Page 1
+
Installer reference guide
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
ERHQ011-014-016BA
ERLQ011-014-016CA
EHVZ16S18CB
Installer reference guide
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
English
Page 2

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
1 General safety precautions 3
1.1 About the documentation .......................................................... 3
1.1.1 Meaning of warnings and symbols.............................. 3
1.2 For the installer.......................................................................... 4
1.2.1 General ....................................................................... 4
1.2.2 Installation site ............................................................ 4
1.2.3 Refrigerant .................................................................. 4
1.2.4 Brine............................................................................ 5
1.2.5 Water .......................................................................... 5
1.2.6 Electrical ..................................................................... 5
2 About the documentation 6
2.1 About this document.................................................................. 6
2.2 Installer reference guide at a glance ......................................... 6
3 About the box 7
3.1 Overview: About the box ........................................................... 7
3.2 Outdoor unit............................................................................... 7
3.2.1 To unpack the outdoor unit ......................................... 7
3.2.2 To handle the outdoor unit.......................................... 7
3.2.3 To remove the accessories from the outdoor unit....... 7
3.3 Indoor unit ................................................................................. 8
3.3.1 To unpack the indoor unit ........................................... 8
3.3.2 To remove the accessories from the indoor unit......... 8
4 About the units and options 8
4.1 Overview: About the units and options...................................... 8
4.2 Identification .............................................................................. 9
4.2.1 Identification label: Outdoor unit ................................. 9
4.2.2 Identification label: Indoor unit .................................... 9
4.3 Combining units and options ..................................................... 9
4.3.1 Possible options for the outdoor unit........................... 9
4.3.2 Possible options for the indoor unit............................. 9
4.3.3 Possible combinations of indoor unit and outdoor
unit .............................................................................. 10
5 Application guidelines 11
5.1 Overview: Application guidelines............................................... 11
5.2 Setting up the space heating system ........................................ 11
5.2.1 Multiple rooms – TwoLWT zones............................... 11
5.3 Setting up the domestic hot water tank ..................................... 12
5.3.1 System layout – Integrated DHW tank........................ 12
5.3.2 Selecting the volume and desired temperature for
the DHW tank.............................................................. 12
5.3.3 Setup and configuration – DHW tank.......................... 13
5.3.4 DHW pump for instant hot water................................. 13
5.3.5 DHW pump for disinfection ......................................... 13
5.4 Setting up the energy metering ................................................. 13
5.4.1 Produced heat............................................................. 13
5.4.2 Consumed energy....................................................... 13
5.4.3 Normal kWh rate power supply................................... 14
5.4.4 Preferential kWh rate power supply............................ 14
5.5 Setting up the power consumption control ................................ 14
5.5.1 Permanent power limitation ........................................ 14
5.5.2 Power limitation activated by digital inputs ................. 15
5.5.3 Power limitation process ............................................. 15
5.6 Setting up an external temperature sensor ............................... 15
6 Preparation 16
6.1 Overview: Preparation............................................................... 16
6.2 Preparing installation site .......................................................... 16
6.2.1 Installation site requirements of the outdoor unit ........ 16
6.2.2 Additional installation site requirements of the
outdoor unit in cold climates ....................................... 17
6.2.3 Installation site requirements of the indoor unit .......... 17
6.3 Preparing refrigerant piping....................................................... 18
6.3.1 Refrigerant piping requirements.................................. 18
6.3.2 Refrigerant piping insulation ........................................ 18
6.4 Preparing water piping ............................................................... 18
6.4.1 Water circuit requirements ........................................... 18
6.4.2 Formula to calculate the expansion vessel pre-
pressure ....................................................................... 19
6.4.3 To check the water volume and flow rate .................... 19
6.4.4 Changing the pre-pressure of the expansion vessel.... 20
6.4.5 To check the water volume: Examples ........................ 21
6.5 Preparing electrical wiring .......................................................... 21
6.5.1 About preparing electrical wiring.................................. 21
6.5.2 About preferential kWh rate power supply ................... 21
6.5.3 Overview of electrical connections except external
actuators ...................................................................... 22
6.5.4 Overview of electrical connections for external and
internal actuators ......................................................... 22
7 Installation 23
7.1 Overview: Installation ................................................................. 23
7.2 Opening the units ....................................................................... 23
7.2.1 About opening the units ............................................... 23
7.2.2 To open the outdoor unit.............................................. 23
7.2.3 To open the indoor unit ................................................ 23
7.2.4 To open the switch box cover of the indoor unit .......... 23
7.3 Mounting the outdoor unit........................................................... 23
7.3.1 About mounting the outdoor unit.................................. 23
7.3.2 Precautions when mounting the outdoor unit............... 24
7.3.3 To provide the installation structure ............................. 24
7.3.4 To install the outdoor unit............................................. 24
7.3.5 To provide drainage ..................................................... 24
7.3.6 To prevent the outdoor unit from falling over ............... 25
7.4 Mounting the indoor unit............................................................. 25
7.4.1 About mounting the indoor unit.................................... 25
7.4.2 Precautions when mounting the indoor unit................. 25
7.4.3 To install the indoor unit............................................... 25
7.5 Connecting the refrigerant piping ............................................... 25
7.5.1 About connecting the refrigerant piping ....................... 25
7.5.2 Precautions when connecting the refrigerant piping.... 26
7.5.3 Guidelines when connecting the refrigerant piping...... 26
7.5.4 Pipe bending guidelines............................................... 26
7.5.5 To flare the pipe end .................................................... 26
7.5.6 To braze the pipe end .................................................. 27
7.5.7 Using the stop valve and service port .......................... 27
7.5.8 To connect the refrigerant piping to the outdoor unit ... 28
7.5.9 To connect the refrigerant piping to the indoor unit ..... 29
7.5.10 To determine if oil traps are required ........................... 29
7.6 Checking the refrigerant piping .................................................. 29
7.6.1 About checking the refrigerant piping .......................... 29
7.6.2 Precautions when checking the refrigerant piping ....... 29
7.6.3 Checking refrigerant piping: Setup............................... 29
7.6.4 To check for leaks........................................................ 29
7.6.5 To perform vacuum drying ........................................... 30
7.7 Charging refrigerant ................................................................... 30
7.7.1 About charging refrigerant ........................................... 30
7.7.2 Precautions when charging refrigerant ........................ 30
7.7.3 To determine the additional refrigerant amount........... 30
7.7.4 To determine the complete recharge amount.............. 30
7.7.5 To charge additional refrigerant ................................... 31
7.7.6 To fix the fluorinated greenhouse gases label ............. 31
7.8 Connecting the water piping....................................................... 31
7.8.1 About connecting the water piping............................... 31
7.8.2 Precautions when connecting the water piping............ 31
7.8.3 To connect the water piping......................................... 31
7.8.4 To connect the recirculation piping .............................. 32
7.8.5 To connect the pressure relief valve to the drain......... 32
7.8.6 To fill the water circuit .................................................. 32
7.8.7 To fill the domestic hot water tank ............................... 33
7.8.8 To insulate the water piping ......................................... 33
7.9 Connecting the electrical wiring.................................................. 33
7.9.1 About connecting the electrical wiring.......................... 33
7.9.2 About electrical compliance ......................................... 33
Installer reference guide
2
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 3

1 General safety precautions
7.9.3 Precautions when connecting the electrical wiring ..... 34
7.9.4 Guidelines when connecting the electrical wiring ....... 34
7.9.5 Specifications of standard wiring components............ 34
7.9.6 To connect the electrical wiring on the outdoor unit.... 34
7.9.7 To reposition the air thermistor on the outdoor unit .... 35
7.9.8 To connect the electrical wiring on the indoor unit...... 36
7.9.9 To connect the main power supply ............................. 37
7.9.10 To connect the backup heater power supply .............. 37
7.9.11 To connect the user interface ..................................... 38
7.9.12 To connect the shut-off valve ...................................... 39
7.9.13 To connect the electrical meters ................................. 39
7.9.14 To connect the domestic hot water pump ................... 39
7.9.15 To connect the alarm output ....................................... 39
7.9.16 To connect the power consumption digital inputs ....... 40
7.9.17 To connect the safety thermostat (normal closed
contact) ....................................................................... 40
7.10 Finishing the outdoor unit installation ........................................ 40
7.10.1 To finish the outdoor unit installation .......................... 40
7.10.2 To close the outdoor unit ............................................ 41
7.11 Finishing the indoor unit installation .......................................... 41
7.11.1 To fix the user interface cover to the indoor unit ......... 41
7.11.2 To close the indoor unit............................................... 41
8 Configuration 41
8.1 Overview: Configuration ............................................................ 41
8.1.1 To connect the PC cable to the switch box................. 41
8.1.2 To access the most used commands ......................... 42
8.1.3 To copy the system settings from the first to the
second user interface.................................................. 42
8.1.4 To copy the language set from the first to the second
user interface .............................................................. 43
8.1.5 Quick wizard: Set the system layout after first power
ON............................................................................... 43
8.2 Basic configuration .................................................................... 43
8.2.1 Quick wizard: Language / time and date..................... 43
8.2.2 Quick wizard: Standard............................................... 44
8.2.3 Quick wizard: Options ................................................. 45
8.2.4 Quick wizard: Capacities (energy metering) ............... 47
8.2.5 Space heating control ................................................. 48
8.2.6 Domestic hot water control ......................................... 50
8.2.7 Contact/helpdesk number........................................... 50
8.3 Advanced configuration/optimization......................................... 50
8.3.1 Space heating operation: advanced ........................... 50
8.3.2 Domestic hot water control: advanced........................ 53
8.3.3 Heat source settings ................................................... 56
8.3.4 System settings........................................................... 57
8.4 Menu structure: Overview user settings .................................... 61
8.5 Menu structure: Overview installer settings............................... 62
9 Commissioning 63
9.1 Overview: Commissioning......................................................... 63
9.2 Precautions when commissioning ............................................. 63
9.3 Checklist before commissioning................................................ 63
9.4 Checklist during commissioning ................................................ 63
9.4.1 To check the minimum flow rate ................................. 64
9.4.2 Air purge function........................................................ 64
9.4.3 To perform a test run .................................................. 65
9.4.4 To perform an actuator test run .................................. 65
9.4.5 Underfloor heating screed dryout................................ 66
10 Hand-over to the user 67
11 Maintenance and service 67
11.1 Overview: Maintenance and service ......................................... 67
11.2 Maintenance safety precautions................................................ 67
11.2.1 Opening the indoor unit............................................... 67
11.3 Checklist for yearly maintenance of the outdoor unit ................ 67
11.4 Checklist for yearly maintenance of the indoor unit................... 67
11.4.1 To drain the domestic hot water tank .......................... 68
12 Troubleshooting 69
12.1 Overview: Troubleshooting......................................................... 69
12.2 Precautions when troubleshooting ............................................. 69
12.3 Solving problems based on symptoms....................................... 69
12.3.1 Symptom: The unit is NOT heating as expected ......... 69
12.3.2 Symptom: The compressor does NOT start (space
heating or domestic water heating).............................. 69
12.3.3 Symptom: The pump is making noise (cavitation) ....... 70
12.3.4 Symptom: The pressure relief valve opens.................. 70
12.3.5 Symptom: The water pressure relief valve leaks ......... 70
12.3.6 Symptom: The space is NOT sufficiently heated at
low outdoor temperatures ............................................ 70
12.3.7 Symptom: The pressure at the tapping point is
temporarily unusually high ........................................... 71
12.3.8 Symptom: Decoration panels are pushed away due
to a swollen tank .......................................................... 71
12.3.9 Symptom: Tank disinfection function is NOT
completed correctly (AH-error)..................................... 71
12.4 Solving problems based on error codes ..................................... 71
12.4.1 Error codes: Overview ................................................. 71
13 Disposal 73
13.1 Overview: Disposal..................................................................... 73
13.2 About pump down ...................................................................... 73
13.3 To pump down............................................................................ 73
14 Technical data 74
14.1 Piping diagram: Outdoor unit...................................................... 74
14.2 Piping diagram: Indoor unit ........................................................ 75
14.3 Wiring diagram: Outdoor unit ..................................................... 76
14.4 Wiring diagram: Indoor unit ........................................................ 77
14.5 ESP curve: Indoor unit ............................................................... 79
15 Glossary 81
16 Field settings table 82
1 General safety precautions
1.1 About the documentation
▪ The original documentation is written in English. All other
languages are translations.
▪ The precautions described in this document cover very important
topics, follow them carefully.
▪ The installation of the system, and all activities described in the
installation manual and the installer reference guide must be
performed by an authorized installer.
1.1.1 Meaning of warnings and symbols
DANGER
Indicates a situation that results in death or serious injury.
DANGER: RISK OF ELECTROCUTION
Indicates a situation that could result in electrocution.
DANGER: RISK OF BURNING
Indicates a situation that could result in burning because of
extreme hot or cold temperatures.
DANGER: RISK OF EXPLOSION
Indicates a situation that could result in explosion.
WARNING
Indicates a situation that could result in death or serious
injury.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
3
Page 4
1 General safety precautions
WARNING: FLAMMABLE MATERIAL
CAUTION
Indicates a situation that could result in minor or moderate
injury.
NOTICE
Indicates a situation that could result in equipment or
property damage.
INFORMATION
Indicates useful tips or additional information.
Symbol Explanation
Before installation, read the installation and
operation manual, and the wiring instruction sheet.
Before performing maintenance and service tasks,
read the service manual.
For more information, see the installer and user
reference guide.
1.2 For the installer
1.2.1 General
If you are not sure how to install or operate the unit, contact your
dealer.
NOTICE
Improper installation or attachment of equipment or
accessories could result in electric shock, short-circuit,
leaks, fire or other damage to the equipment. Only use
accessories, optional equipment and spare parts made or
approved by Daikin.
WARNING
Make sure installation, testing and applied materials
comply with applicable legislation (on top of the
instructions described in the Daikin documentation).
CAUTION
Wear adequate personal protective equipment (protective
gloves, safety glasses,…) when installing, maintaining or
servicing the system.
WARNING
Tear apart and throw away plastic packaging bags so that
nobody, especially children, can play with them. Possible
risk: suffocation.
DANGER: RISK OF BURNING
▪ Do NOT touch the refrigerant piping, water piping or
internal parts during and immediately after operation. It
could be too hot or too cold. Give it time to return to
normal temperature. If you must touch it, wear
protective gloves.
▪ Do NOT touch any accidental leaking refrigerant.
WARNING
Provide adequate measures to prevent that the unit can be
used as a shelter by small animals. Small animals that
make contact with electrical parts can cause malfunctions,
smoke or fire.
CAUTION
Do NOT touch the air inlet or aluminium fins of the unit.
NOTICE
▪ Do NOT place any objects or equipment on top of the
unit.
▪ Do NOT sit, climb or stand on the unit.
NOTICE
Works executed on the outdoor unit are best done under
dry weather conditions to avoid water ingress.
In accordance with the applicable legislation, it might be necessary
to provide a logbook with the product containing at least: information
on maintenance, repair work, results of tests, stand-by periods,…
Also, at least, following information must be provided at an
accessible place at the product:
▪ Instructions for shutting down the system in case of an emergency
▪ Name and address of fire department, police and hospital
▪ Name, address and day and night telephone numbers for
obtaining service
In Europe, EN378 provides the necessary guidance for this logbook.
1.2.2 Installation site
▪ Provide sufficient space around the unit for servicing and air
circulation.
▪ Make sure the installation site withstands the unit's weight and
vibration.
▪ Make sure the area is well ventilated. Do NOT block any
ventilation openings.
▪ Make sure the unit is level.
Do NOT install the unit in the following places:
▪ In potentially explosive atmospheres.
▪ In places where there is machinery that emits electromagnetic
waves. Electromagnetic waves may disturb the control system,
and cause malfunction of the equipment.
▪ In places where there is a risk of fire due to the leakage of
flammable gases (example: thinner or gasoline), carbon fibre,
ignitable dust.
▪ In places where corrosive gas (example: sulphurous acid gas) is
produced. Corrosion of copper pipes or soldered parts may cause
the refrigerant to leak.
1.2.3 Refrigerant
If applicable. See the installation manual or installer reference guide
of your application for more information.
NOTICE
Make sure refrigerant piping installation complies with
applicable legislation. In Europe, EN378 is the applicable
standard.
NOTICE
Make sure the field piping and connections are not
subjected to stress.
WARNING
During tests, NEVER pressurize the product with a
pressure higher than the maximum allowable pressure (as
indicated on the nameplate of the unit).
Installer reference guide
4
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 5
1 General safety precautions
WARNING
Take sufficient precautions in case of refrigerant leakage. If
refrigerant gas leaks, ventilate the area immediately.
Possible risks:
▪ Excessive refrigerant concentrations in a closed room
can lead to oxygen deficiency.
▪ Toxic gas may be produced if refrigerant gas comes
into contact with fire.
DANGER: RISK OF EXPLOSION
Pump down – Refrigerant leakage. If you want to pump
down the system, and there is a leakage in the refrigerant
circuit:
▪ Do NOT use the unit's automatic pump down function,
with which you can collect all refrigerant from the
system into the outdoor unit. Possible consequence:
Self-combustion and explosion of the compressor
because of air going into the operating compressor.
▪ Use a separate recovery system so that the unit's
compressor does NOT have to operate.
WARNING
Always recover the refrigerant. Do NOT release them
directly into the environment. Use a vacuum pump to
evacuate the installation.
NOTICE
After all the piping has been connected, make sure there is
no gas leak. Use nitrogen to perform a gas leak detection.
NOTICE
▪ To avoid compressor breakdown, do NOT charge more
than the specified amount of refrigerant.
▪ When the refrigerant system is to be opened,
refrigerant must be treated according to the applicable
legislation.
WARNING
Make sure there is no oxygen in the system. Refrigerant
may only be charged after performing the leak test and the
vacuum drying.
▪ In case re-charge is required, refer to the nameplate of the unit. It
states the type of refrigerant and necessary amount.
▪ The unit is factory charged with refrigerant and depending on pipe
sizes and pipe lengths some systems require additional charging
of refrigerant.
▪ Only use tools exclusively for the refrigerant type used in the
system, this to ensure pressure resistance and prevent foreign
materials from entering into the system.
▪ Charge the liquid refrigerant as follows:
If Then
A siphon tube is present
(i.e., the cylinder is marked with
"Liquid filling siphon attached")
Charge with the cylinder upright.
▪ Open refrigerant cylinders slowly.
▪ Charge the refrigerant in liquid form. Adding it in gas form may
prevent normal operation.
CAUTION
When the refrigerant charging procedure is done or when
pausing, close the valve of the refrigerant tank
immediately. If the valve is not closed immediately,
remaining pressure might charge additional refrigerant.
Possible consequence: Incorrect refrigerant amount.
1.2.4 Brine
If applicable. See the installation manual or installer reference guide
of your application for more information.
WARNING
The selection of the brine MUST be in accordance with the
applicable legislation.
WARNING
Take sufficient precautions in case of brine leakage. If
brine leaks, ventilate the area immediately and contact
your local dealer.
WARNING
The ambient temperature inside the unit can get much
higher than that of the room, e.g. 70°C. In case of a brine
leak, hot parts inside the unit can create a hazardous
situation.
WARNING
The use and installation of the application MUST comply
with the safety and environmental precautions specified in
the applicable legislation.
1.2.5 Water
If applicable. See the installation manual or installer reference guide
of your application for more information.
NOTICE
Make sure water quality complies with EU directive
98/83EC.
1.2.6 Electrical
DANGER: RISK OF ELECTROCUTION
▪ Turn OFF all power supply before removing the
switch box cover, connecting electrical wiring or
touching electrical parts.
▪ Disconnect the power supply for more than 1 minute,
and measure the voltage at the terminals of main circuit
capacitors or electrical components before servicing.
The voltage MUST be less than 50 V DC before you
can touch electrical components. For the location of the
terminals, see the wiring diagram.
▪ Do NOT touch electrical components with wet hands.
▪ Do NOT leave the unit unattended when the service
cover is removed.
A siphon tube is NOT present Charge with the cylinder upside
down.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
WARNING
If NOT factory installed, a main switch or other means for
disconnection, having a contact separation in all poles
providing full disconnection under overvoltage category III
condition, MUST be installed in the fixed wiring.
Installer reference guide
5
Page 6

2 About the documentation
WARNING
▪ ONLY use copper wires.
▪ Make sure the field wiring complies with the applicable
legislation.
▪ All field wiring must be performed in accordance with
the wiring diagram supplied with the product.
▪ NEVER squeeze bundled cables and make sure they
do not come in contact with the piping and sharp
edges. Make sure no external pressure is applied to the
terminal connections.
▪ Make sure to install earth wiring. Do NOT earth the unit
to a utility pipe, surge absorber, or telephone earth.
Incomplete earth may cause electrical shock.
▪ Make sure to use a dedicated power circuit. NEVER
use a power supply shared by another appliance.
▪ Make sure to install the required fuses or circuit
breakers.
▪ Make sure to install an earth leakage protector. Failure
to do so may cause electric shock or fire.
▪ When installing the earth leakage protector, make sure
it is compatible with the inverter (resistant to high
frequency electric noise) to avoid unnecessary opening
of the earth leakage protector.
NOTICE
Precautions when laying power wiring:
▪ Do not connect wiring of different thicknesses to the
power terminal block (slack in the power wiring may
cause abnormal heat).
▪ When connecting wiring which is the same thickness,
do as shown in the figure below.
▪ For wiring, use the designated power wire and connect
firmly, then secure to prevent outside pressure being
exerted on the terminal board.
▪ Use an appropriate screwdriver for tightening the
terminal screws. A screwdriver with a small head will
damage the head and make proper tightening
impossible.
▪ Over-tightening the terminal screws may break them.
Install power cables at least 1 metre away from televisions or radios
to prevent interference. Depending on the radio waves, a distance of
1metre may not be sufficient.
WARNING
▪ After finishing the electrical work, confirm that each
electrical component and terminal inside the electrical
components box is connected securely.
▪ Make sure all covers are closed before starting up the
unit.
NOTICE
Only applicable if the power supply is three‑phase, and the
compressor has an ON/OFF starting method.
If there exists the possibility of reversed phase after a
momentary black out and the power goes on and off while
the product is operating, attach a reversed phase
protection circuit locally. Running the product in reversed
phase can break the compressor and other parts.
2 About the documentation
2.1 About this document
Target audience
Authorised installers
Documentation set
This document is part of a documentation set. The complete set
consists of:
▪ General safety precautions:
▪ Safety instructions that you must read before installing
▪ Format: Paper (in the box of the indoor unit)
▪ Indoor unit installation manual:
▪ Installation instructions
▪ Format: Paper (in the box of the indoor unit)
▪ Outdoor unit installation manual:
▪ Installation instructions
▪ Format: Paper (in the box of the outdoor unit)
▪ Installer reference guide:
▪ Preparation of the installation, good practices, reference data,…
▪ Format: Digital files on http://www.daikineurope.com/support-
and-manuals/product-information/
▪ Addendum book for optional equipment:
▪ Additional info about how to install optional equipment
▪ Format: Paper (in the box of the indoor unit) + Digital files on
http://www.daikineurope.com/support-and-manuals/productinformation/
Latest revisions of the supplied documentation may be available on
the regional Daikin website or via your dealer.
The original documentation is written in English. All other languages
are translations.
Technical engineering data
▪ A subset of the latest technical data is available on the regional
Daikin website (publicly accessible).
▪ The full set of latest technical data is available on the Daikin
extranet (authentication required).
2.2 Installer reference guide at a glance
Chapter Description
General safety
precautions
About the documentation What documentation exists for the
About the box How to unpack the units and remove
About the units and
options
Application guidelines Various installation setups of the system
Preparation What to do and know before going
Installation What to do and know to install the
Configuration What to do and know to configure the
Safety instructions that you must read
before installing
installer
their accessories
▪ How to identify the units
▪ Possible combinations of units and
options
on‑site
system
system after it is installed
Installer reference guide
6
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 7
3 About the box
21
102~114 kg
1×
2
1
a
1×
c
1×
b
2×
d
1×
e
1×
f
1×
g
1×
Chapter Description
Commissioning What to do and know to commission the
system after it is configured
Hand‑over to the user What to give and explain to the user
Maintenance and service How to maintain and service the units
Troubleshooting What to do in case of problems
Disposal How to dispose of the system
Technical data Specifications of the system
Glossary Definition of terms
Field settings table Table to be filled in by the installer, and
kept for future reference
Note: There is also an installer settings
table in the user reference guide. This
table has to be filled in by the installer
and handed over to the user.
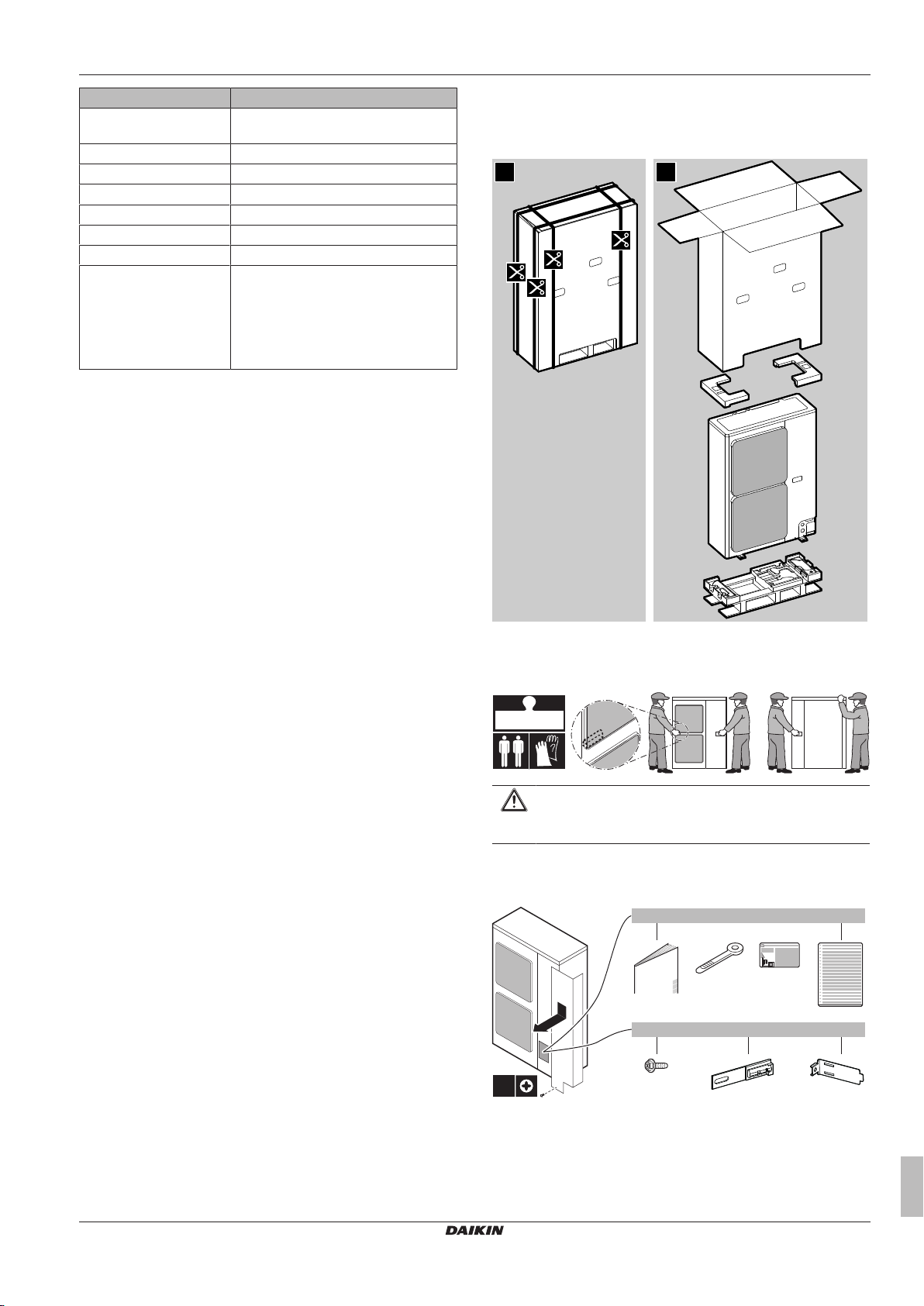
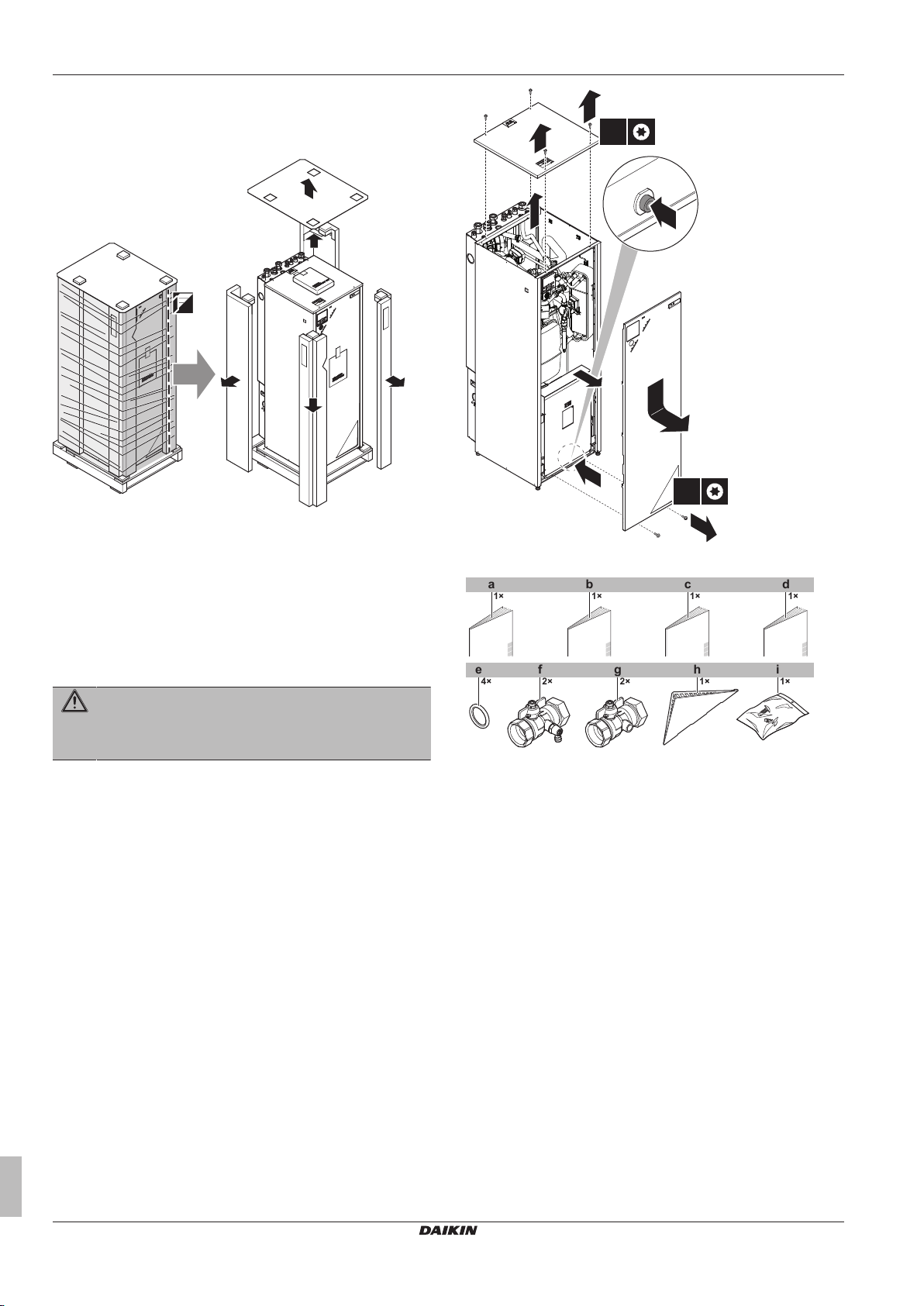
3 About the box
3.1 Overview: About the box
This chapter describes what you have to do after the boxes with the
outdoor and indoor unit are delivered on-site.
It contains information about:
▪ Unpacking and handling the units
▪ Removing the accessories from the units
Keep the following in mind:
▪ At delivery, the unit must be checked for damage. Any damage
must be reported immediately to the carrier's claims agent.
▪ Bring the packed unit as close as possible to its final installation
position to prevent damage during transport.
3.2 Outdoor unit
3.2.1 To unpack the outdoor unit
3.2.2 To handle the outdoor unit
Carry the unit slowly as shown:
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
CAUTION
To avoid injury, do NOT touch the air inlet or aluminium
fins of the unit.
3.2.3 To remove the accessories from the outdoor unit
a Outdoor unit installation manual
b Cable tie
c Fluorinated greenhouse gases label
d Multilingual fluorinated greenhouse gases label
e Screw (only for ERLQ)
f Thermistor fixing plate (spare) (only for ERLQ)
g Thermistor fixture (only for ERLQ)
Installer reference guide
7
Page 8
4 About the units and options
a~e+i
h
f+g
5
4
1
2
3
4
4×
2×
1×
1× 1× 1× 1×
2× 1×4×
a b c d
f
2×
g h ie
3.3 Indoor unit
3.3.1 To unpack the indoor unit
3.3.2 To remove the accessories from the indoor unit
1 Remove the screws at the top of the unit.
2 Remove the top panel.
3 Remove the screws at the front of the unit.
4 Push on the button on the bottom of the front plate.
5 Remove the front plate.
WARNING: Sharp edges
Take the front plate on the upper part instead of the lower
part. Watch your fingers, there are sharp edges on the
lower part of the front plate.
6 Remove the accessories.
a General safety precautions
b Addendum book for optional equipment
c Indoor unit installation manual
d Operation manual
e Sealing ring for shut-off valve
f Shut-off valve with drain/fill point
g Shut-off valve
h User interface cover
i 2 screws for fixing the user interface.
7 Reinstall the top panel and the front plate.
4 About the units and options
4.1 Overview: About the units and options
This chapter contains information about:
▪ Identifying the outdoor unit
▪ Identifying the indoor unit
▪ Combining outdoor and indoor units
▪ Combining the outdoor unit with options
▪ Combining the indoor unit with options
Installer reference guide
8
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 9
4 About the units and options
4.2 Identification
NOTICE
When installing or servicing several units at the same time,
make sure NOT to switch the service panels between
different models.
4.2.1 Identification label: Outdoor unit
Location
Model identification
▪ ERLQ: Contains components (insulation, bottom plate heater,…)
to prevent freeze-up in areas with low ambient temperature and
high humidity.
▪ ERHQ: Does NOT contain these components.
Example: ERLQ011CAW1
Code Explanation
ER European split outdoor pair heat pump
L H=Low water temperature – ambient zone:
0~−10°C
L=Low water temperature – ambient zone:
−10~−20°C
Q Refrigerant R410A
011 Capacity class
CA Model series
W1 Power supply
4.2.2 Identification label: Indoor unit
Location
Code Description
S Integrated tank material: Stainless steel
18 Integrated tank volume
CB Model series
3V Backup heater model
4.3 Combining units and options
4.3.1 Possible options for the outdoor unit
Demand PCB (KRP58M51) (only for ERLQ)
▪ Limits the maximum current. However, this also decreases the
heating/cooling capacity of the system.
▪ Only the "Setting of demand running" function of the demand PCB
is applicable.
▪ For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the
demand PCB.
Snow cover (EK016SNC) (only for ERLQ)
▪ Prevents the outdoor unit from being snowed up.
▪ Recommended in areas with low ambient temperatures or heavy
snowfall.
▪ For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the
snow cover.
Drain plug kit (EKDK04) (only for ERHQ)
▪ Gathers the condensate from the outdoor unit and guides it away
through 1 plug in the bottom plate.
▪ For ERLQ: Drain plug kit is not applicable.
▪ For ERHQ: Drain plug kit is option.
▪ Cannot be combined with bottom plate heater.
▪ For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the
drain plug kit.
Bottom plate heater (EKBPHTH16A) (only for ERHQ in
combination with C* indoor unit)
▪ Prevents freeze-up of the bottom plate.
▪ Recommended in areas with low ambient temperature and high
humidity.
▪ For ERLQ: Bottom plate heater is standard (factory-mounted).
▪ For ERHQ: Bottom plate heater is option.
▪ Cannot be combined with drain plug kit.
▪ If you install EKBPHTH16A, you also have to install the digital I/O
PCB (EKRP1HB).
▪ For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the
bottom plate heater and addendum book for optional equipment.
Model identification
Example: EHVZ04S18CB3V
Code Description
E European model
HV Floor-standing indoor unit with integrated tank
Z Dual-zone model
04 Capacity class
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
4.3.2 Possible options for the indoor unit
User interface (EKRUCBL*)
The user interface and a possible additional user interface are
available as an option.
The additional user interface can be connected:
▪ To have both:
▪ control close to the indoor unit,
▪ room thermostat functionality in the principal space to be
heated.
▪ To have an interface containing other languages.
Following user interfaces are available:
Installer reference guide
9
Page 10

