Bushnell NORTHSTAR GOTORV 78-8890, NORTHSTAR GOTORV 78-8840, NORTHSTAR GOTORV 78-8846, NORTHSTAR GOTORV 78-8850, NORTHSTAR GOTORV 78-8831 User Manual

WITH REALVOICE™ OUTPUT
INSTRUCTION
78-8840, 78-8850, 78-8890 MAKSUTOV-CASSEGRAIN
78-8831 76MM REFLECTOR
MANUAL
78-8846 114MM REFLECTOR
Lit.#: 98-0433/05-05

CONTENTS
ENGLISH ....................................................................... 2
FRANÇAIS .....................................................................35
ESPAÑOL ......................................................................
DEUTSCH ....................................................................103
ITALIANO ...................................................................
PORTUGUÊS ...............................................................
69
137
171

Congratulations on the purchase of your Bushnell Northstar Goto Telescope with Real Voice Output! This is
the first telescope ever created that actually speaks to you to educate you about the night sky. Consider this
feature as your personal astronomy assistant.
After reading through this manual and preparing for your observing session as outlined in these pages you
can start enjoying the Real Voice Output feature by doing the following:
To activate your telescope, simply turn it on! The Real Voice Output feature is built in to the remote control
handset.
Along the way the telescope will speak various helpful comments during the alignment process. Once aligned,
the Real Voice Output feature will really shine anytime the enter key is depressed when an object name or
number is displayed at the bottom right of the LCD viewscreen. That object description will be spoken to
you as you follow along with the scrolling text description.
If at anytime you wish to disable the speaking feature, you can cancel the speech by pressing the “Back”
button on the remote control keypad.
It is our sincere hope that you will enjoy this telescope for years to come!
2.
NEVER LOOK DIRECTLY AT THE SUN
WITH YOUR TELESCOPE
❂
PERMANENT DAMAGE TO YOUR EYES
MAY OCCUR

WHERE DO I START?
Your Bushnell telescope can bring the wonders of the universe to your eye. While this
manual is intended to assist you in the set-up and basic use of this instrument, it does not
cover everything you might like to know about astronomy. Although Northstar will give a
respectable tour of the night sky, it is recommended you get a very simple star chart and a
flashlight with a red bulb or red cellophane over the end. For objects other than stars and
constellations, a basic guide to astronomy is a must. Some recommended sources appear
on our website at www.bushnell.com. Also on our website will be current events in the
sky for suggested viewing. But, some of the standbys that you can see are:
The Moon
Try viewing at different phases of the moon. Lunar highlands, lunar maria (lowlands called
“seas” for their dark coloration), craters, ridges and mountains will astound you.
Saturn
This is one of the most satisfying objects in the sky to see simply because it looks like it
does in pictures. Imagine seeing what you’ve seen in textbooks or NASA images from your
backyard!
Jupiter
dark stripes or bands both above and below its equator. These are the north and south
equatorial belts. Also interesting are Jupiter’s four major moons. Pay close attention to their
positions from night to night. They appear to be lined up on either side of Jupiter.
Mars
the year and try to catch a glimpse of the white polar ice caps.
Venus—just like the moon, Venus changes phases from month to month. At times Venus
appears brilliantly in the night sky, just as if you were looking at a distant crescent moon.
Nebulae
others are brought to you by this telescope.
Star Clusters
Galaxies—One of the greatest and most interesting galaxies is our neighbor the Andromeda
Galaxy. Enjoy this and many others.
—a wonderful view of our lunar neighbor can be enjoyed with any magnification.
—even at the lowest power you should be able to see Saturn’s rings and moons.
—the largest planet in our solar system is spectacular. Most noted features are its
—The Great Red Planet appears as a reddish-orange disk. Look at different times of
—The Great Orion Nebula is a very well known night sky object. This and many
—
View millions of stars densely packed in a cluster that resembles a ball.
3.
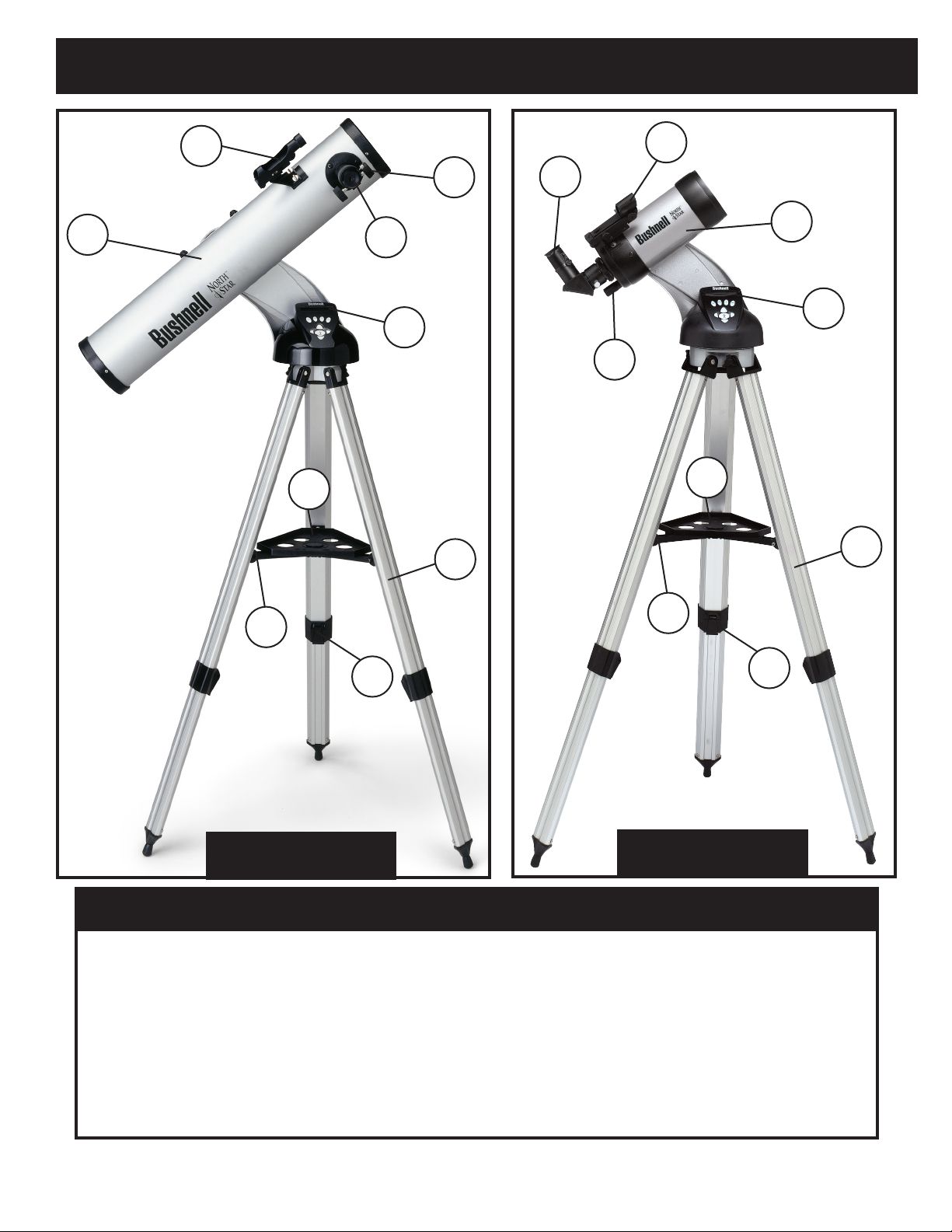
PARTS DIAGRAMS
8.
1.
6.
2.
7.
3.
9.
1.
2.
8.
7.
3.
6.
9.
4.
5.
78-8831 / 78-8846
Telescope Parts Diagram
1. Red Dot Finderscope
2. 1.25" Format Eyepiece
3. Rack and Pinion Focusing Mechanism
4. Accessory Tray Brace
5. Quick-Release Tripod Leg Lever
4.
5.
78-8840, 78-8850,
78-8890
6. Quick-Release Accessory Tray
7. Remote Computer Controller
8. Main Telescope Tube
9. Quick-Release Adjustable Aluminum Tripod
4.
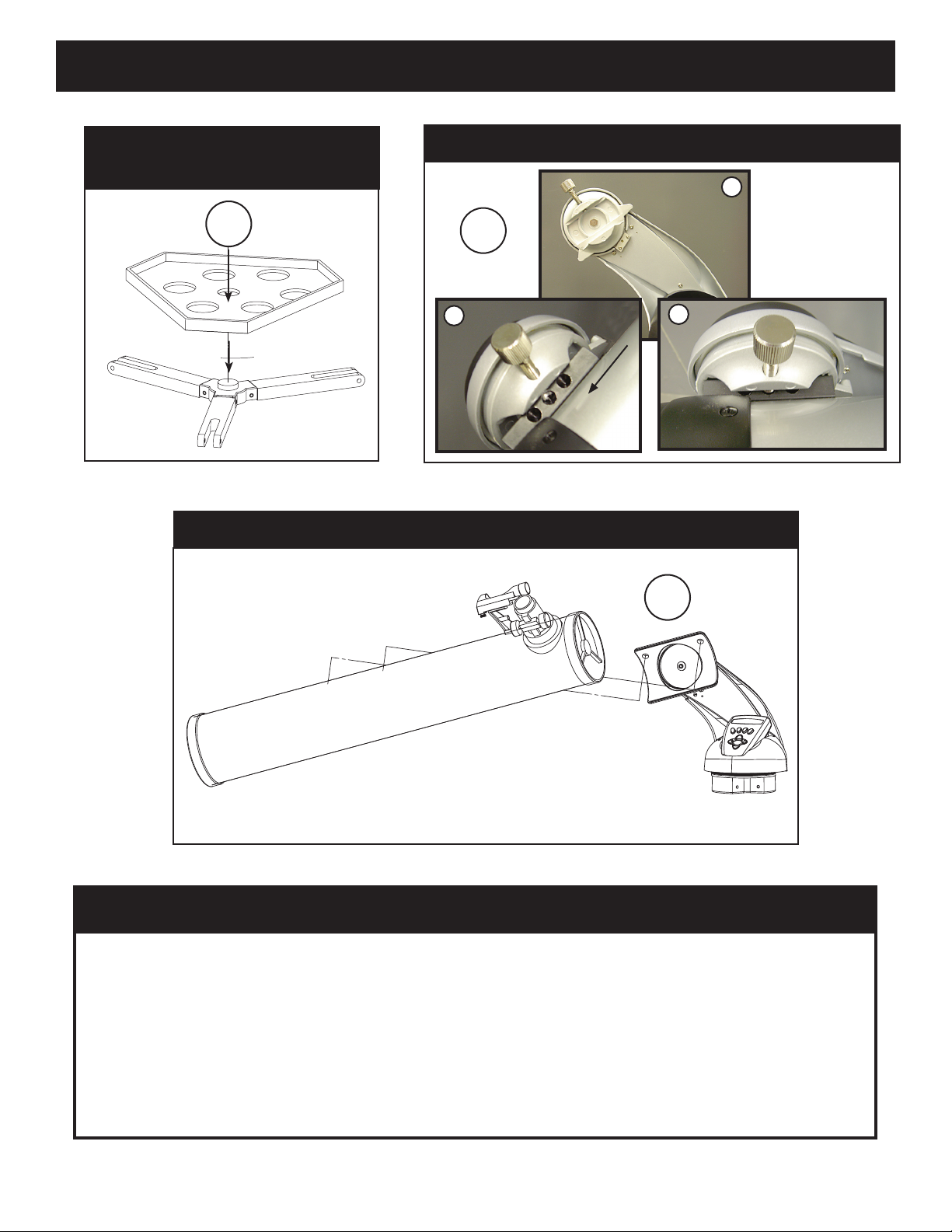
QUICK ASSEMBLY DIAGRAM
78-8831 / 78-8846 / 78-8840
78-8850 / 78-8890
1.
78-8840, 78-8850, 78-8890
2.
B
78-8831 / 78-8846
A
C
PARTS LIST
• Adjustable Aluminum Tripod Assembly
(Pre-assembled to Northstar Computerized Star Locator Base)
• Quick Release Accessory Tray
• Northstar Telescope with finger attachment nuts
2.
• Red Dot Finderscope
• 2 Eyepiece
• Barlow Lens (Reflectors Only)
• 90˚ Erecting Prism (Maksutov Only)
s
5.

DETAILED ASSEMBLY
No tools are required for assembly of your telescope.
Remove all components from the carton and identify all components. It is a good idea to lay all the parts out in front of you before
assembly. Since your telescope is a precision optical system the parts require careful handling—particularly the onboard computer,
telescope, eyepieces, and various accessory lenses.
SET UP TRIPOD AND ACCESSORY TRAY
1. Stand Northstar Computerized Star Locator Assembly and attached tripod legs in the upright position.
Spread tripod legs to a comfortable distance.
2. Fold down the accessory tray braces and place the Quick Release Accessory Tray on top of braces.
(See Quick Assembly Diagram)
3. Turn accessory tray until it snaps into place.
4. Adjust tripod leg height to suit by opening tripod leg lever and extending tripod legs to desired height.
Clamp Tripod Leg lever closed when complete.
ATTACH TELESCOPE TUBE
1. Locate Main Telescope Tube.
2. Remove Telescope Tube Thumb Nuts from side of Telescope Tube (78-8831 and 78-8846 only). For 78-8890, back out silver lug
screw on Telescope Mount top.
3. Position Main Telescope Tube Attachment Bolts through Telescope Tube Bracket at the top of the Northstar Computerized
Star Locator Assembly (78-8831 and 78-8846 only). For 78-8890, slide black telescope tube bracket into telescope mount
receiver. Make sure telescope is pointing in the correction direction. (Logo on telescope tube should be right-side up.)
4. Reattach Telescope Tube Thumb Nuts to Main Telescope Tube Attachment Bolts once Main Telescope Tube and Northstar
Computerized Star Locator Assembly are assembled together (78-8831 and 78-8846 only). For 78-8890, tighten silver lug screw
on Telescope Mount top into desired depression on the black telescope tube bracket.
ATTACH FINAL TELESCOPE ACCESSORIES
1. Locate Red Dot Finderscope.
For Reflector Telescopes: Remove Finderscope attachment nuts from Main Telescope Tube. Place Finderscope
Assembly over Finderscope Attachment Bolts and reattach Finderscope thumb nuts to Finderscope Mount Bolts.
NOTE: The large end of the finderscope should face the open end of telescope tube.
2. Attach Low Power Eyepiece.
For Reflector Telescope Models: Insert lowest power eyepiece in the focusing mechanism by backing out
eyepiece set screw and inserting eyepiece fully.
3. Tighten all set screws to secure accessories.
SELECTING AN EYEPIECE
You should always start viewing with the lowest power eyepiece, which in this case is the 20 mm lens. Note: the base power of each
eyepiece is determined by the focal length of the telescope objective lens. A formula can be used to determine the power of each
eyepiece: telescope OBJECTIVE lens focal length divided by EYEPIECE focal length = MAGNIFICATION (e.g. Using the 20 mm
lens, a sample calculation could look like this: 750 mm / 20 = 38x or 38 power. Telescope models will vary in focal length.)
(Reflectors Only)
Included with this telescope is a Barlow lens. Barlow lenses are used to double or triple the power of your telescope. Place your
Barlow between the focusing tube and the eyepiece. Using the example above, your 3x Barlow lens would give you a total power of
114x or 114 power. (38 x 3 = 114x or 114 power). The magnification calculation would look like this: 750 mm /20mm = 38 power.
38 power x 3=114 power.
6.

