Dell MX5108n User Manual

Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration
and Troubleshooting Guide
Abstract
This document provides the steps for configuring and troubleshooting the
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX networking switches in SmartFabric mode. It
includes examples for ethernet connections to Dell EMC Networking,
Cisco Nexus, and Fibre Channel networks.
Dell EMC Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
This document replaces the Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric
Mode Deployment Guide, which is now deprecated.
September 2019
2 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
Revisions
Date
Description
September 2019
OpenManage Enterprise-Modular 1.10.00 and SmartFabric OS10.5.0.1 updates, Fibre
Channel connectivity, additional troubleshooting information
May 2019
Initial Release
The information in this publication is provided “as is.” Dell Inc. makes no representations or warranties of any kind with respect to the information in this
publication, and specifically disclaims implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
Use, copying, and distribution of any software described in this publication requires an applicable software license.
© 2019 Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. All Rights Reserved. Dell, EMC, Dell EMC and other trademarks are trademarks of Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. Other
trademarks may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Dell believes the information in this document is accurate as of its publication date. The information is subject to change without notice.

3 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
Table of contents
Revisions............................................................................................................................................................................. 2
1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................................................... 8
1.1 Typographical conventions ............................................................................................................................... 10
1.2 Attachments ...................................................................................................................................................... 10
2 SmartFabric Services for PowerEdge MX: An overview ............................................................................................ 11
2.1 Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10 ............................................................................................................................ 11
2.2 Operating modes .............................................................................................................................................. 11
2.2.1 Full Switch mode .............................................................................................................................................. 12
2.2.2 SmartFabric mode ............................................................................................................................................ 12
2.3 Changing operating modes .............................................................................................................................. 14
2.4 MX9116n Fabric Switching Engine (FSE): virtual ports ................................................................................... 15
2.5 Virtual Link Trunking ......................................................................................................................................... 16
2.6 Fibre Channel (FC) connectivity ...................................................................................................................... 17
2.6.1 NPIV Proxy Gateway (NPG) ............................................................................................................................. 17
2.6.2 Direct Attached (F_port) ................................................................................................................................... 18
2.6.3 FCoE (FSB) ...................................................................................................................................................... 18
2.7 Networks and automated QoS ......................................................................................................................... 19
2.8 Server templates, virtual identities, networks, and deployment ....................................................................... 20
2.8.1 Templates ......................................................................................................................................................... 20
2.8.2 Virtual identities and identity pools ................................................................................................................... 21
2.8.3 Deployment ....................................................................................................................................................... 21
3 SmartFabric mode requirements, guidelines, and restrictions ................................................................................... 22
3.1 Create multi-chassis management group ......................................................................................................... 22
3.2 Upstream network requirements ...................................................................................................................... 22
3.2.1 Physical connectivity ........................................................................................................................................ 22
3.2.2 Spanning Tree Protocol .................................................................................................................................... 23
3.3 VLAN scaling guidelines ................................................................................................................................... 23
3.4 Configuring port speed and breakout ............................................................................................................... 24
3.5 Switch slot placement for SmartFabric mode ................................................................................................... 24
3.5.1 Two MX9116n Fabric Switching Engines or FSEs in different chassis ............................................................ 24
3.5.2 Two MX5108n Ethernet switches in the same chassis .................................................................................... 25
3.5.3 Two MX9116n Fabric Switching Engines or FSEs in the same chassis .......................................................... 26
3.6 Switch-to-Switch cabling ................................................................................................................................... 26
3.6.1 VLT backup link ................................................................................................................................................ 27
3.7 NIC teaming guidelines .................................................................................................................................... 27

4 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
3.8 Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) behavior .................................................................................................. 28
3.9 Other restrictions and guidelines ...................................................................................................................... 28
4 Creating a SmartFabric .............................................................................................................................................. 30
4.1 Physically cable MX chassis and upstream switches ....................................................................................... 30
4.2 Define VLANs ................................................................................................................................................... 30
4.2.1 Define VLANs for FCoE .................................................................................................................................... 31
4.3 Create the SmartFabric .................................................................................................................................... 32
4.4 Configure uplink port speed or breakout, if needed ......................................................................................... 33
4.5 Create Ethernet uplink ...................................................................................................................................... 34
4.6 Configure Fibre Channel universal ports .......................................................................................................... 36
4.7 Create Fibre Channel uplinks .......................................................................................................................... 36
4.8 Configuring the upstream switch and connect uplink cables ........................................................................... 37
5 Deploying a server ..................................................................................................................................................... 38
5.1 Server preparation ............................................................................................................................................ 38
5.1.1 Reset server CNAs to factory defaults (if required) .......................................................................................... 38
5.1.2 Configure NIC partitioning on CNAs ................................................................................................................. 38
5.1.3 Configure other server settings ........................................................................................................................ 40
5.2 Create a server template .................................................................................................................................. 40
5.3 Create identity pools ......................................................................................................................................... 42
5.4 Associate server template with networks – no FCoE ....................................................................................... 42
5.5 Associate Server Template with networks - FCoE ........................................................................................... 43
5.6 Deploy a server template .................................................................................................................................. 44
6 SmartFabric operations .............................................................................................................................................. 46
6.1 Viewing the fabric ............................................................................................................................................. 46
6.2 Editing the fabric ............................................................................................................................................... 48
6.3 Editing uplinks ................................................................................................................................................... 49
6.4 Editing VLANs on a deployed server ................................................................................................................ 50
6.5 Managing Fibre Channel Zoning on the MX9116n FSE .................................................................................. 51
6.6 Connecting non-MX Ethernet Devices to the fabric ......................................................................................... 53
6.7 Delete SmartFabric ........................................................................................................................................... 53
6.8 Module replacement process in SmartFabric ................................................................................................... 54
6.8.1 Physically replace the IOM ............................................................................................................................... 54
6.8.2 Identify the master IOM in a fabric .................................................................................................................... 54
6.8.3 Execute process of Module Replacement with Linux command ...................................................................... 55
7 Switch operations ....................................................................................................................................................... 56
7.1 Switch management page overview ................................................................................................................. 56

5 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
7.1.1 Switch overview ................................................................................................................................................ 56
7.1.2 Hardware tab .................................................................................................................................................... 58
7.1.3 Firmware tab ..................................................................................................................................................... 59
7.1.4 Alerts tab ........................................................................................................................................................... 59
7.1.5 Settings tab ....................................................................................................................................................... 60
7.2 Configuring Ethernet ports ................................................................................................................................ 62
7.3 Upgrade Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10 ............................................................................................................. 64
8 Validating the SmartFabric deployment ..................................................................................................................... 67
8.1 View the MCM group topology ......................................................................................................................... 67
8.2 View the SmartFabric status ............................................................................................................................. 68
8.3 View port status ................................................................................................................................................ 70
8.4 CLI commands .................................................................................................................................................. 71
8.4.1 show switch-operating-mode ............................................................................................................................ 71
8.4.2 show discovered-expanders ............................................................................................................................. 71
8.4.3 show unit-provision ........................................................................................................................................... 71
8.4.4 show lldp neighbors .......................................................................................................................................... 71
8.4.5 show qos system .............................................................................................................................................. 73
8.4.6 show policy-map ............................................................................................................................................... 73
8.4.7 show class-map ................................................................................................................................................ 73
8.4.8 show vlt domain-id ............................................................................................................................................ 73
8.4.9 show vlt domain-id vlt-port-detail ...................................................................................................................... 74
8.4.10 show interface port channel summary ......................................................................................................... 74
9 SmartFabric troubleshooting ...................................................................................................................................... 75
9.1 Troubleshooting errors encountered for port group breakout .......................................................................... 75
9.2 Troubleshooting Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) .............................................................................................. 77
9.2.1 Verify if STP is enabled on upstream switches ................................................................................................ 77
9.2.2 Verify if type of STP is the same on MX and upstream switches ..................................................................... 77
9.3 Verify VLT/vPC configuration on upstream switches ....................................................................................... 78
9.4 Discovery of FEM and compute sleds .............................................................................................................. 78
9.5 Troubleshooting uplink errors ........................................................................................................................... 79
9.5.1 Toggle auto negotiation .................................................................................................................................... 79
9.5.2 Set uplink ports to administratively up .............................................................................................................. 80
9.5.3 Verify MTU size ................................................................................................................................................ 80
9.5.4 Verify auto negotiation settings on upstream switches .................................................................................... 80
9.5.5 Verify LACP ...................................................................................................................................................... 81
9.6 Troubleshooting FC/FCoE ................................................................................................................................ 83

6 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
9.7 SmartFabric Services – Troubleshooting commands ....................................................................................... 85
9.7.1 show smartfabric personality ............................................................................................................................ 85
9.7.2 show smartfabric cluster ................................................................................................................................... 85
9.7.3 show smartfabric cluster member ..................................................................................................................... 85
9.7.4 show smartfabric details ................................................................................................................................... 86
9.7.5 show smartfabric uplinks .................................................................................................................................. 86
9.7.6 show smartfabric networks ............................................................................................................................... 87
9.7.7 show smartfabric validation-error ..................................................................................................................... 87
9.7.8 show smartfabric nodes .................................................................................................................................... 87
10 Uplink configuration scenarios ................................................................................................................................... 89
10.1 Scenario 1 - SmartFabric deployment with Dell EMC PowerSwitch Z9100-ON upstream switches ............... 89
10.1.1 Dell EMC PowerSwitch Z9100-ON switch configuration .............................................................................. 90
10.1.2 Dell EMC PowerSwitch Z9100-ON validation .............................................................................................. 92
10.2 Scenario 2 - SmartFabric connected to Cisco Nexus 3232C switches ............................................................ 94
10.2.1 Cisco Nexus 3232C switch configuration ..................................................................................................... 95
10.2.2 Configuration validation ................................................................................................................................ 97
10.3 Scenario 3: Connect MX9116n FSE to Fibre Channel storage - NPIV Proxy Gateway mode ..................... 100
10.3.1 Configuration validation .............................................................................................................................. 101
10.4 Scenario 4: Connect MX9116n FSE to Fibre Channel storage - FC Direct Attach ....................................... 104
10.4.1 Configuration validation .............................................................................................................................. 105
10.5 Scenario 5: Connect MX5108n to Fibre Channel storage - FSB ................................................................... 107
10.5.1 SmartFabric configuration steps ................................................................................................................ 108
10.6 Scenario 6: Configure Boot from SAN ............................................................................................................ 109
10.6.1 Configure NIC Boot Device ........................................................................................................................ 109
10.6.2 Configure BIOS settings ............................................................................................................................. 111
10.6.3 Connect FCoE LUN .................................................................................................................................... 112
10.6.4 Set up install media connection ................................................................................................................. 112
10.6.5 Set up OS driver install media using Lifecycle Controller .......................................................................... 112
A Hardware used in this document .............................................................................................................................. 114
A.1 Dell EMC PowerSwitch S3048-ON................................................................................................................. 114
A.2 Dell EMC PowerSwitch Z9100-ON ................................................................................................................. 114
A.3 Dell EMC PowerSwitch S4148U-ON .............................................................................................................. 114
A.4 Dell EMC PowerSwitch Z9264F-ON............................................................................................................... 114
A.5 Dell EMC Unity 500F storage array ................................................................................................................ 115
A.6 Cisco Nexus 3232C ........................................................................................................................................ 115
B Dell EMC Unity information ...................................................................................................................................... 116

