Page 1

Specifications
CONTROL BOARD
MODEL
Rev. 1.00 Issued on October 10, 2006
BD2-2220/2221
Page 2
Revision
Rev. Date Comment
1.00 2006.10.10 Newly issued
CITIZEN is a registered trade mark of CITIZEN WATCH CO., LTD., Japan.
CITIZEN es una marca registrada de CITIZEN WATCH CO., LTD., Japón.
Page 3

CONTENTS
1. GENERAL OUTLINE......................................................................................1
1.1 FEATURES................................................................................................................1
1.2 ACCESSORIES ..........................................................................................................2
1.3 MODEL CLASSIFICATION............................................................................................2
1.4 CONFIGURATION (BLOCK DIAGRAM)........................................................................... 3
2. BASIC SPECIFICATIONS .............................................................................4
2.1 PRINTING SPECIFICATIONS .......................................................................................4
2.2 CHARACTER AND BARCODE SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................5
2.3 PRINT PAPER SPECIFICATIONS (THERMAL PAPER)........................................................6
2.4 MECHANISM AND PERIPHERALS USED .........................................................................7
2.5 POWER SUPPLY........................................................................................................7
2.5.1 Specifications...................................................................................................................7
2.5.2 Precautions......................................................................................................................7
2.6 ENVIRONMENT: TEMPERATURE, HUMIDITY...................................................................8
3. APPEARANCE SPECIFICATIONS ..................................................................9
4. CONNECTOR CONNECTION ....................................................................... 10
4.1 INTERFACE CONNECTORS.........................................................................................10
4.1.1 Interface Connector Pin Assignment (CN1) .......................................................................10
4.1.2 USB Interface Connector Pin Assignment (CN8) * Only USB model .....................................11
4.1.3 CN1 Connection Example ................................................................................................12
4.2 MECHANISM CONNECTOR (CN2) ..............................................................................13
4.2.1 Mechanism Connector Pin Assignment (CN2) .................................................................... 13
4.2.2 FFC-compliant Cable.......................................................................................................14
4.3 HEAD UP, PAPER-END DETECTING CONNECTOR (CN3, CN7) .......................................14
4.4 MOTOR CONNECTOR (CN4).....................................................................................15
4.5 AUTO CUTTER CONNECTOR (CN5) ............................................................................15
4.6 PAPER NEAR-END SENSOR CONNECTOR (CN6) * OPTION ...........................................16
4.6.1 Paper Near-End Sensor Connector Pin Assignment (CN6)...................................................16
4.6.2 Reference Circuits ..........................................................................................................16
5. OPERATION PANEL ...................................................................................17
5.1 OUTPUT LED .........................................................................................................17
5.2 DETAILS ON ERROR AND LED INDICATION.................................................................17
5.3 FEED SWITCH ........................................................................................................24
5.3.1 Self-printing...................................................................................................................25
5.3.2 Hexadecimal Dump Printing ............................................................................................26
5.3.3 Memory Switch Setting Mode ..........................................................................................27
Page 4

6. INTERFACES .............................................................................................. 28
6.1 BIDIRECTIONAL PARALLEL INTERFACE (IEEE1284) ...................................................28
6.1.1 Specification ..................................................................................................................28
6.1.2 Description of Input/Output Signals .................................................................................29
6.1.3 Connection to Parallel Port ..............................................................................................32
6.2 RS-232C SERIAL INTERFACE ..................................................................................33
6.2.1 Specification ..................................................................................................................33
6.2.2 Description of Input/Output Signals .................................................................................33
6.2.3 Connection to Serial Port.................................................................................................36
6.3 USB INTERFACE.....................................................................................................36
7. FUNCTION SELECTION.............................................................................. 37
7.1 JUMPER ................................................................................................................37
7.2 DIP SWITCH (ONLY SERIAL INTERFACE) ...................................................................37
7.3 MEMORY SWITCHES................................................................................................38
8. PRINT CONTROL COMMANDS ...................................................................40
9. CHARACTER CODE TABLE.......................................................................... 43
9.1 CODE PAGE............................................................................................................43
9.1.1 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC437 (USA, Europe Standard)....................................................43
9.1.2 Codepage 00H to 7FH & Katakana ................................................................................... 44
9.1.3 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC850/858 (Multilingual).............................................................45
9.1.4 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC860 (Portuguese)....................................................................46
9.1.5 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC863 (Canadian-French)............................................................47
9.1.6 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC865 (Nordic)...........................................................................48
9.1.7 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC852 (Eastern Europe).............................................................. 49
9.1.8 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC866 (Russian).........................................................................50
9.1.9 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC857 (Turkish) .........................................................................51
9.1.10 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC864 (Arabic)...........................................................................52
9.1.11 Codepage 00H to 7FH & WPC1252...................................................................................53
9.1.12 Codepage 00H to 7FH & Thaicode18................................................................................54
9.2 INTERNATIONAL CHARACTER CODE TABLE .................................................................55
Page 5

1. GENERAL OUTLINE
・This control board is used for controlling LT222X/232X through computer, etc.
・As it has a variety of functions, it can meet various kinds of applications.
* This specification applies only to control board BD2-2220/2221
* The information contained herein is subject to change without prior notice.
* Transfer, copy, reproduction, or alteration of this document is prohibited without permission of
Citizen Systems Japan Co., Ltd.
1.1
Features
1) Ultra-small design
2) High speed (150 mm/sec) printing
3) Applicable to the width of 80 mm (LT232X) and 58 mm (LT222X).
4) Built-in input buffer
5) Barcode printing (By special command)
6) Free printing layout by page mode
7) Registration of user-defined characters and logos into flash memory
8) Auto cutter control
9) No paper and paper near-end detection
10) Various kinds of functional selection by memory switch
11) Support JIS level 1 and level 2
12) User-defined characters are available. (94 characters)
13) Mounting hole position is the same as that of LT2X20.
1
Page 6
Accessories
1.2
After unpacking the product, make sure the following components are present.
Control board ... 1
Interface cable ... 1 (A cable of 300 mm long)*
Mech FFC ... 1 (With 100-mm-long cable)
* Mini-USB cable is not supplied for USB model.
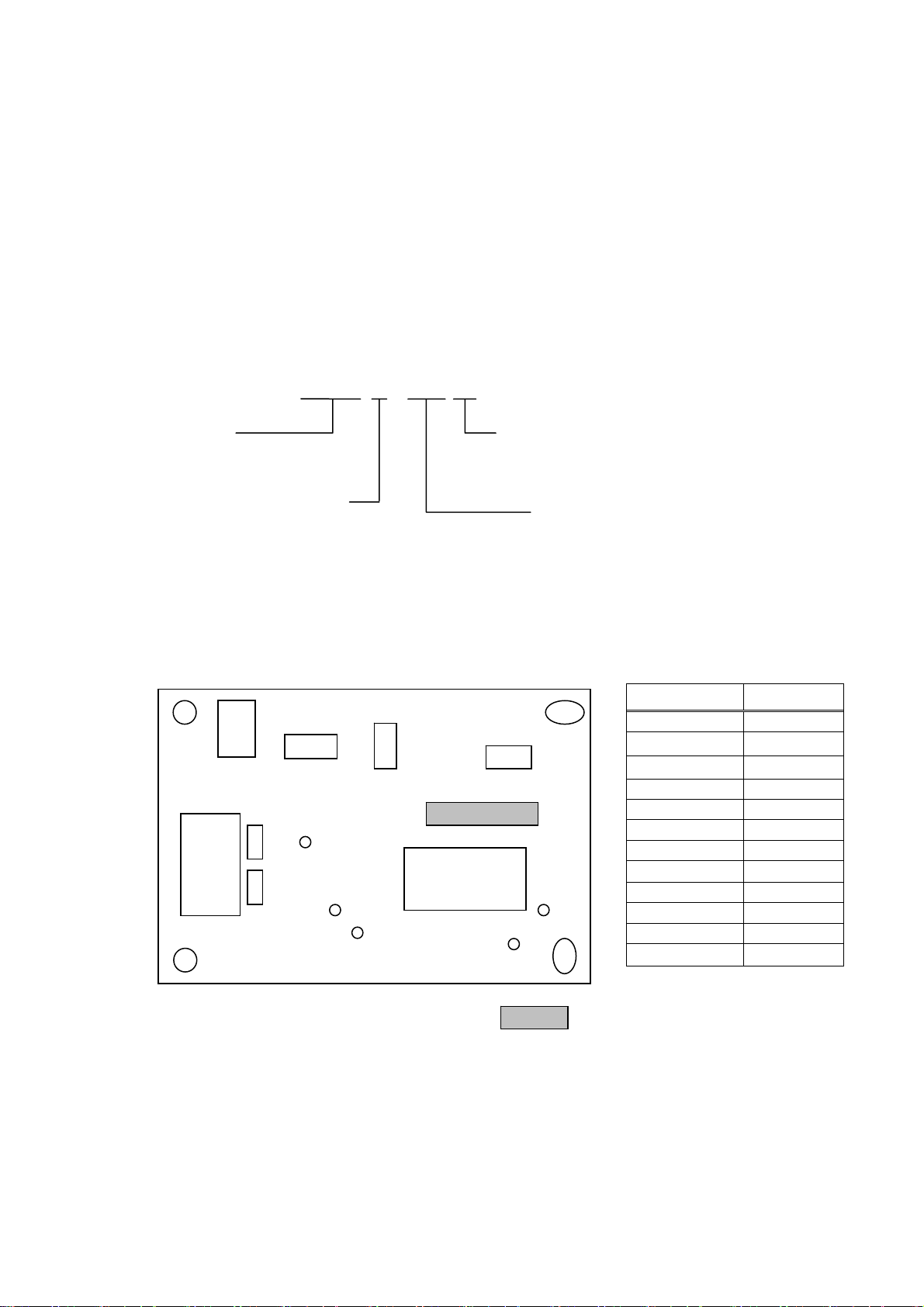
1.3
Model Classification
BD2 ― 222 0 RS J
Model name
Mechanism used
0: LT2X20
1: LT2X21
Destination
J: Japan (Kanji supported)
U: Universal standard
Interface
RS: Serial RS-232C
PA: Parallel IEEE1284
UB: USB
Control board model can be identified by the stamp on the jumper side of the control board.
Stamped designation is shown below.
JP2
BD2-222
JP3 JP5
JP1
JP4
Model Name Designation
BD2-2220RSJ 0RSJ
BD2-2220PAJ 0PAJ
BD2-2220UBJ 0UBJ
BD2-2220RSU 0RSU
BD2-2220PAU 0PAU
BD2-2220UBU 0UBU
BD2-2221RSJ 1RSJ
BD2-2221PAJ 1PAJ
BD2-2221UBJ 1UBJ
BD2-2221RSU 1RSU
BD2-2221PAU 1PAU
BD2-2221UBU 1UBU
Stamped designation:
2
Page 7
V
V
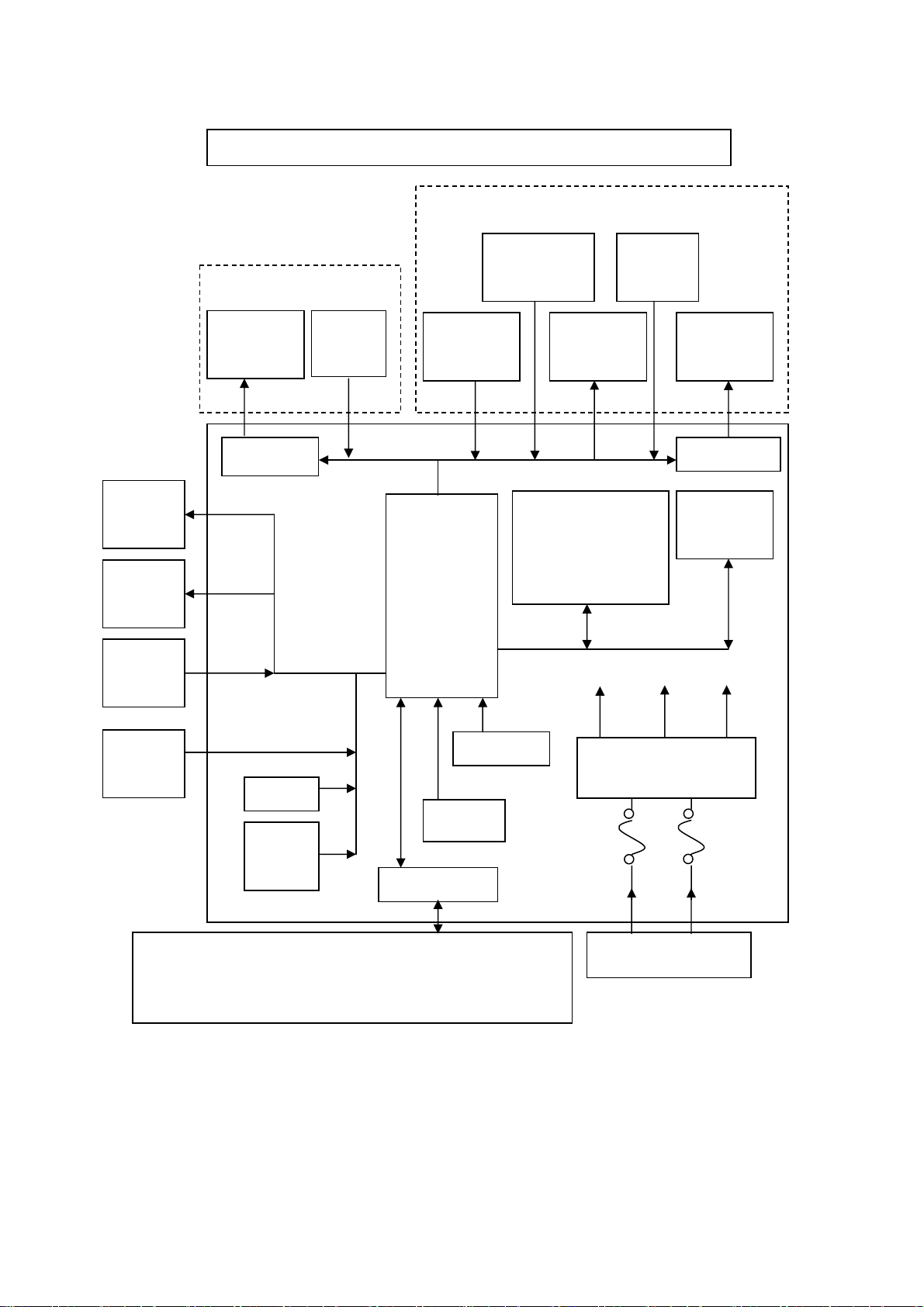
Configuration (Block Diagram)
1.4
BD2-2220/2221 BLOCK DIAGRAM
MECHANISM
CUTTER
HEAD
Thermistor
PE
SENSOR
CUTTER
MOTOR
CUTTER
SW
HEAD UP
SENSOR
PRINTER
HEAD
STEPPING
MOTOR
DRIVER
DRIVER
ERROR
LED
PE LED
CPU
FLASH MEMORY
8Mbit: Foreign
16Mbit: Domestic
SDRAM
16Mbit
SENSOR
PNE
DC5.0V DC3.3
DC24.0
FEED
SW
DIP SW
VOLT
SENSOR
INTERFACE
OSC
POWER SUPPLY
RESET
Serial Interface Parallel Interface USB Interface
RS-232C IEEE1284 Ver 1.1
Centronics
DC24.0V DC5.0V
3
Page 8