DETAILED ASSEMBLY (CONTINUED)
M
FOCUSING TELESCOPE
1. After selecting the desired eyepiece, aim main telescope tube at a land-based target at least 200 yards away
(e.g. a telephone pole or building).
2. Fully extend Focusing Tube by turning Rack and Pinion Focusing Mechanism.
3. While looking through selected eyepiece (in this case the 20 mm), slowly retract Focusing Tube by turning Rack and Pinion
Focusing Mechanism until object comes into focus.
M
ATTACH REMOTE COMPUTER CONTROLLER AND BATTERY
1. Locate Remote Computer Controller and coil cord.
2. Locate Battery Door on Northstar Computerized Star Locator Base.
3. Remove Battery Door and insert one 9V battery.
4. Replace Battery Door.
5. Attach Remote Computer Controller with coil cord to Northstar Computerized Star Locator Base.
M
ALIGNING FINDERSCOPE
Look through Main Telescope Tube and establish a well-defined target. (see Focusing Telescope section)
Remove plastic insulator from between Red Dot Finderscope battery and battery clip.
Turn Red Dot Finderscope on.
Looking through Red Dot Finderscope, turn adjustment wheels until the red dot is precisely centered on the same object already
centered in Main Telescope Tube’s field of view.
Now, objects located first with the Red Dot Finderscope will be centered in the field of view of the main telescope.
NEVER LOOK DIRECTLY AT THE SUN
WITH YOUR TELESCOPE
❂
PERMANENT DAMAGE TO YOUR EYES
MAY OCCUR
7.

M
ENJOYING YOUR NEW TELESCOPE
1. First determine your targeted object. Any bright object in the night sky is a good starting point
One of the favorite starting points in astronomy is the moon. This is an object sure to please
any budding astronomer or experienced veteran. When you have developed proficiency at this
level, other objects become good targets. Saturn, Mars, Jupiter, and Venus are good second steps
to take.
2. The first thing you need to do after assembling the telescope as planned is center the desired object
in the finderscope’s cross hairs. Provided you did a reasonable job aligning the finderscope, a quick
look through the main telescope tube at low power should reveal the same image. With the lowest
power eyepiece (the one with the largest number printed on it) you should be able to focus the
same image that you saw through the finderscope. Avoid the temptation to move directly to the
highest power. The low power eyepiece will give you a wider field of view, and brighter image—thus
making it very easy to find your target object. At this point with a focused image in both scopes,
you’ve passed the first obstacle. If you don’t see an image after attempting to focus it in, you
might consider aligning your finderscope again. Once you pass this step, you’ll will enjoy the time
spent ensuring a good alignment. Every object you center in the finderscope will be easily found in
the main telescope tube, which is important for continuing your exploration of the night sky.
3. The low power eyepieces are perfect for viewing the full moon, planets, star clusters, nebulae, and
even constellations. These should build your foundation. However, for more detail, try bumping
up in magnification to higher power eyepieces on some of these objects. During calm and crisp
nights, the light/dark separation line on the moon (called the “Terminator”) is marvelous at high
power. You can see mountains, ridges and craters jump out at you due to the highlights. Similarly,
you can move up to higher magnifications on the planets and nebulae. Star clusters and individual
stars are best viewed through the low power no matter what.
4. The recurring astronomical theater we call the night sky is an ever-changing billboard. In other
words, the same movie does not play all the time. Rather, the positions of the stars change not
only hourly as they seem to rise and set, but also throughout the year. As the earth orbits the sun
our perspective on the stars changes on a yearly cycle about that orbit. The reason the sky seems
to move daily just as the sun and the moon “move” across our sky is that the earth is rotating about
its axis. As a result you may notice that after a few minutes or a few seconds depending on what
power you are viewing at, the objects in your telescope will move. At higher magnifications especially,
you will notice that the moon or Jupiter will “race” right out of the field of view. To compensate,
just move your telescope to “track” it in the necessary path.
8.

M
HELPFUL HINTS
1. Your telescope is a very sensitive instrument. For best results and fewer vibrations set your
telescope up on a level location on the ground rather than your concrete
wooden deck. This will provide a more stable foundation for viewing, especially if you’ve
drawn a crowd with your new telescope.
2.
If possible view from a location that has relatively few lights. This will allow you to see much
fainter objects. You’d be surprised how much more you’ll see from your local lake or park
when compared to a backyard in the city.
3. Using your telescope out a window is NEVER recommended.
4. View objects that are high in the sky if possible. Waiting until the object rises well above the
horizon will provide a brighter and crisper image.
several layers of earth’s atmosphere. Ever wonder why the moon appears orange as it sets on
the horizon?
than you would directly
are probably viewing on a very humid night.) During nights of unstable atmosphere, viewing
through a telescope can be frustrating if not impossible. Astronomers refer to crisp, clear
nights as nights of “good seeing.
It’s because you are looking through a considerable more amount of atmosphere
overhead. (Note: If objects high in the sky are distorted or wavy, you
”
Objects on the horizon are viewed through
driveway or your
9.
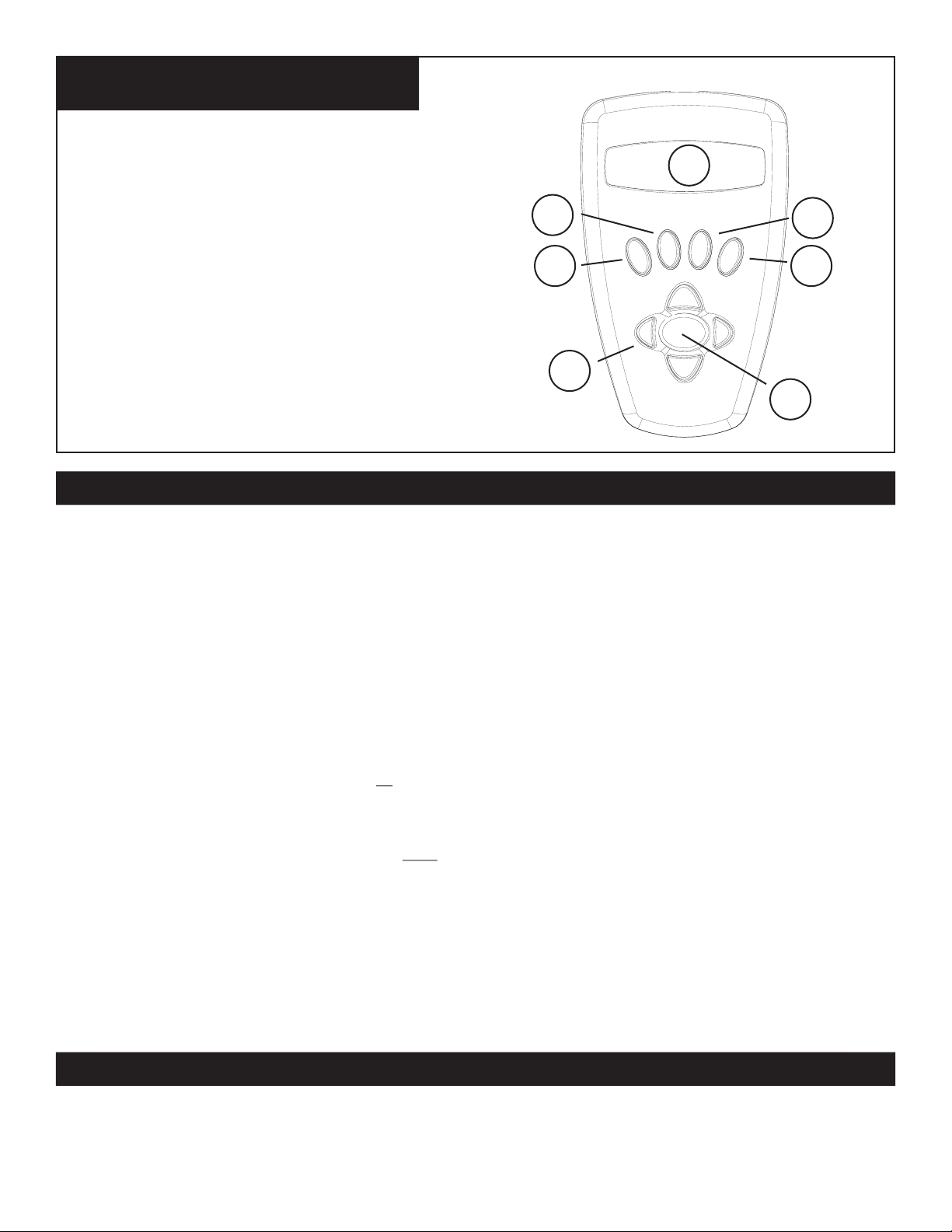
NORTHSTAR COMPUTER
INTERFACE DIAGRAM
1. On/Off Button (On Northstar Base)
2. Back Button
6.
3. Enter Button
3.
4.
4. Scroll Up Button
2.
5.
5. Scroll Down Button
6. LCD Display
7. “GO” Button
8. Motorized Movement Buttons (4)
8.
7.
9. Battery Door (On Northstar Base)
BUTTON FUNCTIONS
ALL BUTTONS ARE ILLUMINATED FOR NIGHTTIME USE.
On/Off Button: The On/Off Button will turn the Northstar Computerized Star Locator on and off. This button flashes or strobes
on and off during normal use. To turn the unit off, simply depress and hold the On/Off button for three seconds and release. (Note:
The Northstar Computerized Star Locator will automatically turn itself off after 10 minutes of inactivity.)
Back Button:
level of input. If at anytime you wish to disable the speaking feature, you can cancel the speech by pressing the “Back” button on
the remote control keypad.
This button functions to navigate to the previous level within the operating framework and/or back to the previous
Enter Button:
selected level. When an object name or number is listed on the screen, the ENTER button can also be pressed to hear a spoken
description and display a scrolling text description of the object.
Scroll Up Button:
text/number option, the scroll button will display the various choices within that menu. (Note: To select an option that you have
scrolled to, just press the ENTER button.)
Scroll Down Button:
blinking text/number option, the scroll button will display the various choices within that menu. (Note: To select an option that
you have scrolled to, just press the ENTER button.)
“GO” Button:
the telescope will automatically find and follow the selected object until another object is selected and the “GO” button is pushed
again.
Motorized Movement Buttons: These four multi-directional buttons will allow the user to override the tracking system and move
the telescope utilizing the motors manually to another desired location. The longer these buttons are depressed, the faster the
Northstar will move until it reaches its maximum speed.
This button functions to select certain menu choices. By pressing the ENTER button Northstar will advance to the
This button functions to scroll up through various menus within Northstar. Anytime you encounter a blinking
This button functions to scroll down through various menus within Northstar. Anytime you encounter a
The GO button will automatically center any object displayed on the LCD display. By pushing the “GO” button,
LCD DISPLAY
The Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) is a two-line, sixteen character display. The LCD is illuminated for use during nighttime viewing
just like the buttons.
10.

