Page 1

Hardware Data Sheet Section III Addendum
ET1810 / ET1811 / ET1812 and ET1815 / ET1816
Slave Controller
IP Core for Altera® and Xilinx® FPGAs
Section I – Technology
(Online at http://www.beckhoff.com)
Section II – Register Description
(Online at http://www.beckhoff.com)
Section III – Hardware Description
(Online at http://www.beckhoff.com)
Section III – Addendum
Design Flow Compatibility, FPGA Device Support, Known issues
Version 2.1
Date: 2015-05-12
Page 2

DOCUMENT ORGANIZATION
Version
Comment
1.0
Initial release
1.1
Update to EtherCAT IP Core V3.0.2/V3.00c
1.2
Update to EtherCAT IP Core V2.4.3/V2.04d
1.3
Update to Altera Quartus 13.0 SP1 and Xilinx Vivado 2013.2
1.4
Update to Altera Quartus 13.1, Xilinx Vivado 2013.3, and ISE14.7
1.5
Update to EtherCAT IP Core V3.0.5/V3.00f
Update to Xilinx Vivado 2013.4, editorial changes
1.6
Update to EtherCAT IP Core V3.0.6/V3.00g
Update to Xilinx Vivado 2014.1
1.7
Update to Altera Quartus 14.0, Xilinx Vivado 2014.2
Added Altera MAX10, Xilinx Kintex UltraScale, and Virtex UltraScale
1.8
Update to EtherCAT IP Core V3.0.9/V3.00j
Update to Xilinx Vivado 2014.3
Added known designflow issues chapters
1.9
Update to EtherCAT IP Core V3.0.9 Patch 1/V3.00j Patch 1
2.0
Update to EtherCAT IP Core V2.4.4/V2.04e and V3.0.10/V3.00k
Update to Altera Quartus 14.1, Xilinx Vivado 2014.4
Added Altera Arria 10
2.1
Update to Altera Quartus 15.0, Xilinx Vivado 2015.1
Trademarks
Beckhoff®, TwinCAT®, EtherCAT®, Safety over EtherCAT®, TwinSAFE® and XFC® are registered trademarks of and licensed by
Beckhoff Automation GmbH & Co. KG. Other designations used in this publication may be trademarks whose use by third
parties for their own purposes could violate the rights of the owners.
Patent Pending
The EtherCAT Technology is covered, including but not limited to the following German patent applications and patents:
DE10304637, DE102004044764, DE102005009224, DE102007017835 with corresponding applications or registrations in
various other countries.
Disclaimer
The documentation has been prepared with care. The products described are, however, constantly under development. For that
reason the documentation is not in every case checked for consistency with performance data, standards or other
characteristics. In the event that it contains technical or editorial errors, we retain the right to make alterations at any time and
without warning. No claims for the modification of products that have already been supplied may be made on the basis of the
data, diagrams and descriptions in this documentation.
Copyright
© Beckhoff Automation GmbH & Co. KG 05/2015.
The reproduction, distribution and utilization of this document as well as the communication of its contents to others without
express authorization are prohibited. Offenders will be held liable for the payment of damages. All rights reserved in the event of
the grant of a patent, utility model or design.
DOCUMENT ORGANIZATION
The Beckhoff EtherCAT Slave Controller (ESC) documentation covers the following Beckhoff ESCs:
ET1200
ET1100
EtherCAT IP Core for Altera® FPGAs
EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx® FPGAs
ESC20
The documentation is organized in three sections. Section I and section II are common for all Beckhoff
ESCs, Section III is specific for each ESC variant.
The latest documentation is available at the Beckhoff homepage (http://www.beckhoff.com).
Section I – Technology (All ESCs)
Section I deals with the basic EtherCAT technology. Starting with the EtherCAT protocol itself, the
frame processing inside EtherCAT slaves is described. The features and interfaces of the physical
layer with its two alternatives Ethernet and EBUS are explained afterwards. Finally, the details of the
functional units of an ESC like FMMU, SyncManager, Distributed Clocks, Slave Information Interface,
Interrupts, Watchdogs, and so on, are described.
Since Section I is common for all Beckhoff ESCs, it might describe features which are not available in
a specific ESC. Refer to the feature details overview in Section III of a specific ESC to find out which
features are available.
Section II – Register Description (All ESCs)
Section II contains detailed information about all ESC registers. This section is also common for all
Beckhoff ESCs, thus registers, register bits, or features are described which might not be available in
a specific ESC. Refer to the register overview and to the feature details overview in Section III of a
specific ESC to find out which registers and features are available.
DOCUMENT HISTORY
Section III – Hardware Description (Specific ESC)
Section III is ESC specific and contains detailed information about the ESC features, implemented
registers, configuration, interfaces, pinout, usage, electrical and mechanical specification, and so on.
Especially the Process Data Interfaces (PDI) supported by the ESC are part of this section.
Additional Documentation
Application notes and utilities can also be found at the Beckhoff homepage. Pinout configuration tools
for ET1100/ET1200 are available. Additional information on EtherCAT IP Cores with latest updates
regarding design flow compatibility, FPGA device support and known issues are also available.
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum II
Page 3