2. BASIC SPECIFICATIONS
Printing Specifications
2.1
1) Print method: Line thermal print method (Thermal printing system)
2) Dot configuration: LT222X: 432 dots/line, LT232X:576 dots/line
3) Dot density: 8 dots/mm (203 dpi)
4) Print area: LT222X: Max. 54 mm, LT232X: Max. 72 mm
5) Number of print columns:
LT222X: Max. 36 columns, LT232X: Max. 48 columns (12×24: Font A)
LT222X: Max. 48 columns, LT232X: Max. 64 columns (9×24: Font B)
LT222X: Max. 54 columns, LT232X: Max. 72 columns (8×16: Font C)
LT222X: Max. 18 columns, LT232X: Max. 24 columns (24×24: Kanji Font A)
LT222X: Max. 27 columns, LT232X: Max. 36 columns (16×16: Kanji Font C)
6) Character spacing: Selectable by use of command
7) Print speed: Max. 1200 dot-lines/sec (150 mm/sec)
8) Paper feed: Feed pitch: 0.125 mm
9) Line feed width: 4.23 mm (1/6 inch) settable by user
10) Print head: Line thermal print head
11) Emulation: ESC/POS compliant
Notes:
• The above printing speed is under the condition of 24.0 V, 25°C, printing duty of 12.5%.
• Print speed may be delayed depending on the setting of printing condition or combination of
commands.
4
Page 9
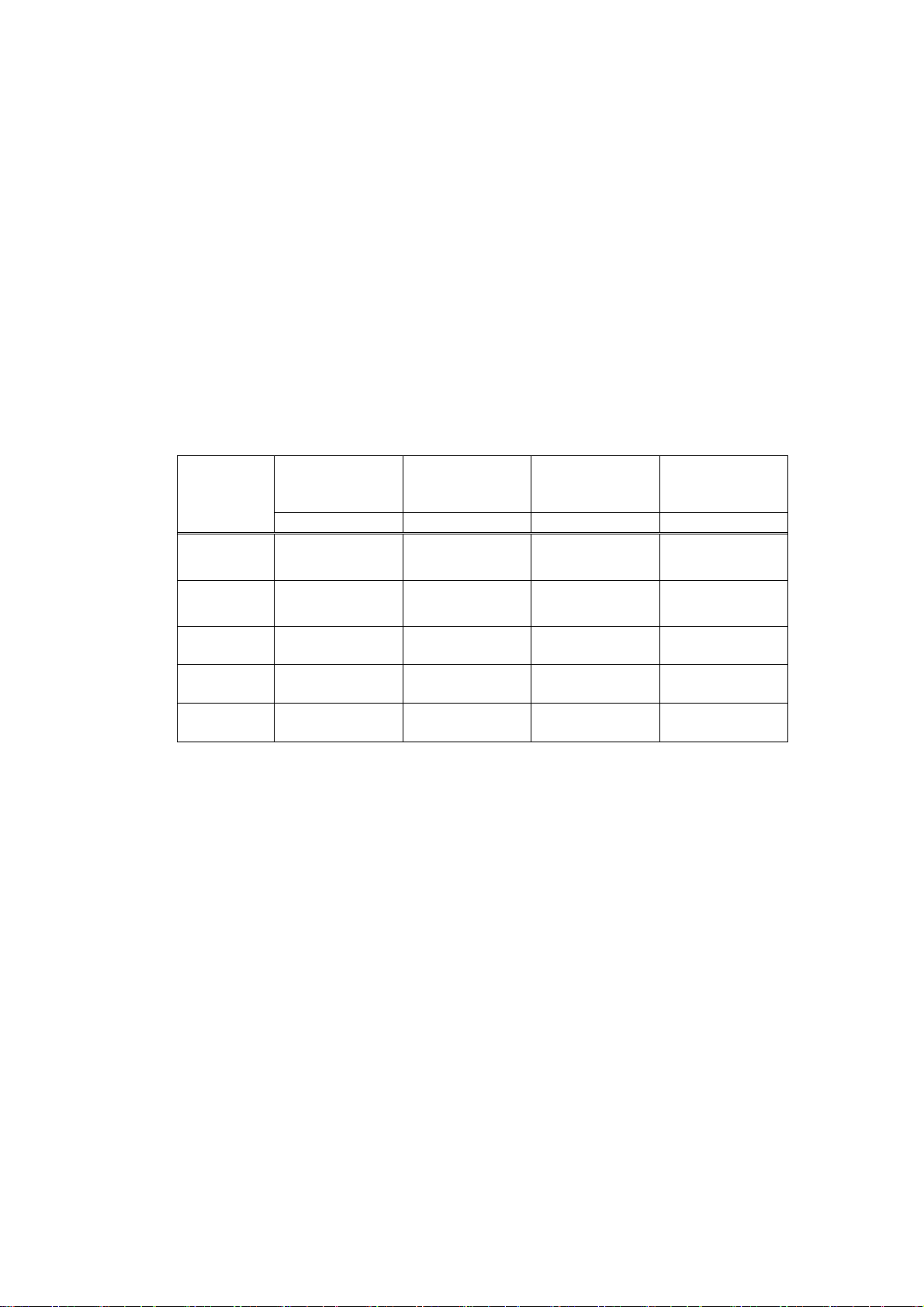
Character and Barcode Specifications
2.2
1) Character type
ANK characters: 96characters
Code pages: 128 characters × 12 pages
International characters: 12 characters × 14 countries
Japanese Kanji: JIS (JIS C6226-1983)
Non-kanji: 577 characters
JIS level 1: 2965 characters
JIS level 2: 3388 characters
(Only when destination is Japan)
2) Character size/configuration
Table 1 Character Size
Font A
12×24
Standard Double Height Double Width
W×H (mm) W×H (mm) W×H (mm) W×H (mm)
1.5×3.0 1.5×6.0 3.0×3.0 3.0×6.0
Double Height
and Double
Width
Font B
9×24
Font C
8×16
Kanji A
24×24
Kanji C
16×16
1.13×3.0 1.13×6.0 2.26×3.0 2.26×6.0
1.0×2.0 1.0×4.0 2.0×2.0 2.0×4.0
3.0×3.0 3.0×6.0 6.0×3.0 6.0×6.0
2.0×2.0 2.0×4.0 4.0×2.0 4.0×4.0
Notes:
• Actual character may be smaller than the above as it includes space inside character font.
• Characters can be enlarged up to 8 times height and width in multiple steps of standard size.
3) Barcode
: UPC-A
: UPC-E
: JAN/EAN-8
: JAN/EAN-13
: ITF
: CODE39
: CODE93
: CODE128
: CODABAR (NW-7)
5
Page 10
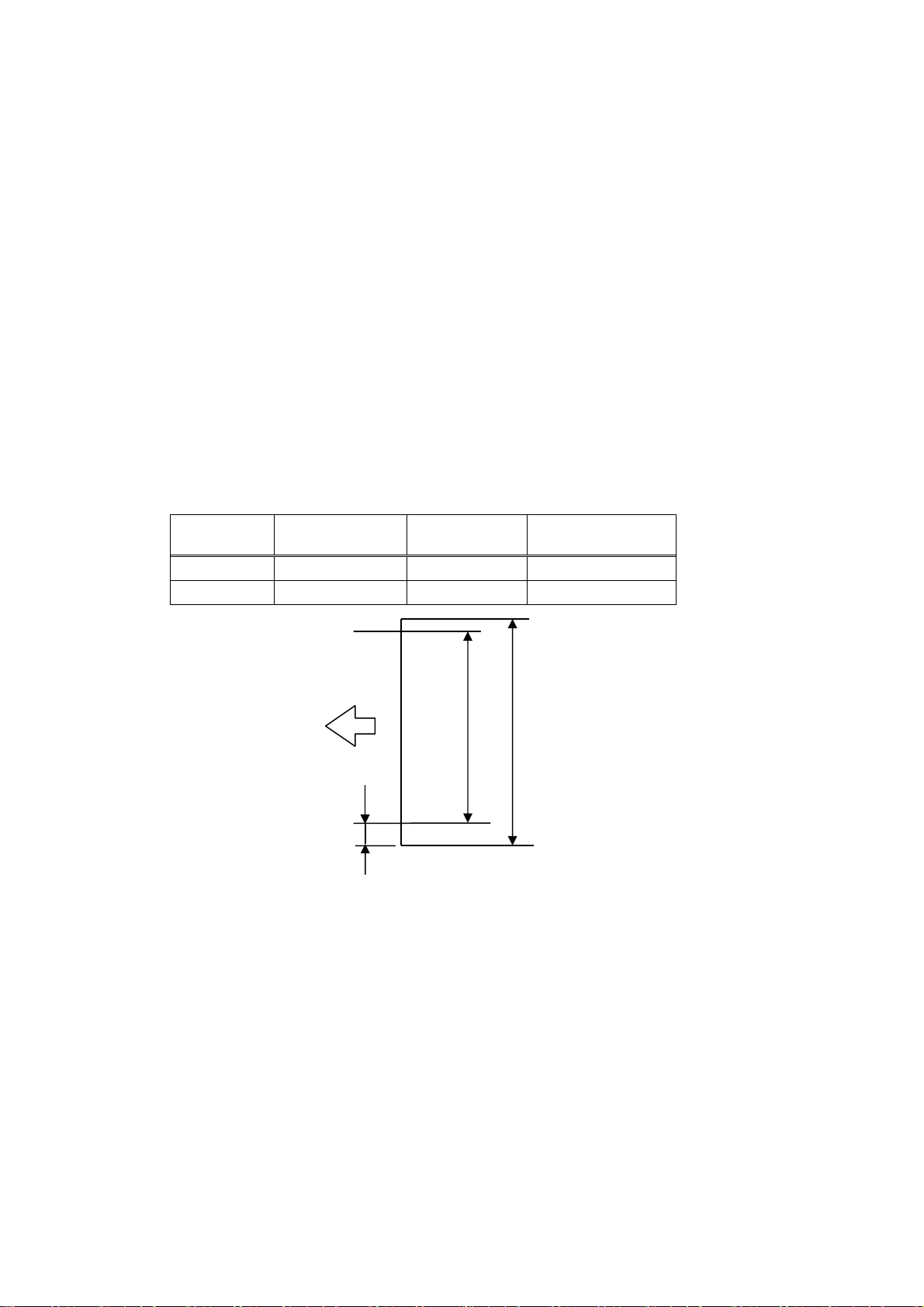
Paper Width
Print Paper Specifications (Thermal Paper)
2.3
1) Paper width : LT222X: 58 +0,-1mm, LT232X: 80 +0,-1mm
2) Paper thickness : 60µm ~ 150µm
3) Recommended paper
Nippon Paper Industries TF50-KS-E2D
Mitsubishi Paper P220AC Or equivalent
Print density setting should be changed according to the type and thickness of paper.
Change the density setting by the Customize value setting GS ( E command. (See “7.3
Memory Switch”.)
*When paper other than the specified, difference in print density may occur.
*Pay full attention to temperature, humidity, and environment when storing printed paper.
Otherwise, the printed data may be lost.
*For the details of paper, refer to the specifications of each mechanism.
4) Effective print width (Print area)
Mechanism
LT222X 58+0,-1 2±2 54
LT232X 80+0,-1 4±2 72
Paper Width
(mm)
Left Margin
(mm)
Effective Print
Width (mm)
Paper feed
direction
HHHHHHH……HHHH
Effective Print Width
Left margin
5) Other
・Chromophoric surface: Roll outside
・Terminating process: Do not apply paste to fix the roll paper and core.
Do not fold paper at the end of the paper.
6
Page 11

