Page 1

Installing and Administering Avaya J100
series IP Phones in third-party call
control setup
Release 3.0
Issue 2
August 2018
Page 2

©
2018, Avaya Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Note
Using a cell, mobile, or GSM phone, or a two-way radio in close
proximity to an Avaya IP telephone might cause interference.
Documentation disclaimer
“Documentation” means information published in varying mediums
which may include product information, operating instructions and
performance specifications that are generally made available to users
of products. Documentation does not include marketing materials.
Avaya shall not be responsible for any modifications, additions, or
deletions to the original published version of Documentation unless
such modifications, additions, or deletions were performed by or on
the express behalf of Avaya. End User agrees to indemnify and hold
harmless Avaya, Avaya's agents, servants and employees against all
claims, lawsuits, demands and judgments arising out of, or in
connection with, subsequent modifications, additions or deletions to
this documentation, to the extent made by End User.
Link disclaimer
Avaya is not responsible for the contents or reliability of any linked
websites referenced within this site or Documentation provided by
Avaya. Avaya is not responsible for the accuracy of any information,
statement or content provided on these sites and does not
necessarily endorse the products, services, or information described
or offered within them. Avaya does not guarantee that these links will
work all the time and has no control over the availability of the linked
pages.
Warranty
Avaya provides a limited warranty on Avaya hardware and software.
Refer to your sales agreement to establish the terms of the limited
warranty. In addition, Avaya’s standard warranty language, as well as
information regarding support for this product while under warranty is
available to Avaya customers and other parties through the Avaya
Support website:
https://support.avaya.com/helpcenter/
getGenericDetails?detailId=C20091120112456651010 under the link
“Warranty & Product Lifecycle” or such successor site as designated
by Avaya. Please note that if You acquired the product(s) from an
authorized Avaya Channel Partner outside of the United States and
Canada, the warranty is provided to You by said Avaya Channel
Partner and not by Avaya.
“Hosted Service” means an Avaya hosted service subscription that
You acquire from either Avaya or an authorized Avaya Channel
Partner (as applicable) and which is described further in Hosted SAS
or other service description documentation regarding the applicable
hosted service. If You purchase a Hosted Service subscription, the
foregoing limited warranty may not apply but You may be entitled to
support services in connection with the Hosted Service as described
further in your service description documents for the applicable
Hosted Service. Contact Avaya or Avaya Channel Partner (as
applicable) for more information.
Hosted Service
THE FOLLOWING APPLIES ONLY IF YOU PURCHASE AN AVAYA
HOSTED SERVICE SUBSCRIPTION FROM AVAYA OR AN AVAYA
CHANNEL PARTNER (AS APPLICABLE), THE TERMS OF USE
FOR HOSTED SERVICES ARE AVAILABLE ON THE AVAYA
WEBSITE,
HTTPS://SUPPORT.AVAYA.COM/LICENSEINFO UNDER
THE LINK “Avaya Terms of Use for Hosted Services” OR SUCH
SUCCESSOR SITE AS DESIGNATED BY AVAYA, AND ARE
APPLICABLE TO ANYONE WHO ACCESSES OR USES THE
HOSTED SERVICE. BY ACCESSING OR USING THE HOSTED
SERVICE, OR AUTHORIZING OTHERS TO DO SO, YOU, ON
BEHALF OF YOURSELF AND THE ENTITY FOR WHOM YOU ARE
DOING SO (HEREINAFTER REFERRED TO INTERCHANGEABLY
AS “YOU” AND “END USER”), AGREE TO THE TERMS OF USE. IF
YOU ARE ACCEPTING THE TERMS OF USE ON BEHALF A
COMPANY OR OTHER LEGAL ENTITY, YOU REPRESENT THAT
YOU HAVE THE AUTHORITY TO BIND SUCH ENTITY TO THESE
TERMS OF USE. IF YOU DO NOT HAVE SUCH AUTHORITY, OR IF
YOU DO NOT WISH TO ACCEPT THESE TERMS OF USE, YOU
MUST NOT ACCESS OR USE THE HOSTED SERVICE OR
AUTHORIZE ANYONE TO ACCESS OR USE THE HOSTED
SERVICE.
Licenses
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS AVAILABLE ON THE AVAYA
WEBSITE, HTTPS://SUPPORT.AVAYA.COM/LICENSEINFO,
UNDER THE LINK “AVAYA SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS (Avaya
Products)” OR SUCH SUCCESSOR SITE AS DESIGNATED BY
AVAYA, ARE APPLICABLE TO ANYONE WHO DOWNLOADS,
USES AND/OR INSTALLS AVAYA SOFTWARE, PURCHASED
FROM AVAYA INC., ANY AVAYA AFFILIATE, OR AN AVAYA
CHANNEL PARTNER (AS APPLICABLE) UNDER A COMMERCIAL
AGREEMENT WITH AVAYA OR AN AVAYA CHANNEL PARTNER.
UNLESS OTHERWISE AGREED TO BY AVAYA IN WRITING,
AVAYA DOES NOT EXTEND THIS LICENSE IF THE SOFTWARE
WAS OBTAINED FROM ANYONE OTHER THAN AVAYA, AN AVAYA
AFFILIATE OR AN AVAYA CHANNEL PARTNER; AVAYA
RESERVES THE RIGHT TO TAKE LEGAL ACTION AGAINST YOU
AND ANYONE ELSE USING OR SELLING THE SOFTWARE
WITHOUT A LICENSE. BY INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING OR
USING THE SOFTWARE, OR AUTHORIZING OTHERS TO DO SO,
YOU, ON BEHALF OF YOURSELF AND THE ENTITY FOR WHOM
YOU ARE INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING OR USING THE
SOFTWARE (HEREINAFTER REFERRED TO
INTERCHANGEABLY AS “YOU” AND “END USER”), AGREE TO
THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS AND CREATE A BINDING
CONTRACT BETWEEN YOU AND AVAYA INC. OR THE
APPLICABLE AVAYA AFFILIATE (“AVAYA”).
Avaya grants You a license within the scope of the license types
described below, with the exception of Heritage Nortel Software, for
which the scope of the license is detailed below. Where the order
documentation does not expressly identify a license type, the
applicable license will be a Designated System License as set forth
below in the Designated System(s) License (DS) section as
applicable. The applicable number of licenses and units of capacity
for which the license is granted will be one (1), unless a different
number of licenses or units of capacity is specified in the
documentation or other materials available to You. “Software” means
computer programs in object code, provided by Avaya or an Avaya
Channel Partner, whether as stand-alone products, pre-installed on
hardware products, and any upgrades, updates, patches, bug fixes,
or modified versions thereto. “Designated Processor” means a single
stand-alone computing device. “Server” means a set of Designated
Processors that hosts (physically or virtually) a software application
to be accessed by multiple users. “Instance” means a single copy of
the Software executing at a particular time: (i) on one physical
machine; or (ii) on one deployed software virtual machine (“VM”) or
similar deployment.
License types
Designated System(s) License (DS). End User may install and use
each copy or an Instance of the Software only: 1) on a number of
Designated Processors up to the number indicated in the order; or 2)
up to the number of Instances of the Software as indicated in the
order, Documentation, or as authorized by Avaya in writing. Avaya
may require the Designated Processor(s) to be identified in the order
by type, serial number, feature key, Instance, location or other
specific designation, or to be provided by End User to Avaya through
electronic means established by Avaya specifically for this purpose.
Shrinkwrap License (SR). You may install and use the Software in
accordance with the terms and conditions of the applicable license
agreements, such as “shrinkwrap” or “clickthrough” license
accompanying or applicable to the Software (“Shrinkwrap License”).
Heritage Nortel Software
“Heritage Nortel Software” means the software that was acquired by
Avaya as part of its purchase of the Nortel Enterprise Solutions
Business in December 2009. The Heritage Nortel Software is the
software contained within the list of Heritage Nortel Products located
https://support.avaya.com/LicenseInfo under the link “Heritage
at
Nortel Products” or such successor site as designated by Avaya. For
Heritage Nortel Software, Avaya grants Customer a license to use
Heritage Nortel Software provided hereunder solely to the extent of
the authorized activation or authorized usage level, solely for the
purpose specified in the Documentation, and solely as embedded in,
for execution on, or for communication with Avaya equipment.
Charges for Heritage Nortel Software may be based on extent of
activation or use authorized as specified in an order or invoice.
Page 3
Copyright
Except where expressly stated otherwise, no use should be made of
materials on this site, the Documentation, Software, Hosted Service,
or hardware provided by Avaya. All content on this site, the
documentation, Hosted Service, and the product provided by Avaya
including the selection, arrangement and design of the content is
owned either by Avaya or its licensors and is protected by copyright
and other intellectual property laws including the sui generis rights
relating to the protection of databases. You may not modify, copy,
reproduce, republish, upload, post, transmit or distribute in any way
any content, in whole or in part, including any code and software
unless expressly authorized by Avaya. Unauthorized reproduction,
transmission, dissemination, storage, and or use without the express
written consent of Avaya can be a criminal, as well as a civil offense
under the applicable law.
Virtualization
The following applies if the product is deployed on a virtual machine.
Each product has its own ordering code and license types. Note,
unless otherwise stated, that each Instance of a product must be
separately licensed and ordered. For example, if the end user
customer or Avaya Channel Partner would like to install two
Instances of the same type of products, then two products of that
type must be ordered.
Third Party Components
“Third Party Components” mean certain software programs or
portions thereof included in the Software or Hosted Service may
contain software (including open source software) distributed under
third party agreements (“Third Party Components”), which contain
terms regarding the rights to use certain portions of the Software
(“Third Party Terms”). As required, information regarding distributed
Linux OS source code (for those products that have distributed Linux
OS source code) and identifying the copyright holders of the Third
Party Components and the Third Party Terms that apply is available
in the products, Documentation or on Avaya’s website at:
support.avaya.com/Copyright or such successor site as designated
by Avaya. The open source software license terms provided as Third
Party Terms are consistent with the license rights granted in these
Software License Terms, and may contain additional rights benefiting
You, such as modification and distribution of the open source
software. The Third Party Terms shall take precedence over these
Software License Terms, solely with respect to the applicable Third
Party Components to the extent that these Software License Terms
impose greater restrictions on You than the applicable Third Party
Terms.
The following applies only if the H.264 (AVC) codec is distributed with
the product. THIS PRODUCT IS LICENSED UNDER THE AVC
PATENT PORTFOLIO LICENSE FOR THE PERSONAL USE OF A
CONSUMER OR OTHER USES IN WHICH IT DOES NOT RECEIVE
REMUNERATION TO (i) ENCODE VIDEO IN COMPLIANCE WITH
THE AVC STANDARD (“AVC VIDEO”) AND/OR (ii) DECODE AVC
VIDEO THAT WAS ENCODED BY A CONSUMER ENGAGED IN A
PERSONAL ACTIVITY AND/OR WAS OBTAINED FROM A VIDEO
PROVIDER LICENSED TO PROVIDE AVC VIDEO. NO LICENSE IS
GRANTED OR SHALL BE IMPLIED FOR ANY OTHER USE.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION MAY BE OBTAINED FROM MPEG LA,
L.L.C. SEE
Service Provider
THE FOLLOWING APPLIES TO AVAYA CHANNEL PARTNER’S
HOSTING OF AVAYA PRODUCTS OR SERVICES. THE PRODUCT
OR HOSTED SERVICE MAY USE THIRD PARTY COMPONENTS
SUBJECT TO THIRD PARTY TERMS AND REQUIRE A SERVICE
PROVIDER TO BE INDEPENDENTLY LICENSED DIRECTLY FROM
THE THIRD PARTY SUPPLIER. AN AVAYA CHANNEL PARTNER’S
HOSTING OF AVAYA PRODUCTS MUST BE AUTHORIZED IN
WRITING BY AVAYA AND IF THOSE HOSTED PRODUCTS USE
OR EMBED CERTAIN THIRD PARTY SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
BUT NOT LIMITED TO MICROSOFT SOFTWARE OR CODECS,
THE AVAYA CHANNEL PARTNER IS REQUIRED TO
INDEPENDENTLY OBTAIN ANY APPLICABLE LICENSE
AGREEMENTS, AT THE AVAYA CHANNEL PARTNER’S EXPENSE,
DIRECTLY FROM THE APPLICABLE THIRD PARTY SUPPLIER.
WITH RESPECT TO CODECS, IF THE AVAYA CHANNEL
PARTNER IS HOSTING ANY PRODUCTS THAT USE OR EMBED
THE G.729 CODEC, H.264 CODEC, OR H.265 CODEC, THE
HTTP://WWW.MPEGLA.COM.
https://
AVAYA CHANNEL PARTNER ACKNOWLEDGES AND AGREES
THE AVAYA CHANNEL PARTNER IS RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY
AND ALL RELATED FEES AND/OR ROYALTIES. THE G.729
CODEC IS LICENSED BY SIPRO LAB TELECOM INC. SEE
WWW.SIPRO.COM/CONTACT.HTML. THE H.264 (AVC) CODEC IS
LICENSED UNDER THE AVC PATENT PORTFOLIO LICENSE FOR
THE PERSONAL USE OF A CONSUMER OR OTHER USES IN
WHICH IT DOES NOT RECEIVE REMUNERATION TO: (I) ENCODE
VIDEO IN COMPLIANCE WITH THE AVC STANDARD (“AVC
VIDEO”) AND/OR (II) DECODE AVC VIDEO THAT WAS ENCODED
BY A CONSUMER ENGAGED IN A PERSONAL ACTIVITY AND/OR
WAS OBTAINED FROM A VIDEO PROVIDER LICENSED TO
PROVIDE AVC VIDEO. NO LICENSE IS GRANTED OR SHALL BE
IMPLIED FOR ANY OTHER USE. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
FOR H.264 (AVC) AND H.265 (HEVC) CODECS MAY BE
OBTAINED FROM MPEG LA, L.L.C. SEE
WWW.MPEGLA.COM.
Compliance with Laws
You acknowledge and agree that it is Your responsibility for
complying with any applicable laws and regulations, including, but not
limited to laws and regulations related to call recording, data privacy,
intellectual property, trade secret, fraud, and music performance
rights, in the country or territory where the Avaya product is used.
Preventing Toll Fraud
“Toll Fraud” is the unauthorized use of your telecommunications
system by an unauthorized party (for example, a person who is not a
corporate employee, agent, subcontractor, or is not working on your
company's behalf). Be aware that there can be a risk of Toll Fraud
associated with your system and that, if Toll Fraud occurs, it can
result in substantial additional charges for your telecommunications
services.
Avaya Toll Fraud intervention
If You suspect that You are being victimized by Toll Fraud and You
need technical assistance or support, call Technical Service Center
Toll Fraud Intervention Hotline at +1-800-643-2353 for the United
States and Canada. For additional support telephone numbers, see
the Avaya Support website:
successor site as designated by Avaya.
Security Vulnerabilities
Information about Avaya’s security support policies can be found in
the Security Policies and Support section of
support.avaya.com/security.
Suspected Avaya product security vulnerabilities are handled per the
Avaya Product Security Support Flow (
support.avaya.com/css/P8/documents/100161515).
Downloading Documentation
For the most current versions of Documentation, see the Avaya
Support website:
as designated by Avaya.
Contact Avaya Support
See the Avaya Support website:
product or Hosted Service notices and articles, or to report a problem
with your Avaya product or Hosted Service. For a list of support
telephone numbers and contact addresses, go to the Avaya Support
website:
designated by Avaya), scroll to the bottom of the page, and select
Contact Avaya Support.
Regulatory Statements
Australia Statements
Handset Magnets Statement:
Industry Canada (IC) Statements
RSS Standards Statement
https://support.avaya.com (or such successor site as
Danger:
The handset receiver contains magnetic devices that can
attract small metallic objects. Care should be taken to avoid
personal injury.
https://support.avaya.com, or such successor site
https://support.avaya.com or such
https://support.avaya.com for
HTTP://
https://
https://
Page 4

This device complies with Industry Canada licence-exempt RSS
standard(s). Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference, including
interference that may cause undesired operation of the
device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada
applicables aux appareils radio exempts de licence. L'exploitation est
autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes:
1. L'appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage, et
2. L'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage
radioélectrique subi, même si le brouillage est susceptible
d'en compromettre le fonctionnement.
Radio Transmitter Statement
Under Industry Canada regulations, this radio transmitter may only
operate using an antenna of a type and maximum (or lesser) gain
approved for the transmitter by Industry Canada. To reduce potential
radio interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain
should be so chosen that the equivalent isotropically radiated power
(EIRP) is not more than that necessary for successful
communication.
Conformément à la réglementation d'Industrie Canada, le présent
émetteur radio peut fonctionner avec une antenne d'un type et d'un
gain maximal (ou inférieur) approuvé pour l'émetteur par Industrie
Canada. Dans le but de réduire les risques de brouillage
radioélectrique à l'intention des autres utilisateurs, il faut choisir le
type d'antenne et son gain de sorte que la puissance isotrope
rayonnée équivalente ne dépasse pas l'intensité nécessaire à
l'établissement d'une communication satisfaisante.
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme
NMB-003 du Canada.
Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC & IC RSS102 radiation exposure
limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment
should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm
between the radiator & your body. This transmitter must not be colocated or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
Cet équipement est conforme aux limites d'exposition aux
rayonnements ISEDétablies pour un environnement non contrôlé.
Cet équipement doit être installé et utilisé avec un minimum de 20
cm de distance entre la source de rayonnement et votre corps.
Industry Canada (IC) Statements
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conformeà la norme
NMB-003 du Canada.
Japan Statements
Class B Statement
This is a Class B product based on the standard of the VCCI Council.
If this is used near a radio or television receiver in a domestic
environment, it may cause radio interference. Install and use the
equipment according to the instruction manual.
Denan Power Cord Statement
Danger:
Please be careful of the following while installing the
equipment:
• Please only use the connecting cables, power cord, and
AC adapters shipped with the equipment or specified by
Avaya to be used with the equipment. If you use any
other equipment, it may cause failures, malfunctioning,
or fire.
• Power cords shipped with this equipment must not be
used with any other equipment. In case the above
guidelines are not followed, it may lead to death or
severe injury.
本製品を安全にご使用頂くため、以下のことにご注意ください。
• 接続ケーブル、電源コード、AC アダプタなどの部品は、必ず
製品に同梱されております添付品または指定品をご使用くだ
さい。添付品指定品以外の部品をご使用になると故障や動作
不良、火災の原因となることがあります。
• 同梱されております付属の電源コードを他の機器には使用し
ないでください。上記注意事項を守らないと、死亡や大怪我
など人身事故の原因となることがあります。
México Statement
The operation of this equipment is subject to the following two
conditions:
1. It is possible that this equipment or device may not cause
harmful interference, and
2. This equipment or device must accept any interference,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
La operación de este equipo está sujeta a las siguientes dos
condiciones:
1. Es posible que este equipo o dispositivo no cause
interferencia perjudicial y
2. Este equipo o dispositivo debe aceptar cualquier
interferencia, incluyendo la que pueda causar su operación
no deseada.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) Statement
This equipment must be connected to PoE networks without routing
to the outside plant.
U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Statements
Compliance Statement
The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate
the equipment.
To comply with the FCC RF exposure compliance requirements, this
device and its antenna must not be co-located or operating to
conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is
subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received,
including interferences that may cause undesired
operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designated to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interferences in a residential installation. This equipment
generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If
this equipment does cause harmful interferences to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Page 5

• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for
help.
Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth
for an uncontrolled environment . This equipment should be installed
and operated with minimum distance of 8 in or 20 cm between the
radiator and your body. This transmitter must not be co-located or
operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
ENERGY STAR® compliance statement
As an ENERGY STAR partner, Avaya Inc. has determined that this
product meets the ENERGY STAR guidelines for energy efficiency.
Information on the ENERGY STAR program can be found at
www.energystar.gov. ENERGY STAR and the ENERGY STAR mark
are registered trademarks owned by the U.S. Environmental
Protection Agency.
EU Countries
This device when installed complies with the essential requirements
and other relevant provisions of EMC Directive 2014/30/EU and LVD
Directive 2014/35/EU. A copy of the Declaration may be obtained
http://support.avaya.com or Avaya Inc., 4655 Great America
from
Parkway, Santa Clara, CA 95054–1233 USA.
WiFi transmitter
• Frequencies for 2412-2472 MHz, transmit power: 17.8 dBm
• Frequencies for 5180-5240 MHz, transmit power: 19.14 dBm
General Safety Warning
• Use only the Avaya approved Limited Power Source power
supplies specified for this product.
• Ensure that you:
- Do not operate the device near water.
- Do not use the device during a lightning storm.
- Do not report a gas leak while in the vicinity of the leak.
- For Accessory Power Supply – Use Only Limited Power
Supply Phihong Technology Co. Ltd. Model:
PSAC12R-050, Output: 5VDC, 2.4A.
Trademarks
The trademarks, logos and service marks (“Marks”) displayed in this
site, the Documentation, Hosted Service(s), and product(s) provided
by Avaya are the registered or unregistered Marks of Avaya, its
affiliates, its licensors, its suppliers, or other third parties. Users are
not permitted to use such Marks without prior written consent from
Avaya or such third party which may own the Mark. Nothing
contained in this site, the Documentation, Hosted Service(s) and
product(s) should be construed as granting, by implication, estoppel,
or otherwise, any license or right in and to the Marks without the
express written permission of Avaya or the applicable third party.
Avaya is a registered trademark of Avaya Inc.
All non-Avaya trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and
other countries.
Page 6

Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction............................................................................................................ 9
Purpose.................................................................................................................................. 9
Chapter 2: J100 Series IP Phone overview........................................................................... 10
J100 Series IP Phone models................................................................................................ 10
Hardware specification........................................................................................................... 11
Power specifications.............................................................................................................. 12
Supported codecs................................................................................................................. 12
Chapter 3: Initial setup and connectivity.............................................................................. 14
Hardware setup..................................................................................................................... 14
Wi-Fi overview................................................................................................................ 14
Wall mounting Avaya J100 Series IP Phones..................................................................... 21
Phone installation.................................................................................................................. 23
Phone installation process............................................................................................... 23
Broadsoft Device Management............................................................................................... 50
Device management configuration.................................................................................... 50
Chapter 4: Configuring the phone using web interface...................................................... 51
Logging in and logging out of the web UI................................................................................. 51
Changing password......................................................................................................... 52
Configuring environment settings............................................................................................ 52
Configuring date and time...................................................................................................... 52
Configuring Ethernet settings................................................................................................. 54
Ethernet settings field descriptions.................................................................................... 55
Configuring Wi-Fi settings...................................................................................................... 58
Wi-Fi settings field descriptions........................................................................................ 58
Configuring network settings.................................................................................................. 60
Network settings field description...................................................................................... 61
Configuring management settings........................................................................................... 63
Management settings field descriptions............................................................................. 63
Configuring settings............................................................................................................... 65
Settings field descriptions................................................................................................. 66
Configuring certificates.......................................................................................................... 72
Certificates field descriptions............................................................................................ 73
Configuring SIP settings......................................................................................................... 75
SIP settings field descriptions........................................................................................... 76
Debugging............................................................................................................................ 80
Debugging field descriptions............................................................................................ 81
Chapter 5: Cloud configurations........................................................................................... 85
Configuration through a cloud server....................................................................................... 85
Phone setup process on a cloud server................................................................................... 85
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 6
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 7

Contents
Settings file contents on a cloud server................................................................................... 86
MAC address file contents on a cloud server........................................................................... 86
Chapter 6: Security configurations....................................................................................... 87
Security overview.................................................................................................................. 87
Access control and security.................................................................................................... 87
Certificate management......................................................................................................... 88
Identity certificates........................................................................................................... 89
Trusted certificates.......................................................................................................... 90
OCSP trust certificates..................................................................................................... 91
Parameter configuration for secure installation......................................................................... 91
Chapter 7: Phone administration.......................................................................................... 93
Accessing the Admin menu during phone startup..................................................................... 93
Accessing the Admin menu after log in.................................................................................... 93
Accessing the Ethernet IPv4 settings...................................................................................... 93
IP configuration field description....................................................................................... 94
Using the debug mode........................................................................................................... 95
Setting the Ethernet interface control...................................................................................... 95
Group identifier..................................................................................................................... 96
Setting the group identifier............................................................................................... 97
Setting event logging............................................................................................................. 97
Restarting the phone............................................................................................................. 98
Configuring SIP settings......................................................................................................... 98
Setting Site Specific Option Number (SSON)......................................................................... 100
Using the VIEW administrative option................................................................................... 100
VIEW field description.......................................................................................................... 101
Setting the 802.1x operational mode..................................................................................... 101
Resetting system values...................................................................................................... 102
Chapter 8: Feature configuration........................................................................................ 104
Features............................................................................................................................. 104
Calendar............................................................................................................................. 104
Calendar configuration................................................................................................... 105
Call Forward....................................................................................................................... 108
Configuring Call Forward by using the web interface........................................................ 108
Call Forward configuration............................................................................................. 108
Call Park............................................................................................................................. 109
Voicemail............................................................................................................................ 109
Configuring Voicemail by using the web interface............................................................. 110
Voicemail configuration.................................................................................................. 110
Recents.............................................................................................................................. 111
Recents configuration..................................................................................................... 111
Contacts list......................................................................................................................... 111
Configuring Groups list by using the web interface............................................................ 111
Contacts list configuration.............................................................................................. 112
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 7
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 8

Contents
Chapter 9: Backup and restore............................................................................................ 114
Backup and restore process................................................................................................. 114
Chapter 10: Resources......................................................................................................... 116
Documentation.................................................................................................................... 116
Finding documents on the Avaya Support website............................................................ 116
Viewing Avaya Mentor videos............................................................................................... 117
Support............................................................................................................................... 117
Chapter 11: Appendix........................................................................................................... 118
Appendix A: List of configuration parameters......................................................................... 118
Appendix B: Public CA Certificates....................................................................................... 177
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 8
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 9

Chapter 1: Introduction
Purpose
This document contains information about preparing Avaya J100 Series IP Phones for installation,
deployment, initial administration, and administration tasks including data and security.
This document is intended for the deployment engineers or support personnel who install,
administer, and maintain Avaya J100 Series IP Phones.
The deployment engineers or the support personnel must have the following knowledge, skills,
and tools:
Knowledge
• DHCP
• SIP
• Configuring 802.1x and VLAN
Skills
How to administer and configure:
• DHCP server
• HTTP or HTTPS server
• Microsoft Exchange Server
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 9
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 10
Chapter 2: J100 Series IP Phone overview
Avaya J100 Series IP Phones are series of phones that you can use for unified communication. The
series leverages the enterprise IP network and eliminates the need of a separate voice network. It
offers superior audio quality with amplified handset and customization with low power requirements
in a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) environment.
This series works with Avaya Aura®, IP office, and Third-Party Call Control environments to provide
a flexible architecture where you can:
• Make conference calls more efficiently and enhance customer interactions with high-quality
audio.
• Gain access to information quickly through easy-to-read and high-resolution displays.
• Create a survivable, scalable infrastructure that delivers reliable performance and flexible
growth as business needs change.
• Increase performance by deploying Gigabit Ethernet within your infrastructure.
• Reduce energy costs by using efficient Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) including sleep mode,
which lowers energy consumption significantly.
• Enhance audio quality by using amplified handset mode.
J100 Series IP Phone models
Phone model
J129 IP Phone A SIP-based phone with a monochrome display that supports
J139 IP Phone A SIP-based phone with a color display that supports four call
J169 IP Phone A SIP-based phone with a grayscale display that supports eight
J179 IP Phone A SIP-based phone with a color display that supports eight call
Description
single line call appearance.
appearances with two lines of call display.
call appearances with four lines of call display.
The phone can also support up to three button modules each
supporting 24 application lines.
appearances with four lines of call display.
The phone can also support up to three button modules each
supporting 24 application lines.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 10
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 11
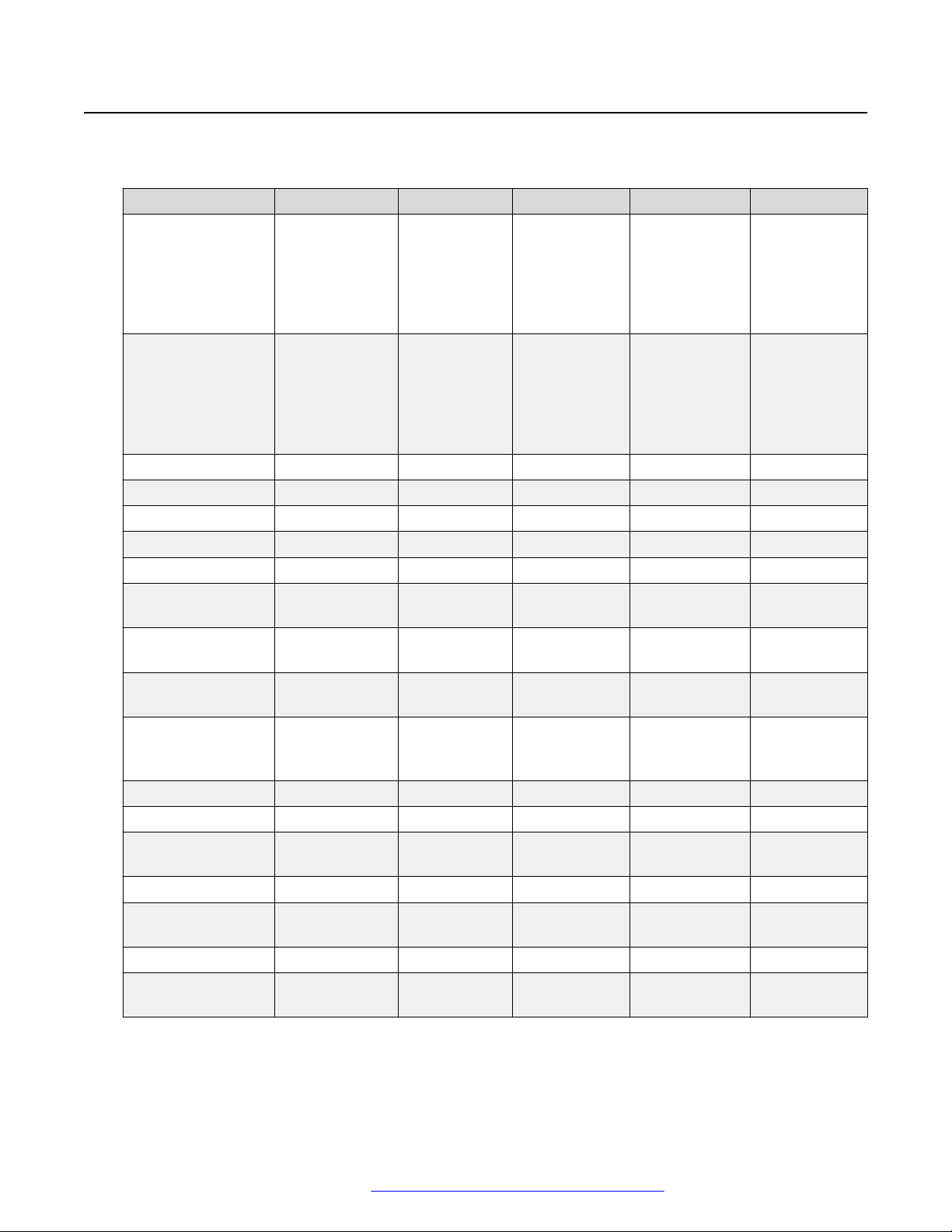
Hardware specification
Hardware specification
Avaya J100 Series IP Phones support the following hardware specifications:
Standard J129 J139 J169 J179 JBM24
Phone dimensions
with the stand in
high position:
Phone dimensions
with the wall mount
Wall mountable Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Stand Dual position Dual position Dual position Dual position Dual position
Call appearances 1 4 8 8 N/A
Touch screen N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Display type Monochrome Colored Grayscale Colored Grayscale
Display 2.3”, 128 x 32
Dual color call
indicator
Ethernet switch Dual 10/100 Dual
Wi-Fi support Yes (As an
Softkeys call control 3 4 4 4 N/A
Wired Handset Yes Yes Yes Yes N/A
Amplified Handset
mode
Wired Headset No Yes Yes Yes N/A
Expansion module
capable
Optional DC Power No Yes Yes Yes N/A
GSPPOE power
adapter
156 mm (6.1 in)
Wide x 170 mm
(6.7 in) Deep x
175mm (6.9 in)
Tall
156 mm (6.1 in)
Wide x 100 mm
(3.9 in) Deep x
198 mm (7.8 in)
Tall
pixel
0 4 8 8 24
optional
module)
Yes, with 20dB
of gain
No No Yes (3) Yes (3) N/A
Yes Yes Yes Yes N/A
179 mm (7.0
in) Wide x 170
mm (6.7 in)
Deep x
177mm (7.0
in) Tall
179 mm (7.0
in) Wide x 100
mm (3.9 in)
Deep x 219
mm (8.6 in)
Tall
2.8”, 320 x
240 pixel
10/100/1000
No No Yes (As an
Yes, with
20dB of gain
187 mm (7.4
in) Wide x 175
mm (6.9 in)
Deep x 183
mm (7.2 in)
Tall
187 mm (7.4
in) Wide x 100
mm (3.9 in)
Deep x 225
mm (8.9 in)
Tall
3.5”, 320 x 240
pixel
Dual
10/100/1000
Yes, with 20dB
of gain
187 mm (7.4
in) Wide x 175
mm (6.9 in)
Deep x 183
mm (7.2 in) Tall
187 mm (7.4
in) Wide x 100
mm (3.9 in)
Deep x 225
mm (8.9 in) Tall
3.5”, 320 x 240
pixel
Dual
10/100/1000
optional
module)
Yes, with 20dB
of gain
89 mm (3.5 in)
Wide x 175
mm (6.9 in)
Deep x 183
mm (7.2 in)
Tall
89 mm (3.5 in)
Wide x 100
mm (3.9 in)
Deep x 225
mm (8.9 in)
Tall
N/A
N/A
N/A
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 11
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 12
J100 Series IP Phone overview
Power specifications
The J100 Series IP Phones can use different power sources like LAN based Power, the Global
Single Port PoE Injector (GSPPOE) or power module (DC power jack).
The following table lists the various power requirements with or without peripherals.
Device Power requirement
J129 IP Phone • IEEE 802.3af
• GSPPOE - Avaya 48V PoE power inserter (Optional Component)
J139 IP Phone • IEEE 802.3af
• GSPPOE - Avaya 48V PoE power inserter (Optional Component)
• 5V DC Power adapter with barrel jack (Optional Component)
J169 IP Phone • IEEE 802.3af POE (Class 1) without JBM 24 button module
• 802.3af PoE (Class 2) if using any JBM24 button module
• GSPPOE - Avaya 48V PoE power inserter (Optional Component)
• 5V DC Power adapter with barrel jack (Optional Component)
J179 IP Phone • IEEE 802.3af POE (Class 1) without JBM 24 button or wireless module
• 802.3af PoE (Class 2) if using any JBM24 button module or wireless module
• GSPPOE - Avaya 48V PoE power inserter (Optional Component)
• 5V DC Power adapter with barrel jack (Optional Component)
Note:
Power the phone with GSPPOE or 5V DC power adapter if the JBM 24
button module and the wireless module are in use simultaneously.
Supported codecs
Avaya J100 Series IP Phones supports the following codecs and call control protocol:
Codecs
Call control
protocol
Codecs • G.711a
J129 J139 J169 J179
SIP SIP SIP SIP
• G.711µ
• G.729
• G.729a
• G.729ab
• G.726
• G.711a
• G.711µ
• G.729
• G.729a
• G.729ab
• G.726
• G.711a
• G.711µ
• G.729
• G.729a
• G.729ab
• G.726
• G.711a
• G.711µ
• G.729
• G.729a
• G.729ab
• G.726
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 12
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 13

Codecs J129 J139 J169 J179
• G722 • G722 • G722 • G722
Supported codecs
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 13
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 14
Chapter 3: Initial setup and connectivity
Hardware setup
Wi-Fi overview
The Wi-Fi module enables the phone to connect to a network through a wireless network. If the
phone loses connection to one Wi-Fi network, it continues to operate with another redundantly
configured wireless network or Ethernet network. A Wi-Fi status icon displays when Wi-Fi is in
use. If the phone is connected to Ethernet switch and the Ethernet link goes down, a pop-up
message displays to change network connectivity to Wi-Fi.
You can configure Wi-Fi network by :
• Setting Wi-Fi parameters by using the Settings file
• Configuring Wi-Fi from the phone UI
• Configuring Wi-Fi parameters from the web UI
Note that VLAN and LLDP functionalities are not supported over a wireless network.
Related links
J100 wireless module on page 14
Configuring Wi–Fi using phone UI on page 17
List of Wi-Fi configuration parameters on page 17
J100 wireless module
Avaya J129 IP Phone and Avaya J179 IP Phone support wireless module. The wireless module is
an optional component and you can order this module separately.
Note:
Avaya J139 IP Phone and Avaya J169 IP Phone do not support the J100 wireless module.
Related links
Wi-Fi overview on page 14
Installing the Wireless Module on page 15
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 14
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 15
Installing the Wireless Module
Before you begin
Get the following items:
• Phillips #1 screw driver to install the screw of the J100 Wireless Module.
• A flat screw driver that fits in the opening of the module panel.
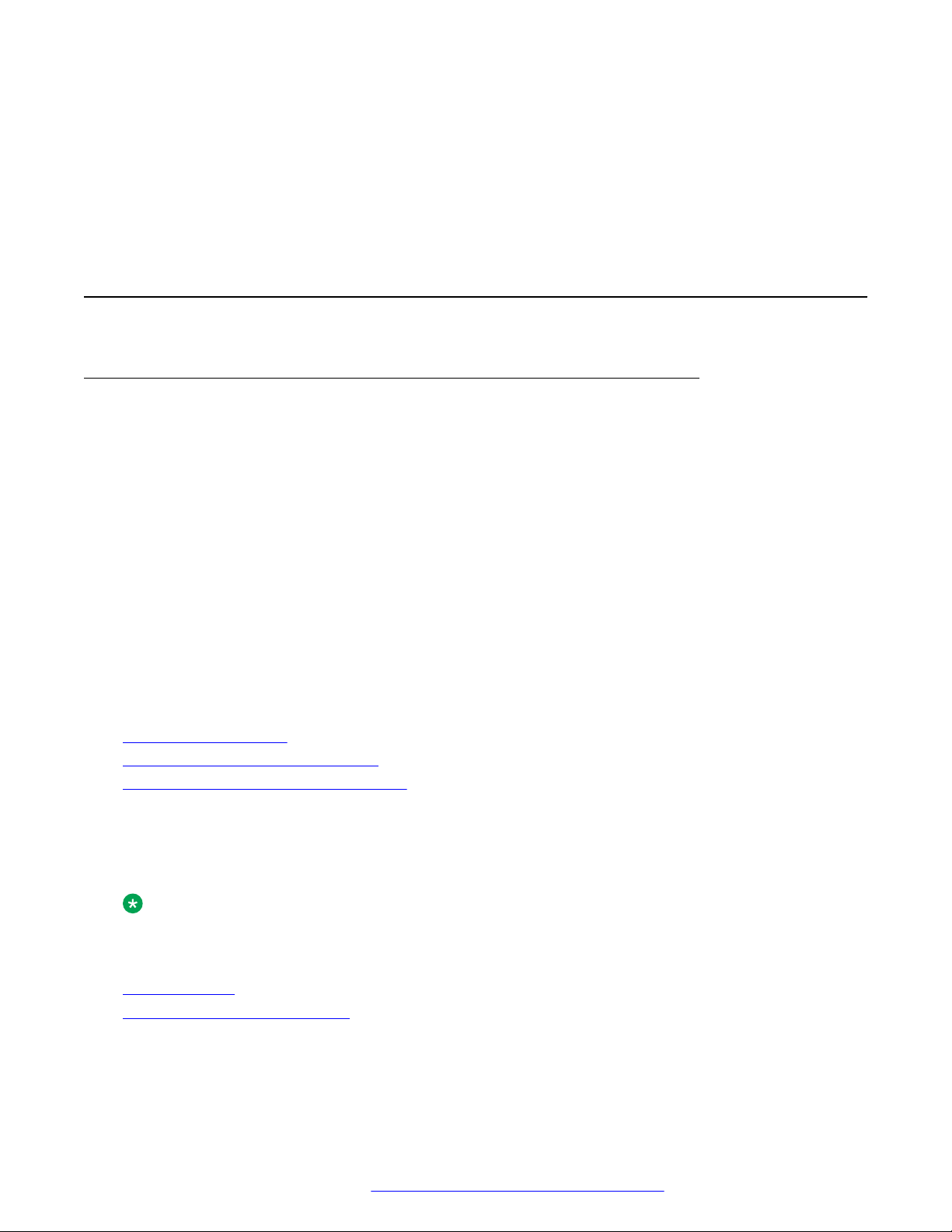
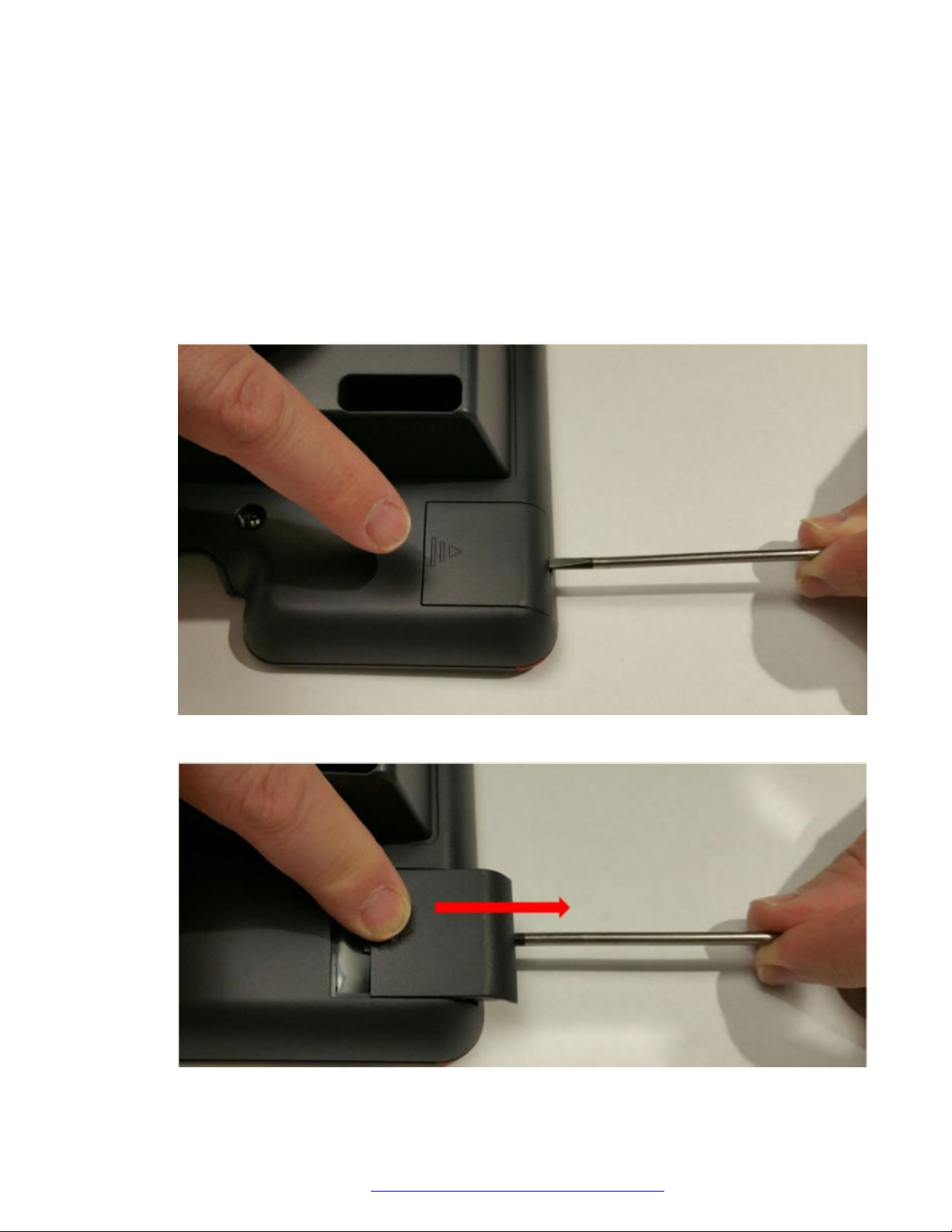
Procedure
1. Insert the screw driver in the opening of the module panel to release the latch. Do not pry
open the panel.
Hardware setup
2. To remove the module panel, slide the panel out in the direction of the arrow.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 15
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 16

