Page 1

D-Link
2.4 GHz / 5 GHz Tri-Mode Dualband
Wireless Router
Air Xpert DI-774
Manual
Building Networks for People
Page 2

Contents
Package Contents ................................................................................ 3
Introduction ........................................................................................... 4
Wireless Basics .................................................................................... 6
Getting Started.................................................................................... 10
Using the Configuration Menu ............................................................. 12
Networking Basics .............................................................................. 41
Troubleshooting .................................................................................. 70
Technical Specifications...................................................................... 76
Contacting Technical Support.............................................................. 79
Package Contents
Contents of Package:
n
D-Link Air Xpert DI-774 2.4GHz/5GHz Tri-Mode Dualband
Wireless Router
Power Adapter – 5V DC, 3.0A
n
Manual on CD
n
Quick Installation Guide
n
Ethernet Cable
n
Warranty and Registration ................................................................... 80
Note: Using a power supply with a different voltage rating than the one included with the
DI-774 will cause damage and void the warranty for this product.
If any of the above items are missing, please contact your reseller.
System Requirements For Configuration:
Computer with Windows, Macintosh, or Linux-based
n
operating system with an installed Ethernet adapter
32
Page 3
Introduction
The new D-Link Air Xpert DI-774 Tri-Mode Dualband Wireless Router is a
next generation broadband router that simultaneously serves both 802.11a
wireless networks at 54 Mbps (72 Mbps in Turbo mode), 802.11g wireless
networks at 54Mbps, and 802.11b.
The DI-774 will automatically obtain an IP address and forward additional IP
addresses to multiple clients for a seamless Ethernet network connection
and shared Internet access.
At up to 54Mbps in both the 5GHz and 2.4GHz frequency ranges, the D-Link
Air Xpert DI-774 router delivers data at speeds 5 times faster than previous
wireless standards.
After completing the steps outlined in the Quick Installation Guide (included
in your package) not only will you have the ability to share information and
resources, but you will also be able to enjoy the freedom that wireless
networking delivers.
The DI-774’s web-based user interface (accessible from most Internet browser
applications), the DI-774 will work with most popular operating systems, including
Windows, Macintosh, Linux and can be easily integrated into a large network. Please
take a look at the Getting Started section in this manual to see an example of an
Infrastructure network using the DI-774.
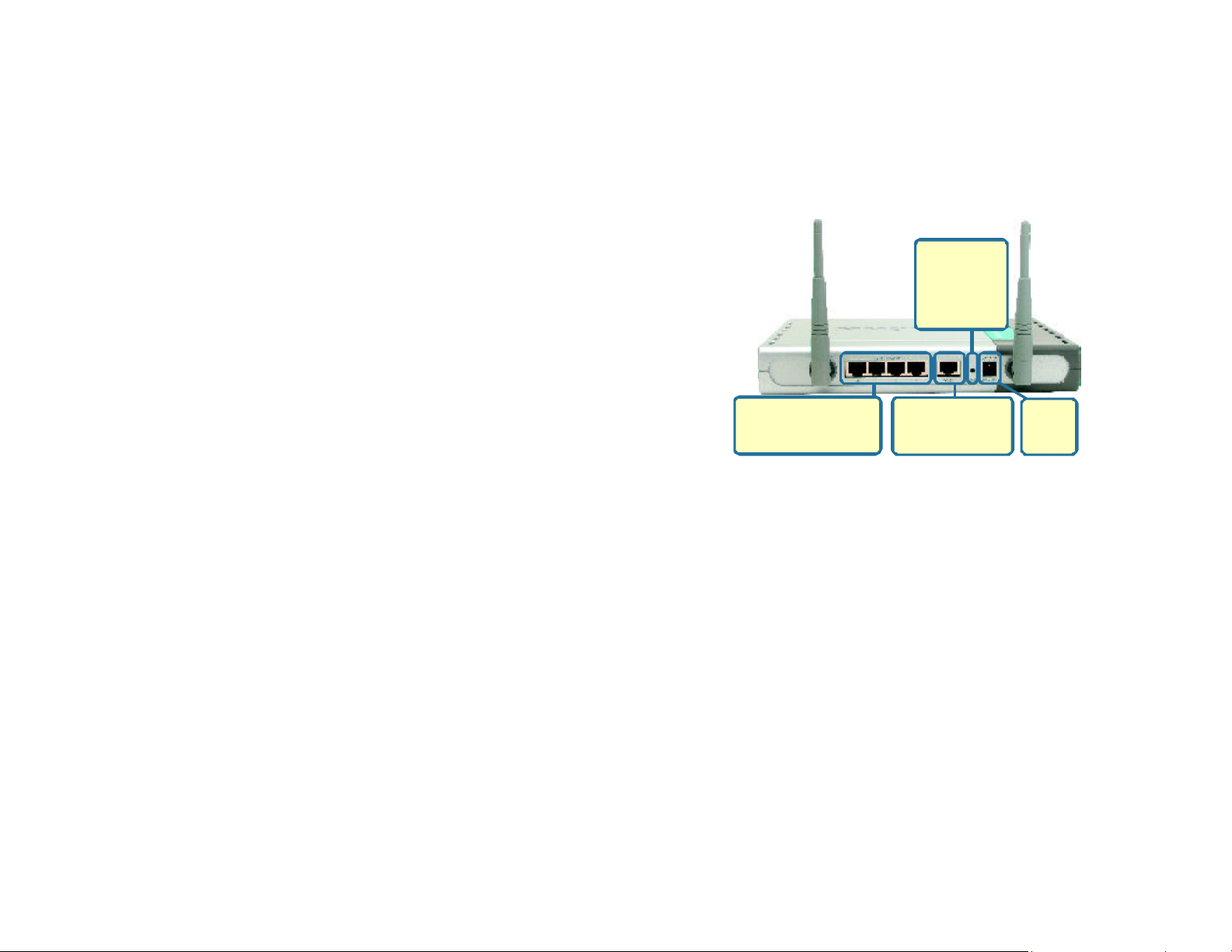
Connections
Pressing the
Reset Button
restores the
router to its
original factory
default settings.
LAN ports automatically
sense cable type when
connecting to Ethernetenabled computers.
The WAN port is the
connection for the
Ethernet cable to the
Cable or DSL modem
Receptor
for the
Power
Adapter
Features & Benefits
Supports data transfer rates of up to 54 Mbps in 2.4GHz and 5 GHz
n
frequency spectrums
Wireless range of up to 900 feet*
n
n
802.11a, 802.11g, and 802.11b compatible
Supports up to 152-bit WEP Encryption at 2.4GHz, and up to 152-bit WEP
n
with Enhanced Dynamic Keying at 5 GHz
n
Eight non-overlapping channels in 5GHz; Three non-overlapping channels in
2.4 GHz
Utilizes Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Orthogonal
n
Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) at 2.4GHz
Utilizes Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
n
n
Easy-to-use Web-based configuration
User level security
n
n
3 Year Warranty (USA only)
*Environmental Factors may Adversely Affect Range.
54
Page 4

LEDS
Wireless Basics
LED stands for Light-Emitting Diode. The DI-774 has the following LEDs:
LED LED Activity
Power
M1
M2
WAN
WLAN
802.11a
WLAN
802.11g
Local Network
(Ports 1-4)
A steady light indicates a connection to a power source
A solid light indicates that the DI-774 is ready
A solid light indicates that the unit is defective
A solid light indicates connection on the WAN port.
This LED blinks during data transmission.
A solid light indicates that the 802.11a wireless segment is ready. The LED blinks during 802.11a wireless
data transmission.
A solid light indicates that the 802.11g wireless segment is ready. The LED blinks during 802.11g wireless
data transmission.
A solid light indicates a connection, a blinking light
indicates data transmission to an Ethernet-enabled
computer on ports 1-4.
Wireless Basics
D-Link wireless products are based on industry standards to provide easy-touse and compatible high-speed wireless connectivity within your home,
business or public access wireless networks. Strictly adhering to the IEEE
standard, the D-Link wireless family of products will allow you to securely
access the data you want, when and where you want it. You will be able to
enjoy the freedom that wireless networking delivers.
A wireless local area network (WLAN) is a cellular computer network that
transmits and receives data with radio signals instead of wires. Wireless
LANs are used increasingly in both home and office environments, and public
areas such as airports, coffee shops and universities. Innovative ways to
utilize WLAN technology are helping people to work and communicate
more efficiently. Increased mobility and the absence of cabling and other
fixed infrastructure have proven to be beneficial for many users.
Wireless users can use the same applications they use on a wired network.
Wireless adapter cards used on laptop and desktop systems support the
same protocols as Ethernet adapter cards.
Under many circumstances, it may be desirable for mobile network devices
to link to a conventional Ethernet LAN in order to use servers, printers or an
Internet connection supplied through the wired LAN. A Wireless Router is a
device used to provide this link.
People use wireless LAN technology for many different purposes:
Mobility - Productivity increases when people have access to data in any
location within the operating range of the WLAN. Management decisions
based on real-time information can significantly improve worker efficiency.
Low Implementation Costs – WLANs (Wireless Local Area Networks)
are easy to set up, manage, change and relocate. Networks that frequently
change, both physically and logically, can benefit from WLANs ease of
implementation. WLANs can operate in locations where installation of wiring
may be impractical.
Installation Speed and Simplicity - Installing a wireless LAN system
can be fast and easy and can eliminate the need to pull cable through walls
and ceilings.
Network Expansion - Wireless technology allows the network to go where
wires cannot go.
Scalability – Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) can be configured in
a variety of topologies to meet the needs of specific applications and
installations. Configurations are easily changed and range from peer-to-peer
networks suitable for a small number of users to larger infrastructure
networks to accommodate hundreds or thousands of users, depending on
the number of wireless devices deployed.
76
Page 5