Mechanism and Peripherals Used
2.4
The following mechanism and peripheral units can be connected to this control board.
1) Thermal mechanism
58 mm Paper: LT222X
80 mm Paper: LT232X
2) Auto cutter
ACS-220/230 series
3) Paper near-end sensor (Option)
* For the details of specification, etc., refer to the relevant manual.
2.5
Power Supply
2.5.1 Specifications
1) Operating voltage
Driver power supply Vp:+24.0 VDC ±5%
Logic unit power supply Vdd:+5.0 VDC ±5%
:+3.3 VDC ±5% (*+5.0 VDC internal conversion in board)
2) Current consumption
Driver current Ip: Average current: Approx. 0.46 A (At ANK slide)
Peak current: Approx. 4.9 A (At full dot printing)
Logic unit current Idd: Average current: Approx. 230 mA (At ANK slide)
Approx. 200 mA (At standby)
2.5.2 Precautions
1. When powering on, enter Vp within 100 ms after Vdd.
2. When powering off, turn Vdd after Vp.
3. Before connecting or disconnecting the connector, be sure to turn the printer power off.
4. Be sure to use Vdd and Vp within the specified range.
5. Be sure to use the printer by connecting both Vp and P-GND.
6. For the power supply at Vp side, use the power supply with peak current removed.
7
Page 12
Cautions
・Using the power supply other than specified, bad effect may occur in printing operation, etc.
・Using the current without removing peak current may result in degradation of printing quality
depending on the printing status or occurrence of low-voltage error.
・Use the power supply that can be turned off easily to prepare for emergencies.
・Power supply with overvoltage protection, overcurrent protection, and various protection
circuits is recommended.
・This control board requires two different supply voltages. Use sufficient care not to make
erroneous wiring or operation. Error in operation may not only break the control board but
also have bad effect on human body or peripheral equipment.
・Though this control board has CN2 that has the same pin allocation as BD2-2880, it is different
in supply voltage. Use sufficient care in handling this control board.
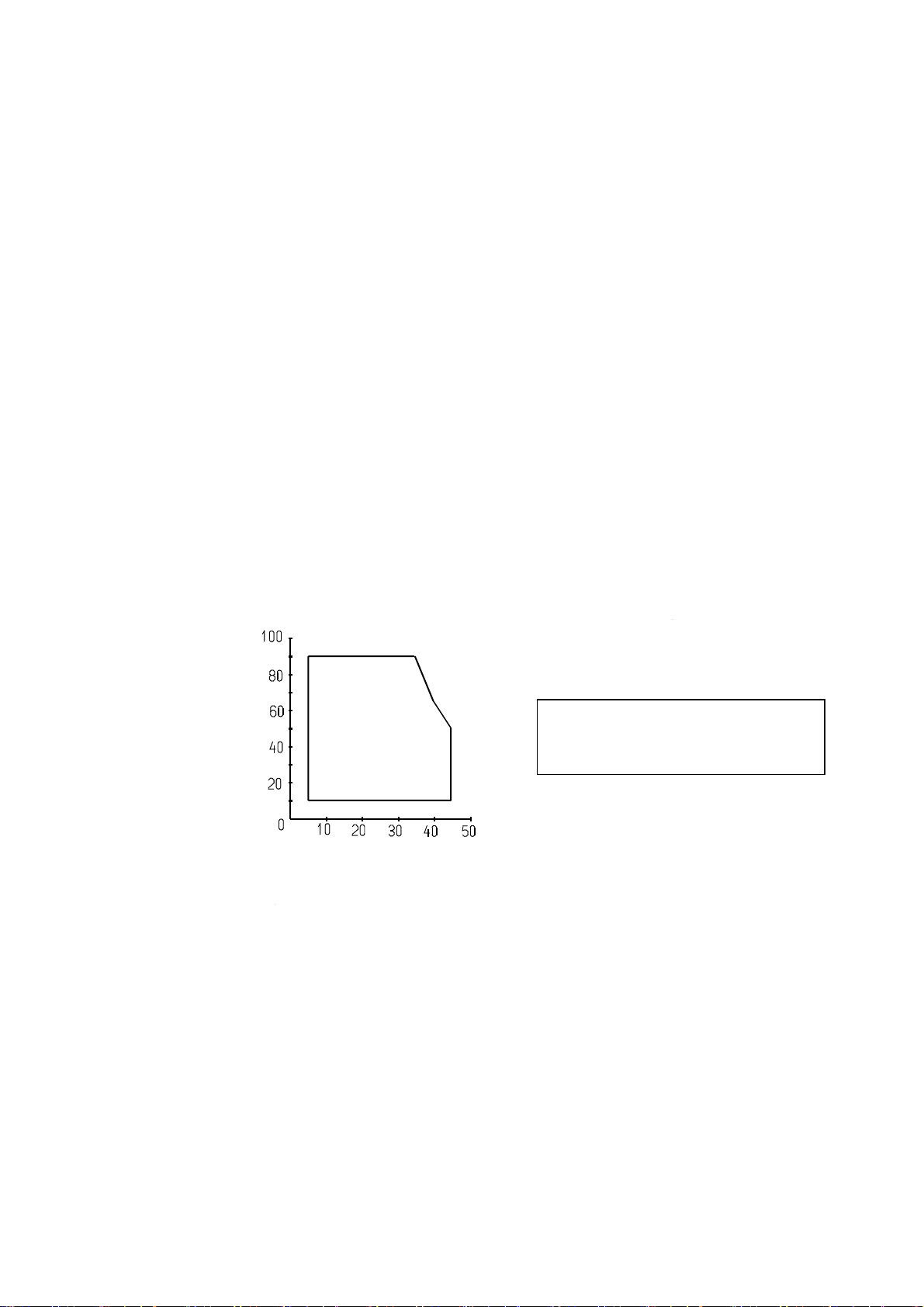
2.6
Environment: Temperature, Humidity
1) Operating
Temperature: 5°C ~ 45°C
Humidity: 10%RH ~ 90%RH (No dew condensation)
Relative humidity (% RH)
2) Storage (excluding roll paper)
Temperature: −20°C ~ 60°C
Humidity: 10% RH ~ 90% RH (No dew condensation)
Note: For storage at high temperature, high humidity, the combination of 40°C, 90% RH (no
condensation) shall be the worst value.
34°C, 90%
40°C, 65%
Operating
environment
range
Environment temperature (°C)
45°C, 50%
Relative humidity (%RH)
Operating environment range
Environment temperature (°C)
8
Page 13
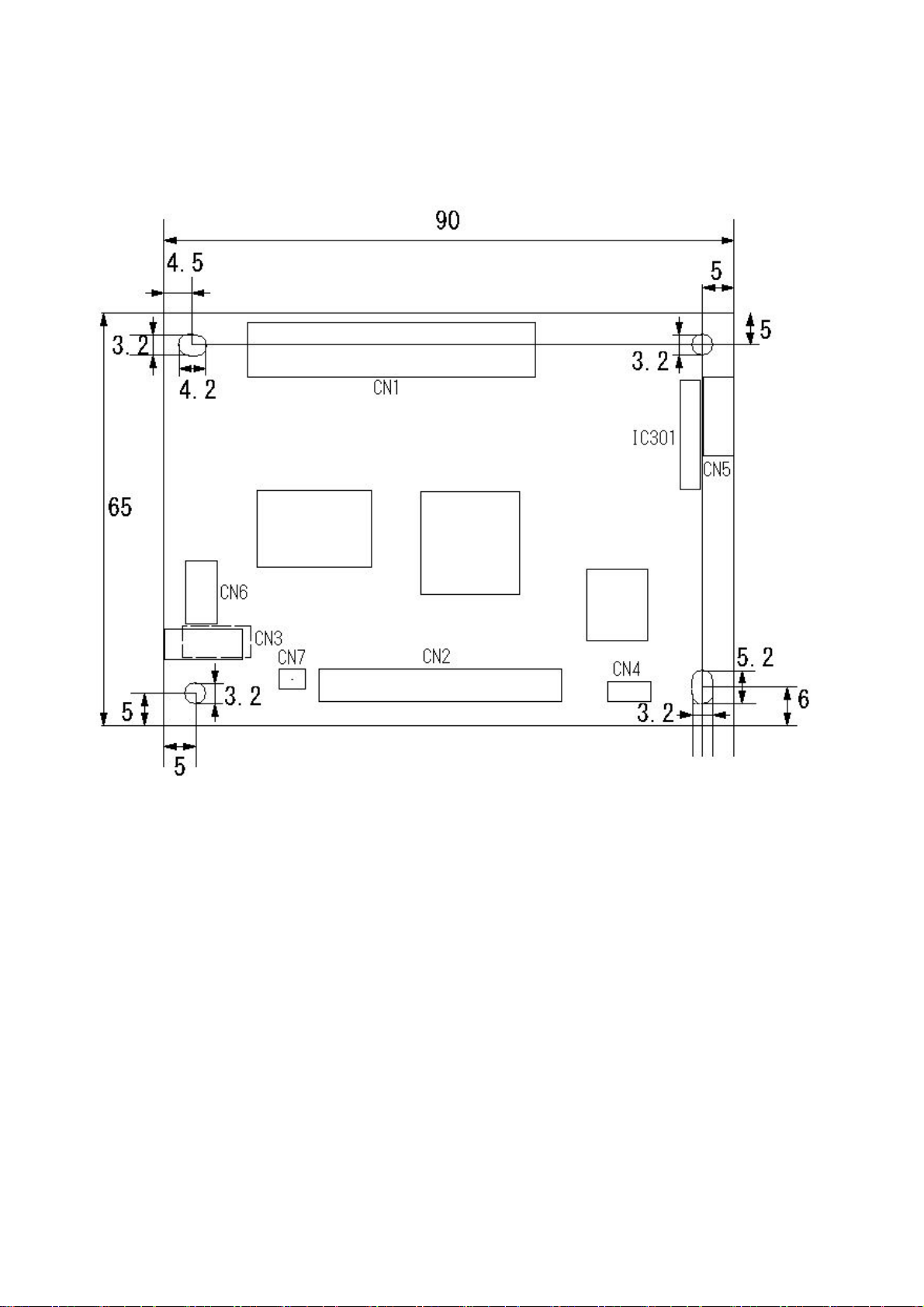
3. APPEARANCE SPECIFICATIONS
Weight : Approx. 37g (Only main body)
Dimensions Unit: mm
* Board size and screw hole position are common to all models.
9
Page 14
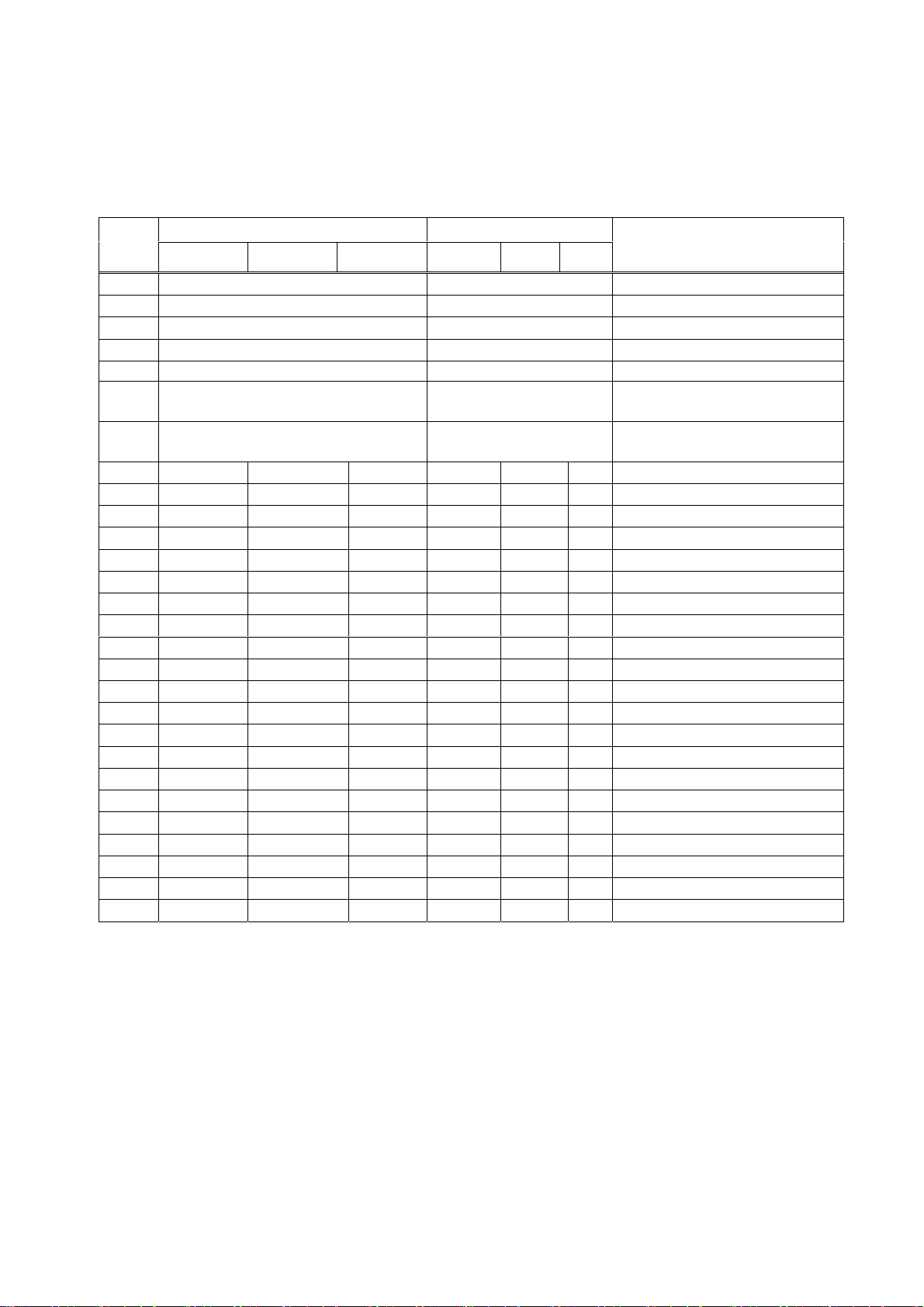
4. Connector Connection
4.1 Interface Connectors
4.1.1 Interface Connector Pin Assignment (CN1)
Pin assignment
Signal Name Input/Output
Pin
RS PA UB RS PA UB
Function
1-2 Vdd
3-4 GND
5-10 Vp
11-16 P-GND
17 nFEED-SW Input FEED Switch (Paper feed)
18 nERROR Output
19 nPEOUT Output
20 DTR N.C N.C Output
21 TXD N.C
22 RXD N.C
23 DSR N.C
24 N.C DATA0
25 N.C DATA1
26 N.C DATA2
27 N.C DATA3
28 N.C DATA4
29 N.C DATA5
30 N.C DATA6
31 N.C DATA7
32 N.C nSTROBE
33 N.C BUSY
34 N.C nFAULT
35 N.C nSELECT
36 N.C PE
37 N.C nACK
38 N.C nAUTOFD
39 N.C nSELECTIN
40 N.C nRESET
Connector used : RS PA 53313-4015 (Molex) UB 53313-2015 (Molex)
Cable supplied
Housing : RS PA 51089-4005 (Molex) UB 51089-2005 (Molex)
Terminal used : 50212 (Molex)
Cable used : AWG26 (UL1007) or equivalent
Cable length : 300mm (Cut at the end)
* Signal name beginning with “n” indicates Low active signal.
-
-
-
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
Output
Input
Input
-
-
-
-
- -
- -
- -
- -
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Input
Input
Input
Circuit PS (+5V)
Circuit GND
Drive PS (+24V)
Drive GND
ERROR output (directly
connectable)
PE LED output (directly
connectable)
Serial interface DTR
Serial interface TXD
Serial interface RXD
Serial interface DSR
-
Parallel interface DATA0
-
Parallel interface DATA1
-
Parallel interface DATA2
-
Parallel interface DATA3
-
Parallel interface DATA4
-
Parallel interface DATA5
-
Parallel interface DATA6
-
Parallel interface DATA7
-
Parallel interface nSTROBE
-
Parallel interface BUSY
-
Parallel interface nFAULT
-
Parallel interface nSELECT
-
Parallel interface PE
-
Parallel interface nACK
-
Parallel interface nAUTOFD
-
Parallel interface nSELECTIN
-
Parallel interface nRESET
10
Page 15

