Page 1

®
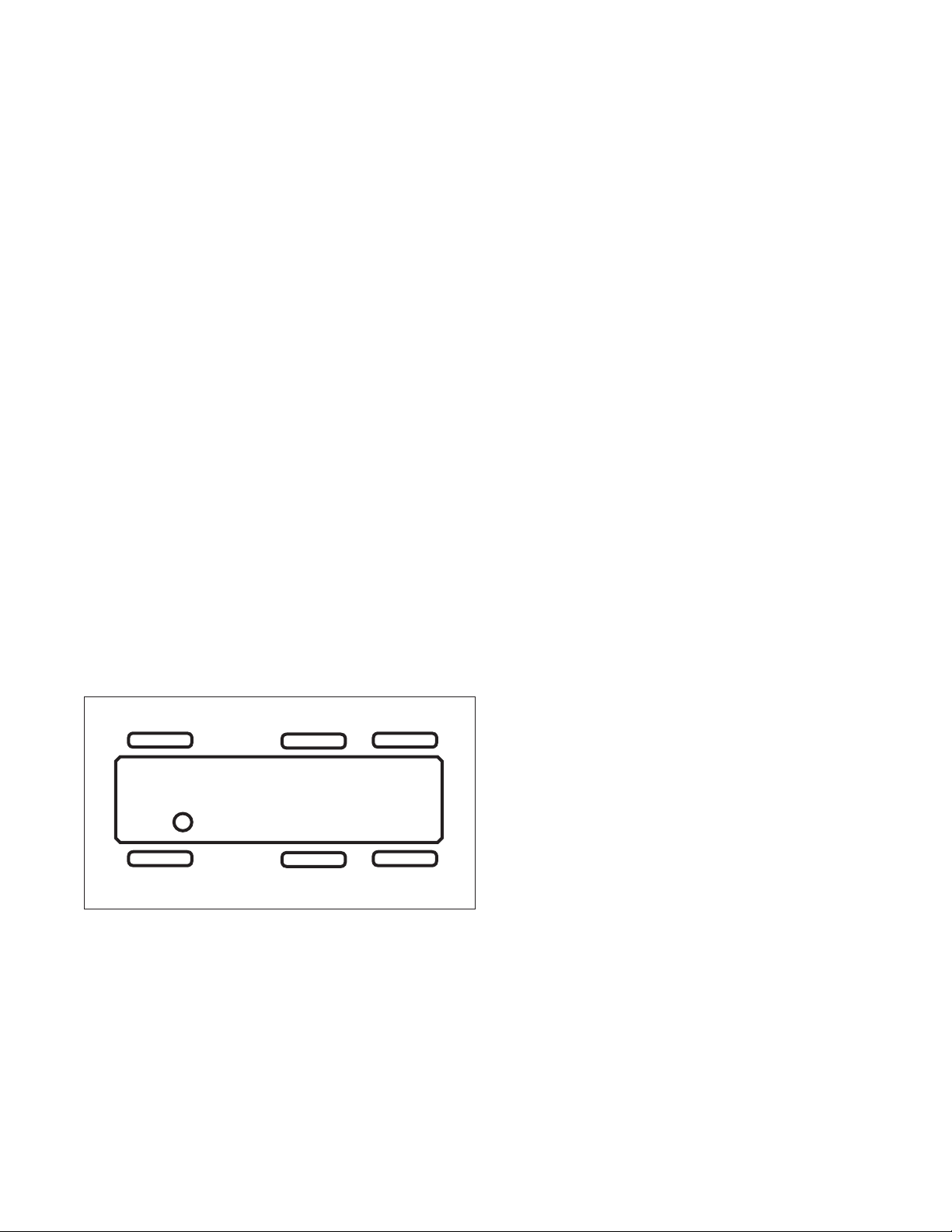
The Bendix® ESP® EC-80™ Controller
SD-13-4986
INTRODUCTION
The Bendix® ESP® EC‑80™ Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
is a member of a family of three Bendix®‑brand electronic
Antilock Braking System (ABS) devices used to help
improve the braking characterist ics of air‑braked heavy‑
and medium‑duty trucks, tractors, and buses:
1. The Bendix® ABS ESP® ECU uses wheel speed sensors
to monitor four wheel‑ends to detect wheel‑slip or wheel
lock‑up during braking. The system inter venes when
needed — using Pressure Modulator Valves (PMVs)
to adjust and/or pulse the brake pressure — in order
to optimize the contact bet ween the t ires and t he road
surface.
2. The Bendix® Automatic T raction Control (ATC ) EC‑80
ECU provides standard ABS; improves vehicle traction
during acceleration; and aid lateral stability while driving
through curves. The Bendix® A TC E CU communicates
with the engine’s Controller to provide Engine Torque
Limiting (ETL), and/or use Differential Braking (DB) to
make brake applications at individual wheels.
3. The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller provides — in
addition to the ABS and ATC functions described
above — advanced braking features referred to as the
Bendix® ESP® Electronic Stability Program. The Bendix
ESP EC‑80 Controller analyzes the vehicle's motion
compared to the driver 's intended path and provides
Yaw Control (YC) and Roll Stability Program (RSP)
capabilities. When necessary, the s ystem will intervene
to reduce the engine throt tle, and/or apply the brakes
at one or more of the wheel ends — to help the vehicle
return to the intended direction.
™
Label Shows ECU
Designation
FIGURE 1 - THE BENDIX® ESP® EC‑80™ CONTROLLER
The driver is always responsible for the control
and safe ope rat io n of th e vehicl e at a ll ti me s. The
Bendix® ABS system does not replace the need
for a skilled, alert professional driver, reacting
appropriately and in a timely manner, and using
safe driving practices.
TABLE OF CONTENTS Page
Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3‑4
Indicator Lamps and Power‑Up Sequence . . . . . 8‑9
ABS Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9‑10
ATC Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11‑12
ESP ABS With Stability Control . . . . . . . . . . . 12‑13
Important Safety Information About
The ESP Stability System . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13‑14
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17‑62
See page 63 for the full Table of Contents
®
Bendix
™
EC‑80
System Name
ABS “Standard”
ATC “Premium”
ESP
®
EC‑60™ ECU)
Designations
“Advanced”
Previous
(Bendix
®
ECU; Pressure Modulator Valves (PMVs);
Four Wheel Speed Sensors.
Items above, plus: Automatic Traction
Control (ATC) Valve; Option of two more
Wheel Speed Sensors and PMVs.
All items above, plus: Yaw Rate Sensor;
Steering Angle Sensor; Load Sensor;
Steer‑axle ATC valve; Brake Demand
Sensor; and an Additional PMV
Key Components
ESP® is a registered trademark of DaimlerChrysler and is used by BCVS under license.
Key System Features
(ECU Designation Shown
on the ECU Label)
ABS [Antilock Braking]
(EC‑80 ABS)
ABS plus ATC [Traction Control]
(EC‑80 ATC)
ABS plus ATC plus ESP
[Yaw Control (YC) and
Roll Stability Program (RSP
(EC‑80 ESP)
®
ECU
Connector
Locations
Provided
Two SD‑13‑4983
Three SD‑13‑4983
Four
)].
See
Service Data
Sheet
SD‑13‑4986
(This
Document)
1
Page 2
GENERAL SAFETY GUIDELINES
WARNING! PLEASE READ AND FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS
TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH:
When working on or around a vehicle, the following guidelines should be observed AT ALL TIMES:
▲ Park the vehicle on a level surface, apply the
parking brakes and always block the wheels.
Always wear personal protection equipment.
▲ Stop the engine and remove the ignition key
when working under or around the vehicle.
When working in the engine compartment,
the engine sho uld be shut off and the ig nition
key should be removed. Where circumst ances
require that the engine be in operation, EXTREME
CAUTION should be used to prevent personal
injury resulting from contact with moving,
rotating, leaking, heated or electrically-charged
components.
▲ Do not att empt to install, remove, dis assemble
or assemb le a component until you have re ad,
and thoroughly understand, the recommended
procedures. Use only the proper tools and
observe all precautions pertaining to use of those
tools.
▲ If the wor k is being per formed on th e vehicle’s
air brake system, or any auxiliary pressurized air
systems, make ce rta in to drain th e air pressur e
from all rese rvoirs before be ginning ANY work
on the vehicle. I f th e vehicle i s equip ped wi th a
Bendix® AD-IS® air dryer system, a Bendix® DRM™
dryer re se rvoir modul e, o r a B en di x® AD-9si™ air
dryer, be sure to drain the purge reservoir.
▲ Following the vehicle manufacturer’s
recommended procedures, deactivate the
electrical system in a manner that safely removes
all electrical power from the vehicle.
▲ Never exceed manufacturer’s recommended
pressures.
▲ Never connect or disconnect a hose or line
containing pressure; it may whip. Never remove
a compone nt or plug unless you ar e certai n all
system pressure has been depleted.
▲ Use only genuine Bendix
parts, components and kits. Replacement
hardware, tubing, hose, ttings, etc. must be of
equivalent size, type and strength as original
equipment and be designed speci cally for such
applications and systems.
▲ Component s with st rippe d threads o r damaged
part s should be replaced ra ther than repaired.
Do not attempt repairs requiring machining or
welding unless speci cally stated and approved
by the vehicle and component manufacturer.
▲ Prior to retur ning the vehicle to ser vice, make
certain all components and systems are restored
to their proper operating condition.
▲ For vehicles with Automatic Traction Control
(ATC), the ATC function m ust be disabled (ATC
indicator lamp should be ON) prior to performing
any vehicle maintenance where one or more
wheels on a d rive axle ar e lifted of f the groun d
and moving.
▲ The power MUST be t emporarily disco nnected
from the radar sensor whenever any tests USING
A DYNAMOMETER are conducted on a Bendix
Wingman® Advanced™-equipped vehicle.
®
brand replacement
®
▲ You should consult the vehicle manufacturer's operating and service manuals, and any related literature,
in conjunction with the Gu ideli nes above.
Even with the Bendix® ESP® system with the EC-80™
Controller, the driver remains responsible for ensuring
vehicle stability during operation. The braking system
can only function within the limits of physics. The
system helps mitigate potential vehicle stability
incidents, but cannot prevent them in all cases.
Other factors such as driving too fast for road, trafc
or weather conditions, oversteering, an excessively
high vehicle Center of Gravity (CG), or poor road
conditions can cause vehicle instability that is beyond
the capability of any stability system to mitigate. In
addition, the effectiveness of Bendix ESP system
with the EC-80 Controller can be greatly reduced on
vehicles towing multiple trailer combinations.
2
The Bendix ESP system with the EC-80 Controller
(see page 12) may only be used on vehicles tested and
approved by Bendix engineering. The tests produce
a validated parameter data set for use by the vehicle’s
Bendix ESP EC-80 Electronic Control Unit (ECU).
When replacing an ECU, only specic Controllers —
with the correct parameter set — may be used. See
“Obtaining a N ew Bendix ES P EC‑ 80 C ontroller ” on
page 17 for further details.
Bendix ESP system with the EC-80 Controller-equipped
ve hi c les should not be dr i v e n on hi g h -ba n k e d ro a d s —
such as those found on high-speed test or race tracks.
Test per sonnel must have the Be ndix ESP system's
stability features disabled prior to operating a vehicle
on such tracks.
Page 3

For vehicles with the (optional) Hill Start Aid (HSA) system
(sometimes referred to as a “Hill Start Assist”, or simply “Hill
Start ”), this feature interfac es between the transmis sion
and the braking system. HSA helps the driver prevent
the vehicle from rolling downhill w hen m oving up a steep
incline from a stationar y position. See page 6 for more
information.
YAW CONTROL (YC)
A Bendix® EC‑80™ ESP® Controller includes Yaw Control
(YC) functionality. Yaw Control has the ability to apply
brakes to individual wheel ends, as well as applying the
trailer brakes, to counteract trailer “pus h” that — during
cert ain maneuvers — could lead to a loss‑ of‑control or
a jackknife incident. See " Yaw Stability" on page 13 for
further details.
ROLL STABILITY PROGRAM (RSP)
®
The Bendix
ABS solution that helps decrease vehicle speed by
reducing the engine's throttle and applying all vehicle
brakes as needed, mitigating the vehicle's tendency to
roll over. RSP focuses on reducin g the vehicle’s speed
below the critical ro ll thre sho ld dur in g direc ti on‑changing
maneuvers — such as driving on curved highway exit
ramps or obstacle avoidance maneuvers on dry, high
friction sur faces. See " ESP ABS with Stabilit y Control"
on page 12 for further details.
Roll Stability Program (RSP), is an all‑a xle
The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller 's ESP/RSP function
utilizes the following additional components:
• A Steer Axle T raction Control V alve (may be integral
to the service brake Relay Valve or a stand‑alone
device)
Sensor
Clamping
Sleeve
Straight Speed
90° Speed
Sensors
FIGURE 2 - BENDIX® WS‑24™ WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
Delivery
(Port 2)
™
M-40X
Modulator
Exhaust (Port 3)
Sensors
Supply
(Port 1)
Electrical
Connector
During an RSP syste m intervent ion, the vehicle
automatically decelerates. RSP can slow the
vehicle with or without the operator applying
the brake p edal, and even when the o perator is
applying the throttle.
COMPONENTS
The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller’s ABS function utilizes
the following components:
• Bendix® WS‑24™ Wheel Speed Sensors (four or
six, depending on the conguration), each with a
clamping sleeve. [Refer to SD-13-4860]
• Bendix® M‑40QR™ or M‑40‑HF™ Pressure Modulator
Valves (four, ve, or six may be present) [refer to
SD-13-4958]. For legacy systems where a Bendix®
M‑32™ or M‑32QR™ Pressure Modulator Valve is
used, refer to SD-13-4870.
• A dash‑mounted tractor ABS Indicator Lamp
• A service brake Relay Valve
• A dash‑mounted trailer ABS Indicator Lamp
• An optional blink code Activation Switch
• An optional ABS Off‑road Switch
FIGURE 3 - EXAMPLE OF A BENDIX M‑40X™ MODULATOR
• A dash‑mounted ESP Status/Indicator Lamp (also
serves as the ATC Status/Indicator Lamp)
• A Bendix® SAS‑60™ Steering Angle Sensor
(mounted to the steering column ‑ See Figure 4)
When replacing a steering wheel, take care not to
damage the Steering Angle Sensor or interfere with
its operation, and the Steering Angle Sensor must be
recalibrated (see Troubleshooting section.)
Straight
Connector
FIGURE 4 - EXAMPLES OF STEERING ANGLE SENSORS
90° Connectors
3
Page 4
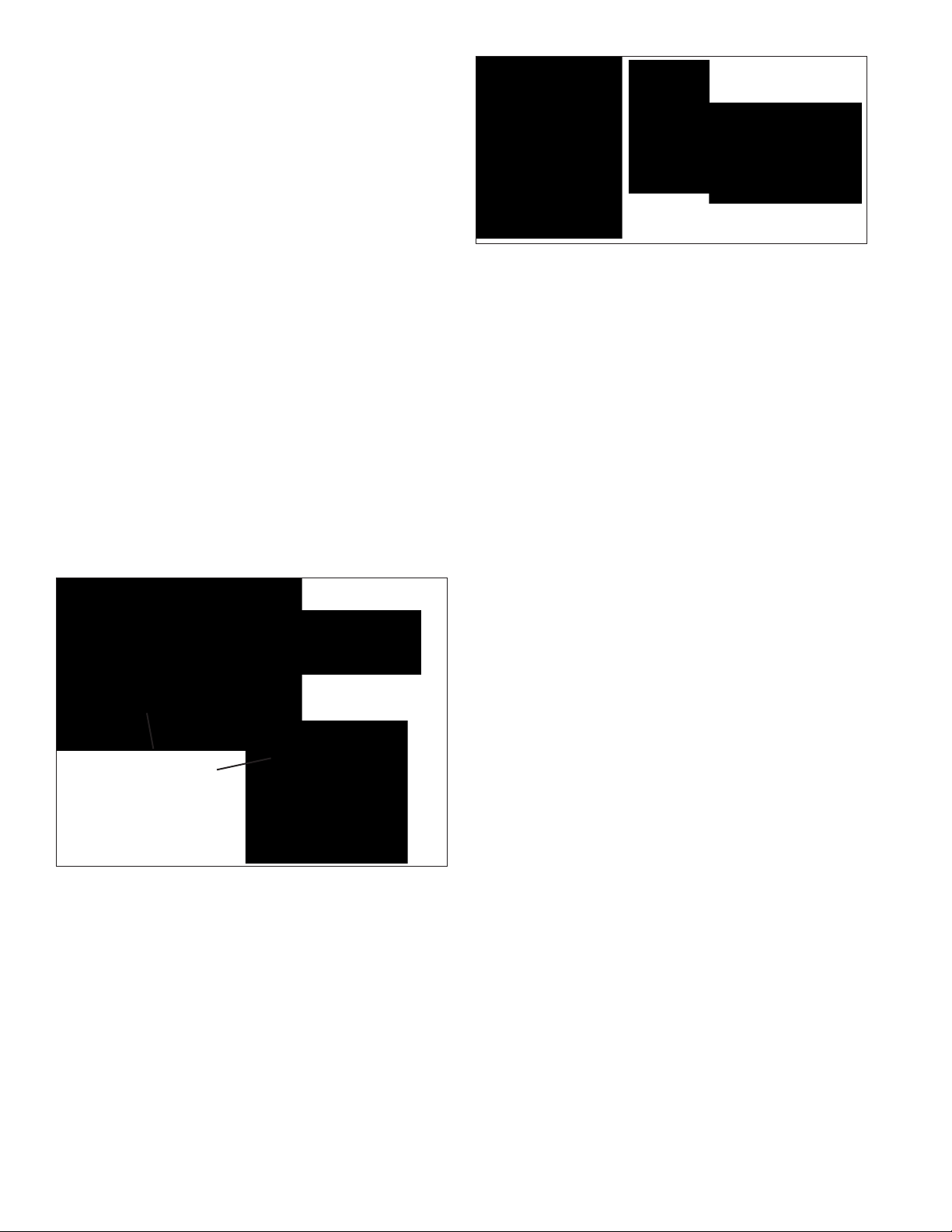
• Bendix® YAS‑60™ or YAS‑70X™ Yaw Rate/Lateral
Acceleration Sensors (typically mounted to a cross‑
member near the back of the vehicle cab). See
Figure 5.
• Brake Demand Sensors (installed in the primary
and secondary delivery circuits)
• A Load Sensor (typically installed in the suspension
air bag)
• An additional Modulator Valve (Bendix® M‑40QR™ or
M‑40HF™ Pressure Modulator Valve) that controls
the pressure applied to the trailer brakes during a
system intervention
The Bendix® ESP® EC‑ 80™ Controller's ATC function
utilizes the following additional components:
• A drive axle Traction Control V alve (may be integral
to the service brake relay valve or a stand‑alone
device)
• A dash‑mounted ATC Status/Indicator Lamp
• A J1939 serial communication Control Module
• A J1939‑ or ECU hardware‑provided Stop Lamp
Switch Input
• An optional ATC Mud/Snow Switch (sometimes
referred to as an ATC off‑road switch)
Brake Demand/
Load Sensor
®
Bendix® RV-3
Pressure
Reducing Valve
FIGURE 6 - ADDITIONAL VALVES NECESSARY FOR THE
HILL START AID FEATURE
™
Bendix® AT-3
Traction Control
Valve
™
Bendix
Double Check
Valve
DC-4
®
BENDIX® ETRAC™ AUTOMA TED AIR
SUSPENSION TRANSFER SYSTEM
The Bendix® eTrac™ automated air pressure transfer system
is used on 6 x 2 semi‑trac tors that feature Bendix® ATC
and ESP Antilock Brake Systems (ABS). This system
complements the Bendix® S MART AT C™ traction control
feature of our ABS system to provide improved traction at
low speeds (e.g. pulling away on an inclined ramp, or in
slippery conditions such as mud or snow‑covered surfaces,
etc.) When active, the Bendix eTrac system vents — or
“dumps” — the air pressure of the tag axle susp ension
air bags, and increases the air pressure in t he drive a xle
suspension air bags to a pre‑determined maximum. This
action helps the drive axle to gain more traction.
See SD-13-21021 for more information about the Bendix®
eTrac™ Automated Air Suspension Transfer System.
Yaw/Lateral
Accelerator Sensors
(Two examples
shown.)
FIGURE 5 - YAW AND BRAKE DEMAND/LOAD SENSORS
The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller's Hill Start Aid function
utilizes the following additional components:
• A Bendix® AT‑3™ Traction Control Valve
• A dash‑mounted Hill Start Status/Indicator Lamp
• A dash‑mounted Enable/Disable Switch
• A Bendix® RV‑3™ Pressure Reducing Valve
• A Bendix® DC‑4® Double Check Valve
ECU MOUNTING
The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller is not protected against
moisture, and must be mounted in an environmentally
protected area.
All wire harness connectors must be properly seated. The
use of secondary locks is strongly recommended.
The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller utilizes connectors from
the AMP MCP 2.8 product family.
HARDWARE CONFIGURATIONS
Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controllers support applications up to
six sensor/six modulator (6S/6M) installations with ATC
and drag torque control. They can also support Hill Start
functions. All 12 volt models suppor t Power Line Carr ie r
(PLC). 24 volt models do not support PLC. See Figure 7
for more details.
4
Page 5
ABS
Off-
Road
ATC
ATC
Mud/Snow
Blink
Codes
ESP/
RSP
HSA
Hill Start
Aid Feature
Bendix
eTrac
system*
Optional Optional Optional 12/24 4/5/6 4/6
For information about the Bendix® eTrac™ automated air suspension transfer system, see SD‑13‑21021
*
FIGURE 7 - BENDIX® ESP® EC‑80™ CONTROLLER FEATURES
BENDIX® ESP® EC-80™ CONTROLLERS USE
POWER LINE CARRIER (PLC)
All new towing vehicles built since March 1, 2001 , have had
an in‑cab trailer ABS Indicator Lamp installed.
Trailers built since Marc h 1, 2001, transmit the status of
the trailer ABS over the power line (the blue wire of the
J560 connector) to the tractor using a Power Line Carrier
(PLC ) signal. See Figures 8 and 9. Typically the signal is
broadcast by the trailer ABS Electronic Control Unit (ECU).
®
™
Voltage
Input
PLC
Modu-
lators
(PMVs)
Retarder
Relay
Sensors
Serial
Communication
J1939
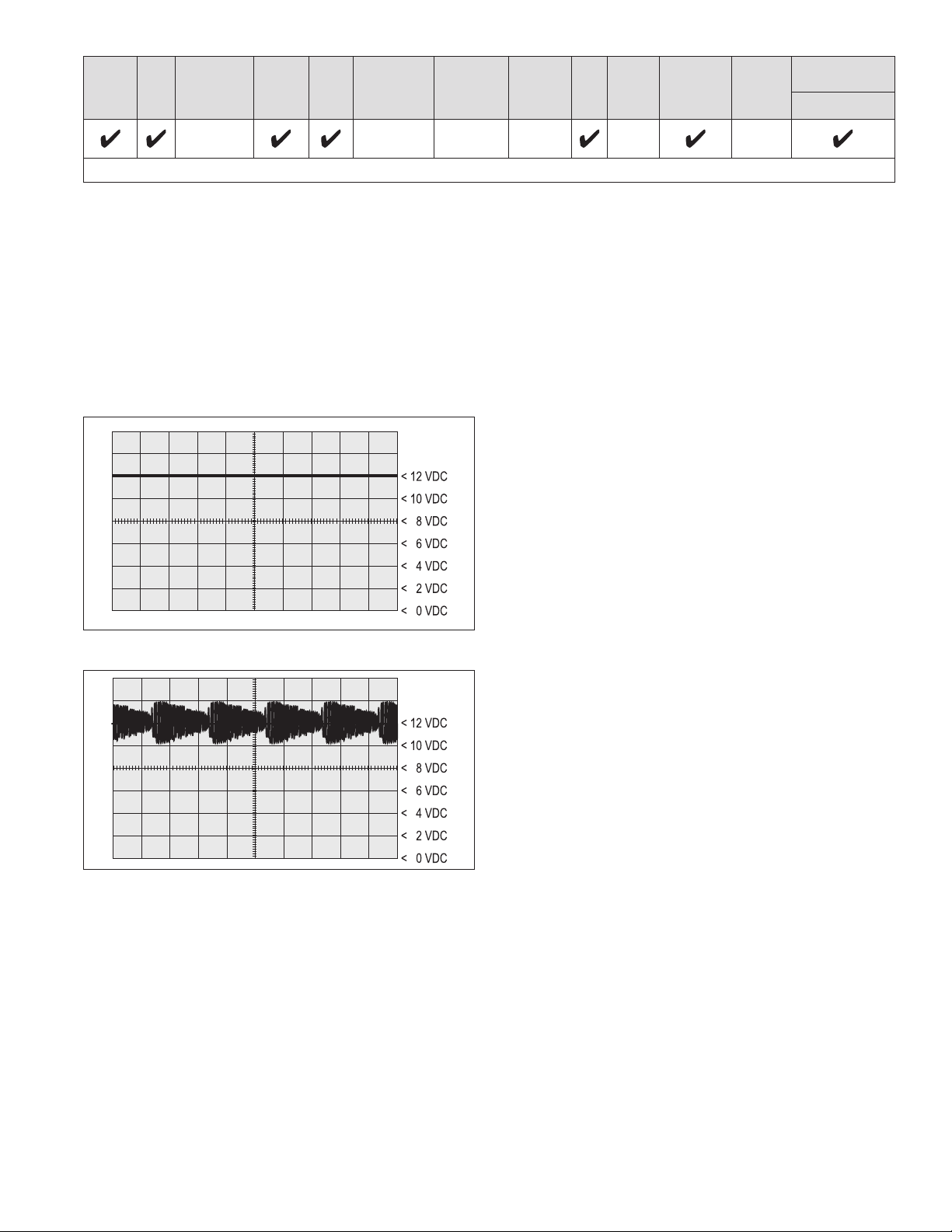
Suggested oscilloscope settings are AC coupling, with one
volt/div, 100 µsec /div. The signal should be measured at
the ignition power input of the Bendix EC‑80 Controller.
Note: An ABS trailer equipped with PLC, or a PLC
diagnostic tool, must be connected to the vehicle in order
to generate a PLC signal on the power line.
BENDIX ESP EC-80 CONTROLLER INPUTS
Battery and Ignition Inputs
The Bendix ESP EC‑ 80 Controller oper ates at a nominal
supply voltage of 12 or 24 volts, depending on the ECU.
The battery input is connected through a 3 0 amp fuse
directly to the battery.
The ignition input is applied by the ignit ion switch circuit
through a 5 amp fuse.
FIGURE 8 - POWER LINE WITHOUT PLC SIGNAL
FIGURE 9 - POWER LINE WITH PLC SIGNAL
The application of PLC technology fo r the heavy vehicle
industry in North America is known as “PLC4Trucks.”
The Bendix® ESP® EC‑ 80™ Controller supports PLC
communications in accordance with SAE J2497.
PLC SIGNAL
An oscillosc ope can be used to measure or identif y the
presence of a PLC signal on the power line. The PLC
signal is an amplitude and frequency‑modulated signal.
Depending on the ltering and load on the power line,
the PLC signal amplitude can range from 5.0 mVp‑p to
7.05 Vp‑p.
Ground Input
The Bendix ESP EC‑ 80 Controller supp orts one gr ound
input. See pages 52 and 53 for wiring system schematics.
ABS Indicator Lamp Ground Input
The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller requires a second
ground input (X1‑12) for the ABS indicator lamp. The X1
wire harness co nnector contains an AB S indicator lamp
interlock (X1‑15), which shorts the ABS indicator lamp
circuit (X1‑18) to ground if the connector is removed from
the ECU.
Bendix® WS-24™ Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed data is provided to the B endix ESP EC‑ 8 0
Controller from the Bendix® WS‑24™ wheel speed sensor
(see Figure 2). Vehic les have an exciter ring (or “tone
ring”) as part of the wheel assembly. As the wheel
turns, the teeth of the exciter ring pass the whee l speed
sensor, generating an AC signal. The Bendix ESP EC‑80
Controller receives the AC signal, which varies in voltage
and frequency as the wheel speed changes.
Vehicle axle configurations determine the number of
Bendix WS‑24 wheel speed se nsors that must be used.
A vehicle with a single rear axle requires four wheel speed
sensors. Vehicles with two rear axles can utilize six wheel
speed sensors for optimal performance.
5
Page 6