4 About the units and options
▪ EKRUCBL1 contains following languages: German, French,
Dutch, Italian.
▪ EKRUCBL2 contains following languages: English, Swedish,
Norwegian, Finnish.
▪ EKRUCBL3 contains following languages: English, Spanish,
Greek, Portuguese.
▪ EKRUCBL4 contains following languages: English, Turkish,
Polish, Romanian.
▪ EKRUCBL5 contains following languages: German, Czech,
Slovenian, Slovakian.
▪ EKRUCBL6 contains following languages: English, Croatian,
Hungarian, Estonian.
▪ EKRUCBL7 contains following languages: English, German,
Russian, Danish.
Languages on the user interface can be uploaded by PC software or
copied from an user interface to the other.
For installation instructions, see "7.9.11 To connect the user
interface"on page38.
Simplified user interface (EKRUCBS)
▪ The simplified user interface can only be used in combination with
the main user interface.
▪ The simplified user interface acts as room thermostat and needs
to be installed in the room that you want it to control.
For installation instructions, see the installation and operation
manual of the simplified user interface.
Room thermostat (EKRTWA, EKRTR1, RTRNETA)
You can connect an optional room thermostat to the indoor unit. This
thermostat can either be wired (EKRTWA) or wireless (EKRTR1 and
RTRNETA). Thermostat RTRNETA can only be used in heating-only
systems.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the room
thermostat and addendum book for optional equipment.
Remote sensor for wireless thermostat (EKRTETS)
You can use a wireless indoor temperature sensor (EKRTETS) only
in combination with the wireless thermostat (EKRTR1).
For installation intructions, see the installation manual of the room
thermostat and addendum book for optional equipment.
Digital I/O PCB (EKRP1HB)
The digital I/O PCB is required to provide following signals:
▪ Alarm output
▪ Space heating On/OFF output
▪ Changeover to external heat source
▪ Only for EHVZ16S18 model: Control signal for bottom plate heater
kit EKBPHTH16A.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the digital
I/O PCB and addendum book for optional equipment.
Demand PCB (EKRP1AHTA)
To enable the power saving consumption control by digital inputs
you must install the demand PCB.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the
demand PCB and addendum book for optional equipment.
Remote indoor sensor (KRCS01-1)
By default the internal user interface sensor will be used as room
temperature sensor.
As an option the remote indoor sensor can be installed to measure
the room temperature on another location.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the remote
indoor sensor and addendum book for optional equipment.
INFORMATION
▪ The remote indoor sensor can only be used in case the
user interface is configured with room thermostat
functionality.
▪ You can only connect either the remote indoor sensor
or the remote outdoor sensor.
Remote outdoor sensor (EKRSCA1)
By default the sensor inside the outdoor unit will be used to measure
the outdoor temperature.
As an option the remote outdoor sensor can be installed to measure
the outdoor temperature on another location (e.g. to avoid direct
sunlight) to have an improved system behaviour.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the remote
outdoor sensor.
INFORMATION
You can only connect either the remote indoor sensor or
the remote outdoor sensor.
PC configurator (EKPCCAB)
The PC cable makes a connection between the switch box of the
indoor unit and a PC. It gives the possibility to upload different
language files to the user interface and indoor parameters to the
indoor unit. For the available language files, contact your local
dealer.
The software and corresponding operating instructions are available
on http://www.daikineurope.com/support-and-manuals/software-
downloads/.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the PC
cable and "8Configuration"on page41.
Heat pump convector (FWXV)
For providing space heating, it is possible to use heat pump
convectors (FWXV).
For installation instructions, refer to the installation manual of the
heat pump convectors, and the addendum book for optional
equipment.
LAN adapter for smartphone control + Smart Grid applications
(BRP069A61)
You can install this LAN adapter to:
▪ Control the system via a smartphone app.
▪ Use the system in various Smart Grid applications.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the LAN
adapter.
LAN adapter for smartphone control (BRP069A62)
You can install this LAN adapter to control the system via a
smartphone app.
For installation instructions, see the installation manual of the LAN
adapter.
4.3.3 Possible combinations of indoor unit and outdoor unit
Outdoor unit Indoor unit
EHVZ16
ERHQ011+ERLQ011 O
ERHQ014+ERLQ014 O
ERHQ016+ERLQ016 O
Installer reference guide
10
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 11
5 Application guidelines
j
k
j
HPC1
FHL1 FHL2 FHL3
HPC2 HPC3
B
A
C
E
D
M
a b c
g hf
d e
i
i
hh
h
5 Application guidelines
5.1 Overview: Application guidelines
The purpose of the application guidelines is to give a glance of the
possibilities of the Daikin heatpump system.
NOTICE
▪ The illustrations in the application guidelines are meant
for reference only, and are NOT to be used as detailed
hydraulic diagrams. The detailed hydraulic
dimensioning and balancing are NOT shown, and are
the responsibility of the installer.
▪ For more information about the configuration settings to
optimize heatpump operation, see "8Configuration"on
page41.
This chapter contains application guidelines for:
▪ Setting up the space heating system
▪ Setting up the domestic hot water tank
▪ Setting up the energy metering
▪ Setting up the power consumption
▪ Setting up an external temperature sensor
5.2 Setting up the space heating system
The Daikin heat pump system supplies leaving water to heat
emitters in one or more rooms.
Because the system offers a wide flexibility to control the
temperature in each room, you need to answer the following
questions first:
▪ How many rooms are heated by the Daikin heatpump system?
▪ Which heat emitter types are used in each room and what is their
design leaving water temperature?
Once the space heating requirements are clear, Daikin recommends
to follow the setup guidelines below.
NOTICE
If an external room thermostat is used, the external room
thermostat will control the room frost protection. However,
the room frost protection is only possible if the leaving
water temperature control on the unit's user interface is
turned ON.
INFORMATION
In case an external room thermostat is used and room frost
protection needs to be guaranteed in all conditions, then
you have to set auto emergency [A.6.C] to 1.
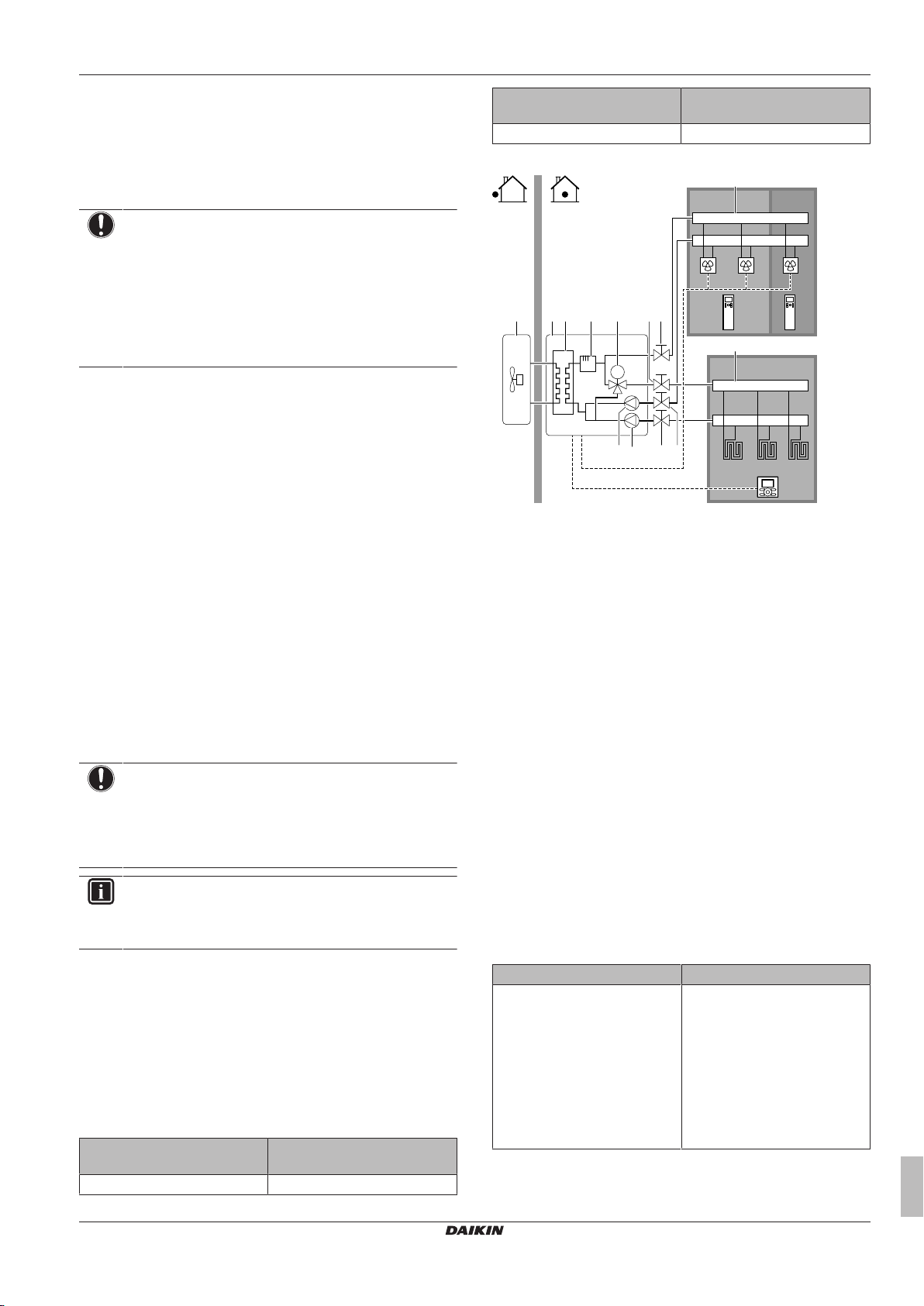
5.2.1 Multiple rooms – TwoLWT zones
This unit is designed to deliver water at 2 different temperatures. A
typical installation consists of underfloor heating at a lower
temperature and radiators at a higher water temperature.
In this document:
▪ Main zone = Zone with the lowest design temperature
▪ Additional zone = Zone with the highest design temperature
Typical example:
Living room (main zone) Underfloor heating: 35°C
Room (zone) Heat emitters: Design
temperature
Room (zone) Heat emitters: Design
temperature
Bed rooms (additional zone) Heat pump convectors: 45°C
Setup
A Additional leaving water temperature zone
B Room 1
C Room 2
D Main leaving water temperature zone
E Room 3
a Outdoor unit
b Indoor unit
c Heat exchanger
d Backup heater
e Motorised 3-way valve (mixing the main zone)
f Additional pump
g Main pump
h Shut-off valve
i Collector (field supply)
j Remote controller of the heat pump convectors (field
supply)
k User interface (field supply)
HPC1...3 Heat pump convectors (field supply)
FHL1...3 Floor heating loops (field supply)
▪ For the main zone: the room temperature is controlled by the user
interface, which is used as room thermostat.
▪ For the additional zone:
▪ The external thermostat is directly connected to the indoor unit.
▪ The desired room temperature is set via the external thermostat
and the thermostatic valves of the radiators in each room.
▪ The heating demand signal from the external thermostat is
connected to the digital input on the indoor unit (X2M/1a and
X2M/4). The indoor unit will only supply the desired additional
leaving water temperature when there is an actual demand.
Configuration
Setting Value
Unit temperature control:
▪ #: [A.2.1.7]
▪ Code: [C-07]
2 (RT control): Unit operation is
decided based on the ambient
temperature of the user interface.
Note:
▪ Main room = user interface
used as room thermostat
functionality
▪ Other rooms = external room
thermostat functionality
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
11
Page 12
5 Application guidelines
M
M
a b c d ge h ii
i
j
j
fki
HPC1
UI
FHL1 FHL2 FHL3
HPC2 HPC3
Setting Value
Number of water temperature
zones:
1 (2 LWT zones): Main +
additional
▪ #: [A.2.1.8]
▪ Code: [7-02]
In case of heatpump convectors:
External room thermostat for the
additional zone:
▪ #: [A.2.2.5]
1 (Thermo ON/OFF): When the
used external room thermostat or
heatpump convector can only
send a thermo ON/OFF
condition.
▪ Code: [C-06]
Shut-off valve output Set to follow the thermo demand
of the main zone.
Benefits
▪ Comfort. The smart room thermostat functionality can decrease
or increase the desired leaving water temperature based on the
actual room temperature (modulation).
▪ Efficiency.
▪ Depending on the demand, the indoor unit supplies different
leaving water temperature matching the design temperature of
the different heat emitters.
▪ Underfloor heating has the best performance with Altherma LT.
5.3 Setting up the domestic hot water tank
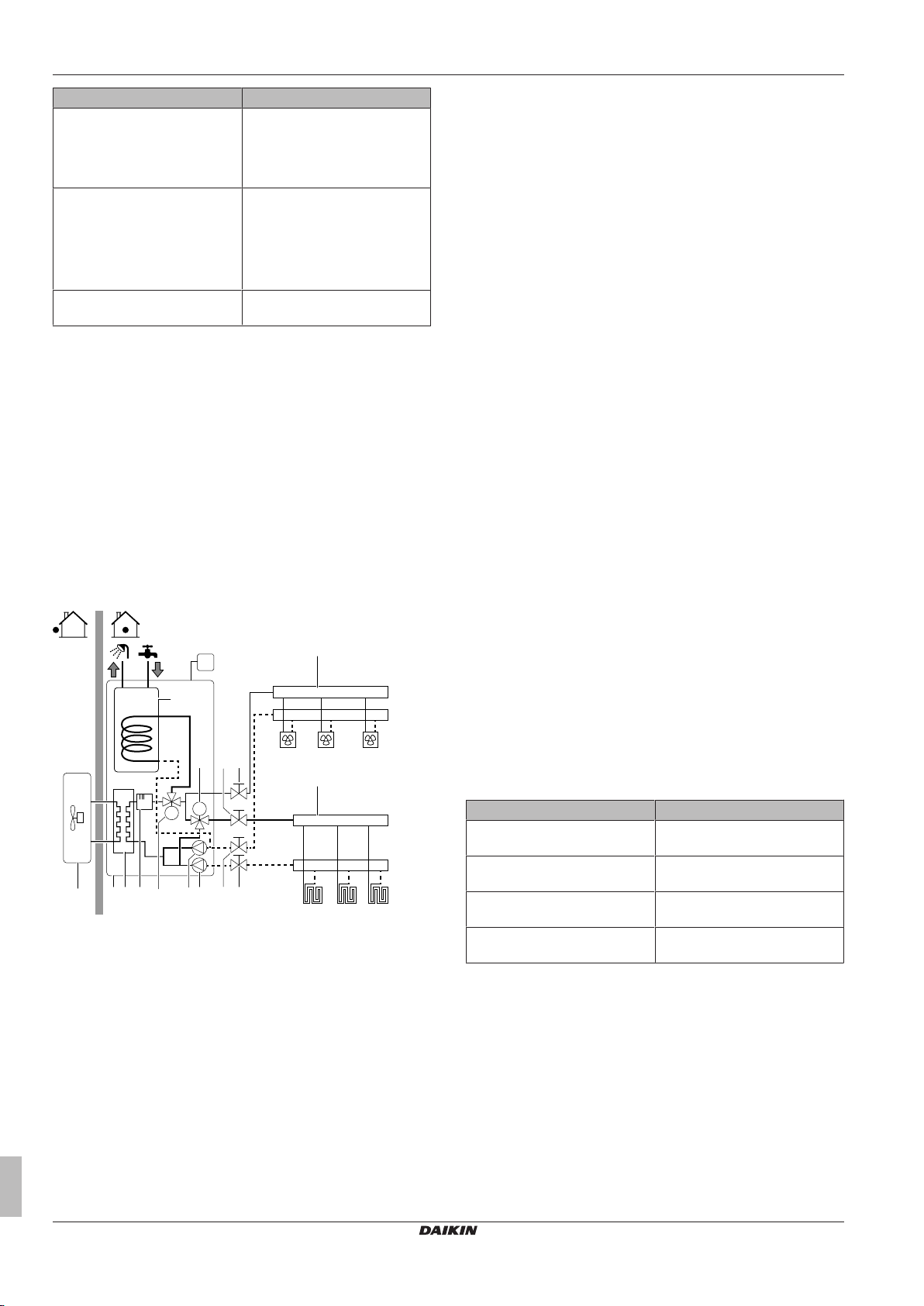
5.3.1 System layout – Integrated DHW tank
5.3.2 Selecting the volume and desired temperature for the DHW tank
People experience water as hot when its temperature is 40°C.
Therefore, the DHW consumption is always expressed as equivalent
hot water volume at 40°C. However, you can set the DHW tank
temperature at a higher temperature (example: 53°C), which is then
mixed with cold water (example: 15°C).
Selecting the desired temperature for the DHW tank consists of:
1 Determining the DHW consumption (equivalent hot water
volume at 40°C).
2 Determining the desired temperature for the DHW tank.
Energy saving tips
▪ If the DHW consumption differs from day to day, you can program
a weekly schedule with different desired DHW tank temperatures
for each day.
▪ The lower the desired DHW tank temperature, the more cost
effective. By selecting a larger DHW tank, you can lower the
desired DHW tank temperature.
▪ The heatpump itself can produce domestic hot water of maximum
55°C (50°C if outdoor temperature is low). The electrical
resistance integrated in the heat pump can increase this
temperature. However, this consumes more energy. Daikin
recommends to set the desired DHW tank temperature below
55°C to avoid using the backup heater.
▪ The higher the outdoor temperature, the better the performance of
the heatpump.
▪ If energy prices are the same during the day and the night,
Daikin recommends to heat up the DHW tank during the day.
▪ If energy prices are lower during the night, Daikin recommends
to heat up the DHW tank during the night.
▪ When the heatpump produces domestic hot water, it cannot heat
up a space. When you need domestic hot water and space
heating at the same, Daikin recommends to produce the domestic
hot water during the night when there is lower space heating
demand.
Determining the DHW consumption
Answer the following questions and calculate the DHW consumption
(equivalent hot water volume at 40°C) using the typical water
volumes:
a Outdoor unit
b Indoor unit
c Heat exchanger
d Backup heater
e Motorised 3‑wave valve (switch between space heating
and domestic hot water)
f Motorised 3‑way valve (mixing the main zone)
g Main pump
h Additional pump
i Shut-off valve
j Collector (field supply)
k Domestic hot water tank
FHL1...3 Floor heating loops (field supply)
UI User interface (field supply)
HPC1...3 Heat pump convectors (field supply)
Installer reference guide
12
Question Typical water volume
How many showers are needed
per day?
How many baths are needed per
1shower = 10min×10l/min =
100l
1bath = 150l
day?
How much water is needed at the
1sink = 2min×5l/min = 10l
kitchen sink per day?
Are there any other domestic hot
—
water needs?
Example: If the DHW consumption of a family (4 persons) per day is
as follows:
▪ 3 showers
▪ 1 bath
▪ 3 sink volumes
Then the DHW consumption = (3×100l)+(1×150l)+(3×10l)=480l
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 13
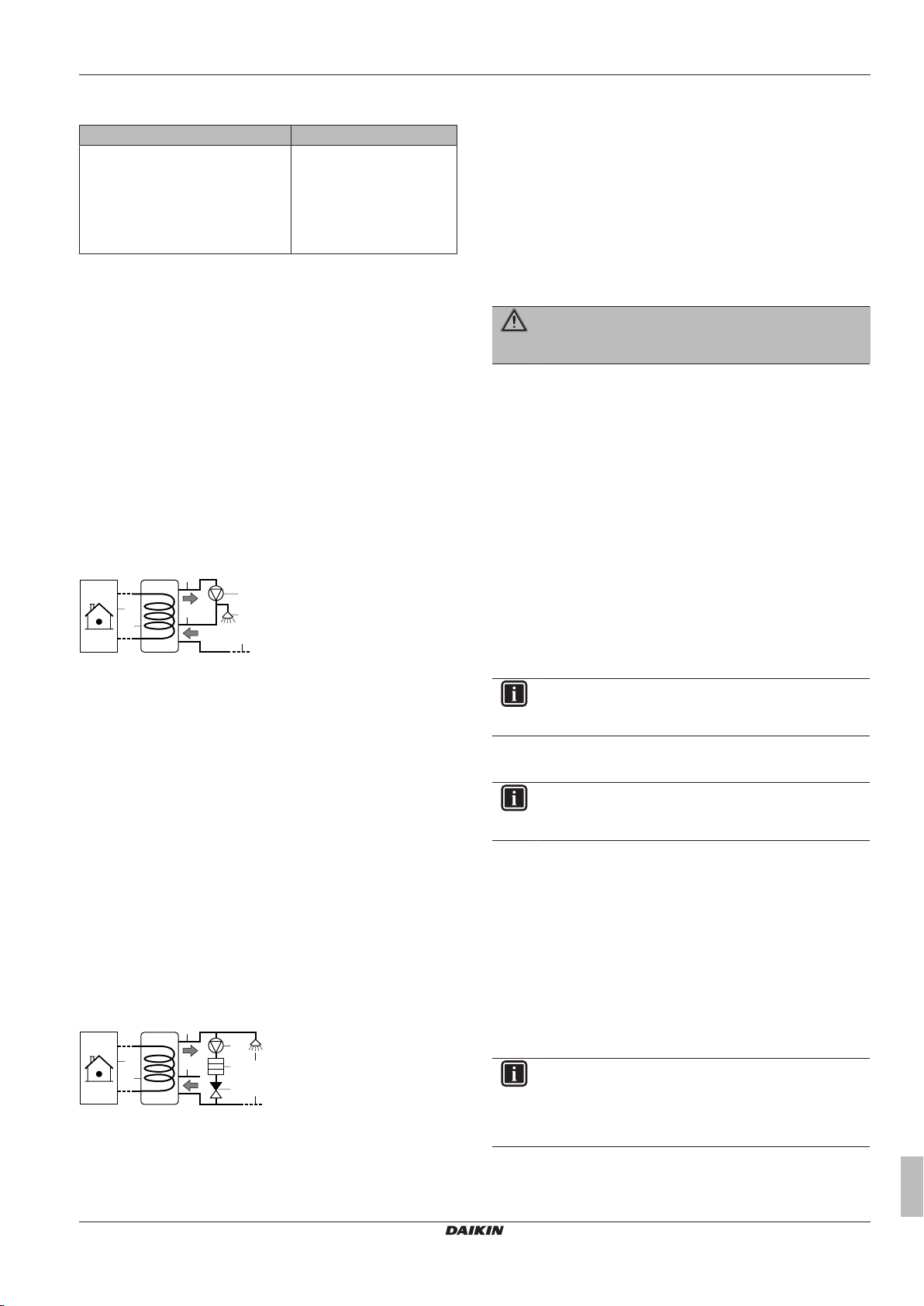
5 Application guidelines
c
f
a
b
g
h
i
c
a
b
d f
e g
h
i
Determining the volume and desired temperature for the DHW
tank
Formula Example
V1=V2+V2×(T2−40)/(40−T1) If:
▪ V2=180l
▪ T2=54°C
▪ T1=15°C
Then V1=280l
V1DHW consumption (equivalent hot water volume at 40°C)
V2Required DHW tank volume if only heated once
T2DHW tank temperature
T1Cold water temperature
5.3.3 Setup and configuration – DHW tank
▪ For large DHW consumptions, you can heat up the DHW tank
several times during the day.
▪ To heat up the DHW tank to the desired DHW tank temperature,
you can use the following energy sources:
▪ Thermodynamic cycle of the heatpump
▪ Electrical backup heater
▪ For more information about optimizing the energy consumption for
producing domestic hot water, see "8Configuration"on page41.
5.3.4 DHW pump for instant hot water
Setup
a Indoor unit
b DHW tank
c DHW pump (field supply)
f Shower (field supply)
g Cold water
h Domestic hot water OUT
i Recirculation connection
▪ By connecting a DHW pump, instant hot water can be available at
the tap.
▪ The DHW pump and the installation are field supply and the
responsibility of the installer.
▪ For more information about connecting the recirculation
connection: see "7Installation"on page23.
Configuration
▪ For more information, see "8Configuration"on page41.
▪ You can program a schedule to control the DHW pump via the
user interface. For more information, see the user reference
guide.
5.3.5 DHW pump for disinfection
Setup
i Recirculation connection
▪ The DHW pump is field-supplied and its installation is the
responsibility of the installer.
▪ The temperature of the DHW tank can be set to maximum 60°C. If
applicable legislation requires higher temperature for disinfection,
you can connect a DHW pump and heater element as shown
above.
▪ If applicable legislation requires disinfection of the water piping
until the tapping point, you can connect a DHW pump and heater
element (if needed) as shown above.
▪ To ensure a complete disinfection, you have to open the tapping
point.
WARNING
When opening the tapping point, the water temperature
can be up to 55°C.
Configuration
The indoor unit can control DHW pump operation. For more
information, see "8Configuration"on page41.
5.4 Setting up the energy metering
▪ Via the user interface, you can read out the following energy data:
▪ Produced heat
▪ Consumed energy
▪ You can read out the energy data:
▪ For space heating
▪ For domestic hot water production
▪ You can read out the energy data:
▪ Per month
▪ Per year
INFORMATION
The calculated produced heat and consumed energy are
an estimation, the accuracy cannot be guaranteed.
5.4.1 Produced heat
INFORMATION
The sensors used to calculate the produced heat are
calibrated automatically.
▪ The produced heat is calculated internally based on:
▪ The leaving and entering water temperature
▪ The flow rate
▪ Setup and configuration: No additional equipment needed.
5.4.2 Consumed energy
You can use the following methods to determine the consumed
energy:
▪ Calculating
▪ Measuring
a Indoor unit
b DHW tank
c DHW pump (field supply)
d Heater element (field supply)
e Non‑return valve (field supply)
f Shower (field supply)
g Cold water
h Domestic hot water OUT
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
INFORMATION
You cannot combine calculating the consumed energy
(example: for backup heater) and measuring the
consumed energy (example: for outdoor unit). If you do so,
the energy data will be invalid.
Calculating the consumed energy
▪ Only applicable for EHVZ04+08.
Installer reference guide
13
Page 14
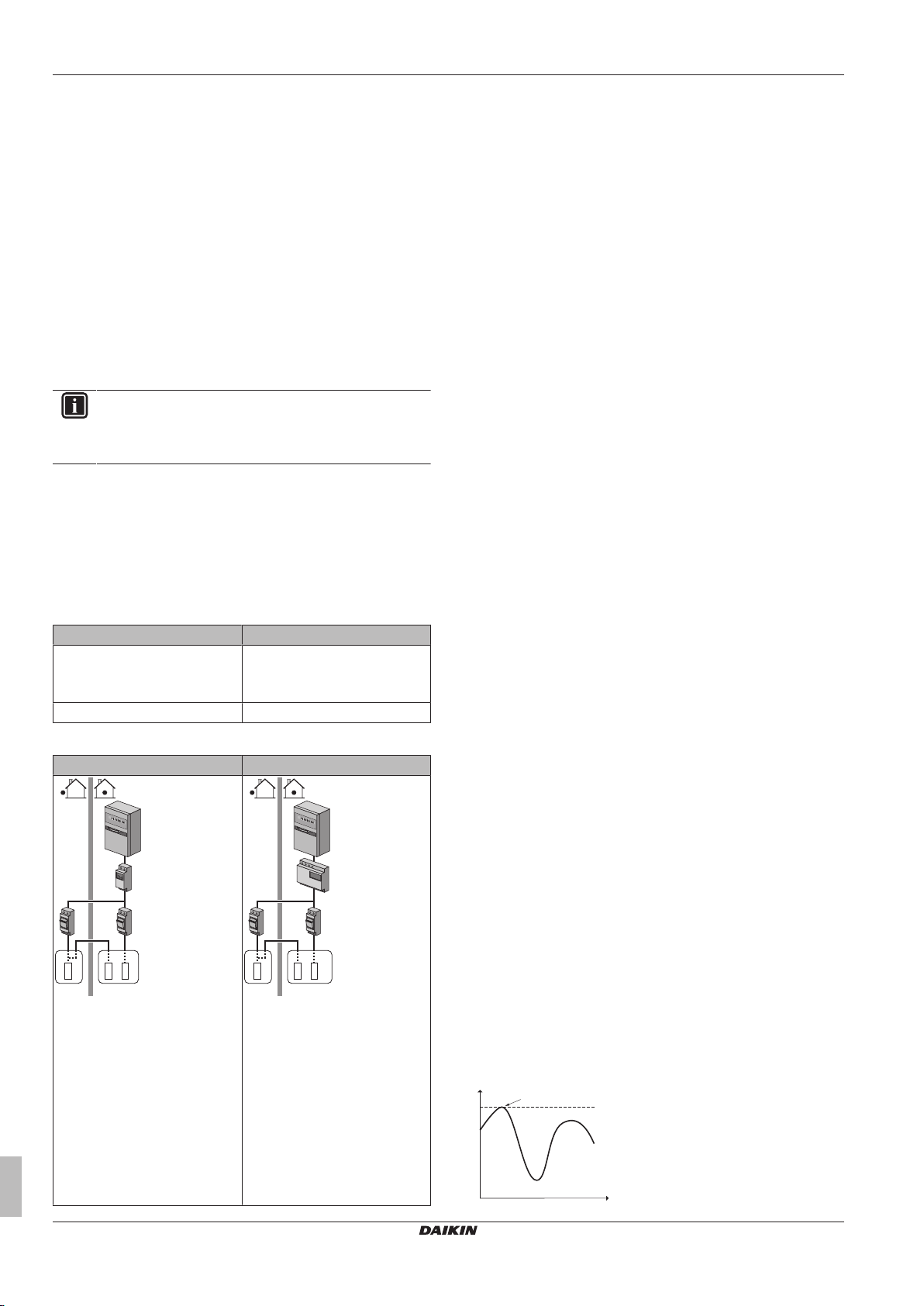
5 Application guidelines
b
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
c c
fed
A B
a
b
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
gfe
A B
c d
a
P
i
t
DI
a
b
▪ The consumed energy is calculated internally based on:
▪ The actual power input of the outdoor unit
▪ The set capacity of the backup heater
▪ The voltage
▪ Setup and configuration: To get accurate energy data, measure
the capacity (resistance measurement) and set the capacity via
the user interface for the backup heater (step1).
Measuring the consumed energy
▪ Applicable for all models.
▪ Preferred method because of higher accuracy.
▪ Requires external power meters.
▪ Setup and configuration: When using electrical power meters, set
the number of pulses/kWh for each power meter via the user
interface. Consumed energy data for EHVZ16 model will only be
available if this setting is configured.
INFORMATION
When measuring the electrical power consumption, make
sure ALL power input of the system is covered by the
electrical power meters.
5.4.3 Normal kWh rate power supply
General rule
One power meter that covers the entire system is sufficient.
Setup
Connect the power meter to X5M/7 and X5M/8.
Power meter type
In case of… Use a… power meter
▪ Single-phase outdoor unit
▪ Backup heater supplied from a
single-phase grid
Three-phase outdoor unit Three-phase
Example
Single-phase power meter Three-phase power meter
Single-phase
Exception
▪ You can use a second power meter if:
▪ The power range of one meter is insufficient.
▪ The electrical meter cannot easily be installed in the electrical
cabinet.
▪ 230 V and 400 V three-phase grids are combined (very
uncommon), because of technical limitations of power meters.
▪ Connection and setup:
▪ Connect the second power meter to X5M/9 and X5M/10.
▪ In the software the power consumption data of both meters is
added so you do NOT have to set which meter covers which
power consumption. You only need to set the number of pulses
of each power meter.
▪ See "5.4.4 Preferential kWh rate power supply"on page 14 for
an example with two power meters.
5.4.4 Preferential kWh rate power supply
General rule
▪ Power meter1: Measures the outdoor unit.
▪ Power meter 2: Measures the rest (i.e. indoor unit and backup
heater).
Setup
▪ Connect power meter1 to X5M/7 and X5M/8.
▪ Connect power meter2 to X5M/9 and X5M/10.
Power meter types
▪ Power meter1: Single- or three-phase power meter according to
the power supply of the outdoor unit.
▪ Power meter2: Use a single-phase power meter.
5.5 Setting up the power consumption control
▪ The power consumption control:
▪ Is only applicable for EHVZ04+08.
▪ Allows you to limit the power consumption of the entire system
(sum of outdoor unit, indoor unit and backup heater).
▪ Configuration: Set the power limitation level and how it has to
be achieved via the user interface.
▪ The power limitation level can be expressed as:
▪ Maximum running current (inA)
▪ Maximum power input (inkW)
▪ The power limitation level can be activated:
▪ Permanently
▪ By digital inputs
A Outdoor unit
B Indoor unit
a Electrical cabinet (L1/N)
b Power meter (L1/N)
c Fuse (L1/N)
d Outdoor unit (L1/N)
e Indoor unit (L1/N)
f Backup heater (L1/N)
Installer reference guide
14
A Outdoor unit
B Indoor unit
a Electrical cabinet (L1/L2/L3/N)
b Power meter (L1/L2/L3/N)
c Fuse (L1/L2/L3/N)
d Fuse (L1/N)
e Outdoor unit (L1/L2/L3/N)
f Indoor unit (L1/L2/L3/N)
g Backup heater (L1/N)
5.5.1 Permanent power limitation
Permanent power limitation is useful to assure a maximum power or
current input of the system. In some countries, legislation limits the
maximum power consumption for space heating and DHW
production.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 15
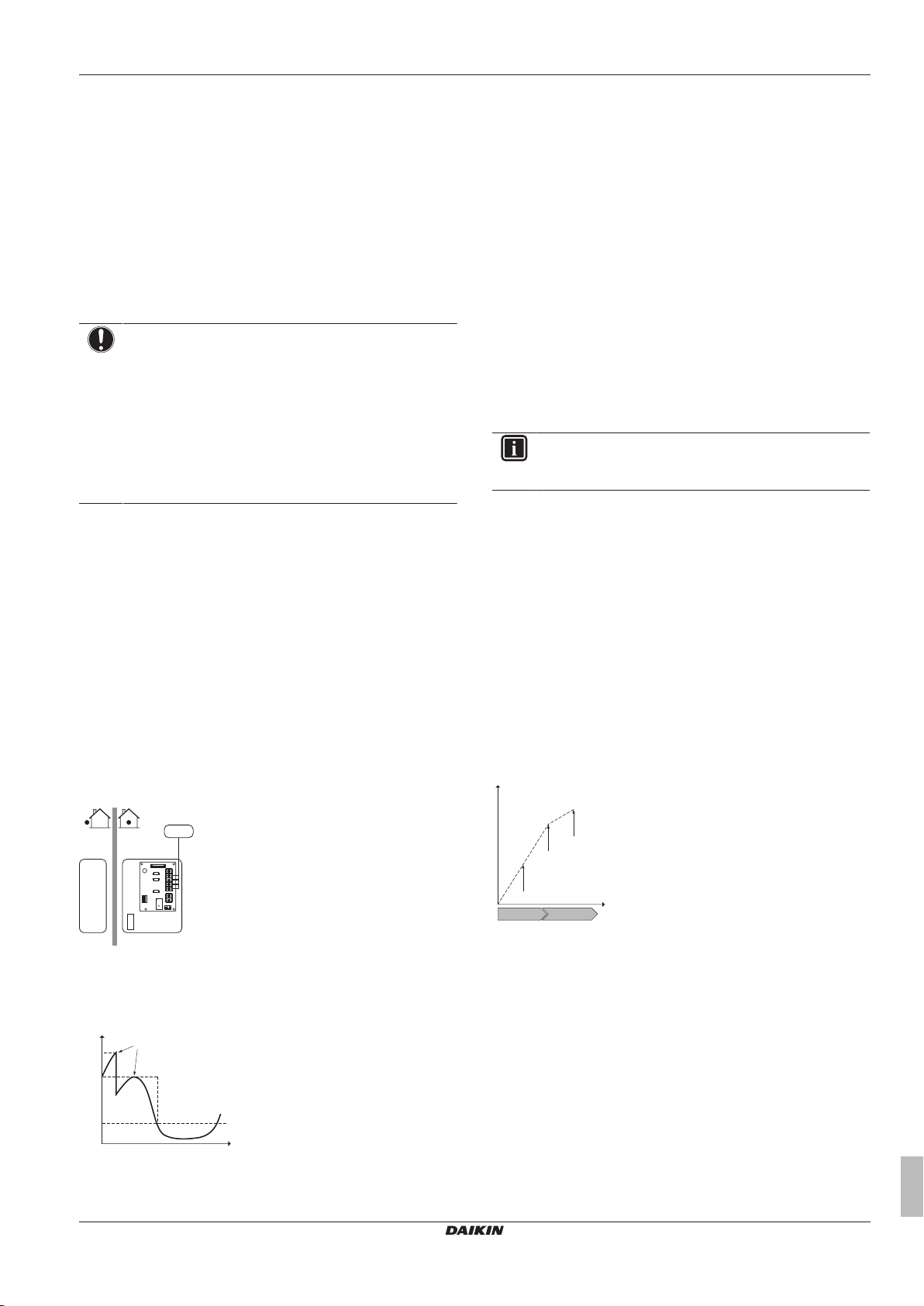
5 Application guidelines
a
b
A B
C
1
2
3
4
5
A8P
P
i
t
DI4
DI3
DI1
a
b
P
h
C
e
a
b
c
A B
PiPower input
t Time
DI Digital input (power limitation level)
a Power limitation active
b Actual power input
Setup and configuration
▪ No additional equipment needed.
▪ Set the power consumption control settings in [A.6.3.1] via the
user interface (for the description of all settings, see
"8Configuration"on page41):
▪ Select full time limitation mode
▪ Select the type of limitation (power in kW or current in A)
▪ Set the desired power limitation level
NOTICE
Mind the following guidelines when selecting the desired
power limitation level:
▪ Set a minimum power consumption of ±3.6 kW to
guarantee defrost operation. Otherwise, if defrosting is
interrupted several times, the heat exchanger will
freeze up.
▪ Set a minimum power consumption of ±3 kW to
guarantee space heating and DHW production by
allowing the backup heater step1.
5.5.2 Power limitation activated by digital inputs
Power limitation is also useful in combination with an energy
management system.
The power or current of the entire Daikin system is limited
dynamically by digital inputs (maximum four steps). Each power
limitation level is set via the user interface by limiting one of the
following:
▪ Current (in A)
▪ Power input (in kW)
The energy management system (field supply) decides the activation
of a certain power limitation level. Example: To limit the maximum
power of the entire house (lighting, domestic appliances, space
heating…).
b Actual power input
Setup
▪ Demand PCB (option EKRP1AHTA) needed.
▪ Maximum four digital inputs are used to activate the
corresponding power limitation level:
▪ DI1 = weakest limitation (highest energy consumption)
▪ DI4 = strongest limitation (lowest energy consumption)
▪ For the specifications of the digital inputs, and for where to
connect them, refer to the wiring diagram.
Configuration
Set the power consumption control settings in [A.6.3.1] via the user
interface (for the description of all settings, see "8Configuration"on
page41):
▪ Select activation by digital inputs.
▪ Select the type of limitation (power in kW or current in A).
▪ Set the desired power limitation level corresponding to each digital
input.
INFORMATION
In case more than 1 digital input is closed (at the same
time), the digital input priority is fixed: DI4 priority>…>DI1.
5.5.3 Power limitation process
The outdoor unit has better efficiency than the electrical heater.
Therefore, the electrical heater is limited and turned OFF first. The
system limits power consumption in the following order:
1 Turns OFF the backup heater.
2 Limits the outdoor unit.
3 Turns OFF the outdoor unit.
Example
If the configuration is as follows: Power limitation level does NOT
allow operation of backup heater (step1).
Then power consumption is limited as follows:
A Outdoor unit
B Indoor unit
C Energy management system
a Power limitation activation (4 digital inputs)
b Backup heater
PiPower input
t Time
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
DI Digital inputs (power limitation levels)
a Power limitation active
PhProduced heat
CeConsumed energy
A Outdoor unit
B Backup heater
a Limited outdoor unit operation
b Full outdoor unit operation
c Backup heater step1 turned ON
5.6 Setting up an external temperature sensor
You can connect one external temperature sensor. It can measure
the indoor or outdoor ambient temperature. Daikin recommends to
use an external temperature sensor in the following cases:
Installer reference guide
15
Page 16
6 Preparation
b
c
a
Indoor ambient temperature
▪ In room thermostat control, the user interface is used as room
thermostat and it measures the indoor ambient temperature.
Therefore, the user interface must be installed on a location:
▪ Where the average temperature in the room can be detected
▪ That is NOT exposed to direct sunlight
▪ That is NOT near a heat source
▪ That is NOT affected by outside air or air draught because of,
for example, door opening/closing
▪ If this is NOT possible, Daikin recommends to connect a remote
indoor sensor (option KRCS01-1).
▪ Setup: For installation instructions, see the installation manual of
the remote indoor sensor.
▪ Configuration: Select room sensor [A.2.2.B].
Outdoor ambient temperature
▪ In the outdoor unit, the outdoor ambient temperature is measured.
Therefore, the outdoor unit must be installed on a location:
▪ At the north side of the house or at the side of the house where
the most heat emitters are located
▪ That is NOT exposed to direct sunlight
▪ If this is NOT possible, Daikin recommends to connect a remote
outdoor sensor (option EKRSCA1).
▪ Setup: For installation instructions, see the installation manual of
the remote outdoor sensor.
▪ Configuration: Select outdoor sensor [A.2.2.B].
▪ During suspend (see "8 Configuration"on page 41), the outdoor
unit is turned down to reduce the standby energy losses. As a
result, the outdoor ambient temperature is NOT read out.
▪ If the desired leaving water temperature is weather dependent, the
full time outdoor temperature measurement is important. This is
another reason to install the optional outdoor ambient temperature
sensor.
INFORMATION
The external outdoor ambient sensor data (either averaged
or instantaneous) is used in the weather-dependent control
curves. To protect the outdoor unit, the internal sensor of
the outdoor unit is always used.
6 Preparation
6.1 Overview: Preparation
This chapter describes what you have to do and know before going
on-site.
It contains information about:
▪ Preparing the installation site
▪ Preparing the refrigerant piping
▪ Preparing the water piping
▪ Preparing the electrical wiring
NOTICE
This unit is designed for operation on 2 temperature zones:
▪ underfloor heating in the main zone (water
temperature 35°C), this is the zone with the lowest
water temperature,
▪ radiators in the additional zone (water temperature
45°C), this is the zone with the highest water
temperature.
6.2.1 Installation site requirements of the outdoor unit
INFORMATION
Also read the following requirements:
▪ General installation site requirements. See the
"General safety precautions" chapter.
▪ Service space requirements. See the "Technical data"
chapter.
▪ Refrigerant piping requirements (length, height
difference). See further in this "Preparation" chapter.
▪ Select a place where rain can be avoided as much as possible.
▪ Take care that in the event of a water leak, water cannot cause
any damage to the installation space and surroundings.
Do NOT install the unit in the following places:
▪ Sound sensitive areas (e.g. near a bedroom), so that the
operation noise will cause no trouble.
Note: If the sound is measured under actual installation
conditions, the measured value might be higher than the sound
pressure level mentioned in Sound spectrum in the data book due
to environmental noise and sound reflections.
▪ In places where a mineral oil mist, spray or vapour may be
present in the atmosphere. Plastic parts may deteriorate and fall
off or cause water leakage.
It is NOT recommended to install the unit in the following places
because it may shorten the life of the unit:
▪ Where the voltage fluctuates a lot
▪ In vehicles or vessels
▪ Where acidic or alkaline vapour is present
Seaside installation. Make sure the outdoor unit is NOT directly
exposed to sea winds. This is to prevent corrosion caused by high
levels of salt in the air, which might shorten the life of the unit.
Install the outdoor unit away from direct sea winds.
Example: Behind the building.
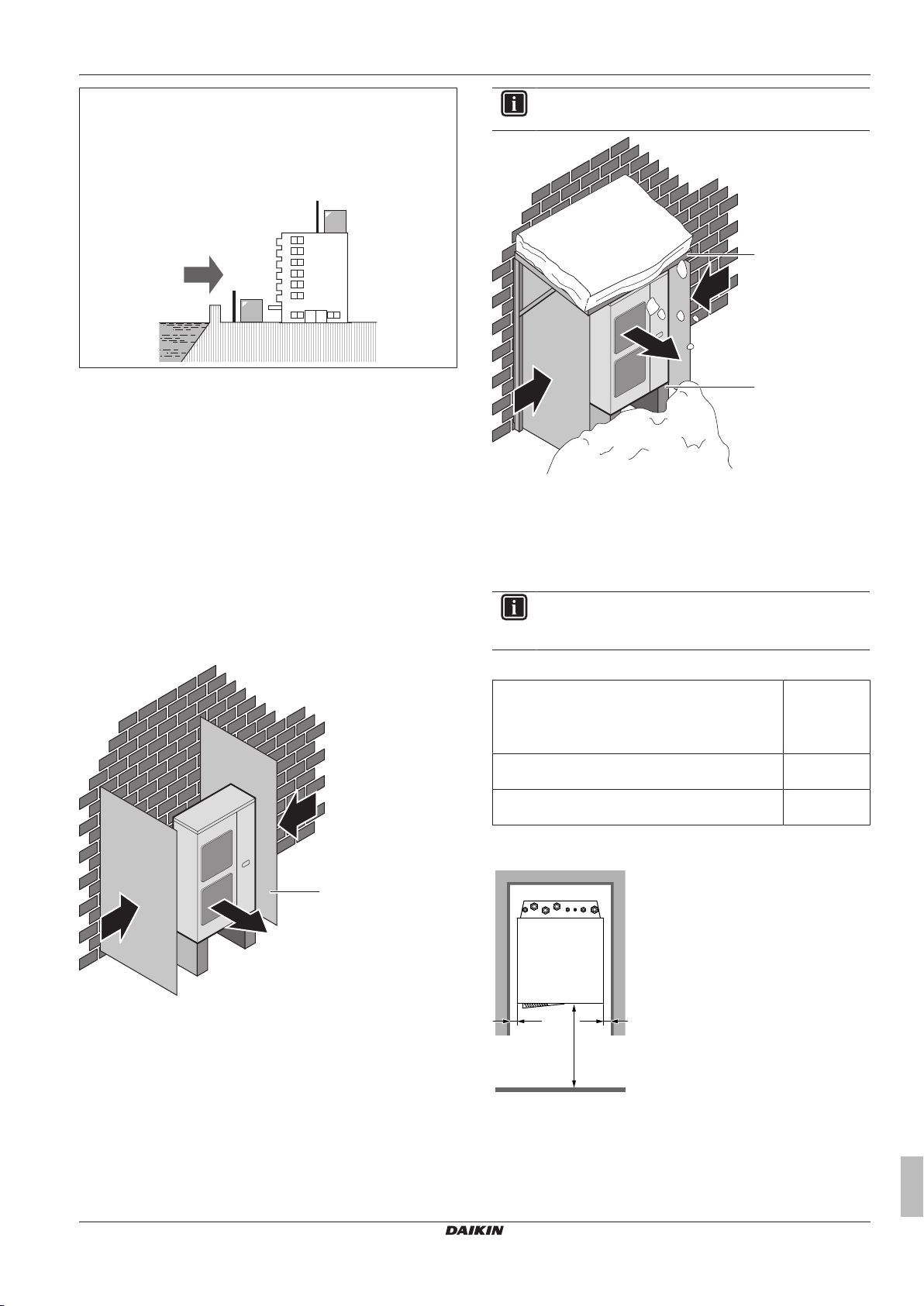
6.2 Preparing installation site
Do NOT install the unit in places often used as work place. In case
of construction works (e.g. grinding works) where a lot of dust is
created, the unit must be covered.
Choose the installation location with sufficient place for carrying the
unit in and out of the site.
Installer reference guide
16
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 17
6 Preparation
a
b
c
d
c
d
a
b
c
b
a
b
c
c
d
>500
>10>10
(mm)
If the outdoor unit is exposed to direct sea winds, install a
windbreaker.
▪ Height of windbreaker≥1.5×height of outdoor unit
▪ Mind the service space requirements when installing the
windbreaker.
a Sea wind
b Building
c Outdoor unit
d Windbreaker
Strong winds (≥18 km/h) blowing against the outdoor unit’s air outlet
causes short circuit (suction of discharge air). This may result in:
▪ deterioration of the operational capacity;
▪ frequent frost acceleration in heating operation;
▪ disruption of operation due to decrease of low pressure or
increase of high pressure;
▪ a broken fan (if a strong wind blows continuously on the fan, it
may start rotating very fast, until it breaks).
It is recommended to install a baffle plate when the air outlet is
exposed to wind.
It is recommended to install the outdoor unit with the air inlet facing
the wall and NOT directly exposed to the wind.
INFORMATION
You can use the optional snow cover (EK016SNC).
a Snow cover or shed
b Pedestal (minimum height=150mm)
c Prevailing wind direction
d Air outlet
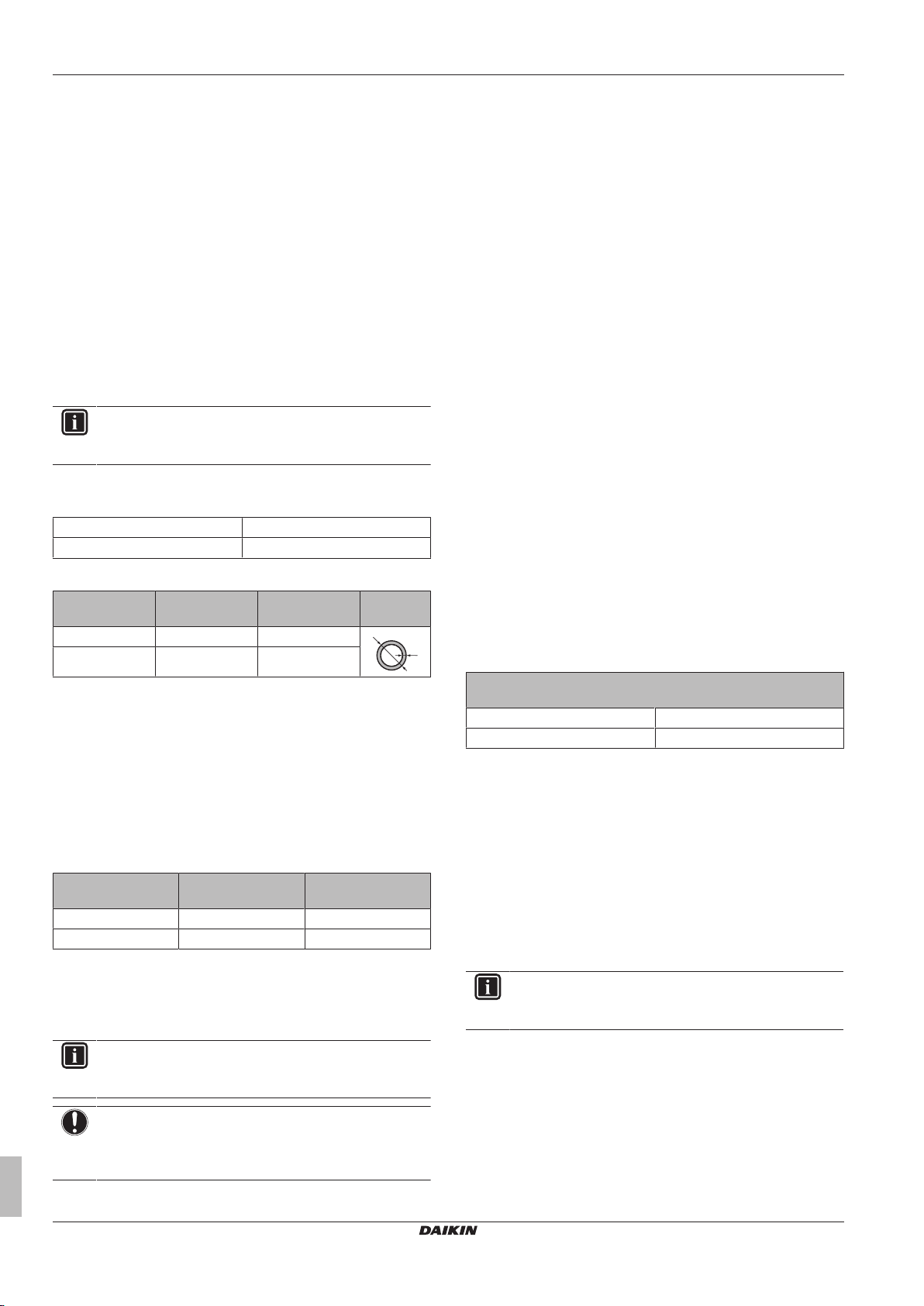
6.2.3 Installation site requirements of the indoor unit
INFORMATION
Also read the precautions and requirements in the
"General safety precautions" chapter.
▪ Mind the measurement guidelines:
Maximum refrigerant piping length between indoor
unit and outdoor unit
Minimum refrigerant piping length between indoor
ERHQ: 75m
ERLQ: 50m
(95m)
(70m)
(a)
(a)
3m
unit and outdoor unit
Maximum height difference between indoor unit and
30m
outdoor unit
(a) Parenthesised figure represents the equivalent length.
▪ Mind the following spacing installation guidelines:
a Baffle plate
b Prevailing wind direction
c Air outlet
The outdoor unit is designed for outdoor installation only, and for
ambient temperatures ranging 10~43°C in cooling mode and –
25~25°C in heating mode.
6.2.2 Additional installation site requirements of the outdoor unit in cold climates
Protect the outdoor unit against direct snowfall and take care that the
outdoor unit is NEVER snowed up.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Do NOT install the unit in places such as:
▪ In places where a mineral oil mist, spray or vapour may be
present in the atmosphere. Plastic parts may deteriorate and fall
off or cause water leakage.
Installer reference guide
17
Page 18
6 Preparation
t
Ø
▪ Sound sensitive areas (e.g. near a bedroom), so that the
operation noise will cause no trouble.
▪ The foundation must be strong enough to bear the weight of the
unit. Take the weight of the unit with a domestic hot water tank full
of water into account.
Make sure, in the event of a water leak, water cannot cause any
damage to the installation space and surroundings.
▪ In places with high humidity (max. RH=85%), for example a
bathroom.
▪ In places where frost is possible. Ambient temperature around the
indoor unit should be >5°C.
▪ The indoor unit is designed for indoor installation only and for
ambient temperatures ranging from 5~35°C.
6.3 Preparing refrigerant piping
6.3.1 Refrigerant piping requirements
INFORMATION
Also read the precautions and requirements in the
"General safety precautions" chapter.
▪ Piping material: Phosphoric acid deoxidised seamless copper.
▪ Piping diameter:
Liquid piping Ø9.5mm (3/8")
Gas piping Ø15.9mm (5/8")
▪ Piping temper grade and thickness:
Outer diameter
(Ø)
9.5mm (3/8") Annealed (O) ≥0.8mm
15.9mm (5/8") Annealed (O) ≥1.0mm
(a) Depending on the applicable legislation and the unit's
Temper grade Thickness (t)
maximum working pressure (see "PS High" on the unit
name plate), larger piping thickness might be required.
6.3.2 Refrigerant piping insulation
▪ Use polyethylene foam as insulation material:
▪ with a heat transfer rate between 0.041 and 0.052W/mK (0.035
and 0.045kcal/mh°C)
▪ with a heat resistance of at least 120°C
▪ Insulation thickness
Ambient
temperature
≤30°C 75% to 80% RH 15mm
>30°C ≥80% RH 20mm
Humidity Minimum thickness
(a)
▪ Connecting piping – Legislation. Make all piping connections in
accordance with the applicable legislation and the instructions in
the "Installation" chapter, respecting the water inlet and outlet.
▪ Connecting piping – Force. Do NOT use excessive force when
connecting the piping. Deformation of the piping can cause
malfunctioning of the unit.
▪ Connecting piping – Tools. Only use appropriate tooling to
handle brass, which is a soft material. If NOT, pipes will get
damaged.
▪ Connecting piping – Air, moisture, dust. If air, moisture or dust
gets into the circuit, problems may occur. To prevent this:
▪ Only use clean pipes
▪ Hold the pipe end downwards when removing burrs.
▪ Cover the pipe end when inserting it through a wall, to prevent
dust and/or particles entering the pipe.
▪ Use a decent thread sealant to seal connections.
▪ Closed circuit. Use the indoor unit ONLY in a closed water
system. Using the system in an open water system will lead to
excessive corrosion.
▪ Glycol. For safety reasons, it is NOT allowed to add any kind of
glycol to the water circuit.
▪ Piping length. It is recommended to avoid long runs of piping
between the domestic hot water tank and the hot water end point
(shower, bath,…) and to avoid dead ends.
▪ Piping diameter. Select the water piping diameter in relation to
the required water flow and the available external static pressure
of the pump. See "14 Technical data"on page74 for the external
static pressure curves of the indoor unit.
▪ Water flow. You can find the minimum required water flow for
indoor unit operation in the following table. In all cases, this flow
needs to be guaranteed. When the flow is lower, the indoor unit
will stop operation and display error 7H.
Minimum required flow rate during defrost/backup heater
operation
04+08 models 12l/min
16 model 15l/min
▪ Field supply components – Water. Only use materials that are
compatible with water used in the system and with the materials
used in the indoor unit.
▪ Field supply components – Water pressure and temperature.
Check that all components in the field piping can withstand the
water pressure and water temperature.
▪ Water pressure. The maximum water pressure is 4 bar. Provide
adequate safeguards in the water circuit to ensure that the
maximum pressure is NOT exceeded.
▪ Water temperature. All installed piping and piping accessories
(valve, connections,…) MUST withstand the following
temperatures:
6.4 Preparing water piping
6.4.1 Water circuit requirements
INFORMATION
Also read the precautions and requirements in the
"General safety precautions" chapter.
NOTICE
In case of plastic pipes, make sure they are fully oxygen
diffusion tight according to DIN 4726. The diffusion of
oxygen into the piping can lead to excessive corrosion.
Installer reference guide
18
INFORMATION
The following illustration is an example and might NOT
match your system layout.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 19
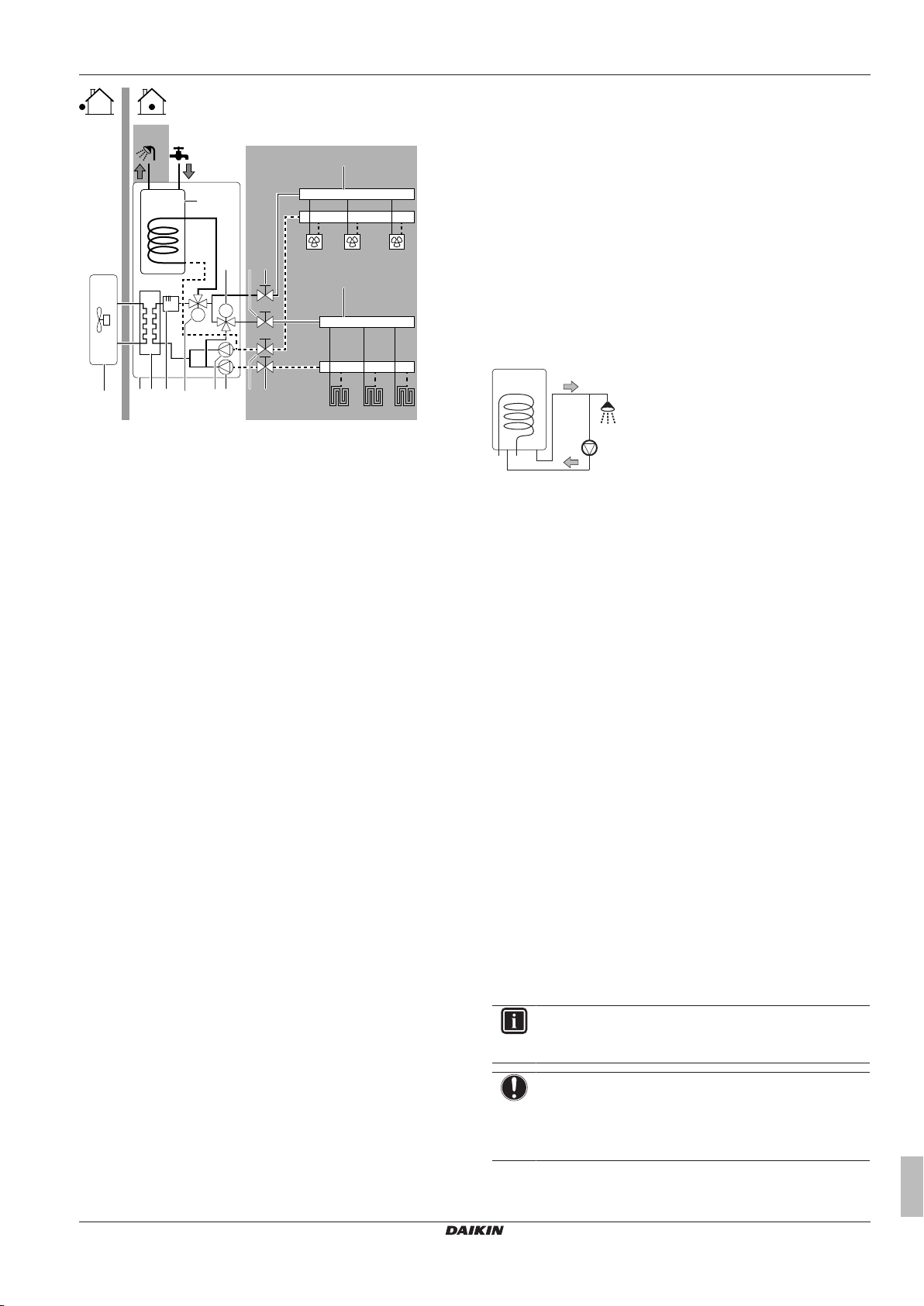
89°C
75°C
M
M
a b c d ge h ii
i
j
j
fki
HPC1
FHL1 FHL2 FHL3
HPC2 HPC3
a Outdoor unit
c
d
a b
b Indoor unit
c Heat exchanger
d Backup heater
e Motorised 3‑way valve (switch between space heating and
domestic hot water)
f Motorised 3‑way valve (mixing the main zone)
g Main pump
h Additional pump
i Shut-off valve
j Collector (field supply)
k Domestic hot water tank
HPC1...3 Heat pump convector (field supply)
FHL1...3 Floor heating loop (field supply)
▪ Drainage – Low points. Provide drain taps at all low points of the
system in order to allow complete drainage of the water circuit.
▪ Drainage – Pressure relief valve. Provide a proper drain for the
pressure relief valve to avoid water dripping out of the unit. See
"7.8.5 To connect the pressure relief valve to the drain" on
page32.
▪ Air vents. Provide air vents at all high points of the system, which
must also be easily accessible for servicing. An automatic air
purge is provided in the indoor unit. Check that the air purge is
NOT tightened too much, so that automatic release of air in the
water circuit is possible.
▪ Zn-coated parts. Never use Zn-coated parts in the water circuit.
Because the unit's internal water circuit uses copper piping,
excessive corrosion may occur.
▪ Non-brass metallic piping. When using non-brass metallic
piping, insulate the brass and non-brass properly so that they do
NOT make contact with each other. This to prevent galvanic
corrosion.
▪ Valve – Change‑over time. When using a 2-way valve or a 3-way
valve in the water circuit, the maximum change-over time of the
valve must be 60seconds.
▪ Filter. It is strongly recommended to install an additional filter on
both heating water circuits. Especially to remove metallic particles
from foul heating piping, it is recommended to use a magnetic or
cyclone filter, which can remove small particles. Small particles
may damage the unit and will NOT be removed by the standard
filter of the heat pump system.
▪ Domestic hot water tank – Capacity. To avoid stagnation of
water, it is important that the storage capacity of the domestic hot
water tank meets the daily consumption of domestic hot water.
▪ Domestic hot water tank – After installation. Immediately after
installation, the domestic hot water tank must be flushed with fresh
water. This procedure must be repeated at least once a day the
first 5 consecutive days after installation.
6 Preparation
▪ Domestic hot water tank – Standstills. In cases where during
longer periods of time there is no consumption of hot water, the
equipment MUST be flushed with fresh water before usage.
▪ Domestic hot water tank – Disinfection. For the disinfection
function of the domestic hot water tank, see "8.3.2Domestic hot
water control: advanced"on page53.
▪ Thermostatic mixing valves. In accordance with the applicable
legislation, it may be necessary to install thermostatic mixing
valves.
▪ Hygienic measures. The installation must be in compliance with
the applicable legislation and may require additional hygienic
installation measures.
▪ Recirculation pump. In accordance with the applicable
legislation, it may be required to connect a recirculation pump in
between the hot water end point and the recirculation connection
of the domestic hot water tank.
a Recirculation connection
b Hot water connection
c Shower
d Recirculation pump
6.4.2 Formula to calculate the expansion vessel pre-pressure
The pre-pressure (Pg) of the vessel depends on the installation
height difference (H):
Pg=0.3+(H/10) (bar)
6.4.3 To check the water volume and flow rate
The indoor unit has an expansion vessel of 10litre with a factory set
pre-pressure of 1bar.
To make sure that the unit operates properly:
▪ You must check the minimum and maximum water volume.
▪ You might need to adjust the pre-pressure of the expansion
vessel.
Minimum water volume
Check that the total water volume in the installation is minimum
10 litre for EHVZ04+08 and 20litre for EHVZ16, the internal water
volume of the indoor unit NOT included. Do NOT split up the
minimum water volume over the 2 temperature zones.
It is sufficient to foresee the minimum water volume on the main
zone. In case of underfloor heating, this is easily done by 1 floor
heating loop that never will be closed by a (remotely) controlled
valve.
It is NOT required to foresee the minimum water volume on the
additional zone.
INFORMATION
In critical processes, or in rooms with a high heat load,
extra water might be required.
NOTICE
When circulation in each space heating/cooling loop is
controlled by remotely controlled valves, it is important that
the minimum water volume is guaranteed, even if all of the
valves are closed.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
19
Page 20
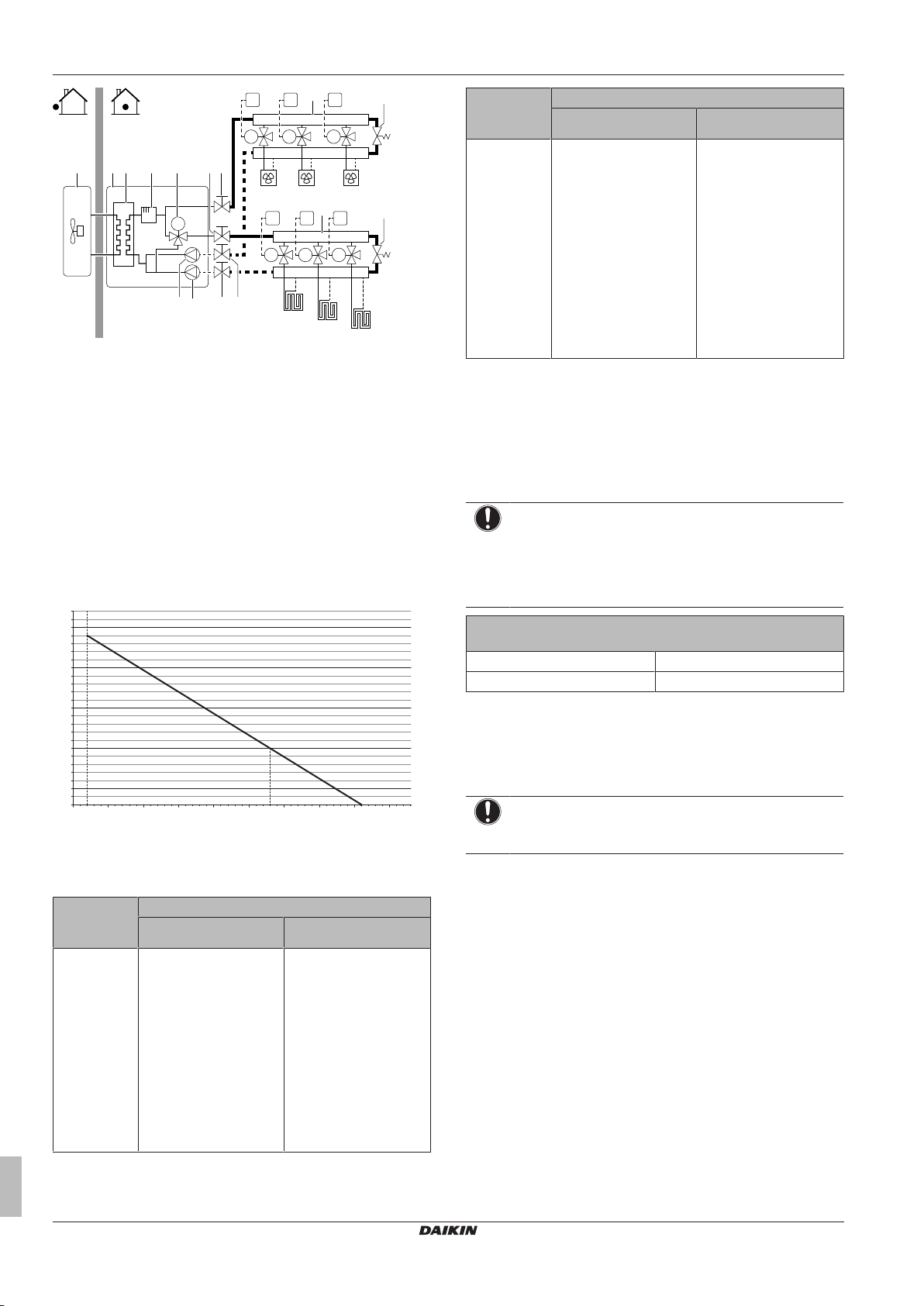
6 Preparation
T1
M1
T1
M1
T2M2T3
M3
M
FHL1
FHL2
FHL3
M2 M3
T2 T3
HPC1 HPC2 HPC3
a b c
g hf
d e
i
i
hh
h
j
j
0.3
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
100500
20
150 200 250 300 350 400 450
a
b
a Outdoor unit
b Indoor unit
c Heat exchanger
d Backup heater
e Motorised 3‑way valve (mixing the main zone)
f Additional pump
g Main pump
h Shut-off valve
i Collector (field supply)
j By-pass valve (field supply)
FHL1...3 Floor heating loop (field supply)
HPC1...3 Heat pump convector (field supply)
T1...3 Individual room thermostat (optional)
M1...3 Individual motorised valve to control loop FHL1...3 and
HPC1...3 (field supply)
Maximum water volume
Use the following graph to determine the maximum water volume for
the calculated pre-pressure.
Installation
height
difference
(a)
≤280l >280l
>7m Do the following:
▪ Increase the pre-
pressure according to
the required
installation height
difference. The prepressure should
Water volume
The expansion vessel of
the indoor unit is too
small for the installation.
In this case, it is
recommended to install
an extra vessel outside
the unit.
increase by 0.1 bar for
each metre above 7 m.
▪ Check if the water
volume does NOT
exceed the maximum
allowed water volume.
(a) This is the height difference (m) between the highest point
of the water circuit and the indoor unit. If the indoor unit is
at the highest point of the installation, the installation height
is 0m.
Minimum flow rate
Check that the minimum flow rate (required during defrost/backup
heater operation) in the installation is guaranteed in all conditions on
each zone separately.
NOTICE
When circulation in each or certain space heating loops is
controlled by remotely controlled valves, it is important that
the minimum flow rate is guaranteed, even if all valves are
closed. In case the minimum flow rate cannot be reached,
a flow error 7H will be generated (no heating/operation).
a Pre-pressure (bar)
b Maximum water volume (l)
Example: Maximum water volume and expansion vessel prepressure
Installation
height
difference
(a)
≤280l >280l
≤7m No pre-pressure
adjustment is required.
Water volume
Do the following:
▪ Decrease the pre-
pressure according to
the required installation
height difference. The
pre-pressure should
decrease by 0.1 bar for
each metre below 7 m.
▪ Check if the water
volume does NOT
exceed the maximum
allowed water volume.
Minimum required flow rate during defrost/backup heater
operation
04+08 models 12l/min
16 model 15l/min
See the recommended procedure as described in "9.4 Checklist
during commissioning"on page63.
6.4.4 Changing the pre-pressure of the expansion vessel
NOTICE
Only a licensed installer may adjust the pre-pressure of the
expansion vessel.
When changing the default pre-pressure of the expansion vessel
(1bar) is required, take following guidelines into account:
▪ Only use dry nitrogen to set the expansion vessel pre-pressure.
▪ Inappropriate setting of the expansion vessel pre-pressure will
lead to malfunction of the system.
Changing the pre-pressure of the expansion vessel should be done
by releasing or increasing nitrogen pressure through the Schrader
valve of the expansion vessel.
Installer reference guide
20
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 21
180 l
a
a Schrader valve
6.4.5 To check the water volume: Examples
Example 1
The indoor unit is installed 5 m below the highest point in the water
circuit. The total water volume in the water circuit is 100l.
No actions or adjustments are required.
Example 2
The indoor unit is installed at the highest point in the water circuit.
The total water volume in the water circuit is 350l.
Actions:
▪ Because the total water volume (350l) is more than the default
water volume (280l), the pre-pressure must be decreased.
▪ The required pre-pressure is:
Pg = (0.3+(H/10))bar = (0.3+(0/10))bar=0.3bar.
▪ The corresponding maximum water volume at 0.3 bar is 410 l.
(See the graph in the chapter above).
▪ Because 350 l is lower than 410 l, the expansion vessel is
appropriate for the installation.
6 Preparation
WARNING
▪ If the power supply has a missing or wrong N-phase,
equipment might break down.
▪ Establish proper earthing. Do NOT earth the unit to a
utility pipe, surge absorber, or telephone earth.
Incomplete earthing may cause electrical shock.
▪ Install the required fuses or circuit breakers.
▪ Secure the electrical wiring with cable ties so that the
cables do NOT come in contact with sharp edges or
piping, particularly on the high-pressure side.
▪ Do NOT use taped wires, stranded conductor wires,
extension cords, or connections from a star system.
They can cause overheating, electrical shock or fire.
▪ Do NOT install a phase advancing capacitor, because
this unit is equipped with an inverter. A phase
advancing capacitor will reduce performance and may
cause accidents.
WARNING
▪ All wiring must be performed by an authorized
electrician and must comply with the applicable
legislation.
▪ Make electrical connections to the fixed wiring.
▪ All components procured on the site and all electrical
construction must comply with the applicable
legislation.
WARNING
The backup heater MUST have a dedicated power supply
and MUST be protected by the safety devices required by
the applicable legislation.
WARNING
ALWAYS use multicore cable for power supply cables.
6.5.2 About preferential kWh rate power supply
6.5 Preparing electrical wiring
6.5.1 About preparing electrical wiring
INFORMATION
Also read the precautions and requirements in the
"General safety precautions" chapter.
INFORMATION
Also read "7.9.5 Specifications of standard wiring
components"on page34.
NOTICE
For applications with preferential kWh rate power supply:
The interruption of the outdoor unit power supply may not
be more than 2 hours to guarantee optimised startup
conditions for the compressor.
Electricity companies throughout the world work hard to provide
reliable electric service at competitive prices and are often
authorized to bill clients at benefit rates. E.g. time-of-use rates,
seasonal rates, Wärmepumpentarif in Germany and Austria, ...
This equipment allows for connection to such preferential kWh rate
power supply delivery systems.
Consult with the electricity company acting as provider at the site
where this equipment is to be installed to know whether it is
appropriate to connect the equipment in one of the preferential kWh
rate power supply delivery systems available, if any.
When the equipment is connected to such preferential kWh rate
power supply, the electricity company is allowed to:
▪ interrupt power supply to the equipment for certain periods of time;
▪ demand that the equipment only consumes a limited amount of
electricity during certain periods of time.
The indoor unit is designed to receive an input signal by which the
unit switches into forced off mode. At that moment, the outdoor unit
compressor will not operate.
Whether the power supply is interrupted or not, the wiring to the unit
is different.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
21
Page 22
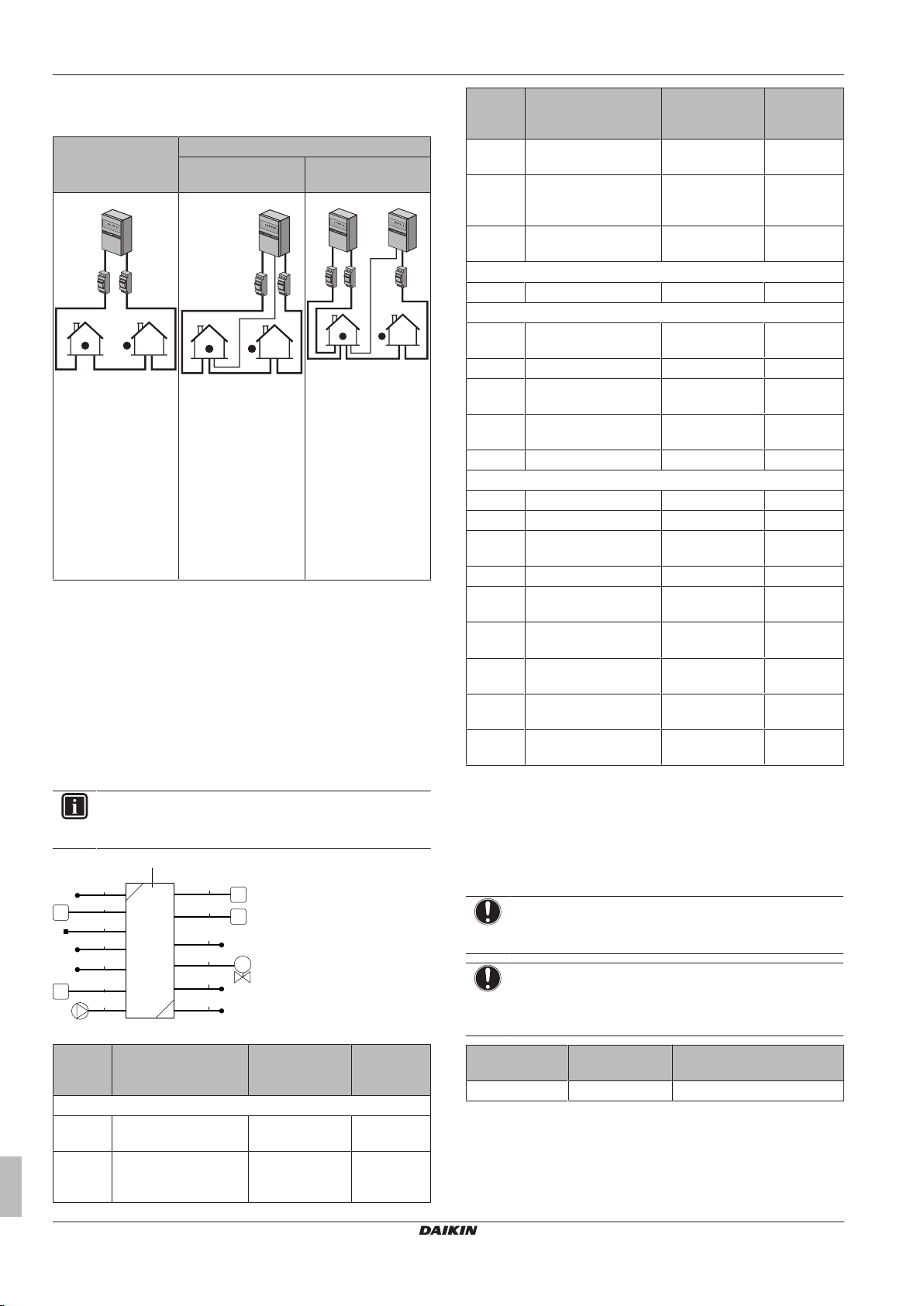
6 Preparation
1
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
2
a
3
1
4
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
2
b
3
5 3
a
b
14
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
5
8
0
1
5
0
0
0
2
M
a
16
21
22
19
15
20
24
23
12
6
13
17
18
6.5.3 Overview of electrical connections except external actuators
Normal power
supply
a Normal power supply
b Preferential kWh rate power supply
1 Power supply for outdoor unit
2 Power supply and interconnection cable to indoor unit
3 Power supply for backup heater
4 Preferential kWh rate power supply (voltage free contact)
5 Normal kWh rate power supply (to power the indoor unit
PCB in the event of power supply interruption of the
preferential kWh rate power supply)
Preferential kWh rate power supply
Power supply is
NOT interrupted
Power supply is
interrupted
During preferential
During preferential
kWh rate power
supply activation,
power supply is NOT
interrupted. The
outdoor unit is turned
off by the control.
Remark: The
electricity company
must always allow the
power consumption
of the indoor unit.
kWh rate power
supply activation,
power supply is
interrupted
immediately or after
some time by the
electricity company.
In this case, the
indoor unit must be
powered by a
separate normal
power supply.
6.5.4 Overview of electrical connections for external and internal actuators
The following illustration shows the required field wiring.
INFORMATION
The following illustration is an example and might NOT
match your system layout.
Item Description Wires Maximum
running
current
3 Power supply for
See table below. —
backup heater
4 Preferential kWh rate
2
(d)
power supply (voltage
free contact)
5 Normal kWh rate power
2 6.3A
supply
User interface
6 User interface 2
(e)
Optional equipment
11 Power supply for
2
(b)
bottom plate heater
12 Room thermostat 2 or 3 100mA
13 Outdoor ambient
2
(b)
temperature sensor
14 Indoor ambient
2
(b)
temperature sensor
15 Heat pump convector 2 100mA
Field supplied components
16 Shut-off valve 2 100mA
17 Electricity meter 2 (per meter)
18 Domestic hot water
2
(b)
(b)
pump
19 Alarm output 2
20 Changeover to external
2
(b)
(b)
heat source control
21 Space heating
2
(b)
operation control
22 Power consumption
digital inputs
23 Safety thermostat for
2 (per input
signal)
2
(b)
(b)
the main zone
24 Safety thermostat for
2
(d)
the additional zone
(a) Refer to name plate on outdoor unit.
(b) Minimum cable section 0.75mm².
(c) Cable section 2.5mm².
(d) Cable section 0.75mm² till 1.25mm²; maximum length:
50m. Voltage-free contact shall ensure the minimum
applicable load of 15VDC, 10mA.
(e) Cable section 0.75mm² till 1.25mm²; maximum length:
500m. Applicable for both single user interface and dual
user interface connection.
NOTICE
More technical specifications of the different connections
are indicated on the inside of the indoor unit.
(b)
(b)
(b)
a Indoor unit
Item Description Wires Maximum
Outdoor unit and indoor unit power supply
1 Power supply for
2 Power supply and
outdoor unit
interconnection cable to
indoor unit
Installer reference guide
22
2+GND or
3+GND
3
running
current
(a)
(c)
NOTICE
A safety thermostat (normal closed contact) MUST be
installed for the main zone. See "7.9.17 To connect the
safety thermostat (normal closed contact)"on page40.
Backup heater
type
Power supply Required number of
conductors
*3V 1× 230V 2+GND
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 23
7 Installation
3
45°~90°
(4)
2
1
1×
2
3
4
5
1
2
4×
2×
4×
7 Installation
7.1 Overview: Installation
This chapter describes what you have to do and know on-site to
install the system.
Typical workflow
Installation typically consists of the following stages:
1 Mounting the outdoor unit.
2 Mounting the indoor unit.
3 Connecting the refrigerant piping.
4 Checking the refrigerant piping.
5 Charging refrigerant.
6 Connecting the water piping.
7 Connecting the electrical wiring.
8 Finishing the outdoor installation.
9 Finishing the indoor installation.
INFORMATION
Depending on the units and/or the installation conditions, it
might be necessary to connect electrical wiring before you
can charge refrigerant.
7.2 Opening the units
7.2.3 To open the indoor unit
1 Loosen and remove the screws at the bottom of the unit.
2 Push on the button at the bottom of the front plate.
WARNING: Sharp edges
Take the front plate on the upper part instead of the lower
part. Watch your fingers, there are sharp edges on the
lower part of the front plate.
3 Slide the front panel of the unit downwards and remove it.
CAUTION
The front panel is heavy. Be careful NOT to jam your
fingers when opening or closing the unit.
4 Loosen and remove the 4 screws that fix the top panel.
5 Remove the top panel from the unit.
7.2.1 About opening the units
At certain times, you have to open the unit. Example:
▪ When connecting the refrigerant piping
▪ When connecting the electrical wiring
▪ When maintaining or servicing the unit
DANGER: RISK OF ELECTROCUTION
Do NOT leave the unit unattended when the service cover
is removed.
7.2.2 To open the outdoor unit
DANGER: RISK OF ELECTROCUTION
DANGER: RISK OF BURNING
7.2.4 To open the switch box cover of the indoor unit
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
7.3 Mounting the outdoor unit
7.3.1 About mounting the outdoor unit
When
You have to mount the outdoor and indoor unit before you can
connect the refrigerant and water piping.
Installer reference guide
23
Page 24
7 Installation
(mm)
>150
620
350
(345-355)
4× M12
a
20
a
4× M12
≥150 mm
58
16
16
71
11710270
45 376 191
a b
c
d (4×)
Typical workflow
Mounting the outdoor unit typically consists of the following stages:
1 Providing the installation structure.
2 Installing the outdoor unit.
3 Providing drainage.
4 Preventing the unit from falling over.
5 Protecting the unit against snow and wind by installing a snow
cover and baffle plates. See "Preparing installation site" in
"6Preparation"on page16.
7.3.2 Precautions when mounting the outdoor unit
INFORMATION
Also read the precautions and requirements in the
following chapters:
▪ General safety precautions
▪ Preparation
7.3.3 To provide the installation structure
Check the strength and level of the installation ground so that the
unit will not cause any operating vibration or noise.
Fix the unit securely by means of foundation bolts in accordance
with the foundation drawing.
Prepare 4 sets of anchor bolts, nuts and washers (field supply) as
follows:
7.3.4 To install the outdoor unit
7.3.5 To provide drainage
▪ Make sure that condensation water can be evacuated properly.
▪ Install the unit on a base to make sure that there is a proper
drainage in order to avoid ice accumulation.
▪ Prepare a water drainage channel around the foundation to drain
waste water surrounding the unit.
▪ Avoid drain water flowing over the footpath, so that it does not
become slippery in case of ambient freezing temperatures.
▪ If you install the unit on a frame, install a waterproof plate within
150 mm of the bottom side of the unit in order to prevent the
invasion of water in the unit and to avoid the drain water dripping
(see the following illustration).
Installer reference guide
24
a Make sure not to cover the drain holes of the bottom plate
of the unit.
INFORMATION
The recommended height of the upper protruding part of
the bolts is 20mm.
NOTICE
Fix the outdoor unit to the foundation bolts using nuts with
resin washers (a). If the coating on the fastening area is
stripped off, the nuts rust easily.
INFORMATION
You can use the optional drain plug kit (EKDK04) (only for
ERHQ).
NOTICE
If drain holes of the outdoor unit are covered by a mounting
base or by floor surface, raise the unit to provide a free
space of more than 150mm under the outdoor unit.
Drain holes
Model Bottom view (mm)
ERHQ_V3
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 25
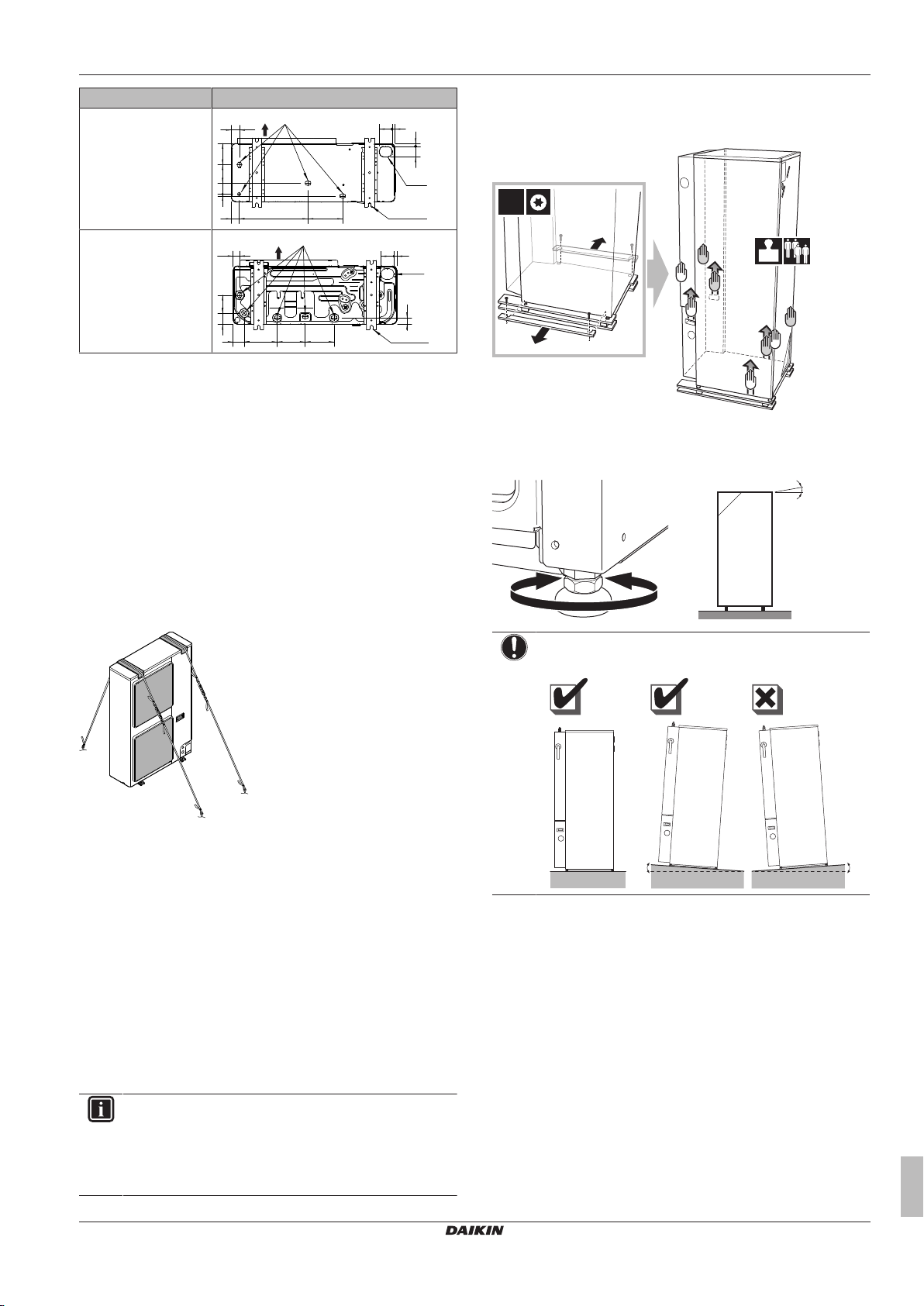
7 Installation
45
43 378
10 60
58 16
71 16
191
117102
a b
c
d (4×)
35
36
61 99
1671
60 159154182
a b
c
d (4×)
135 kg
4×
≤1°
0°
1°1°
Model Bottom view (mm)
ERHQ_W1
ERLQ
a Discharge side
b Drain holes
c Knockout hole (piping intake - downwards route)
d Anchor points
7.3.6 To prevent the outdoor unit from falling over
In case the unit is installed in places where strong wind can tilt the
unit, take following measure:
1 Prepare 2 cables as indicated in the following illustration (field
supply).
2 Place the 2 cables over the outdoor unit.
3 Insert a rubber sheet between the cables and the outdoor unit
to prevent the cable from scratching the paint (field supply).
4 Attach the cable’s ends. Tighten those ends.
7.4.3 To install the indoor unit
1 Lift the indoor unit from the pallet and place it on the floor.
2 Slide the indoor unit into position.
3 Adjust the height of the leveling feet to compensate for floor
irregularities. The maximum allowed deviation is 1°.
NOTICE
Do NOT tilt the unit backwards:
7.4 Mounting the indoor unit
7.4.1 About mounting the indoor unit
When
You have to mount the outdoor and indoor unit before you can
connect the refrigerant and water piping.
Typical workflow
Mounting the indoor unit typically consists of the following stages:
1 Installing the indoor unit.
7.4.2 Precautions when mounting the indoor unit
INFORMATION
Also read the precautions and requirements in the
following chapters:
▪ General safety precautions
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
▪ Preparation
7.5 Connecting the refrigerant piping
7.5.1 About connecting the refrigerant piping
Before connecting the refrigerant piping
Make sure the outdoor and indoor unit are mounted.
Typical workflow
Connecting the refrigerant piping involves:
▪ Connecting the refrigerant piping to the outdoor unit
▪ Connecting the refrigerant piping to the indoor unit
▪ Installing oil traps
▪ Insulating the refrigerant piping
Installer reference guide
25
Page 26
7 Installation
a b
c
d
R=0.4~0.8
45°
±2
90°
±2
A
a b
A
▪ Keeping in mind the guidelines for:
▪ Pipe bending
▪ Flaring pipe ends
▪ Brazing
▪ Using the stop valves
7.5.2 Precautions when connecting the refrigerant piping
INFORMATION
Also read the precautions and requirements in the
following chapters:
▪ General safety precautions
▪ Preparation
DANGER: RISK OF BURNING
CAUTION
▪ Do NOT use mineral oil on flared part.
▪ Do NOT reuse piping from previous installations.
▪ NEVER install a drier to this R410A unit to guarantee
its lifetime. The drying material may dissolve and
damage the system.
NOTICE
Take the following precautions on refrigerant piping into
account:
▪ Avoid anything but the designated refrigerant to get
mixed into the refrigerant cycle (e.g. air).
▪ Only use R410A when adding refrigerant.
▪ Only use installation tools (e.g. manifold gauge set) that
are exclusively used for R410A installations to
withstand the pressure and to prevent foreign materials
(e.g. mineral oils and moisture) from mixing into the
system.
▪ Install the piping so that the flare is NOT subjected to
mechanical stress
▪ Protect the piping as described in the following table to
prevent dirt, liquid or dust from entering the piping.
▪ Use caution when passing copper tubes through walls
(see figure below).
Unit Installation period Protection method
Outdoor unit >1month Pinch the pipe
<1month Pinch or tape the pipe
Indoor unit Regardless of the
period
INFORMATION
Do NOT open the refrigerant stop valve before checking
the refrigerant piping. When you need to charge additional
refrigerant it is recommended to open the refrigerant stop
valve after charging.
7.5.3 Guidelines when connecting the refrigerant piping
Take the following guidelines into account when connecting pipes:
▪ Coat the flare inner surface with ether oil or ester oil when
connecting a flare nut. Tighten 3 or 4 turns by hand, before
tightening firmly.
▪ Always use 2 wrenches together when loosening a flare nut.
▪ Always use a spanner and torque wrench together to tighten the
flare nut when connecting the piping. This to prevent nut cracking
and leaks.
a Torque wrench
b Spanner
c Piping union
d Flare nut
Piping size
(mm)
Tightening
torque (N•m)
Flare
dimensions (A)
Flare shape
(mm)
(mm)
Ø9.5 33~39 12.8~13.2
Ø15.9 63~75 19.3~19.7
7.5.4 Pipe bending guidelines
Use a pipe bender for bending. All pipe bends should be as gentle
as possible (bending radius should be 30~40mm or larger).
7.5.5 To flare the pipe end
CAUTION
▪ Incomplete flaring may cause refrigerant gas leakage.
▪ Do NOT re-use flares. Use new flares to prevent
refrigerant gas leakage.
▪ Use flare nuts that are included with the unit. Using
different flare nuts may cause refrigerant gas leakage.
1 Cut the pipe end with a pipe cutter.
2 Remove burrs with the cut surface facing down so that the
chips do not enter the pipe.
a Cut exactly at right angles.
b Remove burrs.
3 Remove the flare nut from the stop valve and put the flare nut
on the pipe.
4 Flare the pipe. Set exactly at the position as shown in the
following illustration.
Installer reference guide
26
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 27
7 Installation
a b
c
a b c d e
f
f
c
d
a
b
a
b
Flare tool for
R410A (clutch
type)
Conventional flare tool
Clutch type
(Ridgid-type)
Wing nut type
(Imperial-type)
A 0~0.5mm 1.0~1.5mm 1.5~2.0mm
5 Check that the flaring is properly made.
a Flare’s inner surface must be flawless.
b The pipe end must be evenly flared in a perfect circle.
c Make sure the flare nut is fitted.
7.5.6 To braze the pipe end
The indoor unit and outdoor unit have flare connections. Connect
both ends without brazing. If brazing should be needed, take the
following into account:
▪ When brazing, blow through with nitrogen to prevent creation of
large quantities of oxidised film on the inside of the piping. This
film adversely affects valves and compressors in the refrigerating
system and prevents proper operation.
▪ Set the nitrogen pressure to 20kPa (0.2bar) (just enough so it
can be felt on the skin) with a pressure-reducing valve.
▪ Do NOT apply excessive force to the valve stem. Doing so may
break the valve body.
▪ Always make sure to secure the stop valve with a spanner, then
loosen or tighten the flare nut with a torque wrench. Do NOT place
the spanner on the stem cap, as this could cause a refrigerant
leak.
a Spanner
b Torque wrench
▪ When it is expected that the operating pressure will be low (e.g.
when cooling will be performed while the outside air temperature
is low), sufficiently seal the flare nut in the stop valve on the gas
line with silicon sealant to prevent freezing.
Silicon sealant, make sure there is no gap.
To open/close the stop valve
1 Remove the valve cover.
2 Insert a hexagon wrench (liquid side: 4mm, gas side: 6mm)
into the valve stem and turn the valve stem:
a Refrigerant piping
b Part to be brazed
c Taping
d Manual valve
e Pressure-reducing valve
f Nitrogen
▪ Do NOT use anti-oxidants when brazing pipe joints.
Residue can clog pipes and break equipment.
▪ Do NOT use flux when brazing copper-to-copper refrigerant
piping. Use phosphor copper brazing filler alloy (BCuP), which
does not require flux.
Flux has an extremely harmful influence on refrigerant piping
systems. For instance, if chlorine based flux is used, it will cause
pipe corrosion or, in particular, if the flux contains fluorine, it will
deteriorate the refrigerant oil.
7.5.7 Using the stop valve and service port
To handle the stop valve
Take the following guidelines into account:
▪ The stop valves are factory closed.
▪ The following illustration shows each part required in handling the
valve.
Counterclockwise to open.
Clockwise to close.
3 When the valve stem cannot be turned any further, stop turning.
The valve is now opened/closed.
To handle the stem cap
▪ The stem cap is sealed where indicated with the arrow. Do NOT
damage it.
▪ After handling the stop valve, tighten the stem cap, and check for
refrigerant leaks.
Item Tightening torque (N∙m)
Stem cap, liquid side 13.5~16.5
Stem cap, gas side 22.5~27.5
a Service port and service port cap
b Valve stem
c Field piping connection
d Stem cap
▪ Keep both stop valves open during operation.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
To handle the service cap
▪ Always use a charge hose equipped with a valve depressor pin,
since the service port is a Schrader type valve.
▪ After handling the service port, tighten the service port cap, and
check for refrigerant leaks.
Item Tightening torque (N∙m)
Service port cap 11.5~13.9
Installer reference guide
27
Page 28
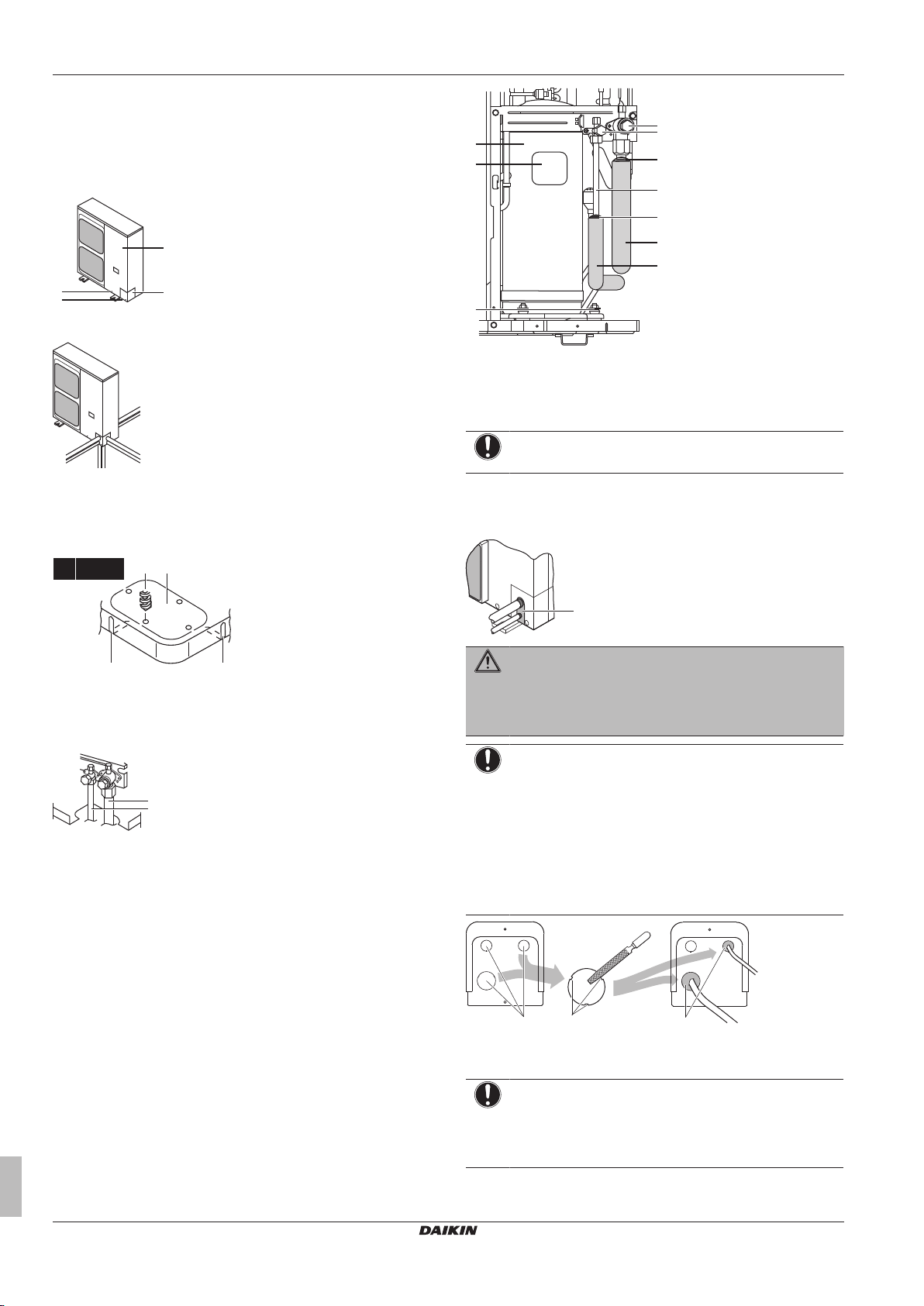
7 Installation
c
a
b
d
a
b
c
d
cc
ba
4× Ø6 mm
a
b
d
c
e
b
a
g
g
h
h
f
a
b
c
a
7.5.8 To connect the refrigerant piping to the outdoor unit
1 Do the following:
▪ Remove the service cover (a) with screw (b).
▪ Remove the piping intake plate (c) with screw (d).
2 Choose a piping route (a, b, c or d).
3 If you have chosen the downwards piping route:
▪ Drill (a, 4×) and remove the knockout hole (b).
▪ Cut out the slits (c) with a metal saw.
6 If the outdoor unit is installed above the indoor unit, cover the
stop valves (h, see above) with sealing material to prevent
condensed water on the stop valves from moving to the indoor
unit.
NOTICE
Any exposed piping might cause condensation.
7 Reattach the service cover and the piping intake plate.
8 Seal all gaps (example: a) to prevent snow and small animals
from entering the system.
4 Do the following:
▪ Connect the liquid pipe (a) to the liquid stop valve.
▪ Connect the gas pipe (b) to the gas stop valve.
5 Do the following:
▪ Insulate the liquid piping (a) and the gas piping (b).
▪ Make sure the piping and piping insulation do NOT touch the
compressor (c), the compressor terminal cover (d), and the
compressor bolts (e). If the liquid pipe insulation might touch
the compressor terminal cover, adjust the height of the
insulation (f=no insulation around the compressor terminal
cover (d)).
▪ Seal the insulation ends (sealant etc.) (g).
Installer reference guide
28
WARNING
Provide adequate measures to prevent that the unit can be
used as a shelter by small animals. Small animals that
make contact with electrical parts can cause malfunctions,
smoke or fire.
NOTICE
Precautions when making knockout holes:
▪ Avoid damaging the casing.
▪ After making the knockout holes, we recommend you
remove the burrs and paint the edges and areas
around the edges using repair paint to prevent rusting.
▪ When passing electrical wiring through the knockout
holes, wrap the wiring with protective tape to prevent
damage.
a Knockout hole
b Burr
c Sealant etc.
NOTICE
Make sure to open the stop valves after installing the
refrigerant piping and performing vacuum drying. Running
the system with the stop valves closed may break the
compressor.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 29

