
Figure 71: Example of Gateway-to-Gateway IPsec VPN tunnel using two DSR routers connected
to the Internet......................................................................................................................................... 111
Figure 72: Example of three IPsec client connections to the internal network through the DSR
IPsec gateway ....................................................................................................................................... 112
Figure 73: VPN Wizard launch screen .............................................................................................................. 113
Figure 74: IPsec policy configuration ................................................................................................................. 116
Figure 75: IPsec policy configuration continued (Auto policy via IKE) ................................................... 117
Figure 76: IPsec policy configuration continued (Auto / Manual Phase 2) ........................................... 119
Figure 77: PPTP tunnel configuration – PPTP Client................................................................................... 121
Figure 78: PPTP VPN connection status.......................................................................................................... 121
Figure 79: PPTP tunnel configuration – PPTP Server ................................................................................. 122
Figure 80: L2TP tunnel configuration – L2TP Server................................................................................... 123
Figure 81: OpenVPN configuration..................................................................................................................... 125
Figure 82: OpenVPN Remote Network ............................................................................................................. 126
Figure 83: OpenVPN Authentication .................................................................................................................. 127
Figure 84: Example of clientless SSL VPN connections to the DSR...................................................... 130
Figure 85: List of groups......................................................................................................................................... 131
Figure 86: User group configuration................................................................................................................... 132
Figure 87: SSLVPN Settings................................................................................................................................. 133
Figure 88: Group login policies options............................................................................................................. 134
Figure 89: Browser policies options ................................................................................................................... 135
Figure 90: IP policies options................................................................................................................................ 136
Figure 91: Available Users with login status and associated Group ....................................................... 137
Figure 92: User configuration options................................................................................................................ 138
Figure 93: List of SSL VPN polices (Global filter).......................................................................................... 139
Figure 94: SSL VPN policy configuration ......................................................................................................... 140
Figure 95: List of configured resources, which are available to assign to SSL VPN policies ........ 142
Figure 96: List of Available Applications for SSL Port Forwarding .......................................................... 144
Figure 97: SSL VPN client adapter and access configuration .................................................................. 145
8

Unified Services Router User Manual
Figure 98: Configured client routes only apply in split tunnel mode........................................................ 146
Figure 99: List of configured SSL VPN portals. The configured portal can then be associated with
an authentication domain .................................................................................................................. 147
Figure 100: SSL VPN Portal configuration....................................................................................................... 149
Figure 101: USB Device Detection ..................................................................................................................... 151
Figure 102: USB SharePort................................................................................................................................... 152
Figure 103: SMS Service – Send SMS ............................................................................................................. 153
Figure 104: SMS Service – Receive SMS ....................................................................................................... 154
Figure 105: Certificate summary for IPsec and HTTPS management ................................................... 155
Figure 106: Advanced Switch Settings.............................................................................................................. 156
Figure 107: User Login policy configuration .................................................................................................... 157
Figure 108: Admin Settings ................................................................................................................................... 158
Figure 109: Remote Management from the WAN ......................................................................................... 159
Figure 110: SNMP Users, Traps, and Access Control ................................................................................ 160
Figure 111: SNMP system information for this router .................................................................................. 161
Figure 112: Date, Time, and NTP server setup ............................................................................................. 162
Figure 113: Facility settings for Logging ........................................................................................................... 164
Figure 114: Log configuration options for traffic through router................................................................ 166
Figure 115: IPv6 Log configuration options for traffic through router ..................................................... 167
Figure 116: E-mail configuration as a Remote Logging option................................................................. 168
Figure 117: Syslog server configuration for Remote Logging (continued)............................................ 169
Figure 118: VPN logs displayed in GUI event viewer .................................................................................. 170
Figure 119: Restoring configuration from a saved file will result in the current configuration being
overwritten and a reboot .................................................................................................................... 171
Figure 120: Firmware version information and upgrade option ................................................................ 172
Figure 121: Firmware upgrade and configuration restore/backup via USB.......................................... 173
Figure 122: Dynamic DNS configuration .......................................................................................................... 174
Figure 123: Router diagnostics tools available in the GUI ......................................................................... 175
Figure 124: Sample trace route output.............................................................................................................. 176
Figure 125: Localization ......................................................................................................................................... 177
Figure 126: Device Status display ...................................................................................................................... 179
Figure 127: Device Status display (continued) ............................................................................................... 180
Figure 128: Resource Utilization statistics ....................................................................................................... 181
Figure 129: Resource Utilization data (continued) ........................................................................................ 182
Figure 130: Resource Utilization data (continued) ........................................................................................ 183
Figure 131: Physical port statistics ..................................................................................................................... 184
9

Unified Services Router User Manual
Figure 132: AP specific statistics......................................................................................................................... 185
Figure 133: List of current Active Firewall Sessions..................................................................................... 186
Figure 134: List of connected 802.11 clients per AP.................................................................................... 187
Figure 135: List of LAN hosts ............................................................................................................................... 188
Figure 136: List of current Active VPN Sessions ........................................................................................... 189
10

Unified Services Router User Manual
Chapter 1. Introduction
D-Link Unified Services Routers offer a s ecure, high performance networking solution
to address the growing needs of small and medium bus iness es. Integrated high -s peed
IEEE 802.11n and 3G wireless technologies offer comparable performance to
traditional wired networks , but with fewer limitations. Optimal network security is
provided via features such as virtual private network (VPN) tunnels, IP Security
(IPs ec), Point-to -Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP), Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP),
and Secure So ckets Layer (SSL). Empower your road warriors with clientless remote
access anywhere and anytime using SSL VPN tunnels .
With the D-Link Unified Services Router you are able to experience a diverse set of
benefits:
Comprehensive Management Capabilities
The DSR-500, DSR-500N, DSR-1000 and DSR-1000N include dual-WAN
Gigabit Ethernet which provides policy -bas ed s ervice management ensuring
maximum productivity for your busines s operations. The failover feature
maintains data traffic without dis connecting when a landline connection is lost.
The Outbound Load Balancing feature adjusts outgoing traffic across two WAN
interfaces and optimizes the system performance resulting in high availability.
The second WAN port can be configured as a DMZ port allowing you to isolate
servers from your LAN.
DSR-150/150N/250 /250N have a single W AN interface, and thus it does not
support Auto Failover and Load Balancing s cenarios.
Superior Wireless Performance
Des igned to deliver s uperior wireless performance, the DSR-500N and DSR1000N include 802.11 a/b/g/n, allowing for operation on either the 2.4 GHz or
5 GHz radio bands . Multiple In Multiple Out (MIMO) technology allows the
DSR-500N and DSR-1000N t o pro v ide h igh d a t a ra t es wit h min imal “d e a d
s p o ts ” t h rou g h o u t t h e wire le s s c o v erage a rea.
DSR-150N, 250N and DSR-500N s upports the 2.4GHz radio band only.
Flexible Deployment Options
The DSR-1000 / 1000N supports Third Generation (3G) Networks via an
extendable USB 3G dongle. This 3G network capability offers an additional
secure data connection for networks that provide critical s ervices . The DSR 1000N can be configured to automatically switch to a 3G network whenever a
phys ical link is lost.
Robust VPN features
A fully featured virtual private network (VPN) provides your mobile workers
and branch offices with a s ecure link to your network. The DSR150/150N/250/ 250N, DSR-500/500N and DSR-1000 /1000N are capable of
simultaneously managing 5, 5, 10, 20 Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) VPN tunnels
res pectively, empowering your mobile users by providing remote access to a
11

Unified Services Router User Manual
central corporate databas e. Site -to-site VPN tunnels use IP Security (IPs ec)
Protocol, Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP), or Lay er 2 Tunneling
Protocol (L2TP) to facilitate branch office connectivity through encrypted
virtual links. The DSR-150/ 150N, DSR-250/250N, DSR-500/500N and DSR-
1000/1000N support 10, 25, 35 and 75 s imultaneous IPSec VPN tunnels
res pectively .
Efficient D-Link Green Technology
As a concerned member of the global community, D-Link is devoted to
providing eco-friendly products . D-Link Green WiFi and D-Link Green
Ethernet save power and prevent waste. The D-Link Green WLAN s cheduler
reduces wireles s power automatically during off-peak hours. Likewise the DLink Green Ethernet program adjusts power usage based on the detected cable
length and link s tatus. In addition, compliance with RoHS (Res triction of
Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment)
directives make D-Link Green certified devices the environmentally responsible
choice.