Wireless Basics
1. The DI-774 is compatible with other D-Link Air Xpert A,B, and G
products, which include:
♦ 5GHz Wireless Cardbus Adapters used with laptop computers
(DWL-AG650)
♦ 5GHz Wireless PCI Adapters used with desktop computers
(DWL-AG520)
2. The DI-774 is also compatible with the D-Link AirPlusXtremeG 802.11g
wireless family, which includes :
♦ High-Speed 2.4GHz Wireless Cardbus Adapters used with laptop
computers (DWL-G650)
♦ High-Speed 2.4GHz Wireless PCI cards used with desktop
computers (DWL-G520)
3. The DI-774 is also compatible with the D-Link AirPlus 802.11b wireless
family, which includes :
Wireless Basics
OFDM reduces the amount of crosstalk (interference) in signal
transmissions. D-Link Air Xpert products will automatically sense the best
possible connection speed to ensure the greatest speed and range possible.
The DI-774 is also interoperable with existing compatible 2.4GHz wireless
devices with data transfer speeds of up to 54Mbps (with the D-Link
AirPlusXtremeG family of wireless devices,) as well as standard 802.11b
technology ( the D-Link AirPlus family of wireless devices), with speeds of up
to 11Mbps.
Installation Considerations
The D-Link Air Xpert DI-774 lets you access your network, using a wireless
connection, from virtually anywhere. Keep in mind, however, that the
number, thickness and location of walls, ceilings or other objects that the
wireless signals must pass through may limit the range. Typical ranges vary
depending on the types of materials and background RF (radio frequency)
noise in your home or business. The key to maximizing wireless range is to
follow these basic guidelines:
♦ High-Speed 2.4GHz Wireless Cardbus Adapters used with laptop
computers (DWL-650+)
♦ High-Speed 2.4GHz Wireless PCI cards used with desktop
computers (DWL-520+)
Standards-Based Technology
The versatile DI-774 Wireless Router integrates 802.11a , 802.11b and
802.11g standards into a single unit.
The 802.11a and 802.11g standards designate that devices may operate at
an optimal data rate of 54 Mbps. This means that in most environments,
within the specified range of this device, you will be able to transfer large files
quickly or even watch a movie in MPEG format over your network without
noticeable delays. This technology works by transmitting high-speed digital
data over a radio wave utilizing OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division
Multiplexing) technology. OFDM works by splitting the radio signal into
multiple smaller sub-signals that are then transmitted simultaneously at
different frequencies to the receiver.
1. Keep the number of walls and ceilings between the DI-774 and your
receiving device (e.g., the DWL-AG650) to a minimum each wall or ceiling
can reduce your D-Link Air Xpert Wireless product’s range from 3-90 feet
(1-30 meters.) Position your receiving devices so that the number of walls
or ceilings is minimized.
2. Be aware of the direct line between routers and computers. A wall that is
1.5 feet thick (.5 meters), at a 45-degree angle appears to be almost 3 feet
(1 meter) thick. At a 2-degree angle it looks over 42 feet (14 meters) thick!
Try to make sure that devices are positioned so that the signal will travel
straight through a wall or ceiling for better reception.
3. Building Materials make a difference - a solid metal door or aluminum
studs may have a negative effect on range. Try to position wireless
devices and computers with wireless adapters so that the signal passes
through drywall or open doorways and not other materials.
4. Keep your product away (at least 3-6 feet or 1-2 meters) from electrical
devices or appliances that generate RF noise.
98
Page 6
Getting Started
Getting Started
1
Right out of the box, with its default settings, the DI-774
will connect with other D-Link Air, AirPlus,
AirXtremeG, and Air Xpert products.
With a single IP Address from your Broadband Internet Service provider you
can share the Internet with all the computers on your local network, without
sacrificing speed or security, using D-Link Air networking products.
IP ADDRESS
Note: If you are using a DHCP-capable router in your network setup,
such as the DI-774, you will not need to assign a static IP Address.
If you need to assign IP Addresses to the computers on the network,
please remember that the
the same IP Address range as all the computers in the network, and
the Subnet mask must be exactly the same for all the computers in the
network.
For example: If the first computer is assigned an IP Address of
192.168.0.2 with a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0, then the second
computer can be assigned an IP Address of 192.168.0.3 with a Subnet
Mask of 255.255.255.0, etc.
IMPORTANT: If computers or other devices are assigned the same
IP Address, one or more of the devices may not be visible on the
network.
IP Address for each computer must be in
2
4
3
5
Please remember that D-Link Air wireless devices are pre-configured to connect
together, right out of the box, with the default settings.
For a typical wireless setup at home (as shown above), please do the
following:
You will need broadband Internet access (Cable/DSL)
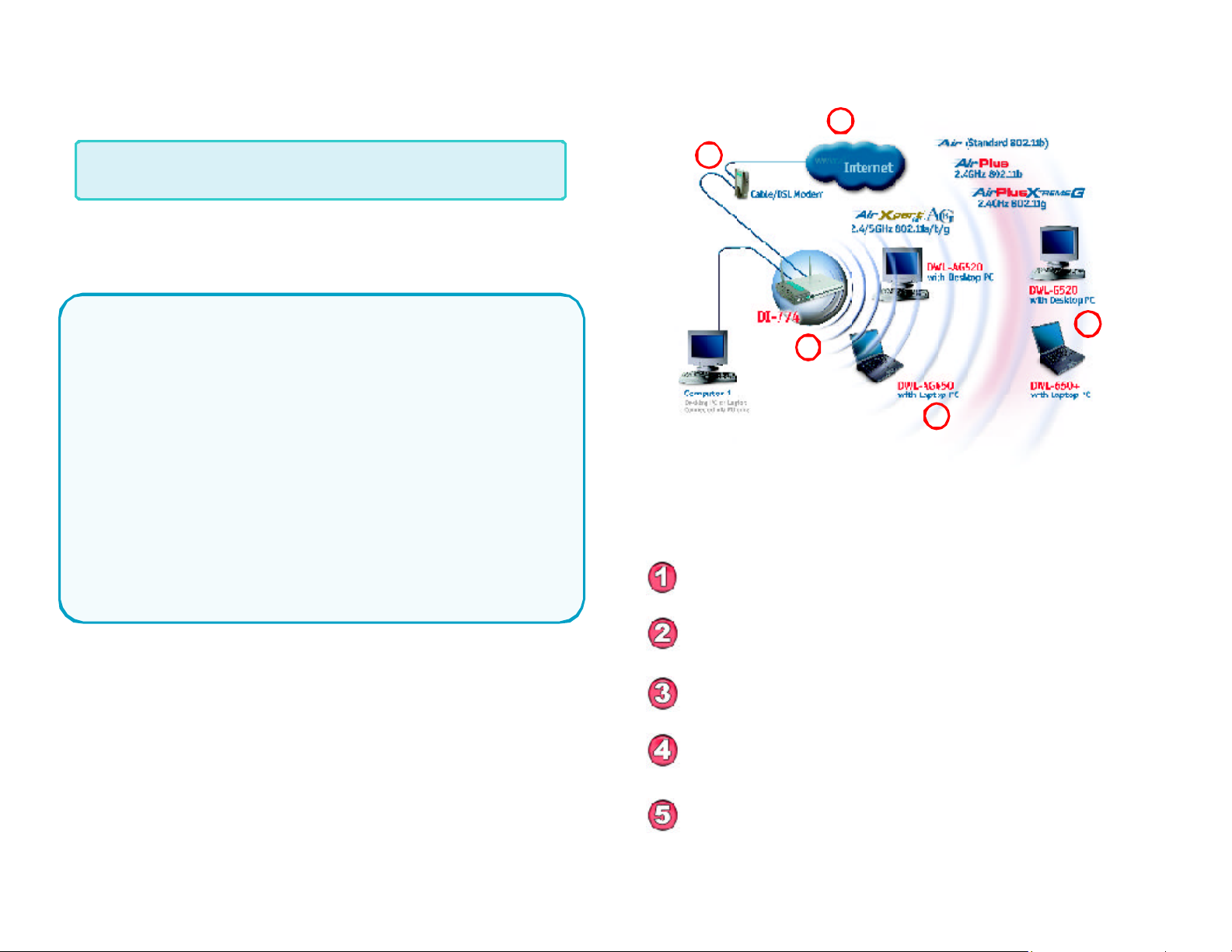
An Infrastructure wireless network contains an Access Point. The
Infrastructure Network example, shown here, contains the following D-Link
network devices:
A wireless Broadband Router - D-Link Air Xpert DI-774
A laptop computer with a wireless adapter - D-Link Air Xpert DWL-AG650
or Air PlusXtremeG DWL-G650
A desktop computer with a wireless adapter - D-Link Air Xpert DWL-AG520
or Air PlusXtremeG DWL-G520
A Cable modem - D-Link DCM-201
Consult with your Cable/DSL provider for proper installation of the modem
Connect the modem to the DI-774 router (see the Quick Installation Guide
included with the DI-774. )
If you are connecting a desktop computer to your network, you can install the
D-Link Air Xpert (DWL-AG520) wireless PCI adapter into an available PCI slot.
(See the Quick Installation Guide included with the DWL-AG520)
If you are connecting a laptop computer to your network, install the drivers for
the wireless cardbus adapter (D-Link Air Xpert DWL-AG650) into a laptop
computer . (See the Quick Installation Guide included with D-Link AirXtremeG
DWL-AG650.)
1110
Page 7
Using the Configuration Menu
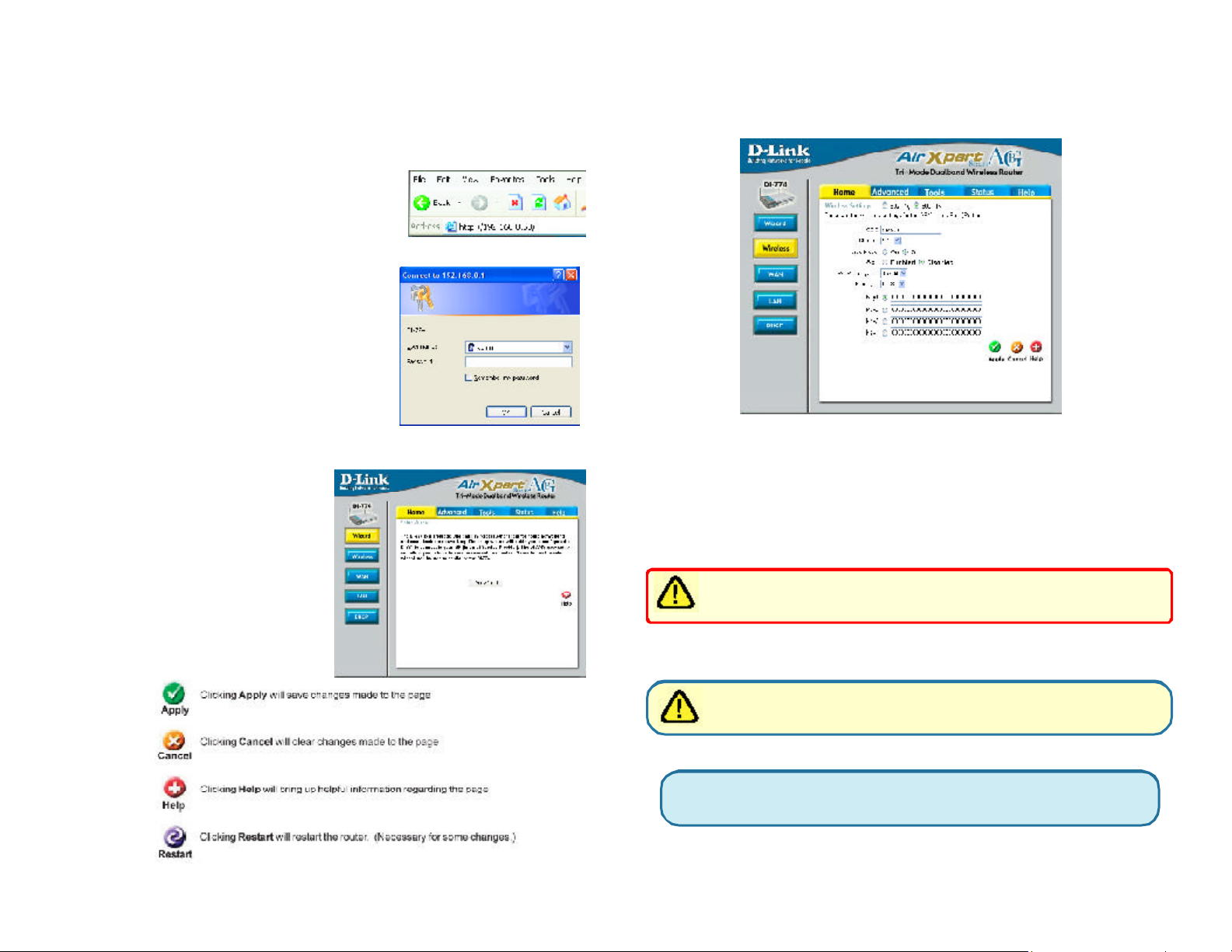
Whenever you want to configure your network or the DI-774, you can access the
Configuration Menu by opening the web-browser and typing in the IP Address of the
DI-774. The DI-774 default IP Address is shown below:
n Open the web browser
n Type in the IP Address of
the Router (http://192.168.0.1)
Note: if you have changed the default IP Address assigned to the DI-774, make sure to
enter the correct IP Address.
n Type admin in the User
Name field
n
blank
n
Leave the Password
Click OK
Connect to 192.168.0.1
admin
Using the Configuration Menu
Home > Wireless > 802.11a
The Home>Wizard screen will appear. Please refer to the Quick Installation
Guide for more information regarding the Setup Wizard.
Home > Wizard
Wireless Settings- choose 802.11a or 802.11g. Here, 802.11a is selected.
SSID-
Channel-
Turbo Mode-
If you enable Turbo mode on the DI-774, make sure to also enable Turbo
mode on all 802.11a wireless clients or a wireless connection will not be
established.
“default” is the default setting. All devices on the network must
share the same SSID. If you change the default setting, the
SSID may be up to 32 characters long.
52 is the default channel for 802.11g. All devices on the network
must share the same channel.
select ON or OFF. The default setting is OFF.
WEP- select Enabled or Disabled. Disabled is the default setting.
WEP Encryption-
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) If you enable encryption on the DI-774
make sure to also enable encryption on all 802.11a wireless clients or
wireless connection will not be established.
select the level of encryption desired: 64, 128 or 152-bit
Key Type- select HEX or ASCII
Hexadecimal digits consist of the numbers 0-9 and the letters A-F
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) is a code for
representing English letters as numbers from 0-127
Keys 1-4-
input up to 4 WEP keys; select the one you wish to use.
1312
Page 8
Using the Configuration Menu
Using the Configuration Menu
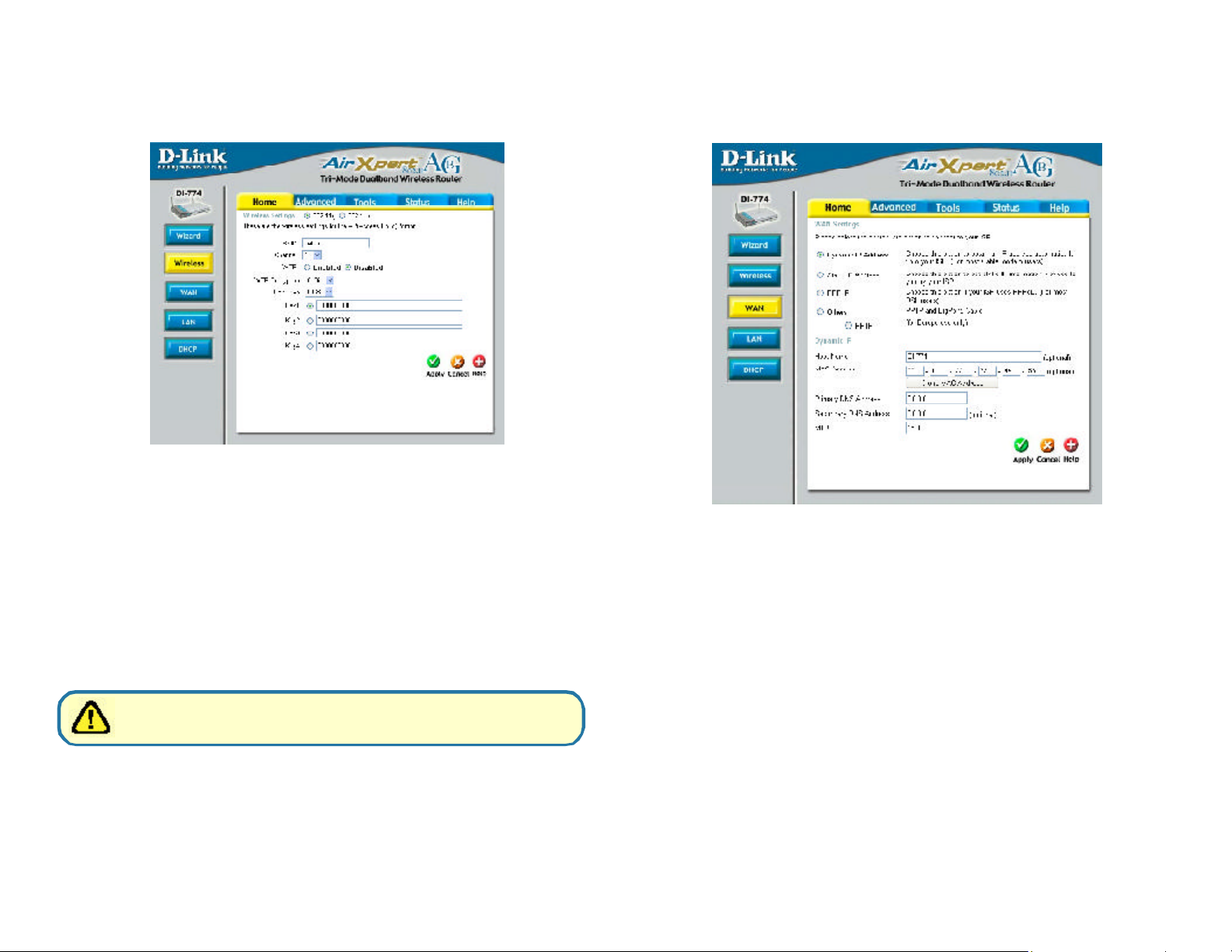
Home > Wireless > 802.11g
Wireless Settings- choose 802.11a or 802.11g. Here, 802.11g is selected.
SSID- “default” is the default setting. All devices on the network must
share the same SSID. The SSID may be up to 32 characters
long.
Channel-
1 is the default channel for 802.11g. All devices on the network
must share the same channel.
WEP- select Enabled or Disabled. Disabled is the default setting.
Dynamic
IP Address-
Host Name-
Home > WAN > Dynamic IP Address
most Cable modem users will select this option to obtain an IP
Address automatically from their ISP (Internet Service Provider).
this is optional, but may be required by some ISPs. The host
name is the device name of the Router.
WEP Encryption-
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) If you enable encryption on the DI-774
make sure to also enable encryption on all 802.11g wireless clients or
wireless connection will not be established.
Key Type-
Keys 1-4-
select the level of encryption desired: 64, 128 or 152-bit
select HEX or ASCII
input up to 4 WEP keys; select the one you wish to use.
MAC Address- the default MAC Address is set to the WAN’s physical interface
MAC address on the Router.
Clone
MAC Address-
Primary/Secondary
DNS-
MTU-
copy the MAC address of the Ethernet card installed by your
ISP, and replace the WAN MAC address with this Ethernet card
MAC address. It is not recommended that you change the default MAC address unless required by your ISP.
enter a DNS Address if you do not wish to use the one provided
by your ISP.
enter an MTU value only if required by your ISP. Otherwise,
leave this section to its default setting of 1500.
1514
Page 9
Using the Configuration Menu
Using the Configuration Menu
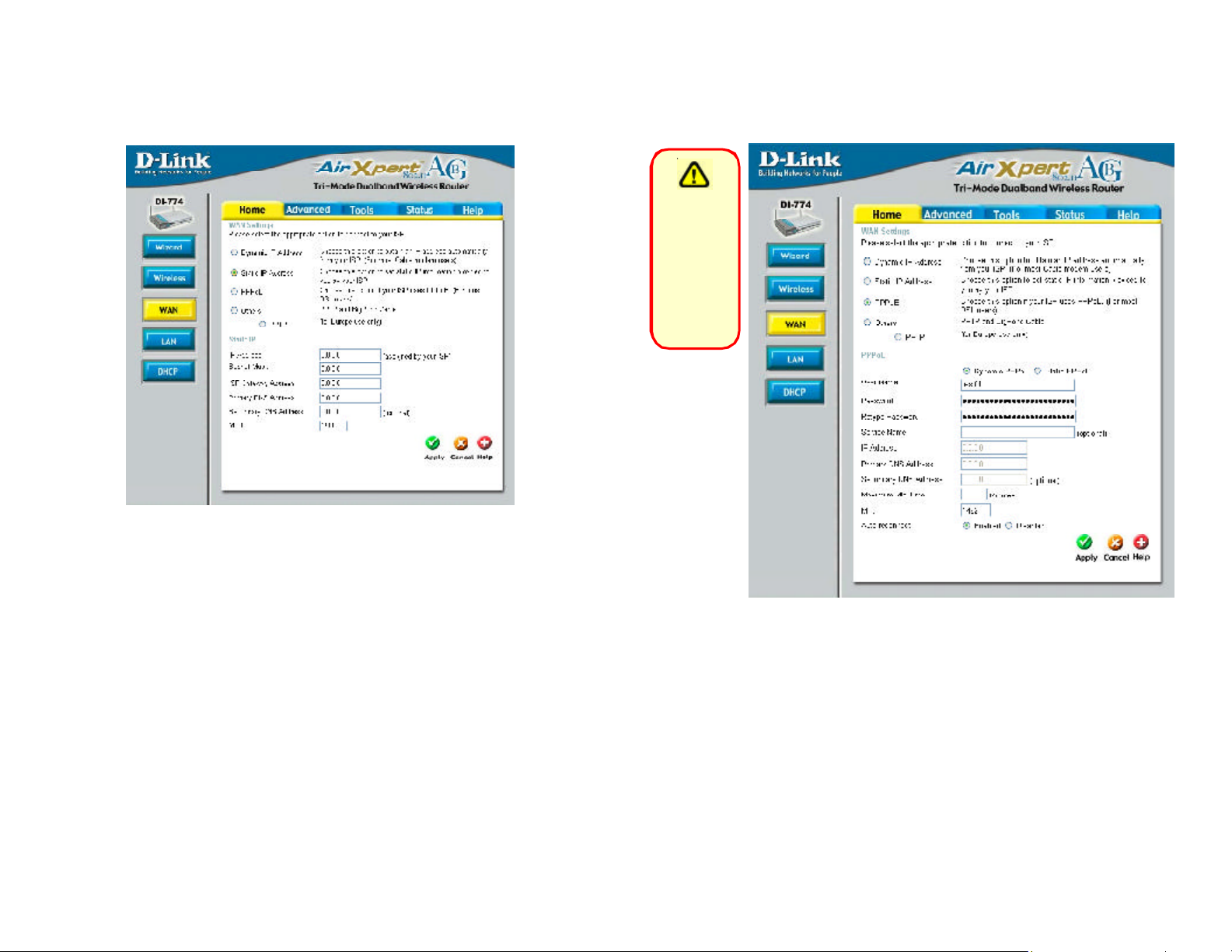
Home > WAN > Static IP Address
Static IP Address-
IP Address-
select this option to set static IP information provided to you
by your ISP.
input the IP Address provided by your ISP
Home > WAN > PPPoE
Please be
sure to
remove any
existing
PPPoE client
software
installed
on your
computers.
Subnet Mask-
ISP
Gateway Address-
Primary / Secondary
DNS Address-
MTU-
input your Subnet mask. (All devices in the network must
have the same subnet mask.)
input the Gateway address
enter a DNS Address if you do not wish to use the one provided by your ISP.
enter an MTU value only if required by your ISP. Otherwise,
leave this section to its default setting of 1500.
PPPoE-
Choose this option if your ISP uses PPPoE.
will select this option.)
Dynamic PPPoE- receive an IP Address automaticcally from
your ISP.
Static PPPoE- you have an assigned (static) IP Adress.
(Most DSL users
User Name- your PPPoE username provided by your ISP.
Password- your PPPoE password provided by your ISP.
Retype Password- re-enter the PPPoE password
Service Name-
enter the Service Name provided by your ISP (optional).
IP Address- this option is only available for Static PPPoE. Enter the static IP
Address for the PPPoE connection.
1716
Page 10
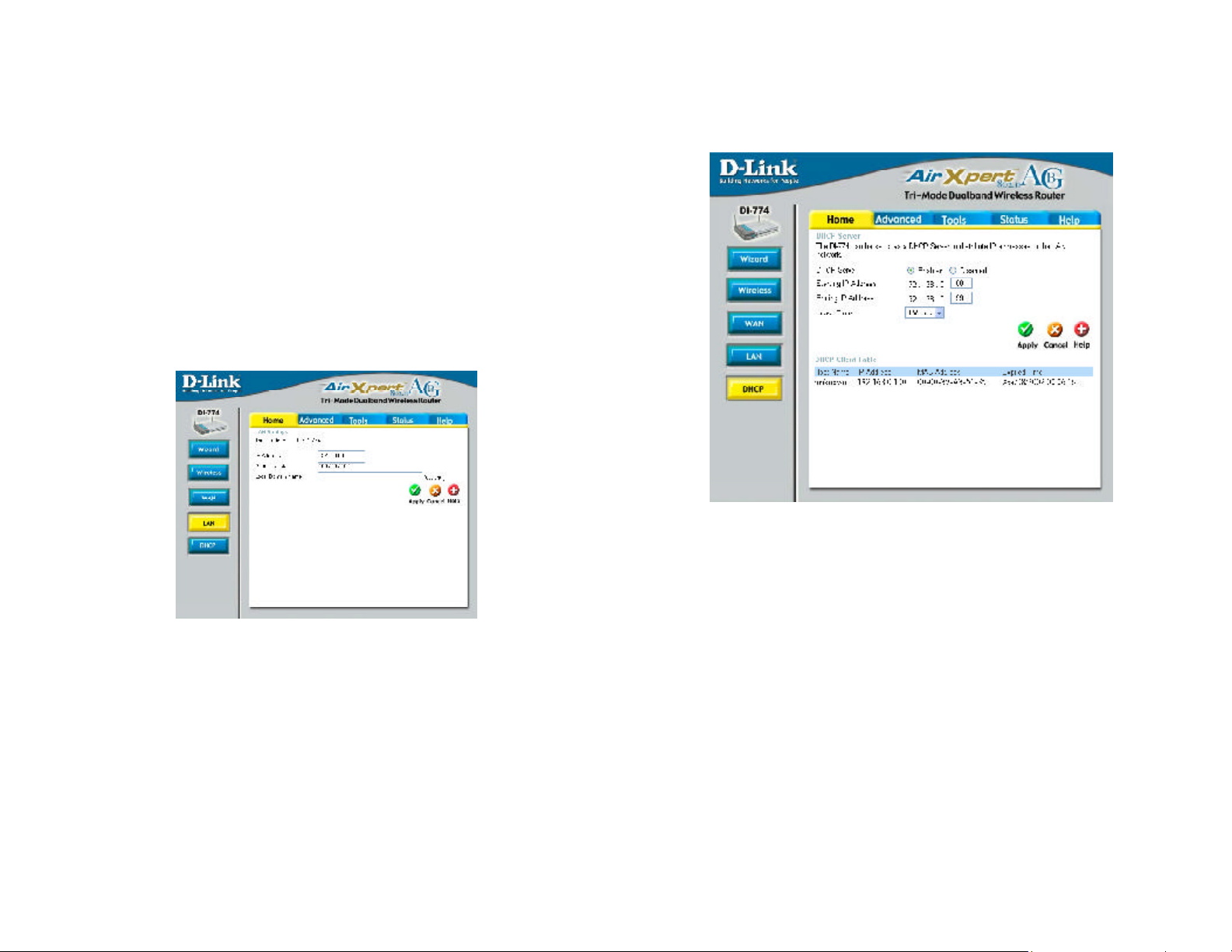
Using the Configuration Menu
Home > WAN > PPPoE continued
Primary/Secondary
DNS-
enter a DNS Address if you do not wish to use the one provided
by your ISP.
Using the Configuration Menu
Home > DHCP
Maximum
Idle Time-
MTU-
Auto-reconnect-
enter a maximum idle time during which Internet connection is
maintained during inactivity. To disable this feature, enter zero
or enable Auto-reconnect.
Maximum Transmission Unit-1472 is default-you may need to
change the MTU to conform with your ISP.
if enabled, the DI-774 will automatically connect to your ISP after your system is restarted or if the connection is dropped.
Home > LAN
LAN is short for Local Area Network. This is considered your internal network. These
are the IP settings of the LAN interface for the DI-774. These settings may be referred to
as Private settings. You may change the LAN IP address if needed. The LAN IP address
is private to your internal network and cannot be seen on the Internet.
IP Address-
Subnet Mask-
Local Domain
the IP address of the LAN interface. The default IP address is:
192.168.0.1
the subnet mask of the LAN interface.
The default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0
domain name assigned to the router
Name-
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Control Protocol. The DI-774 has a built-in DHCP server.
The DHCP Server will automatically assign an IP address to the computers on the LAN/
private network. Be sure to set your computers to be DHCP clients by setting their TCP/
IP settings to “Obtain an IP Address Automatically.” When you turn your computers on,
they will automatically load the proper TCP/IP settings provided by the DI-774. The
DHCP Server will automatically allocate an unused IP address from the IP address pool
to the requesting computer. You must specify the starting and ending address of the IP
address pool.
DHCP Server-
select Enabled or Disabled
Starting
IP Address- the starting IP address for the DHCP server’s IP assignment
Ending
IP Address-
the ending IP address for the DHCP server’s IP assignment
Lease Time- the length of time of the DHCP lease
DHCP Client
displays a list of DHCP clients assigned by the router
Table-
1918
Page 11
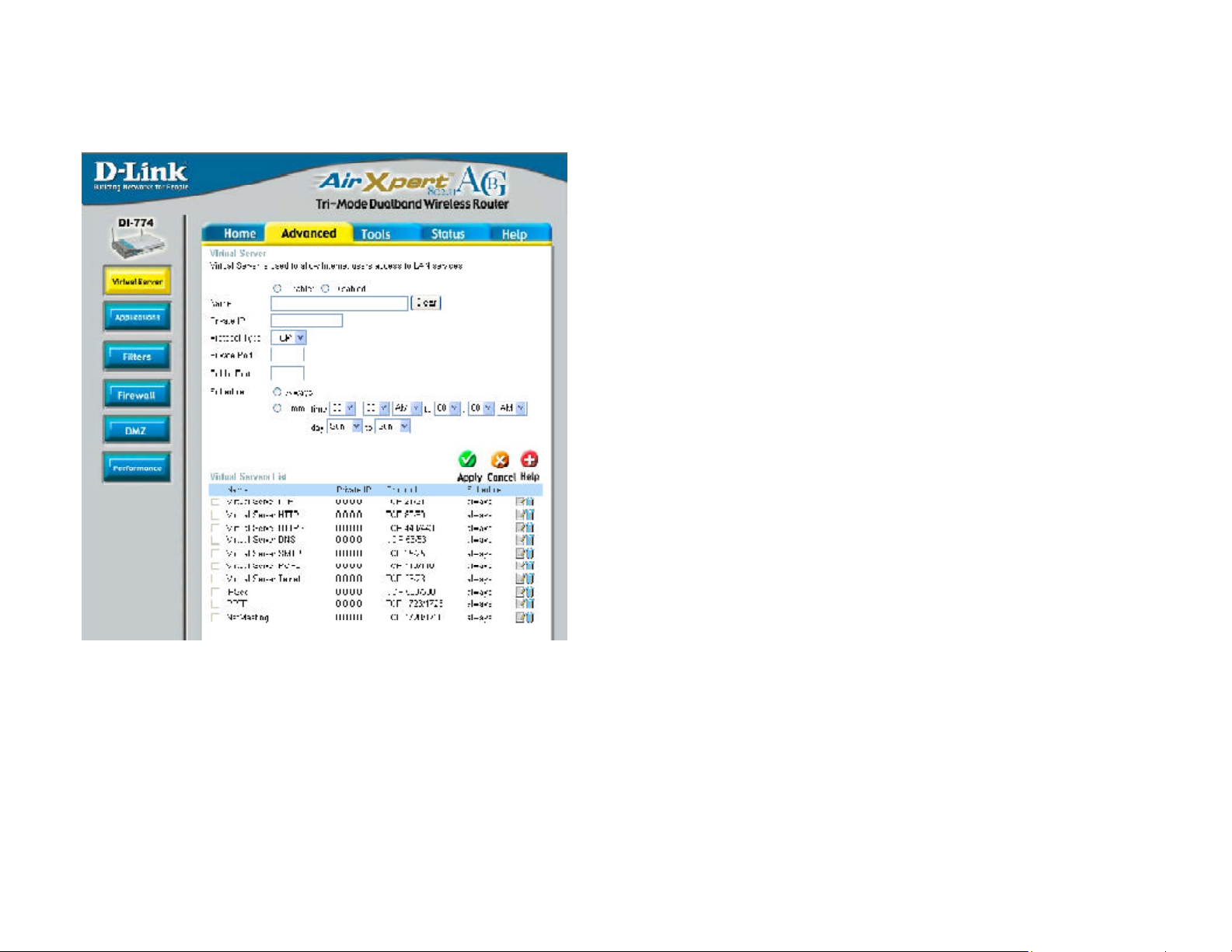
Using the Configuration Menu
Advanced > Virtual Server
Using the Configuration Menu
Advanced > Virtual Server continued
The DI-774 is also capable of port-redirection meaning incoming traffic to a particular
port may be redirected to a different port on the server computer.
Each virtual service that is created will be listed at the bottom of the screen in the
Virtual Servers List. There are pre-defined virtual services already in the table. You
may use them by enabling them and assigning the server IP to use that particular
virtual service.
The DI-774 can be configured as a virtual server so that remote users accessing Web
or FTP services via the public IP address can be automatically redirected to local
servers in the LAN (Local Area Network).
The DI-774 firewall feature filters out unrecognized packets to protect your LAN
network so all computers networked with the DI-774 are invisible to the outside world.
If you wish, you can make some of the LAN computers accessible from the Internet
by enabling Virtual Server. Depending on the requested service, the DI-774 redirects
the external service request to the appropriate server within the LAN network.
Virtual ServerName-
Private IP-
select Enabled or Disabled
enter the name referencing the virtual service
the server computer in the LAN (Local Area Network) that will be
providing the virtual services.
Protocol Type- the protocol used for the virtual service
Private Port-
the port number of the service used by the Private IP computer
Public Port- the port number on the WAN (Wide Area Network)side that will
be used to access the virtual service.
Schedule-
Example #1:
If you have a Web server that you wanted Internet users to access at all times, you
would need to enable it. Web (HTTP) server is on LAN (Local Area Network)
computer 192.168.0.25. HTTP uses port 80, TCP.
Name: Web Server
Private IP: 192.168.0.25
Protocol Type: TCP
Private Port: 80
Public Port: 80
Schedule: always
The schedule of time when the virtual service will be enabled.
The schedule may be set to Always, which will allow the
particular service to always be enabled. If it is set to Time,
select the time frame for the service to be enabled. If the
system time is outside of the scheduled time, the service will
be disabled.
2120
Page 12
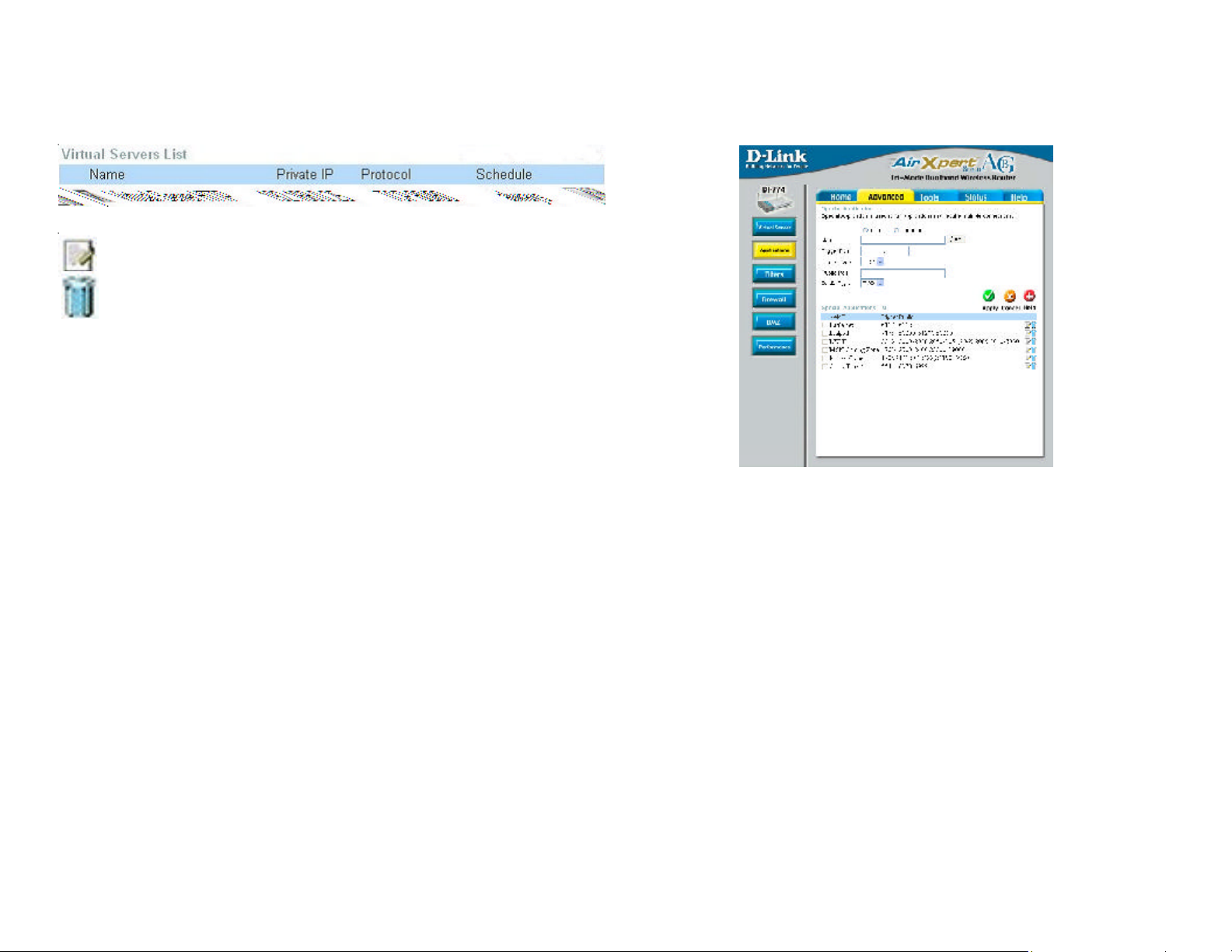
Using the Configuration Menu
Using the Configuration Menu
Advanced > Virtual Server continued
Click on this icon to edit the virtual service
Example #2:
If you have an FTP server that you wanted Internet users to access by WAN port
2100 and only during the weekends, you would need to enable it as such. FTP
server is on LAN computer 192.168.0.30. FTP uses port 21, TCP.
Name: FTP Server
Private IP: 192.168.0.30
Protocol Type: TCP
Private Port: 21
Public Port: 2100
Schedule: From: 01:00AM to 11:00PM, Sat to Sun
Click on this icon to delete the virtual service
All Internet users who want to access this FTP Server
must connect to it from port 2100. This is an example of
port redirection and can be useful in cases where there
are many of the same servers on the LAN network.
Advanced > Applications
Some applications require multiple connections, such as Internet gaming, video
conferencing, Internet telephony and others. These applications have difficulties
working through NAT (Network Address Translation). Special Applications makes
some of these applications work with the DI-774. If you need to run applications that
require multiple connections, specify the port normally associated with an application
in the “Trigger Port” field, select the protocol type as TCP or UDP, then enter the
public ports associated with the trigger port to open them for inbound traffic.
The DI-774 provides some predefined applications in the table on the bottom of the
web page. Select the application you want to use and enable it.
Note! Only one PC can use each Special Application tunnel.
Name:
this is the name referencing the special application.
Trigger Port: this is the port used to trigger the application. It can be either
a single port or a range of ports.
Trigger Type: this is the protocol used to trigger the special application.
Public Port:
this is the port number on the WAN side that will be used to
access the application. You may define a single port or a
range of ports. You can use a comma to add multiple ports or
port ranges.
Public Type: this is the protocol used for the special application.
2322
Page 13
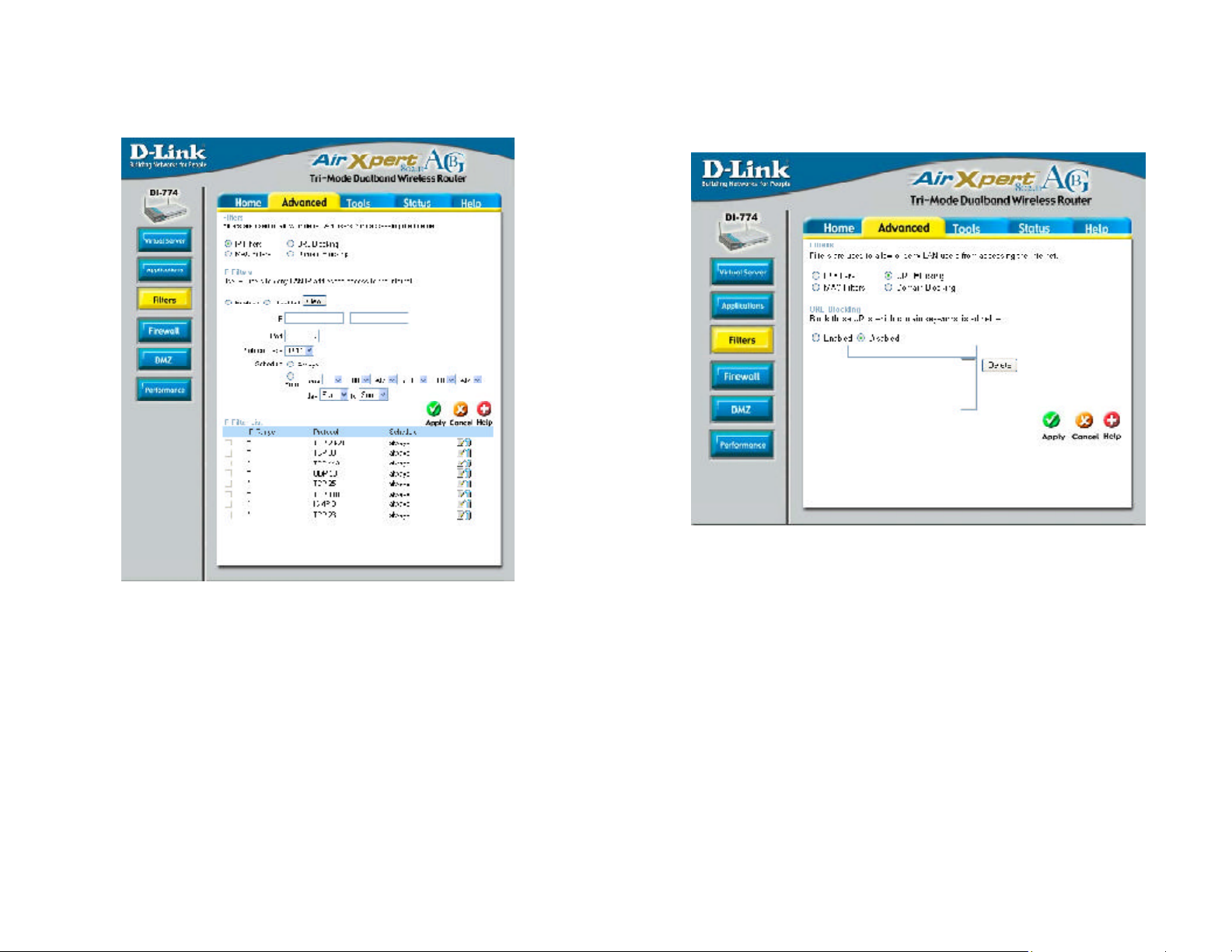
Using the Configuration Menu
Using the Configuration Menu
Advanced > Filters > IP Filters
Filters are used to deny or allow LAN (Local Area Network) computers from accessing
the Internet. The DI-774 can be setup to deny internal computers by their IP or MAC
addresses. The DI-774 can also block users from accessing restricted web sites.
IP Filters-
IP-
Port-
Use IP Filters to deny LAN IP addresses from accessing the
Internet. You can deny specific port numbers or all ports for
the specific IP address.
the IP address of the LAN computer that will be denied
access to the Internet.
the single port or port range that will be denied access to the
Internet.
select the protocol typeProtocol Types-
Advanced > Filters > URL Blocking
URL Blocking is used to deny LAN computers from accessing specific web sites by
its URL. A URL is a specially formatted text string that defines a location on the
Internet. If any part of the URL contains the blocked word, the site will not be
accessible and the web page will not display.
Filters-
URL Blocking-
select the filter you wish to use; in this case, URL Blocking
was chosen.
select Enabled or Disabled.
Keywords- block URLs which contain keywords listed below.
Enter the keywords in this space.
Schedule-
this is the schedule of time when the IP Filter will be enabled.
2524
Page 14

