Canon LBP7200cdn Service Manual

Service Manual
LBP7200 Series
LBP7200Cdn
Feb 4 2009

Application
This manual has been issued by Canon Inc. for qualified persons to learn technical theory, insta llati on, ma intenance, and repair
of products. This manual covers all localities where the products are sold. For this reason, there may be information in this
manual that does not apply to your locality.
Corrections
This manual may contain technical inaccuracies or typographical errors due to improvements or changes in products. When
changes occur in applicable products or in the contents of this manual, Canon will release technical information as the need
arises. In the event of major changes in the contents of this manual over a long or short period, Canon will issue a new edition
of this manual.
The following paragraph does not apply to any countries where such provisions are inconsistent with local law.
Trademarks
The product names and company names used in this manual are the registered trademarks of the individual companies.
Copyright
This manual is copyrighted with all rights reserved. Under the copyright laws, this manual may not be copied, reproduced or
translated into another language, in whole or in part, without the written consent of Canon Inc.
COPYRIGHT © 2001 CANON INC.
Printed in Japan
Caution
Use of this manual should be strictly supervised to avoid disclosure of confidential information.

Symbols Used
This documentation uses the following symbols to indicate special information:
Symbol Description
Indicates an item of a non-specific nature, possibly classified as Note, Caution, or Warning.
Indicates an item requiring care to avoid electric shocks.
Indicates an item requiring care to avoid combustion (fire).
Indicates an item prohibiting disassembly to avoid electric shocks or problems.
Indicates an item requiring disconnection of the power plug from the electric outlet.
Indicates an item intended to provide notes assisting the understanding of the topic in question.
Memo
Introduction
REF.
Indicates an item of reference assisting the understanding of the topic in question.
Provides a description of a service mode.
Provides a description of the nature of an error indication.

Introduction
The following rules apply throughout this Service Manual:
1. Each chapter contains sections explaining the purpose of specific functions and the relationship between electrical and mechanical systems with reference to the timing of operation.
In the diagrams, represents the path of mechanical drive; where a signal name accompanies the symbol , the arrow indicates the
direction of the electric signal.
The expression "turn on the power" means flipping on the power switch, closing the front door, and closing the delivery unit door, which results in
supplying the machine with power.
2. In the digital circuits, '1'is used to indicate that the voltage level of a given signal is "High", while '0' is used to indicate "Low".(The voltage value, however, differs from circuit to circuit.) In addition, the asterisk (*) as in "DRMD*" indicates that the DRMD signal goes on when '0'.
In practically all cases, the internal mechanisms of a microprocessor cannot be checked in the fi eld. Ther efore, the operations of the microprocessors
used in the machines are not discussed: they are explained in terms of fro m sensors to the input of the DC controller PCB and from the output of the
DC controller PCB to the loads.
The descriptions in this Service Manual are subject to change without notice for product improvement or other purposes, and major changes will be communicated in the form of Service Information bulletins.
All service persons are expected to have a good understanding of the contents of this Service Manual and all relevant Service Information bulletins and be
able to identify and isolate faults in the machine."

Contents
Contents
Chapter 1 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
1.1 Features .....................................................................................................................................................1- 1
1.1.1 Feature....................................................................................................................................................................1- 1
1.2 Product Specifications................................................................................................................................1- 1
1.2.1 Product Specifications.............................................................................................................................................1- 1
1.3 Detailed Specifications ...............................................................................................................................1- 2
1.3.1 Print Speed................................................................................................................................................. ... ..........1- 2
1.4 Name of Parts.............................................................................................................................................1- 3
1.4.1 External View............................................ ................................................... ....................................... .....................1- 3
1.4.2 Cross Sectional View...............................................................................................................................................1- 4
1.5 Using the Machine......................................................................................................................................1- 5
1.5.1 Control Panel........................................................................................................................... .. ..............................1- 5
1.6 Safety .........................................................................................................................................................1- 6
1.6.1 Safety of the Laser Light........................................................................................................................... .. ... ..........1- 6
1.6.2 Safety of Toner...................................................................................................................................... ..................1- 6
1.6.3 Handling the Laser Unit...........................................................................................................................................1- 6
1.6.4 Points to note at disassembly/installation procedure...............................................................................................1- 7
Chapter 2 TECHNICAL REFERENCE
2.1 Functional Configuration........ .......................................... ... ... .......................................... .... .......................2- 1
2.1.1 Outline.....................................................................................................................................................................2- 1
2.2 Basic Sequense..........................................................................................................................................2- 1
2.2.1 Basic Sequence of Operation................................................................... ....................................... ... .....................2- 1
2.3 LASER EXPOSURE SYSTEM...................................................................................................................2- 1
2.3.1 Overview/Configuration................................................................................................................ ...........................2- 1
2.3.1.1 Outline...................................................................................................................................................................................... 2- 1
2.3.2 Laser Scanner Motor Control ..................................................................................................................................2- 2
2.3.2.1 Fault Detection......................................................................................................................................................................... 2- 2
2.4 IMAGE FORMATION SYSTEM..................................................................................................................2- 2
2.4.1 Overview/Configuration................................................................................................................ ...........................2- 2
2.4.1.1 Outline...................................................................................................................................................................................... 2- 2
2.4.1.2 Image-formation Process.........................................................................................................................................................2- 3
2.4.1.3 Latent image formation block................................................................................................................................................... 2- 3
2.4.1.4 Development block ...................... ..................... ..................... ..................... ............................................................................. 2- 4
2.4.1.5 Transfer block .......................................................................................................................................................................... 2- 4
2.4.1.6 Fixing block..............................................................................................................................................................................2- 5
2.4.1.7 ITB cleaning block....................................................................................................................................................................2- 6
2.4.1.8 Photosensitive drum cleaning block ......................................................................................................................................... 2- 6
2.4.2 High-Voltage Control................................................................................................................. ... ...........................2- 7
2.4.2.1 Outline...................................................................................................................................................................................... 2- 7
2.4.3 Image Stabilizaton Control ......................................................... .............................................................................2- 8
2.4.3.1 Overview of the Image Stabilization Control Mechanism......................................................................................................... 2- 8
2.4.3.2 Image density correction control (D-max control) .................................................................................................................... 2- 8
2.4.3.3 Image gradation correction control (D-half control).................................................................................................................. 2- 9
2.4.3.4 Color displacement correction control...................................................................................................................................... 2- 9
2.4.4 Drum Cartridge......................................................................................................................................... ...............2- 9
2.4.4.1 Developing roller engagement/disengagement control............................................................................................................ 2- 9
2.4.5 Transfer Unit..........................................................................................................................................................2- 10
2.4.5.1 Pad transfer ........................................................................................................................................................................... 2- 10
2.5 Pickup/Feeding/Delivery System..............................................................................................................2- 11

Contents
2.5.1 Overview/Configuration..........................................................................................................................................2- 11
2.5.1.1 Overview................................................................................................................................................................................2- 11
2.5.2 Detecting Jams......................................................................................................................................................2- 12
2.5.2.1 Jam Detection Outline............................................................................................................................................................ 2- 12
2.5.2.2 Delay Jams ............................................................................................................................................................................ 2- 12
2.5.2.3 Stationary Jams ..................................................................................................................................................................... 2- 12
2.5.2.4 Other Jams ............................................................................................................................................................................ 2- 13
2.5.3 Cassette Pickup.....................................................................................................................................................2- 13
2.5.3.1 Separation Roller Method ...................................................................................................................................................... 2- 13
2.6 FIXING UNIT SYSTEM ............................................................................................................................2- 14
2.6.1 Overview/Configuration..........................................................................................................................................2- 14
2.6.1.1 Outline.................................................................................................................................................................................... 2- 14
2.6.2 Various Control Mechanisms.................................................................................................................................2- 14
2.6.2.1 Controlling the Speed of the Fixing Unit ................................................................................................................................2- 14
2.6.2.2 Fixing Temperature Control ................................................................................................................................................... 2- 15
2.6.3 Protective Functions ..............................................................................................................................................2- 15
2.6.3.1 Protective function ................................................................................................................................................................. 2- 15
2.6.3.2 Fixing unit failure detection .................................................................................................................................................... 2- 15
2.7 EXTERNAL AND CONTROLS SYSTEM .................................................................................................2- 16
2.7.1 Power Supply............................................................................................................ ... ..........................................2- 16
2.7.1.1 Power Supply......................................................................................................................................................................... 2- 16
2.7.1.2 Other Function ....................................................................................................................................................................... 2- 17
2.8 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM ....................................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .................................2- 17
2.8.1 Construction...........................................................................................................................................................2- 17
2.8.1.1 Outline.................................................................................................................................................................................... 2- 17
2.8.1.2 Motor control..........................................................................................................................................................................2- 18
2.8.1.3 Safety..................................................................................................................................................................................... 2- 18
2.8.2 Main Controller.......................................................................................................................................................2- 18
2.8.2.1 Outline.................................................................................................................................................................................... 2- 18
2.8.2.2 Overview of the Block ............................................................................................................................................................ 2- 19
Chapter 3 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
3.1 EXTERNAL AND CONTROLS SYSTEM ...................................................................................................3- 1
3.1.1 Rear Cover...............................................................................................................................................................3- 1
3.1.1.1 Removing rear cover................................................................................................................................................................ 3- 1
3.1.1.2 Pre-procedure for removing rear cover lib unit ........................................................................................................................3- 1
3.1.1.3 Removing rear cover lib unit .................................................................................................................................................... 3- 1
3.1.2 Rear Upper Cover....................................................................................................................................................3- 1
3.1.2.1 Removing upper rear cover (left) .............................................................................................................................................3- 1
3.1.2.2 Pre-procedure for removing lower rear cover .......................................................................................................................... 3- 1
3.1.2.3 Removing lower rear cover......................................................................................................................................................3- 1
3.1.3 Right Cover..................................................................................................................................... .........................3- 3
3.1.3.1 Removing right cover...............................................................................................................................................................3- 3
3.1.3.2 Pre-procedure for removing right frame cover......................................................................................................................... 3- 3
3.1.3.3 Removing right frame cover.....................................................................................................................................................3- 3
3.1.4 Left Cover ................................................................................................................................................................3- 4
3.1.4.1 Pre-procedure for removing left cover .....................................................................................................................................3- 4
3.1.4.2 Removing left cover ................................................................................................................................................................. 3- 4
3.1.5 Upper Cover......................................................................................................................... ....................................3- 5
3.1.5.1 Pre-procedure for removing upper cover.................................................................................................................................3- 5
3.1.5.2 Removing upper cover.............................................................................................................................................................3- 5
3.1.6 Front Cover..................................................................................................................................... .........................3- 6
3.1.6.1 Pre-procedure for removing front cover...................................................................................................................................3- 6
3.1.6.2 Removing front cover...............................................................................................................................................................3- 6
3.1.7 Drive Unit................... ... .................................................. .........................................................................................3- 8
3.1.7.1 Pre-procedure for removing drive unit .....................................................................................................................................3- 8
3.1.7.2 Removing drive unit ................................................................................................................................................................. 3- 8
3.1.8 Duplexing Drive Unit................................................................................................................................................3- 9

