Daikin ERHQ011-014-016BA, ERLQ011-014-016CA, EHBH/X16CA Installation manuals
+
Installer reference guide
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
ERHQ011-014-016BA
ERLQ011-014-016CA
EHBH/X16CA
Installer reference guide
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
English

Table of contents
Table of contents
About the documentation ................................
1
1.1
About this document .................................................................
General safety precautions ..............................
2
2.1
About the documentation ..........................................................
2.1.1 Meaning of warnings and symbols ............................
2.2
For the installer .........................................................................
2.2.1 General ......................................................................
2.2.2 Installation site ...........................................................
2.2.3 Refrigerant .................................................................
2.2.4 Water .........................................................................
2.2.5 Electrical ....................................................................
About the box ....................................................
3
3.1
Indoor unit .................................................................................
3.1.1 To unpack the indoor unit ..........................................
3.1.2 To remove the accessories from the indoor unit ........
About the units and options ............................
4
4.1
Identification ..............................................................................
4.1.1 Identification label: Indoor unit ...................................
4.2
Possible combinations of units and options ..............................
4.2.1 List of options for indoor unit ......................................
4.2.2 Possible combinations of indoor unit and outdoor
unit .............................................................................
4.2.3 Possible combinations of indoor unit and domestic
hot water tank ............................................................
Application guidelines ......................................
5
5.1
Overview: Application guidelines ..............................................
5.2
Setting up the space heating/cooling system ...........................
5.2.1 Single room ................................................................
5.2.2 Multiple rooms – One LWT zone ...............................
5.2.3 Multiple rooms – Two LWT zones .............................
5.3
Setting up an auxiliary heat source for space heating ..............
5.4
Setting up the domestic hot water tank .....................................
5.4.1 System layout – Integrated DHW tank .......................
5.4.2 System layout – Standalone DHW tank .....................
5.4.3 Selecting the volume and desired temperature for
the DHW tank ............................................................
5.4.4 Setup and configuration – DHW tank ........................
5.4.5 Combination: Standalone DHW tank + Solar panels .
5.4.6 DHW pump for instant hot water ................................
5.4.7 DHW pump for disinfection ........................................
5.5
Setting up the energy metering .................................................
5.5.1 Produced heat ...........................................................
5.5.2 Consumed energy .....................................................
5.5.3 Normal kWh rate power supply ..................................
5.5.4 Preferential kWh rate power supply ...........................
5.6
Setting up the power consumption control ................................
5.6.1 Permanent power limitation .......................................
5.6.2 Power limitation activated by digital inputs ................
5.6.3 Power limitation process ............................................
5.7
Setting up an external temperature sensor ...............................
Preparation ........................................................
6
6.1
Preparing installation site ..........................................................
6.1.1 Installation site requirements of the indoor unit .........
6.2
Preparing water piping ..............................................................
6.2.1 Water circuit requirements .........................................
6.2.2 Formula to calculate the expansion vessel pre-
pressure .....................................................................
6.2.3 To check the water volume ........................................
6.2.4 Changing the pre-pressure of the expansion vessel .
6.2.5 To check the water volume: Examples ......................
6.3
Preparing electrical wiring .........................................................
6.3.1 About preparing electrical wiring ................................
6.3.2 About preferential kWh rate power supply .................
6.3.3 Overview of electrical connections except external
actuators ....................................................................
6.3.4 Overview of electrical connections for external and
internal actuators .......................................................
Installation .........................................................
7
7.1
Opening the units ......................................................................
20
25
7.1.1 To open the indoor unit ..............................................
7.1.2 To open the switch box cover of the indoor unit ........
7.2
Mounting the indoor unit ...........................................................
7.2.1 To install the indoor unit .............................................
7.2.2 To install the drain pan kit ..........................................
7.3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
4
4
4
4
5
5
5
5
6
6
6
6
6
8
7
7
8
8
8
8
10
11
13
14
14
14
15
15
16
16
16
16
16
17
17
17
18
18
18
19
19
20
20
20
20
22
22
22
23
23
23
23
23
24
25
9
10
11
12
Connecting the water piping .....................................................
7.3.1 To connect the water piping .......................................
7.3.2 To fill the water circuit ................................................
7.3.3 To fill the domestic hot water tank .............................
7.3.4 To insulate the water piping .......................................
7.4
Connecting the electrical wiring ................................................
7.4.1 About electrical compliance .......................................
7.4.2 To connect the electrical wiring on the indoor unit .....
7.4.3 To connect the main power supply ............................
7.4.4 To connect the backup heater power supply .............
7.4.5 To connect the user interface ....................................
7.4.6 To connect the shut-off valve .....................................
7.4.7 To connect the electrical meters ................................
7.4.8 To connect the domestic hot water pump ..................
7.4.9 To connect the alarm output ......................................
7.4.10 To connect the space cooling/heating ON/OFF
output .........................................................................
7.4.11 To connect the changeover to external heat source ..
7.4.12 To connect the power consumption digital inputs ......
7.5
Finishing the indoor unit installation ..........................................
7.5.1 To fix the user interface cover to the indoor unit ........
7.5.2 To close the indoor unit .............................................
Configuration ....................................................
8.1
Overview: Configuration ...........................................................
8.1.1 To connect the PC cable to the switch box ................
8.1.2 To access the most used commands ........................
8.1.3 To copy the system settings from the first to the
second user interface ................................................
8.1.4 To copy the language set from the first to the second
user interface .............................................................
8.1.5 Quick wizard: Set the system layout after first power
8.2
8.3
8.4
8.5
ON .............................................................................
Basic configuration ...................................................................
8.2.1 Quick wizard: Language / time and date ...................
8.2.2 Quick wizard: Standard ..............................................
8.2.3 Quick wizard: Options ................................................
8.2.4 Quick wizard: Capacities (energy metering) ..............
8.2.5 Space heating/cooling control ....................................
8.2.6 Domestic hot water control ........................................
8.2.7 Contact/helpdesk number ..........................................
Advanced configuration/optimization ........................................
8.3.1 Space heating/cooling operation: advanced ..............
8.3.2 Domestic hot water control: advanced .......................
8.3.3 Heat source settings ..................................................
8.3.4 System settings .........................................................
Menu structure: Overview .........................................................
Menu structure: Overview installer settings ..............................
Commissioning .................................................
9.1
Overview: Commissioning ........................................................
9.2
Checklist before test run ...........................................................
9.3
Air purge function ......................................................................
9.3.1 To perform a manual air purge ..................................
9.3.2 To perform an automatic air purge ............................
9.3.3 To interrupt air purge .................................................
9.4
To perform a test run ................................................................
9.5
To perform an actuator test run ................................................
9.5.1 Possible actuator test runs ........................................
9.6
Underfloor heating screed dryout .............................................
9.6.1 To program an underfloor heating screed dryout
schedule ....................................................................
9.6.2 To start an underfloor heating screed dryout .............
9.6.3 To readout the status of an underfloor heating
screed dryout .............................................................
9.6.4 To interrupt an underfloor heating screed dryout .......
Hand-over to the user .......................................
Maintenance and service .................................
11.1
Maintenance safety precautions ...............................................
11.1.1 Opening the indoor unit .............................................
11.2
Checklist for yearly maintenance for indoor unit .......................
Troubleshooting ................................................
12.1
General guidelines ....................................................................
25
25
25
25
26
26
26
27
27
27
27
27
28
28
29
30
31
32
32
32
32
32
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
34
34
34
34
35
35
35
37
39
39
42
43
44
44
47
51
52
56
57
58
58
58
58
58
59
59
59
59
59
59
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
61
61
61
61
Installer reference guide
2
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
12.2
Solving problems based on symptoms .....................................
12.2.1 Symptom: The unit is NOT heating or cooling as
expected ....................................................................
12.2.2 Symptom: The compressor does NOT start (space
heating or domestic water heating) ............................
12.2.3 Symptom: The pump is making noise (cavitation) .....
12.2.4 Symptom: The pressure relief valve opens ...............
12.2.5 Symptom: The water pressure relief valve leaks .......
12.2.6 Symptom: The space is NOT sufficiently heated at
low outdoor temperatures ..........................................
12.2.7 Symptom: The pressure at the tapping point is
temporarily unusual high ............................................
12.2.8 Symptom: Decoration panels are pushed away due
to a swollen tank ........................................................
12.2.9 Symptom: Tank disinfection function is NOT
12.3
Glossary .............................................................
13
Technical data ...................................................
14
14.1
14.2
14.3
14.4
14.5
14.6
14.7
14.8
14.9
14.10
14.11
completed correctly (AH-error) ..................................
Solving problems based on error codes ...................................
12.3.1 Error codes: Overview ...............................................
Dimensions and service space .................................................
14.1.1 Dimensions and service space: Indoor unit ...............
Components .............................................................................
14.2.1 Components: Indoor unit ...........................................
14.2.2 Components: Switch box (indoor unit) .......................
Functional diagrams .................................................................
14.3.1 Functional diagram: Indoor unit .................................
Piping diagram ..........................................................................
14.4.1 Piping diagram: Indoor unit ........................................
Wiring diagram ..........................................................................
14.5.1 Wiring diagram – components: Indoor unit ................
Technical specifications ............................................................
14.6.1 Technical specifications: Indoor unit ..........................
Operation range ........................................................................
14.7.1 Operation range: Heating and cooling .......................
14.7.2 Operation range: Domestic hot water ........................
14.7.3 Drain pan necessity ...................................................
Sound spectrum ........................................................................
14.8.1 Sound spectrum: Outdoor unit ...................................
ESP curve .................................................................................
14.9.1 ESP curve: Indoor unit ...............................................
Performance .............................................................................
Combination table .....................................................................
64
66
1 About the documentation
62
62
62
62
62
63
63
63
63
63
63
64
Document Contains… Format
Installer
reference
guide
Preparation of the
installation, technical
specifications, good
CD/DVD (in the box of the
indoor unit)
practices, reference data,
…
Addendum
book for
optional
equipment
Additional info about how
to install optional
equipment
Paper (in the box of the
indoor unit)
CD/DVD (in the box of the
indoor unit)
Latest revisions of the supplied documentation may be available on
the regional Daikin website or via your dealer.
2 General safety precautions
66
66
67
67
67
68
68
69
69
70
70
76
76
78
78
79
80
81
81
82
82
83
86
2.1 About the documentation
▪ The original documentation is written in English. All other
languages are translations.
▪ The precautions described in this document cover very important
topics, follow them carefully.
▪ All activities described in the installation manual must be
performed by an authorized installer.
2.1.1 Meaning of warnings and symbols
DANGER
Indicates a situation that results in death or serious injury.
DANGER: RISK OF ELECTROCUTION
Indicates a situation that could result in electrocution.
DANGER: RISK OF BURNING
Indicates a situation that could result in burning because of
extreme hot or cold temperatures.
1 About the documentation
1.1 About this document
Target audience
Authorized installers
Documentation set
This document is part of a documentation set. The complete set
consists of:
Document Contains… Format
General
safety
precautions
Indoor unit
installation
manual
Outdoor unit
installation
manual
Safety instructions that
you must read before
Paper (in the box of the
indoor unit)
installing
Installation instructions
Installation instructions Paper (in the box of the
outdoor unit)
WARNING
Indicates a situation that could result in death or serious
injury.
CAUTION
Indicates a situation that could result in minor or moderate
injury.
NOTICE
Indicates a situation that could result in equipment or
property damage.
INFORMATION
Indicates useful tips or additional information.
2.2 For the installer
2.2.1 General
If you are not sure how to install or operate the unit, contact your
dealer.
NOTICE
Improper installation or attachment of equipment or
accessories could result in electric shock, short-circuit,
leaks, fire or other damage to the equipment. Only use
accessories, optional equipment and spare parts made or
approved by Daikin.
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
Installer reference guide
3

2 General safety precautions
WARNING
Make sure installation, testing and applied materials
comply with applicable legislation (on top of the
instructions described in the Daikin documentation).
CAUTION
Wear adequate personal protective equipment (protective
gloves, safety glasses,…) when installing, maintaining or
servicing the system.
WARNING
Tear apart and throw away plastic packaging bags so that
nobody, especially children, can play with them. Possible
risk: suffocation.
DANGER: RISK OF BURNING
▪ Do NOT touch the refrigerant piping, water piping or
internal parts during and immediately after operation. It
could be too hot or too cold. Give it time to return to
normal temperature. If you must touch it, wear
protective gloves.
▪ Do NOT touch any accidental leaking refrigerant.
NOTICE
Provide adequate measures to prevent that the unit can be
used as a shelter by small animals. Small animals that
make contact with electrical parts can cause malfunctions,
smoke or fire.
▪ In places where corrosive gas (example: sulphurous acid gas) is
produced. Corrosion of copper pipes or soldered parts may cause
the refrigerant to leak.
2.2.3 Refrigerant
NOTICE
Make sure refrigerant piping installation complies with
applicable legislation. In Europe, EN378 is the applicable
standard.
NOTICE
Make sure the field piping and connections are not
subjected to stress.
WARNING
During tests, NEVER pressurize the product with a
pressure higher than the maximum allowable pressure (as
indicated on the nameplate of the unit).
WARNING
Take sufficient precautions in case of refrigerant leakage. If
refrigerant gas leaks, ventilate the area immediately.
Possible risks:
▪ Excessive refrigerant concentrations in a closed room
can lead to oxygen deficiency.
▪ Toxic gas may be produced if refrigerant gas comes
into contact with fire.
CAUTION
Do NOT touch the air inlet or aluminum fins of the unit.
NOTICE
▪ Do NOT place any objects or equipment on top of the
unit.
▪ Do NOT sit, climb or stand on the unit.
In accordance with the applicable legislation, it might be necessary
to provide a logbook with the product containing at least: information
on maintenance, repair work, results of tests, stand-by periods,…
Also, at least, following information must be provided at an
accessible place at the product:
▪ Instructions for shutting down the system in case of an emergency
▪ Name and address of fire department, police and hospital
▪ Name, address and day and night telephone numbers for
obtaining service
In Europe, EN378 provides the necessary guidance for this logbook.
2.2.2 Installation site
▪ Provide sufficient space around the unit for servicing and air
circulation.
▪ Make sure the installation site withstands the unit’s weight and
vibration.
▪ Make sure the area is well ventilated.
▪ Make sure the unit is level.
Do NOT install the unit in the following places:
▪ In potentially explosive atmospheres.
▪ In places where there is machinery that emits electromagnetic
waves. Electromagnetic waves may disturb the control system,
and cause malfunction of the equipment.
▪ In places where there is a risk of fire due to the leakage of
flammable gases (example: thinner or gasoline), carbon fibre,
ignitable dust.
WARNING
Always recover the refrigerants. Do NOT release them
directly into the environment. Use a vacuum pump to
evacuate the installation.
2.2.4 Water
NOTICE
Make sure water quality complies with EU directive
98/83 EC.
2.2.5 Electrical
DANGER: RISK OF ELECTROCUTION
▪ Turn OFF all power supply before removing the
switch box cover, connecting electrical wiring or
touching electrical parts.
▪ Disconnect the power supply for more than 1 minute,
and measure the voltage at the terminals of main circuit
capacitors or electrical components before servicing.
The voltage must be less than 50 V DC before you can
touch electrical components. For the location of the
terminals, see the wiring diagram.
▪ Do NOT touch electrical components with wet hands.
▪ Do NOT leave the unit unattended when the service
cover is removed.
WARNING
If not factory installed, a main switch or other means for
disconnection, having a contact separation in all poles
providing full disconnection under overvoltage category III
condition, shall be installed in the fixed wiring.
Installer reference guide
4
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11

a
a
WARNING
▪ Only use copper wires.
▪ All field wiring must be performed in accordance with
the wiring diagram supplied with the product.
▪ NEVER squeeze bundled cables and make sure they
do not come in contact with the piping and sharp
edges. Make sure no external pressure is applied to the
terminal connections.
▪ Make sure to install earth wiring. Do NOT earth the unit
to a utility pipe, surge absorber, or telephone earth.
Incomplete earth may cause electrical shock.
▪ Make sure to use a dedicated power circuit. NEVER
use a power supply shared by another appliance.
▪ Make sure to install the required fuses or circuit
breakers.
▪ Make sure to install an earth leakage protector. Failure
to do so may cause electric shock or fire.
▪ When installing the earth leakage protector, make sure
it is compatible with the inverter (resistant to high
frequency electric noise) to avoid unnecessary opening
of the earth leakage protector.
Install power cables at least 1 meter away from televisions or radios
to prevent interference. Depending on the radio waves, a distance of
1 meter may not be sufficient.
WARNING
▪ After finishing the electrical work, confirm that each
electrical component and terminal inside the electrical
components box is connected securely.
▪ Make sure all covers are closed before starting up the
unit.
3 About the box
a Installation manual, operation manual, CD/DVD
INFORMATION
Do NOT throw away the upper cardboard cover. On the
inside of the cardboard cover, the installation pattern is
printed.
3.1.2 To remove the accessories from the indoor unit
The installation manual indoor unit, operation manual, and CD/DVD
are located in the upper part of the box. Follow the procedure below
to remove the other accessories.
1 Remove the tape.
3 About the box
▪ At delivery, the unit must be checked for damage. Any damage
must be reported immediately to the carrier’s claims agent.
▪ Bring the packed unit as close as possible to its final installation
position to prevent damage during transport.
3.1 Indoor unit
3.1.1 To unpack the indoor unit
2 Tilt the bottom side of the front panel upwards and remove it.
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
3 Remove the accessories.
Installer reference guide
5

4 About the units and options
h
f
g
i
j
a
1x
b
1x
c
1x
d
1x
g
2x
h
1x
f
1x
i
1x
e
1x
l
4x
k
1x
j
2x
Model identification
Example: E HB H 04 CA 3V
Code Description
E European model
HB HB=Wall-mounted indoor unit
H ▪ H=Heating only
▪ X=Heating/cooling
04 Capacity class:
▪ 04=4 kW
▪ 08=8 kW
▪ 16=16 kW
CA Series
3V Backup heater model
▪ 3V
▪ 9W
4.2 Possible combinations of units and options
a General safety precautions
b Addendum book for optional equipment
c Indoor unit installation manual
d Operation manual
e CD/DVD
f User interface kit: user interface, 4 fixing screws, 2
plugs
g Shut-off valve
h User interface cover
i Top plate of indoor unit
j Screws
k Sound plate
l Screws for fixing sound plate
4 Remove the accessories k+l. These accessories are located at
the bottom of the packaging.