Diagnostic Blink Code Switch
A momentary switch that grounds the ABS Indicator Lamp
output is used to place the ECU into the diagnostic blink code
mode and is typically located on the vehicle’s dash panel.
Optional ABS Off-Road Switch and Indicator
Lamp Operation
Vehicle operators use an optional dash‑mounted switch to
place the Bendix® ESP® EC‑ 8 0™ Controller into the ABS
off‑road m ode. See "Optional A BS Off- Road Mode" on
page 10 for further details. In some c ases, ECUs may
also be put into the ABS off‑road mode by one of the other
vehicle control module s, using a J193 9 message to the
Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller.
(If you need to know if a specic Bendix ESP EC‑80
Controller uses a J1939 message to operate the lamp,
contact the Bendix Tech Team. E‑mail the Tech Team
at ABS@bendix.com (be sure to specify the ECU par t
number), or call 1‑800‑AIR‑BRAKE (1‑800‑245‑2725).
The ABS off-road mode should not be used on
normal, paved road surfaces because vehicle
stability and steerability may be adversely affected.
When the ECU is placed in the ABS off-road mode,
the ABS Indicator Lamp will ash constantly (at a
rate of onc e per 2 .5 secon ds) to notif y th e vehicle
operator that the off-road mode is active.
Optional ATC Mud/Snow (Off-Road) Switch and
Indicator Lamp Operation (also see page 8.)
The Bendix ESP system uses a dash‑mounted switch for the
operator to place the ECU into the ATC Mud/Snow mode.
Optional Hill Start/Hill Start Assist Feature
Switch and Lamp Operation (see also page 8.)
ESP Controllers use a dash‑mounted switch for the
operator to place the ECU into the hill star t mode. This
feature interfaces between the transmission and the
braking system to help the driver prevent the vehicle from
rolling downhill when moving up a steep incline fro m a
stationary position.
With Hill Start Aid Feature option you lose the ABS
off-road function and the retarder relay output.
When the ECU is placed in the Hill Start Aid (HSA) feature
mode, the HSA Indicator Lamp will ash constantly (at a
rate of once per 2.5 seconds) to notify the vehicle operator
that the HSA mode is active. The ECU receives J1939
messages from the t ransmissi on to engage the H S/HSA
components. When engaged, the system applies 44 psi to
the rear brakes for three (3) seconds then releases. This
function is totally controlled by the automatic transmission.
6
Stop Lamp Switch (SLS)
The Bendix ESP EC‑ 80 Controller monitors the vehic le
stop lamp status. Certain vehicle functions, such as
ATC and All‑Wheel Drive (AWD), use the status of the
stop lamp to determine when the driver makes a brake
application. This c an be provided to the ECU via J1939
communications, or hardware input.
Brake Demand Sensors
The brake demand sensors provide the Controller with an
indication of driver‑applied brake pressure. One is installed
in the primary air brake circuit, and another is installed in
the secondary air brake circuit.
Load Sensor
The load sensor provides the Controller with an indication
of the vehicle load. It is typic ally installed in one of the
suspension air bags.
Bendix® SAS-70X™ Steering Angle Sensor
Bendix® brand Steering Angle Sensors (SAS) are used to
report the steering wheel position to the Controller, utilizing
a dedicated serial communications link that is shared with
the Y a w Rat e Sensor. The Controller supplies the power
and ground inputs to the Bendix® SAS‑70X™ sensor.
The Bendix SAS‑70X sensor is available with two different
styles of wire harness connectors. (See Figure 4.)
Bendix® YAS-60™ or Y AS-70X™ Yaw Rate/Lateral
Acceleration Sensors
Bendix® brand yaw rate/lateral acceler ation sensors are
used to provide the Controller an indication of vehicle
lateral acceleration an d rotati on around t he ver ti c al ax is.
This information is provided to t he Controller, utilizing a
dedicated serial c ommunications link that is sha red with
the Bendix® SAS‑60™ sensor. The Controller supplies the
power and ground inputs to the yaw rate sensor.
BENDIX® ESP® EC-80™ CONTROLLER
OUTPUTS
Bendix® M-40QR™ and M-40HF™ Pressure
Modulator Valves (PMVs)
The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller operates Bendix®
M‑40QR™ and M‑40HF™ Pressure Modulator Valves
(PMVs) to modify the dr iver‑applied air pressure to the
servic e brakes during ABS, ATC, RSP or YC activation
(see pages 9-13). The PMV is an electropneumatic
control valve and is the last valve that air passes through
on its way to the brake chamber. The modulator hold and
release solenoids are activated to "modulate" or "control"
the brake pressure during an antilock braking event. The
hold solenoid is normally open and the release solenoid is
normally closed, such that the PMV nominally allows air to
ow through. This design allows for air delivery to brake
chambers in the event of electrical trouble.
Page 7

The Bendix® ESP® EC‑ 80™ Controller also utilizes an
additional Pressure Modulator Valve (PMV) for control
of the trailer service brakes during stability interventions.
Traction Control Valve (TCV)
Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controllers use two TCVs, one on the
steer axle and one on the dr i ve a x l e. The TCV may be a
separate valve or integrated into the rear axle relay valve.
The Controller will activate the drive axle TCV during
differential braking ATC events.
During stabilit y interventions, the Controller will act ivate
both the steer axle and drive axle TCVs as required.
Stop Lamp Output
The Controller provides an output to control a relay
that illuminates the vehicle stop lamps during stability
interventions. This information is also available using the
J1939 serial communications link.
ABS Indicator Lamp Control with Optional
Diagnostic Blink Code Switch
The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller has internal circuitry to
control the ABS Indicator Lamp on the dash panel.
The ABS Lamp Illuminates:
1. During power up (e.g. when the vehicle is started) for
approximately three (3) seconds and turns off after the
self‑test is completed, providing no Diagnostic Trouble
Codes (DTCs) are present on the ECU;
2. When full ABS operation is not available due to the
presence of a DTC on the ECU;
3. If the ECU is unplugged or has no power;
4. When the ECU is placed into the ABS off‑road
mode (the lamp ashes steadily at a rate of once per
2.5 sec.); or
5. To display blink codes for diagnostic purposes after the
external diagnostic switch is activated.
The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller may communicate
with other vehicle control modules to operate the ABS
Indicator Lamp using serial communications. (If you
need to know if this Bendix ESP EC‑ 80 Controll er uses
serial communications to operate the lamp; e‑mail ABS@
bendix.com, (be sure to specify the ECU part number), or
call 1‑800‑AIR‑BRAKE/1‑800‑247‑2725 and speak to the
Bendix Tech Team.)
Indicator Lamp Control Using Serial
Communications Links
As mentioned above, depending on the vehicle
manufacturer, the dash indicator lamps (ABS, ATC,
ESP, and trailer ABS) may be controlled using serial
communications links. In the se cases, the Bendix ESP
EC‑80 Controller will send a serial communications
message over the J1939 link, indicating the required status
of the lamp(s). Another vehicle contro l module receives
the message and controls the indicator lamp(s).
Dynamometer Mode Indicator Lamp Operation
When the Bendix ESP EC‑ 80 Controller is put into the
Dynamometer mode for testing purposes, the ATC
Indicator Lamp will be illuminated.
Retarder Relay Disable Output
The retarder relay disable output may be used to control a
retarder disable relay. When congured to use this output,
the ECU will energize the retarder disable relay and inhibit
the use of the retarder as needed.
If the ECU is congured for the Hill Start/ Hill Start Assist
feature (HS/HSA), the retarder relay output pin is used to
control the Hill St art status lamp. As a result, the vehic l e
loses the retarder relay function when it has the Hill Start
feature.
SAE J1939 Serial Communications
A Controller Area Network (CAN) data link (SAE J1939 ) is
provided for communication. This link is used for various
functions, such as:
• Diagnostic purposes.
• To disable retarding devices during ABS operation.
• To request that the torque converter disable lock‑up
during ABS operation
• To share information such as wheel speed and ECU
status with other vehicle control modules.
Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controllers utilize the J1939 data link
for:
• ATC and drag torque control functions.
• Vehicle stability functions.
Trailer ABS Indicator Lamp Control
The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller will activate a trailer ABS
Indicator Lamp (located on the dash panel) that indicates
the status of the trailer ABS unit on one, or more trailers, or
dollies that are equipped with PLC functionality. T ypically ,
the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller directly controls the
trailer ABS Indicator Lamp based on the information it
receives from the trailer ABS, via PLC.
Alternatively, some vehicles require the Bendix ESP EC‑80
Controller to activate the trailer A BS Indicator Lamp by
communicating with other vehicle Controllers using serial
communications.
(If you need to know if this Bendix ESP EC‑ 80 Controller
uses a serial communications message to operate the
lamp, e‑mail ABS@bendix.com (be sure to specify the ECU
part number), or call 1‑800‑AIR‑BRAKE (1‑800‑245‑2725)
and speak to the Bendix Tech Team.)
Interaxle Differential Lock Control
(AWD Transfer Case)
Bendix ESP EC‑ 80 Controllers c an control the intera xle
differential lock (AWD transfer case) . This is recommended
on AWD vehicles, but the ECU must be specially congured
to provide this feature. E‑mail ABS@bendix.com for more
details.
7
Page 8
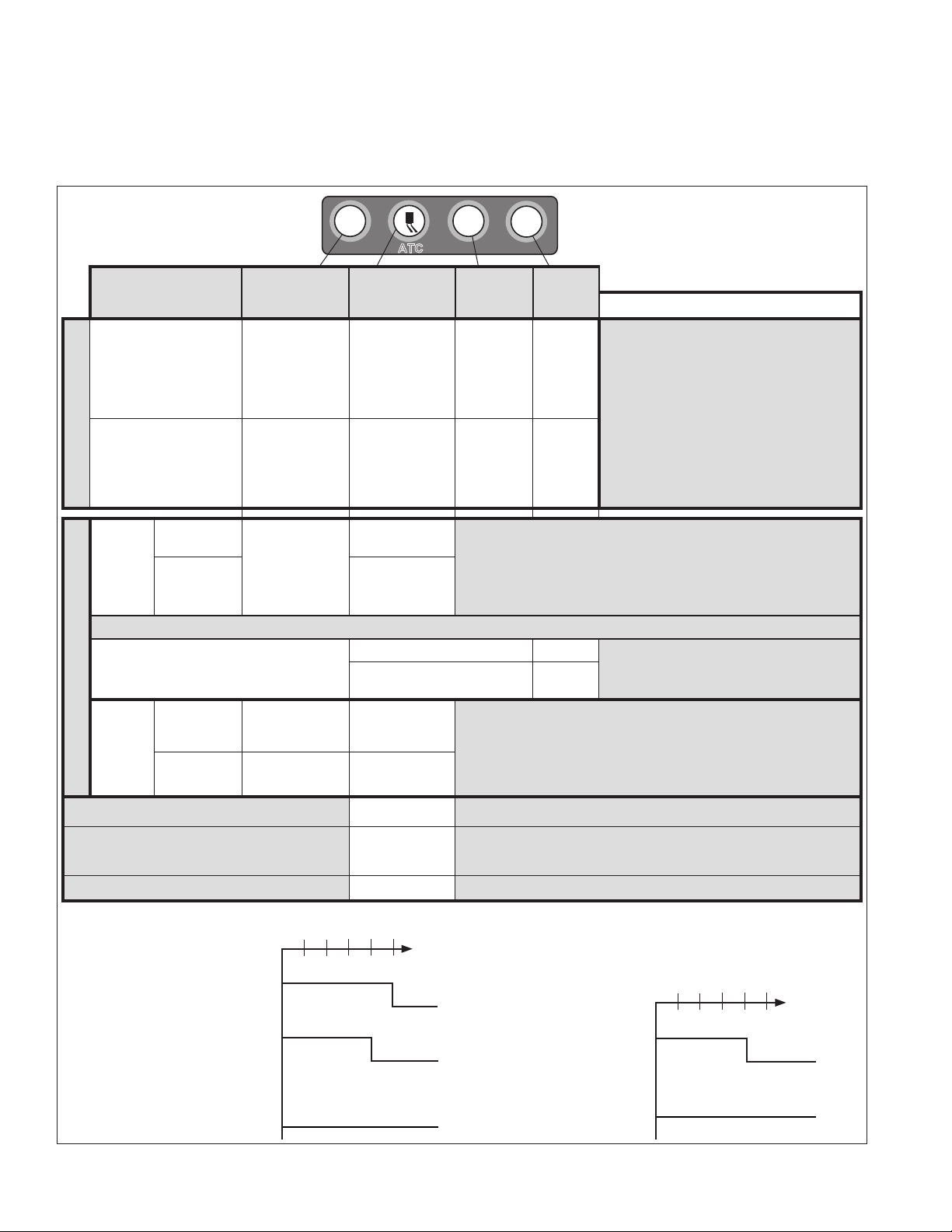
INDICATOR LAMPS AND POWER-UP
ATC
SEQUENCE
NOTICE: The vehicle operator should Verif y the proper
operation of all installed indicator lamps (ABS, ATC/ESP,
and trailer ABS) when applying ignition power and during
vehicle operation. See Figure 10.
Lamps that do not illuminate as expected when ignitio n
power is applied, or remain illuminated, indicate the need
for maintenance.
Dash Lamp Behavior for the
ABS
Bendix® ESP® EC-80™ Controller
Mode
Ignition on ‑ start up
[trailer with Power Line
Carrier (PLC)]
3 seconds after ignition
At Vehicle Startup
[with no Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs)]
ABS
Off-Road
Mode
Vehicles with Hill Start Aid (HSA):
Special Mode Operation
Deep
Mud/
Snow/
Mode
During an Automatic Traction Control (ATC) Event Flashes quickly • Reduces wheel slip during acceleration at low speeds
During Dynamometer Mode
Normal
During an ATC
Event
‑— OR, depending on vehicle options (a vehicle can have either ABS off‑road or HSA) —
During HSA Mode
(“Hill Start” / “Hill Start Assist”)
Normal OFF
During an
ATC/ESP
Event
During an ESP Event Flashes quickly •
ABS
Lamp
ON for
three (3)
seconds*
Lamp OFF* Lamp OFF* Lamp OFF**
Lamp ashes
slowly (every 2.5
seconds)
OFF Flashes quickly
ATC/ESP Lamp
ON for 2.5
seconds*
Lamp OFF
Flashes quickly
During HSA Event Lamp OFF
HSA Manually Disabled
Flashes slowly
(every 2.5
seconds)
Lamp ON
(ATC
Disabled)
TRLR
ABS Lamp
seconds**
• Uses dash switch
• Not for rm road surfaces
• Allows more wheel lock‑up (less ABS intervention)
• Mode only applies under 25 mph (Over 25 mph, the system reverts to
• Disables ATC monitoring functions
• When not in Dynamometer Mode, an illuminated lamp indicates an
ATC DTC is present
HSA
Trailer
ON for
three (3)
full ABS ‑ including ATC/ESP — and upon exiting off‑road mode, the
ATC lamp extinguishes.)
• Uses dash switch
• Increases allowable wheel slip during ATC interventions
• Not for rm road surfaces
System intervenes to reduce the risk of rollovers, loss‑of‑control, etc.
HSA
Lamp
ON for
three (3)
seconds*
Lamp
OFF*
Flashes
slowly
Comments
If any of the described lamp behaviors
*
do not occur — or if the lamp remains
on during operation — have the vehicle
serviced by a qualied mechanic as
soon as possible to restore full system
functionality.
Some vehicle manufacturers may
**
illuminate the trailer ABS indicator lamp
at power‑up regardless of whether a
PLC signal is detected from the trailer or
not. Consult the vehicle manufacturer’s
documentation for more details.
• The HSA lamp is illuminated only at power‑
up, or if an HSA DTC is present
0.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 (sec.)1.5
Power
Application
ATC/ESP System
Status Indicator
at Start-Up
ATC/ESP
enabled
No ESP
or ATC
ABS System
Status Indicators
at Start-Up
Powered Vehicle ABS
Indicator Lamp
Trailer ABS
Indicator Lamp
(PLC Detected)**
Trailer ABS
Indicator Lamp**
(PLC Not Detected)
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
FIGURE 10 - BENDIX® ESP® EC‑80™ CONTROLLER INDICATOR LAMP BEHAVIOR
8
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
0.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 (sec.)1.5
Power
Application
Page 9
ABS Indicator Lamp Operation (Bulb Check)
The Bendix® ESP® EC‑80™ Controller will illuminate the
ABS Indicator Lamp for approximately three seconds when
ignition power is applied, after which the lamp will extinguish
if no Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are detected.
The Controller will illuminate the ABS Indicator Lamp
whenever full ABS operation is not available due to a DTC.
In most cases, partial ABS is still available.
ATC/ESP Status/Indicator Lamp Operation
The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller will illuminate the A TC/
ESP lamp for approximately 2.5 seconds when i gnition
power is applied, after which t he lamp will extinguish if
no DTCs are detected. The Controller will continuously
illuminate the AT C/ESP Indicator Lamp whenever ESP or
ATC is disabled due to a DTC.
During an ESP or ATC intervention, the lamp will ash
rapidly (2.5 times per second). When the C ontroller is
placed in the ATC Mud/Snow (off‑ road) mode, the lamp
will ash slowly at a rate of once every 2.5 seconds.
Trailer ABS Indicator Lamp Operation
The Controller will control the Trailer ABS Indicator Lamp
when a PLC signal (SAE J2497) from a trailer ABS ECU
is detected.
Hill Start Assist (HSA) Indicator Lamp Operation
Vehicles with HSA enabled, will illuminate the HSA
Indicator Lamp when ignition power is applied. The lamp
will extinguish if there are no issues with the HSA system.
This test is performed only when the vehicle is stationary
(if the vehicle moves, the Chuff Test will not be performed).
The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller will per form a PMV
Chuff Test on all installed modulators in the following order:
• Steer Axle Right PMV;
• Steer Axle Left PMV;
• Drive Axle Right PMV;
• Drive Axle Left PMV;
• Additional Axle Right PMV;
• Additional Axle Left PMV; then
• Drive Axle TCV
The pattern will then repeat itself. See Figure 11.
Vehicles with a Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller — following
the completion of the second round of PMV & TCV Chuff
Tests — the Controller (if congured to do so) will perform
a test to cross‑ check the trailer PMV o peration with the
vehicle stop lamps. If the trailer PMV c irc uit i s mis‑wired
(including the steer axle TCV), the PMV will exhaust a large
amount of air, or none at all.
NOTICE: If there are any active DTCs, the stop lamp
cross‑check portion of the Chuff Test will not be carried out
until all DTCs are fully diagnosed and the corresp onding
repairs are succes sfully conduc ted. The ESP/ATC dash
indicator will also illuminate when there are ac tive ABS,
ATC or ESP DTCs.
The ECU will not perform the PMV Chuff T est when wheel
speed sensors show that the vehicle is in motion.
Pressure Modulator Valve (PMV) and Traction
Control Valve (TCV) Chuff Test
Right Steer
Driver
Left Steer
FIGURE 11 - VEHICLE ORIENTATION (TYPICAL)
After the performance of the conguration test, the Bendix
ESP EC‑80 Controller will perform a Bendix‑patented PMV
and TCV Chuff Test. The Chuff Te st is an elect ric al and
pneumatic PMV test that can assist maintenance personnel
in verifying proper PMV wiring and installation.
When ignition power is applied, eac h m odulator so le noi d
is briey energized. If the air system is fully charged and
the servic e brake pedal is depres sed during i gnition, the
modulator creates a single, sharp audible “chuf f” of air
pressure. The modulators are energized in a certain
pattern: right front; left front; right rear; then left rear.
Right Drive
Left Drive
Right
Additional
Left
Additional
ABS OPERATION
Bendix® ABS uses wheel speed s ensors, ABS pres sure
modulator valves, and an ECU to control either four or six
wheels of a vehicle. The Bendix ESP EC‑ 80 Controlle r
monitors individual wheel tur ning motion during brak ing,
and adjusts or modulates the brake pressure at the wheel
end. When excessive wheel slip — or wheel lock‑up — is
detected, the Bendix ESP EC‑ 80 Controller will act ivate
the pressure modulator valves to automatically reduce
the brake pressure at one or more of the wheel ends.
By these actions, the A BS system helps to maintain the
vehicle's lateral stability and steerability during heavy brake
applications and during braking on slippery surfaces.
Steer Axle Control
Although both wheels of the steer axle have their own
wheel speed sensor and pres sure modulator valve, the
Bendix ESP EC‑ 80 Controller blends the applied braking
force between the two steering axle brakes. This Bendix
patented brake application control, called Modified
Individual Regulation (MIR), is designed to help reduce
steering wheel pull during an ABS event on road surfaces
with poor tracti on, or areas of poor tracti on (e.g. asphalt
road surfaces with patches of ice).
9
Page 10

Single Drive Axle Control (4x2 Vehicle)
For vehicles with a single rear drive axle (4x2) , the brakes
are operated independently by the Bendix® ESP® EC‑80™
Controller, based on the individual wheel behavior.
Dual Drive Axle Control (4S/4M Conguration)
For vehicles with dual drive axles (6x4) using a 4S/4M
conguration, one ABS modulator controls both of the
right‑side rear whe els; the other modulator c ontrols both
of the left‑side r ear wheels. Both wheels on each side
receive equal brake pressure during an A BS stop. The
rear wheel speed sensors must b e installed on the axle
with the lightest load.
Dual Rear Axle Control (6S/6M Conguration)
For vehicles with dual rear axles (6x4, 6x2) using a 6S/6M
conguration, the rear wheels are controlled independently.
Therefore, brake application pressure at each wheel is
adjusted according to the individual wheel behavior on
the road surface.
6x2 Vehicles with 6S/5M Conguration
6x2 vehicles can utilize a 6S/5M conguration, with the
additional axle (a non‑driven rear axle) having two sensors,
but only one Pressure Modulator Valve (PMV). In this case,
the PMV controls both wheels on the additional axle. The
additional axle wheels would receive equal brake pressure,
based on the wheel that is currently experiencing the most
wheel slip.
Normal Braking
During normal braking, brake pressure is delivered through
the ABS PMV and into the brake chamber. If the ECU
does not detect excessive wheel slip, it will not activate
ABS control, and normal vehicle service braking is applied.
Retarder Brake System Control
On surfac es with low trac tion, applic ation of the retar der
can lead to high levels of wheel slip at the drive axle wheels,
which can adversely affect vehicle stability.
T o prevent this, the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller switches
off the retarder as soon as a lock‑up is detected at one (or
more) of the drive axle wheels.
When the ECU is placed in the A BS off‑road mode (on
vehicles equipped with this optional feature), it will switch
off the retarder only w hen ABS is active on a steer a xle
wheel and a drive axle wheel.
Optional ABS Off-Road Mode
On some road conditi ons, particularly when the drivin g
surface is s oft, the stopping distance with conventional
ABS may be longer than witho ut ABS. This can occur
when a locked wheel on soft ground or loose gravel plows
up the road surface in front of the tire, changing the rolling
friction value. Alt hough vehicle stopping dist ance with a
locked wheel (in the absence of ABS) may be shorter than
corresponding stopping distanc e with conventional ABS
control, vehicle steerability and stability would be reduced.
Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controllers have an optional dash
switch that initiates a modied ABS control mode (known
as "off‑road A BS") that more effectively ac commodates
these soft road c onditions to shorten stopping distanc e
while maintaining optimal vehicle steerability and stability.
Note: Off‑road mode is not available if the vehicle is
equipped with Hill Start / Hill Start Assist (HS or HSA).
The ABS off-road mode should not be used on
normal, paved road surfaces because vehicle
stability and steerability may be reduced. The ABS
Indicator Lamp will ash slowly to indicate to the
driver that the ABS off-road mode is engaged.
When ABS off-road mode is engaged, stability
functions are disabled at speeds below approximately
25 mph/40 kph. The A TC/ESP dash lamp will illuminate
to indicat e to the driver that t he stability syst em is
disabled.
The vehicle manufacturer should provide the optional ABS
off‑road function only for vehicles that operate on unpaved
surfaces — or that are used in off‑road applications — and
is responsible for ensuring that vehicles equipped with the
ABS off‑road function meet all FMVSS‑121 requirements
and have adequate operator indicators and instructions.
The vehicle operator activates the off‑road function with a
switch on the dash panel. A ashing ABS Indicator Lamp
indicates to the driver that the A BS off‑road function is
engaged. To exit the ABS of f‑road mode, depress and
release the switch. A new ignition cycle w ill also cause
the ECU to exit the ABS off‑road mode.
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Vehicles
AWD vehicles with an engaged interaxle differential (steer
axle to rear axle) / AWD transfer case, may have negative
effects on ABS performance. Optimum ABS performance
is achieved when the lockable differentials are disengaged,
allowing individual wheel control.
Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controllers can be programmed
specically for this conguration to control the differential
lock/unlock solenoid in the AWD transfer case. When
programmed to do so, the ECU will disengage the locked
interaxle/AWD transfer case during an ABS event and
reengage it once the ABS event has ended.
10
Page 11

ATC OPERATION
ATC Functional Overview
Just as ABS improves vehicle stabilit y during braking,
Automatic T raction Control (A TC ) improves vehicle stability
and traction during vehicle acceleration. The Bendix®
ESP® EC‑ 80™ Controller's ATC function uses the same
wheel speed information and modulator control as the
ABS function. The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller detects
excessive drive wheel speed; compares the speed to the
front, non‑driven wheels; and reacts to help bring the wheel
spin under control. The Controller can be congured to use
engine torque limiting and/or differential braking to control
wheel spin. For optimal AT C performance, both methods
are recommended.
ATC/ESP Lamp Output/ATC Mud/Snow Switch
Input
Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controllers operate the AT C/ESP dash
lamp as follows.
The ATC/ESP dash lamp illuminates:
1. During power up (e.g. when the vehicle is started) for
approximately 2.5 seconds and turns off after the self
test is completed, providing no Diagnostic Trouble
Codes (DTCs) are present.
2. When ESP or ATC is disabled for any reason.
3. During an ESP or ATC event (the lamp will ash rapidly
at a rate of 2.5 times per second).
4. When the ECU is placed in the ATC off‑road mode
(the lamp will ash steadily at a rate of once every 2.5
seconds). This noties the vehicle operator that the
ATC Mud/Snow mode is active.
5. When the ECU is placed in the ABS off‑road mode.
When in this mode, ESP will be disabled below 25 mph
and its inactive status will be indicated by a steadily
illuminated A TC/ESP lamp.
Differential Braking
Differential br aking within ATC is automatically activated
when drive wheel(s) on one side of the vehicle are spinning
excessively. This typically occurs on road sur faces
with patches of ice. The tract ion system will then lightly
apply the brake to the drive wheel(s) that are spinning
excessively. The vehicle differential will then drive the
wheels on the other side of the vehicle.
Differential braking (as part of A TC functionality) is available
at vehicle speeds up to 25 mph/40 kph.
Disabling ATC Differential Braking
ATC differential braking is disabled under the following
conditions:
1. During power up (e.g. when the vehicle is started), until
the ECU detects a service brake application.
2. If the ECU receives a J1939 message indicating that
the vehicle is parked.
3. When the dynamometer test mode is active. The
Dynamometer test mode is entered using the diagnostic
Blink Code Switch or by using a diagnostic tool (such
as Bendix® ACom® Diagnostics).
4. In response to a serial communications request from
a diagnostic tool.
5. If ATC Differential Braking function is activated for a
long time period to avoid overheating of the brakes. It
would take approximately three (3) continuous minutes
of activation for the time‑out to occur. Once timed‑out,
approximately two (2) minutes of "cool off" time would
be required before A TC Dif ferential Braking can be used
again.
6. When certain DTC conditions are detected.
Traction Control with Engine Torque Limiting
The Bendix ESP EC‑ 80 Controller uses Engine Torque
Limiting to control drive ‑ axl e wheel slip. This is c ommu ‑
nicated to the engine contro l module (using J19 39), and
is available at all vehicle speeds.
Bendix® SMART ATC™ System
The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller has an additional feature
known as the Bendix® SMART ATC™ system. This system
monitors the accelerator pedal position (using J1939)
to help provide optimum traction and vehicle stability.
By determining the driver’s throttle input and adapting the
target slip of the drive wheels to the dr iving s ituation, th e
Bendix SMART ATC system allows higher wheel slip when
the accelerator pedal is applied above a preset level.
The wheel slip allowed by the Bendix SMART AT C system
is decreased when dri ving through a cur ve for improved
stability.
Disabling ATC Engine Control and the Bendix
SMART A TC System
A TC Engine Control and the Bendix SMART AT C system
will be disabled under the following conditions:
1. In response to a serial communications request from
an off‑board tool;
2. At power‑up until the ECU detects a service brake
application;
3. If the ECU receives a J1939 message indicating that
the vehicle is parked;
4. If the dynamometer test mode is active. This may be
accomplished via an off‑board tool or the diagnostic
Blink Code Switch; or
5. When certain DTC conditions are detected.
11
Page 12
Optional ATC Mud/Snow (Off-Road) Mode
In some road conditions, the vehicle operator may desire
additional drive wheel slip when ATC is active. The Bendix®
ESP® EC‑8 0™ Controller has an optional c o ntro l m od e to
permit this desired performance.
The vehicle operator can activate the Mud/Snow function
with a switch on the dash panel. Alter nately, a J1939
message may be used to place the vehicl e in this mo de.
The ATC/ESP Indicator Lamp will ash steadily at a rate
of once every 2.5 seconds to conrm that the ATC mud/
snow mode is engaged.
T o exit the A TC Mud/Snow mode, depress and release the
ATC Mud/Snow switch.
BENDIX ESP EC-80 ABS WITH STABILITY
CONTROL
Overview
The Bendix ESP system with the EC‑80 Controller reduces
the risk of rollovers, jackkning and other loss‑of‑control
events. Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controllers include Roll
Stability Program (RSP®) and Y aw Control (YC) functions.
During operation, the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller
constantly compares performance models to the vehicle’s
Drag Torque Control Functional Overview
Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controllers have a feature referred to
as drag torque control which reduces wheel slip on a driven
axle due to driveline iner t ia. This c on dition i s address ed
by increasing the engine torque to overcome the inertia.
Drag torque control increases vehicle stabilit y on low‑
traction road sur faces during down‑shifting or retarder
braking.
actual movement, using wheel speed sensor s; a lateral
acceleration sensor, a yaw rate sensor, and a steering
angle sensor. If the vehicle shows a tendency to leave an
appropriate travel path, or if criti cal threshold values are
approached, the system will intervene to assist the driver.
A Real World Example
Of How The RSP
System Operates:
Excessive speed for road
conditions creates forces
that exceed the threshold
at which a vehicle is likely
to rollover on a higher‑
friction surface.
The system automatically reduces
engine torque and applies the
service brakes (based on the
projected rollover risk) to reduce
the vehicle speed, thereby
reducing the tendency to roll over.
A Real World Example Of How Yaw Control
Operates:
Excessive speed exceeds the threshold, creating a
situation where a vehicle is likely to spin and jackknife.
®
The Bendix
and selectively applies brakes to reduce the tendency
to jackknife.
Y aw Control system reduces engine throttle
FIGURE 12 - RSP EXAMPLE
12
FIGURE 13 - YAW CONTROL EXAMPLE
Page 13