CONTENTS
CONTENTS
1 Overview 1
2 EtherCAT IP Core for Altera FPGAs 1
2.1 FPGA design tool compatibility 1
2.2 FPGA device compatibility 3
2.3 FPGA device license support 4
2.4 Known Designflow Issues 5
2.4.1 General Quartus issues 5
2.4.1.1 Qsys: Avalon read error 5
2.4.2 Quartus 14 5
2.4.2.1 Quartus 14.1 Arria 10: Tristate drivers are not properly
connected 5
2.4.2.2 Quartus 14.0 and later: Cyclone III example designs are not
synthesizable 5
2.4.2.3 Quartus 14.0 with EtherCAT IP Core V3.0.0-V3.0.6: DE2-115
example designs are not working 5
3 EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx FPGAs 6
3.1 FPGA design tool compatibility 6
3.3.4 Vivado 2013 11
3.3.4.1 Vivado 2013.2 with EtherCAT IP Core until V3.00f: IP License
issue 11
3.3.5 ISE/EDK/PlanAhead 14.7 12
3.3.5.1 ISE: Crash in libSecurity_FNP.dll 12
3.3.5.2 ISE/EDK/PlanAhead: Additional BUFG inserted 12
3.3.5.3 ISE/EDK/PlanAhead: CLOCK_DEDICATED_ROUTE=FALSE
constraint required 12
4 Appendix 13
4.1 Support and Service 13
4.1.1 Beckhoff’s branch offices and representatives 13
4.2 Beckhoff Headquarters 13
3.2 FPGA device compatibility 7
3.3 Known Designflow Issues 8
3.3.1 General Vivado issues 8
3.3.1.1 Vivado Upgrade IP: Warning on port differences 8
3.3.1.2 The resource consumption of the EtherCAT IP Core is too high8
3.3.1.3 EtherCAT IP Core is not part of the IP Catalog 8
3.3.2 Vivado 2015 9
3.3.2.1 Vivado 2015.1: The resource consumption (Slice LUTs) of the
EtherCAT IP Core is too high 9
3.3.2.2 Vivado 2015.1: ZC702_AXI_VIVADO example design invalid
constraints 9
3.3.2.3 Vivado 2015.1: ZC702_AXI_VIVADO example design does not
meet timing requirements 9
3.3.2.4 Vivado 2015.1: ZC702_AXI_VIVADO example design and
EtherCAT IP cores outside the Zynq block design fails in SDK 9
3.3.3 Vivado 2014 10
3.3.3.1 Vivado 2014.4: ZC702_AXI_VIVADO example design and
EtherCAT IP cores outside the Zynq block design fails in SDK10
3.3.3.2 Vivado 2014.3: Abnormal program termination
(EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION) 10
3.3.3.3 Vivado until 2014.3: Tri-state buffers inside EtherCAT IP Core10
3.3.3.4 Vivado until 2014.2: The resource consumption of the EtherCAT
IP Core is too high 10