4 About the units and options
4.1 Identification
NOTICE
When installing or servicing several units at the same time,
make sure NOT to switch the service panels between
different models.
4.1.1 Identification label: Indoor unit
Location
Installer reference guide
6
4.2.1 List of options for indoor unit
User interface (EKRUCAL1, EKRUCAL2)
The user interface is delivered as an accessory with the unit. An
additional user interface is optionally available.
The additional user interface can be connected:
▪ To have both:
▪ control close to the indoor unit
▪ room thermostat functionality in the principal space to be
heated
▪ To have an interface containing other languages
The additional user interface EKRUCAL1 contains the 6 common
languages: English, German, French, Dutch, Italian, Spanish.
The additional user interface EKRUCAL2 contains other languages:
English, Swedish, Norwegian, Czech, Turkish, Portuguese.
Languages on the user interface can be uploaded by PC software or
copied from an user interface to the other.
For installation instructions, see "7.4.5 To connect the user interface"
on page 30.
Room thermostat (EKRTWA, EKRTR1)
You can connect an optional room thermostat to the indoor unit. This
thermostat can either be wired (EKRTWA) or wireless (EKRTR1).
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the room
thermostat and addendum book for optional equipment.
Remote sensor for wireless thermostat (EKRTETS)
You can use a wireless indoor temperature sensor (EKRTETS) only
in combination with the wireless thermostat (EKRTR1).
For installation intructions, see the installation manual of the room
thermostat and addendum book for optional equipment.
Digital I/O PCB (EKRP1HB)
The digital I/O PCB is required to provide following signals:
▪ Alarm output
▪ Space heating/cooling On/OFF output
▪ Changeover to external heat source
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11

4 About the units and options
▪ Only for EHVH/X16 models: Control signal for bottom plate heater
kit EKBPHTH16A.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the digital
I/O PCB and addendum book for optional equipment.
Demand PCB (EKRP1AHTA)
To enable the power saving consumption control by digital inputs
you must install the demand PCB.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the
demand PCB and addendum book for optional equipment.
Remote indoor sensor (KRCS01-1)
By default the internal user interface sensor will be used as room
temperature sensor.
As an option the remote indoor sensor can be installed to measure
the room temperature on another location.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the remote
indoor sensor and addendum book for optional equipment.
INFORMATION
▪ The remote indoor sensor can only be used in case the
user interface is configured with room thermostat
functionality.
▪ You can only connect either the remote indoor sensor or
the remote outdoor sensor.
Remote outdoor sensor (EKRSCA1)
By default the sensor inside the outdoor unit will be used to measure
the outdoor temperature.
As an option the remote outdoor sensor can be installed to measure
the outdoor temperature on another location (e.g. to avoid direct
sunlight) to have an improved system behaviour.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the remote
outdoor sensor.
INFORMATION
You can only connect either the remote indoor sensor or
the remote outdoor sensor.
PC configurator (EKPCCAB*)
The PC cable makes a connection between the switch box of the
indoor unit and a PC. It gives the possibility to upload different
language files to the user interface and indoor parameters to the
indoor unit. For the available language files, contact your local
dealer.
The software and corresponding operating instructions are available
on Daikin Extranet.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the PC
cable.
Drain pan kit (EKHBDPCA2)
The drain pan is required to drain accumulated condensation from
the indoor unit. It is required during low temperature cooling
operation of the indoor unit and when the leaving water temperature
is <18°C.
For installation of this option into the indoor unit, refer to the
installation manual delivered with this option kit.
Solar kit (EKSOLHW)
The solar kit is required to connect the solar application with the
domestic hot water tank.
For installation, see the installation manual of the solar kit and
addendum book for optional equipment.
Domestic hot water tank
The domestic hot water tank can be connected to the indoor unit for
providing domestic hot water.
The domestic hot water tank is available in 2 types:
▪ Stainless steel tank (EKHWS and EKHWSU (only for UK))
There are 3 types available: 150, 200, and 300 liter.
▪ Enamelled tank (EKHWE and EKHWET (wallmounted version))
There are 3 types of EKHWE: 150, 200, and 300 liter.
There is 1 type of EKHWET: 150 liter.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the
domestic hot water tank and addendum book for optional equipment.
4.2.2 Possible combinations of indoor unit and outdoor unit
Outdoor unit Indoor unit
EHBH16CA3V EHBX16CA3V EHBH16CA9W EHBX16CA9W
ERHQ011BAV3 O O O O
ERHQ014BAV3 O O O O
ERHQ016BAV3 O O O O
ERLQ011CAV3 O O O O
ERLQ014CAV3 O O O O
ERLQ016CAV3 O O O O
ERHQ011BAW1 O O O O
ERHQ014BAW1 O O O O
ERHQ016BAW1 O O O O
ERLQ011CAW1 O O O O
ERLQ014CAW1 O O O O
ERLQ016CAW1 O O O O
4.2.3 Possible combinations of indoor unit and domestic hot water tank
Indoor unit Domestic hot water tank
EKHWS EKHWSU EKHWE EKHWET
EHBH16CA3V O O O O
EHBX16CA3V O O O O
EHBH16CA9W O O O O
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
Installer reference guide
7
5 Application guidelines
B
A
a
B
A
b
a
Indoor unit Domestic hot water tank
EKHWS EKHWSU EKHWE EKHWET
EHBX16CA9W O O O O
5 Application guidelines
5.1 Overview: Application guidelines
The purpose of the application guidelines is to give a glance of the
possibilities of the Daikin heat pump system.
NOTICE
▪ The illustrations in the application guidelines are meant
for reference only, and are NOT to be used as detailed
hydraulic diagrams. The detailed hydraulic
dimensioning and balancing are NOT shown, and are
the responsibility of the installer.
▪ For more information about the configuration settings to
optimize heat pump operation, see "8 Configuration" on
page 33.
This chapter contains applications guidelines for:
▪ Setting up the space heating/cooling system
▪ Setting up an auxiliary heat source for space heating
▪ Setting up the domestic hot water tank
▪ Setting up the energy metering
▪ Setting up the power consumption
▪ Setting up an external temperature sensor
5.2 Setting up the space heating/cooling system
The Daikin heat pump system supplies leaving water to heat
emitters in one or more rooms.
Because the system offers a wide flexibility to control the
temperature in each room, you need to answer the following
questions first:
▪ How many rooms are heated (or cooled) by the Daikin heat pump
system?
▪ Which heat emitter types are used in each room and what is their
design leaving water temperature?
Once the space heating/cooling requirements are clear, Daikin
recommends to follow the setup guidelines below.
▪ The under floor heating or radiators are directly connected to the
indoor unit.
▪ The room temperature is controlled by the user interface, which is
used as room thermostat. Possible installations:
▪ User interface (standard equipment) installed in the room and
▪ User interface (standard equipment) installed at the indoor unit
Configuration
Unit temperature control:
▪ #: [A.2.1.7]
▪ Code: [C-07]
Number of water temperature
zones:
▪ #: [A.2.1.8]
▪ Code: [7-02]
Benefits
▪ Cost effective. You do NOT need an additional external room
thermostat.
▪ Highest comfort and efficiency. The smart room thermostat
functionality can decrease or increase the desired leaving water
temperature based on the actual room temperature (modulation).
This results in:
▪ Stable room temperature matching the desired temperature
▪ Less ON/OFF cycles (more quiet, higher comfort and higher
▪ Lowest possible leaving water temperature (higher efficiency)
▪ Easy. You can easily set the desired room temperature via the
user interface:
▪ For your daily needs, you can use preset values and schedules.
▪ To deviate from your daily needs, you can temporarily overrule
a User interface used as room thermostat
used as room thermostat
and used for control close to the indoor unit + user interface
(optional equipment EKRUCAL) installed in the room and used
as room thermostat
Setting Value
2 (RT control): Unit operation is
decided based on the ambient
temperature of the user interface.
0 (1 LWT zone): Main
(higher comfort)
efficiency)
the preset values and schedules, use the holiday mode…
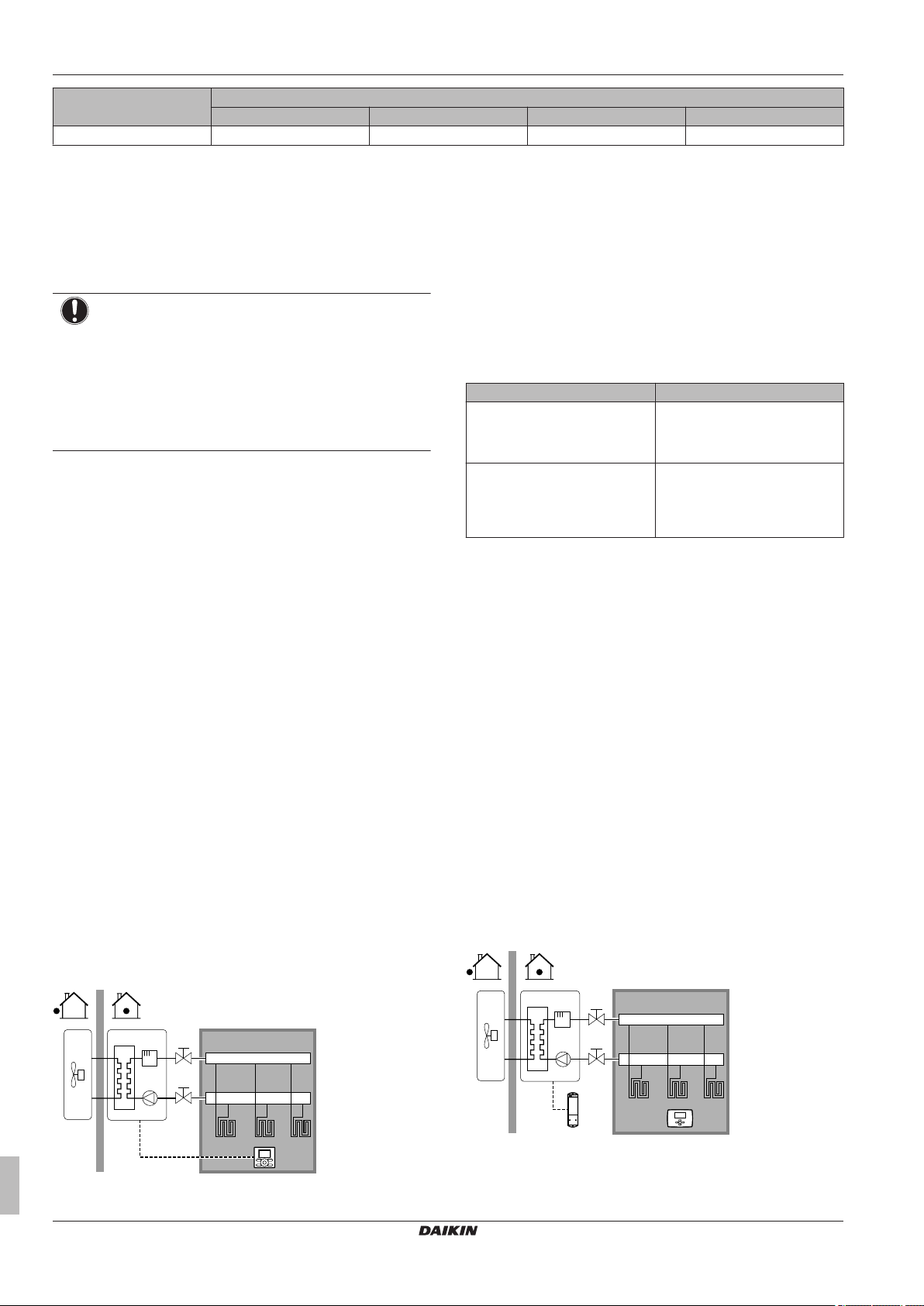
5.2.1 Single room
Under floor heating or radiators – Wired room thermostat
Setup
A Main leaving water temperature zone
B One single room
Installer reference guide
8
Under floor heating or radiators – Wireless room thermostat
Setup
A Main leaving water temperature zone
B One single room
a Receiver for wireless external room thermostat
b Wireless external room thermostat
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
B
A
a
B
A
a
M1
5 Application guidelines
▪ The under floor heating or radiators are directly connected to the
indoor unit.
▪ The room temperature is controlled by the wireless external room
thermostat (optional equipment EKRTR1).
Configuration
Setting Value
Unit temperature control:
▪ #: [A.2.1.7]
▪ Code: [C-07]
Number of water temperature
zones:
▪ #: [A.2.1.8]
▪ Code: [7-02]
External room thermostat for the
main zone:
▪ #: [A.2.2.4]
▪ Code: [C-05]
Benefits
▪ Wireless. The Daikin external room thermostat is available in a
wireless version.
▪ Efficiency. Although the external room thermostat only sends
ON/OFF signals, it is specifically designed for the heat pump
system.
▪ Comfort. In case of under floor heating, the wireless external
room thermostat prevents condensation on the floor during cooling
operation by measuring the room humidity.
1 (Ext RT control): Unit operation
is decided by the external
thermostat.
0 (1 LWT zone): Main
Configure according to the setup:
▪ 1 (Thermo ON/OFF): When
the used external room
thermostat or heat pump
convector can only send a
thermo ON/OFF condition. No
separation between heating or
cooling demand.
▪ 2 (C/H request): When the
used external room thermostat
can send a separate heating/
cooling thermo ON/OFF
condition.
INFORMATION
When using multiple heat pump convectors, make sure
each one receives the infrared signal from the remote
controller of the heat pump convectors.
Configuration
Setting Value
Unit temperature control:
▪ #: [A.2.1.7]
▪ Code: [C-07]
Number of water temperature
zones:
▪ #: [A.2.1.8]
▪ Code: [7-02]
External room thermostat for the
main zone:
▪ #: [A.2.2.4]
▪ Code: [C-05]
Benefits
▪ Cooling. The heat pump convector offers, besides heating
capacity, also excellent cooling capacity.
▪ Efficiency. Optimal energy efficiency because of the interlink
function.
▪ Stylish.
1 (Ext RT control): Unit operation
is decided by the external
thermostat.
0 (1 LWT zone): Main
1 (Thermo ON/OFF): When the
used external room thermostat or
heat pump convector can only
send a thermo ON/OFF
condition. No separation between
heating or cooling demand.
