Page 1

查询TEA1506供应商
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
Product specification 2003 Sep 09
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
FEATURES
Distinctive features
• Universal mains supply operation (70 to 276 V AC)
• High level of integration; giving a low external
component count.
Green features
• Valley or zero voltage switching for minimum switching
losses
• Efficient quasi-resonant operation at high power levels
• Frequency reductionat low power standby for improved
system efficiency (≤3W)
• Cycle skipping mode at very low loads.
Protection features
• Safe restart mode for system fault conditions
• Continuous mode protection by means of
demagnetization detection (zero switch-on current)
• Accurateand adjustable overvoltage protection(latched
in TEA1506; safe restart in TEA1506A)
• Short winding protection
• Undervoltage protection (foldback during overload)
• Overtemperature protection
• Low and adjustable overcurrent protection trip level
• Soft (re)start.
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
APPLICATIONS
Besides typical application areas, i.e. TV and monitor
supplies, the devicecan be usedin adapters andchargers
and all applications that demand an efficient and
cost-effective solution up to 150 W. Unlike the other
GreenChipII control ICs, the TEA1506 has no internal
high voltage start-up source and needs to be started by
means of an external bleeder resistor.
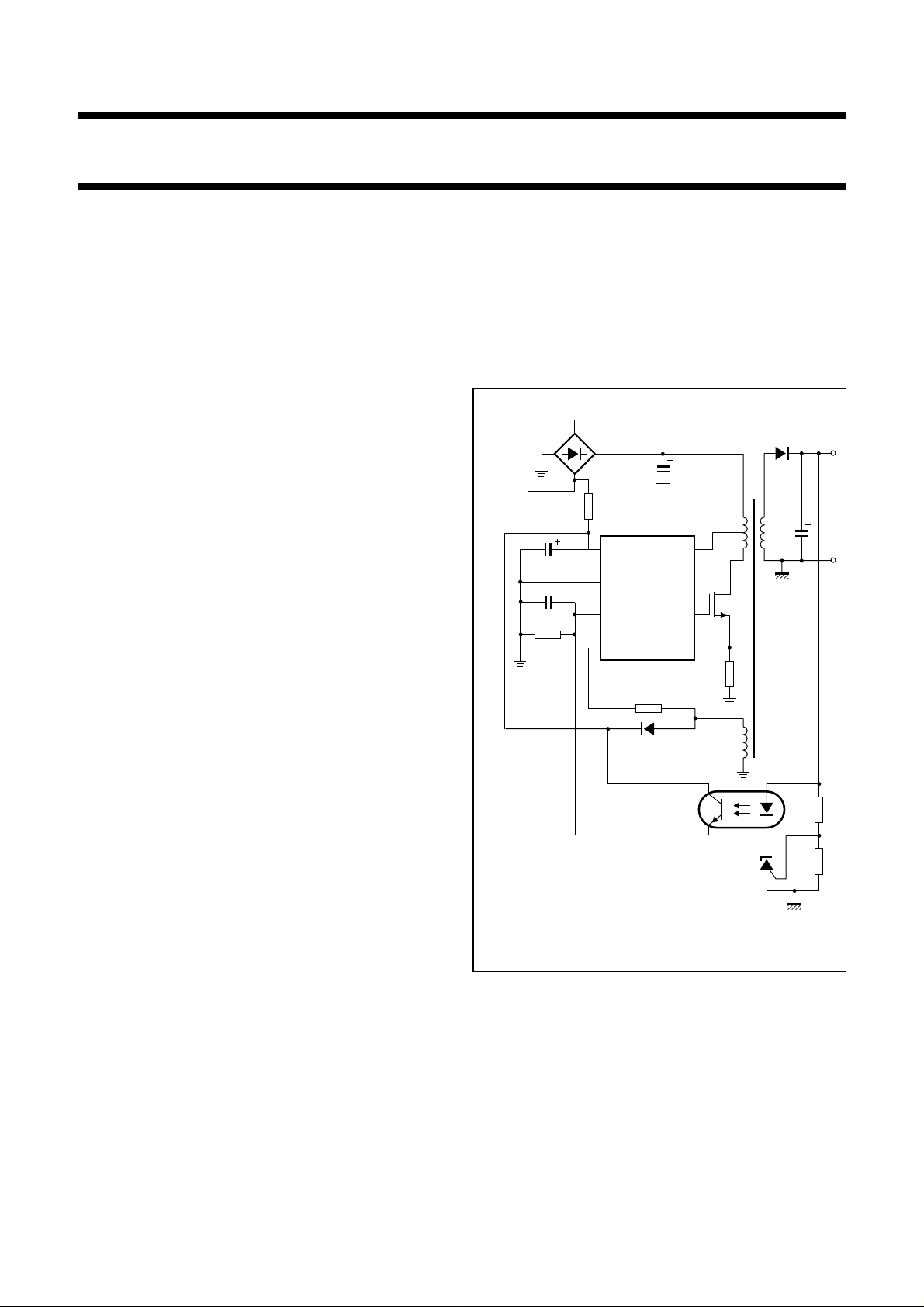
1
2
TEA1506P
TEA1506AP
3
4
8
7
6
5
2003 Sep 09 2
MDB504
Fig.1 Basic application diagram.
Page 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The GreenChip
Switched Mode Power Supply (SMPS) control ICs. A high
level of integration leads to a cost effective power supply
with a low number of external components.
(1) GreenChip is a trademark of Koninklijke Philips
Electronics N.V.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE NUMBER
TEA1506P DIP8 plastic dual in-line package; 8 leads (300 mil) SOT97-1
TEA1506AP
TEA1506T SO14 plastic small outline package; 14 leads; body width 3.9 mm SOT108-1
TEA1506AT
(1)
II is the second generation of green
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
The special built-in green functions allow the efficiency to
be optimum at all power levels. This holds for
quasi-resonant operation at high power levels, as well as
fixed frequency operation with valley switching at medium
power levels. At low power (standby) levels, the system
operates at a reduced frequency and with valley detection.