7 Installation
b a
a
b
10 m
R410A
a
b d e
f
c
7.5.9 To connect the refrigerant piping to the indoor unit
1 Connect the liquid stop valve from the outdoor unit to the
refrigerant liquid connection of the indoor unit.
a Refrigerant liquid connection
b Refrigerant gas connection
2 Connect the gas stop valve from the outdoor unit to the
refrigerant gas connection of the indoor unit.
NOTICE
It is recommended that the refrigerant piping between
indoor and outdoor unit is installed in a ducting or the
refrigerant piping is wrapped with finishing tape.
7.5.10 To determine if oil traps are required
If oil flows back into the outdoor unit's compressor, this might cause
liquid compression or deterioration of oil return. Oil traps in the rising
gas piping can prevent this.
If Then
The indoor unit is installed
higher than the outdoor
unit
Install an oil trap every 10m (height
difference).
Typical workflow
Checking the refrigerant piping typically consists of the following
stages:
1 Checking for leaks in the refrigerant piping.
2 Performing vacuum drying to remove all moisture, air or
nitrogen from the refrigerant piping.
If there is a possibility of moisture being present in the refrigerant
piping (for example, water may have entered the piping), first carry
out the vacuum drying procedure below until all moisture has been
removed.
7.6.2 Precautions when checking the refrigerant piping
INFORMATION
Also read the precautions and requirements in the
following chapters:
▪ General safety precautions
▪ Preparation
NOTICE
Use a 2-stage vacuum pump with a non-return valve that
can evacuate to a gauge pressure of −100.7 kPa
(−1.007 bar)(5 Torr absolute). Make sure the pump oil
does not flow oppositely into the system while the pump is
not working.
NOTICE
Use this vacuum pump for R410A exclusively. Using the
same pump for other refrigerants may damage the pump
and the unit.
7.6.3 Checking refrigerant piping: Setup
The outdoor unit is
installed higher than the
indoor unit
7.6 Checking the refrigerant piping
7.6.1 About checking the refrigerant piping
The outdoor unit's internal refrigerant piping has been factory tested
for leaks. You only have to check the outdoor unit's external
refrigerant piping.
Before checking the refrigerant piping
Make sure the refrigerant piping is connected between the outdoor
unit and the indoor unit.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
a Rising gas piping with oil trap
b Liquid piping
Oil traps are NOT required.
a Pressure gauge
b Nitrogen
c Refrigerant
d Weighing machine
e Vacuum pump
f Stop valve
7.6.4 To check for leaks
NOTICE
Do NOT exceed the unit's maximum working pressure (see
"PS High" on the unit name plate).
NOTICE
Make sure to use a recommended bubble test solution
from your wholesaler. Do not use soap water, which may
cause cracking of flare nuts (soap water may contain salt,
which absorbs moisture that will freeze when the piping
gets cold), and/or lead to corrosion of flared joints (soap
water may contain ammonia which causes a corrosive
effect between the brass flare nut and the copper flare).
Installer reference guide
29
Page 30