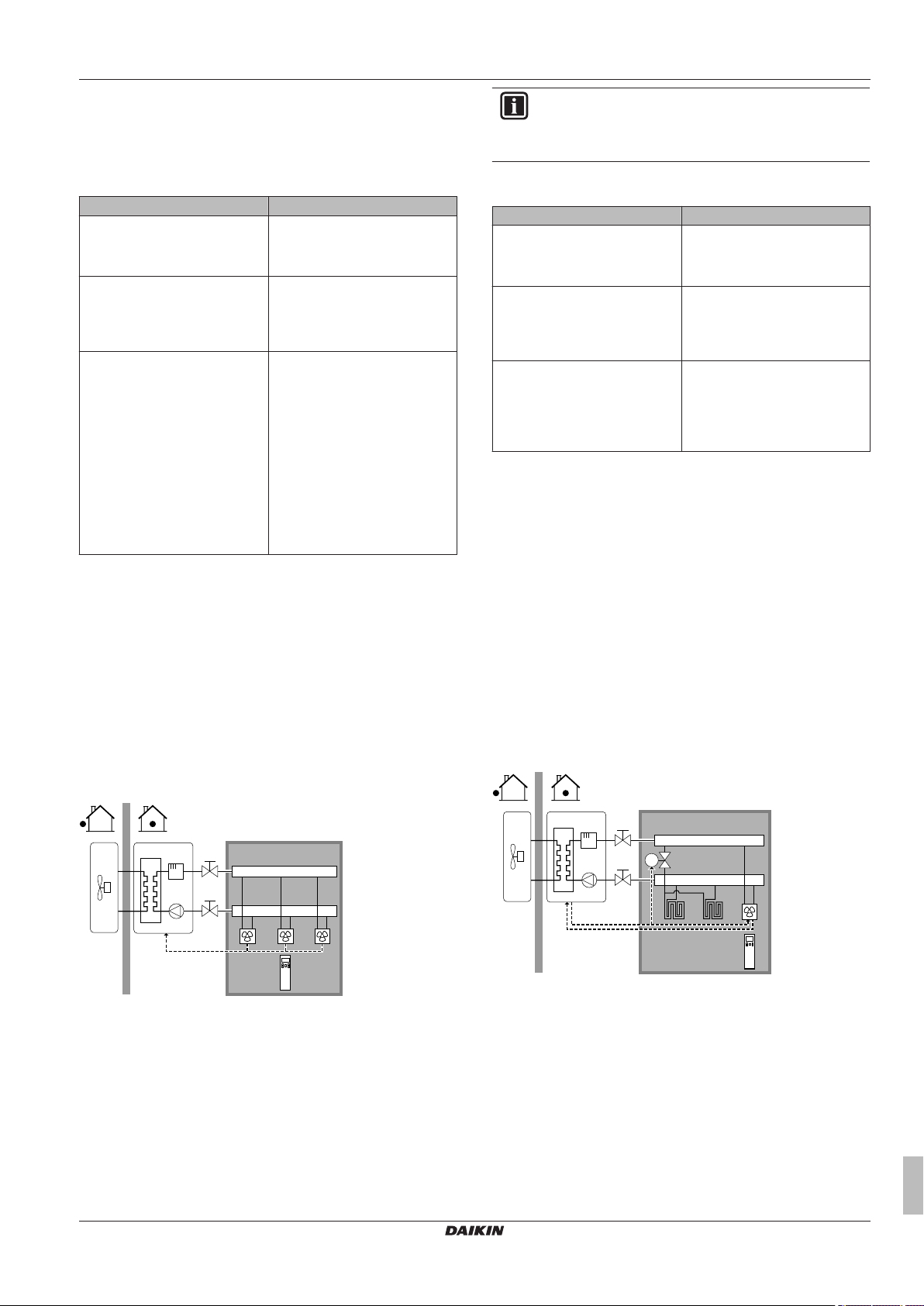
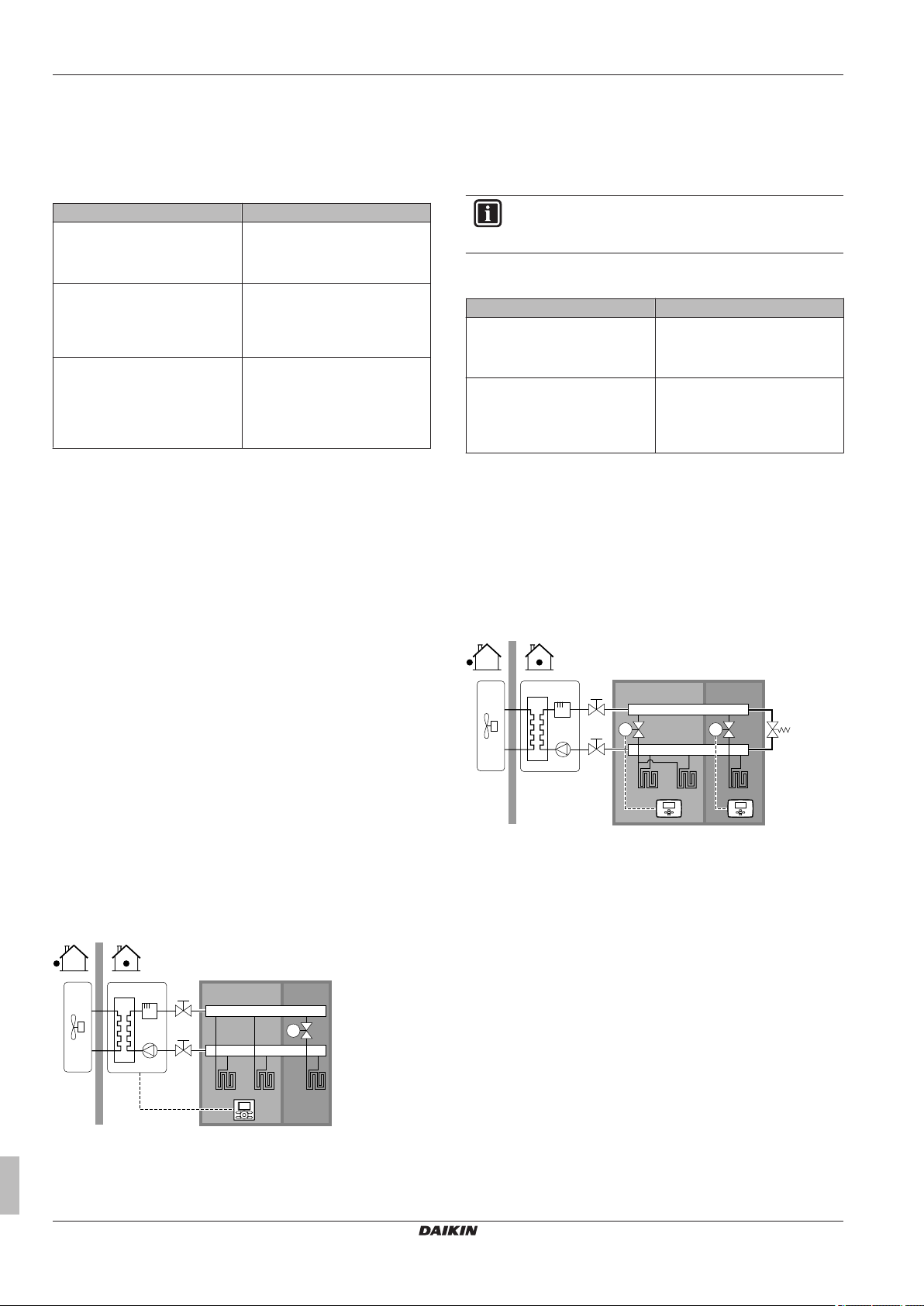
Combination: Under floor heating + Heat pump convectors
▪ Space heating is provided by:
▪ The under floor heating
▪ The heat pump convectors
▪ Space cooling is provided by the heat pump convectors only. The
under floor heating is shut off by the shut-off valve.
Heat pump convectors
Setup
A Main leaving water temperature zone
B One single room
a Remote controller of the heat pump convectors
▪ The heat pump convectors are directly connected to the indoor
unit.
▪ The desired room temperature is set via the remote controller of
the heat pump convectors.
▪ The space heating/cooling demand signal is sent to one digital
input on the indoor unit (X2M/1 and X2M/4).
▪ The space operation mode is sent to the heat pump convectors by
one digital output on the indoor unit (X2M/33 and X2M/34).
Setup
A Main leaving water temperature zone
B One single room
a Remote controller of the heat pump convectors
▪ The heat pump convectors are directly connected to the indoor
unit.
▪ A shut-off valve (field supply) is installed before the under floor
heating to prevent condensation on the floor during cooling
operation.
▪ The desired room temperature is set via the remote controller of
the heat pump convectors.
▪ The space heating/cooling demand signal is sent to one digital
input on the indoor unit (X2M/1 and X2M/4)
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
Installer reference guide
9
5 Application guidelines
T
B C
A
a
M2M1
B C
A
a a
b
▪ The space operation mode is sent by one digital output (X2M/33
and X2M/34) on the indoor unit to:
▪ The heat pump convectors
▪ The shut-off valve
Configuration
Setting Value
Unit temperature control:
▪ #: [A.2.1.7]
▪ Code: [C-07]
Number of water temperature
zones:
▪ #: [A.2.1.8]
▪ Code: [7-02]
External room thermostat for the
main zone:
▪ #: [A.2.2.4]
▪ Code: [C-05]
Benefits
▪ Cooling. Heat pump convectors provide, besides heating
capacity, also excellent cooling capacity.
▪ Efficiency. Under floor heating has the best performance with
Altherma LT.
▪ Comfort. The combination of the two heat emitter types provides:
▪ The excellent heating comfort of the under floor heating
▪ The excellent cooling comfort of the heat pump convectors
1 (Ext RT control): Unit operation
is decided by the external
thermostat.
0 (1 LWT zone): Main
1 (Thermo ON/OFF): When the
used external room thermostat or
heat pump convector can only
send a thermo ON/OFF
condition. No separation between
heating or cooling demand.
5.2.2 Multiple rooms – One LWT zone
If only one leaving water temperature zone is needed because the
design leaving water temperature of all heat emitters is the same,
you do NOT need a mixing valve station (cost effective).
Example: If the heat pump system is used to heat up one floor where
all the rooms have the same heat emitters.
▪ The under floor heating of the main room is directly connected to
the indoor unit.
▪ The room temperature of the main room is controlled by the user
interface used as thermostat.
▪ A thermostatic valve is installed before the under floor heating in
each of the other rooms.
INFORMATION
Mind situations where the main room can be heated by
another heating source. Example: Fireplaces.
Configuration
Setting Value
Unit temperature control:
▪ #: [A.2.1.7]
▪ Code: [C-07]
Number of water temperature
zones:
▪ #: [A.2.1.8]
▪ Code: [7-02]
Benefits
▪ Cost effective.
▪ Easy. Same installation as for one room, but with thermostatic
valves.
2 (RT control): Unit operation is
decided based on the ambient
temperature of the user interface.
0 (1 LWT zone): Main
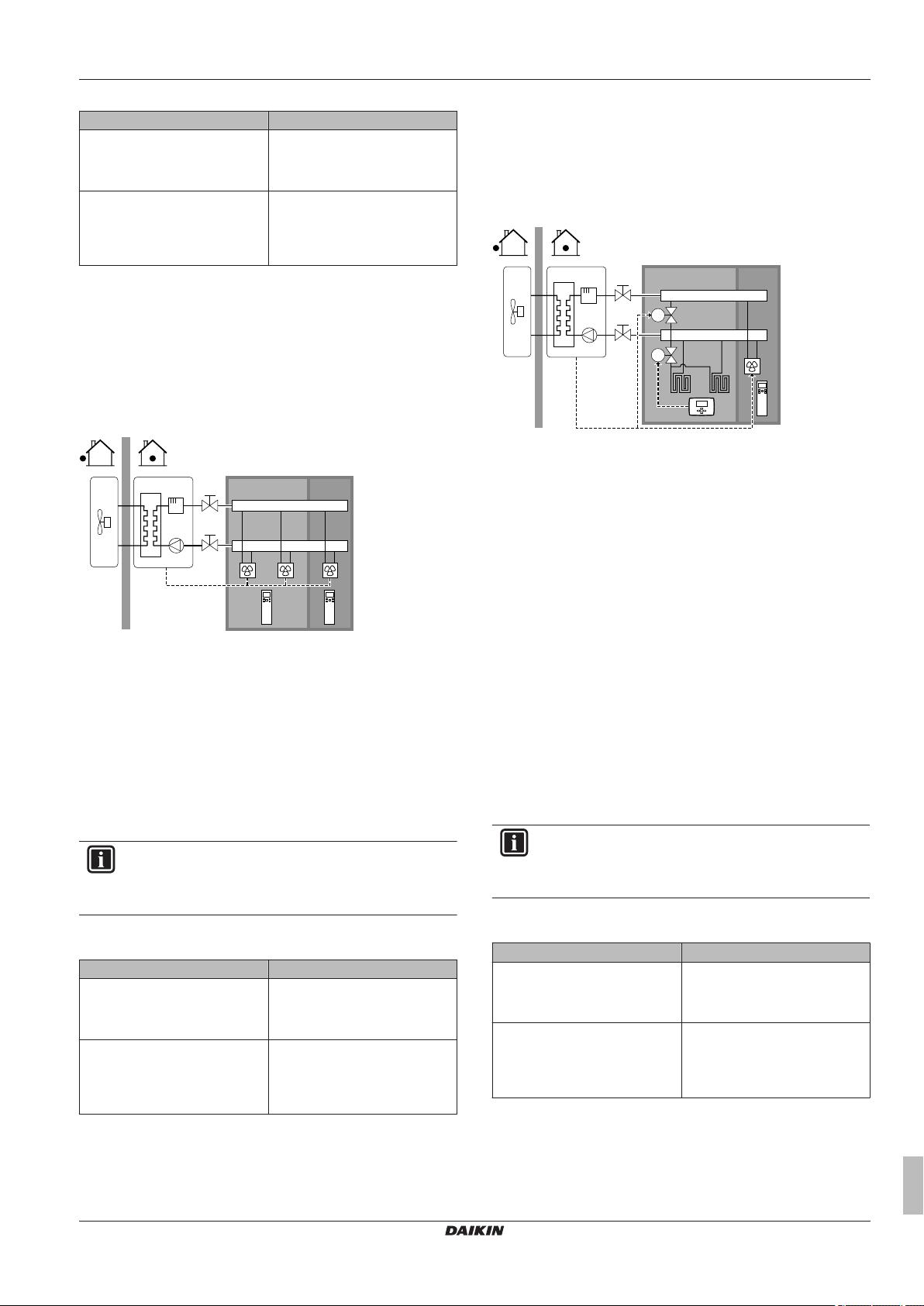
Under floor heating or radiators – Multiple external room thermostats
Setup
Under floor heating or radiators – Thermostatic valves
If you are heating up rooms with under floor heating or radiators, a
very common way is to control the temperature of the main room by
using a thermostat (this can either be the user interface or an
external room thermostat), while the other rooms are controlled by
so-called thermostatic valves, which open or close depending on the
room temperature.
Setup
A Main leaving water temperature zone
B Room 1
C Room 2
a User interface
Installer reference guide
10
A Main leaving water temperature zone
B Room 1
C Room 2
a External room thermostat
b Bypass valve
▪ For each room, a shut-off valve (field supplied) is installed to avoid
leaving water supply when there is no heating or cooling demand.
▪ A bypass valve must be installed to make water recirculation
possible when all shut-off valves are closed.
▪ The user interface connected to the indoor unit decides the space
operation mode. Mind that the operation mode on each room
thermostat must be set to match the indoor unit.
▪ The room thermostats are connected to the shut-off valves, but do
NOT have to be connected to the indoor unit. The indoor unit will
supply leaving water all the time, with the possibility to program a
leaving water schedule.
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
B
A
a a
C
b
B C
A
a
M1
M1
5 Application guidelines
Configuration
Setting Value
Unit temperature control:
▪ #: [A.2.1.7]
▪ Code: [C-07]
Number of water temperature
zones:
▪ #: [A.2.1.8]
▪ Code: [7-02]
Benefits
Compared with under floor heating or radiators for one room:
▪ Comfort. You can set the desired room temperature, including
schedules, for each room via the room thermostats.
0 (LWT control): Unit operation is
decided based on the leaving
water temperature.
0 (1 LWT zone): Main
Heat pump convectors
Setup
A Main leaving water temperature zone
B Room 1
C Room 2
a Remote controller of the heat pump convectors
▪ The desired room temperature is set via the remote controller of
the heat pump convectors.
▪ The user interface connected to the indoor unit decides the space
operation mode.
▪ The heating or cooling demand signals of each heat pump
convector are connected in parallel to the digital input on the
indoor unit (X2M/1 and X2M/4). The indoor unit will only supply
leaving water temperature when there is an actual demand.
INFORMATION
To increase comfort and performance, Daikin recommends
to install the valve kit option EKVKHPC on each heat pump
convector.
Configuration
Setting Value
Unit temperature control:
▪ #: [A.2.1.7]
▪ Code: [C-07]
Number of water temperature
zones:
▪ #: [A.2.1.8]
▪ Code: [7-02]
Benefits
Compared with heat pump convectors for one room:
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
1 (Ext RT control): Unit operation
is decided by the external
thermostat.
0 (1 LWT zone): Main
▪ Comfort. You can set the desired room temperature, including
schedules, for each room via the remote controller of the
heat pump convectors.
Combination: Under floor heating + Heat pump convectors
Setup
A Main leaving water temperature zone
B Room 1
C Room 2
a External room thermostat
b Remote controller of the heat pump convectors
▪ For each room with heat pump convectors: The heat pump
convectors are directly connected to the indoor unit.
▪ For each room with under floor heating: Two shut-off valves (field
supply) are installed before the under floor heating:
▪ A shut-off valve to prevent hot water supply when the room has
no heating demand
▪ A shut-off valve to prevent condensation on the floor during
cooling operation of the rooms with heat pump convectors
▪ For each room with heat pump convectors: The desired room
temperature is set via the remote controller of the heat pump
convectors.
▪ For each room with under floor heating: The desired room
temperature is set via the external room thermostat (wired or
wireless).
▪ The user interface connected to the indoor unit decides the space
operation mode. Mind that the operation mode on each external
room thermostat and remote controller of the heat pump
convectors must be set to match the indoor unit.
INFORMATION
To increase comfort and performance, Daikin recommends
to install the valve kit option EKVKHPC on each heat pump
convector.
Configuration
Setting Value
Unit temperature control:
▪ #: [A.2.1.7]
▪ Code: [C-07]
Number of water temperature
zones:
▪ #: [A.2.1.8]
▪ Code: [7-02]
0 (LWT control): Unit operation is
decided based on the leaving
water temperature.
0 (1 LWT zone): Main
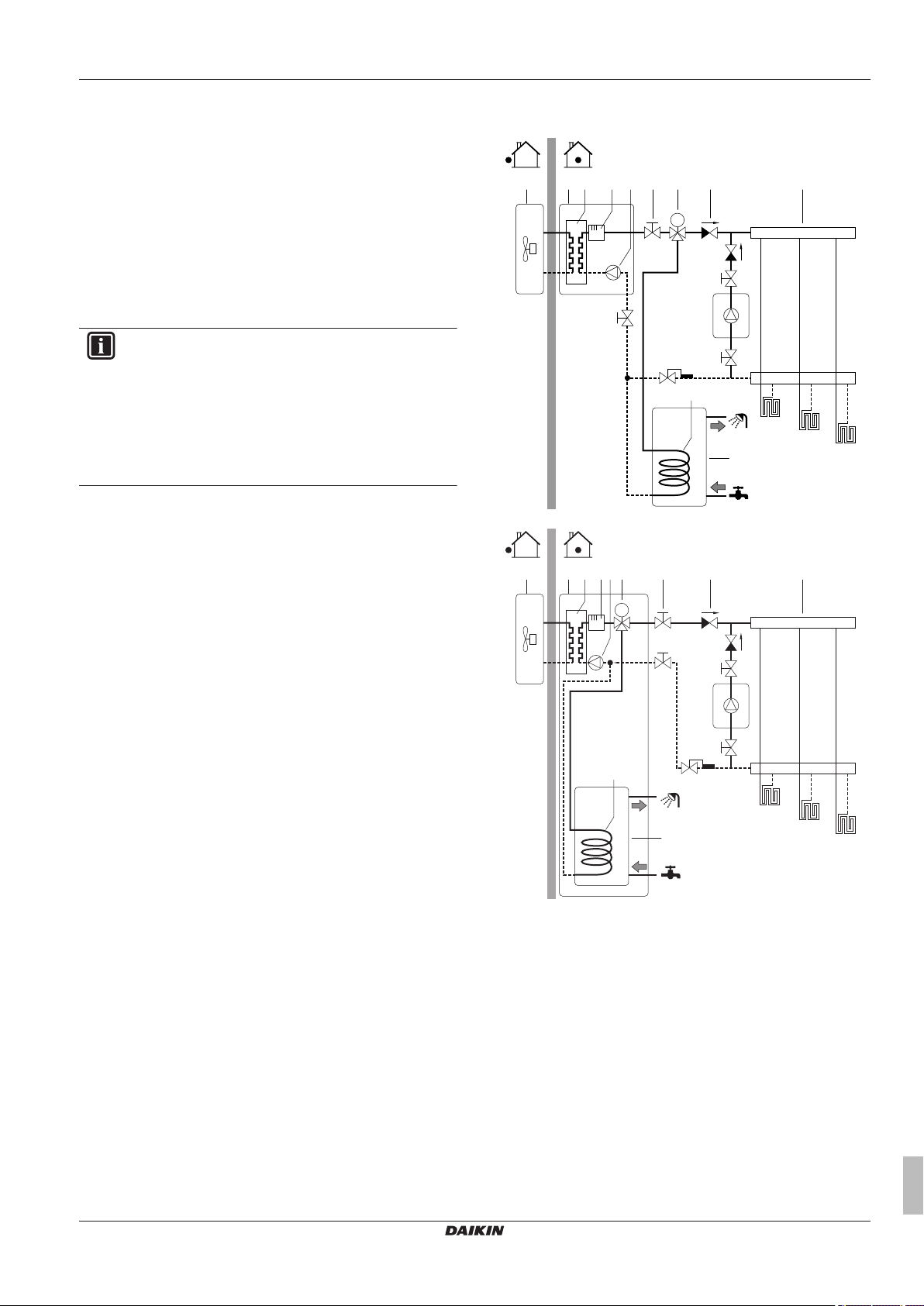
5.2.3 Multiple rooms – Two LWT zones
If the heat emitters selected for each room are designed for different
leaving water temperatures, you can use different leaving water
temperature zones (maximum 2).