Highly efficient and reliable supplies can easily be
designed using the GreenChipII control IC.
PACKAGE
2003 Sep 09 3
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
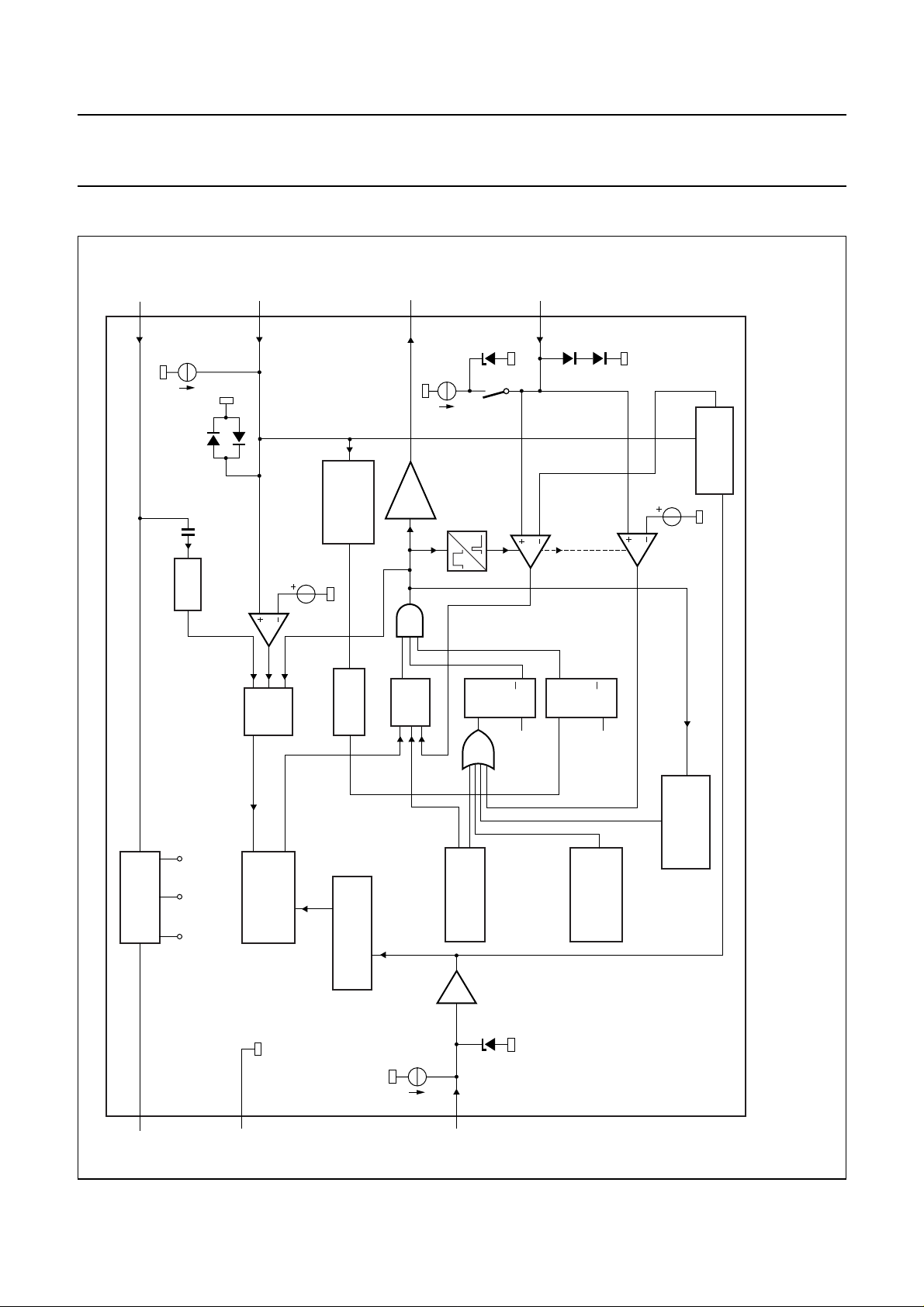
BLOCK DIAGRAM
4
DEM
(7)
OVER-
VOLTAGE
DRAIN
8
(14)
prot(DEM)
I
clamp
DRIVER
6
(11)
DRIVER
PROTECTION
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
sense
I
5
(9)
0.5 V
ss
I
S2
soft
start
OVERPOWER
0.88 V
LEB
blank
OCP
short
winding
MDB505
PROTECTION
, full pagewidth
SUPPLY
MANAGEMENT
VALLEY
UVLO start
supply
internal
100
LOGIC
VOLTAGE
OSCILLATOR
CONTROLLED
mV
UP/DOWN
COUNTER
CONTROL
FREQUENCY
LOGIC
SQ
RESET
POWER-ON
−1
3.8 V
Q
R
UVLO
SQ
< 4.5 V
CC
V
OVER-
TEMPERATURE
Q
R
or UVLO
(TEA1506AT)
PROTECTION
ON-TIME
MAXIMUM
PROTECTION
Fig.2 Block diagram.
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2003 Sep 09 4
prot(CTRL)
I
3
1
(2)
CC
V
2
(3)
GND
(6)
CTRL
TEA1506P;
(TEA1506T;
TEA1506AP
TEA1506 AT)
Pin numbers in parenthesis represent the SO version.
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
PINNING
SYMBOL
V
CC
GND 2 3 ground
CTRL 3 6 control input
DEM 4 7 input from auxiliary winding for demagnetization timing; overvoltage and
I
sense
DRIVER 6 11 gate driver output
HVS 7 12, 13 high voltage safety spacer; not connected
DRAIN 8 14 drain of external MOS switch; input for valley sensing and initial internal
n.c. − 1, 4, 5, 8,10not connected
PIN
DESCRIPTION
DIP8 SO14
1 2 supply voltage
overpower protection
5 9 programmable current sense input
supply
handbook, halfpage
V
CC
GND
CTRL
DEM
1
2
TEA1506P
TEA1506AP
3
4
MDB506
8
7
6
5
DRAIN
HVS
DRIVER
I
sense
Fig.3 Pin configuration DIP8.
handbook, halfpage
n.c.
