BENDIX SD-13-4983 User Manual

®
Bendix® EC-80™ ABS / ATC Controllers
Two Connectors
Are Used
SD-13-4983
Bendix® EC‑80™ ATC ControllerBendix® EC‑80™ ABS Controller
Three Connectors
Are Used
See SD‑13‑21021 for the Bendix® eTrac™ Automated Air
Suspension Transfer System
Bendix® EC‑80™ ESP(+) Controllers will be featured in
SD‑13‑4986.
INTRODUCTION
Bendix® EC‑80™ ABS and ATC controllers are members
of a family of electronic Antilock Braking System
(ABS) devices designed to help improve the braking
characteristics of air braked vehicles ‑ including heavy‑ and
medium‑duty buses, trucks, and tractors. ABS controllers
are also known as Electronic Control Units (ECUs).
Bendix® ABS uses wheel speed sensors, ABS modulator
valves, and an ECU to control either four or six wheels of
a vehicle. By monitoring individual wheel turning motion
during braking, and adjusting or pulsing the brake pressure
at each wheel, the Bendix EC‑80 controller is able to
optimize slip between the tire and the road surface. When
excessive wheel slip, or wheel lock‑up is detected, the
Bendix EC‑80 controller will activate the Pressure Modulator
Valves to simulate a driver pumping the brakes. However,
the Bendix EC‑80 controller is able to pump the brakes on
individual wheels (or pairs of wheels) independently, and
with greater speed and accuracy than a driver.
In addition to the ABS function, the ATC version of the
Bendix EC‑80 controller provides an Automatic Traction
Control (ATC) feature. Bendix® ATC can improve vehicle
traction during acceleration, plus lateral stability while
driving through curves. ATC utilizes Engine Torque
Limiting (ETL) where the ECU communicates with the
engine’s controller and/or Differential Braking (DB) where
individual wheel brake applications are used to improve
vehicle traction.
Bendix EC‑80 ATC controllers also have the capability to
provide a Hill Start Assist (HSA) feature. HSA interfaces
FIGURE 1 - BENDIX® EC‑80™ ABS AND ATC CONTROLLERS
The driver is always responsible for the control
and safe operation of the vehicle at all times. The
Bendix® ABS system does not replace the need
for a skilled, alert professional driver, reacting
appropriately and in a timely manner, and using
safe driving practices.
TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE
Introduction...................................1‑2
Component/ECU Mounting.......................2‑3
ABS Off‑Road Switch and Indicator Lamp Operation.....4
Bendix EC‑80 Controller Outputs ....................4
Indicator Lamp Behavior.........................5‑6
Power‑Up Sequence ...........................6‑7
ABS Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
ATC Operation ................................8‑9
Dynamometer Test Mode .......................9‑10
Automatic Tire Size Calibration ....................10
ABS Partial Shutdown ...........................10
System Reconguration .........................11
Blink Codes ...................................13
Diagnostic Modes...............................14
Using hand‑held or PC‑based diagnostics ............16
Diagnostic Trouble Code Index ....................18
Troubleshooting: Wiring .......................32‑37
Glossary ......................................39
Appendix: J1939 SPN and FMI Codes............40‑43
1

GENERAL SAFETY GUIDELINES
WARNING! PLEASE READ AND
FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS
TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH:
When working on or around a vehicle, the following
guidelines should be observed AT ALL TIMES:
▲ Park the vehicle on a level surface, apply the parking
brakes and always block the wheels. Always wear
personal protection equipment.
▲ Stop the engine and remove the ignition key when
working under or around the vehicle. When working
in the engine compartment, the engine should be shut
off and the ignition key should be removed. Where
circumstances require that the engine be in operation,
EXTREME CAUTION should be used to prevent personal
injury resulting from contact with moving, rotating,
leaking, heated or electrically-charged components.
▲ Do not attempt to install, remove, disassemble or
assemble a component until you have read, and
thoroughly understand, the recommended procedures.
Use only the proper tools and observe all precautions
pertaining to use of those tools.
▲ If the work is being performed on the vehicle’s air brake
system, or any auxiliary pressurized air systems, make
certain to drain the air pressure from all reservoirs
before beginning ANY work on the vehicle. If the vehicle
is equipped with a Bendix
Bendix
®
DRM™ dryer reservoir module, or a Bendix
AD-9si™ air dryer, be sure to drain the purge reservoir.
▲
Following the vehicle manufacturer’s recommended
procedures, deactivate the electrical system in a manner
that safely removes all electrical power from the vehicle
▲ Never exceed manufacturer’s recommended pressures.
▲ Never connect or disconnect a hose or line containing
pressure; it may whip. Never remove a component or
plug unless you are certain all system pressure has
been depleted.
▲ Use only genuine Bendix
components and kits. Replacement hardware, tubing,
hose, ttings, etc. must be of equivalent size, type
and strength as original equipment and be designed
speci cally for such applications and systems.
▲ Components with stripped threads or damaged parts
should be replaced rather than repaired. Do not
attempt repairs requiring machining or welding unless
speci cally stated and approved by the vehicle and
component manufacturer.
▲ Prior to returning the vehicle to service, make certain all
components and systems are restored to their proper
operating condition.
▲ For vehicles with Automatic Traction Control (ATC),
the ATC function must be disabled (ATC indicator
lamp should be ON) prior to performing any vehicle
maintenance where one or more wheels on a drive axle
are lifted off the ground and moving.
▲ The power MUST be temporarily disconnected
from the radar sensor whenever any tests USING A
DYNAMOMETER are conducted on a Bendix
Advanced
™
-equipped vehicle.
▲ You should consult the vehicle manufacturer's
operating and service manuals, and any related
literature, in conjunction with the Guidelines above.
2
®
AD-IS® air dryer system, a
®
brand replacement parts,
®
Wingman®
between the transmission and braking system to help the
driver prevent the vehicle from rolling backwards when
moving forward from a stationary position on steep inclines.
Bendix® EC‑80™ ATC controllers have a drag torque
control feature which reduces driven‑axle wheel slip (due
to driveline inertia) by communicating with the engine’s
controller and increasing the engine torque.
COMPONENTS/ECU MOUNTING
The Bendix EC‑80 controller’s ABS function uses:
• Bendix® WS‑24™ wheel speed sensors (4 or 6,
depending on ECU and conguration). Each sensor is
installed with a Bendix® Sensor Clamping Sleeve
• Bendix® M‑32™ / M‑32QR™ / M‑40X™ Pressure
Modulator Valves (4, 5, or 6 depending on ECU and
conguration)
• Dash‑mounted tractor ABS indicator lamp
• Service brake relay valve
• Dash‑mounted trailer ABS indicator lamp (used on all
towing vehicles manufactured after March 1, 2001)
• Optional blink code activation switch
• Optional ABS off‑road switch. (Off‑road feature is not
available on all ECUs ‑ See Chart 1.)
®
90° Speed
Sensors
.