In this document:
Installer reference guide
11

5 Application guidelines
B
A
a a
C
E
D
b
c
d
▪ Main zone = Zone with the lowest design temperature in heating,
and the highest design temperature in cooling
▪ Additional zone = The other zone
CAUTION
When there is more than one leaving water zone, you must
always install a mixing valve station in the main zone to
decrease (in heating)/increase (in cooling) the leaving
water temperature when the additional zone has demand.
Typical example:
Room (zone) Heat emitters: Design
Living room (main zone) Under floor heating:
▪ In heating: 35°C
▪ In cooling: 20°C (only
Bed rooms (additional zone) Heat pump convectors:
▪ In heating: 45°C
▪ In cooling: 12°C
Setup
A Additional leaving water temperature zone
B Room 1
C Room 2
D Main leaving water temperature zone
E Room 3
a Remote controller of the heat pump convectors
b User interface
c Mixing valve station
d Pressure regulating valve
INFORMATION
A pressure regulating valve should be implemented before
the mixing valve station. This is to guarantee the correct
water flow balance between the main leaving water
temperature zone and the additional leaving water
temperature zone in relation to the required capacity of
both water temperature zones.
▪ For the main zone:
▪ A mixing valve station is installed before the under floor heating.
▪ The pump of the mixing valve station is controlled by the
ON/OFF signal on the indoor unit (X2M/5 and X2M/7; normal
closed shut-off valve output).
▪ The room temperature is controlled by the user interface, which
is used as room thermostat.
temperature
refreshment, no real cooling
allowed)
▪ For the additional zone:
▪ The heat pump convectors are directly connected to the indoor
unit.
▪ The desired room temperature is set via the remote controller of
the heat pump convectors for each room.
▪ The heating or cooling demand signals of each heat pump
convector are connected in parallel to the digital input on the
indoor unit (X2M/1 and X2M/4). The indoor unit will only supply
the desired additional leaving water temperature when there is
an actual demand.
▪ The user interface connected to the indoor unit decides the space
operation mode. Mind that the operation mode on each remote
controller of the heat pump convectors must be set to match the
indoor unit.
Configuration
Setting Value
Unit temperature control:
▪ #: [A.2.1.7]
▪ Code: [C-07]
Number of water temperature
zones:
▪ #: [A.2.1.8]
▪ Code: [7-02]
In case of heat pump convectors:
External room thermostat for the
additional zone:
▪ #: [A.2.2.5]
▪ Code: [C-06]
Shut-off valve output Set to follow the thermo demand
Shut-off valve If the main zone must be shut off
At the mixing valve station Set the desired main leaving
Benefits
▪ Comfort.
▪ The smart room thermostat functionality can decrease or
increase the desired leaving water temperature based on the
actual room temperature (modulation).
▪ The combination of the two heat emitter systems provides the
excellent heating comfort of the under floor heating, and the
excellent cooling comfort of the heat pump convectors.
▪ Efficiency.
▪ Depending on the demand, the indoor unit supplies different
leaving water temperature matching the design temperature of
the different heat emitters.
▪ Under floor heating has the best performance with Altherma LT.
2 (RT control): Unit operation is
decided based on the ambient
temperature of the user interface.
Note:
▪ Main room = user interface
used as room thermostat
functionality
▪ Other rooms = external room
thermostat functionality
1 (2 LWT zones): Main +
additional
1 (Thermo ON/OFF): When the
used external room thermostat or
heat pump convector can only
send a thermo ON/OFF
condition. No separation between
heating or cooling demand.
of the main zone.
during cooling mode to prevent
condensation on the floor, set it
accordingly.
water temperature for heating
and/or cooling.
Installer reference guide
12
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
a b c d e f g h j
FHL1
FHL2
FHL3
M
h
i
il
k
f
m
n
a b c de f
f
g h j
FHL1
FHL2
FHL3
M
h
i
il
k
m
n
5 Application guidelines
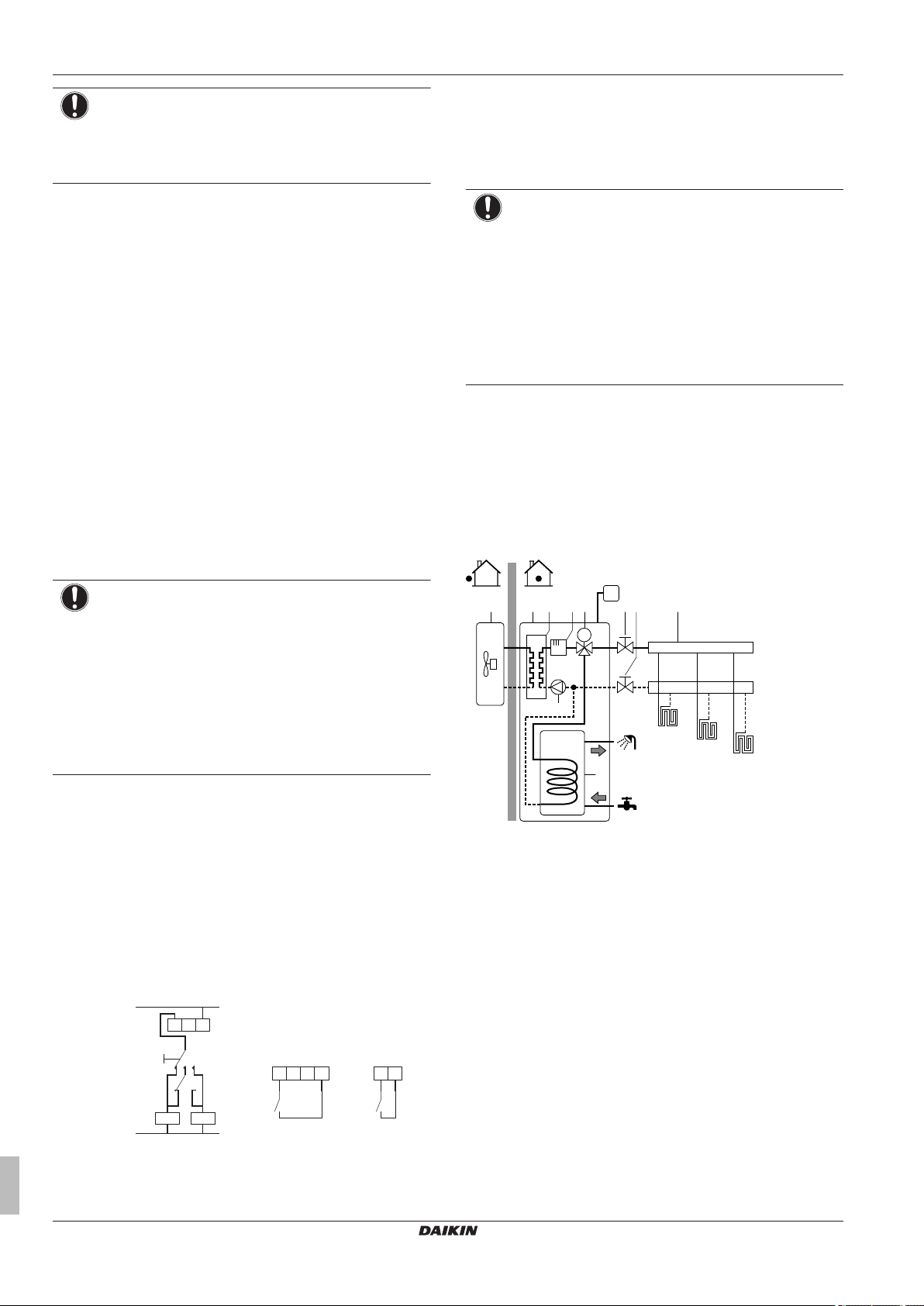
5.3 Setting up an auxiliary heat source for space heating
▪ Space heating can be done by:
▪ The indoor unit
▪ An auxiliary boiler (field supply) connected to the system
▪ When the room thermostat requests heating, the indoor unit or the
auxiliary boiler starts operating depending on the outdoor
temperature (status of the changeover to external heat source).
When the permission is given to the auxiliary boiler, the space
heating by the indoor unit is turned OFF.
▪ Bivalent operation is only possible for space heating, NOT for
domestic hot water production. Domestic hot water is always
produced by the DHW tank connected to the indoor unit.
INFORMATION
▪ During heating operation of the heat pump, the
heat pump operates to achieve the desired temperature
set via the user interface. When weather-dependent
operation is active, the water temperature is determined
automatically depending on the outdoor temperature.
▪ During heating operation of the auxiliary boiler, the
auxiliary boiler operates to achieve the desired water
temperature set via the auxiliary boiler controller.
Setup
▪ Integrate the auxiliary boiler as follows:
Only for EHBH/X
Only for EHVH/X
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
a Outdoor unit
b Indoor unit
c Heat exchanger
d Backup heater
e Pump
f Shut-off valve
g Motorised 3‑way valve (delivered with DHW tank)
h Non-return valve (field supply)
i Shut-off valve (field supply)
j Collector (field supply)
k Auxiliary boiler (field supply)
l Aquastat valve (field supply)
m DHW tank (EHBH/X: option)
n Heat exchanger coil
FHL1...3 Under floor heating
Installer reference guide
13
5 Application guidelines
L
N
H
Com
A
K2AK1A
X2M
B
TI
K2AK1A
Indoor/Auto/Boiler
1 2 3 4 X Y
Indoor
FHL1
FHL2
FHL3
M
UI
a b c d hh if
e
g
NOTICE
▪ Make sure the auxiliary boiler and its integration in the
system complies with applicable legislation.
▪ Daikin is NOT responsible for incorrect or unsafe
situations in the auxiliary boiler system.
▪ Make sure the return water to the heat pump does NOT exceed
55°C. To do so:
▪ Set the desired water temperature via the auxiliary boiler
controller to maximum 55°C.
▪ Install an aquastat valve in the return water flow of the
heat pump.
▪ Set the aquastat valve to close above 55°C and to open below
55°C.
▪ Install non-return valves.
▪ Make sure to only have one expansion vessel in the water circuit.
An expansion vessel is already premounted in the indoor unit.
▪ Install the digital I/O PCB (option EKRP1HB).
▪ Connect X1 and X2 (changeover to external heat source) on the
PCB to the auxiliary boiler thermostat.
▪ To setup the heat emitters, see "5.2 Setting up the space heating/
cooling system" on page 8.
Configuration
Via the user interface (quick wizard):
▪ Set the use of a bivalent system as external heat source.
▪ Set the bivalent temperature and hysteresis.
NOTICE
▪ Make sure the bivalent hysteresis has enough
differential to prevent frequent changeover between
indoor unit and auxiliary boiler.
▪ Because the outdoor temperature is measured by the
outdoor unit air thermistor, install the outdoor unit in the
shadow so that it is NOT influenced or turned ON/OFF
by direct sunlight.
▪ Frequent changeover may cause corrosion of the
auxiliary boiler. Contact the manufacturer of the
auxiliary boiler for more information.
K1A Auxiliary relay for activation of indoor unit (field
supply)
K2A Auxiliary relay for activation of boiler (field supply)
Indoor Indoor unit
Auto Automatic
Boiler Boiler
NOTICE
▪ Make sure the auxiliary contact has enough differential
or time delay to prevent frequent changeover between
indoor unit and auxiliary boiler.
▪ If the auxiliary contact is an outdoor temperature
thermostat, install the thermostat in the shadow so that
it is NOT influenced or turned ON/OFF by direct
sunlight.
▪ Frequent changeover may cause corrosion of the
auxiliary boiler. Contact the manufacturer of the
auxiliary boiler for more information.
5.4 Setting up the domestic hot water tank
The DHW tank can be:
▪ Integrated in the indoor unit
▪ Installed standalone as option
5.4.1 System layout – Integrated DHW tank
Only for EHVH/X.
Changeover to external heat source decided by an auxiliary
contact
▪ Only possible in external room thermostat control AND one
leaving water temperature zone (see "5.2 Setting up the space
heating/cooling system" on page 8).
▪ The auxiliary contact can be:
▪ An outdoor temperature thermostat
▪ An electricity tariff contact
▪ A manually operated contact
▪ …
▪ Setup: Connect the following field wiring:
Installer reference guide
14
BTIBoiler thermostat input
A Auxiliary contact (normal closed)
H Heating demand room thermostat (optional)
a Outdoor unit
b Indoor unit
c Heat exchanger
d Backup heater
e Pump
f Motorised 3‑way valve
g DHW tank
h Shut-off valve
i Collector (field supply)
FHL1...3 Under floor heating
UI User interface
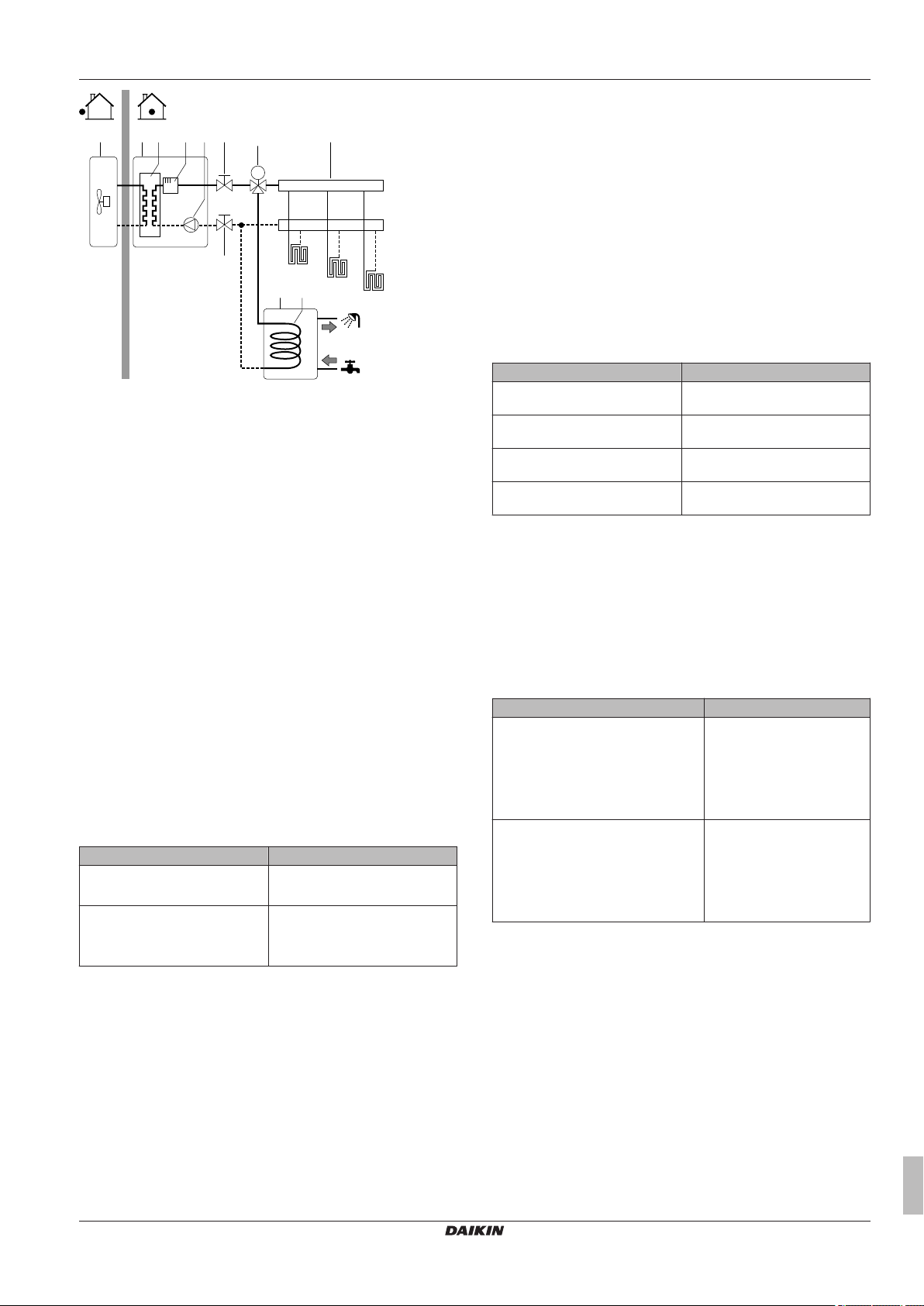
5.4.2 System layout – Standalone DHW tank
Only for EHBH/X.
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
FHL1
FHL2
FHL3
M
a b c d e hf g
f
i j
a Outdoor unit
b Indoor unit
c Heat exchanger
d Backup heater
e Pump
f Shut-off valve
g Motorised 3‑way valve
h Collector (field supply)
i DHW tank
j Heat exchanger coil
FHL1...3 Under floor heating
5.4.3 Selecting the volume and desired temperature for the DHW tank
People experience water as hot when its temperature is 40°C.
Therefore, the DHW consumption is always expressed as equivalent
hot water volume at 40°C. However, you can set the DHW tank
temperature at a higher temperature (example: 53°C), which is then
mixed with cold water (example: 15°C).
Selecting the volume and desired temperature for the DHW tank
consists of:
1 Determining the DHW consumption (equivalent hot water
volume at 40°C).
2 Determining the volume and desired temperature for the DHW
tank.
Possible DHW tank volumes
Type Possible volumes
Integrated DHW tank ▪ 180 l
Standalone DHW tank ▪ 150 l
Energy saving tips
▪ If the DHW consumption differs from day to day, you can program
a weekly schedule with different desired DHW tank temperatures
for each day.
▪ The lower the desired DHW tank temperature, the more cost
effective. By selecting a larger DHW tank, you can lower the
desired DHW tank temperature.