Bendix® Roll Stability Program (RSP®)
Bendix RSP — an element of the overall Bendix® ESP®
system with the EC‑8 0™ Controller — addresses r ollover
conditions. In the c ase of a potential roll event, the ECU
will override the throttle and quickly apply brake pressure
at all wheel ends to slow the vehicle co mbination. The
level of braking application during an RS P event will be
proportional to roll risk. See Figure 12.
Yaw Stability
Y aw stability counteracts the tendency of a vehicle to spin
about its vertic al axis. Dur ing operation — if t he frict ion
between the road surface and the tires is not sufcient
to oppose lateral (side) forces — one or more of the tires
can slide, causing the truck/tractor to spin. These events
are referred to as either an "under‑steer" situation (where
there is a lack of vehicle response to steering input due to
tire slide on the steer axle), or an "over‑steer" (where the
tractor's rear end slides out due to tire slide on the rear axle)
situation. Generally, shorter wheelbase vehicles (tractors,
for instance) have less natural yaw stability, while longer
wheelbase vehicles (straight trucks, for instance) have
greater natural yaw stability. Factors that inuence yaw
stability are: wheelbase, suspension, steering g eometry,
weight distribution front to rear, and vehicle track width.
Yaw Control
Yaw control responds to a wide range of low‑ to high‑
friction sur face scenarios including rollover, jackknife
and loss‑of‑control. It is the recommended system for all
power vehicles and especially cr itical for trac tors pulling
trailers. In the case of vehic le slide (over‑steer or under‑
steer situations), the system will reduce the throttle and
then brake one or more of the “four corners” of the vehicle
(in addition to potentially applying the trailer brakes) , thus
applying a counter‑force to better align the vehicle with an
appropriate path of travel.
For example, in an over ‑steer situation, the system applies
the “outside” front brake; while in an under‑steer condition,
the “inside” rear brake is applied. (See Figure 13)
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
ABOUT THE BENDIX® ESP® SYSTEM
The Bendix ESP EC-80 Controller may reduce
the vehicle speed automatically.
The Bendix® ESP® system can make the
vehicle decelerate automatically and can
slow the vehicle w ith or wit h o ut the operator
applying the brake — and even when the
throttle is being applied.
T o minimize une xpected deceleration and reduce the
risk of a collision, the operator must:
• Avoid aggressive driving maneuvers, such as sharp
turns or abrupt lane changes at high speeds, which
might trigger the stability system; and
• Always operate the vehicle safely, drive defensively ,
anticipate obstacles and pay attention to road,
weather and trafc conditions. Bendix ABS, ATC
and ESP systems are no substitute for prudent,
careful driving.
Towing Doubles Or Triples May Reduce The
Effectiveness Of Stability Systems
The Bendix ESP syst em wi t h th e EC-80 Con t roll er i s
designed and optimized for trucks and for tractors that
tow single trailers. If a tractor equipped with Bendix
ESP is used to powe r multiple trail er combination s
(known as “doubl es” or “trip les”) the eff ectiveness
of the Bendi x ESP system may be greatly r educed.
Extremely careful driving is always required when
towing doubles or triples. Excessive speed and
aggres s i v e ma n e uv e r s — such as sha r p tu r ns , su d den
steering inputs, or abrupt lane changes — should be
avoided.
Limitations Of Stability Systems
The effectiveness of the Bendix ESP system with the
EC‑80 Controller may be greatly reduced if:
• The load shifts due to improper retention, accident
damage, or the inherently mobile nature of some loads
(for example, hanging meat, live animals or partially
laden tankers),
• The vehicle has an unusually high — or off‑set — center
of gravity (CG),
• One side of the vehicle drops off the pavement at an
angle that is too large to be counteracted by a reduction
in speed,
• The vehicle is used to haul double or triple trailer
combinations,
• If very rapid steering changes are attempted at high
speeds,
• There are mechanical problems with suspension
leveling of the tractor or trailer resulting in uneven loads,
• The vehicle is maneuvering on a high banked road
creating either additional side forces due to the weight
(mass) of the vehicle, or a deviation between expected
& actual yaw rates,
• Gusty winds are strong enough to cause signicant
side forces on the vehicle and any towed vehicles.
13
Page 14

To Maximize The Effectiveness Of The Bendix®
®
System with the EC-80™ Controller:
ESP
• Loads must be properly secured at all times.
• Drivers need to exercise extreme caution at all times,
plus avoid sharp turns, sudden steering adjustments
or abrupt lane changes at high speeds, particularly if:
› the vehicle hauls loads that could shift;
› the vehicle or load has a high or off‑set center of
gravity (CG) when loaded; or
› the vehicle tows doubles or triples.
Truck Chassis Modications
If the vehicle’s chassis components are altered (for
example, a wheel base extension or reduction; tag
axle addition or rem oval; a major body change suc h as
conversion of a tractor into a truck; or an axle, suspension,
or steering system component modication) the Bendix
®
ESP
system must be disabled. Have a qualied mechanic
®
replace the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Co ntr o lle r w it h a B e ndi x®
®
ESP
ATC EC‑80™ Controller and secure the X4 connector
(which will no longer be used). The ATC/ESP indicator
lamp would continue to function as an A TC indicator lamp,
and should be designated as ATC only.
If a modied vehicle does not have the Bendix
®
ESP® system disabled, serious vehicle braking
and performance issues could result, including
unnecess ary ESP syst em inter vention s. This can
lead to a loss-of-control of the vehicle.
In addition, remove all cab signage (e.g. visor
labels, etc.) that were used to show that the Bendix
ESP system was installed. Make any necessar y
notations in the vehicle manual(s), so that drivers do
not misunderstand which ABS options are installed
on the vehicle.
Sensor Location Modications
The location and orientation of the Steering Angle Sensor
and Y aw Rate Sensor must not be altered. When servicing,
an identical component must be used in the same
orientation (using OEM brackets & torque requirements).
During installation follow the OEM leveling guidelines.
Steering Angle Sensor Re-Calibration
Whenever maintenance or repair work is performed to the
steering mechanism, linkage, steering gear, adjustment of
the wheel track, or if the steering angle sensor is replaced,
a recalibration of the Steering Angle Sensor must be
performed.
If the Steering Angle Sensor is not recalibrated, the
yaw control system ma y not function properly, which
can result in incidents leading to loss of vehicle
control. See page 19 of this document for more
details on this procedure.
DYNAMOMETER TEST MODE
Bendix ATC and ESP systems must be disabled prior
to conducting any dynamometer testing. When the
Dynamometer Test Mode is engaged, the Bendix ATC
EC‑80 Controller's brake control and engine control —
along with drag torque contr ol and Bendix ESP system
functions — are disabled. This test mode is used to avoid
torque reduction or torque increase and brake control
activation when the vehicle is operated on a dynamometer
for testing purposes.
The Dynamometer Test Mode may be activated by pressing
and releasing the diagnostic Blink Code Switch ve times
or by using a hand‑held or PC‑based diagnostic tool.
During Dynamometer Test Mode the AT C lamp remains ON.
Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controllers will remain engaged in
the Dynamometer Test Mode even if power to the ECU
is removed and re‑applied. To exit the test mode, press
and release the Blink Code S witch three time s, or use a
hand‑held or PC‑based diagnostic tool.
AUTOMATIC TIRE SIZE CALIBRATION
The ECU requires a precise rolling circ umference ratio
between steer axle and dr ive axle tires in order for the
Bendix ABS, ATC, and ESP systems to perform in an
optimal manner. For this reason, a continuously monitoring
process takes place in which the precise ratio is calculated.
This calculated value is stored in the ECU memory
provided the following conditions are met:
1. Rolling‑circumference ratio is within the permissible
range;
2. Vehicle speed is greater than approximately
12 mph/19 kph;
3. No acceleration or deceleration is taking place; and
4. There are no active speed sensor Diagnostic Trouble
Codes (DTCs).
The ECU is provided with a ratio value of 1.00 as a default
setting. If the automatic tire size alignment c alculates a
different value, this is used to overwrite the original gure
in the memor y. This process adapts t he ABS and ATC
function to the vehicle.
14
Page 15
Acceptable Tire Sizes
The speed calculatio n for an exciter ring with 100 teeth
is based on a default tire size of 510 revolutions per mile.
This gure is based on the actual rolling circumference of
the tires, which varies with tire size, tire wear, tire pressure,
vehicle loading, etc.
The ABS response sensitivity is reduced when the actual
rolling circumference is excessive on all wheels. For a 100
tooth exciter ring, the minimum number of tire revolutions
per mile is 376, and the maximum is 665. T he ECU will
set a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) if the number of
revolutions is out of this range.
In addition, the size of the steer axle tire s compared to
the drive axle tires als o has to be within t he A BS system
design. To avoid DTCs, the ratio of the effective rolling
circumference of the steer a xle, divided by the effective
rolling circumference of th e drive axle, must be bet ween
0.85 to 1.15.
Drive Axle/Additional Axle Wheel Speed Sensor
DTC
The Bendix ATC and E SP systems are disabled. In a four
sensor system, ABS on the affected wheel is disabled, but
ABS on all other wheels remains active.
In a six sensor system, ABS remains active by using input
from the remaining rear wheel speed sensor on the same
side.
ATC Modulator DTC
The Bendix ATC and ESP systems are disabled. ABS
remains active.
J1939 Communication DTC
The Bendix ATC and ESP systems are disabled. ABS
remains active.
ECU DTC
The Bendix ABS, ATC, and ESP systems are disabled.
The system reverts to normal braking.
The Bendix® ESP® system with t he EC- 80 Cont roller
effectiveness relies on the accuracy of vehicle speed.
If a major ch a n g e on the tire siz e s is ma d e — su c h that
the odometer setting needs to be changed to correct
for the new tires — the Bendix ESP EC-80 Controller's
setting o f tire sizes must al so be reprogramme d to
revised values.
SYSTEM IMPACT DURING ACTIVE
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCs)
ABS PARTIAL SHUTDOWN
Depending on which component the DTC is detected,
the Bendix ABS, ATC, and ESP system functions may
be fully or partially disabled. Even with the ABS indicator
lamp illuminated, the Bendix ESP EC‑ 80 Controller m ay
still provide ABS function on wheels that are not affected.
The ABS system Controller shoul d be servic ed as soon
as possible.
Steer Axle ABS Modulator DTC
ABS on the affected wheel is disabled. ABS and ATC on
all other wheels remains active. The Bendix ESP system
with the EC‑80 Controller is disabled.
Drive Axle/Additional Axle ABS Modulator DTC
ATC is disabled. ABS on the af fec ted wheel i s disabled.
ABS on all other wheels remains active. The Bendix ESP
EC‑80 system is disabled.
Steer Axle Wheel Speed Sensor DTC
The wheel with the DTC is still controlled by using input
from the remaining wheel speed sensor on the steer axle.
ABS remains active on the rear wheels. The Bendix ATC
and ESP systems are disabled.
Voltage DTC
While voltage is out of range, Bendix ABS, A TC, and E SP
systems are disabled. The system reverts to normal
braking. When the co rrect voltage level is restored, full
ABS and ATC function is available. The operating voltage
range is 9.0 to 17.0 VDC for 12 volt systems, and 20 to 33.5
volts for 24 volt systems.
Steering Angle Sensor DTC
The Bendix ESP system is disabled. Bendix ABS and ATC
systems remain active.
Yaw Rate/Lateral Acceleration Sensor DTC
The Bendix ESP system is disabled. Bendix ABS and ATC
systems remain active.
Brake Demand Pressure Sensor DTC
The Bendix ESP system is disabled. Bendix ABS and ATC
systems remain active.
Load Sensor DTC
The Bendix ESP system is disabled. Bendix ABS and ATC
systems remain active.
Steer Axle Traction Control Valve (TCV) DTC
The Bendix ESP system is disabled. Bendix ABS and ATC
systems remain active.
Trailer Pressure Modulator Valve (PMV) DTC
The Bendix ESP system is disabled. Bendix ABS and ATC
systems remain active.
15
Page 16

SYSTEM RECONFIGURATION
The Bendix® ESP® EC‑ 80™ Controller is designed to
allow the technician to change the default system settings
(chosen by the vehicle OEM) to provide additional or
customized features.
Depending on the model, the customizable features include
ABS control settings, engine module c ommunication etc.
Many of these settings can be recongured using a hand‑
held or PC‑ based sof t ware, such as t he Bendix® ACom®
Diagnostic software.
ECU RECONFIGURATION
Reconguring a Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller may be
carried out by using the B link Code S witch or by using a
hand‑held or PC‑based diagnostic tool.
Note: During the reconfiguration process — and
independently from any reconguration being carried out
by the technician — the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) will
automatically check the J1939 serial link and communicate
with other vehicle modules. In particular, if the serial link
shows that the vehicle has a retarder device present, the
ECU will congure itself to communicate with the retarder
device for improved ABS per formance. For example, if
the ECU detects the presence of a retarde r disable r elay
during a reconguration, it will congure itself to control the
relay to disable the retarding device as needed.
DATA STORAGE
Depending on the product type and version, Bendix®
brand ECUs may store data related to troubleshooting,
diagnostics, service needs, vehicle system operating
status, and vehicle operator inputs. No personally
identifying data (e.g. name, gender or age) is recorded.
Bendix will not acces s stored ECU data or share it with
others except: with the consent of the vehicl e owner; in
response to an ofcial request by law enforcement or
other governmental agency; as par t of Bendix’s defense
of litigation; or, as otherwise required by law. Data that
Bendix receives may also be used for research purposes
or made available to others for research purposes, where
a need is shown and the data is not linked to a specic
vehicle or owner.
Bendix brand antilock ECUs are not designed to store
data for purposes of acc ident rec onstruc tion and Bendi x
ACom Diagnostic Software is not intended to retrieve data
for purposes of accident reconstruction. Bendix makes no
representations as to the acc uracy of data retrieved and
interpreted from Bendix ECUs for purpose s of accident
reconstruction.
Reconguration Using the Blink Code Switch
With ignition power removed from the Bendix ESP EC‑80
Controller, depress the Blink Code Switch. After the
ignition power is activated, depress and release the switch
seven (7) times to initiate a reconguration event.
Diagnostic Tool
A reconguration event may be initiated using a hand‑held
or PC‑based diagnostic tool to communicate with the ECU
over the SAE J1939 diagnostic link.
6S/5M Conguration
A Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller will congure for 6S/5M
operation when a reconguration event is initiated, and the
ECU detects that an additional‑axle Pressure Modulating
Valve (PMV) is wired as follows:
PMV Connector ECU Connector
Hold Right Additional Axle Hold
Release Left Additional Axle Release
Common Right Additional Axle Common
16
Page 17

Troubleshooting: General
GENERAL SAFETY GUIDELINES
Read and follow the General Safety Guidelines shown on
page two (2) of this document.
REMOVAL OF THE BENDIX® ESP® EC-80™
CONTROLLER ASSEMBL Y
1. Turn vehicle ignition off.
2. Remove as much contamination as possible prior to
disconnecting electrical connections.
3. Note the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller assembly
mounting position on the vehicle.
4. Disconnect the electrical connectors from the Controller.
5. Remove and retain the mounting bolts that secure the
Controller.
The VIN of th e vehicle is stored in the Be ndix ESP
EC-80 Controller's internal memor y, and is crosschecked by the E lectronic Co ntrol Unit (ECU) using
information obtained from other vehicle Controller( s).
If the VI N stored i n the ECU doe s not match t he VI N
obtained from the other vehicle Controller(s), the ECU
will generate an ECU Internal VIN Mismatch Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC).
Accordingl y, d o not attempt to move a Bend ix ESP
EC-80 Controller from one vehicle to another.
OBTAINING A NEW BENDIX® ESP® EC-80™
CONTROLLER
Should the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller require
replacement, certain steps must be followed:
1. Record the vehicle model, VIN, year and date of
manufacture from the vehicle.
2. Record the part number of the Bendix ESP EC‑80
Controller.
3. Provide this information to your local OEM vehicle
service department to obtain a new Bendix ESP EC‑80
ECU. The OEM service department will install the same
parameter set in the new Controller that was loaded into
the original ECU at the vehicle OEM assembly facility .
INSTALLING A NEW BENDIX ESP EC-80
CONTROLLER
When replacing the Bendix ESP EC-80 Controller,
verif y with the OEM service depart ment that the unit
you are installing has the correct parameter set.
Failure to do so could re sult in a loss of f eature s or
degraded ESP performance.
For further information, contact either the vehicle
manufacturer, Bendix, or your local authorized Bendix
distributor.
1. Position and secure the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller
in the original mounting orientation using the mounting
bolts retained during removal. Use no more torque than
is necessary to rmly secure the ECU into position.
Over‑tightening the mounting hardware can cause
damage to the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller.
2. Reconnect the electrical connectors to the Bendix
EC‑80 Controller.
3. Apply power and monitor the Bendix ESP EC‑80
Controller power‑up sequence to Verify the proper
system operation.
See Troubleshooting: Wiring section beginning on page 45
for more information on wire harnesses.
The Bendix ESP system with the EC-80 Controller is
validated with specic Bendix
Always use Bendix brand replacement parts to
prevent compromising system performance.
Bendix is not a ble t o validat e th e safe an d relia ble
use of substitute or alternate components that
may be available f rom other ma nufactu rers, since
supplier s of a non-Ben dix brand ABS com ponent
may implement design changes in their component
(without the knowledge or approval of Bendix) which
could negatively af fect antilock system reliabilit y
and braking performance issues.
®
brand components.
17
Page 18
STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MAINTENANCE
Service Checks:
1. Check all wiring and connectors. Some installations
also include an intermediate connector from the
steering angle sensor to the main vehicle wire harness.
Make sure all connections are free from visible damage.
2. Examine the sensor. Make sure the sensor, its
mounting screws, and the interface between the hub
and the steering column are not damaged.
Diagnostics:
®
The Bendix
in conjunction with a Bendix® ESP® EC‑80™ Controller. No
independent diagnostics can be performed on the sensor.
See pages 38-39 for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
associated with this device.
Removal:
1. Remove steering column sheathing.
2. Depending upon manufacturer, the steering angle
sensor could be located either near the steering wheel,
necessitating the removal of the steering wheel, or
near the joint to the vehicle steering mechanism,
necessitating the disconnection of this linkage.
3. Unplug sensor cable assembly from body of sensor.
Squeeze the mounting tabs and pull gently on the
connector until it disengages.
4. Unscrew all three of the mounting screws that hold the
body of the sensor to the steering column body.
5. Slide the sensor over the column to remove. Take note
if the sensor label is facing upward or downward.
Installation:
1. Obt ain a new senso r. The sensor is not repairable in
the eld.
2. Slide the sensor over the column. The center hub of the
sensor must be aligned with the c o r re sp onding n otch
in the column. Dif ferent column manufacturers may
implement this hub alignment in dif ferent ways. The
sensor label should be facing in the same direction as
the removed sensor.
brand steering angle sensor is only operational
3. Assemble to column non‑moving plate with three self‑
locking screws.
4. Tighten screws to steering column manufacturer's
recommended torque specication.
5. Reconnect the connector. Ensure that there will be no
force applied to the sensor be cause the c onnec tor is
pulling on the sensor body.
6. If the wire harness leading to the sensor is being
replaced, ensure that it is adequately tie wrapped
so that the full motion of the steer ing column can b e
achieved without pulling apart the connectors.
7. Reinstall the column sheathing. The sensor is not
protected against dirt or water intrusion, so care
must be taken not to introduce these elements during
installation.
STEERING ANGLE SENSOR CALIBRATION
The steering angle sensor calibration can only be achieved
when the sensor is powered by the Bendix ESP EC‑ 80
Controller. No stand‑alone sensor calibration can be
carried out. The calibration procedure is performed
using Bendix® ACom® Diagnostic software V6.7. 2.5 or
higher. See “Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes:
Steering Angle Sensor (Bendix® SAS-60™)” for the
calibration procedure using this tool. The sensor must be
recalibrated using ACom Diagnostic Software after any of
these situations:
• Replacement of the steering angle sensor;
• Any opening of the connector hub from the steering angle
sensor to the column;
• Any maintenance or repair work on the steering linkage,
steering gear or other related mechanism;
• Adjustment of the wheel alignment or wheel track; or
• Af ter an accident that may have led to damage of the
steering angle sensor or assembly
If the steering angle sensor is not properly
recalibrated as needed, the yaw control system may
not funct io n p roperly, which can re sul t in a l o ss o f
vehicle control.
18
Page 19

Y AW RA TE/LATERAL ACCELERA TION
SENSOR MAINTENANCE
Different generations of yaw rate/lateral acceleration
sensors are not compatible. Only replace these
sensors with exactly the same device.
Service Checks:
1. Check all wiring and connectors. Make sure all
connections are free from visible damage.
2. Examine the sensor. Make sure the sensor, its
mounting bolts, and the mounting bracket are not
damaged.
3. Check t he vent hole in under body of sens or housing.
The vent hole should remain free from paint and debris
at all times.
Diagnostics:
The yaw rate sensor is only operational in conjunction with
a Bendix® ABS, ATC or ESP® system with the EC‑80
Controller. No independent d iagnostics can be performed
on the sensor. See pages 40-41 for Diagnostic Trouble
Codes associated with this device.
Removal:
1. Unplug the sensor cable assembly from body of sensor.
The connector must be t wisted and pulled gently to
release.
2. In some mounting congurations, the sensor can be
removed independently from its mounting bracket.
Otherwise, remove entire assembly, then remove
sensor from bracket.
3. Take note of the direction in which th e connector is
pointed.
Installation:
1. Obt ain a new senso r. The sensor is not repairable in
the eld.
The location of the Yaw Rate Sensor on the vehicle,
the means o f fa ste ning t he un it to t he vehi cle , and
the sensor's orien t at io n, M UST NOT BE A LTERED.
When ser vicing, an ident ical component mu st be
used in the sa me or ien tat ion (using OE M brac kets
& torque requirements). During installation,
follow the OE M leveling guidelin es. If any of the se
requirements are not followed, the Bendix ESP
system may not function properly, which can result
in incidents leading to loss of vehicle control.
™
2. Assembly yaw rate sensor housing to mounting bracket.
The bracket must be the same design as used on the
original vehicle conguration.
3. For Bendix® YAS‑60™ Yaw Rate Sensors, the correct
fasteners are three M8 size bolts, and the xing torque
should be 20 Nm (±2 Nm). For Bendix® Y AS‑70X™ Yaw
Rate Sensors, the correct fasteners are two M10 size
bolts (1.5 mm pitch angle), or OEM‑supplied hardware,
and the xing torque should be 46 Nm (±9 Nm). Note
that the Bendix YAS‑70X sensor has two alternate
designs, one with an aligning post — see the kit
instruction sheet for more information. In all cases,
the connector should be facing in the same direction
as the removed sensor. The unit must not be installed
upside‑down where there is a pressure‑balancing hole.
4. The sensor should be as level as possible and parallel
to the road surface when installed on the vehicle.
5. Reconnect the connector. Ensure that there will be no
force applied to the sensor be cause the c onnec tor is
pulling on the sensor body.
When removing o r installing the sensor, care must
be used to prevent damage. Do not strike or pr y
the sensor. Do not use an imp act tool to in stall th e
mounting hardware.
Sensor Location Modications
The location and orientation of the Yaw Rate Sensor must
not be altered. When servi cing, an identical c omponent
must be used in the same orientation (using OEM brackets
& torque requirements). During installation follow the OEM
leveling guidelines.
Yaw Rate Sensor Calibration:
The yaw rate sensor calibration can only be achieved via
the Bendix ESP system with the EC‑ 80 Controller. The
sensor must be recalibrated after any of these situations:
• Replacement of the sensor
• Af ter an accident that may have led to damage of the
yaw rate sensor
The calibration procedure is performed using Bendix
ACom® Diagnostic Software V6.7.2.5 or higher.
See “Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Y aw Rate
Sensor” for the calibration procedure.
®
19
Page 20

BRAKE DEMAND SENSOR CALIBRATION
Calibration must be performed under the following conditions:
• After servicing any pressure sensor related Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs)
• Replacement of any sensor
The calibration procedure is performed using Bendix®
ACom® Diagnostic Software V6.7.2.5 (or higher).
See “Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Brake
Demand Sensor/Load Sensor” for the calibration procedure.
PRESSURE SENSOR INSTALLATION
REQUIREMENTS
Service Checks:
1. Check all wiring and connectors. Make sure all
connections are free from visible damage.
2. Examine the sensor. Make sure the sensor and its
interface to the pressure location are not damaged.
Diagnostics:
See the test diagram supplied by the Bendix ACom
Diagnostic Software. The pressure sensor can be
independently diagnosed when supplied with a ve volt
voltage supply to the B location and ground to the A
location shown in the test diagram. Signal output on
the C location shoul d read approximately 0.5V if t here is
no pressure applied. The signal outp ut should increase
proport ionately as pres sure is applie d, up to a maximum
of 4.5V at 150 psi.
Removal:
1. Unp lug sensor cable assembly f rom body of sensor.
Pull gently on the mounting tab and co nnector until it
disengages.
2. Remove sensor from its pressure mounting using
approved air brake push in tting tools.
Installation:
1. Obt ain a new senso r. The sensor is not repairable in
the eld.
2. Insert sensor into pressure tting using approved tools.
3. Reconnect the connector. Ensure that there will be no
force applied to the sensor be cause the c onnec tor is
pulling on the sensor body.
4. If the wire harness leading to the sensor is being
replaced, ensure that it is adequately tie wrapped.
20
Pressure Sensor Calibration:
There is no need for pressure se nsor calibr ation as long
as the part replaced is identical to the part removed and a
component approved for use with the Bendix® ESP® system
with EC‑80™ Controllers. However, replacement of brake
demand sensors or clearing of demand pressure sensor
related DTCs require the following:
1. Use Bendix ACom Diagnostic Sof tware V6.7.2.5 (or
higher) to clear the active pressure sensor DTC.
2. Carrying out the demand pressure sensor initialization
procedure which involves applying ser vice brakes of
90 psi or greater for three (3) seconds (while stationary).
Once this procedure is carried out successfully, if there are
no other active DTCs, the A T C/ESP indicator lamp will no
longer be illuminated.
Page 21

