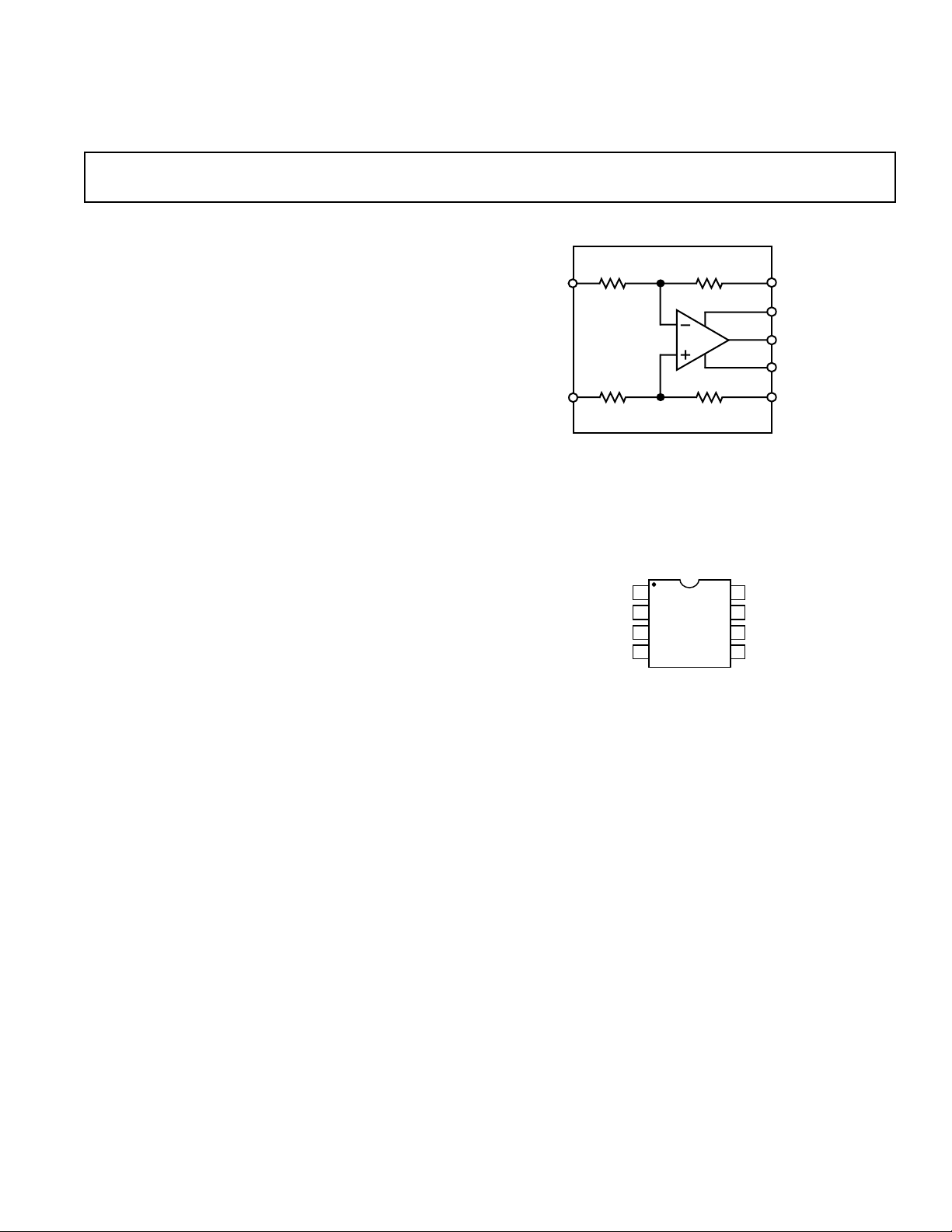
12k
12k
6k
6k
–IN
+IN
SSM2143
V
OUT
REFERENCE
V+
V–
SENSE
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
1
2
3
45
6
7
8
REF
–IN
+IN
V–
OP-482
NC
V+
SENSE
SSM2143
TOP VIEW
(NOT TO SCALE)
NC = NO CONNECT
V
OUT
–6 dB Differential
a
FEATURES
High Common-Mode Rejection
DC: 90 dB typ
60 Hz: 90 dB typ
20 kHz: 85 dB typ
Ultralow THD: 0.0006% typ @ 1 kHz
Fast Slew Rate: 10 V/ms typ
Wide Bandwidth: 7 MHz typ (G = 1/2)
Two Gain Levels Available: G = 1/2 or 2
Low Cost
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SSM2143 is an integrated differential amplifier intended to
receive balanced line inputs in audio applications requiring a
high level of immunity from common-mode noise. The device
provides a typical 90 dB of common-mode rejection (CMR),
which is achieved by laser trimming of resistances to better than
0.005%.