7 Installation
1 Charge the system with nitrogen gas up to a gauge pressure of
at least 200 kPa (2 bar). It is recommended to pressurize to
3000kPa (30bar) in order to detect small leaks.
2 Check for leaks by applying the bubble test solution to all
connections.
3 Discharge all nitrogen gas.
7.6.5 To perform vacuum drying
1 Vacuum the system until the pressure on the manifold indicates
−0.1MPa (−1bar).
2 Leave as is for 4-5minutes and check the pressure:
If the pressure… Then…
Does not change There is no moisture in the
system. This procedure is
finished.
Increases There is moisture in the
system. Go to the next step.
3 Evacuate for at least 2 hours to a pressure on the manifold of
−0.1MPa (−1bar).
4 After turning OFF the pump, check the pressure for at least
1hour.
5 If you do NOT reach the target vacuum or cannot maintain the
vacuum for 1hour, do the following:
▪ Check for leaks again.
▪ Perform vacuum drying again.
NOTICE
Make sure to open the stop valves after installing the
refrigerant piping and performing vacuum drying. Running
the system with the stop valves closed may break the
compressor.
INFORMATION
After opening the stop valve, it is possible that the pressure
in the refrigerant piping does NOT increase. This might be
caused by e.g. the closed state of the expansion valve in
the outdoor unit circuit, but does NOT present any problem
for correct operation of the unit.
Typical workflow – Charging additional refrigerant typically consists
of the following stages:
1 Determining if and how much you have to charge additionally.
2 If necessary, charging additional refrigerant.
3 Filling in the fluorinated greenhouse gases label, and fixing it to
the inside of the outdoor unit.
Completely recharging refrigerant
Before completely recharging refrigerant, make sure the following is
done:
1 All refrigerant is recovered from the system.
2 The outdoor unit's external refrigerant piping is checked (leak
test, vacuum drying).
3 Vacuum drying on the outdoor unit's internal refrigerant piping is
performed.
NOTICE
Before completely recharging, perform vacuum drying on
the outdoor unit's internal refrigerant piping as well. To do
so, use the internal service port of the outdoor unit
(between the heat exchanger and the 4‑way valve). Do
NOT use the service ports of the stop valves, because
vacuum drying cannot be performed properly from these
ports.
Typical workflow – Completely recharging refrigerant typically
consists of the following stages:
1 Determining how much refrigerant to charge.
2 Charging refrigerant.
3 Filling in the fluorinated greenhouse gases label, and fixing it to
the inside of the outdoor unit.
7.7.2 Precautions when charging refrigerant
INFORMATION
Also read the precautions and requirements in the
following chapters:
▪ General safety precautions
▪ Preparation
7.7 Charging refrigerant
7.7.1 About charging refrigerant
The outdoor unit is factory charged with refrigerant, but in some
cases the following might be necessary:
What When
Charging additional refrigerant When the total liquid piping
length is more than specified
(see later).
Completely recharging refrigerant Example:
▪ When relocating the system.
▪ After a leak.
Charging additional refrigerant
Before charging additional refrigerant, make sure the outdoor unit's
external refrigerant piping is checked (leak test, vacuum drying).
INFORMATION
Depending on the units and/or the installation conditions, it
might be necessary to connect electrical wiring before you
can charge refrigerant.
Installer reference guide
30
7.7.3 To determine the additional refrigerant amount
If the total liquid
piping length is…
≤10m Do NOT add additional refrigerant.
>10m R=(total length (m) of liquid
piping–10m)×0.054
R=Additional charge (kg)(rounded in units
of 0.1kg)
INFORMATION
Piping length is the one way length of liquid piping.
Then…
7.7.4 To determine the complete recharge amount
INFORMATION
If a complete recharge is necessary, the total refrigerant
charge is: the factory refrigerant charge (see unit name
plate) + the determined additional amount.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 31

7 Installation
b
Contains fluorinated greenhouse gases
2
1
1
1
2
2
kg
tCO2eq
GWP × kg
1000
=
=
+
kg
=
kg
=
GWP: XXX
RXXX
a
f
c
d
e
fac e d b
7.7.5 To charge additional refrigerant
WARNING
▪ Only use R410A as refrigerant. Other substances may
cause explosions and accidents.
▪ R410A contains fluorinated greenhouse gases. Its
global warming potential (GWP) value is 2087.5. Do
NOT vent these gases into the atmosphere.
▪ When charging refrigerant, always use protective
gloves and safety glasses.
CAUTION
To avoid compressor breakdown, do NOT charge more
than the specified amount of refrigerant.
Prerequisite: Before charging refrigerant, make sure the refrigerant
piping is connected and checked (leak test and vacuum drying).
1 Connect the refrigerant cylinder to both the service port of the
gas stop valve and the service port of the liquid stop valve.
2 Charge the additional refrigerant amount.
3 Open the stop valves.
If pump down is needed in case of dismantling or relocating the
system, see "13.3To pump down"on page73 for more details.
7.7.6 To fix the fluorinated greenhouse gases label
1 Fill in the label as follows:
Typical workflow
Connecting the water piping typically consists of the following
stages:
1 Connecting the water piping to the indoor unit.
2 Connecting the recirculation piping.
3 Connecting the pressure relief valve to the drain.
4 Filling the water circuit.
5 Filling the domestic hot water tank.
6 Insulating the water piping.
7.8.2 Precautions when connecting the water piping
INFORMATION
Also read the precautions and requirements in the
following chapters:
▪ General safety precautions
▪ Preparation
7.8.3 To connect the water piping
NOTICE
Do NOT use excessive force when connecting the piping.
Deformation of the piping can cause malfunctioning of the
unit.
To facilitate service and maintenance, 4 shut-off valves are provided.
Mount these valves on the space heating water inlets and space
heating water outlets. Mind their position. The orientation of the
integrated drain and fill valves is important for servicing.
a If a multilingual fluorinated greenhouse gases label is
delivered with the unit (see accessories), peel off the
applicable language and stick it on top of a.
b Factory refrigerant charge: see unit name plate
c Additional refrigerant amount charged
d Total refrigerant charge
e Greenhouse gas emissions of the total refrigerant charge
expressed as tonnes CO2-equivalent
f GWP = Global warming potential
NOTICE
In Europe, the greenhouse gas emissions of the total
refrigerant charge in the system (expressed as tonnes
CO2-equivalent) is used to determine the maintenance
intervals. Follow the applicable legislation.
Formula to calculate the greenhouse gas emissions:
GWP value of the refrigerant × Total refrigerant charge [in
kg] / 1000
2 Fix the label on the inside of the outdoor unit near the gas and
liquid stop valves.
7.8 Connecting the water piping
7.8.1 About connecting the water piping
Before connecting the water piping
Make sure the outdoor and indoor unit are mounted.
NOTICE
This unit is designed for operation on 2 temperature zones:
▪ underfloor heating in the main zone (water
temperature 35°C), this is the zone with the lowest
water temperature,
▪ radiators in the additional zone (water temperature
45°C), this is the zone with the highest water
temperature.
1 Install the shut-off valves on the space heating water pipes.
a Space heating additional zone water out
b Space heating additional zone water in
c Domestic hot water out
d Domestic cold water in (cold water supply)
e Space heating main zone water out
f Space heating main zone water in
NOTICE
It is recommended to install shut-off valves to domestic
cold water in and domestic hot water out connections.
These shut-off valves are field supplied.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
31
Page 32

7 Installation
4×
b
a
c
a
ab
NOTICE
To avoid damage to the surroundings in case of water
leakage, it is recommended to close the cold water inlet
shut‑off valves during periods of absence.
2 Screw the indoor unit nuts on the shut-off valves.
3 Connect the domestic hot water in and out pipes to the indoor
unit.
NOTICE
Install air purge valves at all local high points.
NOTICE
▪ A drain device and pressure relief device should be
installed on the cold water inlet connection of the
domestic hot water cylinder.
▪ To avoid back siphonage, it is recommended to install a
non-return valve on the water inlet of the domestic hot
water tank in accordance with the applicable legislation.
▪ It is recommended to install a pressure reducing valve
on the cold water inlet in accordance with the
applicable legislation.
▪ An expansion vessel should be installed on the cold
water inlet in accordance with the applicable legislation.
▪ It is recommended to install the pressure relief valve on
a higher position than the top of the domestic hot water
tank. Heating of the domestic hot water tank causes
water to expand and without pressure relief valve the
water pressure inside the tank can rise above the tank
design pressure. Also the field installation (piping,
tapping points, etc.) connected to the tank is subjected
to this high pressure. To prevent this, a pressure
relieve valve needs to be installed. The overpressure
prevention depends on the correct operation of the field
installed pressure relief valve. If this is NOT working
correctly, overpressure will deform the tank and water
leakage may occur. To confirm good operation, regular
maintenance is required.
6 Connect the recirculation piping to the recirculation connection
(b) and route the piping through the hole at the backside of the
unit (a).
a Piping intake hole
b Recirculation connection
c Cut-out location
7 Reattach the top insulation, expansion vessel, and casing.
7.8.5 To connect the pressure relief valve to the drain
The blow out of the pressure relief valve is coming out of the
backside of the unit.
7.8.4 To connect the recirculation piping
Prerequisite: Only required if you need recirculation in your system.
1 Loosen and remove the 4 screws that fix the top panel.
2 Remove the top panel from the unit.
a Pressure relief blow-out
The blow out should be connected to an appropriate drain according
to the applicable legislation. It is recommended to use a tundish.
7.8.6 To fill the water circuit
1 Connect the water supply hose to the fill valve.
3 Disconnect and remove the expansion vessel of the top
insulation.
4 Remove the top insulation.
5 Cut out part (c) on the left or right side from the top insulation.
Tank capacity Cut out position
180l Left OR right
Installer reference guide
32
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 33

7 Installation
INFORMATION
Please fill with water through connection a OR b. Both
circuits (main and additional) will be filled.
2 Open the fill valve.
3 Make sure that the automatic air purge valve is open (at least 2
turns).
4 Fill the circuit with water until the manometer indicates a
pressure of ±2.0bar.
5 Purge as much air as possible from the water circuit.
6 Close the fill valve.
7 Disconnect the water supply hose from the fill valve.
NOTICE
The water pressure indicated on the manometer will vary
depending on the water temperature (higher pressure at
higher water temperature).
However, at all times water pressure shall remain above
1bar to avoid air entering the circuit.
7.8.7 To fill the domestic hot water tank
1 Open every hot water tap in turn to purge air from the system
pipe work.
2 Open the cold water supply valve.
3 Close all water taps after all air is purged.
4 Check for water leaks.
5 Manually operate the field-installed pressure relief valve to
ensure a free water flow through the discharge pipe.
7.8.8 To insulate the water piping
The piping in the complete water circuit MUST be insulated to
prevent condensation during defrost operation and reduction of the
heating capacity.
If the temperature is higher than 30°C and the humidity is higher
than RH 80%, the thickness of the insulation materials should be at
least 20 mm to prevent condensation on the surface of the
insulation.
7.9 Connecting the electrical wiring
7.9.1 About connecting the electrical wiring
Before connecting the electrical wiring
Make sure:
▪ The refrigerant piping is connected and checked
▪ The water piping is connected
Typical workflow
Connecting the electrical wiring typically consists of the following
stages:
1 Making sure the power supply system complies with the
electrical specifications of the heat pump.
2 Connecting the electrical wiring to the outdoor unit.
3 Repositioning the air thermistor on the outdoor unit.
4 Connecting the electrical wiring to the indoor unit.
5 Connecting the main power supply.
6 Connecting the backup heater power supply.
7 Connecting the user interface.
8 Connecting the shut–off valves.
9 Connecting the electrical meters.
10 Connecting the domestic hot water pump.
11 Connecting the alarm output.
12 Connecting the changeover to an external heat source.
13 Connecting the power consumption digital inputs.
14 Connecting the safety thermostat.
7.9.2 About electrical compliance
ERHQ_V3
Equipment complying with EN/IEC 61000‑3‑12 (European/
International Technical Standard setting the limits for harmonic
currents produced by equipment connected to public low-voltage
systems with input current >16A and ≤75A per phase.).
ERLQ_V3
Equipment complying with:
▪ EN/IEC 61000‑3‑11 provided that the system impedance Z
less than or equal to Z
at the interface point between the user's
max
supply and the public system.
▪ EN/IEC 61000‑3‑11 = European/International Technical
Standard setting the limits for voltage changes, voltage
fluctuations and flicker in public low-voltage supply systems for
equipment with rated current ≤75A.
▪ It is the responsibility of the installer or user of the equipment to
ensure, by consultation with the distribution network operator if
necessary, that the equipment is connected only to a supply
with a system impedance Z
less than or equal to Z
sys
max
▪ EN/IEC 61000‑3‑12 provided that the short-circuit power Ssc is
greater than or equal to the minimum Ssc value at the interface
point between the user's supply and the public system.
▪ EN/IEC 61000‑3‑12 = European/International Technical
Standard setting the limits for harmonic currents produced by
equipment connected to public low-voltage systems with input
current >16A and ≤75A per phase.
▪ It is the responsibility of the installer or user of the equipment to
ensure, by consultation with the distribution network operator if
necessary, that the equipment is connected only to a supply
with a short-circuit power Ssc greater than or equal to the
minimum Ssc value.
is
sys
.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Model Z
max
Minimum S
sc
value
ERLQ011CAV3
0.22Ω 525kVA
ERLQ014CAV3
ERLQ016CAV3
ERLQ_W1
Equipment complying with EN/IEC 61000‑3‑12 (European/
International Technical Standard setting the limits for harmonic
currents produced by equipment connected to public low-voltage
systems with input current >16A and ≤75A per phase.).
Installer reference guide
33
Page 34

7 Installation
b a
cb
c
aa
A
AA´
A´
c b ba c
a
B
B
a b
c
b
a
d
V3
1~ 50 Hz
230 V
W1
3N~ 50 Hz
400 V
L1 L3L2
L1 L3L2
Only for indoor units
See "7.9.10 To connect the backup heater power supply" on
page37.
7.9.3 Precautions when connecting the electrical wiring
INFORMATION
Also read the precautions and requirements in the
following chapters:
▪ General safety precautions
▪ Preparation
DANGER: RISK OF ELECTROCUTION
WARNING
ALWAYS use multicore cable for power supply cables.
7.9.4 Guidelines when connecting the electrical wiring
Keep the following in mind:
▪ If stranded conductor wires are being used, install a round crimp-
style terminal on the tip. Place the round crimp-style terminal on
the wire up to the covered part and fasten the terminal with the
appropriate tool.
a Stranded conductor wire
b Round crimp-style terminal
▪ Use the following methods for installing wires:
7.9.5 Specifications of standard wiring components
Component V3 W1
ERHQ ERLQ ERHQ ERLQ
Power supply
cable
(a)
MCA
31.9A 34.2A 13.5A 16.3A
Voltage 230V 400V
Phase 1~ 3N~
Frequency 50Hz
Wire sizes Must comply with applicable
legislation
Interconnection cable Minimum cable section of 2.5mm²
and applicable for 230V
Recommended field fuse 32A 40A 20A
Earth leakage circuit breaker Must comply with applicable
legislation
(a) MCA=Minimum circuit ampacity. Stated values are
maximum values (see electrical data of combination with
indoor units for exact values).
7.9.6 To connect the electrical wiring on the outdoor unit
NOTICE
▪ Follow the wiring diagram (delivered with the unit,
located at the inside of the service cover).
▪ Make sure the electrical wiring does NOT obstruct
proper reattachment of the service cover.
1 Remove the service cover. See "7.2.2 To open the outdoor
unit"on page23.
2 Strip insulation (20mm) from the wires.
Wire type Installation method
Single core wire
Stranded conductor
wire with round
crimp-style terminal
Tightening torques
M4 (X1M) 1.2~1.8
M5 (X1M) 2.0~3.0
M5 (earth) 3.0~4.0
34
Installer reference guide
a Curled single core wire
b Screw
c Flat washer
a Terminal
b Screw
c Flat washer
Item Tightening torque (N•m)
a Strip wire end to this point
b Excessive strip length may cause electrical shock or
leakage.
3 Connect the interconnection cable and power supply as follows:
a Interconnection cable
b Power supply cable
c Earth leakage circuit breaker
d Fuse
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 35

7 Installation
d
b
a
V3 W1
e
h
f
d
g
e
h
f
g
c
c
a
b
a
b
a
b
2
3
1
a b c d e
A B
1
3
2
4
5
a Switch box
b Stop valve attachment plate
c Earth
d Cable tie
e Interconnection cable
f Power supply cable
Only if bottom plate heater is installed (option for ERHQ):
g Bottom plate heater cable
h Power supply cable of the bottom plate heater (from the
indoor unit)
INFORMATION
ERLQ units control the bottom plate heater internally (field
wiring NOT required).
4 Fix the cables (power supply, interconnection cable and power
supply of the bottom plate heater (if applicable)) with a cable tie
to the stop valve attachment plate.
5 Route the wiring through the frame and connect it to it.
Connecting to the
frame
When cables are routed from the unit, a
protection sleeve for the conduits (PG
insertions) can be inserted at the knockout
hole.
When you do not use a wire conduit,
protect the wires with vinyl tubes to
prevent the edge of the knockout hole from
cutting the wires.
A Inside of the outdoor unit
B Outside of the outdoor unit
a Wire
b Bush
c Nut
d Frame
e Hose
6 Reattach the service cover. See "7.10.2To close the outdoor
unit"on page41.
7 Connect an earth leakage circuit breaker and fuse to the power
supply line.
7.9.7 To reposition the air thermistor on the outdoor unit
This task is only required for ERLQ.
Required accessories:
Thermistor fixture.
Use the one from the accessory bag.
Thermistor fixing plate.
Reuse the one attached to the unit. If necessary,
you can use the spare one from the accessory
bag.
Routing through
the frame
Choose one of the 3 possibilities:
a Power supply, earth wiring, and bottom
plate heater wire (if applicable)
b Interconnection cable
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
35
Page 36

7 Installation
7
6
7
8
9
10
11
a b+c
a
b+c
3 Routing of the wiring inside the unit should be as follows:
7.9.8 To connect the electrical wiring on the indoor unit
1 To open the indoor unit, see "7.2.3To open the indoor unit"on
page23 and "7.2.4To open the switch box cover of the indoor
unit"on page23.
2 Wiring should enter the unit from the top:
Routing Possible cables (depending on unit type and installed options)
a
Low voltage
b
High voltage power supply
▪ Preferential power supply contact
▪ User interface
▪ Power consumption digital inputs (field supply)
▪ Outdoor ambient temperature sensor (option)
▪ Indoor ambient temperature sensor (option)
▪ Electrical meters (field supply)
▪ Safety thermostat for the main zone (field supply)
▪ Safety thermostat for the additional zone (field supply)
▪ Interconnection cable
▪ Normal kWh rate power supply
▪ Preferential kWh rate power supply
▪ Power supply for backup heater
▪ Power supply for bottom plate heater (option)
4 Fix the cable with cable ties to the cable tie mountings to
ensure strain relief and to make sure that it does NOT come in
contact with the piping and sharp edges.
INFORMATION
To access the domestic hot water temperature sensor, the
switch box can be tilted. The switch box should NOT be
removed from the unit.
Installer reference guide
36
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 37

Routing Possible cables (depending on unit type and installed options)
X2M
X5M
A5P
X1M
K3M
K2M
1 2 3
1 2 3
X6YB
X6YA
X6Y
3031
X1A
X6YA
X19A
a
X2M
X5M
A5P
X1M
K3M
K2M
1 2 3
1 2 3
X6YB
X6Y
X1A
L N
L N
30 31
S1S
3 4
X19A
abc
c
High voltage control signal
▪ Heat pump convector (option)
▪ Room thermostat (option)
▪ Shut-off valve (field supply)
▪ Domestic hot water pump (field supply)
▪ Alarm output
▪ Changeover to external heat source control
▪ Space heating operation control
7 Installation
CAUTION
Do NOT push or place redundant cable length in the unit.
7.9.9 To connect the main power supply
1 Connect the main power supply.
In case of normal kWh rate power supply
Legend: see illustration below.
INFORMATION
In case of preferential kWh rate power supply, connect
X6Y to X6YB. The necessity of separate normal kWh rate
power supply to indoor unit (b) X2M30/31 depends on the
type of preferential kWh rate power supply.
Separate connection to the indoor unit is required:
▪ if preferential kWh rate power supply is interrupted
when active, OR
▪ if no power consumption of the indoor unit is allowed at
the preferential kWh rate power supply when active.
INFORMATION
The preferential kWh rate power supply contact is
connected to the same terminals (X5M/3+4) as the safety
thermostat for the additional zone. It is only possible for the
system to have EITHER preferential kWh rate power
supply OR a safety thermostat for the additional zone.
7.9.10 To connect the backup heater power supply
CAUTION
To guarantee the unit is completely earthed, always
connect the backup heater power supply and the earth
cable.
Make sure that the power supply is in accordance with the backup
heater capacity, as listed in the table below.
In case of preferential kWh rate power supply
Connect X6Y to X6YB.
a Interconnection cable (=main power supply)
b Normal kWh rate power supply
c Preferential power supply contact
2 Fix the cable with cable ties to the cable tie mountings.
Backup
heater type
Backup
heater
capacity
Power
supply
Maximum
running
current
Z
(Ω)
max
*3V 3kW 1~230V 13A —
1 Connect the backup heater power supply. A double‑pole fuse is
used for F1B.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
37
Page 38

