Page 1
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TEA6300
TEA6300T
Sound fader control circuit
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC01
May 1990
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Sound Fader Control circuit (SOFAC) is an I2C-bus
controlled preamplifier for car radios.
Features
• Source selector for three stereo inputs
• Inputs and outputs for noise reduction circuits
• Volume and balance control; control range of 86 dB in
steps of 2 dB
• Bass and treble control from + 15 dB (treble 12 dB)
to −12 dB in steps of 3 dB
• Fader control from 0 dB to −30 dB in steps of 2 dB
• Fast muting
• Low noise suitable for DOLBY* B and C NR (noise
reduction)
• Signal handling suitable for compact disc
2
• I
C-bus control for all functions
• ESD protected
TEA6300
TEA6300T
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
V
V
f
r
α
CC
i(rms)
i(rms)
CS
Supply voltage 7,0 8,5 13,2 V
Input sensitivity for full power at the output stage − 50 − mV
Input signal handling − 1,65 − V
Frequency response 35 − 20 000 Hz
Channel separation; f = 250 Hz to 10 kHz 70 92 − dB
THD Total harmonic distortion − 0,05 − %
(S+N)/N Signal plus noise-to-noise ratio − 80 − dB
T
amb
Operating ambient temperature range −40 −+ 85 °C
* Dolby is a registered trademark of Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corporation, San Francisco, California (U.S.A.).
PACKAGE OUTLINES
28-lead dual in-line; plastic (SOT117); SOT117-1; 1996 August 15.
28-lead mini-pack; plastic (SO28; SOT136A); SOT136-1; 1996 August 15.
May 1990 2
Page 3
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
May 1990 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
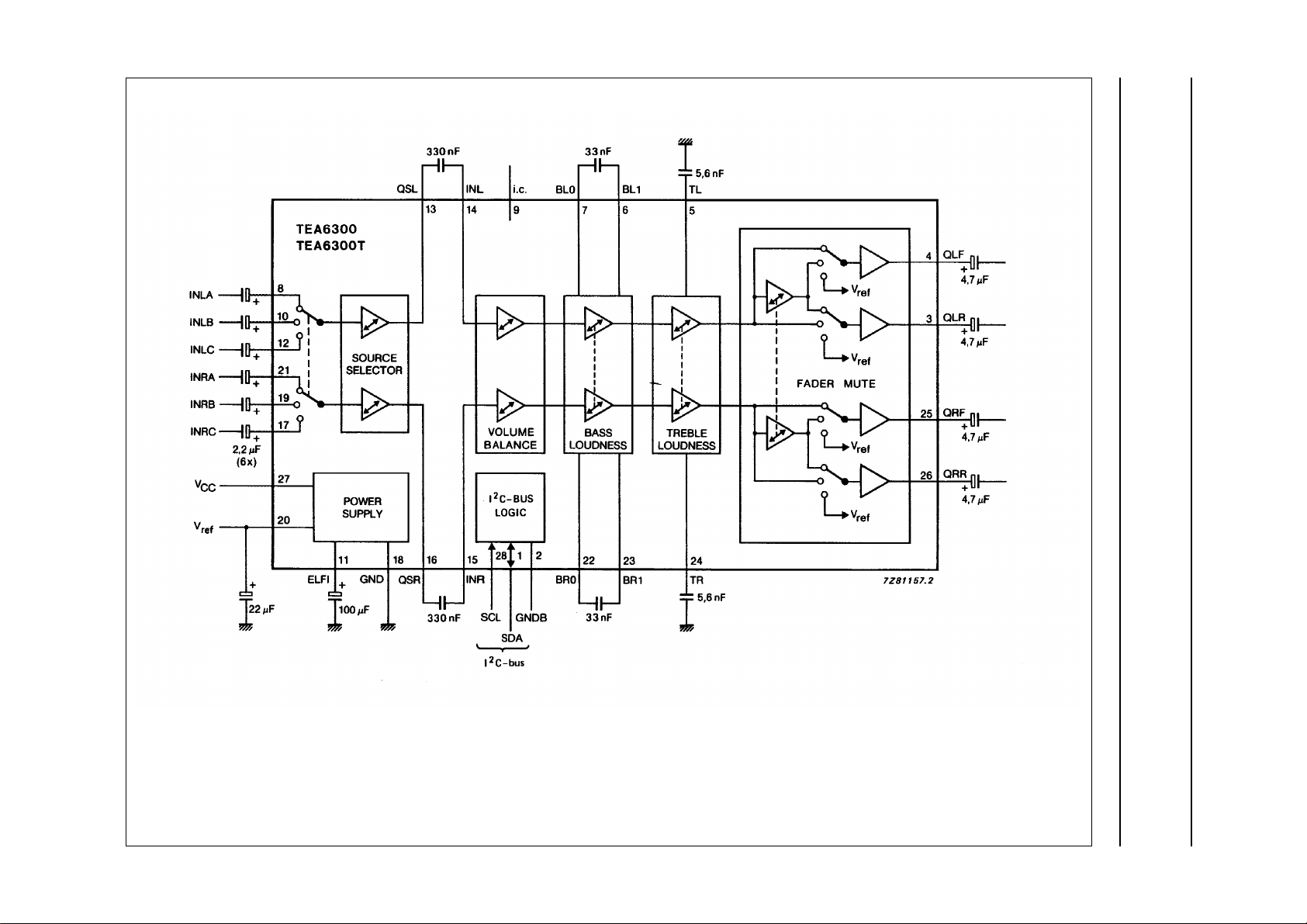
Fig.1 Block diagram.