3.3.3.5 Vivado until 2014.1: The ZC702 AXI Vivado example design is
not synthesizable 11
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum III
Page 4
Overview
IP Core
version
Release
date
Tool
compatibility
Version compatibility
SoPC
Builder
Qsys
5.1
SP2
6.1
7.0
7.1
SP1
7.2
SP2
8.0
9.0
SP1
9.1
10.0
10.1
11.0
11.1
SP2
12.0
SP1
12.1
SP1
13.0
SP1
13.1.4
14.01
14.11
15.01
1.0.0
7/2006
●
- ●
1.1.0
11/2006
●
- ●
1.1.1
1/2007
●
- ● ● ● ●
2.0.0
8/2007
●
- ● ● ● ●
2.2.0
6/2008
●
- ● ● ● ● ● ●
2.2.1
6/2009
●
- - - - - - - ●
2.3.0
12/2009
●
- - - - - - - - ●
2.3.1
2/2010
●
- - - - - - - - ●
2.3.2
3/2010
●
- - - - - - - - ● ● ●
○
2.4.0
3/2011
●
○
- - - - - - - - - ● ●
●
-
2.4.0
Patch 5
6/2012
●
○
- - - - - - - - - ● ● ● ●
2.4.3
7/2013
●
●
- - - - - - - - - ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● 2.4.4
1/2015
●
●
- - - - - - - - - ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ● 3.0.0
3/2013
●
●
- - - - - - - - - - ● ● ●
●
3.0.1
3/2013
●
●
- - - - - - - - - - ● ● ●
●
●
3.0.2
5/2013
●
●
- - - - - - - - - - ● ● ●
●
● ●
3.0.5
2/2014
●
●
- - - - - - - - - - ● ● ●
●
● ●
3.0.6
4/2014
●
●
- - - - - - - - - - ● ● ●
●
● ● ○
3.0.9
9/2014
●
●
- - - - - - - - - - ● ● ●
●
● ● ● ●
3.0.10
1/2015
●
●
- - - - - - - - - -
● ● ● ●
1
1 Overview
This document provides latest release notes, documentation addendum, supported IP Core design flows, and supported IP Core FPGA types for the following Beckhoff EtherCAT Slave Controllers:
EtherCAT IP Core for Altera® FPGAs (up to V2.4.3 / V3.0.10)
EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx® FPGAs (up to V2.04d Patch 1 / V3.00k)
Refer to the ESC data sheets for further information. The ESC data sheets are available from the Beckhoff homepage (http://www.beckhoff.com).
2 EtherCAT IP Core for Altera FPGAs
2.1 FPGA design tool compatibility
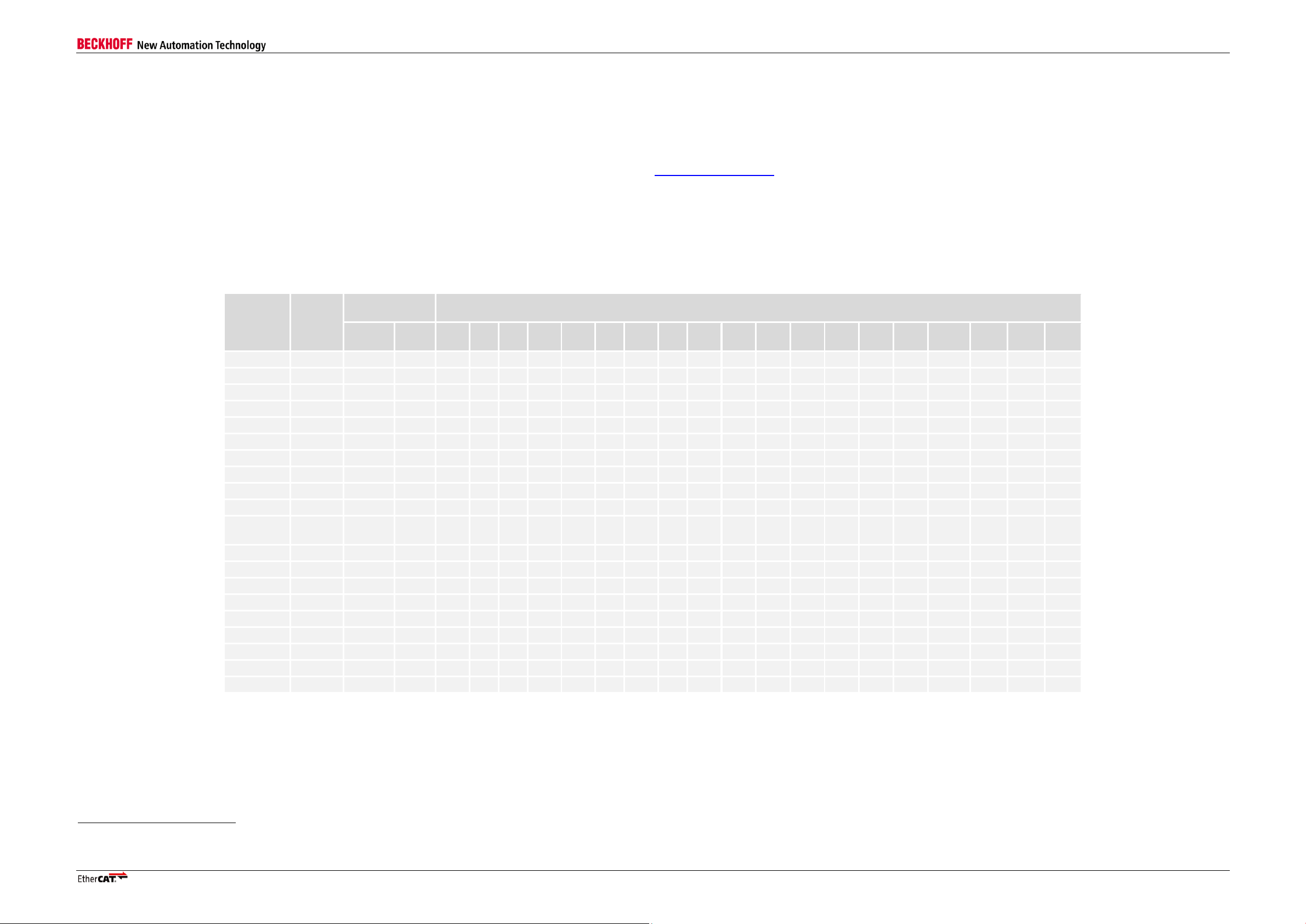
Starting with V2.4.0, Qsys is supported (the example designs of V2.4.0 are SoPC builder based).
Table 1: EtherCAT IP Core for Altera FPGAs compatibility with Altera Quartus II / NIOS EDS
Cyclone III devices are not supported anymore by Quartus, corresponding example designs cannot be synthesized. Refer to known issues for more details.
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum 1
Page 5