M
MODE OVERVIEW OF PRODUCT
Explore: The Explore Mode of Northstar provides the ability to explore various astronomical objects categorized
by object type. These objects would fall under one or more of the following types of objects: Deep Sky, Planets,
Constellations, and Stars. Each of these subheadings would also have subcategories of objects beneath their menu
structure. (See Menu Tree for full list of menu functions and options.)
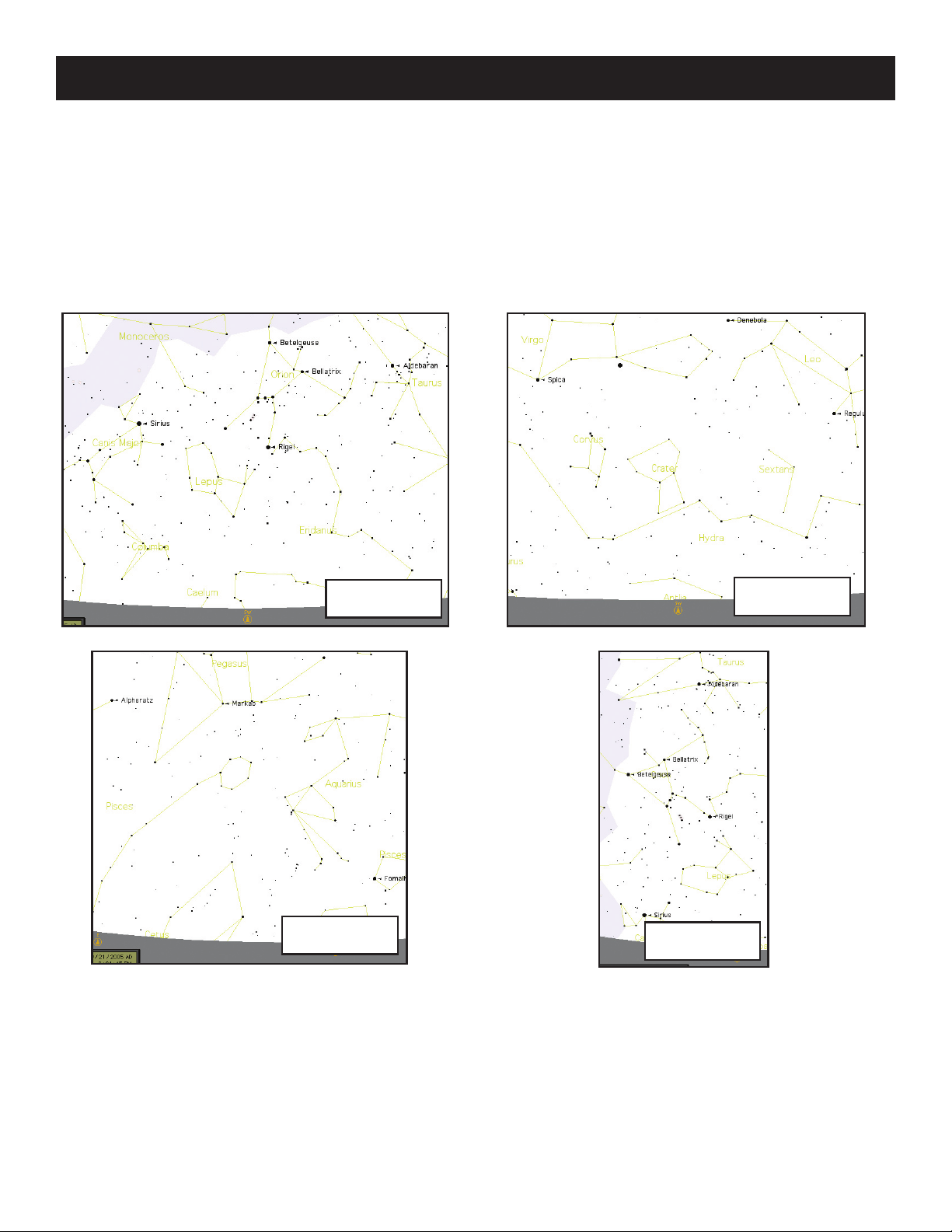
Sky Tour: The Sky Tour Mode of Northstar provides the ability to take a quick tour of the best and brightest objects for any
given month of the year. If the date has been input into the system, the Sky Tour Mode will automatically default to that
month. Objects can be chosen by using the scroll up or down arrows and pressing ENTER. To find out more information
about any given object press the ENTER button while that object is displayed to see the scrolling text message.
Telescope:
Coordinates for Right Ascension (RA) and Declination (DEC) as well as Altitude (ALT) and Azimuth (AZ) are displayed
simultaneously. In addition, in the lower right-hand corner will be the abbreviation for the current constellation that the
telescope is pointed at.
Identify: The Identify Mode of Northstar provides the ability to identify any object within your telescope field of view
Subcategories for different classes of identifiable objects are included as well as an Identify Any option.
Align Earth:
information non-astronomers would readily know. By entering simple information such as time, date, city, etc. a first time
telescope user can explore the immense Northstar database of astronomical objects within minutes.
Align Star:
knowledge. By knowing where two stars are located in the sky, a novice user can circumvent the city, date, and time input
and quickly start utilizing the Northstar database to locate amazing astronomical objects.
Align Object:
of your observing session. This might come in very handy if the family dog has just bumped the telescope out of alignment.
By using this mode you can center the telescope on any known object and select align object to quickly recalibrate the
Northstar alignment allowing continued enjoyment for the duration of the evening.
The Telescope Mode of Northstar provides real-time data on where the telescope is pointing. Astronomical
The Align Earth Mode of Northstar provides the ability to easily align your telescope utilizing common
The Align Star Mode of Northstar provides the ability to align your telescope utilizing some astronomical
The Align Object Mode of Northstar provides the ability to refine your telescope alignment during the middle
11.
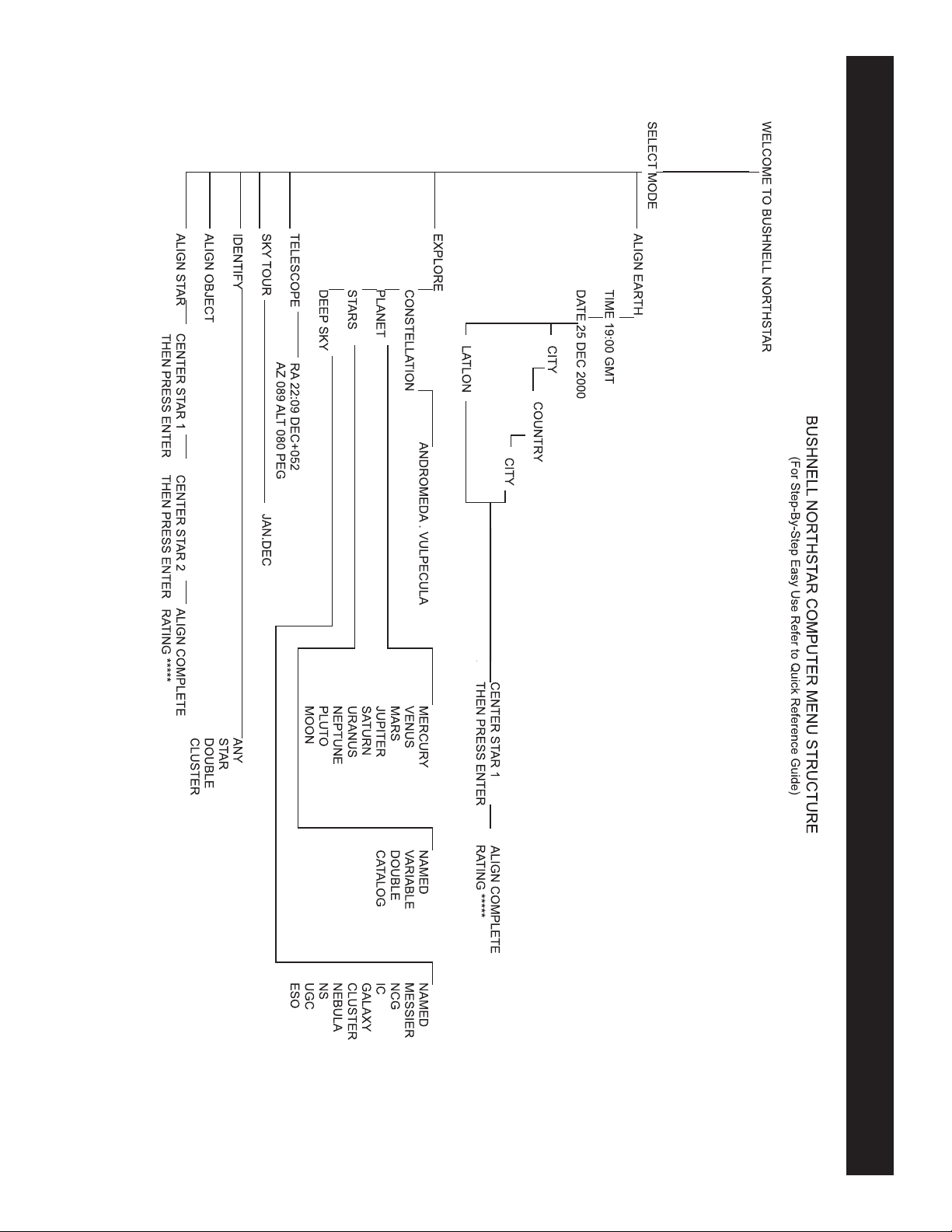
M
MENU TREE

M
ALIGNING NORTHSTAR FOR THE FIRST TIME
(NOTE: Make certain that the telescope is set up on a level surface.)
STEP 1:
Before turning the telescope on, remove the remote control handset. When you turn the telescope on, a spoken and scrolling
message will occur:
BUSHNELL NORTHSTAR Vx.x
Following this message, the telescope will execute a diagnostic check and level the telescope tube in relation to the telescope mount.
Then the default menu will appear:
SELECT MODE
ALIGN EARTH ][
This mode assumes that even if the telescope user is a first time user and does not know anything about astronomy that they
can be successful aligning the telescope in a few simple steps.
The ALIGN EARTH option is flashing.
Press ENTER to choose ALIGN EARTH option.
NOTE: ANY FLASHING ITEM ON THE DISPLAY IS A MENU CHOICE. OTHER CHOICES ARE AVAILABLE BY USING
THE SCROLL UP OR SCROLL DOWN BUTTONS.
STEP 2: SET THE TIME
By using the SCROLL UP and SCROLL DOWN buttons and the ENTER button, the time can easily be set as well as the
time zone. Each flashing option will need to be changed to read the appropriate number. Once the appropriate number is
displayed, accept the number by pressing ENTER. Then set the next flashing option until the time and time zone are set.
STEP 3: SET THE DATE
Again by using the SCROLL UP and SCROLL DOWN buttons and the ENTER button, the date can easily be set. Each
flashing option will need to be changed to read the appropriate number or month. Once the appropriate number is displayed,
accept the number by pressing ENTER. Then set the next flashing option until the day, month and year are set.
STEP 4: SET THE LOCATION
The next screen will display:
ALIGN EARTH
CITY ][
CITY will be flashing. By pressing the ENTER button, the display will change to:
COUNTRY
U.S.A.][
The country will be flashing.
13.
M
ALIGNING NORTHSTAR FOR THE FIRST TIME (Continued)
Again by using the SCROLL UP and SCROLL DOWN buttons and the ENTER button, the COUNTRY can be chosen.
When the appropriate Country is found and the ENTER button is pushed, choose the city that you are closest to by pressing ENTER
when it is displayed.
NOTE: CHOOSE THE CITY CLOSEST TO YOUR VIEWING LOCATION. THIS IS NOT A CRITICAL STEP AND THE
ALIGNMENT WILL BE REFINED AUTOMATICALLY AS WE PROGRESS.
A scrolling message indicates to CENTER STAR 1 THEN PRESS ENTER
To center your guide star, simply choose a star that you know from the list on the screen.
SPRING
FALL
Note: As you become more familiar with other stars in the sky throughout the year, you can choose the ALIGN STAR mode to
eliminate most of the set up data. In ALIGN STAR mode, you must need to know only 2 star positions to align your NorthStar™.
WINTER
SUMMER
By looking through the eyepiece, center the star in the field of view by using the Motorized Movement Buttons or move the
telescope by hand and press ENTER.
14.
M
ALIGNING NORTHSTAR FOR THE FIRST TIME (Continued)
After this step is completed, you will see a display that reads:
ALIGN COMPLETE
RATING *****
(Note: The more stars that appear on the second line of the display the better, up to 5)
Note: As you become more familiar with other stars in the sky throughout the year, you can choose the ALIGN STAR
mode to eliminate most of the set up data. In ALIGN STAR mode, you must need to know only 2 star positions to align
your NorthStar™.
M
USING NORTHSTAR FOR THE FIRST TIME
After EARTH ALIGN, the display will then read:
SELECT MODE
EXPLORE ][
Select EXPLORE by pressing ENTER. SCROLL UP and DOWN to see what flashing menu choices you have. Choose
PLANET. These are the most interesting. Even if you are a first time telescope user, PLANET objects can be very
exciting.
Press ENTER when the display reads:
EXPLORE
PLANET
This will take you into a list of named PLANET objects. By using the SCROLL UP or SCROLL DOWN buttons, you can
explore several items in the object list.
PLANET
JUPITER ][
Press ENTER to choose the PLANET you wish to view. The display will then be:
PLANET
{120 ]52 JUPITER
NOTE: IF AN OBJECT IS BELOW THE HORIZON, THE DISPLAY WILL PERIODICALLY DISPLAY THE WORD
“HORIZON.”
SCROLL UP or SCROLL DOWN to see other PLANETS in the list. Notice the display shows you directions to each object.
But what if you are a first time user wanting to find out more about the object? Wouldn’t it be nice to know what the object
is before moving the telescope?
PRESS ENTER when:
PLANET
{120 ]52 JUPITER
any other PLANET item is displayed. You will see a scrolling message telling you the coordinates for the object, how bright it
is, how big it is, what its proper name is, what constellation it is in, and a brief description of what the object is. For JUPITER
it reads:
JUPITER fifth planet from sun.
Largest planet in solar system.
16 moons. Orbit is 11.86 years.
Diameter 143,000 km. Named for roman king of gods.
15.

M
USING NORTHSTAR FOR THE FIRST TIME (Continued)
Now imagine that you are a parent trying to impress your children (or vice versa). Ten minutes into your first observing
session you are already learning astronomical objects. This is a great educational tool !!!!
To find the object, just press the “GO” button and that object will be right in the telescope’s eyepiece!
By pressing the BACK button, you move back to the previous level each time the button is pressed. Press the button three
times and you are back at the main level menu. The display will read:
SELECT MODE
EXPLORE ][
SCROLL UP or SCROLL DOWN to select
SELECT MODE
SKY TOUR ][.
Press ENTER.
This mode will take you through the best and brightest objects for each month. If you have done the ALIGN EARTH
alignment and entered the date, it will automatically take you to the current month. Don’t know what some of these
obscure objects and abbreviations mean? Just press the ENTER key for more information.
Press the BACK button until you get back to the main menu:
SELECT MODE
SKY TOUR ][.
SCROLL UP or SCROLL DOWN until the display reads:
SELECT MODE
IDENTIFY ][
PRESS ENTER
This mode will default to the level
IDENTIFY ANY
By selecting this option with the ENTER key, it will IDENTIFY the object that you are currently viewing OR the closest
object to where your telescope is currently pointed. You also have the options to choose other types of IDENTIFY menus.
These will IDENTIFY the closest CLUSTERS, NEBULAS, etc. to your current telescope position.
To select the final mode press ENTER at the display:
SELECT MODE
TELESCOPE ][
The display reads something like:
16.
RA18:53 DEC+38.7
AZ280 ALT+62 LYR
The TELESCOPE mode gives you dynamic real-time information on your telescope’s current position in terms of
astronomical coordinates. Play around with this mode by moving the telescope around. Notice the three letter abbreviation
in the lower right portion of the display. This dynamically displays the current CONSTELLATION that the telescope is
pointing at. These names are abbreviated in this mode. Definitions for the abbreviations will be in the catalog index.

Catalog Index
The following appendix information is more thorough information than that listed in the
main instruction manual. For sake of space, the complete 20,000 object catalog is not listed.
However, we have included the entire star list and the entire Messier object lists for your
information. In addition, the constellation abbreviations are defined that are found in the
Northstar system.
Catalog Index
17.