Support for the 3G wireles s WAN USB dongle is only available for DSR-1000 and
DSR-1000N.
1.1 About this User Manual
This document is a high level manual to allow new D-Link Unified Services Router
users to configure connectivity, setup VPN tunnels, es tablis h firewall rules and
perform general administrative tasks. Typical deployment and use cas e scenarios are
described in each section. For more detailed setup ins tructions and explanations of
each configuration parameter, refer to the online help that can be access ed from each
page in the router GUI.
1.2 Typographical Conventions
The following is a list of the various terms , followed by an example of how that term
is represented in this document:
Product Name – D-Link Unified Services Router.
o Model numbers DSR-500/ 500N/1000/1000N/250/250N/150/150N
GUI Menu Path/GUI Navigation – Monitoring > Router Status
Important note –
12

Chapter 2. Configuring Your Network:
LAN Setup
It is assumed that the user has a machine for management connected to the LAN to the
router. The LAN connection may be through the wired Ethernet ports available on the
router, or once the initial setup is complete, the DSR may also be managed through its
wireles s interface as it is bridged with the LAN. A cc e s s t h e ro u te r’s graphical us er
interface (GUI) for management by us ing any web browser, s uch as Microsoft Internet
Explorer or Mozilla Firefox:
Go to http://192.168.10.1 (defa u lt IP ad dres s ) to dis play the ro u t e r’s
management login s creen.
Default login credentials for the management GUI:
Username: admin
Pass word: admin
If t he rou t e r’s LAN IP ad d res s wa s chang ed, u s e th a t IP addres s in the navigation
bar of the brows er to access the router’s management UI.
2.1 LAN Configuration
Setup > Network Settings > LAN Configuration
By default, the router functions as a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
server to the hosts on the WLAN or LAN network. With DHCP, PCs and other LAN
devices can be assigned IP addresses as well as addresses for DNS servers, W indows
Internet Name Service (WINS) servers , and the default gateway. With the DHCP
server enabled t he ro ut er’s IP ad dr es s s erves as t h e gatewa y ad d res s for LAN and
WLAN clients . The PCs in the LAN are as signed IP addresses from a pool of
addresses specified in this procedure. Each pool address is tested before it is assigned
to avoid duplicate address es on the LAN.
For mos t ap plications the default DHCP and TCP/IP s ettings are satisfactory. If you
want another PC on your network to be the DHCP s erver or if you are manually
configuring the network settings of all of your PCs , set t h e DHCP mo d e t o ‘n o ne’ .
DHCP relay can be used to forward DHCP leas e information from another LAN
d ev ic e th a t is t h e ne t work’s DHCP serv e r; t h is is pa rt ic u larly us e fu l for wire les s
clients.
Ins tead of us ing a DNS s erver, you can us e a Windows Internet Naming Service
(W INS) server. A WINS server is the equivalent of a DNS server but us es the
NetBIOS protocol to resolve hostnames. The router includes the WINS server IP
address in the DHCP configuration when acknowledging a DHCP request from a
DHCP client.
You can also enable DNS proxy for the LAN. When this is enabled the router then as
a p roxy for all DNS re q u e s ts an d commun ic a t e s with t h e ISP’s DNS s e rv e rs . W he n
dis abled all DHCP clients receive the DNS IP address es of the ISP.
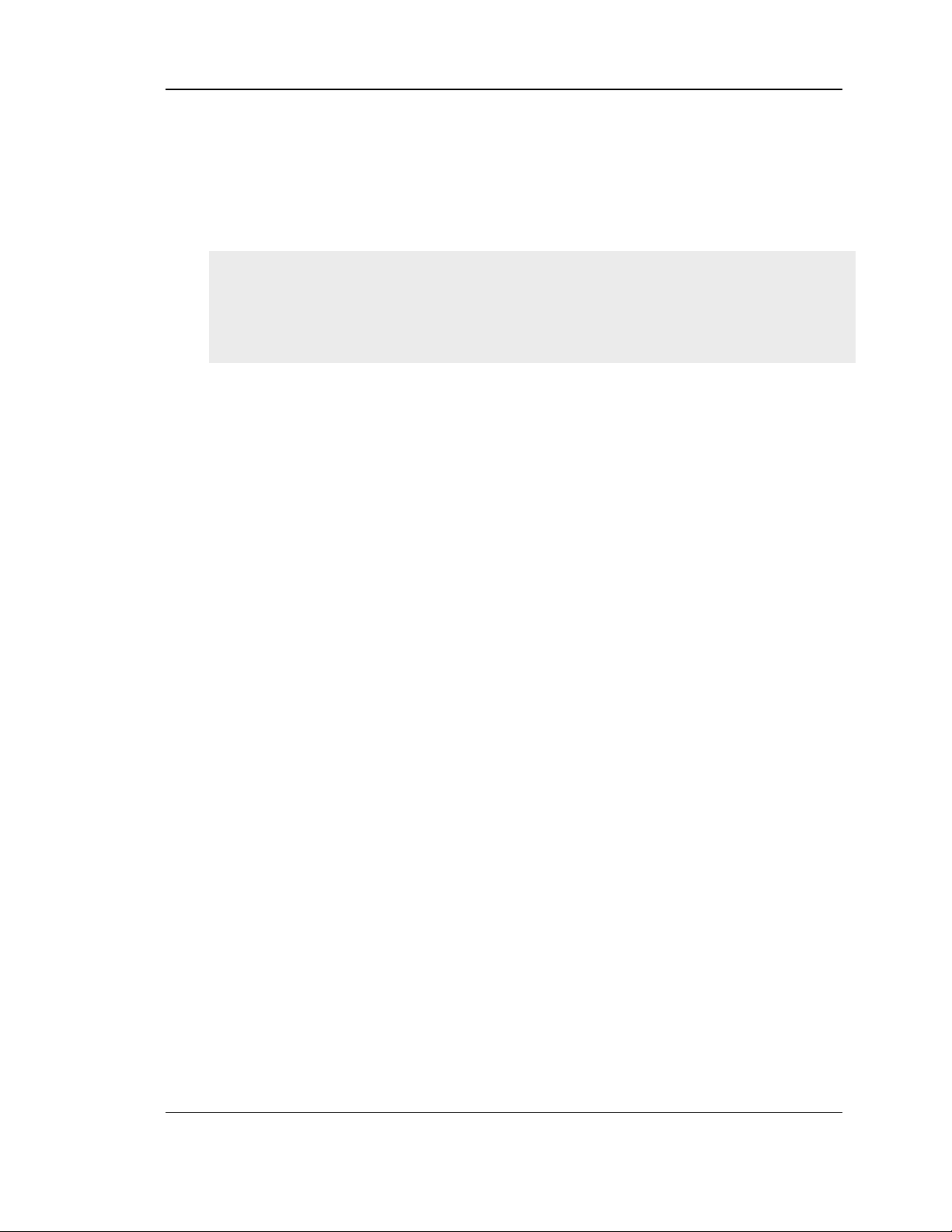
Unified Services Router User Manual
To configure LAN Connectivity, please follow the s teps below:
1. In the LAN Setup page, enter the following information for your router:
IP address (factory default: 192.168.10.1).
If you change the IP address and click Save Settings, the GUI will not res pond.
Open a new connection to the new IP addres s and log in again. Be s ure the LAN
host (the machine used to manage the router) has obtained IP address from newly
ass igned pool (o r has a static IP ad dres s in the ro u t e r’s LA N su b n e t ) before
accessing the router via changed IP addres s.
Subnet mask (factory default: 255.255.255.0).
2. In the DHCP section, select the DHCP mode:
No n e: t h e ro ut er’s DHCP s erv er is d is ab led fo r t h e LA N
DHCP Server. With this option the router assigns an IP address within the
specified range plus additional specified information to any LAN device
that reques ts DHCP s erved address es .
DHCP Relay: With this option enabled, DHCP clients on the LAN can
receive IP address leases and corres ponding information from a DHCP
server on a different subnet. Specify the Relay Gateway, and when LAN
clients make a DHCP request it will be pas sed along to the s erver
accessible via the Relay Gateway IP address .