4.1.2 USB Interface Connector Pin Assignment (CN8) * Only USB model
Pin assignment
1 2 3 4 5
Series Min B plug
* Do not use a cable of longer than 5 m.
Pin
1 VBus(+5V)
2 -Data(D-) Input/Output USB D3 +Data(D+) Input/Output USB D+
4 N.C
5 GND
Signal
Name
Input/Output Function
-
-
-
USB PS
Not connectable
USB GND
11
Page 16
V
V
A
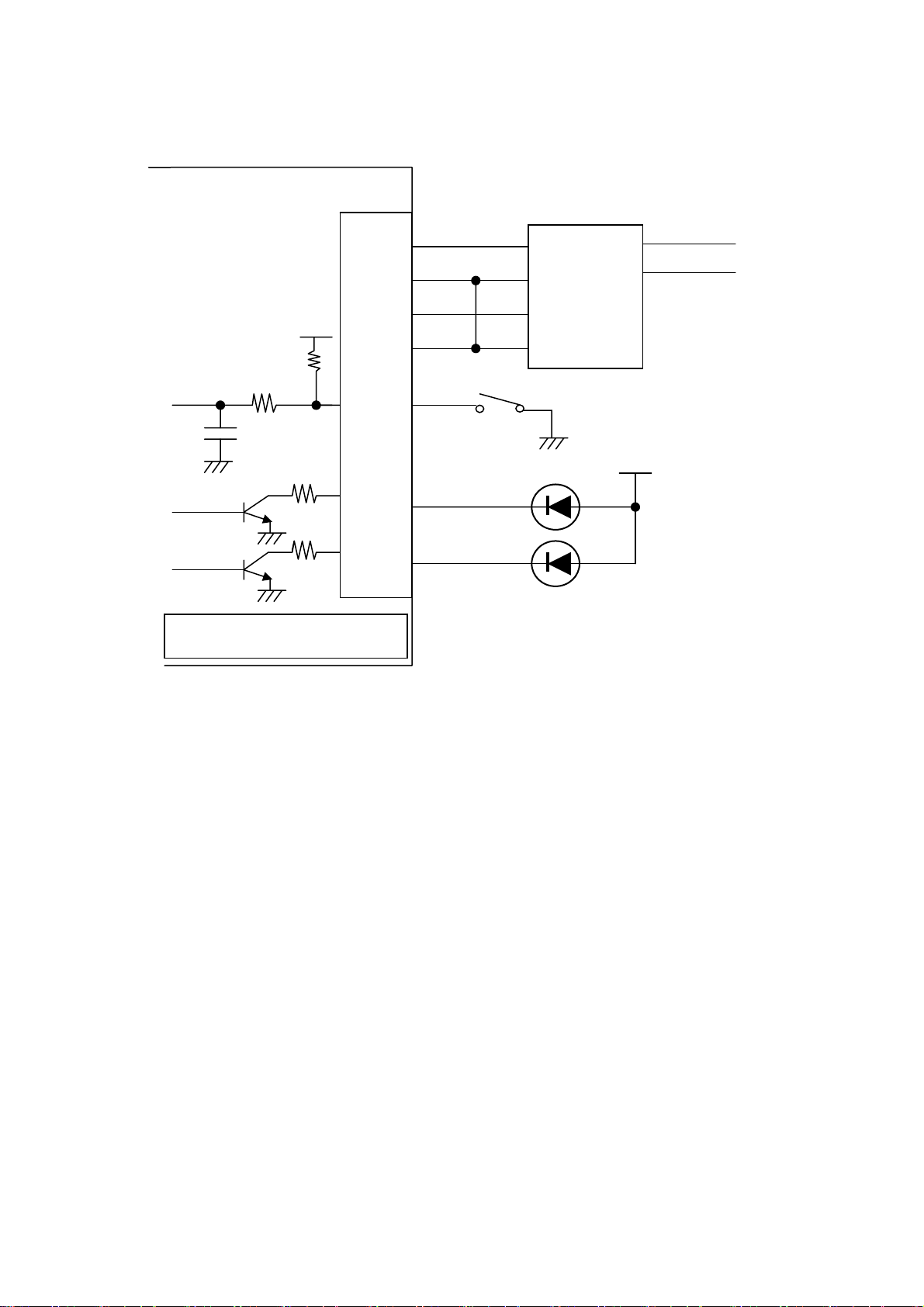
4.1.3 CN1 Connection Example
* For each interface connection, refer to each item.
Vdd
10kΩ
1000pF
100Ω
330Ω
CN1
1、2
3、4
5~10
11~16
17
18
Vdd
GND
Vp
P-GND
FEED SW
ERROR LED
+24
SW
+5
GND
GND
Constant
voltage
PS
GND for power supply or CN1-3, 4
+5V
330Ω
19
PEOUT LED
Control Board
Notes:
1) As resistance 330Ω is inserted in the circuit so that current value of ERROR LED and PEOUT
LED is 10 mA, use the LED with forward voltage of 2 V or so. Using LED exceeding 10 mA
may break the control board.
2) Power supply for circuit (Vdd and GND) will operate if it is applied to only one pin. However,
driving power supply (Vp and P-GND) shall be fed to all pins to retain current capacity.
3) Note that though a ceramic capacitor is provided in the circuit to prevent chattering, great
chattering may occur depending on the switch. In this case, the user is requested to take an
appropriate measure.
4) Do not conduct such operation that only paper feeding continues for more than 5 minutes.
Excessive single operation of paper feed motor may cause failure. * In case of printing
operation (12.5% coloring), continuous operation over 5 minutes causes no trouble.
5) The RESET terminal is pulled up with 3.3 kΩ at the circuit side. If it is not in use, it must be
set as Non Connect.
6) Serial interface is equipped with RS-232C driver and receiver. Be sure to use in RS-232C
level.
7) Unused pin shall be insulated so that cable end may not contact other terminal or part.
C100~240V
5V line of PS or CN1-1, 2
12
Page 17
Mechanism Connector (CN2)
4.2
4.2.1 Mechanism Connector Pin Assignment (CN2)
Pin assignment
Pin
1 ~ 4 Vp - Thermal head PS
5 N.C - N.C
6 CLK Output Clock signal for data transmission
7 LAT Output Print data latch signal
8 N.C STB2 - Output N.C Strobe signal 2
9 STB1 Output Strobe signal 1
10 TM - Thermistor
11 ~ 19 GND - GND
20 TM - Thermistor
21 Vdd - Thermal head driver PS
22 STB3 STB4 Output Strobe signal 3 Strobe signal 4
23 STB2 STB3 Output Strobe signal 2 Strobe signal 3
24 DI Output Print data serial output
25 ~ 28 Vp - Thermal head PS
Connector used: 52045-2845 (Molex) or equivalent
52045-2845 (Molex)or equivalent
* Note that assignment of connector pins and control board pins is reversed.
Signal Name Input/Output Function
LT222X LT232X LT222X LT232X LT222X LT232X
13
Page 18
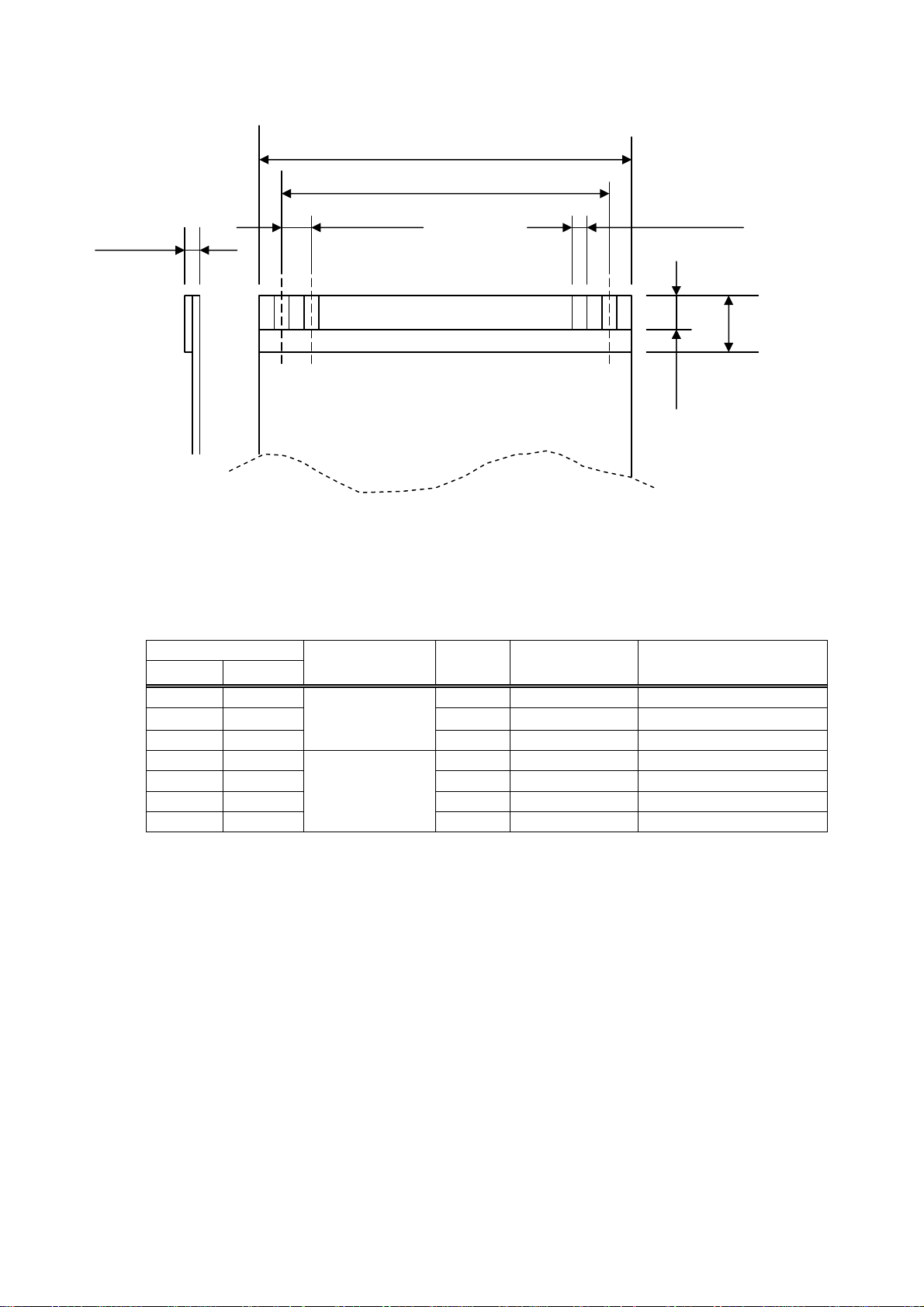
4.2.2 FFC-compliant Cable
36.25±0.1
33.75±0.1
0.3±0.05
1.25±0.05 0.8±0.03
Conductive side
4.3 Head Up, Paper-End Detecting Connector (CN3, CN7)
Min.4
Unit: mm
7
Reinforcing
board
dimension
Pin assignment
Pin
LT2X20 LT2X21
CN3-1 - HU-A Output
CN3-2 CN7-1 GND
CN3-3 CN7-2
CN3-4 CN3-4 PE-C Output
CN3-5 CN3-5 PE-K Input
CN3-6 CN3-6 PE-A Output
CN3-7 CN3-7
Connector used LT2X20 CN3:52045-0745 (Molex) or equivalent
LT2X21 CN3:5597-04CPB (Molex) or equivalent
LT2X21 CN7:53047-0210 (Molex) or equivalent
* In case of LT2X21, 4-pin type is used for CN3 and CN7 is short-circuited by JP4. (Platen
open sensor, if any, shall be removed.)
Sensor
Head Up sensor
Paper sensor
Signal
Name
HU-C Input Head Up signal input
PE-E Input Paper-End signal input
Input/Output Function
-
14
Page 19