▪ The heat pump itself can produce domestic hot water of maximum
55°C (50°C if outdoor temperature is low). The electrical
resistance integrated in the heat pump can higher this
temperature. However, this consumes more energy. Daikin
recommends to set the desired DHW tank temperature below
55°C to avoid using the electrical resistance.
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
5 Application guidelines
▪ The higher the outdoor temperature, the better the performance of
the heat pump.
▪ If energy prices are the same during the day and the night,
Daikin recommends to heat up the DHW tank during the day.
▪ If energy prices are lower during the night, Daikin recommends
to heat up the DHW tank during the night.
▪ When the heat pump produces domestic hot water, it cannot heat
up a space. When you need domestic hot water and space
heating at the same, Daikin recommends to produce the domestic
hot water during the night when there is lower space heating
demand.
Determining the DHW consumption
Answer the following questions and calculate the DHW consumption
(equivalent hot water volume at 40°C) using the typical water
volumes:
Question Typical water volume
▪ 260 l
▪ 200 l
▪ 300 l
How many showers are needed
per day?
How many baths are needed per
day?
How much water is needed at the
kitchen sink per day?
Are there any other domestic hot
water needs?
Example: If the DHW consumption of a family (4 persons) per day is
as follows:
▪ 3 showers
▪ 1 bath
▪ 3 sink volumes
Then the DHW consumption = (3x100 l) + (1x150 l) + (3x10 l) = 480 l
Determining the volume and desired temperature for the DHW
tank
Formula Example
V1 = V2 + V2 x (T2−40) / (40−T1) If:
V2 = V1 x (40−T1) / (T2−T1) If:
V1: DHW consumption (equivalent hot water volume at 40°C)
V2: Required DHW tank volume if only heated once
T2: DHW tank temperature
T1: Cold water temperature
1 shower = 10 min x 10 l/min =
100 l
1 bath = 150 l
1 sink = 2 min x 5 l/min = 10 l
—
▪ V2 = 180 l
▪ T2 = 54°C
▪ T1 = 15°C
Then V1 = 280 l
▪ V1 = 480 l
▪ T2 = 54°C
▪ T1 = 15°C
Then V2 = 307 l
5.4.4 Setup and configuration – DHW tank
▪ For large DHW consumptions, you can heat up the DHW tank
several times during the day.
▪ To heat up the DHW tank to the desired DHW tank temperature,
you can use the following energy sources:
▪ Thermodynamic cycle of the heat pump
▪ Electrical backup heater (for integrated DHW tank)
▪ Electrical booster heater (for standalone DHW tank)
▪ Solar panels
Installer reference guide
15
5 Application guidelines
M
a
c
db
c.1
c.2
c.3
e
c.4
f
≥0.5 m
c
f
a
b
g
h
i
c
a
b
d f
e g
h
i
▪ For more information about:
▪ Optimizing the energy consumption for producing domestic hot
water, see "8 Configuration" on page 33.
▪ Connecting the electrical wiring of the standalone DHW tank to
▪ For more information about connecting the recirculation
connection:
▪ for integrated DHW tank, see "7 Installation" on page 25,
▪ for separate DHW tank, see installation manual of DHW tank.
the indoor unit, see the installation manual of the DHW tank.
▪ Connecting the water piping of the standalone DHW tank to the
indoor unit, see the installation manual of the DHW tank.
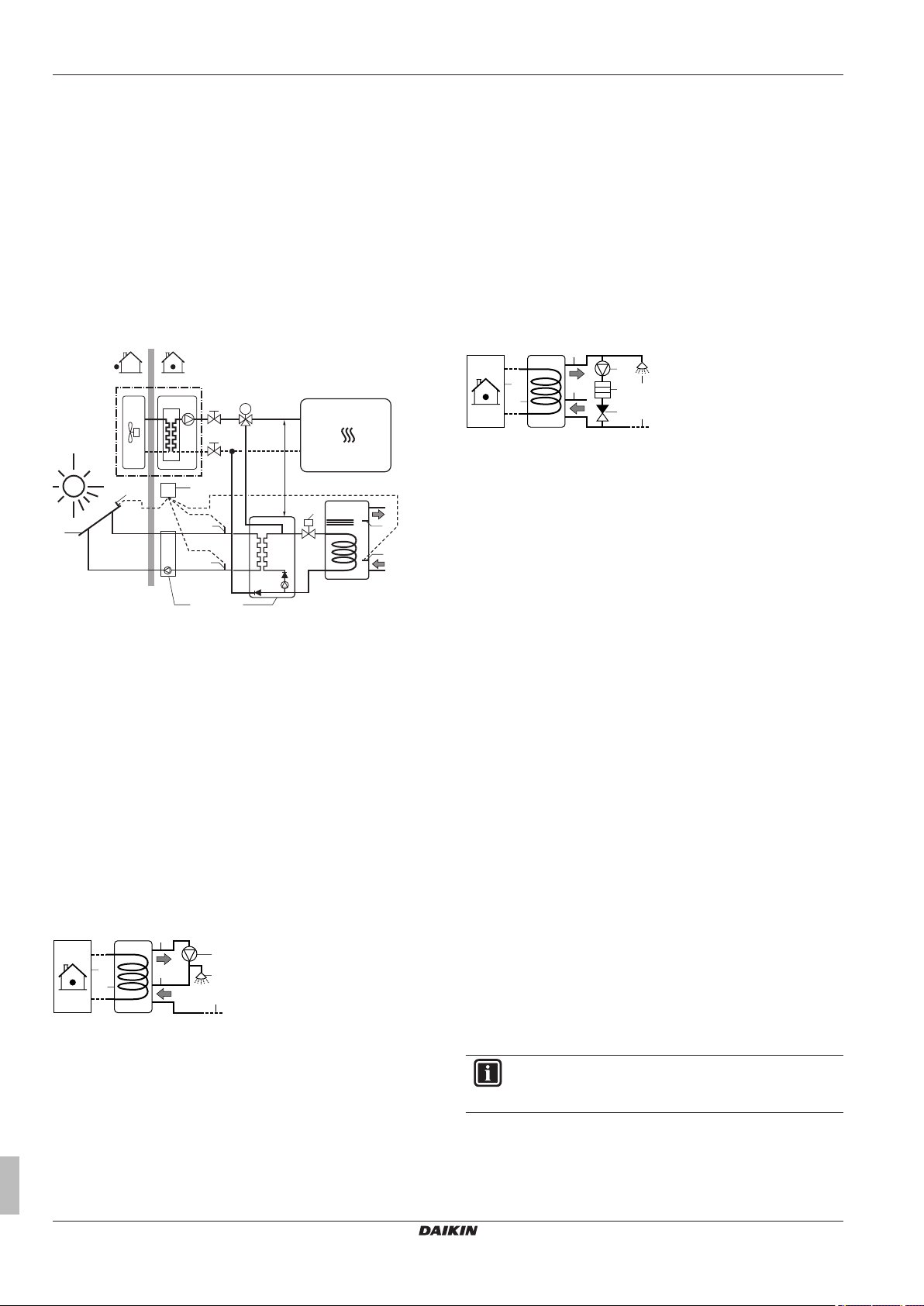
5.4.5 Combination: Standalone DHW tank + Solar panels
Configuration
▪ For more information, see "8 Configuration" on page 33.
▪ You can program a schedule to control the DHW pump via the
user interface. For more information, see the user reference
guide.
By connecting the DHW tank to solar panels, the DHW tank can be
heated by solar energy.
5.4.7 DHW pump for disinfection
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the solar
kit and addendum book for optional equipment.
Setup
a Indoor unit
b DHW tank
c DHW pump
d Heater element
e Non‑return valve
f Shower
g Cold water
h Domestic hot water OUT
i Recirculation connection
▪ The DHW pump and the installation are field supply and the
responsibility of the installer.
a Solar panels
b Solar pump station
c Solar pump station controller with temperature
sensors
c1 Tank temperature sensor
c2 Return temperature sensor to solar panels
c3 Supply temperature with flow meter from solar
▪ For the integrated DHW tank, the temperature of the DHW tank
can be set to maximum 60°C. If applicable legislation requires
higher temperature for disinfection, you can connect a DHW pump
and heater element as shown above.
▪ If applicable legislation requires disinfection of the water piping
until the tapping point, you can connect a DHW pump and heater
element (if needed) as shown above.
panels
c4 Solar panel temperature sensor
d Solar kit
e DHW temperature sensor of the unit
f Solenoid 2-way valve (only for UK). Obligatory for
Configuration
The indoor unit can control DHW pump operation. For more
information, see "8 Configuration" on page 33.
compliance to UK building regulation G3.
Heating system
Example of unit
5.4.6 DHW pump for instant hot water
5.5 Setting up the energy metering
▪ Via the user interface, you can read out the following energy data:
▪ Produced heat
▪ Consumed energy
Setup
▪ You can read out the energy data:
▪ For space heating
▪ For space cooling
▪ For domestic hot water production
▪ You can read out the energy data:
a Indoor unit
b DHW tank
c DHW pump
f Shower
g Cold water
h Domestic hot water OUT
▪ Per month
▪ Per year
INFORMATION
The calculated produced heat and consumed energy are
an estimation, the accuracy cannot be guaranteed.
i Recirculation connection
▪ By connecting a DHW pump, instant hot water can be available at
the tap.
▪ The DHW pump and the installation are field supply and the
responsibility of the installer.
Installer reference guide
16
5.5.1 Produced heat
▪ Applicable for all models.
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
b
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
c c
fed
g
A B C
a
b
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
gfe
h
A B C
c c d
a
5 Application guidelines
▪ The produced heat is calculated internally based on:
▪ The leaving and entering water temperature
▪ The flow rate
▪ The power consumption of the booster heater (if applicable) in
the domestic hot water tank
▪ Setup and configuration:
▪ No additional equipment needed.
▪ Only in case a booster heater is present in the system, measure
its capacity (resistance measurement) and set the capacity via
the user interface. Example: If you measure a booster heater
resistance of 17.1 Ω, the capacity of the heater at 230 V is
3100 W.
5.5.2 Consumed energy
You can use the following methods to determine the consumed
energy:
▪ Calculating
▪ Measuring
INFORMATION
You cannot combine calculating the consumed energy
(example: for backup heater) and measuring the
consumed energy (example: for outdoor unit). If you do so,
the energy data will be invalid.
Calculating the consumed energy
▪ Only applicable for EHBH/X04+08 and EHVH/X04+08.
▪ The consumed energy is calculated internally based on:
▪ The actual power input of the outdoor unit
▪ The set capacity of the backup heater and booster heater
▪ The voltage
▪ Setup and configuration: To get accurate energy data, measure
the capacity (resistance measurement) and set the capacity via
the user interface for:
▪ The backup heater (step 1 and step 2)
▪ The booster heater
Measuring the consumed energy
▪ Applicable for all models.
▪ Preferred method because of higher accuracy.
▪ Requires external power meters.
▪ Setup and configuration:
▪ For the specifications of each type of meter, see "14 Technical
data" on page 66.
▪ When using electrical power meters, set the number of
pulses/kWh for each power meter via the user interface.
Consumed energy data for EHVH/X16 and EHBH/X16 models
will only be available if this setting is configured.
INFORMATION
When measuring the electrical power consumption, make
sure ALL power input of the system is covered by the
electrical power meters.
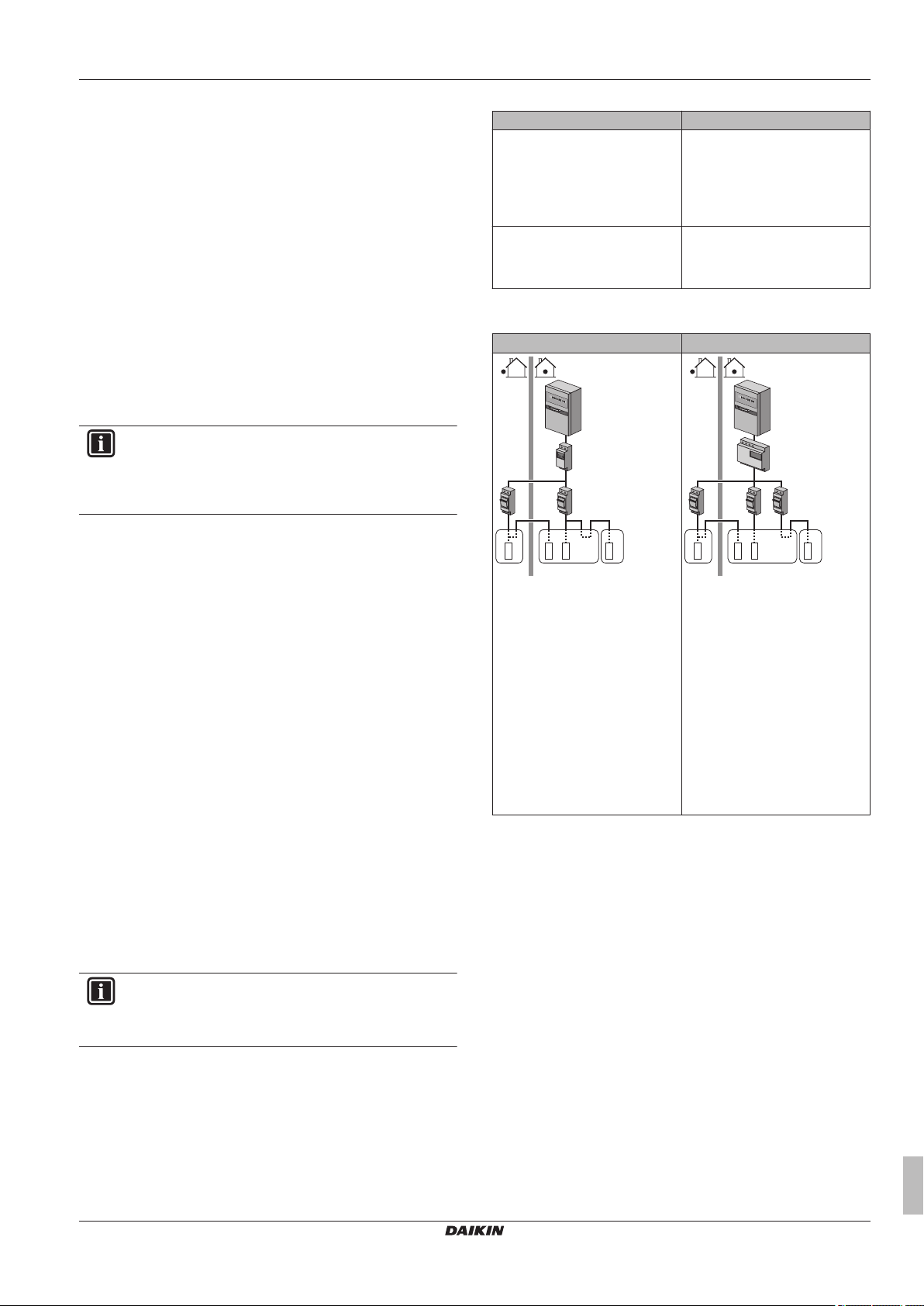
5.5.3 Normal kWh rate power supply
General rule
One power meter that covers the entire system is sufficient.
Power meter type
In case of… Use a… power meter
▪ Single-phase outdoor unit
Single-phase
▪ Backup heater supplied from a
single-phase grid (i.e. the
backup heater model is *3V or
*9W connected to a singlephase grid)
In other cases (i.e. a three-phase
Three-phase
outdoor unit and/or a *9W
backup heater model connected
to a three-phase grid)
Example
Single-phase power meter Three-phase power meter
A Outdoor unit
B Indoor unit
C DHW tank
a Electrical cabinet (L1/N)
b Power meter (L1/N)
c Fuse (L1/N)
d Outdoor unit (L1/N)
e Indoor unit (L1/N)
f Backup heater (L1/N)
g Booster heater (L1/N)
A Outdoor unit
B Indoor unit
C DHW tank
a Electrical cabinet (L1/L2/L3/N)
b Power meter (L1/L2/L3/N)
c Fuse (L1/L2/L3/N)
d Fuse (L1/N)
e Outdoor unit (L1/L2/L3/N)
f Indoor unit (L1/L2/L3/N)
g Backup heater (L1/L2/L3/N)
h Booster heater (L1/N)
Exception
▪ You can use a second power meter if:
▪ The power range of one meter is insufficient.
▪ The electrical meter cannot easily be installed in the electrical
cabinet.
▪ 230 V and 400 V three-phase grids are combined (very
uncommon), because of technical limitations of power meters.
▪ Connection and setup:
▪ Connect the second power meter to X5M/9 and X5M/10.
▪ In the software the power consumption data of both meters is
added so you do NOT have to set which meter covers which
power consumption. You only need to set the number of pulses
of each power meter.
▪ See "5.5.4 Preferential kWh rate power supply" on page 17 for
an example with two power meters.