Using the Configuration Menu
Using the Configuration Menu
Advanced > Filters > MAC Filters
Use MAC (Media Access Control) Filters to allow or deny LAN (Local Area Network)
computers by their MAC addresses from accessing the Internet. You can either
manually add a MAC address or select the MAC address from the list of clients that
are currently connected to the Broadband Router.
Filters- select the filter you wish to use; in this case, MAC filters was
chosen.
MAC Filters- choose Disable MAC filters; allow MAC addresses listed be-
low; or deny MAC addresses listed below.
NameMAC AddressDHCP Client-
enter the name here.
enter the MAC Address.
select a DHCP client from the pull-down list; click Clone to copy
that MAC Address
Advanced > Filters > Domain Blocking
Domain Blocking is used to allow or deny LAN (Local Area Network) computers from
accessing specific domains on the Internet. Domain blocking will deny all requests to a
specific domain such as http and ftp. It can also allow computers to access specific
sites and deny all other sites.
FiltersDomain Blocking:
Disabled-
Allow-
Deny-
select the filter you wish to use; in this case, Domain Blocking
was chosen.
select Disabled to disable Domain Blocking
allows users to access all domains except Blocked Domains
denies users access to all domains except
Permitted Domains
Permitted
Domains-
Blocked Domains-
enter the Permitted Domains in this field
enter the Blocked Domains in this field
2726
Page 15