V
CC
GND
n.c.
n.c.
CTRL
DEM
1
2
3
4
TEA1506AT
5
6
7
TEA1506T
MDB507
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
DRAIN
HVS
HVS
DRIVER
n.c.
I
sense
n.c.
Fig.4 Pin configuration SO14.
2003 Sep 09 5
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The TEA1506 is the controller of a compact flyback
converter, and is situated at the primary side. An auxiliary
winding of the transformer provides demagnetization
detection and powers the IC after start-up.
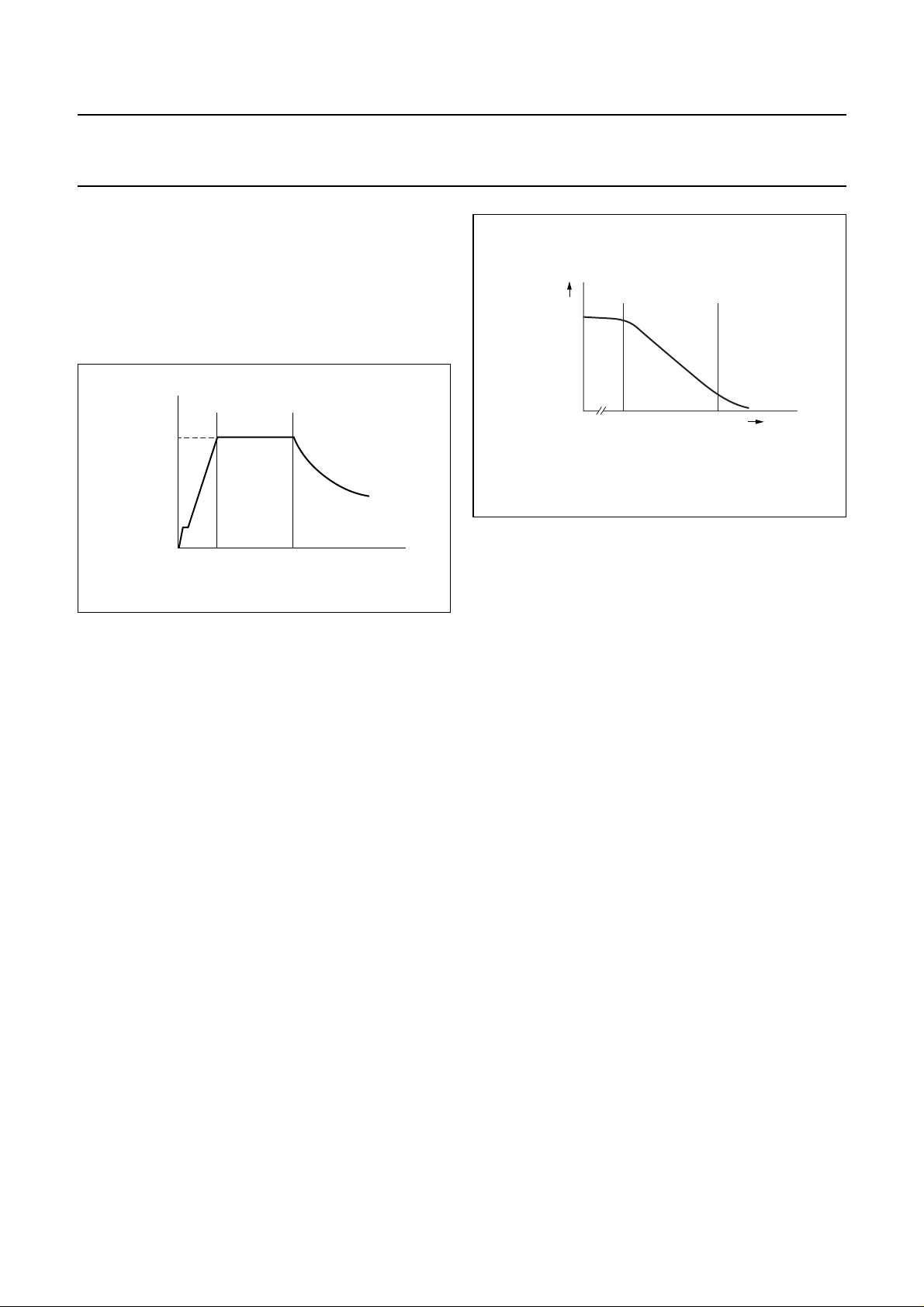
The TEA1506 can operate in multi modes (see Fig.5).
handbook, halfpage
(kHz)
f
VCO fixed quasi resonant
175
25
Fig.5 Multi modes operation.
MGU508
P (W)
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
V
handbook, halfpage
sense(max)
0.52 V
Fig.6 V
sense(max)
1 V
(typ)
1.5 V
(typ)
voltage as function of V
The moment the voltage on pin VCC drops below the
undervoltage lock-out level, the IC stops switching and
re-enters the safe restart mode.
Supply management
MGU233
V
CTRL
CTRL
.
The next converter stroke is started only after
demagnetization of the transformer current (zero current
switching), while the drain voltage has reached the lowest
voltage to prevent switching losses (green function). The
primary resonant circuit of the primary inductance and
draincapacitorensuresthis quasi-resonant operation. The
design can be optimized in such a way that zero voltage
switching can be reached over almostthe universal mains
range.
To prevent very high frequency operation at lower loads,
the quasi-resonant operation changes smoothly in fixed
frequency PWM control.
At very low power (standby) levels, the frequency is
controlled down, via the VCO, to a minimum frequency of
approximately 25 kHz.
Start-up and undervoltage lock-out
Initially the IC is in the save restart mode. As long as V
is below the V
level, the supply current is nearly
CC(start)
CC
zero.