FIGURE 2 - BENDIX® WS‑24™ WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
M-32QR
Modulator
™
Delivery
(Port 2)
Supply
(Port 1)
Electrical
Connector
Exhaust (Port 3)
™
M-40X
Modulators
FIGURE 3 - BENDIX® M‑32™ AND M‑40X™ MODULATORS
Sensor
Clamping
Sleeve
Straight Speed
Sensors
™
M-32
Modulator
The Automatic Traction Control (ATC) function uses the
following additional components:
• Traction control valve (may be integral to the service
brake relay valve or a stand‑alone device)
• Dash‑mounted ATC status/indicator lamp
• J1939 serial communication to engine control module
• Stop lamp switch input (may be provided using the ECU
hardware input or J1939)
• Optional ATC off‑road switch
The Hill Start (HSA) function uses the following components:
• Traction Control Valve (TCV)
• Dash‑mounted HSA status/indicator lamp
• Dash‑mounted Enable/Disable switch
• RV‑3 Pressure Reducing Valve
• DC‑4 Double Check valve
ECU MOUNTING
Bendix® EC‑80™ controllers are cab‑mounted. They are
not protected against moisture and must be mounted in
an environmentally protected location.
All wire harness connectors must be properly seated. The
use of secondary locks is strongly recommended.
Bendix EC-80 ATC Controllers
Bendix EC‑80 ATC controllers support applications up to
six sensor/six modulator (6S/6M) installations with ATC and
drag torque control. They can support HSA functions. All
12 volt models support Power Line Carrier (PLC). 24 volt
models do not support PLC. See Chart 1 for more details.
BENDIX EC-80 CONTROLLERS WITH PLC
Since March 1, 2001, all towing vehicles must have an
in‑cab trailer ABS indicator lamp. Trailers transmit the
status of the trailer ABS over the power line (the blue wire
of the J560 connector) to the tractor using a PLC signal.
See Figures 4 and 5.
FIGURE 4 - POWER LINE WITHOUT PLC SIGNAL
All unused ECU connectors must be covered and
receive any necessary protection from moisture, etc.
ECUs utilize connectors from the AMP MCP 2.8 product
family.
HARDWARE CONFIGURATIONS
Bendix® EC-80™ ABS Controllers
Bendix EC‑80 ABS controllers support four sensor/four
modulator (4S/4M) applications. Certain models support
Power Line Carrier (PLC) communications, with all models
supporting 12 volt installations. See Chart 1 for more
details.
ECU Mounting
Bendix EC-80 ABS
controller
Bendix EC-80 ABS
PLC controller
Bendix EC-80 ATC
controller
Bendix EC-80 ATC
controller
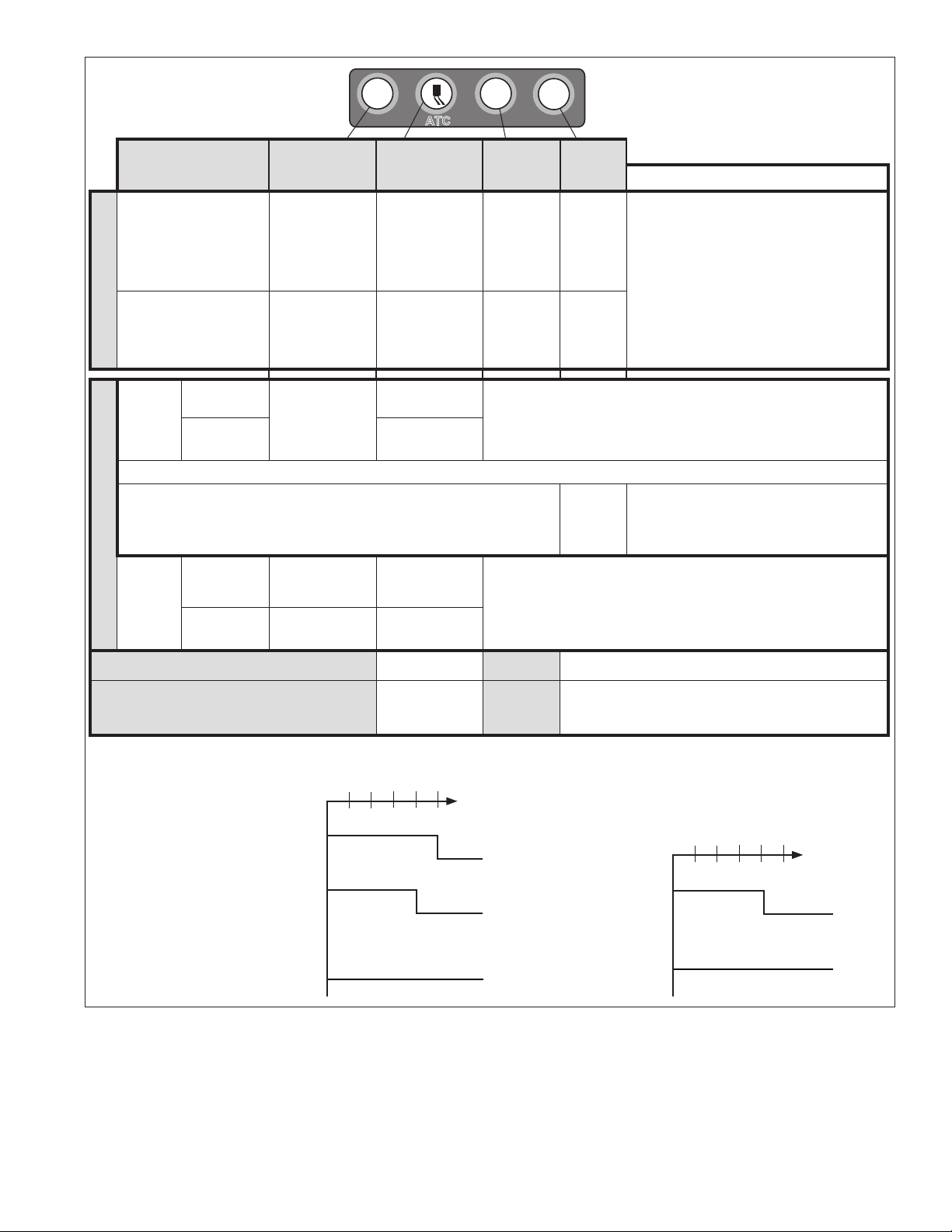
Cab 12 4 4 - - - -
Cab 12 4 4 - - -
Cab 12 4/6 4/5/6
Cab 24 4/6 4/5/6 -
Input
Voltage
Sensors PMVs ATC
FIGURE 5 - POWER LINE WITH PLC SIGNAL
Typically the signal is broadcast by the trailer ABS ECU.
The application of PLC technology for the heavy vehicle
industry is known as “PLC4Trucks.” The Bendix EC‑80
Serial
Blink
Codes
CHART 1 - BENDIX® EC‑80™ CONTROLLERS AVAILABLE
Commu‑
nication
J1939
PLC
ABS
Off-
Road
ATC
Off-
Road
Retarder
Relay
3

PLC controller and the Bendix EC‑80 ATC controller (12
volt versions) support PLC communications in accordance
with SAE J2497.
Identifying a Bendix EC-80 Controller with PLC
Refer to the information panel on the ECU label to see if
the controller provides PLC.