If DHCP is being enabled, enter the following DHCP server parameters:
Starting and Ending IP Address es : Enter the first and last continuous
addresses in the IP address pool. Any new DHCP client joining the LAN is
ass igned an IP address in this range. The defau lt starting address is
192.168.10.2. The default ending address is 192.168.10.100. Thes e
addresses should be in the same IP addres s subn e t as th e r o u t e r’s LA N IP
address. You may wis h to save part of the subnet range for devices with
statically ass igned IP addres ses in the LAN.
Primary and Secondary DNS servers : If configured domain name sys tem
(DNS) servers are available on the LA N enter their IP addres ses here.
WINS Server (optional): Enter the IP addres s for the W INS server or, if
pres ent in you r network, the Windows NetBios server.
14
Unified Services Router User Manual
Lease Time: Enter the time, in hours, for which IP addres ses are leased to
clients.
Relay Gateway: Enter the gateway address. This is the only configuration
parameter required in this s ection when DHCP Relay is selected as its
DHCP mode
3. In the DNS Host Name Mapping section:
Hos t Name: Provide a valid host name
IP address : Provide the IP address of the hos t n ame,
4. In the LAN proxy section:
Enable DNS Proxy: To enable the router to act as a proxy for all DNS
re q u es ts a n d co mmu n icat e with th e ISP’s DNS s ervers , c lick t h e checkb o x.
5. Click Save Settings to apply all changes.
Figure 1: Se tup page for LAN TCP/IP s ettings
15

Unified Services Router User Manual
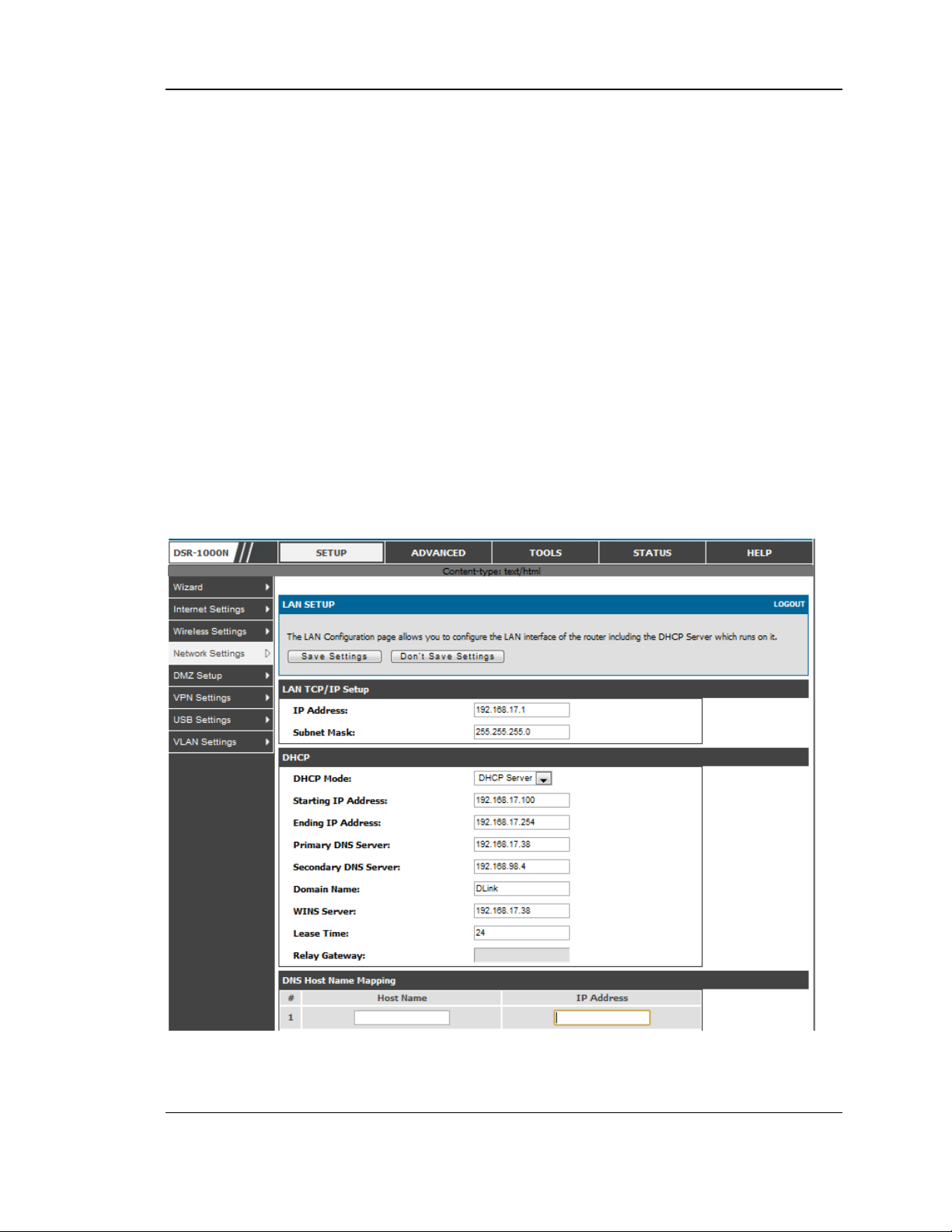
2.1.1 LAN DHCP Reserved IPs
Setup > Network Settings > LAN DHCP Reserved IPs
This router DHCP server can assign TCP/IP configurations to computers in the LAN
explicitly by adding client's network interface hardware address and the IP add ress to
be ass igned to that client in DHCP s erver's database. Whenever DHCP server receives
a request from client, hardware address of that client is compared with the hardware
address list present in the database, if an IP address is already assigned to that
computer or device in the database , the customized IP address is configured
otherwis e an IP address is ass igned to the client automatically from the DHCP pool.
Computer Name: The user defined name for the LAN hos t.
IP Address es: The LAN IP addres s of a host that is res erved by the DHCP server.
MAC Address es: The MAC address that will be as signed the res erved IP address
when it is on the LAN.
As sociate with IP/MAC Binding: W hen the user enables this option the Computer
Name, IP and MAC addres ses are ass ociated with the IP/MAC binding.
The actions that can be taken on lis t of reserved IP address es are:
Select: Selects all the res erved IP address es in the list.
Edit: Opens the LAN DHCP Reserved IP Configuration page to edit the selected
binding rule.
Delete: Deletes the selected IP address reservation(s)
Add: Opens the LAN DHCP Reserved IP Configuration page to add a new binding
rule.