Initial setup and connectivity
3. Insert the J100 Wireless Module to the edge connector.
4. Use the Phillips #1 screwdriver to fasten the module.
5. Slide the module panel inward to close.
Related links
J100 wireless module on page 14
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 16
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 17
Hardware setup
Configuring Wi–Fi using phone UI
About this task
Use this procedure to configure a Wi-Fi network by using phone UI. Note that switching networks
causes a reboot of the phone.
Procedure
1. Press Main Menu > Administration.
2. In the Access code field, enter the administration password.
3. Press Enter.
4. Select Network Interfaces.
5. Use the right arrow key to change Network mode to Wi-Fi.
6. Configure the following fields:
• Network config: Specifies if the WLAN is connected automatically or manually.
• SSID: Specifies the network name for the WLAN you are using. Use the navigation key
to select another SSID.
• Wi-Fi networks: Displays available WLAN.
7. Use the navigation key to select a WLAN and press Connect.
8. Press one of the following:
• Save
• Cancel
• Change
Related links
Wi-Fi overview on page 14
List of Wi-Fi configuration parameters
Parameter Name
WIFISTAT 1 Specifies the network interface to
Default Value Description
be used for network connectivity.
Value operation:
• 0: Phone connects to only
Ethernet network.
• 1: Phone connects to Ethernet
network, unless manually
switched to Wi—Fi
• 2: Phone connects to the Wi—
Fi network with the SSID
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 17
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 18
Initial setup and connectivity
Parameter Name Default Value Description
defined in the 46xxsettings.txt
parameter WLAN_ESSID
ENABLE_NETWORK_CONFIG_
BY_USER
1 Enables network configuration to
be modified by the user.
Value operation:
• 0: Disabled
• 1: Enabled
WLAN_ESSID N/A Specifies the wireless network to
be used.
The name of the SSID ranges up
to 32 characters.
WLAN_SECURITY none Specifies the security standard to
be used for the wireless network.
Value operation:
• none: No security standard is
defined.
• wep: WEP security standard is
defined.
• wpa2psk: WPA2 security
standard with pre-shared key is
defined.
• wpapsk: WPA security standard
with pre-shared key is defined.
• wpa2e: WPA enterprise security
standard is defined.
WEP_DEFAULT_KEY N/A Specifies the index of WEP
default key.
Value operation:
• 1
• 2
• 3
• 4
WLAN_COUNTRY US Specifies the ISO country code
representing the Wi-Fi regulatory
domain.
WLAN_ENABLE_80211D 0 Enables the phone to configure
its Wi-Fi regulatory domain to
match the 802.11d.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 18
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 19
Hardware setup
Parameter Name Default Value Description
Value operation:
• 0: Disable
• 1: Enable
WEP_KEY_LEN 128 bit Specifies the length of the WEP
key.
Value operation:
• 40 bit
• 64 bit
• 128 bit
WLAN_PASSWORD N/A Specifies the pre-configured Wi-Fi
network password. This
parameter is applicable if the
WIFISTAT is enabled and
WLAN_SECURITY is wpa2psk,
or WLAN_SECURITY is wpa2e,
WLAN_WPA2E_EAP_METHOD
is PEAP and
WLAN_WPA2E_EAP_PHASE2 is
MSCHAPV2.
The password must be from 8-63
characters. Note that the space
and ASCII 0x20, are not
supported.
WEP_KEY_1 to WEP_KEY_4 N/A Specifies the name of the WEP
key.
The name of the 40 bit key and
128 bit key are of 10 hex digits
and 26 hex digits respectively.
WLAN_WPA2E_EAP_METHOD PEAP Specifies the pre-configured
802.1x EAP method. This
parameter is applicable if
WIFISTAT parameter is enabled
and WLAN_SECURITY is set as
wpa2e.
Value operation:
• PEAP
• TLS
WLAN_WPA2E_IDENTITY N/A Specifies the 802.1x name of pre-
configured Wi-Fi network. This
parameter is applicable if
WIFISTAT parameter is enabled
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 19
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 20
Initial setup and connectivity
Parameter Name Default Value Description
and WLAN_SECURITY is set as
wpa2e.
The name must be from one to 32
characters.
Note that the space character and
ASCII 0x20, are not supported.
WLAN_WPA2E_ANONYMOUS_I
DENTITY
WLAN_L2QUAD 6 Specifies the layer 2 priority value
N/A Specifies the 802.1x anonymous
name of pre-configured Wi-Fi
network. This parameter is
applicable if WIFISTAT parameter
is enabled,
WLAN_WPA2E_EAP_METHOD
is set to PEAP and
WLAN_SECURITY is set as
wpa2e.
The name must be from one to 32
characters.
Note that the space character and
ASCII 0x20, are not supported.
for audio frames generated by the
telephone.
Valid value is from zero to seven.
WLAN_DSCPAUD 46 Specifies the layer 3
Differentiated Services (DiffServ)
Code Point for audio frames
generated by the telephone.
Valid value is from zero to 63.
WLAN_L2QSIG 3 Specifies the layer 3
Differentiated Services (DiffServ)
Code Point for audio frames
generated by the telephone.
Valid value is from zero to 63.
SET WLAN_DSCPSIG 34 Specifies the layer 3
Differentiated Services (DiffServ)
Code Point for signaling frames
generated by the telephone.
Valid value is from zero to 63.
Related links
Wi-Fi overview on page 14
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 20
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 21
Hardware setup
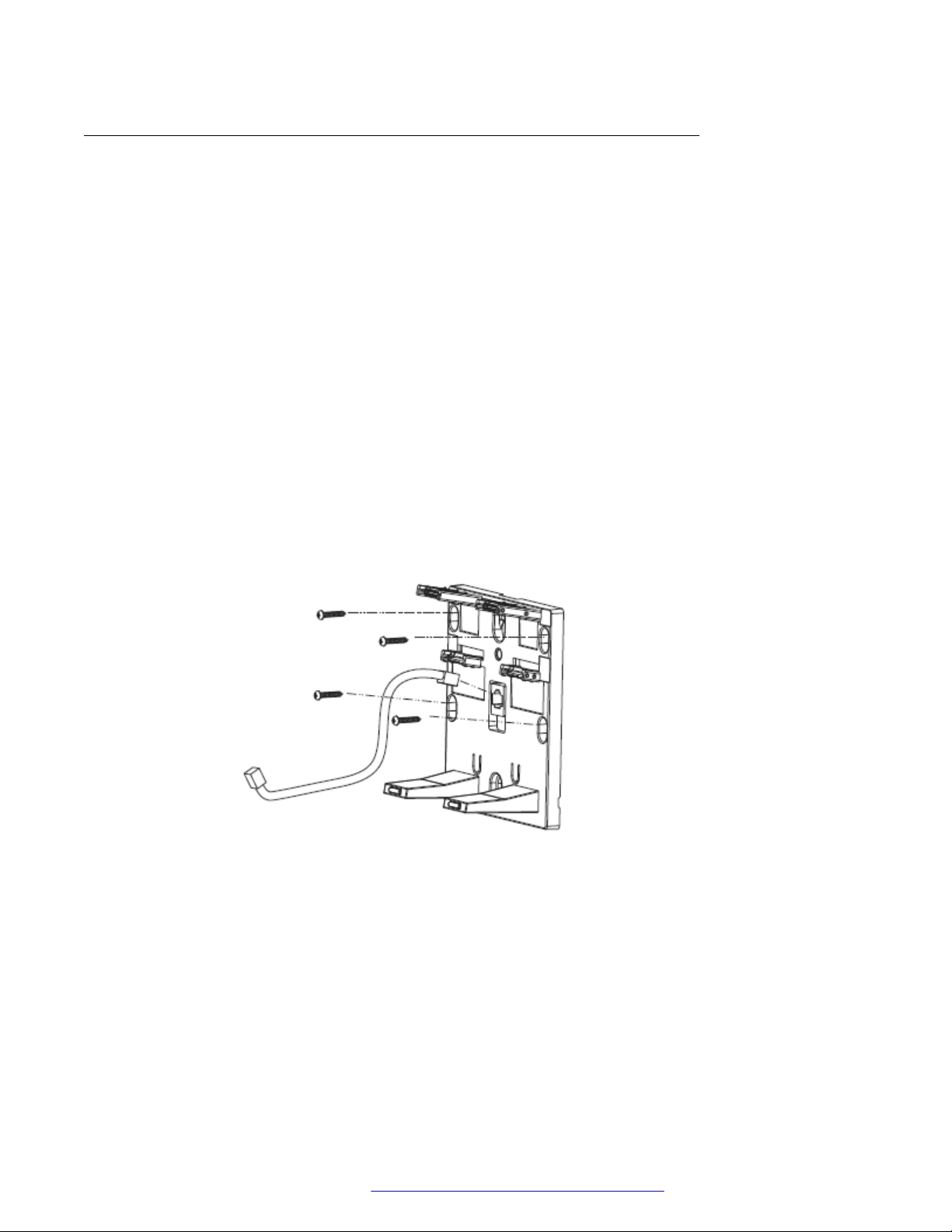
Wall mounting Avaya J100 Series IP Phones
About this task
Wall mounting kit and procedure of Avaya J100 Series IP Phones are similar except the wall
mounting bracket. Wall mounting brackets look different for Avaya J169/J179 IP Phone and Avaya
J129 IP Phone. You can order the kit separately, using the part numbers that correspond to the
phone.model. For example, the part number of the wall mount bracket is 700512707. The
procedure describes the wall mounting procedure with illustrations as reference.
Before you begin
Get the following items:
• Wall mounting kit that contains a wall mount bracket, and an Ethernet cable.
• Four #8 screws. The screws are not provided with the wall mounting kit.
Procedure
1. Do one of the following:
• Place the bracket on the wall, drill holes, and then drill-in the #8 screws.
• If there is a pre-installed wall plate, place the wall mount bracket over the wall plate. In
this case, you do not need the screws.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 21
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 22

Initial setup and connectivity
2. Attach one end of the Ethernet cable to the 10/100 network port of the phone and the other
end to the wall jack.
3. Attach the phone to the wall mount bracket by inserting the two upper tabs of the wall
mount bracket into the slots on the back of the phone. The lower pair of tabs rest against
the back of the phone and ensure that the phone does not move when the keys are
pressed.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 22
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 23

Phone installation
Phone installation process
You can install Avaya J100 Series IP Phones in the following ways:
• With the Device Enrollment Server (DES) discovery process: The installation process begins
after the phone is connected to a network. This is an automated process.
• Without the DES discovery process: The installation process includes a series of preconfiguration tasks.
Related links
Phone installation with DES on page 23
Phone installation without DES on page 24
Phone installation with DES
DES server
Phone installation
Device Enrollment Server (DES) redirects the out of box phone to the configuration file server after
the phone is connected to a network and the installation procedure begins automatically. The DNS
address of the DES server is hard coded to the phone firmware and the administrator can install
the phone by connecting the out of box phone to a network. After the first boot process, the
administrator can disable the DES functionality by setting DES_STAT=0 in DHCP option 242 or
from the settings file by putting the parameter DES_STAT=0.
Installing the phone by using the DES eliminates the need of manual configuration of provision
server.
Note:
DES only works if a provisioning server has been configured in the Avaya DES service for the
phone's MAC address. This is configured by the service provider.
Installing the phone using DES server
After the phone boots up, it prompts to enable or disable DES discovery. You can select one of the
following:
• Yes: The phone contacts the DES server and the DES server redirects the phone to the
configuration file server. The phone receives all the configuration related parameters and
upgrade file from the file server for installation.
• No: The phone skips the DES server discovery process. The administrator must provide all
the configuration related parameters through the following methods:
- Phone UI
- Web UI
- DCCP
- LLDP
After a time out of 30 seconds of the prompt the phone initiates DES discovery and contacts the
provision server for configuration parameter if a provisioning server is not obtained from DHCP. If
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 23
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 24

