Dell PowerConnect 7024P, PowerConnect M6348, PowerConnect 7048R, PowerConnect 7024F, PowerConnect 8024F User Manual
...Page 1

Dell™ PowerConnect™
8132/8164/8132F/8164F/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/
7048R-RA/8024/8024F/M6220/M6348/M8024/M8024-k
PowerConnect
5.1.1.7 Firmware Release Notes
Date: July 2013
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2003 – 2013 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the written pe r m is sion of Dell I nc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademark s used in this t ex t: Dell, the DE LL logo and PowerC o nnect are trademarks of D el l Inc; Intel and Pentium ar e r eg istered trademarks and
Celeron is a trademark of Intel Corporation; Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other trademarks and tr ade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entity claiming the marks and names or thei r products. Dell
Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own. All rights reserved. This document m ay not, in whole or
in part, be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated, or reduced to any electronic medium or machine-readable form without the prior written
consent of Dell. Dell reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products or specifications referred to herein to im prove
reliability, functionality or design.
Reproduction, adaptation or translation without prior written permission is prohibited, except as allowed under the copyrigh t laws.
Page 2
Table of Contents
Introduction 1
Global Support 1
Firmware Specifications 1
Firmware Upgrade 2
Firmware Downgrade 3
Boot Code Downgrade 4
Hardware Supported 4
Support Matrix 5
Supported Firmware Functionality 6
Added Functionality in this Release 7
Changed Functionality in this Release 14
Issues Resolved 22
CLI Reference Guide Updates 55
User’s Configuration Guide Updates 59
Known Issues 61
Known Restrictions and Limitations 70
System – 5.0.1.3 71
System – 5.0.0.4 71
Management – 4.2.1.3 72
Layer 2 – 4.2.0.4 73
Layer 3 – 4.2.0.4 74
Management – 4.2.0.4 74
Data Center – 4.2.0.4 75
End of Release Notes 76
2 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 3

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
PC8100v5.1.1.7.stk
PCM8024kv5.1.1.7.stk
5.1.1.7
5.1.1.7
July 2013
July 2013
Version Numbering Convention
Version number
Description
PowerConnect
5 1 1
7
Four part version number
Denotes an ad hoc release of the product software.
Denotes a scheduled maintenance release of the product software.
Denotes a major version number.
Introduction
This document provides specific information for the Dell PowerConnect
8132/8164/8132F/8164F/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA/8024/8024F/M6220/M6348/M8024/M8024-k
switches firmware versi on 5.1.1.7.
It is recommended that this release note be thoroughly reviewed prior to installing or upgrading of this product.
Global Support
For information regardi ng the latest available firmware, release note revisio ns, or additional assistance, please visit
support.dell.com.
Firmware Specifications
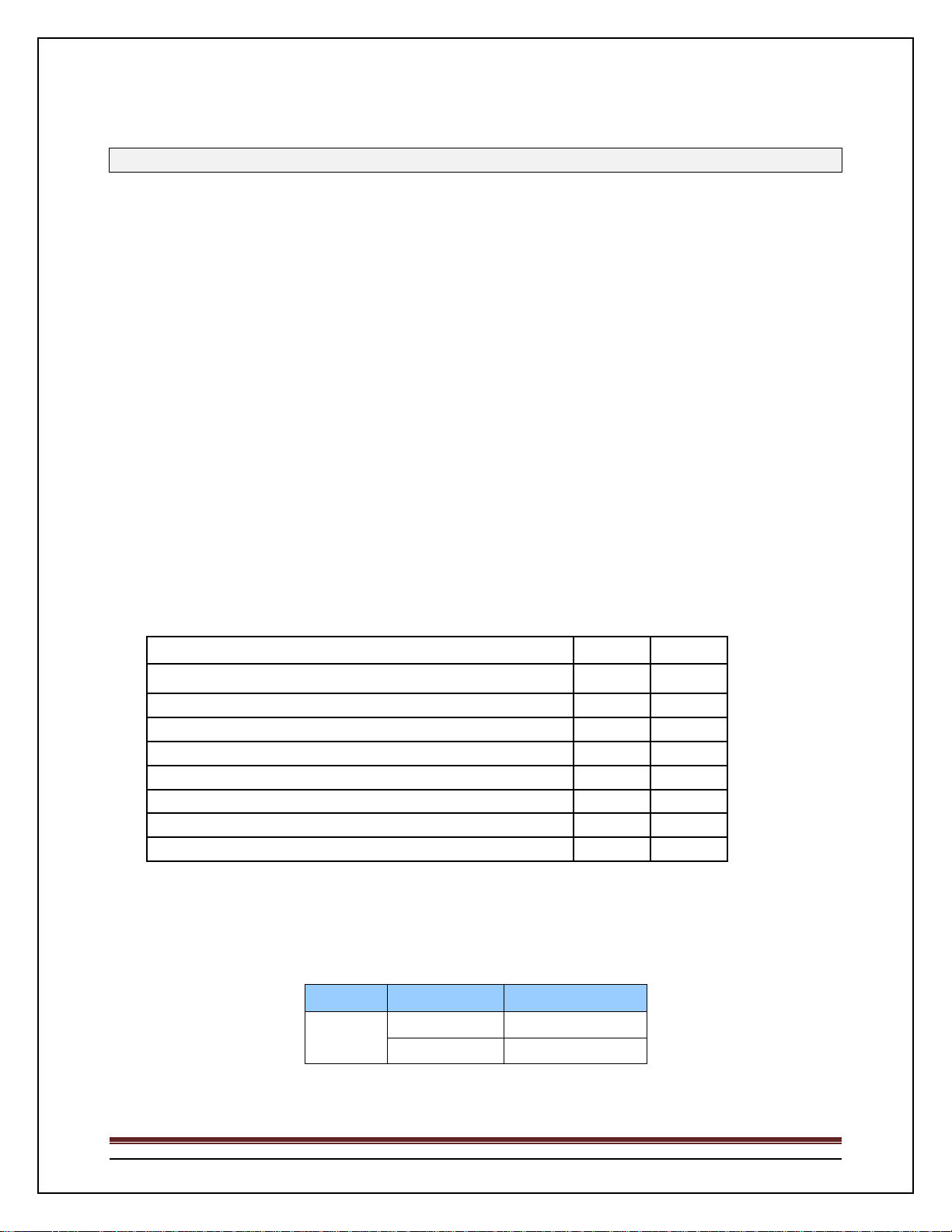
Firmware Version
Firmware Image Name Version Number Release Date
PCM6220v5.1.1.7.stk
PC7000_M6348v5.1.1.7.stk
PC8024v5.1.1.7.stk
PCM8024v5.1.1.7.stk
Series
5.1.1.7
5.1.1.7
5.1.1.7
5.1.1.7
Denotes the build number.
July 2013
July 2013
July 2013
July 2013
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 1
Page 4

Firmware Upgrade
NOTE: Administrators upgrading PowerConnect 7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/
7048R/7048R-RA/8024/8024F/M6220/M6348/M8024/ M8024k switches from 2.x.x.x or
3.x.x.x or 4.x.x.x or 5.x.x.x versions of firmware MUST follow the instructions
documented in the
Upgrading PowerConnect Switches from Version 2.x.x.x or 3.x.x.x
or 4.x.x.x or 5.x.x.x to 5.1.1.7 Firmware procedure. Failure to follow the procedure s
described in that document when upgrading from 2.x.x.x or 3.x.x.x or 4.x. x.x or 5.x.x.x
firmware may result in an inoperable switch!
NOTE: After upgradi ng the switch firmware version to 5.1.1.7, the CPLD (Complex
Programmable Logic Device) code update is required on M8024-k and P C8024/P C80 24F
switches via serial console if switch is running with the older CPLD version. The latest
CPLD version available for M8024k switch is Version 5 and for PC8024/PC8024F switch is
Version 6. Administrators upgrading PowerConnect 8024/ 8 0 2 4F/M8024k switches MUST
follow the CPLD update instructions documented in the
Upgrading PowerConnect
Switches from Version 2.x.x.x or 3.x.x.x or 4.x.x.x or 5.x.x.x to 5.1.1.7 Firmware
procedure.
NOTE: Administrators upgrading PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F switches
MUST follow the instr u ctions documented in the
Upgrading PowerConnect
8132_8164_8132F_8164F switche s from Version 5.x.x.x to 5.1.1.7
Firmware procedure. Failure t o follow the pro cedures described in that document w h en
upgrading firmware may result in an inoperable switch!
NOTE: OMNM (Open Manage Network Manager) v5.2 SP1 supports firmware
management of PowerConnect 7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048RRA/8024/8024F/M6220/M6348/M8024/M8024-k to deploy the firmware version 4.1.x.x or
later. OMNM v5.2 SP1 supports PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F t o deploy the
firmware version 5.0.0.4
2 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 5
PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Part Numbers for PowerConnect 81xx
A1 CPU
B1 CPU
PowerConnect 8132 (US, Canada, Mexico, South Ame r ic a)
TRJ78
PTM0F
PowerConnect 8132F
W0HV1
NWHGV
PowerConnect 8132F (all other countries)
7D1GN
KWHG3
H0F6C
N00C1
PowerConnect 8164 (all other countries)
P8RHX
Y2FJ0
PowerConnect 8164F (US, Canada, Mexico, South America)
VTWN8
4PHP2
PowerConnect 8164F
1JWM5
8KHT1
Firmware Downgrade
Downgrading from 5.1.1.7 to an earlier release is supported on most PowerConnect series switches (except PC81xx series
with B1 CPU versions, see note below); however, migration of configuration information from a later release to an earl ier
release is not supported. The existing configuration may or may not work with the earlier version of firmware, therefore, it is best
to be physically present at the switch site and to be prep ar ed to access the switch over the s er ial port if necessary when
downgrading firmware.
Auto-downgrade of a stack is not enabled by default. If downgrading a stack, be sure to enable auto-downgrade before activating
the earlier versions of firmware on the stack master.
Recent versions of the PowerConnect 81xx series switches support newer versions of CPU (B1). The B1 version of CPU
requires firmware release version 5.1.0.1 or later and cannot be downgraded to earlier firmware releases. In addition, if this unit is
to be deployed as a member within a stack, the entire stack will be required to run 5.1.0.1 or later firmware. Here are some st eps
to help determ i ne what CPU is in the PowerConnect 8100 Series switch:
1. Run show version from the CLI prompt.
2. If there is no CPU version line, then t he stack is r unning 5.0.x.x firmware . Since 5.0.x.x can onl y run on
A1 CPU switches, then all switches in the stack (or a standalone) contain A1 CPUs.
3. If there is a CPU version line (like below):
CPU Version....................... XLP308H-A1
(It will display the CPU version in the last two characters - either A1 or B1).
4. On a stack, r un show version m where m is the unit number assigned to the stack member to see each CPU
version for each member in the stack.
In addition here are the part numbers for reference:
PowerConnect 8132 (all other countries) 0C90P X20W5
(US, Canada, Mexico, So u th America)
PowerConnect 8164 (US, Canada, Mexico, South Ame r ic a)
(all other countries)
Recent versions of the PowerConnect M8024-K modular switches have hardware changes that require firmware version 4.1.0.19
or higher. Power C onne c t M 8 02 4-K with a new PPID label cannot be downgraded to the firmware version below 4.1.0.19. If a
downgrade is attempted, the firmware activatio n procedure will detect th at earlier firmware version is not compatible with the
switch hardware and abort the activation procedure. Any PowerConnect M8024-K with the old PPID label can accept any
version of the switch firmware.
MODEL OLD PPID NEW PPID
M8024K
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 3
2F07F A00 2F07F A01
57821 A00 57821 A01
Page 6
Boot Code Downgrade
Never downgrade the boot code! The 5.1.1.7 boot code supports all earlier versions of firmware and never needs downgrading.
Hardware Supported
• Dell PowerConnect 8132 Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect 8164 Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect 8132F Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect 8164F Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect M6220 Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect M6348 Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect 7024 Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect 7048 Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect 7024P Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect 7048P Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect 7024F Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect 7048R Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect 7048R-RA Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect 8024 Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect 8024F Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect M8024 Ethernet Switch
• Dell PowerConnect M8024-k Ethernet Switch
4 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 7
PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
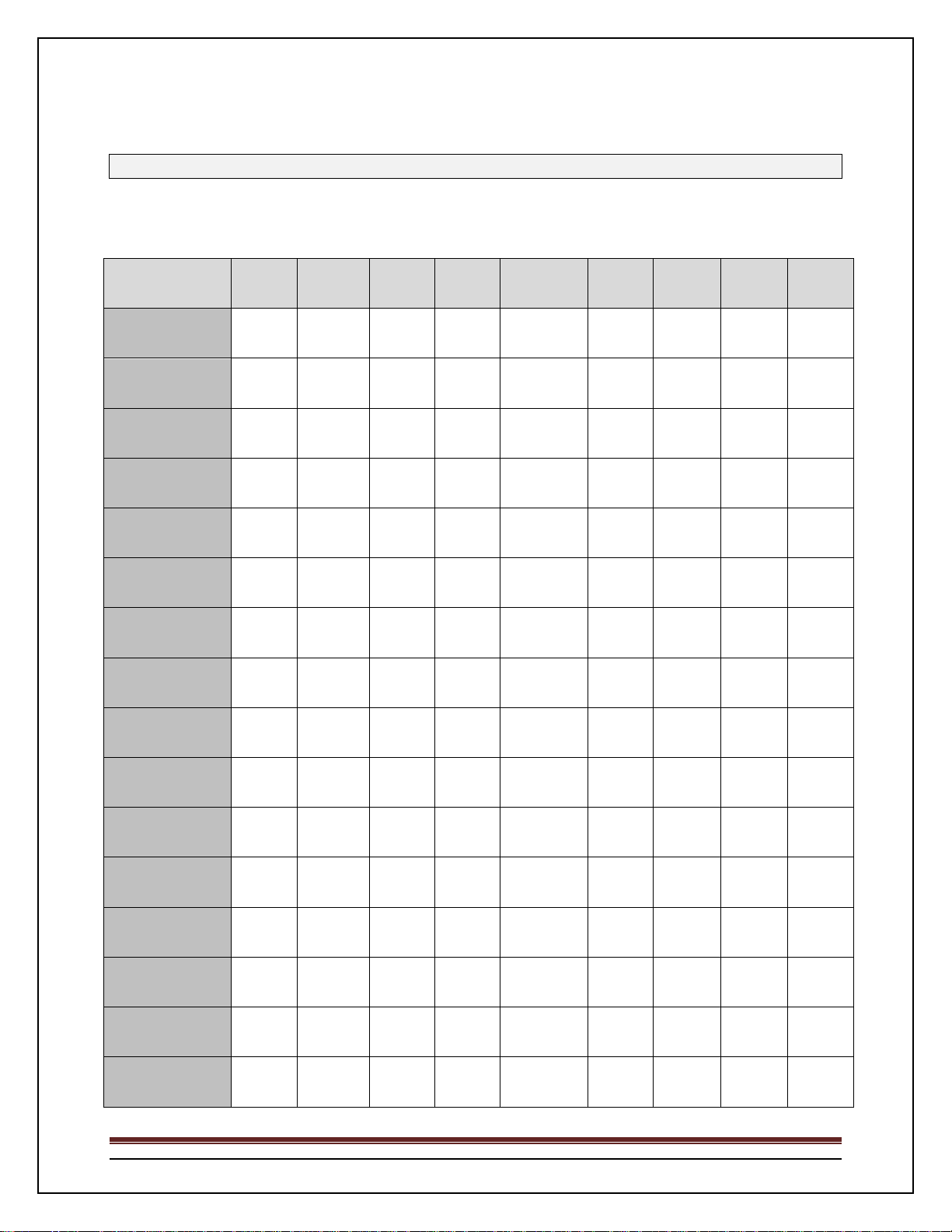
Support Matrix
Since not all functionality is supported on all switches, the following matrix identifies the major differences among the
PowerConnect switch models. A check mark indicates support for the feature. All other features listed in the release notes ar e
supported on all switches.
Feature/Switch
Dell PowerConnect
M6220 Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
M6348 Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
7024 Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
7048 Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
7024P Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
7048P Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
7024F Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
7048R Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
7048R-RA Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
8024 Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
8024F Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
M8024 Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
M8024-k Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
8132 Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
8164 Ethernet
Switch
Dell PowerConnect
8132F/8164F
Ethernet Switch
Priority
Flow
Control
DCBx ETS PoE+
iSCSI
Optimization
USB
grEEEn
Ethernet
Hot
Swap
Cards
WRED
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 5
Page 8

Supported Firmware Functionality
For more details regarding all the supported firmware features and functionality, please refer to the Dell PowerConnect Series
CLI Reference Guide and the Dell PowerConnect Series User’s Configuration Guide.
6 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 9