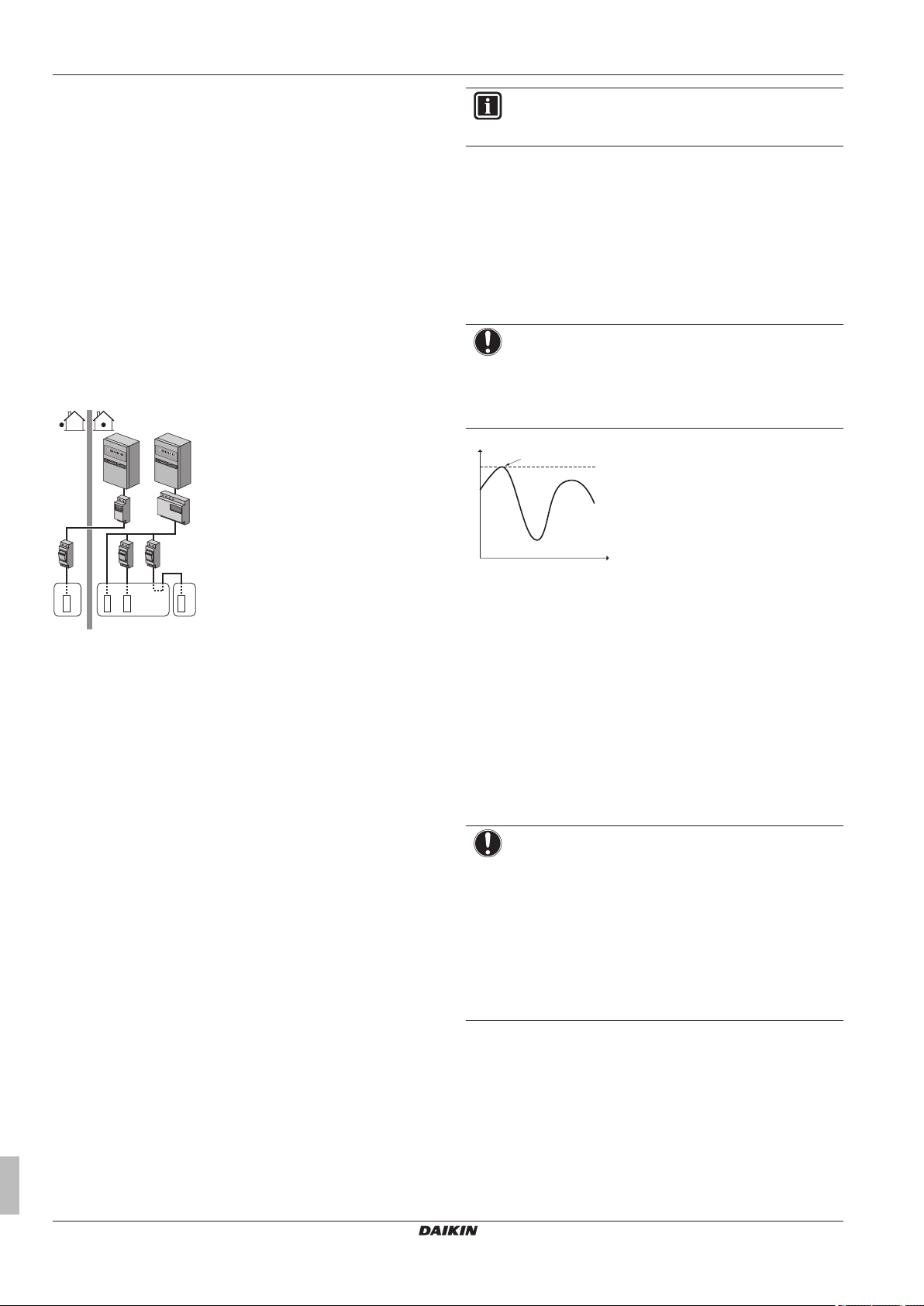
5.5.4 Preferential kWh rate power supply
Setup
Connect the power meter to X5M/7 and X5M/8.
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
General rule
▪ Power meter 1: Measures the outdoor unit.
Installer reference guide
17
5 Application guidelines
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
e ef
ihg
j
A B C
ba
d
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
c
P
i
t
DI
a
b
▪ Power meter 2: Measures the rest (i.e. indoor unit, backup heater
and optional booster heater).
Setup
▪ Connect power meter 1 to X5M/7 and X5M/8.
▪ Connect power meter 2 to X5M/9 and X5M/10.
Power meter types
▪ Power meter 1: Single- or three-phase power meter according to
the power supply of the outdoor unit.
▪ Power meter 2:
▪ In case of a single-phase backup heater configuration, use a
single-phase power meter.
▪ In other cases, use a three-phase power meter.
Example
Single-phase outdoor unit with a three-phase backup heater:
INFORMATION
Power consumption control CANNOT be used in
applications with booster heater.
5.6.1 Permanent power limitation
Permanent power limitation is useful to assure a maximum power or
current input of the system. In some countries, legislation limits the
maximum power consumption for space heating and DHW
production. Example: The maximum power input depends on the
area of the house and an annual fee has to be paid to the electrical
company according to the size of the installed field fuse. By
permanently limiting the maximum power or current of the system,
you can install smaller field fuses.
NOTICE
When the current control is intended to reduce the installed
field fuse sizes, the field fuse will trip to protect the field
wires in case of overcurrents caused by the unit. Make
sure the selection of the field fuse complies with applicable
legislation.
5.6 Setting up the power consumption control
▪ The power consumption control:
▪ Is only applicable for EHBH/X04+08 and EHVH/X04+08.
▪ Allows you to limit the power consumption of the entire system
(sum of outdoor unit, indoor unit, backup heater and optional
booster heater).
▪ Configuration: Set the power limitation level and how it has to
be achieved via the user interface.
▪ The power limitation level can be expressed as:
▪ Maximum running current (in A)
▪ Maximum power input (in kW)
▪ The power limitation level can be activated:
▪ Permanently
▪ By digital inputs
Installer reference guide
18
A Outdoor unit
B Indoor unit
C DHW tank
a Electrical cabinet (L1/N): Preferential kWh rate power
supply
b Electrical cabinet (L1/L2/L3/N): Normal kWh rate
power supply
c Power meter (L1/N)
d Power meter (L1/L2/L3/N)
e Fuse (L1/N)
f Fuse (L1/L2/L3/N)
g Outdoor unit (L1/N)
h Indoor unit (L1/L2/L3/N)
i Backup heater (L1/L2/L3/N)
j Booster heater (L1/N)
PiPower input
t Time
DI Digital input (power limitation level)
a Power limitation active
b Actual power input
Setup and configuration
▪ No additional equipment needed.
▪ Set the power consumption control settings in [A.6.3.1] via the
user interface (for the description of all settings, see
"8 Configuration" on page 33):
▪ Select full time limitation mode
▪ Select the type of limitation (power in kW or current in A)
▪ Set the desired power limitation level
NOTICE
Mind the following guidelines when selecting the desired
power limitation level:
▪ Set a minimum power consumption of ±3.6 kW to
guarantee defrost operation. Otherwise, if defrosting is
interrupted several times, the heat exchanger will
freeze up.
▪ Set a minimum power consumption of ±3 kW to
guarantee space heating and DHW production by
allowing at least one electrical heater (backup heater
step 1 or booster heater).
5.6.2 Power limitation activated by digital inputs
Power limitation is also useful in combination with an energy
management system.
The power or current of the entire Daikin system is limited
dynamically by digital inputs (maximum four steps). Each power
limitation level is set via the user interface by limiting one of the
following:
▪ Current (in A)
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
a
b
c
A B C
D
1
2
3
4
5
A8P
P
i
t
DI1
DI3
DI4
a
b
P
h
C
e
a
b
c
d
e
A B C
5 Application guidelines
▪ Power input (in kW)
The energy management system (field supply) decides the activation
of a certain power limitation level. Example: To limit the maximum
power of the entire house (lighting, domestic appliances, space
heating…).
A Outdoor unit
B Indoor unit
C DHW tank
D Energy management system
a Power limitation activation (4 digital inputs)
b Backup heater
c Booster heater
If… has priority Then set the heater priority
via the user interface to…
Domestic hot water production Booster heater.
Result: The backup heater will
be turned OFF first.
Space heating Backup heater.
Result: The booster heater will
be turned OFF first.
2 Turns OFF all electrical heaters.
3 Limits the outdoor unit.
4 Turns OFF the outdoor unit.
Example
If the configuration is as follows:
▪ Power limitation level does NOT allow operation of both booster
heater and backup heater (step 1 and step 2).
▪ Heater priority = Booster heater.
Then power consumption is limited as follows:
Setup
▪ Demand PCB (option EKRP1AHTA) needed.
▪ Maximum four digital inputs are used to activate the
▪ For the specification and the connection of the digital inputs, see
Configuration
Set the power consumption control settings in [A.6.3.1] via the user
interface (for the description of all settings, see "8 Configuration" on
page 33):
▪ Select activation by digital inputs.
▪ Select the type of limitation (power in kW or current in A).
▪ Set the desired power limitation level corresponding to each digital
5.6.3 Power limitation process
The outdoor unit has better efficiency than the electrical heaters.
Therefore, the electrical heaters are limited and turned OFF first.
The system limits power consumption in the following order:
1 Limits certain electrical heaters.
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
PiPower input
t Time
DI Digital inputs (power limitation levels)
a Power limitation active
b Actual power input
corresponding power limitation level:
▪ DI1 = weakest limitation (highest energy consumption)
▪ DI4 = strongest limitation (lowest energy consumption)
"14.5 Wiring diagram – components: Indoor unit" on page 70.
input.
INFORMATION
In case more than 1 digital input is closed (at the same
time), the digital input priority is fixed: DI4 priority>…>DI1.
PhProduced heat
CeConsumed energy
A Outdoor unit
B Booster heater
C Backup heater
a Limited outdoor unit operation
b Full outdoor unit operation
c Booster heater turned ON
d Backup heater step 1 turned ON
e Backup heater step 2 turned ON
5.7 Setting up an external temperature sensor
You can connect one external temperature sensor. It can measure
the indoor or outdoor ambient temperature. Daikin recommends to
use an external temperature sensor in the following cases:
Indoor ambient temperature
▪ In room thermostat control, the user interface is used as room
thermostat and it measures the indoor ambient temperature.
Therefore, the user interface must be installed on a location:
▪ Where the average temperature in the room can be detected
▪ That is NOT exposed to direct sunlight
▪ That is NOT near a heat source
▪ That is NOT affected by outside air or air draught because of,
for example, door opening/closing
▪ If this is NOT possible, Daikin recommends to connect a remote
indoor sensor (option KRCS01-1).
▪ Setup: For installation instructions, see the installation manual of
the remote indoor sensor.
▪ Configuration: Select room sensor [A.2.2.B].
Installer reference guide
19
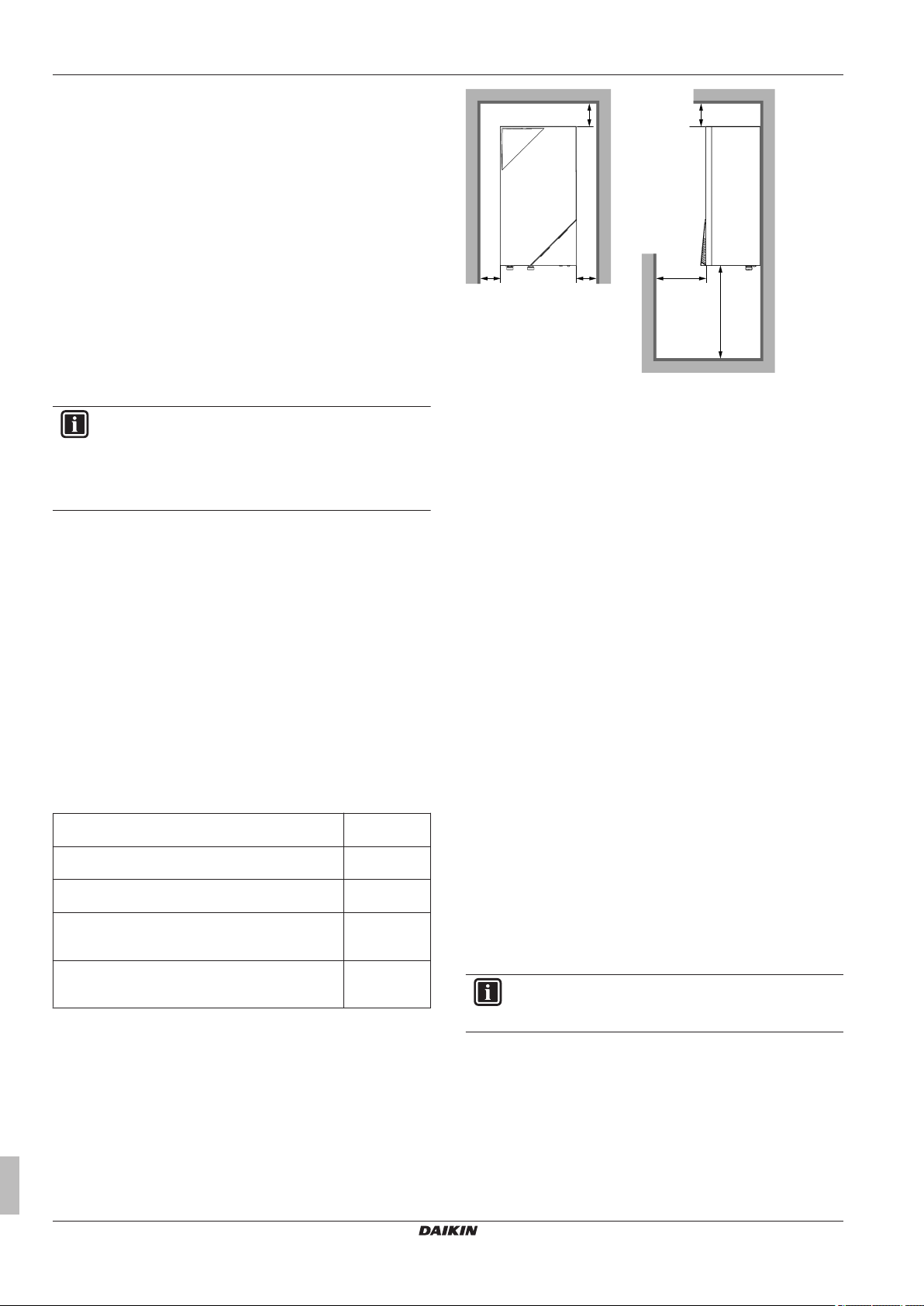
6 Preparation
≥1150
200
200
10 10 500
(mm)
Outdoor ambient temperature
▪ In the outdoor unit, the outdoor ambient temperature is measured.
Therefore, the outdoor unit must be installed on a location:
▪ At the north side of the house or at the side of the house where
the most heat emitters are located
▪ That is NOT exposed to direct sunlight
▪ If this is NOT possible, Daikin recommends to connect a remote
outdoor sensor (option EKRSCA1).
▪ Setup: For installation instructions, see the installation manual of
the remote indoor sensor.
▪ Configuration: Select outdoor sensor [A.2.2.B].
▪ During suspend (see "8 Configuration" on page 33), the outdoor
unit is turned down to reduce the standby energy losses. As a
result, the outdoor ambient temperature is NOT read out.
▪ If the desired leaving water temperature is weather dependent, the
full time outdoor temperature measurement is important. This is
another reason to install the optional outdoor ambient temperature
sensor.
INFORMATION
The external outdoor ambient sensor data (either averaged
or instantaneous) is used in the weather-dependent control
curves and in the automatic heating/cooling changeover
logic. To protect the outdoor unit, the internal sensor of the
outdoor unit is always used.
6 Preparation
6.1 Preparing installation site
Do NOT install the unit in places often used as work place. In case
of construction works (e.g. grinding works) where a lot of dust is
created, the unit must be covered.
Choose the installation location with sufficient place for carrying the
unit in and out of the site.
6.1.1 Installation site requirements of the indoor unit
▪ Mind the measurement guidelines:
Maximum refrigerant piping length between indoor
unit and outdoor unit
Minimum refrigerant piping length between indoor
unit and outdoor unit
Maximum height difference between indoor unit and
outdoor unit
Maximum distance between the 3‑way valve and
the indoor unit (for installations with domestic hot
water tank)
Maximum distance between the domestic hot water
tank and the indoor unit (for installations with
domestic hot water tank)
(a) Check the outdoor unit installation manual.
(b) When <5 m, you need to recharge the outdoor unit (check the outdoor
unit installation manual).
▪ Mind the following spacing installation guidelines:
75 m
3 m
30 m
3 m
10 m
(a)
(b)
Do NOT install the unit in places such as:
▪ Where there is mist of mineral oil, oil spray or vapour.
Plastic parts may deteriorate, and cause them to fall out or water
to leak.
▪ Do NOT install the unit in sound sensitive areas (e.g. near a
bedroom and the like), so that the operation noise will cause no
trouble.
Note: If the sound is measured under actual installation
conditions, the measured value will be higher than the sound
pressure level mentioned in "14.8 Sound spectrum" on page 81
due to environmental noise and sound reflections.
▪ The foundation must be strong enough to bear the weight of the
unit. Take the weight of the unit with a domestic hot water tank full
of water into account.
Make sure, in the event of a water leak, water cannot cause any
damage to the installation space and surroundings.
▪ In places with high humidity (max. RH=85%), for example a
bathroom.
▪ In places where frost is possible. Ambient temperature around the
indoor unit should be >5°C.
▪ The indoor unit is designed for indoor installation only and for
ambient temperatures ranging 5~35°C in cooling mode and
5~30°C in heating mode.
6.2 Preparing water piping
6.2.1 Water circuit requirements
▪ Use the indoor unit only in a closed water system.
Using the system in an open water system will lead to excessive
corrosion.
▪ The maximum water pressure is 4 bar.
Provide adequate safeguards in the water circuit to ensure that
the maximum pressure is NOT exceeded.
▪ All installed piping and piping accessories (valve, connections,…)
must withstand the following temperatures:
INFORMATION
The following illustration is an example and may NOT
match your system layout.