Initial setup and connectivity
the administrator selects Yes in the prompt, the phone forces DES discovery and it overrides the
provision server provided by DHCP.
Related links
Phone installation process on page 23
Phone installation without DES
This section describes the procedure to install the phone without invoking the DES discovery
process.
Related links
Phone installation process on page 23
Prerequisites on page 24
Administration methods on page 24
Installation checklist on page 25
Phone deployment in third-party call control setup on page 26
Prerequisites
Check the prerequisites to ensure that you have the required software and hardware before you
install the Avaya J100 Series IP Phones.
Software requirements
Ensure that your network already has the following components installed and configured:
• A DHCP server for providing dynamic IP addresses to the Avaya J100 Series IP Phones.
• A file server, an HTTP or an HTTPS for downloading the software distribution package and
the settings file.
For more information about installing and configuring the components, see their respective
documentation.
Hardware requirements
Ensure that the LAN uses:
• Ethernet Category 5e or Ethernet Category 6 cabling.
• Either the 802.3at PoE or the 802.3af PoE injector specification.
Related links
Phone installation without DES on page 24
Administration methods
You can use the following methods to administer the devices. The following table lists the
configuration parameters that you can administer through each of the corresponding methods.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 24
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 25
Phone installation
Method Can administer
IP addresses Tagging and
VLAN
Web UI
DHCP —
LLDP — — —
Settings file —
Network Time
Server
Quality of
Service
Applicationspecific
parameters
Administration
menu on the
phone
— —
Precedence of the methods
Most of the parameters are configured through multiple methods. If you configure a parameter
through more than one method, the device applies the settings of the method that has a higher
precedence. The following list shows the precedence of the methods in the highest to lowest
order:
1. Administration menu on the phone. When the parameter USE_DHCP is set to 1, the phone
gets the DHCP values from the DHCP rather than admin menu of the phone.
2. Settings file.
3. DHCP.
4. LLDP. There is an exception of LLDP getting a higher precedence than the Settings file
and DHCP when the layer 2 parameters, such as L2QVLAN, L2Q, L2QAUD, L2QVID,
L2QSIG, DSCPAUD, DSCPSIG, DSCPVID, and PHY2VLAN are set through LLDP.
Note:
When parameters of the Settings file are removed, or are not used, they reset to their default
value.
Related links
Phone installation without DES on page 24
Installation checklist
Use this checklist to gather, record, and verify the information during the installation.
No.
1 Check the prerequisites Prerequisites on page 24
2 Administer the VLAN VLAN overview on page 27
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
Task Reference
Table continues…
setup 25
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 26
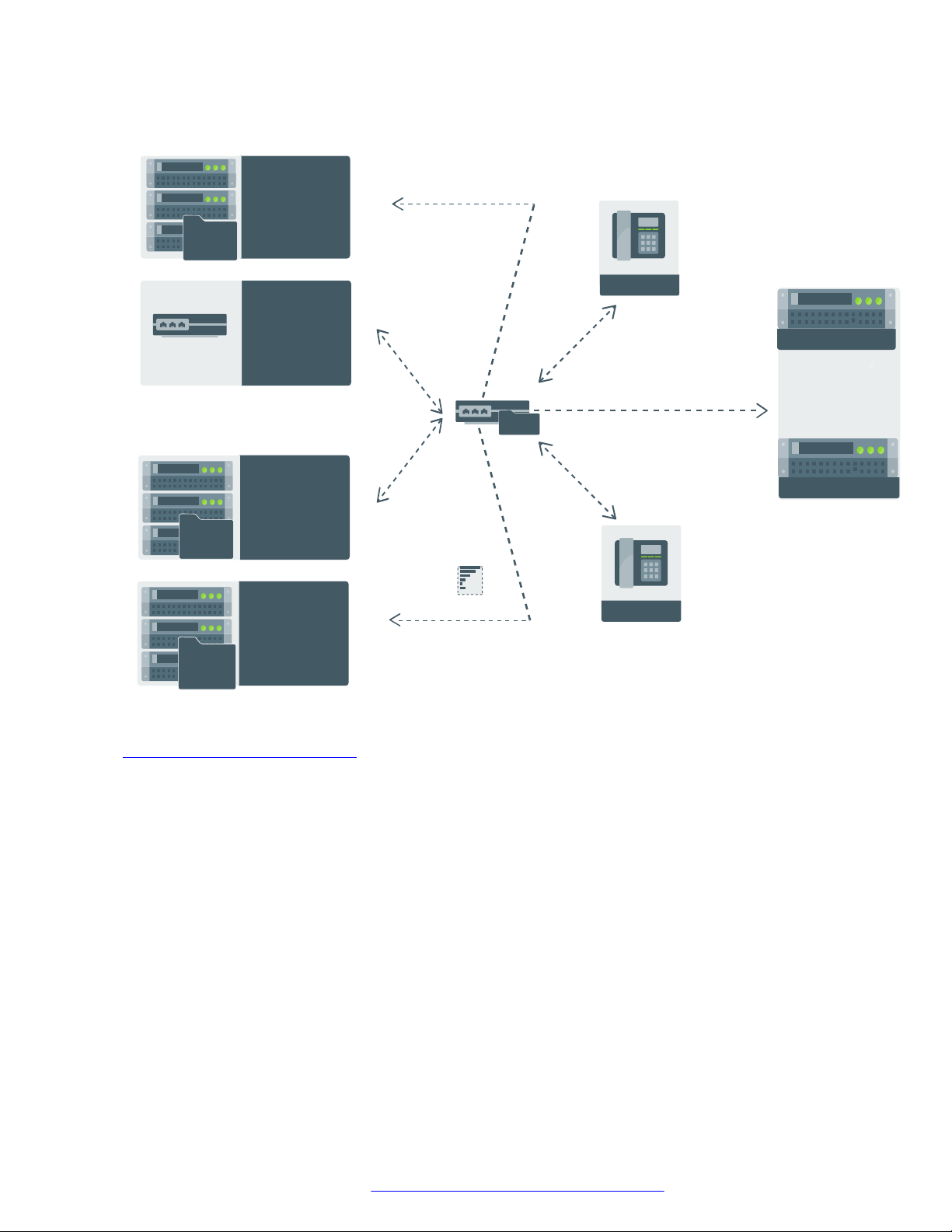
IP PHONE
IP PHONE
D H C P
Provides IP address
& sets configurable
parameters for
provisioning
46xxsettings.txt
Sets the system
parameters for
configuration
Configures
user,
communication,
and session profile
WAN Link
Manages power
and provides
configurable
parameters
for provisioning
Provides Software
distribution package
and Settings file
N e t w o r k
F i l e
S e r v e r
Network server /
Switch (LLDP)
Manages power
& provides configurable
parameters for
provisioning
D N S
Provides domain name
server address
R o u t e r
Session Border
Controller
Avaya Aura
®
System Manager
Primary Call Server
Secondary Call Server
®
Initial setup and connectivity
No. Task Reference
3 Configure the servers Provisioning server
configuration on page 47
4 Configure the settings file Configuration parameters on
page 118
5 Configure the upgrade file Device upgrade process on
page 49
6 Install the phone Installing the phone on page 48
Related links
Phone installation without DES on page 24
Phone deployment in third-party call control setup
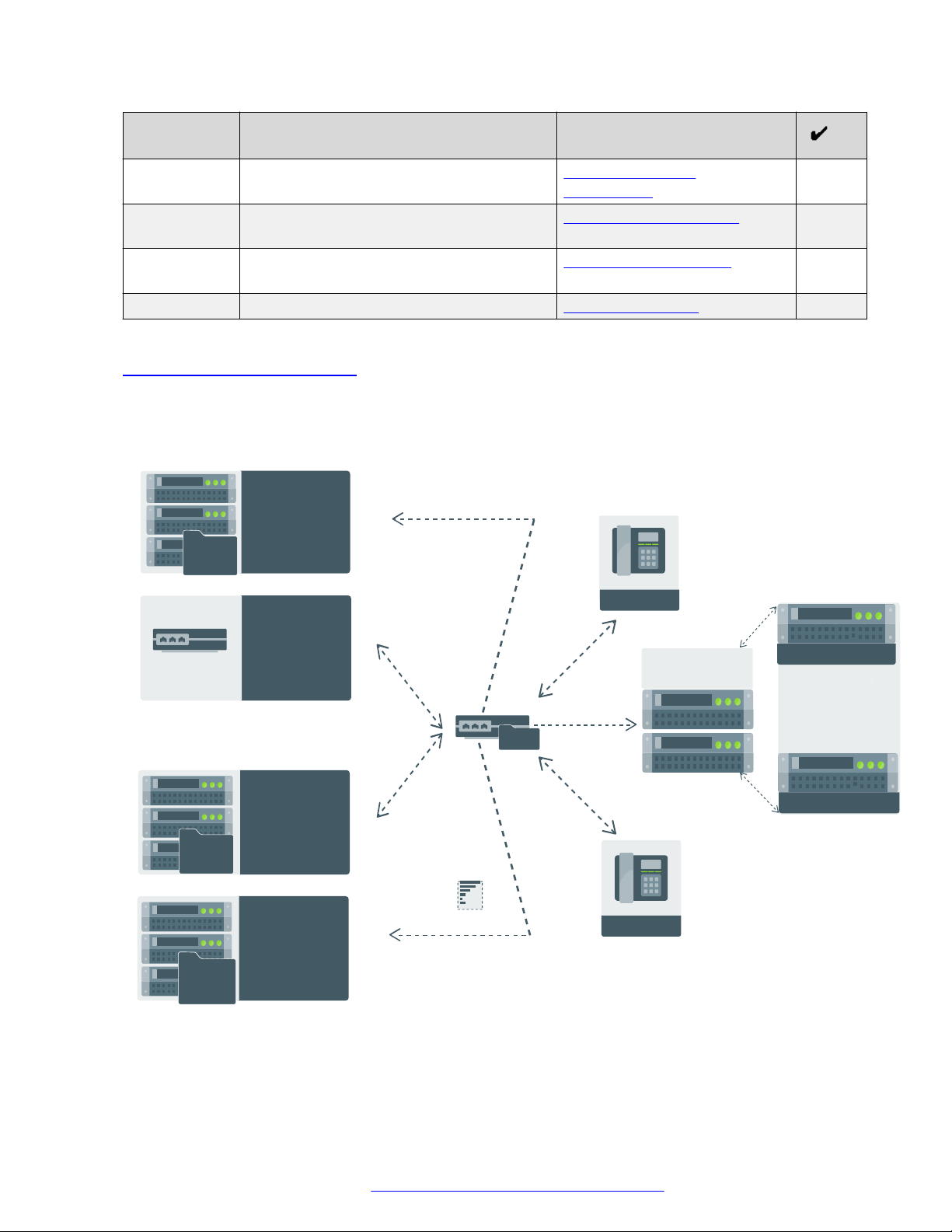
Phone setup with Session Border Controller (SBC)
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
setup 26
Page 27
Phone setup without Session Border Controller (SBC)
IP PHONE
IP PHONE
D H C P
Provides IP address
& sets configurable
parameters for
provisioning
46xxsettings.txt
Sets the system
parameters for
configuration
Configures
user,
communication,
and session profile
WAN Link
Manages power
and provides
configurable
parameters
for provisioning
Provides Software
distribution package
and Settings file
N e t w o r k
F i l e
S e r v e r
Network server /
Switch (LLDP)
Manages power
& provides configurable
parameters for
provisioning
D N S
Provides domain name
server address
R o u t e r
Avaya Aura
®
System Manager
Primary Call Server
Secondary Call Server
®
Phone installation
Related links
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
Phone installation without DES on page 24
Virtual LAN (VLAN) overview
VLANs provide a means to segregate your network into distinct groups or domains. They also
provide a means to prioritize the network traffic into each of these distinct domains. For example,
a network may have a Voice VLAN and a Data VLAN. Grouping devices that have a set of
common requirements can greatly simplify network design, increase scalability, improve security,
and improve network management. Therefore, you must always use VLANs in your network.
The networking standard that describes VLANs is IEEE 802.1Q. This standard describes, in detail,
the 802.1Q protocol and how Ethernet frames get an additional 4 byte tag inserted at the
beginning of the frame. This additional VLAN tag describes the VLAN ID that a particular device
belongs to, and the priority of the VLAN tagged frame. Voice and video traffic typically get a higher
priority in the network as they are subject to degradation caused by network jitter and delay.
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
setup 27
Page 28

Initial setup and connectivity
VLAN separation
The Avaya J100 Series IP Phones has an internal network switch that is capable of using VLANs
to segregate traffic between the LAN port, the PC port and the internal port that goes to the CPU
of the phone. You can have VLAN functionality on this switch and configure the switch to isolate
the traffic destined for the CPU of the phone from the data destined to the PC port.
The configuration of the internal switch of the phone can be done through the Settings file,
LLDP or DHCP. It is preferable to configure the VLAN settings on the internal switch of the phone
through DHCP or LLDP as these protocols are run prior to, and during, network initialization. If that
is not possible then the Settings file configuration parameters can be used and the VLAN can
be started in automatic mode, which is the default mode.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 28
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 29

Attached device.
For example, computer
Network access
switch
Ethernet line
interface (PHY 1)
Computer port
(PC port)
(PHY2)
ingress egress ingress egress
LAN port
PC port
Internal Ethernet switch
CPU port
egress ingress
Phone's CPU
Phone
Phone installation
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 29
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 30

Initial setup and connectivity
VLAN separation modes
Avaya J100 Series IP Phones supports two VLAN separation modes:
• No VLAN separation mode: In this mode the CPU port of the port receives untagged frames
and tagged VLAN frames on any VLAN irrespective of whether the phone sends untagged
frames or tagged frames. This traffic can be received from the PC port or LAN port. The
filtering of the frames is done by the CPU itself. In order to reduce unnecessary traffic to the
CPU, the administrator should configure only the necessary VLANs on the external switch
port, in particular, voice VLAN and data VLAN.
• Full VLAN separation mode: This is the default mode. In this mode the CPU port of the phone
receives tagged frames with VLAN ID = L2QVLAN whether they are from the LAN port or PC
port. The PC port receives untagged or tagged frames with VLAN ID = PHY2VLAN from the
LAN port. The PC port cannot send any untagged frames or tagged frames with any VLAN
ID, including the voice VLAN ID, to the CPU. Frames received externally on the PC port can
only be sent to the LAN port if they are untagged frames or tagged frames with VLAN ID=
PHY2VLAN. In this mode, there is a complete separation between CPU port and PC port. In
order to configure Avaya J100 Series IP Phones to work in this mode all the following
conditions must be met:
- VLANSEPMODE = 1 (default)
- L2Q = 0 (auto, default) or 1 (tag)
- L2QVLAN is not equal to 0
- PHY2VLAN is not equal to 0
- L2QVLAN is not equal to PHY2VLAN
- The phone actually sends tagged VLAN frames. This means that the DHCP server on
voice VLAN (L2QVLAN) is reachable and the phone receives IP address on voice VLAN.
If one of these conditions is not met then the phone works in no VLAN separation mode where all
kinds of traffic reaches the CPU port of the phone.
Note:
The phone can send tagged VLAN frames on the voice VLAN (L2QVLAN), but still not work in
full VLAN separation mode. For example, when PHY2VLAN = 0 or VLANSEPMODE = 0.
External switch configuration
Configure the following for the external switch port:
• Bind VLAN to the voice VLAN (L2QVLAN) and the data VLAN (PHY2VLAN). It is important to
restrict the VLAN binding when in No VLAN separation mode. This is because there is no
filtering by the internal phone switch and the CPU of the phone is subject to all the traffic
going through the phone. When in Full VLAN separation mode, the internal phone switch will
filter any tagged VLAN frames with VLANs other than voice VLAN (L2QVLAN) and data
VLAN (PHY2VLAN) in any case. However, you must configure only the necessary VLANs on
the external switch port.
• Set the default VLAN as the data VLAN (PHY2VLAN). This is the VLAN assigned by the
external switch port to untagged frames received from phone LAN port.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 30
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 31

Phone installation
• Configure one of the following for egress tagging:
- Data VLAN is untagged and voice VLAN is tagged.
- Data VLAN and voice VLAN are both tagged. You must configure this option to have Full
VLAN separation.
Sending egress voice VLAN frames untagged from the external switch port to the phone LAN port
means that there is no VLAN separation between the voice VLAN and data VLAN.
Exceptions to the VLAN forwarding rules
Exceptions to the VLAN forwarding rules are as follows:
• LLDP frames are always exchanged between the following in all VLAN separation modes:
- The LAN port and CPU port
- The CPU port and LAN port
• Spanning tree frames are always exchanged between the LAN port and PC port in all VLAN
separation modes.
• 802.1x frames are always exchanged between the following in all VLAN separation modes
according to DOT1XSTAT and DOT1X configuration:
- The LAN and CPU port or PC port
- The PC and CPU port or LAN port
- The CPU port and LAN port
Special considerations
Special use of VLAN ID=0
The phone adds a VLAN tag to the egress voice frames with a VLAN ID=0 in certain
configurations. For example, to utilize the priority functionality of the VLAN frame only and not the
VLAN ID properties. In this case, use the parameter L2QAUD or L2QSIG to set the value of the
VLAN priority portion of the VLAN tag.
Automatic failback of VLAN tagging
The phone connects to a network when the value of L2QVLAN does not match with the VLAN
being assigned to the network access switch. When the phone starts to connect, it tries to contact
the DHCP server with a VLAN ID=L2QVLAN. If the phone does not receive a DHCPOFFER with
that particular VLAN ID, then it eventually fails back. The phone tries to contact the DHCP server
again if the VLAN functionality of the phone is set to one of the following:
• L2Q=1: With a VLANID =0
• L2Q=0: Without any VLAN tag
The VLANTEST parameter determines how long the phone waits for a recognizable
DHCPOFFER. If VLANTEST= 0, then the phone does not fail back and keeps sending DHCP
requests by using tagged VLAN frames with VLAN ID = L2QVLAN.
VLAN support on the computer or PC port
In full VLAN separation mode, the phone only supports one VLAN on the computer port. In no
VLAN separation mode, all VLANs pass between the LAN and PC ports. However, the CPU port
receives all traffic even on VLANs that are not equal to L2QVLAN.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 31
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 32

Initial setup and connectivity
VLAN parameters
The following configuration parameters are used to configure VLAN functionality on the network
switch internal to the phone.
Parameter name Default value Description
L2Q 0 Specifies the VLAN tagging is
enabled or disabled.
Value operation:
• 0: Auto. VLAN tagging is turned
on when the network can
support VLAN tagging and
L2QVLAN is non zero.
• 1: On. VLAN tagging is turned
on when the network can
support VLAN tagging. The IP
phone sends tagged frames
with VLAN = L2QVLAN, even if
L2QVLAN is set to 0.
VLANTEST
• 2: Off. VLAN functionality is
disabled.
L2Q is configured through:
• Local admin procedure
• A name equal to value pair in
DHCPACK message
• SET command in a settings file
• DHCP option 43
• LLDP
60 Specifies the number of seconds
that the phone waits prior to
failing back to a different VLAN ID
if no response is received from
the DHCP server.
Valid values are 0 through 999.
Value operation:
• 0: The phone continues to
attempt a DHCP REQUEST
forever.
VLANTEST is configured through:
• Settings file
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 32
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 33

Phone installation
Parameter name Default value Description
• A name equal to value pair in
DHCPACK message
VLANSEPMODE 1 Specifies whether the VLAN
separation is enabled or disabled.
Value operation:
• 0: Disabled
• 1: Enabled
VLANSEPMODE is configured
through the settings file.
PHY2TAGS 0 Determines whether or not VLAN
tags are stripped on Ethernet
frames going out of the Computer
(PC) port.
Value operation:
• 0: Strip tags. VLAN tags are
stripped from Ethernet frames
leaving the computer (PC) port
of the phone.
• 1: Does not strip tags. VLAN
tags are not stripped from
Ethernet frames leaving the
Computer (PC) port of the
phone.
PHY2TAGS is configured through
the settings file.
L2QVLAN 0 Specifies the voice VLAN ID to be
used by IP phones.
Valid values are 0 through 4094.
L2QVLAN is configured through:
• Local admin procedure
• A name equal to value pair in
DHCPACK message
• SET command in a settings file
• DHCP option 43
• LLDP
PHY2VLAN 0 Specifies the value of the 802.1Q
VLAN ID that is used to identify
network traffic going into and
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 33
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 34

Initial setup and connectivity
Parameter name Default value Description
coming out of the internal CPU of
the phone.
Valid values are 0 through 4094.
PHY2VLAN is configured
through:
• SET command in a settings file
• LLDP
L2QAUD 6 Specifies the value of the VLAN
priority portion of the VLAN tag
when the phone generates
tagged Ethernet frames from the
internal CPU of the phone. These
values are inserted into the VLAN
tag for audio frames (RTP, RTCP,
SRTP, SRTCP). All other frames
except those specified by the
L2QSIG parameter are set to
priority 0.
Valid values are 0 through 7.
L2QAUD is configured through:
• SET command in a settings file
• LLDP
L2QSIG 6 Specifies the value of the VLAN
priority portion of the VLAN tag
when the phone generates
tagged Ethernet frames from the
internal CPU of the phone. These
values are inserted into the VLAN
tag for signaling frames (SIP). All
other frames except those
specified by the L2QAUD
parameter are set to priority 0.
Valid values are 0 through 7.
L2QSIG is configured through:
• SET command in a settings file
• LLDP
Configuration through LLDP
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is an open standards, layer 2 protocol that IP phones use to
advertise their identity and capabilities and to receive administration from Ethernet switches. LAN
equipment can use LLDP to manage power and administer VLANs, DSCP, and 802.1p priority
fields.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 34
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 35

Phone installation
The transmission and reception of LLDP is specified in IEEE 802.1AB-2005. The use TypeLength-Value (TLV) elements specified in IEEE 802.1AB-2005, TIA TR-41 Committee - Media
Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED, ANSI/TIA-1057), and Proprietary elements. LLDP Data Units
(LLDPDUs) are sent to the LLDP Multicast MAC address.
The running SIP software support IEEE 802.1AB if the value of the configuration parameter
LLDP_ENABLED is “1” (On) or “2” (Auto). If the value of LLDP_ENABLED is “0” (off), the
transmission and reception of Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is not supported. When the
value of LLDP_ENABLED is “2”, the transmission of LLDP frames does not begin until an LLDP
frame is received. The first LLDP frame is transmitted within 2 seconds after the first LLDP frame
is received. After transmission begins, an LLDPDU is transmitted every 30 seconds. A delay of up
to 30 seconds in phone initialization might occur if the file server address is delivered by LLDP and
not by DHCP.
These phones do not transmit 802.1AB multicast LLDP packets from an Ethernet line interface to
the secondary line interface and vice versa.
By using LLDP, you can configure the following:
• Call server IP address
• File server
• PHY2VLAN
• L2QVLAN and L2Q
LLDPDU transmitted by the phones
Category
Basic Mandatory Chassis ID IPADD of phone, IANA Address Family Numbers enumeration
Basic Mandatory Port ID MAC address of the device.
Basic Mandatory Time-To-Live 120 seconds.
Basic Optional System Name The Host Name sent to the DHCP server in DHCP option 12.
Basic Optional System
Basic Optional Management
IEEE 802.3
Organization
Specific
TIA LLDP MED LLDP-MED
TLV Name (Type) TLV Info String (Value)
value for IPv4, or subtype 5:Network address.
Bit 2 (Bridge) will be set in the System Capabilities if the phone
Capabilities
Address
MAC / PHY
Configuration /
Status
Capabilities
has an internal Ethernet switch. If Bit 2 is set in Enabled
Capabilities then the secondary port is enabled.
Mgmt IPv4 IP address of device.
Interface number subtype = 3 (system port). Interface number
= 1.
OID = SNMP MIB-II sysObjectID of the device.
Reports auto negotiation status and speed of the uplink port on
the device.
Media Endpoint Discovery capabilities = 00-33 (Inventory,
Power-via-MDI, Network Policy, MED Caps).
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 35
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 36

Initial setup and connectivity
Category TLV Name (Type) TLV Info String (Value)
TIA LLDP MED Network Policy Tagging Yes/No, VLAN ID for voice, L2 Priority, DSCP Value.
TIA LLDP MED Inventory –
MODEL - Full Model Name.
Hardware Revision
TIA LLDP MED Inventory –
Firmware version.
Firmware Revision
TIA LLDP MED Inventory –
Software version or filename.
Software Revision
TIA LLDP MED Inventory – Serial
Device serial number.
Number
TIA LLDP MED Inventory –
Avaya.
Manufacturer
Name
TIA LLDP MED Inventory – Model
MODEL with the final Dxxx characters removed.
Name
Avaya Proprietary Call Server IP
Call Server IP Address. Subtype = 3.
address
Avaya Proprietary IP Phone
addresses
Phone IP address, Phone Address Mask, Gateway IP
Address. Subtype = 4.
Avaya Proprietary File Server File Server IP Address. Subtype = 6.
Avaya Proprietary 802.1Q Framing 802.1Q Framing = 1 if tagging or 2 if not.
Basic Mandatory End-of-LLDPDU Not applicable.
TLV impact on system parameter values
System parameter
name
PHY2VLAN IEEE 802.1 Port
L2QVLAN and L2Q IEEE 802.1 VLAN
TLV name Impact
VLAN ID
Name
The value of the PHY2VLAN parameter on the phone is
configured from the value of the Port VLAN identifier in the
TLV.
The value is changed to the TLV VLAN Identifier. L2Q is set to
1 (ON).
A check is made as to whether a reset is necessary to obtain a
new IP address due to a change in the values of the
parameters L2Q or L2QVLAN.
VLAN Name TLV is ignored if:
• The value of USE_DHCP is 0 and the value of IPADD is not
0.0.0.0.
• The current value of L2QVLAN was set by a TIA LLDP MED
Network Policy TLV.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 36
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 37