Troubleshooting: Blink Codes and Diagnostic Modes
ELECTRONIC CONTROL UNIT (ECU)
DIAGNOSTICS
The Bendix® ESP® EC‑80™ Controller contains self‑testing
diagnostic circuitry that continuously checks for the normal
operation of internal components and circuitry, as well as
external ABS components and wiring.
Active Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
When an erroneous system condition is detected, the
Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller:
1. Illuminates the appropriate indicator lamp(s) and
disengages part or all of the Bendix ABS, ATC and
ESP system functions. (See ABS Partial Shutdown,
on page 15.);
2. Places the appropriate DTC information in the Electronic
Control Unit (ECU) memory; and
3. Communicates the appropriate DTC information over
the serial communications diagnostic link as required.
Hand‑held or PC‑based diagnostic tools attach to the
vehicle diagnostic connector, typically located on or
under the dash (see Figure 14).
BLINK CODES
Blink codes allow a technician to troubleshoot ABS
problems without using a hand‑held or PC‑based
diagnostic tool. Instead, information about the ABS system
is communicated by the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller using
the ABS indicator lamp to display sequences of blinks.
Note: The Bendix ESP EC-80 Controller will not enter the
diagnostic blink co de mode if the wheel speed sensors
show that the vehicle is in motion. If the ECU is in the
diagnostic blink code mode and then detects vehicle
motion, it will exit the blink code mode.
In addition, by operating the Blink Code Switch as
described below, one of several diagnostic modes can be
entered. See Diagnostic Modes below.
Blink Code Switch Activation
When activating the Blink Code Switch:
1. Wait at least two seconds after “ignition on.” (Except
when entering Reconguration Mode ‑ see System
Reconguration section on page 16.)
2. For the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller to recognize that
the switch is activated “on,” the technician must press
for at least 0.1 seconds, but less than ve (5) seconds.
(If the switch is held for more than ve (5) seconds, the
ECU will register a malfunctioning switch.)
3. Pauses between pressing the switch when a sequence
is required, (e.g. when changing mode) must not be
longer than two (2) seconds.
4. After a pause of three‑and‑a‑half (3.5) seconds, the
ECU will begin responding with output information
blinks. See Figure 15 for an example.
FIGURE 14 - TYPICAL VEHICLE DIAGNOSTIC
CONNECTOR LOCATIONS (J1939)
FIGURE 15 - EXAMPLE OF A BLINK CODE MESSAGE
21
Page 22

Blink Code Timing
The Bendix® ESP® EC‑80™ Controller responds with
a sequence of blink codes. The overall blink code
response from the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is called
a “message.” Each message includes, depending on the
mode selected by the technici an, a sequence of one or
more groups of blinks. Simply record the number of blinks
for each sequence and then use the troubleshooting index
on page 26 for active or inactive Diagnostic T rouble Codes
(DTCs) and you will be directed to the page that provides
troubleshooting information.
NOTE:
1. Sequences of blinks illuminate the ABS indicator lamp
for half a second, with half‑second pauses between
them.
2. Pauses between blink code digits are one‑and‑a‑half
(1.5) seconds.
3. Pauses between blink code messages are two‑and‑a‑
half (2.5) seconds.
4. The lamp remains on for ve (5) seconds at the end of
messages.
Once the ABS indicator lamp begins displaying a sequence
of codes, it continues until all blink c ode m essag es have
been displayed and then returns to the normal o perating
mode. During this time, the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller
will ignore any additional Blink Code Switch activation.
All DTCs, with the exception of voltage and J1939 DTCs,
will remain in an active state for the remainder of the
power cycle.
Voltage DTCs will clear automatically when the voltage
returns within the required limits. All Bendix ABS functions
will be re‑engaged.
J1 939 DTCs will clear automatically when communications
are re‑established.
DIAGNOSTIC MODES
In order to communicate with the Bendix ESP EC‑80
Controller, there are several modes that the technician can
select to allow information to b e retrieved, or other ECU
functions to be accessed.
Diagnostic Modes
To enter the various diagnostic modes:
No. of
Times to
Press the
Blink Code
Switch
1 Active Diagnostic T rouble Code (DT C) Retriev al
2 Inactive DTC Retrieval
3 Clear Active DTCs
4 System Conguration Check
5 Dynamometer Test
7* Recongure ECU
* To enter the Reconguration Mode, the switch must be held
in before the application of ignition power. Once the power is
supplied, the switch is released and then pressed se ven times.
FIGURE 16 - DIAGNOSTIC MODES
Active Diagnostic Trouble Code Mode
For troubleshooting, typically the Active and Inactive
DTC Retrieval Modes are used. The technician presses
the Blink Code Switch o nce and the A BS indicator lamp
ashes a rst group of two codes, and if there are more
DTCs recorded, this is followed by a second set of codes,
etc. (See page 26 for a director y of these codes.) All
active DTCs may also be retrieved using a hand‑held or
PC‑based diagnostic tool, such as the Bendix® ACom®
Diagnostic Software.
To clear active DTCs (as problems are xed), simply
clear (or “self‑heal”) by removing and re‑applying ignition
power. The only exception is for wheel speed sensor
DTCs, which clear when power is removed, re‑applied, and
the ECU detects valid wheel speed from all wh eel spe ed
sensors. Alternately, codes may be cleared by pressing the
diagnostic Blink Code Switch three (3) times (to en t er the
Clear Active Diagnostic Trouble Code Mode) or by using
a hand‑held or PC ‑based diagno stic tool. Hand‑ held or
PC‑based diagn ost ic too ls are ab le to c lear w he el spe ed
sensor DTCs without the vehicle being driven.
System Mode Entered
22
Page 23
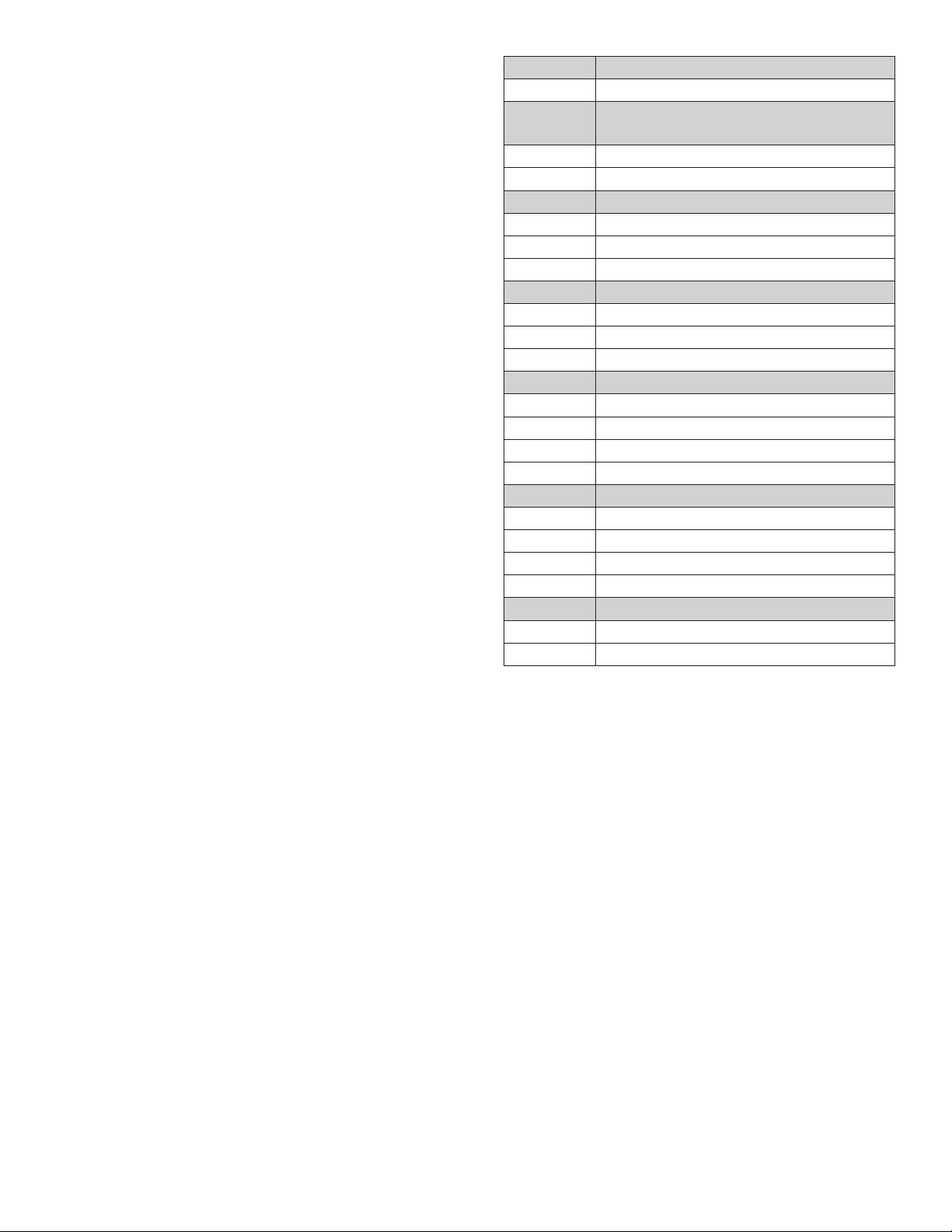
Inactive Diagnostic Trouble Code Mode
The Bendix® ESP® EC‑80™ Controller stores past
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and c omments (such
as conguration changes) in its memory. This record is
commonly referred to as “event history.” When an active
DTC is cleared, the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) stores it
in the event history memory as an inactive DTC.
Using blink codes, the techni cian may review all inactive
DTCs stored on the ECU. The ABS indicator lamp
will display inactive diagnostic blink codes when the
diagnostic Blink Code Switc h is depres sed and release d
two times. See page 26 for the index showing DTCs and
the troubleshooting guide page to read.
Inactive DTCs, and event history, may be retrieved and
cleared by using a hand‑held or PC‑based diagnostic tool,
such as the Bendix® ACom® Diagnostic Software.
Clearing Active DTCs
The ECU will clear active DTCs when the diagnostic Blink
Code Switch is depressed and released three (3) times.
System Conguration Check Mode
The ABS indicator lamp will display system conguration
information when the diagnostic Blink Code Switch is
depressed and released four t imes. The lamp will blink
out conguration information codes using the following
patterns. (See Figure 17).
In this mode the ECU tells the technician — by means of a
series of seven (7) blink codes — the type of ABS system
that the ECU has been set up to expect. For example, if
the fourth blink code is the number two (2) , the technician
knows that a 6S/4M sensor/modulator conguration has
been set.
Dynamometer Test Mode
The Dynamometer Test Mode is used to disable Bendix®
ESP® & ATC system functions when needed (e.g. when
performing any vehicle maintenance where the wheels are
lifted of f the ground an d moving, including dy namometer
testing). Note: For Bendix ESP and ABS EC‑80
Controller s, this mode will remain engage d even if
power to the ECU is r emoved and r e‑ap pli ed . To exit
the Dynamometer Test Mode, press and release the Blink
Code Switch three (3) times, or use a hand‑ held or PC‑
based diagnostic tool.
1st Number System Power
1 12 Volts
2nd
Number
4 4 Sensors
6 6 Sensors
3rd Number Pressure Modulator Valves
4 4 Modulators
5 5 Modulators
6 6 Modulators
4th Number ABS Conguration
1 4S/4M or 6S/6M
2 6S/4M
3 6S/5M
5th Number Traction Control Conguration
2 No ATC
3 ATC Engine Control Only
4 ATC Brake Control Only
5 Full ATC (Engine Control & Brake Control)
6th Number Retarder Conguration
1 No Retarder
2 J1939 Retarder
3 Retarder Relay
4 J1939 Retarder, Retarder Relay
7th Number Stability Conguration
1 No Stability Program
2 Electronic Stability Program (ESP)
FIGURE 17 - SYSTEM CONFIGURATION CHECK
Wheel Speed Sensors
Recongure ECU Mode
Controller reconfiguration is carried out by using the
Recongure ECU Mode. (See page 16.)
Note: To enter the Reconguration Mode, the Blink Code
Switch must be held in before the app lication of ignition
power. Once the power is supplied, the switch is released
and then pressed seven times.
Other Methods
Troubleshooting and DTC clearing (as well as recongura‑
tion) may also be carried out using hand‑held or PC‑based
diagnostic tools such as the Bendi x® Remote Diagnostic
Unit (RDU™), Bendix ACom Diagnostic Software, or similar
tools.
23
Page 24

Troubleshooting: Using PC-Based or
Hand-Held Diagnostic Tools
BENDIX® ACOM® DIAGNOSTIC SOFTWARE
FIGURE 18 - BENDIX® ACOM® DIAGNOSTICS
Bendix® ACom® Diagnostic Software is a PC‑based
program and is designed to meet RP‑1210 industry
standards developed by the Truck Maintenance C ouncil
(TMC). This software provides the technician with access
to all the available Bendix® EC‑ 80™ ESP® Controller's
diagnostic information and configuration capability,
including:
• ECU information;
• Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and repair
information;
• Conguration (ABS, ATC, and more);
• Wheel speed information;
• Perform component tests; and
• Save and print information
Note: Bendix ACom Diagno st ic Softwar e V6 .7.2.5 (or
higher) is required to calibrate the Steering Angle
Sensor, the Yaw Rate/Lateral Acceleration Sensor, the
Brake Demand Sensors and the Load Sensor.
When using ACom Diagnostic Software V6.7.2.5 (or
higher) to diagnose the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller, the
computer’s serial or parallel p ort ne eds to be connected
to the vehicle’s diagnostic connector.
BENDIX® RDU™ (REMOTE DIAGNOSTIC
UNIT)
The Bendix® RDU™ tool (Bendix part number K 101596N001)
provides the technician with a visual indication of Antilock
Braking System (ABS) component Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) information. Note: Previous versions of the
RDU tool are not compatible with the Bendix ESP EC-80
Controller. The Bendix RDU tool is specically designed
for use with Bendix® brand ABS systems and Bendix makes
no claims for its operation and/or usability with other brands
of ABS systems.
LED lights
illuminate
Diagnostic
Trouble
Codes
(10 locations
in total)
FIGURE 19 - THE BENDIX® REMOTE DIAGNOSTIC UNIT
Features of the Bendix RDU Tool
The Bendix RDU tool at taches to the 9‑pin diagnostic
connector in the cab of the vehicle.
The Bendix RDU tool allows the technician to:
• Troubleshoot ABS system component problems using
DTC reporting via LEDs;
• Reset DTCs on Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controllers by
holding a magnet over the reset in the center of the RDU
tool for less than six (6) seconds; and
• Enter the Self‑Conguration Mode used by Bendix ESP
EC‑8 0 Controlle rs by holding a magnet over the reset
area for greater than six (6) seconds but less than 30
seconds.
How the Bendix RDU Operates
See Figure 14 for typical vehicle connector locations.
When the Bendix RDU tool is plugged into the diagnostic
connector, all the LEDs will illuminate, and the green LED
will ash four (4) times to indicate communications have
been established.
If the Bendix ESP EC‑ 8 0 Contro ller has no act ive DTCs,
only the green LED will remain illuminated.
If the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller has at least one active
DTC, the RDU tool displays the rst DTC by illuminating the
red LEDs, indicating the malfunc tioning A BS c omponent
and its location on t he vehicle (See Figure 20.) If t here
are multiple DTCs on the ABS system, the RDU tool will
display one DTC rst, then — once that DTC has been
repaired and cleared — the next code will be displayed.
24
Page 25

Typical Combination
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are:
• Right steer sensor
• Left steer sensor
• Right drive sensor
• Left drive sensor
• Right additional sensor
• Left additional sensor
• Right steer modulator
• Left steer modulator
• Right drive modulator
• Left drive modulator
• Right additional
modulator
• Left additional modulator
• Rear Axle Traction
modulator
• ECU
• Engine serial
communication
• MOD red LED illuminated, shows the "Common"
connection of one o r more modulators is shor ted to
battery or ground
• VLT (Flashing indicates either over‑ or under‑voltage
condition)
To pinpoint the root cause and to ensure the system
Diagnostic Trouble Code is properly corrected the rst time,
additional troubleshooting may be necessary.
Note: The Bendix® RDU™ tool is not capable of diagnosing
certain Bendix® ESP® EC-80™ system-specific DTCs
including additional sensors: steering angle sensors, yaw
sensors, pressure sensors, or modulator valves (trailer
pressure modulating valves or front axle trac tion control
valves.)
LED DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
LFT ‑ Left
RHT ‑ Right
DRV ‑ Drive Axle
ADD ‑ Additional
STR ‑ Steer Axle
VLT ‑ Power
ECU ‑ ABS Controller
Example: If the
Diagnostic Trouble Code
is "Right Steer Axle
Sensor", the Bendix RDU
tool will display one green
and three red LEDs
FIGURE 20 - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES AS
DISPLAYED ON THE BENDIX
SEN ‑ Wheel Speed
Sensor
MOD ‑ Pressure Modulator
Valve
TRC ‑ Traction Control
LEDs
Green
VLT
Red
SEN
STR
RHT
®
RDU™ TOOL
Bendix® RDU™ Reset Function
The magnetic reset switch is located in t he center top of
the Bendix RDU tool. Activation r equires a magnet with
30 gauss minimum.
The reset operations are:
1. If the magnet is held over the switch for less than 6
seconds the "clear current DTCs" command is sent.
2. If the magnet is held over the switch for more than 6
seconds, but less than 30 seconds, the Bendix ABS
"self‑conguration command" is sent.
Additionally, it is recommended at the end of any inspection
that the user switches off and restores the power to
the Bendix ESP EC‑ 80 Controller, then check the ABS
Indicator Lamp operatio n and Bendix RDU tool to see if
they indicate any remaining DTCs.
Bendix RDU Communication Problems
If the Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller does not respond to the
RDU tool’s request for DTCs, the RDU tool will illuminate
each red LED in a clockwise pattern. This pattern indicates
the loss of communication and will continue until the Bendix
ESP EC‑8 0 C o ntr oll er re sp o nds an d communication has
been established.
Possible sources of communication problems are:
1. A problem with the J1939 link at the in‑cab off‑board
diagnostic connector (9 or 6 Pin);
2. The Be ndix ESP EC‑80 Contro ller does not support
PID194;
3. No power is being supplied to the Bendix ESP EC‑8 0
Controller and/or the diagnostic connector;
4. The J1939 bus is overloaded with information and the
RDU can not arbitrate access; or
5. A malfunctioning Bendix RDU tool.
Other Information
For more information on Bendix® ACom® Diagnostics
Software o r RP‑1210 compliant tools, go to ww w.bendix.
com or visit your local authorized Bendix distributor.
See pages 56-62 for Appendices showing J1939 SID, FMI,
codes and their Bendix blink code equivalents.
www.bendix.com
For the latest information, and for free downloads of
the Bendix® ACom® Diagnostic Software, and its User
Guide, visit the Bendix website at www.bendix.com.
Bendix Technical Assistance Team
For direct telephone technical support, call the Bendix
technical assistance team at:
1-800-AIR-BRAKE (1‑800‑247‑2725 option 2, then 1) ,
Monday through Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. ET,
and follow the instructions in the recorded message.
E‑mail the Bendix Technical Assistance Team at:
techteam@bendix.com.
25
Page 26

Active or Inactive Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
INDEX
How to interpret the first digit of messages received
when Active or Inactive Diagnostic Trouble Code Mode
is entered.
1st
Blink
Code
Number
1 ............................... No DTCs (1,1)
2 ............. Wheel Speed Sensors ‑ pages 27‑28
3 ............. Wheel Speed Sensors ‑ pages 27‑28
4 ............. Wheel Speed Sensors ‑ pages 27‑28
5 ............. Wheel Speed Sensors ‑ pages 27‑28
6 ........................Power Supply ‑ page 29
7 .......... Pressure Modulator Valves ‑ pages 30‑31
8 .......... Pressure Modulator Valves ‑ pages 30‑31
9 .......... Pressure Modulator Valves ‑ pages 30‑31
10 .........Pressure Modulator Valves ‑ pages 30‑31
11 ..........................J1939 ‑ pages 32‑33
12 ...................Miscellaneous ‑ pages 34‑35
13 ..............................ECU ‑ page 36
14 ............ Wheel Speed Sensors ‑ pages 27‑28
15 ............ Wheel Speed Sensors ‑ pages 27‑28
16 .........Pressure Modulator Valves ‑ pages 30‑31
17 .........Pressure Modulator Valves ‑ pages 30‑31
18 ....... Drive Axle Traction Control Valve ‑ page 37
19 .......Steer Axle Traction Control Valve ‑ page 37
20 ....Trailer Pressure Modulator Valve ‑ pages 30‑31
21 ............Steering Angle Sensor ‑ pages 38‑39
22 ................Yaw Rate Sensor ‑ pages 40‑41
23 ............Lateral Acceleration Sensor ‑ page 42
24 ..........Brake Demand/Load Sensors ‑ page 43
25 .................Valves Miscellaneous ‑ page 44
26 ...............J1939 ESP‑Related ‑ page 45‑47
Troubleshooting Tests
Example: For a message sequence of:
3, 2 12, 4
For the rst sequence go to page 27 and
for the second sequence go to page 34.
See Page 56-62 for APPENDIX B: J1939 SPN and FMI Codes and their Bendix Blink Code Equivalents
26
Page 27

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
Wheel Speed Sensors
1st. Blink
Code
2 Left Steer Axle Sensor
3 Right Steer Axle Sensor
4 Left Drive Axle Sensor
5 Right Drive Axle Sensor
14 Left Additional Axle Sensor
15 Right Additional Axle Sensor
2nd.
Blink
Code
Location
Diagnostic Trouble
Code Description
1 Excessive Air Gap
2 Output Low at
Drive‑off
3 Open or Shorted
Repair Information
Adjust the sensor to contact the exciter ring. Rotate the wheel and verify a minimum
of 0.25 VAC sensor output at ~ 0.5 RPS . Verify the c onditi on of the sens or head.
Verify the mount ing of t he exciter r ing an d co ndit ion of t he teet h. Verif y the p rop er
bearing end‑play. Verify the condition and retention of the clamping sleeve. Verify
the sensor lead routing and clamping.
Verify 1500 – 2500 ohms is found across the sensor leads. V erify no continuity between
the sensor leads and ground or voltage. Verify no continuity between the sensor leads
and the other sensors. Check for corroded/damaged wiring or connectors between
the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) and the wheel speed sensor.
4 Loss of Sensor Signal
5 Wheel End
6 Erratic Sensor Signal
7 Tire Size Calibration
10 Conguration Error
Adjust the sensor to contact the exciter ring. Rotate the wheel and verify a minimum
of 0.25 VAC sensor output at ~ 0.5 RPS. Verify the condition of sensor head. Verify
the mounting of the exciter ring and condition of the teeth. Verify the proper bearing
end‑play. V erify the condition and retention of the clamping sleeve. Verify the sensor
lead routing and clamping. Check for corroded/damaged wiring or connectors between
the ECU and the wheel speed sensor.
Verify the mounting of exciter ring and the condition of teeth. V erify the proper bearing
end‑play. V erify the condition and retention of the clamping sleeve. V erify the sensor
lead routing and clamping. Check the mechanical function of brake. Check for kinked
or restricted air hoses.
Adjust the sensor to contact the exciter ring. Rotate the wheel and verify a minimum
of 0.25 VAC sensor output at ~ 0.5 RPS. Verify the condition of sensor head. Verify
the mounting of the exciter ring and condition of the teeth. Verify the proper bearing
end‑play. V erify the condition and retention of the clamping sleeve. Verify the sensor
lead routing and clamping. Check for corroded/damaged wiring or connectors between
the ECU and the wheel speed sensor.
Verify the correct tire size as desired. Verify the proper tire ination. Verify the correct
number of exciter ring teeth.
The ECU is congured for four sensors, but it has detected the presence of additional
sensors. Verify the sensor wiring and the ECU conguration.
27
Page 28
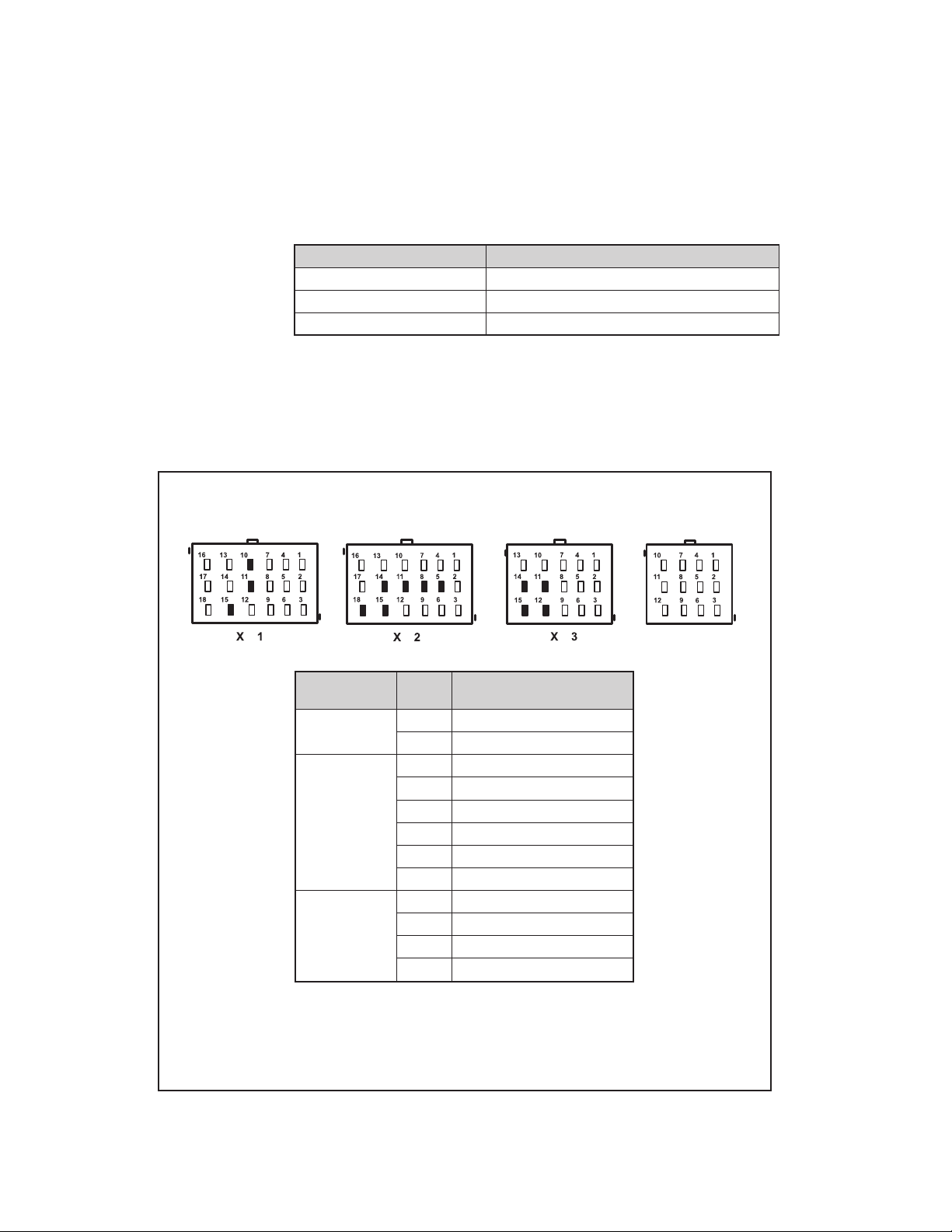
X4
Speed Sensor Repair Tests:
1. Take all measurements at the Elec tronic C ontrol Unit
(ECU) harness connector pins in order to the check wire
harness and sensor. Probe the connector carefully so
that the terminals are not damaged.
2. The wheel speed sensor measurements should read:
Location Measurement
Sensor
Sensor to voltage or ground Open Circuit (no continuity)
Sensor output voltage >0.25 of VAC sensor output at ~ 0.5 revs/sec.
3. Clear the DTC after the issue is corrected. The sensor
DTC will remain until the power is cycled to the ABS
ECU and vehicle is driven above 15 MPH or the DTC
was cleared using either the diagnostic Blink Code
Switch or a diagnostic tool.
Cab-mount ECU: Looking into
the wire harness connector
1500 ‑ 2500 Ohms
Connector Pin
X1
18 Way
X2
18 Way
X3
15 Way
(if ECU is
congured for
6 sensors)
Wheel Speed Sensor
Location
10 Right Drive Axle (+)
11
Right Drive Axle (‑)
5 Left Steer Axle (+)
Left Steer Axle (‑)
8
11 Right Steer Axle (+)
Right Steer Axle (‑)
14
15 Left Drive Axle (+)
Left Drive Axle (‑)
18
11 Left Additional Axle (+)
14
Left Additional Axle (‑)
12 Right Additional Axle (+)
Right Additional Axle (‑)
15
28
Page 29

Troubleshooting Diagn ostic Trouble Codes (D TC s ): P ower S upply
X4
1st. Blink
Code
6 Power Supply
2nd.
Blink
Code
1
2
Location
Diagnostic Trouble
Code Description
Battery Voltage Too
Low
Battery Voltage Too
High
Measure the battery voltage under load. Check the vehicle battery and associated
components. Check for damaged wiring. Check for damaged or corroded connectors
and connections.
Measure the bat tery voltage under load. Ensur e that battery voltage is c orrect
for the Electronic Control Unit (ECU). Check the vehic le batter y and associated
components. Check for damaged wiring. Check for damaged or corroded connectors
and connections.
Power Supply Tests:
1. Take all measurements at the ECU harness
connector.
2. Place a load (e.g. an 1157 stop lamp) across the
battery or ignition and ground connection, measure
the ignition and battery voltage with the load. Ignition
to Ground should measure between 9 to 17 VDC.
Battery to Ground should also measure between 9 to
17 VDC.
Repair Information
3. Check for damaged wiring, damaged or corroded
connectors and connections.
4. Check the condition of the vehicle battery and
associated components, verify that the ground
connection is good and tightened.
5. Check the alternator output for excessive noise.
Cab-mount ECU:
Looking into wire
harness connector
Connector Pin Power Supply Test
X1
18 Way
1 Ground
2 Ignition
16 Battery
29
Page 30