Motor Connector (CN4)
4.4
Pin assignment
Pin
1 MOTOR A+ Output Motor driving signal A+
2 MOTOR B- Output Motor driving signal B3 MOTOR A- Output Motor driving signal A4 MOTOR B+ Output Motor driving signal B+
Connector used: 53047-0410 (Molex)
Signal
Name
4.5
Auto Cutter Connector (CN5)
Pin assignment
Pin
1 M+ Output Cutter Motor driving signal M+
2 M- Output Cutter Motor driving signal M3 GND
4 SW Input Cutter Switch input signal
Connector used: 5267-04A-X (Molex)
* Use dedicated cutter (ACS-220/230 series) for cutter.
* If cutter is not used, short the auto cutter feature of JP1.
Signal
Name
Input/Output Function
Input/Output Function
-
GND
15
Page 20

Paper Near-End Sensor Connector (CN6) * Option
4.6
4.6.1 Paper Near-End Sensor Connector Pin Assignment (CN6)
Pin assignment
Pin
1 PNE-A Output Photo interrupter anode
2 PNE-C Input Photo interrupter collector
3 GND
Connector used: 5267-03A-X (Molex)
* At the time of shipment, pins 2 and 3 are short-circuited by JP5 and paper detection is
disabled (always paper present is defined). In actual use, purchase the above connector.
Signal
Name
Input/Output Function
-
Photo interrupter cathode, emitter
4.6.2 Reference Circuits
Photo interrupter is used.
CPU
10kΩ
100Ω
68kΩ
Mechanical switch is used.
Vcc
3.3V
330Ω
1000
Control board
1
2
3
Photo interrupter GP2S24
Sensor
1
NC
2
SW
3
* In the above circuit, reflection type photo interrupter is taken as an example. With the above
sensor, the clearance from paper must be about 1 mm. As electric characteristic varies with
the sensor used, understand the sensor before use.
* Voltage detection range at the control board side (across 2 and 3) is.
0 ~ 0.4V: Paper Present
1V or more: No Paper
This is not warranted in the state other than the above.
Paper
1mm
16
Page 21

5. OPERATION PANEL
5.1 Output LED
1) PE LED
ON : Paper-End detection
OFF : Paper Present detection
2) ERROR LED
ON : Head Up (LT2220/2320 is used), Platen Open (LT2221/2321 is used). Paper-End
Blinking : Hex dump mode, memory switch setting mode, various errors, waiting for macro
execution
OFF : Normal operation
5.2
Details on Error and LED Indication
1) Error to recover automatically
(1) Head overheat error
Explanation: For overheat protection, when the temperature of head increases (approx.
65°C or more), the printing is stopped and ERROR LED blinks.
When the temperature of head declines (approx. 60°C or less), the printing
operation is started automatically.
PE LED: OFF
ERROR LED: Blinks with long illumination at ON
Restore Condition: Automatically restored by temperature decrease
PE LED ERROR LED
OFF
Blinks with long
illumination at ON
17
Page 22

Head Up error (LT2220/2320 is used and MSW3-8 OFF is set.)
(2)
Explanation: ERROR LED blinks during printing and when Head Up is set (with Head Up
lever raised).
PE LED: OFF
ERROR LED: Blinks with long illumination at ON
Restore Condition: Set Head Down (with Head Up lever down).
PE LED ERROR LED
OFF
(3) Platen Open Error (LT2221/2321 is used and MSW3-8 OFF is set.)
Explanation: ERROR LED blinks during printing and when Platen Open is set (with Platen
Open lever held down and platen retaining unit opened).
PE LED: OFF
ERROR LED: Blinks with long illumination at ON
Restore Condition: Close platen (close platen retaining unit and raise the Platen Open
lever).
PE LED ERROR LED
OFF
Blinks with long
illumination at ON
Blinks with long
illumination at ON
18
Page 23

2) Restorable error
(1) Head Up error (LT2220/2320 is used and MSW3-8 ON is set.)
Explanation: ERROR LED blinks during printing and with Head Up.
PE LED: OFF
ERROR LED: Blinks with long illumination at ON
Restore Condition: After Head Down, clear the error by a command.
* For details of DLE ENQ 1, DLE ENQ 2, and DLE DC4 (fn=8), refer to Command Reference.
PE LED ERROR LED
OFF
(2) Platen Open error (LT2221/2321 is used and MSW3-8 ON is set.)
Explanation: ERROR LED blinks during printing and when platen is opened.
PE LED: OFF
ERROR LED: Blinks with long illumination at ON
Restore Condition: After Platen Close, clear the error by a command.
* For details of DLE ENQ 1, DLE ENQ 2, and DLE DC4 (fn=8), refer to Command Reference.
PE LED ERROR LED
OFF
Blinks with long
illumination at ON
Blinks with long
illumination at ON
19
Page 24

Cutter lock error
(3)
Explanation: Cutter operation is disabled. Abnormality occurred.
PE LED: OFF
ERROR LED: ERROR LED repeats blinking 2 times fast and blinking 1 time slow.
Restore Condition: Remove the fault and restore by pressing the FEED switch (with
MSW3-1 set to OFF) or by DLE EMQ 1 or 2 command (with MSW3-1
set to ON).
PE LED ERROR LED
OFF
3) Error impossible to restore
(1) Memory check error
Explanation: CPU self-diagnoses the circuit. When it detects abnormality in external RAM
PE LED: OFF
ERROR LED: Blinking quickly
Restore Condition: Irreparable
memory, ERROR LED blinks quickly.
However, it can be restored by turning power OFF, replacing external
RAM, and removing the cause of the abnormality.
PE LED ERROR LED
OFF
Repeats blinking 2 times fast
and blinking 1 time slow.
ERROR LED blinks
quickly.
20
Page 25

Low voltage error
(2)
Explanation: Occurs when the Vp voltage supplied to the printer is lowered.
If occurred, immediately turn the power OFF.
PE LED: OFF
ERROR LED: ERROR LED repeats blinking 3 times fast and blinking 1 time slow.
Restore Condition: Irreparable
However, it can be restored by turning the power OFF and then
raising the Vp voltage to the range of DC 16.9 to 27.8 V.
PE LED ERROR LED
OFF
(3) High voltage error
Explanation: Occurs when the Vp voltage supplied to the printer is raised.
If occurred, immediately turn the power OFF.
PE LED: OFF
ERROR LED: ERROR LED repeats blinking 4 times fast and blinking 1 time slow.
Restore Condition: Irreparable
However, it can be restored by turning the power OFF and then
raising the Vp voltage to the range of DC 16.9 to 27.8 V.
PE LED ERROR LED
OFF
Repeats blinking 3 times fast
and blinking 1 time slow.
Repeats blinking 4 times fast
and blinking 1 time slow.
21
Page 26

) Others
4
(1) Paper near-end
Explanation of status: When the diameter of the roll paper deceases to a certain degree
(* differs with the status of using Near-End sensor), the Paper
Near-End sensor responds and allows PE LED to light to indicate
roll paper is low.
PE LED: ON
ERROR LED: OFF
Restore Condition: Set another paper roll.
PE LED ERROR LED
ON OFF
(2) Paper-end
Explanation of status: When roll paper becomes empty, the paper sensor in the paper
path near the print head detects the paper end and causes PE LED
and ERROR LED to light and the printing operation to stop.
PE LED: ON
ERROR LED: ON
Restore Condition: Set another paper roll.
PE LED ERROR LED
ON ON
22
Page 27

Head Up (when LT2220/2310 is used)
(3)
Explanation: When Head Up is set, ERROR LED lights.
PE LED: OFF
ERROR LED: ON
Restore Condition: Set Head Down.
PE LED ERROR LED
OFF ON
(3) Platen Open (when LT2221/2321 is used)
Explanation: When Platen is opened, ERROR LED lights.
PE LED: OFF
ERROR LED: ON
Restore Condition: Close Platen.
PE LED ERROR LED
OFF ON
(4) Waiting for a macro execution
Explanation: The printer is waiting for a macro execution by ESC/POS’s commands.
PE LED: OFF
ERROR LED: ERROR LED blinks slowly.
Restore Condition: Push the FEED SW.
PE LED ERROR LED
OFF
Repeats blinking slow.
23
Page 28

Feed Switch
5.3
Function
• When pressed once, paper feed of one line occurs based on the amount of line feed set by ESC 2
and ESC 3.
However, paper feed is not available in the following cases.
(1) When the FEED switch is set to disable by ESC c 5
(2) When paper-end detector detected no paper
(3) With Head Up. (LT2220/2310 is used)
(4) With Platen Open (LT2221/2321 is used)
(5) When error occurred
(6) When waiting for macro execution (execution of macro by the FEED switch), pressing the
FEED switch causes the macro to be executed.
• At the time of Cutter Lock error, pressing the FEED switch after removing the cause clears the
error. (Depending on the status of MSW3-1)
24
Page 29