Installer reference guide
20
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
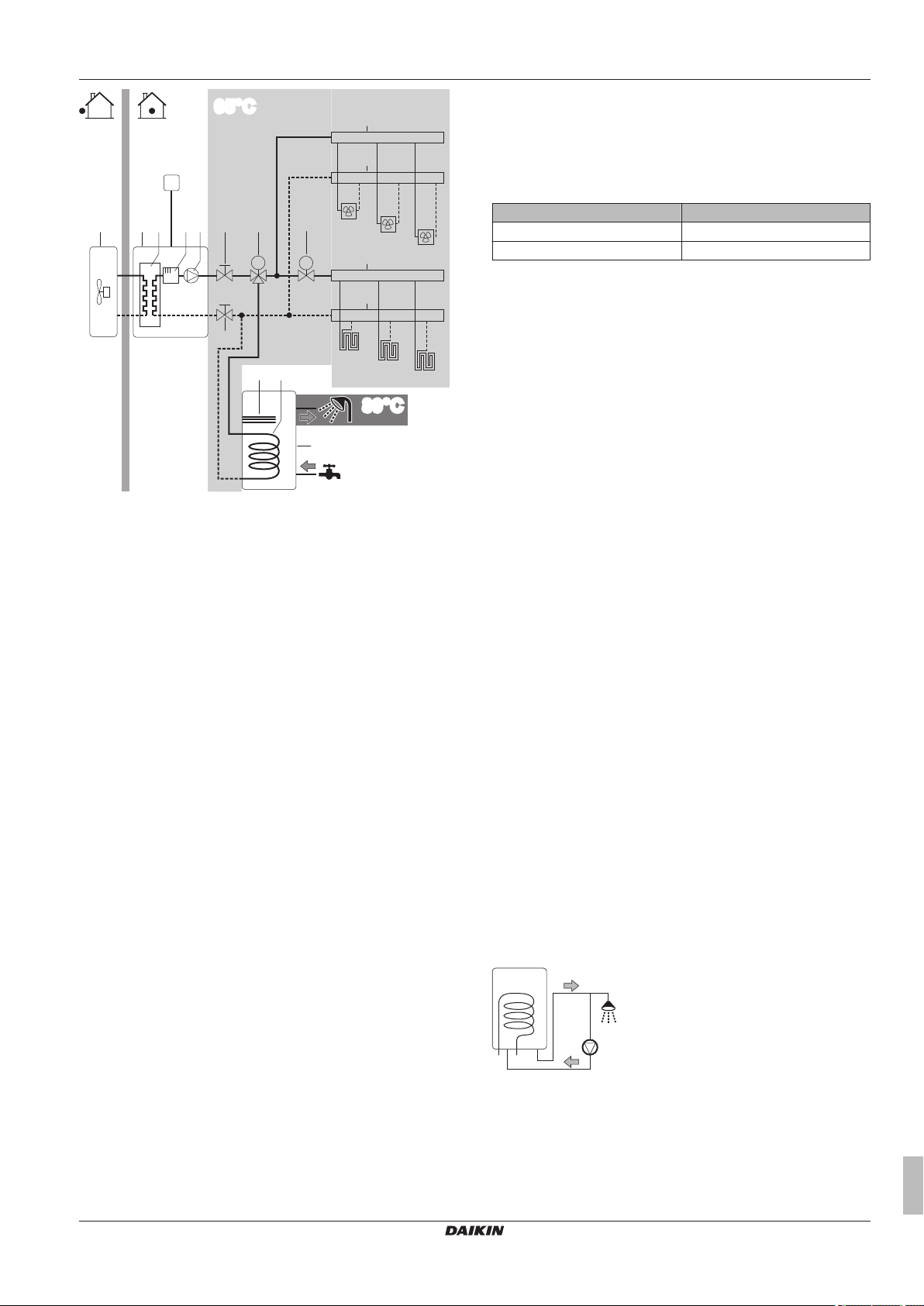
M
HPC1
HPC2
HPC3
i
M
FHL1
FHL2
FHL3
j
l k
fd ecba
f
g
h
i
i
i
T
65°C
89°C
c
d
a b
a Outdoor unit
b Indoor unit
c Heat exchanger
d Backup heater
e Pump
f Shut-off valve
g Motorised 3-way valve (supplied with the domestic
hot water tank)
h Motorised 2-way valve (field supply)
i Collector
j Domestic hot water tank
k Heat exchanger coil
l Booster heater
HPC1...3 Heat pump convector (optional)
FHL1...3 Floor heating loop
T Room thermostat (optional)
▪ Make all water piping connections in accordance with the
applicable legislation and the outlook diagram that is delivered
with the unit, respecting the water inlet and outlet.
▪ Do NOT use excessive force when connecting the piping.
Deformation of the piping can cause malfunctioning of the unit.
▪ Provide drain taps at all low points of the system in order to allow
complete drainage of the water circuit.
▪ Provide a proper drain for the pressure relief valve to avoid water
coming into contact with electrical parts.
▪ Provide air vents at all high points of the system, which must also
▪ Only use materials that are compatible with water used in the
▪ Check that all components in the field piping can withstand the
▪ When using non-brass metallic piping, insulate the brass and non-
▪ Never use Zn-coated parts in the water circuit. Because the unit's
▪ Only use appropriate tooling to handle brass, which is a soft
be easily accessible for servicing. An automatic air purge is
provided in the indoor unit. Check that the air purge is NOT
tightened too much, so that automatic release of air in the water
circuit is possible.
system and with the materials used in the indoor unit.
water pressure and water temperature.
brass properly so that they do NOT make contact with each other.
This to prevent galvanic corrosion.
internal water circuit uses copper piping, excessive corrosion may
occur.
material. If NOT, pipes will get damaged.
6 Preparation
▪ Select the water piping diameter in relation to the required water
flow and the available external static pressure of the pump. See
"14 Technical data" on page 66 for the external static pressure
curves of the indoor unit.
▪ You can find the minimum required water flow for the indoor unit
operation in the following table. When the water flow is lower, flow
error 7H will be displayed and the indoor unit will be stopped.
Model Minimum water flow (l/min)
04 5
08+16 11
▪ When using a 3-way valve in the water circuit make sure that the
domestic hot water circuit and the floor heating circuit is fully
separated.
▪ When using a 2-way valve or a 3-way valve in the water circuit,
the maximum change-over time of the valve must be 60 seconds.
▪ It is strongly recommended to install an additional filter on the
heating water circuit. Especially to remove metallic particles from
the filed heating piping, it is advised to use a magnetic or cyclone
filter, which can remove small particles. Small particles may
damage the unit and will NOT be removed by the standard filter of
the heat pump system.
▪ If air, moisture or dust gets into the water circuit, problems may
occur. To prevent this:
▪ Only use clean pipes
▪ Hold the pipe end downwards when removing burrs.
▪ Cover the pipe end when inserting it through a wall, to prevent
dust and/or particles entering the pipe.
▪ Use a decent thread sealant to seal connections.
▪ For safety reasons, it is NOT allowed to add any kind of glycol to
the water circuit.
▪ To avoid stagnation of water, it is important that the storage
capacity of the domestic hot water tank meets the daily
consumption of domestic hot water.
In cases where during longer periods of time there is no
consumption of hot water, the equipment must be flushed with
fresh water before usage.
The disinfection function provided on the equipment is specified in
the operation manual of the indoor unit.
▪ It is recommended to avoid long runs of piping between the
domestic hot water tank and the hot water end point (shower,
bath,…) and to avoid dead ends.
▪ The installation must be in compliance with the applicable
legislation and may require additional hygienic installation
measures.
▪ In accordance with the applicable legislation, it may be necessary
to install thermostatic mixing valves.
▪ Immediately after installation, the domestic hot water tank must be
flushed with fresh water. This procedure must be repeated at least
once a day the first 5 consecutive days after installation.
▪ In accordance with the applicable legislation, it may be required to
connect a recirculation pump in between the hot water end point
and the recirculation connection of the domestic hot water tank.
a Recirculation connection
b Hot water connection
c Shower
d Recirculation pump
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
Installer reference guide
21
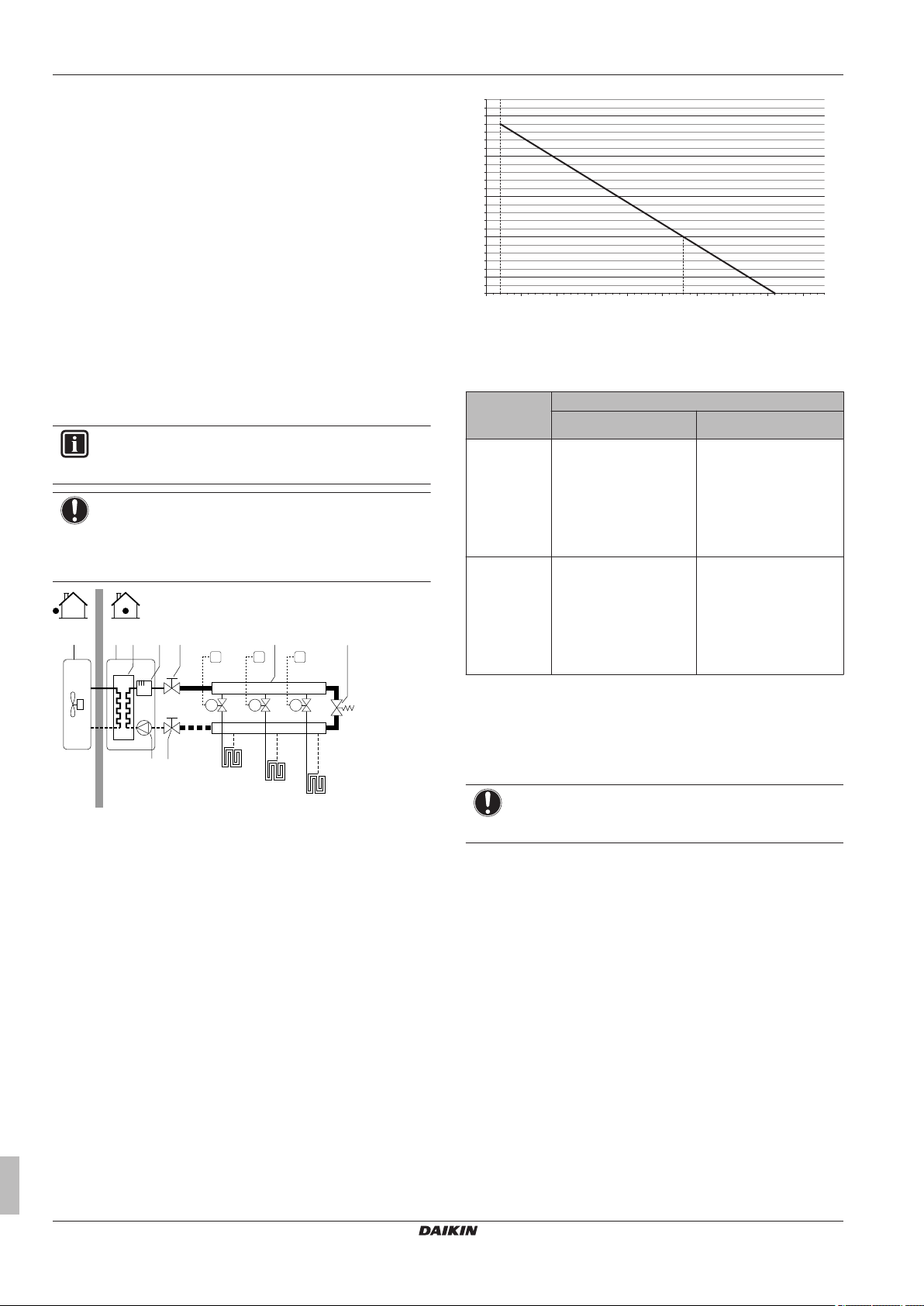
6 Preparation
FHL1
FHL2
FHL3
M1
T1
M2T2M3
T3
fdcba
f
g h
e
0.3
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
10050
0
20
150 200 250 300 350 400 450
a
b
6.2.2 Formula to calculate the expansion vessel pre-pressure
The pre-pressure (Pg) of the vessel depends on the installation
height difference (H):
Pg=0.3+(H/10) (bar)
6.2.3 To check the water volume
The indoor unit has an expansion vessel of 10 litre with a factory set
pre-pressure of 1 bar.
To make sure that the unit operates properly:
▪ You must check the minimum and maximum water volume.
▪ You might need to adjust the pre-pressure of the expansion
vessel.
Minimum water volume
Check that the total water volume in the installation is minimum
20 liter, the internal water volume of the indoor unit NOT included.
INFORMATION
In critical processes, or in rooms with a high heat load,
extra water might be required.
NOTICE
When circulation in each space heating loop is controlled
by remotely controlled valves, it is important that the
minimum water volume is guaranteed, even if all of the
valves are closed.
a Pre-pressure (bar)
b Maximum water volume (l)
Example: Maximum water volume and expansion vessel prepressure
Installation
height
difference
(a)
≤280 l >280 l
≤7 m No pre-pressure
adjustment is required.
Water volume
Do the following:
▪ Decrease the pre-
pressure.
▪ Check if the water
volume does NOT
exceed the maximum
allowed water volume.
>7 m Do the following:
▪ Increase the pre-
pressure.
The expansion vessel of
the indoor unit is too
small for the installation.
▪ Check if the water
volume does NOT
exceed the maximum
allowed water volume.
(a) This is the height difference (m) between the highest point of the
water circuit and the indoor unit. If the indoor unit is at the highest
point of the installation, the installation height is 0 m.
a Outdoor unit
b Indoor unit
c Heat exchanger
d Backup heater
e Pump
f Shut-off valve
g Collector (field supply)
h By-pass valve (field supply)
FHL1...3 Floor heating loop (field supply)
T1...3 Individual room thermostat (optional)
M1...3 Individual motorised valve to control loop FHL1...3
(field supply)
Maximum water volume
Use the following graph to determine the maximum water volume for
the calculated pre-pressure.
6.2.4 Changing the pre-pressure of the expansion vessel
NOTICE
Only a licensed installer may adjust the pre-pressure of the
expansion vessel.
When changing the default pre-pressure of the expansion vessel
(1 bar) is required, take following guidelines into account:
▪ Only use dry nitrogen to set the expansion vessel pre-pressure.
▪ Inappropriate setting of the expansion vessel pre-pressure will
lead to malfunction of the system.
Changing the pre-pressure of the expansion vessel should be done
by releasing or increasing nitrogen pressure through the schräder
valve of the expansion vessel.
Installer reference guide
22
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11

a
WARNING
▪ All wiring must be performed by an authorized
electrician and must comply with the applicable
legislation.
▪ Make electrical connections to the fixed wiring.
▪ All components procured on the site and all electrical
construction must comply with the applicable
legislation.
WARNING
The backup heater should have a dedicated power supply.
6 Preparation
a Schräder valve
6.2.5 To check the water volume: Examples
Example 1
The indoor unit is installed 5 m below the highest point in the water
circuit. The total water volume in the water circuit is 100 l.
No actions or adjustments are required.
Example 2
The indoor unit is installed at the highest point in the water circuit.
The total water volume in the water circuit is 350 l.
Actions:
▪ Because the total water volume (350 l) is more than the default
water volume (280 l), the pre-pressure must be decreased.
▪ The required pre-pressure is:
Pg = (0.3+(H/10)) bar = (0.3+(0/10)) bar=0.3 bar.
▪ The corresponding maximum water volume at 0.3 bar is 410 l.
(See the graph in the chapter above).
▪ Because 350 l is lower than 410 l, the expansion vessel is
appropriate for the installation.
6.3 Preparing electrical wiring
WARNING
Always use multicore cable for power supply cables.
6.3.2 About preferential kWh rate power supply
Electricity companies throughout the world work hard to provide
reliable electric service at competitive prices and are often
authorized to bill clients at benefit rates. E.g. time-of-use rates,
seasonal rates, Wärmepumpentarif in Germany and Austria, ...
This equipment allows for connection to such preferential kWh rate
power supply delivery systems.
Consult with the electricity company acting as provider at the site
where this equipment is to be installed to know whether it is
appropriate to connect the equipment in one of the preferential kWh
rate power supply delivery systems available, if any.
When the equipment is connected to such preferential kWh rate
power supply, the electricity company is allowed to:
▪ interrupt power supply to the equipment for certain periods of time;
▪ demand that the equipment only consumes a limited amount of
electricity during certain periods of time.
The indoor unit is designed to receive an input signal by which the
unit switches into forced off mode. At that moment, the outdoor unit
compressor will not operate.
Whether the power supply is interrupted or not, the wiring to the unit
is different.
6.3.1 About preparing electrical wiring
WARNING
▪ If the power supply has a missing or wrong N-phase,
equipment will break down.
▪ Establish proper earthing. Do NOT earth the unit to a
utility pipe, surge absorber, or telephone earth.
Incomplete earthing may cause electrical shock.
▪ Install the required fuses or circuit breakers.
▪ Secure the electrical wiring with cable ties so that the
cables do NOT come in contact with the piping or sharp
edges, particularly on the high-pressure side
▪ Do NOT use taped wires, stranded conductor wires,
extension cords, or connections from a star system.
They can cause overheating, electrical shock or fire.
▪ Do NOT install a phase advancing capacitor, because
this unit is equipped with an inverter. A phase
advancing capacitor will reduce performance and may
cause accidents.
6.3.3 Overview of electrical connections except external actuators
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
Installer reference guide
23
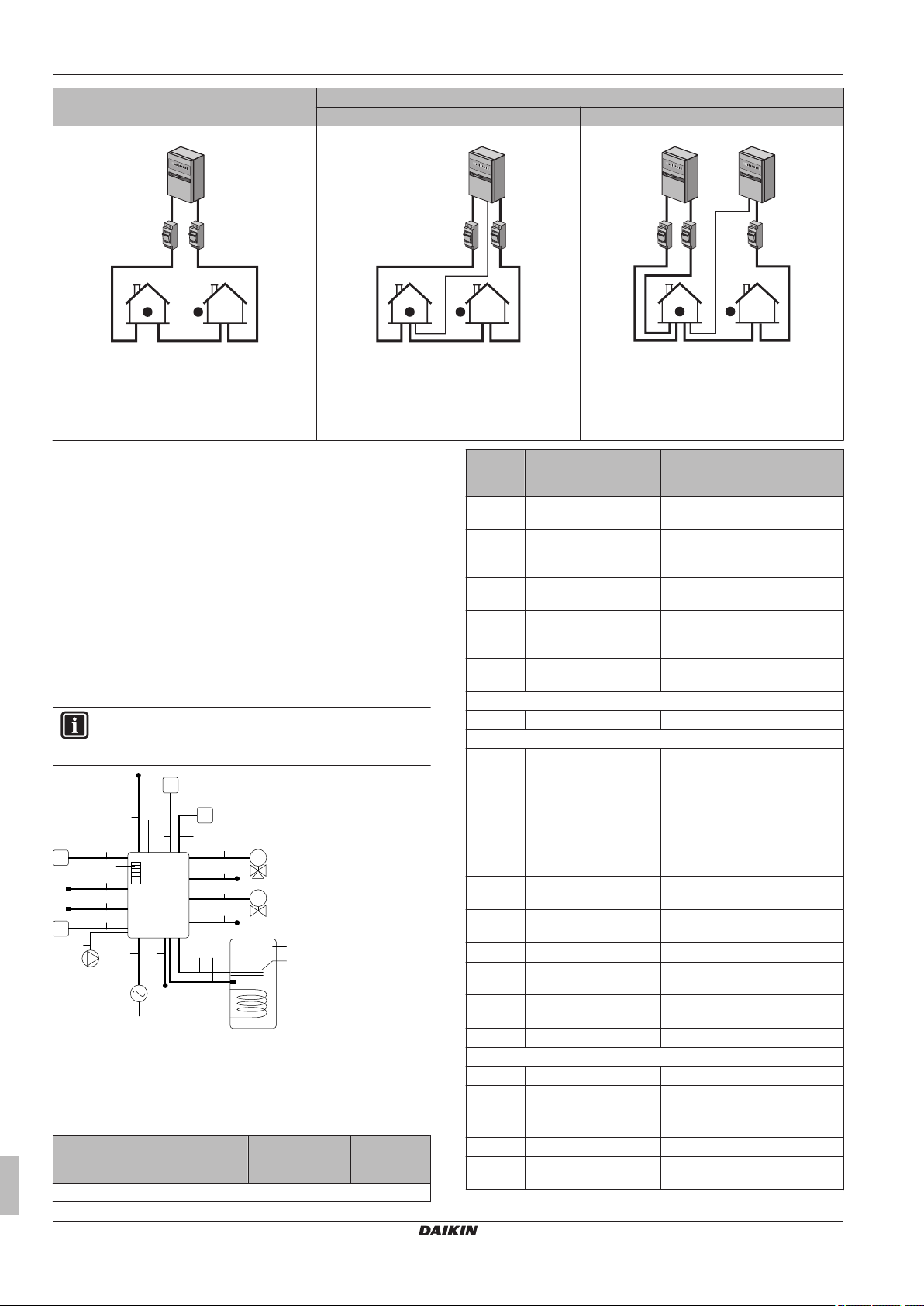
6 Preparation
1
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
2
a
3
1
4
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
2
b
3
5 3
a
b
14
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
2
M
M
6
7
c
16
21
d
e
8 10
a
9
19
12
14
b
20
15
13
14
17
18
Normal power supply Preferential kWh rate power supply
Power supply is NOT interrupted Power supply is interrupted
During preferential kWh rate power supply
activation, power supply is NOT interrupted.