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
Pressure Modulator Valves (PMVs)
1st. Blink
Code
7 Left Steer Axle
8 Right Steer Axle
9 Left Drive Axle
10 Right Drive Axle
16 Left Additional Axle
17 Right Additional Axle
20 Trailer PMV
2nd.
Blink
Code
1
2
Location
Diagnostic Trouble
Code Description
Release Solenoid
Shorted to Ground
Release Solenoid
Shorted to Voltage
Repair Information
Verify no co ntinuit y b et ween th e PMV l eads an d groun d. Verif y 4.9 to 5. 5 ohms
from REL to CM N & H LD to C M N , and 9. 8 to 11 ohms from REL to HLD. Chec k
for corr oded/dama ged wir ing or c onnecto rs bet ween the Electronic Control Unit
(ECU) and PMV.
Verify no co ntinui t y between the PM V lea ds and vol ta ge. Verif y 4. 9 to 5. 5 ohm s
from REL to CM N & H LD to C M N , and 9. 8 to 11 ohms from REL to HLD. Chec k
for corroded/damaged wiring or connectors between the ECU and PMV.
3
4
5
6
7
8
Release Solenoid
Open Circuit
Hold Solenoid Shorted
to Ground
Hold Solenoid Shorted
to Voltage
Hold Solenoid Shorted
to Open Circuit
CMN Open Circuit Verify 4.9 to 5.5 ohms from REL to CMN & HLD to CMN, and 9.8 to 11 ohms from
Conguration Error
Verify 4.9 to 5.5 ohms from REL to CMN & HLD to CMN, and 9.8 to 11 ohms from
REL to HLD. Check for c orroded/damaged w iring or connector s between the
ECU and PMV.
Verify no co ntinuit y b et ween th e PMV l eads an d groun d. Verif y 4.9 to 5. 5 ohms
from REL to CM N & H LD to C M N , and 9. 8 to 11 ohms from REL to HLD. Chec k
for corroded/damaged wiring or connectors between the ECU and PMV.
Verify no co ntinui t y between the PM V lea ds and vol ta ge. Verif y 4. 9 to 5. 5 ohm s
from REL to CMN & HLD CMN, and 9.8 to 11 ohms from REL to HLD. Check for
corroded/damaged wiring or connectors between the ECU and PMV.
Verify 4.9 to 5.5 ohms from REL to CMN & HLD to CMN, and 9.8 to 11 ohms from
REL to HLD. Check for c orroded/damaged w iring or connector s between the
ECU and PMV.
REL to HLD. Check for corroded/damaged wiring or connectors between the ECU
and PMV. This is potentially a miswired or internal mechanical problem.
A mis‑match exists between the ECU conguration and the modulator installation
and wiring. Verify the PMV wiring and installation. Verify the ECU conguration.
Special Note regarding Trailer PMV: Pneumatic issues can result in this DTC being
set. Verify all lines are free from debris or other obstructions, kinks, etc.
30
Page 31
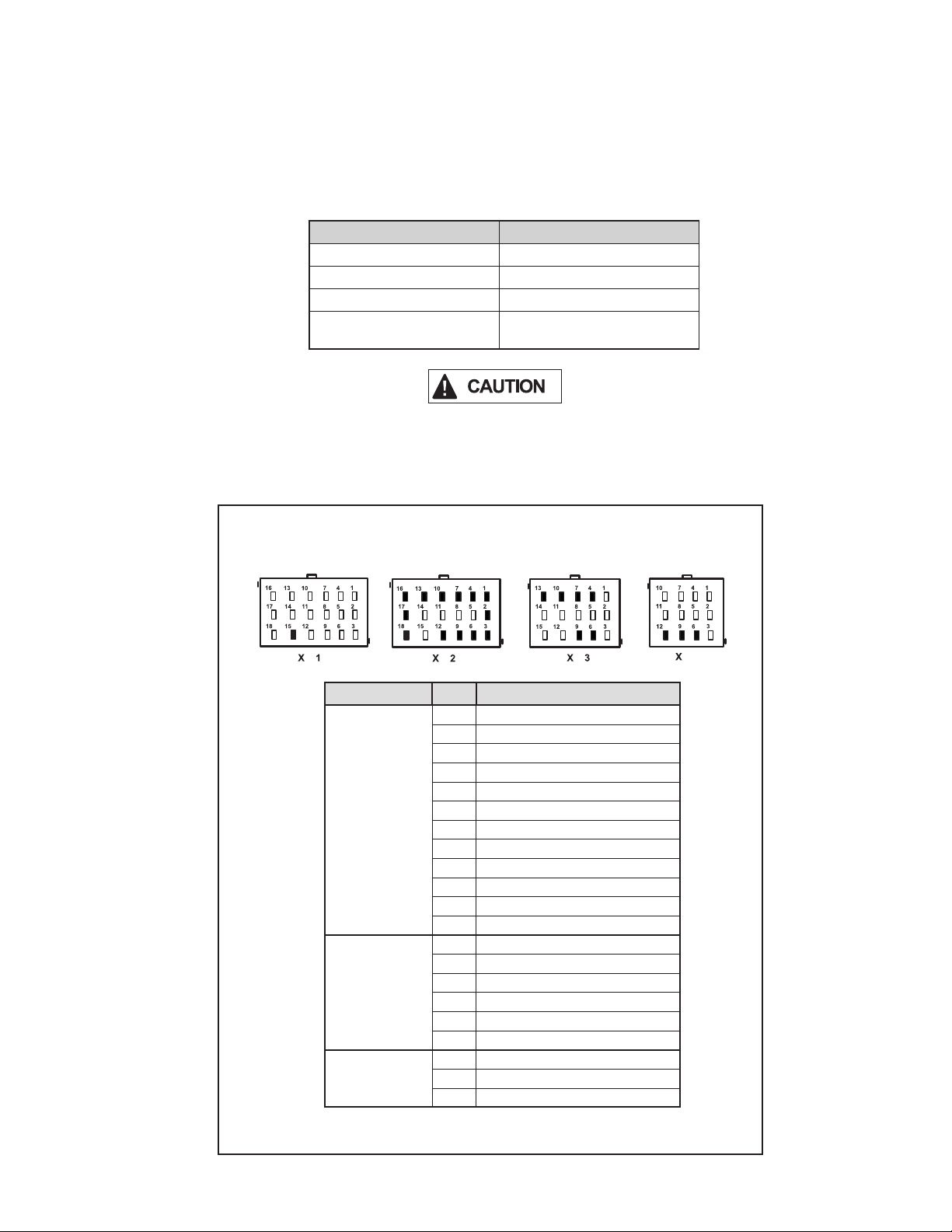
Pressure Modulator Valve (PMV) Repair Tests:
4
1. T ake all measurements at the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) harness
connector pins in order to check wire harness and PMV. Probe the
connector carefully so that the terminals are not damaged.
2. The pressure modulator resistance should read:
Location Measurement
Release to Common 4.9 to 5.5 Ohms
Hold to Common 4.9 to 5.5 Ohms
Release to Hold 9.8 to 11.0 Ohms
Release, Hold, Common to
Voltage or Ground
Open Circuit (no continuity)
When troubleshooting modulator Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs),
check inactive DTCs and the event history for over-voltage or
excessive noise DTCs. If one of these is found, troubleshoot these
DTCs rst before the PMV.
Cab-mount ECU: Looking into
the wire harness connector
Connector Pin PMV Location
1 Left Steer Axle Hold
2 Left Steer Axle Release
3 Left Steer Axle Common
4 Right Steer Axle Hold
6 Right Steer Axle Common
X2
18 Way
X3
15 Way (if
the ECU is
congured for
6 modulators)
X4
12 Way
7 Right Steer Axle Release
9 Right Drive Axle Common
10 Right Drive Axle Hold
13 Right Drive Axle Release
12 Left Drive Axle Common
16 Left Drive Axle Hold
17 Left Drive Axle Release
4 Left Additional Axle Hold
6 Left Additional Axle Common
7 Left Additional Axle Release
9 Right Additional Axle Common
10 Right Additional Axle Hold
13 Right Additional Axle Release
6 Trailer PMV Hold
9 Trailer PMV Release
12 Trailer PMV Common
31
Page 32

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
J1939 Serial Communications
1st. Blink
Code
11
2nd.
Blink
Code
Location:
J1939
Diagnostic Trouble
Code Description
1 J1939 Serial Link
2 J1939 Electronic
Retarder Time‑out
or Invalid Signal
3 J1939 Electronic Engine
Controller 1 Time‑out
or Invalid Signal
4 J1939 Electronic Engine
Controller 2 Time‑out
or Invalid Signal
5 J1939 AIR Message
Time‑out or Invalid
Signal
6 ESP J1939 CAN
Message Time‑out
Repair Information
There is loss of communications between the Bendix
other devices connected to t he J1939 link. Check for damaged or reversed J1939
wiring. Check for corroded or damaged connectors. Ver ify the Electronic Control
Unit (ECU) conguration. Check for other devices inhibiting J1939 communications.
Check for damag ed or reversed J1939 wiring. Check fo r corroded or dam aged
connecto rs. Verify t he presenc e of a retarde r on the J1939 link. Verify th e ECU
conguration. Verify that the retarder is congured to broadcast ERC1. Check for
other devices inhibiting J1939 communications.
Check for damag ed or reversed J1939 wiring. Check fo r corroded or dam aged
connectors. Verify the presence of ECU on the J1939 link. Verify the ECU
conguration. Verify the ECU is congured to broadcast EEC1. Check for other
devices inhibiting J1939 communications.
Check for damag ed or reversed J1939 wiring. Check fo r corroded or dam aged
connectors. Verify the presence of Engine ECU on the J1939 link. Verify the ECU
conguration. Verify that there is an EEC2 broadcast from the address congured
in the ABS ECU. Check for other devices inhibiting J1939 communications.
Invalid pressure signals received from a vehicle Controller. Verify the prope r
operation of brake demand sensors. Check wiring between brake demand sensors
and the vehicle C ontroller. Verify the prope r programming of vehicl e Controller.
Check for damag ed or reversed J1939 wiring. Check fo r damaged or corro ded
connectors. Check for other device inhibiting J1939 communications.
Invalid ESP message s on the J1939 link. Check fo r damaged o r reversed J1939
wiring. Check for damaged or corroded connectors. Verify the presence of engine
and / or retarder on J1939. V erify the proper programming of engine and/or retarder.
Check for other devices inhibiting J1939 communications.
®
ESP® EC‑80™ Controller and
32
7 J1939 Transmission
Communication for HSA
8 Time‑out or invalid data
on XBR
10 J1939 Electronic
Transmission Controller
1 Time‑out or Invalid
Signal
11 AUXIO CAN message
Time‑out
12 J1939 Hill Start Feature
Switch Signal Not
Available
14 J1939 CAN Message
related to ESP is
incomplete
There is loss of c ommunicatio ns between the EC‑ 80 ECU and the tr ansmission
ECU over the J1939 link. Check for damage d or reversed J1939 wiring. Chec k
for damaged or corroded connectors. Verify the presence of transmission ECU on
J1939 link. Check for other devices inhibiting J1939 communications.
Check for damag ed or reversed J1939 wiring. Check fo r damaged or corro ded
connecto r s. Ch ec k fo r oth er devi c e s inhi bit ing J1939 com muni c at io ns. Verify the
ECU conguration. Verify XBR message being broadcast from address 42.
There is loss of c ommunications bet ween the Bendix EC‑ 80 Controller an d the
transmission ECU over the J1939 link. Check for damaged or reversed J1939 wiring.
Check for co rrode d or damage d connec tors. Verif y the pre sence of eng ine ECU
on the J1939 link. Verify the ECU conguration. Check for other devices inhibiting
J1939 communications.
Check for damag ed or reversed J1939 wiring. Check fo r damaged or corro ded
connecto r s. Ch ec k fo r oth er devi c e s inhi bit ing J1939 com muni c at io ns. Verify the
EC U co n g u r a t i o n. Verify AUX IO br o a d c a s t fr o m address congured in EC‑ 8 0 ECU.
Check for damag ed or reversed J1939 wiring. Check fo r damaged or corro ded
connectors. Ve r if y the EC U co n gu r a t i o n . Verif y EB C1 being broadcast with a val i d
SPN 577 parameter. Check for other devices inhibiting J1939 communications.
Check for damag ed or reversed J1939 wiring. Check fo r damaged or corro ded
connecto r s. Ch ec k fo r oth er devi c e s inhi bit ing J1939 com muni c at io ns. Verify the
ECU conguration. Verify ESP messages.
Page 33

X4
2nd.
Blink
Code
15 J1939 Electronic Engine
16 J1939 Electronic
20 J1939 EAC1 Time‑out
21 CAN Message
22 CAN Message
23 J1939 CCVS Time‑out
24 J1939 TCO
26 J1939 Address Conict
Diagnostic Trouble
Code Description
Controller 3 Time‑out or
Invalid Signal
Transmission Controller
2 Time‑out
or Invalid Signal
CGW_C1 Time‑out or
invalid signal
ASC1_CLCS Time‑out
or invalid signal
or Invalid Signal
(Tachograph)
Time‑out
ABS Address
Repair Information
®
There is loss of communications between the Bendix
the engine Elec t ro ni c C o ntr o l Uni t (ECU) over the J1939 link. Chec k fo r da ma ge d
or reversed J1939 wiring. Che ck for cor r o d e d o r d a m ag e d connectors. Verify the
presence of engine ECU on the J1939 link. Verify the ECU conguration. Check
for other devices inhibiting J1939 communications.
There is loss of c ommunications bet ween the Bendix EC‑ 80 Controller an d the
transmission ECU over the J1939 link. Check for damaged or reversed J1939 wiring.
Check for co rrode d or damage d connec tors. Verif y the pre sence of eng ine ECU
on the J1939 link. Verify the ECU conguration. Check for other devices inhibiting
J1939 communications..
Verify 60 ohm s of re sist an c e between X1 pin 7 and X1 pin 8. Check for damaged
or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for damaged or corroded connectors. Verify that
the message i s being transmit ted. Verify data for Elec tronic Ax le Controller 1 i s
correct. Verify the ECU conguration.
Verify 60 ohms of resistance between X1 pin 7 and X1 pin 8. Check for damaged or
reversed J1939 wiring. Check for damaged or corroded connectors. Verify that the
message is being transmitted. Verify that the data for differential lock(s) is correct.
Verify the ECU conguration.
Verify 60 ohm s of re sist an c e between X1 pin 7 and X1 pin 8. Check for damaged
or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for damaged or corroded connectors. Verify that
the message is being transmitted. Verify that the data for Air Suspension Control 1
is correct. Verify the ECU conguration.
Verify 60 ohms of resistance between X1 pin 7 and X1 pin 8. Check for damaged or
reversed J 1939 wiring. Check f or damaged or corroded connectors. V erify message
is being transmitted. Verify the ECU conguration.
Verify 60 ohms of resistance between X1 pin 7 and X1 pin 8. Check for damaged or
reversed J 1939 wiring. Check f or damaged or corroded connectors. V erify message
is being transmitted. Verify the ECU conguration.
Verify only one A BS ECU is con nected on J1939 bus, broad casting O Bh (equals
13 decimal).
ESP® EC‑80™ Controller and
27 J1939 Address Conict
TPMS Address
28 J1939 Proprietary XBR
Message Out of Range
29 J1939 CAN Messages
Are Not Being
Transmitted/Received
Verify only one TPMS ECU is connected on J1939 bus, broadcasting 33h.
Verify 60 ohm s of re sist an c e between X1 pin 7 and X1 pin 8. Check for damaged
or reversed J1939 wiring. Che ck for damaged o r corrod ed connectors. Check fo r
messages being transmitted/received.
Verify 60 ohm s of re sist an c e between X1 pin 7 and X1 pin 8. Check for damaged
or reversed J1939 wiring. Che ck for damaged o r corrod ed connectors. Check fo r
messages being transmitted/received.
J1939 Troubleshooting Tests:
1. Take all measurements at ECU harness
connector.
2. Check for damaged or reversed J1939
wiring.
3. Check for corroded or damaged wiring
connector problems such as (opens or
shorts to voltage or ground).
4. Check for other J1939 devices which
may be loading down (inhibiting) J1939
communication.
Cab-mount ECU:
Looking into wire harness connector
Connector Pin J1939
X1
18 Way
7 J1939 Low
8 J1939 High
33
Page 34

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Miscellaneous
1st. Blink
Code 12
2nd.
Blink
Code
1 Stop Lamp Switch
2 Stop Lamp Switch
3 ATC or ESP Disabled
4 Retarder Relay Open
5 Retarder Relay Circuit
6 ABS Indicator Lamp
7 PMV Common
8 PMV Common
9 ATC Disabled to
11 Wheel Speed
Diagnostic Trouble
Code Description
Not Detected
Defective
or Dynamometer Test
Mode Active
Circuit or Shorted to
Ground
Shorted to Voltage
Circuit DTC
Shorted to Ground
Shorted to Voltage
Prevent Brake Fade
Sensors Reversed on
an Axle
Location:
Miscellaneous
Repair Information
The Electronic Control Unit (ECU) has not detected the presence of the stop lamp switch
since igniti on power was applie d (note that stop lamp switch input may be ap plied to
the Bendix
and release service b rake. Check f or brake switc h input into ECU (see system wir ing
schematic). With servi ce brake released, ch eck for presenc e of the stop lamp bulb.
With service brake applied, verify system voltage is now present at the stop lamp switch
input to the ECU. Check for damaged wiring between ECU, stop lamp switch and bulb.
Check for c orroded or d amaged conn ectors. Che ck for damaged o r reversed J1939
wiring. Check for corroded or damaged connectors on J1939 link. Verify the presence
of engine ECU on the J1939 link. Verify the ECU conguration.
Apply and rel ease ser vi ce bra ke. Check for br ake switch input into ECU (see system
wiring schematic). With service brake released, check for presence of the stop lamp bulb.
With service brake applied, verify system voltage is now present at the stop lamp switch
input to the ECU. Check for damaged wiring between ECU, stop lamp switch and bulb.
Check for c orroded or d amaged conn ectors. Che ck for damaged o r reversed J1939
wiring. Check for corroded or damaged connectors on J1939 link. Verify the presence
of engine ECU on the J1939 link. Verify the ECU conguration.
AT C or ESP is disabled. ECU has been placed in the Dynamometer Test Mode by either
the diagnosti c Blink Code Sw itch or a hand ‑held or PC ‑base d diagnostic too l. Clear
DTCs to exit Dynamometer Test Mode.
Verify vehicle contains a retarder relay. Verify the ECU conguration. Check wiring
between ECU and retarder relay. Verify no continuity between retarder disable output of
Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller and ground. Verify condition and wiring of the retarder relay.
Check wiri ng betwe en ECU and retard er relay. Verify no conti nuity bet ween ret arder
disable output of Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller and voltage. Verify condition and wiring
of the retarder relay.
Check operation of diagnostic Blink Code Switch. Check wiring of diagnostic Blink Code
Switch (verif y A B S wir e is not g rou nde d whe re us ed) and A BS I ndic at or L amp. Verif y
ABS Indicator Lamp ground input. On some vehicles with multi‑plex dashes, the ground
wire may not be present - see ECU 19 DTC.
Verify no continuity between the Release, Hold and CMN of all Pressure Modulator Valves
(PMVs), Traction Control Valve (TCV), HSA, Diff Lock Solenoid and ground. Check for
corroded/damaged wiring or connectors between the ECU and CMN of all PMVs, TCV,
and Diff Lock Solenoid. See the extended troubleshooting for this code in Appendix A.
Verify no co ntinuity betwee n the Re leas e, Hol d and C MN of a ll PM Vs, TCV, HSA, Diff
Lock Solenoid and voltage. Check for corroded/damaged wiring or connectors between
the ECU and CMN of all PMVs, TCV, and Diff Lock Solenoid.
The Bendix
prevent excessive heating of the foundation brakes.
Sensors are rever sed (lef t to ri ght) on one of the a xles. Verif y th e prope r installat ion,
connection, and wiring of the sensors.
®
ESP® EC‑ 80™ Controlle r using either hard‑w ire input or J1939). Apply
®
ATC (Automatic Traction Control) system is temporarily disabled to
14 Sensor CAN Supply
Voltage Error
17 ABS disabled due to
off‑road mode
19 Maximum number
of PMV cycles
exceeded
34
Incorrect supply voltage for the Steering Angle Sensor (SAS) and the Yaw Rate sensor .
Verify the proper voltage at the sensor connectors. Verify the wiring between the ECU
and the sensors. Verify the proper output voltage from ECU. Note: When checking for
voltage at YAW/LAS & SAS, the voltage will only be present momentarily at key ON.
The ABS indicator lamp will be ashing, indicating the ECU is in the off‑road ABS mode.
Remove and re‑apply ignition power.
Replace all PMV valves and clear the DTC.
Page 35

2nd.
Blink
Code
Diagnostic Trouble
Code Description
Repair Information
20 Maximum Number
of TCV Cycles
Exceeded
22 ESP Sensor Voltage
Out of Range
24 HS Feature Lamp
Open or Shorted
to Ground
25 HS Feature Solenoid
Open or Shorted
to Ground
26 HS Feature Solenoid
Shorted to Voltage
27 Brake Lamp Input
Mismatch With Brake
Lamp Output
28 Air system/
Mechanical
Component
Replace all Traction Control Valve (TCV) valves and clear the Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC).
Incorrect supply voltage is detected for the Bendix
®
SAS‑60™ and the Yaw Rate sensor.
Verify the pro per voltage at se nsor conne ctors. Verif y wiring bet ween the Ele ctronic
Control Unit (ECU) and th e sensors. Verify the prope r output voltage from ECU.
Note: When check ing fo r voltag e at YAW/L AS & SAS, the vol tage wi ll on ly be pr esent
momentarily at key ON.
Verify no co ntinuity bet ween the Hi ll Star t / Hill Star t As sist lamp and grou nd. Verify
continuity between the lamp and the ECU. Check the wiring between the lamp and the
ECU. Check the lamp and the condition of its wiring.
The Hill Start / Hill Start Assist solenoid is shorted to ground or has a broken wire. Verify
no continuity between the solenoid and ground. Check for corroded/damaged wiring or
connectors between the ECU and the solenoid.
Verify no continuity between the Hill Start / Hill Start Assist Solenoid and voltage. Check
for corroded/damaged wiring or connectors between the ECU and Solenoid.
There is a brake lamp input mismatch with the brake lamp output.
Verify brakes are operating correctly. Verify that there is not over‑braking at one or more
wheel end(s). Check the pneumatic plumbing and the exhaust port of the PCVs, TCVs,
and relay valves and conrm that the air is being exhausted from all brake chambers.
Verify tire sizes on the vehicle match the ABS ECU conguration. Verify wheel speed
sensors and tone ring are properly adjusted and in good condition.
29 Air system/
Mechanical
Component
30 ESP Disabled due to
Off Road Mode
31 HS Feature Lamp
Shorted to Voltage
32 I/O 2 or 3 Shorted
High (EC‑80‑ATC)
OR
I/O 2 or 3 shorted
High or Stop Lamp
Output error (ESP
EC‑80)
33 HS Feature Solenoid
Open Circuit
34 eTrac Valve Solenoid
Shorted to Voltage
35 eTrac Valve Solenoid
Shorted to Ground
Verify that the t ires a re in go od c on diti on. Verif y th at no pne umati c hose s are t w isted
or kinked. Verify that t he b rakes are o pe rat ing c o r rec tl y. Verify that th e whe el sp ee d
sensor and tone ring are properly adjusted. Verify tire size.
Electronic S tabilit y has been dis abled due to t he vehicle be ing in the AB S or ATC off
road mode. Cycle ABS Off Road or ATC Mud snow switch.
Verify that there is no resistance measured between the battery and HSA lamp output
of the ECU. Check the wir ing betwee n the ECU and the Hill St art / Hi ll Star t Assist
lamp. Check the lamp and condition of its wiring.
Check for a short‑circuit condition between voltage and the I/O 2 and I/O 3 circuits.
Verify resistance across the Hill Sta rt / Hill Start Assist solenoi d. C heck the ECU and
HSA solenoid for corroded or damaged wiring and/or connectors.
Verify the resistance between voltage and the Bendix
®
eTrac™ solenoid is open. Check
for corroded or damaged wiring or connectors between the ECU and the e T rac solenoid.
Verify the resistance between ground and the Bendix eT rac solenoid is open. Check for
corroded or damaged wiring or connectors between the ECU and the eTrac solenoid.
36 Reserved
38 Invalid ABS Warning
Lamp Conguration
Reserved
Check X1‑12 if pin/wire inst all ed. X2‑12 should have no terminal or conne c ti on. ABS
Warning Lamp is controlled via J1939.
35
Page 36

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): ECU
1st. Blink
Code
13
Location:
ECU
Diagnostic
2nd
Blink
Code
1 ECU DTC (5FC)
2 ECU DTC (5CD)
3
4 ECU DTC (2678C)
5 ECU DTC (1C)
6 ECU DTC (6CD)
7
8 ECU DTC (56)
9 ECU DTC (CAC3)
10 ECU DTC (5F3)
11 ECU DTC (F1A)
12 ECU DTC (F14)
13
14 ECU DTC (C6)
15 ECU DTC (CF)
16 ECU DTC (C0)
17 ECU DTC (C8C)
18 ECU DTC (CC)
Trouble Code
Description
(With HEX
designation)
ECU DTC (10)
Conguration
mismatch
Conguration
mismatch
Repair Information
Check for damaged or corroded connectors. Check for damaged
wiring. Clear D iagnostic Trouble Code s (DTCs). If DTCs return,
contact the Bendix Tech T eam at 1‑800‑AIR‑BRAKE (1‑800‑247‑2725,
option 2, then 1) for further troubleshooting assistance.
Verify components installed match the Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
conguration.
Check for damaged or corroded connectors. Check for damaged
wiring. Clear DTCs. If DTCs return, c o ntac t th e Ben dix Tech Team
at 1‑80 0 ‑ AIR‑ B R A KE (1‑80 0 ‑247‑2725, option 2, then 1) for further
troubleshooting assistance.
Verify components installed match ECU conguration.
Check for damaged or corroded connectors. Check for damaged
wiring. Clear DTCs. If DTCs return, c o ntac t th e Ben dix Tech Team
at 1‑80 0 ‑ AIR‑ B R A KE (1‑80 0 ‑247‑2725, option 2, then 1) for further
troubleshooting assistance.
Parameter le was not downloaded. To verify that the vehicle specic
parameters have been lo aded, c ontac t Bendix fo r more inf ormat ion
at 1‑800‑AIR‑BRAKE (1‑800‑247‑2725).
36
19 ECU DTC (63)
20 ECU DTC (6E)
21 ECU DTC (6C)
22 ECU DTC (63C)
25
26
28 ECU DTC (7CD)
29 ECU DTC (5D)
ECU Internal VIN
Mismatch
Valve Conguration
Mismatch
Check for damaged or corroded connectors. Check for damaged
wiring. Clear DTCs. If DTCs return, c o ntac t th e Ben dix Tech Team
at 1‑80 0 ‑ AIR‑ B R A KE (1‑80 0 ‑247‑2725, option 2, then 1) for further
troubleshooting assistance.
The ECU internally‑stored VIN does not match the VIN of the vehicle.
Ensure that the ECU is insta lled on the c orr ect vehicl e. Verify the
ECU programming. Verify engine programming.
Check for damaged or corroded connectors. Check for damaged
wiring. Clear DTCs. If DTCs return, c o ntac t th e Ben dix Tech Team
at 1‑80 0 ‑ AIR‑ B R A KE (1‑80 0 ‑247‑2725, option 2, then 1) for further
troubleshooting assistance.
Check for damaged or corroded connectors. Check for damaged
wiring including power and ground wiring. Clear DTCs. If DTCs return,
contact the Bendix Tech T eam at 1‑800‑AIR‑BRAKE (1‑800‑247‑2725,
option 2, then 1) for further troubleshooting assistance.
Page 37