TEA6300T
TEA6300
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
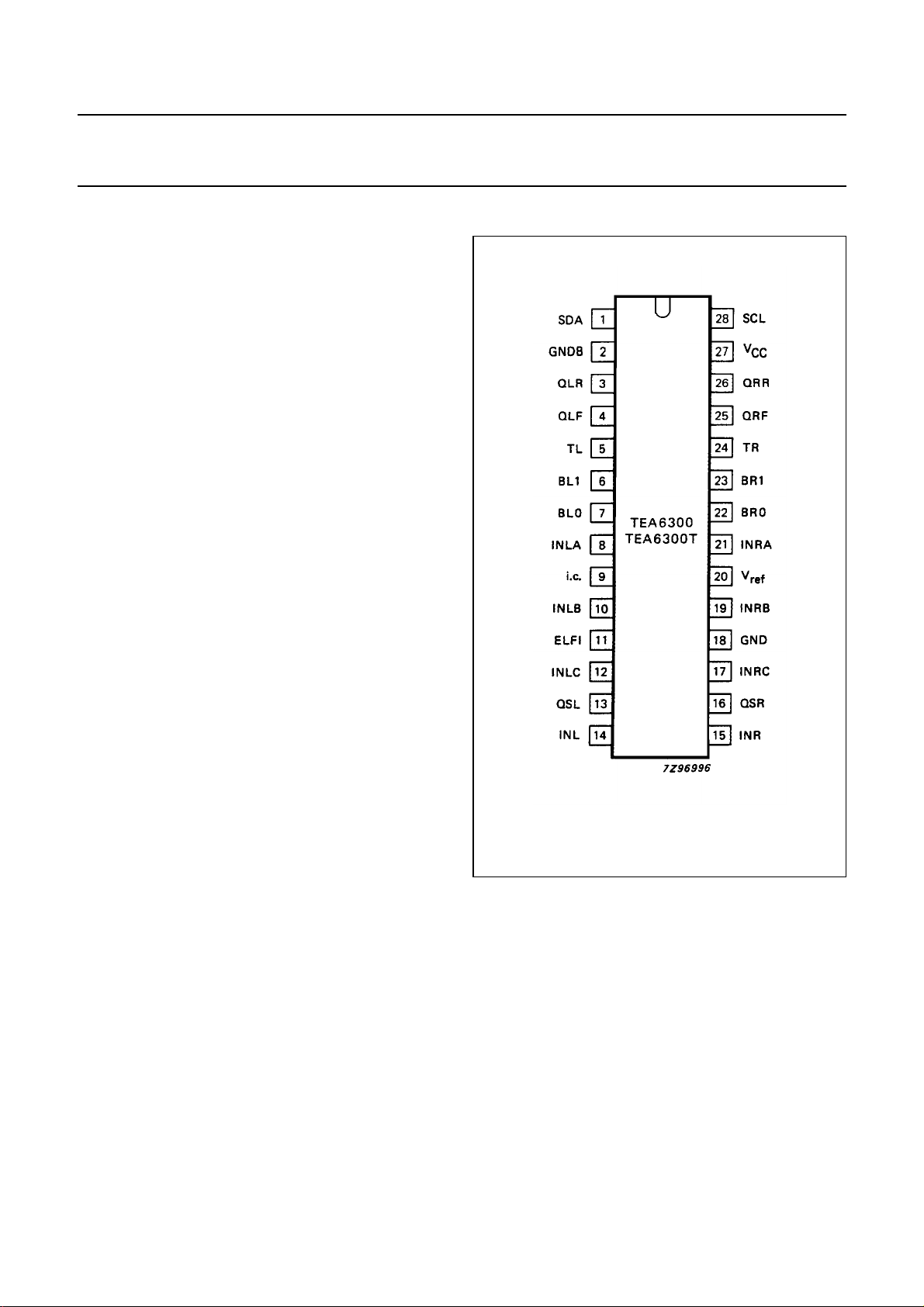
PINNING
2
2
C-bus)
C-bus)
1 SDA serial data input/output (I
2
2 GNDB ground for I
3 QLR output left rear
4 QLF output left front
5 TL treble control capacitor; left channel
6 BL1 bass control capacitor; left channel
7 BL0 bass control capacitor; left channel
8 INLA input left source A
9 i.c. internally connected
10 INLB input left source B
11 ELFI electronic filtering for supply
12 INLC input left source C
13 QSL output source selector left
14 INL input left control part
15 INR input right control part
16 QSR output source selector right
17 INRC input right source C
18 GND ground
19 INRB input right source B
20 V
21 INRA input right source A
22 BRO bass control capacitor; right channel
23 BR1 bass control capacitor; right channel
24 TR treble control capacitor; right channel
25 QRF output right front
26 QRR output right rear
27 V
28 SCL serial clock input (I
reference voltage (1/2 VCC)
ref
supply voltage
CC
C-bus terminals
TEA6300
TEA6300T
Fig.2 Pinning diagram.