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Added Functionality in this Release
This section contains a list of features added in this rele ase that are new for at least one switch listed in the Hardware Supported
section above.
Release 5.1.1.7
No Added Functionality in this Release
Release 5.1.0.1
IGMP Snooping Improvements
IP Multicast Enhancements
Support for B1 CPU – only on PC8100 series
New Browser Support
• Mozilla Firefox 14
• Internet Explorer 9
• Google Chrome 21
Static Route Maximum Increased to 512 (for all switches except for M6220 series)
USB Auto-configuration expanded for multiple MAC Address support
Ability to reset stack port counters
Increased Maximum number of dot1x clients per port to 24
Commands to remove signed certificates/Keys
Support for Additional transceivers/optics
Release 5.0.1.3
Added PoE DC Disconnect HW support – on PC7000 series
Release 5.0.0.4
Added Native EEE Support for the PC8100 10GBaseT Ports
802.1Qaz (ETS) – on 8100 series
Support for 40 Gig (QSFP+) interfaces
Support for Bootcode upgrade from pre-4.x image to 5.x image without manual system reset.
Local Preference for LAG
Private VLAN
CLI output filtering
Routing Improvements for OSPF
UDLD
Administrative Profiles
AAA Authorization
TACACS+ Ac countin g
Stacking over QSFP+ ports
QSFP+ diagnostics
sFlow Support on Port Channels
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 7
Page 10
Release 4.2.2.3
No Added Functionality in this Release
Release 4.2.1.3
No Added Functionality in this Release
Release 4.2.0.4
DCBx on M8024-k/8024/8024F
FIP Snooping Bridge on M8024-k/8024/8024F
Add EEE Support for the PC7000 10GBaseT Ports
GUI EEE Power Savings Charts
RP Failover Performance Improvement
Flexible Dynamic LAG Limits
CLI Help Usability Improvements
Ability to Show Static Route Entries
CMC XML Support
Stacking Over Ethernet Por ts
Change Dell EqualLogic iSCSI Auto Detect to default
Add CLI Macro (Port Profile) for Dell Compellent Storage Equipment
Provide Dell EqualLogic DCBx TLV Auto Detect and Configuration on M8024-k/8024/8024F
Release 4.1.1.9
No Added Functionality in this Release
Release 4.1.0.19
Media-type CLI command
Added new command "media-type" to co nfigure an interface to select the specified media on a combo port. It is
recommended the administrators select the specific media type for the particular type of network connection they
expect to use. Users may observe a single port flap when the media type is changed from RJ45 to auto-select RJ45 and
only the corresponding SFP port is enabled. Refer to the CLI Reference Guide Up dates section below for th e complete
syntax.
Release 4.1.0.6
IPv4-Only Mode Optimization
PowerConnect switches allocate the maximum sizes for routing tables (and others, as applicable) for both IPv4 and
IPv6. Switch Performance Optimization allows the operator to optimize the allocation of switch silicon tables for
either IPv4 only or mixed IPv4/IPv6 operation. The template specified limits are enforced by routing components
when routes are bein g l earned. When IPv4 only mode is select ed, the following capabilities are disabled:
• DHCPv6 r elay
• DHCPv6 server
• IPv6 routing/forwarding
• OSPFv3
• IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
• Configured v6-over-v4 tunnels
• Automatic (6to4) tunnels
8 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 11
PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Blocked Destination
MAC Address
Blockcdp
Used to block CDP
PDU’s
N/A
0x2000
Blockvtp
Used to block VTP
PDU;s
N/A
0x2003
Blockdtp
Used to block DTP
PDU’s
N/A
0x2004
Blockudld
Used to block UDLD
PDU’s
N/A
0x0111
Blockpagp
Used to block PAGP
PDU’s
N/A
0x0104
Blocksstp
Used to block SSTP
PDU’s
N/A
0x010b
Blockall
Used to block all defined
Protocol Filtering PDU’s
01:00.0C:CC:CC:C0
N/A
Auto-Install
Link Local Protocol Filtering
• IPv6 Multicast
A reboot is required when changing to or from IPv4 mode.
USB based auto-install is an easy way to quickly bring up a switch with a known configuration. Network based autoinstall is useful in rolling out a configuration or firmware update to a group of switches or in maintaining a central
repository of switch configurations and firmware where the switches always obtain their firmware and configuration
from a central server.
The following clarifications are helpful in understanding the processing steps in auto-install:
• Always power on the switch that is desired to be the stack master first
• Auto-install never p ro ceeds if a startup-config file is present o n the (master) switch
• USB auto -install is attempted first. Network auto-install only proceeds if USB auto-install fails.
• If there are multiple .setup files present on the USB flash device, the powerconnect.setu p file is selected
• If a valid .setup file is not found on the USB flash device, the single .text file is used
• If multiple .text files are present, the powerconnect.text file is used.
Network based auto-install utilizes information obtained from a DHCP server. Refer to the documentation for a
discussion of the DHCP options used by Auto-Install.
When auto-install downloads a firmware image to switch memory, it compares the version to the current switch image.
If different, the image in memory is copied to the switch backup image and activatio n of the image is attempted. If
activation succeeds, the switch is rebooted and auto-install then attempts configuration file download.
Auto-in s tall configuration files are executed as a script. For more details on Auto-Install, refer to the User’s Guide.
Link Local Protocol Filtering blocks Cisco link local protocols from being flooded in the network. By default,
PowerConnect switches process and r es pond to Cisco CDP packets. However, i n networks where this capability is not
desirable or other Cisco proprietary packets are flooded over the network, the administrator can disable flooding of
Cisco link local protocols. The following table identifies the matching criteria for filtering Cisco proprietary packets:
Rule Type Rule Purpose
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 9
Ether Type
Page 12
DHCP Server
The PowerConnect Series switches support a si mpl e DH C P server capability for domains that do not wish to deploy a
redundant DHCP address assignment solution or who have need of a temporary solution while (re)deploying their
DHCP server solution.
In configuring DHCP scopes, be aware that the DHCP pool address and netmask must exactly match a VLAN address
and netmask assignment for D H CP addresses to be served over that VLAN.
Only a single manual IP address can be assigned to a pool. The address must have a netmask of 32 .
GMRP
The GARP Multicast Registration Protocol provides a mechanism that allows networking devices to dynamically
register (and de-register) Group membership information with the MAC networking devices attached to the same
segment, and for that information to be disseminated across all networking devices in the bridged LAN that support
Extended Filtering Services. The PowerConnect Series switches support GMRP as specified in IEEE 802.1Q 1998.
WRED
Weighted Random Early Drop is supported on certain PowerConnect series switches. Refer to the table at t he
beginning of this section for further information. CoS queue configuration involves the following hardware port queue
configuration parameters:
• schedul er type: strict vs. weighted
• minimum guaran teed bandwidth
• maximum allowed bandwidth (i.e. shaping)
• queue manage ment type: tail drop vs. WRED
• tail drop par ameters: threshold
• WRED parameters: minimum threshold, maximum threshold, drop probability
Tail drop and WRED parameters are specified individually for each supported drop precedence level.
In addition, the following are specified on a per-interface basis:
• queue management type: tail drop vs. WRED (only if per-queue configuration is not supported)
• WRED decay exponent
Switch administrators should remember to configure ingress ports as trusted or un-trusted. By default ingress ports
trust dot1p values.
Stack Firmware Synchronization
Stack firmware synchronization updates all stack members to the active firmware versi on on the master switch. Stack
firmware synchronization is enabled b y defaul t. Stack firmware downgrade is enabled by default.
Multicast VLAN Registration
Multicast VLAN Registration provides a method of coalescing multicast traffic requested by users on multiple VLANs
onto a single VLAN when carried over the network.
MVR does not require t ha t ei t her source or recei v e r ports uti li z e V LAN tagging.
Network planners are re min ded that multicast groups in the 224.0.0.x range are reserved for multicast control plane
traffic. Network planners should select multicast groups in another range for normal multicast traffic, e.g. 239.0.1.x
iSCSI Optimization
iSCSI Optimization automatically configures ports for use with the iSCSI protocol and tracks iSCSI sessions on the
PowerConnect 7000 and 8000 Series switches as well as t he PCM6348. Dell EqualLogic arrays are automatically
detected and configuration of Dell EqualLogic connected ports is perfor med automatically.
Administrators are advised that the configuration performed by enabling iSCSI optimization is not automatically
reversed on disabling the feature. The administrator will need to manually remove the configurat ion s e t ti ng s w he n
migrating Dell EqualLogic servers or iSCSI initiator ports to other ports or switches.
10 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 13
PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Detection of Dell EqualLogic arrays is keyed on receipt of the mandatory System Description TLV in the LLDP
packet. Disabling LLDP will effectively disable Dell EqualLogic array detection.
Dell EqualLogic arra ys are required to be upgraded to fir mwar e 5.0.2 or later in order to use the iSCSI Optimization
feature.
LLDP
Administrators should ensure that LLDP-MED is enabled in order to operate EEE. Disabli ng LLDP or LLD P-MED
will effectively disable EEE, IEEE 802.3at PoE+ high power negotiation and Dell EqualLogic array detection in the
iSCSI Optimization feature.
Connectivity Fault Management
Connectivity Fault Management performs Metro Et hernet maintenance functions. Dell PowerConnect CFM supports
the following functions defined in IEEE 802.1ag Draft 8.1:
• Path disco very (link trace messages)
• Fault detect ion (continuity check messa ge)
• Fault verification and isolation (loopback and link trace messages)
• Fault notification (alarm indication signal or SNMP trap).
Management IP Address Conflict Detection
Management IP address conflict detection activel y lo oks for duplicate IP address as s ignment and logs conflicts. Only
the last identified IPv4 address conflict is retained for display by a show command. Administrators may examine the
in- memory logs or the output from a SYSLOG server to identify the historical IP address conflicts. If console logging
is enabled for traps, a message will appear on the console indicating that an address conflict has o ccurred.
Email Alerting
Email alerting allows administrators to be notified via email regarding system events. Multiple email addresses can be
configured. The system will attempt to resol ve mai l servers specified with a FQDN immediately and, if su ccess fu l,
store the mail-server as an I P address. If a new IP address is subsequently assigned t o the mail server, the oper ator will
need to re-assign the email address on the switch.
Only the Mail User Agent functionality of RFC 4409 is implemented. The PowerConnect switch does not implem e nt
SMTP server functionality.
802.1X Monitor Mode
Monitor mode is a special debug mode that assists network administrators in configuring 802.1X authenticators. Users
attempting to authenticate using the authenticator are always granted access when monitor mode is enabled. All
interactions with th e s upplicant and the authenti cation server are logged.
Administrators are cautioned against enabling monitor mode in a deployed network where 802.1X users may gain
access to sensitive n etwork resources.
Time Controlled ACLs
Time controlled ACLs allow administrators to apply ACLs based on the time of day. Both periodic and absolute time
periods may be configured.
Administrators are cautioned that invalid (overlapping) periodic entries within a time range will prevent the time range
from being applied. Administrators are advised to t es t their periodic entries an d validate that they become active as
expected before deploying the time ranges in a production network. Administrators can check if a time range is act ive
by using the show time-range command.
It is recommended to enable ACL logging to ensure notice of ACL activation and de-activation.
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 11
Page 14
SNTP over IPv6
SNTP operates over IPv4 and IPv6 and may be configured using IPv4 or IPv6 addresses or DNS.
Strong Passwords
The strong passwords featu r e allows administrators to specify that local switch pas swords meet certain characteristics
considered to enhance network security.
Administrators are advi sed that the minimum character classes configuration must be enabled (value equal to 1 or
greater) along with enabling the strong password feature before the other minimum character class configurations are
enforced. These character class configurations are:
• Minimum number of uppercase letters.
• Minimum number of lowercase letters.
• Minimum number of numeric characters.
• Minimum number of special characters
The password strength restrictions do not apply to users configured for the internal authentication server.
Switch Auditing
Switch auditing enhances network security by logging sensitive administrative actions. Switch auditing logs the
following actions:
• Successful login
• Unsuccessful attempt to login
• Logout out from the switch
• Timed out logout from the switch
• Download file to the switch
• Upload file from the switch
• Remove file from the flash
• File changes on the flash
• Clear configu ration
• Add or remove user
• Change user acces s level
Use of a SYSLOG server for monitoring network events is highly recommended.
Authentication
The PowerConnect switches support authentication via a number of methods. The methods are specified in named
lists. Lists may be assigned to the enable and login access methods. The supported authentication methods are:
• Enable
• Line
• RADIUS
• TACACS
• IAS
• Local
• None
Methods are attempted in the order specified in the authentication list. If the authentication method rejects
authentication, the user login is rejected. If an authentication method fail s , e.g. unable to contact the authentication
server, the next method in the list is attempted. The IAS, local and none methods can never fail so, if specified, must
be last in the list.
The 802.1X authentication list cannot be named and only supports the RADIUS, IAS, or none authentication methods.
The 802.1X authentication can only have a single method.
12 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 15
PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Internal Authentication Server
The PowerConnect Series switches support 802.1X authentication of network users from an internal authentication
database. IAS users are given access to network resources. IAS is not a valid method for login or enable
authentication.
The IAS database can be downloaded to the switch using the “ias-users” target in the copy command. The i as -users
file takes the form of a configuration script, as follows:
configure
aaa ias-user username client-1
password my-password1
exit
aaa ias-user username client-2
password aa5c6c251fe374d5e306c62496c3bcf6 encrypted
exit
aaa ias-user username 1f3ccb1157
password 1f3ccb1157
exit
IAS users may also be configured via the web interface.
DNS Client
The PowerConnect Series switches support name resolu tion via an embedded DNS client. When a DNS name is
specified, it is attempted to be resolved against the configured DNS servers immediately. The PowerConnect switches
will store the resolved IP address. If the IP address of the host resolved via DNS changes, th e administrator will need
to update the configured IP address, either via DNS or manually.
If the switch is configured to obtain an address via DHCP, DNS server information received from the DHCP server is
used to populate the DNS client configuration.
Port Profiles (CLI Macros)
The PowerConnect series of switches provid es a convenient way to save and share common configurations through the
use of CLI macros. A CLI macro is a set of commands having a unique name. When a CLI macro is applied, the CLI
commands contained within the macro are executed and added to the running configuration. When the macro is
applied to an interface, th e exi sting interface configur ations are not lost; the new commands are added to the interface
and are saved in the running configuration.
A CLI macro may have keywords (variables) which are replaced by values provided when th e macro is applied (up to 3
keywords per macro). M acros can be applied to specific i nterfaces, a range of int er faces, or the global configuration.
Administrators may add their own macros or utilize the built-in macros.
Administrators are cautioned to ensure that a macro does not change command modes (e.g., change from inter fa ce
configuration mode to global configuration mode).
The software includes 6 built-in macros:
• profile-global - the global configuration used to enable RSTP and loop guard.
• profile-desktop - the int er face co nfiguration for incr eased network security and reliability when connecting a
desktop device, such as a PC, to a switch port.
• profile-phone - the in terface configuration used when connecting a desktop device such as a PC with an IP
phone to a switch port.
• profile-switch - the interface confi guration used when connecting an access switch and a distribution switch
or between access switches.
• profile-router - the interface configur ation used when connecting the switch and a WAN router.
• profile-wireless- the interface configur ation used when connecting the switch and a wireless access point.
Built-in macros may not be deleted or altered by the operator.
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 13
Page 16

Changed Functionality in this Release
This section contains commentary on significant differences from previous releases of firmware on PowerConnect switches, e.g.
the 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA/M6348/M6220/M8024/8024/8024F/M8024-k
switches. Dell PowerConnect series switches closely conform to networking industry standard operational capabilities and
administrative interfaces. The differences below should be studied carefully as attempting to configure or operate the
PowerConnect switches in the same manner as for previous releases of firmware for PowerConnect
8132/8164/8132F/8164F/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA/M6348/M6220/M8024/8024/8024F/M8024-k
switches may lead to unexpected results.
Release 5.1.1.7
No Changed Functionality in this Release
Release 5.1.0.1
IGMP Snooping
IGMP snooping is enabled by default.
Traffic addressed to res er ved multicast IP addr es ses is flooded.
Unregistered multicast is flooded to all ports in the VLAN until a multicast router port is identified.
Once mrouter port is identified the traffic is forwarded to mrouter port and listener ports only.
PIMSM
PIMSM Rendezvous Points can be positioned anywhere in the network, not just as the first hop router. Although
multiple Rendezvous Points can be configured, only one Rendezvous Point is active at any time.
Auto-Configuration
Auto-configuration recognizes any of the assigned internal switch’s MAC addresses when present in an autoconfiguration file. The switch re-writes the file to use th e base MAC address of the switch.
Dot1x Clients
The maximum number of 802.1x clients (i.e. supplicants) that can be authenticated per port is increased to 24. This
increase does not include a corresponding increase in the maximum number of 802.1x clients that are supported on an
entire switch or stack.
Release 5.0.1.3
No Changed Functionality in this Release
Release 5.0.0.4
Stacking Ports C hange
The maximum number of ports that can be configured for stacking per switch is limited to 8. This is done to ensure that
the Hardware limits for maximum stack trunk members are not exceeded.
Stacking Over QSFP+ Ports
Stacking is supported over standard QSFP+ ports at either 1x10G or 4x10G mode. The ports must be configured as
stacking ports.
14 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 17
PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Bootcode upgrade
Bootcode program is enhanced to automatically upgrade bootcode on migrating switches from pre-4.x version to 5.x
version.
Release 4.2.2.3
No Changed Functionality in this Release
Release 4.2.1.3
VoIP Phone Limits
The limitation on the number of VoIP phones has been increased to 576 phones for the
7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F
switches.
Release 4.2.0.4
LAG Limits
Ports can be formed into LAGs in a more flexible manner. The system supports up to 128 total LAGs. Up to 144 ports
can be assigned to dynamic LAGs. Up to 72 LAGs can be configured as dynamic. A LAG may contain up to 8 ports.
The M8024 supports 12 total LAGs (static or dynamic) with up to 24 ports assigned to dynamic LAGs.
Stacking Over Ethernet Por ts only on M8024-k/8024/8024F
Stacking is supported over standard Ethernet SFP+ ports. The ports must be configured as stacking ports.
iSCSI Default Changes
iSCSI optimization is enabled by default. iSCSI optimization will reconfigure ports that are attached to Dell
EqualLogic arrays to utilize spanning-tree portfast and unicast storm disable.
PowerConnect
Release 4.1.1.9
No Changed Functionality in this Release
Release 4.1.0.19
PHY microcode upgrade process
The PHY microcode upgrade process has been enhanced to upgrade the PHY microcode to the latest version base d on
PHY revision. If the user experiences problems links on the combo ports after the upgrade completes, a reboot may be
required in order to activate the new PHY firmware.
Asymmetric flow control
Asymmetric flow control is implemented for the PC8024X, PCM8024, PCM6348, PC70XX, and PCM8024-k
switches. The switch does not generate pause frames when congest ed. It will honor pause frames as per industry
standards.
Release 4.1.0.6
Authentication
The enable and line authentication methods will no longer perform authentication if a password for the method is not
configured. Previously, these methods would always succeed if no password was configured. To achieve the same
functionality, add the “none” method to the list after enable or line method.
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 15
Page 18
NOTE: It is recommended that administrators attach the service/out-of-
management of PowerConnect switches over the operational network.
The default authentication list for telnet and SSH has been changed to enableNetList. The only authentication method
contained in enableN etList is enabled. The net effect of these two changes is that a password is required to enter
privileged exec mode when using telnet or SSH.
Administrators wishing to maintain the previous PowerConnect behavior can set the default authentication list for
telnet and SSH to enableList, which has the enable and none authentication methods (no password required to enter
privileged exec mode). The following commands ch ange the telnet authentication method to enableList.
console(config)# line telnet
console(config)# enable authentication enableList
console(config)# exit
New Web Interface
The Web interface has been enhanced with new navigation features for ease of use.
CLI Syntax Changes
The CLI has changed significantly to be compatible with the PowerConnect switch standard CLI. Configurations for
previous releases may not be compatible with th is release and may need to be updated.
document for more info.
Unit/Slot/Port Naming Conventions
In-band interfaces are na med based on stack unit, slot, and port. Units range from 1-12. Slots range from 0-2. Ports
range from 1-48. Slots for plug-in modules are numbered 1 and 2. Fixed ports belong to slot 0.
The service port is still addressed using the out-of-band keyword.
Management VLAN Deprecated
The PowerConnect series switches do not have an in-band management VLAN by default. Administrators can
designate a VLAN for support of in-band management operations.
VLAN interface configuration mode enables routing
When executing the “in terface vlan x” command, routing is automatically enabled on that VLAN.
Service/Out-of-band Ethernet Port Defaults to DHCP Addressing
By default, the service/out-of-band Ethernet port will attempt to obtain an address via DHCP.
Refer Configuration Migration
band Ethernet port to a physically separate network for out-of-band
network management. The service port does not offer routing or
switching capabilities nor does it offer enhanced protection from DOS
attacks. Configure a VLAN on one or more in-band interfaces for
LACP Ports Inactive Until Attached
Ports in a LAG configured to use LACP (dynamic LAG) remain inactive (discard received traffic) u ntil they become
attached to the LAG. LACP ports that are attached to a LAG will enter the discarding state if they become detached
from the LAG for any reason.
Port level configuration for a port that is configured in a dynamic LAG is disregarded. Remove the port from the LAG
to restore use of the port level configuration.
Ports in a static LAG begin forwarding on link up. Ports in a static LAG disregard port level configuration. Configure
static LAG functions on the static LAG interface.
16 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 19

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
NOTE: It is recommended that administrators disable portfast and auto-
portfast on physical interfaces configured in a LAG. Portfast and autoportfast can interfere with an interface entering into LAG mode on a
reboot and possibly enable a packet sto rm .
Spanning Tree Changes
Administrators may assign more than 1024 VLANs to MSTP instances. Only VLANs that are configured on the
switch will forward traffic.
The PowerConnect swit ches implements the 802.1Q-2005 standard which builds on 802.1D-2004. 802.1D-2004
incorporates the 802.1t, 802.1w and 802.1s revisions. Port path costs are calculated based on the interface speed as
shown below and are dynamically recalculated on interface a ctivation and link sp eed changes.
External Port Path Cost values (Port Path Cost in 17.14 of 802.1D-2004) are applicable in STP, RSTP, and MST modes
(Ref. Table 17-3 802.1D-2004). Use the spanning-tree cost command in interface mode to set the external port path
cost.
Link Speed
10 Gb/s 2000
1 Gb/s 20000
100 Mb/s 200000
10 Mb/s 2000000
1 Mb/s 20000000
Internal Port Path Cost values are specific to MST mode only (Ref. Table 13-3 802.1Q-2005). Use the spanning-tree
mst <instance> cost command in interface mode to set the internal port path cost.
Link Speed
10 Gb/s 2000
1 Gb/s 20000
100 Mb/s 200000
10 Mb/s 2000000
1 Mb/s 20000000
User Configurable CLI Banners
Administrators may configure banners for the following: MOTD, login, and exec. The banners may consist of multiple
lines of text. Each new line will consume an extra two characters (CR/LF) that count against the maximum lengt h
banner that can be configured.
Captive Portal
Captive portal has been extended to support user logout and localization.
802.1Q
The following changes have been made to the operation of VLANs.
VLAN Membership:
Default Value
Default Value
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 17
Page 20
VRRP
By default, trunk ports participate in all VLANs. VLANs created after a trunk port is created are added to all trunk
ports. VLANs deleted are removed from all trunk ports. The operator may configure a trunk port to explicitly disallow
certain VLANs.
Native VLAN Configuration on T runk Ports:
It is now possible to configure the native VLAN on a port in trunk mode. Trunk mode ports will accept untagged
frames but will always transmit tagged frames except for the native VLAN which will always transmit untagged
frames. It is also possible to configure a trunk port to drop untagged frames by filtering on the native VLAN, e.g. by
using the switchport trunk allowed vlan remove command.
A trunk port always has a native VLAN (default is VLAN 1), so the default behavior is that untagged packets are
treated as if they are tagged in VLAN 1. To drop untagged packets, configure switchport trunk allowed vlan remove
<vlan> which has th e side effect of dropping tagged packets in that VLAN as well IIRC.
Switchport Mode Configuration Preserved:
When switching between switchport modes (access , trunk, and general), the switchport configuration applicable to the
selected mode is maintained. This means that when switching from one mode to another and back, the port will have
the same configuration as it had in the original mode. Only the configuration applicable to the selected mode is active
on the port.
The following enhancements have been made to the operation of VRRP to increase usability and robustness of
operation in the network:
Preemption Delay:
Per the VRRP RFC 3768, when preemption is enabled, the backup router discards advertisements until the master
down-timer fires. When the preemption delay timer is set to a non-zero val ue and the backup switch r eceives a PDU
with a lower priority from the master, then backup switch waits for the preemption delay value be fore advertising itself
as the master.
Timer Advertis e me nt Lear ni n g:
In VRRP, all participating routers should be configured with coherent advertisement timer interval values. The
operator can now enable t imer learning which causes a backup router to learn the master advertisement interval and
change its master down interval accordingly.
Ping-able VRRP Interfaces:
RFC 3768 specifies that a r outer may only accept IP packets s ent to the virtual router’s IP address if the router is the
address owner (master). In practice, this restriction makes it more difficult to troubleshoot network connectivity
problems.
This capability adds support for responding to pings by the VRRP master, but does not allow the VRRP Master to
accept other types of packets. A configuration option controls whether the router responds to Echo Requests sent to a
VRRP IP address. When enabled, the VRRP master responds to both fragmented and un-fragmented ICMP Echo
Request packets. The VRRP master responds to Echo Requests sent to the virtual router’s primary address or any of its
secondary addresses. When the VRRP master responds with an Echo Reply, the source IPv4 address is the VRRP
address and source MAC address is the virtual router’s MAC address. The VRRP master does not respond to pings
sent from the master.
Members of the virtual r outer who are in backup stat e discard ping packets destin ed to VRRP addresses, just as they
discard any Ethernet frame sent to a VRRP MAC address.
Fragmentation and Reassembly:
18 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 21