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
X4
Traction Control Valves (TCV)
1st. Blink
Code
18 Drive Axle Traction Control Valve
19 Steer Axle Traction Control Valve
NOTE: When troubleshooting Traction
Control Valve DTCs, it may be useful to look
for a potential connection between them and
ECU DTCs (in particular, DTCs 1 3‑8 and 13‑18
shown on page 36).
Location
2nd.
Blink
Code
1
2
3
4
Diagnostic Trouble
Code Description
TCV Solenoid Shorted
to Ground
TCV Solenoid Shorted
to Voltage
TCV Solenoid Open
Circuit
TCV Conguration Error The ECU is not congured for ESP or ATC, but has detected the presence
Repair Information
Verify 7 to 19 ohms betwe en Tracti on Control Valve (TCV) and TCV
common. Verif y no continu ity bet ween TCV leads and ground. Ch eck
for corroded/damaged wiring or connectors between the ECU and TCV.
Verify 7 to 19 ohms between TCV and TCV common. Verify no continuity
between TCV leads and voltage. Check for corroded/damaged wiring or
connectors between ECU and TCV.
Verify 7 to 19 ohms between TCV and TCV common. Check for corroded/
damaged wiring or connectors between ECU and TCV.
of a TCV. Verify TCV wiring. I nspe ct fo r the p rese nc e of a TCV. Verif y
the ECU conguration.
ATR valve inspections should include: looking for kinked air hoses; inside the harness socket on the valve for
removed or corroded connector pins; and a test to verify that the ATC valve solenoids are functioning correctly.
Traction Control Valve (TCV) Repair Tests:
1. Take all measurements at ECU harness connector pins in order to check wire harness
and traction control valve. Probe the connector carefully so that the terminals are not
damaged.
2. Tractor Control Valve resistance measurements should read:
Location Measurement
TCV to TCV Common 7 to 19 Ohms
Cab-mount ECU:
Looking into wire
harness connector
Connector Pin Traction Control Test
X1
18 Way
Release, Hold, Common
to Voltage or Ground
Drive Axle Traction
4
Control Valve Common
Drive Axle Traction
5
Control Valve
Open Circuit (no continuity)
Connector Pin Traction Control Test
Steer Axle Traction
3
X3
15 Way
Control Valve Common
Steer Axle Traction
5
Control Valve
37
Page 38

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
Steering Angle Sensor (SAS) [Bendix® SAS-60™ Sensor]
1st. Blink
Code
21
Blink
Code
Location:
Steering Angle Sensor
2nd.
Diagnostic Trouble
Code Description
SAS Not Calibrated Steering Angle Sensor (SAS) has not been calibrated.
1
SAS Calibration
2
in Progress
SAS Static Signal SAS signal incorrect. Verify the proper installation of the SAS. Verify proper wiring
3
SAS Signal Out
4
of Range
SAS Signal Reversed SAS s ignal is reversed. Verify t he proper install ation of the SAS. Verify p roper
5
SAS Invalid Signal SAS signal is invalid. Verify the proper installation of the SAS. Verify proper wiring
6
Repair Information
Perform SAS calibration procedure.
SAS calibration procedure is underway.
between the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) and the SAS. Check SAS output.
SAS signal incorrect. Verify the proper installation of the SAS. Verify proper wiring
between the ECU an d the SAS. Check SAS output. Per form SAS calibrati on
procedure.
wiring between the ECU and the SAS. Check SAS output.
between the ECU an d the SAS. Check SAS outp ut. Verify that cor rect SAS is
being used.
SAS Gradient Error SAS signal is invalid. Verify the proper installation of the SAS. Verify proper wiring
7
between the ECU an d the SAS. Check SAS outp ut. Verify that cor rect SAS is
being used.
SAS CAN Time‑out Loss of CAN communications between the ECU and the SAS. Verify proper wiring
8
between the ECU and the SAS. Check SAS output.
SAS Long Term
9
Calibration Error
SAS Plausibility Check E CU has detected incorrect SAS signal as compared to the Yaw Rate sensor signal.
10
SAS detected but
11
not congured
SAS calibration error. Verify the proper installation of the SAS. Verify proper wiring
between the ECU and the SAS. Check SAS output. Verify that correct SAS is being
used. Verify proper ECU programming. Perform SAS calibration procedure.
Verify the proper installation of the SAS. Verify proper wiring between the ECU and
the SAS. Check SAS output. Verify that correct SAS is being used. Verify proper
ECU programming. Perform SAS calibration procedure.
Verify the ECU is congured for ESP.
38
Page 39

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
®
Steering Angle Sensor (SAS) [Bendix
(continued)
Steering Angle Sensor (SAS) Connector
Looking into wire harness connector
(Note: When checking for voltage at YAW/LAS & SAS, the voltage will only be present momentarily at key ON).
Steering Angle Sensor Tests
1. Measure resistance between input voltage and ground
at the sensor wiring harness connector.
Verify continuity between the Electronic Control Unit
(ECU) and SAS‑60 and Yaw Rate Sensor (typically
Y AS‑70 or YAS‑60).
Connector Pin Function
2 Voltage Input
1 Ground Input
11 Power
10 Common
ECU
12 Way
SAS
X4
4. T o perform a calibration procedure of the Steering Angle
Sensor, Bendix® ACom® Diagnostic Software V6.7.2.5
or higher is required. Using the program, select the
“Configuration” option, followed by the “Calibrate”
option. The following screen should be displayed.
SAS-60™ Sensor]
2. Verify wiring between the Steering Angle Sensor and
the ECU.
SAS Wire
Harness
Terminal
4 7 Verify Continuity
3 8 Verify Continuity
ECU Wire
Harness
Terminal
Measurement
3. Verify wiring between the Steering Angle Sensor and
power/ground.
SAS Wire Harness
Terminal
4 to Voltage &
Ground
3 to Voltage &
Ground
Measurement
Verify open circuit (no
continuity)
Verify open circuit (no
continuity)
5. Follow the prompts to perform a calibration of the
Steering Angle Sensor.
6. To test the Steering Angle Sensor, ACom V6.7.2.5, or
higher, is required. Using Bendix ACom V6.7.2.5 or
higher, select the “Component Test” option, followed
by the “ESP Test” option. The following screen should
be displayed.
7. Follow the prompts to perform a test of the Steering
Angle Sensor.
39
Page 40

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
Yaw Rate Sensor (YRS)
1st. Blink
Code
22
Blink
Code
Yaw Rate Sensor
2nd.
Diagnostic Trouble
Code Description
YRS Signal Out of
1
Range
YRS Sensor
2
Reversed Signal
YRS Invalid Signal
3
YRS Gradient Error
4
YRS CAN Time‑out Loss of CAN communic ations bet ween th e ECU and the YRS. Verif y pro per wiri ng
5
YRS Static BITE
6
Error
YRS Dynamic BITE
7
Error
YRS Fast Calibration
8
Error
YRS Static
9
Calibration Error
Location:
Repair Information
The YRS signal i s inc or r ec t. Verify the prop er in sta llat ion o f the Y RS. Verify proper
wiring between the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) and the YRS. Check the YRS output.
Perform the YRS calibration procedure.
The YRS signal is reversed. Verify the proper installation of the YRS. Verify the wiring
between the ECU and the YRS. Check the YRS output.
The YRS signal i s invalid. Verify the prope r installation of th e YRS. Verify prop er
wiring bet ween the ECU and the Y RS. Check the YRS ou tput. Verify that c orrect
YRS is being used.
between the ECU and the YRS. Check the YRS output.
The YRS signal f ail s st at i c s el f ‑ te st . Verify the prop er i nstallation of th e Y RS. Verify
proper wir ing between the ECU and th e YRS. Check the YRS o utput. Verify that
correc t YRS is being used. Verify pro per ECU programming. Per form the YRS
calibration procedure.
The YRS signal f ai ls s e l f‑test conducted while vehicl e i s in m ot ion. Verify the p r op e r
installation of the YRS. Verify proper wiring between the ECU and the YRS. Check the
YRS output. Verify that correct YRS is being used. Verify proper ECU programming.
Perform the YRS calibration procedure.
There is a YRS calibration error. Verify the proper installation of the YRS. Verify proper
wiring between the ECU and the YRS. Check the YRS output. Verify that correct YRS is
being used. Verify proper ECU programming. Perform the YRS calibration procedure..
40
10
12
13
14
15
16
17
YRS Normal
Calibration Error
YRS Plausibility
Check (Ref Yaw
Rate)
YRS Plausibility Error
(Inside Model Based
Limits)
YRS Plausibility
Error (Outside Model
Based Limits)
YRS ‑ SAS Signal
Cross‑check
Incomplete
YRS ‑ Vibration
Detected
YRS Detected But
Not Congured
There is a YRS calibration error. Verify the proper installation of the YRS. Verify proper
wiring between the ECU and the YRS. Check the YRS output. Verify that correct YRS
is being used. Verify proper ECU programming. Perform the YRS calibration procedure.
The ECU has detected an inc or rec t YRS si gnal. Verif y the pr oper i nstall ation of t he
YRS. Verify pro per wir ing bet ween the ECU and th e YRS. Chec k the YRS out put.
Verify that correct YRS is being used. Verify proper ECU programming. Perform the
YRS calibration procedure.
The ECU (if congured) must conrm that YRS and SAS signals match. The vehicle
must be exposed to an S‑shaped driving maneuver for this DTC to automatically clear.
If the DTC does not clear even after the S‑shaped driving maneuver, check and correct
the orientation of the YRS and then repeat the maneuver.
Inspect the Y RS mounting a nd verif y it is sec urely mounte d. Note that the Y RS may
not be reloc ated from the OEM‑ installed position o n vehicle without writ ten Bendix
Engineering approval.
Verify that the ECU is congured for ESP.
Page 41

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
Yaw Rate Sensor (YRS) (continued)
Yaw Connector
Looking into wire harness connector
(Note: When checking for voltage at YAW/LAS & SAS, the voltage will only be present momentarily at key ON.).
Yaw Rate Sensor Tests
1. Verify continuity between the Electronic Control Unit
(ECU) and the Yaw Rate Sensor (typically YAS‑70 or
YAS‑60).
Connector Pin Function
2 Voltage Input
1 Ground Input
11 Power
10 Common
ECU
12 Way
YRS
X4
4. To perform a calibration procedure of the Yaw Rate
Sensor, ACom® Diagnostic Software V6.7.2.5 (or
higher) is required. Using the program, select the
“Configuration” option, followed by the “Calibrate”
option. The following screen should be displayed.
2. Verify wiring between the Yaw Rate Sensor and the
ECU.
YRS Wire
Harness
Terminal
4 7 Verify Continuity
3 8 Verify Continuity
ECU Wire
Harness
Terminal
Measurement
3. Verify wiring between the Y aw Rate Sensor and power/
ground.
YRS Wire Harness
Terminal
4 to Voltage &
Ground
3 to Voltage &
Ground
Measurement
Verify open circuit (no
continuity)
Verify open circuit (no
continuity)
5. Follow the prompts to perform a calibration of the Yaw
Rate Sensor.
6. T o test the Y aw Rate Sensor , ACom V6.7.2.5, or higher ,
is required. Using Bendix ACom V6.7.2.5 or higher,
select the “Component Test” option, followed by the
“ESP Test” option. The following screen should be
displayed.
7. Follow the prompts to perform a test of the Yaw Rate
Sensor.
41
Page 42

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
Lateral Acceleration Sensor (LAS)
1st. Blink
Code
23
Blink
Code
Location:
Lateral Acceleration
Sensor
2nd.
Diagnostic Trouble
Code Description
LAS Signal Out of
1
Range
2 LAS Calibration in
Progress
3 LAS Static
Calibration Error
4 LAS Long Term
Calibration Error
Repair Information
LAS signal inc orr ect. Verif y the pro per installati on of the Y RS/L AS. Verif y
proper wiring between the Electronic Co ntr o l U nit (ECU) and the YRS/LAS.
Check YRS/LAS output. Perform LAS calibration procedure.
LAS calibration procedure is underway.
LAS calibr ation e r ror. Verify the proper installati on of th e YRS/LAS. Verify
proper wiring between the ECU and the YRS/LAS. Check YRS/LAS output.
Verify that correct YRS/LAS is being used. Verify proper ECU programming.
Perform LAS calibration procedure.
LAS calibr ation e r ror. Verify the proper installati on of th e YRS/LAS. Verify
proper wiring between the ECU and the YRS/LAS. Check YRS/LAS output.
Verify that correct YRS/LAS is being used. Verify proper ECU programming.
Perform LAS calibration procedure.
5 LAS Plausibility
Error (Inside ECU‑
specic Limits)
6 LAS Plausibility
Error (Outside ECU
–specic Limits)
7 Erratic ESP Sensor
Signal
(Note: When checking for voltage at YRS/LAS & SAS, the voltage will only be present momentarily at key ON.).
1. Follow the steps shown in the Yaw Rate Sensor
troubleshooting section for calibration and
troubleshooting of the Lateral Acc eleration Sensors
(previous page).
ECU has detected an incorrect LAS signal. Verify the proper installation of the
YRS/LAS. Verify proper wiring between the ECU and the YRS/LAS. Check
YRS/LAS output. Verify that correct YRS/LAS is being used. Verify proper
ECU programming. Perform LAS calibration procedure.
ECU has detected an incorrect LAS signal. Verify the proper installation of the
YRS/LAS. Verify proper wiring between the ECU and the YRS/LAS. Check
YRS/LAS output. Verify that correct YRS/LAS is being used. Verify proper
ECU programming. Perform LAS calibration procedure.
ECU has detected an erratic signal. Verify the proper installation of the YRS/
LAS. Verify proper wiring between the ECU and the YRS/LAS. Check YRS/
LAS output. Verify that correct YRS/LAS is being used. Verify proper ECU
programming. Perform LAS calibration procedure.
42
Page 43
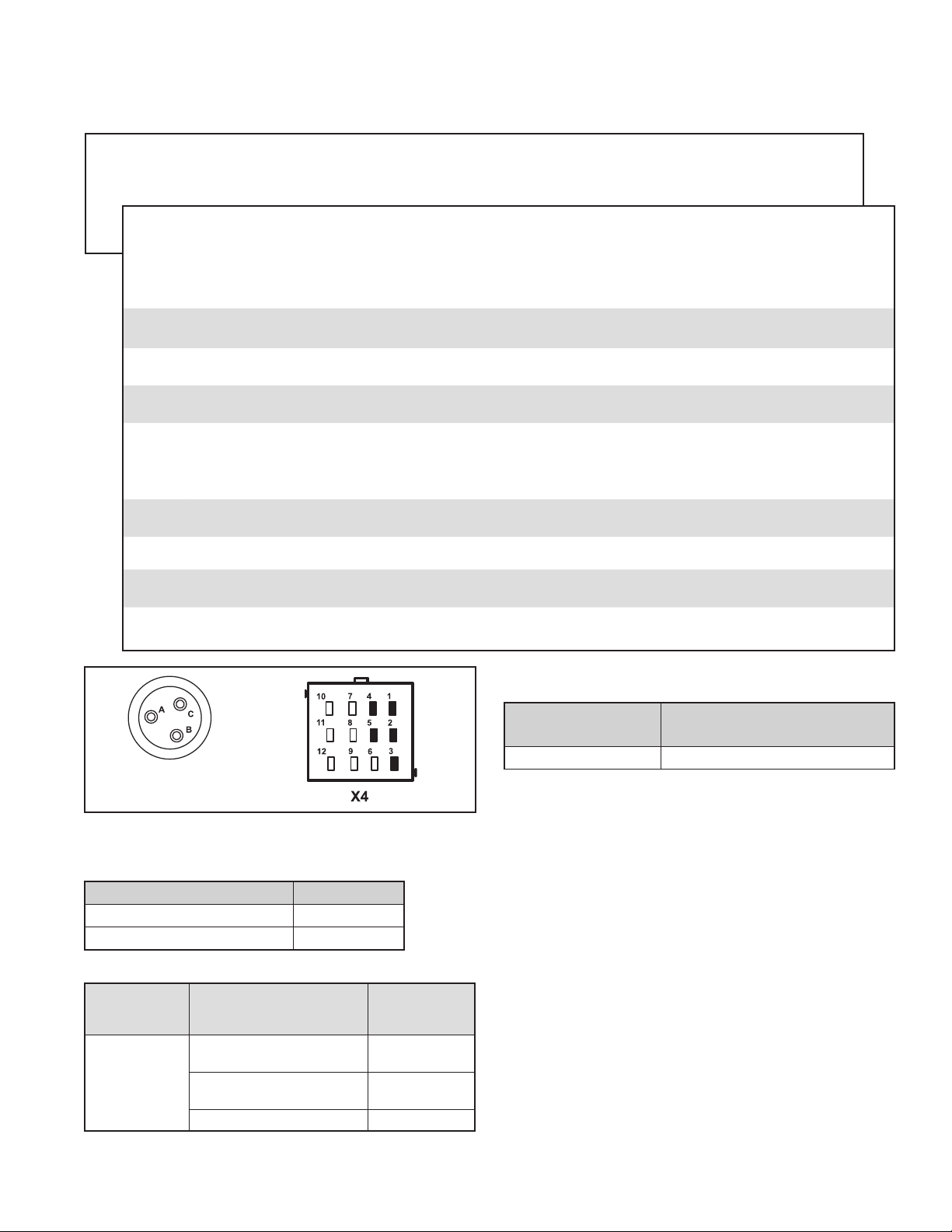
Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
Brake Demand/Load Sensors
1st. Blink
Code
24
2nd.
Blink
Code
1 PS1 Open or
2 PS2 Open or
3 PS3 Open or
4 PS1/2
5 PS Supply
6 PS Not
7 PS Error Verify operation of pressure sensor.
8 PS Supply
9 PS Not
Location:
Brake Demand/
Load Sensor
Diagnostic Trouble
Code Description
Shorted
Shorted
Shorted
Plausibility Error
Voltage Error
Calibrated
Voltage Error
Congured
Repair Information
Check wiring between Brake Demand Sensor (primar y brake circuit) and
Electronic Control Unit (ECU). Verify operation of pressure sensor.
Check wiring between Brake Demand Sensor (secondary brake circuit) and ECU.
Verify operation of pressure sensor.
Check wiring between Load Sensor and ECU. Verify operation of pressure sensor.
ECU has detected an invalid pressure sensor signal from one of the Brake
Demand Sensors.
Incorrect supp ly voltage to the sensors. Verif y the proper voltage at sensor
connectors. Verify wiring between the ECU and the sensors. Verify the proper
output voltage from the ECU (Specically, ensure that X4‑4 PS_SPL is not
shorted to ground).
Perform static sensor calibration procedure. (NOTE: When replacing an ECU,
this DTC may occur.)
Incorre ct supply voltage to senso rs. Verify the prope r voltage at sensor con nectors.
Verify wiring between ECU and the sensors. Verify the proper output voltage from ECU.
Check for presence of pressure sensors. Make sure ESP is enabled.
Looking into wire
harness connector
Brake Demand/Load Sensor Tests
1. Verify continuity between the ECU and the pressure
sensor power and ground.
Power and Ground Input Test Measurement
B = Power Input X4 ‑ 4 Power
A = Ground Input X4 ‑ 1 Common
2. Verify wiring between the Load Sensor and the ECU.
Load Sensor
Wire Harness
Terminal
C
ECU Wire Harness
Terminal
X4 ‑ 2 Brake Demand
Sensor (primary brake circuit)
X4 ‑ 5 Brake Deman d Sen sor
(secondary brake circuit)
X4 ‑ 3 Load Sensor Verify Continuity
Measurement
Verify Continuity
Verify Continuity
3. Verify wiring between the Load Sensor and power/
ground.
Load Sensor
Harness Terminal
C to Voltage & Ground Verify open circuit (no continuity)
Measurement
4. T o perform a calibration procedure of the Brake Demand
Sensor(s), ensure that the air system is fully charged.
Apply ignition power, and wait 30 seconds. Perform
a full application of the service brake and hold for 5
seconds. Release the service brake.
5. To test the Brake Demand Sensor and/or the Load
Sensor, Bendix® ACom® Diagnostic Software V6.7.2.5
or higher is required. Using the program, select the
“Component Test” option, followed by the “ESP Test”
option. The following screen should be displayed.
6. Follow the prompts to test the Brake Demand Sensor(s)
and/or the Load Sensor.
43
Page 44
Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
Valves Miscellaneous
1st. Blink
Code
25
Blink
Code
Location:
Valves
2nd.
Diagnostic Trouble
Code Description
Differential Lock
1
Solenoid Open
2 Differential Lock
Solenoid Shorted to
Ground
3 Differential Lock
Solenoid Shorted to
Voltage
4 I/O 3 Open Circuit Verify resistance for I/O3 c ircuit. Check for cor roded / damaged wiring o r
5 I/O 3 shorted to
Ground
Verify resistance between Diff solenoid and Diff common. Check for corroded
/damaged wriing or connec tors between the Elec tronic Control Unit (ECU)
and the Diff solenoid.
Verify no continuity b etween the D iff Loc k Solenoid an d ground. Check for
corroded /damaged wiring or connectors between the ECU and Diff Lock
Solenoid.
Verify no continuity b etween th e Dif f Lock S olenoid and volt age. Check for
corroded /damaged wiring or connectors between the ECU and Diff Lock
Solenoid.
connector between ECU and I/O.
Check for a short circuit condition between ground and the I/O 3 circuit
Verify resistance between Input /Output and ground is open
Repair Information
6 I/O 3 Shorted to
Battery
7 Output Conguration
Error ‑ Diff
8 Output Conguration
Error ‑ I/O 3
Check for a shor t circuit condition between voltage and the I/O 3 circuit
Verify resistance between Input /Output and voltage is open
Mismatch between ECU conguration and Diff valve
Mismatch between ECU conguration and I/O3
44
Page 45

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
Bendix® ESP® system-related
1st. Blink
Code
2nd.
Blink
26
Code
Location:
®
J1939 Bendix
Diagnostic Trouble Code
system-related
Description
1 J1939 CAN Time‑out of ESP
Message
2 Time‑out or Invalid CAN data
–CCVS 2 ESP Message
3 Time‑out or Invalid CAN data
–Electronic Engine Controller 1
ESP Message
4 Time‑out or Invalid CAN data
–EEC2 ESP Message
5 Time‑out or Invalid CAN data
– Driveline Line Retarder ESP
Message
6 Time‑out or Invalid CAN data –
Engine Retarder ESP Message
7 Time‑out or Invalid CAN
data – Exhaust Retarder ESP
Message
8 Time‑out or Invalid CAN data –
PROP XBR ESP Message
9 Time‑out or Invalid CAN data
– Transmission Retarder ESP
Message
10 Time‑out or Invalid CAN data
–Electronic Transmission
Controller 1 ESP Message
11 Time‑out or Invalid AUXI/O –
ESP Message
ESP®
Repair Information
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded conn ectors . Verify mes sage is be ing transmi tted on J1939 link.
Verify the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded conn ectors . Verify mes sage is be ing transmi tted on J1939 link.
Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded connector s. Verify the pres ence of engine ECU on J1939 link.
Verify mess age is b ein g tra nsmitted on J1939 link. Verify dat a for d ri ver 's
demand torque, act ual engine to rque, engin e speed is c or rect. Verif y th e
ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded connector s. Verify the pres ence of engine ECU on J1939 link.
Verify mess age is being transmitte d on J1939 link. Verify ac celeration
pedal positi on and acceleration p edal status is correc t. Verif y the ECU
conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded connectors. Verif y the presence of a retar der on J19 39 Link.
Verify that the message is being transmitted. Verify that the data is correct
for torque / speed control. Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded connectors. Verif y the presence of a retar der on J19 39 Link.
Verify that the message is being transmitted. Verify that the data is correct
for torque / speed control. Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded connectors. Verif y the presence of a retar der on J19 39 Link.
Verify that the message is being transmitted. Verify that the data is correct
for torque / speed control. Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded con nector s. Verif y the pres ence of Rad ar on J1939 link. Verify
message is being transmitted. Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corroded connectors. Verify the presence of a retarder on J1939 Link. Verify
that the message is being transmitted. Verify that the data in torque/speed
control. Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded con nector s. Verif y the pres ence of tr ansmiss ion ECU on J1939
link. Verify that t he me ss age i s bein g tra nsmit te d. Verif y th at the dat a fo r
shift in process, torque conguration lock , driveline engaged is correct.
Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corroded connectors. Verify that the message is being transmitted. Verify
that the data for reference torque is correct. Verify the ECU conguration
45
Page 46

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
J1939 Bendix® ESP® system-related (continued)
1st. Blink
Code
26
Blink
Code
Location:
®
J1939 Bendix
system-related
2nd.
Diagnostic Trouble Code
Description
12 Time‑out or invalid data for
Conguration of Electronic
Engine Controller 1 ESP
Message
13 Invalid Data Transfer Time‑out
of EC1 ESP Message
14 Time‑out or invalid data for
Conguration of Driveline Line
Retarder ESP Message
15 Time‑out or invalid CAN data
–Electronic Engine Controller
ESP Message
ESP®
Repair Information
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded c on nec tor s. Verif y t he p rese nc e of eng ine on J1939 link. Verif y
that the mess age is being transm itted. Verify th at the data for referen ce
torque is correct. Verify the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded c on nec tor s. Verif y t he p rese nc e of eng ine on J1939 link. Verif y
that the mess age is being transm itted. Verify th at the data for referen ce
torque is correct. Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corroded connectors. Verify the presence of a retarder on J1939 link. Verify
that the mess age is being transm itted. Verify th at the data for referen ce
torque is correct. Verify the ECU conguration
Check for damaged or re versed J1 939 wiring. Check for damaged or corroded
connecto rs. Verif y the p resenc e of engin e ECU on J1939 link. Verify th e
presence of engine ECU on J1939 link. Verify the ECU conguration
16 Time‑out or invalid CAN data
–Electrionic Transmission
Controller 2‑ message required
for ESP
17 Time‑out or invalid data
for Conguration of Engine
Retarder ESP Message
18 Time‑out or invalid data for
Conguration of Exhaust
Retarder ESP Message
19 Time‑out or invalid data for
Conguration of Transmission
Retarder ESP Message
20 Invalid Data Transfer Time‑out
of Driveline Line Retarder ESP
Message
21 Invalid Data Transfer Time‑out
of Engine Retarder ESP
Message
22 Invalid Data Transfer Time‑out
of Exhaust Retarder ESP
Message
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded con nector s. Verif y the pres ence of tr ansmiss ion ECU on J1939
link. Verify that t he me ss age i s bein g tra nsmit te d. Verif y th at the dat a fo r
current gear is correct. Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corroded connectors. Verify the presence of a retarder on J1939 link. Verify
message is being transmitted. Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corroded connectors. Verify the presence of a retarder on J1939 link. Verify
message is being transmitted. Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded con nector s. Verif y the pres ence of Rad ar on J1939 link. Verify
the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corroded connectors. Verify the presence of a retarder on J1939 link. Verify
message is being transmitted. Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corroded connectors. Verify the presence of a retarder on J1939 link. Verify
message is being transmitted. Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corroded connectors. Verify the presence of a retarder on J1939 link. Verify
the presence of a retarder on J1939 link. Verify message is being transmitted.
Verify the ECU conguration
46
Page 47

Troubleshooting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
J1939 Bendix® ESP® system-related (continued)
1st. Blink
Code
26
2nd.
Blink
Code
23 Time‑out or invalid CAN data –
24 Time‑out or invalid CAN data –
25 Invalid Data Transfer Time‑out
26
27 Time‑out of message or invalid
Location:
J1939 ESP-related
Diagnostic Trouble Code
Description
CCVS ESP Message
TCO ESP Message
of Driveline Line Retarder
ESP Message
ESP‑related CM3 Time‑out
at J1939
data received from transmission
transfer information on J1939 ‑
message required for ESP
Repair Information
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corro ded conn ectors . Verify mes sage is be ing transmi tted on J1939 link.
Verify data for park brake, brake lamp switch, clutch and tachograph. Verify
the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corroded connectors. Verify message is being transmitted. Verify the ECU
conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corroded connectors. Verify the presence of a retarder on J1939 link. Verify
message is being transmitted. Verify the ECU conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corroded connectors. Verify message is being transmitted. Verify the ECU
conguration
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corroded connectors. Verify message is being transmitted. Verify the ECU
conguration
28 Time‑out or invalid CAN data –
Electronic Axle Controller 1ESP
Message
Check for dama ged or reversed J1939 wiring. Check for da maged or
corroded connectors. Verify message is being transmitted. Verify the ECU
conguration
47
Page 48