May 1990 4
Page 5
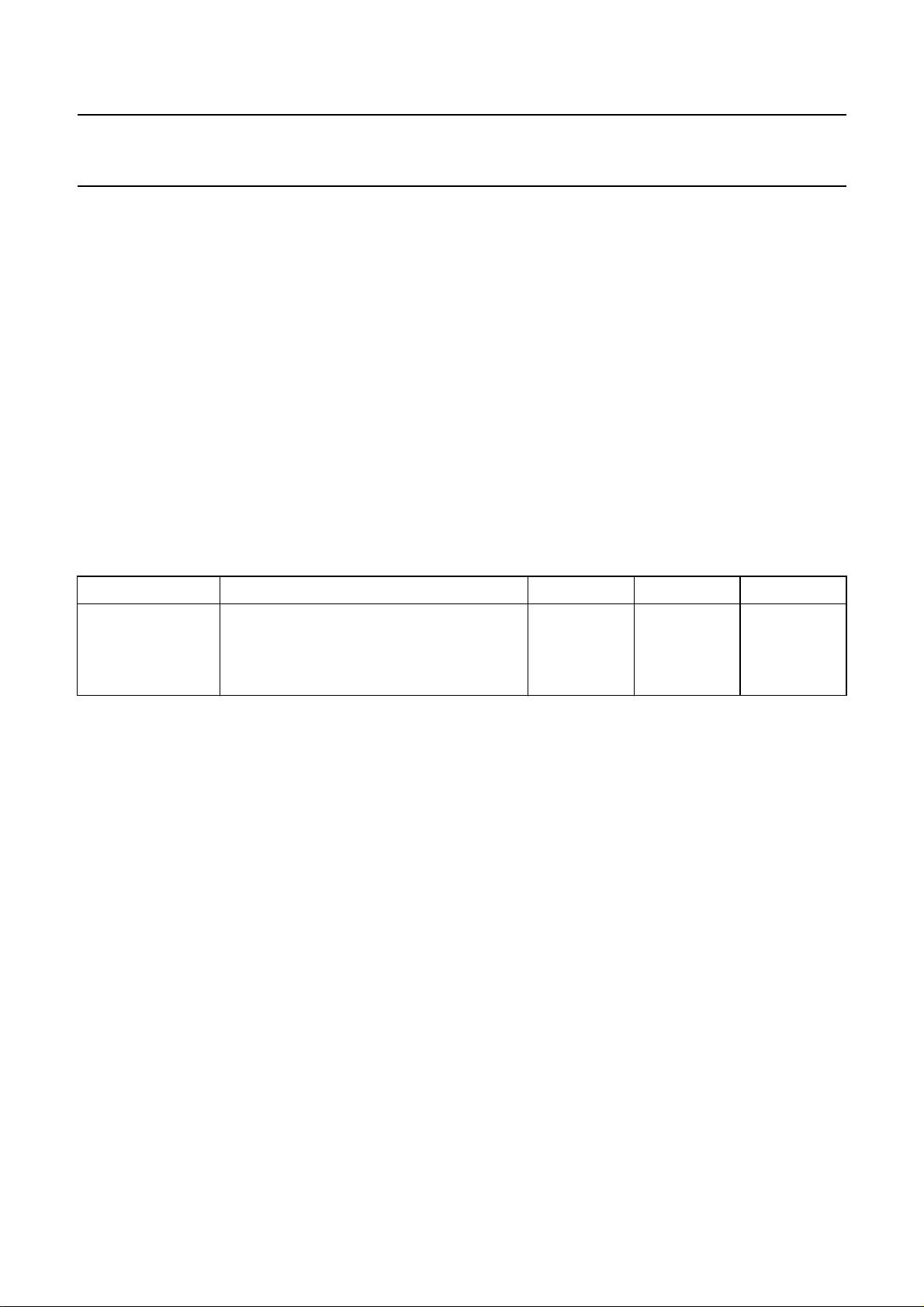
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
TEA6300
TEA6300T
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The source selector selects three stereo channels −RF part (AM/FM), recorder and compact disc. As the outputs of the
source selector and the inputs of the main control part are available, additional circuits such as compander and equalizer
systems may be inserted into the signal path. The AC signal setting is performed by resistor chains in combination with
multi-input operational amplifiers. The advantage of this principle is the combination of low noise, low distortion and a
high dynamic range for the circuit.
The separate volume controls of the left and the right channel facilitate correct balance control. The range and balance
control is software programmable.
Because the TEA6300 has four outputs a low-level fader is included. The fader control is independent of the volume
control and an extra mute position is built in for the front, the rear or for all channels. The last function may be used for
muting during preset selection. An extra pop suppression circuit is built in for pop-free switching on and off. As all
switching and control functions are controllable via the two-wire I
microcomputer and the TEA6300 is required.
The on-chip power-on-reset sets the TEA6300 to the general mute mode.