5.3.1 Self-printing
1) Function
Function to enable the printer setting status to be verified by printing
2) Start of self-printing
When the power is turned on with the FEED switch pressed and held in print ready state,
printer status is printed on the roll paper.
Explanation of printed item is as shown below.
(1) Printer type name BD2-2220
(2) ROM version VX.XXXXXX
(3) Mechanism used
(4) Interface setting
(5) Buffer size
(6) Content of DIP switch setting (Only serial interface)
(7) Jumper settings (Only JP1 to 3. JP4, 5 are not printed.)
(8) Content of memory switch
(9) Font A (20H ~ FFH)
(10) Font B (20H ~ FFH)
(11) Font C(20H ~ FFH)
(12) Kanji Font A 192 characters (Only Kanji specification)
(13) Kanji Font C 192 characters (Only Kanji specification)
(14) Line is fed up to cut position.
3) End of self-printing
Print a specified print pattern and perform resetting after printing for initialization.
25
Page 30

5.3.2 Hexadecimal Dump Printing
1) Function
Prints the data sent from the host in hexadecimal code and the corresponding characters.
2) Starting hexadecimal dump
With paper set and Head Up (or Platen Open), turn the power on while pressing and holding
the FEED switch. Set Head Down (or Platen Close). Then “HEX dump print mode” is printed
on the roll paper followed by the printing of data received thereafter in hexadecimal numbers
and corresponding characters.
Example: When dump printing is executed in Kanji mode.
Example: When dump printing is executed in non-Kanji mode.
• During hexadecimal dump, command other than Real time command has no function.
• When print data is less than one line, offline factor occurs to print the line.
3) End of hexadecimal dump
• Press the FEED switch consecutively three times. In this case “Completed” is printed and
paper is fed to the cut position and then a reset occurs. Otherwise, turn the power OFF or
perform a reset by the I/F signal.
HEXダンプ印字モード
1B 40 31 32 33 34 35 36 .@123456
37 38 39 30 0A 7890.
HEX DUMP PRINT MODE
1B 40 31 32 33 34 35 36 .@123456
37 38 39 30 0A 7890.
Completed
Completed
26
Page 31

5.3.3 Memory Switch Setting Mode
1) Settable memory switch
MSW1、MSW2、MSW3
2) Starting memory switch setting mode
With paper set and Head Up (or Platen Open), turn the power on while pressing and holding
the FEED switch and then press the FEED switch twice, set Head Down (or Platen Close) to
start the setting mode.
After the setting mode is started, the guidance of setting content and operation method is
printed.
3) Selecting memory switch
By pressing FEED SW shortly (less than 500 ms), the memory switches to be set is selected in
the following order.
In doing so, the status of selected memory switch is printed. However, when f is selected,
the verification of flash memory writing is printed.
(1) MSW1
(2) MSW2
(3) MSW3
(4) Recording / Initialization of the setting
* By pressing the FEED switch long (2s or more) when c to e is selected, setting the
selected memory switch is started. (Goes to the following 4) Setting memory switch.)
* By pressing the FEED switch long when (4) is selected, current memory switch settings are
all written into the flash memory and Reset operation is carried out. (Goes to the
following 5) Terminating memory switch setting mode.)
By pressing the FEED switch long with Head Up (or Platen Open) when (4) is selected, a reset
operation is executed with current memory switch settings discarded and factory setting
restored. (Goes to the following 5) Terminating memory switch setting mode.)
4) Setting memory switch
(1) Print the status of bit which is currently set.
(2) Pressing the FEED switch short (less than 500 ms) causes the selected bit to be inverted.
Here, if the bit is ON, error LED lights.
(3) Pressing the FEED switch long (more than 2s) causes current bit to be saved. If any
change occurs, the status of the bit is printed.
Setting the following bits is started.
The order of change of bit is shown below.
Bit 0 → Bit 1 →…→ Bit 6 → Bit 7 → Bit 0 →…
(4) The setting is terminated with Head Up (or Platen Open). Then by Head Down, current
status of memory switch is printed and returns to 3) Selecting memory switch.
5) Terminating memory switch setting mode
After setting, the settings are saved and initializing operation (Reset) is carried out and
normal printable condition is restored.
27
Page 32

6. INTERFACES
6.1 Bidirectional Parallel Interface (IEEE1284)
6.1.1 Specification
1) Compatibility Mode (Host → Printer Communication: Centronics Compliant)
(1) Outline
Compatibility Mode is a standard of Centronics interface that has been used for long.
(2) Specification
Data transfer system: 8 bit parallel
Synchronization: By the nStrobe signal supplied from outside
Handshake: By the nAck signal and Busy signal
Signal level: All signals are TTL compatible.
2) Reverse Mode (Printer → Host Communication)
Transfer of status data from this printer to the host is made in the Nibble or Byte Mode.
(1) Outline
This mode specifies the data transfer from the asynchronous printer controlled by the
host.
Data transfer in the Nibble Mode is carried out through existing control line and data is
transferred in steps of 4 bits (Nibble).
In the Byte Mode, data is transferred through the 8-bit data line treated for bidirectional
transmission.
In any case, as concurrent execution with Compatibility Mode is not available,
communication is made in half duplex mode.
When using this mode, use CN1-38 and 39 pins in addition to the parallel interface
terminal of the interface cable.
CN1-38 pin: nAUTOFD
CN1-39 pin: nSELECTIN
Unless these two pins are used, bidirectional communication cannot be implemented. If
you don’t want to use bidirectional communication, set the terminal to be Non Connect.
* The first “n” of a signal name indicates “LOW” active signal. If any one of the above
signals is missing, bidirectional communication is impossible. Always use twisted pair line
for signal lines of interface while connecting the return side to the signal ground level. All
the interface conditions shall be based on C-MOS level and satisfy the following
characteristics. Rising and falling time of each signal shall be 0.5 µs. Never carry out
data transfer by ignoring the nAck signal or Busy signal. Otherwise, data transfer may
result in loss of data. Interface cable shall be minimum necessary length.
28
Page 33

6.1.2 Description of Input/Output Signals
1) Input/Output Signals
Explanation of input/output signals
[1] Input/Output Signals (Compatibility Mode)
(1) Input signals to the printer
・DATA0 ~ 7: 8 bit parallel signal (positive logic)
・nSTROBE: Strobe signal for reading out 8-bit data (negative logic)
・nRESET: Applies reset by the nRESET signal in Compatibility Mode.
(Can be disabled by the setting:Msw3-3)
Reset signal is invalid for nSelectIn/1284-Active “HIGH”.
nSELECT
nRESET
150 msec min
・nSELECTIN : Signal to set “HIGH” when transferring to the IEEE 1284 mode
(negative logic)
(2) Output signals from the printer
・nACK: 8-bit data request signal (negative logic)
・BUSY: Signal to indicate the printer is in the Busy state.
State to become BUSY
1. Period from Reset (including reset by NV memory write
command, I/F signal, and test print command) or just after
printer power on to printer operation ready state.
2. Under test printing
3. Input buffer full state (Refer to “(4) Buffer full state”.)
4. During Head Up (or Platen Open)
5. Under line feeding with FEED switch
6. Waiting for pressing FEED switch at the execution of macro
7. No paper state
8. Error state
BUSY regardless of memory SW setting under the above 1 to 3
conditions.
Does not become BUSY in other case as specified by setting.
29
Page 34

・SELECT: Always non-active (“LOW”).
・nFAULT: Signal to set “LOW” when the printer is in the error state (negative
logic).
・PE: Signal to be output with No paper or near-end state (by command
setting) (positive logic)
Note: When using a command followed by FROM writing, printer may temporarily
become BUSY (DTR) at the time of write operation. In this case, as the
printer cannot make any processing, data transmitted may possibly be
discarded.
2) Electrical Characteristics
[1] Input signal level (nStrobe, Data0 ~ 7)
All input signals are C-MOS level.
”HIGH ” level: 2.0V min.
”LOW ” level: 0.8V max.
[2] Output signal level
All output signals are C-MOS level.
”HIGH ” level: 4.4V min.
”LOW ” level: 0.1V max.
[3] I/O conditions
All input/output signals are pulled up with 3.3 kΩ.
[Printer side] [Host side]
Vcc
Twisted pair wire
[Printer side] [Host side]
Vcc
Twisted pair wire
3.3KΩ
3.3KΩ
30
Page 35

T2T6 T1T3T4T
3) Timing chart (Compatibility Mode)
Data input and print timing
Power supply
DATA
nSTROBE
BUSY
nACK (Note)
5
T1,T2,T3 : 0.5 µs MIN
T4 : 270ns MAX
T5 : 2.3 µs TYP
T6 : 1200ms MIN (At power on)
Figure Timing Chart
Note: ACK output position can be changed to ACK in BUSY, ACK while BUSY, or ACK after
BUSY by the setting of customize value.
4) Buffer full state
Buffer full state is when the remaining capacity of input buffer is as shown below.
Table Input Buffer Full
Set Value Buffer Full Clear
4K bytes Remaining 128 bytes Remaining 256 bytes
45 bytes Remaining 16 bytes Remaining 26 bytes
・When the remaining capacity of input buffer is 0 byte, data received is read and
discarded.
31
Page 36

5) Reverse Mode (Nibble/Byte) mode allows status to be transmitted from the printer.
(Using GS a, DLE EOT n, GS r, of GS I command)
・The transmitting buffer of the printer is 99 bytes. The host must transfer to Reverse
Mode to prevent loss of status. Being in the Reverse Idle state is desired when using
ASB. If this is not possible, always monitor the presence or absence of the transmitting
data from the printer. The ASB not transmitted but accumulated is transmitted
together (OR) with the latest status.
・Identification of information on each status is available.
Command, Code Status
GS I
GS r
XON
XOFF
DLE EOT
ASB (1st byte)
ASB (2nd byte)
6.1.3 Connection to Parallel Port
1) Connection to 36-pin/25-pin parallel port
CN1
36-pin
Parallel interface
Identification of Status
<0**0****>B
<0**0****>B
<00010001>B
<00010011>B
<0**1**10>B
<0**1**00>B
<0**0****>B
CN1
25-pin
Parallel interface
2) Connection to other parallel port
To connect to the connector other than the above, verify the status of various signals and
connect properly.
32
Page 37

RS-232C Serial Interface
6.2
6.2.1 Specification
1) Synchronization: Asynchronous
2) Baud rate
2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200 bps (User selection)
3) Word configuration
Start bit: 1 bit
Data bit: 7 bits or 8 bits (User selection)
Parity bit: Odd, even, or no parity (User selection)
Stop bit: 1 bit or more
4) Signal polarity
RS-232C
・Mark =Logic ”1” (-3V to-12V)
・Space =Logic ”0” (+3V to +12V)
6.2.2 Description of Input/Output Signals
1) Input/Output Signals
(1) RD
Receive Data
When the host is connected, the unstable TD signal that can occur at the rise (fall) of
host power is defined as a break signal and the data is read and discarded.
(When the host power is turned off, the host may cause unstable state in TD. Printing
of such data shall be avoided.)
(2) TD
Transmit Data
(3) DSR
When DTR/DSR control is selected, data is transmitted after confirming that this signal
is a space.
When XON/XOFF control is selected, data is transmitted by ignoring DSR.
(4) DTR
Space sets the printer is in the Busy state and mark sets the printer in the Ready state.
Condition to become Busy can be switched by the setting (MSW1-3).
33
Page 38

・State to become BUSY
1.Period from Reset (including reset by NV memory write command, I/F signal, and
test print command) or just after printer power on to printer operation ready state.
2.Under test printing
3.Input buffer full state (Refer to “(2) Buffer full state”.)
4.During Head Up (or Platen Open)
5.Under line feeding with FEED switch
6.Waiting for pressing FEED switch at the execution of macro
7.No paper state
8.Error state
BUSY regardless of memory SW setting under the above 1 to 3 conditions. Does not
become BUSY in other case as specified by setting.
Note: When XON/XOFF control is selected, mark state occurs only in the state of 1
and 2. In other case, space state is set. Used to know the status of
connection between the printer and host.
The state other than item 3 is defined as offline.
XON/XOFF output condition
・XON transmission
1.Period from Reset (includin g reset by NV memory write command, I/F signal,
and test print command) or just after printer power on to printer operation
ready state.
2.When input buffer full state is cleared. Does not output if the printer is
offline even memory switch setting is OFF.
3.When the printer changed from offline to online. Does not output in buffer
full state.
・XOFF transmission
1.When input buffer becomes buffer full state.
2.When the printer changed from online to offline. Does not output in buffer
full state.
34
Page 39