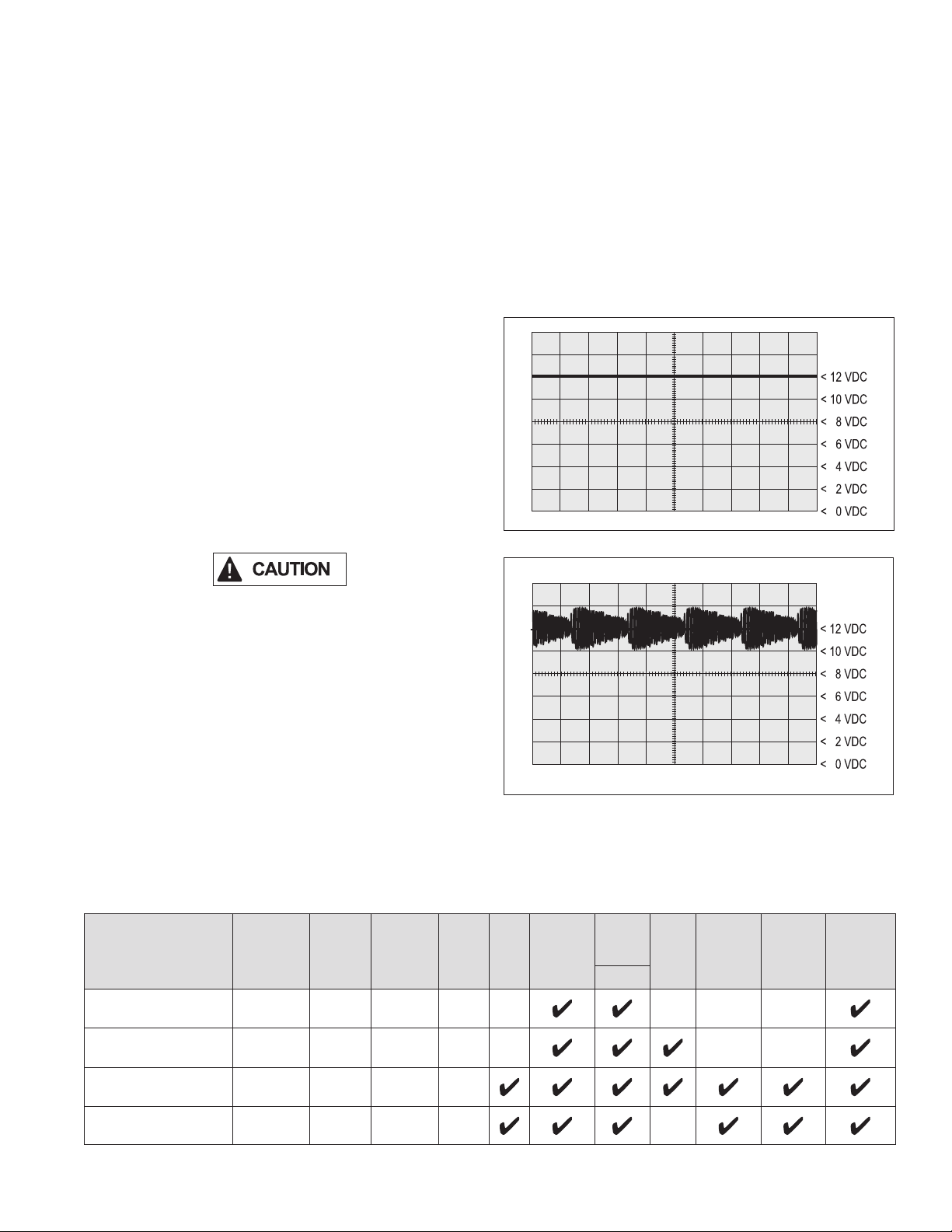
An oscilloscope can be used to measure or identify the
presence of a PLC signal on the power line. The PLC
signal is an amplitude and frequency‑modulated signal.
Depending on the ltering and load on the power line,
the PLC signal amplitude can range from 5.0 mVp‑p
to 7.0 Vp‑p. Suggested oscilloscope settings are AC
coupling, 1 volt/div, 100 µsec/div. The signal should be
measured at the ignition power input of the Bendix EC‑80
controller.
Note: An ABS trailer equipped with PLC or a PLC
diagnostic tool must be connected to the vehicle in order
to generate a PLC signal on the power line.
To conrm if a specic ECU uses PLC or not, see the
Controller Specications box below.
BENDIX EC-80 CONTROLLER INPUTS
Battery and Ignition Inputs
The ECU operates at a nominal supply voltage of 12 or
24 volts, depending on the ECU. The battery input is
connected through a 30 amp fuse directly to the battery.
The ignition input is applied by the ignition switch through
a 5 amp fuse.
Vehicle axle congurations and ATC features determine
the number of Bendix WS‑24™ wheel speed sensors that
must be used. A vehicle with a single rear axle requires
four wheel speed sensors. Vehicles with two rear axles
can utilize six wheel speed sensors for optimal ABS and
ATC performance.
Diagnostic Blink Code Switch
A momentary switch that grounds the ABS indicator lamp
output is used to place the ECU into the diagnostic blink
code mode and is typically located on the vehicle’s dash
panel.
ABS OFF-ROAD SWITCH AND INDICATOR
LAMP OPERATION
The ABS off-road mode should not be used on normal,
paved road surfaces because vehicle stability and
steerability may be affected. When the ECU is placed
in the ABS off-road mode, the ABS indicator lamp will
ash constantly to notify the vehicle operator that the
off-road mode is active.
Bendix EC‑80 ATC controllers use a dash‑mounted switch
to place the ECU into the ABS off‑road mode. In some
cases, ECUs may also be put into the ABS off‑road mode
by one of the other vehicle control modules, using a J1939
message to the Bendix EC‑80 controller.
If you need to know if a specic ECU uses a J1939 message
to operate the lamp, see the Controller Specications box
below.
Ground Input
The Bendix EC‑80 controller supports one ground input.
See pages 35-37 for electrical system schematics.
ABS Indicator Lamp Ground Input
Bendix EC‑80 ECUs require a second ground input (X1‑12)
for the ABS indicator lamp. The X1 wire harness connector
contains an ABS indicator lamp interlock (X1‑15), which
shorts the ABS indicator lamp circuit (X1‑18) to ground if
the connector is removed from the ECU.
Bendix® WS-24™ Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed data is provided to the Bendix EC‑80 controller
from the Bendix® WS‑24™ wheel speed sensor (see Figure
2). Vehicles have an exciter ring (or “tone ring”) as part of
the wheel assembly, and as the wheel turns, the teeth of
the exciter ring pass the wheel speed sensor, generating
an AC signal. The Bendix EC‑80 controller receives the
AC signal, which varies in voltage and frequency as the
wheel speed changes.
Controller Specications: If you need to know exact information about an ECU e.g. if it uses PLC, serial
communications, etc., e-mail ABS@Bendix.com, specifying the ECU part number, or call:
1-800-AIR-BRAKE, 1-800-247-2725, option 2, then 1, and speak to the Bendix TechTeam.
Stop Lamp Switch (SLS)
Bendix EC‑80 ATC ECUs monitor the vehicle stop lamp
status. Certain vehicle functions, such as ATC and All‑
Wheel Drive (AWD), use the status of the stop lamp to know
the driver’s intention. This can be provided to the ECU via
J1939 communications or hardware input.