Contents
3.1.8.1 Pre-procedure for removing duplex reverse drive unit............................................................................................................. 3- 9
3.1.8.2 Removing duplex reverse drive unit.........................................................................................................................................3- 9
3.1.9 Operation Panel Unit .............................................................................................................................................3- 10
3.1.9.1 Pre-procedure for removing control panel ............................................................................................................................ 3- 10
3.1.9.2 Removing control panel ......................................................................................................................................................... 3- 10
3.1.10 DC Controller PCB........................................ .................................................. ... ..................................................3- 10
3.1.10.1 Pre-procedure for removing DC controller PCB...................................................................................................................3- 10
3.1.10.2 Removing DC controller PCB............................................................................................................................................... 3- 10
3.1.11 Connecting PCB..................................................................................................................................................3- 10
3.1.11.1 Pre-procedure for removing relay PCB................................................................................................................................3- 10
3.1.11.2 Removing relay PCB............................................................................................................................................................ 3- 10
3.1.12 Main Controller PCB.............................................................. ... ...........................................................................3- 11
3.1.12.1 Pre-procedure for removing main controller PCB ................................................................................................................ 3- 11
3.1.12.2 Removing main controller PCB............................................................................................................................................3- 11
3.1.12.3 Pre-procedure for removing sub power supply PCB............................................................................................................3- 11
3.1.12.4 Removing sub power supply PCB........................................................................................................................................ 3- 11
3.1.13 Driver PCB................................ ... .................................................. ......................................................................3- 12
3.1.13.1 Pre-procedure for removing driver PCB............................................................................................................................... 3- 12
3.1.13.2 Removing driver PCB...........................................................................................................................................................3- 12
3.1.14 Power Supply Board................................................................. ... ......................................... ...............................3- 13
3.1.14.1 Pre-procedure for removing power supply unit .................................................................................................................... 3- 13
3.1.14.2 Removing power supply unit................................................................................................................................................3- 13
3.1.15 High-voltage PCB................................................................................................................................................3- 14
3.1.15.1 Pre-procedure for removing high voltage power supply PCB .............................................................................................. 3- 14
3.1.15.2 Removing high voltage power supply PCB..........................................................................................................................3- 14
3.1.16 Fan.......................................................................................................................................................................3- 15
3.1.16.1 Pre-procedure for removing fan (1)......................................................................................................................................3- 15
3.1.16.2 Removing fan (1)..................................................................................................................................................................3- 15
3.1.16.3 Pre-procedure for removing duplex feeding fan................................................................................................................... 3- 16
3.1.16.4 Removing duplex feeding fan...............................................................................................................................................3- 16
3.2 LASER EXPOSURE SYSTEM.................................................................................................................3- 16
3.2.1 Laser Scanner Unit................................................................................................................................................3- 16
3.2.1.1 Pre-procedure for removing laser scanner unit......................................................................................................................3- 16
3.2.1.2 Removing laser scanner unit ................................................................................................................................................. 3- 16
3.3 IMAGE FORMATION SYSTEM................................................................................................................3- 19
3.3.1 Drum/ITB Motor.....................................................................................................................................................3- 19
3.3.1.1 Pre-procedure for removing drum motor................................................................................................................................ 3- 19
3.3.1.2 Removing drum motor ........................................................................................................................................................... 3- 19
3.3.2 Developing Rotary Motor.......................................................................................................................................3- 19
3.3.2.1 Pre-procedure for removing developing motor ...................................................................................................................... 3- 19
3.3.2.2 Removing developing motor .................................................................................................................................................. 3- 19
3.3.3 ITB Unit..................................................................................................................................................................3- 20
3.3.3.1 Removing ITB unit ................................................................................................................................................................. 3- 20
3.3.4 RD Sensor Unit.............................................................................................. ........................................................3- 21
3.3.4.1 Pre-procedure for removing RD sensor unit .......................................................................................................................... 3- 21
3.3.4.2 Removing RD sensor unit...................................................................................................................................................... 3- 21
3.4 PICKUP/FEEDING/DELIVERY SYSTEM.................................................................................................3- 22
3.4.1 Pickup Motor..........................................................................................................................................................3- 22
3.4.1.1 Pre-procedure for removing pick-up motor ............................................................................................................................ 3- 22
3.4.1.2 Removing pick-up motor........................................................................................................................................................3- 22
3.4.2 Pickup Unit ............................................................................................................................................................3- 23
3.4.2.1 Pre-procedure for removing pick-up unit................................................................................................................................ 3- 23
3.4.2.2 Removing pick-up unit ........................................................................................................................................................... 3- 23
3.4.2.3 Removing MP tray pick-up unit..............................................................................................................................................3- 24
3.4.3 Delivery Unit..........................................................................................................................................................3- 25
3.4.3.1 Pre-procedure for removing delivery unit............................................................................................................................... 3- 25
3.4.3.2 Removing delivery unit........................................................................................................................................................... 3- 25
3.4.4 Cassette Pickup Roller..........................................................................................................................................3- 26
3.4.4.1 Removing cassette pick-up roller.......................................................................................................................................... 3- 26

Contents
3.4.5 Cassette Separation Roller....................................................................................................................................3- 26
3.4.5.1 Removing cassette separation roller...................................................................................................................................... 3- 26
3.4.6 Manual Pickup Roller.............................................................................................................................................3- 27
3.4.6.1 Removing MP tray pick-up roller............................................................................................................................................ 3- 27
3.4.7 Manual Separation Pad .........................................................................................................................................3- 27
3.4.7.1 Removing MP tray separation pad......................................................................................................................................... 3- 27
3.4.8 Duplexing Feeding Unit..........................................................................................................................................3- 27
3.4.8.1 Pre-procedure for removing duplex feeding unit....................................................................................................................3- 27
3.4.8.2 Removing duplex feeding unit............................................................................................................................................... 3- 27
3.4.9 Secondary Transfer Feeding Unit..........................................................................................................................3- 28
3.4.9.1 Removing secondary transfer feeding unit ............................................................................................................................3- 28
3.4.10 Re-Pickup Guide Unit...........................................................................................................................................3- 28
3.4.10.1 Pre-procedure for removing re-pick-up guide unit................................................................................................................ 3- 28
3.4.10.2 Removing re-pick-up guide unit ........................................................................................................................................... 3- 28
3.5 FIXING SYSTEM......................................................................................................................................3- 29
3.5.1 Fixing Assembly.....................................................................................................................................................3- 29
3.5.1.1 Pre-procedure for removing fixing unit................................................................................................................................... 3- 29
3.5.1.2 Removing fixing unit............................................................................................................................................................... 3- 29
3.5.2 Fixing Film Unit........................... .................................................. ... ......................................................................3- 30
3.5.2.1 Pre-procedure for removing fixing film unit ............................................................................................................................ 3- 30
3.5.2.2 Removing fixing film unit........................................................................................................................................................3- 30
3.5.3 Fixing Pressure Roller................................................................................. ... ... .....................................................3- 31
3.5.3.1 Pre-procedure for removing fixing pressure roller.................................................................................................................. 3- 31
3.5.3.2 Removing fixing pressure roller .............................................................................................................................................3- 31
3.5.4 Fixing Motor....................................................................... ....................................................................................3- 32
3.5.4.1 Pre-procedure for removing fixing motor ...............................................................................................................................3- 32
3.5.4.2 Removing fixing motor ........................................................................................................................................................... 3- 32
Chapter 4 MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
4.1 Periodically Replaced Parts ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ...................................................4- 1
4.1.1 Periodically Replaced Parts.....................................................................................................................................4- 1
4.2 Consumables .............................................................................................................................................4- 1
4.2.1 Life Expectancy of Consumable Parts.....................................................................................................................4- 1
4.3 Periodical Service.......................................................................................................................................4- 1
4.3.1 Periodic Service.......................................................................................................................................................4- 1
4.4 Cleaning .....................................................................................................................................................4- 1
4.4.1 Cleaning method.................................................................................................................................................... ..4- 1
Chapter 5 TROUBLESHOOTING
5.1 MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT......................... .... .........................................................................5- 1
5.1.1 Test Print..................................................................................................................................................................5- 1
5.1.1.1 Test Print.................................................................................................................................................................................. 5- 1
5.1.2 Adjustment of Laser Exposure System...................................................................................................................5- 1
5.1.2.1 After Replacing the laser scanner unit.....................................................................................................................................5- 1
5.1.3 Adjustment of Electrical Components.....................................................................................................................5- 2
5.1.3.1 After Replacing the DC controller PCB....................................................................................................................................5- 2
5.1.3.2 After Replacing the Main Controller PCB................................................................................................................................. 5- 2
5.2 SERVICE TOOLS ......................................................................................................................................5- 3
5.2.1 Standard Tools........................................................................................................................ .................................5- 3
5.2.2 Solvents and Oils.................................................... .. ...................................................... .........................................5- 3
5.3 ERROR CODE..................................................................... ... ... .... ... ... ......................................................5- 3
5.3.1 Error Code ......................................................................................................................................... ......................5- 3
5.4 Version Up..... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... ................................................................5- 5
5.4.1 Outline.................................................................................................................................................................... ..5- 5
5.4.1.1 Overview of Version Upgrading ............................................................................................................................................... 5- 5