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
NOTE: By default, multicast frames are flooded by the switch. Utilize the
multicast frames.
Fragmentation and reassembly of VRRP packets is not supported.
DHCP Relay
The following enhancements have been made to the operation of DHCP Relay to bring the implementation into
conformance with RFC 4649:
DHCPv6 Relay Circuit Id/Remote I d Types
RFC 4649 specifies the IANA assignment of the Relay Circuit Id sub-option and Remote Id option. The
implementation has been changed so that the administrator can no longer assign a numerical value to these TLVs as the
IANA assigned number is now used. The administrator can still enable or disable the insertion of these TLVs in
messages sent to the DHCP server.
Relay Information Option:
The operator has the ability to enable DHCP Relay Information Options both globally and on a physical interface. The
interface configuration overrides the glob al configuration for the selected interface.
Relay Information Option Check:
When DHCP Option-82 insertion is enabled for a rel ay agent, the server should echo received Option 82 unaltered back
toward the client. The relay agent is required to strip Option 82 information before relaying the BOOTPREPLY to the
DHCP client. When enabled, the Relay Information Option Check will cause the BOOTPREPLY packet to be dropped
if invalid sub-options are echoed by the DHCP server.
L2 Address Table
The administrator can disable MAC address table aging.
The administrator can configure static forwarding of a MAC address on a specific VLAN.
mac address-table multicast filtering command to disable flooding of
LLDP Enhancements
Multiple Neighbor Support:
Multiple neighbors are supported on a single LLDP interface. The number of recognized neighbors is limited to two
per port or 834 LLDP neighbors on a fully stacked set of switches. There is no restriction on the number of neighbors
connected to an LLDP port. If more LLDP neighbors are pr es ent than are supported, then only the last two neighbors
that communicate with the local LLDP interface are recognized and any addit ional neighbors are ignored.
EEE Support:
Support is added to process/communicate the EEE TLV to partner devices. The EEE TLV is an 802.3 organizationally
specific TLV used to r eport on the EEE Data Link Layer capabilities.
LLDP-MED Support:
LLDP-MED uses LLDP’s organizationally specific TLV extensions and defines new TLVs which make it easier to
deploy VoIP in a wired or wireless LAN/MAN environment. The LLDP implementation supports the following TLVs:
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 19
Page 22
Mandatory 802.1AB TLVs
• Chassis ID TLV (subtype shall default to MAC Address)
• Port ID TLV (subtype shall default to MAC address
• TTL TLV
• MAC/PHY configuration/status TLV
• End of LLDP PDU
Optional 802.1AB TLV
• Systems Capabilities TLV
• Po wer via MDI TLV
NOT recommended
Mandatory LLDP-MED TLVs
• LLDP-MED Capabilities TLV
This TLV allows the network connectivity device to definitively determine wheth er particular connected
devices do support LLDP-MED and to discover which specific LLDP-MED TLVs the particular end point
devices are capable of su pporting as well as what specific device class they belo ng to.
• Network Policy TLV
This TLV allows the device to advertise its VLAN and associat ed Layer 2 priority and Layer 3 DSCP
attributes which apply for a set of specific protocol applications on this port.
• Location Identification TLV
This TLV provides the advertisement of location identifier information Class II endpoint Devices. This is
expected to be related to wire map or similar network topology data, such that the configuration of the
network Connectivity device is able to uniquely identify the physical location of the connected MED
endpoint.
• Extended Power-via-MDI TLV
This TLV allows for advanced power management between endpoints and network connectivity devices. It
transmits fine grained power requirement detail s . This TLV provides significantly more value than the
802.1AB Power via MDI TLV.
• EEE TLV
The EEE TLV is used to exchange information about the EEE Data Link Layer capabilities. Devices that
require longer wake up times prior to being able to accep t data on their receive path s may use the Data Link
Layer capabilities to negotiate for extended system wake up times from the transmitting link partner. This
mechanism may allow for more or less aggressive energ y savi ng modes.
D yna mic V LA N As sig n me nt
Dynamic VLAN assignment is intended to support the connection of hosts to a router with enhanced levels of service,
typically either security or QoS. This release supports dynamic VLAN assignment as assign ed from the RADIUS
server as part of port authentication. The following additional checks are performed in support of dynamic VLAN
assignment:
Before assigning the port to RADIUS assigned VLAN, dot1x checks if the given VLAN is in the VLAN database or
not. If the assigned VLAN is not in the VLAN database and dynamic VLAN assignment is enabled , a VLAN is
created on the port over which the client is authenticated. Each time a client is de-authenticated on an interface with a
particular VLAN, a check verifies if there any other interface which a VLAN member is . If there is no interface as a
member, the VLAN is deleted. This behavior is same for MAC b ased authentication as well.
Usability Enhancements
In the output of the show running-config command, the slot and member configuration is commented with the
switch/slot type in human comprehensible form.
When in interface config mode, CLI users can navigate to a different interface b y enter ing the appropriat e interface
command without leaving interface config mode.
CLI users can log out of the switch using the exit command (exit is an alias for quit).
The CLI Reference Guide is updated with acceptable character sets and maximum length s fo r s tring parameters to
commands.
Management ACLs permit specification of service any as shorthand for enabling all services access for in-band
management.
for transmission in order to conserve LLDPDU space.
20 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 23
PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
VLANs may be administratively assigned to MSTIs in excess of the switch physical limits and without regard to
whether the VLAN is actually configured. Frames are only forwarded on VLANs assigned to interfaces.
Administrators can re-enter SYSLOG server config mode for a particular SYSLOG server entry without requiring the
deletion and re-creatio n of the entry.
Administrators can configure the web timeout by navigating to: System -> Management Security -> Telnet Server ->
Telnet Session Timeou t.
User configured banners (login, exec, MOTD) appear in the running config.
By default, auto-install supports image downgrade for network installs, specific version USB installs (using a .setup
file), and stack firmware s ynchronization.
A comprehensible message and recommendation is issued when configuring multiple services (telnet, http, etc.) to
listen on the same TCP port.
The terminal length command allows user control over terminal paging.
Simple Mode
The PowerConnect M8024-k is the only modular switch that defaults to the simple mode of operation. Simple mode
contains a restrict ed set of commands suitable for control of a port aggregation device that can be deployed in a
network without requiring updates to the network by a network administrator. Users needing switch capabilities which
require the network administrator to modify the network configuration can exit simple mode using the no mode simple
command.
AAA Authentication
In prior releases, more than one method could be specified for dot1x authentication even though only the first method
was attempted. The CLI and Web now only accept a single method for dot1x authentication.
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 21
Page 24
Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected Platforms
All 5.1 supported
Stack member crash with
Switch crash occurs
Corrected the SDM Templat e
PC8132
Stack member crash when
Switch crash occurs
Corrected a stack data plane
PC8132
PC8164F
Stack member crash from
Switch crash occurs
Enhanced DMA retry logic to
PC8132
Stack member crash in
Switch crash occurs
Corrected multicast routing
PC8132
PC8164F
PC8132
PCM6220
PCM6348
All 5.1 supported
PC8132
PC8164F
PC8132
PC8164F
All 5.1 supported
Issues Resolved
The following issues from previous releases have been corrected. The issues listed here may have been discovered on any of the
switches listed on the title page.
Release 5.1.1.7
Switch crashes in
tIomEvtMon() task once per
week.
Switch crashes in tCptvPrtl
task.
“SDM Template mismatch”
error
“ISO count mismatch has
been detected”
DMA hang
mcastMapTask
Stack master can move on
stack reload
iomEventLog() might result
in switch crash
FRU service tag value up dates
from CMC might result in buffer
overflow as service tag and
other related tag fields are
updated in the switch.
Switch crash occurs in captive
portal after a reload whi ch
brings down the entire switch
occasionally when an SDM
Template id mismatch occu rs.
occasionally when th e stack unit
detects that it is isolated.
occasionally when packet DMA
from the switching fabric to the
CPU stops.
occasionally with routing and
multicast traffic.
On a stack reload the st ack
master can move to a different
switch based on the plug-in
modules being used.
Communications error in the
m1000e Chassis CMC can result
in a crash.
Correct buffer overflow.
Corrected captive portal
initialization problem
ID problem so that invalid
SDM template ids will be
ignored.
communications problem.
allow DMA status information
to update completely.
problem.
Corrected stack master timing
problem when 10GBaseT
plug-in modules are used.
Corrected index r a nge error on
data received from the CMC
PCM6220
PCM6348
PCM8024
PCM8024-k
platforms
PC8132F
PC8164
PC8164F
PC8132F
PC8164
PC8132F
PC8164
PC8164F
PC8132F
PC8164
PC8132F
PC8164
PC8164F
PCM8024
PCM8024K
Switch crash in DHCP
server task
Stack member crash in
bcmRLINK task
Stack member crash in
DMA processing
Port detection mechanism
fails with SNMP Query
using Q-BRIDGE-MIB
22 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Switch crash in DHCP server
task
Switch crash in bcmRLINK task
due to unit id being out of range
Switch crash in DMA
processing due to memory
corruption
dot1qVlanFd bId S NMP object
returns incremental indexes of
the VLANs.
Corrected memory corruption
problem.
Corrected memory corruption
in ATP process.
Corrected in problem in cache
coherency which was causi ng
data corruption.
Corrected problem so that the
object will return VLAN IDs
platforms
PC8132F
PC8164
PC8132F
PC8164
platforms
Page 25

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
All 5.1 supported
All 5.1 supported
All 5.1 supported
MIB file parsing errors
Errors related to undefined
Corrected parsing errors.
All 5.1 supported
WebUI config issues with
Copy-from/Copy-to WEB UI
Corrected copying for duplex
All 5.1 supported
Trunk port tags traffic after
All 5.1 supported
All 5.1 supported
All 5.1 supported
PC70xx returns the chassis
PC70xx returns the chassis
Corrected default value for
All PC70xx platforms
PCM6220
PC8024
Need to throw
All 5.1 supported
All 5.1 supported
PC8132
Incorrect stats for "show
logging email statistics"
Telnet to port 80 hangs
management
Switch Hangs after using
Web GUI -> SNMP ->
Access Control
"No of email Failures so far" in
command "show logging email
statistics" is incrementing even
if there are no failures.
Console hangs when telnet
session to localhost is initiated
Switch Hangs when navigating
to SNMP -> Access Control ->
Show All page
Corrected problem in checking
for non-urgent messages.
Corrected task communication
problem in telnet tasks.
Corrected problem accessing
access control data structure
platforms
platforms
platforms
pre-provisioned por t s in
stacked environment
upgrading from v3.x
firmware
Web UI issue attributed to
ip local-proxy-arp setting
Stack fail-over causing loss
of access to ESX VM
environment
service tag as N/A instead
of NULL
IPv6 VLAN interface fails
to handle size specification
objects in 802.1ag MIB ar e
displayed when snmpwalk is
performed on nets nmp software.
functionality doesn't work
properly on IE 8
Switchport mode trunk &
switchport trunk commands
changed from previous firmware
version
Attribute to ip local-proxy-arp
enabled by default on routed
VLANs if WebUI is used to
configure.
Switch will send tagged traffic
out of the ports in native vlan.
service tag as N/A and it causes
issue with network management
system applications.
ipv6 ping fails when the size
parameter is specified
parameters
Corrected configuration
migration problem
Corrected default attribute.
Corrected problem in native
VLAN check.
chassis service tag.
Corrected packet
fragmentation problem
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
PCM8024
PCM8024K
PCM6348
PC70xx
ERROR/Warnings on
switch when PIM SM
neighbor exceeds 256
neighbor count
Traffic loss after restarting
traffic after power cable
pull/insert, high CPU
utilization.
OOB interface loses the
static default gateway
configuration after multiple
failover
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 23
PIM SM neighbor count gets
beyond 256 random neighbors
gets deleted without any error or
warning messages.
After restarting multicast traffic
for hard power cycle of a switch
in the network there may be
multicast data lost.
Out of Band interface state is
down during initiate failover
event causing default gateway
configuration failure.
Add validation such that no
new neighbors are entertained
if the router maximum
neighbor capacity is reached.
Corrected problem in event
notification logic.
Corrected link state check in
the service port.
platforms
platforms
PC8132F
PC8164
PC8164F
Page 26

M8024-K switch can cause
Temp range difference between
Modified fan speed change
PCM8024-K
All 5.1 supported
PC8132
Routing issue, null address
ARP replies destined to the
Corrected problem when
All 5.1 supported
With Traffic Running,
The ping packets destined to
Corrected ping priority
All 5.1 supported
Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected Platforms
M6220 crashes when
Switch crashes when using this
Fixed memory issue in a loop
All 5.0 supported
All 5.0 supported
All 5.0 supported
Incorrect SFP interface log
The wrong port may get
Calculate the correct i nt ernal
Platforms that support
transceiver modules
All 5.0 supported
Simple mode In-band IP
"ip address vlan" command
Put "ip address vlan" after
PCM8024-k
ARP entries are purged for
L3 egress objects are not
Use the SDK init function to
All 5.0 supported
high fan speed with CMC
4.2
All entries in IGMP
snooping are added and
deleted immediately in a
specific time for 5 minutes
Manager is rebooted while
doing clear config due to
crash in mcastMapTask.
in ARP table after VLAN
manipulation
cannot PING VRRP IP
from VRRP backup router
Release 5.1.0.1
M8024k and CMC with FW 4.2
and above causing chassis fan
speed stuck at 100%
Group entries in IGMP snooping
are added and deleted
immediately in a specific time
for 5 minutes
During multicast traffic flow, on
initiating a NSF failover, the
unit acting as standby crashes
and there will be traffic lo s s.
DUT L3 MAC address will be
dropped.
VRRP Master IP are coming in
the same CPU CoS queu e as the
unresolved data packets. Since
these ping packets are not
prioritized, they are getting
dropped at the CoS queues itself
resulting in ping to fail
parameters and added new
temperature handling logic.
Corrected timer rollover
problem that happens every
49.71 days
Corrected data copy pro blem
when check pointing MFC
data.
removing ARP table entries
problem.
platforms
PC8132F
PC8164
PC8164F
platforms
platforms
issuing command “show
interfaces switchport po1”
Cannot apply ACL on
VLAN 'out bound'
direction from GUI
Default VLAN cannot be
made static from GUI
messages on stack
SNMP management IP
address can only be set
from WebUI and lost after
reboot.
address missing after
reboot.
unknown reason
command
User needed to use CLI Fixed the issue to be able to
apply in both directions from
the web
Cannot change VLAN member
ports settings
reported in the trap notification
command is missing in the CLI
in Simple Mode
disappears from the runningconfig after reboot
programmed correctly resulting
in incorrect L3 forwarding.
Fixed VLAN membership web
page
interface number
Added CLI command support
"port-aggregator group"
commands in the text config
set defaults for egress object.
platforms
platforms
platforms
XFP, SFP a n d SFP+
platforms
PCM6220
PCM6348
PCM8024
platforms
24 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 27

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
All platforms that support
All 5.0 supported
Get the mask from the
All 5.0 supported
M8024-k, M8024, M6348
CLI commands are not
Enabling password recovery will
Fixed the issue to enable
All 5.0 supported
PC8024 and PC81xx
Check if any weight is
Platforms running DCBX
Switch GUI forcing 100Mb
Switch GUI set all external ports
Corrected port speed
M6348
PowerConnect
Vlan membership information
Javascript fixed to pick correct
M6348
email addresses with
A valid email id with an
Underscore is now considered
All 5.0 supported
All 5.0 supported
OOB Static IP unreachable
after stack failover
http[s] authentication
against RADIUS only
allows privilege level 1
access
SNMP v1/2 community
manager address no lon ger
functions with network
address.
Switch service tag not
displayed by “show system
id” command
After failover stack loses static
IP address configured on OOB
interface.
HTTPS authentica t ion through
RADIUS grants only read-only
access.
When a subnet IP is set as
SNMP community IP addr es s
then snmp requests from hosts
of that subnet are not accepted
on the box.
Switch service tag not displayed
with “show system id”
command
Proper checks prevent using
the previous DHCP mode.
parse RADIUS server respo nse
properly
community IP address
configured and set it instead of
the hard coded value.
Added retry to get the Service
Tag value
the OOB interface
platforms
platforms
authorized after Passwor d
Recovery
LINK UP on all interfaces
during POST,
FCoE -M8024-k setting
TSA map to link strict and
assigning bandwidth
allocation to TC
speed on External ports
when cloning port
configurations
M6348/General port GUI
issue
M6348 - service tag not
displayed in GUI
underscore "_" are reject ed
phone port configuration
macro incomplete
not allow the user to run CLI
commands on the serial console.
Links are UP and flapping
during power reset and reloads.
In the CEE mode there is no
way to specify the TSA mode in
the ETS TLV
to 100Mb speed when cloning
port configurations.
on web is displayed and applied
incorrectly
Service tag shows up as none on
GUI
underscore cannot be used
The macro never returns and
appears to hang
commands from serial console
also
Changed the CPLD and reset
logic
configured for the TCGs, if so
set the mode to ETS.
processing from WEB
enum values
Synchronization issue fixed to
retry and get the tag
information
valid character
Fixed the issue and return error
platforms
and including ETS
M6348
platforms
platforms
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 25
Page 28
Release 5.0.1.3
Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected Platforms
Re-enable Auto
The Auto Negotiation can't be enabled back
Corrected error in Port
All 5.0 supported
VLAN ACL
members
ACL prevented traffic from reaching
Prevented VLAN ACL from
All 5.0 supported
All 5.0 supported
All 5.0 supported
All 5.0 supported
All 5.0 supported
All PC70XX Switches
All 5.0 supported
Change PoE
PoE controller Disconnect Type was
PoE controller Disconnect
PC7024P
All 5.0 supported
All 5.0 supported
PC8132
PC8164F
Negotiation
using GUI
doesn't work
properly
blocks traffic
across stack
Power supply
logging
'no ipv4 or ipv6
address found in
response for
request id' error
phone port
configuration
macro
incomplete
web session
timeout
RX Equalizer
setting on
Stacking ports.
interface speed
options
on "Port Configuration->Show All" page
once it has been disabl e d.
destination
Power Supply messages are only sent to the
log file.
'no ipv4 or ipv6 address found in response
for request id' error message flooding the
switch
The phone port is missing some needed
commands
Web session would timeout regardless of
the timeout setting
RX Equalizer was not set on the stacking
port which caused stacking errors to be
reported.
Invalid speed option s mess age i s not clear Changed the message repo rted
Configuration page.
being applied to stack ports.
Elevated failure messages to
ERROR severity
Corrected problem that was
causing extra error messages to
be displayed.
Added missing commands to
the pone port macro.
Corrected the hard t imeout to
be one hour.
Added RX Equalizer value.
when an invalid speed option
is input.
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
Disconnect
Type to DC
disconnect
stacking with
extension
modules
DHCP Req pkts
are not being
forwarded to
Voice VLAN
Component
Netlogic
memory and B0
CPU support
changed to DC Disconnect.
Stacking with redundant stack rings caused
packet flooding on the stacking links.
When using Avaya phone on a switch
running dot1x, the phone will NOT get
authenticated and thus will not boot
Netlogic memory and B0 CPU support Added support for Netlogic
26 Syst e m Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Type was changed to DC
Disconnect.
Corrected problem with st ack
link queuing.
Corrected DHCP forwarding
problem.
memory and B0 CPU.
PC7048P
platforms
platforms
PC8132F
PC8164
Page 29

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected Platforms
OpenManage UI
Port description does not accept space
Correction the por t des c r ipt ion
All 4.2 supported
"show spanning-
The user may think that th er e is traffic over
Corrected the counters.
All 4.2 supported
using the web.
All 4.2 platforms that
All 4.2 supported
"encapsulation"
The user could only set VLAN
Added support for the
All 4.2 supported
M8024-k
The user could not get accurate information
Corrected the information
PCM8024-k
"spanning-tree
The user could not see the configuration of
Corrected the output of the
All 4.2 supported
Inconsistent
The user may be able to configure an
Corrected the error handling so
All 4.2 supported
All 4.2 supported
Release 5.0.0.4
does not accept
blank space
character for
port descripti on
tree detail"
counters are
non-zero for
inactive
interfaces
Unable to
remove 0.0.0.0
as default
gateway on
OOB interface
When
connecting via
SSH, the user is
not prompted to
acknowledge the
MOTD
command is
unavailable in
interface range
mode
interfaces that are supposed to be inactive as
far as spanning tree is co ncerned.
The user may not be able to remove the
default gateway for th e O O B interface
causing unwanted traffic to go over the
OOB interface.
The user may log in without having
acknowledged the MOTD.
encapsulation on a sin gl e VLAN at a time.
validation to accept spaces.
Added support for setting the
gateway to 0.0.0.0.
Add functionality to send the
acknowledge question when
new SSH connection is
created, but after
authentication.
encapsulation command in
interface range VLAN mode.
platforms
platforms
support the OOB interface
platforms
platforms
OpenManage
Web UI stack
view display
transmit holdcount"
command's
value is not
reflected in
show command
behavior in
single and range
interface mode
of "spanningtree port
CLI command
"no passwords
strength
excludekeyword"
requires
<keyword>
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 27
about a stack of M8024-k switches from the
stack view web page.
the hold-count parameter.
invalid spanning tree port priority in range
mode.
The user could not reset the excluded
keywords to the factory default of no
excluded keywords with a single command.
It was necessary to remove each excluded
keyword one at a time.
displayed on the stack view
web page.
"show spanning-tree detail"
command to include the
configuration of the hold-count
parameter.
that the invalid priority is not
used.
Correctly implemented the
"no" form of the "passwords
strength exclude-keyword"
command.
platforms
platforms
platforms
Page 30

Inline help for
The help text might lead the user to think
Corrected the help text so that
All 4.2 supported
Some of the
Some of the options of "show ip pim"
Added missing options to the
All 4.2 supported
Configuration
Configuration command "logging
Added checks to return error
All 4.2 supported
dot1dTpPortMa
dot1dTpPortMaxInfo is displaying
Excluded the MAC header
All 4.2 supported
If a user
No error message was given.
Added a message once an exit
All 4.2 supported
All 4.2 supported
"spanning-tree
loopguard" is
incorrect.
options of "show
ip pim"
command are
not available in
user EXEC
mode.
command
"logging
<hostname>"
accepts more
than 63
characters.
xInfo is
displaying
maximum frame
size that
includes MAC
header.
attempts to
create a
certificate
request with
information that
is not identical
to the key
generated, the
user is not gi ve n
an error/
informative
response letting
them know there
is a conflict
between their
key and their
request.
OIDagentInvent
orySupportedUn
itExpectedCode
Ver provides
incorrect display
string 1.0.176.0
the command only applied to a single port
instead of all ports.
command are not availabl e in user EXEC
mode.
<hostname>" accepts more t han 63
characters, but saves only 63 characters in
running-config.
maximum frame size that includes MAC
header.
agentInventorySupportedUnitExpectedCode
Ver object returns incorrect values.
it indicates that the command
applies to all ports.
CLI tree.
when hostname is larger than
63 characters.
length when retrieving the OID
information
is issued from the request or
generate command. This is to
tell the user whether th e
operation was successful or
not.
Made the OID that is in p rivate
MIB obsolete as it's not
required.
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
28 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 31