RATINGS
Limiting values in accordance with the Absolute Maximum System (IEC 134)
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
P
tot
T
stg
T
amb
Supply voltage (pin 27-18) − 16 V
Maximum power dissipation − 1W
Storage temperature range −55 +150 °C
Operating ambient temperature range −40 + 85 °C
2
C-bus, no external interface between the
May 1990 5
Page 6
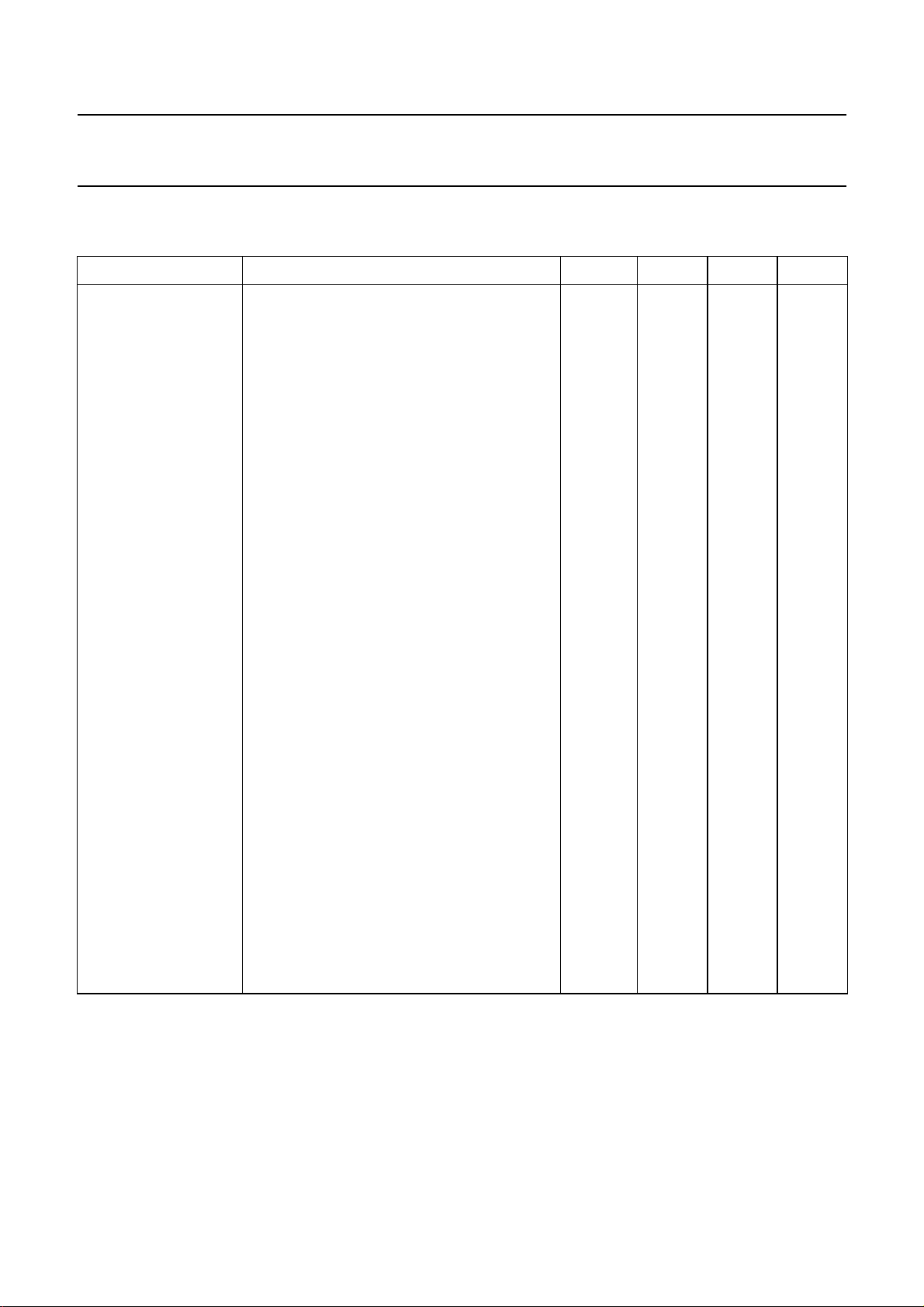
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
CHARACTERISTICS
V
= 8,5 V; RS = 600 Ω; RL = 10 kΩ; f = 1 kHz; T
CC
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
I
CC
I
CC
I
CC
V
DC
V
REF
G
v
V
o(rms)
V
o(rms)
V
i(rms)
f
r
α
CS
THD V
THD V
THD V
RR
100
RR
range
Supply voltage 7,0 8,5 13,2 V
Supply current − 26 − mA
Supply current at 8,5 V −−33 mA
Supply current at 13,2 V −−44 mA
DC voltage
inputs, outputs and reference 0,45 0,5 0,55 V
Internal reference voltage (pin 20)
V
= 0,5 V
ref
CC
Maximum voltage gain
bass and treble linear, fader off 19 20 21 dB
Output voltage level
for P
at the output stage − 500 − mV
max
for start of clipping − 1000 − mV
Input sensitivity
at Vo = 500 mV − 50 − mV
Frequency response
bass and treble linear; roll-off
frequency −1 dB 35 − 20 000 Hz
Channel separation
G
= 0 dB; bass and treble linear;
v
frequency range 250 Hz to 10 kHz 70 92 − dB
Total harmonic distortion
frequency range 20 Hz to 12,5 kHz
= 50 mV; Gv= 20 dB − 0,1 0,3 %
i
= 500 mV; Gv = 0 dB − 0,05 0,2 %
i
= 1,6 V; Gv= −10 dB − 0,2 0,5 %
i
Ripple rejection
V
< 200 mV; Gv = 0 dB;
r(rms)
bass and treble linear;
at f = 100 Hz − 70 − dB
at f = 40 Hz to 12,5 kHz − 60 − dB
= 25 °C; test circuit Fig.10; unless otherwise specified
amb
− 4,25 − V
TEA6300
TEA6300T
CC
May 1990 6
Page 7
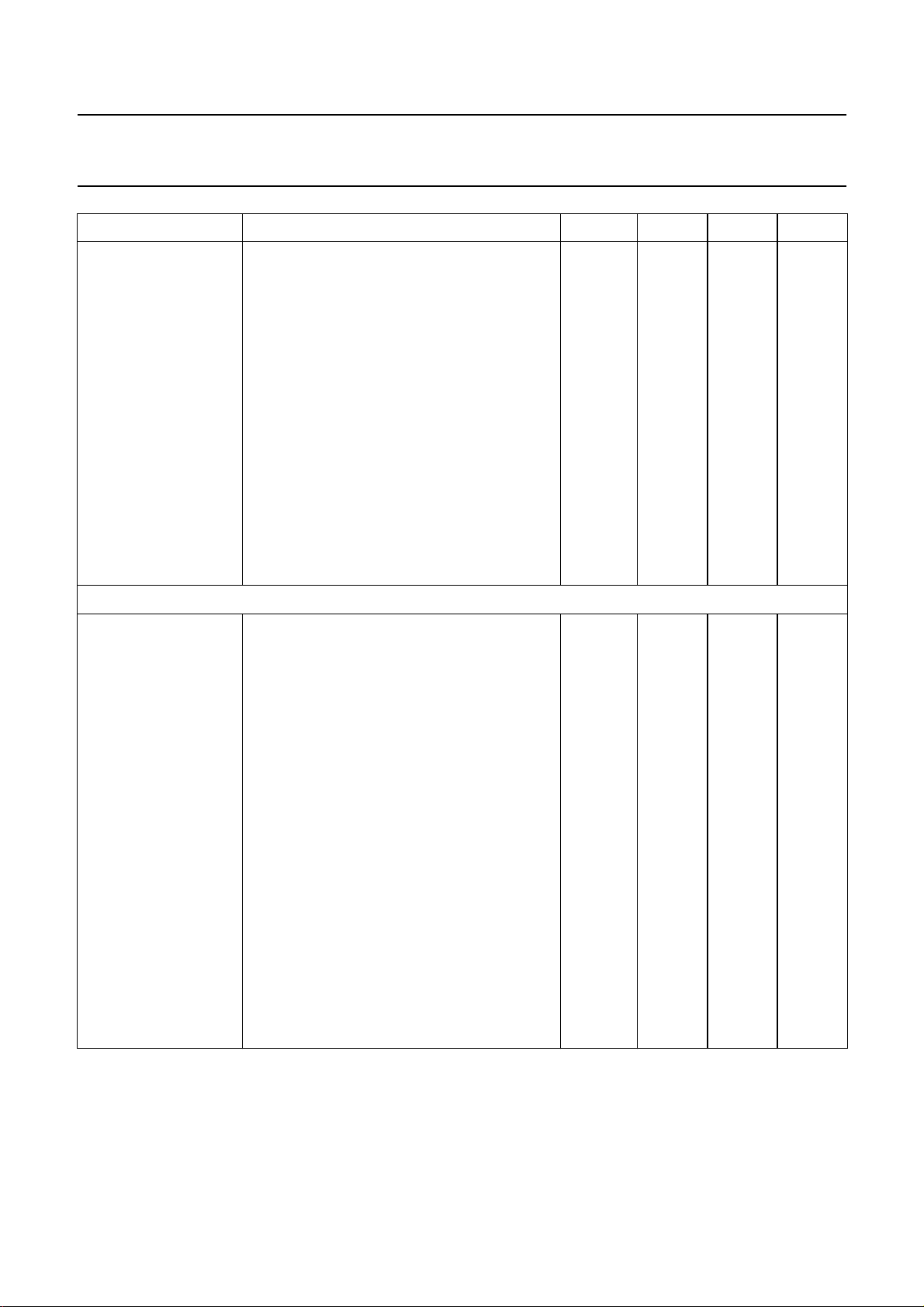
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
TEA6300
TEA6300T
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Signal plus noise-to-noise ratio
bass and treble linear; notes 1 and 2
CCIR 468-2 weighted; quasi peak
(S + N)/N V
(S + N)/N V
(S + N)/N V
(S + N)/N V
(S + N)/N V
(S + N)/N V
P
no
α
B
Source selector
Z