16
Unified Services Router User Manual
Figure 2: LAN DHCP Reserved IPs
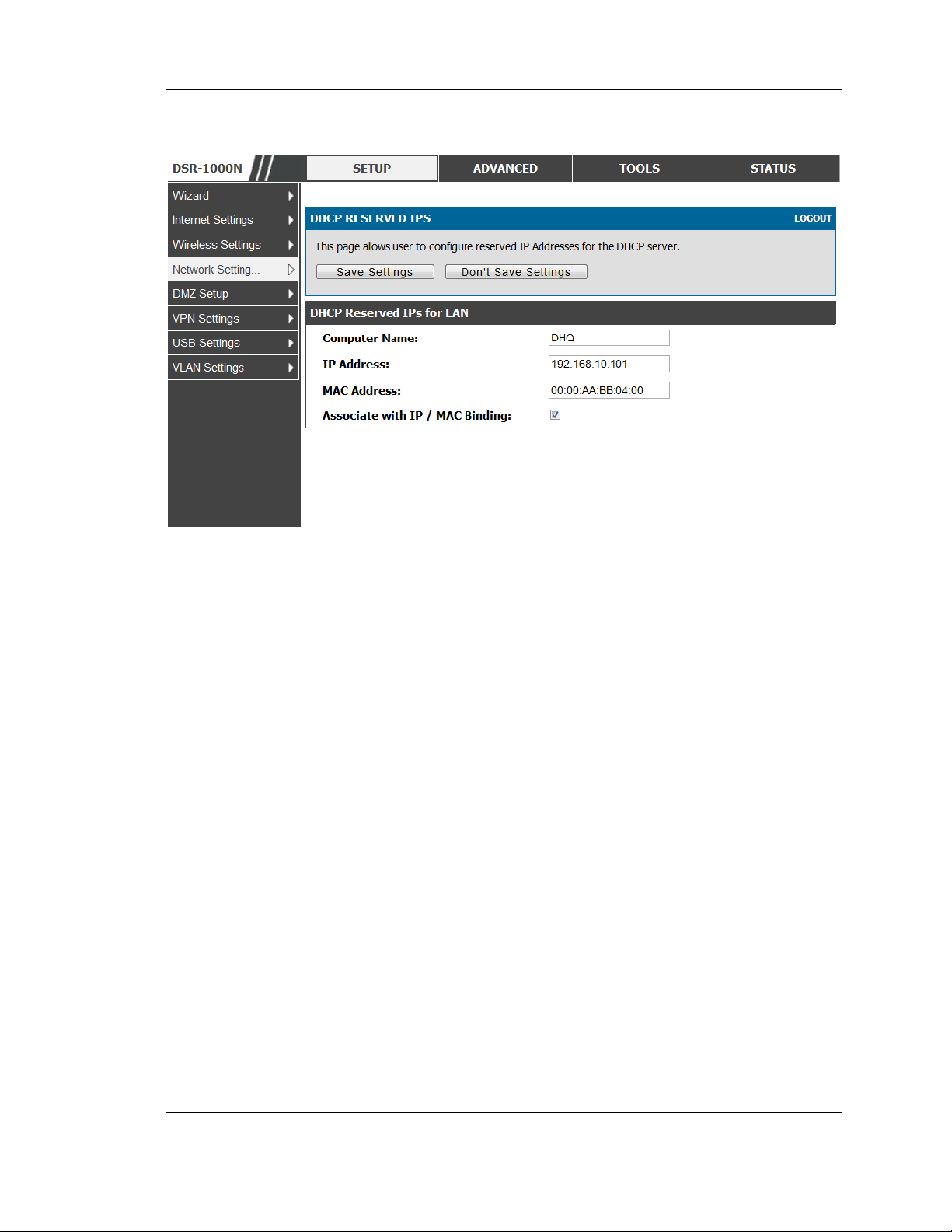
2.1.2 LAN DHCP Leased Clients
Setup > Network Settings > LAN DHCP Leased Clients
This page provides the lis t of clients connect to LAN DHCP server.
17
Unified Services Router User Manual
Figure 3: LAN DHCP Lease d Clients
IP Addres ses : The LAN IP address of a host that matches the reserved IP list.
MAC Addres ses : The MAC address of a LAN hos t that has a configured IP address
res ervation.
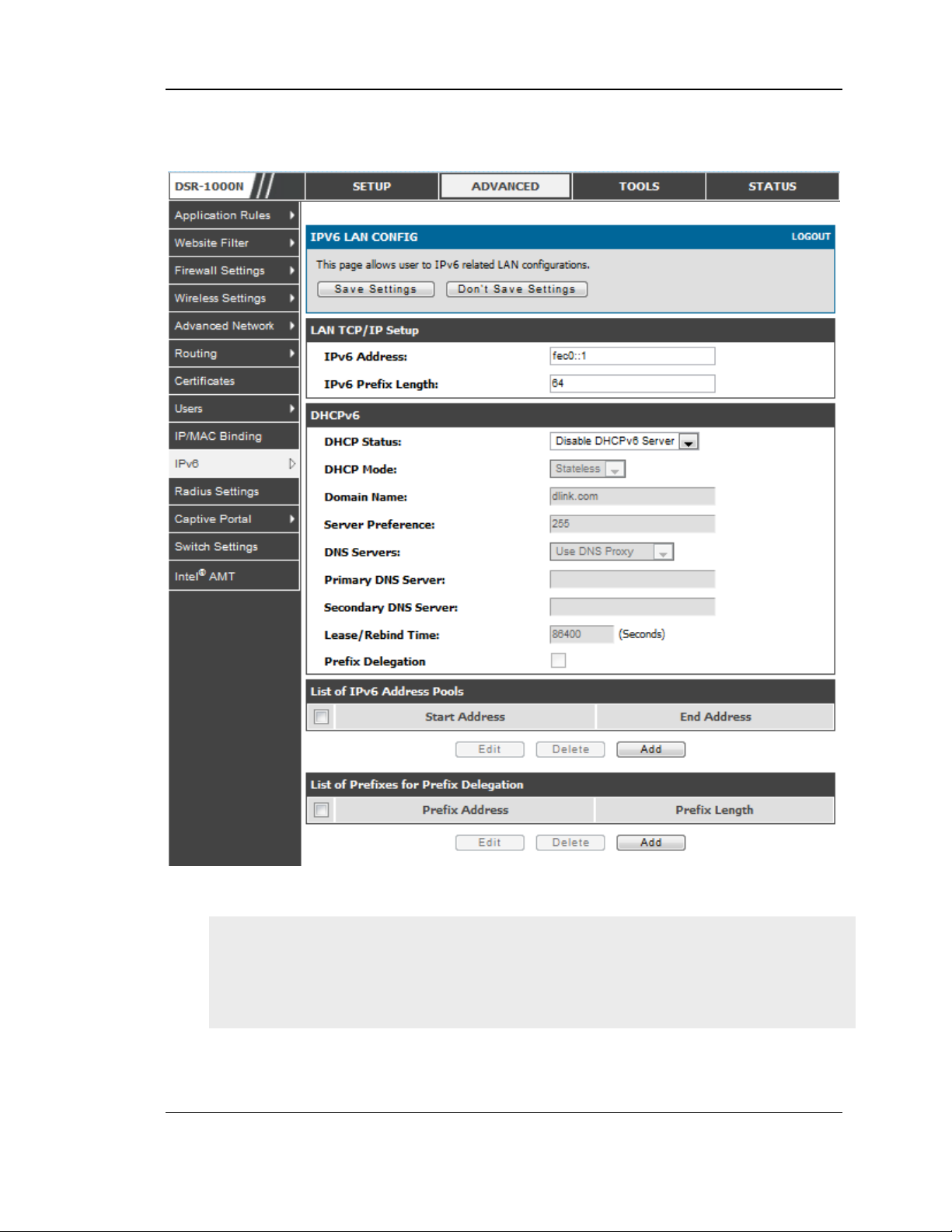
2.1.3 LAN Configuration in an IPv6 Network
Advanced > IPv6 > IPv6 LAN > IPv6 LAN Config
(1) In IPv6 mode, the LAN DHCP server is enabled by default (similar to IPv4
mode). The DHCPv6 server will serve IPv6 addresses from configured address
pools with the IPv6 Prefix Length ass igned to the LAN.
IPv4 / IPv6 mode mus t be enabled in the Advanced > IPv6 > IP mode to enable
IPv6 configuration options.
LAN Settings
The default IPv6 LAN address for the router is fec0::1. You can change this 128 bit
IPv6 address based on your network requirements. The other field that defines the
LAN settings for the router is the prefix length. The IPv6 network (s ubnet) is
identified by the initial bits of the address called the prefix. By default this is 64
bits long. All hosts in the network have common initial bits for their IPv6 address ;
th e n umb e r o f c o mmo n in it ial b its in th e netwo rk’s add res s es is s e t b y t h e pre fix
length field.
18
Unified Services Router User Manual
Figure 4: IPv6 LAN and DHCPv6 configuration
If you change the IP address and click Save Settings, the GUI will not res pond.
Open a new connection to the new IP addres s and log in again. Be s ure the LA N
host (the machine used to manage the router) has obtained IP address from newly
ass igned pool (or has a static IP address in th e rou t e r’s LA N sub n e t ) b e fore
accessing the router via changed IP addres s.
19

Unified Services Router User Manual
As with an IPv4 LAN network, the router has a DHCPv6 server. If enabled , the
router as signs an IP address within the specified range plus additional specified
information to any LAN PC that reques ts DHCP served address es .
The followin g s ettings are us ed to configure the DHCPv6 server:
DHCP Mode: The IPv6 DHCP server is either stateless or stateful. If s tateless is
selected an external IPv6 DHCP s erver is not required as the IPv6 LAN hos ts
are auto-configured by this router. In this case the router advertis ement daemon
(RADVD) must be configured on this device and ICMPv6 router discovery
mess ages are used by the host for auto -configuration. There are no managed
addresses to serve the LAN nodes. If stateful is selected the IPv6 LAN hos t will
rely on an external DHCPv6 server to provide required configuration settings
The domain name o f the DHCPv6 server is an optional setting
Server Preference is used to indicate the pre ference level of this DHCP s erver.