Additional features of the device include a slew rate of 10 V/µs
and wide bandwidth. Total harmonic distortion (THD) is less
than 0.004% over the full audio band, even while driving low
impedance loads. The SSM2143 input stage is designed to
handle input signals as large as +28 dBu at G = 1/2. Although
primarily intended for G = 1/2 applications, a gain of 2 can be
realized by reversing the +IN/–IN and SENSE/REFERENCE
connections.
When configured for a gain of 1/2, the SSM2143 and SSM2142
Balanced Line Driver provide a fully integrated, unity gain
solution to driving audio signals over long cable runs. For
similar performance with G = 1, see SSM2141.
Line Receiver
SSM2143
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
PIN CONNECTIONS
Epoxy Mini-DIP (P Suffix)
and
SOIC (S Suffix)
REV. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 617/329-4700 Fax: 617/326-8703
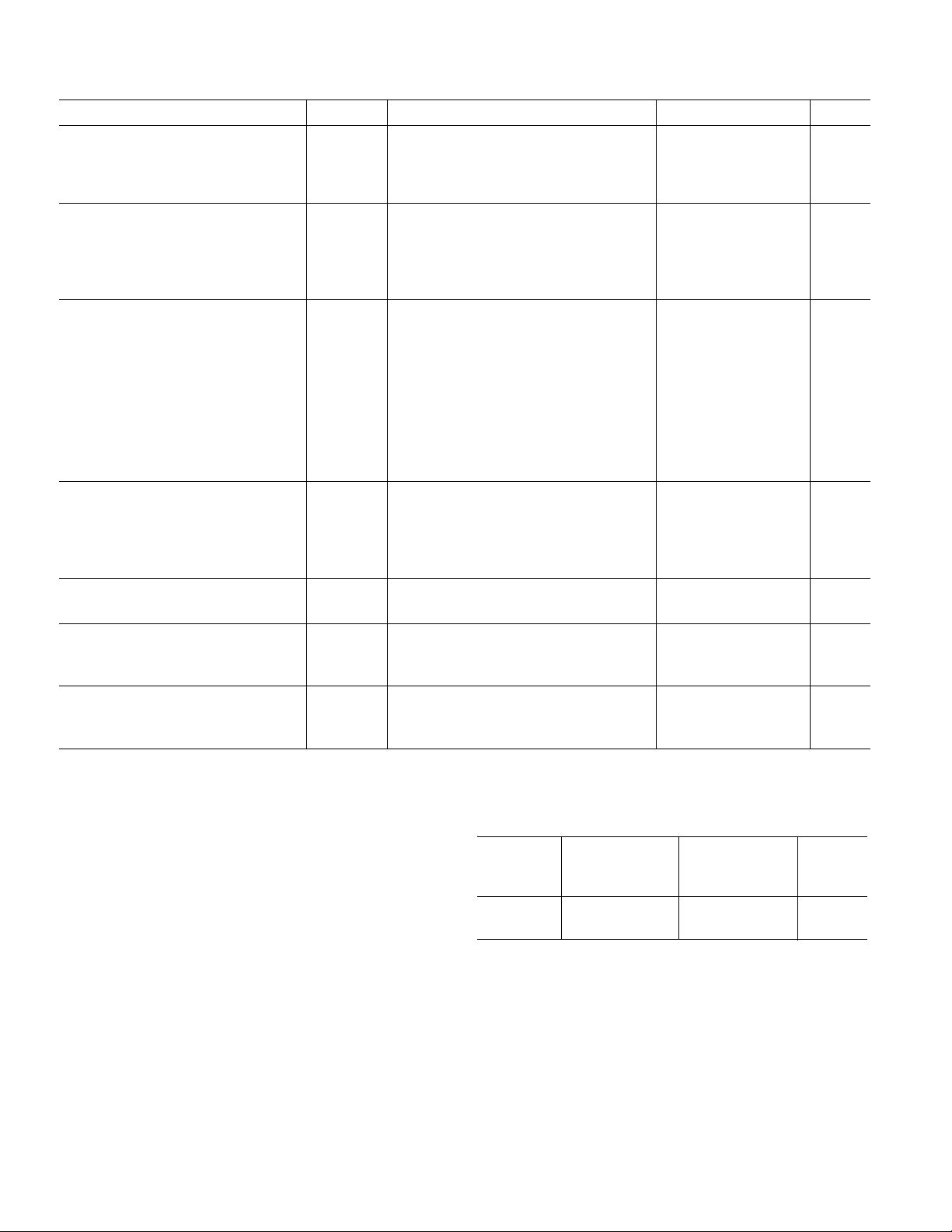
(VS = 615 V, –408C ≤ TA ≤ +858C, G = 1/2, unless otherwise noted.