Phone installation
System parameter
TLV name Impact
name
L2Q, L2QVLAN,
L2QAUD,
DSCPAUD
TIA LLDP MED
Network Policy
(Voice) TLV
L2Q, L2QVLAN TIA LLDP MED
Network Policy
(Voice Signaling)
• The VLAN name in the TLV does not contain the substring
“voice” in lower-case, upper-case or mixed-case ASCII
characters anywhere in the VLAN name.
L2Q - set to 2 (off) if T (the Tagged Flag) is set to 0 and to 1
(on) if T is set to 1.
L2QVLAN - Set to the VLAN ID in the TLV.
L2QAUD - Set to the Layer 2 Priority value in the TLV.
DSCPAUD - Set to the DSCP value in the TLV.
A check is made as to whether a reset is necessary to obtain a
new IP address due to a change in the values of the
parameters L2Q or L2QVLAN.
This TLV is ignored if:
• The value of USE_DHCP is 0 and the value of IPADD is not
0.0.0.0.
• The Application Type is not 1 (Voice) or 2 (Voice Signaling).
• The Unknown Policy Flag (U) is set to 1.
L2Q - set to 2 (off) if T (the Tagged Flag) is set to 0 and to 1
(on) if T is set to 1.
L2QVLAN - Set to the VLAN ID in the TLV.
SIP_CONTROLL
ER_LIST
TLSSRVR and
HTTPSRVR
Proprietary Call
Server TLV
Proprietary File
Server TLV
L2QAUD - Set to the Layer 2 Priority value in the TLV.
DSCPAUD - Set to the DSCP value in the TLV.
A check is made as to whether a reset is necessary to obtain a
new IP address due to a change in the values of the
parameters L2Q or L2QVLAN.
This TLV is ignored if:
• The value of USE_DHCP is 0 and the value of IPADD is not
0.0.0.0.
• The Application Type is not 1 (Voice) or 2 (Voice Signaling).
• The Unknown Policy Flag (U) is set to 1.
SIP_CONTROLLER_LIST will be set to the IP addresses in
this TLV value.
Note:
This parameter cannot be used in an environment where
both SIP phones and H.323 phones exist.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 37
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 38

Initial setup and connectivity
System parameter
name
L2Q Proprietary 802.1 Q
TLV name Impact
If the value of TLV = 1, L2Q is set to 1 (On).
Framing
If the value of TLV = 2, L2Q is set to 2 (Off).
If the value of TLV = 3, L2Q is set to 0 (Auto).
A check is made as to whether a reset is necessary to obtain a
new IP address due to a change in the values of the
parameters L2Q or L2QVLAN.
This TLV is ignored if:
• The value of USE_DHCP is 0 and the value of IPADD is not
0.0.0.0.
• The current L2QVLAN value was set by an IEEE 802.1
VLAN name.
• The current L2QVLAN value was set by a TIA LLDP MED
Network Policy (Voice) TLV.
TCP and UDP ports
Avaya J100 Series IP Phones use different protocols, such as TCP, TLS, and UDP to
communicate with other equipment in the network. Part of this communication identifies which
TCP or UDP ports each piece of equipment uses to support each protocol and each task within
the protocol. Depending on your network, you need to know what ports or ranges are used in the
operation of the phones.
Received packets (destination = SIP phone)
Destination port
The number used in the
Source Port field of the
packets that the HTTP
client of the phone sends
The number used in the
Source Port field of the
SSL packets that the
HTTP client of the phone
sends
68 Any Received DHCP
SIP messages initiated
by the call server should
be sent to the port
number specified by the
value of SIPPORT
Source port Use Protocol
Any Packets that the HTTP
client of the phone
receives
Any SSL packets that the
HTTP client of the phone
receives
messages
Any Received signaling
protocol
UDP or TCP
TCP
TCP
UDP
TCP
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 38
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 39

Destination port Source port Use Protocol
UDP or TCP
(TCP). Responses to
SIP messages initiated
by the phone should be
sent to the number used
in the Source Port field
of the message from the
phone.
The number used in the
Source Port field of the
Any Received DNS
messages
UDP
DNS query that the
phone sends
The number used in the
Source Port field of the
Any Received SNTP
messages
UDP
SNTP query that the
phone sends
161 Any Received SNMP
UDP
messages
Phone installation
Transmitted packets (source = SIP phone)
Destination port
53 Any unused port number Transmitted DNS
67 68 Transmitted DHCP
80, unless explicitly
specified otherwise
123 Any unused port number Transmitted SNTP
The number used in the
Source Port field of the
SNMP query packet
received by the phone
443, unless explicitly
specified otherwise
514 Any unused port number Transmitted Syslog
Source port Use Protocol
messages
messages
Any unused port number Packets transmitted by
the HTTP client of the
phone
messages
161 Transmitted SNMP
messages
Any unused port number TLS/SSL packets
transmitted by the HTTP
client of the phone.
messages
UDP or TCP
UDP
UDP
TCP
UDP
UDP
TCP
UDP
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 39
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 40

Initial setup and connectivity
Destination port Source port Use Protocol
The port number
specified in the test
request message
System-specific Any unused port number Transmitted signaling
FEPORT + 1 (if
FEPORT is even) or
FEPORT -1 (if FEPORT
is odd) or the port
number specified in a
CNA RTP test request
plus or minus one, as
with FEPORT
RTCPMONPORT PORTAUD + 1 (if
System-specific Any unused port number Transmitted signaling
50000 Transmitted SLA Mon
agent test results
messages
protocol packets
PORTAUD + 1 (if
PORTAUD is even) or
PORTAUD – 1 (if
PORTAUD is odd) or the
port number reserved for
CNA RTP tests plus or
minus one, as for
PORTAUD, above
PORTAUD is even) or
PORTAUD – 1 (if
PORTAUD is odd)
RTCP packets
transmitted to the farend of the audio
connection
RTCP packets
transmitted to an RTCP
monitor
protocol packets
UDP or TCP
™
UDP
TCP
UDP
UDP
UDP
Configuration through DHCP
Avaya J100 Series IP Phones connect to the DHCP server during the boot up. You can configure
the DHCP server to provide the following information to the device:
• IP address
• Subnet mask
• IP address of the router
• IP address of the HTTP or HTTPS file server
• IP address of the SNTP server
• IP address of DNS
You can configure the DHCP server to:
• Dynamically assign IP addresses to the Avaya J100 Series IP Phones.
• Provision device and site-specific configuration parameters through various DHCP options.
DHCP options
You can configure the following options in the DHCP server:
Option
Option 1 Specifies the subnet mask of the network.
Description
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 40
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 41

Phone installation
Option Description
Option 3 Specifies the gateway IP address list. The list can contain up to 127 total ASCII
characters. Separate more than one IP address with commas with no intervening
spaces.
Option 6 Specifies the DNS server address list. The list can contain up to 127 total ASCII
characters. Separate more than one IP address with commas with no intervening
spaces.
The phone supports DNS and the dotted decimal addresses. The phone attempts to
resolve a non-ASCII-encoded dotted decimal IP address by checking the contents of
DHCP Option 6. At least one address in option 6 must be a valid, nonzero, dotted
decimal address, otherwise the DNS address fails.
Option 12 Specifies the host name.
AVohhhhhh, where:
• AV stands for Avaya.
• o is one of the following values based on Object Unique Identifier (OUI) derived
from the first three octets of the phone MAC address:
- A if OUI is 00-04-0D
- B if OUI is 00-1B-4F
- E if OUI is 00-09-6E
- L if OUI is 00-60-1D
- T if the OUI is 00-07-3B
- X if the OUI is anything else
• hhhhhh are the ASCII characters for the hexadecimal representation of the last
three octets of the phone MAC address.
Option 15 Specifies the domain name. The domain name is required to resolve DNS names
into IP addresses.
Configure this option if you use a DNS name for the HTTP server. Otherwise, you
can specify a domain as part of customizing the HTTP server.
This domain name is appended to the DNS addresses specified in option 6 before
the phone attempts to resolve the DNS address. The phone queries the DNS
address in the order they are specified in option 6. If there is no response from an
address, the phone queries the next DNS address.
As an alternative to administering DNS by DHCP, you can specify the DNS server
and domain name in the HTTP script file. If you use the script file, you must
configure the DNSSRVR and DOMAIN parameters so that you can use the values of
these parameters in the script.
Note:
Administer option 6 and option 15 appropriately with DNS servers and domain
names respectively.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 41
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 42

Initial setup and connectivity
Option Description
Option 42 Specifies the SNTP IP address list. List servers in the order of preference. The
minimum length is 4 and the length must be a multiple of 4.
Option 43 Specifies the encapsulated vendor-specific options that clients and servers use to
exchange the vendor-specific information. Option 43 is processed only if the first
code in the Option is 1 with a value of 6889. The value 6889 is an Avaya enterprise
number. All values are interpreted as strings of ASCII characters that are accepted
with or without a null termination character. Any invalid value is ignored and the
corresponding parameter value is not set.
Option 51 Specifies the DHCP lease time. If this option is not received, the DHCPOFFER is not
accepted. Assign a lease time of six weeks or greater. If this option has a value of
FFFFFFFF hex, the IP address lease is assumed to be infinite, so that the renewal
and rebinding procedures are not necessary even if options 58 and 59 are received.
Expired leases causes the device to reboot.
Option 52 Specifies the overload option. If this option is received in a message, the device
interprets the sname and file parameters.
Option 53 Specifies the DHCP message type. The value can be one of the following:
• 1 for DHCPDISCOVER
• 3 for DHCPREQUEST
For DHCPREQUEST sent to renew the device IP address lease:
• If a DHCPACK is received in response, a log event record is generated with a Log
Category of DHCP.
• If a DHCPNAK is received in response, the device immediately ceases IP address
usage, generates a log event record, sets IPADD to 0.0.0.0, and enters the DHCP
INIT state.
Option 55 Specifies the parameter request list. Acceptable values are:
• 1 for subnet mask
• 3 for router IP addresses
• 6 for domain name server IP addresses
• 7 for log server
• 15 for domain name
• 42 for NTP servers
Option 57 Specifies the maximum DHCP message size.
Set the value to 1500.
Set the value to 1000.
Option 58 Specifies the DHCP lease renew time. If not received or if this value is greater than
that for option 51, the default value of T1, renewal timer is used.
Option 59 Specifies the DHCP lease rebind time. If not received or if this value is greater than
that for Option 51, the default value of T2, rebinding timer is used.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 42
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 43

Phone installation
Option Description
Option 242 Specifies the site-specific option. This option is optional. If you do not configure this
option, ensure that one of the following parameters is configured appropriately
elsewhere:
• HTTPSRVR
• TLSSRVR
DHCP vendor-specific option
You can set DHCP vendor-specific parameters by using DHCP option 43. The supported codes for
Option 43 and the corresponding parameters are as follows:
Code Parameter
1 Does not set any parameter. The value must be 6889.
2 HTTPSRVR
3 HTTPDIR
4 HTTPPORT
5 TLSSRVR
6 TLSDIR
7 TLSPORT
8 TLSSRVRID
9 L2Q
10 L2QVLAN
11 PHY1STAT
12 PHY2STAT
14 SIG
15 SIP_CONTROLLER_LIST
DHCP lease time
The DHCP standard states that when a DHCP lease expires, the device should immediately
cease using its assigned IP address. However, if the network has problems and the only DHCP
server is centralized or if the DHCP server itself has problems, the device will not receive
responses to its request for a renewal of the lease. In this case the device is not usable until the
server can respond. Configure system such that once the IP address is assigned to the device,
the device continues using that address after the DHCP lease expires, until a conflict with another
device is detected.
The system parameter DHCPSTD allows an administrator to specify that the device will either:
• Comply with the DHCP standard by setting DHCPSTD to 1.
• Continue to use its IP address after the DHCP lease expires by setting DHCPSTD to 0.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 43
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 44

Initial setup and connectivity
The latter case is the default. If the default is invoked, after the DHCP lease expires the phone
continues to broadcast DHCPREQUEST messages for its current IP address, and it sends an
ARP Request for its own IP address every five seconds.
The messages continue to be sent until the device receives a DHCPACK, a DHCPNAK, or an
ARP reply. After receiving a DHCPNAK or ARP reply, the device immediately stops using the
current IP address. The device displays the DHCPNAK: message for five seconds and then, sets
the IP address to 0.0.0.0. Duplicate address detection is no longer performed and the device
enters the DHCP INT state.
Depending on the DHCP application you choose, the application might not immediately recycle
expired DHCP leases. An expired lease might remain reserved for the original client a day or
more. If the client and the DHCP server are in two different time zones, the clocks of the
computers are not in sync, or the client is not on the network when the lease expires, there is time
to correct the situation.
The following example shows the implication of having a reservation period.
Assume that there are two IP addresses, therefore two possible DHCP leases. Assume that there
are three IP devices in the network, two of which are using the two available IP addresses. When
the lease for the first two devices expires, the third device cannot get a lease until the reservation
period expires. Even if the other two devices are removed from the network, the third device
remains without a lease until the reservation period expires.
Parameter configuration through DHCP
Parameter Set to
DHCP lease
time
DHCP lease
renew time
DHCP lease
rebind time
DOMAIN Option 15, if received
DNSSRVR Option 6, if received, which might be a list of IP addresses
HTTPSRVR The siaddr parameter, if that parameter is non-zero
IPADD The yiaddr parameter
LOGSRVR Option 7, if received
MTU_SIZE Option 26
NETMASK Option 1, if received
ROUTER Option 3, if received, which might be a list of IP addresses
SNTPSRVR Option 42
Option 51, if received
Option 58, if received
Option 59, if received
DHCP site-specific option
You can set the values of site-specific configuration parameters through a DHCP option. The
default DHCP option to set the site-specific configuration parameters is 242. You can also use any
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 44
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 45

Phone installation
option between 128 to 254. Whichever option you select , you must specify that number in the
Site-Specific Option Number (SSON) parameter by using the device interface.
The following is an example of the DHCP 242 option string that specifies the HTTPSRVR and the
Voice VLAN that the device must connect to.
HTTPSRVR=10.138.251.67,L2QVLAN=1104
The following table lists the site-specific configuration parameters that you can define for the
device:
Parameter Description
ADMIN_PAS
SWORD
HTTPDIR Specifies the path to prepend to all configurations and data files that the device might
Specifies the security string used to access local procedures. The string can contain
alphanumeric characters. The default is 27238. This parameter replaces PROCPSWD as
it provides a more secure password syntax.
request when starting up. This path is relative to the root of the HTTP file server and also
to the directory in which the device configuration and date files are stored. The path might
contain maximum 127 characters without spaces. HTTPDIR is the path for all HTTP
operations.
The command is SET HTTPDIR=<path>. In configurations where the upgrade and
binary files are in the default directory on the HTTP server, do not use HTTPDIR=<path>.
HTTPPORT Specifies the destination port for HTTP requests. The default is 80.
HTTPSRVR The firmware files are digitally signed, so TLS is not required for security.
ICMPDU Controls the extent to which ICMP Destination Unreachable messages are sent in
response to messages sent to closed ports so as not to reveal information to potential
hackers. The default is 1, which sends Destination Unreachable messages for the closed
ports used by traceroute.
ICMPRED Controls whether ICMP Redirect messages are processed. The default is 0 in which
redirect messages are not processed.
L2Q Specifies the 802.1Q tagging mode. The default is 0 for automatic.
L2QVLAN Specifies the VLAN ID of the voice VLAN. The default is 0.
PHY1STAT Controls the Ethernet line interface speed. The default is 1 for auto-negotiate.
PHY2STAT Controls the secondary Ethernet interface speed. The default is 1 for auto-negotiate.
PROCPSWD Specifies the security string used to access local procedures. The string can contain only
four numeric characters. The default is 27238.
PROCSTAT Controls whether local procedures are enabled. The default is 0 for enabled.
REUSETIME Specifies the time in seconds for IP address reuse. The default is 60 seconds.
SIP_CONTR
OLLER_LIST
TLSDIR Specifies the path to all file names used in HTTPS GET operations during initialization.
Specifies the SIP proxy or registrar server IP or DNS addresses. The list contains 0 to 255
characters. The IP address must be in the dotted decimal name format, separated by
commas and without intervening spaces. The default is null.
The path name is prepended. The string can be from 0 to 127 characters long.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 45
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 46

Initial setup and connectivity
Parameter Description
TLSPORT Specifies the destination TCP port used for requests to https servers in the range of 0 to
65535. The default is 443, which is the standard HTTPS port.
TLSSRVR Specifies the IP address or DNS name of the file server that is used to download the
configuration files. Firmware files can also be downloaded using HTTPS.
Note:
Transport Layer Security is used to authenticate the server.
VLANTEST Specifies the number of seconds to wait for DHCPOFFER on a non-zero VLAN. The
default is 60 seconds.
Downloading and saving the software
Before you begin
Ensure that your file server is set up.
Procedure
1. Go to the
https://support.avaya.com/ website.
2. In the Enter Your Product Here field, enter Avaya J100 Series IP Phones.
3. In the Choose Release field, click the required release number.
4. Click the Downloads tab.
The system displays a list of the latest downloads.
5. Click the appropriate software version.
The system displays the Downloads page.
6. In the File field, click the zipped file and save the file on the file server.
7. Extract the zipped file and save it at an appropriate location on the file server.
8. From the latest downloads list, click the Settings file.
The system displays the Downloads page.
9. In the File field, click the Settings file and save the file at an appropriate location on the
file server.
Software distribution package
Note:
For any new software release, ensure that you download the latest software distribution
package and read any Product Support Notices (PSNs) associated with the new release. Both
are available on the Avaya support website
Review the release notes and any Read Me files associated with a distribution package.
Ensure that the Settings file is not cached in your browser. To do this, clear the browser cache
before downloading the settings file from the Avaya support Web site, so that you don’t get an
old version.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 46
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 47

Phone installation
Software distribution package containing the files needed to operate the Avaya J100 Series IP
Phones are packaged together in a ZIP format. You can download the package from the Avaya
support website.
SIP software distribution package contains:
• One or more software files
• One upgrade file, J100Supgrade.txt.
• Language files. For example, Mlf_J129_BrazilianPortuguese.xml,
Mlf_J129_Chinese.xml.
• File named release.xml that is used by the Avaya Software Update Manager application.
Avaya Software Update Manager upgrades and maintains firmware for Avaya managed
devices.
Note:
You can configure a third-party root certificates by using the TRUSTCERTS parameter in the
46xxsettings.txt file. The supported file format is PEM.
Configuring the Settings file
About this task
Use this procedure to modify the Settings file with appropriate values to provision the device
configuration parameters.
Procedure
1. On the file server, go to the location where you downloaded the 46xxsettings.txt
Settings file.
2. Open the Settings file in a text editor.
3. Set the required parameters.
4. Save the Settings file.
Provisioning Server configuration
A file server is an HTTP or an HTTPS server that is required to download and save the software
distribution package and the settings file.
On restarting, the phone checks for software updates and settings files on the specified file
servers.
You can provide the file server addresses to phones through one of the following methods:
• DHCP
• LLDP
• Device interface
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 47
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 48

Initial setup and connectivity
Installing the phone
Before you begin
You must do the following:
• Configure the file server.
• Download and extract the firmware zip file to your file server.
• Configure the 46xxsettings.txt file.
Procedure
1. Set up the phone hardware.
2. Plug the Ethernet cable to the phone.
The phone powers up and starts to initialize.
3. The initialization procedure consists of the following processes:
a. The phone checks for LLDP messages.
b. The phone sends a DHCP DISCOVER message to discover the DHCP server in the
network and invokes the DHCP process.
If the phone does not receive a provisioning server address from the configuration
setup, the phone displays the Configure Provision Server screen.
c. In the Configure Provision Server screen, press the Config softkey and enter the
address of the provisioning server. The provisioning server address can be in the form
of IP address or a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). To enter the dot symbol (.)
in the field, press the alphanumeric softkey to toggle to the alphanumeric mode.
d. The phone verifies the VLAN ID, and starts tagging the data and voice packets
accordingly.
e. The phone sends and identifies an upgrade script file, gets the Settings file, the
language files, and any firmware updates.
• If configured to use simple certificate enrollment protocol (SCEP), the phone
downloads a valid device certificate.
• The phone displays only the Admin softkey for 15 seconds, and then the Admin
and the Login softkeys.
Note:
For subsequent restarts, if the user login is automatic and the supplied
credentials are valid, the Login softkey is not displayed.
4. Do one of the following:
• To access the user login screen, press the Login softkey.
• To access the Admin menu, press the Admin softkey and enter the admin menu
password.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 48
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 49