DHCP advertise mess ages with the highes t server preference value to a LA N
host are preferred over other DHCP server advertise mess ages . The default is
255.
The DNS server details can be manually entered here (primary/s econdary
optio ns. An alternative is to allow the LAN DHCP client to receive the DNS
server details from the ISP directly. By selecting Us e DNS proxy, this router
acts as a proxy for all DNS requests and communicates wit h th e ISP ’s DNS
servers (a W AN configuration parameter).
Primary and Secondary DNS servers : If there is configured domain name
sys tem (DNS) s ervers available on the LAN enter the IP addresses here.
Lease/Rebind time sets the duration of the DHCPv6 leas e from this router to the
LAN client.
IPv6 Address Pools
This feature allows you to define the IPv6 delegation prefix for a range of IP
addresses to be s erved b y the gatewa y ’s DHCPv6 s e rver. Using a delegation prefix
you can automate the process of informing other networking equipment on the LAN
of DHCP information s pecific for the ass igned prefix.
Prefix Delegation
The followin g settings are used to configure the Prefix Delegation:
Prefix Delegation: Select this option to enable prefix delegation in DHCPv6
server. This option can be selected only in Stateless Address Auto
Configuration mode of DHCPv6 s erver.
20

Unified Services Router User Manual
Prefix A ddres s: IPv6 prefix addres s in the DHCPv6 s erver prefix pool
Prefix Length: Length prefix address
2.1.4 Configuring IPv6 Router Advertisements
Router Advertis ements are analogous to IPv4 DHCP as signments for LAN clients, in
that the router will ass ign an IP address and s upporting network information to
devices that are configured to accept s uch details. Router Advertisement is required
in an IPv6 network is required for stateless auto configuration of the IPv6 LAN. By
configuring the Router Advertisement Daemon on this router, the DSR will lis ten on
the LAN for router s olicitations and respond to these LAN hosts with rout er
advis ements .
RADVD
Advanced > IPv6 > IPv6 LAN > Router Advertisement
To support stateless IPv6 auto configuration on the LAN, set the RADVD s tatus to
Enable. The following settings are used to configure RADVD:
Advertise Mode: Select Unsolicited Multicast to send router advertis ements
(RA’s ) to all in te rfa c e s in t h e mu lt icas t gr o u p . To re s tric t RA’s to wellknown IPv6 address es on the LAN, and thereby reduce overall network
traffic, select Unicast only.
Advertise Interval: When advertisements are uns olicited multicast packets ,
this interval s ets the maximum time between advertisements from the
interface. The actual duration between advertis ements is a random value
between one third of this field and this field. The default is 30 s econds.
RA Flags: Th e rout er a d vertis eme n ts (RA ’s ) can be s en t wit h o n e o r b o th o f
these flags. Chose Managed to use the administered /stateful protocol for
address auto configuration. If the Other flag is selected the host uses
administered/stateful protocol for non-address auto configuration.
Router Preference: this low/medium/high parameter determines the
preference associated with the RADVD proces s of the router. This is us eful
if there are other RADVD enabled devices on the LAN as it helps avoid
conflicts for IPv6 clients.
MTU: The router advertisement will s et this maximum transmiss ion unit
(MTU) value for all nodes in the LAN that are auto configured by the router.
The default is 1500.
Router Lifetime: T h is v a lu e is p res ent in RA ’s a n d indic at es the u sefu lnes s
of this router as a default router for the interface. The default is 3600
21
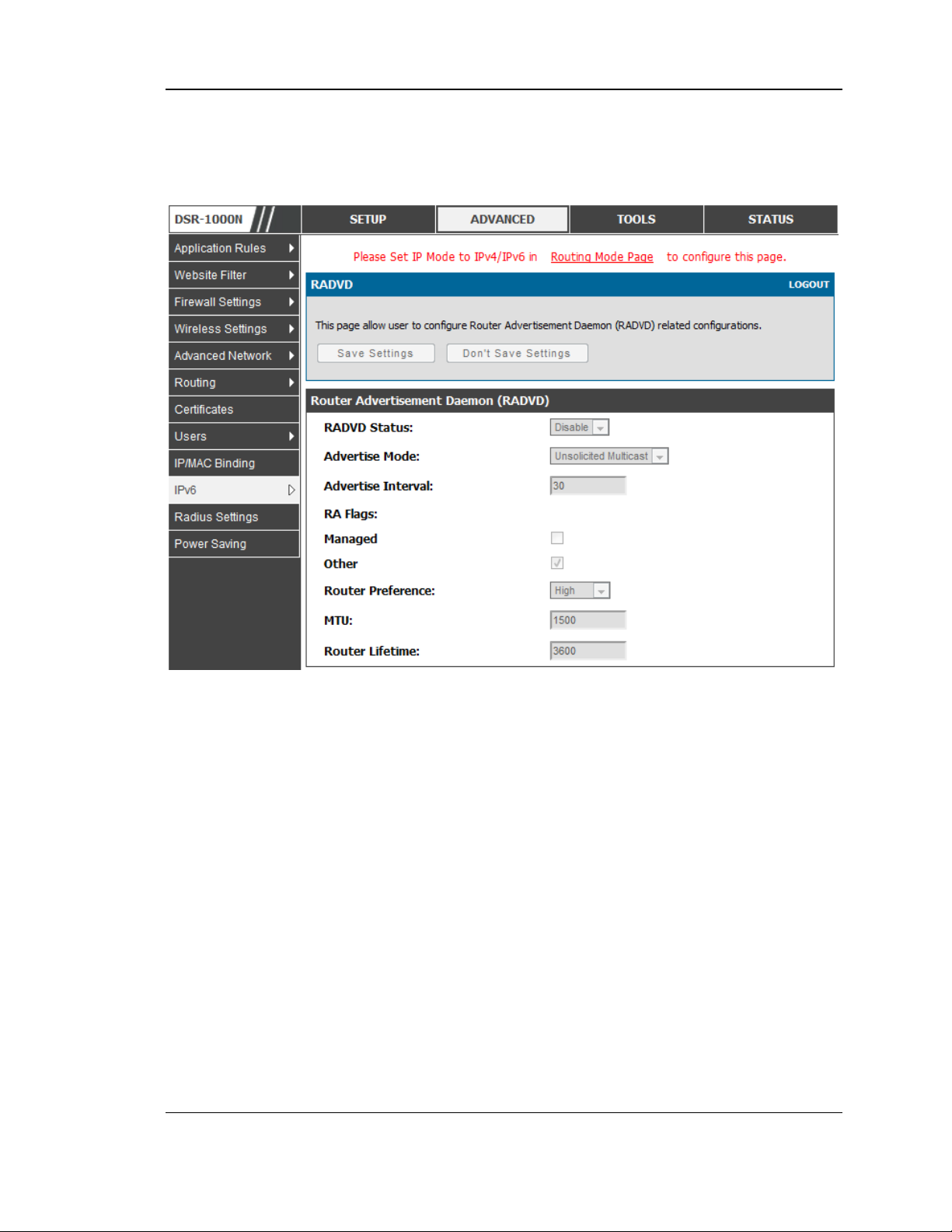
Unified Services Router User Manual
seconds. Upon expiration of this value, a new RADVD exchange must take
place between the host and this router.
Figure 5: Configuring the Route r Advertisement Daemon
Advertisement Prefixes
Advanced > IPv6 > IPv6 LAN > Advertisement Prefixes
The router advertisements configured with advertisement prefixes allow this router
to inform hos ts how to perform stateless address auto configuration. Router
advertisements contain a list of subnet prefixes that allow the router to determine
neighbours and whether the hos t is on the same link as the router.
The followin g prefix options are available for the router advertis ements :
IPv6 Prefix Type : To ensure hosts s upport IPv6 to IPv4 tunnel s elect the
6to4 prefix type. Selecting Global/Lo cal/ISATAP will allow the nodes to
support all other IPv6 routing options
SLA ID: The SLA ID (Site-Level Aggregation Identifier) is available when
6to4 Prefixes are s elected. This s h ou ld b e t h e in t e rfa c e ID o f the ro u t e r’s
LAN interface used for router advertis ements .