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
All 4.2 supported
All 4.2 supported
CLI command
The user would not always get the correct
Corrected the logic in the
All 4.2 supported
All 4.2 supported
All 4.2 supported
All 4.2 supported
1. Changes are
not applied to
the correct
interfaces on the
pages
"System>sFlow>Sampler
Configuration"
"System>sFlow->Poll
Configuration"
2. Incorrect
error message is
displayed when
not configured
Receiver index
is applied
to interface on
"System>sFlow->Poll
Configuration"
page.
"show ip route
configured
...longerprefixes" reports
that default
gateway is not
configured,
which is
incorrect.
1. Changes were not applied to the correct
interfaces on the GUI pages referred to.
2. An incorrect error message wa s
displayed.
The default gateway would not be shown on
executing "show ip route configured"
1. Used initialized buffers.
2. Correct the error messag e.
Corrected the implementat ion
of this command so that it
functions correctly.
platforms
platforms
"show ip route
192.168.2.2 /24"
not ignoring
host bits.
CLI command
"show spanningtree detail"
missing
information.
"ipv6 pim joinprune interval"
command does
not work
Macro input
string does not
accept more
than 20
characters
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 29
list of routes from the "show ip route"
command.
The user could not see the configured
values for spanning tree max hops.
The user could not change the configuration
of the IPv6 PIM join interval.
The interface string length is lim ited to 20
characters for the "macro global apply"
command.
implementation of the "show
ip routes" command so that the
appropriate list of routes are
shown, depending upon which
optional parameters are given.
Changed the output of the
"show spanning-tree" and
"show spanning-tree detail"
commands to include the
configured value of max hops.
Corrected the implementat ion
of this command so that it
functions correctly.
Increased the acceptab le string
length for the "macro global
apply" command to 256
characters.
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
Page 32

startup-config
startup-config failed error message is
Corrected the implementat ion
All 4.2 supported
In stacking
CLI output for command "show system
Corrected pagination in the
All 4.2 supported
PC8024F
Alignment
The alignment issues make it d ifficult for
Corrected alignment issue
All 4.2 supported
All 4.2 supported
All 4.2 supported
All 4.2 supported
"show interface
The user sees the info but it looks messy
Corrected formatting i s s ues
PC8024
All 4.2 supported
Port channel
The members of the stack other than the
Corrected the logic to check
All 4.2 supported
failed error
message is
displayed when
finishing the
Dell Easy Setup
Wizard
environment,
"show system
temperature"
command output
is corrupted
Error message
for port enable /
disable on IE on
8024F combo
ports
issues in the
output of "show
voice vlan
interface"
command
CLI command
"show ip igmp
snooping"
output is
truncated.
vrrp ip
command
accepts invalid
IP addresses
CLI command
"isdp enable"
does not work
for a range of
ports
displayed when finishing the Dell Easy
Setup Wizard
temperature" is corru pted when
pagination is used.
When a copper port was disabled, port was
getting set in no negotiating mode.
the customer to read the page.
The displayed info is not complete on page. Corrected the implementation
Switch allowed user to misconfigure VRRP
IP
User cannot enable isdp on range of
interfaces
of this command so that it
functions correctly.
command handler.
Corrected by disabling
negotiation on combo ports
of this command so that it
functions correctly.
Added checks to return error
when invalid VRRP IP address
is given.
Added support to "isdp enable"
command in interface range
mode
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
Priority-FlowControl"
command output
is not formatted
correctly
CLI command
"show ip route
192.168.2.2 /24"
not ignoring
host bits.
goes down
during master
failover.
30 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
and is hard to read.
The user would not always get the correct
list of routes from the "show ip route"
command.
master unit and thei r por t channels, i.e. the
Standby units and their port channel
interfaces, are now not affected by a master
failover and the port channel stays up
during failover.
Corrected the logic in the
implementation of the "show
ip routes" command so that the
appropriate list of routes are
shown, depending upon which
optional parameters are given.
for active port channels in the
new Standby master unit.
PC8024F
PCM8024-K
platforms
platforms
Page 33

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
switches
emWeb
The switch crashes when it receives the url
Corrected URL length problem
All
general mode
vlan
The general mode for switchport won't
Corrected memory
All
SNMP OIDs
switch crash
Walk of any member of
Corrected unit number range
All
Stack ARP
ARP replies to a routing interface are not
interfaces.
Corrected ARP repl y policy
All
Stack member
GUI.
Stack member unit ports were not displayed
Corrected power LED element
PCM8024-K
No response to
jumbo (ping)
Third IP fragment was being dropped in
Corrected jumbo Ping packet
All
Ports connected
after reboot.
When customer is using the Intel X520
Corrected port configuration
PC8024
switch reboots
randomly
switch reboots randomly
Corrected memory corruption
problem.
All
Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected Platforms
IP routing
enabled.
Traffic will get forwarded by software when
Telnet existing
"New Telnet Sessions" are changed to
Disabled.
OOB interface
Out-Of-Band interface will be unreachable
PCM8024-k
rebooting possible crash
dump w/
vlan does not
show up after a
reload, it shows
up in access
1.3.6.1.4.1.674.1
0895.3000.1.2.1
10.7.x causing
Problem
units port
display is
missing in web
ICMP with
with the maximum characters.
work properly in several cases , such as,
script apply, nsf failover and save and
reload.
envMonFanStatusEntry and
envMonSupplyStatusEntry with 67109251
index causes crash.
received at the CPU after cl ear ing the
config and reconfiguring the routing
properly.
jumbo Ping packe t.
initialization problem
check.
problem
id name problem which was
causing this display problem.
problem.
to Intel X520
NIC do not
return online
NICs, sometimes the ports never came back
up after a reboot of the switch.
Release 4.2.2.3
unexpectedly
after reboot
despite its not
having been
session is
interrupted
when "New
Telnet Sessions"
is set to "Block".
unreachable
after failover
global routing is not enabled.
Block, All the current telnet sessions are
closed and using "Telnet Ser ver Admin
Mode" to set Disable will only block new
telnet sessions.
after a stack failover
timing issue.
Correct the default act ion so
that global forwarding is
enabled for the hard ware.
Functionality was corrected so
that "New Telnet Sessions"
will only block new telnet
sessions and "Telnet Server
Admin Mode" will close all
the sessions if the mode is
Corrected MAC address for
new manager.
PC8024F
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
PCM6220
PCM6348
PCM8024
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 31
Page 34

Switch CLI help
Warning message printed during execution
mode only.
Timeout during
root
SNMP walk on root ends with timeout
"show interfaces
value
"show interfaces switchport" command
Error while
access-group
Error message when trying to apply ACLs
Walk of
VLANs
Walk of agentDaiVlanStatsTable returns
OOB interface
so
When the Setup Wizard is used the OOB
Unable to create
Web GUI
Unable to create new VLAN with its name
"Failed to get
messages in logs
"Failed to get CPU cosq 0 drop counters,
Default "ip
error repeatedly
Default "ip address dhcp" command on
agentPortSpeed
error
Mistakes in the
ifIndiscards is
is in trunk mode
ifIndiscards is still counting VLAN discards
does not locate
the 'initiate
failover'
command
properly
SNMP walk on
switchport"
command shows
incorrect
General Mode
Tagged VLANs
adding an
access-list to an
agentDaiVlanSt
atsTable returns
statistics for all
the 4096
configured with
default IP via
Setup Wizard
though not to do
of the deprecated "movemanagement"
command incorrectly
states that "initiate failover" command is
executed from privileged EXEC mode
whereas it's available from stack config
shows incorrect General Mode Tagged
VLANs value.
to VLANs.
statistics for all the 4096 VLANs even they
do not exist in the system
interface IP address is incorrectly set to
192.168.2.1 static IP by default
Corrected the warning message All 4.2 supported
platforms
Corrected delay that cau sed
timeout.
Corrected the display of the
General Mode Tagged VLANs
value.
Corrected the condition that
resulted in the error.
Corrected the VLAN Stats
Table data.
Corrected the settin g of the
OOB interface IP addr es s .
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
PC8024
PCM8024
PCM8024-k
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
VLAN ID and
name VLAN in
CPU cosq 0
drop counters,
error -16"
address dhcp"
command on
VLAN 1
causing "failed
to bind socket"
DuplexStatus
SNMP MIB
object
documentation
still counting
VLAN discards
if the interface
switchport mode
using the Web GUI
error -16" messages in logs
VLAN 1 causing "failed to bind socket"
error repeatedly
agentPortSpee dDuplexStatus SN MP MIB
object description
if the interface switchport mode is in trunk
mode (acceptable frame type is all)
Corrected the VLAN creation
GUI
Corrected the retri eval of cosq
0 counters.
Corrected DHCP socket
problem.
Corrected MIB object
description.
Corrected ifIndiscards counter
collection.
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
32 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 35

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Switch doesn't
TLVs.
Switch doesn't register all the 576 devices if
SNMP and LOG
ifAdminStatus
When setting ifAdminStatus “adminState
Cannot type
reboot of switch
After reboot external ser ial connection can
Web GUI
Explorer 9
Device View doesn't display one port on IE
Switchport
running config
"switchport general allowed vlan add 1
Cannot rename
Cannot rename vlan1 running v4.2.1.3.
SNMP Port
When setting VLAN un-tagging for a
DNS client error
rebooted.
Upgrade of 3.1.4.5 to 4.1.0.6 DNS client
Terminal Length
4.1
Terminal length is not setting per-session is
Trunk port
reboot
Trunk port multiple VLAN assignment
FIP snooping
script apply.
FIP snooping session i s not getting
register all the
576 devices if
LLDP-MED has
all the optional
LLDP-MED has all the optional LLDPMED Location TLVs.
Corrected the allocation of
LLDP-MED Location TLVs.
All 4.2 supported
platforms
errors when
setting
input into
external serial
connector after
doesn't display
port 24 if using
Internet
general
configuration,
VLAN1 tagged
not saved in
vlan1
tag/untag issue
2d is not valid” errors are produced.
become inoperative.
9. (IE9 is currently unsupported)
tagged" is not displayed in running config
It is correct that the defaul t VLAN cannot
be renamed (same as a Cisco switch).
specific port using the
dot1qVlanStaticUntaggedPorts object,
All the other ports are automatically added
to that particular V LAN as tag ged.
Corrected error check when
using invalid testing options.
Corrected initialization of
serial connection.
Corrected problem for IE9. All 4.2 supported
Corrected check of enabled
VLAN.
Updated error message to
reflect this behavior.
Corrected the port un-tagging
set.
All 4.2 supported
platforms
PCM6220
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
in logs and
switch locks up
and needs to be
setting not
working as in
multiple vlan
assignment
doesn't work
properly after
session is not
getting
established after
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 33
error “osapiSocketRecvFr om returned error
“ in logs and switch locks up and needs to
be rebooted.
an enhancement scheduled for the next
release.
doesn't work properly after reboot.
established after script apply.
Corrected service por t link
status during upgrade.
Corrected a problem with
terminal scrolling.
Corrected command pars ing
problem.
Corrected FIP snooping
command problem.
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
Page 36

"ip http secure-
build.
ip http secure-server command not getting
Data loop in
A data loop occurs in the port-aggregator if
Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected Platforms
The “show fiber
up.
The “show fiber optical-transceiver"
Unable to ping
MTU size configured on the combo ports
cpCaptivePortal
The description of the
Corrected the description in
LLDP
TLV
When Port-Description is set as no
0.
The CLI shows
The "show interface advanced firmware"
Can't assign a
Config migration for the "name <vlan
command.
No default route
route table
"Show ip route" commands will not display
terminal length 0.
CLI command
CLI command "show dot1x users" is
command.
server"
command not
getting migrated
from 4.1.0.19
build to 4.2.1.3
Simple mode
when adding
VLAN
applied when we migrate from 4.1.0.19 to
4.2.1.3 release
a new VLAN is added to an interface.
Release 4.2.1.3
opticaltransceiver"
command shows
LOS even
though link is
with jumbo
frames set
command was reporting incorrect values
when optical transceivers that did not
support diagnostics were used.
will be lost after a save and reload and also
when changes the media p r eferences are
made.
Corrected command pars ing
problem.
Corrected the VLAN creation
error.
Correct diagnostics so that
diagnostics for unsupported
transceivers are not d isplayed.
Corrected the storing of the
MTU size
All 4.2 supported
platforms
PCM6220
PCM6348
PCM8024
PCM8024-k
All 4.2 supported
platforms
PC72xx and PC80xx
platforms
WebLangCode.
1.1 display s en
when mib says
only supported
value active (1)
Assignment of
port ID for PortDescription
incorrect media
type 10GBASET for fiber ports
name to a
VLAN
or static
showing in ip
"show dot1x
users" is missing
cpCaptivePortalConfigWebLangCode
object doesn't correspond to the values it
returns.
description in LLDP port configuration, the
TLV should contain the Port Interface name
as the port description by default instead of
shows incorrect information under "Type"
column.
name>" command was not correct.
route even though there were routes is in the
router(static routes, ospf routes) for
missing
the fastpath_captive_portal.mx
file
Corrected the default P ortDescription.
Removed the Type column
which was not valid.
Corrected the config migration
for the "name <vlan name>"
Corrected the display of the
"Show ip route" command.
Corrected the command tree
for the "show dot1x users"
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
34 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 37

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Missing port
EgressPorts)
Changing VLAN configuration for general
The VRP P track
The VRRP track port priority in the running
Firmware won't
logging email
The hyphen is part of the allowed characters
Internal ports
Internal ports were up while switch is
Corrected the initialization of
Continuous log
default settings
POE log message comes up during power
DNS client error
The meaning of the DNS error message:
unclear.
VRRP
Issues
Ping to a remote host will not work if
VLAN
GUI
VLAN membership port names are not
Radius crash
Sometimes switch crashes when receiving
platforms
In a Stack, the
breaks CLI
CLI output for command "show system
QOS on port
There is no way to see the match packet
channel number > " was added.
membership
from SNMP
(dot1qVlanStati
cUntaggedPorts
and
dot1qVlanStatic
mode affected trunk mode configuration
and there from the port membership
returned via SNMP.
Corrected the issue. All 4.2 supported
platforms
port priority
changes in the
running config
allow domain
names with
hyphen "-" in
are up during
most of the
switch POST
message at
config is retrieving the operational value
instead of the configured value.
available for the email address.
booting, this was causing traffic loss in
network.
up sometimes.
“DNS Client: osapiS ocketRecvFrom
returned error for addr 0x1214BCA8” is
Corrected the retri eval of the
configured value
Added the hyphen to the
allowed characters for email
addresses.
the internal ports. CPLD Code
Update is required.
1. Update the CPLD using the
command 'dev cpldUpdate'
Console#dev cpldUpdate
2. Power cycle the switch.
(Power Cycle from CMC
WebUI. Do not run “reload”
from the console prompt)
Removed unwanted message. PC7024P/PC7048P
Corrected the text o f the
message.
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
PCM8024-K
All 4.2 supported
platforms
Intermittent
Connectivity
membership
port names not
consistent in
"show system
temperature"
CLI command
channel
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 35
switch acts as VRRP master
consistent.
of Radius packets
temperature" is corru pted when
pagination is used because the stack
displays much more data.
counts of a policy-map on a port-channel.
Corrected a VRRP
communication issue.
Corrected the port numbers
displayed in the GUI.
Corrected the crash. All 4.2 supported
Corrected the paginat ion issue. All 4.2 supported
Command "show policy-map
interface port-channel <port-
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
Page 38

Dropped VLAN
Customer is really not able to use this
PC7048 Combo
Combo ports are randomly not transmitting
Order of
changed
The "show running-config" command
Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected Platforms
PowerConnect
specification
sFlow implementation is not per
Using config
console
Doesn’t affect any iscsi traffic. Constant log
PC8024
8024 stack does
If a user logs in via console - motd and
All 4.2 supported
Simple Switch
default
FC not functional
All 4.2 supported
OSPF error
With 128 IPv4 & IPv6 interfaces & OSFP
routing.
All 4.2 supported
frames are
included in
Discards
counters.
ports are not
passing traffic.
switchport
commands in
running-config
counter to monitor their network outage
activity.
traffic, but receiving frames when media
type preference set as SFP
shows the detailed switchport configuration
before the switchport mode. This caused
problems with some scripts.
Release 4.2.0.4
sFlow
implementation
is not per
wizard to setup
8024 causes
iscsi error
messages off
out-of-band in
specification
messages with the erro r “Can’t create static
rule”.
Corrected by not ignoring the
dropped VLAN frames in the
Discards counter
Corrected by adding a property
to bypass the lane initialization
when media-type preferences
is set.
Corrected the orde r of runningconfigurati on output.
Issues corrected and passes
conformance test
Issue is corrected.
All 4.2 supported
platforms
PC70xx
All 4.2 supported
platforms
All 4.2 supported
platforms
not follow
similar banner
execution for
console, telnet
and ssh
should have FC
enabled by
message after
reboot
login banners are execut ed
If a user logs in via ssh - only exec banner
is executed
If a user logs in via telnet - all 3 banners are
executed
configured a reboot caused the following
error messages to be gen er ated:
Failed to send message to O SPF mapping
thread in
ospfMapRoutingEventChangeCallBack()
These lost events could lead to incorrect
Behavior is now as follows:
Add motd banner display for
telnet connection before motd
acknowledge question is
asked.
Remove motd banner after
motd acknowledge question.
FC is enabled by default in
simple switch mode.
Issue has been correct ed.
platforms
platforms
platforms
36 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 39

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
show crypto key
After generating DSA & RSA keys,
There is no impact on the keys themselves.
All 4.2 supported
Web GUI AR P
The Web GUI does not display the
All 4.2 supported
The copper auto
fails to link up
The copper ports 1-24 fail on 8024 to
PC8024
PCM6220 -
page on the GUI
The current stacking port status does not
All 4.2 supported
PC8024 -
interface
If user changes VLAN me mbers h i p
All 4.2 supported
Implement
M8024-K
The dot1qVlanStaticTable is not available
All 4.2 supported
Trunk mode
with Cisco
tagged native vlan traffic.
All 4.2 supported
PCM6220 -
sftp
Switch hangs and needs a hard reboot.
All 4.2 supported
mypubkey
generates two
error messages
executing the command "show crypto key
mypubkey" generates the following error
messages:
<187> APR 23 09:09: 22 19 2.168.1.2-1
OSAPI[162603 39 2]: osapi_file. c ( 657 ) 426
%% File close failed for descriptor 37
<187> APR 23 09:09: 22 19 2.168.1.2-1
OSAPI[162603 39 2]: osapi_file. c ( 657 ) 427
%% File close failed for descriptor 37
Resolved
platforms
table does not
match the CLI
ARP table
negotiation
process fails at
100mb FD and
Wrong
information for
current link
status in port
configuration
VLAN
membership
change on
interface affects
unrelated
dot1qVlanStatic
Table in
static/local ARP entries. However, once an
external port is linked up some, but not all,
of the Static/local appear in the Web GUI.
negotiate at 100Mb FD.
display “stacking linkup”
configurati on on tr u nk port via the WEB he
loses ports configuration on access ports
and access ports are put into default VLAN.
on M8024-k.
All ARP entries are now
shown.
8024 copper ports negotiate to
100M FD.
The web stack display has
been updated to accur ately
reflect the correct information
as well as address some style
issues.
Issue is resolved.
the dot1qStaticVlanTable is
implemented for the M8024-k
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
native vlan
implementation
not compatible
Switch hangs
when user tries
to transfer a file
from the flash to
the server using
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 37
Native vlan implementation is incompatible
with Cisco. Switch will egress native vlan
traffic as tagged and Cisco will drop ingress
Implementation of native vlan
changed to be compatible with
Cisco.
None – issue is resolved.
platforms
platforms
Page 40

No message
The switch does not log an error message
refused, but no error message is logged.
All 4.2 supported
CLI command
correctly
The CLI command "show ip v6 interface"
All 4.2 supported
2nd and 4th
problems
Ports report to be fiber ports and not copper
PC8024/PC8024F
WebGui Secure
On the WebGui under Management
on the Web UI
All 4.2 supported
Web UI MSTP
MSTIs
In the "MSTP Interface Settings" page of
All 4.2 supported
Flowcontrol
module
Flowcontrol negotiation iss ue s be t ween
PC8024/PC8024F
PC8024 - GUI -
When you change the port setting, for
problem when using the command prompt.
All 4.2 supported
Unable to config
pops up
Unable to configure Secure Shell from web
All 4.2 supported
Web interface
iSCSI item.
The web page for iSCSI fails to open when
All 4.2 supported
logged for "Max
number of SSH
login sessions
exceeded"
"show ipv6
interface" does
not paginate
block of copper
ports 5-8 and
13-16 think they
are fiber ports,
possible
Shell SSH
Remote Access
Instance pull
down menu
displays 4k
when the maximum number of SSH
sessions has been exceeded.
The switch does accept 5 SSH sessions
normally, when the 6th session connection
is attempted via SSH, the connection is
does not paginate corr ectly when a large
number of interfaces/ad dresses are
configured.
ports.
Security,
Secure HTTP, Secure Shell does not work
the Web UI, the Instance pull down menu
has a range of 1-4094 MSTIs.
A Log message "Unable to
find a free connection.
Exceeded the maximum
number of allowed
connections." has been added.
Pagination mechanism
corrected.
Corrected error checking logic
to correctly select fiber ports
for fiber diags and copper ports
for copper diags.
Issue is corrected
Issue is corrected
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
negotiation
issues with
10GBase-T
Under Port
Configuration
page get error
on 10GB ports
when you
change any
setting
secure ssh from
web interface.
error
'sshcfg_load
start' missing
fails to provide
an iSCSI web
page when
selecting the
6200 and 8024/8024F
example the duplex settings or description,
from the GUI under switching -> Ports ->
Port Configuration you will get outputs
error when changing port settings on 10G
ports. The popup says 10G speed is invalid.
Error message attached. This is a problem
with code ve r s ion 4.1.0.6 under the GUI no
interface. Error pops up.
selected with OpenManage.
.
Driver update applied.
Erroneous pop-up message
removed.
Corrected web page
Corrected web index p age
platforms
platforms
platforms
38 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 41

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Line "no
The following is displayed when startup-
All 4.2 supported
Web GUI
Switching-->Port-->Port Configuration
PCM6348
Advertise LLDP
LLDP advertises the switch's MAC address
All 4.2 supported
PCM6348 - Log
Messages repeated in t he switch logs
sender MAC is 76:f7:b9:cf:06:7e.
All 4.2 supported
Firmware
the GUI
Port VLAN membership will not be shown
PCM6220
passive-interface
Vl32" in startupconfig does not
get loaded on
startup
config is loaded:
Applying Global configuration, please wait
...
Applying Interface configuration, please
wait ...
******* The following lines in "startupconfig" failed:
******* Line 57:: no passive-interface
Vl32
Corrected stored config
platforms
Admin Duplex
setting on 10G
Fiber ports
Management
Address as IP
Address
assigned to
OOB interface
message output
Select a ten gigabit in terface Te1/0/1 and
you can see that "Admin duplex" and
"speed" are still active and can be changed,
but when you apply it gives an error
message saying "
Error failed to set current auto negotiation
with disable".
as the Management Address. Request to
advertise the management IPv4 or IPv6
address instead.
<190> APR 28 19:39: 22 10 . 1.208.10-1
STATSMGR[239558880]:
collector.c(1066) 3445 %% Failure in
function collector Get
<190> APR 28 19:39: 22 10 . 1.208.10-1
STATSMGR[239558880]: presenter.c(102)
3446 %% ERROR!! Failure in preStatsGet
0x0002011e
<188> APR 28 16:40: 31 10 . 1.208.10-1
ARP[301140128]: ipmap_arp_api.c(855)
3325 %% Received ARP Reply on interface
Vl208 with bad target IP address
255.255.255.255. Sender IP is 10.1.209.60,
Invalid selections disabled on
page load.
The following behavior is now
implemented:
1) Will advertise service port
address if it is there
2) If service port is not th ere,
then will send network address
3) If both of the above are not
there and if it is routing
interface will send IP address
of the routing interface
4) If none of the above not
there, will send MAC address.
SNMP walk/gets on counters
for CPU/vlan routing ports not
supported by platform no
longer log a warning message
platforms
platforms
missing port
VLAN
membership in
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 39
in the GUI.
Web code updated to display
VLAN membership
Page 42