Device upgrade process
1. During boot-up, the phone receives the file server address from DHCP, LLDP, or the device
interface.
2. The phone contacts the provisioning server to download the firmware upgrade file,
J100Supgrade.txt.
3. In J100Supgrade.txt, the APPNAME parameter contains the firmware version.
4. The phone compares the currently installed software version with the version specified in
the APPNAME parameter.
5. If the firmware version specified in the APPNAME parameter is higher, the phone
downloads the software files for upgrade.
6. The phone automatically restarts to apply the upgraded firmware
Tip:
The upgrade events are logged under NOTICES level in the Syslog file.
Post installation checklist
Phone installation
To ensure that the phone is properly installed and running properly, verify that the following
requirements are complete.
No.
1 Has the phone acquired an IP
2 Are you able to make a call from the
3 Are you able to perform backup-
3 Are you able to modify the phone's
4 Are you able to upgrade your phone? Device upgrade process on
5 Have you installed the appropriate
6 It is critical that you verify Emergency
Task Reference
address?
phone?
restore?
Configuration parameters on
Settings file parameters and end user
settings.
private network authentication
certificates?
calling is working properly in your
network. It may be necessary to
make arrangements with the
appropriate authorities to test this
functionality.
page 118
page 49
For more information, see
Administering emergency
numbers
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 49
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 50

Initial setup and connectivity
Broadsoft Device Management
With the Broadsoft Device Management feature, you can download device-specific configuration
files from the BroadWorks server in Avaya J100 Series IP Phones.The phone does not require a
third-party provisioning server and connects automatically to the Broadsoft server.
You must have a user name and password to access the configuration files in the BroadWorks
server.
To support Broadsoft Device Management feature, the phone must support:
• HTTP Authentication.
• HTTP redirection using “302 Found”.
• SIP NOTIFY request from the Broadsoft server to access or reset the device.
Device management configuration
The configuration parameter for the Broadsoft Device Management is:
Parameter name Default Value Description
ENABLE_OOD_RESET_NOTIFY 0 Specifies whether the phone
supports Out Of Dialog (OOD)
SIP NOTIFY message with
Event:resync or Event:check-sync
only.
Value operation:
• 0: OOD is not supported.
• 1: OOD is supported.
The phone restart using SIP
NOTIFY request.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 50
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 51

Chapter 4: Configuring the phone using
web interface
Logging in and logging out of the web UI
About this task
Use this procedure to log in or log out of the web UI. Note that the system prompts you to change
your default password only after the first log in.
Before you begin
• On the phone UI, use the admin menu to do the following:
- Change the status of Web Server to On admin menu.
- Obtain the IP address of the phone Administration menu.
Procedure
1. In your browser, enter the IP address of the phone and press Enter.
2. On the login page, type the following:
• Username: The user name is always admin.
• Password: The default password is 27238.
3. Click Login.
The system displays the Change Default Password.
4. In the Change Default Password dialog box, type the following:
• New password
• Confirm password
5. Click Update.
The system displays the login page.
6. To log out of the web UI, click Logout.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 51
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 52

Configuring the phone using web interface
Changing password
Procedure
1. Log in to the web GUI using your username and current password.
2. In the left pane of the screen, click Password.
The System section is displayed.
3. In the System section, enter your old password in the Old Password field, enter your new
password in the New Password field, re-enter your new password in the Confirm
Password field, and click Save.
• Your password must be between 8 to 31 alphanumeric characters including upper, lower
and special characters.
• Your password should contain at least 2 digits.
• Allowed special characters are ~!@#$%^&*_-+=`|\(){}[]:;'<>,.?/.
Configuring environment settings
Procedure
1. Log in to the web interface as an administrator.
2. In the navigation pane, click Environment Settings.
3. In the Environment Setting area, enable the following fields:
• AURA environment: To set Avaya Aura as your environment.
• Discover AVAYA environment: To discover whether the phone supports Avaya Aura
SIP AST feature.
• IP Office: To set IP Office as your environment.
• 3PCC environment: To set a third-party call controller as your environment.
Configuring date and time
Procedure
1. Log in to the web interface as an administrator.
2. In the navigation pane, click Date & Time.
3. In the SNTP area, configure the following:
• SNTP Server: Type the SNTP server IP address .
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 52
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 53

Configuring date and time
• SNTP SYNC Interval: Type the SNTP synchronization time interval to re-synchronize
the phone’s local time . The valid time interval is from 60 to 2880 minutes. The default
synchronization time is 1440 minutes.
• GMT Offset: Type the GMT Offset value in hours and minutes between the local
standard time and Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). The offset value ranges from 0:00 to
±12:59.
4. In the Daylight Saving area, configure the following:
• Daylight Saving Mode: The options are :
- Automatic daylight saving time:
- Manual daylight saving activated (time set to DSTOFFSET):
- Manual daylight saving adjustment (as specified by DSTSTART and DSTSTOP):
• DST Offset: Specifies the offset time between standard time and daylight savings time.
The options are:
- 0
- 1 hour
- 2 hour
• DST Start: Specifies the daylight savings time start date and time with a format of either
odddmmmht or Dmmmht; where:
- o represents a one-character ordinal adjective. For example, 1 for first, 2 for second,
3 for third, 4 for fourth, or L for last.
- D represents 1 or 2 ASCII digits or character representing the date of the month.
- ddd represents a three-characters containing the English abbreviation for the day of
the week. For example, Sun for Sunday, Mon for Monday.
- mmm represents a three-character English abbreviation for the month. For example,
Jan for January, Feb for February.
- h represents one-numeric digit representing the time to make the adjustment at hAM
(0h00 in military format).
The valid values of h are "0" to "9";
- t represents one-character for the time zone to which to make the adjustment. For
example, “L” for local time or “U” for Universal Time.
• DST Stop: Specifies the daylight savings time stop date and time with a format of either
odddmmmht or Dmmmht; where:
- o represents a one-character ordinal adjective. For example, 1 for first, 2 for second,
3 for third, 4 for fourth, or L for last.
- D represents 1 or 2 ASCII digits or character representing the date of the month.
- ddd represents a three-characters containing the English abbreviation for the day of
the week. For example, Sun for Sunday, Mon for Monday.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 53
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 54

Configuring the phone using web interface
- mmm represents a three-character English abbreviation for the month. For example,
Jan for January, Feb for February.
- h represents one-numeric digit representing the time to make the adjustment at hAM
(0h00 in military format).
The valid values of h are "0" to "9";
- t represents one-character for the time zone to which to make the adjustment. For
example, “L” for local time or “U” for Universal Time.
5. Click one of the following :
• Save: To save the configuration changes.
• Reset to Default: To revert to the default values.
• Help: To view the online help.
Configuring Ethernet settings
Procedure
1. Log in to the web interface as an administrator.
2. In the navigation pane, click Ethernet.
3. Configure the following areas:
• IP Configuration
• 802.1X
• VLAN
• QoS
• LLDP
• Interface
4. Click one of the following :
• Save
• Reset to Default
• Help
Related links
Ethernet settings field descriptions on page 55
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 54
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 55

Configuring Ethernet settings
Ethernet settings field descriptions
Name Description
IP Configuration
Use DHCP Provides the IP address to your phone automatically or manually.
The options are:
• Yes: To assign the IP address automatically to your phone.
• No: To assign the IP address manually to your phone.
Note that, to assign the IP address manually, you must also configure
the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway IP Address fields
manually.
Continue to use DHCP
information after lease expiry
Specifies whether the DHCP information can be used after the lease
expires.
The options are:
• Yes: To use the assigned IP address after the DHCP lease expires.
• No: To stop using the assigned IP address after the DHCP lease
expires.
IP Address re-use time Specifies the time in seconds to re-use the assigned IP address after
the DHCP lease expires. The default value is 60 seconds.
IP Address Specifies the IP address of the phone. .
Subnet Mask Specifies the network mask address. To assign the network mask
address manually to your phone, type the address in the corresponding
field.
Gateway IP Address Specifies the IP address of the gateway. To assign the gateway IP
address manually to your phone, type the address in the corresponding
field.
802.1X
Supplicant Operating Mode Specifies the 802.1X supplicant operating mode.
The options are:
• Disabled
• Unicast
• Multicast
Pass-through Operating Mode Specifies the 802.1X pass-through operating mode.
Pass-through refers to the forwarding of EAPOL frames between the
phone's Ethernet line interface and the secondary PC Ethernet
interface.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 55
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 56

Configuring the phone using web interface
Name Description
The options are:
• Without proxy logoff
• With proxy logoff
• disabled
Authentication Mode Specifies the authentication method to be used by 802.1X.
The options are:
• MD5
• TLS
VLAN
VLAN Specifies whether the VLAN tagging is enabled or disabled.
The options are:
• Auto: To support VLAN functionality by using the phone network.
• On: To support the VLAN functionality by using the internal switch of
the phone.
• Off: To disable the VLAN functionality of the phone.
VLAN ID Specifies the VLAN ID. To assign a VLAN ID, type the VLAN ID.
Configure this parameter if the phone uses a different VLAN than the
default data VLAN.
VLAN Separation Mode Specifies the VLAN separation mode.
The options are :
• Disable
• Enable
VLAN Test - Wait Time for
DHCP Offer
Specifies the wait time interval in seconds to receive a DHCPOFFER
on a non-zero VLAN. The default value is 60 seconds.
PC Port VLAN ID Specifies the VLAN ID of the PC port.
Tags to PC Eternet Interface Specifies whether the VLAN tags are stripped from Ethernet frames
that leave the computer (PC) port.
The options are:
• Do not remove
• Remove
QoS
Audio Priority (Layer 2) Specifies the Layer 2 priority value for audio (RTP and RTCP) streams.
Valid priority values are 0 to 7.
Signaling Priority (Layer 2) Specifies the Layer 2 priority value for signaling protocol messages.
Valid priority values are 0 to 7.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 56
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 57

Configuring Ethernet settings
Name Description
Audio DiffServ (Layer 3) Specifies the layer 3 Differentiated Services (DiffServ) code point for
audio frames generated by the phone. Valid values are 0 to 63.
Signaling DiffServ (Layer 3) Specifies the layer 3 Differentiated Services (DiffServ) code point for
signaling frames generated by the phone. Valid values are 0 to 63.
LLDP
LLDP Specifies the status of LLDP.
The options are:
• Disabled
• Enabled
• Enabled- only if LLDP frame is received
Interface
Ethernet Specifies the speed and duplex settings for the Ethernet line interface.
The options are:
• auto-negotiate
• 10Mbps half-duplex
• 10Mbps full-duplex
• 100Mbps half-duplex
• 100Mbps full-duplex
PC Ethernet Specifies the speed and duplex settings for the secondary (PC)
Ethernet interface.
The options are:
• auto-negotiate
• 10Mbps half-duplex
• 10Mbps full-duplex
• 100Mbps half-duplex
• 100Mbps full-duplex
• Disable
PC Ethernet auto-MDIX Specifies the status of the auto-MDIX Value Operation.
The options are:
• Enable
• Disable
Related links
Configuring Ethernet settings on page 54
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 57
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 58

Configuring the phone using web interface
Configuring Wi-Fi settings
Procedure
1. Log in to the web interface as an administrator.
2. In the navigation pane, click Wi-Fi.
3. Configure the following areas :
• WiFi Setting
• IP Configuration
• WEP
• WPA2 Enterprise (802.1x)
• QoS
4. Click one of the following:
• Save
• Reset to Default
• Help
Related links
Wi-Fi settings field descriptions on page 58
Wi-Fi settings field descriptions
Name
WiFi Setting
Country Specifies the country code to define the Wi-Fi radio parameters
Use of 802.11d Configures the 802.11d specifications automatically to the local
SSID Specifies the network name for the WLAN you are using.
Password Specifies the password for the SSID.
Description
permitted by the local regulatory domain.
regulatory domain for the WLAN network.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable
You can also type the SSID in this field.
You can also type the password in this field.
Note that the maximum length of a password is 63 characters.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 58
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 59

Configuring Wi-Fi settings
Name Description
Security Specifies the WLAN security standard for your WiFi network.
The options are:
• None
• WEP Security
• WPA2 security with pre-shared key
• WPA security with pre-shared key
• WPA2 Enterprise security (802.1x auth.)
IP Configuration
Use DHCP Provides the IP address to your phone automatically. You can
also manually assign the IP address.
The options are:
• Yes: To assign the IP address automatically to your phone. To
display the IP address automatically
• No: To assign the IP address manually to your phone.
If you assign the IP address manually, you must also configure
the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway IP Address fields
manually.
IP Address Specifies the IP address of the phone. You can also type the IP
address in this field.
Subnet Mask Specifies the network mask address. You can also type the
network mask address in this field.
Gateway IP Address Specifies the IP address of the gateway. You can also type the
gateway IP address in this field.
WEP
WEP Authentication Specifies the type of WEP authentication method used by your
WiFi network.
The options are:
• Open systems
• Shared key
WEP Key Length Specifies the passcode key length for your WEP security.
The options are:
• 40 bit
• 64 bit
• 128 bit
WEP Default Key Specifies the default key for your WiFi network.
You can select a default key from WEP key 1 to 4.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 59
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 60

Configuring the phone using web interface
Name Description
WEP Key 1–4 Specifies the WEP key values for the WiFi network.
You can configure up to 4 WEP keys.
Note that the maximum length of a WEP key is 26 alphanumeric
characters that can include the following:
• Blank
• 0–9
• A-F
Blank, 0 to 9, A to F. make a vertical list
WPA2 Enterprise (802.1x)
EAP Authentication Method Specifies the type of EAP authentication method.
The options are:
• PEAP
• TLS
EAP Phase 2 Authentication Method
Authentication Identity
Authentication Anonymous Identity
QoS
Audio Priority (Layer 2) Specifies the Layer 2 priority value for RTP and RTCP audio
streams. Valid priority values are 0 to 7.
Signaling Priority (Layer 2) Specifies the Layer 2 priority value for signaling protocol
messages. Valid priority values are 0 to 7.
Audio DiffServ (Layer 3) Specifies the layer 3 Differentiated Services (DiffServ) code
point for audio frames generated by the phone. Valid values are
0 to 63.
Signaling DiffServ (Layer 3) Specifies the layer 3 Differentiated Services (DiffServ) code
point for signaling frames generated by the phone. Valid values
are 0 to 63.
Related links
Configuring Wi-Fi settings on page 58
Configuring network settings
Procedure
1. Log in to the web interface as an administrator.
2. In the navigation pane, click Network.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 60
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 61

3. Configure the following areas :
• Network
• DNS
• ICMP
• TCP
• Web Server
4. Click one of the following:
• Save
• Reset to Default
• Help
Related links
Network settings field description on page 61
Configuring network settings
Network settings field description
Name
Network
Network Mode of Operation Specifies the network mode used by the phone.
DNS
DNS Server Specifies the IP addresses of the DNS servers
DNS Domain Specifies the domain name of the IP address. You
ICMP
Destination Unreachable Message Control Specifies the type of the ICMP destination
Description
The operations are:
• Ethernet only
• Ethernet
• Wi-Fi
added to the network. You can type the DNS
servers in this field.
can type the DNS domain name in this field.
unreachable messages .
The options are:
• No
• Limited Port Unreachable messages
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 61
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 62

Configuring the phone using web interface
Name Description
• Protocol and Port Unreachable messages
Redirect Message Control Specifies whether the ICMP redirect messages are
processed or not.
The options are:
• Yes
• No
TCP
Send TCP Keep Alive Message Specifies whether the TCP/IP keep-alive messages
are enabled or disabled at the system.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable
TCP Keep Alive Time Specifies the wait time interval of the phone before
sending out the TCP keep-alive message (TCP
ACK message) to the far-end.
The valid time interval range is from 10 to 3600
seconds.
TCP Keep Alive Interval Specifies the TCP keep-alive packet re-
transmission interval
The valid time interval range is from 5 to 60
seconds.
Web Server
Web Server Specifies whether the web server is enabled or
disabled.
The options are :
• Enable
• Disable
HTTP Listen Port Specifies the port number of the web server when
the web interface is accessed using HTTP.
The default port number is 80.
HTTPS Listen Port Specifies the port number of the web server when
the web interface is accessed using HTTPS.
The default port number is 443.
Use custom certificate for Web Server Specifies whether to use the custom server
certificate when the web interface is accessed using
HTTPS.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 62
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 63

Name Description
The options are:
• No
• Yes
Related links
Configuring network settings on page 60
Configuring management settings
Procedure
1. Log in to the web interface as an administrator.
2. In the navigation pane, click Management.
3. Configure the following areas:
Configuring management settings
• Device Enrollment Server
• HTTP Provisioning Server
• HTTPS Provisioning Server
• Configuration
• Firmware
• Backup/Restore User Data
4. Click one of the following:
• Save
• Reset to Default
• Help
Related links
Management settings field descriptions on page 63
Management settings field descriptions
Name
HTTP Provisioning Server
HTTP Server Address Specifies the IP address of the of the provisioning
Description
file server.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 63
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 64

Configuring the phone using web interface
Name Description
HTTP Server Directory Path Specifies the path to prepare all configurations and
data files the device might request when starting up,
that is, the path, relative to the root of the HTTP file
server, to the directory in which the device
configuration and date files are stored.
HTTP Port Specifies the HTTP port address.
The default port number is 80.
HTTPS Provisioning Server
HTTPS Server Address Specifies the IP address of the HTTPS provisioning
file server.
HTTPS Server Directory Path Specifies the path to prepare all configurations and
data files the device might request when starting up,
that is, the path, relative to the root of the HTTPS
file server, to the directory in which the device
configuration and date files are stored.
HTTPS Port Specifies the HTTPS port address.
The default is 443.
Configuration
Import Configuration File Enable user to import a configuration file. To import
a configuration file, click Choose File to browse
your local PC or any PC connected to the network,
select the file and click Import.
The administrator needs to restart the phone after
the configuration file is uploaded.
Export Configuration File Enable user to export a configuration file. To export
a configuration file, click Export .
Firmware
Software Version Specifies the software version of the SIP software
Backup Software Version Specifies the backup software version.
Firmware Upgrade Enable user to import the upgrade file from the local
PC or any PC connected to the network.
To upload the firmware upgrade file, click Choose
File to browse your local PC, select the file and
click Upgrade.
The phone reboots after you select Yes in the
prompt.
Language
Language File Enables the user to upload language files to the
phone from the local PC. To import a language file
from your local PC or any PC connected to the
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 64
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 65

Configuring settings
Name Description
network, click Choose File to browse to your local
PC, select the language file and click Import.
Language File Uploaded Specifies the available language files for the phone
to be used.
Related links
Configuring management settings on page 63
Configuring settings
Procedure
1. Log in to the web interface as an administrator.
2. In the navigation pane, click Settings.
3. Configure the following areas:
• Language
• Feature access
• Phone Menu Option
• Call Log
• Contacts
• Emergency Call
• Phone Lock
• Other
• Audio
• Dialing
• Enhanced Local Dialing Rules
• Admin
4. Click one of the following:
• Save
• Reset to Default
• Help
Related links
Settings field descriptions on page 66
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 65
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 66

Configuring the phone using web interface
Settings field descriptions
Language
Name Description
Language
Available Language File Specifies the name of the default system language file used in
the phone.
You can delete the default language file by clicking Delete.
Import Language File You can browse and import a language file from your local
machine by clicking Choose File > Import.
Language file to upload Specifies the language file to be uploaded.
Phone Language Specifies the phone language file.
Feature Access
Call Forward Specifies the status of the call forward feature .
The options are:
• Do not allow
• Allow
Number of Ring cycle before Call
Forward
Do Not Disturb Specifies the status of the DND feature .
DND Priority over Call Forward
(Unconditional, Busy)
Auto Answer Specifies the status of the Auto Answer feature.
Mute on Auto Answer Specifies the mute status when Auto Answer feature is enabled.
Hold Reminder Timer Specifies the number of seconds after which the phone plays
Specifies the number of ring cycles before the call is forwarded
The default delay is one ring cycle.
The options are:
• Do not allow
• Allow
Specifies the IP address of the gateway. You can type or ethe
gate way IP address in this field.
The options are:
• Do not allow
• Allow
The options are:
• Yes
• No
the hold reminder tone .
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 66
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 67