Using the Configuration Menu
Using the Configuration Menu
Advanced > Firewall
Firewall Rules is an advanced feature used to deny or allow traffic from passing
through the DI-774. It works in the same way as IP Filters with additional settings.
You can create more detailed access rules for the DI-774. When virtual services are
created and enabled, it will also display in Firewall Rules. Firewall Rules contains all
network firewall rules pertaining to IP (Internet Protocol).
In the Firewall Rules List at the bottom of the screen, the priorities of the rules are
from top (highest priority) to bottom (lowest priority.)
Advanced > DMZ
Note: The DI-774 MAC Address filtering rules have precedence over the Firewall
Rules.
Firewall RulesName-
ActionSource-
enable or disable the Firewall Rules
enter a name for the rule
allow or deny IP traffice through the router
enter the IP Address range
Destination- enter the IP Address range ; the Protocol;
and the Port Range
Schedule-
select Always or enter the Time.
If you have a client PC that cannot run Internet applications properly from behind the
DI-774, then you can set the client up to unrestricted Internet access. It allows a
computer to be exposed to the Internet. This feature is useful for gaming purposes.
Enter the IP address of the internal computer that will be the DMZ host. Adding a
client to the DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) may expose your local network to a variety of
security risks, so only use this option as a last resort.
DMZ-
IP Address-
enable or disable the DMZ. The DMZ (Demilitarized Zone)
allows a single computer to be exposed to the Internet.
enter the IP Address of the computer to be in the DMZ
2928
Page 16