SSM2143–SPECIFICA TIONS
Typical specifications apply at TA = +258C)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
AUDIO PERFORMANCE
Total Harmonic Distortion Plus Noise THD+N V
= 10 V rms, RL = 10 kΩ, f = 1 kHz 0.0006 %
IN
Signal-to-Noise Ratio SNR 0 dBu = 0.775 V rms, 20 kHz BW, RTI –107.3 dBu
Headroom HR Clip Point = 1% THD+N +28.0 dBu
DYNAMIC RESPONSE
Slew Rate SR R
Small Signal Bandwidth BW
–3 dB
= 2 kΩ, CL = 200 pF 6 10 V/µs
L
RL = 2 kΩ, CL = 200 pF
G = 1/2 7 MHz
G = 2 3.5 MHz
INPUT
Input Offset Voltage V
IOS
Common-Mode Rejection CMR V
VCM = 0 V, RTI, G = 2 –1.2 0.05 +1.2 mV
= ±10 V, RTO
CM
f = dc 70 90 dB
f = 60 Hz 90 dB
f = 20 kHz 85 dB
f = 400 kHz 60 dB
Power Supply Rejection PSR V
= ±6 V to ±18 V 90 110 dB
S
Input Voltage Range IVR Common Mode ±15 V
Differential ±28 V
OUTPUT
Output Voltage Swing V
O
RL = 2 kΩ±13 ±14 V
Minimum Resistive Load Drive 2kΩ
Maximum Capacitive Load Drive 300 pF
Short Circuit Current Limit I
SC
+45, –20 mA
GAIN
Gain Accuracy –0.1 0.03 0.1 %
REFERENCE INPUT
Input Resistance 18 kΩ
Voltage Range ±10 V
POWER SUPPLY
Supply Voltage Range V
Supply Current I
Specifications subject to change without notice.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
SY
S
VCM = 0 V, RL = ∞±2.7 ±4.0 mA
ORDERING GUIDE
±6 ±18 V
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±18 V
Common-Mode Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±22 V
Differential Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±44 V
Output Short Circuit Duration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Continuous
Operating Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature (T
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +150°C
J
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 60 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . +300°C
Model Range Description Option
SSM2143P –40°C to +85°C 8-Pin Plastic DIP N-8
SSM2143S* –40°C to +85°C 8-Pin SOIC SO-8
*Contact sales office for availability.