i
Z
o
R
L
C
L
α
S
G
v
V
b int/Vref
V
i(rms)
V
i(rms)
THD Vi= 500 mV; RL= 10 kΩ−−0,1 %
V
no
V
o
= 50 mV; Vo= 46 mV; Po= 50 mW − 65 − dB
i
= 500 mV; Vo= 45 mV; Po= 50 mW − 67 − dB
i
= 50 mV; Vo= 200 mV; Po= 1 W 65 70 − dB
i
= 500 mV; Vo= 200 mV; Po= 1 W 65 78 − dB
i
= 50 mV; Vo= 500 mV; Po= 6 W − 70 − dB
i
= 500 mV; Vo= 500 mV; Po= 6 W − 85 − dB
i
Noise output power
mute position, only contribution of
TEA6300; power amplifier for 25 W −−10 nW
Crosstalk (20 log V
bus(p-p)/Vo(rms)
)
between bus inputs and signal outputs
GV= 0 dB; bass and treble linear − 110 − dB
Input impedance 20 30 40 kΩ
Output impedance −−100 Ω
Output load resistance 10 −−kΩ
Output load capacity 0 − 200 pF
Input isolation
not selected source; frequency range
40 Hz to 12,5 kHz − 80 − dB
Voltage gain
RL≥ 10 kΩ−0−dB
Internal bias voltage ratio − 1 −
Maximum input voltage level (RMS value)
THD < 0,5% − 1,65 − V
THD < 0,5%; VCC= 7,5 V − 1,5 − V
Total harmonic distortion
Noise output voltage
weighted CCIR 468-2, quasi peak − 920µV
DC offset voltage
between any inputs −−10 mV
May 1990 7
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
TEA6300T
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Control part
Source selector disconnected,
source resistance 600 Ω
Z
i
Z
o
R
L
C
L
V
i(rms)
V
no
V
no
V
no
V
no
Volume control
G
c
∆G
a
∆G
a
∆G
t
α
m
DC step offset
Input impedance 35 50 65 kΩ
Output impedance − 100 150 Ω
Output load resistance 5 −−kΩ
Output load capacity 0 − 2500 pF
Maximum input voltage
THD < 0,5%; G
= −10 dB;
v
bass and treble linear − 2,0 − V
Noise output voltage
weighted acc CCIR 468-2, quasi-peak,
bass and treble linear, fader off
Gv= 20 dB − 110 220 µV
Gv= 0 dB − 25 50 µV
Gv= −66 dB − 19 38 µV
mute position − 11 22 µV
Continuous control range − 86 − dB
Step resolution − 2 − dB
Attenuator set error
(Gv= + 20 to −50 dB) −−2dB
Attenuator set error
(Gv= + 20 to −66 dB) −−3dB
Gain tracking error
balance in mid position,
bass and treble linear −−2dB
Mute attenuation 72 90 − dB
Between any adjoining step
and any step to mute
Gv= 0 to −66 dB − 0,2 10 mV
G