Using the Configuration Menu
Advanced > Performance > 802.11a
Using the Configuration Menu
Advanced > Performance > 802.11b+
Wireless
Performance-
Data Rate-
select 802.11a or 802.11g. Here, 802.11a has been
chosen. This screen displays the wireless performance
features of the Access Point portion of the DI-774.
Auto is the default selection. Select from the drop down menu
for your selection.
Transmit Power- full is the default selection. Select from the drop down menu for
your selection.
Beacon interval- beacons are packets sent by the DI-774 to synchronize a wire-
less network. Specify a value. 100 is the default setting and is
recommended.
RTS Threshold-
Fragmentation-
DTIM interval-
Authentication-
Open System -
Shared Key - in this mode, in order to access the DI-774 on the network, the
this value should remain at its default setting of 2346. If inconsistent data flow is a problem, only a minor modification should
be made.
this value should also remain at its default setting of 2346. If
you experience a high packet error rate, you may slightly increase your Fragmentation value within the range of 256-2346.
Setting the Fragmentation value too low may result in poor performance.
(Delivery Traffic Indication Message) 1 is the default setting. A
DTIM is a countdown informing clients of the next window for
listening to broadcast and multicast messages.
select Open system or Shared Key
the DI-774 will be visible to all devices on the network. This is the
default setting
device must be listed in the MAC Address Control List
Wireless
Performance-
TX Rates-
Transmit Power-
Beacon interval-
Select 802.11a or 802.11g. 802.11g is selected here. Displayed
in this window are the Wireless Performance features for the
Access Point portion of the DI-774.
Auto is the default selection. Select from the drop down menu
for your selection.
full is the default selection. Select from the drop down menu for
your selection.
beacons are packets sent by the DI-774 to synchronize a wireless network. Specify a value. 100 is the default setting and is
recommended.
RTS Threshold- this value should remain at its default setting of 2346. If incon-
sistent data flow is a problem, only a minor modification should
be made.
Fragmentation-
DTIM interval-
Authentication-
Open System -
Shared Key -
this value should also remain at its default setting of 2346. If you
experience a high packet error rate, you may slightly increase
your Fragmentation value within the range of 256-2346. Setting
the Fragmentation value too low may result in poor performance.
(Delivery Traffic Indication Message) 1 is the default setting. A
DTIM is a countdown informing clients of the next window for
listening to broadcast and multicast messages.
select Open system or Shared Key
the DI-774 will be visible to all devices on the network. This is the
default setting
in this mode, in order to access the DI-774 on the network, the
device must be listed in the MAC Address Control List
3130
Page 17