7 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
B.1 Determine Unity 500F storage array FC WWPNs .......................................................................................... 116
B.2 CNA FCoE port WWPNs ................................................................................................................................ 117
B.3 Configure Unity FC storage ............................................................................................................................ 118
B.3.1 Create a storage pool ..................................................................................................................................... 118
B.3.2 Add hosts ........................................................................................................................................................ 119
B.3.3 Create LUNs and configure host access ........................................................................................................ 119
C Additional information ............................................................................................................................................... 121
C.1 Delete MCM group.......................................................................................................................................... 121
C.2 Reset chassis using RACADM ....................................................................................................................... 121
C.3 Reset SmartFabric OS10 switch to factory defaults ....................................................................................... 121
C.4 Reset Cisco Nexus 3232C to factory defaults ................................................................................................ 121
C.5 Connect to IO Module console port via RACADM .......................................................................................... 122
D Validated components .............................................................................................................................................. 123
D.1 Scenarios 1 and 2 ........................................................................................................................................... 123
D.1.1 Dell EMC PowerSwitches ............................................................................................................................... 123
D.1.2 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX7000 chassis and components ............................................................................. 123
D.1.3 Cisco Nexus switches ..................................................................................................................................... 124
D.2 Scenarios 3 and 4 ........................................................................................................................................... 124
E Technical resources ................................................................................................................................................. 125
F Support and feedback .............................................................................................................................................. 126

8 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
1 Introduction
Our vision at Dell EMC is to be the essential infrastructure company from the edge, to the core, and to the
cloud. Dell EMC Networking ensures modernization for today’s applications and for the emerging cloud-native
world. Dell EMC is committed to disrupting the fundamental economics of the market with an open strategy
that gives you the freedom of choice for networking operating systems and top-tier merchant silicon. The Dell
EMC strategy enables business transformations that maximize the benefits of collaborative software and
standards-based hardware, including lowered costs, flexibility, freedom, and security. Dell EMC provides
further customer enablement through validated deployment guides which demonstrate these benefits while
maintaining a high standard of quality, consistency, and support.
The Dell EMC PowerEdge MX is a unified, high-performance data center infrastructure. PowerEdge MX
provides the agility, resiliency, and efficiency to optimize a wide variety of traditional and new, emerging data
center workloads and applications. With its kinetic architecture and agile management, PowerEdge MX
dynamically configures compute, storage, and fabric, increases team effectiveness, and accelerates
operations. The responsive design delivers the innovation and longevity that customers need for their IT and
digital business transformations.
As part of the PowerEdge MX platform, Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10 includes SmartFabric Services.
SmartFabric Services is a network automation and orchestration solution that is fully integrated with the MX
Platform.
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX7000 chassis
This document provides information about SmartFabric OS10 SmartFabric Services running on the
PowerEdge MX platform. This document also provides examples for the deployment of two PowerEdge
MX7000 chassis and the setup and configuration of SmartFabric Services. In SmartFabric mode, switches

9 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
operate as a Layer 2 I/O aggregation fabric and are managed through the Open Manage Enterprise - Modular
(OME-M) graphical user interface or console.
This guide also demonstrates connectivity with different upstream switch options, including:
• Dell EMC PowerSwitch Z9100-ON
• Cisco Nexus 3232C
• Fibre Channel connectivity methods: NPG, Direct Attach, and FSB modes
Note: The examples in document assume that the MX7000 chassis are configured in a Multi-Chassis
Management group and that no errors have been found. Additionally, this guide assumes the reader has a basic
understanding of the PowerEdge MX platform.
Four important terminologies and their definitions are as follows:
Scalable Fabric – This is exclusive to the MX7000 platform. This is an architecture comprised of the Dell
EMC Networking MX9116n Fabric Switching Engine (FSE) and Dell EMC Networking MX7116n Fabric
Expander Module (FEM) allowing a fabric to span up to ten MX7000 chassis. This creates a single network
fabric enabling efficient east/west traffic flows between participating chassis. Scalable Fabric is supported in
both SmartFabric and Full Switch modes.
SmartFabric mode - SmartFabric mode leverages SmartFabric Services (see below) to create a Layer 2
network leveraging one to ten MX7000 chassis. Switches operating in SmartFabric mode are administered
through the OpenManage Enterprise - Modular (OME-M) GUI interfaces that provide complete lifecycle
management of the network fabric.
Full Switch mode – When operating in Full Switch mode, the switch can perform any functionality supported
by the version of SmartFabric OS10 running on the switch. Most of the configuration is performed using the
CLI, not the OME-M GUI.
SmartFabric Services (SFS) – In PowerEdge MX, SFS technology provides the underlying network
automation and orchestration to support all automated network operations. SFS is the underlying technology
for all Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10 automation efforts including PowerEdge MX, Isilon back-end storage
networking, VxRail network automation, and so on.
Table 1 outlines what this document is and is not. Also, this guide assumes a basic understanding of the
PowerEdge MX platform.
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide - is/is not
This guide is
This guide is not/does not
A reference for the most used features of
SmartFabric operating mode
A guide for all features of the MX7000 platform
A secondary reference to the Release Notes
Take precedence over the Release Notes
Note: For a general overview and details of PowerEdge MX networking concepts, see the Dell EMC PowerEdge
MX Network Architecture Guide.

10 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
1.1 Typographical conventions
The CLI and GUI examples in this document use the following conventions:
Monospace Text CLI examples
Underlined Monospace Text CLI examples that wrap the page
Italic Monospace Text Variables in CLI examples
Bold Monospace Text Commands entered at the CLI prompt, or to highlight information in CLI
output
Bold text UI elements and information entered in the GUI
1.2 Attachments
This document in .pdf format includes one or more file attachments. To access attachments in Adobe Acrobat
Reader, click the icon in the left pane halfway down the page, then click the icon.
11 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
2 SmartFabric Services for PowerEdge MX: An overview
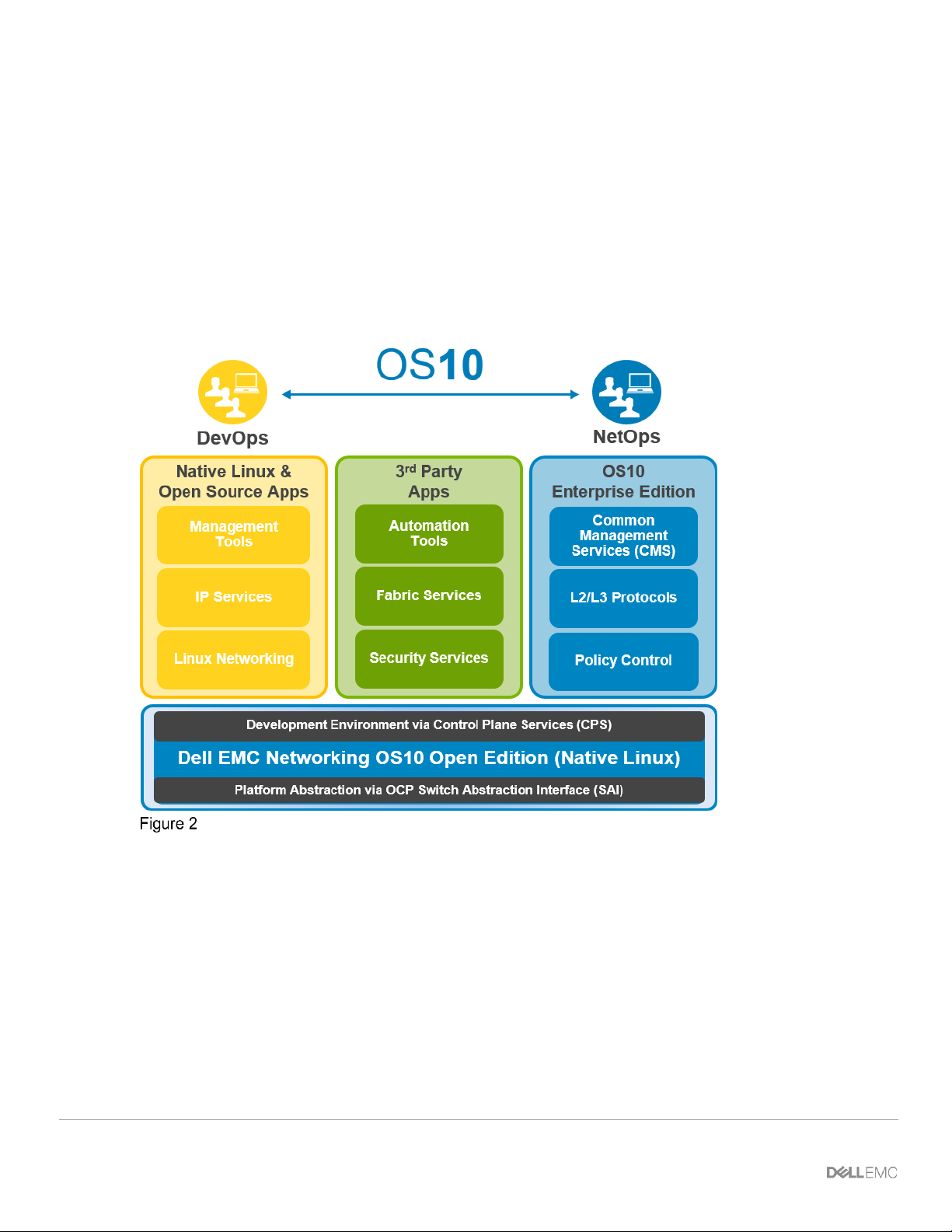
2.1 Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10
The networking market is transitioning from a closed, proprietary stack to open hardware supporting a variety
of operating systems. Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10 is designed to allow multi-layered disaggregation of the
network functionality. While OS10 contributions to Open Source provide users freedom and flexibility to pick
their own third-party networking, monitoring, management and orchestration applications, SmartFabric OS10
bundles industry hardened networking stack featuring standard L2 and L3 protocols over a standard and well
accepted CLI interface.
Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10 High Level Architecture
2.2 Operating modes
The Dell EMC Networking MX9116n Fabric Switching Engine (FSE) and MX5108n Ethernet Switch operate in
one of two modes:
• Full Switch mode (Default) – All switch-specific SmartFabric OS10 capabilities are available
• SmartFabric mode – Switches operate as a Layer 2 I/O aggregation fabric and are managed
through the Open Manage Enterprise-Modular (OME-M) console
The following SmartFabric OS10 CLI commands have been added specifically for the PowerEdge MX
platform:
12 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
• show switch-operating-mode – displays the current operating mode (SmartFabric or
Full Switch) of a supported switch
• show discovered-expanders – displays the MX7116n FEMs attached to the MX9116n
FSEs
• show unit-provision – displays or configures the unit ID and service tag of a MX7116n
FEM attached to a MX9116n FSE
Note: For more information, see the SmartFabric OS10 User Guide for PowerEdge MX I/O Modules on the
Support for Dell EMC Networking MX9116n - Manuals and documents and Support for Dell EMC Networking
MX5108- Manuals and documents web pages.
2.2.1 Full Switch mode
In Full Switch mode, all SmartFabric OS10 features and functions supported by the hardware are available to
the user. In other words, the switch operates the same way as any other SmartFabric OS10 switch.
Configuration is primarily done using the CLI, however, the following items can be configured or managed
using the OME-M GUI:
1. Initial switch deployment: Configure hostname, password, SNMP, NTP, etc.
2. Set ports administratively up or down, configure MTU
3. Monitor health, logs, alerts, and events
4. Update the SmartFabric OS10 software
5. View physical topology
6. Switch power management
Full Switch mode is typically used when a desired feature or function is not available when operating in
SmartFabric mode. For more information about Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10 operations, see Dell EMC
Networking OS Info Hub.
2.2.2 SmartFabric mode
A SmartFabric is a logical entity that consists of a collection of physical resources, such as servers and
switches, and logical resources such as networks, templates, and uplinks. The OpenManage Enterprise –
Modular (OME-M) console provides a method to manage these resources as a single unit.
In the PowerEdge M1000e and FX2 platforms, I/O Aggregation (IOA) was implemented to simplify the
process to connect blade servers to upstream networks, so server administrators and generalists could
manage uplinks, downlinks, and VLAN assignments without needing to be fluent with the CLI.
SmartFabric Services mode builds on this IOA functionality providing:
1. Data center modernization
• I/O Aggregation
• Plug-and-play fabric deployment
• Single interface to manage all switches in the fabric
2. Lifecycle management
• Fabric-wide SmartFabric OS10 updates
• Automated or user enforced roll back to last well-known state