BENDIX EC-80 CONTROLLER OUTPUTS
Bendix® M-32™, M-32QR™ and M-40X™ Pressure
Modulator Valves (PMV)
The Bendix M‑32, M‑32QR and M‑40X pressure modulator
valves (PMV) are operated by the Bendix EC‑80 controller
to modify driver applied air pressure to the service brakes
during ABS or ATC activation (See pages 6‑8). The PMV
is an electro‑pneumatic control valve and is the last valve
that air passes through on its way to the brake chamber.
The modulator hold and release solenoids are activated
to precisely modify the brake pressure during an antilock
braking event. The hold solenoid is normally open and the
release solenoid is normally closed.
4
Dash Lamps
ATC
ABS
TRLR
HSA
Mode
Ignition on ‑ start up
(trailer with PLC)
3 seconds after ignition
At Vehicle Startup
(with no Diagnostic
Trouble Codes)
ABS
Off-Road
Mode
Deep
Special Mode Operation
Mud/
Snow/
Mode
Normal
During an ATC
Event
Vehicles with Hill Start Feature: During HSA Mode Lamp OFF
Normal OFF
During an ATC
Event
ABS
Lamp
ON for 3 sec‑
onds*
Lamp OFF* Lamp OFF* Lamp OFF**
Lamp ashes
slowly (every 2.5
seconds)
‑— OR, depending on vehicle options (a vehicle can have either ABS off‑road or HSA) —
OFF Flashes quickly
ATC
Lamp
ON for 2.5
seconds*
Lamp OFF
Flashes quickly
Flashes slowly
(every 2.5
seconds)
Trailer
ABS Lamp
ON for 3
seconds**
• Uses dash switch
• Not for rm road surfaces
• Allows more wheel lock‑up (less ABS intervention)
• Mode only applies under 25 mph (Over 25 mph, the system reverts to
full ABS ‑ including ATC, and ATC lamp goes off.)
• Uses dash switch
• Increases allowable wheel slip during ATC interventions
• Not for rm road surfaces
HSA
Lamp
ON for 3
seconds*
Lamp
OFF*
Comments
If any of the described lamp behaviors do
*
not occur — or if the lamp remains on during
operation — have the vehicle serviced by a
qualied mechanic as soon as possible to
restore full system functionality.
Some vehicle manufacturers may illuminate
**
the trailer ABS indicator lamp at power‑up
regardless of whether a PLC signal is
detected from the trailer or not. Consult
the vehicle manufacturer’s documentation
for more details.
• The HSA lamp is illuminated only at power‑
up, or if an HSA DTC is present
• If the driver disables HSA, the HSA lamp will
ash slowly
During an Automatic Traction Control (ATC) Event Flashes quickly • Reduces wheel slip during acceleration at low speeds
During Dynamometer Mode
ABS System
Status Indicators
at Start-Up
Powered Vehicle ABS
Indicator Lamp
Trailer ABS
Indicator Lamp
(PLC Detected)**
Trailer ABS Indicator
Lamp**
(PLC Not Detected)
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
0.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 (sec.)1.5
Lamp ON
(ATC
Disabled)
Power
Application
• Disables ATC monitoring functions
• When not in Dynamometer Mode, an illuminated lamp
indicates an ATC DTC is present
ATC System
Status Indicator
at Start-Up
ATC
enabled
No ATC
0.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 (sec.)1.5
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Power
Application
CHART 2 - BENDIX® EC‑80™ INDICATOR LAMP BEHAVIOR
Traction Control Valve (TCV)
Bendix EC‑80 ATC controllers will activate the TCV during
differential braking ATC events. The TCV may be a
separate valve or integrated into the rear axle relay valve.
ABS Indicator Lamp Control with Optional
Diagnostic Blink Code Switch
Bendix® EC‑80™ controllers have internal circuitry to control
the ABS indicator lamp on the dash panel.
5

The ABS Lamp Illuminates:
1. During power‑up (e.g. when the vehicle is started) and
turns off after the self‑test is completed, providing no
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are present on the
tractor.
2. If the ECU is unplugged or has no power.
3. When the ECU is placed into the ABS off‑road mode
(the lamp ashes rapidly).
4. To display blink codes for diagnostic purposes after the
external diagnostic switch is activated.
Certain Bendix® EC‑80™ controllers communicate with
other vehicle control modules to operate the ABS indicator
lamp using. To conrm if a specic ECU uses serial
communications, see the Controller Specications box
on page 4.
Indicator Lamp Control Using Serial
Communications Links
As mentioned above, depending on the vehicle
manufacturer, the dash indicator lamps (ABS, ATC and
trailer ABS) may be controlled using serial communications
link. In these cases, the Bendix EC‑80 controller will send
a serial communications message over the J1939 links
indicating the required status of the lamp(s). Another
vehicle control module receives the message and controls
the indicator lamp(s).
Retarder Relay Disable Output
The retarder relay disable output may be used to control
a retarder disable relay.
When congured to use this output, the ECU will energize
the retarder disable relay and inhibit the use of the retarder
as needed.
SAE J1939 Serial Communications
A Controller Area Network (CAN) data link (SAE J1939) is
provided for communication. This link is used for various
functions, such as:
• To disable retarding devices during ABS operation
• To request that the torque converter disable lock‑up
during ABS operation
• To share information such as wheel speed and ECU
status with other vehicle control modules
Bendix EC‑80 ATC controllers utilize the J1939 data link
for ATC and drag torque control functions.
Trailer ABS Indicator Lamp Control
Certain models of the Bendix EC‑80 controller activate a
trailer ABS indicator lamp (located on the dash panel) that
indicates the status of the trailer ABS unit on one, or more
trailers or dollies. Typically, the Bendix EC‑80 controller
directly controls the trailer ABS indicator lamp based on
the information it receives from the trailer ABS.
Alternatively, some vehicles require the Bendix EC‑80
controller to activate the trailer ABS indicator lamp by
communicating with other vehicle controllers using serial
communications. To conrm if a specic ECU uses serial
communications, see the Controller Specications box on
page 4.
ATC Lamp Output/ATC Off-Road Switch Input
The ATC dash lamp is controlled by the Bendix EC‑80 ATC
ECU. The ATC lamp illuminates:
1. During power‑up (e.g. when the vehicle is started for
approximately 2.5 seconds) and turns off after the
self‑test is completed, providing no Diagnostic Trouble
Codes are present.
2. When ATC is disabled for any reason.
3. During an ATC event (the lamp will ash rapidly at a
rate of 2.5/second).
4. When the ECU is placed in the ATC off‑road mode (the
lamp will ash steadily every 2.5 seconds). This noties
the vehicle operator that the off‑road mode is active.
Interaxle Differential Lock Control (AWD Transfer Case)
A Bendix EC‑80 ATC ECU can control the interaxle
differential lock (AWD transfer case). This is recommended
on AWD vehicles, but the ECU must be specially congured
to provide this feature. For help with conguring an ECU,
use the information in the Controller Specications box on
page 4 to contact Bendix.
POWER-UP SEQUENCE
The vehicle operator should verify proper operation
of all installed indicator lamps (ABS, ATC, and trailer
ABS) when applying ignition power and during vehicle
operation. See Chart 2 on page 5.
Lamps that do not illuminate as expected when ignition
power is applied, or remain illuminated, indicate the need
for maintenance.
ABS Indicator Lamp Operation
The ECU will illuminate the ABS indicator lamp for
approximately three seconds when ignition power is
applied, after which the lamp will extinguish if no Diagnostic
Trouble Codes are detected.