Using the Configuration Menu
CTS Mode-
None-
Always-
Auto- CTS wilCTS will monitor the wireless network and automati-
Tools> Admin
CTS (Clear To Send) is a function used to minimize collisions
among wireless devices on a wireless local area network
(LAN). CTS will make sure the wireless network is clear
before a wireless client attempts to send wireless data.
Enabling CTS will add overhead and may lower wireless
throughput.
CTS is typically used in a pure 802.11g environment. If CTS
is set to “None” in a mixed mode environment populated by
802.11b clients, wireless collisions may occur frequently.
CTS will always be used to make sure the wireless LAN is
clear before sending data.
cally decide whether to implement CTS based on the amount
of traffic and collisions that occurs on the wireless network.
l always be used to make sure the wireless LAN is clear
before sending data.
Using the Configuration Menu
Remote Management
Remote Management allows the DI-774 to be configured from the Internet by a web
browser. A username and password is still required to access the Web-Management
interface. In general, only a member of your network can browse the built-in web
pages to perform “Administrator” tasks. This feature enables you to perform
“Administrator” tasks from the remote (Internet) host.
IP Address: Internet IP address of the computer that has access to the Router. It is
not recommended that you set the IP address to * (star), because this allows any
Internet IP address to access the Router, which could result in a loss of security for
your network. If you elect to enable Remote Management, make sure to enter the
IP Address of the remote computer allowed to configure the DI-774.
Port: For security purposes, select a separate port number used to access the
Router. (The following is an example only; you may use a different port number.)
Example: http://x.x.x.x:8080 where x.x.x.x is the WAN IP address of the Router
and 8080 is the port used for the Web-Management interface.
Tools > Time
Administrator
Login Name
User
Login Name
Admin Password-
User Password-
admin is the default login name for the Admin account. Admin
account has read/write access to the router.
user is the default login name for the User account. User ac-
count has read-only access to the router.
the default setting is blank - no password. To change the pass-
word, enter and confirm the new password.
the default setting is blank - no password. To change the pass-
word, enter and confirm the new password.
Time settings- in this window you can choose the time zone ; set the time;
and enable or disable Daylight Savings Time.
Default
NTP Server-
NTP is short for Network Time Protocol. NTP synchronizes computer clock times in a network of computers.
This field is optional.
3332
Page 18

Using the Configuration Menu
Using the Configuration Menu
Tools > System
Tools > Firmware
System Settings
Save Settings to
Local Hard Drive-
Load Settings from
Local Hard Drive-
Restore to Factory
Default Settings- click Restore to restore the factory default settings
click Save to save the current settings to the local Hard Drive
click Browse to find the settings, then click Load
Firmware Upgrade-
Browse-
click on the link in this screen to find out if there is an updated
firmware; if so, download the new firmware to your hard drive.
after you have downloaded the new firmware, click Browse in
this window to locate the firmware update on your hard drive.
Click Apply to complete the firmware upgrade.
3534
Page 19

Using the Configuration Menu
Using the Configuration Menu
Tools > Misc
Ping Test-
the Ping Test is used to send Ping packets to test if a computer
is on the Internet. Enter the IP Address that you wish to Ping,
and click Ping
Restart Device- click Reboot to restart the DI-774
Block WAN Ping-
Discard Ping
from WAN side-
VPN
Pass Through-
if you choose to block WAN Ping, the WAN IP Address of the
DI-774 will not respond to pings. Blocking the Ping may provide
some extra security from hackers.
click Enabled to block the WAN ping
the DI-774 supports VPN (Virtual Private Network) pass-through
for both PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) and IPSec
(IP Security). Once VPN pass-through is enabled, there is no
need to open up virtual services. Multiple VPN connections
can be made through the DI-774. This is useful when you have
many VPN clients on the LAN network.
PPTP- select Enabled or Disabled
IPSec- select Enabled or Disabled
DDNS-
fill in the required fields to use the Dynamic Domain Name Service (DDNS) feature.
Status > Device Info
Device Information- This screen displays information about the DI-774
Status > Log
View Log- this screen displays the activity on the DI-774
Log Settings-
for advanced features, click on Log Settings
3736
Page 20

Using the Configuration Menu
Status > Log > Log Settings
Using the Configuration Menu
Status > Stats
SMTP Server /
IP Address-
Email Address-
Log Type-
enter the proper SMTP Server information or the IP address
enter the email address of the receipient who will receive the
email logs.
admin can specify which surveillance they want to log. Check
mark the box for specific activities.
Traffic Statistics-
Status > Wireless
Connected
Wireless
Client List-
displays the receive and transmit packets that are passing
through the DI-774. Click on Refresh, for the most recent infor-
mation. Click Reset to reset the counters back to zero.
displays the wireless clients that are connected
to the Access Point function of the DI-774.
3938
Page 21

Using the Configuration Menu
Help
Networking Basics
Using the Network Setup Wizard in Windows XP
In this section you will learn how to establish a network at home or work,
using Microsoft Windows XP.
Note: Please refer to websites such as http://www.homenethelp.com
and http://www.microsoft.com/windows2000 for information about
networking computers using Windows 2000, ME or 98.
Go to Start>Control Panel>Network Connections
Select Set up a home or small office network
Help- displays the complete Help menu. For help at anytime, click
the Help tab in the Configuration menu.
When this screen appears, Click Next.
4140
Page 22

Networking Basics
Networking Basics
Please follow all the instructions in this window:
Click Next
In the following window, select the best description of your computer. If your
computer connects to the internet through a gateway/router, select the
second option as shown.
Enter a Computer description and a Computer name (optional.)
Click Next
Enter a Workgroup name. All computers on your network should have the
same Workgroup name.
Click Next
Click Next
4342
Page 23

Networking Basics
Please wait while the Network Setup Wizard applies the changes.
When the changes are complete, click Next.
Networking Basics
In the window below, select the option that fits your needs. In this example, Create
a Network Setup Disk has been selected. You will run this disk on each of the
computers on your network. Click Next.
Please wait while the Network Setup Wizard configures the computer.
This may take a few minutes.
Insert a disk into the Floppy Disk Drive, in this case drive A.
Format the disk if you wish, and click Next.
4544
Page 24

Networking Basics
Please read the information under Here’s how in the screen below. After you com-
plete the Network Setup Wizard you will use the Network Setup Disk to run the
Network Setup Wizard once on each of the computers on your network. To continue
click Next.
Networking Basics
Please read the information on this screen, then click Finish to complete the
Network Setup Wizard .
The new settings will take effect when you restart the computer. Click Yes to
restart the computer.
You have completed configuring this computer. Next, you will need to run the
Network Setup Disk on all the other computers on your network. After running the Network Setup Disk on all your computers, your new wireless network will be ready to use.
4746
Page 25

Networking Basics
Naming your Computer
To name your computer, please follow these directions:In Windows XP:
Click Start (in the lower left corner of the screen)
n
Right-click on My Computer
n
Select Properties and click
n
Networking Basics
Naming your Computer
n In this window, enter the
Computer name
Select Workgroup and enter
n
the name of the Workgroup
All computers on your network
n
must have the same
Workgroup name.
Click OK
n
Checking the IP Address in Windows XP
Select the Computer
n
Name Tab in the System
Properties window.
n
You may enter a Computer Description if you
wish; this field is optional.
To rename the computer
n
and join a domain, Click
Change.
The wireless adapter-equipped computers in your network must be in the same IP Address range (see Getting Started in this manual for a definition of IP Address Range.) To
check on the IP Address of the adapter, please do the following:
Right-click on the
n
Local Area
Connection icon
in the task bar
Click on Status
n
4948
Page 26

Networking Basics
Checking the IP Address in Windows XP
This window will appear.
Click the
n
Support tab
Click Close
n
Assigning a Static IP Address in Windows XP/2000
Note: Residential Gateways/Broadband Routers will automatically assign IP Addresses to the computers on the network, using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) technology. If you are using a DHCP-capable Gateway/Router you
will not need to assign Static IP Addresses.
If you are not using a DHCP capable Gateway/Router, or you need to assign a Static IP
Address, please follow these instructions:
Networking Basics
Assigning a Static IP Address in Windows XP/2000
Double-click on
n
Network
Connections
n
Go to Start
n
Double-click on
Control Panel
Right-click on Local Area
n
Connections
Double-click on
n
Properties
5150
Page 27

Networking Basics
Assigning a Static IP Address
in Windows XP/2000
Click on Internet Protocol
n
(TCP/IP)
Click Properties
n
Networking Basics
Assigning a Static IP Address with Macintosh OSX
Go to the Apple Menu and se-
n
lect System Preferences
n
cClick on Network
Select Built-in Ethernet in the
n
Show pull-down menu
Input your IP address and
n
subnet mask. (The IP
Addresses on your network
must be within the same
range. For example, if one
computer has an IP Address
of 192.168.0.2, the other
computers should have IP
Addresses that are
sequential, like 192.168.0.3
and 192.168.0.4. The
subnet mask must be the
same for all the computers
on the network.
Enter the IP Address
n
of the Default
Gateway (in this case
it is 192.168.0.1 for
the DI-774)
n
Input your DNS server
address.
The DNS server address will be supplied by your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
If the DNS Server address is not available from your ISP, you may input 192.168.0.1
in this field.
n Click OK
Select Manually in the
n
Configure pull-down menu
n Input the Static IP Address,
the Subnet Mask and the
Router IP Address in the
appropriate fields
Input the Domain Name
n
Server address. Your ISP
(Internet Service Provider)
will provide the IP address of
the DNS Server. If the DNS
Server address is not available from your ISP, you may
input 192.168.0.1 in this field.
Click Apply Now
n
5352
Page 28

