+OUT FORCE
– OUT FORCE
– OUT SENSE
+OUT SENSE
10kΩ
10kΩ
50Ω
50Ω
V
IN
GND
ALL RESISTORS 30kΩ
UNLESS OTHERWISE
INDICATED
a
REV. C
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113
©1991–2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
Balanced Line Driver
SSM2142
FEATURES
Transformer-Like Balanced Output
Drives 10 V RMS Into a 600 V Load
Stable When Driving Large Capacitive Loads and Long
Cables
Low Distortion
0.006% typ 20 Hz–20 kHz, 10 V RMS into 600 V
High Slew Rate
15 V/ms typ
Low Gain Error
(Differential or Single-Ended); 0.7% typ
Outputs Short-Circuit Protected
Available In Space-Saving 8-Pin Mini-DIP Package
Low Cost
APPLICATIONS
Audio Mix Consoles
Distribution Amplifiers
Graphic and Parametric Equalizers
Dynamic Range Processors
Digital Effects Processors
Telecommunications Systems
Industrial Instrumentation
Hi-Fi Equipment
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SSM2142 is an integrated differential-output buffer
amplifier that converts a single-ended input signal to a balanced
output signal pair with high output drive. By utilizing low noise
thermally matched thin film resistors and high slew rate
amplifiers, the SSM2142 helps maintain the sonic quality of
audio systems by eliminating power line hum, RF interference,
voltage drops, and other externally generated noise commonly
encountered with long audio cable runs. Excellent rejection of
common-mode noise and offset errors is achieved by laser
trimming of the onboard resistors, assuring high gain accuracy.
The carefully designed output stage of the SSM2142 is capable
of driving difficult loads, yielding low distortion performance
despite extremely long cables or loads as low as 600 Ω, and is
stable over a wide range of operating conditions.
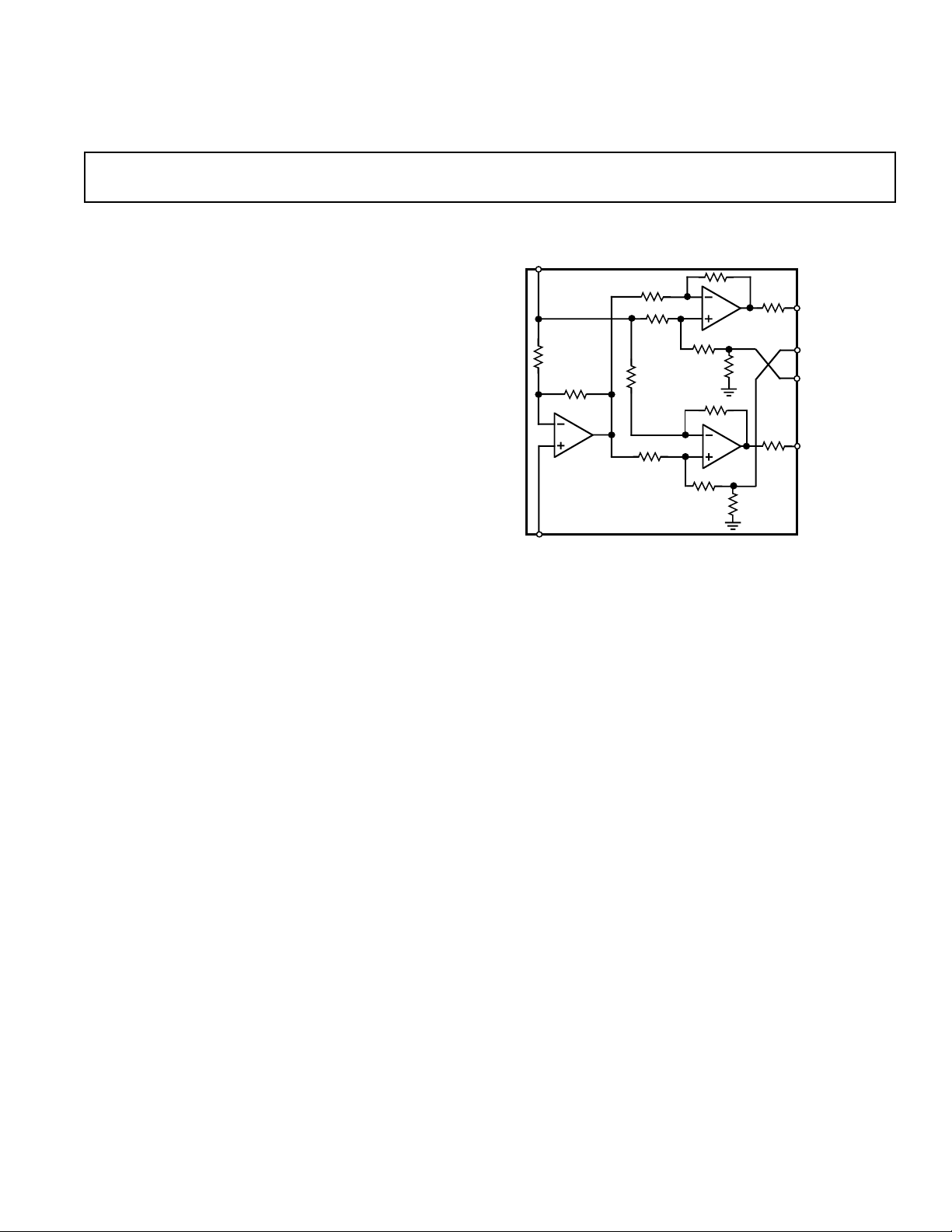
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Based on a cross-coupled, electronically balanced topology, the
SSM2142 mimics the performance of fully balanced
transformer-based solutions for line driving. However, the
SSM2142 maintains lower distortion and occupies much less
board space than transformers while achieving comparable
common-mode rejection performance with reduced parts count.