The ECU will illuminate the ABS indicator lamp whenever
full ABS operation is not available due to a Diagnostic
Trouble Code. In most cases, partial ABS is still available.
ATC Status/Indicator Lamp Operation
The ECU will illuminate the ATC lamp for approximately
2.5 seconds when ignition power is applied, after which
the lamp will extinguish, if no Diagnostic Trouble Codes
are detected.
6
The ECU will illuminate the ATC indicator lamp whenever
ATC is disabled due to a Diagnostic Trouble Code.
Trailer ABS Indicator Lamp Operation
Certain models of the ECU will control the Trailer ABS
indicator lamp when a PLC signal (SAE J2497) from a
trailer ABS ECU is detected.
Pressure Modulator Valve Chuff Test
Bendix® EC‑80™ controllers will perform a Bendix‑patented
Pressure Modulator Valve (PMV) Chuff Test. The Chuff
Test is an electrical and pneumatic PMV test that can assist
maintenance personnel in verifying proper PMV wiring and
installation.
With brake pressure applied, a properly installed PMV will
perform one sharp audible exhaust of air by activating the
hold solenoid twice and the release solenoid once. If the
PMV is wired incorrectly, it will produce two exhausts of
air, or none at all.
The Bendix EC‑80 controller will perform a PMV chuff test
on all installed modulators in the following order:
• Steer Axle Right PMV
• Steer Axle Left PMV
• Drive Axle Right PMV
• Drive Axle Left PMV
• Additional Axle Right PMV
• Additional Axle Left PMV
The pattern will then repeat itself. See Figure 6.
The ECU will not perform the PMV Chuff Test when wheel
speed sensors show that the vehicle is in motion.
Right Steer
Right Drive
Right
Additional
ABS OPERATION
Bendix® ABS uses wheel speed sensors, ABS modulator
valves, and an ECU to control either four or six wheels of
a vehicle. By monitoring individual wheel turning motion
during braking, and adjusting or pulsing the brake pressure
at each wheel, the Bendix EC‑80 controller is able to
optimize slip between the tire and the road surface. When
excessive wheel slip, or wheel lock‑up, is detected, the
Bendix EC‑80 controller will activate the pressure modulator
valves to simulate a driver pumping the brakes. However,
the Bendix EC‑80 controller is able to pump the brakes on
individual wheels (or pairs of wheels), independently, and
with greater speed and accuracy than a driver.
Steer Axle Control
Although both wheels of the steer axle have their own wheel
speed sensor and pressure modulator valve, the Bendix
EC‑80 controller blends the applied braking force between
the two steering axle brakes. This Bendix‑patented brake
application control, called Modied Individual Control (MIC),
is designed to help reduce steering wheel pull during an
ABS event on road surfaces with poor traction (or areas
of poor traction, e.g., asphalt road surfaces with patches
of ice).
Single Drive Axle Control (4x2 Vehicle)
For vehicles with a single rear drive axle (4x2), the brakes
are operated independently by the Bendix EC‑80 controller,
based on the individual wheel behavior.
Dual Drive Axle Control (4S/4M Conguration)
For vehicles with dual drive axles (6x4) using a 4S/4M
conguration, one ABS modulator controls both right-side
rear wheels, and the other modulator controls both left‑
side rear wheels. Both wheels on each side receive equal
brake pressure during an ABS stop. The rear wheel speed
sensors must be installed on the axle with the lightest load.
Driver
Left Steer
FIGURE 6 - VEHICLE ORIENTATION (TYPICAL)
Left Drive
Additional
Left
Dual Rear Axle Control (6S/6M Conguration)
For vehicles with dual rear axles (6x4, 6x2) using a 6S/6M
conguration, the rear wheels are controlled independently.
Therefore, brake application pressure at each wheel is
adjusted according to the individual wheel behavior on
the road surface.
6x2 Vehicles with 6S/5M Conguration
6x2 vehicles can utilize a 6S/5M conguration, with the
additional axle (a non‑driven rear axle) having two sensors,
but only one pressure modulator valve. In this case, the
PMV controls both wheels on the additional axle. The
additional axle wheels would receive equal brake pressure,
based on the wheel that is currently experiencing the most
wheel slip.
7

Normal Braking
During normal braking, brake pressure is delivered through
the ABS PMV and into the brake chamber. If the ECU
does not detect excessive wheel slip, it will not activate
ABS control, and the vehicle stops with normal braking.
Retarder Brake System Control
On surfaces with low traction, application of the retarder can
lead to high levels of wheel slip at the drive axle wheels,
which can adversely affect vehicle stability.
To avoid this, the Bendix EC‑80 controller switches off the
retarder as soon as a lock‑up is detected at one (or more)
of the drive axle wheels.
When the ECU is placed in the ABS off‑road mode, it will
switch off the retarder only when ABS is active on a steer
axle wheel and a drive axle wheel.
Optional HSA Mode
As a driver begins to move a vehicle forward when stopped
facing up an incline (or backs‑up a vehicle when facing
down a slope), vehicles without Bendix Hill Start Aid/Assist
(HSA) may experience rolling downhill during the delay
between the release of the brakes and providing enough
torque to move the vehicle up the slope.
For vehicles with Bendix HSA, the ECU receives a J1939
message from the transmission when it will need the
assistance of the brakes to avoid the vehicle rolling. The
HSA components apply brake pressure to select wheel‑end
brakes. After three (3) seconds from the driver brake
release, the HSA system releases the brake pressure.
The three‑second delay allows the drive‑line components
to activate while the vehicle is held in place.
The ABS off-road mode should not be used on normal,
paved road surfaces because vehicle stability and
steerability may be reduced. The flashing ABS
indicator lamp communicates the status of this mode
to the driver.
The vehicle manufacturer should provide the optional
ABS off‑road function only for vehicles that operate on
unpaved surfaces or that are used in off‑road applications.
The vehicle OEM is responsible for ensuring that
vehicles equipped with the ABS off‑road function meet all
FMVSS‑121 requirements and have adequate operator
indicators and instructions.
The vehicle operator activates the off‑road function with a
switch on the dash panel. A ashing ABS indicator lamp
indicates to the driver that the ABS off‑road function is
engaged. To exit the ABS off‑road mode, depress and
release the switch.
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Vehicles
AWD vehicles with an engaged interaxle differential (steer
axle to rear axle)/AWD transfer case may have negative
effects on ABS performance. Optimum ABS performance
is achieved when the lockable differentials are disengaged,
allowing individual wheel control.
Bendix EC‑80 ATC controllers can be programmed
specically for this conguration to control the differential
lock/unlock solenoid in the AWD transfer case. When
programmed to do so, the ECU will disengage the locked
interaxle/AWD transfer case during an ABS event and
reengage it once the ABS event has ended.
When using the HSA function, the ABS off-road
function and the Retarder Relay output are temporarily
disabled.
Optional ABS Off-Road Mode
On some road conditions, particularly when the driving
surface is soft, the stopping distance with ABS may be
longer than without ABS. This can occur when a locked
wheel on soft ground plows up the road surface in front of
the tire, changing the rolling friction value. Although vehicle
stopping distance with a locked wheel may be shorter than
corresponding stopping distance with ABS control, vehicle
steerability and stability is reduced.