Operating
Temperature Package Package
Thermal Resistance
8-Pin Plastic DIP (P): θ
8-Pin SOIC (S): θ
= 103, θJC = 43 . . . . . . . . . °C/W
JA
= 150, θJC = 43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . °C/W
JA
–2–
REV. 0
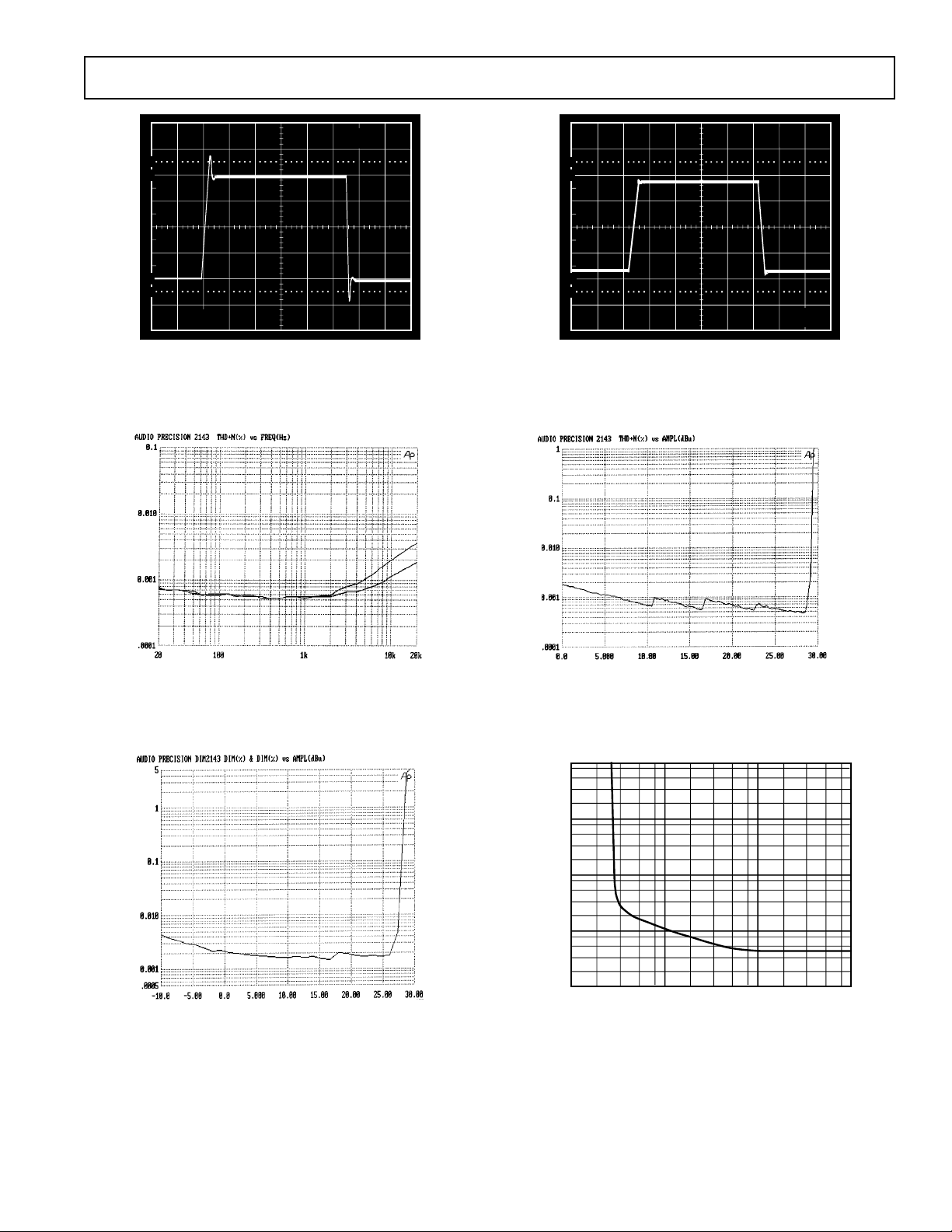
100
SSM2143
1µs
90
100
90
10
0%
50mV
Figure 1. Small-Signal Transient Response (VIN = ±200 mV,
G = 1/2, R
= 2 kΩ, VS = ±15 V, TA = +25°C)
L
Figure 3. THD+N vs. Frequency (VS = ±15 V,
V
= 10 V rms, with 80 kHz Filter)
IN
10
0%
5V
5µs
Figure 2. Large Signal Transient Response (VIN = +24 dBu,
G = 1/2, R
= 2 kΩ VS = ±15 V, TA = +25°C)
L
Figure 4. Headroom (VS = ±15 V, RL = 10 kΩ,
with 80 kHz Filter)
Figure 5. Dynamic Intermodulation Distortion, DIM-100
(V
= ±15 V, RL = 100 kΩ)
S
REV. 0
1.0
0.1
0.01
THD+N – %
0.001
0.0001
100 10k
1k
LOAD RESISTANCE – Ω
Figure 6. THD+N vs. Load (VS = ±15 V, VIN = 10 V rms, with
1 kHz Sine, 80 kHz Filter)
–3–
100k

SSM2143
1M
1k
100
100k
10k
FREQUENCY – Hz
0
TA = +25°C
V
S
= ±15V
OUTPUT IMPEDANCE – Ω
2
10
6
4
8
VS = ±15V
T
= +25°C
A
40
30
20
10
0
–10
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN – dB
–20
VS = ±15V
T
= +25°C
A
Figure 7. Closed-Loop Gain vs. Frequency, 20 Hz to 20 kHz
(Gain of 1/2 Normalized to 0 dB)
180
135
90
45
0
–45
PHASE – Degrees
–90
–135
–180
100
1k
FREQUENCY – Hz
100k10k
TA = +25°C
= ±15V
V
S
R
= 2kΩ
L
1M 10M
Figure 9. Closed-Loop Phase vs. Frequency
–30
1k100 100k10k
FREQUENCY – Hz
1M
10M
Figure 8. Closed-Loop Gain vs. Frequency, 100 Hz to
10 MHz
120
100
80
60
40
COMMON-MODE REJECTION – dB
20
0
FREQUENCY – Hz
= ±15V
V
S
TA = +25°C
1M1k100 100k10k
Figure 10. Common-Mode Rejection vs. Frequency
140
V
= ±15V
S
TA = +25°C
–PSRR
Figure 12. Closed-Loop Output Impedance vs. Frequency
–4–
REV. 0
120
100
80
60
40
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION – dB
20
0
10 100 1M100k1k 10k
FREQUENCY – Hz
+PSRR
Figure 11. Power Supply Rejection vs. Frequency