The SSM2142 in tandem with the SSM2141 differential
receiver establishes a complete, reliable solution for driving and
receiving audio signals over long cables. The SSM2141 features
an Input Common-Mode Rejection Ratio of 100 dB at 60 Hz.
Specifications demonstrating the performance of this typical
system are included in the data sheet.
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
(VS = 618 V, –408C ≤ TA ≤ +858C, operating in differential mode unless otherwise
– FORCE
– SENSE
GROUND
V
IN
+ FORCE
+ SENSE
+V
–V
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
REV. C
–38
–35
SSM2142–SPECIFICATIONS
noted. Typical characteristics apply to operation at TA = +258C.)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
INPUT IMPEDANCE Z
INPUT CURRENT I
IN
IN
VIN = ±7.071 V ±750 ±900 µA
10 kΩ
GAIN, DIFFERENTIAL 5.8 5.98 dB
GAIN, SINGLE-ENDED Single-Ended Mode 5.7 5.94 dB
GAIN ERROR, DIFFERENTIAL RL = 600 Ω 0.7 2 %
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION
RATIO STATIC PSRR VS = ±13 V to ±18 V 60 80 dB
OUTPUT COMMON-MODE REJECTION OCMR See Test Circuit; f = 1 kHz –45 dB
OUTPUT SIGNAL BALANCE RATIO SBR See Test Circuit; f = 1 kHz –40 dB
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION
Plus Noise THD+N 20 Hz to 20 kHz, 0.006 %
VO = 10 V rms, RL = 600 Ω
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO SNR VIN = 0 V –93.4 dBu
HEADROOM HR CLIP Level = 10.5 V rms +93.4 dBu
SLEW RATE SR 15 V/µs
OUTPUT COMMON-MODE
VOLTAGE OFFSET
1
V
OOS
RL = 600 Ω –250 25 250 mV
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT
VOLTAGE OFFSET V
OOD
RL = 600 Ω –50 15 50 mV
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT
VOLTAGE SWING VIN = ±7.071 V ±13.8 ±14.14 V
OUTPUT IMPEDANCE Z
SUPPLY CURRENT I
OUTPUT CURRENT, SHORT CIRCUIT I
NOTES
1
Output common-mode offset voltage can be removed by inserting dc blocking capacitors in the sense lines. See Applications Information.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
SY