22

Unified Services Router User Manual
IPv6 Prefix: When us ing Global/Local/ISA TAP prefixes, this field is us ed to
define the IPv6 network advertised by this router.
IPv6 Prefix Length: This value indicates the number contiguous , higher
order bits of the IPv6 address that define up the network portion of the
address. Typically this is 64.
Prefix Lifetime: This defines the duration (in seconds ) that the reques ting
node is allowed to us e the advertised prefix. It is analogous to DHCP lease
time in an IPv4 network.
Figure 6: IPv6 Adve rtise me nt Prefix settings
2.2 VLAN Configuration
The router supports virtual network isolation on the LAN with the use of VLANs.
LAN devices can be configured to communicate in a s ub network defined by VLAN
identifiers. LAN ports can be as signed unique VLAN IDs s o that traffic to and from
that phys ical port can be isolated from the general LA N. VLAN filtering is
particularly useful to limit broadcast packets of a device in a large network
VLAN support is disabled by default in the router. In the VLAN Configuration page,
enable VLAN support on the router and then proceed to the next section to define the
virtual network.
Setup > VLAN Settings > Available VLAN
The Available VLAN page shows a list of configured VLANs by name and VLAN ID.
A VLAN membership can be created by clicking the Add button below the Lis t of
Available VLANs .
A VLAN membership entry consists of a VLAN identifier and the numerical VLAN
ID which is as signed to the VLAN membership. The VLAN ID value can be any
23
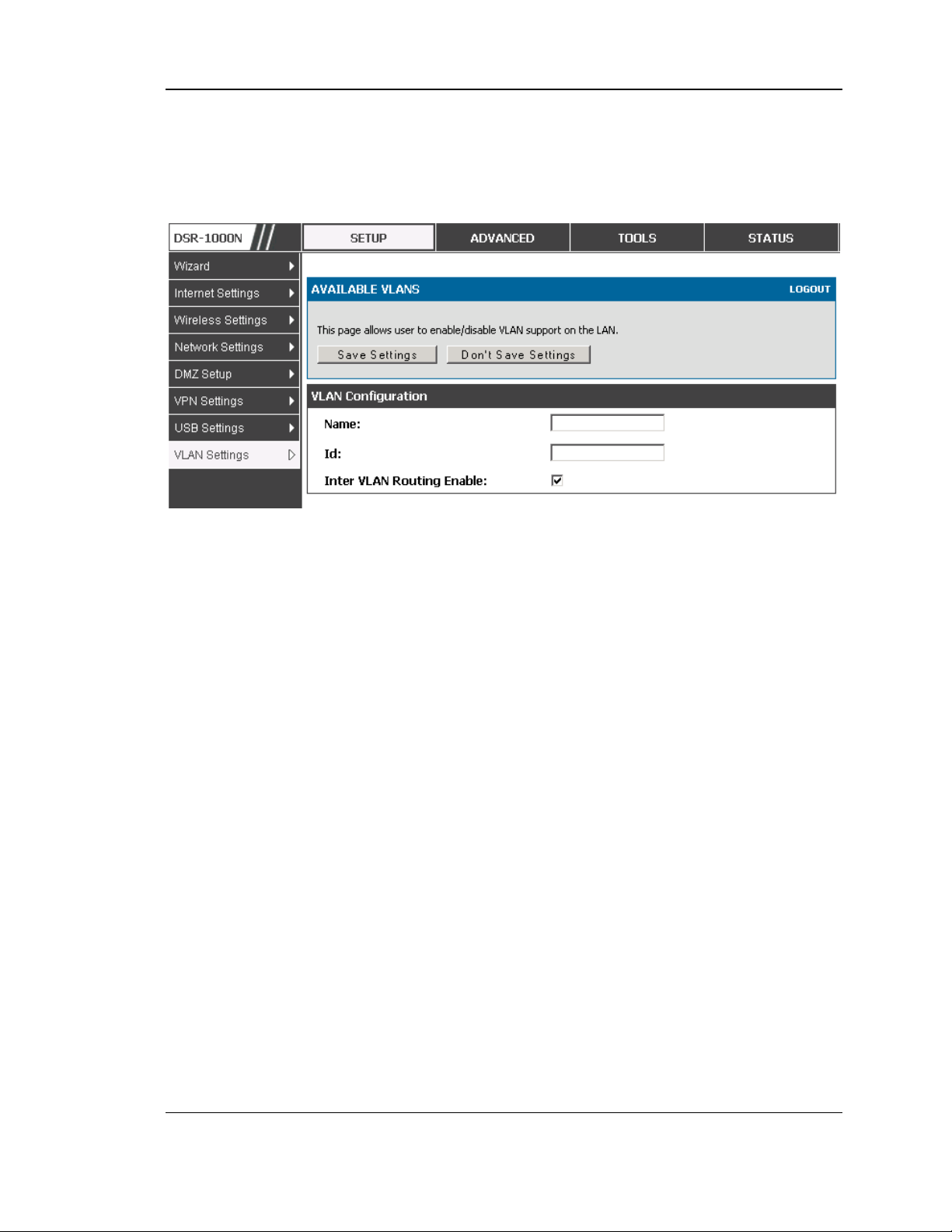
Unified Services Router User Manual
number from 2 to 4091. VLAN ID 1 is reserved for the default VLAN, which is us ed
for untagged frames received on the interface. By enabling Inter VLAN Routing, you
will allow traffic from LAN hos ts belonging to this VLAN ID to pas s through to other
configured VLAN IDs that have Inter VLAN Routing enabled.
Figure 7: Adding VLAN me mberships to the LAN
2.2.1 Associating VLANs to ports
In order to tag all traffic through a specific LAN port with a VLAN ID, you can
ass ociate a VLAN to a physical port.
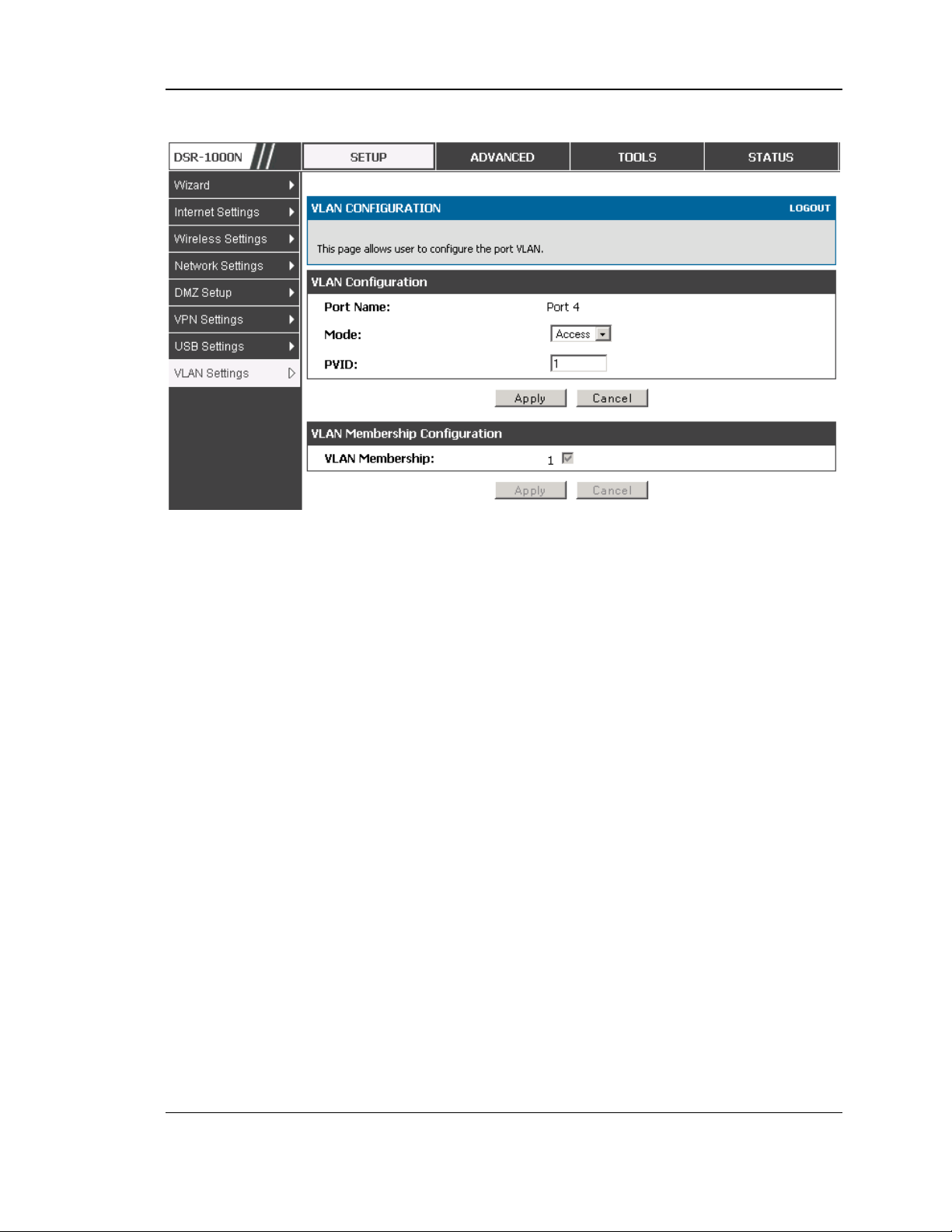
Setup > VLAN Settings > Port VLAN
VLAN membership properties for the LAN and wireles s LAN are lis ted on this page.