Networking Basics
Selecting a Dynamic IP Address with Macintosh OSX
Go to the Apple Menu and select
n
System Preferences
Click on Network
n
Select Built-in Ethernet in the
n
Show pull-down menu
Select Using DHCP in the
n
Configure pull-down menu
Click Apply Now
n
The IP Address, Subnet
n
mask, and the Router’s IP
Address will appear in a few
seconds
Networking Basics
Checking the Wireless Connection by Pinging in Windows XP and
2000
Go to Start > Run >
n
type cmd. A window
similar to this one
will appear. Type
ping
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx,
where xxx is the IP
Address of the
Wireless Router or
Access Point. A
good wireless
connection will show
four replies from the
Wireless Router or
Acess Point, as
shown.
Checking the Wireless Connection by Pinging in Windows Me
and 98
Go to Start > Run
n
> type command.
A window similar to
this will appear.
Type ping
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
where xxx is the IP
Address of the
Wireless Router or
Access Point. A
good wireless
connection will
show four replies
from the wireless
router or access
point, as shown.
5554
Page 29

Networking Basics
Adding and Sharing Printers in Windows XP
Networking Basics
Adding a local printer (a printer connected directly to a computer)
After you have run the Network Setup Wizard on all the computers in your network
(please see the Network Setup Wizard section at the beginning of Networking
Basics,) you can use the Add Printer Wizard to add or share a printer on your
network.
Whether you want to add a local printer (a printer connected directly to one computer,)
share an LPR printer (a printer connected to a print server) or share a network
printer (a printer connected to your network through a Gateway/Router,) use the Add
Printer Wizard . Please follow the directions below:
First, make sure that you have run the Network Setup Wizard on all of the
computers on your network.
On the following pages, we will show you these 3 ways to use the Add Printer Wizard:
1. Adding a local printer
2. Sharing network printer
3. Sharing an LPR printer
(Other Networking Tasks)
For help with other tasks, that we have not covered here, in home or small office
networking, see Using the Shared Documents folder and Sharing files and folders
in the Help and Support Center in Microsoft Windows XP.
A printer that is not shared on the network and is connected directly to one computer
is called a local printer. If you do not need to share your printer on a network,
follow these directions to add the printer to one computer.
Go to
n
Start>
Printers
and Faxes
Click on Add a printer
n
5756
Page 30

Networking Basics
Adding a local printer
Click Next
n
Networking Basics
Adding a local printer
Select and highlight
n
the correct driver for
your printer.
Click Next
n
(If the correct driver is
not displayed, insert the
CD or floppy disk that
came with your printer
and click Have Disk.)
Select Local printer
n
attached to this
computer
(Deselect Automati-
n
cally detect and install
my Plug and Play
printer if it has been
selected.)
Click Next
n
Select Use the
n
following port:
From the pull-down
n
menu select the correct
port for your printer
(Most computers use the LPT1: port,
as shown in the illustration.)
Click Next
n
At this screen, you can
n
change the name of
the printer (optional.)
Click Next
n
Select Yes, to print a
n
test page. A successful
printing will confirm that
you have chosen the
correct driver.
Click Next
n
5958
Page 31

Networking Basics
Adding a local printer
This screen gives you information about your printer.
Click Finish
When the test page has printed,
Networking Basics
Adding a local printer
Go to Start> Printers
n
and Faxes
A successful installation will display
the printer icon as shown at right.
You have successfully added a local
printer.
Click OK
Sharing a network printer
After you have run the Network Setup Wizard on all the computers on your net-
work, you can run the Add Printer Wizard on all the computers on your network.
Please follow these directions to use the Add Printer Wizard to share a printer on
your network:
Go to Start>
n
Printers and Faxes
6160
Page 32

Networking Basics
Sharing a network printer
Click on
n
Add a printer
Click Next
n
Networking Basics
Sharing a network printer
Select Browse for
n
a printer
Click Next
n
Select the printer you
would like to share
Click Next
n
Select
n
Network Printer
Click Next
n
Click Finish
n
6362
Page 33

Networking Basics
Sharing a network printer
Networking Basics
Sharing an LPR printer
To check for proper
n
installation:
Go to Start > Printers
n
and Faxes
The printer icon will appear at right,
indicating proper installation.
You have completed adding the
printer.
To share this printer
on your network:
Remember the printer
n
name
Run the Add Printer
n
Wizard on all the
computers on your
network
To share an LPR printer (using a print server,) you will need a Print Server such as
the DP-101P+. Please make sure that you have run the Network Setup Wizard on
all the computers on your network. To share an LPR printer, please follow these
directions:
Go to Start >
n
Printers and
Faxes
Click on Add
n
a Printer
The screen to the
right will appear
Click Next
n
Select
n
Local
Printer...
Make sure you have
n
already run the
Network Setup
Wizard on all the
network computers
After you run the Add Printer
Wizard on all the computers in the
network, you can share the printer.
Click Next
n
6564
Page 34

Networking Basics
Sharing an LPR printer
Select Create a new port
n
Networking Basics
Sharing an LPR printer
From the pull-down menu,
n
select Standard TCP/IP
Port, as shown.
Click Next
n
Please read the
n
instructions on this
screen
Click Next
n
Enter the Printer IP
n
Address and the Port
Name, as shown.
In this
n
screen,
select
Custom
Click
n
Settings
Enter the Port
n
Name and the
Printer Name
or
IP Address.
Select LPR
n
Enter a
n
Queue Name
(if your PrintServer/
Gateway has
more than
one port, you
will need a
Queue
name.)
Click Nextn
Click OKn
6766
Page 35

Networking Basics
Sharing an LPR printer
This screen will show you
n
information about your
printer.
Click Finish
n
n
Select the printer you
are adding from the list
of Printers.
Insert the printer driver disk
n
that came with your printer.
Networking Basics
Sharing an LPR printer
You can rename your printer if
n
you choose. It is optional.
Please remember the name of
n
your printer. You will need this
information when you use the
Add Printer Wizard on the
other computers on your
network.
Click Next
n
Select Yes, to print a test page.
n
Click Have Disk
n
If the printer driver is already installed,
do the following:
Select Keep existing
n
driver
Click Next
n
Click Next
n
This screen will display information about your printer.
Click Finish to complete the
n
addition of the printer.
Please run the Add Printer
n
Wizard on all the computers
on your network in order to
share the printer.
Note: You must run the Network Setup Wizard on all the computers on your network before
you run the Add Printer Wizard.
6968
Page 36

Troubleshooting
This Chapter provides solutions to problems that can occur during the installation and
operation of the DI-774 Wireless Broadband Router. We cover various aspects of the
network setup, including the network adapters. Please read the following if you are
having problems.
Note: It is recommended that you use an Ethernet connection to
configure the DI-774 Wireless Broadband Router.
1.The computer used to configure the DI-774 cannot access the
Configuration menu.
Check that the Ethernet LED on the DI-774 is ON. If the
n
LED is not ON, check that the cable for the Ethernet
connection is securely inserted.
Check that the Ethernet Adapter is working properly. Please
n
see item 3 (Check that the drivers for the network
adapters are installed properly) in this Troubleshooting
section to check that the drivers are loaded properly.
n
Check that the IP Address is in the same range and subnet
as the DI-774. Please see Checking the IP Address in
Windows XP in the Networking Basics section of this
manual.
Note: The IP Address of the DI-774 is 192.168.0.1. All the computers on the
network must have a unique IP Address in the same range, e.g., 192.168.0.x.
Any computers that have identical IP Addresses will not be visible on the
network. They must all have the same subnet mask, e.g., 255.255.255.0
Do a Ping test to make sure that the DI-774 is responding.
n
Go to Start>Run>Type Command>Type ping 192.168.0.1.
A successful ping will show four replies.
Note: If you have
changed the default IP
Address, make sure to
ping the correct IP Address assigned to the
DI-774.
Troubleshooting
2. The wireless client cannot access the Internet in the
Infrastructure mode.
Make sure the wireless client is associated and joined with the correct Access
Point. To check this connection:
in the taskbar> select View Available Wireless Networks. The Connect to
Wireless Network screen will appear. Please make sure you have selected the
correct available network, as shown in the illustrations below.
Check that the IP Address assigned to the wireless adapter is within the
n
same IP Address range as the access point and gateway. (Since the
DI-774 has an IP Address of 192.168.0.1, wireless adapters must have
an IP Address in the same range, e.g., 192.168.0.x. Each device must
have a unique IP Address; no two devices may have the same IP
Address. The subnet mask must be the same for all the computers on
the network.) To check the IP Address assigned to the wireless adapter,
double-click on the Local Area Connection icon in the taskbar >
select the Support tab and the IP Address will be displayed. (Please
refer to Checking the IP Address in the Networking Basics section of
this manual.)
If it is necessary to assign a Static IP Address to the wireless adapter,
n
please refer to the appropriate section in Networking Basics. If you are
entering a DNS Server address you must also enter the Default
Gateway Address. (Remember that if you have a DHCP-capable
router, you will not need to assign a Static IP Address. See
Networking Basics: Assigning a Static IP Address. )
Right-click on the Local Area Connection icon
default
7170
Page 37

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
3. Check that the drivers for the network adapters are
installed properly.
You may be using different network adapters than those illustrated here, but this
procedure will remain the same, regardless of the type of network adapters you are
using.
Select the
n
Hardware
Tab
Double-click
n
on Network
Adapters
Right-click on D-Link
n
AirPro DWL-A650
Wireless Cardbus
Adapter
Select Properties
n
to check that the
drivers are
installed properly
Click Device
n
Manager
Look under Device
n
Status to check that the
device is working
properly
Click OK
n
7372
Page 38

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
4. What variables may cause my wireless products to lose reception?
D-Link products let you access your network from virtually anywhere you want.
However, the positioning of the products within your environment will affect the
wireless range. Please refer to Installation Considerations in the Wireless
Basics section of this manual for further information about the most advantageous placement of your D-Link wireless products.
5. Why does my wireless connection keep dropping?
Antenna Orientation- Try different antenna orientations for the DI-774.
n
Try to keep the antenna at least 6 inches away from the wall or other
objects.
If you are using 2.4GHz cordless phones, X-10 equipment or other home
n
security systems, ceiling fans, and lights, your wireless connection will
degrade dramatically or drop altogether. Try changing the Channel on
your Router, Access Point and Wireless adapter to a different Channel
to avoid interference.
Keep your product away (at least 3-6 feet) from electrical devices that
n
generate RF noise, like microwaves, Monitors, electric motors, etc.
6. Why can’t I get a wireless connection?
To establish a wireless connection, while enabling Encryption on the DI-774,
you must also enable encryption on the wireless client.
7. Resetting the DI-774 to Factory Default Settings
After you have tried other methods for troubleshooting your network, you
may choose to Reset the DI-774 to the factory default settings.
Remember that D-Link Air Xpert products network together, out of the
box, at the factory default settings.
To hard-reset the D-Link Air Xpert DI-774 to Factory Default Settings, please
do the following:
n
Locate the Reset button on the back of the DI-774
Use a paper clip to press the Reset button
n
Hold for about 10 seconds and then release
n
For 802.11a, the Encryption settings are: 64, 128 or 152 bit. Make sure
n
that the encryption bit level is the same on the Router and the Wireless
Client.
For 802.11g, the Encryption settings are: 64, 128, or 152 bit. Make sure
n
that the encryption bit level is the same on the Router and the Wireless
Client.
Make sure that the SSID on the Router and the Wireless Client are exactly the
same. If they are not, wireless connection will not be established. Please note
that there are two separate SSIDs for 802.11a and 802.11g. The default SSID
for both 802.11a and 802.11g is default.
After the DI-774 reboots (this may take a few minutes)
n
it will be reset to the factory Default settings
7574
Page 39