6
LOAD RESISTANCE – Ω
10 1k
100
10k
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – V rms
0V
7.5V
2.5V
12.5V
5.0V
10.0V
V = ±15V
T = +25°C
S
A
TA = +25°C
V
S
= ±15V
FREQUENCY – Hz
1
10010
1k
10k
120
0
60
20
40
100
80
VOLTAGE NOISE DENSITY – nV/ Hz
10
90
100
0%
5mV
10ms
5µV
0V
–5µV
5
4
3
2
1
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – V rms
T
= +25°C
A
VS = ±15V
G = 1/2
R
= 2kΩ
L
SSM2143
0
1k
100k10k 1M 10M
FREQUENCY – Hz
Figure 13. Output Voltage Swing vs. Frequency
40
T = +25°C
A
30
20
10
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – V p–p
0
0
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
±20±5 ±15±10
Figure 15. Output Voltage Swing vs. Supply Voltage
Figure 14. Output Voltage Swing vs. Load Resistance
Figure 16. Voltage Noise Density vs. Frequency
100
90
Figure 17. Low Frequency Voltage Noise from 0.1 Hz
to 10 Hz*
REV. 0
10
0%
*The photographs in Figure 17 through Figure 19 were taken at VS = ±15 V and TA = +25°C, using an external amplifier with a gain of 1000.
1s
0.5µV
0V
–0.5µV
5mV
Figure 18. Voltage Noise from 0 kHz to 1 kHz*
–5–

SSM2143
SLEW RATE – V/µs
4
16
10
6
8
14
12
TEMPERATURE – °C
7525
50
–50
–25 1000
R = 2kΩ
V = ±15V
L
S
TEMPERATURE – °C
75
25
50–50 –25
100
0
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE – µV
400
0
300
100
200
V = ±15V
S
100
90
10
0%
5mV
1ms
5µV
0V
–5µV
Figure 19. Voltage Noise from 0 kHz to 10 kHz*
0.10
V = ±15V
S
V = ±10V
0.08
0.06
0.04
GAIN ERROR – %
0.02
0
–50
–25
25 50
0
TEMPERATURE – °C
IN
R = 0Ω
S
75
100
Figure 21. Gain Error vs. Temperature
5
V = ±15V
S
4
Figure 20. Slew Rate vs. Temperature
Figure 22. Input Offset Voltage vs. Temperature
4.0
TA = +25°C
3.5
3
2
SUPPLY CURRENT – mA
1
0
–25
–50
0
TEMPERATURE – °C
50
7525
100
Figure 23. Supply Current vs. Temperature
*The photographs in Figure 17 through Figure 19 were taken at VS = ±15 V and TA = +25°C, using an external amplifier with a gain of 1000.