Catalog Index
CONSTELLATION ABBREVIATIONS
18.
Andromeda (And)
Antila (Ant)
Apus (Aps)
Aquarius (Aqr)
Aquila (Aql)
Ara (Ara)
Aries (Ari)
Auriga (Aur)
Bootes (Boo)
Caelum (Cae)
Camelopardis (Cam)
Cancer (Cnc)
Canes Venatici (CVn)
Canis Major (CMa)
Canis Minor (CMi)
Capricornus (Cap)
Carina (Car)
Cassiopeia (Cas)
Centaurus (Cen)
Cepheus (Cep)
Cetus (Cet)
Chameleon (Cha)
Circinus (Cir)
Columbia (Col)
Coma Berenices (Com)
Corona Australis (CrA)
Corona Borealis (CrB)
Corvus (Crv)
Crater (Crt)
Crux (Cru)
Cygnus (Cyg)
Delphinus (Del)
Dorado (Dor)
Draco (Dra)
Equuleus (Equ)
Eridanus (Eri)
Fornax (For)
Gemini (Gem)
Grus (Gru)
Hercules (Her)
Horologium (Hor)
Hydra (Hya)
Hydrus (Hyi)
Indus (Ind)
Lacerta (Lac)
Leo (Leo)
Leo Minor (LMi)
Lepus (Lep)
Libra (Lib)
Lupus (Lup)
Lynx (Lyn)
Lyra (Lyr)
Mensa (Men)
Microscopium (Mic)
Monoceros (Mon)
Musca (Mus)
Norma (Nor)
Octans (Oct)
Ophiuchus (Oph)
Orion (Ori)
Pavo (Pav)
Pegasus (Peg)
Perseus (Per)
Phoenix (Phe)
Pictor (Pic)
Pisces (Psc)
Piscis Austrinus (PsA)
Puppis (Pup)
Pyxis (Pyx)
Reticulum (Ret)
Sagitta (Sge)
Sagittarius (Sgr)
Scorpius (Sco)
Sculptor (Scl)
Scutum (Sct)
Serpens (Ser)
Sextans (Sex)
Taurus (Tau)
Telescopium (Tel)
Triangulum (Tri)
Triangulum Australe (TrA)
Tucana (Tuc)
Ursa Major (UMa)
Ursa Minor (UMi)
Vela (Vel)
Virgo (Vir)
Volcans (Vol)
Vulpecula (Vul)
Catalog Index
NAME - NAME
RA - RIGHT ASCENSION (hours min.min)
DEC - DECLINATION (degrees)
MAG - MAGNITUDE
SIZE - SIZE
CON - CONSTELLATION
Messier Catalog
MESSIER CATALOG NAME RA DEC MAG SIZE CON DESCRIPTION
M001 Crab nebula supernova remnant NGC 1952 05 34.5 +22.0 8.4 6' Tau nebula
M002 NGC 7089 21 33.5 -0.8 6 7' Aqr globular cluster highly resolved
M003 NGC 5272 13 42.2 +28.4 6 18' Cvn globular cluster highly resolved
M004 NGC 6121 16 23.6 -26.5 5.9 26' Sco globular cluster highly resolved
M005 NGC 5904 15 18.6 +02.1 6.2 13' Ser globular cluster highly resolved
M006 butterfly NGC 6405 17 40.1 -32.2 4.6 25' Sco open cluster rich
M007 NGC 6475 17 53.9 -34.8 5 1° Sco open cluster bright scattered
M008 Lagoon NGC 6523 18 03.8 -24.4 5 80' Sgr nebula with dust and cluster
M009 NGC 6333 17 19.2 -18.5 8 9' Oph globular cluster mottled
M010 NGC 6254 16 57.1 -4.1 7 8' Oph globular cluster highly resolved
M011 wild duck NGC 6705 18 51.1 -6.3 6 12' Sct open cluster dense
M012 NGC 6218 16 47.2 -2 8 10' Oph globular cluster highly resolved
M013 NGC 6205 16 41.7 +36.5 5.7 23' Her globular cluster highly resolved
M014 NGC 6402 17 37.6 -3.3 9 6' Oph globular cluster
M015 NGC 7078 21 30.0 +12.2 6.5 10' Peg globular cluster highly resolved
M016 Eagle NGC 6611 18 18.8 -13.8 6 7' Ser nebula with dust and cluster
M017 Swan NGC 6618 18 20.8 -16.2 6 45' Sgr nebula
M018 NGC 6613 18 19.9 -17.1 8 7' Sgr open cluster bright scattered
M019 NGC 6273 17 02.6 -26.3 7 5' Oph globular cluster
M020 Trifid NGC 6514 18 02.6 -23 6.3 25' Sgr nebula with dust
M021 NGC 6531 18 04.6 -22.5 7 10' Sgr open cluster rich
M022 NGC 6656 18 36.4 -23.9 6 18' Sgr globular cluster highly resolved
M023 NGC 6494 17 56.8 -19 7 30' Sgr open cluster dense
M024 small star cloud 18 15.9 -18.5 0 1.5° Sgr open cluster bright scattered
M025 IC 4725 18 31.6 -19.3 6 20' Sgr scattered group of stars
M026 NGC 6694 18 45.2 -9.4 9.5 9' Sct open cluster rich
M027 Dumbell NGC 6853 19 59.6 +22.7 8 8' Vul planetary nebula irregular
M028 NGC 6626 18 24.5 -24.9 8 6' Sgr globular cluster highly resolved
M029 NGC 6913 20 23.9 +38.5 7 7' Cyg open cluster bright scattered
M030 NGC 7099 21 40.4 -23.2 8 6' Cap globular cluster highly resolved
M031 Great Andromeda Galaxy NGC 224 00 42.7 +41.3 3.4 3° And very elongated galaxy dusty with bright core
M032 NGC 221 00 42.7 +40.9 8.2 8' And round galaxy with bright core
M033 Pinwheel NGC 598 01 33.9 +30.7 5.7 60' Tri spiral galaxy structure with bright knots
M034 NGC 1039 02 42.0 +42.8 5.2 30' Per open cluster rich
M035 NGC 2168 06 08.9 +24.3 5.1 30' Gem open cluster rich
M036 NGC 1960 05 36.1 +34.1 6 12' Aur open cluster rich
M037 NGC 2099 05 52.4 +32.6 5.6 24' Aur open cluster dense
M038 NGC 1912 05 28.7 +35.8 6.4 21' Aur open cluster rich
M039 NGC 7092 21 32.2 +48.4 5 30' Cyg open cluster bright scattered
M040 Winnecke 4 12 19.8 +58.3 9 50" UMa double star
M041 NGC 2287 06 47.0 -20.7 4.5 38' Cma open cluster dense
M042 Great Orion nebula NGC 1976 05 35.4 -5.5 4 1° Ori nebula
M043 NGC 1982 05 35.6 -5.3 9 20' Ori nebula bright with dust
M044 Behive NGC 2632 08 40.1 +20.0 3.1 1.5° Cnc open cluster bright scattered
M045 Pleiades Pleiades 03 47.0 +24.1 1.5 1.5° Tau scattered group of stars
M046 NGC 2437 07 41.8 -14.8 6.1 27' Pup open cluster dense
M047 NGC 2422 07 36.6 -14.5 4.4 30' Pup open cluster dense
M048 NGC 2548 08 13.8 -5.8 5.8 40' Hya open cluster rich
M049 NGC 4472 12 29.8 +08.0 8.4 8' Vir round galaxy with bright core
M050 NGC 2323 07 03.2 -8.3 6 20' Mon open cluster rich
M051 Whirlpool NGC 5194 13 29.9 +47.2 8.1 11' Cvn spiral galaxy structure attached companion
M052 NGC 7654 23 24.2 +61.6 7 12' Cas open cluster dense
M053 NGC 5024 13 12.9 +18.2 8 10' Com globular cluster highly resolved
M054 NGC 6715 18 55.1 -30.5 9 6' Sgr globular cluster mottled
M055 NGC 6809 19 40.0 -31 7 15' Sgr globular cluster highly resolved
M056 NGC 6779 19 16.6 +30.2 8 5' Lyr globular cluster highly resolved
Catalog Index
19.

M057 Ring NGC 6720 18 53.6 +33.0 9.7 80" Lyr planetary nebula ring with central star
M058 NGC 4579 12 37.7 +11.8 9.8 5' Vir round galaxy with bright core
M059 NGC 4621 12 42.0 +11.7 9.8 2' Vir elongated galaxy with bright core
M060 NGC 4649 12 43.7 +11.6 8.8 3.5' Vir round galaxy with bright core
M061 NGC 4303 12 21.9 +04.5 9.7 5' Vir spiral galaxy structure
M062 NGC 6266 17 01.2 -30.1 6.5 9' Oph globular cluster
M063 Sunflower NGC 5055 13 15.8 +42.0 8.6 9' Cvn elongated galaxy with bright core
M064 Black eye NGC 4826 12 56.7 +21.7 8.6 7.5' Com elongated galaxy dusty
M065 Leo triplet NGC 3623 11 18.9 +13.1 9.3 10' Leo very elongated galaxy with bright core
M066 Leo triplet NGC 3627 11 20.2 +13.0 9 9' Leo spiral galaxy structure
M067 NGC 2682 08 50.4 +11.8 7 30' Cnc open cluster dense
M068 NGC 4590 12 39.5 -26.8 8 9' Hya globular cluster highly resolved
M069 NGC 6637 18 31.4 -32.4 7.5 4' Sgr globular cluster
M070 NGC 6681 18 43.2 -32.3 8 4' Sgr globular cluster
M071 NGC 6838 19 53.8 +18.8 9 6' Sge globular cluster highly resolved
M072 NGC 6981 20 53.5 -12.5 8.6 3' Aqr globular cluster
M073 NGC 6994 20 59.0 -12.6 8.9 ? Aqr asterism
M074 NGC 628 01 36.7 +15.8 9.2 10' Psc spiral galaxy structure
M075 NGC 6864 20 06.1 -21.9 8 3' Sgr globular cluster unresolved
M076 little dumbell NGC 650 01 42.4 +51.6 10.1 2' Per planetary nebula irregular
M077 NGC 1068 02 42.7 -0.1 8.8 7' Cet round galaxy with bright core
M078 NGC 2068 05 46.7 +00.1 8 8' Ori reflection nebula bright
M079 NGC 1904 05 24.5 -24.6 8.4 7.5' Lep globular cluster highly resolved
M080 NGC 6093 16 17.0 -23 7.2 9' Sco globular cluster mottled
M081 Bodes nebula NGC 3031 09 55.6 +69.1 6.9 26' Uma spiral galaxy structure
M082 NGC 3034 09 55.8 +69.7 8.4 9' Uma very elongated galaxy with dust and bright knots
M083 NGC 5236 13 37.0 -29.9 8 10' Hya barred spiral galaxy structure
M084 NGC 4374 12 25.1 +12.9 9.3 4' Vir round galaxy with bright core
M085 NGC 4382 12 25.4 +18.2 9.3 5' Com round galaxy with bright core
M086 NGC 4406 12 26.2 +13.0 9.2 7' Vir round galaxy with bright core
M087 NGC 4486 12 30.8 +12.4 8.6 7' Vir round galaxy with bright core
M088 NGC 4501 12 32.0 +14.4 9.5 6' Com very elongated galaxy with bright core
M089 NGC 4552 12 35.7 +12.6 9.8 3' Vir round galaxy with bright core
M090 NGC 4569 12 36.8 +13.2 9.5 9' Vir very elongated galaxy with bright core
M091 NGC 4548 12 35.4 +14.5 10.2 4.5' Com elongated galaxy with bright core
M092 NGC 6341 17 17.1 +43.1 6.5 8' Her globular cluster highly resolved
M093 NGC 2447 07 44.6 -23.9 6.2 20' Pup open cluster dense
M094 NGC 4736 12 50.9 +41.1 8.2 5' Cvn elongated galaxy with bright core
M095 NGC 3351 10 44.0 +11.7 9.7 4' Leo barred spiral galaxy structure
M096 NGC 3368 10 46.8 +11.8 9.3 6' Leo round galaxy with bright core
M097 Owl NGC 3587 11 14.8 +55.0 11 2.5' Uma planetary nebula irregular
M098 NGC 4192 12 13.8 +14.9 10 8.2' Com very elongated galaxy with bright core
M099 NGC 4254 12 18.8 +14.4 10 5' Com spiral galaxy structure
M100 NGC 4321 12 22.9 +15.8 9.4 7' Com round galaxy with bright core
M101 NGC 5457 14 03.2 +54.4 7.8 20' Uma spiral galaxy structure with bright knots
M102 NGC 5866 15 06.5 +55.8 10 3' Dra very elongated galaxy dusty with bright core
M103 NGC 581 01 33.2 +60.7 7.4 6' Cas open cluster rich
M104 sombrero NGC 4594 12 40.0 -11.6 8.2 7' Vir edge on galaxy dusty
M105 NGC 3379 10 47.8 +12.6 9.3 4' Leo round galaxy with bright core
M106 NGC 4258 12 19.0 +47.3 8.3 18' Cvn spiral galaxy structure with bright knots
M107 NGC 6171 16 32.5 -13.1 9 7' Oph globular cluster
M108 NGC 3556 11 11.5 +55.7 10.1 8' Uma very elongated galaxy with dust and bright knots
M109 NGC 3992 11 57.6 +53.4 9.8 8' Uma elongated galaxy with bright core
M110 NGC 205 00 40.4 +41.7 8 17' And elongated galaxy
Star Catalog
STAR CATALOG NAME RA DEC MAG SIZE CON DESCRIPTION
ST001 O∑∑254 00 01.2 +60 21 7.6 59" Cas colored double star
ST002 30 30 PSC 00 02.0 -6 4.4 * Psc red variable star
ST003 ∑3053 00 02.6 +66 06 5.9 15" Cas colored double star
ST004 SU SU AND 00 04.6 +43.5 8 * And red variable star
ST005 Ced214 Cederblad 214 00 04.7 +67.2 7.8 30' Cep emission nebula
ST006 ∑3062 ADS 61 00 06.3 +58.4 6.4 1.5" Cas double star challenge
ST007 Alpheratz Alpha And 00 08.4 +29 05 2.1 * And star
ST008 ∑2 Struve 2 00 09.3 +79.7 6.6 0.8" Cep double star challenge
ST009 Kappa ß 391 00 09.4 -28 00 6.2 2" Scl double star challenge
ST010 Algenib Gamma PEG 00 13.2 +15.2 2.8 * Peg star
ST011 AD AD Cet 00 14.5 -7.8 4.9 1.5° Cet red variable star
ST012 7 7 CET 00 14.6 -18.9 4.4 * Cet red variable star
ST013 35 Psc
ST014 S S SCL 00 15.4 -32.1 5.5 * Scl variable star
∑12, UU Psc 00 15.0 +08 49 5.8 12" Psc colored double star
20.