= 20 to 0 dB − 215mV
v
In any treble and fader position
G
= 0 to −66 dB −−10 mV
v
In any bass position
Gv= 0 to −66 dB −−20 mV
TEA6300
May 1990 8
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
TEA6300T
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Bass control
Bass control range
G
b
G
b
Treble control
G
t
G
t
G
t
Fader control
G
f
α
m
Digital part
f = 40 Hz; maximum boost 14 15 16 dB
f = 40 Hz; maximum attenuation 11 12 13 dB
Step resolution − 3 − dB
Step error −−0,5 dB
Treble control range
f = 15 kHz; maximum boost 11 12 13 dB
f = 15 kHz; maximum attenuation 11 12 13 dB
f > 15 kHz; maximum boost −−15 dB
Step resolution − 3 − dB
Step error −−0,5 dB
Continuous attenuation
fader control range − 30 − dB
Step resolution − 2 − dB
Attenuator set error −−1,5 dB
Mute attenuation 74 84 − dB
TEA6300
Bus terminals
Input voltage
V
IH
V
IL
HIGH 3 − 12 V
LOW −0,3 −+1,5 V
Input current
I
IH
I
IL
V
OL
AC characteristics
HIGH −10 −+10 µA
LOW −10 −+10 µA
Output voltage LOW; IL= 3 mA −−0,4 V
In accordance with the I2C-bus specification
Power-on-Reset
When RESET is active the GMU (general mute)
bit is set and the I2C-bus receiver is in RESET
position
Increasing supply voltage
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
start of reset −−2,5 V
end of reset 5,2 6,0 6,8 V
Decreasing supply voltage; start of reset 4,2 5,0 5,8 V
Notes to the characteristics
1. The indicated values for output power assume a 6 W power amplifier with 20 dB gain, connected to the output of the
May 1990 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
TEA6300
TEA6300T
circuit. Signal-to-noise ratios exclude noise contribution of the power amplifier.
2. Signal-to-noise ratios on a CCIR 468-2 average meter reading are 4,5 dB better than on CCIR 468-2 quasi peak.
2
C-BUS FORMAT
I
S SLAVE ADDRESS A SUBADDRESS A DATA A P
S = start condition SUBADDRESS = see Table 1
SLAVE ADDRESS = 1000 0000 DATA = see Table 1
A = acknowledge, generated by the slave P = STOP condition
If more than 1 byte of DATA is transmitted, then auto-increment of the subaddress is performed.