–6–
3.0
2.5
2.0
SUPPLY CURRENT– mA
1.5
1.0
0
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – V
±20±5 ±15±10
Figure 24. Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
REV. 0

SSM2143
REFERENCE
OP27
+10V
–10V
6
1
2
3
4
5
7
12k
12k
6k
6k
–IN
+IN
–15V
0.1µF
V
OUT
+15V
0.1µF
SSM2143
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
The SSM2143 is designed as a balanced differential line receiver. It uses a high speed, low noise audio amplifier with four
precision thin-film resistors to maintain excellent common-mode
rejection and ultralow THD. Figure 25 shows the basic differential receiver application where the SSM2143 yields a gain of 1/2.
The placement of the input and feedback resistors can be
switched to achieve a gain of +2, as shown in Figure 26. For
either circuit configuration, the SSM2143 can also be used unbalanced by grounding one of the inputs. In applications requiring a gain of +1, use the SSM2141.
5
SSM2143
1
+15V
0.1µF
7
6k
6k
4
–15V
12k
12k
0.1µF
A = 2
2
6
3
+15V
0.1µF
1
A =
V
2
5
6
V
OUT
1
–IN
+IN
12k
2
SSM2143
3
12k
7
4
–15V
+
0.1µF
6k
6k
Figure 25. Standard Configuration for Gain of 1/2
–IN
+IN
Figure 26. Reversing the
Resistors Results in a
Gain of 2
CMRR
The internal thin-film resistors are precisely trimmed to achieve
a CMRR of 90 dB. Any imbalances introduced by the external
circuitry will cause a significant reduction in the overall CMRR
performance. For example, a 5 Ω source imbalance will result in
a CMRR of 71 dB at dc. This is also true for any reactive source
impedances that may affect the CMRR over the audio frequency
range. These error sources need to be minimized to maintain
the excellent CMRR.
To quantify the required accuracy of the thin film resistor
matching, the source of CMRR error can be analyzed. A resistor
mismatch can be modelled as shown in Figure 27. By assuming
a tolerance on one of the 12 kΩ resistors of ∆R, the equation for
the common-mode gain becomes:
V
OUT
=
V
IN
6k+12k
6k
6k
12k+∆R
+1
–
12k+∆R
6k
which reduces to:
V
OUT
V
IN
1/3∆R
=
12k+∆R
This gain error leads to a common-mode rejection ratio of:
|
CMRR =
Figure 27. A Small Mismatch in Resistance Results in a
Large Common-Mode Error
REV. 0
–IN
+IN
12k + ∆R
12k
|A
|A
6k
DM
CM
6k
|
18k
≅
∆R
CMRR =
V
OUT
18k
∆R
Setting ∆R to 5 Ω results in the CMRR of 71 dB, as stated
above. To achieve the SSM2143’s CMRR of 90 dB, the resistor
mismatch can be at most 0.57 Ω. In other words, to build this
circuit discretely, the resistors would have to be matched to
better than 0.005%!
The following table shows typical resistor accuracies and the
resulting CMRR for a differential amplifier.
% Mismatch CMRR
5% 30 dB
1% 44 dB
0.1% 64 dB
0.005% 90 dB
V
DC OUTPUT LEVEL ADJUST
The reference node of the SSM2143 is normally connected to
ground. However, it can be used to null out any dc offsets in
V
OUT
the system or to introduce a dc reference level other than
ground. As shown in Figure 28, the reference node needs to be
Figure 28. A Low Impedance Buffer Is Required to Adjust
the Reference Voltage.
buffered with an op amp to maintain very low impedance to
achieve high CMRR. The same reasoning as above applies such
that the 6 kΩ resistor has to be matched to better than 0.005%
or 0.3 Ω. The op amp maintains very low output impedance
over the entire audio frequency range, as long as its bandwidth
is well above 20 kHz. The reference input can be adjusted over
a ±10 V range. The gain from the reference to the output is
unity so the resulting dc output adjustment range is also ±10 V.
INPUT ERRORS
The main dc input offset error specified for the SSM2143 is the
Input Offset Voltage. The Input Bias Current and Input Offset
Current are not specified as for a normal operational amplifier.