TheIC will activate theconverteras soon as the voltageon
pin VCC passes the V
CC(start)
level.
The IC supply is taken over by the auxiliary winding as
soon as the output voltage reaches its intended level.
All (internal) reference voltages are derived from a
temperature compensated, on-chip band gap circuit.
Current mode control
Current mode control is used for its good line regulation
behaviour.
The ‘on-time’ iscontrolled by theinternally inverted control
voltage, which is compared with the primary current
information. The primary current is sensed across an
external resistor. The driver output is latched in the logic,
preventing multiple switch-on.
The internal control voltage is inverselyproportional to the
external control pin voltage, with an offset of 1.5 V. This
means that a voltage range from 1 to 1.5 V on pin CTRL
will result in an internal control voltage range from
0.5 to 0 V (a high external control voltage results in a low
duty cycle).
Oscillator
The maximum fixed frequency of the oscillator isset by an
internal current source and capacitor. The maximum
frequency is reduced once the control voltage enters the
VCO control window. Then, the maximum frequency
changeslinearly with thecontrol voltage untilthe minimum
frequency is reached (see Figs 6 and 7).
2003 Sep 09 6
Page 7

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
handbook, halfpage
f
(kHz)
175
25
VCO
VCO
2
level
level
Fig.7 VCO frequency as function of V
handbook, full pagewidth
1
MGU509
175 kHz
V
sense(max) (V)
sense(max)
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
Cycle skipping
At very low power levels, a cycle skipping mode will be
activated. A high control voltage will reduce the switching
frequency to a minimum of 25 kHz. If the voltage on the
control pin is raised even more, switch-on of the external
power MOSFET will be inhibited until the voltage on the
control pin has dropped to a lower value again (see Fig.8).
For system accuracy, it is not the absolute voltage on the
control pin that will trigger the cycle skipping mode, but a
signal derived from the internal VCO will be used.
Remark: If the no-load requirement of the system is such
.
that the output voltage can be regulated to its intended
level at a switching frequency of 25 kHz or above, the
cycle skipping mode will not be activated.
f
osc
1.5 V − V
CTRL
CTRL
X2
V
x
150 mV
The voltage levels dV1 and dV2 are fixed in the IC to 50 mV (typical) and 18 mV (typical) respectively.
current
comparator
V
I
DRIVER
OSCILLATOR
DRIVER
I
sense
f
max
f
min
cycle
skipping
1
0
Fig.8 The cycle skipping circuitry.
dV
2
dV
1
150
Vx (mV)
MGU510
Vx (mV)
2003 Sep 09 7
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
Demagnetization
The system will be in discontinuous conduction mode all
the time. The oscillator will not start a new primary stroke
until the secondary stroke has ended.
Demagnetization features a cycle-by-cycle output
short-circuit protection by immediately lowering the
frequency (longer off-time), thereby reducing the power
level.
Demagnetizationrecognition is suppressedduringthe first
t
time. This suppression may be necessary in
suppr
applications where the transformer has a large leakage
inductance, at low output voltages and at start-up.
If pin DEM is open-circuit or not connected, a fault
condition is assumed and the converter will stop operating
immediately. Operation will recommence as soon as the
fault condition is removed.
Minimum and maximum ‘on-time’
The minimum ‘on-time’ of the SMPS is determined by the
Leading Edge Blanking (LEB) time. The IC limits the
‘on-time’ to 50 µs. When the system desires an ‘on-time’
longer than 50 µs, a fault condition is assumed (e.g.
removed Ciin Fig.12), the IC will stop switching and enter
the safe restart mode.
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
Regarding the TEA1506, the IC will not start switching
again. Subsequently, VCC will drop again to the UVLO
level, etc.
Operation only recommenceswhen the VCCvoltage drops
below a level of about 4.5 V.
Regardingthe TEA1506A, when theV
switching starts again (safe restart mode) when the V
level is reached. This process is repeated as long as the
OVP condition exists.
Theoutput voltage V
atwhich the OVPfunctiontrips,
o(OVP)
can be set by the demagnetization resistor, R
V
N
----------N
=
o OVP()
s
I
(OVP)(DEM)RDEM
aux
× V
+{}
clamp(DEM)(pos)
where Nsis the number of secondary turnsand N
number of auxiliary turns of the transformer.
Current I
(OVP)(DEM)
The value of R
is internally trimmed.
can be adjusted to the turns ratio of the
DEM
transformer, thus making an accurate OVP possible.
levelis reached,
start
DEM
:
aux
start
is the
OverVoltage Protection (OVP)
An OVP mode is implemented in the GreenChip series.
This works for the TEA1506 by sensing the auxiliary
voltage via the current flowing into pin DEM during the
secondary stroke. The auxiliary winding voltage is a
well-defined replica of the output voltage. Any voltage
spikes are averaged by an internal filter.
Ifthe output voltage exceedstheOVP trip level, aninternal
counter starts counting subsequent OVP events. The
counter has been added to prevent incorrect OVP
detections which might occur during ESD or lightning
events. If the output voltage exceeds the OVP trip level a
fewtimes and notagain in asubsequent cycle, theinternal
counter will count down with twice the speed compared
with counting-up. However, when typical 10 cycles of
subsequent OVP events are detected, the IC assumes a
true OVP and the OVP circuit switches the power
MOSFET off. Next, the controller waits until the UVLO
level is reached on pin VCC. When VCC drops to UVLO,
capacitor C
will be recharged to the V
VCC
start
level.
2003 Sep 09 8
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
Valley switching
A new cycle starts when the power MOSFET is switched
on (see Fig.9). After the ‘on-time’ (which is determined by
the ‘sense’ voltage and the internal control voltage), the
switchis opened andthesecondary stroke starts.Afterthe
secondary stroke, the drain voltage shows an oscillation
primary
stroke
1
pCd
×()×
secondary
stroke
with a frequency of approximately
----------------------------------------------2 π× L
where L
is the primary self inductance of the transformer
p
and Cd is the capacitance on the drain node.