M8024 - 1GB
X520-KX4
The M8024 is negotiating 1GB speed
PCM8024
Feature request -
The "Client-DUID" is used to uniquely
Client-DUID parameter has
All 4.2 supported
clock summer-
minutes
Time change offset is applied early.
All 4.2 supported
M6220 - Simple
Modular switch in Simple mode. Interfaces
again.
All 4.2 supported
SSH
after reboot
SSH config is not restored after reboot.
All 4.2 supported
PC8024 -
change
On 4.1.0.6 if VLANS are assigned to a
that are assigned
All 4.2 supported
Web UI displays
After the browser session timeout (default
than 240 minutes
All 4.2 supported
PC8024 - Secure
If you go to system managemen t, Secure
All 4.2 supported
Upgrades to
setup interfaces
The wizard in 4.1.0.9 fails to create any or
All 4.2 supported
PC6220M GUI
issue didn't exist
The issue using CLI stack ports shows up
All 4.2 supported
link being
negotiated on
10GB Intel
Display "clientDUID" in
DHCP binding
table.
time recurring
EU offset 60
zone "GMT" not
offsetting the
time by 60
mode, VLAN
setting not
active when
move port to
another group
connection with the 10GB X520-KX4 Intel
card in the blade server. Issue is only
present with new
identify an individual host receiving DHCP
address configuration.
In the case of a multi-homed host, it is
possible to deter mine that the host has
multiple bindings for different interfaces
and which interfaces belong to each host.
have VLAN settings differen t from default.
If you move port from one aggregation
group to another, VLAN settings are
retained and are listed in running config but
it is not active until system is rebooted or
VLAN information removed and reentered
Incorrect pre-emphasis values
have been corrected.
been added to show "ip dhcp
binding" command output.
Day of month calculation has
been corrected.
None – issue corrected
platforms
platforms
platforms
configuration
not restored
VLAN trunk
assignment CLI
incorrect session
timeout duration
HTTP Random
Characters -
4.1.0.6
4.1.0.9 are
causing network
outages. The
wizard from
4.1.0.9 fails to
trunk, the switch CLI will display the
VLANS not assigned instead of the VLANS
10 minutes), Web UI displays incorrect
session timeout duration in the message
"Your session had been inactive for more
HTTP, you will see ran dom characters
populating the fields. Even if you delete
these entries and re-populate with valid
chars, it will repopulate with invalid
characters making it impo s s ible to generate
a cert using the web int erface.
very few interfaces and there was no config
for any or very few of the ports, thus, the ip,
icmp traffic was not working between ports
as well.
ssh configuration saved
VLANs are displayed in
positive format, i.e. assigned
VLANs are displayed.
The displayed message was
corrected.
The random character
rendering has been co rrected.
Issue with switch upgrade has
been resolved.
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
shows stackports down but
CLI does not. In
previous version
40 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
and counters shows no transfer rate but GUI
shows stack ports down.
Web shows stack ports up if
they are up
platforms
Page 43

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
M6220 -
Customer has multiple M6220 switches,
All 4.2 supported
MIB walk
SNMP MIB walk crashes switch.
All 4.2 supported
M8024 - No
On the web GUI-->system-->management
attachment.
All 4.2 supported
Bug in Simple
Once you select the Tagged -Vlans, there is
only way to unselect those.
All 4.2 supported
M6348 simple
group
Can't remove what running config says is
All 4.2 supported
Banner motd
The "banner motd" config uration changes
All 4.2 supported
Error message
Attempting to assign an ACL to VLAN 1,
All 4.2 supported
Web UI not
Binding an IP ACL as out bound to an
All 4.2 supported
Auto-neg option
Auto-neg is an option in the port
All 4.2 supported
Routing fails on
VLAN
and as part of a network change t hey
wanted to remove a VLAN rout ing interface
that was no longer in use. When they
removed the IP address from this VLAN,
they lost routing across the entire switch.
Ports are now checked to
ensure they are not part of
other routing VLANs before
clearing the ARP poli cy on the
port.
platforms
crashes switch
password min
length error
using web GUI
Switch GUI.
mode issue with
10G ports in
aggregator
configuration
changes after
reload.
via Web UI
refers to
"Management
VLAN"
security-->password management,
If the password min length is unchecked
and applied, there is an entry in the running
config for "no passwords min-length". This
can be verified through CLI. After this, on
enable passwords page if we try to set a
password which is any length less than 8,
we get an error message as shown in the
NO way to unselect them again via GUI.
Using command-line configuration is the
there
after a switch reload.
via Web UI, generates an error message
referring to the Managemen t VLAN.
"Error! Cannot Bind ACLs to Management
VLAN."
A large array is allocated
statically instead o f o n the
stack.
Password ranges are no w
allocated dynamicall y on web
pages.
Tagged VLANs can be
unchecked in simple mode
Add interface command i s
corrected.
Previously, the input
mechanism ignored ANY lines
beginning with an exclamation
point. Now, the CLI engine
will allow lines with a leading
“!” in the banner
the hard coded value has been
removed in favor of the correct
VLAN val u e
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
generating error
for out bound
ACL & applies
the config.
via Web UI is
not grayed out
for 10Gb fiber
ports.
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 41
interface, via Web UI, does not generate an
error message. Further more, the config
gets applied to the interface as an inbound
ACL. When the same action is done via
CLI, an error message is gener ated and the
config is not applied.
configuration via Web UI for 10Gb fiber
ports. Ideally the auto-neg option should be
grayed out for 10Gb fiber ports.
Use of the direction object has
been corrected.
Auto-negotiation selection is
disabled for 10G ports in the
Web as auto-negotiation must
always be enabled.
platforms
platforms
Page 44

CLI command
The CLI command “show interface detail
All 4.2 supported
Creating
config
Using web GUI to create and assign ports
All 4.2 supported
Assigning ACL
via Web UI
When binding an ACL to a VLAN
All 4.2 supported
Incorrect Model
The last revision date has not been revised.
Nov 2003 12:00:0 0
All 4.2 supported
Links do not
Link dependency CLI "show link-
of the members or the depended-on ports.
All 4.2 supported
M8024 does not
configuration
Show spanning-tree mst-config not
PCM8024
Need to increase
than 50
Previous limit was 20.
All 4.2 supported
On the 8024F,
The PowerConnect 8024F ports 1 and 2 will
PC8024F
The CLI
value
When executing the command terminal
All 4.2 supported
The Service tag
platforms.
When executing the “show system id” is not
All 4.2 modular platforms.
"show interface
detail portchannel1" locks
up console
session
VLANs,
assigning ports
using vlan
membership
detail page
causes removal
from running-
Priority to a
VLAN interface
does not get set
numbers and
revision date in
dellref.my
show status
port-channel1” generates the following
errors:
Max number of lines in the scroll buffer
reached. Output will be truncated.
via vlan membership detail page causes
previous vlan ports and sometimes previous
vlan to be removed from running-config.
interface, via Web UI, th e "Ass ign ACL
Priority" field does not get set as it would if
it were configured via CLI.
This could lead a customer to believe they
do not need to update their MIB file.
LAST-UPDATED "200311210000Z" -- 21
dependency" shows "Member ports" and
"Ports depended on" port numbers along
with group id, but does not show the status
The scrolling issue h as been
corrected.
VLAN creation
addition/removal behavior is
corrected.
Web interface has been
corrected.
The MIB has been corrected.
Administrators are advised to
load the new MIBs when
updating to this release.
The display has been updated
to show the requested
information
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
platforms
save complete
MST vlan
the VRRP
routing
instances or
VRID to greater
inserting or
removing the
cable on ports 1
and 2 causes
both ports to
shut down
briefly
command
terminal length
is not setting
terminal length
is being deleted
on modular
working.
flap briefly when cables are r emoved and
reinserted.
length <value>, the value is not updated
after execution.
showing the service tag on modular
platforms.
All MSTP configurations are
now saved.
VRRP instances are now set to
50.
All inter-phy operation is
fixed.
Terminal length settings now
take effect immediatel y.
The service tag was
accidentally being deleted and
is now being saved correctly.
platforms
platforms
42 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 45
PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected
Platforms
PC7048R-RA switch has boxes
PC7048R-RA switch has cpu process boxes
Corrected CPU utilization
PC7048R-RA
The warning message about IP address
one subnet.
Add warning message in
port
Config commands did not
3.1.5.13
Command "spanning-tree mode mstp"
3.1.5.13.
Auto-neg option via Web UI is
ports.
Auto-neg option via Web UI is not grayed
k.
Simple mode, VLAN setting
moved to another group
if a port is moved from one aggregation
retained but not applied until reboot.
Unable to configure secu re
SSH from web interface.
Error message 'sshcfg_load start' missing
is returned.
Secure HTTP Random
Random characters populate the Secure
IP PIMSM BSR/RP Mapping
When the RP or the BSR changes, the data
get software forwarded.
Error messages when issuing a
Accessing unsupported counters causes
Release 4.1.1.9
req cpu process 38-54%
utilization with single power
supply.
Router crashes on OSPF
network type change.
Occasional crash when
configuring VRRP.
Cannot create Dynamic LAG
with Interface range co mmand
PC8024 cannot forward
packets on port9 to port16
while linked on at 100Mb.
Show fiber-por ts opt ic a l transceiver is not displaying
the correct interface numbers.
VRRP routing instances
increased to 50.
DHCP on in-band and out of
band ports
req running betw een 38-54 % utilizat ion if
it’s running either only with primary or
secondary power supply.
The switch can crash when changing the
configuration from the default of broadcast
to point-to-point.
With routing globally disabled, bouncing
VRRP on a host interface occasi onally
causes a crash.
Dynamic LAG cannot b e cr eated from CLI
using interface range command.
PC8024 cannot forward packets on port9
to port16 while linked on at 100Mb.
Instead of reporting on exact ports that had
modules, diagnostics were reported on the
ports that did not have modules
VRRP routing instances increased to 50. Increased VRRP routing
conflict is not printed in case DHCP is
configured on in-band and out-band ports
and they both receive an IP address from
issue when running with one
power supply.
Corrected process
synchronizati o n pr o bl e m
Correct the transition
between routing being
disabled and routing being
enabled.
Correct the command
syntax to "auto " instead of
"active"
Correct interoperability
problem between the PHY
and the switching core.
Corrected register pr oblem
when accessing the SP F+
ports
instances table.
case offered IP addres s is
conflicting with the
configured one on another
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
PC8024
PC8024F
PCM8024
All Platforms
All Platforms
migrate correctly from vers ion
not grayed out for 10Gb fiber
not active when a port is
Characters
is not robust
show statistics command while
traffic running.
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 43
doesn't migrate correctly from version
out for 10Gb fiber ports for the PCM8024-
group to other, VLAN settings are
HTTP web page.
traffic may get affected and in some case
error messages to be displayed.
Correct the command tree to
migrate the old syntax.
Corrected the Web UI. PCM8024-k
Correct initialization when
port is moved.
Corrected Web page error . All Platforms
Corrected Web page data
initialization.
Corrected RP join
processing.
Change the logging priority
of the messages for
unsupported counters so that
they are not output.
All Platforms
PCM6220
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
Page 46

Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected
When network re-configuration happens,
traffic.
Port Configuration page gets
any setting is changed.
IGMPv3 querier sent in error
DNS client error in logs and
Message: “nimCheckIfNumber: internal
"no enable authentication"
telnet line
If LAG port is configured as general trunk
agentLagSummaryAccessVlanID.
PCM6348 - Log message
output
Missing port VLAN
membership in the GUI.
Routing fails on VLAN. Removing a VLAN routing interface
PIM BSR join messages. PIM Join messages using wrong RP
PIM-SM Not al l data passed
down to the RPT.
SNMP walk through unsupported counters
cause error messages
If switch has less than 24 ports, Port
VLAN membership will not be shown in
the GUI.
causes routing to b e lo s t across the entire
switch.
Address
the multicast traffic may not properly
converge thus resulting in loss of some
Platforms
Change the logging priority
of the messages for
unsupported counters so that
they are not output.
Corrected the VLAN port
data issue.
Corrected the VLAN
interface removal problem
Corrected Join without a
Prune condition.
Corrected Join condition. All platforms
All Platforms
PC70xx
PCM6220
All Platforms
errors on 10GB ports when
PIM-SM RP Fails to send
Register Stops.
with source address 0.0.0.0
PIM-SM Jo ining messages
using wrong RP address
Fails to reconfigure and
forward multicast messa ge
switch locks up and needs to
be rebooted.
PIM-DM Prune states
expiring.
Email alerts do not contain log
message.
log message "internal interface
number 183 out of range" is
seen.
does not disable access to
privileged EXEC over the
Port Configuration page gets errors on
10GB ports when any setting is changed.
Register-Stop messages may not be sent
out on the correct interface through to the
First Hop Router.
Switch will get moved to non-querier
mode if an IGMP membership query
arrives with source address 0.0.0.0.
PIM-SM Joining messages using wrong
RP address
Switch fails to reconfigure and forward
multicast messages following link failure
Error message “DNS Client:
osapiSocketRecvFrom returned error for
address 0xAABBCCDD” being logged
The router might end up sending Graft
messages even thou gh there are no
intended hosts.
Current e-mail messages display in e-mail
applications with a blank body, log
message is not displayed.
interface number 183 out of range” is
displayed.
"no enable authentication" does not
disable access to privileged EXEC over
the telnet line
Corrected Web page error . All Platforms
Corrected Register Stops
message error.
Corrected valid address
check for membership query
packet.
Corrected Join message
processing.
Correct an RPF information
problem when link goes
down.
Corrected error in tas k t hat
handles changes of the
Service Port link status
Corrected a PIM-DM
timeout error.
Corrected error in email
header section.
Corrected error in VLAN
create web page
Corrected error in
authenticati on pr oc e s s ing.
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
dot1q_api.c error during MIB
walk
sFlow Timeout settings for
CLI command
44 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
then log message is getting printed when
snmpwalk is accessing the MIB OID
sFlow receiver timeout value should be
optional
Corrected VLAN access
error.
Changed receiver timeout
value to be optional.
All Platforms
All Platforms
Page 47

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
The sFlow agent field isn't being filled into
Stack module inserted in Bay
Summary User Impact Resolution Affected
Platforms
sFlow: Limit of 32 for the
number of interfaces for which
sFlow can be enabled
sFlow: Formatting errors with
some of the records
sFlow: The sample Pool field
is not being incremented
properly
sFlow: The sFlow agent field
isn't being filled in
1 and SFP+ module in Bay 2
CLI "switchport gen eral
acceptable-frame-type"
different options than GUI
startup-config cannot be
restored via tftp
"show ip ospf database" does
not respect configuration of
"terminal length 0"
Occasionally, "clear con fig"
from console triggers
wio_api.c traceback
Radius config stops working
after reboot.
ISDP timers running fast. ISDP entries are timing out and dropping
VRRP hang VRRP los s of mastership causes the switch
IPMC error messages and
forwarding issue.
Dynamic LAG Ports are
flapping/continuous trace
messages.
Simple Switch should have FC
enabled by defa ul t
Need to change message on
console when try to
downgrade anything below
4.1.0.19 release for new DDR
Current limit of 32 for the number of
interfaces for which sFlow can be enabled.
Some of the sFlow records had formatting
errors.
Sample pool field will not be incremented
in the sFlow packet sent t o the collector.
sFlow Packet.
With the presence of stack module at bay1,
SFP+ module in bay2 will not get detected
until the stack-module at bay1 is removed.
The CLI "switchport general acceptableframe-type" contains different options than
GUI.
TFTP script download or saved script
validation will leave the DUT in an
unusable state.
The CLI handler of the "show ip ospf
database" command does not consider the
terminal length configuration.
Occasionally, "clear con fig" from console
triggers wio_api.c t raceback
Radius config stops working after reboot,
needs to be removed and re-added in order
to work again.
off the list before the next update comes
in.
to hang.
Error messages indicating that IPMC table
are not set correctly in hardware.
Lags do not stay up on combo ports. Corrected an error in
Enable Flowcontrol on simple mode. Flowcontrol enabled on
If a switch contains new DDR,
downgrading to 4.1.0.19 is not allowed.
Changed the limit to allow
all sFlow instances.
Corrected sFlow header
problems.
Corrected sample pool field
error.
Corrected problem adding
sFlow agent address.
Corrected error that
prevented the detecting of
SFP+ module in bay 2.
Options are now the same. All Platforms
Corrected script validation
problem.
Corrected terminal len gt h
configurati on ha nd l ing.
Corrected “clear config”
internal message error.
Corrected error in Radius
user authenticatio n
processing.
Corrected an error in the
ISDP timer disable
processing.
Corrected an error in the
VRRP processing of the
new IP address.
Corrected error message
processing which generated
false error messages.
mapping the physical ports
to a LACP logical port.
simple mode.
Modified the downgrade
message.
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
PCM6220
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
PCM8024
PCM8024-k
(with new
DDR)
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 45
Page 48

Release 4.1.0.19
Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected
PC8024F/
All Platforms
All Platforms
PCM8024-k
Combo ports flapping when
fiber port connected to certain
other vendor switches
New M8024/M8024-k cards
have different memory parts
requiring changes to DDR
timings
10GBaseT ports do not come
up
Switch crashes when
executing “show interfaces
detail te1/2/1” command with
no space between “te” and the
unit/slot/port identifier
OOB Default Gateway does
not save when using CLI setup
wizard
Upgrades to 4.1.0.6 are
causing network outages. The
wizard from 4.1.0.6 fails to
setup interfaces
The combo port is not coming
up after performing repeated
plug-out and plug-in.
Line "no passive-interface
Vl32" in startup-config does
not get loaded on startup.
Unable to configure Secure
Shell from web interface.
OpenManage web interface
fails to provide an iSCSI web
page when selecting the iSCSI
item.
Wrong information for current
link status in port
configurati on pa g e .
PFC sends packet after quanta
extension received.
CLI command "show ipv6
interface" does not paginate
correctly.
MOTD Banner appears at t he
wrong time.
Platforms
Users unable to reliably operate over
combo ports
User unable to downgrade t o earlier
version of firmware
Unable to use 10GBaseT ports on
PC7048R-RA
Service inter rupt ion due to crash Issue has been corrected. M8024
There was no way to configure the
gateway on Out-Of-Band interface.
Ports on some devices will not attach. Corrected the Configuration
The fibers port associated with Fiber /
RJ45 combo ports may flap or not link up
with certain other switches.
The "no passive-interface Vl32"
configuration does not get loaded from the
startup-config on startup.
Proper web page operation is prevented. Web page has been
The web page for iSCSI fails to open when
selected with OpenManage.
Incorrect stacking link status is presented
in the Web page.
This can cause FCOE failures when using
PCM8024-k as a tran s it switch between
some switches.
A large number of interfaces cause
information to scroll off the viewing area.
MOTD and Login Banner is not visible
before login for SSH users.
Corrected combo port
flapping issue with new
PHY firmware. Added new
media-type command to
configure the preference on
a combo port
No resolution. Newer IOMs
do not support earlier
versions of firmware.
Corrected internal
addressing of port. Ports
now come up properly.
Add functionality for
configuring gateway on
Out-Of-Band interface.
Wizard to properly apply
the configuration to all
ports.
Add commands to allow
operator to pref er or force
RJ45 or SFP port selection
on combo ports.
Corrected the loading of the
"no passive-interface Vl32"
configuration.
corrected.
Web page has been
corrected.
Web page output has been
corrected.
Switch no longer sends
packet after quanta
extension received.
Fixed the pagination for the
command.
Fixed the banner proc e s s i ng
function.
PC8024
PC8024F
PCM8024
PCM8024-k
PC7048R-RA
M6220
M6348
M8024-k
All Platforms
All Platforms
PC8024
All Platforms
PCM6220
All Platforms
PCM6220
46 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 49

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
PCM8024
All Platforms
PC8024
Model numbers which are
Corrected VLAN instan ce
Correct the handling of
Corrected the ability to
the running-config.
Corrected the port mapping
configuration.
PCM8024
Added an error message.
All Platforms
Corrected the fetch o f
All Platforms
Correct password length
All Platforms
Corrected a memory
All Platforms
Corrected the Web page t hat
PCM8024
Summary User Impact Resolution Affected
Platforms
Summertime function running
early.
Switch does not save complet e
MST VLAN configuration.
Switch failed to generate new
RSA/DSA crypto keys.
Banner MOTD configuration
changes after reload.
VLANs can get removed from
running-config.
Console session locks up. CLI command "show interface detail port-
Fiber diagnostics reporting
incorrect port type.
BROADCOM-REF-MIB
reporting incorrect values.
Switch crashes when full vlan
range assigned to MST
regions.
Config Wizard causes iSCSI
error messages.
SSH configuration not restored
after reboot.
The summertime function resets the time
on the wrong week.
The correct configuration was not being
saved if there are more than 1K VLANs in
a single MST instance.
“Failed to generate RSA key.” message
was produced and keys were not
generated.
After reload a MOTD with an embedded!
Character will be truncated .
Creating vlans, assigning ports using the
vlan membership detail page causes
removal from running-config.
channel1" locks up console session.
When running fibe r diag nostics, Ports 5, 7,
8, 13, 15, 16 report to be fiber ports and
not copper ports.
Incorrect Model numbers and revision date
in BROADCOM-REF-MIB dellref.my
When the full range of VLAN instances is
assigned to a MST region the switch
crashes.
Using the config wizard to setup the
PC8024 causes iSCSI error messages.
The 'ip ssh protocol 2' is not being
included in the running configuration.
Corrected the function that
returns the day of the week
to account for parti cul ar
months and leap years.
Corrected the VLAN
configurati on buffer size.
Fixed error condition when
generating keys.
Fix the MOTD engine to not
ignore the leading ‘!’
character.
Corrected default VLAN
checks when updating
VLAN information.
Corrected buffer overflow
during "show interfaces
detail" execution.
Fixed reporting of valid
copper ports.
described in dellref.my are
corrected.
buffer overflow.
iSCSI admin mode.
place 'ip ssh protocol 2' in
All Platforms
PC8024
PCM8024
PCM8024
All Platforms
PC70XX
PCM6220
PC8024
All Platforms
1GB link being negotiated on
10GB Intel X520-KX4
No message logged for "Max
number of SSH login sessions
exceeded"
VLAN web page not updating. When VLANs are removed using the web,
No password min length error
when using web GUI.
MIB walk crashes switch. When running a large SNMP MIB walk
Unable to deselect VLAN tags
in web GUI.
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 47
Some internal links on the Modular
switches will not link at 10Gb.
When the Max number of SSH sessions is
reached no error is logged.
the GUI doesn’t display the ports that are
members of the VLAN.
If "no passwords min-length" Is set an
error results if the password is less than 8
characters.
the switch crashes.
Once Tagged-Vlans are selected there is
no way to unselect them again via the web
GUI.
to allow proper port
current VLAN data.
range check.
problem in the MIB walk.
allows tagged VLANs to be
unselected.
PCM8024-k
PCM8024-k
Page 50

Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected
Access is allowed to files on
Corrected the web process
All Platforms
Corrected download web
All Platforms
Corrected task table
All Platforms
Corrected task table
All Platforms
Corrected the code looping
All Platforms
Corrected the code looping
All Platforms
Correct the SDRAM test
PCM8024-k
The help page for the PCM8024-k
Corrected the help page.
PCM8024-k
When the switch boots, If the CRC check
of the VPD fails, the switch will hang.
Corrected check for valid
VPD before CRC check.
All Platforms
Improved Performance with High
Improved performance.
PC70XX
PC6348
PCM6220 Web pages did not have the
Updated the PCM6220 web
PCM6220
Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected
the switch without log in
permissions required
Switch crashes when
downloading without the .stk
extension.
Switch crashing when HTTPS
session is enabled.
Switch crashing when trying to
open more than 3 HTTPS
sessions
Mozilla Java Script er r or when
selecting VLANs.
IE7 error when selecting
VLANs.
SDRAM test does not run the
specified number of iterations.
PCM8024-k Web page an d
help page mismatch.
VPD CRC check hang
If the file name is known, th e fil e can be
downloaded through the web browser
without having to be logged in.
Switch crashes when trying to download
code without .stk extension through
HTTPS using HTTP.
Switch is crashing when HTTPS session is
enabled from CLI but not from WEB
Opening more than 3 or more HTTPS
sessions will crash the switch.
In Mozilla, when 1-4085 VLANs are
*selected* in the web page for Tagged
VLAN Java Script error appears.
In IE7, when 1-4085 VLANs are
*selected* in the web page for Tagged
VLAN IE7 error appears.
When running the SDRAM test a <cntl-c>
must be used to exit the test.
Switching--> Network Security--> Dot1x
Authentication--> Authentication Detail
page did not match the page.
Platforms
to require login credentials
before downloading a file.
page.
memory size.
memory size.
error.
error.
iteration loop.
Packet Buffer Optimization.
PCM6220 Stack View needs
PCM70XX styling
Release 4.1.0.6
SSH crash - memPartAlloc:
block too big
PC M8024 switch reset out-ofband address to none when
switchports were changed
Web page shows IP address as
'0.0.0.0' for '1.1.1.1' routing
interface.
Read-Only Web page is
populating all configured IP
and IPv6 ACL names when we
select the ACL Name.
Utilization iSCSI Workloads.
same styling as PC70xx.
Reduced switch functionality. Memory allocation issue is
Inability to access switches via OOB port. The out-of-band address is
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations
Potential operator confusion regarding web
page operations.
pages.
corrected and checked fo r
memory leaks
maintained over switchport
changes.
The web page output has
been corrected.
The web page has been
corrected to only populate
the selected entry.
PCM8024
PCM8024-k
PC8024
Platforms
All
Platforms
PCM8024
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
48 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 51

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Summary User Impact Resolution Affected
Platforms
FAN LED graphic on web page
needs to glow in RED when
FANs are not operational
(stopped).
Incorrect command is being
displayed in running-config,
when boot host dhcp is
disabled.
DUT crashes while configuring
max dynamic VLANs.
Manager of the stack is
changing when trying to learn
maximum number of VLANs
using GVRP.
Switch prompts to save config
data when no changes have
been made
Crash while RFC3918 Group
Capacity test is running
'no' version of 'key' command
is not implemented
Password is not accepting
quotation ( " ) character
Incorrect warning message
displayed while executing the
command "boot system <unit>
image1"
IPV6 command displays wrong
output
LLDP-MED log messages
showing 5 sec difference in
entry age out information
DHCPv6 web issues Potential operator confusion regarding
LLDP MED application should
not allow configuration of
location and inventory transmit
TLV's as underlying
application not pr e s e nt
Inability to determine switch status. Web page has been corrected All
Platforms
Potential operator confusion regarding web
page operations.
Network outage possible. The PowerConnect does not
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch operations.
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch operation.
Network outage possible. The PowerConnect switch
Potential operator frustration with switch
management.
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch configuration.
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch operation.
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch operation.
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch operation.
switch configuration.
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch configuration.
The running config now
shows the correct
configuration
crash when using maximum
dynamic VLANs
The stack manager does not
change during learning with
GVRP
The switch no longer
prompts to save config data
if no changes have been
made
runs the RFC3918 test
without crashing
The no key comman d is
implemented to return the
key configuration to the
default.
Passwords can be enclosed
in quotes (contain embedded
blanks). A password may not
contain a quote. The
accepted character set and
length is documented in the
CLI reference manual.
The error message has been
corrected to indicate that the
unit selected for reboot does
not exist.
The IPv6 output has be e n
corrected to remove the
duplicate display lines in
show ipv6 he lp.
The LLDP timer has been
updated to account for
processing skew.
The acceptable ch ar acter
sets are documented in the
CLI Reference guide.
Location and inventory
TLVs cannot be enabled for
transmission in LLDP MED.
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 49
Page 52

Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected
SysUpTime is not being shown
correctly duri ng an SNMP walk
(Poll interval 1sec)
Log messages need to be
corrected on ip dhcp snooping
rate limit scenario.
The show ip vlan command
output is not proper after morequit prompt is encountered, i.e.
after around 16 routing
interfaces
Invalid error port number
displayed on log message when
vlan is changed to forbidden
mode from access mode
The banner motd XXXXX
does not appear in show
running-config
Web page mac-vlan table too
slow to load.
Confused between ip default
gateway and ip default route
(update manual with how to set
a default route).
Auto Install show boot retry
count line needs to be left
aligned by one space.
Cannot Access Optical
Transceiver Diagnostics Page if
Multiple Submits done prior to
initial refresh completing
Error messages for non-existent
stack members non-informative
Traffic is forwarding when
IPv6 forwarding is disabled
A LAG member comes UP if
configured individually as no
shutdown, even though the
port-channel's state is d own
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch operation.
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch configuration. Inability to diagnose
network issues.
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch configuration.
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch configuration.
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch configuration.
Potential operator frustration with switch
management.
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch configuration.
None. The retry count alignment is
Potential operator frustration with switch
management.
Potential operator confusion regarding
switch configuration.
Incorrect operatio nal state in network. The ipv6 forwarding
Incorrect operatio nal state in network. LAG members are placed in
The correct variable is u sed
to write SysUpTime
Interface representations in
log messages use unit-slotport format.
The paging has been
corrected.
The error message is no
longer issued.
All banner configuration
appear in the running-config
For certain browsers, paging
has been implemented t o
speed up load times.
The ip default route
command is deprecated. Use
the ip default route
command to set a default
route.
corrected
This is a browser dependent
issue (IE 6) that is not seen
in later versions. Th e web
session recovers after d oing
a refresh.
The user can pre-configure
stack units. If the stack unit
does not exist for a switch
configurati on ope r a ti o n, a n
error message indicat ing
same is issued.
command is deprecated. To
disable traff ic forwarding, use
the “no ipv6 unicast-routing”
in place of the “no ipv6
forwarding” command.
the blocking state for
dynamic LAGs and only
come up when the LAG link
comes up.
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
PCM8024
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
PC70XX
PCM8024
All
Platforms
50 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 53

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Summary User Impact Resolution Affected
Platforms
Re-authenticate Now check
box is not highlighted when
edit check box is selected
Block command is not seen in
show running config through
web and cli
FDB entries are getting aged
out before default age-out time,
when both FDB and MFDB
tables are full.
DHCP packets forwarding i s
not proper to/from the trusted
and un-truste d port s
Configuring all ports in all
VLANs takes a long time
Max number of OSPF
neighbors not su pp or te d
Cable fault distance not getting
displayed in WEB in case of
cable with one or more pairs
cut or short.
Ports representation need to be
changed in debug messages
No error message for illegal
characters in various command
parameters
The ARP entry is not seen in
the ARP table when an ARP
reply is sent to DUT.
Mapping Table configuration is
not being displayed on ReadOnly mode user web page.
ACL is getting deleted when
trying to create max+1 rul e.
LLDP-Med TLV information
not registered for jumbo frame
sizes greater than 8000
VLAN binding entries are not
being displayed on Read-Only
mode user web page.
Inability to configure switch. The Re-authenticate Now
check box is highlighted
when the edit check box is
selected
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations.
Incorrect operatio nal state in network. The frame flooding routing
Potential operator frustration with switch
management.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations. Inability to diagnose network
issues.
Potential operator confusion over switch
configuration.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations. Inability to diagnose network
issues.
Potential operator confusion over switch
configuration.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations. Possible security issues.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations.
The block command is a
temporary administrative
assignment and is not
maintained persistently in
the saved or running configs.
On the PCM6220, the
MFDB and FDB tables are a
shared resource. The user is
continually sending new
MFDB entries, which causes
old FDB entries to be
removed to make a place for
the new MFDB entries.
in DHCP snooping now
takes into account trust
status.
VLAN configuration has
been optimized.
The maximum number of
neighbors is supported.
The fault distance is
displayed in the web page.
Ports are now displayed in
C/S/P standard format
The accepted character set
and length is documented in
the CLI reference manual.
ARP entries are stored
properly
The mapping table is
displayed for a read-only
user.
Corrected error checking
logic.
Jumbo LLDP frames are
now processed properly
VLAN binding entries are
available to read only users
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 51
Page 54

Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected
Unable to execute the
command dot1x timeout txperiod 1
In switching> network security
>dot1x authentication web
page in read-only user mode,
the Re-Authenticate Now
check box can be checked
System Device information
web page LED information not
in sync with front panel LED
information.
DHCP snooping static binding
thru DHCP request is denied as
this is an expected behavior.
Mode of transfer is displaying
“unknown,” while
downloading the code from ftp
Allow disabling and enabling
of terminal paging
Web does not allow to
configure image descriptor to
its max length i.e. 255
characters.
CDP (ISDP) is a c tive on portchannels instead of the member
Ethernet interfaces. For
dynamic LAGS, the ISDP
information is not exchanged
on the interface until the portchannel becomes active.
CLI Manual Has No Index Potential operator frustration over switch
Script validation is fails when
max SNTP servers are
configured.
Configured SYSLOG server
parameters cannot b e updated
without deleting and reconfiguring
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations. Possible security issue.
No Potential operator impact expected. This issue was regarding
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations.
Potential operator frustration over switch
configuration.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations. Inability to interoperate with
other switches.
configuration.
Potential operator confusion over switch
configuration.
Potential operator frustration over switch
configuration.
This command is accepted
with a timeout period of 1
second. Corrected range
check on input.
Read-only properties are s et
for the check box
various stylistic aspects of
the system device web page.
The system device web page
conforms to the requirements
as it exists and does
necessarily match th e C LI
with regarding to
capitalization or naming
conventions
Removed the log message
indicating that a bound
DHCP client with an existing
binding sent a DISCOVER.
Added a counter for this
condition to the DHCP
debug statistics.
ftp transfer mode is
displayed
The terminal length
command is now
implemented.
Images descriptors up to
255 characters are allowed
CDP is active on the
member ports for dynamic
LAGs when the LAG is
active.
The CLI manual has an
index.
Corrected CLI validation
check so that existing ser ver
can be entered multiple
times.
Syslog server parameter can
be updated in the CLI
without deleting the server.
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
52 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 55

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
LLDP Assignment of port ID for
Management ACL list needs
SNMP support for D ell-LAN-
Simple mode BPDU w ill pass
single link per aggregator
Fatal error cra sh and reload when
Interface metric not working on
Local system MAC address
channel"
SNMP going unresponsive on
Network perf ormance and
H323 VoIP traffic and
LACP not working with Juniper
PDUs.
Summary User Impact Resolution Affected
Platforms
CLI will not let user configure
available parameter for the given
IGMP command
Inconsistent b ehavior - using
same port number for multiple
services
Port-Descrip tion TLV
"Match every packet" option
TRAP-MIB
thru port-aggregator to other
port-aggregator when using a
Potential operator frustration over switch
configuration.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations. Inability to diagnose network
issues.
Potential operator frustration over switch
configuration. Possible security issue.
Potential operator frustration over switch
configuration.
Network outage if conn ected to Cisco with
BPDU-Guard enabled
IGMP configuration
commands can be enter ed in
interface VLAN mode at any
time.
Attempting to add a service
with a TCP port overlapping
a TCP port used by an
existing service is denied
with an appropriate error
message.
The LLDP port id TLV is
supported by Powe r C onne c t
and can be displayed on peer
devices.
New syntax has been added
to the management ACL to
allow the any specification
for the service type.
The Dell-LAN-TRAP-MIB
is supported.
BPDU flooding is now
disabled on aggregator ports.
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
uplinked to Cisco 6509 - 3.1.3.9 Believe to be ISDP
8024 OSPF passi ve int erface
displayed as partner MAC
address in "show lacp port-
modular switches within 6 hours
connectivity is sues. Evidenced by
“l7utils_inet_addr” messages in
log.
Crashing/Rebooting switch. CPU
PID '17c31570 voipTask' spikes
as seen in the 'show p rocess cpu'.
EX-4200, show inactive port
channel state. System is sending
oversize (132 bytes) LACP
Inability to connect to Cisco 6509 CDP
enabled ports
Interface metric is adverti s ed as 0 when
configured as passive – passive interface
preferred over active in terface
Potential operator confusion over network
topology
Potential operator frustration over switch
operations
Potential operator frustration over switch
operations
Potential operator frustration over switch
operations. Switch degradation in VoIP
deployments.
Potential operator frustration over switch
operations. Inability to interoperate with
Juniper switches.
The switch now handles
CDP mega-packets of size
1376.
The interface metric is
advertised properly when the
interfaces is configured in
passive mode.
The partner MAC address i s
displayed in the Partner
system MAC address field.
SNMP operations have been
corrected and tested without
issue for over 24 hours.
The internal timer operations
have been highly optimized
resulting in lower overall
CPU utilization.
The VOIP QOS code is no
longer processing VoIP
packets when it is admin
disabled.
The LACP process now
sends 128 byte LACP PDUs.
Interoperability with Juniper
switches is verified.
PCM6220
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 53
Page 56

Summary
User Impact
Resolution
Affected
Stack splits into multiple masters
when MU fails.
VLAN name issues in web UI on
switching to new VL A N.
Discards Occ urring After
STP topology changes when an
ARP broadcast traffic not
modular. Old VLAN name is
retained on web page when
Potential operator frustration over switch
operations.
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations.
Issue in SDK MAC reset
function resolved such that
connected unit respond to
master within 1 ms. Stacking
stability verified under the
conditions where issue
occurred.
The correct VLAN name is
always displayed.
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
Firmware Update to current
version 3.1.5 .4.
OOB SSH connection is
established
forwarded through static/dynamic
10Gb LAGs
Potential operator confusion over switch
operations.
Potential operator frustration over switch
operations.
Potential operator frustration over switch
operations. Potential network instability.
The wrong counter was
being displayed in the CLI.
The CLI commands “sho w
statistics port-channel” and
“show statistics <inter f ace>”
are corrected to use the s ame
counter as SNMP.
The SSHD task was starving
other tasks in the system and
causing topology changes.
The SSHD task priority is
now set to the shared time
slice priority.
A field was being utilized in
the LAG hash algorithm that
could result in different hash
indices on different units of a
stack. This field (modid) has
been removed from the hash
selection algorithm.
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
All
Platforms
54 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 57

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
ip igmp snooping querier
query-interval
The guideline under this command refers to the IGMP Snooping Max Response
Max Response Time is 25 sec
terminal monitor
The command does not have any arguments or a particular expected output hence
( in privileged exec mode to display logging messages on terminal )
ip mtu
The guideline should be augmented with the below text:
outgoing interface.
rate-limit cpu direction
input pps
no rate-limit cpu direction
input pps
Use the rate-limit command to reduce the amount of unknown unicast/multicast
Note: This command is not available on the PCM6220 switch.
show system internal pktmgr
internal control sw-rate-limit
The show command is to display the configured CPU rate limit for unknown packets
Note: This command is not available on the PCM6220 switch.
CLI Reference Guide Updates
Release 5.1.1.7
No Updates
Release 5.1.0.1
The following table list s issues found in the CLI Reference Guide after publication:
Command Issue
pps_value
Time. A reference that this can be configured using command ip igmp query-maxresponse-time under IGMP commands is missing. The default IGMP/MLD snooping
an example for this is missing in the guide.
prompt#: terminal monitor
Use the ip mtu command in Interface Configuration mode to set the IP
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) on a routing interface. The IP MTU is
the size of the largest IP packet that can be transmitted on the interface
without fragmentation. Packets that are L2 forwarded in hardware ignore the IP
MTU. Packets that are L3 (VLAN routing) forwarded in hardware observe the IP
MTU. Packets forwarded in software are dropped if they exceed the IP MTU of the
packets forwarded to the CPU. Use the “no” form of the command to set the rate
limit to the default value.
pps_value – range 100-1024 packets per second (100-3000 for PC81xx
switches).
The default ingress rate limit is 1024 packets per second (3000 for PC81xx
switches).
This command allows the administrator to reduce the rate limit for which
unknown un i cast and multicast packets are forwarded and/or copied to the
CPU. It does not affect the rate limits for control plane packets. It is almost
never necessary to use this command to change from the default value. The use
of this command should be restricted to situations in which moderate to high
rates of unknown unicast/multicast are contin ually sent to the switch CPU as
evidenced by the show proc cpu command and where the
ipMapForwardingTask is showing high CPU usage. This will occur most
frequently in networks where a high number of ARPs are continually received
on untrusted ports, high numbers of L2 stations are timing out and reappearing
or multicast flooding is occurring in the network. If problems with L2, L3 or
multicast learning occur after changing this value, set the rate limit back to the
default value and take other steps to correct or mitigate the underlying network
issue directly.
in packets per second.
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 55
Page 58

Release 5.0.1.3
Show snmp filters
Snmp-server filter
The following note should be added to the command usage guidelines.
aaa authorization {exec }
{default | <list_name>}
method1[method2]
no aaa authorization {exec}
{ default|<list_name>}
authorization exec [default
|<list_name>]
no authorization exec
debug aaa authorization
exec
no debug aaa authorization
exec
The following Exec Authorization CLI commands are missing from the CLI reference
Command
Issue
The VLAN name command has been migrated to VLAN Config mode
No Updates
Release 5.0.0.4
Command Issue
Release 4.2.2.3
No Updates
Release 4.2.1.3
When a filter is defined, SNMP treats the filter as having an 'exclude all' statement at
the beginning of the filter. Unless an include statement is specified, all notifications
will be excluded.
guide
aaa authorization {exec } {default | <list_name>} method1[method2]
no aaa authorization {exec} { default|<list_name>}
authorization exec [default |<list_name>]
no authorization exec
debug aaa authorization exec
no debug aaa authorization exec
Storm-control bro a dca s t
name "RDU-NOC
Management VLAN "
Release 4.2.0.4
Please refer Dell PowerConnect CLI Reference Guide for more details
Release 4.1.1.9
No Updates
56 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
The supported syntax is Storm-contr ol broadcast [level rate] where
rate is a parameter to level and defined to be:
The storm-control threshold as percent of port speed. Percent of
port speed is converted to PacketsPerSecond based on 512 byte
average packet size and applied to HW.
If level is not used the default rate is 5.
and is no longer available in interface VLAN mode.
Page 59

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Release 4.1.0.19
The following commands are supported on switches that have combo ports:
Comma n d me di a -type
Syntax:
media-type { auto-select [rj45 | sfp ] | rj45 | sfp }
auto-select rj45 - utilize RJ45 media when both media types are active
auto-select sfp - uti lize the SFP media when both medi a types are active
auto-select – return the selection to the default (auto-select sfp)
rj45 – force connection on the RJ45 port. Power off SFP media port
sfp – force connection on the SFP port. Power off RJ45 media port
Default Configurati o n:
The default is “media-type auto-select sfp”
Command Mode:
Interface Config mode
Description:
Select the media type for the interface. This command is only valid on combo ports.
User Guidelines:
When both media types are co nnected, the preference as determined by the auto-select keyword parameter selects the
active media. When the au to-select keyword is no t specified, the selected media type is powered on and th e alternate
media type is powered off. Note that when the auto-select keyword is used with any media type, the SFP port will remain
powered and the laser, if any, will remain on in order to allow connections over the SFP port.
Examples:
! Select the RJ45 port and power off the SFP port
console(config-if-Te1/0/24)#media-type rj45
! Prefer the RJ45 port and leave the SFP port powered on
console(config-if-Te1/0/24)#media-type auto-select rj45
Command show interfaces media-type
Syntax:
show interfaces media-type
Default Configurati o n:
N/A
Description:
Display the configured and active media type for the combo ports
User Guidelines:
N/A
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 57
Page 60