ST015 ∑13 Struve 13 00 16.2 +76.9 7 0.9" Cep double star challenge
ST016 ST ST CAS 00 17.6 +50.3 9 * Cas red variable star
ST017 Groombridge34
ST018 ∑24 00 18.5 +26 08 7.6 5" And double star
ST019 Iota Iota CET 00 19.4 -8.8 3.5 * Cet star
ST020 VX VX AND 00 19.9 +44.7 8 * And star
ST021 R 00 24.0 +38 35 5.8 Stellar And variable star
ST022 ∑30 00 27.2 +49 59 6.9 15" Cas double star
ST023 AQ AQ AND 00 27.6 +35.6 6.9 * And red variable star
ST024 Beta Beta TUC 00 31.5 -63 4.4 27" Tuc double star
ST025 ∑36 Struve 36 00 32.4 +06.9 5.7 28" Psc double star
ST026 Zeta Zeta CAS 00 37.0 +53.9 3.7 * Cas star
ST027 Delta Delta AND 00 39.3 +30.9 3.3 * And star
ST028 55 00 39.9 +21 26 5.4 6" Psc colored double star
ST029 Schedar Alpha CAS 00 40.5 +56.5 2.2 * Cas star
ST030 O
ST031 HN HN 122 00 45.7 +75.0 5.7 36" Cas double star
ST032 Delta Delta PSC 00 48.7 +07.6 4.4 * Psc star
ST033 Eta 00 49.1 +57 49 3.4 12" Cas colored double star
ST034 65 65 PSC 00 49.9 +27.7 6.3 4.4" Psc colored double star
ST035 Do13 Dolidze 13 00 50.0 +64.1 11 13' Cas scattered group of stars
ST036 Lambda1 Lambda1 TUC 00 52.4 -69.5 6.5 21" Tuc double star
ST037 36 36 AND 00 55.0 +23.6 6 0.8" And double star challenge
ST038 Navi Gamma CAS 00 56.7 +60.7 2.5 * Cas star
ST039 ∑80 00 59.4 +00 47 8.4 26" Cet double star equal magnitude
ST040 ∑79 01 00.1 +44 43 6 8" And double star equal magnitude
ST041 U 01 02.3 +81 51 6.8 Stellar Cep variable star
ST042 Psi-1
ST043 77
ST044 Zeta Zeta PHE 01 08.4 -55.3 3.9 6.4" Phe double star
ST045 Eta Eta CET 01 08.6 -10.2 3.5 * Cet star
ST046 Lux Lydiae Lux Lydiae 01 08.7 +86.3 4.3 * Cep star
ST047 Mirach Beta AND 01 09.7 +35.6 2 * And star
ST048 Zeta Zeta PSC 01 13.7 +07.6 5.6 23" Psc double star
ST049 Kappa Kappa TUC 01 15.8 -68.9 5.1 5.4" Tuc double star
ST050 Z Z PSC 01 16.2 +25.8 8.8 * Psc star
ST051 42
ST052 Psi Psi CAS 01 25.9 +68.1 4.7 25" Cas double star magnitude contrast
ST053 R R SCL 01 27.0 -32.5 6.1 * Scl variable star
ST054 Gamma Gamma PHE 01 28.4 -43.3 3.4 4' Phe star
ST055 Achernar Alpha Eri 01 37.7 -57 14 0.5 * Eri star
ST056 51 51 AND 01 38.0 +48.6 3.6 * And star
ST057 UV UV CET 01 38.8 -18 7 * Cet variable star
ST058 p p ERI 01 39.8 -56.2 5.8 11.5" Eri double star
ST059 Nu Nu PSC 01 41.4 +05.5 4.4 * Psc star
ST060 44 44 CAS 01 43.3 +60.6 5.8 1.6" Cas double star
ST061 Phi Phi PER 01 43.7 +50.7 4.1 * Per star
ST062 ∑162 01 49.3 +47 54 5.8 2" Per triple star challenge
ST063 1 1 ARI 01 50.1 +22.3 6 2.6" Ari double star
ST064 ∑163 01 51.3 +64 51 6.6 35" Cas colored double star
ST065 Zeta Zeta CET 01 51.5 -10.3 3.7 3' Cet double star
ST066 ∑178 01 52.0 +10 48 8.5 3" Ari double star equal magnitude
ST067 Gamma Gamma ARI 01 53.5 +19.3 4.5 8" Ari double star equal magnitude
ST068 Psi Psi PHE 01 53.6 -46.3 4.4 5° Phe red variable star
ST069 Epsilon Epsilon CAS 01 54.4 +63.7 3.4 * Cas star
ST070 ∑186 Struve 186 01 55.9 +01.9 6.8 1" Cet double star challenge
ST071 56 56 AND 01 56.2 +37.3 5.7 3' And double star
ST072 Lambda Lambda ARI 01 57.9 +23.6 4.8 37" Ari double star
ST073 Upsilon Upsilon CET 02 00.0 -21.1 4 * Cet star
ST074 Alpha Alpha PSC 02 02.0 +02.8 4 1.6" Psc double star challenge
ST075 Almach Gamma AND 02 03.9 +42.3 2.2 10" And colored double star
ST076 Hamal Alpha ARI 02 07.2 +23.5 2 * Ari star
ST077 59 And 02 10.9 +39 02 5.6 16" And colored double star
ST078 Iota Iota TRI 02 12.4 +30.3 5 3.8" Tri colored double star
ST079 ∑231 Struve 231 02 12.8 -2.4 5.7 16.5" Cet double star
ST080 ∑228 Struve 228 02 14.0 +47.5 6.6 1.1" And double star challenge
ST081 ∑232 02 14.7 +30 24 8 7" Tri double star equal magnitude
ST082 ∑239 02 17.4 +28 44 7 14" Tri double star
ST083 Mira Omicron CET 02 19.3 -3 2 * Cet variable star
ST084 Iota Iota CAS 02 29.1 +67.4 4 2.2" Cas triple star
ST085 ∑268 02 29.4 +55 31 6.9 3" Per double star
ST086 ∑274 02 31.5 +01 05 7.3 14" Cet double star equal magnitude
ST087 Polaris Alpha UMi 02 31.8 +89 16 2 18" UMi double star
ST088 Omega h 3506 02 33.9 -28 13 5 11" For double star
ST089 30 02 37.0 +24 38 6.5 39" Ari colored double star
∑18 ADS 588 00 42.4 +04.2 7.8 1.5" Psc double star challenge
Groombridge 34 00 18.1 +44.0 8 39" And double star
∑88, 74 Psc 01 05.6 +21 28 5.3 30" Psc double star equal magnitude
∑90 01 05.8 +04 55 6.8 33" Psc double star
∑113 01 19.8 -00 31 6.4 1.6" Cet double star challenge
Catalog Index
21.

ST090 R R TRI 02 37.0 +34.3 5.4 * Tri variable star
ST091 Gamma Gamma CET 02 43.3 +03.2 3.6 2.7" Cet double star
ST092 ∑305 02 47.5 +19 22 7.4 3" Ari double star challenge
ST093 RZ 02 48.9 +69 38 6.2 Stellar Cas variable star
ST094 pi 02 49.3 +17 28 5.2 3" Ari triple star
ST095 Eta
ST096 R R HOR 02 53.9 -49.9 4.7 * Hor variable star
ST097 ∑330 Struve 330 02 57.2 -0.6 7.3 9" Cet double star
ST098 Acamar Theta ERI 02 58.3 -40.3 3.5 8" Eri double star
ST099 Epsilon Epsilon ARI 02 59.2 +29.3 4.6 1.4" Ari double star challenge
ST100 Epsilon 02 59.2 +21 20 4.6 1" Ari double star challenge
ST101 ∑331 03 00.8 +52 20 5.4 12" Per double star
ST102 Menkar Alpha CET 03 02.3 +04.1 2.5 * Cet star
ST103 Rho Rho PER 03 05.2 +38.8 3.4 * Per red variable star
ST104 ∑320 03 06.2 +79 24 5.8 5" Cep colored double star
ST105 h3568 h3568 03 07.5 -79 5.6 15" Hyi double star
ST106 Algol Beta PER 03 08.2 +41.0 2.2 * Per variable star
ST107 Alpha Alpha FOR 03 12.1 -29 4 5" For double star
ST108 h3556 h3556 03 12.4 -44.4 6 3.5" Eri double star
ST109 ∑362 03 16.3 +60 02 8.5 7" Cam double star equal magnitude
ST110 ∑369 03 17.2 +40 29 6.7 3" Per colored double star
ST111 ADS2446 ADS 2446 03 17.7 +38.6 7.8 0.9" Per double star challenge
ST112 Zeta Zeta RET 03 18.2 -62.5 5.2 5' Ret double star
ST113 Tau4 Tau4 ERI 03 19.5 -21.8 3.7 * Eri star
ST114 Toms Topaz Tom's Topaz 03 20.3 +29.0 4.5 9° Ari star
ST115 Mirfak Alpha Per 03 24.3 +49 52 1.8 * Per star
ST116 Y Y PER 03 27.7 +44.2 8.1 * Per variable star
ST117 ∑394 03 28.0 +20 27 7.1 7" Ari double star
ST118 ∑385 Struve 385 03 29.1 +59.9 4.2 2.4" Cam double star
ST119 ∑389 03 30.1 +59 21 6.5 2.7" Cam double star
ST120 Sigma Sigma PER 03 30.6 +48.0 4.4 * Per star
ST121 ∑401 03 31.3 +27 34 6.4 11" Tau double star equal magnitude
ST122 Epsilon Epsilon ERI 03 32.9 -9.5 3.7 * Eri star
ST123 ∑400 Struve 400 03 35.0 +60.0 6.8 1.4" Cam double star
ST124 O
ST125 U1 U(1) CAM (?) 03 41.6 +62.6 8.1 0 Cam variable star
ST126 Omicron Omicron PER 03 44.3 +32.3 3.8 0 Per star
ST127 Pi Pi ERI 03 46.1 -12.1 4.4 * Eri red variable star
ST128 Gamma Gamma HYI 03 47.2 -74.2 3.2 * Hyi star
ST129 30 30 TAU 03 48.3 +11.2 5 9" Tau double star
ST130 F
ST131 BE BE CAM 03 49.5 +65.5 4.5 * Cam star
ST132 Atik Zeta PER 03 54.1 +31.9 2.9 * Per star
ST133 32 32 ERI 03 54.3 -3 5 7" Eri colored double star
ST134 Epsilon 03 57.9 +40 01 2.9 9" Per double star magnitude contrast
ST135 Gamma Gamma ERI 03 58.0 -13.5 3 * Eri star
ST136 Lambda Lambda TAU 04 00.7 +12.5 3.3 * Tau variable star
ST137 O
ST138 SZ
ST139 Omicron2 Omicron2 ERI 04 15.2 -7.7 4.5 83" Eri triple star challenge
ST140 Epsilon Epsilon RET 04 16.5 -59.3 4.4 * Ret star
ST141 Theta Theta RET 04 17.7 -63.3 6.2 4" Ret double star
ST142 Phi Phi TAU 04 20.4 +27.4 5 52" Tau double star
ST143 T 04 22.0 +19 32 8.4 Stellar Tau variable star
ST144 Chi Chi TAU 04 22.6 +25.6 5.5 19.4" Tau double star
ST145 ADS3169 ADS 3169 04 22.7 +15.1 7.3 1.4" Tau double star challenge
ST146 43 43 ERI 04 24.0 -34 4 * Eri red variable star
ST147 ß 184 04 27.9 -21 30 7.3 1.7" Eri double star challenge
ST148 ∑552 04 31.4 +40 01 7 9" Per double star equal magnitude
ST149 1 04 32.0 +53 55 5.4 10" Cam colored double star
ST150 ∑559 04 33.5 +18 01 6.9 3" Tau double star equal magnitude
ST151 46 46 ERI 04 33.9 -6.7 5.7 4' Eri double star
ST152 Aldebaran Alpha TAU 04 35.9 +16.5 0.9 30" Tau colored double star
ST153 Nu Nu ERI 04 36.3 -3.4 3.9 11° Eri star
ST154 53 53 ERI 04 38.2 -14.3 3.9 * Eri star
ST155 ∑572 04 38.5 +26 56 7.3 4" Tau double star equal magnitude
ST156 54 54 ERI 04 40.4 -19.7 4.3 * Eri red variable star
ST157 R R CAE 04 40.5 -38.2 6.7 * Cae variable star
ST158 55
ST159 Iota Iota PIC 04 50.9 -53.5 5.6 12" Pic double star
ST160 ST 04 51.2 +68 10 9.2 Stellar Cam red variable star
ST161 Pi4 Pi4 ORI 04 51.2 +05.6 3.7 * Ori star
ST162 TT TT TAU 04 51.6 +28.5 8 * Tau variable star
ST163 Pi5 Pi5 ORI 04 54.2 +02.4 3.7 * Ori star
ST164 Omicron2 Omicron2 ORI 04 56.4 +13.5 4.1 * Ori star
∑36 O.Struve 36 03 40.0 +63.9 6.8 46" Cam double star
∑531 ADS 2995 04 07.6 +38.1 7.4 1.4" Per double star challenge
∑307 02 50.7 +55 53 3.9 28" Per double star magnitude contrast
Δ 16 03 48.6 -37 37 4.9 8" Eri double star equal magnitude
∑485 04 07.8 +62 20 7 90" Cam double star
∑590 04 43.6 -08 48 6.7 9" Eri double star equal magnitude
22.