3. Fabric automation
• Physical topology compliance
• Server networking managed via templates
• Automated QoS assignment per VLAN
• Automated storage networking
4. Failure remediation
• Dynamically adjusts bandwidth across all inter-switch links in the event of a link failure
• Automatically detects fabric misconfigurations or link level failure conditions
• Automatically heals the fabric on failure condition removal
Note: In SmartFabric mode, MX series switches operate entirely as a Layer 2 network fabric. Layer 3 protocols
are not supported.
When operating in SmartFabric mode, access to certain CLI commands is restricted to SmartFabric OS10
show commands and can run the following subset of CLI configuration commands:
• clock – Configure clock parameters
• end – Exit to the EXEC mode
• exit – Exit from the current mode
• fc alias – Set Fiber Channel name
• fc zone – Set Fiber Channel zone name
• fc zoneset – Set Fiber Channel zoneset name
• help – Display available commands
• hostname – Set the system hostname
• host-description – Define the description for the host
• interface – Configure or select an interface
• ip nameserver – Configure nameserver
• ip ssh server – Configure SSH server
• ip telnet server – Configure Telnet server
• login concurrent-session – Start concurrent session and login
• login statistics – Enable timeframe for the login session
• logging – Configure system logging
• management route – Configure the IPV4/IPv6 management route
• no – Delete or disable commands in configuration mode
• ntp – Configure the network time protocol
• snmp-server – Configure the SNMP server
• tacacs-server – Configure the TACACS server
• username – Create or modify user credentials
• spanning-tree commands:
- disable – Disable spanning tree globally
- mac-flush-timer – Set the time used to flush MAC address entries
- mode – Enable a spanning-tree mode, such as RSTP
13 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
14 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
- rstp – Configure rapid spanning-tree protocol (RSTP) mode
- vlan – Configure spanning-tree on a VLAN range
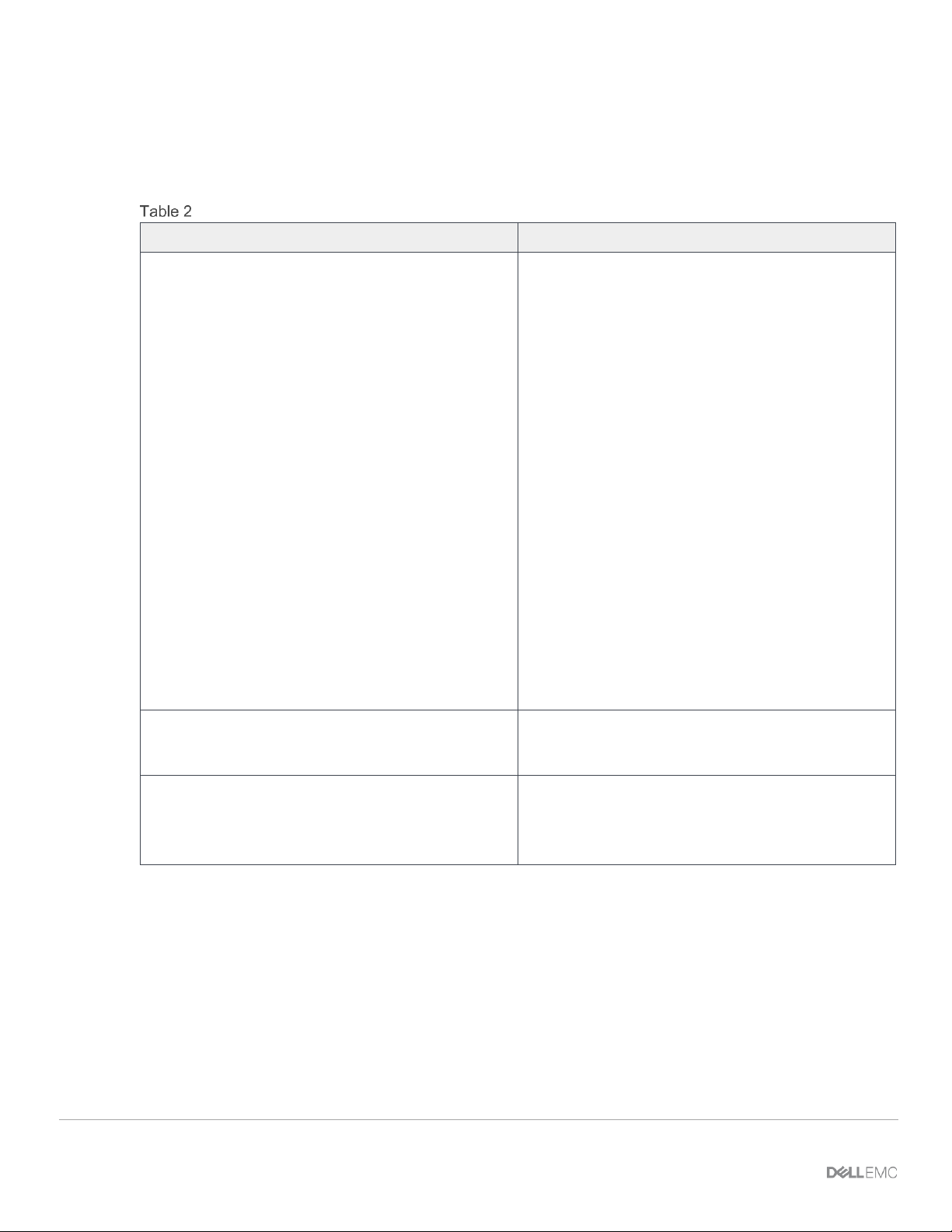
Table 2 outlines the differences between the two operating modes and apply to both the MX9116n FSE and
the MX5108n switches.
IOM operating mode differences
Full Switch mode
SmartFabric mode
Configuration changes are persistent during power
cycle events.
Only the configuration changes made using the
OS10 commands below are persistent across power
cycle events. All other CLI configuration commands
are disabled.
clock
fc alias
fc zone
fc zoneset
hostname
host-description
interface
ip nameserver
ip ssh server
ip telnet server
login concurrent-session
login statistics
logging
management route
ntp
snmp-server
tacacs-server
username
spanning-tree
vlan
All switch interfaces are assigned to VLAN 1 by
default and are in the same Layer 2 bridge domain.
Layer 2 bridging is disabled by default. Interfaces
must join a bridge domain (VLAN) before being able
to forward frames.
All configuration changes are saved in the running
configuration by default. To display the current
configuration, use the show running-
configuration command.
Verify configuration changes using feature-specific
show commands, such as show interface and
show vlan, instead of show runningconfiguration.
2.3 Changing operating modes
In both Full Switch and SmartFabric modes, all configuration changes you make using the OME-M GUI are
retained when you switch modes. Dell EMC recommends using the graphical user interface for switch
configuration in SmartFabric mode and the SmartFabric OS10 CLI for switch configuration in Full Switch
mode.
By default, a switch is in Full Switch mode. When that switch is added to a fabric, it automatically changes to
SmartFabric mode. When you change from Full Switch to SmartFabric mode, all Full Switch CLI
configurations are deleted except for the subset of CLI commands supported in SmartFabric mode.