Command
Issue
show service-policy {in|out}
Examples:
console#show interfaces media-type
Port Configured Media-Type(s) Active
--------- --------------------------- -----Te1/0/21 auto-select, SFP preferred SFP
Te1/0/22 auto-select, SFP preferred SFP
Te1/0/23 auto-select, SFP preferred Down
Te1/0/24 auto-select, SFP preferred Down
Release 4.1.0.6
The Dell PowerConnect CLI Reference Guide is completely new. Users are re ferred to the Dell PowerConnect
Configuration Migration White Paper for information on how to migrate configurations from previous releases of Dell
PowerConnect firmware to the 4.0.0.6 Dell PowerConnect firmware.
The following table lists issues found in the CLI Reference Guide after publication:
show service-policy in
show copper-ports cabl e -
length
The supported syntax is
This command is depr ecated. Use the show copper-ports tdr
command to display the stored information regarding cable lengths
and the test copper-port tdr command to perform a cable length test.
Testing a port brings the port down momentarily.
58 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 61

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
The following paragraphs need to be added to the User’s Guides for all platforms except the PCM6220:
numbers of L2 stations are timing out and reappearing or multicast flooding is occurring in the network. If problems with
and its use.
Issue
The following message needs to be added to warn the user that Hotplug of a module is not supported if one of the ports
The following copper SFP needs to be listed as the supported module. However, diagnostics are not supported on copper
Finisar FCLF-8521-3
When a filter is defined, SNMP treats the filter as having an 'exclude all' statement at the beginning of the filter.
Unless an include statement is specified, all notifications will be excluded.
User’s Configuration Guide Updates
The following table lists issues found in the User’s Configuration Guide after publication:
Release 5.1.1.7
No Updates
Release 5.1.0.1
Issue
Unknown unicast and multicast packets are copied to the CPU on the lowest priority QoS queue. Unknown packets are
those that do not have hardware forwarding entries. Known uni cas t/mul ticast packets are hardware forwarded and are not
queued to the CPU. Control plane packets (e.g. spanning tree BPDUs) are copied or forwarded to the CPU on higher
priority queues. The rate limiting for unknown packets occurs on the internal CPU port and does not affect hardware
based traffic routing/forwarding in any way. Typical ly, the switch will examine the received packets in software to check
if there is a forwarding en try, create a forwarding entry (e.g., add a L2 MAC address or ARP response), and then either
discard the packet or software forward the packet (only occurs during the brief transitional period when the system is
actively adding a hardware forwarding entry but the hardware is not yet updated). Processing delays for higher priority
packets may occur when the internal CPU queue is continually kept busy handling low priority packets.
A command was created to allow the administrator to reduce the rate limit for which unknown unicast and multicast
packets are forwarded and/or copied to the CPU. It does not affect the rate limits for control plane packets. It is almost
never necessary to use this command to change from the default value. The use of this command should be restricted to
situations in which moderate to high rates of unknown unicast/multicast are continually sent to the switch CPU as
evidenced by the show proc cpu command and where the ipMapForwardingTask is showing high CPU usage. This will
occur most frequently in networks where a high number of ARPs are continually received on untrusted ports, high
L2, L3 or multicast learning occur after changing this value, set the rate limit back to the default value and take other
steps to correct or mitigate the underlying network issue directly.
See the CLI Reference Guide updates section of this document for the description of the “rate-limit cpu” CLI command
Release 5.0.1.3
No Updates
Release 5.0.0.4
on the module is operating in stacking mode.
Warning: One of the modular ports is operating in stacking mode.
Hotplug of a module requires system reboot.
Failure to do so will make the system unstable!
SFP’s.
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 59
Page 62

Release 4.2.2.3
No Updates
Release 4.2.1.3
Please refer Dell PowerConnect Users Guide for more details
Release 4.2.0.4
Please refer Dell PowerConnect Users Guide for more details
Release 4.1.1.9
No Updates
Release 4.1.0.19
The default authentication profile has chang ed from "enableList" to "enableNetList:
Telnet and SSH default to using the enab le NetList authentication pr ofile which requires an enable or line
password. The serial console default s to using the enableList authentication pr ofile which does not require the
use of a password. This change increases compatibility with industry standard behaviors. In previous releases,
telnet, SSH and the serial console defaulted to using the enableList profile which does not require a password.
The following table lists changes to the User’s Configuration Guides after publication:
Change Affected Platform
Added examples of how a user would implement VLAN or QoS policy assignment in the Port
Based Security section.
Added a table of the RADIUS attributes supported by the PowerConnect switches in the
Controlling Management Access section.
The valid VLAN range is described as 1 to 4093 (multiple sections) PC70xx
A better description of the RADIUS 'deadtime' parameter is added to the Controlling
Management Access sectio n
The CLI command "monitor session 1 mode" is described in the Configuring Port Mirroring
section
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
All Platforms
60 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 63

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
PC8100 - SCP or SFTP
SCP or SFTP file transfer from PowerConnect
iSCSI connections to drop.
8024 - Routing issue,
Some null mac address (0000.0000.0000) present
PCM6220 v5.0.1.3
monitored
PCM6220 Switch crashes every 30 to 40 days
M6348 Stack - interface
physical interface is up
Due to a race condition, while the lag member
existing members in the lag goes down.
Summary
User Impact
Workaround
Show A AA IAS-USERS
External CDP/ISDP
Occasionally external CDP/ISDP packets are
connected neighbors appear to be seen.
None.
Multicast sources that
If an intermittent multicast source that has been
receiving the multicast stream.
Known Issues
The following are all the outstanding known issues from previous releases. The issues listed here may have been discovered on
any of the switches listed on the title page.
Release 5.1.1.7
Summary User Impact Workaround
file transfers to FreeBS D
and Mac causes switch to
crash and reboot.
8100 switches to a FreeBSD or Mac client/server
causes the switch to crash and reboot. Eventually
connectivity comes back after a few seconds, but
the connectivity loss is long enough to cause
Workaround: None.
Fix is under review and it will be available in
the next maintenance release.
null address in ARP table
after VLAN
manipulation
switch crashes every 3040days while SNMP
in static LAG goes into
inactive state while
Release 5.1.0.1
Molex QSPF DAC Cable
with part number
111040-1104 does not
comply with QSFP
specification SFF-8436.
These cables do not
support 'vo ltage'
diagnostics.
<Username> Command
Missing
in PC8024 ARP table. This happens after vlan
manipulation (like creat e, delete, define IP
address, add and remove on trunk port).Issue
occurs randomly and not immediately (take
between 30min and 1h between vlan
manipulation and routing issue)
when SNMP monitoring with cacti version 0.8.8a
links flap, the lag member that linked up may be
put into standby, when at the same moment any
Voltage is displayed as 0.00 instead of "N/A" for
this diagnostic par ameter.
The “show aaa ias-users [username]” command
seems to have been deprecat ed even though it
still exists in the CLI guide.
Workaround: Reloading the switch resolves the
issue temporally (till next vlan
reconfiguration). Add static entry in ARP table
resolves the issue.
Fix is under review and it will be available in
the next maintenance release.
Workaround: None.
Fix is under review and it will be available in
the next maintenance release.
Workaround: None.
Fix is under review and it will be available in
the next maintenance release.
Ignore the voltage displayed field for this part
or use a SFF-8436 compliant cable.
The same information can be seen within the
running configuration of the switch with the
“show running-config” command.
traffic occasionall y
forwarded onto internal
ports
cease sending multicast
are timed out and
removed from the
multicast forwarding
cache after 150 seconds
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 61
being forwarded to the internal ports. This
results in confusing information from the blade
server point of view as multiple directly
aged out of the multicast forwarding cache
begins sending again before the corresponding
S,G entry has timed out at the RP (185 seconds
per RFC 4601), any *,G entries (joined hosts)
may take up to one IGMP Query interval to begin
The default IGMP query interval is 125
seconds. In practice, this situation is very
unlikely to occur as a multicast source that fails
to send even one packet for 150 seconds is
unlikely to start sending packets before the S,G
entry at the RP times out.
Page 64
Release 5.0.0.4
Summary
User Impact
Workaround
QSFP Base CR4 with
When using the DAC copper cables with QSFP
On PC8100 switches,
to the switch.
This is a corner case issue r equiring many steps
Failure log messages
on root node.
There is no effect besides t he annoyance of these
Speed is not applied to
Since these configuration variables exist for both
speed or duplex.
SFP+ module is still
QSFP to 4x10G
The information that will be stored in the
Status is not shown after
HTTPS session
The user may not be aware that the download has
Console logs/syslogs are
preference.
This will only be seen when disabling the local
The following unwanted
logs
There is no effect to the switch or user, just
The following unwanted
alloc” logs
There is no effect to the switch or user, just
copper DAC cable
lengths greater than 3
meters will not work on
PC8100 switches
sharp decrease in 6to 4
tunnel traffic is observed
when ipv4 static route is
deleted and added back
may show up on console
on doing a SNMP walk
combo (copper) ports
after saving and
reloading the DUT
(8024/8024F).
detected in runningconfig after clear
config on PC8100 with
CR4s (which are rarely used) and cable more
than 3 meters, the switch may not even detect
this device and so link up never happens. Only
the following cables are recommended with thes e
CR4 QSFPs:
111040-1104 – 1m Passive Copper Assembly
111040-1204 – 3m Passive Copper Assembly
to get to this state but if the state is reached, the
user will see less through-put on t he tunne l .
messages while doing an SNMP walk.
copper and fiber modes (combo ports), the speed
and duplex are not saved since the port assumes
that it will only save fiber parameters and thus
the customer will notice that the port autonegotiates after reload instead of goes to a stati c
running-config specific to the 4x10G port (QSFP
to 4x10G) will not be cleared after the clear
config command.
None
Stop traffic for a minute or two so that the stale
entry in the Linux stack is cl ear ed.
None
Always reconfigure the speed on copper combo
ports after reboots on the 8024 / 8 024F.
User can negate these co mmands manually
after a clear config.
the image upload using
HTTP through IPv4
not generated if we
disable LAG local
logs may come up on
console after running the
“clear config” command.
1) dot1s helper
logs
2) snooping logs
3) “ATP RX:
Failed to alloc”
logs may come up on
console after running the
“show tech-support”
command with UDLD
and MSTP configured:
“ATP RX: Failed to
62 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
completed when using the GUI.
LAG config and will not affect the system.
unwanted log messages on console.
unwanted log messages on console.
User must refresh screen or go to version
screen for indication that the download has
completed.
None
None
None
Page 65

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Summary
User Impact
Workaround
On PC8100 switches,
tunnel source.
This only happens after r epeated attempts at
'out of mBlks' logs are
line rate
There is no effect to the switch or user, just
Invalid characters are
statistics” command.
This only happens with this CLI command output
LPI samples are not
GUI.
This can be confusing to the user since the switch
"show fiber port op ti c a l-
This field does not apply to QSFP transceivers
Image uploaded with
networks are very slow.
This might require the User to have to retry the
Use alternate transfer met hods like TFTP, FTP,
Console messages shows
WARNING" often.
Our customers requested this warning to indicate
sensors.
Configure the logging level to be higher than
Finisar LRM 10G SFP+
packets intermittently.
This specific model is not recommended for use
Please use the Avago 10 G-BaseLRM model –
OpenManage displ ays
duration
OpenManage timeout warning window is
None.
Command "show fiber-
transceiver count.
Executing the command “show fiber-ports
None.
Port goes down if the
feature enabled on it.
If the port is operating in Trunk mode and UDLD
Include the port in na ti v e v la n.
SNMP V3 walk may fail
command is issued.
After failover, SNMP V3 walk may fail, as MIB
stop intercommunication.
After a failover, close th e browser and re-open
console gets locked for
20-30 seconds if trying
to add a 6to4 tunnel
source within 30 seconds
of deleting another
observed on console if
ICMPv6 echo reques t s
are sent to OOB port at
shown under reason
column for some entries
in the “show ip ospf
shown for the first time
on selecting a different
unit number using the
transceiver" command i s
showing current as zero
for QSFP transceivers.
adding and deleting a tunnel source and thus the
impact is very small to th e customer.
unwanted log messages on console.
and thus might be bothersome.
will not show the stats for the port after a new
unit is selected but then the stats will show up
after going to new port and then back.
and should display “NA” instead of zero.
Wait for 30 seconds after deleting the tunnel
source and then add a new tunnel source.
None.
The Web interface will not show these
characters.
Select a random port from the web and then reselect the desired port to view the LPI samples.
None.
HTTP method can't be
downloaded back to the
switch if switch and PC
are located in different
networks and the
"Thermal state raised to
transceiver model –
FTLX137D3BCL - drops
incorrect session timeout
ports optical-transceiver"
causes UI to become
slower with multiple
port is excluded from
native vlan with UDLD
after “initiate failover”
download or change the IP address or VLANs on
the switch or PC.
better visibility into the Thermal settings and
with our switches.
displaying the wrong value but uses the set value.
optical-transceiver” with multiple transceivers
inserted will cause the console prompt a long
time to return (possibly up to 60 seconds).
is enabled, the port goes down if it is excluded
from the native vlan.
browser and agent can become out of time and
etc.
“Warning”.
AFBR-707SDZ-D1.
it. SNMPv2 works correctly.
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 63
Page 66

Summary
User Impact
Workaround
OOB static IP entry
address
After receiving an IP address from the DHCP
gateway that is the same as the DHCP IP address.
Use a different IP addres s than the DHCP
Summary
User Impact
Workaround
Stack member units port
web GUI.
Wrong id for the power LED is displayed.
WebUI sFlow Polling
sFlow>Sampler configuration and sFlow>Poll
1/0/9.
"show interfaces
value
Some general mode VLANs tagged to the
M6220 OOB interface
failover
On a failover on a M6220 stack the OOB
CLI command "show ip
information.
"show ip dhcp snooping binding" not displaying
counts.
OOB interface
though told not to do so.
The setup wizard does not honor selection to not
DHCPv6 - M6220,
Relay
By looking at the counters, the client believes it
File modification date &
time & date.
When internal files are modified, they do not get
SNMP walk is not
walk on root port.
SNMP walk on the root port times out.
FIP sessions are getti ng
Users are unlikely to ch ange either the default
cannot be the same as the
DHCP assigned IP
server, the switch gives an er r or and will not
allow an attempt to add a s tatic IP address and
address given.
Release 4.2.2.3
display is missing in
page issues.
Configuration don't work for ports Gig1/0/1 -
None
None
Release 4.2.1.3
Summary User Impact Workaround
switchport " command
shows incorrect General
Mode Tagged VLANs
unreachable after
dhcp snooping binding"
not displaying client
interface may not be displayed using this
command.
interface may not be avail able.
client information. "show ip dhcp snooping
statistics" does not display correct message
Use “show vlan” command to interfaces. No
other workaround.
Recovers when the master is restored.
None
configured with default
IP via Setup Wizard
PC/M 8024/ k - Client
Solicits do Not Seem to
Make it to the Server /
Release 4.2.0.4
Summary User Impact Workaround
time is not getting
updated with current
successful while doing
disconnected for VLAN
switchport mode change
with default vlan
settings.
setup OOB IP address.
is sending solicits; but, the relay and the server
never see the solicitations.
the current time stamp.
VLAN or the FIP VLAN while sessions are
active.
OOB IP address will need to be setup
manually.
None
None
Do not do SNMP walks using root port.
Do not change the FIP VLAN while sessions
are established. The reason is that after a
VLAN is re-assigned or even changed to
general mode, the sessi ons will of course be
disrupted since the FIP snooping occurs on the
VLAN and any change in this will cause
problems on the Cisco Nexus side and will
require an interruption and reestablishment of
the addressing from the CNAs on up.
64 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 67

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Summary
User Impact
Workaround
OpenManage displ ays
After the browser session timeout (default 10
Cannot disable the SFS
Even with SFS allow-downgrade disabled, the
Console port locks up
Radius authenticated Telnet login attempt when
expires.
Flowcontrol is in inactive
combo ports.
Flowcontrol gets automatically disabled and if
7048R replacement
Although the power supplies part number is the
supplies still works correctly.
PowerConnect 7048P :
control
After a long period of time and numerous IP
filling the logs.
SNMP showing packets
doesn't show the same.
SNMP monitoring tool is pulling stats from
but switch doesn't say the same.
PC M6220 Running
master, 4.1.0.19, 4.1.1.7
When ma s t e r member wa s removed from and
Stacked m8024-k or
Customers downgrading a switch stack to a
Failure to follow these i nstructions may cause
time.
The stack will stop passing traffic if all switches
Jumbo frames cause
Transmit Errors is seen on port channel, but not
incorrect session timeout
duration when usi ng
secure HTTP
"allow-downgrade"
feature
when awaiting telnet
Radius response
state when connected to
Partner(Randall) with
power supplies reported
as incompatible
poe_lldp.c(1741) 23137
%% Failed to get pairs
minutes), OpenManage displays incorrect session
timeout durati on in the message "Your session
had been inactive for more than 240 minutes",
which is the actual setting for telnet and ssh.
However, the actual ti meout occurs after the
default period of 10 minutes, so the GUI message
is incorrect.
master will still push the older firmware to a
stack member running a newer version of code.
Radius daemon stopped, causes console port to
be temporarily blocked until Radius timeout
the ports have a need for Flowcontrol, there will
be no pause frames sent.
same, the 7048R reports it as incompatible and
thus the error message is incorrect. The power
phones connected and with at least 5 switches
connected as a stack, PoE error messages start
Disregard the time in this GUI message.
Always make sure the master h as the wanted
version loaded.
Wait for timeout or ensure Radius server is
reachable.
Re-enable Flowcontrol on Randall switch.
Ignore the error message, since there are no
functional issues with this power supply.
Maximum supported IP phones at this time is
64.
discarded while cli
configuration altered
after removal of stacking
8024/8024F switches
running code that
supports Ethernet
stacking should not be
downgraded to ol de r
code that doesn’t support
Ethernet stacking.
PC7048P, in a stack will
error out when all
rebooted at the same
transmit errors on port
channel
M8024 and shows very high discard receive rate
reinserted into an M1000e enclosure, some of the
configuration was missing from running-config.
version of code that does not support stacking are
advised to:
1) Break apart the stack into individual units
2) Clearing the saved config on each unit
3) Renumber each unit to unit 1 using the switch
X renumber 1 command
in the stack are rebooted simultaneously.
on the members of the port channel. Counters
remain inaccurate.
None.
Always write the config before removing
master.
units to crash when booted into the 4.1
firmware. To recover the switch, attach a serial
cable and enter the boot menu (press 2 - Start
Boot Menu at the prompt). From the boot
menu, select 10 - Restore configuration to
factory defaults, and then select 1 - Start
operational code
If this situation happens, it is recommended
that each power switch be r ebooted in sequence
with a four to five minute interval between
each reboot.
None – Inaccurate transmit errors do not cause
functional issues.
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 65
Page 68

Summary
User Impact
Workaround
PC8024F St a c king -
CLI/WebUI shows the stack-ports counters value
CLI command "no snmp-
group" doesn't work
CLI command “no snmp-server community-
Dot1x ias local
The internal datab as e feature, which is a Dell
time.
"ipv6 pim join-prune
working
CLI command “"ipv6 pim join-prune interval 30"
60
Incorrect status being
When PowerConnect 8024F com bo por ts 21 and
Down.
Power supply
There is no impact to the user.
M8024-k Internal port s
switch POST
Network operators may exp er ience a single
None
M8024, M6220,
Submittal Troubles
CSR may be rejected by Certificate Authority
Users can hand edit the CSR to left align all
Sflow conf ig ur a ti ons do
The operator entered a s flow command that takes
time period may have already expired.
The configuration will show in the running
Password strength -
Operator may become confused regarding switch
As is documented in the CLI Reference
strength minimum character-classes
CLI/WebUI : stack-ports
counters value is alwa ys
zero
server community-
authentication method
not working
interval" command is n ot
reported with show
interfaces commands
descriptions should be
modified as "Internal"
and "Remote" or
"External" for main and
secondary power
supplies respectively in
show system.
as zero after stack is formed.
group” is not available.
specific feature, is not working correctly because
this feature requires a user to authenticate using
MD5, which is not supported by Windows at this
does not change the default interval value from
22 are used for stacking, the show interfaces
status command and sho w interfaces media-type
commands report the status to be Detac he d and
None – Stack-Ports counter values as zero
doesn’t affect the PC 8024F stacking
functionality.
None
Use any other form of dot1x authentication.
None
None
None
are up during most of the
M8024k, PC8024F Extra Lines and Tabs in
CSR Cause CA
not get saved to the
config
minimum characters not
enforced
66 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
bounce during reboots of the M8024-k.
a timeout value which makes th e sflow
configuration valid only for a fixed period of
time. As the configuration is temporary (bound
by the timeout value), it is not shown in runningconfig. Storing the vale in the running
config/startup config would be an error as the
operations.
rows and eliminate blank lines before
submission to the CA.
config if the command is used with the
"notimeout" option, e.g.
sflow 1 destination ow ne r 1 not imeout
Manual, the password strength minimums do
not become effective until the user has
configured a non-zero value for passwords
strength minimum character-classes. Please
refer to the documentation for passwords
Page 69

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Summary
User Impact
Workaround
M8024-k OpenManage
Operators using IE 8 may experience issues as
(6) There are two "Slot 0" in display – confusing
Operators should consider using a browser
Inline help for
loopguard" is incorrect.
The inline help indicates that the command
Operators should b e aware that this global
show interfaces
10GBASE-T on 8024F
Operator should be aware that the type is
Ignore the type in the display for this
VLAN name config lost
When upgrading from release 3.1.4.16 to 4.2.0.4
affected.
The user can cut the VLAN na mes and save
Web GUI sFlow
Fails with an error - "Error! Failed to Set
Always configure the receiver owner when
Websense: Order of
The order that the commands “switchport mode
running-config” output.
None.
The “show dot1x
The User Guide states th at there is a “show dot1x
supposed correct command.
Use the “show dot1x interface statistics”
Summary
User Impact
Workaround
LLPF is not supported
The hardware functionality needed to support
Upgrade to a PowerConnect switch that
Web UI stack view
display
"spanning-tree
advanced firmware
displays ports 1-20 as
when upgrade from
3.1.5.16 to 4.2.x .x
configuration , receiver
owner inconsistent with
CLI
follows:
(1) Status LED does not glow to identify Master
(2) Member units do not show "DELL
PowerConnect M8024-k" model info
(3) Member units port display is missing
(4) LED label should be "Unit No." instead of
"Stack No." ?
(5) All Stack No. shown are as "01", instead of
"01", "02", "03", "04" e tc.
applies to a single port.
reported incorrectly on this platform.
the VLAN names only will not be copied to the
upgraded configuration. VLAN numbers are not
'Receiver Owner' with ''
However, it is possible to save the same
configuration (without receiver owner) via the
CLI.
Also, it is also not possible to add any polling
device or sampler configuration on the Web GUI
with this receiverIndex (seen in the show all
option) since an error is thrown stating "Receiver
Index is not configured".
other than IE 8.
CONFIG command app lies to all ports.
command.
these off before the upgrade occurs and then
again reenter them after the upgrade.
using the Web interface.
switchport commands in
running-config changed,
Impacts scripts
statistics” command
within the User Guide is
actually “show dot1x
interface statistics”
command from the CLI.
general” and “switchport general allowed vlan”
are displayed in the running config has been
changed so that now the “allowed” command is
first. This may cause problems with customer’s
scripts that expect a certain order in the “show
statistics” command for displaying dot1x
statistics on the switch when the actual command
for doing this is “show dot1x interface statistics”.
This can be frustrating to the customer if he has
referenced the User Guide to look up the
command.
Release 4.1.1.9
on the PCM6220 switch
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 67
LLPF is not available on the PCM6220 switch.
supports LLPF like a PCM6348 switch.
Page 70