EtherCAT IP Core for Altera FPGAs
Symbol
Description
●
Compatible
○
Synthesis possible, issues with some example designs
-
Incompatible
Not tested
Table 2: Version compatibility legend
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum 2
Page 6

EtherCAT IP Core for Altera FPGAs
IP Core
version
Cyclone
Cyclone
II
Cyclone
III
Cyclone
III LS
Cyclone
IV E
Cyclone
IV GX
Cyclone
V /
Cyclone
V SoC
Arria
GX
Arria
II GX
Arria
II GZ
Arria
V
Arria
V GZ
Arria
10
Stratix/
Stratix
II
Stratix
GX/
Stratix
II GX
Stratix
III
Stratix
IV
Stratix
V
Stratix
10
Intel
Atom
E6x5C
MAX10
1.0.0
● ● - - -
-
-
-
-
-
- -
● - -
-
- - - 1.1.0
● ● - - -
-
-
-
-
-
- -
● - -
-
- - - 1.1.1
● ● - - -
-
-
-
-
-
- -
● - -
-
- - - 2.0.0
● ● ● - -
-
-
●
-
-
- -
● ● ●
-
- - - 2.2.0
● ● ● - -
-
-
●
-
-
- -
● ● ●
●
- - - 2.2.1
● ● ● - -
-
-
●
●
-
- -
● ● ●
●
- - - 2.3.0
● ● ● ● ●
●
-
●
●
-
- -
● ● ●
●
- - - 2.3.1
● ● ● ● ●
●
-
●
●
-
- -
● ● ●
●
- - - 2.3.2
● ● ● ● ●
●
-
●
●
-
- -
● ● ●
●
- - - 2.4.0
● ● ● ● ●
●
-
●
●
●
- -
● ● ●
●
● ● - 2.4.0 Patch 5
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ● ● ●
●
2.4.3
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ● ● ●
●
2.4.4
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ● ● ●
●
3.0.0
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ● ●
●
3.0.1
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ● ●
●
3.0.2
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ● ●
●
3.0.5
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ● ●
●
3.0.6
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ●
●
3.0.9
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ●
●
3.0.10
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
●
○
2
● ● ● ●
●
Symbol
Description
●
Compatible
○
Designflow issues
-
Incompatible
Not tested
2
2.2 FPGA device compatibility
Starting with V2.4.0 Patch 5, the family support check of the MegaWizard plugin has been turned off (a license update is now sufficient for new FPGA families).
Table 3: EtherCAT IP Core for Altera FPGAs compatibility with Altera FPGAs
Issues with Tristate-Drivers, please refer to Known Designflow Issues
Table 4: FPGA compatibility legend
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum 3
Page 7