Bendix® EC‑80™ ATC controllers have an optional control
mode that more effectively accommodates these soft road
conditions to shorten stopping distance while maintaining
optimal vehicle steerability and stability.
8
ATC OPERATION
ATC Functional Overview
Just as ABS improves vehicle stability during braking,
ATC improves vehicle stability and traction during vehicle
acceleration. The Bendix EC‑80 ATC controller’s ATC
function uses the same wheel speed information and
modulator control as the ABS function. The ECU detects
excessive drive wheel speed; compares the speed of the
front, non‑driven wheels; and reacts to help bring the wheel
spin under control. The ECU can be congured to use
engine torque limiting and/or differential braking to control
wheel spin. For optimal ATC performance, both methods
are recommended.
ATC Lamp Operation
The ATC lamp illuminates:
1. During power‑up (e.g. when the vehicle is started for
approximately 2.5 seconds) and turns off after the
self‑test is completed, providing no Diagnostic Trouble
Codes are present.
2. When ATC is disabled for any reason.

3. During an ATC event (the lamp will ash rapidly at a
rate of 2.5/second). When ATC is no longer active, the
ATC active/indicator lamp turns off.
4. When the ECU is placed in the ATC off‑road mode (the
lamp will ash steadily every 2.5 seconds). This noties
the vehicle operator that the off‑road mode is active.
Differential Braking
Differential braking is automatically activated when drive
wheel(s) on one side of the vehicle are spinning. This
typically occurs on asphalt road surfaces with patches of
ice. The traction system will then lightly apply the brake to
the drive wheel(s) that are spinning. The vehicle differential
will then drive the wheels on the other side of the vehicle.
Differential braking is available at vehicle speeds up to
25 MPH.
Disabling ATC Engine Control and Smart ATC™ Traction
Control
ATC Engine Control and Smart ATC™ traction control will
be disabled under the following conditions:
1. In response to a serial communications request from
an off‑board tool.
2. At power‑up until the ECU detects a service brake
application.
3. If the ECU receives a J1939 message indicating that
the vehicle is parked.
4. If the Dynamometer Test Mode is active. This may be
accomplished via an off‑board tool or the diagnostic
blink code switch.
5. When certain Diagnostic Trouble Code conditions are
detected.
Disabling ATC Differential Braking
ATC differential braking is disabled under the following
conditions:
1. During power‑up (e.g. when the vehicle is started), until
the ECU detects a service brake application.
2. If the ECU receives a J1939 message indicating that
the vehicle is parked.
3. When the Dynamometer Test Mode is active. The
Dynamometer Test Mode is entered using the
diagnostic blink code switch or by using a diagnostic
tool (such as Bendix® ACom® Diagnostics).
4. In response to a serial communications request from
a diagnostic tool.
5. During brake torque limiting to avoid overheating of the
brakes.
6. When certain Diagnostic Trouble Code conditions are
detected.
Engine Torque Limiting (ETL) with Smart ATC™
Traction Control
The Bendix® EC‑80™ controller uses Engine Torque Limiting
to control drive axle wheel slip. This is communicated to
the engine control module (using J1939), and is available
at all vehicle speeds.
Optional ATC Off-Road Mode
In some road conditions, the vehicle operator may desire
additional drive wheel slip when ATC is active. The Bendix
EC‑80 ATC controller has an optional control mode to
permit this desired performance.
The vehicle operator can activate the off‑road function with
a switch on the dash panel. Alternately, a J1939 message
may be used to place the vehicle in this mode. The ATC
indicator lamp will ash continually to conrm that the off-
road ATC function is engaged.
To exit the ATC off‑road mode, depress and release the
ATC off‑road switch.
Drag Torque Control Functional Overview
Bendix EC‑80 ATC controllers have a feature referred to as
drag torque control which reduces wheel slip on a driven
axle due to driveline inertia. This condition is addressed
by increasing the engine torque to overcome the inertia.
Drag torque control increases vehicle stability on low‑
traction road surfaces during down‑shifting or retarder
braking.
DYNAMOMETER TEST MODE
Bendix® Smart ATC™ Traction Control
The Bendix EC‑80 ATC controller has an additional feature
known as Smart ATC™ traction control. Smart ATC™
traction control monitors the accelerator pedal position
(using J1939) to help provide optimum traction and vehicle
stability. By knowing the driver’s intention and adapting
the target slip of the drive wheels to the driving situation,
the Smart ATC™ traction control allows higher wheel slip
when the accelerator pedal is applied above a preset level.
The target wheel slip is decreased when driving through a
curve for improved stability.
ATC must be disabled prior to conducting any
dynamometer testing. When the Dynamometer Test
Mode is enabled, ATC brake control and engine control,
along with drag torque control, are turned off. This
test mode is used to avoid torque reduction — or
torque increase and brake control activation — when
the vehicle is operated on a dynamometer for testing
purpose.
The Dynamometer Test Mode may be activated by pressing
and releasing the diagnostic blink code switch ve (5) times
or by using a hand‑held or PC‑based diagnostic tool.
9

The Dynamometer Test Mode will remain active even if
power to the ECU is removed and re‑applied. Press and
release the blink code switch three (3) times, or use a
hand‑held or PC‑based diagnostic tool to exit the test mode.
AUTOMATIC TIRE SIZE CALIBRATION
The ECU requires a precise rolling circumference ratio
between steer axle and drive axle tires in order for ABS
and ATC to perform in an optimal manner. For this reason,
a learning process continuously takes place in which the
precise ratio is calculated. This calculated value is stored in
the ECU memory provided the following conditions are met:
1. Rolling‑circumference ratio is within the permissible
range.
2. Vehicle speed is greater than approximately 15 MPH.
3. No acceleration or deceleration is taking place.
4. There are no active speed sensor Diagnostic Trouble
Codes (DTCs).
The ECU is provided with a ratio value of 1.00 as a default
setting. If the automatic tire size alignment calculates a
different value, this is used to overwrite the original gure
in the memory. This process adapts the ABS and ATC
function to the vehicle.
ABS PARTIAL SHUTDOWN
Depending which component the trouble code is detected
on, the ABS and ATC functions may be fully or partially
disabled. Even with the ABS indicator lamp on, the Bendix
EC‑80™ controller may still provide ABS function on wheels
that are not affected. The ECU should be serviced as soon
as possible.
Steer Axle ABS Modulator Diagnostic Trouble
Code
ABS on the affected wheel is disabled. ABS and ATC on
all other wheels remains active.
Drive Axle/Additional Axle ABS Modulator
Diagnostic Trouble Code
ATC is disabled. ABS on the affected wheel is disabled.
ABS on all other wheels remains active.
Steer Axle Wheel Speed Sensor Diagnostic
Trouble Code
The wheel with the Diagnostic Trouble Code is still
controlled by using input from the remaining wheel speed
sensor on the front axle. ABS remains active on the rear
wheels. ATC is disabled.
®
Acceptable Tire Sizes
The speed calculation for an exciter ring with 100 teeth is
based on a default tire size of 510 revolutions per mile.
This gure is based on the actual rolling circumference of
the tires, and varies with tire size, tire wear, tire pressure,
vehicle loading, etc.