The VLAN Port table dis plays the port identifier, the mode setting for that port and
VLAN membership information. The configuration page is access ed by selecting
one of the four physical ports or a configured access point and clicking Edit.
The edit page offers the following configuration options:
Mode: The mode of this VLAN can be General, Acces s, or Trunk. The
default is acces s.
In General mode the port is a member of a us er s electable set of VLANs.
The port sends and receives data that is tagged or untagged with a VLAN
ID. If the data into the port is untagged, it is assigned the defined PVID. In
the configuration from Figure 4, Port 3 is a General port with PVID 3, s o
untagged data into Port 3 will be as signed PVID 3. A ll tagged data s ent out
of the port with the s ame PVID will be untagged. This is mode is typically
used with IP Phones that have dual Ethernet ports. Data coming from phone
to the switch port on the router will be tagged. Data pass ing through the
phone from a connect ed device will be untagged .
24
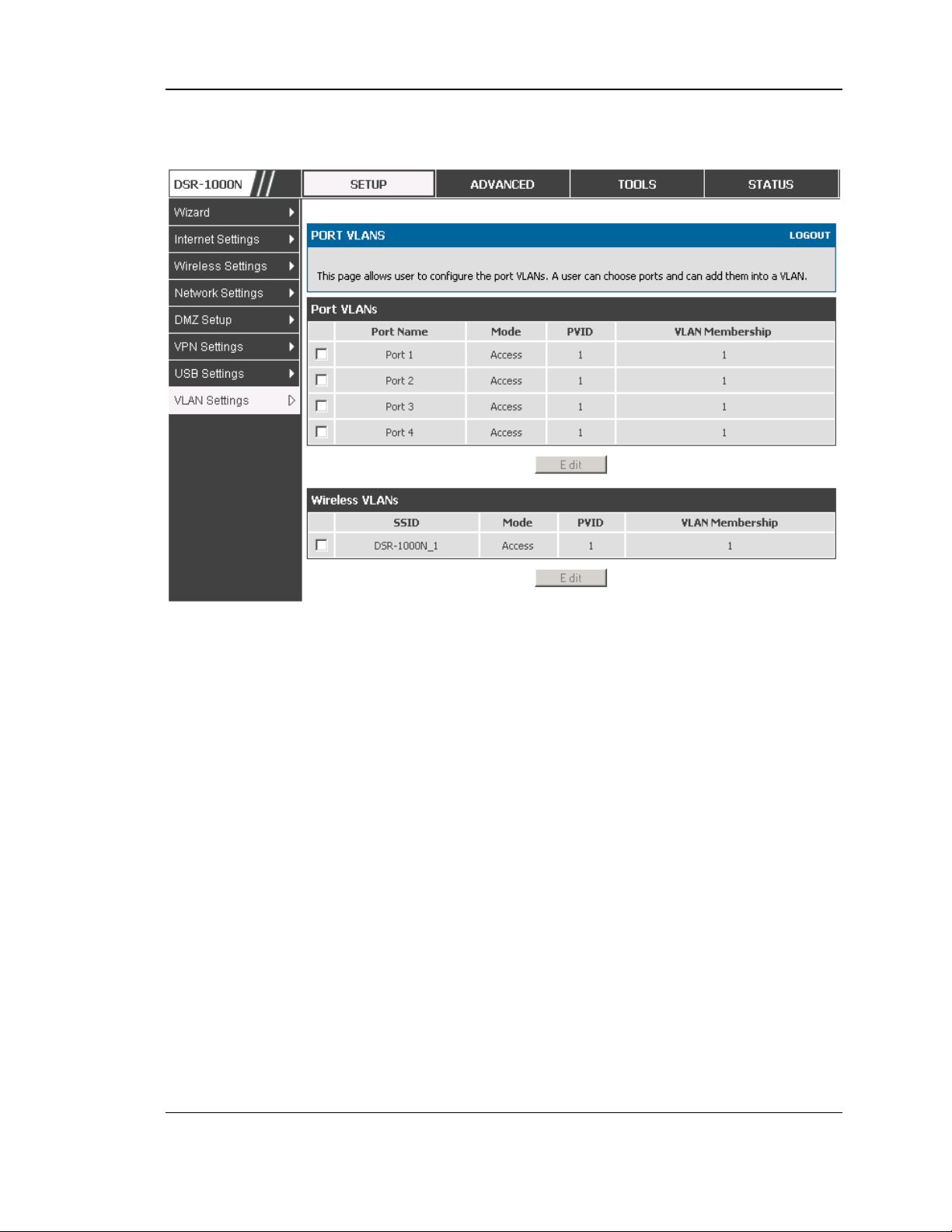
Unified Services Router User Manual
Figure 8: Port VLAN list
In Access mode the port is a member of a s ingle VLAN (and only one). All
data going in to and out of the port is untagged. Traffic through a port in
access mode looks like any other Ethernet frame.
In Trunk mode the port is a member of a user selectable s et of VLANs. All
data going in to and out of the port is tagged. Untagged coming into the port
is not forwarded, except for the default VLAN with PVID=1, which is
untagged. Trunk ports multiplex traffic for multiple VLANs over the same
phys ical link.
Select PVID for the port when the General mode is selected.