Troubleshooting: Connectors
Bendix® ESP® EC-80™ Controller Wire Harness Connector Part Numbers and Pin Assignments:
X1
CONNECTOR
X2
CONNECTORX3CONNECTORX4CONNECTOR
Bendix ESP EC-80 Controller
Controllers utilize four (4) AMP connectors for wire harness connections.
X1 Connector Pin Assignments
Vary by Part Number:
K098920R000
K098921R000
K103428R000
K103429R000
K105094R000
K105095R000
K105096R000
K105097R000
Pin Designation Designation Designation Designation Designation
1 Ground PMV SA Left HLD ABS ORS Pressure Sensor CMN
2 Trailer ABS Indicator HSA Disable Switch PMV SA Left REL
3 Ignition PMV SA Left CMN TCV CMN (SA) Load Sensor Signal
4 TCV CMN (DA) TCV (DA) PMV SA Right HLD PMV AA Left HLD
5 TCV (DA) TCV CMN (DA) WSS SA Left (+) TCV (SA)
ATC/ESP Indicator
6
and ATC ORS
7 J1939 High PMV SA Right REL PMV AA Left REL Sensor CAN Low
8 J1939 Low
9 SLS Input
10 WSS DA Right (+) PMV DA Right HLD PMV AA Right HLD Sensor CAN Common
11
ABS Indicator
12
Ground
13 J1939 High 2 PMV DA Right REL PMV AA Right REL
14 J1939 Low 2
15 ABS Indicator Interlock WSS DA Left (+) WSS AA Right (‑)
16 Battery PMV DA Left HLD
17 Retarder ATC/ESP Indicator PMV DA Left REL
18 ABS Dash Indicator
48
WSS DA Right (‑) WSS SA Right (+) WSS AA Left (+) Sensor CAN Supply
K105303R000
X2 Connector
Pin
Assignments
TPMS Ground PMV SA Right CMN PMV AA Left CMN PMV Trailer HLD
WSS SA Left (‑) Stop Lamp Output Sensor CAN High
TPMS
Communications
Reserved PMV DA Left CMN WSS AA Right (+) PMV Trailer CMN
ATC Disable S witch or
Diagnostic Switch
AWD vehicles only (AWD Transfer Case.)
*
PMV DA Right CMN PMV AA Right CMN PMV Trailer REL
WSS SA Right (‑) WSS AA Left (‑)
WSS DA Left (‑)
X3 Connector
Pin
Assignments
Diff. Lock Solenoid
X4 Connector Pin
Assignments
Brake Demand Primary
*
Circuit Signal
Pressure Sensor
Supply
Brake Demand
Secondary Circuit
Signal
Page 49

Troubleshooting: Wiring
ABS/ATC WIRING
Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Wiring Harness
Connectors
The Bendix® ESP® EC‑ 80™ Controller is designed to
interface with AMP MCP 2.8 connectors as referenced in
Figure 21. Follow all AMP requirements for t he repair of
wire harnesses.
All wire harness connectors must be properly seated. The
use of secondary locks is strongly advised.
All unused ECU connectors must be covered and
receive proper environmental protection.
ABS Wiring Requirements
As a matter of good practice and to ensure maximum
system robustness, always use the maximum size wire
supported by the wire harness connectors for battery,
ignition, ground, Pressure Modulator Valve (PMV), T raction
Control Valve (TCV), Interaxle Differential Lock and
indicator lamp circuits.
All sensor and serial communications circuits (J1 939) must
use twisted pair wir ing (one to two twists pe r inch). See
the appropriate Soci ety of Automotive Engineers (SAE)
document for additional details.
All wires mus t be carefully route d to avoid cont act
with rotating elements. Wiring must be properly
secured approximately every 6 to 12 inches using UV
stabilized, non-metallic hose clamps or bow-tie cable
ties to prevent pinching, binding or fraying.
It is recommended that wir es be routed straight out of a
connector for a minimum of three inc hes before the wi re
is allowed to bend.
Battery and g round wires should be kept to a minimum
length.
If convoluted tubing is used, its I.D. must match the size
of the wire bundle as closely as possible.
Wire harn ess len gths mu st be ca refully se lect ed for
the vehicle. Excess lengths of wire are not to be
wound to form coils, instead re-route, repair or replace
wire harness to avoid the possibilit y of electrical
interference and wire damage. Do not at tempt to
stretch harnesses that are too short, since mechanical
strain can result in wire breakage.
Bendix® SAS-60™ Sensors and YAS-60™, or
YAS-70X™, Sensor Wiring
If it is necessar y to replace the wir ing that connects t he
Bendix SAS‑ 60 or the Yaw Rate sensor to the ECU, it
is import ant to use the same wiring as that used by the
vehicle OEM.
49
Page 50

ABS Component Connector Wire Terminal
In‑Cab Controller Harness
17‑Way AMP
MCP 2.8 (X1)
1718091‑1
927768‑9
1 ‑ 2.5 mm
X1‑12 & 18
In‑Cab Controller Harness
18‑Way AMP
MCP 2.8 (X2)
8‑968974‑1
Wire Seal/
Plug
Terminal
Lock
Terminal Crimp Tool
N/A
2
967634
In‑Cab Controller Harness
15‑Way AMP
MCP 2.8 (X3)
8‑968973‑1
968874
2.5 ‑ 4 mm
2
Controller Harness
12‑Way AMP
MCP 2.8 (X4)
8‑968972‑1
968873
1.0 ‑ 2.5 mm
2
ABS Modulator Harness
AMP T wist‑Lock
(Bayonet)
ATC Modulator Harness
1‑967325‑2
929975‑1
AMP T wist‑Lock
(Bayonet)
1‑967325‑3
ABS Modulator Harness
3‑pin Packard
Metri‑Pack
280 Series
12040977
12077411
TE® Connectivity / AMP Terminal Removal Tool. Newark® Part
No. 78H0240. Manufacturer Part Number 1‑1579007‑6
12015323
N/A
N/A
12034145
539723‑2
539635‑1
12155975
Bendix® WS-24™ Wheel Speed Sensor Connectors
Packard® GT
150 series
Packard
Metripack 150.2
series
Deutsch
DTM06 series
Packard
Metripack 280
series (female)
Packard
Metripack 280
series (male)
®
Yaw Rate Sensor Wire Harness Connectors (4 contact):
Straight Connector: Schlemmer® 9800 351 (shown)
AMP® Connector 2‑967325‑1
ITT® Cannon® Connector 121583‑001
90 degree Connector: Schlemmer 9800 331
Brake Demand Sensor/Load Sensor
Wire Harness Connectors:
Metri‑Pack® (Packard) 1206 5287
Contact Pins:
Packard 1210 3881
Bendix® SAS-60™ Sensor Connectors:
Robert Bosch® 1 928 404 025,
Robert Bosch 1 928 498 001
One Meter Adapter to Connector:
Bendix 5015242 (shown)
Packard 12092162, pins 12064971
FIGURE 21 - BENDIX ESP® EC‑80™ CONTROLLER COMPONENT CONNECTORS
50
Deutsch DT04
series
Standard round
two pin
Yaw Rate Sensor Wire Harness
Contact Pin Terminals:
Schlemmer 7814 125
AMP 0‑962981‑1
ITT Cannon 031‑8717‑120
Page 51

WS-24™ Speed
Sensor
Troubleshooting: Wiring (Continued)
Speed Sensor
Mounting Block
100 Tooth (typical)
Speed Sensor
Exciter Ring
Mounting
Block
Brake Drum
Max. Gap
(Sensor to Exciter)
.015 Inches
WS-24™ Speed
Sensor
100 Tooth
Exciter
Ring
Hub Assembly
Air Disc Brake
Note: Ensure that the sensor wiring is
routed to avoid chang from moving
parts (including rotors and steering
components.)
FIGURE 22 - BENDIX® WS‑24™ WHEEL SPEED SENSOR INSTALLATION (S‑CAM AND AIR DISC BRAKE)
90° Speed
Sensors
Sensor
Clamping
Sleeve
Wheel Speed Sensor Wiring
Route sensor wiring coming o ut of the wheel ends away
from moving brake components. Sensor w ir in g nee ds to
be secured to the axle to prevent ex cess cable length and
wiring damage. It is required that cab le ties be installe d
to the sensor wire within 3 inches (76.2 mm) of the sensor
head to provide strain relief.
Following the axle, the sensor wires must be attached
along the length of the service brake hoses using cable ties
with ultraviolet protection and secured every 6 to 8 inches
(152 to 203 mm). Sufcient – but not excessive – cable
length must be provided to permit full suspension travel and
steering axle movement. Install wires so that they cannot
touch rotating elements such as w heels, brake discs or
drive shafts. Radiation protec tion may be necessar y in
the area of brake discs.
Bendix does not recomm e n d us in g standard tie‑wraps to
secure wiring har nes s es dire c t ly to r ubb er air line s. Thi s
may cause premature wiring failure from the pressure
exerted on the wiring when air pressure is applied through
the air line. Non‑metallic hose clamps or bow‑tie tie‑wraps
are preferred.
The use of grommets or other suitable protection is
required whenever the cable must pass throug h metallic
frame members.
All sensor wiring must utilize twisted pair wire, with
approximately one to two twists per inch.
It is recommended that wir es be routed straight out of a
connector for a minimum of three inc hes before the wi re
is allowed to bend.
Straight Speed
Sensors
51
Page 52

OP LAMP OUTPUT
SA
X4
X4
PMV_TR_REL
PMV_TR_CMN
PMV_TR_HLD
PS_SIG 1
PS_SIG 3
PS_SPL
PS_CMN
PS_SIG 2
CAN_SEN_SPL
CAN_SEN_CMN
CAN_SEN_HI
CAN_SEN_LO
X3
TCV_SA_CMN
TCV_SA
PMV_AL_REL
PMV_AL_CMN
PMV_AL_HLD
PMV_AR_REL
PMV_AR_CMN
PMV_AR_HLD
WSS_AL-
WSS_AL+
WSS_AR-
WSS_AR+
DIFF
ST
ABS ORS
X2
WSS_SL-
WSS_SL+
WSS_SR-
WSS_SR+
PMV_SL_REL
PMV_SL_CMN
PMV_SL_HLD
PMV_SR_REL
PMV_SR_CMN
PMV_SR_HLD
PMV_DL_REL
PMV_DL_CMN
PMV_DL_HLD
PMV_DR_REL
PMV_DR_CMN
PMV_DR_HLD
WSS_DL-
WSS_DL+
X1
WSS_DR-
WSS_DR+
SLS INPUT
ABS IND. GND
IND. INTERLOCK
ABS IND.
TRAILER ABS IND.
IGNITION
GROUND
RETARDER
BATTERY
J1939_HI
J1939_LO
J1587 A
J1587 B
9
12
6
2
3
4
1
5
11
10
8
7
X3
3
5
7
6
4
13
9
10
11 14
15
12
2
8
1
X2
8
5
14
11
3
12
476
17
12
16
9
10 13
15 18
X1
11
10
9
12
15
18
2
3
1
17
16
8
7
14
13
Troubleshooting: Wiring Schematic A
5
21
PMV
3
6
19
2 1
3
6
21
3
6
7
8
8
11
11
88 8 8
11
18
17
11
12
1010
7
13
DIFF
7 7
21
3
21
3
21
3
6 6 6
21
3
6
77
5A
11
30A
4
2
2
TRAILER
PRESSURE
SENSOR 1
(PRIMARY
DELIVERY)
YAW
RATE
AMP
CONNECTOR
PART NUMBER
NUMBER OF
CONTACTS
REF. NO.
SENSOR
STEERING
ANGLE
1718091-1
17 POLE
X1
SENSOR
8-968974-1
8-968973-1
15 POLE
18 POLE
X3
X2
STOP LAMP
RELAY
8-968972-1
X4 12 POLE
NOTES
1. RETARDER CONTROL VIA RELAY OR SAE J1939.
5 PRESSURE MODULATOR VALVE (PMV): BENDIX M-32, M-32QR, M-40X
6 PMV CONNECTOR TWIST-LOCK PACKARD
4 ATC ENGINE CONTROL PER SAE J1939.
2 DIAGNOSTICS PER SAE J1587 OR J1939.
3 DIAGNOSTIC BLINK CODE SWITCH (MOMENTARY SWITCH).
PRESSURE
SENSOR 3
(SUSPENSION)
PRESSURE
SENSOR 2
(SECONDARY
DELIVERY)
9
STEER
AXLE
TRACTION
CONTROL
VALVE
5
21
ADD
PMV
AXLE
LEFT
5
ADD
PMV
AXLE
RIGHT
WSS
ADD
AXLE
LEFT
WSS
LOCK
SOL
WSS
WSS
ADDITIONAL AXLE
ADD
AXLE
RIGHT
ABS
STEER
AXLE
LEFT
STEER
AXLE
RIGHT
STEER
AXLE
LEFT
PMV
WIRE HARNESS CONNECTORS
20
(ORS)
SWITCH
OFF-ROAD
STEER AXLE
STEER
AXLE
RIGHT
PMV
DRIVE
AXLE
LEFT
5 5 5
5
PMV
DRIVE
AXLE
RIGHT
PMV
DRIVE AXLE
WSS
DRIVE
AXLE
LEFT
WSS
DRIVE
AXLE
RIGHT
12
(OPTIONAL)
RETARDER RELAY
ABS DASH
INDICATOR
3
TRAILER ABS
5A
5A
DASH INDICATOR
5A
5A
STOP LAMP
(SLS)
STOP LAMP SWITCH
5A
+12V IGNITION
Use this page for the following
Electronic C ontrol Unit (ECU) part
numbers:
K098920R000
K098921R000
K103428R000
K103429R000
K105094R000
K105095R000
K105096R000
K105097R000
See next page for the alternate wiring
schematic for one other part number.
COMMON (CMN) PIN 2 PIN B
HOLD (HLD) PIN 3 PIN C
RELEASE (REL) PIN 1 PIN A
9 TRACTION CONTROL VALVE (TCV).
7 WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (WSS): BENDIX WS-24
8 WSS WIRING - 18 AWG (TWISTED PAIR REQUIRED).
+12V BATTERY
11 DOTTED LINES: SPECIAL FUNCTION (OPTIONS).
10 SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS - 18 AWG (TWISTED PA IR REQUIRED).
VEHICLE 6 X 4
12 BATTERY AND GROUND - 12 AWG
13 ALL WHEEL DRIVE VEHICLES ONLY. REQUIRES STOP LAMP INPUT (SEE NOTE 18 ).
16. THIS SYSTEM WIRING CONNECTION SCHEMATIC IS FOR AN EC-80 ECU DESIGNED AS A SERVICE REPLACEMENT FOR EC-60 ADVANCED.
ABS INDICATOR.
17 WHEN X1 IS DISCONNECTED FROM ECU, THE INTERLOCK SHORTS THE INDICATOR CIRCUIT TO GROUND, ILLUMINATING THE
18 STOP LAMP SWITCH INPUT REQUIRED FOR ATC AND ALL-WHEEL DRIVE VEHICLES.
15. PRODUCT SPECIFICATION: Y119679
14. ALL WIRE IS CONDUCTOR CROSS-SECTION OF 16 AWG, UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED.
R
R
19 CAN SENSOR WIRING - 18 AWG (FOUR CONDUCTOR TWISTED WIRE REQUIRED).
20 MOMENTARY SWITCH.
MAY BE PROVIDED VIA HARDWARE INPUT OR J1939 COMMUNICATION.
21 ADDITIONAL AXLE WSS AND PMV INSTALLED PER EC-80 CONFIGURATION (6S/4M, 6S/6M).
L
AA
ADDITIONAL
DA
DRIVE
STEER
L
52
TCV_DA_CMN
TCV_DA
54
ESP/ATC IND.
6
18
TRAC
CONTROL
VALVE
(TCV)
9
20
ATC
ESP/ATC
DASH
INDICATOR
(ORS)
SWITCH
OFF-ROAD
FIGURE 23 - STANDARD WIRING SCHEMATIC FOR ECUs LISTED ABOVE
Page 53

Troubleshooting: Wiring Schematic B (Alternate)
SW
SA
X4
X4
PMV_TR_REL
9
PMV_TR_CMN
12
PMV_TR_HLD
6
PS_SIG 1
2
PS_SIG 3
PS_SPL
PS_CMN
PS_SIG 2
CAN_SEN_SPL
CAN_SEN_CMN
CAN_SEN_HI
CAN_SEN_LO
X3
TCV_SA_CMN
TCV_SA
PMV_AL_REL
PMV_AL_CMN
PMV_AL_HLD
PMV_AR_REL
PMV_AR_CMN
PMV_AR_HLD
WSS_AL-
WSS_AL+
WSS_AR-
WSS_AR+
HSA SOLENOID
I/0
TPMS PWR
X2
WSS_SL-
WSS_SL+
WSS_SR-
WSS_SR+
PMV_SL_REL
PMV_SL_CMN
PMV_SL_HLD
PMV_SR_REL
PMV_SR_CMN
PMV_SR_HLD
PMV_DL_REL
PMV_DL_CMN
PMV_DL_HLD
PMV_DR_REL
PMV_DR_CMN
PMV_DR_HLD
WSS_DL-
WSS_DL+
X1
WSS_DR-
WSS_DR+
TPMS COMM
NOT CONNECTED
IND. INTERLOCK
ATC DIS OR DIAG
HSA DISABLE
IGNITION
GROUND
ATC IND
BATTERY
J1939_HI
J1939_LO
CAN LO 2
CAN HI 2
3
4
1
5
11
10
8
7
X3
3
5
7
6
4
13
9
10
11 14
15
12
2
8
1
X2
8
5
14
11
3
12
476
17
12
16
9
10 13
15 18
X1
11
10
9
12
15
18
2
3
1
17
16
8
7
14
13
16
16
17
12
ATC DISABLEORDIAGNOSTIC
8
8
11
88 8 8
SWITCH
30A
1010
5
21
PMV
3
6
TRAILER
Use the wiring schematic on this
page for the following Electronic
Control Unit (ECU) part number:
PRESSURE
SENSOR 1
(PRIMARY
PRESSURE
SENSOR 3
DELIVERY)
(SUSPENSION)
YAW
RATE
SENSOR
K105303R000
See the previous page for a
second list of ECU part numbers.
PRESSURE
SENSOR 2
(SECONDARY
DELIVERY)
If your ECU part numbe r does
not appear on eit her list , pleas e
19
9
STEER
AXLE
TRACTION
CONTROL
VALVE
5
2 1
3
6
5
21
3
6
7
7
HSA
SOL
7 7
21
3
21
3
21
3
6 6 6
5 5 5
21
3
6
5
77
3
ATC
MUD
& SNOW
3
HSA
SWITCH
DISABLE
ATC
LAMP
4
2
20
ADD
PMV
AXLE
LEFT
ADD
PMV
AXLE
RIGHT
WSS
ADD
AXLE
LEFT
WSS
WSS
WSS
ADDITIONAL AXLE
ADD
AXLE
RIGHT
STEER
AXLE
LEFT
STEER
AXLE
RIGHT
STEER
AXLE
LEFT
PMV
WIRE HARNESS CONNECTORS
AMP
CONNECTOR
PART NUMBER
NUMBER OF
CONTACTS
REF. NO.
8-968974-1
1718091-1
18 POLE
17 POLE
X2
X1
8-968973-1
8-968972-1
15 POLE
X3
X4 12 POLE
STEER AXLE
STEER
AXLE
RIGHT
PMV
COMMON (CMN) PIN 2 PIN B
HOLD (HLD) PIN 3 PIN C
NOTES:
1. RETARDER CONTROL VIA SAE J1939.
2 DIAGNOSTICS VIA SAE J1939.
3 MOMENTARY SWITCH.
DRIVE
AXLE
LEFT
PMV
DRIVE
AXLE
RIGHT
PMV
WSS
WSS
DRIVE AXLE
DRIVE
AXLE
LEFT
AXLE
DRIVE
RIGHT
HSA
LAMP
5A
12
4 ATC ENGINE CONTROL PER SAE J1939.
+12V IGNITION
RELEASE (REL) PIN 1 PIN A
7 WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (WSS): BENDIX WS-24.
5 PRESSURE MODULATOR VALVE (PMV): BENDIX M-32, M-32QR, M-40X.
6 PMV CONNECTOR TWIST-LOCK PACKARD
8 WSS WIRING - 18 AWG (TWISTED PAIR REQUIRED).
call 1‑800‑AIR‑BRAKE, option 2,
and speak with the Tech Team.
9 TRACTION CONTROL VALVE (TCV).
11 DOTTED LINES: SPECIAL FUNCTION (OPTIONS).
12 BATTERY AND GROUND - 12 AWG.
10 SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS - 18 AWG (TWISTED PAIR REQUIRED).
+12V BATTERY
16 TPMS WIRING - 3 WIRES.
13. ALL WHEEL DRIVE VEHICLES ONLY. REQUIRES STOP LAMP INPUT (SEE NOTE 18 ).
15. PRODUCT SPECIFICATION: Y119679 AND Y173755.
14. ALL WIRE IS CONDUCTOR CROSS-SECTION OF 16 AWG, UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED.
R
VEHICLE 6 X 4
R
17. WHEN X1 IS DISCONNECTED FROM ECU, BODY CONTROLLER NEEDS TO ILLUMINATE ABS INDICATOR.
19 CAN SENSOR WIRING - 18 AWG (FOUR CONDUCTOR TWISTED WIRE REQUIRED).
18 STOP LAMP SWITCH INPUT REQUIRED FOR ATC AND ALL-WHEEL DRIVE VEHICLES.
IS PROVIDED VIA STOP LAMP SWITCH VIA J1939 COMMUNICATION.
20 ADDITIONAL AXLE WSS AND PMV INSTALLED PER EC-80 CONFIGURATION (6S/4M, 6S/6M).
21. ABS/ESP/TRAILER LAMP VIA J1939. 22. NO ABS OFF ROAD SWITCH. ABS OFF ROAD ACTIVATED WITH ATC MUD AND SNOW.
L
AA
ADDITIONAL
DA
DRIVE
STEER
L
TCV_DA_CMN
TCV_DA
54
TPMS GND
6
18
16
TRAC
CONTROL
VALVE
(TCV)
9
FIGURE 24 - CAB WIRING SCHEMATIC FOR ECU LISTED ABOVE
53
Page 54

GLOSSARY
ABS — Antilock Brake System.
ABS Event — Impend ing whee l loc k situati on that c auses t he
ABS Controller to activate the modulator valve(s).
ABS Indicator Lamp — An amber lamp whi ch indicates the
operating status of an antilock system. When the indicator lamp
is on, ABS is dis abled and t he vehicl e rever ts to nor mal brake
operation.
Air Gap — Distance between the Sensor and tone ring.
ASR — Auto matic Slip Re gulation. A nother na me for trac tion
control.
ATC — Automatic Traction Control. An additional ABS function
in which engine t orque is controlled and br akes are applied
differentially to enhance vehicle traction.
ATC/ESP Lamp — A lamp that indicates when stability functions,
including trac tion contro l, roll stability pr ogram or yaw control
are operating.
Channel — A controlled wheel site.
CAN — Controlle r Area N etwor k. J1939 is an SAE ver sion of
the CAN link.
Clear Cod es — Syste m to erase h istor ic al Diag nosti c Trouble
Codes (DTCs) from the ECU, from either the Diagnostic Switch
or from a hand ‑held diagnosti c tool (only repaired DTCs may
be cleared).
Conguration — The primary objective is to identify a “normal”
set of sensors and m odulators fo r the Electro nic Control U nit,
so that it will identify future missing sensors and modulators.
Diagnostic Connector — Diagnostic receptacle in vehicle cab
for connection of J1939 hand‑held or PC based test equipment.
The tester can initiate test sequences, and can also read system
parameters.
Diagnostic Switch — A switch used to activate blinks codes.
Differential Braking — Application of brake force to a spinning
wheel so that tor que can be applied to wh eels which are not
slipping.
ECU — Electronic Control Unit.
ESP — Electron ic Stability Program. Full stability functi on that
includes RSP & YC subfunctions.
Diagnostic Tr ouble Code — A condition that interferes with the
generation or transmission of response or control signals in the
vehicle's ABS system t hat c oul d lead to t he fu nct io nalit y of t he
ABS system becoming inoperable in whole or in part.
FMVSS-121 — Federal Mot or Vehicle Safety Standar d which
regulates air brake systems.
Hill Start (or “ Hill Start Assist”) HS/HSA — This feature
interfaces between the transmission and braking system to help
the driver prevent the vehicle from rolling downhill when moving
up a steep incline from a stationary position.
IR — Independent Regulat ion. A control method in whi ch a
wheel is cont rolled at optimum slip, a point w here retardation
and stabilit y are maximized. The br ake pressure that is best
for the wheel in question is directed individually into each brake
chamber.
J1939 — A high speed data link used for communications
between the ABS ECU engine, transmission and retarders.
LAS — Lateral Acceleration Sensor.
MIR — Mo d i ed In dependent Reg u l a t i o n . A method of controlling
the opposite sides of a steer axle during ABS operation so that
torque steer and stopping distance are minimized.
PLC — Power Line Carrier. The serial communication protocol
used to commun icate with the trailer over the bl ue full time
power wire.
PMV — Pres sure M odu lator Valve. An air valve wh ic h is use d
to vent or block air to the b rake chambers to limit or reduce
brake torque.
QR — Quick Release. Quick release valves allow faster release
of air from the br ake chamber af ter a brake application. To
balance the system, qu i ck release valves have hold off sprin g s
that produce higher crack pressures (when the valves open).
Relay Valve — Increase s the a ppli cat ion s peed o f the se r vi ce
brake. Installed near b rakes wi th lar ger air c ham ber s (typ e 24
or 30). The treadle valve ac tivates the relay valve with a n air
signal. The relay valve then connects its supply port to its delivery
ports. Equal length air hose must connect the delivery ports of
the relay valve to the brake chambers.
Retard er Relay — A r elay which i s used to disab le a retard er
when ABS is triggered.
RSP
— Roll Stabilit y Program. An all ‑axle A BS solution th at
helps reduce veh icle speed by applying al l vehicle brakes as
needed, reducing the tendency to roll over.
SAS — Steering Angle Sensor.
Sensor Clamping Sleeve — A beryllium c o pp er sl eeve whi c h
has ngers cut into it. It is pre s sed bet wee n an ABS se nsor and
mounting hole to hold the sensor in place.
Stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes — A DTC that occurr ed i n
the past.
TCS — T raction Control System, another name for AT C or ASR.
TCV — Traction Control Valve.
Tone Ring — A ring that is usually pressed into a wheel hub that
has a series of teeth (usually 100) and provides actuation for the
speed sensor. Note maximum run out is .008.
YC — Y aw Control. Helps stabilize rotational dynamics of vehicle.
YRS — Yaw Rate Sensor.
54
Page 55

APPENDIX A: TROUBLESHOOTING A 12-7 BLINK CODE, EQUIVALENT TO A
(SID-93 FMI-4) (SPN-0802 FMI-04) DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC)
Bendix® EC-80™ ESP® Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
1) Remove the X1, X2, X3 and X4 connectors from the ECU.
2) Using X1‑1 as the ground connection, check for resistance
for the entire X2 connector. There should be no resistance
to ground found. Please ll out worksheet on this page.
3) Using X1‑1 as the ground connection, check for resistance
for X1‑4 and X1‑5. There should be no resistance to ground.
4) Using X1‑1 as the ground connection, check for resistance for
X3‑4, X3‑6, X3‑7, X3‑9, X3‑10, X3‑13, X3‑3 and X3‑5. There
should be no resistance to ground. (Even if the vehicle is not
congured for 6S/6M).
5) Using X1‑1 as the ground connection, check for resistance
for X4‑6, X4‑9 and X4‑12. There should be no resistance to
ground.
6) Troubleshoot any pin that has resistance to ground. If no
issues are found continue to step 7.
7) Reconnect the X1 connector only and apply IGN power to the
ECU and using the DTC screen of Bendix® ACom® Diagnostic
Software, clear all DTCs. Re‑check for any DTCs. If the
12‑7 DTC is still present, the problem is the Traction Solenoid
Wiring or Solenoid.
8) If the 12‑7 DTC does not reappear , remove power and connect
the X2 connector, reapply power, then clear all DTCs. If the
12‑7 DTC is no longer present, connect the X3 connector
and clear all DTCs.
9) If at this point the 12‑7 DTC is not present, the problem is
with the X4 connector.
For Peterbilt® & Kenworth® Trucks Only:
Clear all DTCs. If the 12‑7 DTC reappears, the issue is
10)
on the X4 connector. Otherwise, proceed to the next step.
11) Disconnect all modulators and the traction solenoid.
Clear all DTCs. If the DTC does not reappear, connect
one modulator and Traction Solenoid at a time, until the
DTC reappears. Otherwise, continue to the next step.
12) Make sure all modulators and the traction solenoid are
connected. Disconnect the ABS bulkhead connector at
the engine (top‑left side) and remove Pins 1, 2, 11 &12.
Reconnect the connector and apply IGN power to the
ECU. Using Bendix ACom Diagnostics, clear all DTCs.
If the 12‑7 DTC returns, the problem is either the wiring
harness inside the cab or the ECU.
Record Resistances
Below:
X1-1 for ground point
X1 Pin Resistance
X1‑4
X1‑5
X2 Pin Resistance
X2‑1
X2‑2
X2‑3
X2‑4
X2‑5
X2‑6
X2‑7
X2‑8
X2‑9
X2‑10
X2‑11
X2‑12
X2‑13
X2‑14
X2‑15
X2‑16
X2‑17
X2‑18
X3 Pin Resistance
X3‑4
X3‑5
X3‑6
X3‑7
X3‑8
X3‑9
X3‑10
X3‑13
4
X4 Pin Resistance
X4‑6
X4‑9
X4‑12
55
Page 56