Contents
5.5 Service Mode..............................................................................................................................................5- 6
5.5.1 Outline.....................................................................................................................................................................5- 6
5.5.1.1 Outline...................................................................................................................................................................................... 5- 6
5.5.2 Service Mode Table............................... ................................................... ...............................................................5- 8
5.5.2.1 Service Mode List .................................................................................................................................................................... 5- 8
5.5.2.2 Service Chart Print 1................................................................................................................................................................ 5- 8
5.5.2.3 Service Chart Print 2.............................................................................................................................................................. 5- 11
5.5.2.4 Print Status Print....................................................................................................................................................................5- 17
5.5.2.5 Status Print B.........................................................................................................................................................................5- 18
5.6 Special Administrator Mode......................................................................................................................5- 19
5.6.1 Overview................................................................................................................................................................5- 19
5.6.1.1 Preface...................................................................................................................................................................................5- 19
5.6.1.2 Entering the Special Administrator Mode............................................................................................................................... 5- 19
5.6.1.3 Menu List ............................................................................................................................................................................... 5- 22
Chapter 6 APPENDIX
6.1 OUTLINE OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS .......... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... .6- 1
6.1.1 Clutch/Solenoid .......................................................................................................................................................6- 1
6.1.1.1 Cluth/Solenoid.......................................................................................................................................................................... 6- 1
6.1.2 Motor/Fan................................................................................................................................................................6- 2
6.1.2.1 Motor/Fan................................................................................................................................................................................. 6- 2
6.1.3 Sensor.....................................................................................................................................................................6- 3
6.1.3.1 Sensor...................................................................................................................................................................................... 6- 3
6.1.4 PCBs ............................................................................................................................................... ........................6- 4
6.1.4.1 PCBs........................................................................................................................................................................................ 6- 4