The outdoor unit is turned off by the control.
Remark: The electricity company must always
allow the power consumption of the indoor
unit.
a Normal power supply
b Preferential kWh rate power supply
1 Power supply for outdoor unit
2 Power supply and interconnection cable to indoor
unit
3 Power supply for backup heater
4 Preferential kWh rate power supply (voltage free
contact)
5 Normal kWh rate power supply (to power the indoor
unit PCB in the event of power supply interruption of
the preferential kWh rate power supply)
6.3.4 Overview of electrical connections for external and internal actuators
The following illustration shows the required field wiring.
INFORMATION
The following illustration is an example and may NOT
match your system layout.
a Single power supply for outdoor unit, backup heater
and booster heater
b Backup heater
c Indoor unit
Item Description Wires Maximum
Outdoor unit and indoor unit power supply
d Domestic hot water tank
e Booster heater
running
current
During preferential kWh rate power supply
activation, power supply is interrupted
immediately or after some time by the
electricity company. In this case, the indoor
unit must be powered by a separate normal
power supply.
Item Description Wires Maximum
running
current
1 Power supply for
outdoor unit
2 Power supply and
2+GND or
3+GND
3
(a)
(c)
interconnection cable to
indoor unit
3 Power supply for
See table below. —
backup heater
4 Preferential kWh rate
2
(e)
power supply (voltage
free contact)
5 Normal kWh rate power
2 6.3 A
supply
User interface
6 User interface 2
(f)
Optional equipment
7 3‑way valve 3 100 mA
8 Power supply for
4+GND
(c)
booster heater and
thermal protection
(from indoor unit)
9 Power supply for
2+GND 13 A
booster heater (to
indoor unit)
10 Domestic hot water
2
(d)
tank thermistor
11 Power supply for
2
(b)
bottom plate heater
12 Room thermostat 3 or 4 100 mA
13 Outdoor ambient
2
(b)
temperature sensor
14 Indoor ambient
2
(b)
temperature sensor
15 Heat pump convector 4 100 mA
Field supplied components
16 Shut-off valve 2 100 mA
17 Electricity meter 2 (per meter)
18 Domestic hot water
2
(b)
(b)
pump
19 Alarm output 2
20 Changeover to external
2
(b)
(b)
heat source control
(b)
(b)
(b)
(b)
Installer reference guide
24
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
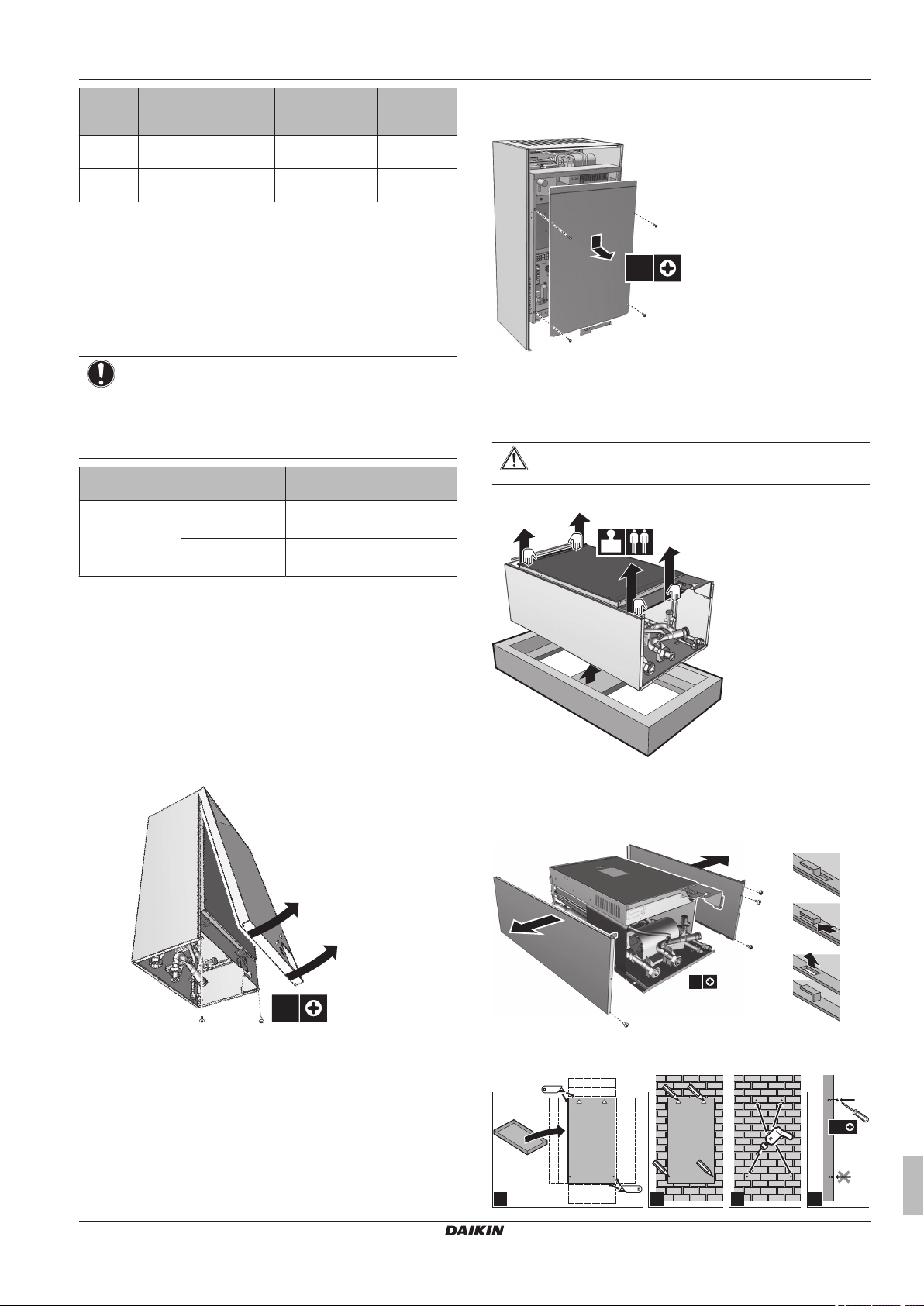
2x
4x
60kg
1
4x
1
2
3
3
2x
21 3 4
7 Installation
Item Description Wires Maximum
running
current
21 Space cool/heat
2
(b)
operation control
22 Power consumption
digital inputs
(a) Refer to name plate on outdoor unit.
(b) Minimum cable section 0.75 mm².
(c) Cable section 2.5 mm².
(d) The thermistor and connection wire (12 m) are delivered with the
domestic hot water tank.
(e) Cable section 0.75 mm² till 1.25 mm²; maximum length: 50 m.
Voltage-free contact shall ensure the minimum applicable load of
15 V DC, 10 mA.
(f) Cable section 0.75 mm² till 1.25 mm²; maximum length: 500 m.
Applicable for both single user interface and dual use interface
connection.
2 (per input
signal)
(b)
NOTICE
More technical specifications of the different connections
are indicated on:
▪ Wiring diagram in the switch box of the unit
▪ "14.5 Wiring diagram" on page 70
Backup heater
type
Power supply Required number of
conductors
*3V 1x 230 V 2+GND
*9W 1x 230 V 2+GND + 2 bridges
3x 230 V 3+GND + 1 bridge
3x 400 V 4+GND
7.1.2 To open the switch box cover of the indoor unit
7.2 Mounting the indoor unit
7.2.1 To install the indoor unit
CAUTION
Do NOT grasp the piping to lift the indoor unit.
1 Lift the unit from the package.
7 Installation
7.1 Opening the units
7.1.1 To open the indoor unit
1 Loosen and remove the 2 screws that fix the front panel.
2 Tilt the front panel towards you and remove the front panel.
2 Remove the screws and sound plate at the bottom of the
package.
3 Remove the 4 screws from the bottom of the unit. Unhook and
remove the side plates.
4 Put the installation pattern (see packing) on the wall and follow
the steps as shown below.
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
Installer reference guide
25

7 Installation
1
2
21
2x
3
2x
1
2
1
2
2
2
3
4x
ab
5 Lift the unit.
6 Tilt the top of the unit against the wall at the position of the 2
inserted screws.
7 Hook the unit against the wall.
7.2.2 To install the drain pan kit
If a drain pan kit (EKHBDPCA2) is required, install it before
connecting the refrigerant and water pipes and the electrical wiring.
To install, see the installation manual of the drain pan kit.
7.3 Connecting the water piping
8 Assemble the unit.
7.3.1 To connect the water piping
NOTICE
Do NOT use excessive force when connecting the piping.
Deformation of the piping can cause malfunctioning of the
unit.
To facilitate service and maintenance, 2 shut-off valves are provided.
Mount the valves on the water inlet and on the water outlet. Mind
their the position. Orientation of the integrated drain valves is
important for servicing.
1 Install the shut-off valves on the water pipes.
a Water inlet
b Water outlet
NOTICE
To avoid damage to the surroundings in case of water
leakage, it is recommended to close the cold water inlet
stop valves during periods of absence.
2 Screw the indoor unit nuts on the shut-off valves.
3 Connect the field piping on the shut-off valves
4 In case of connection with the optional domestic hot water tank,
see the installation manual of the domestic hot water tank.
Installer reference guide
26
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
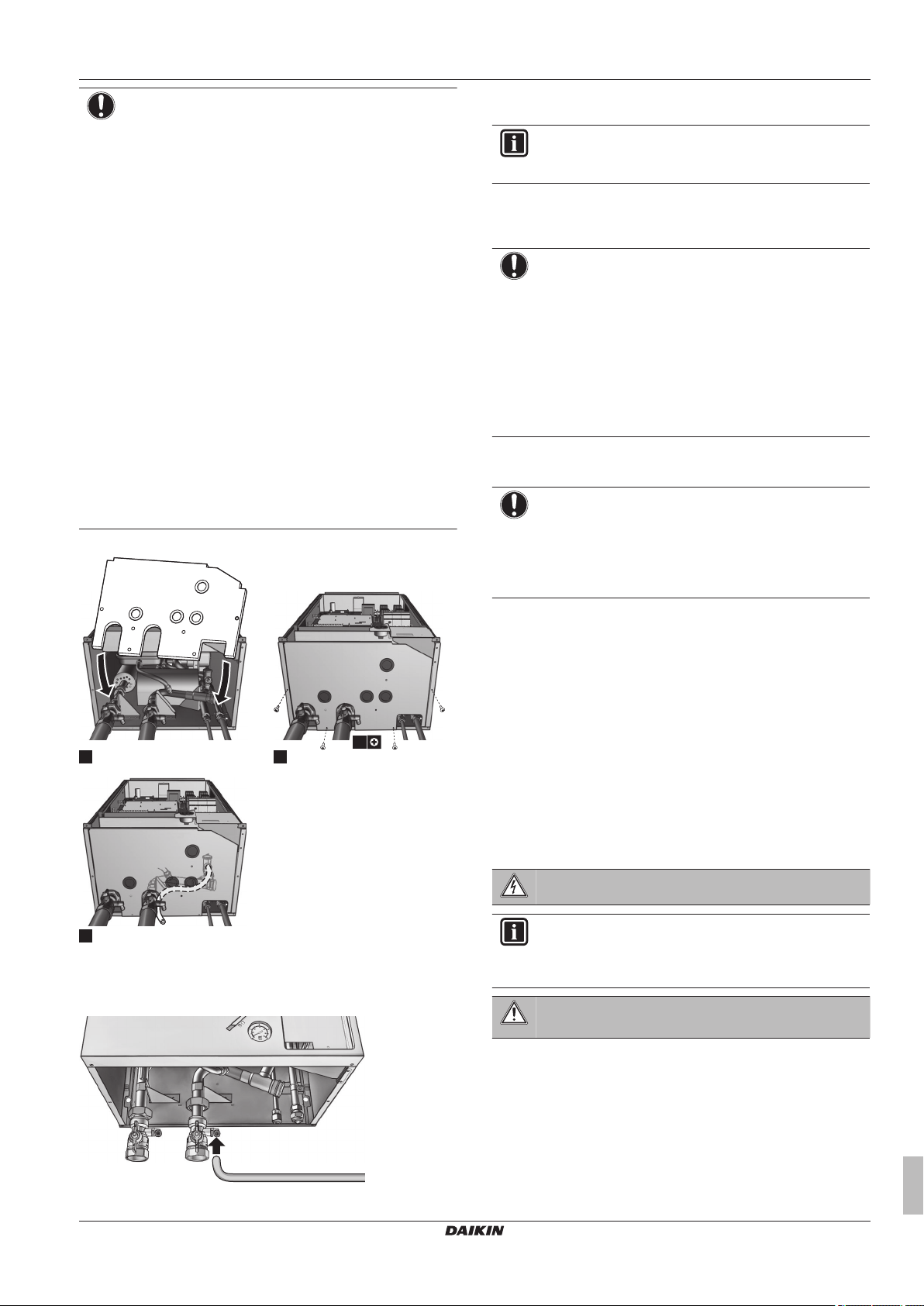
1 2
4x
3
7 Installation
NOTICE
▪ A drain device and pressure relief device should be
installed on the cold water inlet connection of the
domestic hot water cylinder.
▪ To avoid back siphonage, it is recommended to install a
non-return valve on the water inlet of the domestic hot
water tank in accordance with the applicable legislation.
▪ It is recommended to install a pressure reducing valve
on the cold water inlet in accordance with the
applicable legislation.
▪ An expansion vessel should be installed on the cold
water inlet in accordance with the applicable legislation.
▪ It is recommended to install the pressure relief valve on
higher position as top of the domestic hot water tank.
Heating of the domestic hot water tank causes water to
expand and without pressure relief valve the water
pressure inside the tank can rise above the tank design
pressure. Also the field installation (piping, tapping
points, etc.) connected to the tank is subjected to this
high pressure. To prevent this, a pressure relieve valve
needs to be installed.
The overpressure prevention depends on the correct
operation of the field installed pressure relief valve. If
this is NOT working correctly, overpressure will deform
the tank and water leakage may occur. To confirm
good operation, regular maintenance is required.
5 Install the sound plate as shown in the figure below.
3 Make sure that the automatic air purge valve is open (at least 2
turns).
INFORMATION
For location of the air purge valve, see
"14.2.1 Components: Indoor unit" on page 67.
4 Fill the circuit with water until the manometer indicates a
pressure of ±2.0 bar.
5 Purge as much air as possible from the water circuit.
NOTICE
▪ Air in the water circuit can cause malfunctioning of the
backup heater. During filling, it may not be possible to
remove all the air from the circuit. Remaining air will be
removed through the automatic air purge valves during
the initial operating hours of the system. Additional
filling with water afterwards may be required.
▪ To purge the system, use the special function as
described in the chapter "9 Commissioning" on
page 58. This function should be used to purge the
heat exchanger coil of the domestic hot water tank.
6 Close the drain and fill valve.
7 Disconnect the water supply hose from the drain and fill valve.
NOTICE
The water pressure indicated on the manometer will vary
depending on the water temperature (higher pressure at
higher water temperature).
However, at all times water pressure shall remain above
1 bar to avoid air entering the circuit.
7.3.2 To fill the water circuit
1 Connect the water supply hose to the drain and fill valve.
7.3.3 To fill the domestic hot water tank
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the
domestic hot water tank.
7.3.4 To insulate the water piping
The piping in the complete water circuit must be insulated to prevent
condensation during cooling operation and reduction of the heating
and cooling capacity.
If the temperature is higher than 30°C and the humidity is higher
than RH 80%, the thickness of the sealing materials should be at
least 20 mm to prevent condensation on the surface of the sealing.
7.4 Connecting the electrical wiring
DANGER: RISK OF ELECTROCUTION
INFORMATION
More information about the legend and the location of the
wiring diagram of the unit can be found in "14.5 Wiring
diagram" on page 70.
WARNING
Always use multicore cable for power supply cables.
7.4.1 About electrical compliance
2 Open the drain and fill valve.
ERHQ011~016BA+ERLQ011~016CA + EHBH/X16CA
Daikin Altherma - Low Temperature Split
4P313776-1C – 2012.11
Only for ERLQ006CAV3+ERLQ008CAV3
Equipment complying with EN/IEC 61000‑3‑12 (European/
International Technical Standard setting the limits for harmonic
currents produced by equipment connected to public low-voltage
systems with input current >16 A and ≤75 A per phase.).
Installer reference guide
27
 Loading...
Loading...