2) Buffer full state
Buffer full state is when the remaining capacity of input buffer is as shown below.
Table Input Buffer Full
Set Value Buffer Full Clear
4K bytes Remaining 128 bytes Remaining 256 bytes
45 bytes Remaining 16 bytes Remaining 26 bytes
・When the remaining capacity of input buffer is 0 byte, data received is read and
discarded.
3) Data receive error
When any of the following error occurs, data is printed as “?” or read and discarded
(Msw1-4).
・Parity error
・Framing error
・Overrun error
Note: When a command accompanying flash ROM write is used, the printer may
become BUSY (DTR) temporarily at write operation. In this case, as the printer
cannot process anything, the transmitted data may possibly be discarded.
4) Electrical Characteristics
[1]RS-232C circuit (MAX 232 or equivalent)
Input (RD, DSR)
[Printer side] [Host side]
Output (DTR, TD)
35
Page 40

6.2.3 Connection to Serial Port
1) Connection to 25-pin/9-pin serial port
CN1
25-pin
Serial interface
CN1
9-pin
Serial interface
*The above wiring is an example of standard connection to the host. If the cable
is relayed, it is necessary to take such measures as connecting DTR/DSR and
RXD/TXD reversely, etc.
2) Connection to other serial port
To connect to the connector other than the above, verify the status of various signals and
connect properly.
6.3
USB Interface
(1) Whole specification: Based on the specification of USB1.1
(2) Communication speed: USB full-speed mode (12 MHz)
(3) Communication method: USB bulk forwarding method
(4) Power supply: 0 mA (Power is supplied from the printer.)
36
Page 41

7. Function Selection
When using this control board, some functions can be set to default.
7.1
Jumper
Turn the printer power off before changing jumper setting.
Jumper No. Function Open Short
JP1 Auto cutter Enable ●Disable
JP2 Mechanism used ●LT2220/2221 LT2320/2331
JP3 Auto loading ●Enable Disable
JP4* Platen Open sensor ●Enable Disable
JP5 PNE sensor Enable ●Disable
* Disabled (Short) for BD2-2221.
●Default (factory setting)
7.2
DIP switch (Only Serial Interface)
DIP switch is located on the RS-232C serial interface board.
Change the DIP switch setting with power set to OFF.
Switch
No.
1
2 Handshake
3 Bit length 7 bits ● 8 bits
4 Parity check With parity ● None
5 Parity selection Even parity ● Odd parity
6
7
8 Reserved
● Default (factory setting)
Selecting Baud Rate
Switch No.
Baud Rate (bps)
2400 OFF OFF
4800 ON OFF
9600 ● OFF ● ON
19200 ON ON
● Default (factory setting)
Baud rate (38400, 57600, 115200 bps) other than the above can be set by command.
Function ON OFF
Communication
condition setting
method
Baud rate selection See “Selecting Baud Rate” below.
● Depend on DIP switch
setting
XON/XOFF ● DTR/DSR
-
6 7
Depend on customer’s
value setting.
● Fixed
37
Page 42

Memory Switches
7.3
Memory switch is a generic name for the following:
Memory switches MSW1, MSW2, and MSW3
Customize value
Serial Interface Communication Conditions
1) Memory switches MSW1, MSW2, and MSW3
Memory switch setting table
No. Function OFF ON
MSW1-1 Power ON notice setting ● Enable Disable
MSW1-2 Input buffer ● 4K bytes 45 bytes
MSW1-3 Busy condition ● Full/Off line Buffer full
MSW1-4 Receive error character ● Character “?” Disable
MSW1-5 CR mode ● Disable Enable
MSW1-6 Reserved ● Fixed ―
MSW1-7 DSR signal selection ● Disable Enable
MSW1-8 Reserved ● Fixed ―
MSW2-1 Reserved ― ● Fixed
MSW2-2 Reserved ― ● Fixed
MSW2-3 Buffering ● Disable Enable
MSW2-4 Full digit printing ● Line feed WaitData
MSW2-5 Head Down restore * ● Next Top
MSW2-6 Reserved ― ● Fixed
MSW2-7 Reserved ● Fixed ―
MSW2-8 Reserved ● Fixed ―
MSW3-1 Auto Cutter recovery ● L/F Enable L/F Disable
MSW3-2 Reserved ● Fixed ―
MSW3-3 Parallel Reset ● Reset Ignored
MSW3-4 Reserved ● Fixed ―
MSW3-5 Reserved ● Fixed ―
MSW3-6 Reserved ● Fixed ―
MSW3-7 Reserved ● Fixed ―
MSW3-8 Head Up in printing * ● Automatic recovery Recoverable error
● Default (factory setting)
* When LT2221/2321 is used, function for Platen Close/Platen Open is applied.
38
Page 43

2) Customize value
Customize value can be set by the GS (E command.
Function Value
Specify the user NV memory capacity
Select the print density
(Verification required)
(Verification required)
● Default (factory setting)
3) Serial interface communication conditions
Communication conditions can be set by the GS(E command.
Function Value
Baud rate
Parity
Flow control ● DSR/DTR control XON/XOFF control
Data length 7-bit length ● 8-bit length
● Default (factory setting)
1K bytes 64K bytes
128K bytes ● 192K bytes
70% 75%
80% 85%
90% 95%
● 100% 105%
110% 115%
120% 125%
130% ―
ACK-in-Busy ● ACK-while-Busy ACK output position
ACK-after-Busy ―
● 1 2 At Input Buffer Full, BUSY output timing
3 4
2400 bps 4800 bps
● 9600 bps 19200 bps
38400 bps 57600 bps
115200 bps ―
● None Odd
Even ―
39
Page 44

8. PRINT CONTROL COMMANDS
○ Print Control Commands
Control
Command
LF Printing and paper feed
CR Back to printing
FF Printing in page mode and recovery P
ESC FF Printing data in PAGE MODE P
ESC J Printing and feeding paper in minimum pitch
ESC d Printing and feeding the paper by “n” lines
○ Print Character Commands
Control
Command
CAN Canceling print data in PAGE MODE P
ESC SP Setting the right spacing of the character
ESC ! Collectively specifying the printing mode
ESC % Specifying/canceling download character set
ESC & Defining the download characters
ESC - Specifying/canceling underline
ESC ? Deleting download characters
ESC E Specifying/canceling emphasis printing
ESC G Specifying/canceling double strike printing
ESC M Selection of character fonts
ESC R Selecting the international character set
ESC V Specifying/canceling 90°-right-turned characters S
ESC t Selecting the character code table
ESC { Specifying/canceling the inverted characters S
GS ! Specifying the character size
GS B Specifying/canceling the black/white inverted printing
GS b Specifying/canceling the smoothing
○ Print Position Commands
Control
Command
HT Horizontal tab
ESC $ Specifying the absolute positions
ESC D Setting horizontal tab position
ESC T Selecting the character printing direction in PAGE MODE P
ESC W Defining the print area in PAGE MODE P
ESC \
ESC a Aligning the characters S
GS $
GS L Setting the left margin S
GS W Setting the print area width
GS \
Specifying the relative position
Specifying the absolute vertical position of characters in
PAGE MODE
Specifying the relative vertical position of a character in
PAGE MODE
Function Mode GS P
S・P
S・P
S・P ○
S・P
Function Mode GS P
S・P ○
S・P
S・P
S・P
S・P
S・P
S・P
S・P
S・P
S・P
S・P
S・P
S・P
S・P
Function Mode GS P
S・P
S・P ○
S・P
S・P ○
P
S・P ○
S・P ○
○
○
○
40
Page 45

○ Line Feed Span Commands
Control
Command
ESC 2 Specifying 1/6-inch line feed rate
ESC 3 Setting line feed rate of minimum pitch
Function Mode GS P
S・P
S・P ○
○ Bit Image Commands
Control
Command
ESC * Specifying the bit image mode
GS * Defining the download bit image
GS / Printing the downloaded bit image
Function Mode GS P
S・P
S・P
S・P
GS v 0 Printing of raster bit image S
○ Status Commands
Control
Command
DLE EOT Sending status in real-time
GS a Enabling/disabling ASB (Automatic Status Back)
GS r Sending status
Function Mode GS P
S・P
S・P
S・P
○ Paper Detecting Commands
Control
Command
ESC c 3
Selecting the Paper Sensor valid for Paper-end signal
output
ESC c 4 Selecting the Paper Near-end Sensor valid for print stop
Function Mode GS P
S・P
S・P
○ Panel Switch Commands
Control
Command
ESC c 5 Enabling/disabling the panel switches
Function Mode GS P
S・P
○ Macro Commands
Control
Command
GS : Starting/ending macro definition
GS ^ Executing the macro
Function Mode GS P
S・P
S・P
○ Cutter Commands
Control
Command
ESC i Cutting the paper partially
ESC m Cutting the paper partially
GS V Cutting the paper
Function Mode GS P
S・P
S・P
S・P ○
41
Page 46

Bar Code Commands
○
Control
Command
GS H Selecting of printing position of HRI characters
GS f Selecting the font of HRI characters
GS h Specifying the height of the bar code
GS k Printing the bar code
GS w Specifying the horizontal size (magnification) of bar code
Function Mode GS P
S・P
S・P
S・P
S・P
S・P
○ Commands for Flash Memory
Control
Command
FS p
FS q
Printing the bit image in flash memory S
Defining the bit image in flash memory S
Function Mode GS P
○ Printer Setting Commands
Control
Command
Function Mode GS P
GS ( E User-defined command S
GS ( K Selecting print control method S
GS ( M Customizing the printer S
○ Other Commands
Control
Command
DLE ENQ Real-time request to printer
DLE DC4 Clearing buffer
ESC = Data input control
ESC @ Initializing the printer
Function Mode GS P
S・P
S・P
S・P
S・P
ESC L Selecting PAGE MODE S
ESC S Selecting STANDARD MODE P
GS ( A Execution of test printing S
GS I Sending the printer ID
GS P Specifying the basic calculation pitch
S・P
S・P
Notes:
• In the Mode column: S = STANDARD MODE, P = PAGE MODE.
• { = shows the command affected by GS P.
42
Page 47

9. CHARACTER CODE TABLE
9.1 Code Page
9.1.1 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC437 (USA, Europe Standard)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
NUL DLE
0
0 @ P ` p Ç É á ░ └ ╨ α≡
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
XON
XOFF
EOT DC4
ENQ
CAN
HT
LF
ESC
! 1 A Q a q ü æ í ▒ ┴ ╤ β ±
" 2 B R b r é Æ ó ▓ ┬ ╥ Γ ≧
# 3 C S c s â ô ú │ ├ ╙ π ≦
$ 4 D T d t ä ö ñ ┤ ─ ╘ ∑ ⌠
% 5 E U e u à ò Ñ ╡ ┼ ╒ σ ⌡
& 6 F V f v å û a ╢ ╞ ╓ μ÷
' 7 G W g w ç ù o ╖ ╟ ╫ τ
≈
( 8 H X h x ê ÿ ¿ ╕ ╚ ╪ Φ 。
) 9 I Y i y ë Ö ⌐ ╣ ╔ ┘ θ ∙
* : J Z j z è Ü ¬ ║ ╩ ┌ Ω ∙
+ ; K [ k { ï ¢ ½ ╗ ╦ █ δ √
FF FS
C
CR GS
D
E
F
Note: Kanji code table shows the shape of characters but does not show actual print result.
RS
, < L \ l | î £ ¼ ╝ ╠ ▃ ∞ ⁿ
- = M ] m } ì ¥ ¡ ╜ ═ ▌ φ ²
. > N ^ n ~ Ä
Pt
« ╛ ╬ ▐ ∈ ■
/ ? O _ o ・ Å ƒ » ┐ ╧ ▄ ∩
43
Page 48

9.1.2 Codepage 00H to 7FH & Katakana
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
NUL DLE
0
0 @ P ` p ▁ ┴SP-タ ミ ═ ×
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
XON
XOFF
EOT DC4
ENQ
CAN
HT
LF
ESC
! 1 A Q a q ▂ ┬ º ア チ ム ╞ 円
" 2 B R b r ▃ ┤┌イツ メ ╪ 年
# 3 C S c s ▅ ├┘ウテ モ ╡ 月
$ 4 D T d t ▆ ─、エト ヤ ◢ 日
% 5 E U e u ▇ _ ・ オ ナ ユ ◣ 時
& 6 F V f v █ |ヲカニ ヨ ◥ 分
' 7 G W g w ▉ ▕ ァ キ ヌ ラ ◤
秒
( 8 H X h x ▏ ┌ィクネ リ ♠ 〒
) 9 I Y i y ▎ ┐ゥケノ ル ♥ 市
* : J Z j z ▍ └ェコハ レ ♦ 区
+ ; K [ k { ▌ ┘ォサヒ ロ ♣ 町
FF FS
C
CR GS
D
E
F
RS
, < L \ l | ▋ ╭ ャ シ フ ワ ● 村
- = M ] m } ▋ ╮ ュ ス ヘ ン ○ 人
. > N ^ n ~ ▊ ╰ ョ セ ホ “ ╱ ▒
/ ? O _ o ・ + ╯ ッ ソ マ ゜ ╲ SP
44
Page 49