Configuring settings
Name Description
Transfer on Conference hangup Specifies whether a conference call continues after the host
hangs up.
The options are:
• Yes
• No
Phone Menu Options
Settings Specifies whether the Options & Settings menu is provided to
the user .
The options are:
• Do not allow
• Allow
Network Info Screen Specifies whether the Network Information screen is provided to
the user.
The options are:
• Do not allow
• Allow
Logout Specifies whether the logout function is provided to the user.
The options are:
• Do not allow
• Allow
SSL Version Specifies the version of the SSL certificate.
User-ID Field Specifies the option to disable or enable the User-ID Field form
menu.
The options are:
• Do not allow
• Allow
UDP Transport Specifies whether UDP transport is allowed.
The options are:
• Do not allow
• Allow
Network Configuration by User Specifies whether network configuration can be modified by a
user.
The options are:
• Do not Allow to Modify
• Allow to Modify
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 67
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 68

Configuring the phone using web interface
Name Description
Call Log
Call Log Specifies whether to enable or disable complete call log
application.
The options are:
• Do not allow
• Allow
Enable Redial Specifies whether to enable or disable the capability to redial
out of a list of recently dialed numbers instead of performing last
number redial.
The options are:
• Do not allow
• Allow
Note:
Avaya J139 IP Phone does not support this feature.
Contacts
Local Contacts Specifies whether to enable or disable complete Contact
Application feature.
The options are:
• Do not allow
• Allow
Contact Name Format Specifies the format of the contact name to be displayed in the
contact list.
The options are:
• 'Last Name' 'First Name'
• 'First Name' 'Last Name'
Contact Name display logic Specifies how to match a dialed string on an incoming call with
the users contacts.
The options are:
• Match the number completely
• Match shorter number completely to the rightmost digits
of longer number
• Match at least 4 rightmost digits
Emergency Call
Emergency Numbers Specifies the emergency contact number.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 68
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 69

Configuring settings
Name Description
Emergency Softkey Specifies whether the emergency softkey is displayed after the
phone is registered.
The options are:
• Do Not Display
• Display without Confirmation
• Display with Confirmation
Softkey Emergency Number Specifies the number to be used as a softkey for emergency
numbers.
Emergency Softkey on
Unregistration
Specifies whether the emergency softkey is displayed when the
phone is not registered.
The options are:
• Do Not Display
• Display without Confirmation
• Display with Confirmation
Phone Lock
Enable Phone Lock Specifies whether the phone lock feature of the phone is
enabled.
The options are:
• Do Not Allow
• Allow
Phone Lock Idle Time Specifies the idle time after which the phone is locked.
The value is 0 to 10080 minutes.
Others
Softkey Configuration Specifies which feature will show up on which softkey on the
phone screen.
Branding Volume Specifies the level of the Avaya audio brand.
The options are:
• 12db below nominal
• 9db below nominal
• 6db below nominal
• 3db below nominal
• Nominal
• 3db above nominal
• 6db above nominal
• 9db above nominal
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 69
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 70

Configuring the phone using web interface
Name Description
Phone Mute Alert Specifies whether mute alert feature is blocked.
The options are:
• Unblocked
• Blocked
Extend Ringtone Specifies whether extended ring tone feature is enabled.
Group Number Specifies group numbers if available.
The values are 0 to 99.
Audio
Call Progress Tone Country Specifies the country of operation.
AGC Handset Specifies the Automatic Gain Control setting for the handset
interface.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable
AGC Speaker Specifies the Automatic Gain Control setting for the speaker.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable
Handset Sidetone Level Specifies the level of side tone in the handset.
The options are:
• Normal level
• Three levels softer than Normal
• Off
• One level softer than Normal
• Two levels softer than Normal
• Four levels softer than Normal
• Five levels softer than Normal
• Six levels softer than Normal
• One level louder than Normal
• Two levels louder than Normal
Ringtone Style Specifies the style of classic ring tone to be used.
The options are:
• North America
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 70
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 71

Configuring settings
Name Description
• European
Dialing
No Digit Dial Timer Specifies the number of seconds that the telephone waits for a
digit to be dialed after going off-hook and before generating a
warning tone.
The valid range is 0 to 60 seconds.
Inter-digit Wait Timer Specifies the number of seconds that the telephone waits after
a digit is dialed before sending a SIP INVITE.
The valid range is 1 to 10 seconds.
Dial Local Area Code Specifies whether the user must dial the area code of calls
within the same area code.
The options are:
• No
• Yes
Local Area Code Specifies the local area code of the phone.
Enhanced Local Dialing Rules
Enable Local Dialing Rules Specifies whether to process telephone numbers from the
incoming Call Log or Contacts while dialling a number.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable Without Contacts
• Enable With Contacts
Country Code Specifies the country code of the user.
International Access Code Specifies the international access code.
Long Distance Access Code Specifies the long distance access code.
Internal Extension Number Length Specifies the length of an internal extension number.
The valid range is 3 to 13 numeric digits.
National Telephone Number Length Specifies the length of a national telephone number.
The valid range is 5 to 15 numeric digits.
Outside Line Access Code Specifies the pre-fixed number to be used to make a local call
by using a public network.
Remove PSTN access prefix from
outgoing number
Specifies the removal of the PSTN access prefix from the
outgoing number.
The options are:
• No
• Yes
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 71
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 72

Configuring the phone using web interface
Name Description
Admin
Admin Access allowed from Phone Specifies whether the admin access is allowed from the phone.
The options are:
• No
• Yes
Admin Login fail attempt allowed Specifies the number of failed attempts to enter the admin
access code before the admin login is locked.
The options are 1 to 20.
Admin Login Locked Time after fail
attempt
Specifies the time interval in minutes to re-enter the admin
access code after the admin login is locked.
The value is 5 to 1440 minutes.
Related links
Configuring settings on page 65
Configuring certificates
Procedure
1. Log in to the web interface as an administrator.
2. In the navigation pane, click Certificates.
3. Configure the following areas:
• Certificates
• Online Certificates Status Protocol (OCSP)
• SCEP
• PKCS12
• Web Server
4. Click one of the following:
• Save
• Reset to Default
• Help
Related links
Certificates field descriptions on page 73
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 72
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 73

Configuring certificates
Certificates field descriptions
Name Description
Certificates
Available Trusted Certificate Specifies the file names of certificates for authentication.
Upload Trusted Certificate Specifies the trusted certificate used by the phone. You can also
browse and upload the certificates from your local machine by
clicking Choose File > Import.
Trusted Certificates file to upload Specifies the name of the certificate file to be uploaded.
Warning on number of days
before Certificate expiration
FQDN IP Mapping Specifies to validate an FQDN contained in the certificate when an
Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP)
Enable OCSP Specifies the status of OSCP.
Specifies the number of days before the expiration of a certificate
that a warning must first appear on the phone screen.
IP address is used to establish the connection. The parameter is a
comma-separated list of names or value pairs where the name is
an FQDN and the value is an IP address.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable
Action on Unknown Revocation
Status
Nonce in OCSP Request Specifies whether a nonce is included in OCSP requests and
OCSP Address Specifies a URI for an OCSP responder. The URI can be an IP
OCSP Address Preferred Specifies the preferred OCSP responder URI.
Specifies whether a certificate is authenticated when its revocation
status cannot be determined.
The options are:
• Certificate revocation operation is accepted
• Certificate is considered to be revoked and TLS connection
is closed
expected in OCSP responses.
The options are:
• Do not add
• Add
address or a host name.
The options are:
• Use OCSP address configured first and then OCSP field of
AIA extension of the certificate being checked
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 73
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 74

Configuring the phone using web interface
Name Description
• Use OCSP field of AIA extension of the certificate being
checked first and then OCSP address configured
OCSP Trusted Certificates Specifies the trusted OCSP certificates to be downloaded. It also
acts as a separate trusted certificate repository for the OCSP
Trusted Responder Model and contains certificates that the OCSP
responder can trust. This value is required if the OCSP responder
uses a different CA for the server certificate than the root CA.
OCSP Hash Algorithm Specifies the hashing algorithm for an OCSP request. value
operation. discuss
The options are:
• SHA-1
• SHA-256
Use OCSP Caching Specifies whether OCSP caching is in use.
The options are:
• Yes
• No
OCSP Cache Expiry Specifies the time interval for the OCSP cache expiry in minutes.
The valid range is 60 to 10080.
SCEP
SCEP Server Specifies the URL address of the SCEP server.
Common Name Specifies the common name for the subject in an SCEP certificate
request.
Subject Specifies the part of SUBJECT in an SCEP certificate request that
is common for requests from different device. For example,
Organizational Unit, Organization, Location, State, and Country.
CA Identifier Specifies the Certificate Authority Identifier.
Certificate Authority servers may require a specific CA Identifier
string to accept GetCA requests. If the device works with such a
Certificate Authority, the CA identifier string can be set through this
parameter.
Initiate renewal on % of Validity
Interval
Specifies the percentage used to calculate the renewal time
interval out of the device certificate’s Validity Object.
If the renewal time interval has elapsed, the phone starts to contact
the SCEP server periodically to renew the certificate. The range is
0 to 99.
Phone behavior on Pending
request
Specifies the functioning of the device when performing certificate
enrolment.
The options are:
• Poll SCEP server periodically in background
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 74
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 75

Configuring SIP settings
Name Description
• Wait until a certificate is received or rejected
SCEP Password Specifies a challenge password to use with SCEP.
PKCS12
PKCS12 Address Specifies the IPv4 or IPv6 URL address, or FQDN from where a
PKCS#12 file is to be downloaded.
PKCS12 Password Retry Count Specifies the number of attempts allowed for password entry.
Available Identity Certificate Specifies the trust certificates used as trust points for TLS
connections.
Upload Identity Certificate Specifies the trust certificates to be uploaded.
Delete Installed Identity Certificate Allows you to delete any installed identity certificate.
Related links
Configuring certificates on page 72
Configuring SIP settings
Procedure
1. Log in to the web interface as an administrator.
2. In the navigation pane, click SIP.
3. Configure the following areas:
• SIP Account
• SIP Server
• Codecs and DTMF
• RTP
• Timers and Count
• Local Port
• Miscellaneous
4. Click one of the following:
• Save
• Reset to Default
• Help
Related links
SIP settings field descriptions on page 76
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 75
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 76

Configuring the phone using web interface
SIP settings field descriptions
Name Description
SIP Account
Status Displays the SIP account status. The field is automatically populated.
The values are:
• Not Configured
• Not Registered
• Registered
SIP User ID Specifies the SIP user ID provided by the service provider.
You can also type the SIP user ID, which is a combination of the following
values:
• Upper and lower case characters
• Numbers from 0 to 9
• Spaces
• Special characters
Authentication User ID Specifies the authentication ID.
You can also type the authentication user ID in this field if authentication is
enabled on the SIP server.
The authentication user ID is a combination of the following values:
• Upper and lower case characters
• Numbers from 0 to 9
• Spaces
• Special characters
Authentication Password Specifies the authentication password.
You can also type the password in this field if authentication is enabled on
the SIP server.
Note that the password can contain maximum 31 ASCII characters.
SIP Server
SIP Domain Specifies the SIP domain used for SIP registration.
Valid values are 0 to 255 ASCII characters.
Use Proxy Server Specifies whether SIP proxy servers are read-only or can be edited.
The options are:
• Manual: To configure SIP proxy server manually by using the phone or
the web interface.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 76
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 77

Configuring SIP settings
Name Description
• Automatic: To use the SIP proxy server settings received from the
46xxsettings.txt file .
SIP Proxy Server (Manual) Specifies the SIP proxy server domain.
Valid values are 0 to 255 ASCII characters.
SIP Proxy Server
(Automatic)
Specifies the SIP proxy server settings as received from the
46xxsettings.txt file .
Registration Interval Specifies the time interval between two registrations to the SIP proxy.
The default value is 900 seconds.
Valid values are from 30 to 86400 seconds.
Un-registration Wait Timer
(seconds)
Specifies the time for which the phone waits before terminating all SIP
dialog and SIP registrations.
The default value is 32 seconds.
Valid values are from 4 to 3600 seconds.
Registration Wait Timer
(seconds)
Specifies the number of seconds the phone waits for a response message
from registration. If no response message is received within this time, the
phone tries to register again.
The default value is 32 seconds.
Valid values are from 4 to 3600 seconds.
Codecs and DTMF
G.722 Specifies whether the G.722 codec is enabled.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable
G.726 Specifies whether the G.726 codec is enabled.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable
G.729 Specifies whether the G.729A codec is enabled.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable
G.711u law Specifies whether the G.711u law codec is enabled.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 77
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 78

Configuring the phone using web interface
Name Description
G.711a law Specifies whether the G.711a law codec is enabled.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable
Send DTMF Specifies whether the phone sends DTMF tones in-band as regular audio,
or out-of-band using RFC 2833 procedures.
The options are:
• In-band
• Out-of-band
G.726 Payload Specifies the RTP payload type to be used for the G.726 codec.
The default value is 110.
Valid values are from 96 to 127.
DTMF Payload Specifies the RTP payload type to be used for RFC 2833 signaling.
The default value is 120.
Valid values are from 96 to 127.
RTP
Play Tone till RTP Specifies whether the locally generated ringback tone stops when SDP is
received for an early media session, or whether it continues until RTP is
actually received from the far-end party.
The options are:
• Yes
• No
Symmetric RTP Specifies whether the phone must receive RTP if the UDP source port
number is not same as the UDP destination port number.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable
The default value is Enable. tag
RTCP_XR Specifies whether VoIP Metrics Report Block as defined in RTP Control
Protocol Extended Reports (RTCP XR) (RFC 3611) is sent as part of the
RTCP packets to a remote peer or an RTCP monitoring server.
The options are:
• Yes
• No
The default value is No.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 78
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 79

Configuring SIP settings
Name Description
Timers and Count
SIP Timer T1 Specifies an estimate for the Round Trip Time (RTT).
Valid values are from 500 to 10000 milliseconds.
The default value is 500 milliseconds.
SIP Timer T2 Specifies the maximum retransmit interval for non-INVITE requests and
INVITE responses.
Valid values are from 2000 to 40,000 milliseconds.
The default value is 4000 milliseconds.
SIP Timer T4 Specifies the maximum duration for which a message remains in the
network.
Valid values are from 2500 to 10,000 milliseconds.
The default value is 5000 milliseconds.
INVITE Response Timeout Specifies the maximum number of seconds that the phone waits for
another response after receiving a SIP 100 Trying response.
Valid values are from 30 to 180 seconds.
The default value is 60.
Failed Session Removal
Timer
Specifies the time to automatically remove a failed call session.
Valid values are from 5 to 999 seconds.
The default value is 60 seconds.
Outbound Subscription
Duration Request
Specifies the Outbound subscription request duration.
Valid values are from 60 to 31,53,600 seconds.
The default value is 86,400 seconds.
Controller Search Interval Specifies the time that the phone waits to complete the maintenance check
for monitored controllers.
Valid values are from 4 to 3600 seconds.
The default value is 16 seconds.
Local Port
RTP Port (minimum) Specifies the lower limit of a port range to be used by the following
connections:
• RTP
• RTCP
Valid values are from 1024 to 65,003.
The default value is 5004.
RTP Port (range) Specifies the port range to be used by the following connections:
• RTP
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 79
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 80

Configuring the phone using web interface
Name Description
• RTCP
Valid values are from 32 to 64,511.
The default value is 40.
SIP Signaling Port
(minimum)
SIP Signaling Port (range) Specifies the port range to be used for SIP signaling.
Miscellaneous
Conference Factory URI Specifies the URI for network conferencing in third-party call control
Voice Mail Access Code Specifies the number to access the voice mail in a non-Avaya environment.
100rel Specifies whether the 100rel option tag is included in the SIP INVITE
Specifies the lower limit of a port range to be used for SIP signaling.
Valid values are from 1024 to 65,003.
The default value is 5060.
Valid values are from 32 to 64,511.
The default value is 32.
environments.
The value contains 0 to 255 ASCII characters.
header field.
Validate Incoming
messages
Related links
Configuring SIP settings on page 75
Debugging
Procedure
1. Log in to the web interface as an administrator.
The options are:
• Disable: The tag is not included.
• Enable: The tag is included.
Specifies whether AOR received in Request-URI of an incoming call must
be validated with the contact header published by phone during
registration.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable
2. In the navigation pane, click Debugging.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 80
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 81

3. Configure the fields in the following areas:
• Log
• SNMP
• RTCP Monitoring
• Phone Report
• SSH
• SLA Monitor
• Other
4. Click Save.
5. (Optional) Click Generate Phone Report.
6. (Optional) To ping, do the following:
a. In Ping, enter the IP address that you want to ping.
b. Click Ping Test.
Related links
Debugging field descriptions on page 81
Debugging
Debugging field descriptions
Name
Log
Logging Specifies the logging status.
Log Server Specifies the IP or DNS address of the Syslog server.
Log Level Specifies the severity level of the syslog messages. Events with the
Description
The options are:
• Off
• On
The default value is Off.
The value contains 0 to 255 ASCII characters.
selected severity level and above are logged.
The options are:
• Emergencies
• Alerts
• Critical
• Errors
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 81
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 82

Configuring the phone using web interface
Name Description
• Warnings
• Notices
• Information
• Debug
The default value is Emergencies.
Log Categories Specifies the list of log categories. need more info
Enhanced Debugging Specifies the status of enhanced debugging .
The options are:
• Enable
• Disable
SNMP
SNMP String Specifies the SNMP community name string.
The string contains maximum 32 ASCII characters.
SNMP Address Specifies the IP addresses for SNMP queries.
The address contains maximum 255 ASCII characters.
RTCP Monitoring
RTCP Monitor Address Specifies the IP or DNS address of the RTCP monitor.
The address contains maximum 255 ASCII characters.
RTCP Monitor Port Specifies the RTCP monitor port number.
Valid values are 0 through 65535 ASCII characters.
The default value is 5005.
RTCP Monitoring Report
Period
Specifies the interval for sending out RTCP monitoring reports.
Valid values are 5 through 30 seconds.
The default value is 5 seconds.
Phone Report
Maintenance Server Address Specifies the file server address to send the phone report.
The address contains maximum 255 ASCII characters.
SSH
SSH Allowed Specifies whether Secure Shell (SSH) is supported.
The options are:
• Enable
• Disable
SSH Idle Timeout Specifies the time after which SSH is disabled. discuss
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 82
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 83

Debugging
Name Description
The options are:
• Enable
• Disable
• Configured using local craft procedure
The default value is Disable.
SSH Banner File Specifies the file name or URL for a custom SSH banner file.
The file contains maximum 255 ASCII characters.
EASG site certificates Specifies a list of EASG site certificates. Support technicians use these
certificates to generate EASG responses for SSH login without access
to the Avaya network.
The certificate contains maximum 64 ASCII characters.
You can add maximum four certificates.
EASG site Authentication
Factor code
Specifies the Site Authentication Factor code associated with the
EASG site certificate installed.
Valid values are 10 through 20 alphanumeric characters.
Days before EASG certificates
expiration warning
Specifies the number of days before the expiration of EASG product
certificate that a warning message appears on the phone screen.
Valid values are 90 through 730.
The default value is 365.
SLA Monitor
Enable SLA Monitor Agent Specifies the status of the SLA Monitor Agent .
The options are:
• Enable
• Disable
The default value is Disable.
SLA Monitor Server Address Specifies the IP address of the SLA Monitor server in the
aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd format.
The IP address must contain:
• Numbers 0 to 9
• 3 dots
Packet Capture (sniffing) Specifies whether the SLA Monitor agent supports packet capture.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable with payloads removed from RTP packets
• Enable with payloads included in RTP packets
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 83
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 84

Configuring the phone using web interface
Name Description
• Controlled from Admin Menu
The default value is Disable.
Device Control Specifies whether the SLA Monitor agent supports device control.
The options are:
• Disable
• Enable
• Controlled from Admin Menu
The default value is Disable.
Device Performance
Monitoring
UDP Port for discovery and
test messages
Specifies whether the SLA Monitor agent supports access to phone
performance data.
The options are:
• Enable
• Disable
The default value is Disable.
Specifies the port used to receive packets from an SLA Monitor server.
Valid values are 6000 through 65535.
The default value is 50011.
Other
Serial Port Specifies if the port for network traffic is enabled or disabled.
The options are:
• Enable
• Disable
The default value is Disable.
Port Mirroring Specifies the status of port mirroring. Port mirroring is used to monitor
network traffic.
The options are:
• Off
• On
The default value is Off.
Related links
Debugging on page 80
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 84
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 85