Chapter 1 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION

Contents
Contents
1.1 Features..........................................................................................................................................................................1-1
1.1.1 Feature.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.2 Product Specifications....................................................................................................................................................1-1
1.2.1 Product Specifications ................................................................................................................................................................. 1-1
1.3 Detailed Specifications ..................................................................................................................................................1-2
1.3.1 Print Speed................................................................................................................................................................................... 1-2
1.4 Name of Parts.................................................................................................................................................................1-3
1.4.1 External View .............................................................................................................................................................................. 1-3
1.4.2 Cross Sectional View................................................................................................................................................................... 1-4
1.5 Using the Machine.........................................................................................................................................................1-5
1.5.1 Control Panel ............................................................................................................................................................................... 1-5
1.6 Safety .............................................................................................................................................................................1-6
1.6.1 Safety of the Laser Light.............................................................................................................................................................. 1-6
1.6.2 Safety of Toner ............................................................................................................................................................................ 1-6
1.6.3 Handling the Laser Unit............................................................................................................................................................... 1-6
1.6.4 Points to note at disassembly/installation procedure ................................................................................................................... 1-7
1.1 Features
Chapter 1
1.1.1 Feature
1. Small and low-cost printer
The printer uses a flat in-line cartridge method for the first time in the small printer. This lowers the height and reduces the printer siz e. The printer uses the
transfer pad and the separation roller to reduce the parts expenses.
2. Intermediate transfer method
The intermediate transfer method transfers toner images to the Intermediate Transfer Belt (ITB) and transfers the images in four colors onto the print media at
once. It realizes a stabilized color-print on various media without being affected by the primary transfer operation.
3. Improved usability
The printer improves usability by using the pullout cartridge and the front side accessibility to the media. This small-sized printer is user-friendly on the spa ce
of the desktop.
1.2 Product Specifications
1.2.1 Product Specifications
Body installation method Desktop page printer
Photosensitive medium OPC drum
Charging method Roller charging
Exposure method Laser scanning
Development method Contact development
Transfer method Intermediate Transfer Belt (ITB)
Separation method Curvature
Pickup method Cassette: simple retard method
Drum cleaning method rubber blade
Transfer cleaning method Cleaning brush + roller method (drum electrosta ti c col lec tion)
Fixing method On-demand fixing
Delivery method Face-down
Contrast adjustment function Auto
Toner level detection function Available
Toner type Non-magnetic single-component dry toner
Warm-up time 19 seconds or less
Image margin (Leading edge) 5.0+1.5/-1.5mm
Image margin (Trailing edge) 5.0+1.5/-1.5mm
Image margin (Left/right) 5.0+1.0/-1.0mm
Number of gradations 16 gradations
Printing resolution 600dpi x 600dpi
First print time Black and white printing: 15 seconds or less
Print speed (A4) Black and white printing: 20 ppm
Cassette paper size Standard sizes:
Multifeeder paper size Standard sizes:
Cassette paper type Plain paper (60 to 90g/m2),Heavy paper (86 to 263g/m2),Label,Coated
Multifeeder tray paper type Plain paper (60 to 90g/m2),Heavy paper (86 to 263g/
Cassette capacity Approx. 250 sheets (80 g/m2)
Multifeeder tray capacity Approx. 50 sheets (80 g/m2)
Delivery tray stack Approx. 125 sheets (80 g/m2)
Memory Standard: 16MB, option: none
Hard disk Standard: none, option: none
Manual feed tray : pad separation method
-May vary depending on the usage conditions, such as the availability of
the optional accessories and installation environment.
-Approximately 220 seconds when the printer is turned on after a ton er
cartridge is replaced.
Color printing: 15 seconds or less
-May vary depending on the output environment.
Color printing: 20 ppm
-The print speed may drop depending on the settings for the paper size,
paper type, number of pages printed, and fixing mode setting.
-If the printer is used continuously for an extended period of time, the
internal temperature of the printer may increase, activating a safety
mechanism and pausing printing temporarily.
A4, B5, A5, Legal, Letter, Executive, Statement, Foolscap, 16K,
Envelope DL, Envelope COM10, Envelope C5, and Envelope B5
Custom paper sizes:
100.0 to 215.9 mm wide and 148.0 to 355.6 mm long
A4, B5, A5, Legal, Letter, Executive, Statement, Foolscap, 16K,
Envelope DL, Envelope COM10, Envelope C5, Envelope B5, Envelope
Monarch, and Index Card
Custom paper sizes:
76.2 to 215.9 mm wide and 127.0 to 355.6 mm long
paper(120 to 220g/m2),Envelope
m2),Transparency,Label,Coated paper(120 to 220g/m2),Envelope
0021-1249
0022-8863
1-1
Chapter 1
Interface USB:
Auto gradation correction available(A4, B5, Legal, Letter, Executive, and Foolscap)
Operating environment
(Temperature range)
Operating environment
(Humidity range)
Noise Lwad (declared A-weighted sound power level (1 B = 10 dB))
Power supply rating 120 to 127 V (±10%), 50/60 Hz (±2 Hz)
Power consumption (Maximum) 1,070 W or less
Power consumption Average during operation
Dimensions 409 (W) x 490 (W) x 331(H) mm
Weight Printer unit (excluding toner cartridges):Approx. 22.0 kg
Hi-Speed USB/USB
Network:
Shared 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX (RJ-45)
Full duplex/Half duplex
10 to 30 deg
Operating environment
Temperature range: 10 to 30 deg C (50 to 86 deg F)
Humidity range: 20 to 80 % RH (no condensation)
During standby: Background noise level
During operation: 7 B or less
Sound pressure level (bystander position)
During standby: Background noise level
During operation: 56 dB (A) or less
(Declared noise emission in accordance with ISO 9296)
220 to 240 V (±10%), 50/60 Hz (±2 Hz)
Approx. 405 W (120 to 127V)/ Approx. 395 W (220 to 240V)
Average during standby
Approx. 18.5 W (120 to 127V)/ Approx. 20.5 W (220 to 240V)
Average during sleep mode
Approx. 7 W (120 to 127V)/ Approx. 7.5 W (220 to 240V)
Option Csette:4.0Kg
1.3 Detailed Specifications
1.3.1 Print Speed
Name in the driver
(grammage)
Plain paper (70 to 90g/m2)
plain paper L (60 to 74g/m2)
heavy paper 1 (86 to 119g/2)
heavy paper2 (120 to 129g/2)
Heavy paper 3 (130 to 163g/2)
Coat paper1 (120 to 130g/m2)
Coat paper2 (155 to 165g/m2)Coat paper3 (210 to
220g/m2)
Glossy paper
Envelope
Envelope H
Labels
Transparency
speed Paper
1/1
1/2
1/3
1/2
1/3
1/2
1/3
Size
A4
LTR
LGL
A4
LTR
LGL
A4
LTR
LGL
Com10
A4
A4
T-1-1
Unit: prints/min
Single-sided Double-sided
Manual feed
tray
16.0 20.0 20.0 9.1 10.0 10.0
16.6 21.0 21.0 9.2 10.3 10.3
14.1 17.1 17.1 8.5 9.2 9.2
7.4 9.7 9.7 4.5 4.5 4.5
7.4 9.9 9.9 4.6 4.5 4.5
6.5 8.3 8.3 4.2 4.2 4.2
5.0 6.5 6.5 3.0 3.0 3.0
5.0 6.9 6.9 3.0 3.0 3.0
4.4 5.6 5.6 2.8 3.0 3.0
5.4 7.6 7.6 - - -
4.2 4.2 4.2 - - -
7.6 9.7 9.7 - - -
5.0-----
Cassette Option
cassette
Manual feed
tray
Cassette Option
cassette
0021-1262
1-2
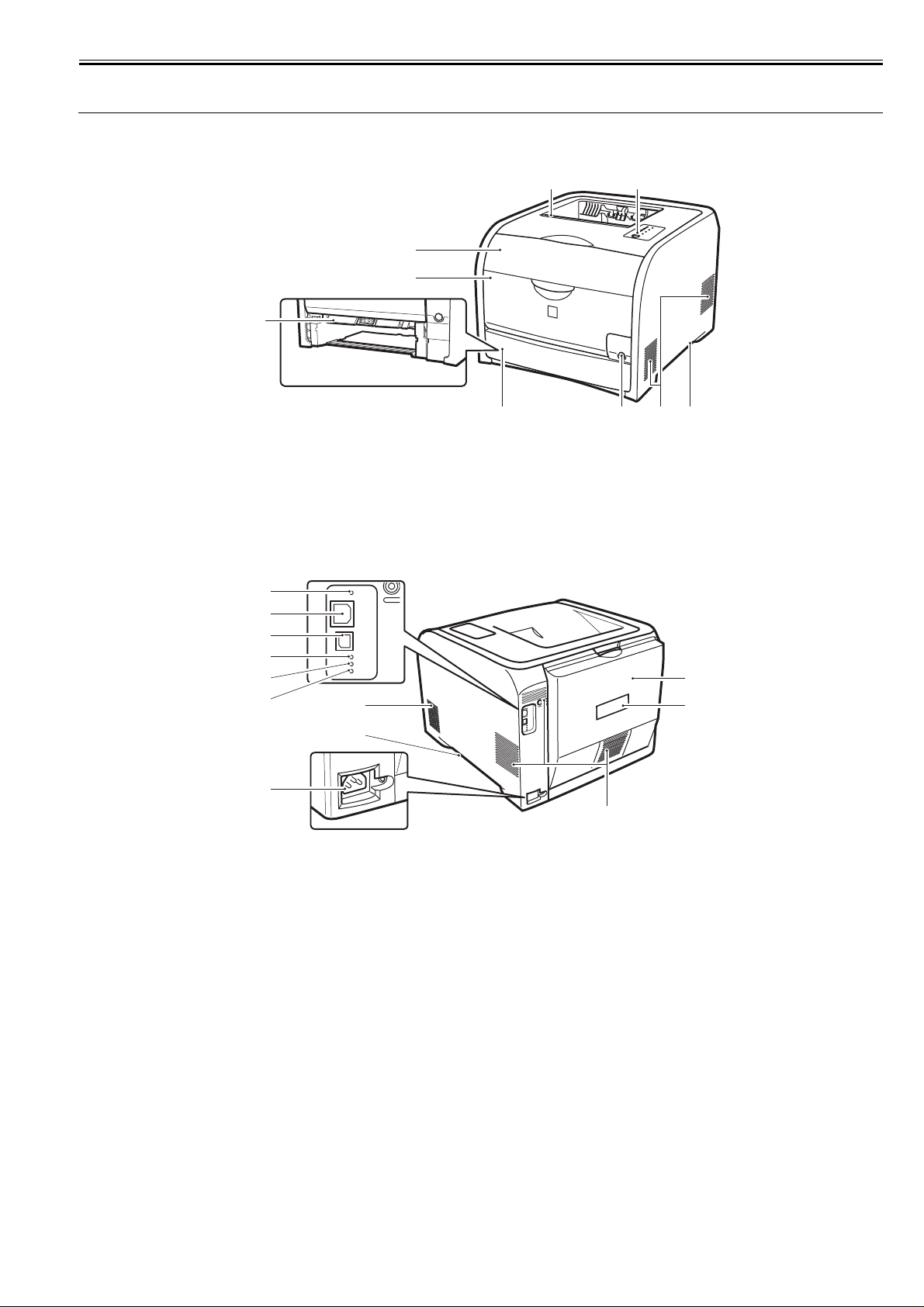
1.4 Name of Parts
Chapter 1
1.4.1 External View
[3]
[1]
Front Cover
[2]
Manual Feed Tray
[3]
Manual Feed Feeding Guide
[4]
Pickup Cassette
Delivery Tray
[5]
[1]
[2]
F-1-1
[4]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[5]
Power Switch
Control Panel
Delivery Tray
Carry Grip
[6]
0021-1265
[7]
[8] [9]
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
F-1-2
[1] Reset button [7] Airway
[2] LAN connector [8] Carry Grip
[3] USB connector [9] Power Code Outlet
[4] 100 lamp (green) [10] Rear Cover
[5] LNK lamp (green) [11] Standard rating-plate label
[6] ERR lamp (orange)
[10]
[11]
[7]
1-3
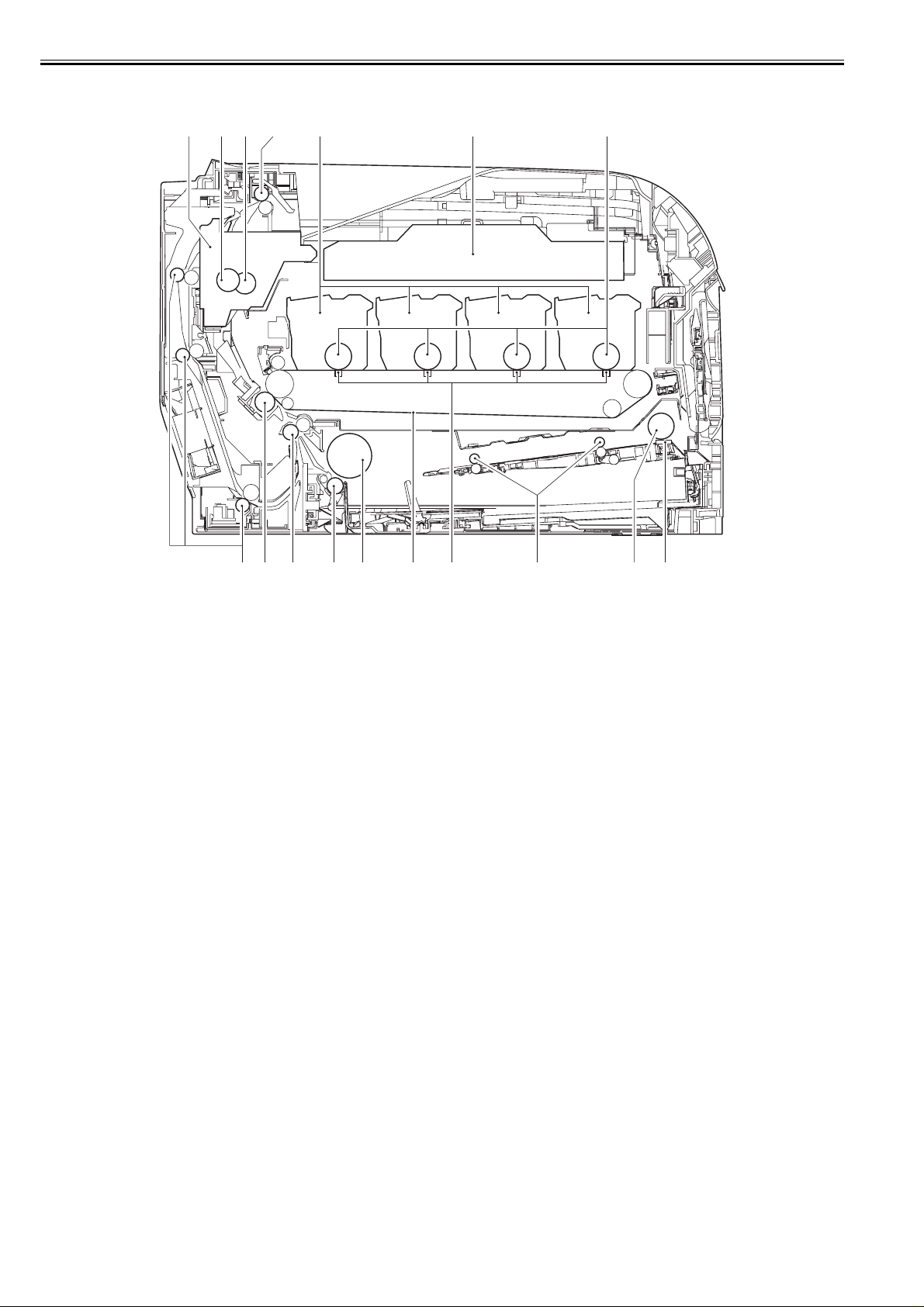
Chapter 1
1.4.2 Cross Sectional View
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7]
0021-1266
[11][12] [10][13][14][15][16][17]
F-1-3
T-1-2
[1] Cross Sectional View [10] Multi tray feed roller
[2] Pressure roller [11] Primary transfer pad
[3] Fixing sleeve [12] ITB Unit
[4] Fixing sleeve [13] Cassette pickup roller
[5] Cartridge [14] Cassette separation roller
[6] Laser scanner unit [15] Registration roller
[7] Photosensitive drum [16] Secondary transfer roller
[8] Multi tray separation pad [17] Duplex feed roller (Duplex model)
[9] Multi tray pickup roller
[8][9]
1-4
1.5 Using the Machine
Chapter 1
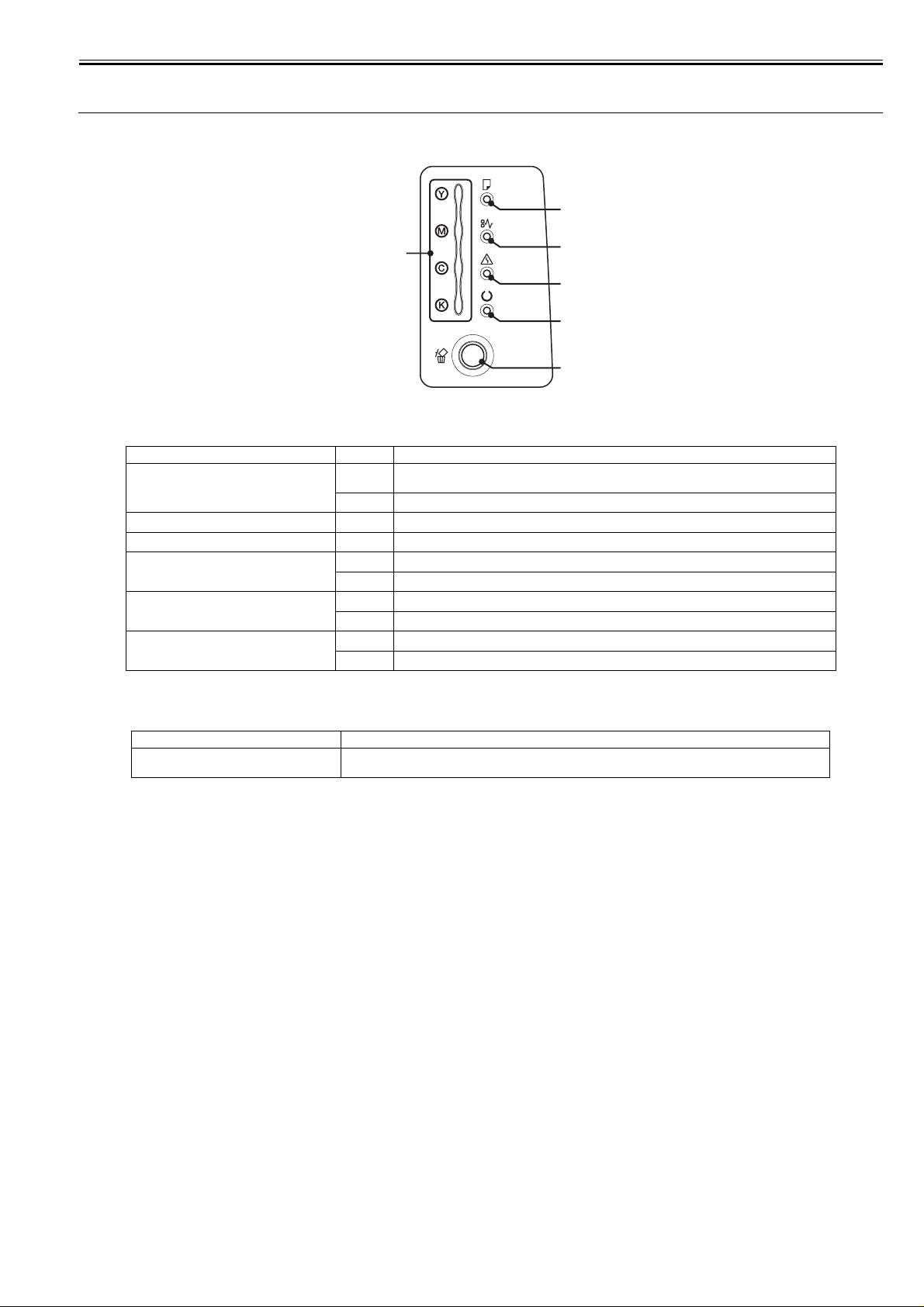
1.5.1 Control Panel
Functions of the LEDs
[1] Toner Indicator
[2] Paper Source Indicator
[3] Paper Jam Indicator
[4] Alarm Indicator
[5] Ready Indicator
[6] Cancel Job Indicator
[2]
[1]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
F-1-4
T-1-3
Name Status Description
Blinking
Blinking
Blinking
Blinking
Blinking
Blinking
Printing cannot be performed because a toner cartridge needs to be replaced, or a toner cartridge is not
installed properly.
On
A toner cartridge needs to be replaced.
There is no paper or paper of the correct size is not loaded.
A paper jam has occurred and printing cannot be performed.
An error has occurred and printing cannot be performed.
On
A service error has occurred.
The printer is busy printing, warming up, or cleaning.
On
The printer is ready to print.
A job is being canceled.
On
The Cancel Job key has been pressed.
0021-1268
Functions of the Control Panel Keys
Name Function
[6] Cancel Job Key Press this key to cancel the job that is currently being printed or a job with an error.
T-1-4
1-5