9.1.3 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC850/858 (Multilingual)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
NUL DLE
0
0 @ P ` p Ç É á ░ └ ð Ó ―
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
XON
XOFF
EOT DC4
ENQ
CAN
HT
LF
ESC
! 1 A Q a q ü æ í ▒ ┴ Ð β ±
" 2 B R b r é Æ ó ▓ ┬ Ê Ô =
# 3 C S c s â ô ú │ ├ Ë Ò ¾
$ 4 D T d t ä ö ñ ┤ ─ È õ ¶
% 5 E U e u à ò Ñ Á ┼ € Õ §
& 6 F V f v å û a  ã Í μ÷
' 7 G W g w ç ù o À Ã Î þ
,
( 8 H X h x ê ÿ ¿ © ╚ Ï Þ °
) 9 I Y i y ë Ö ® ╣ ╔ ┘ Ú ¨
* : J Z j z è Ü ¬ ║ ╩ ┌ Û ∙
+ ; K [ k { ï ø ½ ╗ ╦ █ Ù ¹
FF FS
C
CR GS
D
E
F
RS
, < L \ l | î £ ¼ ╝ ╠ ▃ ý ³
- = M ] m } ì Ø ¡ ¢ ═ ¦ Ý ₂
. > N ^ n ~ Ä × « \ ╬ Ì ¯ ■
/ ? O _ o ・ Å ƒ » ┐ ¤ ▄ ′
45
Page 50

9.1.4 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC860 (Portuguese)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
NUL DLE
0
0 @ P ` p Ç É á ░ └ ╨ α≡
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
XON
XOF
F
EOT DC4
ENQ
CAN
HT
LF
ESC
! 1 A Q a q ü À í ▒ ┴ ╤ β ±
" 2 B R b r é È ó ▓ ┬ ╥ Γ ≧
# 3 C S c s â ô ú │ ├ ╙ π ≦
$ 4 D T d t ã õ ñ ┤ ─ ╘ ∑ ⌠
% 5 E U e u à ò Ñ ╡ ┼ ╒ σ ⌡
& 6 F V f v Á Ú a ╢ ╞ ╓ μ÷
' 7 G W g w ç ù o ╖ ╟ ╫ τ
≈
( 8 H X h x ê Ì ¿ ╕ ╚ ╪ Φ °
) 9 I Y i y Ê Õ Ò ╣ ╔ ┘ θ
* : J Z j z è Ü ¬ ║ ╩ ┌ Ω ∙
+ ; K [ k { Í ¢ ½ ╗ ╦ █ δ √
FF FS
C
CR GS
D
E
F
RS
, < L \ l | Ô £ ¼ ╝ ╠ ▃ ∞ ⁿ
- = M ] m } ì Ù ¡ ╜ ═ ▌ ∅ ₂
. > N ^ n ~ Ã
Pt
« ╛ ╬ ▐ ∈ ■
/ ? O _ o ・ Â Ó » ┐ ╧ ▄ ∩
46
Page 51

9.1.5 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC863 (Canadian-French)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
NUL DLE
0
0 @ P ` p Ç É ¦ ░ └ ╨ α≡
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
XON
XOFF
EOT DC4
ENQ
CAN
HT
LF
ESC
! 1 A Q a q ü È ´ ▒ ┴ ╤ β ±
" 2 B R b r é Ê ô ▓ ┬ ╥ Γ ≧
# 3 C S c s â ô ú │ ├ ╙ π ≦
$ 4 D T d t Â Ë ¨ ┤ ─ ╘ ∑ ⌠
% 5 E U e u à Ï
ゝ
╡ ┼ ╒ σ ⌡
& 6 F V f v ¶ û ³ ╢ ╞ ╓ μ ÷
' 7 G W g w ç ù - ╖ ╟ ╫ τ
≈
( 8 H X h x ê ¤ Î ╕ ╚ ╪ Φ 。
) 9 I Y i y ë Ô ⌐ ╣ ╔ ┘ θ
* : J Z j z è Ü ¬ ║ ╩ ┌ Ω ∙
+ ; K [ k { Ï ¢ ½ ╗ ╦ █ δ √
FF FS
C
CR GS
D
E
F
RS
, < L \ l | Î £ ¼ ╝ ╠ ▃ ∞ ⁿ
- = M ] m } = Ù ¾ ╜ ═ ▌ ∅ ²
. > N ^ n ~ À
Û
« ╛ ╬ ▐ ∈ ■
/ ? O _ o ・ § ƒ » ┐ ╧ ▄ ∩
47
Page 52

9.1.6 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC865 (Nordic)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
NUL DLE
0
0 @ P ` p Ç É á ░ └ ╨ α≡
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
XON
XOFF
EOT DC4
ENQ
CAN
HT
LF
ESC
! 1 A Q a q ü æ í ▒ ┴ ╤ β ±
" 2 B R b r é Æ ó ▓ ┬ ╥ Γ ≧
# 3 C S c s â ô ú │ ├ ╙ π ≦
$ 4 D T d t ä ö ñ ┤ ─ ╘ ∑ ⌠
% 5 E U e u à ò Ñ ╡ ┼ ╒ σ ⌡
& 6 F V f v å û a ╢ ╞ ╓ μ÷
' 7 G W g w ç ù o ╖ ╟ ╫ τ
≈
( 8 H X h x ê ÿ ¿ ╕ ╚ ╪ Φ 。
) 9 I Y i y ë Ö ⌐ ╣ ╔ ┘ θ
* : J Z j z è Ü ¬ ║ ╩ ┌ Ω ∙
+ ; K [ k { Ï ø ½ ╗ ╦ █ δ √
FF FS
C
CR GS
D
E
F
RS
, < L \ l | Î £ ¼ ╝ ╠ ▃ ∞ ⁿ
- = M ] m } Ì Ø ¡ ╜ ═ ▌ ∅ ₂
. > N ^ n ~ Ä
Pt
« ╛ ╬ ▐ ∈ ■
/ ? O _ o ・ Å ƒ ¤ ┐ ╧ ▄ ∩
48
Page 53

9.1.7 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC852 (Eastern Europe)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
NUL DLE
0
0 @ P ` p Ç É á ░ └ đ ó -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
XON
XOFF
EOT DC4
ENQ
CAN
HT
LF
ESC
! 1 A Q a q ü Ĺ í ▒ ┴ Đ β ”
" 2 B R b r é í ó ▓ ┬ Ď Ó 、
# 3 C S c s â ú ú │ ├ Ë Ń ˇ
$ 4 D T d t ä ö Ą ┤ ─ ď ń ˘
% 5 E U e u ů Ľ ą Á ┼ Ň ň §
& 6 F V f v ć Ĭ Ž Â Ă Í Š ÷
' 7 G W g w ç Ś ž Ě ă î š
ゝ
( 8 H X h x ł ś Ę Ş ╚ ĕ Ŕ ゚
) 9 I Y i y ë Ö ę ╣ ╔ ┘ Ú ¨
* : J Z j z Ő Ü ║ ╩ ┌ ŕ ∙
+ ; K [ k { ő Ť ź ╗ ╦ █ Ű ű
FF FS
C
CR GS
D
E
F
RS
, < L \ l | î Č ╝ ╠ ▃ ý Ř
- = M ] m } Ź Ł ş Ż ═ Ţ Ý ř
. > N ^ n ~ Ä × « ż ╬ Ů ţ ■
/ ? O _ o ・ Ć č » ┐ ¤ ▀ ´
49
Page 54

9.1.8 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC866 (Russian)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
NUL DLE
0
0 @ P ` p ΑРа ░ └ ╨ р Ë
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
XON
XOFF
EOT DC4
ENQ
CAN
HT
LF
ESC
! 1 A Q a q Б С б ▒ ┴ ╤ с ë
" 2 B R b r В Т в ▓ ┬ ╥ т Є
# 3 C S c s ГУг│├ ╙ у є
$ 4 D T d t ДФд┤─ ╘ ф Ї
% 5 E U e u Е Х е ╡ ┼ ╒ ц ї
& 6 F V f v Ж Ц ж ╢ ╞ ╓ ц ў
' 7 G W g w З Ч з ╖ ╟ ╫ ч
( 8 H X h x И Ш и ╕ ╚ ╪ х ゚
) 9 I Y i y Й Щ й ╣ ╔ ┘ ш ・
* : J Z j z К Ъ к ║ ╩ ┌ щ ∙
+ ; K [ k { Л Ы л ╗ ╦ █ ъ √
FF FS
C
CR GS
D
E
F
RS
, < L \ l | М Ь м ╝ ╠ ▃ ы
- = M ] m } Н Э н ╜ ═ Ţ э ¤
. > N ^ n ~ О Ю о ╛ ╬ Ů ю ■
/ ? O _ o ・ ПЯп┐ ╧ ▀ я
No
.
50
Page 55

9.1.9 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC857 (Turkish)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
NUL DLE
0
0 @ P ` p Ç É á ░ └ o ó ―
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
XON
XOFF
EOT DC4
ENQ
CAN
HT
LF
ESC
! 1 A Q a q ü æ í ▒ ┴ a β ±
" 2 B R b r é Æ ó ▓ ┬ Ê ô
# 3 C S c s â ô ú │ ├ Ë ò ¾
$ 4 D T d t à ö ñ ┤ ─ È õ ¶
% 5 E U e u ä ò Ñ Á ┼ Õ §
& 6 F V f v å û Ĝ Â ã Í μ ÷
' 7 G W g w ç ù ĝ À Ã Î
ゝ
( 8 H X h x ê Í ¿ © ╚ Ï × ゚
) 9 I Y i y ë Ö ® ╣ ╔ ┘ Ú ¨
* : J Z j z è Ü ¬ ║ ╩ ┌ Û .
+ ; K [ k { ï ø ½ ╗ ╦ █ Ù ¹
FF FS
C
CR GS
D
E
F
RS
, < L \ l | î £ ¼ ╝ ╠ ▃ Ì ³
- = M ] m }
I
Ø ¡ ¢ ═ ¦ ÿ ²
. > N ^ n ~ Ä Ş « ¥ ╬ Ì - ■
/ ? O _ o ・ Å ş » ┐ ¤ ▀ ´ SP
51
Page 56

9.1.10 Codepage 00H to 7FH & PC864 (Arabic)
52
Page 57

9.1.11 Codepage 00H to 7FH & WPC1252
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
NUL DLE
0
0 @ P ` p € ° À Ð à ð
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
XON
XOFF
EOT DC4
ENQ
CAN
HT
LF
ESC
! 1 A Q a q ‘ ¡ ± Á Ñ á ñ
" 2 B R b r ¸ ’ ¢ ² Â Ò â ò
# 3 C S c s ƒ “ £ ³ Ã Ó ã ó
$ 4 D T d t ,, ” ¤ ´ Ä Ô ä Ô
% 5 E U e u
...
‧ ¥ µ Å Õ å Õ
& 6 F V f v † ‐ ¦ ¶ Æ Ö æ ö
' 7 G W g w ‡ ‒ § · Ç × ç
÷
( 8 H X h x ˆ ~ ¨ ¸ È Ø è ø
) 9 I Y i y ‰
© ¹ É Ù é ù
™
* : J Z j z Š š ª º Ê Ú ê ú
+ ; K [ k { ‹ › « » Ë Û ë û
FF FS
C
CR GS
D
E
F
RS
, < L \ l | Œ œ ¬ ¼ Ì Ü ì ü
- = M ] m } ½ Í Ý í ý
. > N ^ n ~ Ž ž ® ¾ Î Þ î þ
/ ? O _ o ・ Ÿ ¯ ¿ Ï ß ï ÿ
53
Page 58

9.1.12 Codepage 00H to 7FH & Thaicode18
54
Page 59

International Character Code Table
9.2
Country 23 24 40 5B 5C 5D 5E 60 7B 7C 7D 7E
0 USA
1 France
2 Germany
3 UK
4 Denmark I
5 Sweden
6 Italy
7 Spain I
8 Japan
9 Norway
10 Denmark II
# $ @ [ ╲ ] ^ ' { | } ~
# $ à ° ç § ^ ' é ù È ¨
# $ § Ä Ö Ü ^ ' ä ö ü β
£ $ @ [ ╲ ] ^ ' { | } ~
# $ @ Æ Ø Å ^ ' æ ø å ~
# ¤ É Ä Ö Å Ü é ä ö å ü
# $ @ ° ╲ é ^ ù à ò è ì
Pt $ @ ¡ Ñ ¿ ^ ' ¨ ñ } ~
# $ @ [ ¥ ] ^ ' { | } ~
# ¤ É Æ Ø Å Ü é æ ø å ü
# $ É Æ Ø Å Ü é æ ø å ü
11 Spain II
12 Latin America
13 Korea
# $ á ¡ Ñ ¿ é ' ì ñ ó ú
# $ á ¡ Ñ ¿ é ü ì ñ ó ú
# $ @ [ ₩ ] ^ ' { | } ~
55
 Loading...
Loading...