Because the SSM2143 has built-in resistors, any bias current
related errors are converted into offset voltage errors. Thus, the
offset voltage specification is a combination of the amplifier’s
offset voltage plus its offset current times the input impedance.
+18V
V
4
IN
3
–18V
ALL CABLE MEASUREMENTS USE
BELDEN CABLE (500').
6
2
1
SSM2142
8
7
5
+18V
2
SSM2143
3
0.1µF
7
5
V
6
4
1
–18V
OUT
0.1µF
Figure 29. SSM2142/SSM2143 Balanced Line Driver/
Receiver System
–7–

SSM2143
SEATING
PLANE
SEE DETAIL
ABOVE
4
5
8
1
0.0688 (1.75)
0.0532 (1.35)
0.0098 (0.25)
0.0075 (0.19)
0.1574 (4.00)
0.1497 (3.80)
0.2440 (6.20)
0.2284 (5.80)
0.1968 (5.00)
0.1890 (4.80)
0.0192 (0.49)
0.0138 (0.35)
0.0500
(1.27)
BSC
0.0098 (0.25)
0.0040 (0.10)
× 45°
0.0196 (0.50)
0.0099 (0.25)
0.0500 (1.27)
0.0160 (0.41)
PIN 1
0°- 8°
LINE DRIVER/RECEIVER SYSTEM
The SSM2143 and SSM2142 provide a fully integrated line driver/
receiver system. The SSM2142 is a high performance balanced
line driver IC that converts an unbalanced input into a balanced
output signal. It can drive large capacitive loads on long cables
making it ideal for transmitting balanced audio signals. When combined with an SSM2143 on the receiving end of the cable, the system maintains high common-mode rejection and ultralow THD.
The SSM2142 is designed with a gain of +2 and the SSM2143
with a gain of 1/2, providing an overall system gain of unity.
The following data demonstrates the typical performance of the
two parts together, measured on an Audio Precision at the
SSM2143’s output. This configuration was tested with 500 feet
500' CABLE
NO CABLE
of cable between the ICs as well as no cable. The combination
of the two parts results in excellent THD+N and SNR and a noise
floor of typically –105 dB over a 20 Hz to 20 kHz bandwidth.
A comment on SSM2142/SSM2143 system headroom is necessary. Figure 31 shows a maximum signal handling of approximately
±22 dBu, but it must be kept in mind that this is measured between the SSM2142’s input and SSM2143’s output, which has
been attenuated by one half. Normally, the system would be shown
as actually used in a piece of equipment, whereby the SSM2143 is
at the input and SSM2142 at the output. In this case, the system
could handle differential signals in excess of +24 dBu at the input
and output, which is consistent with headroom requirements of
most professional audio equipment.
C1598–24–11/91
Figure 30. THD+N vs. Frequency of SSM2142/SSM2143
System (V
= ±18 V, VIN = 5 V rms, with 80 kHz Filter)
S
Figure 31. SSM2142/SSM2143 System Headroom–
= ±18 V, RL = 10 kΩ, 500' Cable)
S
500' CABLE
NO CABLE
See Text—(V
Figure 32. SSM2142/SSM2143 System
DIM-100 Dynamic Intermodulation
Distortion (VS = ±18 V, RL = 10 kΩ)
0.210
(5.33)
MAX
0.200 (5.05)
0.125 (3.18)
Figure 33. SSM2142/SSM2143 System Frequency
Response (V
= ±18 V, VIN = 0 dBV, 500' Cable)
S
5V
100
90
10
0%
10µs
Figure 34. SSM2142/SSM2143 System Large Signal Pulse
Response (V
= ±18 V, RL = 10 kΩ, No Cable)
S
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm).
1
0.430 (10.92)
0.348 (8.84)
0.022 (0.558)
0.014 (0.356)
0.100
(2.54)
BSC
N-8
58
4
0.280 (7.11)
0.240 (6.10)
0.070 (1.77)
0.045 (1.15)
0.060 (1.52)
0.015 (0.38)
0.150
(3.81)
MIN
SEATING
PLANE
0 - 15
0.325 (8.25)
0.300 (7.62)
0.015 (0.381)
0.008 (0.204)
SO-8
–8–
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
REV. 0
 Loading...
Loading...