As soon as the oscillator voltage is high again and the
secondary stroke has ended, the circuit waits for the
handbook, full pagewidth
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
lowest drain voltage before starting a new primary stroke.
This method is called valley detection.
Figure 9 shows the drain voltage together with the valley
signal, the signal indicating the secondary stroke and the
oscillator signal.
In an optimum design, the reflected secondary voltage on
the primary side will force the drain voltage to zero. Thus,
zero voltage switching is very possible, preventing large
1
P
capacitive switching losses
-- -
2
and allowing high frequency operation, which results in
small and cost effective inductors.
secondary
ringing
2
CV
× f××=
drain
valley
secondary
stroke
oscillator
BA
MGU235
A: Start of new cycle at lowest drain voltage.
B: Start of new cycle in a classical PWM system at high drain voltage.
Fig.9 Signals for valley switching.
2003 Sep 09 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
MGU236
handbook, halfpage
−100 µA
(typ)
I
DEM
−24 µA
(typ)
Fig.10 OPP correction curve.
OverCurrent Protection (OCP)
The cycle-by-cycle peak drain current limit circuit uses the
externalsource resistor to measurethecurrent accurately.
This allows optimum size determination of the transformer
core (cost issue). The circuit is activated after the leading
edge blanking time, t
. The OCP circuit limits the ‘sense’
leb
voltage to an internal level.
V
sense(max)
0.52 V
(typ)
0.3 V
(typ)
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
Short winding protection
After the leading edge blanking time, the short winding
protection circuit is activated. If the ‘sense’ voltage
exceeds the short winding protection voltage V
converter will stop switching. Once VCC drops below the
UVLO level, capacitor C
will be recharged and the
VCC
supply will restart again. This cycle will be repeated until
the short-circuit is removed (safe restart mode).
The short winding protection will also protect in case of a
secondary diode short-circuit.
OverTemperature Protection (OTP)
An accurate temperature protection is provided in the
circuit. When the junction temperature exceeds the
thermal shutdown temperature, the IC will enter the safe
restart mode.
When the V
level is reached, switching starts again.
start
This process is repeated as long as the OTP condition
exists.
swp
, the
OverPower Protection (OPP)
Duringthe primary stroke,the rectified mainsinput voltage
is measured by sensing the current drawn from pin DEM.
This current is dependent on the mains voltage, according
to the following formula:
N
where:
N
=
-----------N
aux
p
I
V
≈≈
-------------- -
DEM
R
DEM
aux
×
NV
mains
-------------------------R
DEM
The current information is used to adjust the peak drain
current, which is measured via pin I
. The internal
sense
compensation is such that an almost mains independent
maximum output power can be realized.
The OPP curve is given in Fig.10.
2003 Sep 09 10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
Control pin protection
If pin CTRL is open-circuit or not connected, a fault
conditionis assumed and theconverter will stop switching.
Operation will recommence as soon as the fault condition
is removed.
Soft start-up
To prevent transformer rattle during hiccup, the
transformer peak current is slowly increased by the soft
start function. This can be achieved by inserting a resistor
and a capacitor between pin I
(see Fig.11). An internal current source charges the
capacitor to V = ISS× RSS, with a maximum of
approximately 0.5 V.
The start level and the time constant of the increasing
primary current level can be adjusted externally by
changing the values of RSS and CSS.
V
I
primary(max)
τ R
SSCSS
ocpISSRSS
=
---------------------------------------------- -
×=
The charging currentI
pin I
pin I
is below approximately 0.5 V. If the voltage on
sense
exceeds 0.5 V, the soft start current source will
sense
×()–
R
sense
will flow aslong as the voltage on
SS
start limiting the current ISS. At the V
current source is completely switched off.
Since the soft start current ISSis supplied from pin DRAIN,
the RSSvalue will not affect the VCCcurrent during start-up.
and the sense resistor
sense
level, the I
CC(start)
SS
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
handbook, halfpage
I
SS
0.5 V
Driver
The driver circuit to the gate of the power MOSFET has a
current sourcing capabilityof 135 mA typical and a current
sink capability of 560 mA typical. This permits fast turn-on
and turn-off of the power MOSFET for efficient operation.
A low driver source current has been chosen to limit the
∆V/∆t at switch-on. This reduces Electro Magnetic
Interference (EMI) and also limits the current spikes
across R
sense
.
start-up
R
I
sense
5
V
ocp
C
Fig.11 Soft start.
SS
SS
R
sense
MGU237
2003 Sep 09 11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134); note 1.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
Voltages
V
CC
V
CTRL
V
DEM
V
sense
V
DRAIN
Currents
I
CTRL
I
DEM
I
sense
I
DRIVER
I
DRAIN
General
P
tot
T
stg
T
j
V
esd
supply voltage continuous −0.4 +20 V
voltage on pin CTRL −0.4 +5 V
voltage on pin DEM current limited −0.4 − V
voltage on pin I
sense
current limited −0.4 − V
voltage on pin DRAIN −0.4 +650 V
current on pin CTRL − 5mA
current on pin DEM −250 +250 µA
current on pin I
sense
−1 +10 mA
current on pin DRIVER d < 10 % −0.8 +2 A
current on pin DRAIN − 5mA
total power dissipation T
<70°C − 0.75 W
amb
storage temperature −55 +150 °C
operating junction temperature −20 +145 °C
electrostatic discharge voltage
all pins except pins DRAIN and V
pins DRAIN and V
CC
HBM class 1; note 2 − 2000 V
CC
HBM class 1; note 2 − 1500 V
any pin MM; note 3 − 400 V
Notes
1. All voltages are measured with respect to ground; positive currents flow into the IC; pin VCC may not be current
driven. The voltage ratings are valid provided other ratings are not violated; current ratings are valid provided the
maximum power rating is not violated.