Chapter 1
1.6 Safety
1.6.1 Safety of the Laser Light
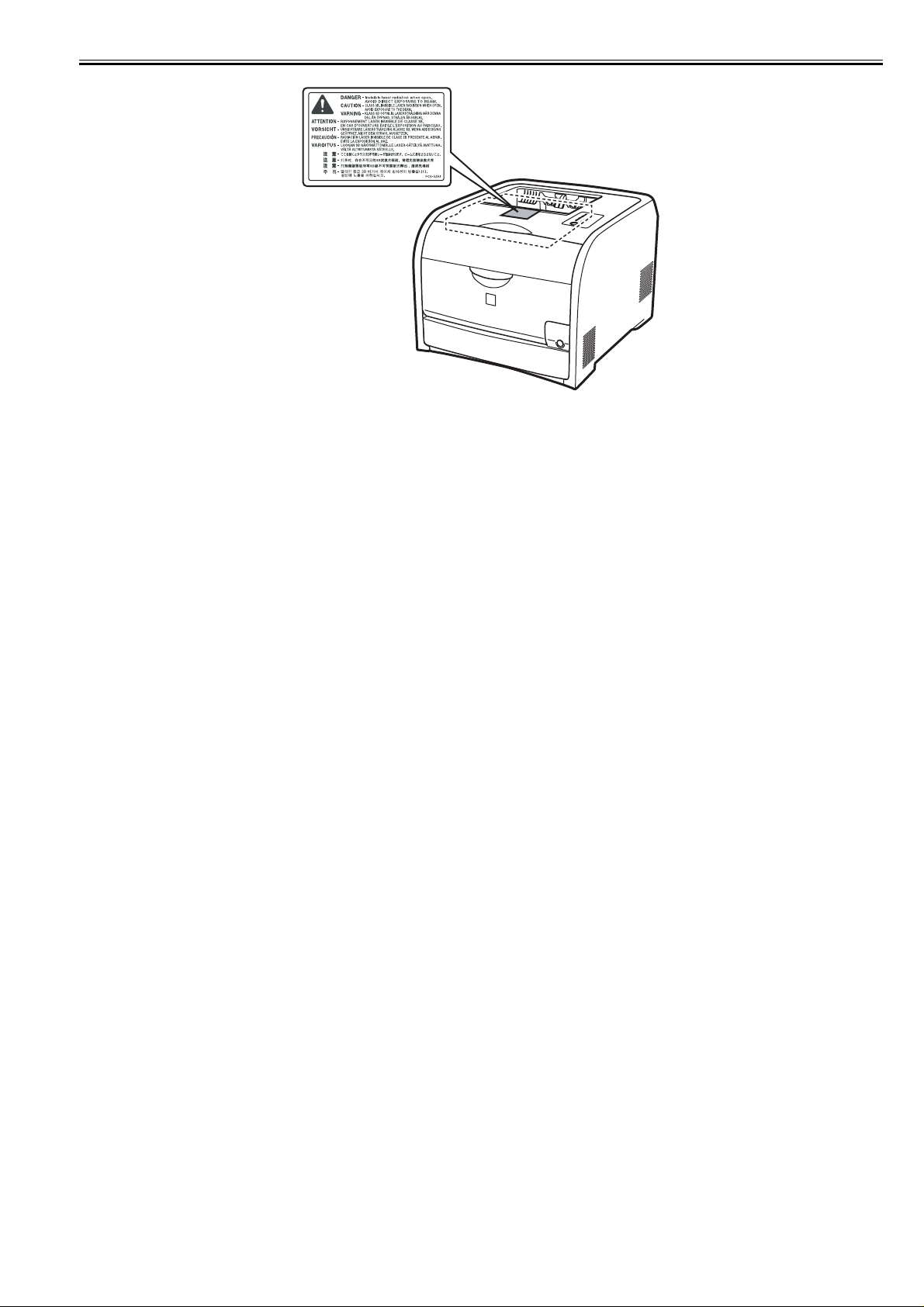
Laser beam radiation may pose a danger to the human body. A laser scanner mounted on the machine is sealed with the protection housing and external cover to
0021-1270
prevent the laser beam from leaking to the outside. The laser beam never leaks out of the scanner as far as users operate the machine normally
The following warnings are given to comply with Safety Principles (EN60950).
Laserstrahlen können für den menschlichen Körper gefährlich sein. Aus diesem Grund ist das optische Lasersystem mit einem Schutzgehäuse und einer Außenabdeckung dicht verschlossen und hat eine Struktur, die keine L aserstrahlen nach außen dringen lässt. Unter der Voraussetzung, dass der Benutzer d ieses Gerät normal
bedient, ist ein Austritt von Laserstrahlen daher ausgeschlossen.
1.6.2 Safety of Toner
1. Toner in General
Toner is a non-toxic material made up of plastic, iron, and small amounts of dye.
Do not throw toner into fire. Doing so can lead to explosion.
0021-1272
2. Contact with Toner
- Toner on the skin or clothes must be removed using dry tissue and then washed with water.
- The use of warm water must be avoided, doing so will cause the toner to turn gel-like and to permanently fuse with the fibers of the clothes.
- Contact with vinyl must also be avoided, as toner can readily react.
3. Store of Copy/Print Output
- Be sure to use transparency cases for storing copy/print output.
Do not use transparency cases made from polyvinyl chloride materials. If the copied surface contacts to the case, toner on the surface of the output dissolves and
the output may adhere to the case.
1.6.3 Handling the Laser Unit
When servicing the area around the laser assembly, be sure to turn off the main power.
If you must servicr while the power is turned on, be sure to keep the followings:
- Do not use a screwdriver or tools that have a high level of reflectance in the laser path.
- Remove watches and rings before starting the work. (They can reflect the laser beam, possibly hitting the eye.)
The machine's covers that can reflect laser light are identified by means of a warning label (Figure). If you must detach a cover showing the label, be sure to take
extra caution during the work.
0021-1273
The following warnings are given to comply with Safety Principles (EN60950).
F-1-5
1-6
F-1-6
Chapter 1
1.6.4 Points to note at disassembly/installation procedure
At disassembly/installation procedure, make sure to follow the instruction below to proceed.
1. Be sure to unplug the power code before disassembly/installation.
2. At installation, follow the procedure in the reverse order of disassembly unless otherwise instructed.
3. Be careful of the screw type (length, diameter) and corresponding part.
4. To check the electrical conductivity, washer equipped screw is used to attach the grounding wire and the varistor etc. When attaching them, be sure to use this
screw.
5. In principle, do not operate the machine without any part.
6. Be sure not to unscrew the screw with painting at disassembly.
0021-1274
1-7