ST165 Iota Iota AUR 04 57.0 +33.2 2.7 * Aur star
ST166 Pi6 Pi6 ORI 04 58.5 +01.7 4.5 * Ori star
ST167 Omega Omega AUR 04 59.3 +37.9 5 5.4" Aur double star
ST168 Hinds Crimson Star R LEP 04 59.6 -14.8 5.9 * Lep variable star
ST169 ∑627 05 00.6 +03 36 6.6 21" Ori double star equal magnitude
ST170 ∑631 Struve 631 05 00.7 -13.5 7.5 5.5" Lep double star
ST171 ∑630 Struve 630 05 02.0 +01.6 6.5 15" Ori double star
ST172 Epsilon 05 02.0 +43 49 2.9 Stellar Aur variable star
ST173 Zeta Zeta AUR 05 02.5 +41.1 3.8 * Aur star
ST174 W W ORI 05 05.4 +01.2 8.6 * Ori variable star
ST175 Epsilon Epsilon LEP 05 05.5 -22.4 3.2 * Lep star
ST176 Eta Eta AUR 05 06.5 +41.2 3.2 * Aur star
ST177 14 O
ST178 TX TX AUR 05 09.1 +39.0 8.5 * Aur variable star
ST179 SY SY ERI 05 09.8 -5.6 9 * Eri variable star
ST180 ∑644 05 10.4 +37 17 6.8 2" Aur double star challenge
ST181 Iota Iota LEP 05 12.3 -11.9 4.5 13" Lep double star
ST182 Rho 05 13.3 +02 52 4.5 7" Ori colored double star
ST183 Rigel Beta ORI 05 14.5 -8.2 0 9.4" Ori double star magnitude contrast
ST184 ∑653 Struve 653 05 15.4 +32.7 5.1 11" Aur triple star
ST185 Capella Alpha Aur 05 16.7 +46 00 0.1 * Aur star
ST186 S 476 05 19.3 -18 30 6.2 39" Lep double star equal magnitude
ST187 h3750 05 20.5 -21 14 4.7 4" Lep double star magnitude contrast
ST188 UV UV AUR 05 21.8 +32.5 7.4 * Aur variable star
ST189 ADS3954 ADS 3954 05 21.8 -24.8 5.5 3.2" Lep double star
ST190 ∑696 Struve 696 05 22.8 +03.6 5 32" Ori double star
ST191 ∑701 Struve 701 05 23.3 -8.4 6 6" Ori double star
ST192 Eta 05 24.5 -02 24 3.4 1.5" Ori double star challenge
ST193 Sigma Sigma AUR 05 24.7 +37.4 5 9" Aur double star
ST194 Theta Theta PIC 05 24.8 -52.3 6.8 38" Pic double star
ST195 Bellatrix Gamma ORI 05 25.1 +06.3 1.6 * Ori star
ST196 ∑698 Struve 698 05 25.2 +34.9 6.6 31" Aur double star
ST197 118
ST198 31 31 ORI 05 29.7 -1.1 4.7 * Ori star
ST199 TL9 TL 9 05 30.0 +17.0 5 5° Tau asterism
ST200 Delta Delta ORI 05 32.0 -0.3 2.2 53" Ori double star
ST201 119 119 TAU 05 32.2 +18.6 4.7 * Tau star
ST202 ∑718 05 32.4 +49 24 7.5 8" Aur double star equal magnitude
ST203 RT RT ORI 05 33.2 +07.2 8 * Ori variable star
ST204 ∑747 Struve 747 05 35.0 -6 4.8 36" Ori double star
ST205 Lambda 05 35.1 +09 56 3.4 4" Ori double star magnitude contrast
ST206 Trapezium Trapezium 05 35.3 -05 23 5.1 13" Ori quadruple star
ST207 Iota
ST208 Epsilon Epsilon ORI 05 36.2 -1.2 1.7 * Ori star
ST209 Phi2 Phi2 ORI 05 36.9 +09.3 4 * Ori star
ST210 Zeta Zeta TAU 05 37.6 +21.1 3 * Tau star
ST211 Sigma 05 38.7 -02 36 3.7 11" Ori quadruple star
ST212 Alpha Alpha COL 05 39.6 -34.1 2.6 * Col star
ST213 Alnitak Zeta ORI 05 40.8 -1.9 2 2.4" Ori double star magnitude contrast
ST214 U2 U(2) CAM (?) 05 42.2 +62.5 7.7 * Cam variable star
ST215 Gamma Gamma LEP 05 44.5 -22.5 3.7 97" Lep double star
ST216 Y Y TAU 05 45.7 +20.7 7.1 * Tau variable star
ST217 Mu Mu COL 05 46.0 -32.3 5.2 * Col star
ST218 Kappa Kappa ORI 05 47.8 -9.7 2 * Ori star
ST219 52
ST220 Beta Beta COL 05 51.0 -35.8 3.1 * Col star
ST221 Delta Delta LEP 05 51.3 -20.9 3.8 * Lep star
ST222 Nu Nu AUR 05 51.5 +39.1 4 30' Aur star
ST223 ∑817 05 54.9 +07 02 8.8 19" Ori double star equal magnitude
ST224 Betelgeuse Alpha Ori 05 55.2 +07 24 0.5 Stellar Ori star
ST225 U U ORI 05 55.8 +20.2 5.3 * Ori variable star
ST226 Theta 05 59.7 +37 13 2.6 3.5" Aur double star magnitude contrast
ST227 Pi Pi AUR 05 59.9 +45.9 4.3 1° Aur red variable star
ST228 Δ23 06 04.8 -48 27 7 2.7" Pup double star equal magnitude
ST229 ∑855 06 09.0 +02 30 6 30" Ori double star
ST230 TU TU GEM 06 10.9 +26.0 7.5 * Gem variable star
ST231 41
ST232 SS SS AUR 06 13.4 +47.0 10 * Aur variable star
ST233 Gamma Gamma MON 06 14.9 -6.3 4 8° Mon star
ST234 Eta Eta GEM 06 14.9 +22.5 3.3 * Gem star
ST235 ∑872 Struve 872 06 15.6 +36.2 6.9 11" Aur double star
ST236 KS KS MON 06 19.7 -5.3 9.5 * Mon variable star
ST237 Zeta Zeta CMA 06 20.3 -30.1 3 8.5° Cma star
ST238 V V MON 06 22.7 -2.2 6 * Mon variable star
ST239 Mirzam Beta CMA 06 22.7 -18 2 * Cma star
∑98 05 07.9 +08 29 5.9 0.7" Ori double star challenge
∑716 05 29.3 +25 09 5.8 5" Tau double star
∑752 05 35.4 -05 55 2.9 11" Ori double star magnitude contrast
∑795 05 48.0 +06 27 6.1 1.3" Ori double star challenge
∑845 06 11.7 +48 42 6.1 8" Aur double star
Catalog Index
23.

ST240 Mu Mu GEM 06 23.0 +22.5 2.9 * Gem star
ST241 8 06 23.8 +04 36 4.3 13" Mon colored double star
ST242 Canopus Alpha Car 06 24.0 -52 42 -0.7 * Car star
ST243 BL BL ORI 06 25.5 +14.7 8.5 * Ori variable star
ST244 15 06 27.8 +20 47 6.6 27" Gem double star
ST245 Beta 06 28.8 -07 02 3.8 3" Mon triple star
ST246 ADS5150 ADS 5150 06 31.8 +38.9 11.5 4.5" Aur double star
ST247 20 20 GEM 06 32.3 +17.8 6.3 20" Gem colored double star
ST248 ADS5188 ADS 5188 06 34.3 +38.1 6.7 43" Aur double star
ST249 CR CR GEM 06 34.4 +16.1 8.5 * Gem variable star
ST250 ∑928 ADS 5191 06 34.7 +38.4 7.6 3.5" Aur double star
ST251 ADS5201 ADS 5201 06 35.1 +37.1 7.4 2.6" Aur double star
ST252 ∑929 ADS 5208 06 35.4 +37.7 7.4 6" Aur double star
ST253 ∑939 Struve 939 06 35.9 +05.3 8.3 30" Mon double star
ST254 ADS5221 ADS 5221 06 36.2 +38.0 8.5 1.3" Aur double star challenge
ST255 Nu1 Nu1 CMA 06 36.4 -18.7 6 17.5" Cma colored double star
ST256 UU UU AUR 06 36.5 +38.5 5.1 * Aur variable star
ST257 ADS5240 ADS 5240 06 36.9 +38.2 9.7 2.2" Aur double star
ST258 ADS5245 ADS 5245 06 37.3 +38.4 8.8 10" Aur double star
ST259 South529 South 529 06 37.6 +12.2 7.6 70" Gem double star
ST260 Innes5 Innes 5 06 38.0 -61.5 6.4 2.4" Pic double star
ST261 ADS5265 ADS 5265 06 38.4 +38.8 9.6 4.6" Aur double star
ST262 Innes1156 Innes 1156 06 39.1 -29.1 8 0.7" Cma double star challenge
ST263 SAO172106 SAO 172106 06 39.5 -30 7.8 2.5° Cma red variable star
ST264 ∑953 06 41.2 +08 59 7.1 7" Mon double star
ST265 VW VW GEM 06 42.2 +31.5 8.7 * Gem variable star
ST266 Sirius Alpha CMA 06 45.1 -16.7 -1 9" Cma double star magnitude contrast
ST267 12
ST268 ∑958 06 48.2 +55 42 5.5 5" Lyn double star equal magnitude
ST269 Kappa Kappa CMA 06 49.8 -32.5 4 * Cma star
ST270 14 14 LYN 06 53.1 +59.5 5.7 0.4" Lyn double star challenge
ST271 GY GY MON 06 53.2 -4.6 9.4 * Mon variable star
ST272 ∑987 06 54.1 -05 51 7.1 1.3" Mon double star challenge
ST273 Omicron1
ST274 Theta Theta CMA 06 54.2 -12 4.1 * Cma star
ST275 38 06 54.6 +13 11 4.7 7" Gem colored double star
ST276 Mu
ST277 BG BG MON 06 56.4 +07.1 9.2 * Mon variable star
ST278 O
ST279 RV RV MON 06 58.4 +06.2 7 * Mon variable star
ST280 Epsilon Epsilon CMA 06 58.6 -29 1.5 7.5" Cma double star
ST281 Sigma Sigma CMA 07 01.7 -27.9 3.5 * Cma star
ST282 Omicron2
ST283 Dunlop38 Dunlop 38 07 04.0 -43.6 5.6 20.5" Pup double star
ST284 Zeta Zeta GEM 07 04.1 +20.6 3.7 * Gem variable star
ST285 ∑1009 07 05.7 +52 45 6.9 4.1" Lyn double star equal magnitude
ST286 R R GEM 07 07.4 +22.7 6 * Gem variable star
ST287 W 07 08.1 -11 55 6.4 Stellar CMa red variable star
ST288 Gamma Gamma VOL 07 08.8 -70.5 4 13.6" Vol double star
ST289 Tau Tau GEM 07 11.1 +30.2 4.4 1.9" Gem double star
ST290 ∑1035 07 12.0 +22 17 8.2 4" Gem double star equal magnitude
ST291 ∑1037 Struve 1037 07 12.8 +27.2 7.2 1.3" Gem double star challenge
ST292 Omega Omega CMA 07 14.8 -26.8 3.9 * Cma star
ST293 h3945 07 16.6 -23 19 4.5 27" CMa colored double star
ST294 Tau h 3948 07 18.7 -24 57 4.4 15" CMa triple star
ST295 Delta 55 Gem 07 20.1 +21 59 3.5 6" Gem double star magnitude contrast
ST296 19
ST297 Gamma Gamma CMI 07 28.2 +08.9 4.3 * Cmi star
ST298 Sigma Sigma PUP 07 29.2 -43.3 3.3 22" Pup double star
ST299 ∑1093 Struve 1093 07 30.3 +50.0 8.8 0.8" Lyn double star challenge
ST300 n HN19, h269 07 34.3 -23 28 5.1 10" Pup double star equal magnitude
ST301 Castor Alpha GEM 07 34.6 +31.9 2 1.8" Gem double star challenge
ST302 Upsilon Upsilon GEM 07 35.9 +26.9 4.1 2.5° Gem red variable star
ST303 ∑1121 07 36.6 -14 29 7.9 7" Pup double star equal magnitude
ST304 K 07 38.8 -26 48 3.8 10" Pup double star equal magnitude
ST305 Procyon Alpha CMi 07 39.3 +05 14 0.4 Stellar CMi star
ST306 Kappa O
ST307 2
ST308 ∑1127 07 47.0 +64 03 7 5" Cam triple star
ST309 ∑1149 07 49.4 +03 13 7.9 22" Cmi double star
ST310 U 07 55.1 +22 00 8.2 Stellar Gem variable star
ST311 Chi Chi CAR 07 56.8 -53 3.5 4° Car star
ST312 Dunlop59 Dunlop 59 07 59.2 -50 6.5 16" Pup double star
ST313 S-h86 S-h 86 08 02.5 +63.1 6 49" Cam double star
ST314 Zeta Zeta PUP 08 03.6 -40 2.3 4° Pup star
∑80 O. Struve (P) 80 06 58.1 +14.2 7.3 2' Gem asterism
∑948 06 46.2 +59 27 4.9 2" Lyn triple star challenge
Omicron1 CMA 06 54.1 -24.2 3.9 * Cma star
∑997 06 56.1 -14 02 5.3 2.8" Cma double star magnitude contrast
Omicron2 CMA 07 03.0 -23.8 3 * Cma star
∑1062 07 22.9 +55 17 5.6 15" Lyn triple star
∑179 07 44.4 +24 23 3.7 7" Gem double star magnitude contrast
∑1138 07 45.5 -14 41 6.1 17" Pup double star equal magnitude
24.

ST315 RT RT PUP 08 05.4 -38.8 8.5 * Pup variable star
ST316 RU RU PUP 08 07.5 -22.9 8.9 * Pup variable star
ST317 Epsilon Epsilon VOL 08 07.9 -68.6 4.4 6" Vol double star
ST318 Gamma Gamma VEL 08 09.5 -47.3 1.9 41" Vel double star
ST319 Zeta 08 12.2 +17 39 4.7 0.6" Cnc triple star challenge
ST320 c c CAR 08 15.3 -62.9 5.3 4" Car double star
ST321 Beta Beta CNC 08 16.5 +09.2 3.5 * Cnc star
ST322 R R CNC 08 16.6 +11.7 6.1 * Cnc variable star
ST323 Kappa Kappa VOL 08 19.8 -71.5 5.4 65" Vol double star
ST324 AC AC PUP 08 22.7 -15.9 8.9 * Pup variable star
ST325 31 31 LYN 08 22.8 +43.2 4.3 15° Lyn star
ST326 Beta Beta VOL 08 25.7 -66.1 3.8 6° Vol star
ST327 h4903 h4903 08 26.3 -39.1 6.5 8" Pup double star
ST328 24
ST329 Phi
ST330 h4104 h4104 08 29.1 -47.9 5.5 3.6" Vel double star
ST331 Δ70 08 29.5 -44 44 5 5" Vel double star
ST332 h4107 08 31.4 -39 04 6.4 4" Vel triple star
ST333 ∑1245 08 35.8 +06 37 6 10" Cnc double star
ST334 Sigma Sigma HYA 08 38.8 +03.3 4.4 * Hya star
ST335 h4128 h4128 08 39.2 -60.3 6.9 1.4" Car double star challenge
ST336 ∑1254 08 40.4 +19 40 6.4 21" Cnc quadruple star
ST337 Alpha Alpha PYX 08 43.6 -33.2 3.7 * Pyx star
ST338 Delta Delta VEL 08 44.7 -54.7 2.1 2.6" Vel double star
ST339 ∑1270 ADS 6977 08 45.3 -2.6 6.4 5" Hya double star
ST340 Iota
ST341 Epsilon 08 46.8 +06 25 3.4 3" Hyd double star magnitude contrast
ST342 ∑1282 08 50.8 +35 03 7.5 4" Lyn double star equal magnitude
ST343 X X CNC 08 55.4 +17.2 5.6 * Cnc variable star
ST344 66
ST345 Rho Rho UMA 09 02.5 +67.6 4.8 1° Uma star
ST346 ∑1311 09 07.5 +22 59 6.9 8" Cnc double star equal magnitude
ST347 Suhail Lambda Vel 09 08.0 -43 26 2.2 Stellar Vel star
ST348 Sigma2 09 10.4 +67 08 4.8 4" Uma double star magnitude contrast
ST349 a a CAR 09 11.0 -59 3.4 50' Car star
ST350 h4188 h4188 09 12.5 -43.6 6.7 2.7" Vel double star
ST351 h4191 09 14.4 -43 13 5.2 6" Vel double star magnitude contrast
ST352 ∑1321 09 14.9 +52 42 8.1 18" Uma double star equal magnitude
ST353 g g CAR 09 16.2 -57.5 4.3 5' Car star
ST354 RT RT UMA 09 18.4 +51.4 8.6 * Uma variable star
ST355 38
ST356 ∑1338 09 21.0 +38 11 6.6 1" Lyn double star challenge
ST357 Alpha Alpha LYN 09 21.1 +34.4 3.1 * Lyn star
ST358 Kappa Kappa VEL 09 22.1 -55 2.5 * Vel star
ST359 ∑1347 09 23.3 +03 30 7.2 21" Hya double star
ST360 Kappa Kappa LEO 09 24.7 +26.2 4.5 2.1" Leo triple star
ST361 ∑1355 09 27.3 +06 14 7.5 2.3" Hya double star equal magnitude
ST362 Alphard Alpha Hya 09 27.6 -08 40 2 Stellar Hya star
ST363 Omega Omega LEO 09 28.5 +09.1 5.9 0.5" Leo double star challenge
ST364 Dunlop76 Dunlop 76 09 28.6 -45.5 7.8 61" Vel double star
ST365 ∑1360 09 30.6 +10 35 8.3 14" Leo double star equal magnitude
ST366 Zeta 09 30.8 -31 53 5.8 8" Ant double star
ST367 N N VEL 09 31.2 -57 3.1 * Vel star
ST368 23
ST369 Lambda Lambda LEO 09 31.7 +23.0 4.3 * Leo star
ST370 R R CAR 09 32.2 -62.8 3.8 * Car variable star
ST371 ∑1369 Struve 1369 09 35.4 +40.0 6.5 25" Lyn double star
ST372 Iota Iota HYA 09 39.9 -1.1 3.9 * Hya star
ST373 Upsilon Upsilon CAR 09 47.1 -65.1 3.1 5" Car double star
ST374 R 09 47.6 +11 26 4.4 Stellar Leo red variable star
ST375 W W SEX 09 51.0 -2 9 * Sex variable star
ST376 Y Y HYA 09 51.1 -23 8.3 * Hya variable star
ST377 Mu Mu LEO 09 52.8 +26.0 3.9 * Leo star
ST378 h4262 ADS 7571 09 54.5 -12.9 8.7 8" Hya double star
ST379 Regulus Alpha Leo 10 08.4 +11 58 1.4 Stellar Leo star
ST380 S S CAR 10 09.4 -61.6 4.5 * Car variable star
ST381 ADS7704 ADS 7704 10 16.3 +17.7 7.2 1.4" Leo double star challenge
ST382 Zeta Zeta LEO 10 16.7 +23.4 3.4 5.5' Leo double star
ST383 q q CAR 10 17.1 -61.3 3.4 * Car star
ST384 h4306 h4306 10 19.1 -64.7 5.6 2.1" Car double star
ST385 Algieba Gamma LEO 10 20.0 +19.8 2.5 4.4" Leo double star
ST386 Mu Mu UMA 10 22.3 +41.5 3 * Uma star
ST387 Mu Mu HYA 10 26.1 -16.8 3.8 * Hya star
ST388 Alpha Alpha ANT 10 27.2 -31.1 4.3 * Ant star
ST389 45 45 LEO 10 27.6 +09.8 6 3.8" Leo double star
∑1224 08 26.7 +24 32 7.1 6" Cnc double star
∑1223 08 26.7 +26 56 6.3 5" Cnc double star equal magnitude
∑1268 08 46.7 +28 46 4 30" Cnc colored double star
∑1298 09 01.4 +32 15 5.9 5" Cnc double star
∑1334 09 18.8 +36 48 3.9 3" Lyn double star challenge
∑1351 09 31.5 +63 03 3.8 23" Uma double star magnitude contrast
Catalog Index
25.