7 Installation
X2M
F1B
X1M
L NL N
X5M
A5P
A2P A2P
a b
1 2
Backup heater type Connections to backup heater power
supply
3kW 1~ 230V (*3V)
2 Fix the cable with cable ties to the cable tie mountings.
7.9.11 To connect the user interface
▪ If you use 1 user interface, you can install it at the indoor unit (for
control close to the indoor unit), or in the room (when used as
room thermostat).
▪ If you use 2 user interfaces, you can install 1 user interface at the
indoor unit (for control close to the indoor unit) + 1 user interface
in the room (used as room thermostat).
# At the indoor unit In the room
1 Connect the user interface cable to the indoor unit.
Fix the cable with cable ties to the cable tie mountings.
a Main user interface
(a)
b Optional user interface
2 Insert a screwdriver into the slots underneath the user
interface and carefully separate the faceplate from the
wallplate.
The PCB is mounted in the faceplate of the user interface.
Be careful NOT to damage it.
INFORMATION
The user interface can only be used as room thermostat of
the main zone.
The procedure differs slightly depending on where you install the
user interface.
3 Use the 2 screws in the accessory
bag to fix the wallplate of the user
interface to the sheet metal of the
Fix the wallplate of
the user interface to
the wall.
unit.
Be careful NOT to distort the shape
of the backside of the user interface
by overtightening the mounting
screws.
4 Connect as shown in 4A. Connect as shown
in 4A, 4B, 4C or 4D.
5 Reinstall the faceplate onto the wallplate.
Be careful NOT to pinch the wiring when attaching the
frontplate to the unit.
(a) The main user interface is required for operation, but has to
be ordered separately (mandatory option).
Installer reference guide
38
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 39

7 Installation
b
a
PCB
1×
a
PCB
b
1×
a
b
PCB
b
1×
a
PCB
b
b
1×
X2M
X1M
K3M
K2M
X2M
X1M
K3M
K2M
5 6 7
M2S
5 6 7
M2S
NO NC
X5M
A5P
78910
S2S S3S
X2M
X1M
K3M
K2M
3534
1~
M
M2P
X2M
X5M
A5P
X1M
A4P
K3M
K2M
29
X1M
YC Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4
a
4A From the rear
4C From the top
a Notch this part for the wiring to pass through with nippers
b Secure the wiring to the front part of the casing using the
4B From the left
4D From the top centre
2 Fix the cable with cable ties to the cable tie mountings.
7.9.14 To connect the domestic hot water pump
1 Connect the domestic hot water pump cable to the appropriate
terminals as shown in the illustration below.
etc.
wiring retainer and clamp.
7.9.12 To connect the shut-off valve
1 Connect the valve control cable to the appropriate terminals as
shown in the illustration below.
NOTICE
Wiring is different for a NC (normal closed) valve and a NO
(normal open) valve.
2 Fix the cable with cable ties to the cable tie mountings.
7.9.15 To connect the alarm output
1 Connect the alarm output cable to the appropriate terminals as
shown in the illustration below.
2 Fix the cable with cable ties to the cable tie mountings.
7.9.13 To connect the electrical meters
INFORMATION
In case of an electrical meter with transistor output, check
the polarity. The positive polarity MUST be connected to
X5M/7 and X5M/9; the negative polarity to X5M/8 and
X5M/10.
1 Connect the electrical meters cable to the appropriate terminals
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
as shown in the illustration below.
a Installation of EKRP1HB is required.
2 Fix the cable with cable ties to the cable tie mountings.
Installer reference guide
39
Page 40

7 Installation
X5M
A5P
A8P
1 2 3 4 5
X801M
S6S
S7S
S8S
S9S
a
X5M
A5P
1211
3 4
X5M
f
b
a
e
d
c
7.9.16 To connect the power consumption digital inputs
1 Connect the power consumption digital inputs cable to the
appropriate terminals as shown in the illustration below.
a Installation of EKRP1AHTA is required.
2 Fix the cable with cable ties to the cable tie mountings.
7.9.17 To connect the safety thermostat (normal closed contact)
Main zone
1 Connect the safety thermostat (normal closed) cable to the
appropriate terminals as shown in the illustration below.
4 Fix the cable with cable ties to the cable tie mountings.
NOTICE
Make sure to select and install the safety thermostat for the
additional zone according to the applicable legislation.
In any case, to prevent unnecessary tripping of the safety
thermostat, it is recommended that …
▪ … the safety thermostat is automatically resettable.
▪ … the safety thermostat has a maximum temperature
variation rate of 2°C/min.
▪ … there is a minimum distance of 2 m between the
safety thermostat and the 3‑way valve.
INFORMATION
After it is installed, do NOT forget to configure the safety
thermostat for the additional zone. Without configuration,
the indoor unit will ignore the safety thermostat contact.
INFORMATION
The preferential kWh rate power supply contact is
connected to the same terminals (X5M/3+4) as the safety
thermostat for the additional zone. It is only possible for the
system to have EITHER preferential kWh rate power
supply OR a safety thermostat for the additional zone.
7.10 Finishing the outdoor unit installation
7.10.1 To finish the outdoor unit installation
2 Fix the cable with cable ties to the cable tie mountings.
INFORMATION
Installation of a safety thermostat (field supply) is required
for the main zone, otherwise the unit will NOT operate.
NOTICE
A safety thermostat MUST be installed on the main zone to
avoid too high water temperatures in this zone. The safety
thermostat is typically a thermostatically controlled valve
with a normal closed contact. When the water temperature
in the main zone is too high, the contact will open and the
user interface will show a 8H‑02 error. ONLY the main
pump will stop.
Additional zone
3 Connect the safety thermostat (normal closed) cable to the
appropriate terminals as shown in the illustration below.
1 Insulate and fix the refrigerant piping and interconnection cable
as follows:
a Gas pipe
b Gas pipe insulation
c Interconnection cable
d Liquid pipe
e Liquid pipe insulation
f Finishing tape
2 Install the service cover.
Installer reference guide
40
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 41

8 Configuration
1
3
2
4
1×
A1P
X10A
7.10.2 To close the outdoor unit
NOTICE
When closing the outdoor unit cover, make sure that the
tightening torque does NOT exceed 4.1N•m.
7.11 Finishing the indoor unit installation
7.11.1 To fix the user interface cover to the indoor unit
1 Make sure that the front panel is removed from the indoor unit.
See "7.2.3To open the indoor unit"on page23.
2 Plug the user interface cover into the hinges.
8 Configuration
8.1 Overview: Configuration
This chapter describes what you have to do and know to configure
the system after it is installed.
Why
If you do NOT configure the system correctly, it might NOT work as
expected. The configuration influences the following:
▪ The calculations of the software
▪ What you can see on and do with the user interface
How
You can configure the system using two different methods.
Method Description
Configuring via the
user interface
Configuring via the
PC configurator
INFORMATION
When the installer settings are changed, the user interface
will request to confirm. When confirmed, the screen will
shortly turn OFF and "busy" will be displayed for several
seconds.
Accessing settings – Legend for tables
You can access the installer settings using two different methods.
However, NOT all settings are accessible via both methods. If so,
the corresponding table columns in this chapter are set to N/A (not
applicable).
First time – Quick wizard. When you turn
ON the user interface for the first time (via
the indoor unit), a quick wizard starts to help
you configure the system.
Afterwards. If necessary, you can make
changes to the configuration afterwards.
You can prepare the configuration off-site on
PC and afterwards upload the configuration
to the system with the PC configurator.
See also: "8.1.1To connect the PC cable to
the switch box"on page41.
3 Mount the front panel to the indoor unit.
7.11.2 To close the indoor unit
1 Close the switch box cover.
2 Reinstall the top plate.
3 Reinstall the front panel.
NOTICE
When closing the indoor unit cover, make sure that the
tightening torque does NOT exceed 4.1N•m.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Method Column in tables
Accessing settings via the breadcrumb in the
menu structure.
Accessing settings via the code in the
overview settings.
See also:
▪ "To access the installer settings"on page42
▪ "8.5Menu structure: Overview installer settings"on page62
#
Code
8.1.1 To connect the PC cable to the switch box
Prerequisite: The EKPCCAB kit is required.
1 Connect the cable with USB connection to your PC.
2 Connect the plug of the cable to X10A on A1P of the switch box
of the indoor unit.
Installer reference guide
41
Page 42

8 Configuration
2
345
H JS T
01
02
06
0a
0e
00 03
07
0b
0f
0000
04
08
0c
00 01
05
09
0d
15
Overview settings
Confirm Adjust Scroll
01
02
06
0a
0e
00 03
07
0b
0f
0000
04
08
0c
00 01
05
09
0d
15
Overview settings
Confirm
Adjust
Scroll
01
02
06
0a
0e
00 03
07
0b
0f
0000
04
08
0c
00 01
05
09
0d
20
Overview settings
Confirm
Adjust
Scroll
Installer settings
The system will restart.
Confirm Adjust
Cancel
OK
15:10
Tue
U5:Auto address
Push 4 sec. to continue
3 Pay special attention to the position of the plug!
3 Go to the corresponding second part of the setting by using the
and button.
NOTICE
Another cable is already connected to X10A. To connect
the PC cable to X10A, therefore temporarily disconnect
this other cable. Do NOT forget to reconnect it afterwards.
8.1.2 To access the most used commands
To access the installer settings
1 Set the user permission level to Installer.
2 Go to [A]:
To access the overview settings
1 Set the user permission level to Installer.
2 Go to [A.8]:
To set the user permission level to Installer
1 Set the user permission level to Adv. end user.
2 Go to [6.4]:
3 Press
Result:
4 If you do NOT press any button for more than 1hour or press
again for more than 4seconds, the installer permission level
switches back to End user.
To set the user permission level to Advanced end user
1 Go to the main menu or any of its submenus:
2 Press
Result: The user permission level switches to Adv. end user.
Additional information is displayed and "+" is added to the menu title.
The user permission level will stay in Adv. end user until set
otherwise.
To set the user permission level to End user
1 Press
Result: The user permission level switches to End user. The user
interface will return to the default home screen.
To modify an overview setting
Example: Modify [1‑01] from 15 to 20.
1 Go to [A.8]:
2 Go to the corresponding screen of the first part of the setting by
using the
INFORMATION
An additional 0-digit is added to the first part of the setting
when you access the codes in the overview settings.
Example: [1‑01]: "1" will result in "01".
Installer reference guide
42
> Installer settings.
> Installer settings > Overview settings.
> Information > User permission level.
for more than 4seconds.
is displayed on the home pages.
for more than 4seconds.
for more than 4 seconds.
> Installer settings > Overview settings.
and button.
Result: The value to be modified is now highlighted.
4 Modify the value by using the
5 Repeat previous steps if you have to modify other settings.
6 Push
7 At installer settings menu, press
Result: The system will restart.
to confirm the modification of the parameter.
and button.
to confirm the settings.
8.1.3 To copy the system settings from the first to the second user interface
.
If a second user interface is connected, the installer must first
proceed below instructions for the proper configuration of the 2 user
interfaces.
This procedure offers you also the possibility to copy the language
set from one user interface to the other one: e.g. from EKRUCBL2 to
EKRUCBL1.
1 When power is turned on for the first time, both user interfaces
display:
2 Push for 4seconds on the user interface on which you want
to proceed to the quick wizard. This user interface is now the
main user interface.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 43

8 Configuration
Synchronization
Data difference detected.
Please select action:
Send data
Confirm
Adjust
Start copy
Are you sure you want to
start the copy operation?
Cancel
OK
Confirm Adjust
Language
Select the desired language
Confirm Adjust
1 2013
Jan
Tue
Confirm Adjust Scroll
Date
What is the date today?
00 : 00
What is the current time?
Time
Confirm
Adjust
Scroll
A.2 1
Scroll
Select
System layout
Standard
Options
Capacities
Confirm layout
Confirm layout
Please confirm the system
layout. The system will
restart and will be ready for
first startup.
OK
Cancel
Confirm
Adjust
INFORMATION
During the quick wizard, the second user interface displays
Busy and will NOT be possible to operate.
3 The quick wizard will guide you.
4 For proper operation of the system, the local data on the two
user interfaces must be the same. If this is NOT the case, both
user interfaces will display:
5 Select the required action:
▪ Send data: the user interface you are operating contains the
correct data and the data on the other user interface will be
overwritten.
▪ Receive data: the user interface you are operating does
NOT contain the correct data and the data on the other user
interface will be used to overwrite.
6 The user interface requests confirmation if you are sure to
proceed.
1 At power ON, the quick wizard starts as long as the system
layout was NOT confirmed yet, by setting the language.
2 Set the current date and time.
3 Set the system layout settings: Standard, Options, Capacities.
For more details, see "8.2Basic configuration"on page43.
7 Confirm the selection on the screen by pushing and all data
(languages, schedules etc.) will be synchronised from the
selected source user interface to the other one.
INFORMATION
▪ During the copying, both controllers will NOT allow
operation.
▪ The copy operation can take up until 90 minutes.
▪ It is recommended to change installer settings, or the
configuration of the unit, on the main user interface. If
not, it can take up to 5 minutes before these changes
are visible in the menu structure.
8 Your system is now set to be operated by the 2 user interfaces.
8.1.4 To copy the language set from the first to the second user interface
See "8.1.3To copy the system settings from the first to the second
user interface"on page42.
8.1.5 Quick wizard: Set the system layout after first power ON
After first power ON of the system, you are guided on the user
interface to do initial settings:
▪ language,
▪ date,
▪ time,
▪ system layout.
By confirming the system layout, you can proceed with the
installation and commissioning of the system.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
4 After configuration, select Confirm layout and press .
5 The user interface re-initialises and you can proceed the
installation by setting the other applicable settings and
commissioning of the system.
When the installer settings are changed, the system will request to
confirm. When confirmation is complete, the screen will shortly turn
OFF and "busy" will be displayed for several seconds.
8.2 Basic configuration
8.2.1 Quick wizard: Language / time and date
# Code Description
[A.1] N/A Language
[1] N/A Time and date
Installer reference guide
43
Page 44

8 Configuration
c
b
a
c
FHL1 FHL2 FHL3
M
HPC1 HPC2 HPC3
8.2.2 Quick wizard: Standard
Backup heater configuration (only for *9W model)
The backup heater in a *9W model is adapted to be connected to
most common European electricity grids. Besides hardware
configuration, the grid type and the relay setting must be set on the
user interface.
# Code Description
[A.2.1.5] [5-0D] BUH type:
▪ 1 (1P,(1/1+2)): 6kW 1~230V (*9W)
▪ 3 (3P,(1/1+2)): 6kW 3~230V (*9W)
▪ 4 (3PN,(1/2)): 6kW 3N~400V (*9W)
▪ 5 (3PN,(1/1+2)): 9 kW 3N~ 400 V
(*9W)
Relay setting
Relay setting Backup heater operation
If backup heater
step 1 is active:
1/1+2 Relay 1 ON Relays 1+2 ON
1/2 Relay 1 ON Relay 2 ON
Space heating settings
The system can heat up a space. Depending on the type of
application, the space heating settings must be made accordingly.
# Code Description
[A.2.1.7] [C-07] Unit control method:
▪ 0 (LWT control): Unit operation is
decided based on the leaving water
temperature regardless the actual
room temperature and/or heating
demand of the room. This is applicable
for both temperature zones.
▪ 1 (Ext RT control): Unit operation is
decided by the external thermostat or
equivalent (e.g. heat pump convector).
This is applicable for both temperature
zones.
▪ 2 (RT control): Unit operation for the
main temperature zone is decided
based on the ambient temperature of
the user interface. The additional
temperature zone is controlled by the
external thermostat.
If backup heater
step 2 is active:
# Code Description
[A.2.1.B] N/A Only if there are 2user interfaces (1
installed in the room, 1 installed at the
indoor unit):
▪ a: At unit
▪ b: In room as room thermostat
▪ c: Remote controller of the heat pump
convectors
User interface location:
▪ At unit: the other user interface is
automatically set to In room and if RT
control is selected act as room
thermostat.
▪ In room (default): the other user
interface is automatically set to At unit
and if RT control is selected to act as
room thermostat. Controlling the main
zone.
Installer reference guide
44
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 45

8 Configuration
M
FHL1 FHL2 FHL3
HPC1 HPC2 HPC3
a
b
a
b c
d
b c
a
b
d
e
f
c
g
b
c
a
d
e
b
b
c
b c
c
# Code Description
[A.2.1.8] [7-02] The system can supply leaving water to
up to 2 water temperature zones. During
configuration, the number of water zones
must be set.
Number of LWT zones: This unit is
designed for 2 leaving water temperature
zones. Do NOT change this setting.
▪ 0 (1 LWT zone): N/A.
▪ 1 (2 LWT zones)(default): 2 leaving
water temperature zones. The zone
with the lowest leaving water
temperature is called the main leaving
water temperature zone. The zone
with the highest leaving water
temperature is called the additional
leaving water temperature zone. In
practice, the main leaving water
temperature zone consists of
underfloor heating and the additional
water temperature zone consists of
radiators or heat pump convectors.
# Code Description
[A.2.1.9] [F-0D] << continuation
▪ 1 (Sample): The pump is ON when
there is heating demand and the
leaving water temperature has NOT
reached the desired temperature yet.
When thermo OFF condition occurs,
the pump runs every 5 minutes to
check the water temperature and
demand heating if necessary.
Remark: Sample is NOT available in
external room thermostat control or
room thermostat control.
▪ a: Space heating control (user
interface)
▪ b: OFF
▪ c: On
▪ d: LWT temperature
▪ e: Actual
▪ f: Desired
▪ g: Pump operation
continued >>
▪ a: Add LWT zone
▪ b: Main LWT zone
# Code Description
[A.2.1.9] [F-0D] When the space heating control is OFF
by the user interface, the pump is always
OFF. When the space heating control is
On, you can select the desired pump
operation mode (only applicable during
space heating). This is applicable for
both temperature zones.
Pump operation mode:
▪ 0 (Continuous): Continuous pump
operation, regardless of thermo ON or
OFF condition. Remark: continuous
pump operation requires more energy
than sample or request pump
operation.
▪ a: Space heating control (user
interface)
▪ b: OFF
▪ c: On
▪ d: Pump operation
continued >>
# Code Description
[A.2.1.9] [F-0D] << continuation
▪ 2 (Request)(default): Pump operation
based on request. Example: Using a
room thermostat creates thermo ON/
OFF condition. When there is no such
demand, the pump is OFF. Remark:
Request is NOT available in leaving
water temperature control.
▪ a: Space heating control (user
interface)
▪ b: OFF
▪ c: On
▪ d: Heating demand (by ext RT or
RT)
▪ e: Pump operation
8.2.3 Quick wizard: Options
Domestic hot water settings
Following settings must be made accordingly.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
45
Page 46

8 Configuration
c
f
b
a
g
c
b
a
d f
e g
# Code Description
[A.2.2.1] [E-05] DHW operation:
Can the system prepare domestic hot
water?
▪ 0 (No): NOT installed.
▪ 1 (Yes)(default): Installed. Remark:
The domestic hot water tank is by
default installed. Do NOT change this
setting.
[A.2.2.A] [D-02] The indoor unit offers the possibility to
connect a field supplied domestic hot
water pump (On/OFF type). Depending
on the installation and configuration on
the user interface, we distinguish its
functionality.
DHW pump:
▪ 0 (No)(default): NOT installed.
▪ 1 (Secondary rtrn): Installed for instant
hot water when water is tapped. The
end-user sets the operation timing
(weekly schedule time) of the
domestic hot water pump when it
should run. Control of this pump is
possible through the indoor unit.
▪ 2 (Disinf. shunt): Installed for
disinfection. It runs when the
disinfection function of the domestic
hot water tank is running. No further
settings are needed.
See also illustrations below.
Domestic hot water pump installed for…
Instant hot water Disinfection
a Indoor unit
b Tank
c Domestic hot water pump (field supply)
d Heater element (field supply)
e Non‑return valve (field supply)
f Shower (field supply)
g Cold water
Thermostats and external sensors
Following combinations are possible to control the unit (not
applicable when [C‑07]=0):
When [C‑07]=2 (RT control)
User interface at
indoor unit
(1)
Room thermostat at
main zone
(2)
External room
thermostat at
additional zone
User interface at
indoor unit
External room
thermostat at main
zone
NOTICE
If an external room thermostat is used, the external room
thermostat will control the room frost protection. However,
the room frost protection is only possible if the leaving
water temperature control on the unit's user interface is
turned ON.
See "5Application guidelines"on page11.
# Code Description
[A.2.2.4] [C-05] Contact type main
In external room thermostat control, the
contact type of the optional room
thermostat or heat pump convector for
the main leaving water temperature zone
must be set. See "5Application
guidelines"on page11.
▪ 1 (Thermo ON/OFF): The connected
external room thermostat or heat
pump convector sends the heating
demand to the indoor unit (X2M/1).
Select this value in case of a
connection to the heat pump
convector (FWXV).
▪ 2 (H/C request)(default): The
connected external room thermostat
sends a heating demand and is
connected to the digital input
(preserved for the main leaving water
temperature zone) on the indoor unit
(X2M/1). Select this value in case of
connection with the wired (EKRTWA)
or wireless (EKRTR1) room
thermostat.
[A.2.2.5] [C-06] Contact type add.
In external room thermostat control with
2 leaving water temperature zones, the
type of the optional room thermostat for
the additional leaving water temperature
zone must be set. See "5Application
guidelines"on page11.
▪ 1 (Thermo ON/OFF): See Contact
type main. Connected on the indoor
unit (X2M/1a).
▪ 2 (H/C request)(default): See Contact
type main. Connected on the indoor
unit (X2M/1a).
External room
thermostat at
additional zone
When [C‑07]=1 (Ext RT control)
(1)Not mandatory.
(2)When there is no user interface installed at the indoor unit, the user interface in the main zone will function as room thermostat AND user interface.
Installer reference guide
46
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 47

8 Configuration
# Code Description
[A.2.2.B] [C-08] External sensor
When an optional external ambient
sensor is connected, the type of the
sensor must be set. See "5Application
guidelines"on page11.
▪ 0 (No)(default): NOT installed. The
thermistor in the user interface and in
the outdoor unit are used for
measurement.
▪ 1 (Outdoor sensor): Installed. The
external outdoor sensor will be used to
measure the outdoor ambient
temperature. Remark: For some
functionality, the temperature sensor
in the outdoor unit is still used.
▪ 2 (Room sensor): Installed. The
temperature sensor in the user
interface is NOT used anymore.
Remark: This value has only meaning
in room thermostat control.
Digital I/O PCB
Modification of these settings is only needed when the optional
digital I/O PCB is installed. The digital I/O PCB has multiple
functionality which need to be configured. See "5 Application
guidelines"on page11.
# Code Description
[A.2.2.6.1] [C-02] Not applicable.
[A.2.2.6.2] [D-07] Not applicable (read only).
[A.2.2.6.3] [C-09] Alarm output
Indicates the logic of the alarm output on
the digital I/O PCB during
malfunctioning.
▪ 0 (Normally open): The alarm output
will be powered when an alarm
occurs. By setting this value, a
distinction is made between the
detection of an alarm, and the
detection of a power failure.
▪ 1 (Normally closed): The alarm output
will NOT be powered when an alarm
occurs.
See also table below (Alarm output
logic).
[A.2.2.6.4] [F-04] Bottom plate heater
Only applicable for EHVZ16. Indicates if
an optional bottom plate heater is
installed on the outdoor unit. The power
of the bottom plate heater is in this case
supplied by the indoor unit.
▪ 0 (No)(default): NOT installed.
▪ 1 (Yes): Installed. Remark: If this
value is set, the output on the digital I/
O PCB cannot be used for space
heating output. See "5 Application
guidelines"on page11.
Alarm output logic
[C-09] Alarm No alarm No power
supply to unit
0 (default) Closed output Open output Open output
1 Open output Closed output
Demand PCB
The demand PCB is used to enable the power consumption control
by digital inputs. See "5Application guidelines"on page11.
# Code Description
[A.2.2.7] [D-04] Demand PCB
Only applicable for EHVZ04+08.
Indicates if the optional demand PCB is
installed.
▪ 0 (No)(default)
▪ 1 (Pwr consmp ctrl)
Energy metering
When energy metering is performed by the use of external power
meters, configure the settings as described below. Select the pulse
frequency output of each power meter in accordance with the power
meter specifications. It is possible to connect (up to 2) power meters
with different pulse frequencies. When only 1 or no power meter is
used, select No to indicate the corresponding pulse input is NOT
used.
# Code Description
[A.2.2.8] [D‑08] Optional external kWh meter1:
▪ 0 (No): NOT installed
▪ 1: Installed (0.1pulse/kWh)
▪ 2: Installed (1pulse/kWh)
▪ 3: Installed (10pulse/kWh)
▪ 4: Installed (100pulse/kWh)
▪ 5: Installed (1000pulse/kWh)
[A.2.2.9] [D‑09] Optional external kWh meter2:
▪ 0 (No): NOT installed
▪ 1: Installed (0.1pulse/kWh)
▪ 2: Installed (1pulse/kWh)
▪ 3: Installed (10pulse/kWh)
▪ 4: Installed (100pulse/kWh)
▪ 5: Installed (1000pulse/kWh)
8.2.4 Quick wizard: Capacities (energy metering)
The capacities of all electrical heaters must be set for the energy
metering and/or power consumption control feature to work properly.
When measuring the resistance value of each heater, you can set
the exact heater capacity and this will lead to more accurate energy
data.
# Code Description
[A.2.3.2] [6-03] BUH: step 1: The capacity of the first
step of the backup heater at nominal
voltage. Nominal value 3kW. Default:
3kW.
Range: 0~10kW (in steps of 0.2kW)
[A.2.3.6] [6-07] Bottom plate heater: Only applies to an
optional bottom plate heater
(EKBPHTH16A). The capacity of the
optional bottom plate heater at nominal
voltage. Default: 0W.
Range: 0~200W (in steps of 10W)
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
47
Page 48

8 Configuration
[1-03]
[1-02]
T
a
T
t
[1-00] [1-01]
8.2.5 Space heating control
The basic required settings in order to configure the space heating of
your system are described in this chapter. The weather-dependent
installer settings define the parameters for the weather-dependent
operation of the unit. When weather-dependent operation is active,
the water temperature is determined automatically depending on the
outdoor temperature. Low outdoor temperatures will result in warmer
water and vice versa. During weather-dependent operation, the user
has the possibility to shift up or down the target water temperature
by a maximum of 5°C.
See the user reference guide and/or operation manual for more
details about this function.
Leaving water temperature: Main zone
# Code Description
[A.3.1.1.1] N/A LWT setpoint mode:
▪ Fixed (default)
The desired leaving water
temperature is:
▪ NOT weather-dependent (i.e. does
NOT depend on the outdoor
ambient temperature)
▪ fixed in time (i.e., NOT scheduled)
▪ Weather dep.: The desired leaving
water temperature is:
▪ weather-dependent (i.e. depends
on the outdoor ambient
temperature)
▪ fixed in time (i.e., NOT scheduled)
continued >>
# Code Description
[A.3.1.1.1] N/A << continuation
▪ Fixed/scheduled: The desired leaving
water temperature is:
▪ NOT weather-dependent (i.e.,
does NOT depend on the outdoor
ambient temperature)
▪ according a schedule. The
scheduled actions consists of
desired shift actions, either preset
or custom.
Remark: This value can only be
set in leaving water temperature
control.
▪ WD/scheduled: The desired leaving
water temperature is:
▪ weather-dependent (i.e., does
depend on the outdoor ambient
temperature)
▪ according a schedule. The
scheduled actions consists of
desired leaving water
temperatures either preset or
custom.
Remark: This value can only be
set in leaving water temperature
control.
# Code Description
[7.7.1.1] [1-00]
Set weather-dependent heating:
[1-01]
[1-02]
[1-03]
▪ Tt: Target leaving water temperature
(main)
▪ Ta: Outdoor temperature
continued >>
# Code Description
[7.7.1.1] [1-00]
[1-01]
[1-02]
[1-03]
<< continuation
▪ [1-00]: Low outdoor ambient
temperature.–40°C~+5°C (default: –
10°C)
▪ [1-01]: High outdoor ambient
temperature. 10°C~25°C (default:
15°C)
▪ [1-02]: Desired leaving water
temperature when the outdoor
temperature equals or drops below
the low ambient temperature.
[9‑01]°C~[9‑00]°C (default: 35°C).
Note: This value should be higher
than [1-03] as for low outdoor
temperatures warmer water is
required.
▪ [1-03]: Desired leaving water
temperature when the outdoor
temperature equals or rises above
the high ambient temperature.
[9‑01]°C~min(45, [9‑00])°C (default:
25°C).
Note: This value should be lower
than [1-02] as for high outdoor
temperatures less warm water is
required.
Leaving water temperature: Additional zone
Only applicable if 2 leaving water temperature zones are present.
Installer reference guide
48
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 49

8 Configuration
[0-00]
[0-01]
T
a
T
t
[0-03] [0-02]
# Code Description
[A.3.1.2.1] N/A LWT setpoint mode:
▪ Fixed (default): The desired leaving
water temperature is:
▪ NOT weather-dependent (i.e. does
NOT depend on the outdoor
ambient temperature)
▪ fixed in time (i.e., NOT scheduled)
▪ Weather dep.: The desired leaving
water temperature is:
▪ weather-dependent (i.e. depends
on the outdoor ambient
temperature)
▪ fixed in time (i.e., NOT scheduled)
▪ Fixed/scheduled: The desired leaving
water temperature is:
▪ NOT weather-dependent (i.e.,
does NOT depend on the outdoor
ambient temperature)
▪ according a schedule. The
scheduled actions are On or OFF.
Remark: This value can only be
set in leaving water temperature
control.
▪ WD/scheduled: The desired leaving
water temperature is:
▪ weather-dependent (i.e., does
depend on the outdoor ambient
temperature)
▪ according a schedule. The
scheduled actions are On or OFF.
Remark: This value can only be
set in leaving water temperature
control.
# Code Description
[7.7.2.1] [0-00]
Set weather-dependent heating:
[0-01]
[0-02]
[0-03]
▪ Tt: Target leaving water temperature
(additional)
▪ Ta: Outdoor temperature
continued >>
# Code Description
[7.7.2.1] [0-00]
[0-01]
[0-02]
[0-03]
<< continuation
▪ [0-03]: Low outdoor ambient
temperature. –40°C~+5°C (default: –
10°C)
▪ [0-02]: High outdoor ambient
temperature. 10°C~25°C (default:
15°C)
▪ [0-01]: Desired leaving water
temperature when the outdoor
temperature equals or drops below
the low ambient temperature.
[9‑05]°C~[9‑06]°C (default: 45°C).
Note: This value should be higher
than [0-00] as for low outdoor
temperatures warmer water is
required.
▪ [0-00]: Desired leaving water
temperature when the outdoor
temperature equals or rises above
the high ambient temperature.
[9‑05]°C~min(45, [9‑06])°C (default:
35°C).
Note: This value should be lower
than [0-01] as for high outdoor
temperatures less warm water is
required.
Leaving water temperature: Delta T source
When both temperature zones have heating demand, both pumps
will operate at full speed. When only 1 temperature zone has heating
demand, only 1 pump will operate and the flow will be controlled to
realize a temperature difference between the entering and the
leaving water of [9‑09] on that zone. Only 1 temperature difference
[9‑09] can be selected, this is then applicable for both temperature
zones.
# Code Description
[A.3.1.3.1] [9-09] Heating: Required temperature
difference between entering and
leaving water. Range: 3°C~10°C (in
steps of 1°C; default value: 5°C).
Leaving water temperature: Modulation
Only applicable in case of room thermostat control. When using the
room thermostat functionality, the customer needs to set the desired
room temperature. The unit will supply hot water to the heat emitters
and the room will be heated. Additionally, also the desired leaving
water temperature must be configured: when turning on the
modulation, the desired leaving water temperature will be calculated
automatically by the unit (based on the preset temperatures, if
weather-dependent is selected, modulation will be done based on
the desired weather-dependent temperatures); when turning off the
modulation, you can set the desired leaving water temperature on
the user interface. Moreover, with the modulation turned on, the
desired leaving water temperature is lowered or raised in function of
the desired room temperature and the difference between the actual
and the desired room temperature. This results in:
▪ stable room temperatures exactly matching the desired
temperature (higher comfort level)
▪ less On/OFF cycles (lower noise level, higher comfort and higher
efficiency)
▪ water temperatures as low as possible to match the desired
temperature (higher efficiency)
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
49
Page 50

8 Configuration
a
+[8-06]
−[8-06]
b
T
a
T
t
# Code Description
[A.3.1.1.5] [8-05] Modulated LWT:
▪ No (default): disabled.
Note: The desired leaving water
temperature needs to be set on the
user interface.
▪ Yes: enabled.
Note: The desired leaving water
temperature can only be read out on
the user interface
N/A [8-06] Leaving water temperature maximum
modulation:
0°C~10°C (default: 3°C)
Requires modulation to be enabled.
This is the value by which the desired
leaving water temperature is increased
or lowered.
INFORMATION
Only applicable for the main zone.
INFORMATION
When leaving water temperature modulation is enabled,
the weather‑dependent curve needs to be set to a higher
position than [8-06] plus the minimum leaving water
temperature setpoint required to reach a stable condition
on the comfort setpoint for the room. To increase
efficiency, modulation can lower the leaving water setpoint.
By setting the weather‑dependent curve to a higher
position, it cannot drop below the minimum setpoint. Refer
to the illustration below.
8.2.6 Domestic hot water control
Configuring the desired tank temperature
The domestic hot water can be prepared in 3 different ways. They
differ from each other by the way the desired tank temperature is set
and how the unit acts upon it.
# Code Description
[A.4.1] [6-0D] Domestic hot water Type:
▪ 0 (Reheat only): Only reheat operation
is allowed.
▪ 1 (Reheat + sched.): The domestic hot
water tank is heated according to a
schedule and between the scheduled
heatup cycles, reheat operation is
allowed.
▪ 2 (Scheduled only): The domestic hot
water tank can ONLY be heated
according to a schedule.
See "8.3.2 Domestic hot water control: advanced" on page 53 for
more details.
INFORMATION
There is a risk of space heating capacity shortage/comfort
problem (in case of frequent domestic hot water operation,
frequent and long space heating interruption will happen)
when selecting [6‑0D]=0 ([A.4.1] Domestic hot water
Type=Reheat only).
Maximum DHWtemperature setpoint
The maximum temperature that users can select for the domestic
hot water. You can use this setting to limit the temperatures at the
hot water taps.
a Weather-dependent curve
b Minimum leaving water temperature setpoint required to
reach a stable condition on the comfort setpoint for the
room.
Leaving water temperature: Emitter type
This setting only applies to the main zone. Only applicable in case of
room thermostat control. Depending on the system water volume
and the heat emitters type, the heat up of a space can take longer.
This setting can compensate for a slow or a quick heating system
during the heat up cycle.
Note: The setting of the emitter type will influence the maximum
modulation of the desired leaving water temperature.
Therefore it is important to set this correctly.
# Code Description
[A.3.1.1.7] [9-0B] Emitter type:
Set for the main temperature zone.
Reaction time of the system:
▪ Quick Example: Small water volume
and fan coils.
▪ Slow Example: Large water volume,
floor heating loops.
INFORMATION
During disinfection of the domestic hot water tank, the
DHWtemperature can exceed this maximum temperature.
INFORMATION
Limit the maximum hot water temperature according to the
applicable legislation.
# Code Description
[A.4.5] [6-0E] Maximum setpoint
The maximum temperature that users
can select for the domestic hot water.
You can use this setting to limit the
temperature at the hot water taps.
Range: 40°C~60°C (default: 60°C).
The maximum temperature is NOT
applicable during disinfection function.
See disinfection function.
8.2.7 Contact/helpdesk number
# Code Description
[6.3.2] N/A Number that users can call in case of
problems.
8.3 Advanced configuration/ optimization
8.3.1 Space heating operation: advanced
Preset leaving water temperature
You can define preset leaving water temperatures:
Installer reference guide
50
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 51

8 Configuration
T
t
T
A
R
L
0°C
T
t
T
A
R
L
0°C
a b
▪ economic (denotes the desired leaving water temperature which
results in the lowest energy consumption)
▪ comfort (denotes the desired leaving water temperature which
results in the highest energy consumption).
Preset values make it easy to use the same value in the schedule or
to adjust the desired leaving water temperature according to the
room temperature (see modulation). If you later want to change the
value, you ONLY have to do it in one place. Depending on whether
the desired leaving water temperature is weather dependent or NOT,
the desired shift values or the absolute desired leaving water
temperature should be specified.
NOTICE
The preset leaving water temperatures are ONLY
applicable for the main zone, as the schedule for the
additional zone consists of On/OFF actions.
NOTICE
Select preset leaving water temperatures in accordance
with the design and selected heat emitters to ensure the
balance between desired room and leaving water
temperatures.
# Code Description
Preset leaving water temperature for the main leaving water
temperature zone in case of NOT weather dependent
[7.4.2.1] [8-09] Comfort (heating)
[9‑01]°C~[9‑00]°C (default: 35°C)
[7.4.2.2] [8-0A] Eco (heating)
[9‑01]°C~[9‑00]°C (default: 33°C)
Preset leaving water temperature (shift value) for the main leaving
water temperature zone in case of weather dependent
[7.4.2.5] N/A Comfort (heating)
–10°C~+10°C (default: 0°C)
[7.4.2.6] N/A Eco (heating)
–10°C~+10°C (default: –2°C)
Temperature ranges (leaving water temperatures)
The purpose of this setting is to prevent selecting a wrong (i.e. too
hot or too cold) leaving water temperature. Therefore the available
desired heating temperature range can be configured.
NOTICE
In case of a floor heating application it is important to limit
the maximum leaving water temperature at heating
operation according to the specifications of the floor
heating installation.
Example: Set the minimum leaving water temperature to 28°C to
avoid NOT to be able to heat up the room: leaving water
temperatures MUST be sufficiently higher than the room
temperatures (in heating).
# Code Description
Leaving water temperature range for the main leaving water
temperature zone (= the leaving water temperature zone with the
lowest leaving water temperature)
[A.3.1.1.2.2] [9-00] Maximum temp (heating)
37°C~55°C (default: 55°C)
[A.3.1.1.2.1] [9-01] Minimum temp (heating)
15°C~37°C (default: 25°C)
Leaving water temperature range for the additional leaving water
temperature zone (= the leaving water temperature zone with the
highest leaving water temperature)
[A.3.1.2.2.2] [9-06] Maximum temp (heating)
37°C~55°C (default: 55°C)
[A.3.1.2.2.1] [9-05] Minimum temp (heating)
15°C~37°C (default: 25°C)
Leaving water temperature overshoot temperature
This function defines how much the water temperature may rise
above the desired leaving water temperature before the compressor
stops. The compressor will startup again when the leaving water
temperature drops below the desired leaving water temperature.
# Code Description
N/A [9-04] 1°C~4°C (default: 1°C)
Leaving water temperature compensation around 0°C
In heating operation, the desired leaving water temperature is locally
increased around an outdoor temperature of 0°C. This
compensation can be selected when using an absolute or a weather
dependent desired temperature (see illustration below). Use this
setting to compensate for possible heat losses of the building due to
the evaporation of melted ice or snow (e.g. in cold region countries).
NOTICE
▪ When adjusting the leaving water temperature ranges,
all desired leaving water temperatures are also
adjusted to guarantee they are between the limits.
▪ Always balance between the desired leaving water
temperature with the desired room temperature and/or
the capacity (according to the design and selection of
the heat emitters). The desired leaving water
temperature is the result of several settings (preset
values, shift values, weather dependent curves,
modulation). As a result, too high or too low leaving
water temperatures could occur which lead to
overtemperatures or capacity shortage. By limiting the
leaving water temperature range to adequate values
(depending on the heat emitter), such situations can be
avoided.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
a Absolute desired LWT
b Weather dependent desired LWT
TAAmbient temperature (°C)
TtDesired leaving water temperature
# Code Description
N/A [D-03] ▪ 0 (disabled) (default)
▪ 1 (enabled) L=2°C,
R=4°C (−2°C<TA<2°C)
▪ 2 (enabled) L=4°C,
R=4°C (−2°C<TA<2°C)
▪ 3 (enabled) L=2°C,
R=8°C (−4°C<TA<4°C)
▪ 4 (enabled) L=4°C,
R=8°C (−4°C<TA<4°C)
Installer reference guide
51
Page 52