Chapter 5: Cloud configurations
Configuration through a cloud server
Cloud server configuration simplifies the process of deployment and is applicable when the phone
must be configured on a third-party vendor server. The cloud vendor assigns a customer reference
number and creates a subdirectory on its file server. The cloud vendor must generate the following
for creating a customer profile:
• Customer username
• Customer password
• Customer extension number
• Customer reference number
The cloud vendor must have a staging area file server to host the customer-specific settings.
Customer-specific settings are generated for each customer through the MAC address of the
phone. A text file containing the MAC address of the phone must be hosted on the staging area
file server. Typically, the text file containing the customer-specific settings can be named with the
phone MAC address.
MACADDR.txt
The staging area file server must host the following files:
• J100Supgrade.txt file
• 46xxsettings.txt file
MACADDR.txt
•
• Software upgrade files available from Avaya
Phone setup process on a cloud server
The phone does the following during the setup process:
1. Boots and discovers the staging area file server address through DHCP.
2. Retrieves and checks the J100Supgrade.txt file for device upgrade if required.
3. Retrieves the 46xxsettings.txt and MACADDR.txt files for customer-specific
configurations.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 85
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 86

Cloud configurations
4. Logs on to the SIP Proxy server of the cloud service provider.
Settings file contents on a cloud server
The cloud server hosts the details of the customer phone through the Settings file. The Settings
file must contain the details to locate the MAC address of the phone along with other system
parameter definitions and value.
Settings file contents
SET parameter_name parameter_value
GET $MACADDR.txt
where, MACADDR.txt is the name of the MAC address file of the phone.
MAC address file contents on a cloud server
The cloud server hosts a MAC address file that contains customer details. This file is unique to
each phone and can also be used for custom settings for a specific order.
MAC address file contents
SET <FORCE_SIP_USERNAME> <Username>
SET <FORCE_SIP_PASSWORD> <Password>
SET <FORCE_SIP_EXTENSION> <Extension_number>
SET <TLSDIR> <Path_to_the_TLS_directory>
SET <HTTPSRVR> <"">
where,
• FORCE_SIP_USERNAME is the name of the parameter that assigns the username.
• FORCE_SIP_PASSWORD is the name of the parameter that assigns the password.
• FORCE_SIP_EXTENSION is the name of the parameter that assigns the extension number.
• TLSDIR is the name of the parameter that locates the subdirectory of the cloud service
provider.
• HTTPSRVR with <"”> is the name of the parameter that removes the cached HTTP file
server address. This redirects the phone to the cloud service provider’s file server.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 86
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 87

Chapter 6: Security configurations
Security overview
SIP-based Avaya J100 Series IP Phones provides several updated security features. When the
phone is in a locked state, a user can only receive calls or make emergency calls. User logs and
data are protected with the user account.
The following security features are available:
• Supports X509v3–compliant certificates.
• Supports Identity certificate installation using the following methods:
- Enrollment using Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP): Creates a private key
and Certificate Signing Request (CSR) using the SCEP interface.
- Importing key and certificate: Uses an encrypted PKCS#12 file format to import the private
key and certificate.
• Supports Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) for public key management.
• Supports Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) for users that use third-party certificates for all
Avaya services including database.
• Supports VLAN separation mode using system parameter.
• Supports synchronization of system clock at configured intervals using system parameter.
• Supports display of SSH fingerprint in the ADMIN menu.
• Displays version of OpenSSH and OpenSSL in the ADMIN menu.
• Maintains the integrity and goes to out-of-service mode under Denial of Service (DoS) attack.
Important:
The ADMIN menu provides access to certain administrative procedures from the phone. You
must change the default password for the ADMIN menu to restrict users from using the
administrative procedures to change the phone configuration.
Access control and security
Phones provide several security features for control and access. These include:
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 87
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 88

Security configurations
Security event logging
Logs are maintained for the following events:
• Successful and failed logins, username lockouts, and registration and authorization attempts
by users and administrators.
• Change in roles.
• Firewall configuration changes.
• Modification or access to critical data, applications, and files.
Private Key storage
The phone stores the private key in PKCS#12 and PEM file formats. The phone sends the device
identity certificate and a private key along with the encrypted password to the WPA supplicants.
MD5 passwords are sent to the WPA supplicants securely.
Temporary Data
The phone deletes any temporary storage data from the program, variables, cache, main memory,
registers, and stack.
IP information
The phone enables the user with ADMIN privileges to see the IP information on the phone screen.
The parameter PROVIDE_NETWORKINFO_SCREEN controls the display information.
OpenSSH/OpenSSL version
The phone displays the version of OpenSSL and OpenSSH on the VIEW screen in the ADMIN
menu. To see this information, set the parameter DISPLAY_SSL_VERSION to 1.
SSH Fingerprint
The phone displays the SSH fingerprint to manually verify that an SSH connection is established
with the correct phone.
Time synchronization
The phone synchronizes the time with the configured NTP servers in intervals. Use the parameter
SNTP_SYNC_INTERVAL to check the time interval for synchronization. The range is 60 to 2880
minutes, and the default is 1440 minutes.
Certificate management
Certificates are used to establish secure communication between network entities. Server or
mutual authentication can be used to establish a secure connection between a client and server.
The client always validates the certificate of the server and maintains a trust store to support this
validation. If the server additionally requires mutual authentication, it requests an identity
certificate from the client. The identity certificate must be provided and validated by the server to
establish mutual authentication. Server must validate the identity certificate to establish a secure
connection..
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 88
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 89

Certificate management
Phones support three types of certificates:
• Trusted certificates
• Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) trust certificates
• Phone identity certificates
The Trusted and OCSP trust certificates are root or intermediate Certification Authority (CA)
certificates that are installed on the phone through the 46xxsettings.txt file.
Enhancements for installing identity certificates:
• SCEP over HTTPS is supported for enrollment.
• PKCS#12 file format is supported for installation.
To check the number of days remaining for Identity certificate expiry, use the parameter
CERT_WARNING_DAYS . The user is notified through a log message if the log level is
maintained as WARNING with the category CERTMGMT. The logs are maintained and displayed
if SYSLOG is enabled.
MIB object tables and IDs are created for certificates installed on the phone. You can view the
certificate attributes through an SNMP MIB browser.
To implement DES, the phone has 64 Public CA certificates built in. For a list of the certificates,
see Appendix B.
Related links
Appendix B: Public CA Certificates on page 177
Identity certificates
Identity certificates are the endpoint or Server certificates. To share the identity, a public key is
presented for identification. X509v3 compliant certificates are supported. Secure communications
that use Transport Layer Security (TLS) or certificates for authentication are supported to
participate in a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). The following mechanisms are supported for
installation:
• Enrolling a certificate : Creates a private key and Certificate Signing Request (CSR). CSR is
sent to the Certificate Authority (CA) using a manual or automatic Simple Certificate
Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) interface. The certificate is validated and accepted when CA
signs the CSR.
• Importing Key and Certificate: Uses an encrypted PKCS #12 file format to import both the
private key and the corresponding certificate.
You can view the following attributes of the certificate using an SNMP MIB browser:
• Serial Number
• Subject Name
• Issuer Name
• Validity Period:notBefore and notAfter dates
• Thumbprint: Hash of the certificate
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 89
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 90

Security configurations
• Basic Contraints
• Subject Alternative Name
• Key Usage Extensions
• Extended Key Usage
To validate the identity of a received certificate, the following process is followed:
• Verification of certificate chain up to the trusted entity.
• Verification of the signature.
• Verification of the revocation status through OCSP.
• Verification of the certification validity (not-before and not-after dates are checked).
• Verification of the certificate usage restrictions.
• Verification of the identity against the certificate.
Subject Alternative Field (SAN)
While validating the certificates, the phone verifies whether the presented certificate has a SAN
field or not. The SAN field simplifies the server configuration. With the SAN field, you can specify
additional host names, such as IP addresses or common names, to use a single SSL Certificate.
• If the certificate does not have the SAN field, the phone validates the Common Name (CN)
fields of the certificate. In this case, you need the following CN fields:
- SIP domain name
- IP address
• If the certificate has the SAN field, the following attributes for an HTTP-TLS connection are
present:
- Provisioning phone with only an IP address
• In the SAN field, IP attribute with IP of HTTPS server is present.
- Provisioning phone with FQDN of HTTPS server
• In the SAN field, IP attribute with the IP address of HTTPS server is present.
• DNS attribute with FQDN of HTTPS server.
Note:
While provisioning the phone with the FQDN of HTTPS server, you need two attributes in the
SAN field:
• DNS attribute with FQDN
• IP attribute IP address
Trusted certificates
Trusted certificates are the root certificates that are used to verify the received certificates. These
certificates are installed on the phone through the http server using settings file and are used to
validate server certificates during a TLS session.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 90
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 91

Parameter configuration for secure installation
OCSP trust certificates
Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) is used to check the certificate revocation status of an
x509 certificate in use. The phone trusts the OCSP server and installs its CA certificates. These
certificates are called OCSP Trust Certificates.
OCSP Trust Certificates are installed in the same way as those for System Manager. However,
OCSP Trust Certificates use a different parameter name called OCSP_TRUSTCERTS. This
parameter follows the same format as that for TRUSTCERTS.
Parameter configuration for secure installation
For a secure installation, configure the following parameters:
Parameter Set to Notes
TRUSTCERTS Provides the file names of certificates to be used for authentication.
It supports both root and intermediate certificates and can contain
up to six certificate files.
AUTH 1 Ensures usage of HTTPS file servers for configuration and software
files download. After AUTH is set to 1 and the device downloads the
trusted certificates, the device can only download files from an
HTTPS server. That server must have certificates that can be
validated using a trusted certificate repository.
SSH_ALLOWED 0 Keeps SSH disabled.
SCEP parameters
Configure the following Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) parameters:
Parameter
MYCERTURL String Null Specifies the URL to access the Simple Certificate
MYCERTCN String $SERIA
Type Default
value
LNO
Description
Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) server. The device attempts
to contact the server only if this parameter is set to other
than its default value.
Specifies the Common name (CN) for SUBJECT in the
SCEP certificate request. The values can be
$SERIALNO or $MACADDR.
If the value includes the string $SERIALNO, that string
will be replaced by the phones serial number.
If the value includes the string $MACADDR, that string
will be replaced by the phones MAC address.
Table continues…
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 91
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 92

Security configurations
Parameter Type Default
Description
value
MYCERTDN String Null Specifies the common part of SUBJECT in SCEP
certificate request. This value defines the part of
SUBJECT in a certificate request including
Organizational Unit, Organization, Location, State, and
Country that is common for requests from different
devices.
MYCERTKEYLEN Numeric 2048 Specifies the private key length in bits to be created in
the device for a certificate enrollment. The range is from
1024 to 2048.
MYCERTRENEW Numeric 90 Specifies the percentage used to calculate the renewal
time interval out of the device certificate’s Validity Object.
If the renewal time interval has elapsed, the phone starts
to periodically contact the SCEP server again to renew
the certificate. The range is from 1 to 99.
MYCERTWAIT Numeric 1 Specifies the functions of the device when performing
certificate enrolment. The options are:
• 0: Periodical check in the background
• 1: Wait until a certificate or a denial is received or a
pending notification is received
MYCERTCAID String CAIdenti
fier
Specifies the Certificate Authority Identifier. Certificate
Authority servers might require a specific CA Identifier
string to accept GetCA requests. If the device works with
such a Certificate Authority, the CA identifier string can
be set through this parameter.
SCEPPASSWORD String $SERIA
LNO
Specifies a challenge password to use with SCEP. The
value of SCEPPASSWORD, if non-null, is included in a
challengePassword attribute in SCEP certificate signing
requests.
If the value contains $SERIALNO, $SERIALNO is
replaced by the value of SERIALNO. If the value contains
$MACADDR, $MACADDR is replaced by the value of
MACADDR without the colon separators.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 92
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 93

Chapter 7: Phone administration
Accessing the Admin menu during phone startup
Before you begin
Ensure you set the following parameters in the Settings file:
• PROCSTAT: To administer the phone using admin menu, set the parameter to zero.
• PROCPSWD or ADMIN_PASSWORD: The default password is 27238. You must change the
default password at the time of initial installation.
Procedure
1. Press Main Menu softkey.
2. On the Access code screen, enter the admin menu password using the dialpad.
3. Press Enter.
Accessing the Admin menu after log in
Procedure
1. Press Main Menu > Administration.
2. In the Access code field, enter the administration password.
3. Press Enter.
Accessing the Ethernet IPv4 settings
Procedure
1. Press Main Menu > Administration.
2. In the Access code field, enter the administration password.
3. Press Enter.
4. Select IP Configuration > Ethernet IPv4.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 93
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 94

Phone administration
The phone displays the parameters for IP configuration.
IP configuration field description
Configuration Parameter Name Description
The following parameters are available in IPv4 menu:
Use DHCP Specifies the access to view or manually enter the
IP address.
Select one of the following:
• YES: Selects the DHCP option to view the IP
addresses.
• No: Selects the DHCP option to enter the IP
addresss.
Phone Specifies the IP address of the phone. The
available format is nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn.
Router Specifies the router IP address. The available
format is nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn.
Mask Specifies the network mask. The available format is
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn.
The following parameters are available in VLAN menu:
802.1Q Choose one of the following options:
• Auto: Automatic mode.
• On: Turns on the configuration.
• Off: Turns off the configuration.
VLAN ID Specifies the ID for VLAN. The available format is
dddd.
VLAN Test Specifies the time in seconds, the phone waits for
the DHCP server response. The available format is
ddd.
The following parameters are available in Servers menu:
HTTP server Specifies the IP address of the HTTP file server.
The available format is nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn.
HTTPS server Specifies the IP address of the HTTPS file server.
The available format is nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn.
DNS server Specifies the IP address of the DNS server. The
available format is nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn.
SNTP server Specifies the time server settings.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 94
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 95

Using the debug mode
Using the debug mode
About this task
Use this procedure to activate or deactivate the debugging options.
Before you begin
You must set a HTTP server in the BRURI parameter in the Settings file that is capable of
receiving a phone report from the phone. BRURI parameters can receive only phone report. It has
no effect on any other debugging setting.
Procedure
1. Press Main Menu > Administration.
2. In the Access code field, enter the admin menu password.
3. Press Enter.
4. Select Debug.
The phone displays the following debug options:
• Phone Report
• Serial port mode
• Port mirroring
• Port Mirroring
• SSH access
• SSH fingerprint
• Clear SSH lockout
• Service mode control
• Service mode record
5. Use the appropriate keys to enable or disable the options.
6. Press Save.
Setting the Ethernet interface control
Procedure
1. Press Main Menu > Admin.
2. In the Access code field, enter the admin menu password.
3. Press Enter.
4. Use the Down Arrow to select Network interface.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 95
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 96

Phone administration
5. Use the Right Arrow key to change Network mode to Ethernet and do one of the
following settings:
• Network config: To change the network configuration to either Auto or Manual.
• Ethernet: To change the Ethernet setting, go to step 6.
• PC Ethernet: To change the PC Ethernet setting, go to step 7.
6. Use the Right Arrow key or the Change softkey to change the Ethernet setting to one of
the following:
• Auto
• 10Mbps half
• 10Mbps full
• 100Mbps half
• 100Mbps full
7. Use the Right Arrow key or the Change softkey to change the PC Ethernet setting to one
of the following:
• Auto
• 10Mbps half
• 10Mbps full
• 100Mbps half
• 100Mbps full
• Disabled
8. Press Save.
Group identifier
A group identifier is a number assigned to a particular community of IP phone users in an
organization. The group identifier number can be a number from 0 to 999 and the default number
is 0.
With a group identifier, you can provide administration settings to each phone used by different
communities of end users. For example, you might want to group users by time zones or work
activities.
You can configure group identifier from the phone UI as a local administration process.
Related links
Setting the group identifier on page 97
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 96
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 97

Setting event logging
Setting the group identifier
About this task
Use this procedure to set or change the group identifier only if the LAN Administrator instructs you
to do so.
Procedure
1. Press Main Menu > Administration.
2. In the Access code field, enter the admin menu password.
3. Press Enter.
4. Select Group.
5. Enter any Group value between 0 to 999.
When you change the Group value, the phone restarts after you exit the admin menu.
6. Press Save.
Related links
Group identifier on page 96
Setting event logging
Procedure
1. Press Main Menu > Administration.
2. In the Access code field, enter the admin menu password.
3. Press Enter.
4. Select Log.
5. Use the Right and Left Arrow keys to select one of the following settings associated with
the corresponding SYSLOG_LEVEL:
• Emergencies: SYSLOG_LEVEL=0
• Alerts: SYSLOG_LEVEL=1
• Critical: SYSLOG_LEVEL=2
• Errors: SYSLOG_LEVEL=3
• Warnings: SYSLOG_LEVEL=4
• Notices: SYSLOG_LEVEL=5
• Information: SYSLOG_LEVEL=6
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 97
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 98

Phone administration
• Debug: SYSLOG_LEVEL=7
6. Press Save.
Restarting the phone
Procedure
1. Press Main Menu > Admin.
2. In the Access code field, enter the admin menu password.
3. Press Enter.
4. Select Restart phone.
5. Press Restart when the phone prompts for confirmation.
A restart does not affect user-specified data and settings, such as contact data or the
phone login and password.
Configuring SIP settings
About this task
Use this procedure to set up SIP-related settings, such as identifying the SIP proxy server.
Procedure
1. Press Main Menu > Admin.
2. In the Access code field, enter the admin menu password.
3. Press Enter.
4. Select SIP.
5. Choose one of the following:
• SIP global settings
• SIP proxy server
6. Press Select or OK to change any of the following SIP global settings:
• Domain: Changes the domain parameter of SIP.
• Avaya Environment: Specifies whether the available SIP Avaya environment is in
effect.
The two modes to detect the available environment are as follows:
- Auto: Detects the Avaya environment automatically.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 98
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 99

Configuring SIP settings
- No: Does not detect the Avaya environment and switches to a non-Aura mode.
Note:
Disable the Avaya Environment configuration from the 46xxsettings.txt file.
• Reg. policy: Specifies the registration policy for SIP.
The two modes are as follows:
- Alternate: Supports registration to one of the active controllers.
- Simultaneous: Supports registration to both the active controllers.
• Failback policy: Specifies the fall back policy.
The two modes are as follows:
- Auto: Active controller automatically recovers after failback.
- Admin: Active controller uses failback policy defined by the administrator.
Note:
Failback policy is not supported on Third-party call control setup.
• Proxy policy: Specifies whether the settings of SIP proxy servers are taken from the
46xxsettings.txt file or can be edited by the user.
The two modes are as follows:
- Auto: The settings are taken from the 46xxsettings.txt file. The user can only
view the settings.
- Manual: The user can edit, delete, or create new server properties.
• User ID Field: Specifies whether during logging in the User ID field will be displayed on
the phone screen or not.
7. Select SIP proxy server to change SIP proxy server settings.
Caution:
Do not configure proxy settings manually while a user is logged in to the phone.
The phone displays the IP address of the server that you selected.
8. Press Details and use the Up and Down Arrow keys to view, add, or change the following
settings:
• Proxy: Specifies the IP address or DNS. The corresponding parameter is
SIP_CONTROLLER_LIST.
• Protocol: Specifies the type of protocol. The options are TCP or UDP. The
corresponding parameter is SIPSIGNAL.
• SIP Port: Specifies the SIP port. If no value is entered, SIP port uses 5060 as the
default port for UDP/TCP.
9. Press Save.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 99
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
Page 100

Phone administration
Setting Site Specific Option Number (SSON)
About this task
The Site Specific Option Number (SSON) is used by the phones to request information from a
DHCP server. This number must match a similar number option set on the DHCP server. The
number option set on the DHCP server defines the various settings required by the phone.
Procedure
1. Press Main Menu > Administration.
2. In the Access code field, enter the administation menu password.
3. Press Enter.
4. Select SSON.
5. In the SSON field, enter the new SSON.
The number must be between 128 to 254.
6. Press Save.
Caution:
Do not perform this procedure if you are using static addressing. Perform this
procedure if you are using DHCP addressing and the DHCP option number is changed
from the default number.
Using the VIEW administrative option
About this task
Use this procedure to view the parameters associated with the admin procedures.
Procedure
1. Press Main Menu > Admin.
2. In the Access code field, enter the admin menu password.
3. Press Enter.
4. Select View.
5. Press Back to return to the main menu.
August 2018 Installing and Administering Avaya J100 series IP Phones in third-party call control
setup 100
Comments on this document? infodev@avaya.com
 Loading...
Loading...