15 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
To change a switch from SmartFabric to Full Switch mode, you must delete the fabric. At that time, all
SmartFabric GUI configuration changes are deleted except for the configurations supported by the subset of
SmartFabric CLI commands (hostname, SNMP settings, etc.) and the changes made to port interfaces,
except for admin state (shutdown/no shutdown), MTU, speed, and auto-negotiation mode.
Note: There is no CLI command to switch between operating modes. Delete the fabric to change from
SmartFabric to Full Switch mode.
The CLI command show switch-operating-mode displays the currently configured operating mode
of the switch. This information is also available on the switch landing page in the OME-M GUI.
2.4 MX9116n Fabric Switching Engine (FSE): virtual ports
A virtual port is a logical switch port that connects to a downstream server and has no physical hardware
location on the switch. Virtual ports are created when an MX9116n Fabric Switching Engine (FSE) on-boards
an MX7116n Fabric Expander Module (FEM). The onboarding process consists of discovery and
configuration.
Note: If the servers in the chassis have dual-port NICs, only QSFP28-DD port 1 on the FEM needs to be
connected. Do not connect QSFP28-DD port 2.
To verify the auto-discovered Fabric Expander Modules, enter the show discovered-expanders
command.
OS10# show discovered-expanders
Service-tag Model Type Chassis-service-tag Chassis-slot Port-group Virtual Slot-Id
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------403RPK2 MX7116n Fabric 1 SKY003Q A2 1/1/1 71
Expander Module
If the FSE is in SmartFabric mode, the attached FEM is automatically configured and virtual ports on the
Fabric Expander Module and a virtual slot ID are created and mapped to 8x25GbE breakout interfaces in
FEM on the Fabric Engine.
An FSE in Full Switch mode automatically discovers the FEM when these conditions are met:
• The FEM is connected to the FSE by attaching a cable between the QSFP28-DD ports on both
devices
• The interface for the QSFP28-DD port-group connected to the FSE is in 8x25GbE FEM mode
• At least one blade server is inserted into the MX7000 chassis containing the FEM
Note: If the FSE is in Full Switch mode, you must manually configure the unit ID of the FEM. See the OS10
Enterprise Edition User Guide — PowerEdge MX I/O Modules for implementation.
Once the FSE discovers the FEM, it creates virtual ports by mapping each 8x25GbE FEM breakout interface
in port groups 1 to 10 to a FEM virtual port. Table 3 shows an example of this mapping.
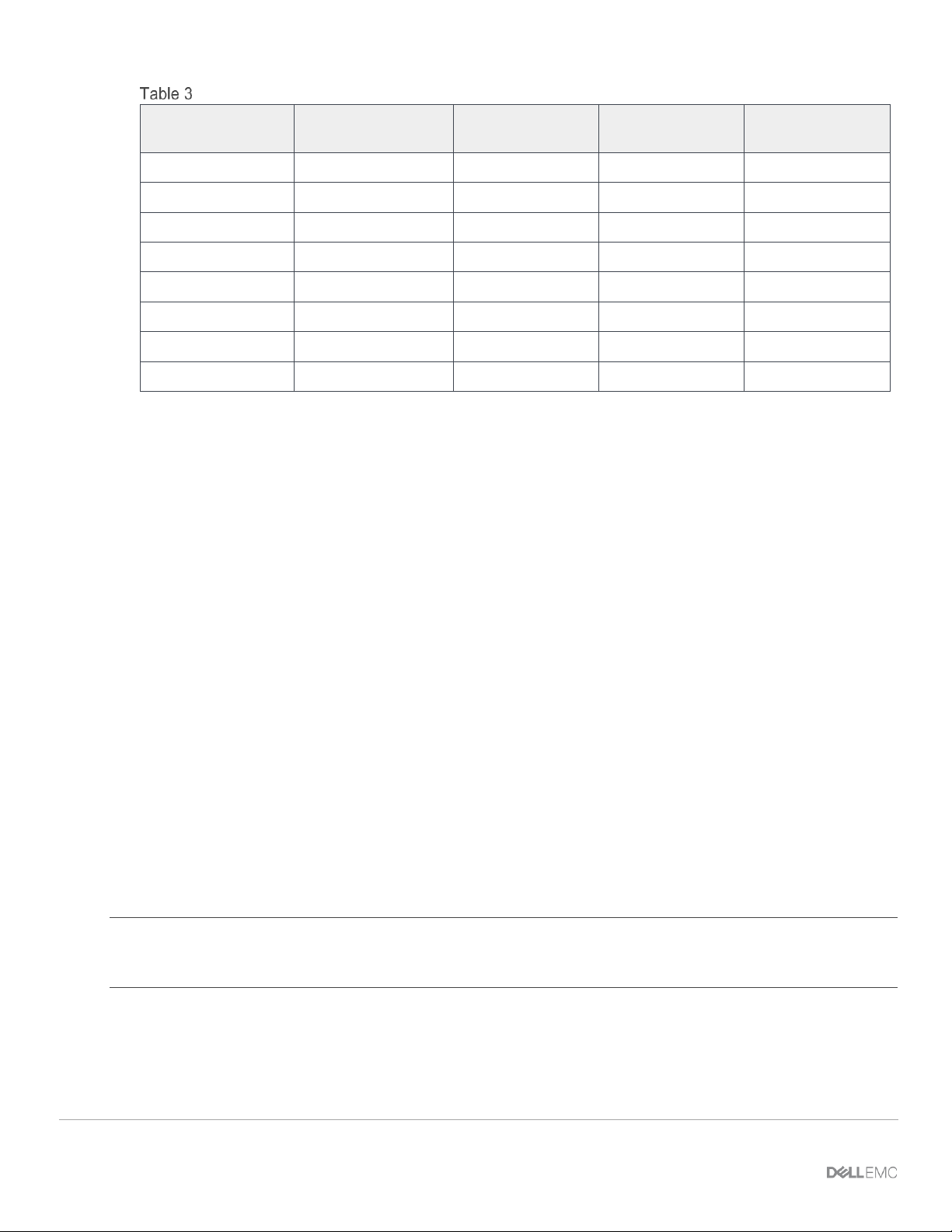
16 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
Virtual port mapping
FEM service tag
FSE QSFP28-DD
port group
FSE 25G
interfaces
FEM unit ID
(virtual slot ID)
FEM virtual ports
12AB3456
portgroup1/1/1
1/1/17:1
71
1/71/1
1/1/17:2
1/71/2
1/1/17:3
1/71/3
1/1/17:4
1/71/4
1/1/18:1
1/71/5
1/1/18:2
1/71/6
1/1/18:3
1/71/7
1/1/18:4
1/71/8
When a QSFP28-DD port group is mapped to a FEM, in the show interface status output, the eight
interfaces display dormant instead of up until a virtual port starts to transmit server traffic:
OS10# show interface status
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Port Description Status Speed Duplex Mode Vlan Tagged-Vlans
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------...
Eth 1/1/17:1 dormant
Eth 1/1/17:2 dormant
Eth 1/1/17:3 dormant
Eth 1/1/17:4 dormant
Eth 1/1/18:1 dormant
Eth 1/1/18:2 dormant
Eth 1/1/18:3 dormant
Eth 1/1/18:4 dormant
...
You can also use the show interface command to display the Fabric Engine physical port-to-Fabric
Expander virtual port mapping, and the operational status of the line:
OS10# show interface ethernet 1/1/30:3
Ethernet 1/1/30:3 is up, line protocol is dormant
Interface is mapped to ethernet1/77/7
Note: If you move a FEM by cabling it to a different QSFP28-DD port on the Fabric Engine, all software
configurations on virtual ports are maintained. Only the QSFP28-DD breakout interfaces that map to the virtual
ports change.
2.5 Virtual Link Trunking
Virtual Link Trunking (VLT) aggregates two identical physical switches to form a single logical extended
switch. However, each of the VLT peers has its own control and data planes and can be configured
individually for port, protocol, and management behaviors. Though the dual physical units act as a single
17 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
logical unit, the control and data plane of both switches remain isolated, ensuring high availability and high
resilience for all its connected devices. This differs from the legacy stacking concept, where there is a single
control plane across all switches in the stack, creating a single point of failure.
With the critical need for high availability in modern data centers and enterprise networks, VLT plays a vital
role connecting with rapid convergence, seamless traffic flow, efficient load balancing, and loop free
capabilities.
With the instantaneous synchronization of MAC and ARP entries, both the nodes remain Active-Active and
continue to forward the data traffic seamlessly.
VLT is required when operating in SmartFabric mode.
For more information on VLT, see the Virtual Link Trunking chapter in the OS10 Enterprise Edition User
Guide - PowerEdge MX I/O Modules and Virtual Link Trunking (VLT) in Dell EMC OS10 Enterprise Edition
Best Practices and Deployment Guide.
2.6 Fibre Channel (FC) connectivity
PowerEdge MX Ethernet I/O modules support Fibre Channel, or FC connectivity in three different ways:
Direct Attach (also called F_port), NPIV Proxy Gateway (NPG), and FIP Snooping Bridge (FSB). The method
to implement depends on the existing infrastructure and application requirements. Consult your Dell EMC
representative for more information.
Configuring FC connectivity in SmartFabric mode is simple and is almost identical across the three
connectivity types.
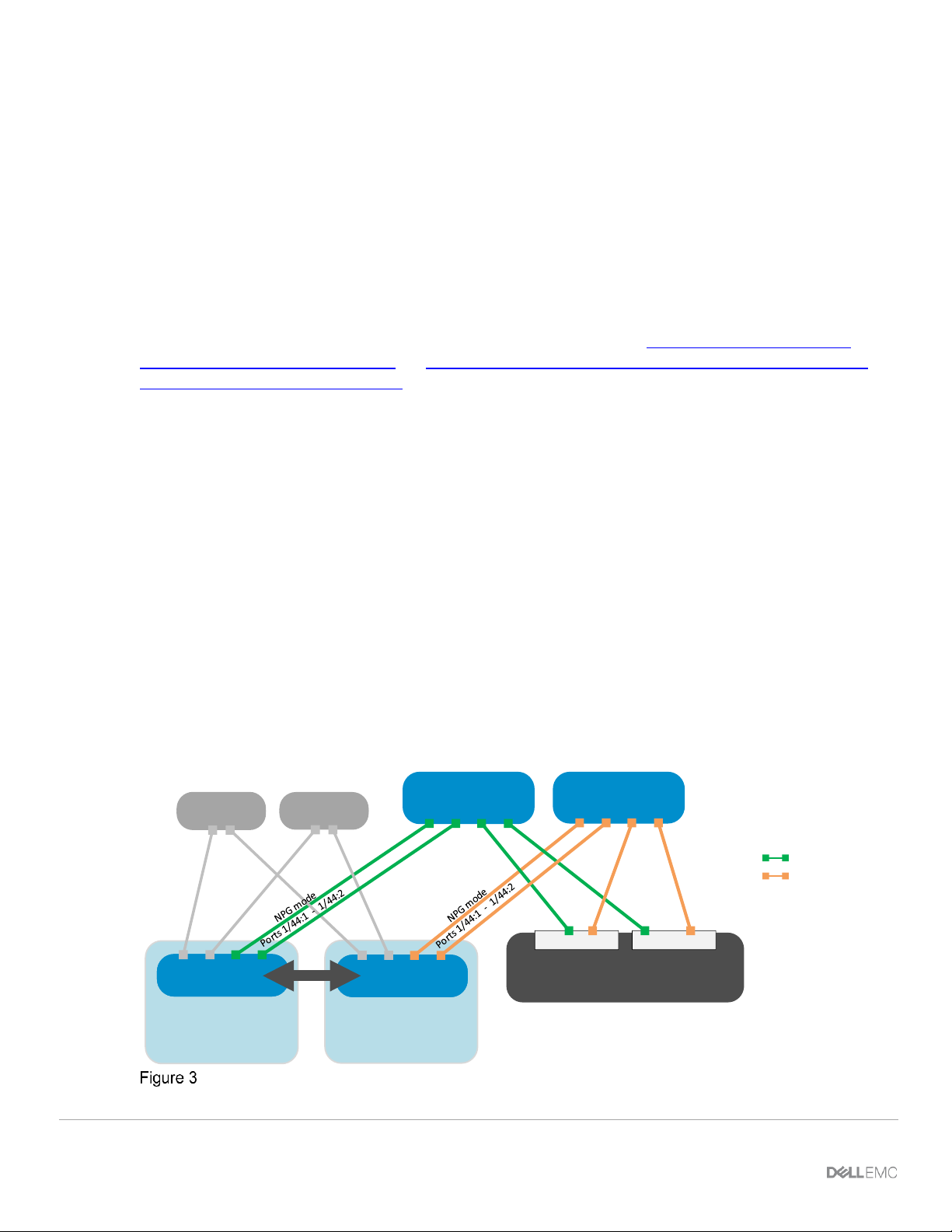
2.6.1 NPIV Proxy Gateway (NPG)
The most common connectivity method, NPIV Proxy Gateway mode (NPG) is used when connecting
PowerEdge MX to a storage area network that hosts a storage array. NPG mode is very simple to implement
as there is very little configuration that needs to be done. The NPG switch converts FCoE from the server to
native FC and aggregates the traffic into an uplink. The NPG switch is effectively transparent to the FC SAN,
which “sees” the hosts themselves. This mode is supported only on the MX9116n FSE.
FC Switch
FC Switch
MX9116n
(Leaf 2)
MX9116n
(Leaf 1)
VLT
MX7000
Spine 2
Spine 1
FC SAN A
Note: Brocade 6510 switches were used in
validating this brownfield example. Other FC
switches may be used as well.
Unity 500F
Unity 500F
Unity 500F
Controller A Controller B
chassis 1
MX7000
chassis 2
FC SAN B
FC (NPG) network to Dell EMC Unity
18 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
For more information on configuration and deployment, see Section 10.3.
2.6.2 Direct Attached (F_port)
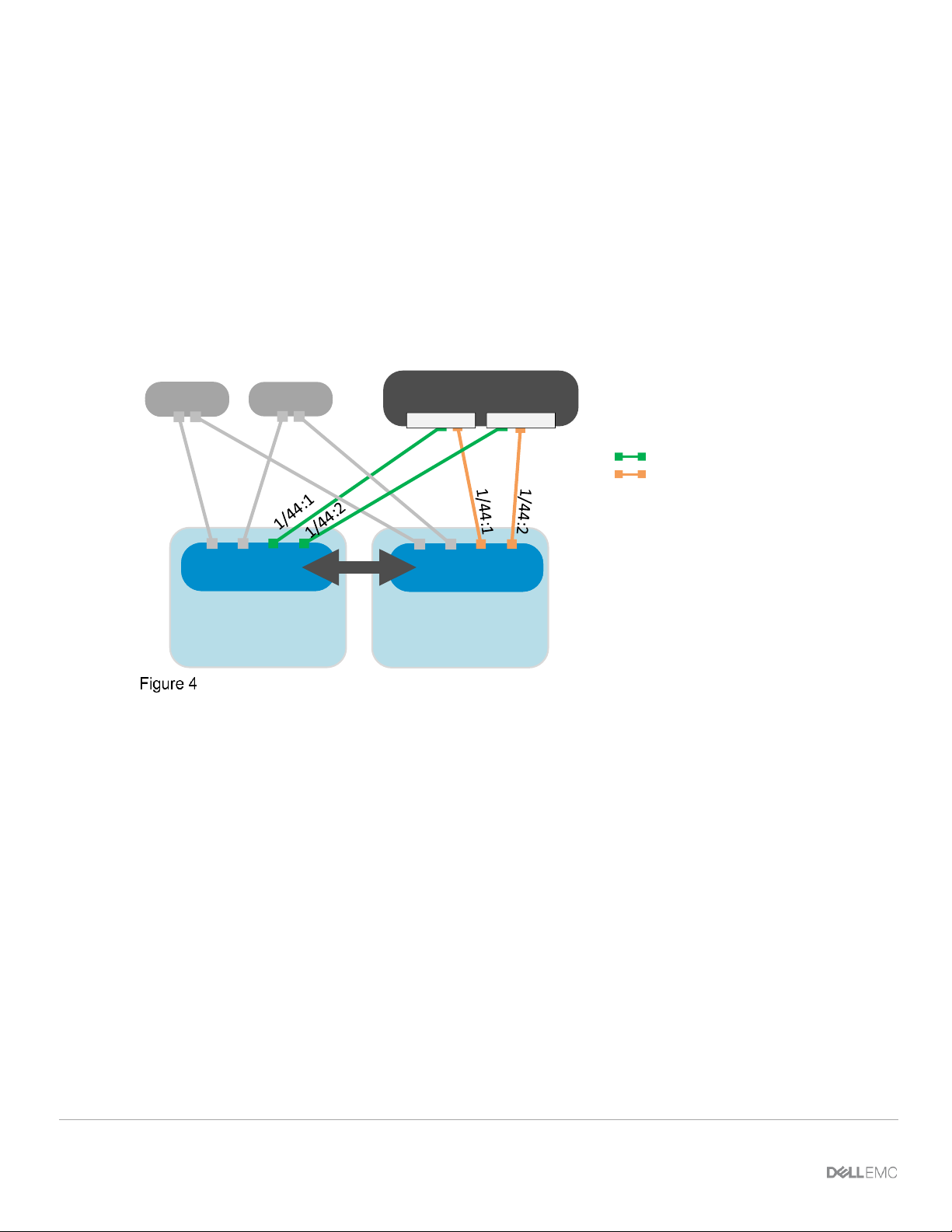
Direct Attached mode, or F_port, is used when FC storage needs to be directly connected to the switch. The
switch supports the required services such as name server and zoning that are typical of FC switches.
This example demonstrates Fibre Channel directly attaching to the Dell EMC Unity 500F storage array.
MX9116n FSE universal ports 44:1 and 44:2 are required for FC connections and operate in F_port mode,
which allows for an FC storage array to be connected directly to the MX9116n FSE. The uplink type enables
F_port functionality on the MX9116n unified ports, converting FCoE traffic to native FC traffic and passing that
traffic to a directly attached FC storage array.
This mode is supported only on the MX9116n FSE.
Unity 500F
MX9116n
(Leaf 2)
MX9116n
(Leaf 1)
VLT
MX7000
Spine 2
Spine 1
FC SAN B
Unity 500F
Controller A Controller B
chassis 1
MX7000
chassis 2
FC SAN A
Fibre Channel (F_Port) direct connect network to Dell EMC Unity
For more information on configuration and deployment, see Section 10.4.
2.6.3 FCoE (FSB)
FCoE Transit, or FSB mode is used when connecting PowerEdge MX to an upstream switch that accepts
FCoE and converts it to native FC, such as the Dell EMC PowerSwitch S4148U. This mode is typically used
when an existing FCoE infrastructure is in place that PowerEdge MX must connect to. In Figure 5, uplink type
enables NPG FC Gateway functionality on the MX9116n FSE unified ports, converting FCoE traffic to native
FC traffic on PowerSwitch S4148U-ON and passing that traffic to an external FC switch.
When operating in FSB mode, the switch snoops FIP packets on FCoE-enabled VLANs and discovers the
following information:
• End nodes (ENodes)
• Fibre Channel forwarders (FCFs)
• Connections between ENodes and FCFs
• Sessions between ENodes and FCFs
Using the discovered information, the switch installs ACL entries that provide security and point-to-point link
emulation.
19 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
This mode is supported on both the MX9116n FSE and the MX5108n Ethernet Switch.
S4148U-ON
(NPG mode)
S4148U-ON
(NPG mode)
Unity 500F
MX5108n
FSB mode
(Leaf 2)
MX5108n
FSB mode
(Leaf 1)
VLT
MX7000 chassis
ToR switch 2
ToR switch 1
FC SwitchFC Switch
Unity 500F
Unity 500F
Controller A Controller B
VLT
FC SAN A
FC SAN B
FCoE SAN A
FCoE SAN B
FCoE (FSB) Network to Dell EMC Unity through NPG switch
For more information on configuration and deployment, see Section 10.5.
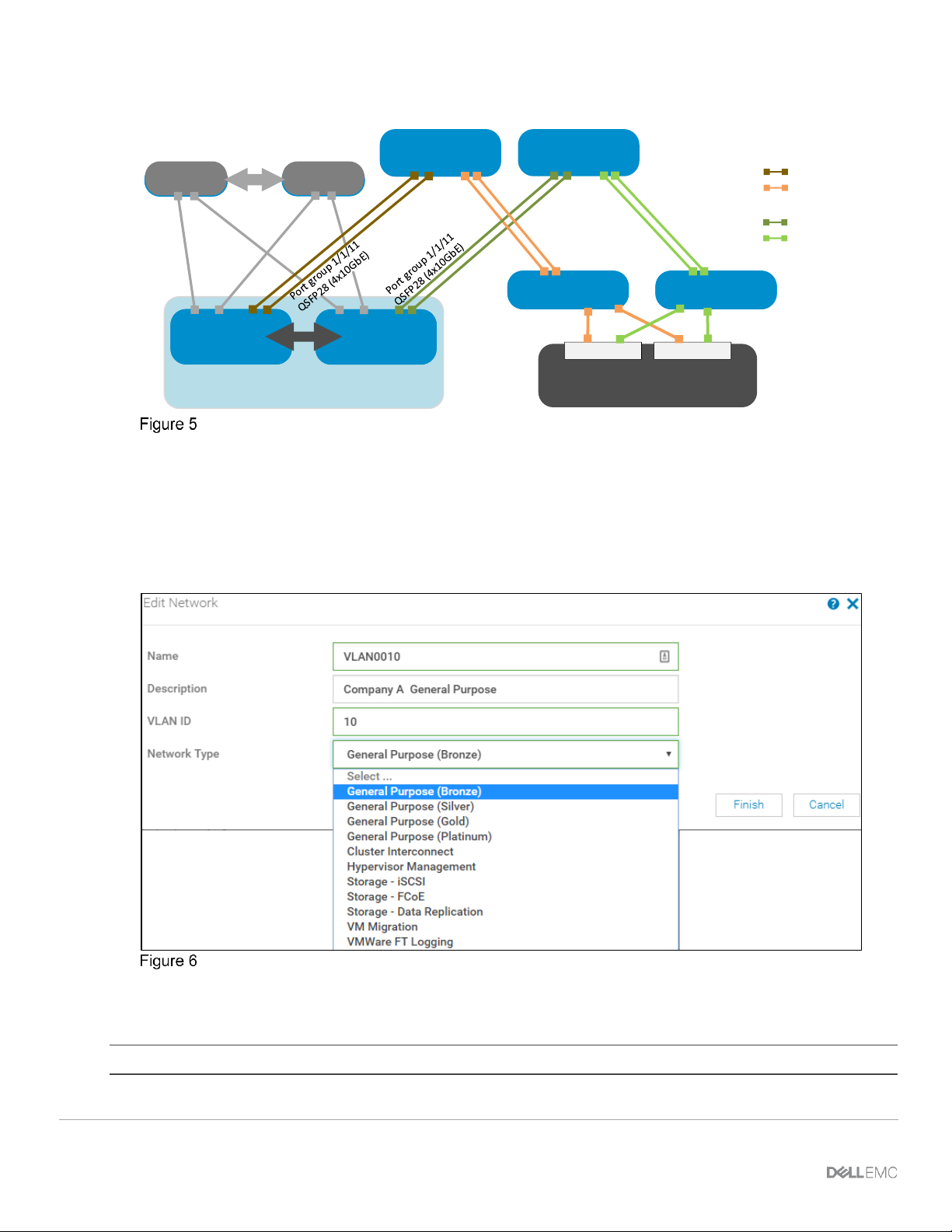
2.7 Networks and automated QoS
In addition to assigning VLANs to server profiles, SmartFabric automates QoS settings based on the Network
Type specified. Figure 6 shows that when defining a VLAN, one of 11 options are pre-defined.
Network types available in SmartFabric mode
Table 4 lists the network types and related settings. The QoS group is the numerical value for the queues
available in SmartFabric mode. Available queues include 2 through 5. Queues 1, 6, and 7 are reserved.
Note: In SmartFabric mode, an administrator cannot change the default weights for the queues.
20 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
Network types and default QoS settings
Network type
Description
QoS group
General Purpose (Bronze)
Used for low priority data traffic
2
General Purpose (Silver)
Used for standard/default priority data traffic
3
General Purpose (Gold)
Used for high priority data traffic
4
General Purpose (Platinum)
Used for extremely high priority data traffic
5
Cluster Interconnect
Used for cluster heartbeat VLANs
5
Hypervisor Management
Used for hypervisor management connections such as the
ESXi management VLAN
5
Storage - iSCSI
Used for iSCSI VLANs
5
Storage - FCoE
Used for FCoE VLANs
5
Storage - Data Replication
Used for VLANs supporting storage data replication such
as for VMware VSAN
5
VM Migration
Used for VLANs supporting vMotion and similar
technologies
5
VMware FT Logging
Used for VLANs supporting VMware Fault Tolerance
5
2.8 Server templates, virtual identities, networks, and deployment
For detailed information on templates, identities, and deployment, see the OpenManage Enterprise - Modular
documentation and the technical paper PowerEdge MX7000: Templates and Profiles.
2.8.1 Templates
A template is a set of system configuration settings referred to as attributes. A template may contain a small
set of attributes for a specific purpose, or all the attributes for a full system configuration. Templates allow for
multiple servers to be configured quickly and automatically without the risk of human error.
Networks (VLANs) are assigned to NICs as part of the server template. When the template is deployed, those
networks are programmed on the fabric for the servers associated with the template.
Note: Network assignment through template only functions for servers connected to a SmartFabric. If a template
with network assignments is deployed to a server connected to a switch in Full Switch mode, the network
assignments are ignored.
OME-M GUI provides options for creating templates:
• Most frequently, templates are created by getting the current system configuration from a server that
has been configured to the exact specifications required (referred to as a “Reference Server”).
• Templates may be cloned or copied and edited.
• A template can be created by importing a Server Configuration Profile (SCP) file. The SCP file may
be from a server or exported by OpenManage Essentials, OpenManage Enterprise, or OME-M.
• OME-M comes prepopulated with several templates for specific purposes.