Chapter 2 TECHNICAL REFERENCE

Contents
Contents
2.1 Functional Configuration............................................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.1.1 Outline.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.2 Basic Sequense...............................................................................................................................................................2-1
2.2.1 Basic Sequence of Operation ....................................................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.3 LASER EXPOSURE SYSTEM.....................................................................................................................................2-1
2.3.1 Overview/Configuration .............................................................................................................................................................. 2-1
2.3.1.1 Outline.............................................................................................................................................................................................................2-1
2.3.2 Laser Scanner Motor Control....................................................................................................................................................... 2-2
2.3.2.1 Fault Detection ................................................................................................................................................................................................2-2
2.4 IMAGE FORMATION SYSTEM.................................................................................................................................2-2
2.4.1 Overview/Configuration .............................................................................................................................................................. 2-2
2.4.1.1 Outline.............................................................................................................................................................................................................2-2
2.4.1.2 Image-formation Process ................................................................................................................................................................................2-3
2.4.1.3 Latent image formation block.........................................................................................................................................................................2-3
2.4.1.4 Development block .........................................................................................................................................................................................2-4
2.4.1.5 Transfer block .................................................................................................................................................................................................2-4
2.4.1.6 Fixing block ....................................................................................................................................................................................................2-5
2.4.1.7 ITB cleaning block..........................................................................................................................................................................................2-6
2.4.1.8 Photosensitive drum cleaning block................. ...................................... ... ......................................................................................................2-6
2.4.2 High-Voltage Control .................................................................................................................................................................. 2-7
2.4.2.1 Outline.............................................................................................................................................................................................................2-7
2.4.3 Image Stabilizaton Control .......................................................................................................................................................... 2-8
2.4.3.1 Overview of the Image Stabilization Control Mechanism..............................................................................................................................2-8
2.4.3.2 Image density correction control (D-max contro l).............................. ...................................... ... ...................................................................2-8
2.4.3.3 Image gradation correction control (D-half control).......................................................................................................................................2-9
2.4.3.4 Color displacement correction control............................................................................................................................................................2-9
2.4.4 Drum Cartridge............................................................................................................................................................................ 2-9
2.4.4.1 Developing roller engagement/disen gagement control. ...................................... ... .........................................................................................2-9
2.4.5 Transfer Unit.............................................................................................................................................................................. 2-10
2.4.5.1 Pad transfer....................................................................................................................................................................................................2-10
2.5 Pickup/Feeding/Delivery System.................................................................................................................................2-11
2.5.1 Overview/Configuration ............................................................................................................................................................ 2-11
2.5.1.1 Overview.......................................................................................................................................................................................................2-11
2.5.2 Detecting Jams........................................................................................................................................................................... 2-12
2.5.2.1 Jam Detection Outline...................................................................................................................................................................................2-12
2.5.2.1.1 Outline................................... ... ...................................... ... .... ................................................................................................................2-12
2.5.2.2 Delay Jams ....................................................................................................................................................................................................2-12
2.5.2.2.1 Pickup delay jam 1 ................................................................................................................................................................................2-12
2.5.2.2.2 Pickup delay jam 2 ................................................................................................................................................................................2-12
2.5.2.2.3 Fixing delivery delay jam......................................................................................................................................................................2-12
2.5.2.3 Stationary Jams .............................................................................................................................................................................................2-12
2.5.2.3.1 Pickup stationary jam............................................................................................................................................................................2-12
2.5.2.3.2 Fixing delivery stationary jam ..............................................................................................................................................................2-13
2.5.2.4 Other Jams.....................................................................................................................................................................................................2-13
2.5.2.4.1 Fixing wrapping-up jam........................................................................................................................................................................2-13
2.5.2.4.2 Inside stationary jam 1 ................................................................ ... .......................................................................................................2-13
2.5.2.4.3 Inside stationary jam 4 ................................................................ ... .......................................................................................................2-13
2.5.2.4.4 Duplex re-pickup jam............................................................................................................................................................................2-13
2.5.2.4.5 Door open jam.......................................................................................................................................................................................2-13
2.5.3 Cassette Pickup .......................................................................................................................................................................... 2-13
2.5.3.1 Separation Roller Method .............................................................................................................................................................................2-13
2.6 FIXING UNIT SYSTEM.............................................................................................................................................2-14
2.6.1 Overview/Configuration ............................................................................................................................................................ 2-14

Contents
2.6.1.1 Outline ..........................................................................................................................................................................................................2-14
2.6.2 Various Control Mechanisms .................................................................................................................................................... 2-14
2.6.2.1 Controlling the Speed of the Fixing Unit...................................................................................................................................................... 2-14
2.6.2.1.1 The speed control of small size paper (throughput down control) ...................................................................................................... 2-14
2.6.2.2 Fixing Temperature Control ......................................................................................................................................................................... 2-15
2.6.2.2.1 Fixing temperature control....................................................................................................................................................................2-15
2.6.3 Protective Functions................................................................................................................................................................... 2-15
2.6.3.1 Protective function........................................................................................................................................................................................ 2-15
2.6.3.2 Fixing unit failure detection..........................................................................................................................................................................2-15
2.7 EXTERNAL AND CONTROLS SYSTEM ............................................................................................................... 2-16
2.7.1 Power Supply............................................................................................................................................................................. 2-16
2.7.1.1 Power Supply................................................................................................................................................................................................2-16
2.7.1.1.1 Low-voltage power supply ...................................................................................................................................................................2-16
2.7.1.2 Other Function ..............................................................................................................................................................................................2-17
2.7.1.2.1 Protective function....................................... ... ...................................... ... ............................................................................................. 2-17
2.7.1.2.2 Power-save mode.................................................. ................................................................................................................................ 2-17
2.8 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM .............. ................................................... ................................................................ 2-17
2.8.1 Construction............................................................................................................................................................................... 2-17
2.8.1.1 Outline ..........................................................................................................................................................................................................2-17
2.8.1.2 Motor control ................................................................................................................................................................................................2-18
2.8.1.3 Safety ............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 2-18
2.8.2 Main Controller.......................................................................................................................................................................... 2-18
2.8.2.1 Outline ..........................................................................................................................................................................................................2-18
2.8.2.2 Overview of the Block..................................................................................................................................................................................2-19
2.1 Functional Configuration
Chapter 2
2.1.1 Outline
The machine may be broadly divided into the following 6 functional blocks: engine control system, laser exposure system, image formation system, pickup/transport/delivery system, fixing system, and externals/auxiliary control system.
0021-1275
Laser exposure system
Image formation system
Engine control
Pickup/transport/delivery system
system
Fixing system
Externals and control system
To external device
F-2-1
2.2 Basic Sequense
2.2.1 Basic Sequence of Operation
The operational sequence of the printer is controlled by the DC controller in the engine control system.
Table describes periods, durations and operations for each period of a print operation from the printer is turned on until the motors stop rotating.
Period Duration Operation
WAIT From the time the power switch is turned on, the door
STBY
(Standby)
INTR
(Initial rotation period)
PRINT From the end of INTR period until the last media
LSTR
(Last rotation
period)
is closed or the Sleep mode is released until the
printer gets ready for a print operation
From the end of WAIT or LSTR period until either
the print command is received from the main
controller or the power switch is turned off
From the time the print command is received from
the main controller during STBY period until the
temperature of the fixing unit reaches the targeted
temperature
completes the fixing operation
From the end of PRINT period until the motors stop
rotating
T-2-1
Brings the printer to printable condition
The printer performs the following during this period:
- Detects the pressure roller pressurized status
- Detects the presence of each cartridge and unit
- Determines the homeposition of the development unit
- Cleans the ITB
- Completes any required calibration, such as color
misregistration and image stabilization control
Maintains the printer in printable condition The printer performs the following
during this period:
- Enters Sleep mode when the main controller sends a sleep command
- Completes any required calibration, such as color misregistration control and
image stabilization control, when the main controller sends a command
Starts up each high-voltage bias, laser scanner unit and fixing unit for preparing a
print operation
Forms the image on the photosensitive drum based on the video signals from the
main controller, transfers and fuses the toner image to the print media The printer
performs color misregistration control and image stabilization control at a specified
print interval after the printer is turned on
Moves the last printed sheet out of the printer and stops the laser scanner unit
operation and high-voltage biases The printer enters INTR period as soon as the
LSTR period is completed if another print command is received from the main
controller
0021-1276
2.3 LASER EXPOSURE SYSTEM
2.3.1 Overview/Configuration
2.3.1.1 Outline
The laser scanner system forms the latent image on the photosensitive drum according to the VIDEO signals sent from the main controller.
0021-1304
2-1
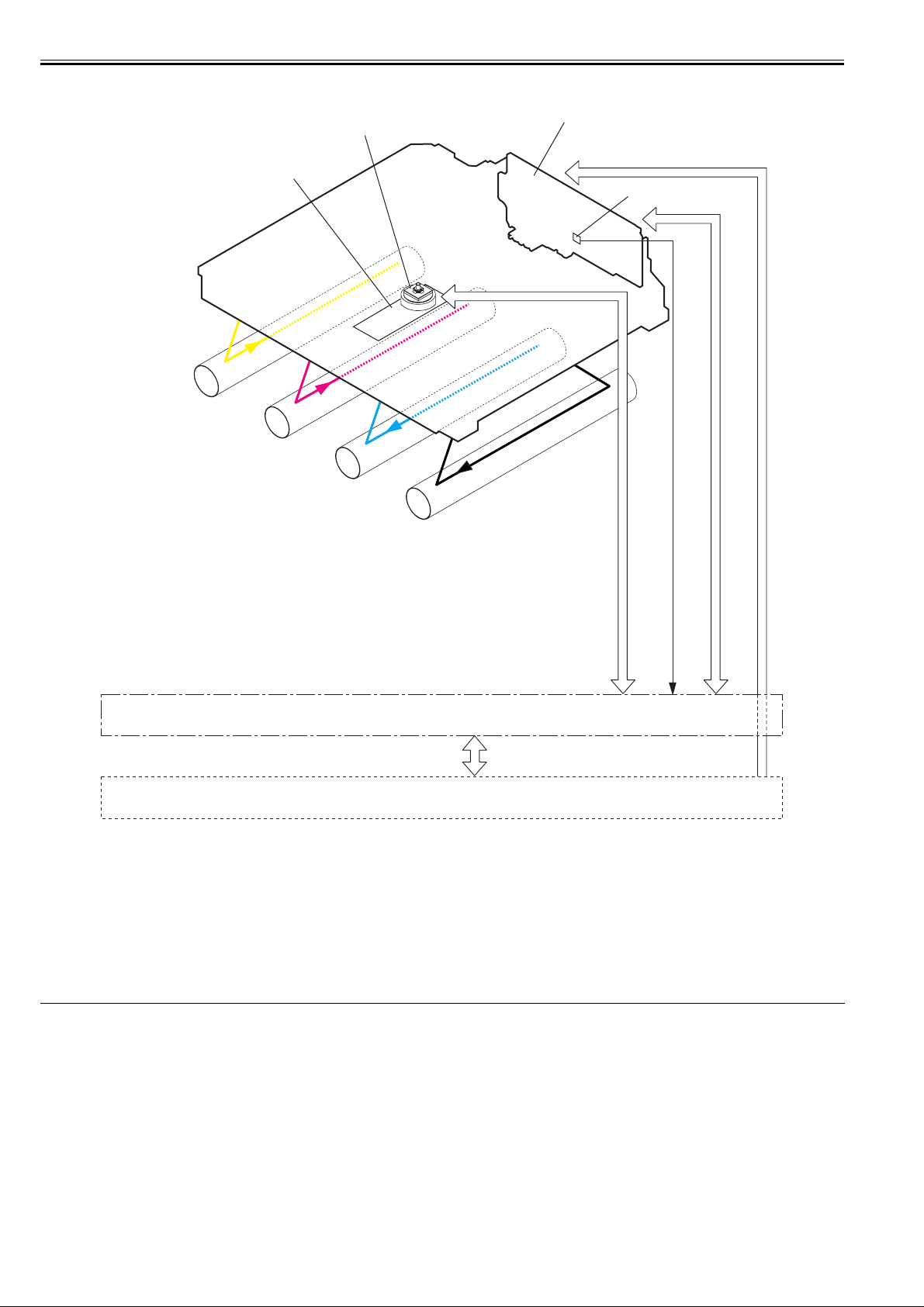
Chapter 2
The main components of the laser scanner unit are the laser driver and the scanner motor unit and are controlled by the signals sent from the DC controller.
Scaner motor unit
Photosensitive drum
(Y)
Photosensitive drum
Polygon mirror
Laser driver PCB
BD PCB
(M)
Photosensitive drum
(C)
Photosensitive drum
(Bk)
LASER CONTROL signal
SCANNER MOTOR
SPEED CONTROL signal
BD INPUT signal
VIDEO signal
DC controller
Main controller
F-2-2
2.3.2 Laser Scanner Motor Control
2.3.2.1 Fault Detection
1. Scanner motor failure
- The scanner motor does not reach a specified rotation within a specified period after starting-up the laser scanner motor.
- The rotation of the scanner motor is out of specified range for a specified period during scanner motor drive.
2. BD failure
- The BD interval is detected at out of a specified value during a print operation.
0021-1305
2.4 IMAGE FORMATION SYSTEM
2.4.1 Overview/Configuration
2.4.1.1 Outline
The image-formation system is the central hub of the printer. It forms the toner image on the media.
The following are the main components of the image-formation system:
- Four cartridges
- ITB
- Laser scanner unit
- Fixing unit
The DC controller controls the laser scanner unit and high-voltage power supply to form the toner image on the photosensitive drums according to the VIDEO
signals. The image is transferred to the print media through the ITB and fixed.
0021-1306
2-2