APPENDIX B: J1939 SPN AND FMI CODES AND THEIR BENDIX® BLINK CODE EQUIVALENTS
Bendix
SPN
(J1939)
168 3 6 2 Battery Voltage Too High ON ON
168 4 6 1 Battery Voltage Too Low ON ON
564 3 25 3 Differential Lock Solenoid Shorted To Voltage ON ON
564 4 25 2 Differential Lock Solenoid Shorted To Ground ON
564 5 25 1 Differential Lock Solenoid Open ON ‑
564 13 25 7 Output Conguration Error ‑ Differential ON ‑
575 14 12 17
576 14 12 3 ATC or ESP Disabled or Dynamometer Test Mode Active ON
614 3 12 32
614 3 25 6 I/O 3 Shorted to Voltage
614 4 25 5 I/O 3 Shorted to Ground
614 5 25 4 I/O 3 Open Circuit
614 13 25 8
615 14 12 19 Maximum Number of Pressure Modulator Valve (PMV) Cycles Exceeded
615 14 12 20 Maximum Number of Traction Control Valve (TCV) Cycles Exceeded ‑ ‑
614 3 12 32
614 3 25 6 I/O 3 Shorted to Voltage
614 4 25 5 I/O 3 Shorted to Ground
614 5 25 4 I/O 3 Open Circuit
614 13 25 8
615 14 12 19 Maximum Number of PMV Cycles Exceeded
615 14 12 20 Maximum Number of TCV Cycles Exceeded ‑ ‑
629 2 13 4 ECU DTC (2678C) ON ON
629 2 13 5 ECU DTC (1C) ON ON
629 2 13 7 Conguration Mismatch ON ON
629 2 13 17 ECU DTC (C8C) ON ON
629 8 12 29 Air System / Mechanical Component ON ON
629 12 13 3 ECU DTC (10) ON ON
629 12 13 14 ECU DTC (C6) ON ON
629 12 13 15 ECU DTC (CF) ON ON
629 12 13 16 ECU DTC (C0) ON ON
629 14 12 28 Air System / Mechanical Component ON ON
629 14 12 30
FMI
(J1939)
‑ 1 1 No DTCs ‑ ‑
®
Blink Code
Equivalent(s)
(1st
Digit)
Digit)
(2nd
Lamp Status
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Description
ABS
Power Supply DTCs
Miscellaneous DTCs
ABS Disabled Due To Special Mode Or Off‑Road ABS Active.
Note: The ABS warning lamp will be ashing indicating the is in ABS off-
road mode
I/O 2 or 3 Shorted High (EC‑80 ATC) OR
I/O 2 or 3 Shorted High or Stop Lamp Output Error (ESP EC‑80)
Output Conguration Error ‑ I/O 3 ‑ ON
I/O 2 or 3 Shorted High (EC‑80 ATC) OR
I/O 2 or 3 Shorted High or Stop Lamp Output Error (ESP EC‑80)
Output Conguration Error ‑ I/O 3 ‑ ON
ECU DTCs (Also see other 629 codes)
Miscellaneous DTCs
ECU DTCs (Also see other 629 codes)
Miscellaneous DTCs
ESP Disabled Due to Off‑Road Mode ‑ ON
ATC/
ESP
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ‑
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ‑
‑
‑
56
Page 57

APPENDIX B: J1939 SPN AND FMI CODES AND THEIR BENDIX® BLINK CODE EQUIVALENTS
®
Bendix
SPN
(J1939)
629 14 13 1 ECU DTC (5FC) ON ON
630 12 13 6 ECU DTC(6CD) ON ON
630 12 13 10 ECU DTC (5F3) ON ON
630 12 13 19 ECU DTC (63)
630 12 13 20 ECU DTC (6E) ON ON
630 12 13 28 ECU DTC (7CD) ON ON
630 13 13 2 ECU DTC (5CD) ON ON
630 13 13 8 ECU DTC (56) ON ON
630 13 13 9 ECU DTC (CA3C) ON ON
630 13 13 18 ECU DTC (CC) ON ON
630 13 13 21 ECU DTC (6C) ON ON
630 13 13 22 ECU DTC (63C) ON ON
630 13 13 25 VIN Mismatch
630 13 13 26 Valve Conguration Mismatch
630 13 13 29 ECU DTC (5D) ON ON
630 14 13 13 Conguration Mismatch ON ON
639 2 11 2 J1939 Electronic Retarder Time‑out or Invalid Signal ON ON
639 2 11 3 J1939 Electronic Engine Controller 1 Time‑out or Invalid Signal
639 2 11 4 J1939 Electronic Engine Controller 2 Time‑out or Invalid Signal
639 2 11 5 J1939 AIR Message Time‑out or Invalid Signal
639 2 11 6 ESP J1939 CAN Message Time‑out
639 2 11 7 Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data for ETC7/VP15
639 2 11 8 Time‑out or Invalid Data on XBR ‑ ‑
639 2 11 10 J1939 Electronic Transmission Controller 1 Time‑out or Invalid Signal ON ‑
639 2 11 11 AUXIO CAN Message Time‑out ‑ ‑
639 2 11 12 J1939 Hill Start Aid Switch Signal Not Available ‑ HSA LAMP ON ‑ ‑
639 2 11 14 J1939 CAN Message Related to ESP is Incomplete ‑ ON
639 2 11 15 J1939 Electronic Engine Controller 3 Time‑out or Invalid Signal
639 2 11 16 J1939 Electronic Transmission Controller 2 Time‑out
639 2 11 20 J1939 EAC1 Time‑out or Invalid Signal
639 2 11 21 CAN Message CGW_C1 Time‑out or Invalid Signal
639 2 11 22 CAN Message ASC1_CLCS Time‑out or Invalid Signal
639 2 11 23 J1939 CCVS Time‑out or Invalid Signal
639 2 11 24 J1939 TCO(Tachograph) Time‑out
639 2 11 28
639 2 26 1 J1939 CAN Time‑out of ESP Message
639 2 26 2 Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – CCVS 2 ESP Message
639 2 26 3
639 2 26 4 Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – EEC2 ESP Message
639 2 26 5 Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – Driveline Line Retarder ESP Message
639 2 26 6 Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – Engine Retarder ESP Message
639 2 26 7 Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – Exhaust Retarder ESP Message
639 2 26 8 Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – PROP XBR ESP Message
639 2 26 9 Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – Transmission Retarder ESP Message
639 2 26 10
639 2 26 11 Time‑out or Invalid AUX I/O – ESP Message
639 2 26 12
FMI
(J1939)
Blink Code
Equivalent(s)
(1st
Digit)
Digit)
(2nd
Lamp Status
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Description
ABS
ECU DTCs (Also see other 629 codes)
J1939 DTCs
J1939 Proprietary XBR Message Out‑of‑Range ‑ ON
Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – Electronic Engine Controller 1 ESP
Message
Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – Electronic Transmission Controller 1 ESP
Message
Time‑out or Invalid Data for Conguration of Electronic Engine Controller 1
ESP Message
ATC/
ESP
‑ ‑
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ‑
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
57
Page 58

APPENDIX B: J1939 SPN AND FMI CODES AND THEIR BENDIX® BLINK CODE EQUIVALENTS
®
Bendix
SPN
(J1939)
639 2 26 13 Invalid Data Transfer Time‑out of EC1 ESP Message
639 2 26 14
639 2 26 15 Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – Electronic Engine Controller ESP Message
639 2 26 16
639 2 26 17 Time‑out or Invalid Data for Conguration of Engine Retarder ESP Message
639 2 26 18
639 2 26 19
639 2 26 20 Invalid Data Transfer Time‑out of Driveline Line Retarder ESP Message
639 2 26 21 Invalid Data Transfer Time‑out of Engine Retarder ESP Message
639 2 26 22 Invalid Data Transfer Time‑out of Exhaust Retarder ESP Message
639 2 26 23 Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – CCVS ESP Message
639 2 26 24 Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – TCO ESP Message
639 2 26 25 Invalid Data Transfer Time‑out of Driveline Line Retarder ESP Message
639 2 26 26 ESP Related CM3 Time‑out at J1939
639 2 26 27
639 2 26 28 Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – Electronic Axle Controller 1ESP Message
639 5 11 29 J1939 CAN Messages Are Not Being Transmitted / Received ON ON
639 12 11 1 J1939 Serial Link ON ON
789 1 2 1 Steer Axle Left WSS Excessive Air Gap ON ON
789 2 2 3 Steer Axle Left WSS Open or Shorted ON ON
789 7 2 5 Steer Axle Left WSS Wheel End ON ON
789 8 2 6 Steer Axle Left Erratic Sensor Signal ON ON
789 9 2 2 Steer Axle Left WSS Signal Low at Drive Off ON ON
789 10 2 4 Steer Axle Left WSS Loss of Sensor Signal ON ON
789 13 2 7 Steer Axle Left WSS Tire Size Calibration ON ON
790 1 3 1 Steer Axle Right WSS Excessive Air Gap ON ON
790 2 3 3 Steer Axle Right WSS Open or Shorted ON ON
790 7 3 5 Steer Axle Right WSS Wheel End ON ON
790 8 3 6 Steer Axle Right Erratic Sensor Signal ON ON
790 9 3 2 Steer Axle Right WSS Signal Low at Drive Off ON ON
790 10 3 4 Steer Axle Right WSS Loss of Sensor Signal ON ON
790 13 3 7 Steer Axle Right WSS Tire Size Calibration ON ON
791 1 4 1 Drive Axle Left WSS Excessive Air Gap ON ON
791 2 4 3 Drive Axle Left WSS Open or Shorted ON ON
791 7 4 5 Drive Axle Left WSS Wheel End ON
791 8 4 6 Drive Axle Left Erratic Sensor Signal ON ON
791 9 4 2 Drive Axle Left WSS Signal Low at Drive Off ON ON
791 10 4 4 Drive Axle Left WSS Loss of Sensor Signal ON ON
791 13 4 7 Drive Axle Left Tire Size Calibration ON ON
792 1 5 1 Drive Axle Right WSS Excessive Air Gap ON ON
792 2 5 3 Drive Axle Right WSS Open or Shorted ON ON
792 7 5 5 Drive Axle Right WSS Wheel End ON ON
792 8 5 6 Drive Axle Right Erratic Sensor Signal ON ON
792 9 5 2 Drive Axle Right WSS Signal Low at Drive Off ON ON
792 10 5 4 Drive Axle Right WSS Loss of Sensor Signal ON ON
792 13 5 7 Drive Axle Right Tire Size Calibration ON ON
793 1 14 1 Additional Axle Left WSS Excessive Air Gap ON ON
FMI
(J1939)
58
Blink Code
Equivalent(s)
(1st
Digit)
Digit)
(2nd
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Description
Time‑out or Invalid Data for Conguration of Driveline Line Retarder ESP
Message
Time‑out or Invalid CAN Data – Electronic Transmission Controller 2‑
Message Required for ESP
Time‑out or Invalid Data for Conguration of Exhaust Retarder ESP
Message
Time‑out or Invalid Data for Conguration of Transmission Retarder ESP Message
Time‑out of message or Invalid Data Received from Transmission Transfer
information on J1939 ‑ Message Required for ESP
Wheel Speed Sensor DTCs
Lamp Status
ABS
ATC/
ESP
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
ON
Page 59

APPENDIX B: J1939 SPN AND FMI CODES AND THEIR BENDIX® BLINK CODE EQUIVALENTS
®
Bendix
SPN
(J1939)
793 2 14 3 Additional Axle Left WSS Open or Shorted ON ON
793 7 14 5 Additional Axle Left WSS Wheel End ON ON
793 8 14 6 Additional Axle Left Erratic Sensor Signal ON ON
793 9 14 2 Additional Axle Left WSS Signal Low at Drive Off ON ON
793 10 14 4 Additional Axle Left WSS Loss of Sensor Signal ON ON
793 13 14 7 Additional Axle Left Tire Size Calibration ON ON
794 1 15 1 Additional Axle Right WSS Excessive Air Gap ON ON
794 2 15 3 Additional Axle Right WSS Open or Shorted ON ON
794 7 15 5 Additional Axle Right WSS Wheel End ON ON
794 8 15 6 Additional Axle Right Erratic Sensor Signal ON ON
794 9 15 2 Additional Axle Right WSS Signal Low at Drive Off ON ON
794 10 15 4 Additional Axle Right WSS Loss of Sensor Signal ON ON
794 13 15 14 Additional Axle Right Tire Size Calibration ON ON
795 5 7 7 Steer Axle Left PMV Common Open Circuit ON ON
795 13 7 8 Steer Axle Left PMV Conguration Error ON ON
796 5 8 7 Steer Axle Right PMV Common Open ON ON
796
797 5 9 7 Drive Axle Left PMV Common Open Circuit ON ON
797 13 9 8 Drive Axle Left PMV Conguration Error ON ON
798 5 10 7 Drive Axle Right PMV Common Open Circuit ON ON
798 13 10 8 Drive Axle Right PMV Conguration Error ON ON
799 5 16 7 AA Left PMV Common Open Circuit ON ON
799 13 16 8 AA Left PMV Conguration Error ON ON
800 5 17 7 Additional Axle Right PMV Common Open Circuit ON ON
800 13 17 8 AA Right PMV Conguration Error ON ON
801 2 12 4 Retarder Relay Open Circuit or Shorted to Ground ON
801 3 12 5 Retarder Relay Open Circuit or Shorted to Voltage ON ‑
802 3 12 8 PMV Common Shorted to Voltage ON ON
802 4 12 7 PMV Commons Shorted to Ground ON ON
802 12 13 11 ECU DTC (F1A) ON ON
802 12 13 12 ECU DTC (F14) ON
805 14 12 9 ATC Disabled to Prevent Brake Fade - -
806 3 18 2 TCV DA Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
806 4 18 1 TCV DA Solenoid Shorted to Ground
806 5 18 3 TCV DA Solenoid Open Circuit
806 13 18 4 TCV DA Valve Conguration Error ON ON
807 3 19 2 TCV SA Solenoid Shorted to Voltage
807 4 19 1 TCV SA Solenoid Shorted to Ground
807 5 19 3 TCV SA Solenoid Open Circuit ON ON
807 13 19 4 TCV SA Valve Conguration Error ON ON
810 7 12 11 Wheel Speed Sensors Reversed on an Axle ON ON
811 2 12 6 ABS Dash Indicator Circuit DTC ON
811 13 12 38
815 13 14 10 Additional Axle WSS Conguration Error ON ON
FMI
(J1939)
13 8 8 Steer Axle Right PMV Conguration Error ON ON
Blink Code
Equivalent(s)
(1st
Digit)
Digit)
(2nd
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Description
Pressure Modulator Valve (PMV) DTCs
Miscellaneous DTCs
Pressure Modulator Valve (PMV) DTCs
Miscellaneous DTCs
Traction Control Valve (TCV) DTCs
Miscellaneous DTCs
Warning Lamp Ground Pin Connected to GND in Conict with Conguration
Settings
Lamp Status
ABS
ATC/
ESP
‑
‑
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑
ON ‑
59
Page 60

APPENDIX B: J1939 SPN AND FMI CODES AND THEIR BENDIX® BLINK CODE EQUIVALENTS
®
Bendix
SPN
(J1939)
932 3 7 5 Steer Axle Left PMV Hold Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
932 4 7 4 Steer Axle Left PMV Hold Solenoid Shorted to Ground ON ON
932 5 7 6 Steer Axle Left PMV Hold Solenoid Open Circuit ON ON
933 3 8 5 Steer Axle Right PMV Hold Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
933 4 8 4 Steer Axle Right PMV Hold Solenoid Shorted to Ground ON ON
933 5 8 6 Steer Axle Right PMV Hold Solenoid Open Circuit ON ON
934 3 9 5 Drive Axle Left PMV Hold Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
934 4 9 4 Drive Axle Left PMV Hold Solenoid Shorted to Ground ON ON
934 5 9 6 Drive Axle Left PMV Hold Solenoid Open Circuit ON ON
935 3 10 5 Drive Axle Right PMV Hold Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
935 4 10 4 Drive Axle Right PMV Hold Solenoid Shorted to Ground ON ON
935 5 10 6 Drive Axle Right PMV Hold Solenoid Open Circuit ON ON
936 3 16 5 AA Left PMV Hold Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
936 4 16 4 AA Left PMV Hold Solenoid Shorted to Ground ON ON
936 5 16 6 AA Left PMV Hold Solenoid Open Circuit ON ON
936 13 16 11
937 3 17 5 AA Right PMV Hold Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
937 4 17 4 AA Right PMV Hold Solenoid Shorted to Ground ON ON
937 5 17 6 AA Right PMV Hold Solenoid Open Circuit ON ON
937 13 17 11
938 3 7 2 Steer Axle Left PMV Release Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
938 4 7 1 Steer Axle Left PMV Release Solenoid Shorted to Ground ON ON
938 5 7 3 Steer Axle Left PMV Release Solenoid Open Circuit ON ON
939 3 8 2 Steer Axle Right PMV Release Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
939 4 8 1 Steer Axle Right PMV Release Solenoid Shorted to Ground ON ON
939 5 8 3 Steer Axle Right PMV Release Solenoid Open ON ON
940 3 9 2 Drive Axle Left PMV Release Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
940 4 9 1 Drive Axle Left PMV Release Solenoid Shorted to Ground ON ON
940 5 9 3 Drive Axle Left PMV Release Solenoid Open Circuit ON ON
941 3 10 2 Drive Axle Right PMV Release Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
941 4 10 1 Drive Axle Right PMV Release Solenoid Shorted to Ground ON ON
941 5 10 3 Drive Axle Right PMV Release Solenoid Open Circuit ON ON
942 3 16 2 AA Left PMV Release Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
942 4 16 1 AA Left PMV Release Solenoid Shorted to Ground ON ON
942 5 16 3 AA Left PMV Release Solenoid Open Circuit ON ON
942 13 16 10
943 3 17 2 AA Right PMV Release Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
943 4 17 1 AA Right PMV Release Solenoid Shorted to Ground ON ON
943 5 17 3 AA Right PMV Release Solenoid Open Circuit ON ON
943 13 17 10
1043 2 12 14 ESP sensor supply too high or too Low
1043 2 12 22
1045 2 12 2 Stop Light Switch Defective ON ON
1045 2 12 27 Brake Lamp Input Mismatch With Brake Lamp Output ON ON
1045 7 12 1 Stop Lamp Switch Not Detected
FMI
(J1939)
Blink Code
Equivalent(s)
(1st
Digit)
Digit)
(2nd
Lamp Status
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Description
ABS
Pressure Modulator Valve (PMV) DTCs
Output Conguration Error ‑ Left Additional Axle Hold ON ON
Output Conguration Error ‑ Additional Axle Right Hold ON ON
Output Conguration Error ‑ Additional Axle Left Release ON ON
Output Conguration Error ‑ Additional Axle Right Release ON ON
Miscellaneous DTCs
U‑ Bat too high or too Low for ESP sensor ‑ ON
ATC/
ESP
‑ ON
‑ ON
60
Page 61

APPENDIX B: J1939 SPN AND FMI CODES AND THEIR BENDIX® BLINK CODE EQUIVALENTS
®
Bendix
SPN
(J1939)
1056 3 20 2 Trailer PMV: Release Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
1056 3 20 5 Trailer PMV: hold Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ON
1056 4 20 1 Trailer PMV: Release Solenoid Shorted to Ground
1056 4 20 4 Trailer PMV: hold Solenoid Shorted to Ground
1056 5 20 3 Trailer PMV: Release Solenoid Open Circuit
1056 5 20 6 Trailer PMV: hold Solenoid Open Circuit
1056 5 20 7 Trailer PMV: Common Open Circuit
1056 13 20 8 Trailer PMV: Conguration Error
1059 2 24 3 PS3 Open or Shorted
1067 2 24 1 PS1 Open or Shorted
1067 3 24 5 PS Supply Voltage High Error
1067 4 24 7 PS Supply Voltage Low Error
1067 6 24 8 PS Supply Voltage Error
1067 7 24 6 PS Not Calibrated
1067 11 24 4
1067 14 24 9 Pressure Sensor not congured.
1068 2 24 2 PS2 Open or Shorted
1238 14 12 37 ATC disable by switch
1807 2 21 3 SAS Static Signal
1807 2 21 4 SAS Signal Out of Range
1807 2 21 5 SAS Signal Reversed
1807 2 21 7 SAS Gradient Error
1807 2 21 9 SAS Long Term Calibration Error
1807 2 21 10 SAS Plausibility Check (Ref YAW Rate)
1807 9 21 8 SAS CAN Time‑out
1807 12 21 6 SAS Signal Invalid
1807 13 21 1 SAS Not Calibrated
1807 13 21 2 SAS Calibration in Progress
1807 13 21 11 SAS Detected But Not Congured
1808 2 22 1 YRS Signal Out of Range
1808 2 22 2 YRS Reversed Signal
1808 2 22 3 YRS Invalid Signal
1808 2 22 4 YRS Gradient Error
1808 2 22 6 YRS Static BITE Error
1808 2 22 7 YRS Dynamic BITE Error
1808 2 22 8 YRS Fast Calibration Error
1808 2 22 9 YRS Static Calibration Error
1808 2 22 10 YRS Normal Calibration Error
1808 2 22 12 YRS Plausibility Check (Ref Yaw Rate)
1808 2 22 13 YRS Plausibility Error (Inside Model Based Limits)
1808 2 22 14 YRS Plausibility Error (Outside Model Based Limits)
1808 2 22 16 YRS Vibration Detected
1808 9 22 5 YRS CAN Time‑out
1808 13 22 17 YRS Detected But Not Congured
1808 14 23 7 Erratic ESP Signal
FMI
(J1939)
Blink Code
Equivalent(s)
(1st
Digit)
(2nd
Digit)
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Description
Pressure Modulator Valve (PMV) DTCs
Brake Demand/Load Sensor DTCs
(PS1/PS2 Plausibility Error) Brake Demand Primary and Secondary Circuit
Pressure Sensor Plausibility Error
Miscellaneous DTCs
Steering Angle Sensor DTCs
Yaw Rate Sensor DTCs
Lamp Status
ABS
ATC/
ESP
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ‑
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
61
Page 62

APPENDIX B: J1939 SPN AND FMI CODES AND THEIR BENDIX® BLINK CODE EQUIVALENTS
®
Bendix
SPN
(J1939)
1809 2 23 1 LAS Signal of Range
1809 2 23 3 LAS Static Calibration Error
1809 2 23 4 LAS Long Term Calibration Error
1809 2 23 5 LAS Plausibility Error (Inside Model Based Limits)
1809 2 23 6 LAS Plausibility Error (Outside Model Based Limits)
1809 13 22 15
1809 13 23 2 LAS Calibration in Progress
2011 31 11 26 ABS ECU CAN Address Conict ON
2051 31 11 27 TPMS ECU CAN Address Conict ‑ TPMS INDICATOR LAMP ON ‑ ‑
2622 2 12 24 HSA lamp Open Circuit or Shorted to GND ON
2622 3 12 26 HSA valve: Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ON ‑
2622 3 12 31 HSA lamp Shorted to Voltage ON ON
2622 4 12 25 HSA valve: Solenoid Shorted to Ground
2622 5 12 33 HSA valve: Solenoid Open Circuit ‑ ‑
2984 3 12 34 Bendix
2984 4 12 35 Bendix eTrac Solenoid Shorted to Ground
FMI
(J1939)
Blink Code
Equivalent(s)
(1st
Digit)
Digit)
(2nd
Lamp Status
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Description
ABS
Lateral Acceleration Sensor DTCs
YRS‑ SAS Signal Cross‑Check Incomplete ‑ ON
Miscellaneous
HS/HSA Hill Start Feature DTCs
Bendix® eTrac™ DTCs
®
eTrac™ Solenoid Shorted to Voltage ‑ ON
ATC/
ESP
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ON
‑ ‑
‑ ON
‑
‑
Figures Used
Figure 1 - Bendix® ESP® EC‑80™ Controller ....................................................................1
Figure 2 - Bendix® WS‑24™ Wheel Speed Sensors .........................................................3
Figure 3 - Example Of A Bendix® M‑40X™ Modulator .....................................................3
Figure 4 - Examples Of Steering Angle Sensors ............................................................3
Figure 5 - Yaw And Brake Demand/Load Sensors ..........................................................4
Figure 6 - Additional Valves Necessary For The Hill Start Feature .................................4
Figure 7 - Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller Features ..........................................................5
Figure 8 - Power Line Without PLC Signal ......................................................................5
Figure 9 - Power Line With PLC Signal ...........................................................................5
Figure 10 - Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller Indicator Lamp Behavior ...............................8
Figure 11 - Vehicle Orientation (Typical) .........................................................................9
Figure 12 - RSP Example ..............................................................................................12
Figure 13 - Yaw Control Example ..................................................................................12
Figure 14 - Typical Vehicle Diagnostic Connector Locations (J1939) ...........................21
Figure 15 - Example Of Blink Code Message ...............................................................21
Figure 16 - Diagnostic Modes........................................................................................22
Figure 17 - System Conguration Check .......................................................................23
Figure 18 - Bendix® ACom® Diagnostics .......................................................................24
Figure 19 - The Bendix® Remote Diagnostic Unit..........................................................24
Figure 20 - Diagnostic Trouble Codes ...........................................................................25
Figure 21 - Bendix EC‑80 Controller Component Connectors ......................................50
Figure 22 - WS‑24 Wheel Speed Sensor Installation (S‑Cam And Air Disc Brake) ......51
Figures 23 & 24 - Troubleshooting: Wiring Schematics ...........................................52‑53
62
Page 63

Full Table of Contents
Introduction .............................................................................................................................................1
Yaw Control (YC) ....................................................................................................................................3
Roll Stability Program (RSP) ..................................................................................................................3
Components ........................................................................................................................................3‑4
Bendix® eTrac™ Automated Air Suspension Transfer System ................................................................4
ECU Mounting ........................................................................................................................................4
Hardware Congurations .......................................................................................................................4
Bendix® ESP® EC‑80™ Controllers USE Power Line Carrier (PLC) .......................................................5
Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller Inputs ..................................................................................................... 5
Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller Outputs ...............................................................................................6‑7
Indicator Lamps And Power‑Up Sequence .........................................................................................8‑9
ABS Operation ..................................................................................................................................9‑10
ATC Operation ..................................................................................................................................11‑12
Bendix® ESP® ABS With Stability Control .......................................................................................12‑13
Important Safety Information About The Bendix ESP System ........................................................ 13‑14
Dynamometer Test Mode ..................................................................................................................... 14
Automatic Tire Size Calibration ............................................................................................................ 14
System Impact During Active Trouble Codes ....................................................................................... 15
ABS Partial Shutdown .......................................................................................................................... 15
System Reconguration .......................................................................................................................16
Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Reconguration .................................................................................... 16
Data Storage ........................................................................................................................................16
Troubleshooting ...........................................................................................................................17-53
Removal Of The Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller Assembly .................................................................. 17
Obtaining A New Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller ................................................................................. 17
Installing A New Bendix ESP EC‑80 Controller ................................................................................... 17
Steering Angle Sensor Maintenance .................................................................................................... 18
Steering Angle Sensor Calibration .......................................................................................................18
Removal Of The Yaw Rate/Lateral Acceleration Sensor ..................................................................... 19
Brake Demand Sensor Calibration ....................................................................................................... 20
Pressure Sensor Installation Requirements ......................................................................................... 20
Troubleshooting: Blink Codes and Diagnostic Modes .....................................................................21‑23
ECU Diagnostics .................................................................................................................................. 21
Blink Codes .......................................................................................................................................... 21
Diagnostic Modes .................................................................................................................................22
Troubleshooting: Using PC‑Based or Hand‑Held Diagnostic Tools ................................................24‑25
Bendix® ACom® Diagnostic Software ...................................................................................................24
Bendix® RDU™ (Remote Diagnostic Unit) ............................................................................................. 24
Active or Inactive Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Index and Troubleshooting Tests .............................26‑47
Troubleshooting: Connectors ...............................................................................................................48
Troubleshooting: Wiring ...................................................................................................................49‑53
Glossary ...............................................................................................................................................54
APPENDIX A: Troubleshooting a 12‑7 Blink Code DTC (SID‑93 FMI‑4) (SPN‑0802 FMI‑04) ...........55
APPENDIX B: J1939 SPN and FMI Codes and their Bendix Blink Code Equivalents ...................56‑62
63
Page 64

Log-on and Learn from the Best
On-line training that's available when you are 24/7/365.
Visit www.brake-school.com.
Any references in this document to AMP, DEUTSCH, ITT, METRI‑PACK, NEWARK, PACKARD, ROBERT BOSCH, SCHLEMMER, TE, and any other
company or trademark ar e solely for iden tic ation an d cross r eferen ce purposes. T he trad emarks a re the pr oper ty of the ir respective c ompan ies.
64
SD‑13‑4986 © 2015 Bendix Commercial Vehicle Systems LLC • All Rights Reserved • 1/15
 Loading...
Loading...