21 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
2.8.2 Virtual identities and identity pools
Some of the attributes included in a template are referred to as identity attributes. Identity attributes identify a
device and distinguish it from all other devices on the network. Since identity attributes must uniquely identify
a device, it is imperative that each device has a unique network identity. Otherwise, devices won’t be able to
communicate with each other over the network.
Devices come with unique manufacturer-assigned identity values preinstalled, such as a factory-assigned
MAC address. Those identities are fixed and never change. However, devices can assume a set of alternate
identity values, called a “virtual identity”. A virtual identity functions on the network using that identity, as if the
virtual identity was its factory-installed identity. The use of virtual identity is the basis for stateless operations.
OME-M console uses identity pools to manage the set of values that can be used as virtual identities for
discovered devices. It controls the assignment of virtual identity values, selecting values for individual
deployments from pre-defined ranges of possible values. This allows the customer to control the set of values
which can be used for identities. The customer doesn’t have to enter all needed identity values with every
deployment request, or remember which values have or have not been used. Identity pools make
configuration deployment and migration much easier to manage.
Identity pools are used in conjunction with template deployment and profile operations. They provide sets of
values that can be used for virtual identity attributes for deployment. After a template is created, an identity
pool may be associated with it. Doing this directs the identity pool to get identity values whenever the
template is deployed to a target device. The same identity pool can be associated with, or used by, any
number of templates. Only one identity pool can be associated with a template.
Each template will have specific virtual identity needs, based on its configuration. For example, one template
may have iSCSI configured, so it needs the appropriate virtual identities for iSCSI operations. Another
template may not have iSCSI configured, but may have FCoE configured, so it will need virtual identities for
FCoE operations but not for iSCSI operations, etc.
2.8.3 Deployment
Deployment is the process of applying a full or partial system configuration on a specific target device. In
OME-M, templates are the basis for all deployments. Templates contain the system configuration attributes
that get sent to the target server, then the iDRAC on the target device applies the attributes contained in the
template and reboots the server if necessary. Often, templates contain virtual identity attributes. As mentioned
above, identity attributes must have unique values on the network. Identity Pools facilitate the assignment and
management of unique virtual identities.