2. Human Body Model (HBM): equivalent to discharging a 100 pF capacitor through a 1.5 kΩ resistor.
3. Machine Model (MM): equivalent to discharging a 200 pF capacitor through a 0.75 µH coil and a 10 Ω resistor.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th(j-a)
thermal resistance from junction to
in free air 100 K/W
ambient
QUALITY SPECIFICATION
In accordance with
‘SNW-FQ-611-D’
.
2003 Sep 09 12
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
CHARACTERISTICS
T
=25°C; VCC= 15 V; all voltages are measured with respect to ground; currents are positive when flowing into
amb
the IC; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Start-up current source (pin DRAIN)
I
DRAIN
BV
DSS
Supply voltage management (pin VCC)
V
CC(start)
V
CC(UVLO)
V
CC(hys)
I
CC(oper)
I
CC(start)
I
CC(protection)
Demagnetization management (pin DEM)
V
th(DEM)
I
prot(DEM)
V
clamp(DEM)(neg)
V
clamp(DEM)(pos)
t
suppr
Pulse width modulator
t
on(min)
t
on(max)
Oscillator
f
osc(l)
f
osc(h)
V
vco(start)
V
vco(nom)
Duty cycle control (pin CTRL)
V
CTRL(min)
V
CTRL(max)
I
prot(CTRL)
supply current drawn from
pin DRAIN
VCC< V
V
CC>Vstart
start
− 500 −µA
− 50 −µA
breakdown voltage 650 −−V
start-up voltage on V
CC
undervoltage lock-out on V
hysteresis voltage on V
CC
supply current under normal
CC
V
CC(start)
− V
CC(UVLO)
no load on pin DRIVER 1.1 1.3 1.5 mA
10.3 11 11.7 V
8.1 8.7 9.3 V
2.0 2.3 2.6 V
operation
supply current in start-up and safe
VCC<V
start
(1)
0
− 70 µA
restart mode
supply current while not switching VCC>V
demagnetization comparator
UVLO
− 0.85 − mA
50 100 150 mV
threshold voltage on pin DEM
protection current on pin DEM V
negative clamp voltage on pin DEM I
positive clamp voltage on pin DEM I
suppression of transformer ringing
=50mV −50
DEM
= −150 µA −0.5 −0.25 −0.05 V
DEM
= 250 µA 0.5 0.7 0.9 V
DEM
(2)
−−10 nA
1.1 1.5 1.9 µs
at start of secondary stroke
minimum on-time − t
leb
− ns
maximum on-time latched 40 50 60 µs
oscillator low fixed frequency V
oscillator high fixed frequency V
peak voltage on pin I
sense
; where
> 1.5 V 20 25 30 kHz
CTRL
< 1 V 145 175 205 kHz
CTRL
see Figs 7 and 8 − VCO
1
− mV
frequency reduction starts
peak voltage on pin I
the frequency is equal to f
minimum voltage on pin CTRL for
sense
; where
osc(l)
− VCO1− 50 − mV
− 1.0 − V
maximum duty cycle
maximum voltage on pin CTRL for
− 1.5 − V
minimum duty cycle
protection current on pin CTRL V
= 1.5 V −1
CTRL
(2)
−0.8 −0.5 µA
2003 Sep 09 13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Valley switch (pin DRAIN)
∆V/∆t
valley
t
valley-swon
Overcurrent and short winding protection (pin I
V
sense(max)
t
PD
V
swp
t
leb
I
SS
Overvoltage protection (pin DEM)
I
OVP(DEM)
Overpower protection (pin DEM)
I
OPP(DEM)
I
OPP50%(DEM)
Driver (pin DRIVER)
I
source
I
sink
V
o(max)
Overtemperature protection
T
prot(max)
T
prot(hys)
valley recognition voltage change −85 −+85 V/µs
delay from valley recognition to
− 150
(2)
− ns
switch-on
)
sense
maximum source voltage OCP ∆V/∆t = 0.1 V/µs 0.48 0.52 0.56 V
propagating delay from detecting
V
sense(max)
to switch-off
∆V/∆t = 0.5 V/µs − 140 185 ns
short winding protection voltage 0.83 0.88 0.96 V
blanking time for current and short
300 370 440 ns
winding protection
soft start current V
OVP level on pin DEM set by resistor R
< 0.5 V 45 60 75 µA
sense
;
DEM
54 60 66 µA
see Section
“OverVoltage
Protection (OVP)”
OPP current on pin DEM to start
OPP correction
set by resistor R
see Section
DEM
;
−−24 −µA
“OverPower
Protection (OPP)”
OPP current on pin DEM; where
−−100 −µA
maximum source voltage is limited
to 0.3 V
source current capability of driver VCC= 9.5 V;
V
DRIVER
=2V
sink current capability of driver VCC= 9.5 V;
maximum output voltage of the
V
V
V
VCC> 12 V − 11.5 12 V
DRIVER
= 9.5 V;
CC
DRIVER
=2V
= 9.5 V
−−135 − mA
− 240 − mA
− 560 − mA
driver
maximum temperature protection
130 140 150 °C
level
hysteresis for the temperature
− 8
(2)
−°C
protection level
Notes
1. For VCC≥ 2V.
2. Guaranteed by design.
2003 Sep 09 14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
APPLICATION INFORMATION
A converterwith the TEA1506consists of aninput filter, atransformer with athird winding (auxiliary), and an output stage
with a feedback circuit.
Capacitor C
via the auxiliary winding during operation.
A sense resistor converts the primary current into a voltage at pin I
maximum primary peak current.
handbook, full pagewidth
(at pin VCC) buffers the supply voltage of the IC, which is powered via the resistor RSduring start-up and
VCC
. The value of this sense resistor defines the
sense
V
mains
i
C
i
D
o
V
oV
C
C
R
VCC
CTRL
CTRL
R
S
V
CC
GND
CTRL
DEM
1
2
TEA1506P
TEA1506AP
3
4
R
DEM
DRAIN
8
HVS
7
DRIVER
6
I
5
sense
n.c.