Configured VLAN members hips will be displayed on the VLAN
Members hip Configuration for the port. By selecting one more VLAN
members hip options for a General or Trunk port, traffic can be routed
between the selected VLAN members hip IDs
25
Unified Services Router User Manual
Figure 9: Configuring VLAN membe rship for a port
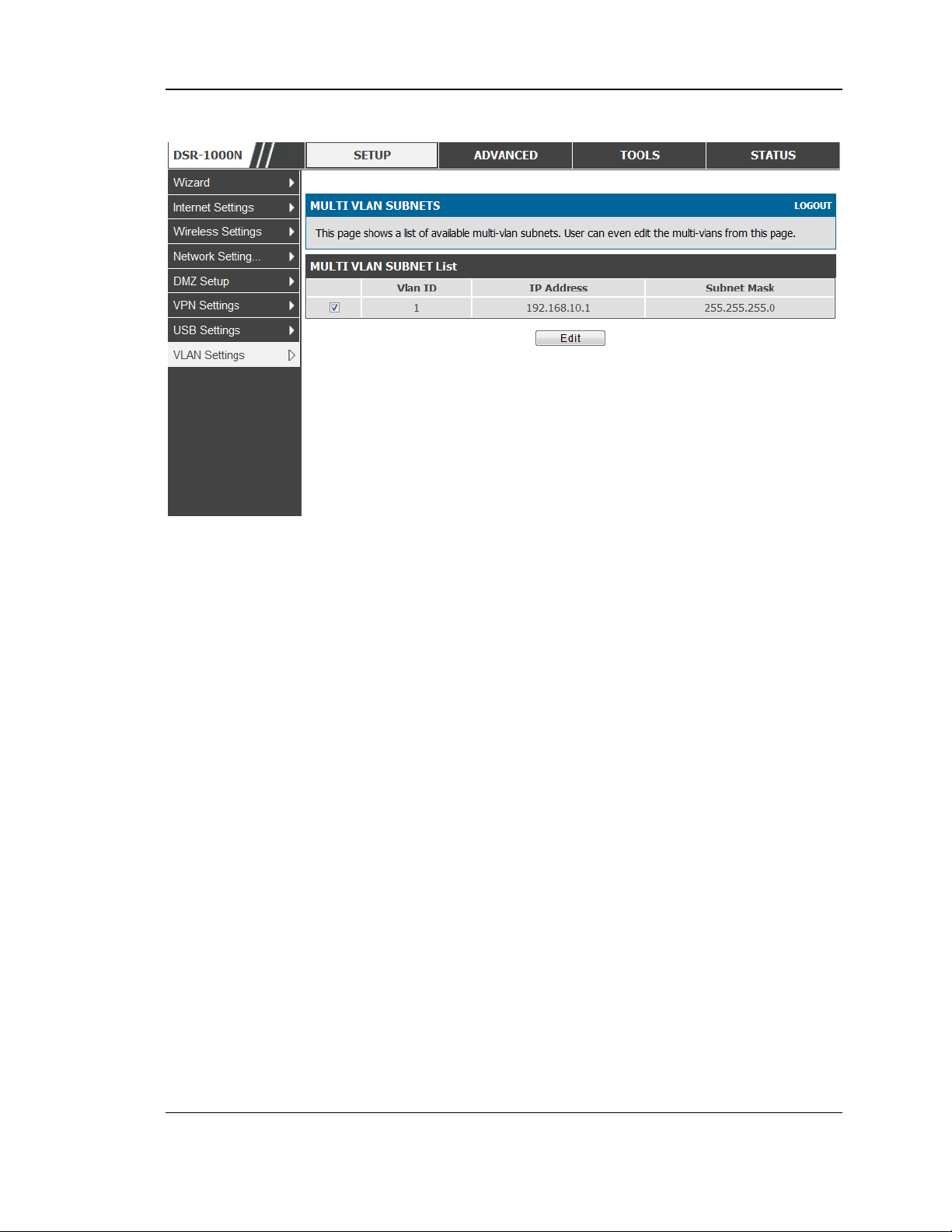
2.2.2 Multiple VLAN Subnets
Setup > VLAN Settings > Multi VLAN Settings
This page shows a list of available multi-VLAN s ubnets. Each configured VLAN ID
can map directly to a subnet within the LAN. Each LAN port can be ass igned a
unique IP address and a VLAN specific DHCP server can be configured to ass ign IP
address leases to devices on this VLAN.
VLAN ID: The PVID of the VLAN that will have all member devices be part of the
same subnet range.
IP Address : The IP address ass ociated with a port as signed this VLAN ID.
Subnet Mas k: Subnet Mask for the above IP A ddres s
26
Unified Services Router User Manual
Figure 10: Multiple VLAN Subnets
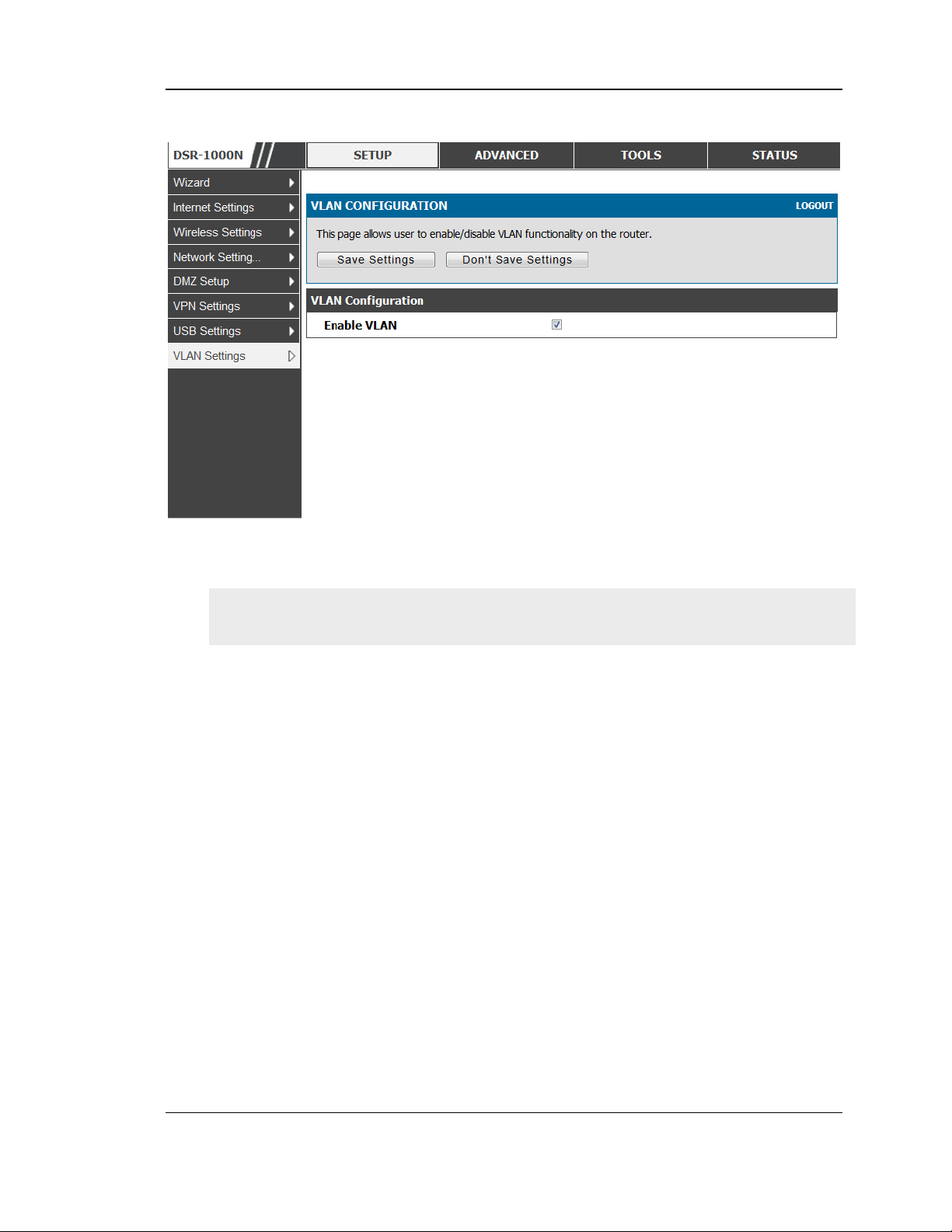
2.2.3 VLAN configuration
Setup > VLAN Settings > VLANconfiguration
This page allows enabling or disabling the VLAN function on the router. Virtual
LANs can be created in this router to provide segmentation capabilities for firewall
rules and VPN policies. The LAN network is cons idered the default VLAN. Check
the Enable VLAN box to add VLAN functionality to the LAN.
27
Unified Services Router User Manual
Figure 11: VLAN Configuration
2.3 Configurable Port: DMZ Setup
DSR-150/150N/250/ 250N does not have a configurable port – there is no DMZ
support.
This router supports one of the physical ports to be configured as a s econdary WAN
Ethernet port or a dedicated DMZ port. A DMZ is a s ub network that is open to the
public but behind the firewall. The DMZ adds an additional layer of security to the
LAN, as specific services/ports t hat are exposed to the internet on the DMZ do not
have to be exposed on the LAN. It is recommended that hosts that mus t be exposed to
the internet (such as web or email s ervers) be placed in the DMZ network. Firewall
rules can be allowed to permit access specific services /p orts to the DMZ from both
the LAN or WAN. In the event of an attack to any of the DMZ nodes, the LAN is not
necess arily vulnerable as well.
Setup > DMZ Setup > DMZ Setup Configuration
DMZ configuration is identical to the LAN configuration. There are no restrictions on
the IP addres s or subnet assigned to the DMZ port, other than the fact that it cannot
be identical to the IP address given to the LAN interface of this gateway.
28
 Loading...
Loading...