22 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
3 SmartFabric mode requirements, guidelines, and restrictions
Before deploying a SmartFabric, ensure that the following requirements, guidelines, and restrictions are
followed. Failure to do so may impact your network.
3.1 Create multi-chassis management group
For a scalable fabric that uses more than one MX chassis, the chassis must be in a Multi-Chassis
Management (MCM) Group. For more information on how to create MCM Group, refer to Dell EMC
OpenManage Enterprise-Modular Edition for PowerEdge MX7000 Chassis.
Note: SmartFabric mode can be enabled on a single chassis having two MX9116n FSEs or two MX5108n
switches. For a SmartFabric implemented using a single chassis, creating an MCM group is not mandatory but
recommended. The chassis must be in an MCM group for a SmartFabric containing more than one MX chassis.
3.2 Upstream network requirements
3.2.1 Physical connectivity
All physical Ethernet connections within an uplink from a SmartFabric are automatically grouped into a single
LACP LAG. Because of this, all ports on the upstream switches must also be in a single LACP LAG. Failure to
do so may create network loops.
A minimum of one physical uplink from each MX switch to each upstream switch is required and that the
uplinks must be connected in a “mesh” or “bowtie” design.
Note: The upstream switch ports must be in a single LACP LAG as shown in the figure below. Creating multiple
LAGs within a single uplink results in a network loop.
Recommended upstream network connectivity

3.2.2 Spanning Tree Protocol
By default, SmartFabric OS10 uses Rapid per-VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (RPVST+) across all switching
platforms including PowerEdge MX networking IOMs. SmartFabric OS10 also supports RSTP.
Note: Dell EMC recommends using RSTP instead of RPVST+ when more than 64 VLANs are required in a fabric
to avoid performance problems.
Caution should be taken when connecting an RPVST+ to an existing RSTP environment. RPVST+ creates a
single topology per VLAN with the default VLAN, typically VLAN 1, for the Common Spanning Tree (CST) with
RSTP.
For non-native VLANs, all bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) traffic is tagged and forwarded by the upstream,
RSTP-enabled switch with the associated VLAN. These BPDUs use a protocol-specific multicast address.
Any other RPVST+ tree attached to the RSTP tree might processes these packets accordingly leading to the
potential of unexpected trees.
Note: When connecting to an existing environment that is not using RPVST+, Dell EMC recommends changing to
the existing spanning tree protocol before connecting a SmartFabric OS10 switch. This ensures same type of
Spanning Tree is run on the SmartFabric OS10 MX switches and the upstream switches.
To switch from RPVST+ to RSTP, use the spanning-tree mode rstp command:
MX9116N-A1(config)# spanning-tree mode rstp
MX9116N-A1(config)# end
To validate the STP configuration, use the show spanning-tree brief command:
MX9116N-A1#show spanning-tree brief
Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp with force-version rstp
Executing IEEE compatible Spanning Tree Protocol
Root ID Priority 0, Address 4c76.25e8.f2c0
Root Bridge hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Bridge ID Priority 32768, Address 2004.0f00.cd1e
Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Flush Interval 200 centi-sec, Flush Invocations 95
Flush Indication threshold 0 (MAC flush optimization is disabled)
Note: STP is required. Operating a SmartFabric with STP disabled creates network loops and is not supported.
3.3 VLAN scaling guidelines
Because SmartFabric mode provides network automation capabilities that Full Switch mode does not, the
number of recommended VLANs differs between the modes. Table 5 provides the recommended maximum
number of VLANs per fabric, uplink, and server port.
Note: These are recommendations, not enforced maximums.
23 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide

24 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
Recommended maximum number of VLANs in SmartFabric mode
OS10 Version
Parameter
Value
10.5.0.1
Recommended Max VLANs per Fabric
256
Recommended Max VLANs per Uplink
256
Recommended Max VLANs per server port
64
10.4.0.R3S
10.4.0.R4S
Recommended Max VLANs per Fabric
128
Recommended Max VLANs per Uplink
128
Recommended Max VLANs per server port
32
3.4 Configuring port speed and breakout
If you need to change the default port speed and/or breakout configuration of an uplink port, you must do that
prior to creating the uplink.
For example, the QSFP28 interfaces that belong to port groups 13, 14, 15, and 16 on MX9116n FSE are
typically used for uplink connections. By default, the ports are set to 1x100GbE. The QSFP28 interface
supports the following Ethernet breakout configurations:
• 1x 100GbE – One 100GbE interface
• 1x 40GbE – One 40GbE interface
• 2x 50GbE – Breakout a QSFP28 port into two 50GbE interfaces
• 4x 25GbE – Breakout a QSFP28 port into four 25GbE interfaces
• 4x 10GbE – Breakout a QSFP28 port into four 10GbE interfaces
The MX9116n FSE also supports Fibre Channel (FC) capabilities via Universal Ports on port-groups 15 and
16. For more information on configuring FC storage on the MX9116n FSE, see Section 10.3 and 10.4.
For more information on interface breakouts, see OS10 User Guide - PowerEdge MX I/O Modules Release
10.4.0E(R3S).
3.5 Switch slot placement for SmartFabric mode
SmartFabric mode supports three specific switch placement options. Attempts to use placements different
than described here is not supported and may result in unpredictable behavior and/or data loss.
Note: The cabling shown in this section, Section 3.5, is the VLTi connections between the MX switches.
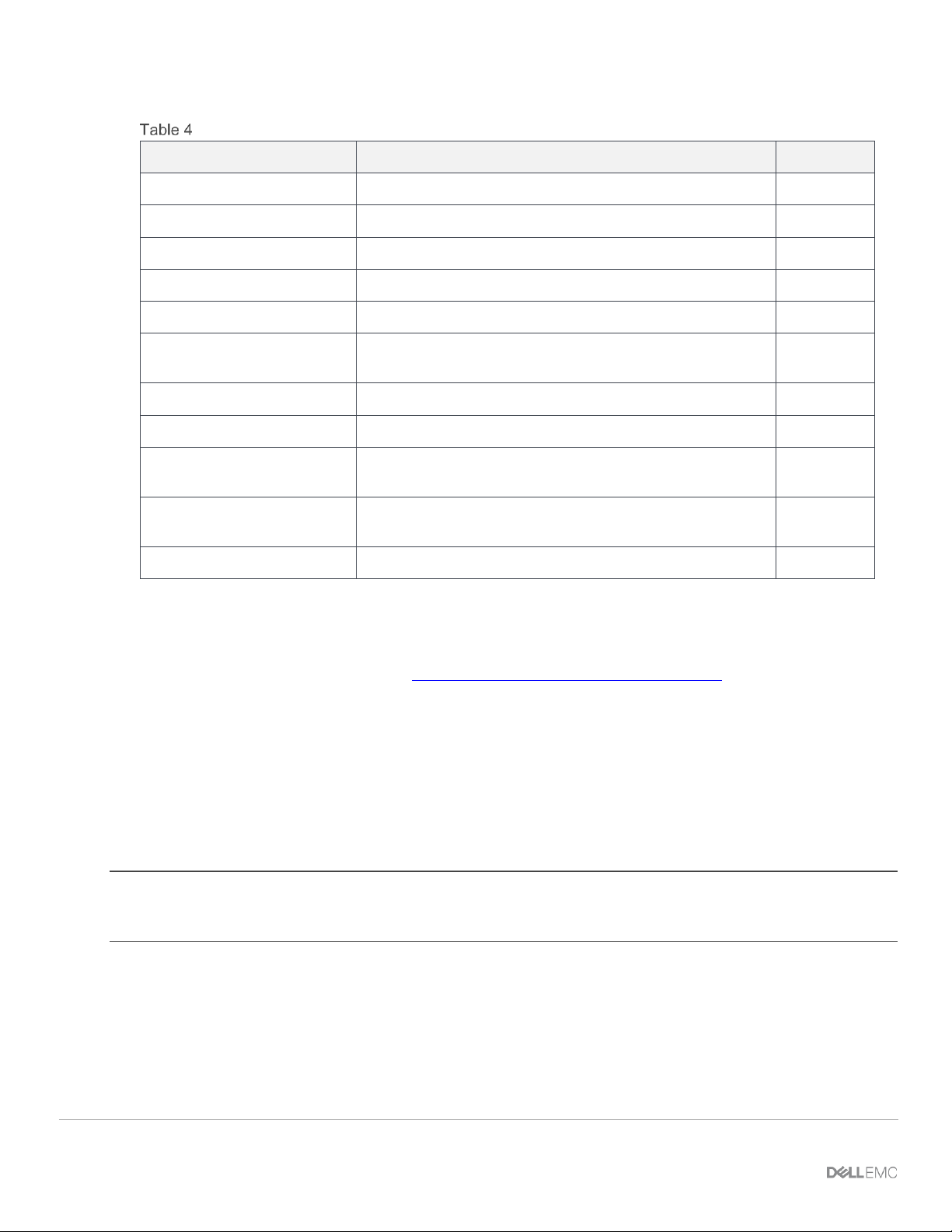
3.5.1 Two MX9116n Fabric Switching Engines or FSEs in different chassis
This is the recommended placement when creating a SmartFabric on top of a Scalable Fabric Architecture.
Placing the FSE modules in different chassis provides redundancy in the event of a chassis failure. This
configuration supports placement in Chassis1 Slot A1 and Chassis 2 Slot A2 or Chassis1 Slot B1 and
Chassis 2 Slot B2. A SmartFabric cannot include a switch in Fabric A and a switch in Fabric B.
25 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
IOM placement – 2 x MX9116n in different chassis
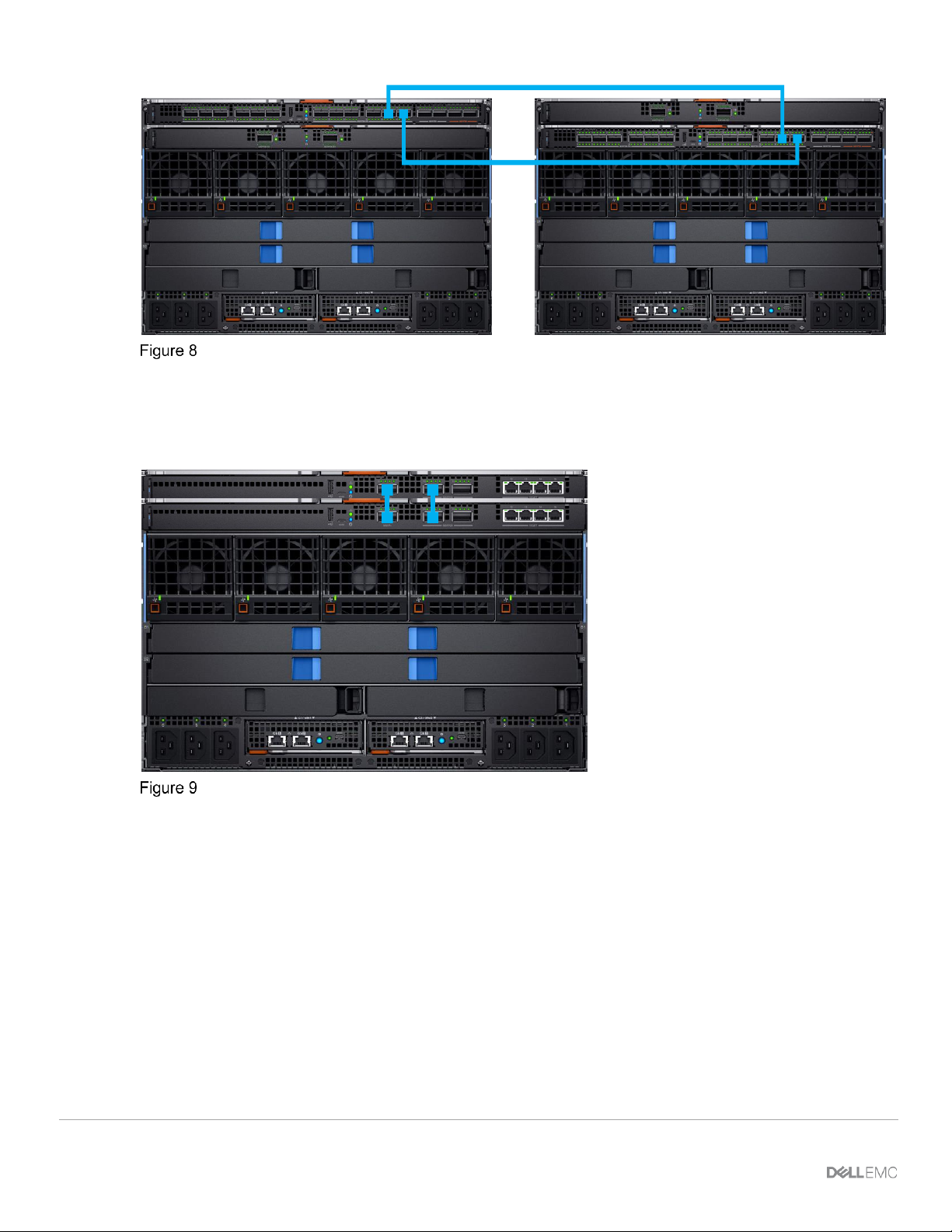
3.5.2 Two MX5108n Ethernet switches in the same chassis
The MX5108n Ethernet Switch is only supported in single chassis configurations, with the switches in either
slots A1/A2 or slots B1/B2. A SmartFabric cannot include a switch in Fabric A and a switch in Fabric B.
IOM placement – 2 x MX5108n in the same chassis
26 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
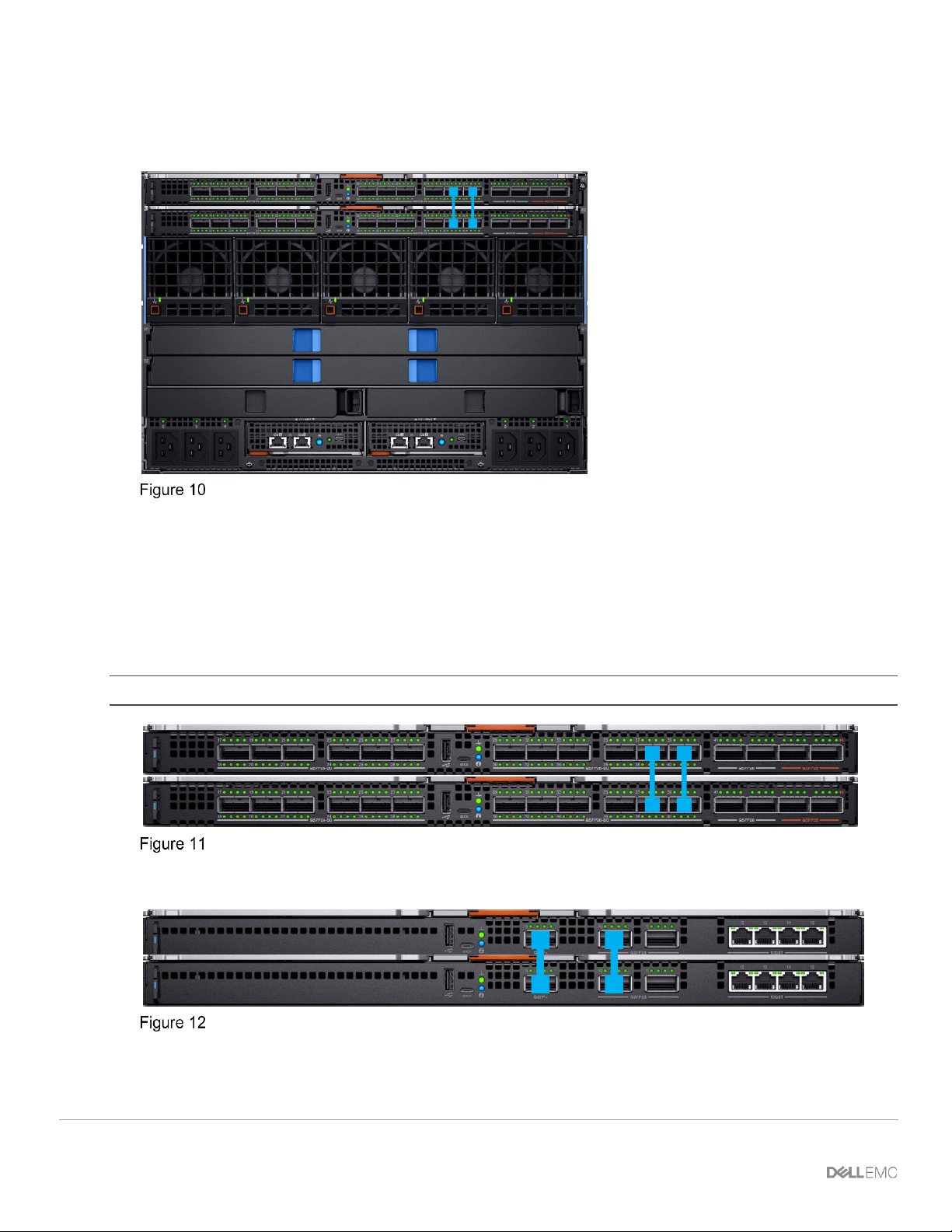
3.5.3 Two MX9116n Fabric Switching Engines or FSEs in the same chassis
This placement should only be used in environments with a single chassis, with the switches in either slots
A1/A2 or slots B1/B2. A SmartFabric cannot include a switch in Fabric A and a switch in Fabric B.
IOM placement – 2 x MX9116n in the same chassis
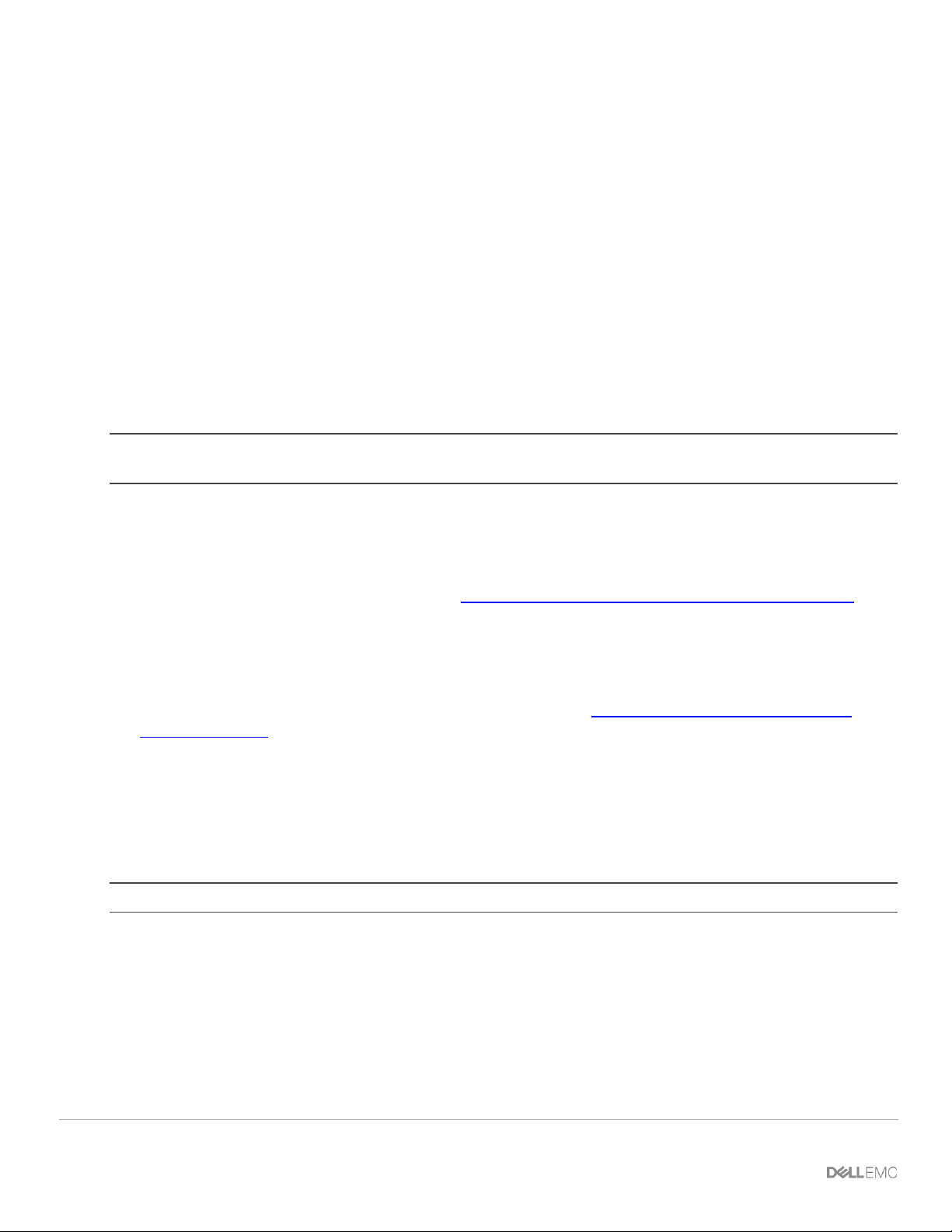
3.6 Switch-to-Switch cabling
When operating in SmartFabric mode, each switch pair runs a VLT interconnect (VLTi) between them. For the
MX9116n FSE, QSFP28-DD port groups 11 and 12 (eth1/1/37-1/1/40) are used.
For the MX5108n, ports 9 and 10 are used. Port 10 operates at 40GbE instead of 100GbE because all VLTi
links must run at the same speed.
Note: The VLTi ports are not user selectable and the connection topology is enforced by the SmartFabric engine.
MX9116n SmartFabric VLTi cabling
MX5108n SmartFabric VLTi cabling