Technical Specifications
Humidity:
• 5%-95%, non-condensing
Standards:
• Draft IEEE 802.11g
• IEEE 802.11b
• IEEE 802.11a
• IEEE 802.3 and IEEE 802.3u
• IEEE 802.3x
Ports:
• (4) 10/100Base-T Ethernet, RJ-45 (UTP)
• (1) WAN Port (Auto MDI/MDIX)
• (1) Power – 5V DC, 3.0A
Network Management:
• Web-Based Interface
Network Architecture:
• Supports Infrastructure Mode
Diagnostic LED:
• Power
• 100M Link/Act
• 10M Link/Act
• 11a WLAN
• 11g WLAN
Range:
• Indoors – up to 328 feet (100 meters)
• Outdoors – up to 1,312 feet (400 meters)
(Auto MDI/MDIX)
Emissions:
• FCC part 15b
• UL1950-3
Physical Dimensions:
• L = 9.25 inches
• W = 6.25 inches
• H = 1.375 inches
802.11a Specifications
Data Rates:
• 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54
Data Security:
• 64, 128, 152-bit w/dynamic keying
• Access Control List
Antenna Type:
• 5dBi dipole antenna with diversity
• Power parameter software configurable
Available Channels:
• Thirteen channels for North America
Frequency Range:
• 5.150 – 5.350 GHz
Modulation Technology:
• Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
Temperature:
Antenna Type:
• 5dBi dipole antenna with diversity
• Operating: 0ºC to 40ºC (32ºF to 104ºF)
• Storing: -25ºC to 60ºC (-77ºF to 140ºF)
7776
Page 40

802.11a Specifications (continued)
Modulation Techniques:
• BPSK
• QPSK
• 16 QAM
• 64 QAM
Contacting Technical Support
You can find the most recent software and user documentation on the D-Link
website.
D-Link provides free technical support for customers within the United States for the
duration of the warranty period on this product.
802.11g Specifications
Data Rates:
• 1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11,12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 Mbps (with Automatic
Fallback)
Data Security:
• 64, 128, 152-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) Encryption
Available Channels:
• Eleven channels for North America. Three non-overlapping.
Frequency Range:
• 2.4 – 2.4835 GHz
Modulation Technology:
• Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (DSSS) - 802.11g
• Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) - 802.11b
• Complementary Code Keying (CCK) - 802.11b
U.S. customers can contact D-Link technical support through our web site,
or by phone.
Tech Support for customers within the United States:
D-Link Technical Support over the Telephone:
(877) 453-5465
24 hours a day, seven days a week.
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://support.dlink.com
email:support@dlink.com
Tech Support for customers within Canada:
D-Link Technical Support over the Telephone:
(800) 361-5265
Monday to Friday 8:30am to 9:00pm EST
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://support.dlink.ca
email:support@dlink.ca
When contacting technical support, please provide the following information:
• Serial number of the unit
• Model number or product name
• Software type and version number
7978
Page 41

Warranty and Registration
(USA only)
Subject to the terms and conditions set forth herein, D-Link Systems, Inc. (“D-Link”) provides this Limited
warranty for its product only to the person or entity that originally purchased the product from:
• D-Link or its authorized reseller or distributor and
• Products purchased and delivered within the fifty states of the United States, the District of
Columbia, U.S. Possessions or Protectorates, U.S. Military Installations, addresses with an
APO or FPO.
Limited Warranty: D-Link warrants that the hardware portion of the D-Link products described
below will be free from material defects in workmanship and materials from the date of original retail
purchase of the product, for the period set forth below applicable to the product type (“Warranty
Period”), except as otherwise stated herein.
3-Year Limited Warranty for the Product(s) is defined as follows:
• Hardware (excluding power supplies and fans) Three (3) Years
• Power Supplies and Fans One (1) Year
• Spare parts and spare kits Ninety (90) days
D-Link’s sole obligation shall be to repair or replace the defective Hardware during the Warranty Period
at no charge to the original owner or to refund at D-Link’s sole discretion. Such repair or replacement will
be rendered by D-Link at an Authorized D-Link Service Office. The replacement Hardware need not be
new or have an identical make, model or part. D-Link may in its sole discretion replace the defective
Hardware (or any part thereof) with any reconditioned product that D-Link reasonably determines is
substantially equivalent (or superior) in all material respects to the defective Hardware. Repaired or
replacement Hardware will be warranted for the remainder of the original Warranty Period from the date
of original retail purchase. If a material defect is incapable of correction, or if D-Link determines in its sole
discretion that it is not practical to repair or replace the defective Hardware, the price paid by the original
purchaser for the defective Hardware will be refunded by D-Link upon return to D-Link of the defective
Hardware. All Hardware (or part thereof) that is replaced by D-Link, or for which the purchase price is
refunded, shall become the property of D-Link upon replacement or refund.
Limited Software Warranty: D-Link warrants that the software portion of the product (“Software”)
will substantially conform to D-Link’s then current functional specifications for the Software, as set forth
in the applicable documentation, from the date of original retail purchase of the Software for a period of
ninety (90) days (“Warranty Period”), provided that the Software is properly installed on approved
hardware and operated as contemplated in its documentation. D-Link further warrants that, during the
Warranty Period, the magnetic media on which D-Link delivers the Software will be free of physical
defects. D-Link’s sole obligation shall be to replace the non-conforming Software (or defective media)
with software that substantially conforms to D-Link’s functional specifications for the Software or to
refund at D-Link’s sole discretion. Except as otherwise agreed by D-Link in writing, the replacement
Software is provided only to the original licensee, and is subject to the terms and conditions of the
license granted by D-Link for the Software. Software will be warranted for the remainder of the original
Warranty Period from the date or original retail purchase. If a material non-conformance is incapable of
correction, or if D-Link determines in its sole discretion that it is not practical to replace the nonconforming Software, the price paid by the original licensee for the non-conforming Software will be
refunded by D-Link; provided that the non-conforming Software (and all copies thereof) is first returned
to D-Link. The license granted respecting any Software for which a refund is given automatically
terminates.
Non-Applicability of Warranty: The Limited Warranty provided hereunder for hardware and software
of D-Link’s products will not be applied to and does not cover any refurbished product and any product
purchased through the inventory clearance or liquidation sale or other sales in which D-Link, the sellers,
or the liquidators expressly disclaim their warranty obligation pertaining to the product and in that case,
the product is being sold “As-Is” without any warranty whatsoever including, without limitation, the
Limited Warranty as described herein, notwithstanding anything stated herein to the contrary.
Submitting A Claim: The customer shall return the product to the original purchase point based on its
return policy. In case the return policy period has expired and the product is within warranty, the
customer shall submit a claim to D-Link as outlined below:
• The customer must submit with the product as part of the claim a written description of the
Hardware defect or Software nonconformance in sufficient detail to allow D-Link to confirm
the same.
• The original product owner must obtain a Return Material Authorization (“RMA”) number from
the Authorized D-Link Service Office and, if requested, provide written proof of purchase of
the product (such as a copy of the dated purchase invoice for the product) before the
warranty service is provided.
• After an RMA number is issued, the defective product must be packaged securely in the
original or other suitable shipping package to ensure that it will not be damaged in transit, and
the RMA number must be prominently marked on the outside of the package. Do not include any
manuals or accessories in the shipping package. D-Link will only replace the defective portion
of the Product and will not ship back any accessories.
• The customer is responsible for all in-bound shipping charges to D-Link. No Cash on Delivery
(“COD”) is allowed. Products sent COD will either be rejected by D-Link or become the
property of D-Link. Products shall be fully insured by the customer. D-Link will not be held
responsible for any packages that are lost in transit to D-Link. The repaired or replaced
packages will be shipped to the customer via UPS Ground or any common carrier selected by
D-Link, with shipping charges prepaid. Expedited shipping is available if shipping charges are
prepaid by the customer and upon request.
• Return Merchandise Ship-To Address
USA: 53 Discovery Drive, Irvine, CA 92618
Canada: 2180 Winston Park Drive, Oakville, ON, L6H 5W1 (Visit http://www.dlink.ca for detailed
warranty information within Canada)
D-Link may reject or return any product that is not packaged and shipped in strict compliance with the
foregoing requirements, or for which an RMA number is not visible from the outside of the package. The
product owner agrees to pay D-Link’s reasonable handling and return shipping charges for any product
that is not packaged and shipped in accordance with the foregoing requirements, or that is determined
by D-Link not to be defective or non-conforming.
What Is Not Covered: This limited warranty provided by D-Link does not cover: Products, if in D-Link’s
judgment, have been subjected to abuse, accident, alteration, modification, tampering, negligence, misuse,
faulty installation, lack of reasonable care, repair or service in any way that is not contemplated in the
documentation for the product, or if the model or serial number has been altered, tampered with, defaced
or removed; Initial installation, installation and removal of the product for repair, and shipping costs;
Operational adjustments covered in the operating manual for the product, and normal maintenance;
Damage that occurs in shipment, due to act of God, failures due to power surge, and cosmetic damage;
Any hardware, software, firmware or other products or services provided by anyone other than DLink; Products that have been purchased from inventory clearance or liquidation sales or other sales in
which D-Link, the sellers, or the liquidators expressly disclaim their warranty obligation pertaining to the
product. Repair by anyone other than D-Link or an Authorized D-Link Service Office will void this
Warranty.
Disclaimer of Other Warranties: EXCEPT FOR THE LIMITED WARRANTY SPECIFIED HEREIN, THE
PRODUCT IS PROVIDED “AS-IS” WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY OF ANY KIND WHATSOEVER INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
AND NON-INFRINGEMENT. IF ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY CANNOT BE DISCLAIMED IN ANY TERRITORY
WHERE A PRODUCT IS SOLD, THE DURATION OF SUCH IMPLIED WARRANTY SHALL BE LIMITED TO
NINETY (90) DAYS. EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY COVERED UNDER THE LIMITED WARRANTY PROVIDED
HEREIN, THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY, SELECTION AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PRODUCT IS
WITH THE PURCHASER OF THE PRODUCT.
8180
Page 42

LIABILITY OF D-LINK UNDER THIS WARRANTY IS LIMITED TO THE PURCHASE PRICE OF THE PRODUCT
COVERED BY THE WARRANTY. THE FOREGOING EXPRESS WRITTEN WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES
ARE EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU OF ANY OTHER WARRANTIES OR REMEDIES, EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR
STATUTORY.
Governing Law: This Limited Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the State of California. Some
states do not allow exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, or limitations on how
long an implied warranty lasts, so the foregoing limitations and exclusions may not apply. This limited
warranty provides specific legal rights and the product owner may also have other rights which vary
from state to state.
Trademarks: D-Link is a registered trademark of D-Link Systems, Inc. Other trademarks or registered
trademarks are the property of their respective manufacturers or owners.
Copyright Statement: No part of this publication or documentation accompanying this Product may
be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative such as translation,
transformation, or adaptation without permission from D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems, Inc., as
stipulated by the United States Copyright Act of 1976. Contents are subject to change without prior
notice. Copyright© 2002 by D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
CE Mark Warning: This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio
interference, in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
FCC Statement: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and
can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communication. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged
to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures :
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
For detailed warranty outside the United States, please contact corresponding local
D-Link office.
FCC Caution:
The manufacturer is not responsible for any radio or TV interference caused by unauthorized
modifications to this equipment; such modifications could void the user’s authority to operate the
equipment.
(1) T he devices are restricted to indoor operations within the 5.15 to 5.25GHz range. (2) For this
device to operate in the 5.15 to 5.25GHz range, the devices must use integral antennas.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. The antenna(s) used for this equipment must be installed to provide a separation
distance of at least eight inches (20 cm) from all persons.
This equipment must not be operated in conjunction with any other antenna.
Register your D-Link product online at http://support.dlink.com/register/
82
(03/28/2003)
 Loading...
Loading...