8 Configuration
[
9-0C
]
a
b
c
d
Leaving water temperature maximum modulation
ONLY applicable in room thermostat control and when modulation is
enabled. The maximum modulation (=variance) on the desired
leaving water temperature decided on the difference between the
actual and desired room temperature, e.g. 3°C modulation means
the desired leaving water temperature can be increased or lowered
by 3°C. Increasing the modulation results in better performance (less
On/OFF, faster heat up), but note that depending on the heat
emitter, there MUST ALWAYS be a balance (refer to the design and
selection of the heat emitters) between the desired leaving water
temperature and the desired room temperature.
# Code Description
N/A [8-06] 0°C~10°C (default: 3°C)
Temperature ranges (room temperature)
ONLY applicable in room thermostat control. In order to save energy
by preventing overheating the room, you can limit the range of the
room temperature.
NOTICE
When adjusting the room temperature ranges, all desired
room temperatures are also adjusted to guarantee they are
between the limits.
# Code Description
Room temp. range
[A.3.2.1.2] [3-06] Maximum temp (heating)
18°C~30°C (default: 30°C)
[A.3.2.1.1] [3-07] Minimum temp (heating)
12°C~18°C (default: 12°C)
Room temperature step
ONLY applicable in room thermostat control and when the
temperature is displayed in °C.
# Code Description
[A.3.2.4] N/A Room temp. step
▪ 1°C (default). The desired room
temperature on the user interface is
settable per 1°C.
▪ 0.5°C. The desired room temperature
on the user interface is settable per
0.5°C. The actual room temperature is
displayed with an accuracy of 0.1°C.
Room temperature hysteresis
ONLY applicable in case of room thermostat control. The hysteresis
band around the desired room temperature is settable. It is
recommended NOT to change the room temperature hysteresis as it
is set for an optimal use of the system.
interface or by the external room sensor. The settings can be used
to compensate for situations where the user interface or external
room sensor CANNOT be installed on the ideal installation location
(see installation manual and/or installer reference guide).
# Code Description
Room temp. offset: Offset on the actual room temperature
measured on the user interface sensor.
[A.3.2.2] [2-0A] –5°C~+5°C, step 0.5°C (default: 0°C)
Ext. room sensor offset: ONLY applicable if the external room
sensor option is installed and configured (see [C-08])
[A.3.2.3] [2-09] –5°C~+5°C, step 0.5°C (default: 0°C)
Room frost protection
Room frost protection prevents the room from getting too cold. This
setting behaves differently depending on the set unit control method
([C‑07]). Perform actions according to the table below:
Unit control method ([C‑07]) Room frost protection
Room thermostat control
([C‑07]=2)
Allow for the room thermostat to
take care of room frost
protection:
▪ Set [2‑06] to "1"
▪ Set the room antifrost
temperature ([2‑05]).
External room thermostat control
([C‑07]=1)
Allow for the external room
thermostat to take care of room
frost protection:
▪ Turn ON the leaving water
temperature home page.
Leaving water temperature
control ([C‑07]=0)
Room frost protection is NOT
guaranteed.
NOTICE
If the system does NOT contain a backup heater, do NOT
change the default room antifrost temperature.
INFORMATION
If a U4 error occurs, room frost protection is NOT
guaranteed.
Refer to the sections below for detailed information on room frost
protection in relation to the applicable unit control method.
[C‑07]=2: room thermostat control
Under room thermostat control, room frost protection is guaranteed,
even if the room temperature home page is OFF on the user
interface. When room frost protection ([2‑06]) is enabled and the
room temperature drops below the room antifrost temperature
([2‑05]), the unit will supply leaving water to the heat emitters to heat
up the room again.
a Room temperature
b Actual room temperature
c Desired room temperature
d Time
# Code Description
N/A [9-0C] 1°C~6°C (default: 1°C)
Room temperature offset
ONLY applicable in case of room thermostat control. You can
calibrate the (external) room temperature sensor. It is possible to
give an offset to the room thermistor value measured by the user
Installer reference guide
52
# Code Description
N/A [2-06] Room frost protection
▪ 0: disabled
▪ 1: enabled (default)
N/A [2-05] Room antifrost temperature
4°C~16°C (default: 12°C)
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 53

8 Configuration
INFORMATION
If a U5 error occurs:
▪ when 1 user interface is connected, room frost
protection is NOT guaranteed,
▪ when 2 user interfaces are connected and the second
user interface used for room temperature control is
disconnected (due to miswiring, damage of the cable),
then room frost protection is NOT guaranteed.
NOTICE
If Emergency is set to Manual ([A.6.C]=0), and the unit is
triggered to start emergency operation, the user interface
will ask confirmation before starting. Room frost protection
is active even if the user does NOT confirm emergency
operation.
[C‑07]=1: external room thermostat control
Under external room thermostat control, room frost protection is
guaranteed by the external room thermostat, provided that the
leaving water temperature home page is ON on the user interface,
and the auto emergency setting ([A.6.C]) is set to "1".
Additionally, limited frost protection by the unit is possible:
In case of… …then the following applies:
Two leaving water temperature
zones
[C‑07]=0: leaving water temperature control
Under leaving water temperature control, room frost protection is
NOT guaranteed. However, if [2‑06] is set to "1", limited frost
protection by the unit is possible:
▪ When the leaving water temperature home page is OFF and the
outdoor ambient temperature drops below 4°C, then the unit will
supply leaving water to the heat emitters to heat up the room
again, and the leaving water temperature setpoint will be lowered.
▪ When the leaving water temperature home page is ON, then the
unit will supply leaving water to the heat emitters to heat up the
room according to normal logic.
Shut-off valve
The following is only applicable in case of 2 leaving water
temperature zones. In case of 1 leaving water temperature zone,
connect the shut-off valve to the heating output.
The shut-off valve, which is in the main leaving water temperature
zone, output is configurable.
INFORMATION
During defrost operation, the shut-off valve is ALWAYS
opened.
▪ When the leaving water
temperature home page is
OFF, and the outdoor ambient
temperature drops below 4°C,
then the unit will supply
leaving water to the heat
emitters to heat up the room
again, and the leaving water
temperature setpoint will be
lowered.
▪ When the leaving water
temperature home page is ON,
the outdoor ambient
temperature drops below 4°C,
then the unit will supply
leaving water to the heat
emitters to heat up the room
again, and the leaving water
temperature setpoint will be
lowered.
Thermo On/OFF: the valve closes, depending on [F‑0B] when there
is no heating demand from the main zone.
# Code Description
[A.3.1.1.6.1] [F-0B] The shut-off valve:
▪ 0 (No)(default): is NOT influenced by
heating demand.
▪ 1 (Yes): closes when there is NO
heating demand.
INFORMATION
The setting [F‑0B] is only valid when there is a thermostat
or external room thermostat request setting (NOT in case
of leaving water temperature setting).
Operation range
Depending on the average outdoor temperature, the operation of the
unit in space heating is prohibited.
Space heating OFF temp: When the averaged outdoor temperature
raises above this value, space heating is turned OFF to avoid
overheating.
# Code Description
[A.3.3.1] [4-02] ▪ EHVZ04+08: 14°C~35°C (default:
25°C)
▪ EHVZ16: 14°C~35°C (default: 35°C)
8.3.2 Domestic hot water control: advanced
Preset tank temperatures
Only applicable when domestic hot water preparation is scheduled
or scheduled + reheat.
You can define preset tank temperatures:
▪ storage economic
▪ storage comfort
▪ reheat
▪ reheat hysteresis
Preset values make it easy to use the same value in the schedule. If
you later want to change the value, you only have to do it in 1 place
(see also operation manual and/or user reference guide).
Storage comfort
When programming the schedule, you can make use of the tank
temperatures set as preset values. The tank will then heat up until
these setpoint temperatures have been reached. Additionally, a
storage stop can be programmed. This feature puts a stop to tank
heating even if the setpoint has NOT been reached. Only program a
storage stop when tank heating is absolutely undesirable.
# Code Description
[7.4.3.1] [6-0A] 30°C~[6‑0E]°C (default: 60°C)
Storage eco
The storage economic temperature denotes the lower desired tank
temperature. It is the desired temperature when a storage economic
action is scheduled (preferably during day).
# Code Description
[7.4.3.2] [6-0B] 30°C~min(50, [6‑0E])°C (default: 45°C)
Reheat
The desired reheat tank temperature is used:
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
53
Page 54

8 Configuration
T
DHW
T
a
[0-0C]
[0-0B]
[0-0E] [0-0D]
t
T
DHW
T
HP ON
T
HP OFF
T
HP MAX
T
U=TBUH OFF
[6-01]
[6-00]
TU= 60°C
T
HP MAX
= 50°C
[6-01] = 2°C
[6-00] = 2°C
HP
BUH
HP
5
10
20
30
40
46
48
50
60
▪ in reheat mode of scheduled + reheat mode: The guaranteed
minimum tank temperature is set by T
–[6‑08], which is either
HP OFF
[6‑0C] or the weather dependent setpoint, minus the reheat
hysteresis. If the tank temperature drops below this value, the tank
is heated up.
▪ during storage comfort, to prioritize the domestic hot water
preparation. When the tank temperature raises above this value,
domestic hot water preparation and space heating is executed
sequentially.
# Code Description
[7.4.3.3] [6-0C] 30°C~min(50, [6‑0E])°C (default: 45°C)
Reheat hysteresis
Only applicable when domestic hot water preparation is scheduled +
reheat.
# Code Description
N/A [6-08] 2°C~20°C (default: 10°C)
Weather dependent
The weather dependent installer settings define the parameters for
the weather dependent operation of the unit. When weather
dependent operation is active the desired tank temperature is
determined automatically depending on the averaged outdoor
temperature: low outdoor temperatures will result in higher desired
tank temperatures as the cold water tap is colder and vice versa. In
case of scheduled or scheduled+reheat domestic hot water
preparation, the storage comfort temperature is weather dependent
(according to the weather dependent curve), the storage economic
and reheat temperature are NOT weather dependent. In case of
reheat only domestic hot water preparation, the desired tank
temperature is weather dependent (according to the weather
dependent curve). During weather dependent operation, the enduser cannot adjust the desired tank temperature on the user
interface.
# Code Description
[A.4.6] N/A Weather dependent desired tank
temperature is:
▪ Fixed (default): disabled. All desired
tank temperature are NOT weather
dependent.
▪ Weather dep.: enabled. In scheduled
or scheduled+reheat mode, the
storage comfort temperature is
weather dependent. Storage economic
and reheat temperatures are NOT
weather dependent. In reheat mode,
the desired tank temperature is
weather dependent.
Note: When the displayed tank
temperature is weather dependent, it
cannot be adjusted on the user
interface.
# Code Description
[A.4.7] [0-0E]
Weather-dependent curve
[0-0D]
[0-0C]
[0-0B]
▪ T
: The desired tank temperature.
DHW
▪ Ta: The (averaged) outdoor ambient
temperature
▪ [0-0E]: low outdoor ambient
temperature: –40°C~5°C (default: –
10°C)
▪ [0-0D]: high outdoor ambient
temperature: 10°C~25°C (default:
15°C)
▪ [0-0C]: desired tank temperature when
the outdoor temperature equals or
drops below the low ambient
temperature: 45°C~[6‑0E]°C (default:
60°C)
▪ [0-0B]: desired tank temperature when
the outdoor temperature equals or
rises above the high ambient
temperature: 35°C~[6‑0E]°C (default:
55°C)
Limits on heat pump operation
In domestic hot water operation, following hysteresis values can be
set for the heat pump operation:
# Code Description
N/A [6-00] The temperature difference determining
the heat pump ON temperature.
Range: 2°C~20°C (default: 2°C)
N/A [6-01] The temperature difference determining
the heat pump OFF temperature.
Range: 0°C~10°C (default: 2°C)
Example: setpoint (TU)>maximum heat pump temperature–[6‑01]
(T
–[6‑01])
HP MAX
Installer reference guide
54
BUH Backup heater
HP Heat pump. If heating up time by the heat pump takes too
T
long, auxiliary heating by the backup heater can take place
Backup heater OFF temperature (TU)
BUH OFF
T
Maximum heat pump temperature at sensor in domestic
HP MAX
hot water tank
T
Heat pump OFF temperature (T
HP OFF
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
−[6-01])
HP MAX
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 55

T
t
[6-00]
HP
5
10
20
30
40
43
45
TU=T
HP OFF
T
HP MAX
T
DHW
T
HP ON
50
t
1
0
1
0
[8-01] [8-02]
[8-00]
t
T
A
0
[8-01]
[5-03] [4-02]
[8-02]
[8-01]+
[8-04]
Heat pump ON temperature (T
HP ON
T
Domestic hot water temperature
DHW
TUUser set point temperature (as set on the user interface)
t Time
HP OFF
−[6-00])
Example: setpoint (TU)≤maximum heat pump temperature–[6‑01]
(T
–[6‑01])
HP MAX
8 Configuration
# Code Description
N/A [8-04] Additional running time for the maximum
running time depending on the outdoor
temperature [4‑02].
Range: 0~95 minutes (default: 95).
[8-02]: Anti-recycling time
Timers for simultaneous request space and domestic hot water
operation
N/A [8-00] Do not change. (default: 1)
N/A [8-01] Maximum running time for domestic hot
N/A [8-02] Anti-recycling time.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
HP Heat pump. If heating up time by the heat pump takes too
long, auxiliary heating by the booster heater can take place
T
Maximum heat pump temperature at sensor in domestic
HP MAX
hot water tank
T
Heat pump OFF temperature (T
HP OFF
T
Heat pump ON temperature (T
HP ON
T
Domestic hot water temperature
DHW
TUUser set point temperature (as set on the user interface)
t Time
HP MAX
HP OFF
−[6-01])
−[6-00])
INFORMATION
The maximum heat pump temperature depends on the
ambient temperature. For more information, see the
operation range.
# Code Description
water operation. Domestic hot water
heating stops even when the target
domestic hot water temperature is NOT
reached. The actual maximum running
time also depends on setting [8‑04].
▪ When system layout = Room
thermostat control: This preset value is
only taken into account if there is a
request for space heating. If there is
NO request for space heating, the tank
is heated until the setpoint has been
reached.
▪ When system layout ≠ Room
thermostat control: This preset value is
always taken into account.
Range: 5~95 minutes (default: 30)
Minimum time between two cycles for
domestic hot water. The actual antirecycling time also depends on setting
[8‑04].
Range: 0~10 hours (default: 0.5) (step:
0.5 hour).
Remark: The minimum time is 1/2 hour
even when the selected value is 0.
1 Heat pump domestic water heating mode (1=active, 0=not
active)
2 Hot water request for heat pump (1=request, 0=no request)
t Time
[8-04]: Additional running time at [4-02]/[F-01]
TAAmbient (outdoor) temperature
t Time
Anti-recycle time
Maximum running time domestic hot water
Disinfection
The disinfection function disinfects the domestic hot water tank by
periodically heating the domestic hot water to a specific temperature.
CAUTION
The disinfection function settings MUST be configured by
the installer according to the applicable legislation.
# Code Description
[A.4.4.2] [2‑00] Operation day:
▪ 0: Each day
▪ 1: Monday
▪ 2: Tuesday
▪ 3: Wednesday
▪ 4: Thursday
▪ 5: Friday
▪ 6: Saturday
▪ 7: Sunday
[A.4.4.1] [2‑01] Disinfection
▪ 0: No
▪ 1: Yes
[A.4.4.3] [2‑02] Start time: 00~23:00, step: 1:00.
[A.4.4.4] [2‑03] Temperature target: 60°C (fixed).
[A.4.4.5] [2‑04] Duration: 40~60 minutes, default: 40
minutes.
Installer reference guide
55
Page 56

8 Configuration
00.00 22.00 24.0001.00 23.00 t
T
DHW
T
H
T
U
[2-02]
[2-03]
[2-04]
T
Domestic hot water temperature
DHW
TUUser set point temperature
THHigh set point temperature [2-03]
t Time
WARNING
Be aware that the domestic hot water temperature at the
hot water tap will be equal to the value selected in field
setting [2-03] after a disinfection operation.
When the high domestic hot water temperature can be a
potential risk for human injuries, a mixing valve (field
supply) shall be installed at the hot water outlet connection
of the domestic hot water tank. This mixing valve shall
secure that the hot water temperature at the hot water tap
never rise above a set maximum value. This maximum
allowable hot water temperature shall be selected
according to the applicable legislation.
CAUTION
Be sure that the disinfection function start time [A.4.4.3]
with defined duration [A.4.4.5] is NOT interrupted by
possible domestic hot water demand.
INFORMATION
In case of error code AH and no interruption of the
disinfection function occurred due to domestic hot water
tapping, following actions are recommended:
▪ When the Domestic hot water > Type > Reheat or
Reheat + sched. is selected, it is recommended to
program the start-up of the disinfection function at least
4 hours later than the last expected large hot water
tapping. This start-up can be set by installer settings
(disinfection function).
▪ When the Domestic hot water > Type > Scheduled only
is selected, it is recommended to program a Storage
eco 3 hours before the scheduled start-up of the
disinfection function to preheat the tank.
INFORMATION
Disinfection function is restarted in case the domestic hot
water temperature drops 5°C below the disinfection target
temperature within the duration time.
8.3.3 Heat source settings
Backup heater
Backup heater operation mode: defines when backup heater
operation is disabled or only allowed during domestic hot water
operation. This setting is only overruled when backup heating is
required during defrost operation or malfunctioning of the outdoor
unit (when [A.6.C] is enabled).
# Code Description
[A.5.1.1] [4‑00] Backup heater operation:
▪ 0: Disabled
▪ 1 (default): Enabled
N/A [5-00] Is backup heater operation allowed
[A.5.1.4] [5‑01] Equilibrium temperature.
INFORMATION
If backup heater operation during space heating needs to
be limited but can be allowed for domestic hot water
operation, then put [4‑00] on 1, [5‑00] on 1, and [5‑01] on –
15°C.
Auto emergency
When the heat pump fails to operate, the backup heater can serve
as an emergency heater and either automatically or nonautomatically take over the heat load.
▪ When auto emergency is set to Automatic and a heat pump failure
occurs, the backup heater will automatically take over the heat
load.
▪ When auto emergency is set to Manual and a heat pump failure
occurs, the domestic hot water and space heating operations will
stop and need to be recovered manually. The user interface will
then ask you to confirm whether the backup heater can take over
the heat load or not.
When the heat pump fails,
house is unattended for longer periods, we recommend to set
[A.6.C] Emergency to Automatic.
# Code Description
[A.6.C] N/A Emergency:
above equilibrium temperature during
space heating operation?
▪ 1: NOT allowed (default)
▪ 0: Allowed
Outdoor temperature below which
operation of the backup heater is
allowed.
Range: –15°C~35°C (default: 0°C) (step:
1°C)
will appear on the user interface. If the
▪ 0: Manual (default)
▪ 1: Automatic
INFORMATION
An AH error occurs if you do the following during
disinfection:
▪ Set the user permission level to Installer.
▪ Go to the DHWtank temperature home page (Tank).
Installer reference guide
▪ Press
to interrupt the disinfection.
56
INFORMATION
The auto emergency setting can be set in the menu
structure of the user interface only.
INFORMATION
If a heat pump failure occurs and [A.6.C] is set to Manual,
the room frost protection function, the underfloor heating
screed dryout function, and the water pipe antifreeze
function will remain active even if the user does NOT
confirm emergency operation.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 57

8 Configuration
T
A
[F-02]
[F-03]
a
b
YC Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4
X1 X2 X3 X4
OFF ON
X2M
SS1
X1M
Bottom plate heater
Applies only to installation with an outdoor unit ERHQ and the option
bottom plate heater kit is installed.
▪ [F-02] Bottom plate heater ON temperature: defines the outdoor
temperature below which the bottom plate heater will be activated
by indoor unit in order to prevent ice build-up in the bottom plate of
the outdoor unit at lower outdoor temperatures.
▪ [F-03] Bottom plate heater hysteresis: defines the temperature
difference between bottom plate heater ON temperature and the
bottom plate heater OFF temperature.
Bottom plate heater
TAOutdoor temperature
a On
b OFF
CAUTION
The bottom plate heater is controlled via EKRP1HB.
# Code Description
N/A [F-02] Bottom plate heater ON temperature:
3°C~10°C (default: 3°C)
N/A [F-03] Hysteresis: 2°C~5°C (default: 5°C)
INFORMATION
Depending on setting [F-04], contact Y2, located on digital
I/O PCB EKRP1HB, controls the optional bottom plate
heater. See the illustration below for the schematic location
of this contact. For the complete wiring, see the wiring
diagram.
8.3.4 System settings
Priorities
# Code Description
N/A [5‑02] Space heating priority.
Defines whether backup heater will
assist the heat pump during domestic
hot water operation.
Consequence: Shorter tank heating
operation time and shorter interruption
of the space heating cycle.
This setting MUST always be 1.
[5‑01] Equilibrium temperature and
[5‑03] Space heating priority
temperature are related to backup
heater. So, you must set [5‑03] equal or
a few degrees higher than [5‑01].
If the backup heater operation is limited
([4‑00]=0) and the outdoor temperature
is lower than setting [5‑03], the
domestic hot water will not be heated
with the backup heater.
N/A [5‑03] Space heating priority temperature.
Defines the outdoor temperature which
below the backup heater will assist
during domestic hot water heating.
Auto-restart
When power returns after a power supply failure, the auto restart
function reapplies the remote controller settings at the time of the
power failure. Therefore, it is recommended to always enable the
function.
If the preferential kWh rate power supply is of the type that power
supply is interrupted, always enable the auto restart function.
Continuous indoor unit control can be guaranteed independent of the
preferential kWh rate power supply status, by connecting the indoor
unit to a normal kWh rate power supply.
# Code Description
[A.6.1] [3‑00] Is the auto restart function of the unit
allowed?
▪ 0: No
▪ 1 (default): Yes
Preferential kWh rate power supply
INFORMATION
The preferential kWh rate power supply contact is
connected to the same terminals (X5M/3+4) as the safety
thermostat for the additional zone. It is only possible for the
system to have EITHER preferential kWh rate power
supply OR a safety thermostat for the additional zone.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
57
Page 58

8 Configuration
3×
1 2 3
# Code Description
[A.2.1.6] [D‑01] Connection to a preferential kWh rate
power supply:
▪ 0 (default): The outdoor unit is
connected to a normal power supply.
▪ 1: The outdoor unit is connected to a
preferential kWh rate power supply.
When the preferential kWh rate signal
is sent by the electricity company, the
contact will open and the unit will go in
forced off mode. When the signal is
released again, the voltage-free
contact will close and the unit will
restart operation. Therefore, always
enable the auto restart function.
▪ 2: The outdoor unit is connected to a
preferential kWh rate power supply.
When the preferential kWh rate signal
is sent by the electricity company, the
contact will close and the unit will go in
forced off mode. When the signal is
released again, the voltage-free
contact will open and the unit will
restart operation. Therefore, always
enable the auto restart function.
Remark: 3 is related to safety
thermostat.
[A.6.2.1] [D‑00] Which heaters are allowed to operate
during preferential kWh rate power
supply?
▪ 0 (default): None
▪ 1: N/A
▪ 2: Backup heater only
▪ 3: N/A
INFORMATION
The preferential kWh rate power supply contact is
connected to the same terminals (X5M/3+4) as the safety
thermostat for the additional zone. It is only possible for the
system to have EITHER preferential kWh rate power
supply OR a safety thermostat for the additional zone.
Power saving function
INFORMATION
Only applicable for ERLQ004~008CAV3.
Defines whether the outdoor unit power supply can be interrupted
(internally by indoor unit control) during stand-still conditions (no
space heating nor domestic hot water demand). The final decision to
allow power interruption of the outdoor unit during standstill depends
on the ambient temperature, compressor conditions and minimum
internal timers.
To enable the power saving function setting, [E‑08] needs to be
enabled on the user interface in combination with the removal of the
power saving connector at the outdoor unit.
NOTICE
The power saving connector at the outdoor unit shall only
be removed when the main power supply to the application
is switched OFF.
In case of ERLQ004~008CAV3
See table below.
Setting 2 is only meaningful if the
preferential kWh rate power supply is of
type1 or indoor unit is connected to a
normal kWh rate power supply (via
X2M/30-31) and the backup heater is
NOT connected to the preferential kWh
rate power supply.
Do NOT use 1 or 3.
[D‑00] Backup heater Compressor
0 (default) Forced OFF Forced OFF
2 Allowed
Safety thermostat for the additional zone
The following setting is related to the safety thermostat for the
additional zone. For more information about the safety thermostat for
the main zone, see "7.9.17To connect the safety thermostat (normal
closed contact)"on page40.
# Code Description
[A.2.1.6] [D‑01] Connection to a safety thermostat
voltage free contact:
▪ 0 (default): No safety thermostat.
▪ 3: Safety thermostat normal closed
contact.
Remark: 1+2 are related to preferential
kWh rate power supply.
# Code Description
N/A [E‑08] Power saving function for outdoor unit:
▪ 0: Disabled
▪ 1 (default): Enabled
In case of ERHQ011~016BAV3, ERHQ011~016BAW1,
ERLQ011~016CAV3, and ERLQ011~016CAW1
Do NOT change the default setting.
# Code Description
N/A [E-08] Power saving function for outdoor unit:
▪ 0 (default): Disabled
▪ 1: Enabled
Installer reference guide
58
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 59

8 Configuration
Power consumption control
Only applicable for EHVZ04+08. See "5 Application guidelines" on
page11 for detailed information about this functionality.
Pwr consumpt. control
# Code Description
[A.6.3.1] [4-08] Mode:
▪ 0 (No limitation)(default): Disabled.
▪ 1 (Continuous): Enabled: You can
set one power limitation value (in A
or kW) to which the system power
consumption will be limited for all the
time.
▪ 2 (Digital inputs): Enabled: You can
set up to four different power
limitation values (in A or kW) to
which the system power
consumption will be limited when the
corresponding digital input asks.
[A.6.3.2] [4-09] Type:
▪ 0 (Current): The limitation values are
set in A.
▪ 1 (Power)(default): The limitation
values are set in kW.
[A.6.3.3] [5-05] Value: Only applicable in case of full
time power limitation mode.
0A~50A, step: 1A (default: 50A)
[A.6.3.4] [5-09] Value: Only applicable in case of full
time power limitation mode.
0kW~20kW, step: 0.5kW (default:
20kW)
Amp. limits for DI: Only applicable in case of power limitation mode
based on digital inputs and based on current values.
[A.6.3.5.1] [5-05] Limit DI1
0A~50A, step: 1A (default: 50A)
[A.6.3.5.2] [5-06] Limit DI2
0A~50A, step: 1A (default: 50A)
[A.6.3.5.3] [5-07] Limit DI3
0A~50A, step: 1A (default: 50A)
[A.6.3.5.4] [5-08] Limit DI4
0A~50A, step: 1A (default: 50A)
kW limits for DI: Only applicable in case of power limitation mode
based on digital inputs and based on power values.
[A.6.3.6.1] [5-09] Limit DI1
0kW~20kW, step: 0.5kW (default:
20kW)
[A.6.3.6.2] [5-0A] Limit DI2
0kW~20kW, step: 0.5kW (default:
20kW)
[A.6.3.6.3] [5-0B] Limit DI3
0kW~20kW, step: 0.5kW (default:
20kW)
[A.6.3.6.4] [5-0C] Limit DI4
0kW~20kW, step: 0.5kW (default:
20kW)
[A.6.3.7] [4-01] Priority: Not applicable.
The outdoor temperature is averaged over the selected time period.
# Code Description
[A.6.4] [1-0A] Outdoor average timer:
▪ 0: No averaging (default)
▪ 1: 12hours
▪ 2: 24hours
▪ 3: 48hours
▪ 4: 72hours
INFORMATION
If the power saving function is activated (see [E‑08]), the
average outdoor temperature calculation is only possible in
case the external outdoor temperature sensor is used. See
"5.6 Setting up an external temperature sensor" on
page15.
Offset temperature external outdoor ambient sensor
Only applicable in case of an external outdoor ambient sensor is
installed and configured.
You can calibrate the external outdoor ambient temperature sensor.
It is possible to give an offset to the thermistor value. The setting can
be used to compensate for situations where the external outdoor
ambient sensor cannot be installed on the ideal installation location
(see installation).
# Code Description
[A.6.5] [2‑0B] –5°C~5°C, step: 0.5°C (default: 0°C)
Forced defrost
You can manually start a defrost operation.
The decision to execute the manual defrost operation is made by the
outdoor unit and depends on ambient and heat exchanger
conditions. When the outdoor unit accepted the forced defrost
operation, will be displayed on the user interface. If is NOT
displayed within 6 minutes after forced defrost operation was
enabled, the outdoor unit ignored the forced defrost request.
# Code Description
[A.6.6] N/A Do you want to start a defrost operation?
Pump operation
When the pump operation function is disabled the pump will stop if
the outdoor temperature is higher than the value set by [4‑02]. When
the pump operation is enabled, the pump operation is possible at all
outdoor temperatures.
# Code Description
N/A [F‑00] Pump operation:
▪ 0 (default): Disabled if outdoor
temperature is higher than [4‑02].
▪ 1: Possible at all outdoor
temperatures.
Pump operation during flow abnormality [F‑09] defines whether the
pump stops at flow abnormality or allow to continue operation when
flow abnormality occurs. This functionality is only valid in specific
conditions where it is preferable to keep the pump active when
Ta<4°C (pump will be activated for 10 minutes and deactivated after
10 minutes). Daikin shall NOT be held liable for any damage
resulting this functionality.
Average timer
The average timer corrects the influence of ambient temperature
variations. The weather-dependent set point calculation is done on
the average outdoor temperature.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
59
Page 60

8 Configuration
[9-0D]=0 [9-0D]=5
a (kPa)
b (l/min)
a (kPa)
b (l/min)
a (kPa)
b (l/min)
a (kPa)
b (l/min)
[9-0D]=6 [9-0D]=7
[9-0D]=8
a (kPa)
b (l/min)
# Code Description
N/A [F‑09] Pump continue operation when flow
abnormality:
▪ 0 (default): Pump will be deactivated.
▪ 1: Pump will be activated when
Ta<4°C (10 minutes ON – 10 minutes
OFF)
Pump speed limitation
Pump speed limitation main zone [9‑0E] and pump speed limitation
additional zone [9‑0D] define the maximum pump speed. In normal
conditions, the default setting should NOT be modified. The pump
speed limitation will be overruled when the flow rate is in the range
of the minimum flow (error 7H).
# Code Description
N/A [9‑0E] Pump speed limitation main zone
▪ 0: No limitation.
▪ 1~4: General limitation. There is
limitation in all conditions. The
required delta T control and comfort
are NOT guaranteed.
▪ 5~8 (default: 6): Limitation when no
actuators. When there is no heating
output, the pump speed limitation is
applicable. When there is heating
output, the pump speed is only
determined by delta T in relation to the
required capacity. With this limitation
range, delta T is possible and the
comfort is guaranteed.
N/A [9‑0D] Pump speed limitation additional zone
▪ 0: No limitation.
▪ 1~4: General limitation. There is
limitation in all conditions. The
required delta T control and comfort
are NOT guaranteed.
▪ 5~8 (default: 6): Limitation when no
actuators. When there is no heating
output, the pump speed limitation is
applicable. When there is heating
output, the pump speed is only
determined by delta T in relation to the
required capacity. With this limitation
range, delta T is possible and the
comfort is guaranteed.
The maximum values depend on the unit type:
a External static pressure
b Water flow rate
Installer reference guide
60
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 61

8.4 Menu structure: Overview user settings
< >
[1]
[2]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[2]
[6.2]
[6.3]
[6.8]
[7.1]
[7.4]
[7.3]
[3]
Set time/date
Date
Time
Daylight Saving Time
Clock type
Holiday
Holiday
Holiday
Holiday
Holiday mode
Holiday mode
Home
Away
From
Until
Until
From
Use day schedule
Operation mode
Heating
Quiet mode
Select schedules
Room temperature
LWT main
LWT additional
Tank temperature
Information
Sensor information
Energy metering
Error handling
User permission level
Actuators
Operation modes
Running hours
Version
Energy metering
Consumed elec.
Produced energy
Error information
Error history
Contact/helpdesk number
Version
User interface
Indoor unit
Outdoor unit
User settings
Display
Temperature lock
Set schedules
Preset values
Unit of measurement
Display
Contrast
Backlit LCD time
User profile
Available home pages
Set schedules
Room temp.
LWT main
LWT additional
DHW temp
Quiet mode
DHW pump
Preset values
Room temperature
LWT main
Tank temperature
Quiet level
DHW
Set weather dependent
Warning history
[7.7]
Set weather dependent
Main
Additional
[7.7.1]
Main
Set weather-dependent heating
[7.7.2]
Additional
Set weather-dependent heating
8 Configuration
INFORMATION
Depending on the selected installer settings, settings will
be visible/invisible.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
61
Page 62

8 Configuration
[A]
[A.2]
[A.2.1]
[A.2.2]
[A.2.2.6]
[A.3]
[A.3.1]
[A.3.1.1]
[A.3.2]
[A.3.3]
[A.4]
[A.4.4]
[A.5]
[A.5.1]
[A.7]
[A.6]
[A.6.3]
[A.6.2]
Installer settings
Language
System layout
Space operation
Domestic hot water (DHW)
Heat sources
System operation
Commissioning
Overview settings
System layout
Standard
Options
Capacities
Confirm layout
Space operation
LWT settings
Room thermostat
Operation range
Domestic hot water
Type
Disinfection
Maximum setpoint
SP mode
Weather-dependent curve
Heat sources
Backup heater
System operation
Auto restart
Preferential kWh rate
Pwr consumpt. control
Averaging time
Ext amb. sensor offset
Commissioning
Test run
UFH screed dryout
Air purge
Actuator test run
Standard
Unit type
Compressor type
Indoor software type
BUH type
Backup heater steps
Forced off contact
Unit control method
Number of LWT zones
Pump operation mode
Power saving possible
User interface location
Options
DHW operation
DHW tank type
Contact type main
Contact type add.
Digital I/O PCB
Demand PCB
External kWh meter
External kWh meter
DHW pump
External sensor
Leaving water
Main
Additional
Delta T source
Room thermostat
Room temp. range
Room temp. offset
Operation range
Space heating OFF temp
Disinfection
Disinfection
Operation day
Start time
Temperature target
Duration
Backup heater
Operation mode
Enable BUH step 2
Prefer. kWh rate PS
Allowed heaters
Forced pump OFF
Pwr consmp ctrl
Mode
Type
Amp. value
kW value
Amp. limits for DI
Digital I/O PCB
Ext. backup heat src
Solar kit
Alarm output
Bottom plate heater
Main
LWT setpoint mode
Temperature range
Modulated LWT
Shut-off valve
Emitter type
[A.3.1.2]
Additional
LWT setpoint mode
Temperature range
Ext. room sensor offset
[A.3.1.3]
Delta T source
Heating
Forced defrost
Room temp. step
kW limits for DI
Priority
Emergency
Equilibrium temp.
LAN adapter
8.5 Menu structure: Overview installer settings
INFORMATION
Depending on the selected installer settings, settings will
be visible/invisible.
Installer reference guide
62
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 63

9 Commissioning
9 Commissioning
9.1 Overview: Commissioning
This chapter describes what you have to do and know to
commission the system after it is configured.
Typical workflow
Commissioning typically consists of the following stages:
1 Checking the "Checklist before commissioning".
2 Performing an air purge.
3 Performing a test run for the system.
4 If necessary, performing a test run for one or more actuators.
5 If necessary, performing an underfloor heating screed dryout.
9.2 Precautions when commissioning
INFORMATION
During the first running period of the unit, the required
power may be higher than stated on the nameplate of the
unit. This phenomenon is caused by the compressor, that
needs a continuous run time of 50 hours before reaching
smooth operation and stable power consumption.
NOTICE
Before starting up the system, the unit MUST be energised
for at least 6hours. The crankcase heater needs to heat
up the compressor oil to avoid oil shortage and
compressor breakdown during startup.
NOTICE
NEVER operate the unit without thermistors and/or
pressure sensors/switches. Burning of the compressor
might result.
NOTICE
Do NOT operate the unit until the refrigerant piping is
complete (when operated this way, the compressor will
break).
9.3 Checklist before commissioning
Do NOT operate the system before the following checks are OK:
You read the complete installation instructions, as
described in the installer reference guide.
The indoor unit is properly mounted.
The outdoor unit is properly mounted.
The following field wiring has been carried out according
to this document and the applicable legislation:
▪ Between the local supply panel and the outdoor unit
▪ Between indoor unit and outdoor unit
▪ Between the local supply panel and the indoor unit
▪ Between the indoor unit and the valves (if applicable)
▪ Between the indoor unit and the room thermostat (if
applicable)
There are NO missing phases or reversed phases.
The system is properly earthed and the earth terminals
are tightened.
The fuses or locally installed protection devices are
installed according to this document, and have not been
bypassed.
The power supply voltage matches the voltage on the
identification label of the unit.
There are NO loose connections or damaged electrical
components in the switchbox.
There are NO damaged components or squeezed
pipes on the inside of the indoor and outdoor units.
Backup heater circuit breaker F1B on the switchbox is
turned ON.
There are NO refrigerant leaks.
The refrigerant pipes (gas and liquid) are thermally
insulated.
The correct pipe size is installed and the pipes are
properly insulated.
There is NO water leak inside the indoor unit.
The shut-off valves are properly installed and fully open.
The stop valves (gas and liquid) on the outdoor unit are
fully open.
The air purge valve is open (at least 2 turns).
The pressure relief valve purges water when opened.
The minimum water volume is guaranteed in all
conditions. See "To check the water volume" in
"6.4Preparing water piping"on page18.
The safety thermostat is connected.
INFORMATION
The software is equipped with an "installer-on-site" mode
([4‑0E]), that disables automatic operation by the unit. At
first installation, setting [4‑0E] is by default set to "1",
meaning automatic operation is disabled. All protective
functions are then disabled. If the user interface home
pages are off, the unit will NOT operate automatically. To
enable automatic operation and the protective functions,
set [4‑0E] to "0".
36 hours after the first power-on, the unit will automatically
set [4‑0E] to "0", ending "installer-on-site" mode and
enabling the protective functions. If – after first
installation – the installer returns to the site, the installer
has to set [4‑0E] to "1" manually.
9.4 Checklist during commissioning
The minimum flow rate during backup heater/defrost
operation is guaranteed in all conditions. See "To check
the water volume and flow rate" in "6.4Preparing water
piping"on page18.
To perform an air purge.
To perform a test run.
To perform an actuator test run.
Underfloor screed dryout function
The underfloor screed dryout function is started (if
necessary).
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
63
Page 64

9 Commissioning
9.4.1 To check the minimum flow rate
Recommended procedure for the additional zone
1 Confirm according to the hydraulic configuration which space
heating loops can be closed due to mechanical, electronic, or
other valves.
2 Close all space heating loops that can be closed (see previous
step).
3 Start the pump test run operation (see "9.4.4 To perform an
actuator test run"on page65).
4 Go to [6.1.8]: > Information > Sensor information > Flow rate
to check the flow rate. During pump test run operation, the unit
can operate below this minimum required flow rate that is
needed during defrost/backup heater operation.
Bypass valve foreseen?
Yes No
Modify the bypass valve setting
to reach the minimum required
flow rate + 2l/min
Recommended procedure for the main zone
5 Confirm according to the hydraulic configuration which space
heating loops can be closed due to mechanical, electronic, or
other valves.
6 Close all space heating loops that can be closed (see previous
step).
7 Create a thermo request on the main zone only.
8 Wait 1 minute until the unit is stabilized.
9 If the additional pump is still assisting (the green LED on the
right hand sided pump is ON), increase the flow until the
additional pump is NOT assisting anymore (LED is OFF).
10 Go to [6.1.8]: > Information > Sensor information > Flow rate
to check the flow rate.
Bypass valve foreseen?
Yes No
Modify the bypass valve setting
to reach the minimum required
flow rate + 2l/min
Minimum required flow rate during defrost/backup heater
operation
04+08 models 12l/min
16 model 15l/min
In case the actual flow rate is
below the minimum flow rate
(required during defrost/backup
heater operation), modifications
at hydraulic configuration are
required. Increase the space
heating loops that can NOT be
closed or install a pressure
controlled bypass valve.
In case the actual flow rate is
below the minimum flow rate
(required during defrost/backup
heater operation), modifications
at hydraulic configuration are
required. Increase the space
heating loops that can NOT be
closed or install a pressure
controlled bypass valve.
9.4.2 Air purge function
When commissioning and installing the unit, it is very important to
remove all air in the water circuit. When the air purge function is
running, the pumps operate without actual operation of the unit and
the removal of air in the water circuit will start.
NOTICE
Before starting the air purge, open the safety valve and
check if the circuit is sufficiently filled with water. Only if
water escapes the valve after opening it, you can start the
air purge procedure.
There are 2 modes for purging air:
▪ Manually: the unit will operate with a custom pump speed and in a
custom position of the 3-way valve (space heating/domestic hot
water). The custom position of the 3-way valve is a helpful feature
to remove all air from the water circuit in the space heating or the
domestic hot water heating mode. The operation speed of the
pump (slow or quick) can also be set.
▪ Automatic: the unit automatically changes the pump speed and
the position of the 3-way valve (space heating/domestic hot water)
between the space heating or the domestic hot water heating
mode.
INFORMATION
For both manual and automatic air purge, 1 temperature
zone is purged with each air purge start. To purge the
other temperature zone, you have to restart the air purge
function. When performing an air purge for the first time,
the main temperature zone will be purged.
Typical workflow
Purging the air from the system should consist of:
1 Performing a manual air purge for both zones
2 Performing an automatic air purge for both zones
INFORMATION
Start by performing a manual air purge on both zones.
When almost all the air is removed, perform an automatic
air purge on both zones. If necessary, repeat performing
the automatic air purge until you are sure that all air is
removed from the system. During air purge function, pump
speed limitation [9‑0D] is NOT applicable.
Make sure that the leaving water temperature home page, room
temperature home page, and domestic hot water home page are
turned OFF.
To perform a manual air purge
INFORMATION
When purging the main zone, make sure the setpoint for
the main zone is at least 5°C higher than the actual water
temperature inside the unit.
Prerequisite: Make sure that the leaving water temperature home
page, room temperature home page, and domestic hot water home
page are turned OFF.
1 Set the user permission level to Installer. See "To set the user
permission level to Installer"on page42.
2 Set the air purge mode: go to [A.7.3.1] > Installer settings >
Commissioning > Air purge > Type.
3 Select Manual and press .
4 Go to [A.7.3.4] > Installer settings > Commissioning > Air
purge > Start air purge and press to start the air purge
function.
Result: The manual air purge starts and the following screen
appears.
Installer reference guide
64
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 65