ST390 Delta HN 50 10 29.6 -30 36 5.7 11" Ant double star magnitude contrast
ST391 p p CAR 10 32.0 -61.7 3.3 * Car star
ST392 Rho Rho LEO 10 32.8 +09.3 3.9 * Leo star
ST393 49 10 35.0 +08 39 5.7 2" Leo double star challenge
ST394 U U ANT 10 35.2 -39.6 8.1 * Ant variable star
ST395 Gamma Gamma CHA 10 35.5 -78.6 4.1 * Cha star
ST396 U U HYA 10 37.6 -13.4 7 * Hya variable star
ST397 Dunlop95 Dunlop 95 10 39.3 -55.6 4.3 52" Vel double star
ST398 35
ST399 R R UMA 10 44.6 +68.8 7.5 * Uma variable star
ST400 VY VY UMA 10 45.1 +67.4 5.9 * Uma variable star
ST401 Delta Delta CHA 10 45.8 -80.5 4.5 4.5' Cha double star
ST402 40
ST403 Nu Nu HYA 10 49.6 -16.2 3.1 * Hya star
ST404 54 54 LEO 10 55.6 +24.8 4.5 6.8" Leo double star
ST405 SAO251342 SAO 251342 11 17.5 -63.5 7 7" Car double star magnitude contrast
ST406 Xi Xi UMA 11 18.2 +31.5 4.5 1.3" Uma double star challenge
ST407 Nu Nu UMA 11 18.5 +33.1 3.5 7" Uma double star
ST408 ∑1529 11 19.4 -01 38 7 10" Leo double star
ST409 h4432 h4432 11 23.4 -65 5.1 2.3" Mus double star
ST410 Iota Iota LEO 11 23.9 +10.5 4 1.3" Leo double star challenge
ST411 83
ST412 Tau Tau LEO 11 27.9 +02.9 5.5 1.5' Leo double star
ST413 Lambda Lambda DRA 11 31.4 +69.3 3.8 20' Dra red variable star
ST414 88
ST415 N 11 32.3 -29 16 5.8 9" Hyd double star equal magnitude
ST416 Innes78 Innes 78 11 33.6 -40.6 6 1" Cen double star challenge
ST417 ∑1552 ∑1552 11 34.7 +16 48 6 3" Leo triple star
ST418 Nu Nu VIR 11 45.9 +06.5 4 * Vir star
ST419 Denebola Beta Leo 11 49.1 +14 34 2.1 Stellar Leo star
ST420 Beta Beta HYA 11 52.9 -33.9 4.7 0.9" Hya colored double star
ST421 O
ST422 65
ST423 Epsilon Epsilon CHA 11 59.6 -78.2 5.4 0.9" Cha colored double star
ST424 ∑1593 12 03.5 -02 26 8.7 1.3" Vir double star challenge
ST425 Zeta Zeta COM 12 04.3 +21.5 6 3.6" Com double star
ST426 Delta Delta CEN 12 08.4 -50.7 2.6 4.5' Cen double star
ST427 ∑1604 12 09.5 -11 51 6.6 10" Crv triple star
ST428 Epsilon Epsilon CRV 12 10.1 -22.6 3 * Crv star
ST429 Rumker14 Rumker 14 12 14.0 -45.7 5.6 2.9" Cen double star
ST430 Delta Delta CRU 12 15.1 -58.7 2.8 * Cru star
ST431 2 2 CVN 12 16.1 +40.7 6 11.5" Cvn colored double star
ST432 Epsilon Epsilon MUS 12 17.6 -68 4.1 * Mus red variable star
ST433 ∑1627 12 18.1 -03 56 6.6 20" Vir double star equal magnitude
ST434 R R CRV 12 19.6 -19.3 6.7 * Crv variable star
ST435 ∑1633 12 20.6 +27 03 6.3 9" Com double star equal magnitude
ST436 Epsilon Epsilon CRU 12 21.4 -60.4 3.6 * Cru star
ST437 M40 Winnecke 4 12 22.4 +58 05 9 50" UMa double star
ST438 17 17 VIR 12 22.5 +05.3 6.5 21" Vir double star
ST439 ∑1639 Struve 1639 12 24.4 +25.6 6.8 1.6" Com double star challenge
ST440 S S CEN 12 24.6 -49.4 9.2 * Cen variable star
ST441 SS 12 25.3 +00 48 6 Stellar Vir red variable star
ST442 Acrux Alpha CRU 12 26.6 -63.1 1 4.4" Cru double star
ST443 3C273 3C 273 12 29.1 +02.0 12.8 * Vir asterism
ST444 Algorab Delta CRV 12 29.9 -16.5 3 24" Crv double star
ST445 Gamma Gamma CRU 12 31.2 -57.1 1.6 110" Cru double star
ST446 ∑1649 Struve 1649 12 31.6 -11.1 8 15" Vir double star
ST447 24 12 35.1 +18 23 5 20" CVn colored double star
ST448 Alpha Alpha MUS 12 37.2 -69.1 2.7 * Mus star
ST449 ADS8612 ADS 8612 12 37.7 -27.1 5.5 1.3" Hya double star challenge
ST450 ∑1669 12 41.3 -13 01 5.3 5" Crv double star equal magnitude
ST451 Gamma Gamma CEN 12 41.5 -49 2.2 1" Cen double star challenge
ST452 Porrima Gamma VIR 12 41.7 -1.4 3.5 3" Vir double star
ST453 Y 12 45.1 +45 26 7.4 Stellar CVn red variable star
ST454 Iota Iota CRU 12 45.6 -61 4.7 27" Cru double star
ST455 Beta Beta MUS 12 46.3 -68.1 3.7 1.4" Mus double star challenge
ST456 Mimosa Beta CRU 12 47.7 -59.7 1.3 * Cru star
ST457 32
ST458 35
ST459 Mu Mu CRU 12 54.6 -57.2 4.3 35" Cru double star
ST460 Delta Delta VIR 12 55.6 +03.4 3.4 * Vir red variable star
ST461 Cor Caroli Alpha CVN 12 56.0 +38.3 3 19" Cvn double star
ST462 RY RY DRA 12 56.4 +66.0 6.8 * Dra variable star
ST463 ∑1699 12 58.7 +27 28 8.8 1.5" Com double star challenge
ST464 Delta Delta MUS 13 02.3 -71.5 3.6 8' Mus star
∑112 O.Struve 112 11 54.6 +19.4 8.4 73" Leo double star
∑1466 10 43.4 +04 44 6.3 7" Sex double star
∑1476 10 49.3 -04 01 6.9 2.5" Sex double star
∑1540 11 26.8 +03 00 6.2 29" Leo triple star
∑1547 11 31.8 +14 21 6.4 16" Leo double star
∑1579 11 55.1 +46 29 6.7 4" Uma double star
∑1694 12 49.2 +83 25 5.3 22" Cam double star equal magnitude
∑1687 12 53.3 +21 14 5.1 29" Com double star magnitude contrast
26.

ST465 Theta Theta MUS 13 08.1 -65.3 5.7 5.3" Mus double star
ST466 Theta 51 Vir,
ST467 Alpha 13 10.0 +17 32 5 0.5" Com double star challenge
ST468 54 13 13.4 -18 50 6.8 5" Vir double star
ST469 J J CEN 13 22.6 -61 4.7 1' Cen double star
ST470 Zeta Mizar 13 23.9 +54 56 2.3 14" Uma double star
ST471 Spica Alpha VIR 13 25.2 -11.2 1 * Vir star
ST472 O
ST473 R 13 29.7 -23 17 4 Stellar Hyd variable star
ST474 ∑1755 Struve 1755 13 32.3 +36.8 7 4.4" Cvn double star
ST475 S S VIR 13 33.0 -7.2 6 * Vir variable star
ST476 25 25 CVN 13 37.5 +36.3 5 1.8" Cvn double star magnitude contrast
ST477 ∑1763 Struve 1763 13 37.6 -7.9 7.9 2.8" Vir double star
ST478 Epsilon Epsilon CEN 13 39.9 -53.5 2.3 * Cen star
ST479 1
ST480 Dunlop141 Dunlop 141 13 41.7 -54.6 5.3 5.3" Cen double star
ST481 T T CEN 13 41.8 -33.6 5.5 * Cen variable star
ST482 Alkaid Eta UMA 13 47.5 +49.3 1.9 * Uma star
ST483 ∑1785 Struve 1785 13 49.1 +27.0 7.6 3.4" Boo double star
ST484 2 2 CEN 13 49.4 -34.5 4.2 * Cen star
ST485 Upsilon Upsilon BOO 13 49.5 +15.8 4.1 * Boo star
ST486 3 3 CEN 13 51.8 -33 4.5 8" Cen double star
ST487 Zeta Zeta CEN 13 55.5 -47.3 2.6 5° Cen star
ST488 Beta Beta CEN 14 03.8 -60.4 0.6 * Cen star
ST489 Pi Pi HYA 14 06.4 -26.7 3.3 * Hya star
ST490 Kappa Kappa VIR 14 12.9 -10.3 4.2 * Vir star
ST491 Kappa 14 13.5 +51 47 4.4 13" Boo colored double star
ST492 ∑1819 14 15.3 +03 08 7.8 0.8" Vir double star challenge
ST493 Arcturus Alpha Boo 14 15.7 +19 11 0 Stellar Boo star
ST494 Iota Iota BOO 14 16.2 +51.4 4.9 39" Boo double star
ST495 R R CEN 14 16.6 -59.9 5.3 * Cen variable star
ST496 ∑1834 Struve 1834 14 20.3 +48.5 8.1 1.3" Boo double star challenge
ST497 ∑1833 14 22.6 -07 46 7.6 6" Vir double star equal magnitude
ST498 Dunlop159 Dunlop 159 14 22.6 -58.5 5 9" Cen colored double star
ST499 ∑1835 14 23.4 +08 26 5.1 6" Boo double star
ST500 SHJ 179 14 25.5 -19 58 6.4 35" Lib double star
ST501 5 5 UMI 14 27.5 +75.7 4.3 * Umi star
ST502 Proxima Proxima CEN 14 29.9 -62.7 10.7 * Cen variable star
ST503 Rho Rho BOO 14 31.8 +30.4 3.6 * Boo star
ST504 h4690 14 37.3 -46 08 5.4 19" Lup double star magnitude contrast
ST505 Alpha
ST506 Pi Pi BOO 14 40.7 +16.4 5 5.6" Boo double star
ST507 pi
ST508 Zeta 14 41.1 +13 44 3.8 1" Boo double star challenge
ST509 Alpha Alpha LUP 14 41.9 -47.4 2.3 * Lup star
ST510 q q CEN 14 42.0 -37.8 4 * Cen star
ST511 Alpha Alpha CIR 14 42.5 -65 3.2 16" Cir double star
ST512 c1 c1 CEN 14 43.7 -35.2 4 17' Cen star
ST513 Epsilon Izar 14 45.0 +27 04 2.4 3" Boo colored double star
ST514 Dunlop Dunlop 169 14 45.2 -55.6 6.2 68" Cir double star
ST515 54 H 97 14 46.0 -25 26 5.2 8" Hya double star
ST516 Alpha Alpha APS 14 47.9 -79 3.8 10° Aps star
ST517 ∑1883 14 48.9 +05 57 7.6 0.7" Vir double star challenge
ST518 Mu 14 49.3 -14 09 5.4 2" Lib double star challenge
ST519 39 14 49.7 +48 43 5.7 3" Boo double star
ST520 58 58 HYA 14 50.3 -28 4.4 * Hya star
ST521 Kochab Beta UMI 14 50.7 +74.2 2.1 * Umi star
ST522 Zubenelgenubi Alpha LIB 14 50.9 -16 2.8 4' Lib double star
ST523 Xi 37 Boo 14 51.4 +19 06 4.6 7" Boo colored double star
ST524 h4715 h4715 14 56.5 -47.9 6 2.4" Lup double star
ST525 33 H 28 14 57.3 -21 22 5.9 23" Lib double star
ST526 Beta Beta LUP 14 58.5 -43.1 2.6 * Lup star
ST527 Pi Pi OCT 15 01.8 -83.2 5.7 18' Oct double star
ST528 44 15 03.8 +47 39 4.8 1.5" Boo double star challenge
ST529 Sigma Sigma LIB 15 04.1 -25.3 3.2 * Lib red variable star
ST530 Dunlop178 Dunlop 178 15 11.6 -45.3 6.7 32" Lup double star
ST531 Kappa Kappa LUP 15 11.9 -48.7 3.9 27" Lup double star
ST532 X X TRA 15 14.3 -70.1 8.1 * Tra variable star
ST533 ∑1932 15 18.3 +26 50 6.6 1.5" CrB double star challenge
ST534 Mu Mu LUP 15 18.5 -47.9 5.1 1.2" Lup double star challenge
ST535 ∑1931 15 18.7 +10 26 7 13" Ser double star
ST536 S S CRB 15 21.4 +31.4 5.8 * Crb variable star
ST537 Phi1 Phi1 LUP 15 21.8 -36.3 3.6 50' Lup star
ST538 Eta 15 23.2 +30 17 5.6 1.0" CrB double star challenge
ST539 Mu 15 24.5 +37 23 4.3 2" Boo triple star
∑∑123 13 27.1 +64 43 6.7 69" Dra colored double star
∑1724 13 09.9 -05 32 4.4 7" Vir triple star challenge
∑1772 13 40.7 +19 57 5.7 5" Boo double star magnitude contrast
Rigil Kentaurus 14 39.6 -60 50 0 20" Cen double star
∑1864 14 40.7 +16 25 4.9 6" Boo double star
Catalog Index
27.