2
Table 1 I
FUNCTION SUBADDRESS
volume left 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 X X VL5 VL4 VL3 VL2 VL1 VL0
volume right 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 X X VR5 VR4 VR3 VR2 VR1 VR0
bass 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 X X X X BA3 BA2 BA1 BA0
treble 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 X X X X TR3 TR2 TR1 TR0
fader 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 X X MFN FCH FA3 FA2 FA1 FA0
switch 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 GMU XXXXSCCSCBSCA
C-bus; subaddress/data
DATA
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Function of the bits:
VL0 to VL5 volume control left
VR0 to VR5 volume control right
BA0 to BA3 bass control
TR0 to TR3 treble control
FA0 to FA3 fader control
FCH select fader channel (front or rear)
MFN mute control of the selected fader channel (front or rear)
SCA to SCC source selector control
GMU mute control (general mute)
for the outputs QLF, QLR, QRF and QRR
X don't care bits (logic 1 during testing)
May 1990 10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
Table 2 Bass setting
G
V
DB BA3 BA2 BA1 BA0
+15 1 1 1 1
+15 1 1 1 0
+15 1 1 0 1
+15 1 1 0 0
+12 1 0 1 1
+ 91010
+61001
+31000
00111
− 30110
− 60101
− 90100
−12 0 0 1 1
DATA
TEA6300
TEA6300T
Table 3 Treble setting
G
V
DB TR3 TR2 TR1 TR0
+12 1 1 1 1
+12 1 1 1 0
+12 1 1 0 1
+12 1 1 0 0
+12 1 0 1 1
+ 91010
+61001
+31000
00111
− 30110
− 60101
− 90100
−12 0 0 1 1
DATA
−12 0 0 1 0
−12 0 0 0 1
−12 0 0 0 0
−12 0 0 1 0
−12 0 0 0 1
−12 0 0 0 0
May 1990 11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
Table 4 Volume setting LEFT
G
V
DB VL5 VL4 VL3 VL2 VL1 VL0
20 111111
18 111110
16 111101
14 111100
12 111011
10 111010
8 111001
6 111000
4 110111
2 110110
0 110101
− 2 110100
− 4 110011
− 6 110010
−8 110001
−10 110000
−12 101111
−14 101110
−16 101101
−18 101100
−20 101011
−22 101010
−24 101001
−26 101000
−28 100111
DATA
TEA6300
TEA6300T
G
V
DB VL5 VL4 VL3 VL2 VL1 VL0
−30 100110
−32 100101
−34 100100
−36 100011
−38 100010
−40 100001
−42 100000
−44 011111
−46 011110
−48 011101
−50 011100
−52 011011
−54 011010
−56 011001
−58 011000
−60 010111
−62 010110
−64 010101
−66 010100
mute left 010011
mute left 010010
..
..
..
mute left 000000
DATA
May 1990 12
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
Table 5 Volume setting RIGHT
G
V
DB VR5 VR4 VR3 VR2 VR1 VR0
20 111111
18 111110
16 111101
14 111100
12 111011
10 111010
8 111001
6 111000
4 110111
2 110110
0 110101
− 2 110100
− 4 110011
− 6 110010
− 8 110001
−10 110000
−12 101111
−14 101110
−16 101101
−18 101100
−20 101011
−22 101010
−24 101001
−26 101000
−28 100111
DATA
TEA6300
TEA6300T
G
V
DB VR5 VR4 VR3 VR2 VR1 VR0
−30 100110
−32 100101
−34 100100
−36 100011
−38 100010
−40 100001
−42 100000
−44 011111
−46 011110
−48 011101
−50 011100
−52 011011
−54 011010
−56 011001
−58 011000
−60 010111
−62 010110
−64 010101
−66 010100
mute right 010011
mute right 010010
..
..
..
mute right 000000
DATA
May 1990 13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
Table 6 Fader function
SETTING DATA
FRONT REAR
DB DB MFN FCH FA3 FA2 FA1 FA0
fader off
0 0 1 11111
0 0 0 11111
fader front
− 2 0 1 11110
−4 0 1 11101
−6 0 1 11100
−8 0 1 11011
−10 0 1 11010
−12 0 1 11001
−14 0 1 11000
−16 0 1 10111
−18 0 1 10110
−20 0 1 10101
−22 0 1 10100
−24 0 1 10011
−26 0 1 10010
−28 0 1 10001
−30 0 1 10000
mute front
−80 0 0 11110
.. .
.. .
.. .
−80 0 0 10000
TEA6300
TEA6300T
SETTING DATA
FRONT REAR
DB DB MFN FCH FA3 FA2 FA1 FA0
fader off
0 01 01111
0 00 01111
fader rear
0 − 21 01110
0 − 41 01101
0 − 61 01100
0 − 81 01011
0 −101 01010
0 −121 01001
0 −141 01000
0 −161 00111
0 −181 00110
0 −201 00101
0 −221 00100
0 −241 00011
0 −261 00010
0 −281 00001
0 −301 00000
mute rear
0 −800 01110
.. .
.. .
.. .
0−800 00000
Table 7 Selected inputs
DATA
SELECTED INPUTS
SCC SCB SCA
data not allowed 1 1 1
data not allowed 1 1 0
data not allowed 1 0 1
INLC, INRC 1 0 0
data not allowed 0 1 1
INLB, INRB 0 1 0
INLA, INRA 0 0 1
data not allowed 0 0 0
May 1990 14
Table 8 Mute control
MUTE DATA
REMARKS
CONTROL GMU
active 1 outputs QLF, QLR
QRF and QRR are
muted
passive 0 no general mute
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
Fig.3 Bass control without T-pass filter.
TEA6300
TEA6300T
Fig.4 Bass control with T-pass filter.
Pin numbers in parentheses refer to the bass control, right channel.