Fixing unit
Cartridge
ITB cleaning unit
Secondary transfer
external roller
Chapter 2
Laser scanner
Laser beam
Photosensitive drum
ITB
Primary transfer pad
High-voltage power supply
DC controller
F-2-3
2.4.1.2 Image-formation Process
The image-formation process consists of the following nine steps divided among six functional blocks:
Step 1: Primary charging
Step 2: Laser-beam exposure
Step 3: Development
Step 4: Primary transfer
Step 5: Secondary transfer
Step 6: Separation
Step 7: Fixing
Step 8: ITB cleaning
Step 9: Drum cleaning
Delivery
Fixing block
7. Fixing
6. Separation
Development
block
3. Development
Static image formation block
2. Laser beam exposure
1. Primary charging
Drum cleaning block
ITB cleaning
block
8. ITB cleaning
5. Secondary transfer
Primary transfer
4.
9. Drum cleaning
0021-1307
Flow of paper
Rotation of ITB/photosensitive drum
Block
Step
Transfer block
Registration
Pickup
F-2-4
2.4.1.3 Latent image formation block
During the two steps that comprise this block, an invisible latent image is formed on the photosensitive drum.
Step 1: Primary charging
To prepare for latent image formation, the surface of the photosensitive drum is charged with a uniform negative potential.
0021-1308
2-3
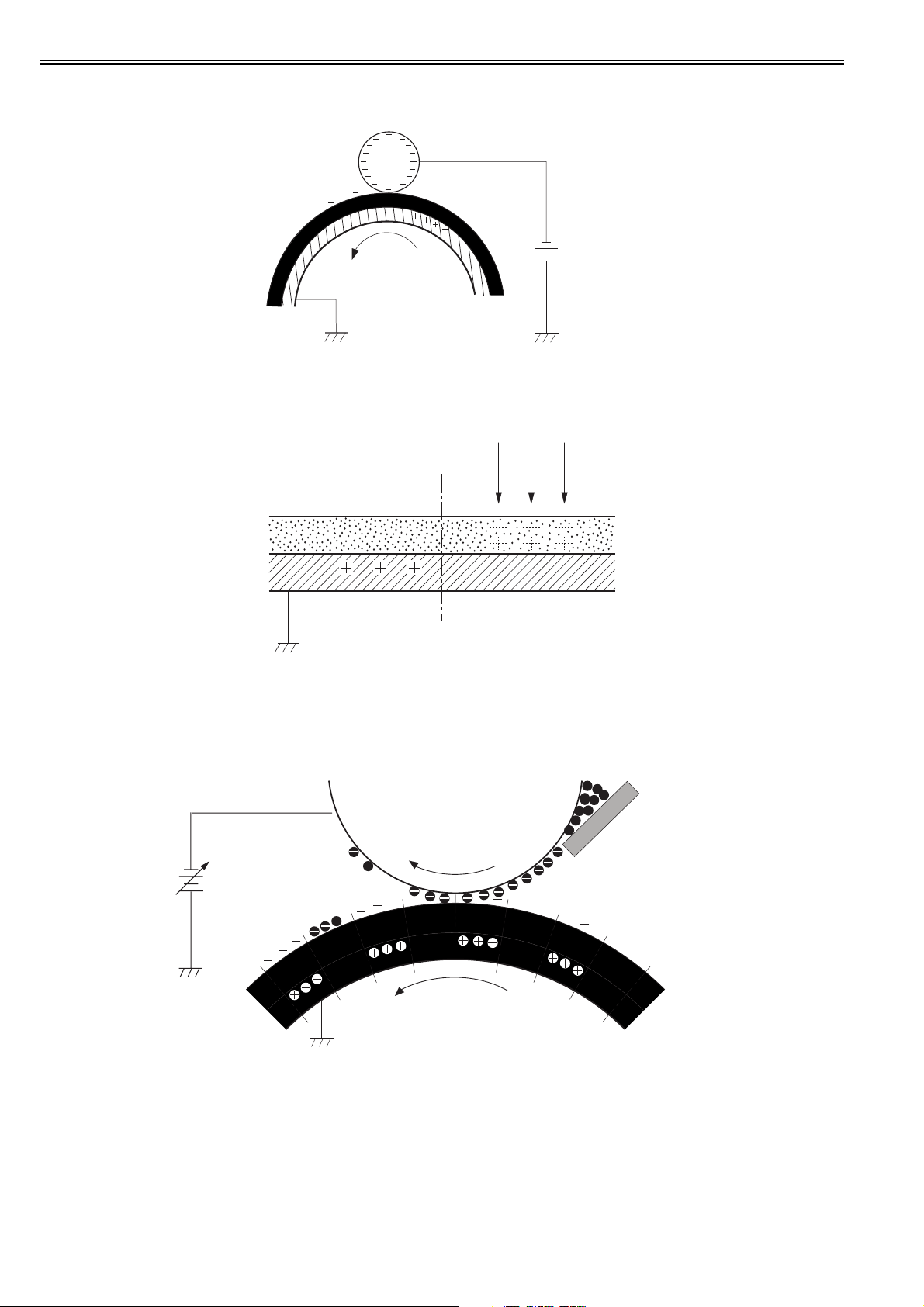
Chapter 2
The primary charging roller charges the photosensitive drum directly. The DC negative bias is applied to the primary charging roller to keep a negative potential
on the drum surface.
Primary charging roller
DC bias
Photosensitive drum
F-2-5
Step 2: Laser-beam exposure
The laser beam scans the photosensitive drum to neutralize the negative charge on portions of the drum surface. An electrostatic latent image forms where the
negative charge was neutralized.
Laser beam
Unexposed area Exposed area
F-2-6
2.4.1.4 Development block
Toner adheres to the electrostatic latent image on the photosensitive drum, which becomes visible.
Step 3: Development
Toner acquires a negative charge from the friction that occurs when the developing cylinder rotates against the developing blade. When the negatively charged
toner comes in contact with the drum, it adheres to the latent image because the drum surface has a higher potential.
Developing blade
Developing cylinder
DC negative bias
Exposed area
Unexposed area
Photosensitive drum
F-2-7
Unexposed area
Exposed area
0021-1309
2.4.1.5 Transfer block
During the three steps that comprise this block, a toner image on the photosensitive drum is transferred to the print media through the ITB.
Step 4: Primary transfer
The toner image on the photosensitive drum is transferred to the ITB. The DC positive bias is applied to the primary transfer pad. The negatively charged toner
transfers to the ITB from the drum surface.
2-4
0021-1310