ST540 Edasich Iota DRA 15 24.9 +59.0 3.3 * Dra star
ST541 Pi
ST542 Lal123 15 33.1 -24 29 7.5 9" Lib double star equal magnitude
ST543 Delta Delta SER 15 34.8 +10.5 4 3.9" Ser double star
ST544 Gamma Gamma LUP 15 35.1 -41.2 2.8 * Lup star
ST545 h4788 h4788 15 35.9 -45 4.7 2.2" Lup double star
ST546 Upsilon Upsilon LIB 15 37.0 -28.1 3.6 3" Lib colored double star
ST547 Omega Omega LUP 15 38.1 -42.6 4.3 * Lup red variable star
ST548 ∑1962 15 38.7 -08 47 5.8 12" Lib double star equal magnitude
ST549 Tau Tau LIB 15 38.7 -29.8 3.7 2° Lib star
ST550 Zeta Zeta CRB 15 39.4 +36.6 5 6.3" Crb double star
ST551 Gamma Gamma CRB 15 42.7 +26.3 4.2 0.3" Crb double star challenge
ST552 Alpha Alpha SER 15 44.3 +06.4 2.7 * Ser star
ST553 R 15 48.6 +28 09 5.7 Stellar CrB variable star
ST554 Kappa Kappa SER 15 48.7 +18.1 4.1 * Ser red variable star
ST555 R R SER 15 50.7 +15.1 5.2 * Ser variable star
ST556 Xi 15 56.9 -33 58 5.2 10" Lup double star
ST557 Rho Rho SCO 15 56.9 -29.2 3.9 * Sco star
ST558 Epsilon Epsilon CRB 15 57.6 +26.9 4.2 * Crb star
ST559 Pi Pi SCO 15 58.9 -26.1 2.9 * Sco star
ST560 T 15 59.5 +25 55 2 Stellar CrB variable star
ST561 Eta Rmk 21 16 00.1 -38 24 3.6 15" Lup double star magnitude contrast
ST562 Delta Delta SCO 16 00.3 -22.6 2.3 * Sco star
ST563 Xi 16 04.4 -11 22 4.2 1" Sco triple star challenge
ST564 Graffias Beta SCO 16 05.4 -19.8 2.5 * Sco star
ST565 Omega1 Omega1 SCO 16 06.8 -20.7 4 14' Sco star
ST566 Kappa 16 08.1 +17 03 5 28" Her colored double star
ST567 Nu 16 12.0 -19 28 4 1" Sco quadruple star
ST568 Delta Delta OPH 16 14.3 -3.7 2.7 * Oph star
ST569 Sigma
ST570 Delta Delta APS 16 20.3 -78.7 4.7 * Aps double star
ST571 Sigma H 121 16 21.2 -25 35 2.9 20" Sco double star magnitude contrast
ST572 Rho Rho OPH 16 25.6 -23.5 5.3 3.1" Oph double star
ST573 V V OPH 16 26.7 -12.4 7.3 * Oph variable star
ST574 Epsilon Epsilon NOR 16 27.2 -47.6 4.8 23" Nor double star
ST575 Iota Iota TRA 16 28.0 -64.1 5.3 20" Tra double star
ST576 ∑2052 Struve 2052 16 28.9 +18.4 7.7 1.7" Her double star
ST577 Antares Alpha SCO 16 29.4 -26.4 1 3" Sco double star challenge
ST578 Lambda Lambda OPH 16 30.9 +02.0 4.2 1.4" Oph double star challenge
ST579 R R DRA 16 32.7 +66.8 6.7 * Dra variable star
ST580 16 16 36.2 +52 55 5.1 3" Dra triple star
ST581 H H SCO 16 36.4 -35.3 4.2 * Sco star
ST582 Zeta Zeta OPH 16 37.2 -10.6 2.6 * Oph star
ST583 SU SU SCO 16 40.6 -32.4 8 * Sco variable star
ST584 Zeta Zeta HER 16 41.3 +31.6 3 1.4" Her colored double star
ST585 Alpha Alpha TRA 16 48.7 -69 1.9 * Tra star
ST586 Eta Eta ARA 16 49.8 -59 3.8 * Ara star
ST587 Epsilon Epsilon SCO 16 50.2 -34.3 2.3 * Sco star
ST588 Mu Mu SCO 16 52.3 -38 3 * Sco star
ST589 20 20 DRA 16 56.4 +65.0 7.1 1.4" Dra double star challenge
ST590 RR RR SCO 16 56.6 -30.6 5.1 * Sco variable star
ST591 Kappa Kappa OPH 16 57.7 +09.4 3.2 75' Oph star
ST592 Zeta Zeta ARA 16 58.6 -56 3.1 * Ara star
ST593 Epsilon1 Epsilon1 ARA 16 59.6 -53.2 4.1 40' Ara star
ST594 Mu 17 05.3 +54 28 4.9 2" Dra double star equal magnitude
ST595 Eta Eta OPH 17 10.4 -15.7 2.4 0.6" Oph double star challenge
ST596 Rasalgethi Alpha HER 17 14.6 +14.4 3 4.6" Her double star equal magnitude
ST597 Delta 17 15.0 +24 50 3.2 10" Her double star magnitude contrast
ST598 Pi Pi HER 17 15.0 +36.8 3.2 7° Her star
ST599 36 17 15.3 -26 36 4.3 5" Oph double star equal magnitude
ST600 39 17 18.0 -24 17 5.2 10" Oph colored double star
ST601 Theta Theta OPH 17 22.0 -25 3.3 * Oph star
ST602 Rho
ST603 Beta Beta ARA 17 25.3 -55.5 2.9 * Ara star
ST604 Gamma Gamma ARA 17 25.4 -56.4 3.3 * Ara star
ST605 Sigma Sigma OPH 17 26.5 +04.1 4.3 4° Oph star
ST606 h4949 h4949 17 26.9 -45.9 6 2.2" Ara double star
ST607 ∑2173 17 30.4 -01 04 6 1.1" Oph double star challenge
ST608 Lambda Lambda HER 17 30.7 +26.1 4.4 * Her star
ST609 Upsilon Upsilon SCO 17 30.8 -37.3 2.7 * Sco star
ST610 Alpha Alpha ARA 17 31.8 -49.9 3 * Ara star
ST611 Nu 17 32.2 +55 11 4.9 62" Dra double star equal magnitude
ST612 Shaula Lambda SCO 17 33.6 -37.1 1.6 35' Sco star
ST613 Rasalhague Alpha Oph 17 34.9 +12 34 2.1 * Oph star
ST614 Iota Iota HER 17 39.5 +46.0 3.8 * Her star
∑1972 15 29.2 +80 26 6.9 31" Umi double star
∑2032, 17 CrB 16 14.7 +33 52 5.2 7" CrB double star
∑2161, 75 Her 17 23.7 +37 09 4.2 4" Her double star
28.

ST615 Psi ∑2241 17 41.9 +72 09 4.9 30" Dra double star
ST616 Kappa Kappa SCO 17 42.5 -39 2.4 2.5° Sco star
ST617 V V PAV 17 43.3 -57.7 5.7 * Pav variable star
ST618 Beta Beta OPH 17 43.5 +04.6 2.8 * Oph star
ST619 61
ST620 SZ SZ SGR 17 45.0 -18.6 9 * Sgr variable star
ST621 SX SX SCO 17 47.5 -35.7 8.5 * Sco variable star
ST622 G G SCO 17 49.9 -37 3.2 2° Sco star
ST623 Y Y OPH 17 52.6 -6.2 6 * Oph variable star
ST624 Xi Xi DRA 17 53.5 +56.9 3.8 * Dra star
ST625 Gamma Gamma DRA 17 56.6 +51.5 2.2 * Dra star
ST626 Barnards Star 17 57.8 +04 34 9.5 Stellar Oph star
ST627 h5003 17 59.1 -30 15 5 6" Sgr colored double star
ST628 ∑2038 Struve 2038 18 00.0 +80.0 5.7 20" Dra double star equal magnitude
ST629 95 18 01.5 +21 36 4.3 6" Her double star equal magnitude
ST630 Tau Tau OPH 18 03.1 -8.2 5.2 1.8" Oph double star challenge
ST631 70
ST632 Theta Theta ARA 18 06.6 -50.1 3.7 * Ara star
ST633 100
ST634 W W LYR 18 14.9 +36.7 7.3 * Lyr variable star
ST635 Eta Eta SGR 18 17.6 -36.8 3.1 * Sgr star
ST636 Kappa Kappa LYR 18 19.9 +36.1 4.3 * Lyr star
ST637 Delta Delta SGR 18 21.0 -29.8 2.7 * Sgr star
ST638 ∑2306 18 22.2 -15 05 7.9 10" Sct double star
ST639 Xi Xi PAV 18 23.2 -61.5 4.4 * Pav star
ST640 39
ST641 21 21 SGR 18 25.3 -20.5 4.9 1.8" Sgr double star challenge
ST642 Alpha Alpha TEL 18 27.0 -46 3.5 6' Tel star
ST643 59 18 27.2 +00 12 5.2 4" Ser colored double star
ST644 Lambda Lambda SGR 18 28.0 -25.4 2.8 * Sgr star
ST645 SS SS SGR 18 30.4 -16.9 9 * Sgr variable star
ST646 Delta Delta TEL 18 31.8 -45.9 5 11' Tel double star
ST647 T T LYR 18 32.3 +37.0 7.8 * Lyr red variable star
ST648 Kappa
ST649 ∑2348 18 33.9 +52 18 6 26" Dra double star
ST650 Alpha Alpha SCT 18 35.2 -8.2 3.9 * Sct star
ST651 O
ST652 O
ST653 Vega Alpha Lyr 18 36.9 +38 47 0 Stellar Lyr star
ST654 X X OPH 18 38.3 +08.8 5.9 * Oph variable star
ST655 HK HK LYR 18 42.8 +37.0 9.5 * Lyr variable star
ST656 ∑2398 Struve 2398 18 43.0 +59.6 8 13" Dra double star
ST657 Epsilon Double-Double, 18 44.3 +39 40 4.7 2" Lyr quadruple star
ST658 Zeta 18 44.8 +37 36 4.4 44" Lyr double star
ST659 ∑2375 18 45.5 +05 30 6.2 2" Ser double star equal magnitude
ST660 5
ST661 R 18 47.5 -05 42 4.5 Stellar Sct variable star
ST662 Beta 18 50.0 +33 24 3.5 47" Lyr double star magnitude contrast
ST663 S S SCT 18 50.3 -7.9 6.8 14.3" Sct double star
ST664 ∑2404 18 50.8 +10 59 6.9 4" Aql double star
ST665 Omicron
ST666 Delta2 Delta2 LYR 18 54.5 +36.9 4.5 * Cyg star
ST667 O
ST668 Sigma Sigma SGR 18 55.3 -26.3 2 * Sgr star
ST669 13 13 LYR 18 55.3 +43.9 3.9 4.. Lyr star
ST670 Theta
ST671 ADS11871 ADS 11871 18 57.0 +32.9 5.4 1" Lyr double star challenge
ST672 ∑2422 Struve 2422 18 57.1 +26.1 8 0.7" Lyr double star challenge
ST673 UV UV AQL 18 58.6 +14.4 8.6 * Aql variable star
ST674 ∑2426 19 00.0 +12 53 7.1 17" Aql colored double star
ST675 BrsO14 19 01.1 -37 03 6.6 13" Cra double star equal magnitude
ST676 h5082 19 03.1 -19 14 6 7" Sgr triple star
ST677 V 19 04.4 -05 41 6.6 Stellar Aql red variable star
ST678 15 19 05.0 -04 02 5.4 38" Aql colored double star
ST679 Gamma 19 06.4 -37 00 5 3" Aql double star equal magnitude
ST680 R 19 06.4 +08 14 5.5 Stellar Aql red variable star
ST681 ∑2449 19 06.4 +07 09 7.2 8" Aql double star
ST682 ∑2474 19 09.1 +34 35 6.5 16" Lyr double star
ST683 ∑2486 19 12.1 +49 51 6.6 8" Cyg double star equal magnitude
ST684 O
ST685 Tau Tau DRA 19 15.5 +73.4 4.5 * Dra star
ST686 RY RY SGR 19 16.5 -33.5 6 * Sgr variable star
ST687 U 19 18.8 +19 37 6.6 Stellar Sge variable star
ST688 V1942 V1942 SGR 19 19.2 -15.9 6.4 * Sgr variable star
ST689 UX 19 21.6 +76 34 5.9 Stellar Dra red variable star
∑359 18 35.5 +23 36 6.3 0.7" Her double star challenge
∑358 ADS 11483 18 35.9 +17.0 6.8 1.6" Her double star challenge
∑525 18 54.9 +33 58 6 45" Lyr colored double star
∑178 O.Struve 178 19 15.3 +15.1 5.7 90" Aql double star
∑2202 17 44.6 +02 34 6.2 21" Oph double star equal magnitude
∑2276 18 05.5 +02 30 4 1.5" Oph double star challenge
∑2280 18 07.8 +26 06 5.9 14" Her double star equal magnitude
∑2323 18 24.0 +58 48 4.9 4" Dra triple star
Δ222 18 33.4 -38 44 5.9 21" CrA double star equal magnitude
∑2379 18 46.5 -00 58 5.8 13" Aql triple star
∑2420 18 51.2 +59 22 4.9 35" Dra double star
∑2417, 63 Ser 18 56.3 +04 11 4.1 22" Ser double star
Catalog Index
29.
 Loading...
Loading...