01:18
Tue
Air purge
l/min
Low
SHC
0.5
Flow rate
Speed
Circuit
Stop
Adjust
Scroll
01:18
Tue
Air purge
l/min
Low
SHC
0.5
Flow rate
Speed
Circuit
Stop
Adjust
Scroll
5 Use the and buttons to scroll to Speed.
6 Use the and buttons to set the desired pump speed.
Result: Low
Result: High
7 If applicable, set the desired position of the 3-way valve (space
heating/domestic hot water). Use the and buttons to scroll to
Circuit.
8 Use the and buttons to set the desired position of the 3-way
valve (space heating/domestic hot water).
Result: SHC
Result: Tank
To perform an automatic air purge
INFORMATION
When purging the main zone, make sure the setpoint for
the main zone is at least 5°C higher than the actual water
temperature inside the unit.
Prerequisite: Make sure that the leaving water temperature home
page, room temperature home page, and domestic hot water home
page are turned OFF.
1 Set the user permission level to Installer. See "To set the user
permission level to Installer"on page42.
2 Set the air purge mode: go to [A.7.3.1] > Installer settings >
Commissioning > Air purge > Type.
3 Select Automatic and press .
4 Go to [A.7.3.4] > Installer settings > Commissioning > Air
purge > Start air purge and press to start the air purge
function.
Result: Air purging will start and the following screen will be
shown.
The automatic air purge function stops automatically after
30minutes, then the installer has to restart the automatic air purge
function for the second temperature zone. This function will also stop
automatically after 30minutes
To interrupt air purge
1 Press and press to confirm the interruption of the air
purge function. When you restart the air purge function, the
other zone will be air purged.
9.4.3 To perform a test run
INFORMATION
The test run only applies to the additional temperature
zone.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
9 Commissioning
Prerequisite: Make sure that the leaving water temperature home
page, room temperature home page, and domestic hot water home
page are turned OFF.
1 Set the user permission level to Installer. See "To set the user
permission level to Installer"on page42.
2 Go to [A.7.1]: > Installer settings > Commissioning > Test
run.
3 Select a test and press . Example: Heating.
4 Select OK and press .
Result: The test run starts. It stops automatically when done
(±30min). To stop it manually, press , select OK and press .
INFORMATION
If 2 user interfaces are present, you can start a test run
from both user interfaces.
▪ The user interface used to start the test run displays a
status screen.
▪ The other user interface displays a "busy" screen. You
cannot use the user interface as long as the "busy"
screen is shown.
If the installation of the unit has been done correctly, the unit will
start up during test operation. During the test mode, the correct
operation of the unit can be checked by monitoring leaving water
temperature (heating mode) and tank temperature (domestic hot
water mode).
To monitor the temperature, go to [A.6] and select the information
you want to check.
9.4.4 To perform an actuator test run
Purpose of the actuator test run is to confirm the operation of the
different actuators (e.g., when you select pump operation, a test run
of the pump will start).
Prerequisite: Make sure that the leaving water temperature home
page, room temperature home page, and domestic hot water home
page are turned OFF.
1 Set the user permission level to Installer. See "To set the user
permission level to Installer"on page42.
2 Make sure the room temperature control, the leaving water
temperature control and the domestic hot water control are
turned OFF via the user interface.
3 Go to [A.7.4]: > Installer settings > Commissioning >
Actuator test run.
4 Select an actuator and press . Example: Pump.
5 Select OK and press .
Result: The actuator test run starts. It automatically stops when
finished. To stop it manually, press , select OK and press .
Possible actuator test runs
▪ Backup heater (step 1) test
▪ Pump test (only the pump of the additional temperature zone)
INFORMATION
Make sure that all air is purged before executing the test
run. Also avoid disturbances in the water circuit during the
test run.
▪ 2-way valve test
▪ 3-way valve test (3-way valve for switching between space
heating and tank heating)
▪ Bottom plate heater test
▪ Bivalent signal test
▪ Alarm output test
Installer reference guide
65
Page 66

9 Commissioning
t
T
A1
25°C (1) 35°C (2)
24h (1) 36h (2)
▪ Heating signal test
▪ Quick heat-up test
▪ Circulation pump test
9.4.5 Underfloor heating screed dryout
This function is used for drying out the screed of an underfloor
heating system very slowly during the construction of a house. It
allows the installer to program and execute this program.
Make sure that the leaving water temperature home page, room
temperature home page, and domestic hot water home page are
turned OFF.
This function can be executed without finishing the outdoor
installation. In this case, the backup heater will perform the screed
dryout and supply the leaving water without heat pump operation.
When no outdoor unit is installed yet, then connect the main power
supply cable to the indoor unit via X2M/30 and X2M/31. See
"7.9.9To connect the main power supply"on page37.
INFORMATION
NOTICE
The installer is responsible for:
NOTICE
To perform an underfloor heating screed dryout, room frost
protection needs to be disabled ([2‑06]=0). By default, it is
enabled ([2‑06]=1). However, due to the "installer-on-site"
mode (see "Checklist before commissioning"), room frost
protection will be automatically disabled for 36 hours after
the first power-on.
If the screed dryout still needs to be performed after the
first 36 hours of power-on, manually disable room frost
protection by setting [2‑06] to "0", and KEEP it disabled
until the screed dryout has finished. Ignoring this notice will
result in cracking of the screed.
NOTICE
For the underfloor heating screed dryout to be able to start,
make sure the following settings are met:
The installer can program up to 20 steps. For each step he needs to
enter:
▪ If Emergency is set to Manual ([A.6.C]=0), and the unit
is triggered to start emergency operation, the user
interface will ask confirmation before starting. The
underfloor heating screed dryout function is active even
if the user does NOT confirm emergency operation.
▪ During underfloor heating screed dryout, pump speed
limitation [9‑0D] is NOT applicable.
▪ contacting the screed manufacturer for the initial
heating instructions to avoid cracking the screed,
▪ programming the underfloor heating screed dryout
schedule according to the above instruction of the
screed manufacturer,
▪ checking the proper functioning of the setup on a
regular basis,
▪ selecting the correct program complying with the type
of the used screed of the floor.
▪ [4‑00]=1
▪ [C‑02]=0
▪ [D‑01]=0
▪ [4‑08]=0
▪ [4‑01]≠1
1 the duration in hours, up to 72hours,
2 the desired leaving water temperature.
Example:
T Desired leaving water temperature (15~55°C)
t Duration (1~72h)
(1) Action step 1
(2) Action step 2
To program an underfloor heating screed dryout schedule
1 Set the user permission level to Installer. See "To set the user
permission level to Installer"on page42.
2 Go to [A.7.2]:
screed dryout > Set dryout schedule.
3 Use the
▪ Use
▪ Use
If a time is selected, you can set the duration between 1 and
72hours.
If a temperature is selected, you can set the desired leaving
water temperature between 15°C and 55°C.
4 To add a new step, select "–h" or "–" on an empty line and
press
5 To delete a step, set the duration to "–" by pressing
6 Press
.
to save the schedule.
It is important that there is no empty step in the program.
The schedule will stop when a blank step is programmed
OR when 20 consecutive steps have been executed.
> Installer settings > Commissioning > UFH
, , , and to program the schedule.
and to scroll through the schedule.
and to adjust the selection.
.
To perform an underfloor heating screed dryout
INFORMATION
Preferential kWh rate power supply cannot be used in
combination with underfloor heating screed dryout.
Prerequisite: Make sure there is ONLY 1 user interface connected
to your system to perform an underfloor heating screed dryout.
Prerequisite: Make sure that the leaving water temperature home
page, room temperature home page, and domestic hot water home
page are turned OFF.
1 Go to [A.7.2]:
screed dryout.
2 Set a dryout program.
3 Select Start dryout and press
4 Select OK and press
Result: The underfloor heating screed dryout starts and following
screen will be shown. It stops automatically when done. To stop it
manually, press
> Installer settings > Commissioning > UFH
.
.
, select OK and press .
Installer reference guide
66
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 67

15:10
1
14d 12h
25°C
Tue
Screed dryout
Current step
Remaining
Desired LWT
Stop
To readout the status of an underfloor heating screed dryout
1 Press .
2 The current step of the program, the total remaining time, and
the current desired leaving water temperature will be displayed.
To interrupt an underfloor heating screed dryout
When the program is stopped by an error, an operation switch off, or
a power failure, the U3 error will be displayed on the user interface.
To resolve the error codes, see "12.4 Solving problems based on
error codes" on page 71. To reset the U3 error, your User
permission level needs to be Installer.
1 Go to the underfloor heating screed dryout screen.
2 Press .
3 Press to interrupt the program.
4 Select OK and press .
Result: The underfloor heating screed dryout program is stopped.
When the program is stopped due to an error, an operation switchoff, or a power failure, you can read out the underfloor heating
screed dryout status.
5 Go to [A.7.2]: > Installer settings > Commissioning > UFH
screed dryout > Dryout status > Stopped at and followed by the
last executed step.
6 Modify and restart the execution of the program.
10 Hand-over to the user
Once the test run is finished and the unit operates properly, please
make sure the following is clear for the user:
▪ Fill in the installer setting table (in the operation manual) with the
actual settings.
▪ Make sure that the user has the printed documentation and ask
him/her to keep it for future reference. Inform the user that he can
find the complete documentation on the url as earlier described in
this manual.
▪ Explain the user how to properly operate the system and what to
do in case of problems.
▪ Show the user what to do in relation to maintaining the unit.
▪ Explain the user about energy saving tips as described in the
operation manual.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
INFORMATION
There is limited access to the menu structure. Only the
following menus can be accessed:
▪ Information.
▪ Installer settings > Commissioning > UFH screed
dryout.
10 Hand-over to the user
11 Maintenance and service
NOTICE
Maintenance must be done by an authorised installer or
service agent.
We recommend to do maintenance at least once a year.
However, applicable legislation might require shorter
maintenance intervals.
NOTICE
In Europe, the greenhouse gas emissions of the total
refrigerant charge in the system (expressed as tonnes
CO2-equivalent) is used to determine the maintenance
intervals. Follow the applicable legislation.
Formula to calculate the greenhouse gas emissions:
GWP value of the refrigerant × Total refrigerant charge [in
kg] / 1000
11.1 Overview: Maintenance and service
This chapter contains information about:
▪ The yearly maintenance of the outdoor unit
▪ The yearly maintenance of the indoor unit
11.2 Maintenance safety precautions
DANGER: RISK OF ELECTROCUTION
DANGER: RISK OF BURNING
NOTICE:Risk of electrostatic discharge
Before performing any maintenance or service work, touch
a metal part of the unit in order to eliminate static electricity
and to protect the PCB.
11.2.1 Opening the indoor unit
CAUTION
The front panel is heavy. Be careful NOT to jam your
fingers when opening or closing the unit.
You just need to remove the front panel of the unit to gain access to
most parts which need maintenance. In rare cases, you may also
need to remove the switch box.
11.3 Checklist for yearly maintenance of the outdoor unit
Check the following at least once a year:
▪ Outdoor unit heat exchanger.
The heat exchanger of the outdoor unit can get blocked up due to
dust, dirt, leaves, etc. It is recommended to clean the heat
exchanger yearly. A blocked heat exchanger can lead to too low
pressure or too high pressure leading to worse performance.
11.4 Checklist for yearly maintenance of the indoor unit
Check the following at least once a year:
▪ Water pressure
▪ Water filters
Installer reference guide
67
Page 68

11 Maintenance and service
1 3
2
5
4
2
×
▪ Water pressure relief valve
▪ Relief valve hose
▪ Pressure relief valve of the domestic hot water tank
▪ Switch box
▪ Descaling
▪ Chemical disinfection
▪ Anode
Water pressure
Check whether the water pressure is above 1bar. If it is lower, add
water.
Water filters
Clean the water filters.
NOTICE
Handle the water filters with care. Do NOT use excessive
force when you reinsert the water filters so as NOT to
damage the water filters mesh.
Water pressure relief valve
Open the valve and check if it operates correctly. The water may be
very hot!
Checkpoints are:
▪ The water flow coming from the relief valve is high enough, no
blockage of the valve or in between piping is suspected.
▪ Dirty water coming out of the relief valve:
▪ open the valve until the discharged water does NOT contain dirt
anymore
▪ flush the system and install an additional water filter (a
magnetic cyclone filter is preferable).
To make sure this water originates from the tank, check after a tank
heat up cycle.
It is recommended to do this maintenance more frequently.
Pressure relief valve hose
Check whether the pressure relief valve hose is positioned
appropriately to drain the water. See "7.8.5To connect the pressure
relief valve to the drain"on page32.
Relief valve of the domestic hot water tank (field supply)
Open the valve and check the correct operation. Water may be very
hot!
Checkpoints are:
▪ The water flow coming from the relief valve is high enough, no
blockage of the valve or in between piping is suspected.
▪ Dirty water coming out of the relief valve:
▪ open the valve until the discharged water does not contain dirt
anymore
▪ flush and clean the complete tank, including the piping between
the relief valve and cold water inlet.
To make sure this water originates from the tank, check after a tank
heat up cycle.
It is recommended to do this maintenance more frequently.
Switch box
▪ Carry out a thorough visual inspection of the switchbox and look
for obvious defects such as loose connections or defective wiring.
▪ Using an ohmmeter, check if contactors K1M, K2M and K3M
operate correctly. All contacts of these contactors must be in open
position when the power is turned OFF.
WARNING
If the internal wiring is damaged, it has to be replaced by
the manufacturer, its service agent or similarly qualified
persons.
Descaling
Depending on water quality and set temperature, scale can deposit
on the heat exchanger inside the domestic hot water tank and can
restrict heat transfer. For this reason, descaling of the heat
exchanger may be required at certain intervals.
Chemical disinfection
If the applicable legislation requires a chemical disinfection in
specific situations, involving the domestic hot water tank, please be
aware that the domestic hot water tank is a stainless steel cylinder
containing an aluminium anode. We recommend to use a nonchloride based disinfectant approved for use with water intended for
human consumption.
NOTICE
When using means for descaling or chemical disinfection,
it must be ensured that the water quality remains compliant
with EU directive 98/83EC.
Anode
No maintenance or replacement required.
11.4.1 To drain the domestic hot water tank
Prerequisite: Switch OFF the power supply.
Prerequisite: Turn OFF the cold water supply.
1 Open the front panel.
2 Remove the 2 screws, unhook and put the switch box aside.
3 The drain hose is located at the right side of the unit. Cut the tie
wraps or tape and bring the flexible drain hose forward.
Installer reference guide
68
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 69

a
a Drain hose
INFORMATION
To drain the tank, all the hot water tapping points need to
be opened to allow air to enter the system.
4 Open the drain valve.
12 Troubleshooting
12.1 Overview: Troubleshooting
This chapter describes what you have to do in case of problems.
It contains information about:
▪ Solving problems based on symptoms
▪ Solving problems based on error codes
Before troubleshooting
Carry out a thorough visual inspection of the unit and look for
obvious defects such as loose connections or defective wiring.
12.2 Precautions when troubleshooting
WARNING
▪ When carrying out an inspection on the switch box of
the unit, always make sure that the unit is disconnected
from the mains. Turn off the respective circuit breaker.
▪ When a safety device was activated, stop the unit and
find out why the safety device was activated before
resetting it. NEVER bridge safety devices or change
their values to a value other than the factory default
setting. If you are unable to find the cause of the
problem, call your dealer.
DANGER: RISK OF ELECTROCUTION
WARNING
Prevent hazard due to the inadvertent resetting of the
thermal cut-out: this appliance must NOT be supplied
through an external switching device, such as a timer, or
connected to a circuit that is regularly turned ON and OFF
by the utility.
DANGER: RISK OF BURNING
12 Troubleshooting
12.3 Solving problems based on symptoms
12.3.1 Symptom: The unit is NOT heating as expected
Possible causes Corrective action
The temperature setting is NOT
correct
The water flow is too low Check and make sure that:
The water volume in the
installation is too low
12.3.2 Symptom: The compressor does NOT start (space heating or domestic water heating)
Possible causes Corrective action
The unit must start up out of its
operation range (the water
temperature is too low)
Check the temperature setting on
the remote controller. Refer to
the operation manual.
▪ All shut-off valves of the water
circuit are completely open.
▪ The water filters are clean.
Clean if necessary.
▪ There is no air in the system.
Purge air if necessary. You
can purge air manually (see
"To perform a manual air
purge"on page64) or use the
automatic air purge function
(see "To perform an automatic
air purge"on page65).
▪ The water pressure is >1 bar.
▪ The expansion vessel is NOT
broken.
▪ The resistance in the water
circuit is NOT too high for the
pump (see the ESP curve in
the "Technical data" chapter).
If the problem persists after you
have conducted all of the above
checks, contact your dealer. In
some cases, it is normal that the
unit decides to use a low water
flow.
Make sure that the water volume
in the installation is above the
minimum required value (see
"6.4.3To check the water volume
and flow rate"on page19).
If the water temperature is too
low, the unit uses the backup
heater to reach the minimum
water temperature first (15°C).
Check and make sure that:
▪ The power supply to the
backup heater is correctly
wired.
▪ The backup heater thermal
protector is NOT activated.
▪ The backup heater contactor is
NOT broken.
If the problem persists after you
have conducted all of the above
checks, contact your dealer.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
69
Page 70

12 Troubleshooting
Possible causes Corrective action
The preferential kWh rate power
supply settings and electrical
connections do NOT match
The preferential kWh rate signal
was sent by the electricity
company
This should match with the
connections as explained in
"6.5Preparing electrical
wiring"on page21 and "7.9.9To
connect the main power
supply"on page37.
Wait for the power to return (2
hours max.).
12.3.3 Symptom: The pump is making noise (cavitation)
Possible causes Corrective action
There is air in the system Purge air manually on both
zones (see "To perform a manual
air purge"on page64) or use the
automatic air purge function on
both zones (see "To perform an
automatic air purge"on page65).
The water pressure at the pump
inlet is too low
Check and make sure that:
▪ The water pressure is >1bar.
▪ The manometer is not broken.
▪ The expansion vessel is NOT
broken.
▪ The pre-pressure setting of the
expansion vessel is correct
(see "6.4.4 Changing the pre-
pressure of the expansion
vessel"on page20).
12.3.4 Symptom: The pressure relief valve opens
Possible causes Corrective action
The expansion vessel is broken Replace the expansion vessel.
The water volume in the
installation is too high
The water circuit head is too high The water circuit head is the
Make sure that the water volume
in the installation is below the
maximum allowed value (see
"6.4.3To check the water volume
and flow rate"on page19 and
"6.4.4Changing the pre-pressure
of the expansion vessel"on
page20).
difference in height between the
indoor unit and the highest point
of the water circuit. If the indoor
unit is located at the highest
point of the installation, the
installation height is considered
0m. The maximum water circuit
head is 10m.
Check the installation
requirements.
12.3.5 Symptom: The water pressure relief valve leaks
Possible causes Corrective action
Dirt is blocking the water
pressure relief valve outlet
Check whether the pressure
relief valve works correctly by
turning the red knob on the valve
counterclockwise:
▪ If you do NOT hear a clacking
sound, contact your dealer.
▪ If the water keeps running out
of the unit, close both the
water inlet and outlet shut-off
valves first and then contact
your dealer.
12.3.6 Symptom: The space is NOT sufficiently heated at low outdoor temperatures
Possible causes Corrective action
The backup heater operation is
not activated
The backup heater equilibrium
temperature has not been
configured correctly
There is air in the system. Purge air manually or
Check and make sure that:
▪ The backup heater operation
mode is enabled. Go to:
▪ [A.5.1.1] > Installer settings
> Heat sources > Backup
heater > Operation mode
[4‑00]
▪ The backup heater overcurrent
fuse has not been turned off. If
it has, check the fuse and turn
it back on.
▪ The thermal protector of the
backup heater has not been
activated. If it has, check the
following, and then press the
reset button in the switch box:
▪ The water pressure
▪ Whether there is air in the
system
▪ The air purge operation
Increase the "equilibrium
temperature" to activate the
backup heater operation at a
higher outdoor temperature. Go
to:
▪ [A.5.1.4] > Installer settings >
Heat sources > Backup heater
> Equilibrium temp. OR
▪ [A.8] > Installer settings >
Overview settings [5‑01]
automatically. See the air purge
function in the "Commissioning"
chapter.
Installer reference guide
70
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 71

12 Troubleshooting
Possible causes Corrective action
Too much heat pump capacity is
used for heating domestic hot
water
Check and make sure that the
"space heating priority" settings
have been configured
appropriately:
▪ Make sure that the "space
heating priority status" has
been enabled. Go to [A.8] >
Installer settings > Overview
settings [5‑02]
▪ Increase the "space heating
priority temperature" to
activate backup heater
operation at a higher outdoor
temperature. Go to [A.8] >
Installer settings > Overview
settings [5‑03]
12.3.7 Symptom: The pressure at the tapping point is temporarily unusually high
Possible causes Corrective action
Failing or blocked pressure relief
valve.
▪ Flush and clean the complete
tank including the piping
between pressure relief valve
and the cold water inlet.
▪ Replace the pressure relief
valve.
12.3.8 Symptom: Decoration panels are pushed away due to a swollen tank
Possible causes Corrective action
Failing or blocked pressure relief
valve.
Contact your local dealer.
12.3.9 Symptom: Tank disinfection function is NOT completed correctly (AH-error)
Possible causes Corrective action
The disinfection function was
interrupted by domestic hot water
tapping
Large domestic hot water tapping
happened recently before the
programmed start-up of the
disinfection function
Program the start-up of the
disinfection function when the
coming 4hours NO domestic hot
water tapping is expected.
When the Domestic hot water >
Type > Reheat or Reheat +
sched. is selected, it is
recommended to program the
start-up the disinfection function
at least 4hours later than the last
expected large hot water tapping.
This start-up can be set by
installer settings (disinfection
function).
When the Domestic hot water >
Type > Scheduled only is
selected, it is recommended to
program a Storage eco 3hours
before the scheduled start-up of
the disinfection function to
preheat the tank.
Possible causes Corrective action
The disinfection operation was
stopped manually: with the user
interface displaying the DHW
home page and its user
permission level set to Installer,
the button was pressed
during disinfection operation.
Do NOT press the button
while the disinfection function is
active.
12.4 Solving problems based on error codes
When a problem happens, an error code appears on the user
interface. It is important to understand the problem and to take
countermeasure before resetting the error code. This should be
done by a licensed installer or by your local dealer.
This chapter gives you an overview of all error codes and the
content of the error code as it appears on the user interface.
For a more detailed troubleshooting guideline for each error, please
see the service manual.
12.4.1 Error codes: Overview
Error codes of the indoor unit
Error code Detailed error
code
7H 01 Water flow problem.
7H 04 Water flow problem during
7H 05 Water flow problem during
7H 06 Water flow problem during
80 00 Returning water temperature
81 01 Mixed water thermistor
81 00 Leaving water temperature
89 01 Heat exchanger frozen.
Description
Auto restart.
domestic hot water production.
Manual reset.
Check the domestic hot water
circuit.
heating/sampling.
Manual reset.
Check the space heating circuit.
defrost.
Manual reset.
Check the plate heat exchanger.
sensor problem.
Please contact your dealer.
abnormality.
Auto reset.
sensor problem.
Please contact your dealer.
1
(1)
On the home screen of your user inter interface, the following information will be displayed:
Bi-zone kit abnormality
detection
Refer to bi-zone kit manual
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
71
Page 72

12 Troubleshooting
Error code Detailed error
Description
code
89 02 Heat exchanger frozen.
89 03 Heat exchanger frozen.
8F 00 Abnormal increase outlet
water temperature (DHW).
8H 00 Abnormal increase outlet
water temperature.
8H 01 Overheating mixed water circuit.
Auto reset.
1
8H 02 Overheating mixed water circuit
(thermostat).
Auto reset.
1
8H 03 Overheating water circuit
(thermostat).
A1 00 Zero cross detection problem.
Power reset required.
Please contact your dealer.
A1 01 EEPROM reading error.
Error code Detailed error
Description
code
H1 00 External temperature
sensor problem.
Please contact your dealer.
HC 00 Tank temperature sensor
problem.
Please contact your dealer.
U3 00 Under floor heating screed
dryout function not completed
correctly.
U4 00 Indoor/outdoor unit
communication problem.
U5 00 User interface
communication problem.
U8 01 Connection with adapter lost
Please contact your dealer.
UA 00 Indoor unit, outdoor unit
matching problem.
Power reset required.
UA 16 Extension/hydro
communication problem.
AA 01 Backup heater overheated.
Power reset required.
Please contact your dealer.
AH 00 Tank disinfection function not
completed correctly.
AJ 03 Too long DHW heat-up time
required.
C0 00 Flow sensor malfunction.
Manual reset.
C4 00 Heat exchanger temperature
sensor problem.
Please contact your dealer.
CJ 02 Room temperature sensor
problem.
Please contact your dealer.
EC 00 Abnormal increase tank
temperature.
UA 17 Tank type problem
UA 21 Extension/hydro
mismatch problem.
INFORMATION
In case of error code AH and no interruption of the
disinfection function occurred due to domestic hot water
tapping, following actions are recommended:
▪ When the Domestic hot water > Type > Reheat or
Reheat + sched. is selected, it is recommended to
program the start-up of the disinfection function at least
4 hours later than the last expected large hot water
tapping. This start-up can be set by installer settings
(disinfection function).
▪ When the Domestic hot water > Type > Scheduled only
is selected, it is recommended to program a Storage
eco 3 hours before the scheduled start-up of the
disinfection function to preheat the tank.
(1)
On the home screen of your user inter interface, the following information will be displayed:
Bi-zone kit abnormality
detection
Refer to bi-zone kit manual
Installer reference guide
72
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 73

13 Disposal
NOTICE
When the minimum water flow is lower than described in
the table below, the unit will temporarily stop operation and
the user interface will display error 7H‑01. After some time,
this error will reset automatically and the unit will resume
operation.
Minimum required flow during heat pump operation
04 models 6l/min
08 models 6l/min
16 models 10l/min
Minimum required flow during defrost operation
04+08 models 12l/min
16 models 15l/min
Minimum required flow during backup heater operation
All models 12l/min
If the 7H-01 error persists, the unit will stop operation and the user
interface will display an error code that needs to be reset manually.
Depending on the problem, this error code is different:
Error code Detailed error
code
7H 04 The water flow problems mainly
7H 05 The water flow problems mainly
7H 06 The water flow problems mainly
INFORMATION
Error AJ-03 is reset automatically from the moment there is
a normal tank heat-up.
INFORMATION
If the unit detects flow when the pump is not running, an
external device might be causing flow, or there might be
something wrong with the flow measuring devices (flow
sensor).
▪ If the flow sensor detects flow when the pump is not
running, the unit will stop operation and the user
interface will display error C0‑00. For the unit to resume
operation, this error needs to be reset manually.
Description
occurred during domestic hot
water operation. Check the
domestic hot water circuit.
occurred during space heating
operation. Check the space
heating circuit.
occurred during defrost
operation. Check the space
heating circuit.
Additionally, this error code might
be an indication of frost damage
to the plate heat exchanger. In
that case, contact your local
dealer.
13 Disposal
NOTICE
Do not try to dismantle the system yourself: the dismantling
of the system, treatment of the refrigerant, oil and other
parts must comply with applicable legislation. Units must
be treated at a specialised treatment facility for reuse,
recycling and recovery.
13.1 Overview: Disposal
Typical workflow
Disposing of the system typically consists of the following stages:
1 Pumping down the system.
2 Bringing the system to a specialized treatment facility.
INFORMATION
For more details, see the service manual.
13.2 About pump down
The unit is equipped with an automatic pump down function, with
which you can collect all refrigerant from the system into the outdoor
unit.
NOTICE
The outdoor unit is equipped with a low pressure switch or
a low pressure sensor to protect the compressor by turning
it OFF. NEVER short-circuit the low pressure switch during
pump down operation.
Before pumping down
NOTICE
Before you pump down, make sure the water temperature
(example: by performing a heating operation) and water
volume (example: by opening all heat emitters) are
sufficiently high. Pump down is done in cooling mode.
13.3 To pump down
DANGER: RISK OF EXPLOSION
Pump down – Refrigerant leakage. If you want to pump
down the system, and there is a leakage in the refrigerant
circuit:
▪ Do NOT use the unit's automatic pump down function,
with which you can collect all refrigerant from the
system into the outdoor unit. Possible consequence:
Self-combustion and explosion of the compressor
because of air going into the operating compressor.
▪ Use a separate recovery system so that the unit's
compressor does NOT have to operate.
1 Turn ON the main power supply switch.
2 Make sure the liquid stop valve and the gas stop valve are
open.
3 Press the pump down button (BS4) for at least 8 seconds. BS4
is located on the PCB in the outdoor unit (see wiring diagram).
Result: The compressor and outdoor unit fan start
automatically.
4 Once operation stops (after 3~5 minutes), close the liquid stop
valve and the gas stop valve.
Result: The pump down operation is finished. The user
interface may display " " and the indoor pump may continue
operating. This is NOT a malfunction. Even if you press the ON
button on the user interface, the unit will NOT start. To restart
the unit, turn OFF the main power supply switch and turn it ON
again.
5 Turn OFF the main power supply switch.
NOTICE
Make sure to reopen both stop valves before restarting the
unit.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
73
Page 74

14 Technical data
R2T
R4T
R6T
R1T
e
d
g
f
a
c
c
b
e
Y1E
Y1S
M1F-M2F
M1C
E1HC
S1NPH
S1PH
R5T
R3T
3TW57765-1A
R2T
R3T
R6T
e
d
g
f
h
a
c
c
b
e
Y1E
Y3S
Y1S
M1F-M2F
M1C
E1HC
S1NPH
S1PH
R1T
R4T
R5T
3TW57915-1A
R2T
R3T
R6T
e
d
g
f
a
c
c
b
e
Y1E
Y3S
Y3E
Y1S
M1F-M2F
M1C
E1HC
S1NPH
S1PH
h
R1T
R4T
R5T
3TW60335-1A
e
14 Technical data
A subset of the latest technical data is available on the regional Daikin website (publicly accessible). The full set of latest technical data is
available on the Daikin extranet (authentication required).
14.1 Piping diagram: Outdoor unit
ERHQ_V3
a Field piping (liquid: Ø9.5 flare connection)
b Field piping (gas: Ø15.9 flare connection)
c Stop valve (with service port 5/16")
d Accumulator
e Filter
f Heat exchanger
g Internal service port 5/16"
E1HC Crankcase heater
M1C Motor (compressor)
M1F‑M2F Motor (upper and lower fan)
R1T Thermistor (air)
R2T Thermistor (discharge)
R3T Thermistor (suction)
R4T Thermistor (heat exchanger)
R5T Thermistor (heat exchanger middle)
R6T Thermistor (liquid)
S1NPH Pressure sensor
S1PH High pressure switch
Y1E Electronic expansion valve
Y1S Solenoid valve (4‑way valve)
Heating
Cooling
ERHQ_W1
a Field piping (liquid: Ø9.5 flare connection)
b Field piping (gas: Ø15.9 flare connection)
c Stop valve (with service port 5/16")
d Accumulator
e Filter
f Heat exchanger
g Internal service port 5/16"
h Capillary tube
E1HC Crankcase heater
M1C Motor (compressor)
M1F‑M2F Motor (upper and lower fan)
R1T Thermistor (air)
R2T Thermistor (discharge)
R3T Thermistor (suction)
R4T Thermistor (heat exchanger)
R5T Thermistor (heat exchanger middle)
R6T Thermistor (liquid)
S1NPH Pressure sensor
S1PH High pressure switch
Y1E Electronic expansion valve
Y1S Solenoid valve (4‑way valve)
Y3S Solenoid valve (injection)
Heating
Cooling
ERLQ
a Field piping (liquid: Ø9.5 flare connection)
b Field piping (gas: Ø15.9 flare connection)
c Stop valve (with service port 5/16")
d Accumulator
e Filter
f Heat exchanger
g Internal service port 5/16"
h Capillary tube
E1HC Crankcase heater
M1C Motor (compressor)
Installer reference guide
74
M1F‑M2F Motor (upper and lower fan)
R1T Thermistor (air)
R2T Thermistor (discharge)
R3T Thermistor (suction)
R4T Thermistor (heat exchanger)
R5T Thermistor (heat exchanger middle)
R6T Thermistor (liquid)
S1NPH Pressure sensor
S1PH High pressure switch
Y1E Electronic expansion valve (main)
Y3E Electronic expansion valve (injection)
Y1S Solenoid valve (4‑way valve)
Y3S Solenoid valve (hot gas pass)
Heating
Cooling
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 75

14.2 Piping diagram: Indoor unit
Field installed
M
M
3D096028-1A
R1T
R4T
R3T
R2T
R5T
R7T
A
A
1
7
7
26
12
14
18
9
21
2
5
6
4
3
13
27
16
19
20
17
10
28
22
23
8
8
29
15
11
24
28
Refrigerant inlet
Refrigerant outlet
Refrigerant side
Water side
Field installed
14 Technical data
1 Space heating – water OUT (additional/direct zone)
2 Space heating – water IN (additional/direct zone)
3 Space heating – water OUT (main/mixed zone)
4 Space heating – water IN (main/mixed zone)
5 Domestic hot water: hot water out
6 Domestic hot water: cold water in
7 Shut-off valve with drain/fill valve
8 Shut-off valve
9 Flow sensor
10 3-way valve (space heating/domestic hot water)
11 3-way valve (mixing valve for the main/mixed zone)
12 Water filter (additional/direct zone)
13 Water filter (main/mixed zone)
14 Pump (additional/direct zone)
15 Pump (main/mixed zone)
16 Backup heater
17 Safety valve
18 Plate heat exchanger
19 R1T – Outlet water heat exchanger thermistor
20 R2T – Outlet water backup heater thermistor
21 R3T – Thermistor (heat exchanger, liquid pipe)
22 R4T – Inlet water thermistor
23 R5T – Tank thermistor
24 R7T – Water outlet thermistor (main/mixed zone)
26 Expansion vessel
27 Air purge
28 Check valve
29 Capillary tube
Screw connection
Flare connection
Quick coupling
Brazed connection
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
75
Page 76

14 Technical data
14.3 Wiring diagram: Outdoor unit
The wiring diagram is delivered with the unit, located at the inside of
the service cover.
Notes:
1 This wiring diagram applies only to the outdoor unit.
2 Symbols (see below).
3 Symbols (see below).
4 Refer to the option manual for connecting wiring to X6A and
X77A.
5 Refer to the wiring diagram sticker (on the back of the service
cover) for how to use the BS1~BS4 and DS1 switches.
6 When operating, do not short-circuit protective device S1PH.
7 Colours (see below).
8 Refer to the service manual for instructions on how to set the
selector switches (DS1). The factory setting of all switches is
OFF.
9 Symbols (see below).
Symbols:
L Live
N Neutral
Field wiring
Terminal strip
Connector
Connector
Connection
Protective earth (screw)
Noiseless earth
Terminal
Option
Wiring dependent on model
Colours:
BLK Black
BLU Blue
BRN Brown
GRN Green
ORG Orange
RED Red
WHT White
YLW Yellow
Legend:
A1P~A4P Printed circuit board
BS1~BS4 Push button switch
C1~C4 Capacitor
DS1 DIP switch
E1H Bottom plate heater
E1HC Crankcase heater
F1U~F8U
(ERHQ_V3 + ERLQ_V3)
▪ F1U, F3U, F4U: Fuse (T 6.3 A /
250V)
▪ F6U: Fuse (T 5.0A / 250V)
▪ F7U, F8U: Fuse (F 1.0A / 250V)
F1U~F9U
(ERHQ_W1 + ERLQ_W1)
H1P~H7P (A2P)
(ERHQ_V3 + ERLQ_V3)
H1P~H7P (A1P)
(ERHQ_W1 + ERLQ_W1)
HAP (A1P)
(ERHQ_V3 + ERLQ_V3)
HAP (A1P, A2P)
(ERHQ_W1 + ERLQ_W1)
K1M, K2M
(ERHQ_W1 + ERLQ_W1)
K1R~K4R Magnetic relay
K10R, K11R
(ERHQ_V3 + ERLQ_V3)
L1R~L4R Reactor
M1C Motor (compressor)
M1F Motor (upper fan)
M2F Motor (lower fan)
PS Switching power supply
Q1DI Earth leakage circuit breaker (field
R1~R4 Resistor
R1T Thermistor (air)
R2T Thermistor (discharge)
R3T Thermistor (suction)
R4T Thermistor (heat exchanger)
R5T Thermistor (heat exchanger middle)
R6T Thermistor (liquid)
R7T
(ERHQ_W1 + ERLQ_W1)
R10T
(ERHQ_V3 + ERLQ_V3)
RC
(ERHQ_V3 + ERLQ_V3)
S1NPH Pressure sensor
S1PH High pressure switch
TC
(ERHQ_V3 + ERLQ_V3)
V1R
(ERHQ_V3 + ERLQ_V3)
V1R, V2R
(ERHQ_W1 + ERLQ_W1)
V2R, V3R
(ERHQ_V3 + ERLQ_V3)
V3R
(ERHQ_W1 + ERLQ_W1)
▪ F1U, F2U: Fuse (31.5A / 500V)
▪ F3U~F6U: Fuse (T 6.3A / 250V)
▪ F7U: Fuse (T 5.0A / 250V)
▪ F8U, F9U: Fuse (F 1.0A / 250V)
Light‑emitting diode (service monitor
orange)
H2P:
▪ Prepare, test: Flickering
▪ Malfunction detection: Light up
Light‑emitting diode (service monitor
orange)
Light‑emitting diode (service monitor
green)
Light‑emitting diode (service monitor
green)
Magnetic contactor
Magnetic relay
supply)
Thermistor (fin)
Thermistor (fin)
Signal receiver circuit
Signal transmission circuit
Power module
Power module
Diode module
Diode module
Installer reference guide
76
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 77

14 Technical data
15
**
/12.2
1
V1T
(ERHQ_V3 + ERLQ_V3)
X1M Terminal strip (power supply)
X1Y Connector (option for ERHQ: bottom
X6A Connector (option)
X77A
(ERHQ_W1 + ERLQ_W1)
Y1E Expansion valve (main)
Insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT)
plate heater)
Connector (option)
Y3E
(ERLQ)
Y1S Solenoid valve (4‑way valve)
Y3S
(ERHQ_W1)
Y3S
(ERLQ)
Z1C~Z9C Noise filter
Z1F~Z4F Noise filter
Expansion valve (injection)
Solenoid valve (injection)
Solenoid valve (hot gas pass)
14.4 Wiring diagram: Indoor unit
See the internal wiring diagram supplied with the unit (on the inside of the indoor unit switch box cover). The abbreviations used are listed
below.
Notes to go through before starting the unit
English Translation
Notes to go through before
starting the unit
X1M Main terminal
X2M Field wiring terminal for AC
X5M Field wiring terminal for DC
User installed options User installed options
Domestic hot water tank Domestic hot water tank
Remote user interface Remote user interface
Ext. indoor thermistor External indoor thermistor
Ext outdoor thermistor External outdoor thermistor
Digital I/O PCB Digital I/O PCB
Demand PCB Demand PCB
Bottom plate heater Bottom plate heater
Main LWT Main leaving water temperature
On/OFF thermostat (wired) On/OFF thermostat (wired)
On/OFF thermostat (wireless) On/OFF thermostat (wireless)
Ext. thermistor External thermistor
Heat pump convector Heat pump convector
Safety thermostat Safety thermostat
Add LWT Additional leaving water
On/OFF thermostat (wired) On/OFF thermostat (wired)
On/OFF thermostat (wireless) On/OFF thermostat (wireless)
Ext. thermistor External thermistor
Heat pump convector Heat pump convector
Position in switch box
English Translation
Position in switch box Position in switch box
Notes to go through before
starting the unit
Earth wiring
Wire number 15
Field supply
Connection ** continues on page
12 column 2
Several wiring possibilities
Option
Not mounted in switch box
Wiring depending on model
PCB
temperature
Legend
A1P Main PCB
A2P User interface PCB
A3P * On/OFF thermostat (PC=power circuit)
A3P * Heat pump convector
A4P * Digital I/O PCB
A4P * Receiver PCB (Wireless On/OFF
thermostat)
A5P Bizone PCB
A6P Current loop PCB
A7P Anode driver PCB
A8P * Demand PCB
B1L Flow sensor
DS1 (A5P) DIP switch
DS1 (A8P) DIP switch
E1A Electrical anode
E3H Backup heater element (3kW)
F1B Overcurrent fuse backup heater
F1T Thermal fuse backup heater
F1U (A4P) * Fuse 5A 250V for digital I/O PCB
F2U (A4P) * Fuse 5A 250V for digital I/O PCB
F1U (A5P) Fuse T 2A 250V for PCB
F2U (A5P) Fuse T 2A 250V for PCB
FU1 (A1P) Fuse T 6.3A 250V for PCB
K1M Contactor backup heater
K2M Relay 3-way valve bypass
K3M Relay 3-way valve flow
K*R (A1P, A4P) Relay on PCB
M1P Additional zone pump
M2P # Domestic hot water pump
M3P Main zone pump
M1S Mixing 3-way valve
M2S # 2-way valve for cooling mode
M3S 3-way valve for space heating/domestic hot
water
PC (A4P) Power circuit
PHC1 (A4P) * Optocoupler input circuit
Q*DI # Earth leakage circuit breaker
Q1L Thermal protector backup heater
Q3L # Safety thermostat
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
77
Page 78