The ABS response sensitivity is reduced when the actual
rolling circumference is excessive on all wheels. For
a 100‑tooth exciter ring, the minimum number of tire
revolutions per mile is 426, and the maximum is 567. The
ECU will set DTCs if the number of revolutions are out of
this range.
Drive Axle/Additional Axle Wheel Speed Sensor
Diagnostic Trouble Code
ATC is disabled. In a four sensor system, ABS on the
affected wheel is disabled, but ABS on all other wheels
remains active.
In a six sensor system, ABS remains active by using input
from the remaining rear wheel speed sensor on the same
side.
ATC Modulator Diagnostic Trouble Code
ATC is disabled. ABS remains active.
J1939 Communication Diagnostic Trouble Code
ATC is disabled. ABS remains active.
ECU Diagnostic Trouble Code
ABS and ATC are disabled. The system reverts to normal
braking.
Voltage Diagnostic Trouble Code
While voltage is out of range, ABS and ATC are disabled.
The system reverts to normal braking. When the correct
voltage level is restored, full ABS and ATC function is
available. Operating voltage range is 9.0 to 17.0 VDC.
10

Reconguring Bendix® EC-80™ Controllers
SYSTEM RECONFIGURATION
The Bendix® EC‑80™ controller is designed to allow the
technician to change the default system settings (chosen
by the vehicle OEM) to provide additional or customized
features. When replacing an ECU, be sure to use an
equivalent Bendix® replacement part number so that the
standard default settings are provided.
Depending on the version, the customizable features include
ABS control settings, engine module communication, etc.
Many of these settings can be recongured using a hand-
held diagnostic tool or PC‑based software, such as the
Bendix® ACom® Diagnostics program.
ECU RECONFIGURATION
Reconguring Bendix EC-80 ABS ECUs
Reconguring a Bendix EC‑80 ABS controller may be
carried out by using the Blink Code Switch or by using a
hand‑held or PC‑based diagnostic tool.
Note: During the reconguration process, and independently
from any reconguration being carried out by the technician,
standard ECUs automatically check the J1939 serial link
and communicate with other vehicle modules. In particular,
if the serial link shows that the vehicle has a retarder device
present, the ECU will congure itself to communicate with
the retarder device for improved ABS performance. For
example, if the ECU detects the presence of a retarder
disable relay during a reconguration, it will congure
itself to control the relay to disable the retarding device
as needed.
Reconguring Bendix EC-80 ATC ECUs
As with non‑ATC ECUs, the Bendix EC‑80 ATC ECU also
carries out — independently from any reconguration
being carried out by the technician — an automatic
check of the J1939 serial link and communicates with
other vehicle modules. This includes checking for ATC
and retarder disable relay operation. In addition, Bendix
EC‑80 ATC controllers will determine the number of wheel
speed sensors and PMVs installed and congure itself
accordingly.
6S/5M Conguration
Bendix EC-80 ATC controllers will congure for 6S/5M
operation when a reconguration event is initiated and the
ECU detects that an additional axle PMV is wired as follows:
PMV Connector ECU Connector
Hold Right Additional Axle Hold
Release Left Additional Axle Release
Common Right Additional Axle Common
See 6S/5M System Schematic (page 37) for details.
Reconguration Using the Blink Code Switch
The reconguration procedure is the same for ATC and
non‑ATC ECUs. With ignition power removed from the
Bendix EC‑80 controller, depress the blink code switch.
After the ignition power is activated, depress and release
the switch seven times to initiate a reconguration.
Diagnostic Tool
A reconguration event may be initiated using a hand-held
or PC‑based diagnostic tool to communicate with the ECU
over the SAE J1939 diagnostic link.
11
Troubleshooting: General
Read and follow the General Safety Guidelines on
page two (2) of this document.
REMOVING THE BENDIX® EC-80™
CONTROLLER ASSEMBLY
1. Turn vehicle ignition off.
2. Remove as much contamination as possible prior to
disconnecting air lines and electrical connections.
3. Note the ECU assembly mounting position on the vehicle.
4. Disconnect the electrical connectors from the ECU.
5. Remove and retain the mounting bolts that secure
the ECU.
INSTALLING A NEW BENDIX
®
EC-80™ CONTROLLER
When replacing the Bendix® EC-80™ controller, verify
that the unit you are installing has the correct default
settings. Failure to do so could result in a loss of
features, such as ATC and PLC, or noncompliance
with U.S. regulations such as FMVSS 121. It is
recommended to use only the correct replacement part
number. However, most conguration settings can
be altered using the Bendix® ACom® ABS Diagnostic
Software program.
Verify correct operation of the Bendix EC‑80 controller
system and indicator lamps prior to putting the vehicle back
into service. Towing vehicles manufactured after March 1,
2001 must support the trailer ABS indicator lamp located
on the dash.
For further information, contact either the vehicle
manufacturer, Bendix® or your local authorized Bendix®
dealer.
1. Position and secure the Bendix EC‑80 controller in the
original mounting orientation using the mounting bolts
retained during removal. When mounting the unit in
the cab, use no more torque than is necessary to rmly
secure the ECU into position. Over‑tightening the
mounting hardware can cause damage to the Bendix
EC‑80 controller.
2. Reconnect the electrical connectors to the ECU.
3. Apply power and monitor the Bendix EC‑80 controller
power‑up sequence to verify proper system operation.
See Troubleshooting: Wiring section beginning on page 32
for more information on wiring harnesses.
12
Troubleshooting: Blink Codes and Diagnostic Modes
ECU DIAGNOSTICS
The Bendix® EC‑80™ controller contains self‑testing
diagnostic circuitry that continuously checks for the normal
operation of internal components and circuitry, as well as
external ABS components and wiring.
Active Diagnostic Trouble Codes
When an erroneous system condition is detected, the
Bendix EC‑80 controller:
1. Illuminates the appropriate indicator lamp(s) and
disengages part or all of the ABS and ATC functions.
(See pages 8-9.)
2. Places the appropriate trouble code information in the
ECU memory.
3. Communicates the appropriate trouble code information
over the serial communications diagnostic link as
required. Hand‑held or PC‑based diagnostic tools
attach to the vehicle diagnostic connector, typically
located on or under the dash (See Figure 7).
FIGURE 7 - TYPICAL VEHICLE DIAGNOSTIC CONNECTOR
LOCATION (J1939)
BLINK CODES
Blink codes allow a technician to troubleshoot ABS
problems without using a hand‑held or PC‑based diagnostic
tool. Instead, information about the ABS system is
communicated by the ECU using the ABS indicator lamp
to display sequences of blinks.
Note: The ECU will not enter the diagnostic blink code
mode if the wheel speed sensors show that the vehicle is in
motion. If the ECU is in the diagnostic blink code mode and
then detects vehicle motion, it will exit the blink code mode.
In addition, by operating the blink code switch as described
below, one of several diagnostic modes can be entered.
See Diagnostic Modes below.
Blink Code Switch Activation
When activating the blink code switch:
1. Wait at least two seconds after “ignition on.” (Except when
entering Reconguration Mode - see Reconguration
section on page 11)
2. For the ECU to recognize that the switch is activated
“on,” the technician must press for at least 0.1 seconds,
but less than 5 seconds. (If the switch is held for more
than 5 seconds, the ECU will register a malfunctioning
switch.)
3. Pauses between pressing the switch when a sequence
is required, (e.g. when changing mode) must not be
longer than 2 seconds.