Fig.5 T-pass filter.
May 1990 15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
TEA6300
TEA6300T
Fig.6 Treble control.
Fig.7 Output noise voltage (CCIR 468-2 weighted: quasi peak).
May 1990 16
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
TEA6300
TEA6300T
Fig.8 Signal-to-noise ratio (CCIT 468-2 weighted; quasi peak) with a 6 W power amplifier (gain 20 dB) without
noise contribution of the power amplifier (see Fig.9).
Fig.9 Recommended level diagram; V
May 1990 17
= 50 mV, Vo = 500 mV for P
i min
max
.
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
APPLICATION INFORMATION
TEA6300
TEA6300T
Fig.10 Test and application circuit.
May 1990 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
PACKAGE OUTLINES
handbook, full pagewidth
DIP28: plastic dual in-line package; 28 leads (600 mil)
D
seating plane
L
Z
28
e
b
TEA6300
TEA6300T
SOT117-1
M
E
A
2
A
A
1
w M
b
1
15
c
(e )
1
M
H
pin 1 index
1
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
A
A
A
UNIT
inches
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
max.
mm
1 2
min.
max.
b
1.7
1.3
0.066
0.051
b
0.53
0.38
0.020
0.014
cD E weM
1
0.32
0.23
0.013
0.009
(1) (1)
36.0
35.0
1.41
1.34
14.1
13.7
0.56
0.54
E
14
(1)
L
3.9
3.4
M
15.80
15.24
0.62
0.60
H
E
17.15
15.90
0.68
0.63
0.252.54 15.24
0.010.10 0.60
e
1
0.15
0.13
Z
max.
1.75.1 0.51 4.0
0.0670.20 0.020 0.16
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT117-1
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
051G05 MO-015AH
REFERENCES
May 1990 19
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
92-11-17
95-01-14
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
SO28: plastic small outline package; 28 leads; body width 7.5 mm
D
c
y
Z
28
15
TEA6300
TEA6300T
SOT136-1
E
H
E
A
X
v M
A
pin 1 index
1
e
0 5 10 mm
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
mm
A
max.
2.65
0.10
A
1
0.30
0.10
0.012
0.004
A2A
2.45
2.25
0.096
0.089
0.25
0.01
b
3
p
0.49
0.32
0.36
0.23
0.019
0.013
0.014
0.009
UNIT
inches
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.15 mm maximum per side are not included.
(1)E(1) (1)
cD
18.1
7.6
17.7
7.4
0.71
0.30
0.69
0.29
14
w M
b
p
scale
eHELLpQ
1.27
0.050
10.65
10.00
0.419
0.394
1.4
0.055
A
2
0.043
0.016
A
1.1
0.4
Q
A
3
θ
ywv θ
Z
0.9
0.4
0.035
0.004
0.016
o
8
o
0
L
p
L
0.25 0.1
0.01
(A )
1
detail X
1.1
0.25
1.0
0.043
0.01
0.039
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT136-1
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
075E06 MS-013AE
REFERENCES
May 1990 20
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
95-01-24
97-05-22
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
SOLDERING
Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
situations reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“IC Package Databook”
DIP
SOLDERING BY DIPPING OR BY WAVE
The maximum permissible temperature of the solder is
260 °C; solder at this temperature must not be in contact
with the joint for more than 5 seconds. The total contact
time of successive solder waves must not exceed
5 seconds.
The device may be mounted up to the seating plane, but
the temperature of the plastic body must not exceed the
specified maximum storage temperature (T
printed-circuit board has been pre-heated, forced cooling
may be necessary immediately after soldering to keep the
temperature within the permissible limit.
R
EPAIRING SOLDERED JOINTS
Apply a low voltage soldering iron (less than 24 V) to the
lead(s) of the package, below the seating plane or not
more than 2 mm above it. If the temperature of the
soldering iron bit is less than 300 °C it may remain in
contact for up to 10 seconds. If the bit temperature is
between 300 and 400 °C, contact may be up to 5 seconds.
SO
REFLOW SOLDERING
Reflow soldering techniques are suitable for all SO
packages.
(order code 9398 652 90011).
). If the
stg max
TEA6300
TEA6300T
Several techniques exist for reflowing; for example,
thermal conduction by heated belt. Dwell times vary
between 50 and 300 seconds depending on heating
method. Typical reflow temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C.
Preheating is necessary to dry the paste and evaporate
the binding agent. Preheating duration: 45 minutes at
45 °C.
AVE SOLDERING
W
Wave soldering techniques can be used for all SO
packages if the following conditions are observed:
• A double-wave (a turbulent wave with high upward
pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave) soldering
technique should be used.
• The longitudinal axis of the package footprint must be
parallel to the solder flow.
• The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves at
the downstream end.
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Maximum permissible solder temperature is 260 °C, and
maximum duration of package immersion in solder is
10 seconds, if cooled to less than 150 °C within
6 seconds. Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
R
EPAIRING SOLDERED JOINTS
Fix the component by first soldering two diagonallyopposite end leads. Use only a low voltage soldering iron
(less than 24 V) applied to the flat part of the lead. Contact
time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to 300 °C. When
using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be soldered in
one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
May 1990 21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Sound fader control circuit
TEA6300
TEA6300T
DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
May 1990 22
 Loading...
Loading...