14 Technical data
R1H (A3P) * Humidity sensor
R1T (A1P) Outlet water heat exchanger thermistor
R1T (A2P) Ambient sensor user interface
R1T (A3P) * Ambient sensor On/OFF thermostat
R2T (A1P) Outlet backup heater thermistor
R2T (A3P) * External sensor (floor or ambient)
R3T Refrigerant liquid side thermistor
R4T Inlet water thermistor
R5T Domestic hot water thermistor
R6T * External indoor or outdoor ambient
thermistor
R7T Mixed leaving water thermistor
S1S # Preferential kWh rate power supply contact
S2S # Electrical meter pulse input 1
S3S # Electrical meter pulse input 2
S4S # Safety thermostat
S6S~S9S # Digital power limitation inputs
SS1 (A4P) * Selector switch
TR1 Power supply transformer
CN1-2, X*A
X*H, X*Y
X*M Terminal strip
Translation of text on wiring diagram
English Translation
3 wire type SPST 3 wire type SPST
Add. LWT zone Additional leaving water
Alarm output Alarm output
Anode Anode
Continuous Continuous current
Demand PCB Demand PCB
DHW pump Domestic hot water pump
DHW pump output Domestic hot water pump output
Digital I/O PCB Digital I/O PCB
Electric pulse meter inputs: 12 V
DC pulse detection (voltage
supplied by PCB)
Ext. ambient sensor option
(indoor or outdoor)
Ext. heat source External heat source
For preferential kWh rate power
supply
For safety thermostat For safety thermostat
Heat pump convector Heat pump convector
Connector
* = Optional
# = Field supply
temperature zone
Electric pulse meter inputs: 12 V
DC pulse detection (voltage
supplied by PCB)
External ambient sensor option
(indoor or outdoor)
For preferential kWh rate power
supply
English Translation
Indoor unit supplied from outdoor Indoor unit supplied from outdoor
Inrush Inrush current
Main LWT zone Main leaving water temperature
zone
Max. load Maximum load
Min. load Minimum load
NC valve Normal closed valve
NO valve Normal open valve
Normal kWh rate power supply Normal kWh rate power supply
Only for *** Only for ***
Only for demand PCB option Only for demand PCB option
Only for digital I/O PCB option Only for digital I/O PCB option
Only for ext. sensor (floor or
ambient)
Only for normal power supply
(standard)
Only for preferential kWh rate
power supply (outdoor)
Only for wired On/OFF
thermostat
Only for wireless On/OFF
thermostat
Only if no *** Only if no ***
Options: boiler output, alarm
output
Options: bottom plate heater OR
On/OFF output
Outdoor unit Outdoor unit
Power limitation digital inputs: 12
V DC / 12 mA detection (voltage
supplied by PCB)
Preferential kWh rate power
supply contact: 16 V DC
detection (voltage supplied by
PCB)
Remote user interface Remote user interface
Safety thermostat Safety thermostat
Safety thermostat contact: 16 V
DC detection (voltage supplied
by PCB)
Shut-off valve Shut-off valve
Space C/H On/OFF output Space cooling/heating On/OFF
Switch box Switch box
To bottom plate heater To bottom plate heater
Use normal kWh rate power
supply for indoor unit
User interface User interface
Only for external sensor (floor or
ambient)
Only for normal power supply
(standard)
Only for preferential kWh rate
power supply (outdoor)
Only for wired On/OFF
thermostat
Only for wireless On/OFF
thermostat
Options: boiler output, alarm
output
Options: bottom plate heater OR
On/OFF output
Power limitation digital inputs:
12VDC / 12mA detection
(voltage supplied by PCB)
Preferential kWh rate power
supply contact: 16VDC
detection (voltage supplied by
PCB)
Safety thermostat contact:
16VDC detection (voltage
supplied by PCB)
output
Use normal kWh rate power
supply for indoor unit
Installer reference guide
78
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 79

Electrical connection diagram
X1Y: 1-2
X1M: 1-2-3
X1M: 1-2-3
A4P:Y2
X2M:29
2x0.75
X2M: 30-31
X5M: 3-4
1
1
A4P: Y1
X2M: 29
230 V
A4P: X1-X2
230 V
230 V
230 V
A4P: X1M: H-C-com
X2M: L-N
A3P: X1M: 1-3
R2T
230 V
X11M : 5-6
X5M: 1-2
2x0.75
2x0.75
X2M: 34-35
230 V
X5M: 5-6
X5M: 7-8
X5M: 9-10
A8P: X801M: 1-5
A8P: X801M: 2-5
A8P: X801M: 3-5
A8P: X801M: 4-5
230 V
A4P: Y2
X2M: 29
2
2
2
X5M: 11-12
2
2
4D096036A
A3P: X1M: C-com-H
Only for *KRP1HB*
Field supply
communication
External sensor
(floor or ambient)
external thermistor (indoor or outdoor)
Only for KRCS01-1 or EKRSCA1
2way valve
Bottom plate heater
Only for *KBPHT*
& depending on model
X1M: L1-L2-L3-N-earth
or L-N-earth
2 core
3 core
Indoor unit
Notes:
- In case of signal cable: keep minimum distance to power cables > 5 cm
Outdoor unit
Cooling/heating
On/OFF output
Electricity meter pulse input 2
Electricity meter pulse input 1
Circulation pump for DHW
M2S (*KHBX units) for cooling mode
Ext. heat source (eg boiler)
alarm indication
2 core
2 core
signal
2 core
signal
signal
2 core
2 core
2 core
signal
2 core
2 core
Only for *KRTW
(wired room thermostat)
External room thermostat / Heat pump convector
(main and/or additional zone)
Optional part
Only for *KRTR
(wireless room thermostat)
Only for *KRTETS
2 core
(3m included)
signal
2 core
2 core
4 core for H only operation
5 core for C/H operation
2 core for H only operation
3 core for C/H operation
Only for
(heat pump convector)
signal
2 core
signal
2 core
signal
2 core
signal
2 core
Power limitation
demand input 4
Power limitation
demand input 3
Power limitation
demand input 2
Power limitation
demand input 1
Field supply
Standard part
Optional part
A2P: P1-P2 user interface
A2P: P1-P2 user interface
Only for *KRUCBL*
communication
2 core
main: X2M: 1-4
add: X2M: 1a-4
main: X2M: 1-2-3-4
add: X2M: 1a-2a-3-4
main: X2M: 1-2-4
add: X2M: 1a-2a-4
NO valve: X2M: 6-7
NC valve: X2M: 5-7
Cooling/heating
On/OFF output
Changeover to
ext. heat source output
Alarm output
Only for *KRP1AHTA
F1B: L-N + earth
2 core
signal
Safety thermostat
Field supply
Field supply
3 core
backup heater power supply (3 kW): 230 V + earth
Safety thermostat
normal kWh rate power supply for indoor unit: 230 V
unit preferential kWh rate power supply:
400 V or 230 V + earth
Only for preferential kWh rate power supply installation
5 or 3 core
2x0.75
2 core
2 core
5 or 3 core
unit power supply: 400 V or 230 V + earth
Only for normal power supply installation
Standard part
Power supply
For more details, please check the unit wiring.
14 Technical data
14.5 ESP curve: Indoor unit
Note: A flow error will occur when the minimum water flow rate is not
reached.
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
79
Page 80

14 Technical data
80
70
60
50
30
40
20
10
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
45
A
B
C
4D097421-1
EHVZ16S18CB
A External static pressure (kPa)
B Water flow rate (l/min)
C Operation range
Additional/direct zone
Main/mixed zone
Operation area is extended to lower flow rates only in case the unit
operates with heat pump only. (Not in startup, no backup heater
operation, no defrost operation).
ESP=External static pressure [kPa] in the space heating circuit.
Flow=Water flow through the unit in the space heating circuit.
Notes:
▪ Selecting a flow outside the area of operation can cause damage
or malfunction of the unit. See also the minimum and maximum
allowed water flow range in the technical specifications.
▪ Water quality MUST be according to EN directive EC98/83EC.
Installer reference guide
80
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Page 81

15 Glossary
Dealer
Sales distributor for the product.
Authorized installer
Technical skilled person who is qualified to install the
product.
User
Person who is owner of the product and/or operates the
product.
Applicable legislation
All international, European, national and local directives,
laws, regulations and/or codes that are relevant and
applicable for a certain product or domain.
Service company
Qualified company which can perform or coordinate the
required service to the product.
Installation manual
Instruction manual specified for a certain product or
application, explaining how to install, configure and maintain
it.
Operation manual
Instruction manual specified for a certain product or
application, explaining how to operate it.
Maintenance instructions
Instruction manual specified for a certain product or
application, which explains (if relevant) how to install,
configure, operate and/or maintain the product or
application.
Accessories
Labels, manuals, information sheets and equipment that are
delivered with the product and that need to be installed
according to the instructions in the accompanying
documentation.
Optional equipment
Equipment made or approved by Daikin that can be
combined with the product according to the instructions in
the accompanying documentation.
Field supply
Equipment not made by Daikin that can be combined with
the product according to the instructions in the
accompanying documentation.
15 Glossary
ERHQ+ERLQ011~016 + EHVZ16S18CB
Daikin Altherma – Low temperature split
4P401677-1B – 2017.04
Installer reference guide
81
Page 82

1/8
Field settings table
[6.8.2] = .... ID66F2
Applicable indoor units
*HVZ04S18CB3V
*HVZ08S18CB3V
*HVZ16S18CB3V
Notes
(*5) *04/08*
(*6) *16*
4P401673-1A - 2017.04
Page 83

2/8
Page 84

3/8
Breadcrumb Field code Setting name Range, step
Default valu
e
Date Value
User settings
└─ Preset values
└─ Room temperature
7.4.1.1 R/W [3-07]~[3-06], step: A.3.2.4
21°C
7.4.1.2 R/W [3-07]~[3-06], step: A.3.2.4
19°C
└─ LWT main
7.4.2.1 [8-09] R/W [9-01]~[9-00], step: 1°C
35°C
7.4.2.2 [8-0A] R/W [9-01]~[9-00], step: 1°C
33°C
7.4.2.5 R/W -10~10°C, step: 1°C
0°C
7.4.2.6 R/W -10~10°C, step: 1°C
-2°C
└─ Tank temperature
7.4.3.1 [6-0A] R/W 30~[6-0E]°C, step: 1°C
60°C
7.4.3.2 [6-0B] R/W 30~min(50, [6-0E])°C, step: 1°C
45°C
7.4.3.3 [6-0C] R/W 30~min(50, [6-0E])°C, step: 1°C
45°C
└─ Quiet level
7.4.4 R/W
0: Level 1 (*6)
1: Level 2 (*5)
2: Level 3
└─ Electricity price
7.4.5.1 [C-0C]
[D-0C]
R/W 0,00~990/kWh
0/kWh
7.4.5.2 [C-0D]
[D-0D]
R/W 0,00~990/kWh
0/kWh
7.4.5.3 [C-0E]
[D-0E]
R/W 0,00~990/kWh
0/kWh
└─ Fuel price
7.4.6 R/W 0,00~990/kWh
0,00~290/MBtu
8,0/kWh
└─ Set weather dependent
└─ Main
└────────────────── Set weather-dependent heating
7.7.1.1 [1-00] Set weather-dependent heating Low ambient temp. for LWT main zone heating
WD curve.
R/W -40~5°C, step: 1°C
-10°C
7.7.1.1 [1-01] Set weather-dependent heating High ambient temp. for LWT main zone heating
WD curve.
R/W 10~25°C, step: 1°C
15°C
7.7.1.1 [1-02] Set weather-dependent heating Leaving water value for low ambient temp. for
LWT main zone heating WD curve.
R/W
[9-01]~[9-00]°C, step: 1°C
35°C
7.7.1.1 [1-03] Set weather-dependent heating Leaving water value for high ambient temp. for
LWT main zone heating WD curve.
R/W [9-01]~min(45, [9-00])°C , step: 1°C
25°C
└─ Additional
└────────────────── Set weather-dependent heating
7.7.2.1 [0-00] Set weather-dependent heating Leaving water value for high ambient temp. for
LWT add zone heating WD curve.
R/W [9-05]~min(45,[9-06])°C, step: 1°C
35°C
7.7.2.1 [0-01] Set weather-dependent heating Leaving water value for low ambient temp. for
LWT add zone heating WD curve.
R/W [9-05]~[9-06]°C, step: 1°C
45°C
7.7.2.1 [0-02] Set weather-dependent heating High ambient temp. for LWT add zone heating
WD curve.
R/W 10~25°C, step: 1°C
15°C
7.7.2.1 [0-03] Set weather-dependent heating Low ambient temp. for LWT add zone heating
WD curve.
R/W -40~5°C, step: 1°C
-10°C
Installer settings
└─ System layout
└─ Standard
A.2.1.1 [E-00] R/O 0~5
0: LT s
p
lit
A.2.1.2 [E-01] R/O
0: 8 (*5)
1: 16
(*6)
A.2.1.3 [E-02] R/O
1: T
yp
e 2
A.2.1.4 [E-03] R/O
1: 1 ste
p
A.2.1.5 [5-0D] R/O
1: 1P,
(
1/1+2
)
A.2.1.6 [D-01] R/W
0: No
1: Open tariff
2: Closed tariff
3: Thermostat
A.2.1.7 [C-07] R/W 0: LWT control
1: Ext RT control
2: RT control
A.2.1.8 [7-02] R/W 0: 1 LWT zone
1: 2 LWT zones
A.2.1.9 [F-0D] R/W 0: Continuous
1: Sample
2: Re
q
ues
t
A.2.1.A [E-04] R/O
0: No (*6)
1: Yes
(*5)
A.2.1.B R/W 0: At unit
1: In room
└─ Options
A.2.2.1 [E-05] R/W
0: No
1: Yes
A.2.2.3 [E-07] R/O 0~6
1: T
yp
e 2
A.2.2.4 [C-05] R/W 1: Thermo ON/OFF
2: C/H re
q
ues
t
A.2.2.5 [C-06] R/W 1: Thermo ON/OFF
2: C/H re
q
ues
t
A.2.2.6.1 [C-02] Digital I/O PCB Ext. backup heat src R/W
0~3
0: No
1: Bivalent
A.2.2.6.2 [D-07] Digital I/O PCB Solar kit R/O
0~1
0: No
A.2.2.6.3 [C-09] Digital I/O PCB Alarm output R/W
0: Normally open
1: Normall
y
closed
A.2.2.6.4 [F-04] Digital I/O PCB Bottom plate heater R/W
0: No
1: Yes
A.2.2.7 [D-04] R/W
0: No
1: Pwr consm
p
ctrl
Forced off contact
Contact type add.
Demand PCB
Pump operation mode
Power saving possible
User interface location
DHW operation
DHW tank type
Contact type main
Indoor software type
Backup heater steps
BUH type
Unit control method
Number of LWT zones
High
Medium
Low
Unit type
Compressor type
Comfort (heating)
Eco (heating)
Storage comfort
Storage eco
Reheat
Field settings table
Installer setting at variance with
default value
Comfort (heating)
Eco (heating)
Comfort (heating)
Eco (heating)
(*5) *04/08*_
(*6) *16*
4P401673-1A - 2017.04
Page 85

4/8
Breadcrumb Field code Setting name Range, step
Default valu
e
Date Value
Field settings table
Installer setting at variance with
default value
A.2.2.8 [D-08] R/W
0: No
1: 0,1 pulse/kWh
2: 1 pulse/kWh
3: 10 pulse/kWh
4: 100 pulse/kWh
5: 1000
p
ulse/kWh
A.2.2.9 [D-09] R/W
0: No
1: 0,1 pulse/kWh
2: 1 pulse/kWh
3: 10 pulse/kWh
4: 100 pulse/kWh
5: 1000
p
ulse/kWh
A.2.2.A [D-02] R/W
0~4
0: No
1: Secondary rtrn
2: Disinf. shunt
A.2.2.B [C-08] R/W
0: No
1: Outdoor sensor
2: Room sensor
└─ Capacities
A.2.3.2 [6-03] R/W 0~10 kW, step: 0,2 kW
3 kW
A.2.3.6 [6-07] R/W 0~200 W, step: 10 W
0 W
└─ Space operation
└─ LWT settings
└────────────────── Main
A.3.1.1.1 R/W 0: Fixed
1: Weather dep.
2: Fixed + scheduled
3: WD + scheduled
A.3.1.1.2.1 [9-01] Temperature range Minimum temp (heating) R/W 15~37°C, step: 1°C
25°C
A.3.1.1.2.2 [9-00] Temperature range Maximum temp (heating) R/W 37~55, step: 1°C
55°C
A.3.1.1.5 [8-05] R/W
0: No
1: Yes
A.3.1.1.6.1 [F-0B] Shut-off valve Thermo On/OFF R/W
0: No
1: Yes
A.3.1.1.7 [9-0B] R/W 0: Quick
1: Slo
w
└────────────────── Additional
A.3.1.2.1 R/W 0: Fixed
1: Weather dep.
2: Fixed + scheduled
3: WD + scheduled
A.3.1.2.2.1 [9-05] Temperature range Minimum temp (heating) R/W 15~37°C, step: 1°C
25°C
A.3.1.2.2.2 [9-06] Temperature range Maximum temp (heating) R/W 37~55, step: 1°C
55°C
└────────────────── Delta T source
A.3.1.3.1 [9-09] R/W 3~10°C, step: 1°C
5°C
└─ Room thermostat
A.3.2.1.1 [3-07] Room temp. range Minimum temp (heating) R/W 12~18°C, step: A.3.2.4
12°C
A.3.2.1.2 [3-06] Room temp. range Maximum temp (heating) R/W 18~30°C, step: A.3.2.4
30°C
A.3.2.2 [2-0A] R/W -5~5°C, step: 0,5°C
0°C
A.3.2.3 [2-09] R/W -5~5°C, step: 0,5°C
0°C
A.3.2.4 R/W 0: 0,5 °C
1: 1 °C
└─ Operation range
14~35°C, step: 1°C
25°C
(*5)
14~35°C, step: 1°C
35°C
(*6)
└─ Domestic hot water (DHW)
└─ Type
A.4.1 [6-0D] R/W 0: Reheat only
1: Reheat + sched.
2: Scheduled onl
y
└─ Disinfection
A.4.4.1 [2-01] R/W 0: No
1: Yes
A.4.4.2 [2-00] R/W 0: Each day
1: Monday
2: Tuesday
3: Wednesday
4: Thursday
5: Friday
6: Saturday
7: Sunda
y
A.4.4.3 [2-02] R/W 0~23 hour, step: 1 hour
23
A.4.4.4 [2-03] R/W
60°C
A.4.4.5 [2-04] R/W 40~60 min, step: 5 min
40 min
└─ Maximum setpoint
A.4.5 [6-0E] R/W 40~60°C, step: 1°C
60°C
└─ SP mode
A.4.6 R/W
0: Fixed
1: Weather de
p
.
└─ Weather dependent curve
A.4.7 [0-0B] Weather-dependent curve Leaving water value for high ambient temp. for
DHW WD curve.
R/W 35~[6-0E]°C, step: 1°C
55°C
A.4.7 [0-0C] Weather-dependent curve Leaving water value for low ambient temp. for
DHW WD curve.
R/W 45~[6-0E]°C, step: 1°C
60°C
A.4.7 [0-0D] Weather-dependent curve High ambient temp. for DHW WD curve. R/W 10~25°C, step: 1°C
15°C
A.4.7 [0-0E] Weather-dependent curve Low ambient temp. for DHW WD curve. R/W -40~5°C, step: 1°C
-10°C
Start time
Temperature target
Duration
R/W
Disinfection
Operation day
Heating
Room temp. offset
Ext. room sensor offset
Room temp. step
A.3.3.1 [4-02] Space heating OFF temp
BUH: step 1
Bottom plate heater
LWT setpoint mode
Modulated LWT
Emitter type
LWT setpoint mode
External kWh meter 1
External kWh meter 2
DHW pump
External sensor
4P401673-1A - 2017.04
(*5) *04/08*_
(*6) *16*
Page 86

5/8
Breadcrumb Field code Setting name Range, step
Default valu
e
Date Value
Field settings table
Installer setting at variance with
default value
└─ Heat sources
└─ Backup heater
A.5.1.1 [4-00] R/W 0~2
0: Disabled
1: Enabled
A.5.1.4 [5-01] R/W -15~35°C, step: 1°C
0°C
└─ System operation
└─ Auto restart
A.6.1 [3-00] R/W 0: No
1: Yes
└─ Preferential kWh rate
A.6.2.1 [D-00] R/W
0~3
0: None
2: BUH onl
y
A.6.2.2 [D-05] R/W 0: Forced off
1: As normal
└─ Pwr consumpt. Control
A.6.3.1 [4-08] R/W
0: No limitation
1: Continuous
2: Di
g
ital inputs
A.6.3.2 [4-09] R/W 0: Current
1: Powe
r
A.6.3.3 [5-05] R/W 0~50 A, step: 1 A
50
A
A.6.3.4 [5-09] R/W 0~20 kW, step: 0,5 kW
20 kW
A.6.3.5.1 [5-05] Amp. limits for DI Limit DI1 R/W 0~50 A, step: 1 A
50
A
A.6.3.5.2 [5-06] Amp. limits for DI Limit DI2 R/W 0~50 A, step: 1 A
50
A
A.6.3.5.3 [5-07] Amp. limits for DI Limit DI3 R/W 0~50 A, step: 1 A
50
A
A.6.3.5.4 [5-08] Amp. limits for DI Limit DI4 R/W 0~50 A, step: 1 A
50
A
A.6.3.6.1 [5-09] kW limits for DI Limit DI1 R/W 0~20 kW, step: 0,5 kW
20 kW
A.6.3.6.2 [5-0A] kW limits for DI Limit DI2 R/W 0~20 kW, step: 0,5 kW
20 kW
A.6.3.6.3 [5-0B] kW limits for DI Limit DI3 R/W 0~20 kW, step: 0,5 kW
20 kW
A.6.3.6.4 [5-0C] kW limits for DI Limit DI4 R/W 0~20 kW, step: 0,5 kW
20 kW
A.6.3.7 [4-01] R/W
0~2
0: None
2: BUH
└─ Averaging time
A.6.4 [1-0A] R/W
0: No averaging
1: 12 hours
2: 24 hours
3: 48 hours
4: 72 hours
└─ Ext amb. sensor offset
A.6.5 [2-0B] R/W -5~5°C, step: 0,5°C
0°C
└─ Boiler efficiency
A.6.A [7-05] R/W
0: Very high
1: High
2: Medium
3: Low
4: Ver
y
low
└─ Emergency
A.6.C R/W
0: Manual
1: Automatic
└─ Overview settings
A.8 [0-00] R/W [9-05]~min(45,[9-06])°C, step: 1°C
35°C
A.8 [0-01] R/W [9-05]~[9-06]°C, step: 1°C
45°C
A.8 [0-02] R/W 10~25°C, step: 1°C
15°C
A.8 [0-03] R/W -40~5°C, step: 1°C
-10°C
A.8 [0-04] R/W
8
A.8 [0-05] R/W
12
A.8 [0-06] R/W
35
A.8 [0-07] R/W
20
A.8 [0-0B] R/W 35~[6-0E]°C, step: 1°C
55°C
A.8 [0-0C] R/W 45~[6-0E]°C, step: 1°C
60°C
A.8 [0-0D] R/W 10~25°C, step: 1°C
15°C
A.8 [0-0E] R/W -40~5°C, step: 1°C
-10°C
A.8 [1-00] R/W -40~5°C, step: 1°C
-10°C
A.8 [1-01] R/W 10~25°C, step: 1°C
15°C
A.8 [1-02] R/W
[9-01]~[9-00], step: 1°C
35°C
A.8 [1-03] R/W [9-01]~min(45, [9-00])°C , step: 1°C
25°C
A.8 [1-04] R/W
1
A.8 [1-05] R/W
1
A.8 [1-06] R/W
20
A.8 [1-07] R/W
35
A.8 [1-08] R/W
22
A.8 [1-09] R/W
18
A.8 [1-0A] R/W
0: No averaging
1: 12 hours
2: 24 hours
3: 48 hours
4: 72 hours
--
--
--
--
-What is the averaging time for the outdoor temp?
Low ambient temp. for DHW WD curve.
Low ambient temp. for LWT main zone heating WD curve.
High ambient temp. for LWT main zone heating WD curve.
Leaving water value for low ambient temp. for LWT main zone heating WD curve.
Leaving water value for high ambient temp. for LWT main zone heating WD curve.
--
--
--
-Leaving water value for high ambient temp. for DHW WD curve.
Leaving water value for low ambient temp. for DHW WD curve.
High ambient temp. for DHW WD curve.
Leaving water value for high ambient temp. for LWT add zone heating WD curve.
Leaving water value for low ambient temp. for LWT add zone heating WD curve.
High ambient temp. for LWT add zone heating WD curve.
Low ambient temp. for LWT add zone heating WD curve.
--
Type
Amp. value
kW value
Priority
Equilibrium temp.
Allowed heaters
Forced pump OFF
Mode
Operation mode
(*5) *04/08*_
(*6) *16*
4P401673-1A - 2017.04
Page 87

6/8
Breadcrumb Field code Setting name Range, step
Default valu
e
Date Value
Field settings table
Installer setting at variance with
default value
A.8 [2-00] R/W 0: Each day
1: Monday
2: Tuesday
3: Wednesday
4: Thursday
5: Friday
6: Saturday
7: Sunda
y
A.8 [2-01] R/W 0: No
1: Yes
A.8 [2-02] R/W 0~23 hour, step: 1 hour
23
A.8 [2-03] R/W
60°C
A.8 [2-04] R/W 40~60 min, step: 5 min
40 min
A.8 [2-05] R/W 4~16°C, step: 1°C
12°C
A.8 [2-06] R/W 0: Disabled
1: Enabled
A.8 [2-09] R/W -5~5°C, step: 0,5°C
0°C
A.8 [2-0A] R/W -5~5°C, step: 0,5°C
0°C
A.8 [2-0B] R/W -5~5°C, step: 0,5°C
0°C
A.8 [3-00] R/W 0: No
1: Yes
A.8 [3-01]
0
A.8 [3-02]
1
A.8 [3-03]
4
A.8 [3-04]
2
A.8 [3-05]
1
A.8 [3-06] R/W 18~30°C, step: A.3.2.4
30°C
A.8 [3-07] R/W 12~18°C, step: A.3.2.4
12°C
A.8 [3-08] R/W
35°C
A.8 [3-09] R/W
15°C
A.8 [4-00] R/W 0: Disabled
1: Enabled
2: Onl
y
DHW
A.8 [4-01] R/W
0~2
0: None
2: BUH
14~35°C, step: 1°C
25°C
(*5)
14~35°C, step: 1°C
35°C
(*6)
A.8 [4-03] R/W
3
A.8 [4-04]
2
A.8 [4-05]
0
A.8 [4-06]
0/1
A.8 [4-07] R/W
1
A.8 [4-08] R/W
0: No limitation
1: Continuous
2: Di
g
ital inputs
A.8 [4-09] R/W 0: Current
1: Powe
r
A.8 [4-0A]
0
A.8 [4-0B] R/W
1
A.8 [4-0D] R/W
3
A.8 [4-0E] Is the installer on site? R/W
0: No
1: Yes
A.8 [5-00] R/W 0: Allowed
1: Not allowe
d
A.8 [5-01] R/W -15~35°C, step: 1°C
0°C
A.8 [5-02] R/W 0: Disabled
1: Enabled
A.8 [5-03] R/W -15~35°C, step: 1°C
0°C
A.8 [5-04] R/W 0~20°C, step: 1°C
10°C
A.8 [5-05] R/W 0~50 A, step: 1 A
50
A
A.8 [5-06] R/W 0~50 A, step: 1 A
50
A
A.8 [5-07] R/W 0~50 A, step: 1 A
50
A
A.8 [5-08] R/W 0~50 A, step: 1 A
50
A
A.8 [5-09] R/W 0~20 kW, step: 0,5 kW
20 kW
A.8 [5-0A] R/W 0~20 kW, step: 0,5 kW
20 kW
A.8 [5-0B] R/W 0~20 kW, step: 0,5 kW
20 kW
A.8 [5-0C] R/W 0~20 kW, step: 0,5 kW
20 kW
A.8 [5-0D] R/O 0~5
1: 1P,
(
1/1+2
)
A.8 [5-0E]
1
A.8 [6-00] R/W 2~20°C, step: 1°C
2°C
A.8 [6-01] R/W 0~10°C, step: 1°C
2°C
A.8 [6-02] R/W
0
A.8 [6-03] R/W 0~10 kW, step: 0,2 kW
3 kW
A.8 [6-04] R/W
0
A.8 [6-05]
0
A.8 [6-06]
0
A.8 [6-07] R/W 0~200 W, step: 10 W
0 W
-What is the capacity of the backup heater step 1?
--
--
-What is the capacity of the bottom plate heater?
What is the requested limit for DI3?
What is the requested limit for DI4?
What type of backup heater installation is used?
-The temperature difference determining the heat pump ON temperature.
The temperature difference determining the heat pump OFF temperature.
What is the requested limit for DI1?
What is the requested limit for DI2?
What is the requested limit for DI3?
What is the requested limit for DI4?
What is the requested limit for DI1?
What is the requested limit for DI2?
--
Is backup heater operation allowed above equilibrium temperature during space
heating operation?
What is the equilibrium temperature for the building?
Space heating priority.
Space heating priority temperature.
Set point correction for domestic hot water temperature.
-- (Do not change this value)
-Which power limitation mode is required on the system?
Which power limitation type is required?
--
--
R/W
--
--
--
--
-What is the BUH operation mode?
Which electric heater has priority?
A.8 [4-02] Below which outdoor temperature is heating allowed?
--
--
--
-What is the maximum desired room temperature in heating?
What is the mimimum desired room temperature in heating?
Room frost protection
Adjust the offset on the measured room temperature
Adjust the offset on the measured room temperature
What is the required offset on the measured outdoor temp.?
Is auto restart of the unit allowed?
--
When should the disinfection function be executed?
Should the disinfection function be executed?
When should the disinfection function start?
What is the disinfection target temperature?
How long must the tank temperature be maintained?
Room antifrost temperature
4P401673-1A - 2017.04
(*5) *04/08*_
(*6) *16*
Page 88

7/8
Breadcrumb Field code Setting name Range, step
Default valu
e
Date Value
Field settings table
Installer setting at variance with
default value
A.8 [6-08] R/W
2~20°C, step: 1°C
10°C
A.8 [6-09]
0
A.8 [6-0A] R/W 30~[6-0E]°C, step: 1°C
60°C
A.8 [6-0B] R/W 30~min(50, [6-0E])°C, step: 1°C
45°C
A.8 [6-0C] R/W 30~min(50, [6-0E])°C, step: 1°C
45°C
A.8 [6-0D] R/W 0: Reheat only
1: Reheat + sched.
2: Scheduled onl
y
A.8 [6-0E] R/W 40~60°C, step: 1°C
60°C
A.8 [7-00] R/W
0
A.8 [7-01] R/W
2
A.8 [7-02] R/W 0: 1 LWT zone
1: 2 LWT zones
A.8 [7-03]
2,5
A.8 [7-04]
0
A.8 [7-05] R/W
0: Very high
1: High
2: Medium
3: Low
4: Ver
y
low
A.8 [8-00]
1 min
A.8 [8-01] R/W 5~95 min, step: 5 min
30 min
A.8 [8-02] R/W 0~10 hour, step: 0,5 hour
0,5 hour
A.8 [8-03] R/W
50
A.8 [8-04] R/W 0~95 min, step: 5 min
95 min
A.8 [8-05] R/W
0: No
1: Yes
A.8 [8-06] R/W 0~10°C, step: 1°C
3°C
A.8 [8-07] R/W
18
A.8 [8-08] R/W
20
A.8 [8-09] R/W [9-01]~[9-00], step: 1°C
35°C
A.8 [8-0A] R/W [9-01]~[9-00], step: 1°C
33°C
A.8 [8-0B]
13
A.8 [8-0C]
10
A.8 [8-0D]
16
A.8 [9-00] R/W 37~55, step: 1°C
55°C
A.8 [9-01] R/W 15~37°C, step: 1°C
25°C
A.8 [9-02] R/W
22
A.8 [9-03] R/W
5
A.8 [9-04] R/W 1~4°C, step: 1°C
1°C
A.8 [9-05] R/W 15~37°C, step: 1°C
25°C
A.8 [9-06] R/W 37~55, step: 1°C
55°C
A.8 [9-07] R/W
5
A.8 [9-08] R/W
22
A.8 [9-09] R/W 3~10°C, step: 1°C
5°C
A.8 [9-0A] R/W
5
A.8 [9-0B] R/W 0: Quick
1: Slo
w
A.8 [9-0C] R/W 1~6°C, step: 0,5°C
1 °C
A.8 [9-0D] R/W 0~8, step:1
0 : 100%
1~4 : 80~50%
5~8 : 80~50%
6
A.8 [9-0E]
6
A.8 [A-00]
0
A.8 [A-01]
0 (*5)
3
(*6)
A.8 [A-02]
0 (*5)
1
(*6)
A.8 [A-03]
0
A.8 [A-04]
0
A.8 [B-00]
0
A.8 [B-01]
0
A.8 [B-02]
0
A.8 [B-03]
0
A.8 [B-04]
0
A.8 [C-00] R/O 0~1
1: Heat
pump p
riorit
y
A.8 [C-01]
0
A.8 [C-02] R/W
0~3
0: No
1: Bivalent
A.8 [C-03] R/W -25~25°C, step: 1°C
0°C
A.8 [C-04] R/W 2~10°C, step: 1°C
3°C
A.8 [C-05] R/W 1: Thermo ON/OFF
2: C/H re
q
ues
t
A.8 [C-06] R/W 0: -
1: Thermo ON/OFF
2: C/H re
q
ues
t
A.8 [C-07] R/W 0: LWT control
1: Ext RT control
2: RT control
Is an external backup heat source connected?
Bivalent activation temperature.
Bivalent hysteresis temperature.
What is the thermo request contact type for the main zone?
What is the thermo request contact type for the add. zone?
What is the unit control method in space operation?
--
--
--
-Domestic heating water priority.
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
What is the desired delta T in heating?
-What emitter type is connected to the main LWT zone?
Room temperature hysteresis.
Pump speed limitation
--
-Leaving water temperature overshoot temperature.
What is the mimimum desired LWT for add. zone in heating?
What is the maximum desired LWT for add. zone in heating?
--
--
--
--
-What is the maximum desired LWT for main zone in heating?
What is the mimimum desired LWT for main zone in heating?
--
Allow modulation of the LWT to control the room temp?
Leaving water temperature maximum modulation.
--
-What is the desired comfort main LWT in heating?
What is the desired eco main LWT in heating?
Boiler efficiency
-Maximum running time for domestic hot water operation.
Anti-recycling time.
-Additional running time for the maximum running time.
What is the maximum temperature setpoint?
--
-How many leaving water temperature zones are there?
--
--
What is the hysteresis to be used in reheat mode?
-What is the desired comfort storage temperature?
What is the desired eco storage temperature?
What is the desired reheat temperature?
What is the desired DHW production type?
(*5) *04/08*_
(*6) *16*
4P401673-1A - 2017.04
Page 89

8/8
Breadcrumb Field code Setting name Range, step
Default valu
e
Date Value
Field settings table
Installer setting at variance with
default value
A.8 [C-08] R/W
0: No
1: Outdoor sensor
2: Room sensor
A.8 [C-09] R/W
0: Normally open
1: Normall
y
closed
A.8 [C-0A]
0
A.8 [C-0C] R/W 0~7
0
A.8 [C-0D] R/W 0~7
0
A.8 [C-0E] R/W 0~7
0
A.8 [D-00] R/W
0~3
0: None
2: BUH onl
y
A.8 [D-01] R/W
0: No
1: Open tariff
2: Closed tariff
3: Thermostat
A.8 [D-02] R/W
0~4
0: No
1: Secondary rtrn
2: Disinf. shunt
A.8 [D-03] R/W
0: Disabled
1: Enabled, shift 2°C (from -2 to 2°C)
2: Enabled, shift 4°C (from -2 to 2°C)
3: Enabled, shift 2°C (from -4 to 4°C)
4: Enabled, shift 4°C
(
from -4 to 4°C
)
A.8 [D-04] R/W
0: No
1: Pwr consm
p
ctrl
A.8 [D-05] R/W 0: Forced off
1: As normal
A.8 [D-07] R/O
0
A.8 [D-08] R/W
0: No
1: 0,1 pulse/kWh
2: 1 pulse/kWh
3: 10 pulse/kWh
4: 100 pulse/kWh
5: 1000
p
ulse/kWh
A.8 [D-09] R/W
0: No
1: 0,1 pulse/kWh
2: 1 pulse/kWh
3: 10 pulse/kWh
4: 100 pulse/kWh
5: 1000
p
ulse/kWh
A.8 [D-0A]
0
A.8 [D-0B]
2
A.8 [D-0C] R/W 0~49
0
A.8 [D-0D] R/W 0~49
0
A.8 [D-0E] R/W 0~49
0
A.8 [E-00] R/O
0~5
0: LT s
p
lit
A.8 [E-01] R/O
0: 8 (*5)
1: 16
(*6)
A.8 [E-02] R/O 0~1
1: T
yp
e 2
A.8 [E-03] R/O 0~2
1: 1 ste
p
A.8 [E-04] R/O
0: No (*6)
1: Yes
(*5)
A.8 [E-05] R/W
0: No
1: Yes
A.8 [E-06] R/O 0: No
1: Yes
A.8 [E-07] R/O 0~6
1: T
yp
e 2
A.8 [E-08] R/W
0: Disabled (*6)
1: Enabled
(*5)
A.8 [E-09]
0
A.8 [E-0A]
0
A.8 [E-0B] R/O
0~1
1: Yes
A.8 [E-0C]
0
A.8 [E-0D]
0
A.8 [F-00] R/W
0: Disabled
1: Enabled
A.8 [F-01] R/W
20
A.8 [F-02] R/W 3~10°C, step: 1°C
3°C
A.8 [F-03] R/W 2~5°C, step: 1°C
5°C
A.8 [F-04] R/W
0: No
1: Yes
A.8 [F-05]
0
A.8 [F-06]
0
A.8 [F-09] R/W
0: Disabled
1: Enabled
A.8 [F-0A]
0
A.8 [F-0B] R/W
0: No
1: Yes
A.8 [F-0C] R/W
1
A.8 [F-0D] R/W 0: Continuous
1: Sample
2: Re
q
ues
t
-Close shut-off valve during thermo OFF?
-What is the pump operation mode?
Forced off contact type
Bottom plate heater ON temperature.
Bottom plate heater hysteresis.
Is a bottom plate heater connected?
--
-Pump operation during flow abnormality.
-Is a bi-zone kit installed?
--
-Pump operation allowed outside range.
--
Is the power saving function available on the outdoor unit?
Can the system prepare domestic hot water?
Is a DHW tank installed in the system?
What kind of DHW tank is installed?
Power saving function for outdoor unit.
--
What is the medium electricity price (Do not use)
What is the low electricity price (Do not use)
Which type of unit is installed?
Which type of compressor is installed?
What is the indoor unit software type?
What is the number of backup heater steps?
-Is an external kWh meter used for power measurement?
Is an external kWh meter used for power measurement?
--
-What is the high electricity price (Do not use)
Which heaters are permitted if prefer. kWh rate PS is cut?
Which type of DHW pump is installed?
Leaving water temperature compensation around 0°C.
Is a demand PCB connected?
Is the pump allowed to run if prefer. kWh rate PS is cut?
Which type of external sensor is installed?
What is the required alarm output contact type?
-High electricity price decimal (Do not use)
Medium electricity price decimal (Do not use)
Low electricity price decimal (Do not use)
4P401673-1A - 2017.04
(*5) *04/08*_
(*6) *16*
Page 90

Page 91

Page 92

4P401677-1B 2017.04
Copyright 2015 Daikin
 Loading...
Loading...