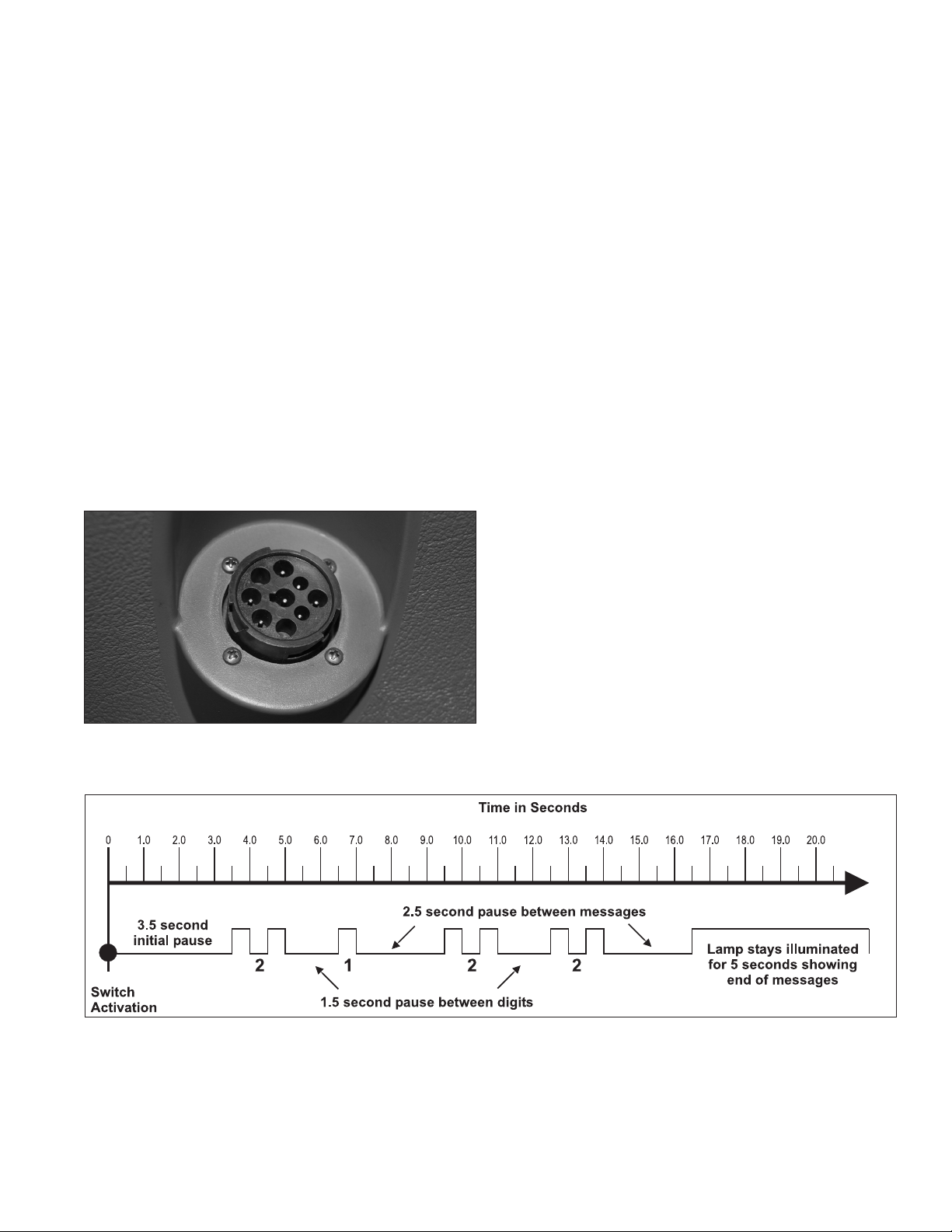
4. After a pause of 3.5 seconds, the ECU will begin
responding with output information blinks. See Figure
10 for an example.
FIGURE 8 - EXAMPLE OF BLINK CODE MESSAGE
13

Blink Code Timing
The ECU responds with a sequence of blink codes. The
overall blink code response from the ECU is called a
“message.” Each message includes, depending on the
mode selected by the technician, a sequence of one or
more groups of blinks. Simply record the number of blinks
for each sequence and then use the troubleshooting index
on page 18 for active or inactive trouble codes. Once you
have located the code, you will be directed to the page
that provides the applicable troubleshooting information.
NOTE:
1. Blink sequences illuminate the ABS indicator lamp for
half a second, with half‑second pauses between them.
2. Pauses between blink code digits are 1.5 seconds.
3. Pauses between blink code messages are 2.5
seconds.
4. The lamp remains on for ve (5) seconds at the end of
messages.
See Figure 8 for an example showing the message: 2,1
followed by 2,2.
Once the ABS indicator lamp begins displaying a sequence
of codes, it continues until all blink code messages have
been displayed and then returns to the normal operating
mode. During this time, the ECU will ignore any additional
blink code switch activation.
All trouble codes, with the exception of voltage and
J1939 trouble codes, will remain in an active state for the
remainder of the power cycle.
Voltage trouble codes will clear automatically when the
voltage returns within the required limits. All ABS functions
will be re‑engaged.
J1939 trouble codes will clear automatically when
communications are re‑established.
DIAGNOSTIC MODES
In order to communicate with the ECU, the controller has
several modes that the technician can select, allowing
information to be retrieved, or other ECU functions to be
accessed.
Diagnostic Modes
To enter the various diagnostic modes:
No. of
Times to
Press the
Blink Code
Switch
1 Active Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) retrieval
2 Inactive DTC retrieval
3 Clear active DTCs
4 System conguration check
5 Dynamometer Test Mode
7* Recongure ECU
* To enter the Reconguration Mode, the switch must be held
in before the application of ignition power. Once the power is
supplied, the switch is released and then pressed seven times.
CHART 3 - DIAGNOSTIC MODES
Active Diagnostic Trouble Code Mode
For troubleshooting, typically the active and inactive
Diagnostic Trouble Retrieval Modes are used. The
technician presses the blink code switch once and the ABS
indicator lamp ashes a rst group of two codes, and if
there are more trouble codes recorded, this is followed by
a second set of codes, etc. (See page 18 for a directory of
these codes.) All active trouble codes may also be retrieved
using a hand‑held or PC‑based diagnostic tool, such as
the Bendix® ACom® Diagnostics software.
To clear active DTCs (as problems are xed), simply clear
(or “self‑heal”) by removing and re‑applying ignition power.
The only exception is for wheel speed sensor trouble
codes, which clear when power is removed, re‑applied, and
the ECU detects valid wheel speed from all wheel speed
sensors. Alternately, codes may be cleared by pressing the
diagnostic blink code switch three (3) times (to enter the
Clear Active Diagnostic Trouble Code Mode) or by using
a hand‑held or PC‑based diagnostic tool. Hand‑held or
PC‑based diagnostic tools are able to clear wheel speed
sensor trouble codes without the vehicle being driven.
System Mode Entered
14
Inactive Diagnostic Trouble Code Mode
The ECU stores past trouble codes and comments (such
as conguration changes) in its memory. This record is
commonly referred to as “event history.” When an active
trouble code is cleared, the ECU stores it in the event
history memory as an inactive trouble code.
 Loading...
Loading...