Chapter 2
Photosensitive
drum
ITB
Primary transfer pad
DC bias
F-2-8
Step 5: Secondary transfer
The toner image on the ITB is transferred to the print media. The DC positive bias is applied to the secondary transfer roller. As the media passes between the
secondary transfer roller and the ITB, the toner image is transferred to the media.
Media
ITB
Static charge eliminator
ITB drive roller
Secondary
transfer external roller
DC bias
F-2-9
Step 6: Separation
The elasticity of the print media and the curvature of the ITB drive roller cause the media to separate from the ITB.
Media
ITB
ITB drive roller
Secondary
transfer external roller
F-2-10
2.4.1.6 Fixing block
The toner image is fixed onto the print media.
Step 7: Fixing
The printer uses an on-demand fixing method to fix the toner image onto the media. The toner image is permanently affixed to the print media by the heat and
pressure.
0021-1311
2-5
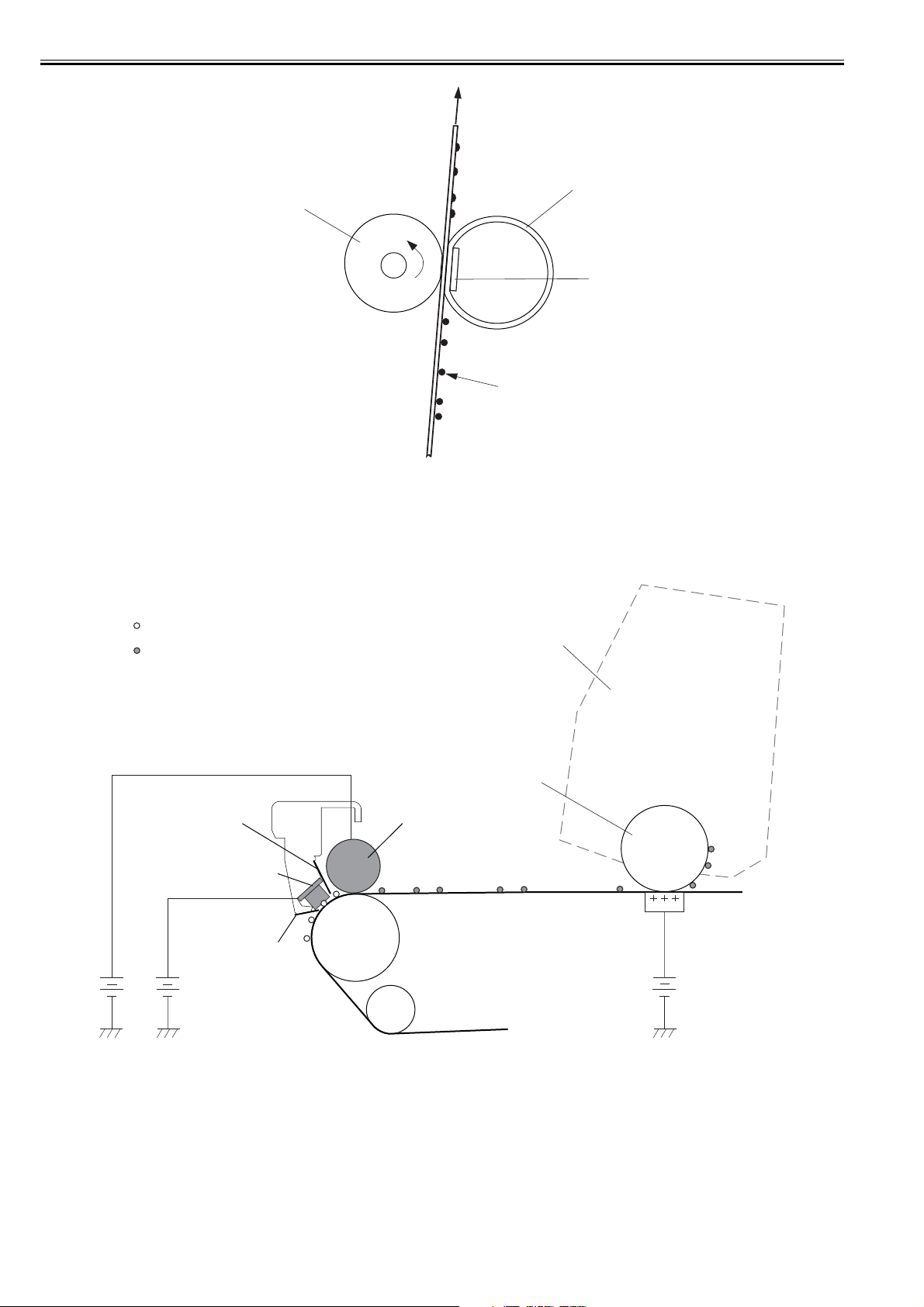
Chapter 2
Fixing film
Pressure roller
Fixing heater
Toner
Media
F-2-11
2.4.1.7 ITB cleaning block
The residual (waste) toner is cleared from the ITB surface.
Step 8: ITB cleaning
The ITB cleaning roller and the cleaning brush are applied with DC positive bias to charge the residual toner positive.
As the primary transfer pad is also applied with DC positive bias, the positively charged residual toner is reverse transferred to the photosensitive drum from the
ITB surface.
Positive potential waste toner
Cartridge
Negative potential waste toner
Photosensitive drum
Partition sheet
ITB cleaning roller
ITB cleaning brush
ITB
0021-1312
Sweeper strip
DC bias
F-2-12
DC bias
2.4.1.8 Photosensitive drum cleaning block
The waste toner is cleared from the photosensitive drum surface.
Step 9: Drum cleaning
The cleaning blade scrapes the waste toner off the surface of the photosensitive drum. The waste toner is deposited in the waste toner container.
2-6
0021-1313
2.4.2 High-Voltage Control
Chapter 2
Cleaning blade
Photosensitive
drum
Waste toner container
Sweeper strip
F-2-13
2.4.2.1 Outline
The high-voltage power supply generates the high-voltage biases that are applied to the primary charging roller, developing roller, primary transfer pad, secondary
transfer roller and ITB cleaning unit. The DC controller controls the high-voltage power supply to generate high-voltage biases.
0021-1314
2-7

Chapter 2
Primary charging
bias circuit
Photosensitive drum
Primary transfer pad
ITB
cleaning unit
Developing bias
Cartridge
circuit
Blade bias circuit
Secondary transfer
external roller
ITB cleaning brush
bias circuit
ITB cleaning roller
bias circuit
Secondary transfer
bias circuit
Primary transfer
bias circuit
High-voltage power supply
DC controller
F-2-14
2.4.3 Image Stabilizaton Control
2.4.3.1 Overview of the Image Stabilization Control Mechanism
The machine uses its image stabilization control mechanism to prevent lowering of image quality (e.g., in the form of a faulty image) otherwise caused by changes
in the environment or deterioration of the photosensitive drum or toner.
The machine's image stabilization control mechanism may be any of 3 types: Image density corrective control (D-max control), Image halftone corrective control
(D-half control), Color Misregistration Corrective Control.
2.4.3.2 Image density correction control (D-max control)
This control is to stabilize the image density of the printer engine.
If the prescribed condition is met, DC controller PCB performs D-max control in the following procedure.
1. Measure the each density detection pattern made on the ITB.
2. According to the measured density of each pattern, controls the primary charge bias and developing bias to get the appropriate density.
The following is the conditions that trigger the image density correction control
- When the power is ON
At power ON, Out-of-Register Colors Correction is suspended until the initial print process is completed and the machine is ready or until 15 min passes after
the power ON. The time setting can be changed from Option > Device Settings > Startup Settings in printer status window.
Startup Settings Calibration Out-of-Register Colors Correction Remarks
Execute Later Performed 15 minutes later Performed 15 minutes later Default
T-2-2
0021-1315
0021-1316
2-8
Execute Immediately (Level 1) Performed 15 minutes later Execute Immediately
Execute Immediately (Level 2) Execute Immediately Execute Immediately
- During toner cartridge replacement
- After a specified sheet number printing (200 sheets)
- If there is major environment change
- after the printing is completed, or 300 minutes after Image density correction control (D-max control)
- If there is calibration execution instruction from user.
MEMO:
- When the calibration is executed, sheet counter reading and elapsed time timer are cleared.
- Calibration is not executed in sleep mode.
Chapter 2
2.4.3.3 Image gradation correction control (D-half control)
This is a control that main controller PCB executes the gradation correction based on result of the halftone density measurement that is executed by DC controller
PCB.
After D-max control, DC controller PCB and main controller PCB execute the D-half control in the following procedure.
1. DC controller PCB measures the each color density detection pattern on ITB that is made by the appropriate primary charge bias that is determined at D-max
control and developing bias, and sends the density data to main controller PCB.
2. Main controller PCB executes the gradation correction to realize the ideal halftone image based on the data.
2.4.3.4 Color displacement correction control
This control is to correct the color displacement that appears due to the variation of laser scanner unit or toner cartridge.
The following objects are controlled by this color displacement correction.
- Write start position in main scanning direction
- Magnification in main scanning direction
- Write start position in sub scanning direction
When one of the following conditions is met, DC controller PCB controls the color displacement/density sensor and displacement sensor.
- At power ON
At power ON, Out-of-Register Colors Correction is suspended until the initial print process is completed and the machine is ready or until 15 min passes after
0021-1317
0021-1318
the power ON. The time setting can be changed from Option > Device Settings > Startup Settings in printer status window.
T-2-3
Startup Settings Calibration Out-of-Register Colors Correction Remarks
Execute Later Performed 15 minutes later Performed 15 minutes later Default
Execute Immediately (Level 1) Performed 15 minutes later Execute Immediately
Execute Immediately (Level 2) Execute Immediately Execute Immediately
- When closing the door after toner cartridge replacement
- After a specified sheet number printing (150 sheets)
- 60 minutes after the power is turned ON
- 240 minutes after the printing is completed, or 240 minutes after color displacement adjustment control execution
- If there is major environment change
MEMO:
- When the calibration is executed, sheet counter reading and elapsed time timer are cleared.
- Calibration is not executed in sleep mode.
The following is the sequences of this control.
1) DC controller calculates the degree of each color displacement by the color displacement detection pattern made on ITB and sends the color displacement information to main controller.
2) Main controller controls the each color video signal according the color displacement data and adjusts the write start position in main scanning direction, the
magnification in main scanning direction and the write start position in sub scanning direction.
At printer engine side, DC controller PCB also controls the scanner motor speed to correct the color displacement in sub scanning direction.
Scanning magnification
This indicates the image size in the main scanning direction.
Since this machine is equipped with the independent photosensitive drum for each color, the photosensitive drum position differs due to the toner cartridge variation
and that leads to the laser wave length difference. Thus, image range differs depending on a color in main scanning direction so that the color displacement occurs
at the edge of the image.
2.4.4 Drum Cartridge
2.4.4.1 Developing roller engagement/disengagement control
The developing cylinder engagement/disengagement control engages the required developing cylinder with the photosensitive drum according to the print mode,
full-color mode or monochrome mode.
The necessary developing cylinder is engaged with the photosensitive drum only when required, preventing a deterioration of the drums and making maximum use
of the life.
The engagement/disengagement of the developing cylinder is controlled by the DC cont roller rotating the main motor and changing the direction of the developing
disengagement cam. The DC controller controls the developing cylinder state, whether en gaged or disengaged, by coun ting the mai n motor rotation after it detects
the signal from the developing homeposition sensor.
All four colors' developing cylinders disengage from the photosensitive drums when the printer is turned on and when a print operation is completed. All four colors'
developing cylinders engage with the photosensitive drums when the full-color mode is designated. Only black's developing cylinder engages with the photosensitive drum when the monochrome mode is designated.
The DC controller determines an abnormality of the developing cylinder engagement/disengagement function and notifies the main controller when it does not
sense the signal from the developing homeposition sensor for a specified period during the developing cylinder engagement/disengagement operation.
0021-1319
2-9
 Loading...
Loading...