N
N
p
power
MOSFET
R
SS
C
SS
R
N
sense
aux
D
micro
C
s
C
o
V
µC
micro
MICRO-
CONTROLLER
R
reg1
R
reg2
MDB508
Fig.12 Flyback configuration with secondary sensing.
2003 Sep 09 15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
handbook, full pagewidth
V
i
V
D
(power
MOSFET)
V
i
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
V
V
gate
V
V
CC
µC
o
start-up
sequence
normal
operation
overvoltage
protection
(TEA1506AP/TEA1506AT)
output
short-circuit
normal
operation
MDB509
Fig.13 Typical waveforms.
2003 Sep 09 16
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
PACKAGE OUTLINES
DIP8: plastic dual in-line package; 8 leads (300 mil)
D
seating plane
A
L
Z
e
b
8
1
w M
b
1
b
2
5
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
SOT97-1
M
E
A
2
A
c
(e )
1
M
H
pin 1 index
E
1
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
A
A
A
UNIT
max.
mm
inches
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm (0.01 inch) maximum per side are not included.
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT97-1
12
min.
max.
050G01 MO-001 SC-504-8
b
1.73
1.14
0.068
0.021
0.045
0.015
IEC JEDEC JEITA
b
1
0.53
0.38
4
0 5 10 mm
scale
b
2
0.36
1.07
0.23
0.89
0.014
0.042
0.009
0.035
REFERENCES
(1) (1)
cD E e M
9.8
6.48
9.2
6.20
0.39
0.26
0.36
0.24
L
e
1
M
3.60
8.25
3.05
7.80
0.14
0.32
0.12
0.31
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
E
10.0
0.39
0.33
H
8.3
w
max.
0.2542.54 7.62
ISSUE DATE
0.010.1 0.3
99-12-27
03-02-13
1.154.2 0.51 3.2
0.0450.17 0.02 0.13
(1)
Z
2003 Sep 09 17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
SO14: plastic small outline package; 14 leads; body width 3.9 mm
D
c
y
Z
14
8
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
SOT108-1
E
H
E
A
X
v M
A
A
2
pin 1 index
4.0
3.8
0.16
0.15
7
w M
b
p
scale
eHELLpQZywv θ
6.2
1.27
5.8
0.244
0.05
0.228
1
e
0 2.5 5 mm
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
UNIT
mm
inches
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.15 mm (0.006 inch) maximum per side are not included.
A
max.
1.75
0.069
A
1
0.25
0.10
0.010
0.004
A
2
1.45
1.25
0.057
0.049
A3b
0.25
0.01
p
0.49
0.36
0.019
0.014
0.25
0.19
0.0100
0.0075
(1)E(1)
cD
8.75
8.55
0.35
0.34
A
1.05
0.041
Q
1
detail X
1.0
0.7
0.4
0.6
0.028
0.039
0.024
0.016
(A )
L
p
L
0.25
0.01 0.004
A
3
θ
0.25 0.1
0.01
(1)
0.7
0.3
0.028
0.012
o
8
o
0
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT108-1
IEC JEDEC JEITA
076E06 MS-012
REFERENCES
2003 Sep 09 18
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
99-12-27
03-02-19
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
SOLDERING
Introduction
Thistext gives a very briefinsightto a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages”
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-holeandsurfacemountcomponentsare mixed on
one printed-circuit board. Wave soldering can still be used
for certain surface mount ICs, but it is not suitable for fine
pitch SMDs. In these situations reflow soldering is
recommended. Driven by legislation and environmental
forces the worldwide use of lead-free solder pastes is
increasing.
Through-hole mount packages
SOLDERING BY DIPPING OR BY SOLDER WAVE
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
cooling) vary between 100 and 200 seconds depending
on heating method.
Typical reflow peak temperatures range from
215 to 270 °C depending on solder paste material. The
top-surface temperature of the packages should
preferably be kept:
• below 220 °C (SnPb process) or below 245 °C (Pb-free
process)
– for all the BGA and SSOP-T packages
– for packages with a thickness ≥ 2.5 mm
– for packages with a thickness < 2.5 mm and a
volume ≥ 350 mm3 so called thick/large packages.
• below 235 °C (SnPb process) or below 260 °C (Pb-free
process) for packages with a thickness < 2.5 mm and a
volume < 350 mm3 so called small/thin packages.
Moisture sensitivity precautions, as indicated on packing,
must be respected at all times.
Typical dwell time of the leads in the wave ranges from
3 to 4 seconds at 250 °C or 265 °C, depending on solder
material applied, SnPb or Pb-free respectively.
Thetotalcontact time of successive solderwavesmustnot
exceed 5 seconds.
The device may be mounted up to the seating plane, but
the temperature of the plastic body must not exceed the
specified maximum storage temperature (T
printed-circuit board has been pre-heated, forced cooling
may be necessary immediately after soldering to keep the
temperature within the permissible limit.
MANUAL SOLDERING
Apply the soldering iron (24 V or less) to the lead(s) of the
package, either below the seating plane or not more than
2 mm above it. If the temperature of the soldering iron bit
is less than 300 °C it may remain in contact for up to
10 seconds. If the bit temperature is between
300 and 400 °C, contact may be up to 5 seconds.
Surface mount packages
REFLOW SOLDERING
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
tothe printed-circuit board byscreen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example,
convection or convection/infrared heating in a conveyor
type oven. Throughput times (preheating, soldering and
stg(max)
). If the
WAVE SOLDERING
Conventional single wave soldering is not recommended
forsurfacemount devices (SMDs) or printed-circuitboards
with a high component density, as solder bridging and
non-wetting can present major problems.
To overcome these problems the double-wave soldering
method was specifically developed.
If wave soldering is used the following conditions must be
observed for optimal results:
• Use a double-wave soldering method comprising a
turbulent wave with high upward pressure followed by a
smooth laminar wave.