EtherCAT IP Core for Altera FPGAs
First date of
license
support
Cyclone/
Cyclone
II
Cyclone
III
Cyclone
III LS
Cyclone
IV E
Cyclone
IV GX
Cyclone
V /
Cyclone
V SoC
Arria
GX
Arria
II GX
Arria
II GZ
Arria
V
Arria
V GZ
Arria
10
Stratix/
Stratix
II
Stratix
GX/
Stratix
II GX
Stratix
III
Stratix
IV
Stratix
V
Stratix
10
Intel
Atom
E6x5C
MAX10
Initial
●
-
- - - - - - - - -
-
●
●
- - - - - - 2007-03-28
●
●
- - - - - - - - -
-
● ● ●
- - - - -
2007-08-16
●
●
- - - - ● - - - -
-
● ● ●
- - - - -
2008-06-03
●
●
- - -
- ● - - - - -
● ● ●
●
- - -
-
2009-05-27
●
●
- - -
-
●
●
- - -
-
● ● ●
●
-
- ● -
2009-07-02
● ● ●
- - -
●
●
- - -
-
● ● ●
●
-
- ● -
2009-11-27
● ● ● - ● - ●
●
- - -
-
● ● ●
●
-
- ● -
2010-06-07
● ● ● ● ● - ●
●
- - -
-
● ● ●
●
-
- ● -
2011-03-22
● ● ● ● ● - ● ● ●
● - -
● ● ●
●
●
- ● -
2012-06-25
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
●
-
-
● ● ● ● ● - ●
-
2013-02-15
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● - ● ● ● ● ● - ●
-
2014-05-06
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● - ● ● ● ● ● - ●
●
2014-05-08
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
●
Symbol
Description
●
Supported
-
Not supported
2.3 FPGA device license support
Every license for the EtherCAT IP Core contains restrictions on supported FPGA devices. All FPGA device families which have license support at the date when the license is generated are unlocked. The following table shows the dates
of introduction of the FPGA license support. All EtherCAT IP Core licenses which are generated past the date will include the marked FPGA devices.
Table 5: EtherCAT IP Core for Altera FPGAs License support
Table 6: License support legend
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum 4
Page 8

EtherCAT IP Core for Altera FPGAs
2.4 Known Designflow Issues
2.4.1 General Quartus issues
2.4.1.1 Qsys: Avalon read error
With Qsys, a 32 bit read access to the EtherCAT IP Core might have gaps between the bytes. The prefetch feature (Data width of smallest Avalon Master is set to 2 or 4 byte), which is available in EtherCAT IP Core versions before
V3.0.0, does not support these gaps, read errors occur as a consequence.
Solution
Set the configuration option Data width of smallest Avalon Master to 1 byte, prefetch is disabled then.
2.4.2 Quartus 14
2.4.2.1 Quartus 14.1 Arria 10: Tristate drivers are not properly connected
With Quartus 14.1 and Arria 10 devices, tristate drivers may not be properly connected (IN and OE pins are swapped during technology mapping). This issue does not depend on internal/external tristate drivers.
Warning message:
Warning (12620): Input port OE of I/O output buffer "PROM_DATA~output" is not connected, but the atom is driving a bi-directional pin
The warning message cannot be ignored since the tristate driver is actually not properly connected. This issue is already approved by Altera.
Solution
None.
2.4.2.2 Quartus 14.0 and later: Cyclone III example designs are not synthesizable
Cyclone III devices are not supported anymore by Quartus 14, corresponding example designs cannot be synthesized
Solution
None. Use previous Quartus versions.
2.4.2.3 Quartus 14.0 with EtherCAT IP Core V3.0.0-V3.0.6: DE2-115 example designs are not working
The DE2-115 example designs are not working when synthesized using Quartus 14.0 (no communication, no display). The reason is that the PLL remains in reset state, because the areset input pin is not connected. Quartus 14.0 seems
to use a different input value for this signal, causing the reset to be active all the time.
Solution
Open Qsys, export the altpll_0 module’s areset_conduit signal, and connect it to GND. The warning regarding this conduit disappears.
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum 5
Page 9

EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx FPGAs
IP Core version
Release
date
Tool compatibility
Version compatibility
ISE
EDK
PlanAhead
Vivado
ISE
8.2.3
EDK
8.2.2
ISE
9.2.4
EDK
9.2.2
10.1.1
11.5
12.1
-
12.3
12.4
13.1
13.2
-
14.2
14.3
-
14.7
2012.3
-
2012.4
2013.1
2013.2
2013.3
-
2013.4
2014.1
2014.2
2014.3
2014.4
2015.1
1.01b
1/2007
● ● -
-
● ●
2.00a
8/2007
● ● -
-
● ●
2.02a
6/2008
● ● -
-
● ● ●
2.03a
12/2009
● ● -
-
- - - ●
2.03b
2/2010
● ● -
-
- - - ●
2.03c
3/2010
● ● -
-
- - - ●
2.03d
6/2010
● ● -
-
- - - - ● ○ ○
●
2.04a
3/2011
● ● -
-
- - - - - ● ●
●
2.04d Patch 1
7/2013
● ● ●
●
- - - - - ● ●
●
● - ● ● ● 2.04e
1/2015
● ● ●
●
- - - - - ● ●
●
● - ● ● ● ● ● ● 3.00c Patch 2
5/2013
● ● ●
●
- - - - -
● - ● ● ● 3.00f
2/2014
● ● ●
●
- - - - -
● - ● ● ● ● 3.00g
4/2014
● ● ●
●
- - - - -
● ● ● ● ● ● 3.00j
9/2014
● ● ●
●
- - - - -
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ○ 3.00k
11/2014
● ● ●
●
- - - - -
● ● ● ○
○
Symbol
Description
●
Compatible
○
Synthesis possible, issues with some example designs
-
Incompatible
Not tested
3 EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx FPGAs
3.1 FPGA design tool compatibility
Table 7: EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx FPGAs compatibility with Xilinx designflow tools
Table 8: Version compatibility legend
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum 6
Page 10

EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx FPGAs
IP Core version
Spartan
-3/
-3E
Spartan
-3A/
-3AN/
-3AN DSP
Spartan
-6
Virtex
-II/
-II Pro/
-II Pro X
Virtex
-4
Virtex
-5
Virtex
-6
Virtex
-7
Virtex
UltraScale
Virtex
UltraScale+
Kintex
-7/
-7 L
Kintex
UltraScale
Kintex
UltraScale+
Artix
-7/
-7 L
Zynq7000
Zynq
UltraScale+
MPSoC
1.01b
● ● ● ● ●
2.00a
● ● ● ● ●
2.02a
● ● ● ● ●
2.03a
● ● ● ● ● ●
2.03b
● ● ● ● ● ●
2.03c
● ● ● ● ● ●
2.03d
● ● ● ● ● ●
2.04a
● ● ● ● ● ●
●
●
●
●
2.04d Patch 1
● ● ● ● ● ●
●
●
●
●
2.04e
● ● ● ● ● ●
●
●
● ●
●
●
3.00c Patch 2
- - ● - - - ●
●
●
●
●
3.00f
- - ● - - - ●
●
●
●
●
3.00g
- - ● - - - ● ● ● ●
● ●
●
3.00j
- - ● - - - ● ● ● ●
● ●
●
3.00k
- - ● - - - ● ● ● ●
● ●
●
Symbol
Description
●
Compatible
-
Incompatible
Not tested
3.2 FPGA device compatibility
Table 9: EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx FPGAs compatibility with Xilinx FPGAs
Table 10: FPGA compatibility legend
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum 7
Page 11

EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx FPGAs
3.3 Known Designflow Issues
3.3.1 General Vivado issues
3.3.1.1 Vivado Upgrade IP: Warning on port differences
When upgrading the ZC702_AXI_VIVADO example design to a newer Vivado version, a warning may be issued regarding port differences:
[IP_Flow 19-3298] Detected external port differences while upgrading IP 'ZYNC_BLOCK_processing_system7_0_0'. These changes may impact your design.
These warnings can be ignored since the different port signals are not used by the example design.
3.3.1.2 The resource consumption of the EtherCAT IP Core is too high
The EtherCAT IP Core has a higher resource consumption when used with Vivado instead of ISE.
Solution
Using the following settings to achieve better design results:
Synthesis settings:
- Option -control_set_opt_threshold 0
- Option -fsm_extraction sequential
- Use this TCL switch:
set_param synth.elaboration.rodinMoreOptions " set rt::extractNetlistGenomes false"
Implementation settings:
- Strategy: Area_Explore
3.3.1.3 EtherCAT IP Core is not part of the IP Catalog
The EtherCAT IP Core is not part of the IP Catalog, because the configuration options required by the EtherCAT IP Core are currently not supported by the IP Packager/IP Catalog until Vivado 2014.3. Additionally, Vivado does not
support Spartan-6 FPGA devices, so ISE support is still required. Maintaining two types of configuration (IPCore_Config tool for ISE and IP Catalog for Vivado) is currently not planned.
Solution
Use The IPCore_Config tool to configure the EtherCAT IP Core, then add it to your project. You can either instantiate the EtherCAT IP Core wrapper directly, or you can use the IP Packager to add it to the IP Catalog (without any
configuration options). The last solution allows for automatically connecting the AXI interface.
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum 8
Page 12

EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx FPGAs
3.3.2 Vivado 2015
3.3.2.1 Vivado 2015.1: The resource consumption (Slice LUTs) of the EtherCAT IP Core is too high
The EtherCAT IP Core has a higher resource consumption with Vivado 2015.1 compared with Vivado 2014.3. The number of Slice LUTs may be about 10% higher.
Solution
Use a previous version.
3.3.2.2 Vivado 2015.1: ZC702_AXI_VIVADO example design invalid constraints
Vivado 2015.1 has renamed clock signals inside the Zynq block design. This causes some constraints to fail with such an error message:
[Vivado 12-1387] No valid object(s) found for set_false_path constraint with option '-to [get_clocks CLKOUT1]'.
Solution
In the ZC702.xdc constraint file, rename all clock references using
CLKOUT1
to the new name
clk_out1_ZYNC_BLOCK_clk_wiz_0_0
3.3.2.3 Vivado 2015.1: ZC702_AXI_VIVADO example design does not meet timing requirements
Vivado introduces BUFGs on the MII_TX_CLK wires, which causes timing failures for paths from ISMNET1_PHY1_MII_TX_CLK and ISMNET1_PHY2_MII_TX_CLK. In addition, it causes suboptimal placement of other signals in the IP
core, which may cause additional timing violations.
Solution
Add this line to the ZC702.xdc constraints file:
set_property BUFFER_TYPE NONE [get_ports ISMNET1_PHY*_MII_TX_CLK]
3.3.2.4 Vivado 2015.1: ZC702_AXI_VIVADO example design and EtherCAT IP cores outside the Zynq block design fails in SDK
Vivado 2015.1 generates an xparameters.h file without base address defines if the EtherCAT IP core (and probably any other AXI slave) is connected externally to the Zynq block design. This causes a compile error for the example
software in the SDK:
../src/EtherCAT_TestApp.c:18:28: error: 'XPAR_ETHERCAT_AXI_BASEADDR' undeclared (first use in this function)
Solution
Change the base address reference in EtherCAT_TestApp.c (line 18) to refer to the actual base address instead of the XPAR_ETHERCAT_AXI_BASEADDR define:
#define ETHERCAT_BASEADDR 0x43C00000
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum 9
Page 13

EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx FPGAs
3.3.3 Vivado 2014
3.3.3.1 Vivado 2014.4: ZC702_AXI_VIVADO example design and EtherCAT IP cores outside the Zynq block design fails in SDK
Vivado 2014.4 generates a wrong hardware description file if the EtherCAT IP core (and probably any other AXI slave) is connected externally to the Zynq block design. This causes the SDK to fail in generating the example software with
such an error message:
[Hsi 55-1464] Hardware instance __EMPTY__ not found in the design
This issue is partially fixed in Vivado 2015.1. A similar answer record (AR63036) can be found on the Xilinx website.
Solution
Please use Vivado 2015.1 (and newer) or 2014.3 to implement this example design and other designs which have the EtherCAT IP Core connected externally to the Zynq block design.
3.3.3.2 Vivado 2014.3: Abnormal program termination (EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION)
Vivado 2014.3 may stop during Technology Mapping with an access violation occasionally. Just repeat the synthesis run again and again until it succeeds (1-6 iterations until success have been seen). This issue is already approved by
Xilinx and should be fixed in 2014.3 Update 1.
The Vivado console stops with these messages:
[...]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------Start Technology Mapping
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------Abnormal program termination (EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION)
Please check '<project name>.runs/synth_1/hs_err_pid6336.log' for details
The mentioned log file contains no further details except for the dump file:
#
# An unexpected error has occurred (EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION)
#
Stack:
no stack trace available, please use hs_err_<pid>.dmp instead.
Solution
Run the synthesis again several times until it succeeds or update Vivado.
3.3.3.3 Vivado until 2014.3: Tri-state buffers inside EtherCAT IP Core
If the EtherCAT IP Core is configured to have internal tri-state buffers (e.g. for EEPROM/MI), Vivado 2014.2 (and maybe others) does not correctly implement the tristate drivers. Instead of a tristate output, a push-pull output is
implemented, which might not even toggle. This issue is approved by Xilinx, it should be solved in 2014.3.
Solution
Execute the following Tcl command in the Vivado GUI Tcl Console:
set_param synth.elaboration.rodinMoreOptions "rt::set_parameter enableTristateBubbleUp 1"
3.3.3.4 Vivado until 2014.2: The resource consumption of the EtherCAT IP Core is too high
The resource consumption of the EtherCAT IP Core is about 30% higher when it is synthesized with Vivado instead of ISE. This issue is approved by Xilinx, it is targeted to be solved in 2014.3.
Solution
Refer to Answer Record 61518 for a Vivado 2014.2 patch (this is not publicly available on the website). After applying the patch, the resource consumption is still higher, but much more acceptable.
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum 10
Page 14

EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx FPGAs
3.3.3.5 Vivado until 2014.1: The ZC702 AXI Vivado example design is not synthesizable
The ZC702 AXI Vivado example design was developed for Vivado 2014.2 and later, and it is incompatible with previous Vivado versions.
Solution
Use Vivado 2014.2 with the patch or a later Vivado version.
3.3.4 Vivado 2013
3.3.4.1 Vivado 2013.2 with EtherCAT IP Core until V3.00f: IP License issue
The license string used by the EtherCAT IP Core before V3.00g is not accepted by Vivado 2013.2. Note that the license key style change was not communicated to Beckhoff.
Solution
use Vivado 2013.3 or later, or
use EtherCAT IP Core V3.00g or later, or
refer to Answer Record 56630 for a Vivado 2013.2 patch required to use the EtherCAT IP Core before V3.00g
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum 11
Page 15

EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx FPGAs
3.3.5 ISE/EDK/PlanAhead 14.7
3.3.5.1 ISE: Crash in libSecurity_FNP.dll
After installing both ISE 14.7 and Vivado 2014.1 on a Microsoft Windows 7 64 bit operating system, a crash occurred while synthesizing the EtherCAT IP Core using ISE 14.7. The crash was caused by libSecurity_FNP.dll. This issue is
approved by Xilinx, but there will not be any future version of ISE.
Solution
Refer to Answer Record 59851 for an ISE 14.7 patch.
3.3.5.2 ISE/EDK/PlanAhead: Additional BUFG inserted
Under certain circumstances, the tools insert additional BUFGs into the clock signals to the EtherCAT IP Core (CLK25, CLK100), or the BUFGs are not placed at optimal sites. This results in an error message suggesting to add a
CLOCK_DEDICATED_ROUTE=FALSE constraint to the clocks. This issue occurs especially when the MAP option “Global optimization” is different from OFF. This issue is reported to Xilinx and present at least until ISE 14.5.
Solution
Either set Global optimization to OFF or add the CLOCK_DEDICATED_ROUTE=FALSE constraint.
3.3.5.3 ISE/EDK/PlanAhead: CLOCK_DEDICATED_ROUTE=FALSE constraint required
The PDI_SPI_SEL, PDI_SPI_DI and MII_RX_CLK0/1/2 signals are used as clock inputs for a few registers at low speed. Since these signals are not placed on dedicated clock inputs – which is not required –, Xilinx ISE sometimes issues
an error, which needs to be suppressed.
Solution
Add an additional constraint for the signals causing the error message (or uncomment the appropriate lines in the example UCF files):
CLOCK_DEDICATED_ROUTE = FALSE
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum 12
Page 16

Appendix
4 Appendix
4.1 Support and Service
Beckhoff and our partners around the world offer comprehensive support and service, making available fast and competent assistance with all questions related to Beckhoff products and system solutions.
4.1.1 Beckhoff’s branch offices and representatives
Please contact your Beckhoff branch office or representative for local support and service on Beckhoff products!
The addresses of Beckhoff's branch offices and representatives round the world can be found on her internet pages: http://www.beckhoff.com
You will also find further documentation for Beckhoff components there.
4.2 Beckhoff Headquarters
Beckhoff Automation GmbH & Co. KG
Huelshorstweg 20
33415 Verl
Germany
Phone: +49 (0) 5246 963-0
Fax: +49 (0) 5246 963-198
E-mail: info@beckhoff.com
Web: www.beckhoff.com
Beckhoff Support
Support offers you comprehensive technical assistance, helping you not only with the application of individual Beckhoff products, but also with other, wide-ranging services:
world-wide support
design, programming and commissioning of complex automation systems
and extensive training program for Beckhoff system components
Hotline: +49 (0) 5246 963-157
Fax: +49 (0) 5246 963-9157
E-mail: support@beckhoff.com
Beckhoff Service
The Beckhoff Service Center supports you in all matters of after-sales service:
on-site service
repair service
spare parts service
hotline service
Hotline: +49 (0) 5246 963-460
Fax: +49 (0) 5246 963-479
E-mail: service@beckhoff.com
Slave Controller – EtherCAT IP Core Data Sheet Addendum 13
 Loading...
Loading...