27 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
3.6.1 VLT backup link
A pair of cables is used to provide redundancy for the VLTi link. A third redundancy mechanism, a VLT
backup link is automatically created when the SmartFabric is created. This link exchanges VLT heartbeat
information between the two switches to avoid a split-brain scenario should the external VLTi links go down.
Based on the node liveliness information, the VLT LAG/port is in up state in the primary VLT peer and in down
state in the secondary VLT peer. When only the VLTi link fails, but the peer is alive, the secondary VLT peer
shuts down the VLT ports. When the node in primary peer fails, the secondary becomes the primary peer.
To see the status of VLT backup link, run show vlt domain-id backup-link.
For example:
OS10# show vlt 255 backup-link
VLT Backup Link
------------------------
Destination : fde1:53ba:e9a0:de14:2204:fff:fe00:a267
Peer Heartbeat status : Up
Heartbeat interval : 30
Heartbeat timeout : 90
Destination VRF : default
3.7 NIC teaming guidelines
While NIC teaming is not required, it is generally suggested for redundancy unless a specific implementation
recommends against it.
There are two main kinds of NIC teaming:
• Switch dependent: Also referred to as LACP, 802.3ad, or Dynamic Link Aggregation, this teaming
method uses the LACP protocol to understand the teaming topology. This teaming method provides
Active-Active teaming and requires the switch to support LACP teaming.
• Switch independent: This method uses the operating system and NIC device drivers on the server
to team the NICs. Each NIC vendor may provide slightly different implementations with different pros
and cons.
NIC Partitioning (NPAR) can impact how NIC teaming operates. Based on restrictions implemented by the
NIC vendors related to NIC partitioning, certain configurations will preclude certain types of teaming.
The following restrictions are in place for both Full Switch and SmartFabric modes:
• If NPAR is NOT in use, both Switch Dependent (LACP) and Switch Independent teaming methods
are supported
• If NPAR IS in use, only Switch Independent teaming methods are supported. Switch Dependent
teaming is NOT supported
If Switch Dependent (LACP) teaming is used, the following restrictions are in place:
• The iDRAC shared LAN on motherboard (LOM) feature can only be used if the “Failover” option on
the iDRAC is enabled
• If the host OS is Windows, the LACP timer MUST be set to “slow” (also referred to as “normal”)
1. Microsoft Windows 2012 R2, see Instructions

28 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
2. Microsoft Windows 2016, see Instructions
Refer to the network adapter or operating system documentation for detailed NIC teaming instructions.
Note: If using VMware ESXi and LACP, it is recommended to use VMware ESXi 6.7.0 Update 2.
Table 6 shows the options that MX Platform provides for NIC Teaming.
NIC Teaming Options on MX Platform
No Teaming
No NIC Bonding/Teaming or Switch Independent
Teaming
LACP Teaming
LACP (Also called 802.3ad or Dynamic Link
Aggregation)
Other
Other (Not recommended. Can have performance
impact on link management)
Note: LACP Fast timer is not currently supported.
3.8 Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) behavior
The default MTU for SmartFabric OS10 interfaces is 1532 bytes. When a SmartFabric is created, the default
MTU for the switch is set to Jumbo (9216 bytes). This introduces the following behaviors:
1. If the MTU is not specifically set on a specific interface, the MTU will be 9216 bytes.
2. If the MTU has been specifically set on a specific interface, the MTU will be the value that has
been specified.
3. If a FCoE VLAN is assigned to an interface, the MTU will be set to 2500 bytes even if the
MTU had been manually set to a different value before the FCoE VLAN was assigned. It is
recommended that you set the MTU back to 9216 bytes after the FCoE VLAN has been
assigned
Please see Section 7.2 for instructions on setting the MTU.
3.9 Other restrictions and guidelines
The following additional restrictions and guidelines are in place when operating in SmartFabric mode:
1. Interconnecting switches in Slots A1/A2 with switches in Slots B1/B2 regardless of chassis is not
supported.
2. When operating with multiple chassis, switches in Slots A1/A2 or Slots B1/B2 in one chassis must be
interconnected only with other Slots A1/A2 or Slots B1/B2 switches respectively. Connecting switches
that reside in Slots A1/A2 in one chassis with switches in Slots B1/B2 in another is not supported.
3. Uplinks must be symmetrical. If one switch in a SmartFabric has two uplinks, the other switch must have
two uplinks of the same speed.
4. You cannot have a pair of switches in SmartFabric mode uplink to another pair of switches in SmartFabric
mode. A SmartFabric can uplink to a pair of switches in Full Switch mode.
5. VLANs 4001 to 4020 are reserved for internal switch communication and must not be assigned to an
interface.

29 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
6. In SmartFabric mode, although you can use the CLI to create VLANs 1 to 4000 and 4021 to 4094, you
cannot assign interfaces to them. For this reason, do not use the CLI to create VLANs in SmartFabric
mode.
7. VLAN 1 is automatically created as the Default/Native VLAN, but it is not required to be used. See
Section 4.2 for more information.
8. When using LACP NIC teaming, the LACP timer must be set to slow.
9. If you assign OME-M to a specific VLAN (VLAN 500, for example), do not create VLAN 500 on the fabric.
30 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
4 Creating a SmartFabric
The general steps required to create a SmartFabric are:
1. Physically cable the MX chassis and upstream switches.
2. Define the VLANs.
3. Create the SmartFabric.
4. If needed, configure uplink port speed and breakout.
5. Create the Ethernet uplink.
6. Configure the upstream switch and connect uplink cables.
These steps make the following assumptions:
• All MX7000 chassis and management modules are cabled correctly and in a Multi-Chassis
Management group.
• The VLTi cables between switches have been connected.
• Open Manage Enterprise - Modular is at version 1.10.00 and OS10 is version 10.5.0.1
Note: All server, network, and chassis hardware has been updated to the latest firmware. See Appendix D for the
minimum recommended firmware versions.
4.1 Physically cable MX chassis and upstream switches
The first step in creating the SmartFabric is to cable the MX chassis and upstream switches.
• For Management Module cabling, see Dell EMC PowerEdge MX Networking Architecture Guide.
• For VLTi cabling of different IOM placements, see Figure 8, Figure 9, and Figure 10.
For information on cabling the MX chassis to the upstream switches, see the example topologies in Section
10 in this document.
For further information on cabling PowerEdge MX in general, see Dell EMC PowerEdge MX Networking
Architecture Guide.
4.2 Define VLANs
Before creating the SmartFabric, the initial set of VLANs should be created. The first VLAN to be created
should be the default, or native VLAN, typically VLAN 1. The default VLAN must be created for any untagged
traffic to cross the fabric.
Note: VLAN1 will be created as a Default VLAN when the first fabric is created.
To define VLANs using the OME-M console, perform the following steps:
1. Open the OME-M console.
2. From the navigation menu, click Configuration > Networks.
3. In the Network pane, click Define.
4. In the Define Network window, complete the following:
• Enter a name for the VLAN in the Name box. In this example, VLAN0010 was used.
• Optionally, enter a description in the Description box. In this example, the description was
entered as “Company A General Purpose”.
 Loading...
Loading...