• For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e):
– larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint
longitudinal axis is preferred to be parallel to the
transport direction of the printed-circuit board;
– smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis
must be parallel to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board.
The footprint must incorporate solder thieves at the
downstream end.
• Forpackageswith leads on four sides,thefootprintmust
be placed at a 45° angle to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board. The footprint must incorporate
solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
During placement andbefore soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
2003 Sep 09 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Typical dwell time of the leads in the wave ranges from
3 to 4 seconds at 250 °C or 265 °C, depending on solder
material applied, SnPb or Pb-free respectively.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
Suitability of IC packages for wave, reflow and dipping soldering methods
MOUNTING PACKAGE
(1)
Through-hole mount DBS, DIP, HDIP, SDIP, SIL suitable
Through-hole-
PMFP
(9)
surface mount
Surface mount BGA, LBGA, LFBGA, SQFP, SSOP-T
TFBGA, VFBGA
DHVQFN, HBCC, HBGA, HLQFP, HSQFP,
HSOP, HTQFP, HTSSOP, HVQFN, HVSON,
SMS
(6)
PLCC
, SO, SOJ suitable suitable −
LQFP, QFP, TQFP not recommended
SSOP, TSSOP, VSO, VSSOP not recommended
MANUAL SOLDERING
Fix the component by first soldering two
diagonally-opposite end leads. Use a low voltage (24 V or
less) soldering iron applied to the flat part of the lead.
Contact time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to
300 °C. When using a dedicated tool, all other leads can
be soldered in one operation within 2 to 5 seconds
between 270 and 320 °C.
not suitable not suitable −
(4)
,
not suitable suitable −
not suitable
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
SOLDERING METHOD
WAVE REFLOW
(3)
(5)
− suitable
suitable −
(6)(7)
suitable −
(8)
suitable −
(2)
DIPPING
Notes
1. Formore detailed information ontheBGA packages refertothe
“(LF)BGAApplication Note
”(AN01026); order a copy
from your Philips Semiconductors sales office.
2. All surface mount (SMD) packages are moisture sensitive. Depending upon the moisture content, the maximum
temperature (with respect to time) and body size of the package, there is a risk that internal or external package
cracks may occur due to vaporization of the moisture in them (the so called popcorn effect). For details, refer to the
Drypack information in the
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages; Section: Packing Methods”
.
3. For SDIP packages, the longitudinal axis must be parallel to the transport direction of the printed-circuit board.
4. These transparent plastic packages are extremely sensitive to reflow soldering conditions and must on no account
be processed through more than one soldering cycle or subjected to infrared reflow soldering with peak temperature
exceeding 217 °C ± 10 °C measured in the atmosphere of the reflow oven. The package body peak temperature
must be kept as low as possible.
5. These packages are not suitable for wave soldering. On versions with the heatsink on the bottom side, the solder
cannot penetrate between the printed-circuit board and the heatsink. On versions with the heatsink on the top side,
the solder might be deposited on the heatsink surface.
6. If wave soldering is considered, then the package must be placed at a 45° angle to the solder wave direction.
The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
7. Wave soldering is suitable for LQFP,QFP and TQFP packages with a pitch (e) larger than 0.8 mm; it is definitely not
suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.65 mm.
8. Wave soldering is suitable for SSOP, TSSOP, VSO and VSSOP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than
0.65 mm; it is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.5 mm.
9. Hot bar soldering or manual soldering is suitable for PMFP packages.
2003 Sep 09 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
GreenChipII SMPS control IC
TEA1506P; TEA1506AP;
TEA1506T; TEA1506AT
DATA SHEET STATUS
LEVEL
I Objective data Development This data sheet contains data from the objective specification for product
II Preliminary data Qualification This data sheet contains data from the preliminary specification.
III Product data Production This data sheet contains data from the product specification. Philips
Notes
1. Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
2. The product status of the device(s) described in this data sheet may have changed since this data sheet was
3. For data sheets describing multiple type numbers,the highest-levelproduct statusdetermines thedata sheet status.
DATA SHEET
STATUS
published. The latest information is available on the Internet at URL http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
(1)
PRODUCT
STATUS
(2)(3)
DEFINITION
development. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to change the
specification in any manner without notice.
Supplementary data will be published at a later date. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to change the specification without
notice, in order to improve the design and supply the best possible
product.
Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes at any time in order
to improve the design, manufacturing and supply. Relevant changes will
be communicated via a Customer Product/Process Change Notification
(CPCN).
DEFINITIONS
Short-form specification The data in a short-form
specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the
same type number and title. For detailed information see
the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition Limiting values given are in
accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System
(IEC 60134). Stress above one or more of the limiting
values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device
atthese or at anyotherconditionsabove those given inthe
Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied.
Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Application information Applications that are
described herein for any of these products are for
illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors make
norepresentationorwarranty that such applications willbe
suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
DISCLAIMERS
Life support applications These products are not
designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or
systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected to result inpersonal injury. Philips
Semiconductorscustomersusingor selling these products
for use in such applications do so at their own risk and
agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any
damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes Philips Semiconductors
reserves the right to make changes in the products including circuits, standard cells, and/or software described or contained herein in order to improve design
and/or performance. Whenthe product is in full production
(status ‘Production’), relevant changes will be
communicated via a Customer Product/Process Change
Notification (CPCN). Philips Semiconductors assumes no
responsibility or liability for the use of any of these
products, conveys no licence or title under any patent,
copyright, or mask work right to these products, and
makes no representations or warranties that these
products are free from patent, copyright, or mask work
right infringement, unless otherwise specified.
2003 Sep 09 21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors – a w orldwide compan y
Contact information
For additional information please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com. Fax: +31 40 27 24825
For sales offices addresses send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Printed in The Netherlands 613502/01/pp22 Date of release: 2003 Sep 09 Document order number: 9397 750 11434
SCA75
 Loading...
Loading...