Summary
User Impact
Workaround
Traffic led solid green
Setting advertisement from other switches or IXIA
None – Traffic LED Solid Green do not cause
Config Lost for the
On boot up, the switch gives an error and rejects
Remove port configuration of 10G module
PC7XXX cable
ports does not work.
DUT delivers more
DUT may draw more power than negotiated at
None – system assumes 5.8W average loss due
Trunk mode VLANs
Not compatible with other vendors trunk modes.
Administrators can configure “general” mode
Speed/duplex command s
Confusion about how to configure links.
Documentation and CLI prompt clearly states
ST : Stack member
No user impact expected. Observed occasional
None required.
vlan protocol gro up
with 1Gb and 100Mb
link speeds on
PC8024/PC8024F
Portchannel on
removing a 2 Port 10 G
Module on the
PCM8024 switch
of 1Gb or 100Mb link speeds to 10G links on
8024, 8024F results in link up and traffic led to be
solid green.
all the config for the portchannel as well as the
TenGig interfaces i n Bay1.
any functional issues.
before removing the module from the bay and
reboot the switch.
Release 4.1.0.19
Summary User Impact Workaround
Log message output snmpwalk will report error log message related to
CPU-port and vlan routing port
Secure HTTP Random
Characters
Under System Management -> Secur e H TTP,
random characters maybe populating some of the
fields.
None – error messages do not cause functional
issues.
The CLI must be used to generate
certifications.
Release 4.1.0.6
Summary User Impact Workaround
diagnostics for the Fiber
power than the PD
requested via LLDP in
high power mode.
L3 routing NSF failover
data plane on dynamic
LAG - loss duration up
to 5 seconds for large
configurations
Fiber port cable diagn ostics are not available for
the PC7XXX.
short cable lengths. PD may draw more power
than negotiate d, but power loss due to cable
impedance is compensated for so that devices
with average or longer cable length will receive
adequate power.
Interruption of voice, video and data service for
duration of loss. Data plane loss during failover
should not exce e d 50 ms.
None.
to cable length and del ivers 5.8W extra power
to ensure device receives requested power.
Disable portfast and auto-portfast on physical
ports configured in a LAG.
transmit tagged frames
only
available for interfaces
which require autonegotiation
response times to ICMP
ping requests in a 12 unit
stack are larger than for
stack master
Issue with protocol based
VLAN configuration
migration.
68 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
outlier response time up to 500 ms for stack
members in a large stack configuration with
heavy traffic. Average response time is well
under 100 ms for stack members. All response
times are well within ping limits.
The command
string parameter in earlier versions; now it
requires an integer par amet er.
required a
VLANs, which transmit PVID frames untagged
and all other VLAN frames tagged. General
mode is compatible with other vendor’s trunk
mode behavior.
which commands are app licable to which
interfaces. Only use speed/duplex commands
on fiber interfaces. Only use speed
auto/duplex aut o co m mands on copper
interfaces.
The software recognizes if the group name is
alphanumeric, however it will not work when
the name of the group is numeric (for example
2, 3, etc.).
Page 71

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Summary
User Impact
Workaround
Read/write user allowed
The user always gets Read-On ly access if using
User can configure the same TACACS user
Configure the acct-port to the default using the
read only access when
authentication method is
used as TACACS.
TFTP gives no reason for
file download failures.
CLI command stack-port
config rejection does not
display the cause.
The 'acct-port' command
does not have 'no'
version.
Non-configuration file
getting loaded to startupconfig through HTTP.
A v6 ping with the v4
header destination address
set to 224.0.0.2 (all routers
addr) is not responded to.
Certain packets match
system rules that elevate
the priority for protocol
packets.
TACACS as a means for HTTP authentication,
even if the TACACS user is Read/Write capable.
Generic failure message i s issued. Administrators can ping the TFTP server from
If a user enters an invalid interface, a generic
error message is issued .
The user can configure the acct-port to the
default using the positive form of the command
Switch does not utilize invalid configuration file
information. Earlier versions of startup-config are
not available for fallback when overwritten with
an invalid startup-config.
Users are not able to ping over 6to4 tunnels using
IPv6 addresses.
Packets may be transmitted out of order when
using priority flow control. Additionally, if the
queue that the packets are put on is not enabled
for lossless PFC, then the packets can be
transmitted even when the port was told to pause.
This may have an effect on connections that
expect packet order to be maintained, e.g. FCoE.
locally and use LOCAL authentication method
for HTTP. The user will be able to get access
based on the local user access level (Read-write
or Read-only).
the switch. Administrators should ensure the
TFTP server is available, the requested file is
available, and the permissi ons are set correctly.
Utilize the show stack-port command to
identify stack port configuration issues.
acct-port 1813 command in Radius accounting
mode.
In this case, an invali d configuration file was
downloaded (on purpose) via the web. When
the switch rebooted, it detected that the
configuration file was invalid and overwrote
the start-up config with the default
configuration (an empty configuration). Users
are advised to maintain off-line copies of
switch configurations.
Users can send pure IPv4 pings to the other end
of the tunnel.
None.
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 69
Page 72

Known Restrictions and Limitations
Description
User Impact
PowerConnect 8100 Series QSFP DAC CR4 40GB cable fails to link up with
S4810(conf-if-fo-0/60)#intf-type cr4 autoneg
Description
User Impact
SNMP walk is not successful while doing walk on root port
Low
Release 5.1.1.7
partner switch (for example. Dell Force10 S4810). After upgrading a Power
Connect 8100 series switch to firmware 5.1.0.1 customers may experience
loss of connectivity when using 40G QSFP CR4 DAC cables with partner
switch. Some partner switch vendors may by default leave auto-negotiation
disabled for CR4 connections. This will cause a negotiation mismatch and
the QSFP CR4 port will not link up.
When https enabled with a 2048 bit key CPU sslt tasks will require a high
CPU processing load for 5 – 10 seconds.
PCM6220 switch does not support “Private VLAN” feature Private VLAN feature requires hardware
High
In 5.1.0.1 firmware a behavioral chan ge, as
per IEEE spec, was made th at means that
when a QSFP CR4 cable is connected the
40gb port has auto-negotiation enabled. In
previous versions of firmware the default
behavior was to leave auto-negotiation
disabled. This change was required in order
to ensure compliancy to the following
specifications:
IEEE 802.3-2012 Secti on 6 / Clause 85.3 /
Clause 82.6 / Clause 73.9 - explains that
auto-negotiation is mandatory for 40GBASECR4 and 100GBASE-CR10.
Workaround:
Enable auto-negotiation on 40G interface of
Dell Force10 S4810 switch like below:
S4810#conf
S4810(conf)#int fortyGigE 0/60
Medium
HTTPS login attempt may timeout.
Workaround:
Use 1024 or lower key.
support that the PCM6220 XGS3 swi tc hi ng
fabric does not contain.
Workaround:
None.
Release 5.1.0.1
The IPMC L2_BITMAP is only updated to reflect ports that should 'not' be
flooded when a multicast stream is 'first' seen on a VLAN.
70 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
SNMP walk on root port may result in a
timeout if executed without specifying any
timeout value.
Workaround:
Execute walk with a recommen ded timeout
value of 2 sec
Moderate
There will be some flooding of multicast
traffic
Workaround: Issue no ip multicast followed
by ip multicast
Page 73

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Description
User Impact
The device manager GUI does not
Moderate – Multiple errors are displayed when trying to bring up the device GUI
Workaround: The User must use an Internet Explorer version prior to IE9 with the
"ip http secure-server" may not be cleared after performin g t he clear config
operation if there is user intervention before prompt returns
Reboot needed when critical message “Failed to add local route for network
X/X on interface X” appears on the console
Release 5.0.1.3
System – 5.0.1.3
Low
Clear config operatio n clears all system
components operational and configuration
information and then builds the default
configurati on. T his ope r a tion takes time to
complete and the prompt may not be returned
immediately. Prompt is returned after the
completion of the operation. Please wait for
the prompt, pressing "enter"/CR is not
needed in this case.
Workaround: Issue clear config one more
time if “ip http secure-server” configu ratio n
is not cleared
High
Route is not added and hence critical
situation. Need a rebo ot to recover.
Stacking
Description User Impact
Under certain conditions 5 or more ports
identified as stacking ports can cause
transmission errors even if the stacking
links are not up.
Low
This problem happens infrequently and setting those ports back to Ethernet mode
has corrected the prob lem.
Release 5.0.0.4
System – 5.0.0.4
System
Description User Impact
8100 switches increment “Internal MAC
Rx Errors” counter, when packets are
received with (size > 1518) and (size <=
MTU size), and the packet contains an
invalid FCS or code error detected or an
IEEE length check error
Web
support IE9 at this time.
Low
For typical IP networks this problem won't be seen because t he length
field/Ethertype will contain a valid value.
with IE9.
GUI.
Note: This is not a limitation if running Release 5.1.0.1 or later versions of
firmware.
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 71
Page 74

iSCSI
“show iscsi sessions” command does not
platforms.
Moderate –
traffic.
Description
User Impact
Show policy-map interface command
Low – the administrator can show the counters on the individual members of the
Show dot1x statistics command is
Low – the administrator can show the statistics on the individual interfaces
Description User Impact
display established sessions on
M8024/M8024-k/PC8024/PC8024F
Release 4.2.1.3
Management – 4.2.1.3
CLI
CLI command ‘show dot1x users’ is
missing in CLI
does not take a port-channel parameter
missing in the CLI
Show crypto key pubkey-chain ssh -
"username" optio n doe s not work
Workaround: Configure partner devices to send tagged, not priority tagged
Low – Use the show dot1x clients command to show the authenticated clients.
port-channel and sum them manually.
None – the administrator must configure and associate a key to a user in order for
the user to be associat ed with an SSH key. The following exampl e creates and
associates an SSH user with a key:
console(config)#us er name asd password XXXXXXXX privilege 15
console(config)#crypto key pubkey-chain ssh
console(config-pubkey-chain)#user-key asd dsa
console(config-pubkey-key)#key-string "ssh-dss
AAAAB3NzaC1kc3MAAACBAJRwUAD3AuRACp1MObBeh1AgyZb18wf9Bt
dip+t+1CbAqiqNEh4lBiew184DSKk0T6SnSSXuCN+bJnQPxJeiQt+OFnmjiYhn
HcvI04Q5KnQhloZcEFgSsmQ7zJnReWtLvUQI0QvBIStanzedmQVGHvDrQ5X
2R729ToSH0ibBrnYtAAAAFQDNord7S9EJvUkKKxVBpWE6/skCmQAAAIB
MjMO+BPP5KXzNWfZhqAhxBSoBvif/z6pzi9xWLlYy99A03zmRYCpcGIoLW
iRHsR7NVpxFqwbqvez8KS0CDJ5aoKKLrpBlpg5ETkYEew/uTZ14lQQRBrzPw
GBfxvTXKCWiI2j5KFa/WKLSnmWJX0/98qpxW/lMXoXsA9iK4pnMKwAAAI
B4Jrt6jmoLybpzgOPOI0DsJ7jQwWacinD0jliz8k+qzCpanhd2wH+DEdj/xO2sFR
fnYlME3hmXoB+7NByVUtheVjuQ2CWhcGFIKm9tbuPC6DtXh1xxT0NJ7rspv
Lgb0s6y/0tk+94ZP5RCoAtLZ7wirShy3/KJ4RE0y2SFZjIVjQ=="
console(config-pubkey-key)#exit
console(config-pubkey-chain)#exit
console(config)#exit
console#show crypto key pubkey-chain ssh username asd
Username : asd
ssh-dss
AAAAB3NzaC1kc3MAAACBAJRwUAD3AuRACp1MObBeh1AgyZb18wf9Bt
dip+t+1CbAqiqNEh4lBiew184DSKk0T6SnSSXuCN+bJnQPxJeiQt+OFnmjiYhn
HcvI04Q5KnQhloZcEFgSsmQ7zJnReWtLvUQI0QvBIStanzedmQVGHvDrQ5X
2R729ToSH0ibBrnYtAAAAFQDNord7S9EJvUkKKxVBpWE6/skCmQAAAIB
MjMO+BPP5KXzNWfZhqAhxBSoBvif/z6pzi9xWLlYy99A03zmRYCpcGIoLW
iRHsR7NVpxFqwbqvez8KS0CDJ5aoKKLrpBlpg5ETkYEew/uTZ14lQQRBrzPw
GBfxvTXKCWiI2j5KFa/WKLSnmWJX0/98qpxW/lMXoXsA9iK4pnMKwAAAI
B4Jrt6jmoLybpzgOPOI0DsJ7jQwWacinD0jliz8k+qzCpanhd2wH+DEdj/xO2sFR
fnYlME3hmXoB+7NByVUtheVjuQ2CWhcGFIKm9tbuPC6DtXh1xxT0NJ7rspv
Lgb0s6y/0tk+94ZP5RCoAtLZ7wirShy3/KJ4RE0y2SFZjIVjQ==
Fingerprint : d9: d1:21:ad:26: 41:ba:43:b1:dc : 5c :6c :b9:57:07:6c
72 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 75

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
SSH RSA or DSA keys can be generated by using the ssh-keygen command on a
Broadcom NIC link always stays up
Low- This is works as designed and is necessary for new features for 12G.
Description
User Impact
Windows Vista® Authentication - The
Low
The maximum number of 802.1x clients
Low – most deployments will have at most 2 802.1x clients per physical port.
The maximum number of configurable
Low as most deployments use a single traffic class. Some limited deployments
Description
User Impact
Maximum number of unicas t static
The maximu m number of unicast MAC and source port filtering entries is 20.
Maximum number of multicast static
The maximum number of multicast MAC and source port filtering entries is 20.
mac addr-table multicast filtering
Description
User Impact
No command to identify external IGMP
There is no specific command to identify an external IGMP querier.
Unix system or with other publicly available utilities.
within the m8024-k status even after
disabling server port through device
manager or turning off server altogether.
Release 4.2.0.4
Layer 2 – 4.2.0.4
802.1x Authentication
Windows Vista® client could fail to
authenticate properly when the option to
cache user credentials is selected.
per port is 4.
traffic classes is 7.
MAC Filtering
The Broadcom NIC 57810S never reports to the internal switch that the link is
down because it needs the link to be up so that internal communications can
continue with iDRAC and for other various components even after disabling the
link on the server side.
Workaround:
1. In Control Panel Network Connections, right-click on the desired
Local Area Connection and select Properties.
2. In the Properties window, select the Authentication tab.
3. Deselect the checkbo x for Cache user information for subsequent
connections to this network.
4. Click OK.
Note: If running Release 5.1.0.1 or later version of firmware, the maximu m
number is 24.
may use up to 3 traffic classes.
filtering entries
filtering entries
Static multicast MAC address table
entries do not show with show command
The maximum number of multicast MAC and destination port filtering entries is
256.
Users must enable MAC filtering using the
command to enable filtering. Static MAC multicast forwarding entries will then
be shown.
LACP
Description User Impact
LAGs Supported Number of LAGs supported:
128 total LAGs of which up to 72 may be dynamic LAGs. Up to 144 ports can be
assigned to dynamic LAGs. The PCM8024 supports 12 LAGs with up to 24 ports
assigned to dynamic LAGs.
IGMP Snooping
querier
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 73
Administrators can use the show ip igmp snooping querier det a il command or
the show ip igmp snooping querier vlan command to display information about
snooping querie rs .
Page 76

IP VLAN MTU Support
Operators may see jumbo packets discarded when oper ating in a routed IP
IPv6 Fragmentation Support
The switch is not fragmenting the datagram and forwards even when the IP MTU
Description
User Impact
Description
User Impact
radius-server mode commands do not
Low - None of the commands in radius-server mode support a "no" form except
Multicast VLAN Registration
Description User Impact
MVR is not supported on LAGs Use of MVR is restricted to physical interfaces.
Layer 3 – 4.2.0.4
IP MTU
Description User Impact
environment. Administrators are advised when operating in a L3 routing
configuration with jumbo frames to adjus t both the link MTU and the VLAN IP
MTU.
IPv6 MTU
Description User Impact
of the forwarding interface is set to a lower value (than the datagram size).
IPv6 frames are not allowed to be fragmented. IPv6 frames forwarded in silicon
can be up to the lesser of 9216 octets or the link MTU. These frames are
forwarded by the switching silicon with no effect. If a frame exceeds the link
MTU for a port, it is discarded silently.
If a packet is sent to the CPU or originated on the CPU and it exceeds the IPv6
MTU, then the packet still will not be fragmented. Instead, an ICMP error
message is returned t o t he sender. The maximum IPv6 MTU is 1500 bytes.
Administrators are advised that when operating in an L2 switching
configuration with jumbo frames, to only adjust the link MTU and let the
system automatically adjust the IPv4/ IPv6 MTU based on the link MTU.
VRRP
The maximu m number of VRRP
instances is 50.
Users can scale VRRP higher than previously.
Management – 4.2.0.4
CLI
have a "no" form.
The maximum command line length is
1536 characters.
USB
Description User Impact
Dir command can only address top-level
directory on USB stick
Only FAT32 formatted devices are
supported.
for the msgauth command. To reset values to the default, delete the server entry
and add it back.
Low - Entries greater than the maximum line length throw an error, e.g. using
multiple interface range qualifiers.
Minimal – users can move files to top-level directory easily
Minimal – FAT32 devices are the de-facto standard for flash devices
74 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
Page 77

PowerConnect 8132/8164/8132F/8164F/8024/8024F/M8024/M8024-k/
M6220/M6348/7024/7048/7024P/7048P/7024F/7048R/7048R-RA
Release Notes
Description
User Impact
Certain browser (IE) versions respond
This behavior is a browser performance limitation . Users may select anot her
Certain browser (FireFox) versions
This behavior is a browser functionality issue. If popups are blocked, the web
Description
User Impact
CLI Comment Character
The '!' indicates the beginning of a comment. All characters following the '!' will
Description
User Impact
VLAN request/Notification counters are
Low – FIP ses s ions are established and are d isplayed in the show commands.
equest/Notification counters are not incremented for priority
Broadcom CNA only supports
Low – Most users prefer automatic setup of CNAs
be able to do so if using BRCM CNAs.
While working with QLogic, it is found that CNA sends two TLVs concerning the
be a use case where host or FCF can choose to create di fferent priorities for
When multiple partitions are present on
the flash drive, only the first partition is
accessible.
Web
Minimal – users will typically re-partition flash drives to maximize space.
slowly when displaying large lists of
information. In these cases , the “All”
display selection may not appear (is
disabled).
automatically block popups after a
certain number of displays within a
session.
supported brow ser to enable “all” display functionality. Alternatively, the user
may utilize the page selector functions to display the appropriate page of
information.
interface will display errors/information using alerts. Users can disable popup
monitoring by browsing to about:config and set dom.popup_maximum to -1
File Management
be treated as a comment (except when configuring a banner where the ! is
accepted at the beginning of a line)
Data Center – 4.2.0.4
Interoperability
not incremented for priority tagged
packets
configuration of VLAN via VLAN
Discovery process
FIP snooping VLAN request or VLAN response counters do not increment when
CNA sends priority tagged frames (i.e. VID 0). It is observed that certain CNAs
sometimes sends FIP VLAN discovery frames as 802.1Q tagged frames with
VID=0 and priority as FCoE priority. FSB snoops FIP packets which are
classified to any of FCoE enabled VLANs. In this case, the default VLAN (1) and
the configured FCoE VLAN. In general, VLAN request messages are exchanged
as untagged so gets associated with VLAN 1. In this case, the BROADCOM CNA
sends priority tagged FIP frames (VID=0) which do not match the FSB snooping
criteria because they do not get associated to any of the F C oE enabled VLANs
hence FCoE VLAN R
tagged packets. These con trol frames are however are forwarded to FCF by FSB
in order to establish a successful session. FIP snooping bridge need to consider
forwarding priority tagged FIP frames to FCF as well in order to interoperate with
CNAs which could send priority tagged packets. The current FSB implementation
does this already.
The Broadcom CNA does not support manual configuration of VLAN. This
means that customers who prefer to set up their FCoE network manually will not
FIP snooping bridge does not forward
the DCBX FIP tlv info from
configuration source
System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7 Page 75
Low – No supported FCF supports this configuration option.
FIP/FCoE traffic. It sends FIP TLV along with FCoE TLV with respective
priorities - in this case same priority for both. Although, it is not a normal use case
but can be used to have different treatment for control and data traffic. Ther e can
Page 78

control (FIP) and FCoE data traffic.
FIP Snooping Over Stack Results in
Low - When trying to accomplish FIP snooping over the stack, the eNode address
supported across the stacks so this is a non-issue.
In cases, where FIP and FCoE use different priorities, it is expected that
intermediate switches are configured to treat them accordingly. In cases where
ports are configured in DCBX auto mode and configuration source carries two
TLVs, one for FIP and other for FCoE with different priorities then it is expected
that FSB/DCB should forward this information to downstream ports.
The PowerConnec t FS B implementation ignores the FIP TLV and does not
forward this information to the peers. In such cases, Host will not know the
special treatment or expected priority for FIP frames. Considering that slow
protocol and this being a corner case situation, this can be a readme and
documented in release notes.
eNode in Ethernet VLAN
is put in the wrong VLAN causing the connections to never occur. FCoE is not
End of Release Notes
76 System Firmware Version 5.1.1.7
 Loading...
Loading...