SC
O
Unloaded, VIN = 0 V 5.5 7.0 mA
45 50 55 Ω
60 70 mA
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±18 V
Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –60°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 60 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . +300°C
Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +150°C
Operating Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Output Short Circuit Duration (Both Outputs) . . . . Indefinite
*Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause
permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only; the functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
–2–
PIN CONNECTIONS
8-Pin Plastic DIP
(P Suffix)
16-Pin Wide Body SOL
(S Suffix)
SSM2142
10
12
FREQUENCY – kHz
10
8
6
4
2
0
20 30 50 100
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – V rms
T
A
= +25°C
V
S
= ±18V
R
L
= 600Ω
DIFF. MODE
0.1% DISTORTION
0.01% DISTORTION
±2
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – Volts
6.5
SUPPLY CURRENT – mA
±6 ±10 ±14 ±18
T
A
= +25°C
V
IN
= 0V
NO LOAD
6.0
5.5
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
300
300
600
+18V
–18V
V = 10V p–p
IN
∆V
OUT
V
IN
SBR = 20 LOG
V
OUT
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
V
Ω
Ω
Ω
REV. C
300Ω
V
OUT
V
300Ω
1
2
3
= 0V
V
S
4
OCMR = 20 LOG
8
7
+18V
6
–18V
5
V
= 10V p–p
CMR
∆V
OUT
V
CMR
600Ω
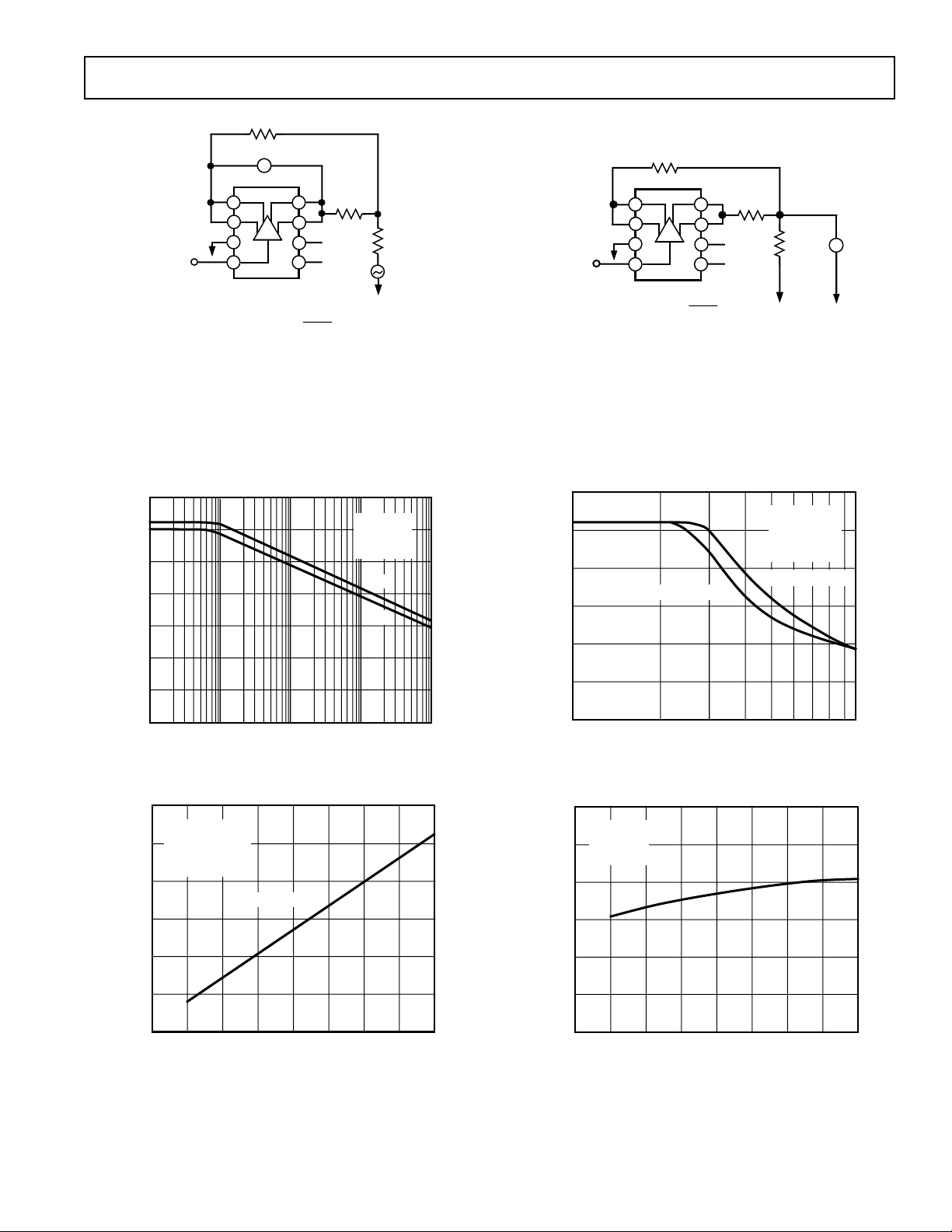
Figure 1. Output CMR Test Circuit
Typical Performance Characteristics
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION – dB
0
10
100 1k 10k 100k
FREQUENCY – Hz
Figure 3. Power Supply Rejection vs. Frequency
12
= +25°C
T
A
= 600Ω
R
L
10
DIFF. MODE
FREQ. = 20kHz
8
0.1% DISTORTION
6
TA = +25°C
= ±18V
V
S
∆V
= ±1V
S
–PSR
+PSR
Figure 2. Signal Balance Ratio (BBC Method) Test Circuit
Figure 4. Maximum Output Voltage Swing vs. Frequency
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – V rms
Figure 5. Output Voltage Swing vs. Supply Voltage
4
2
0
±2
±6 ±10 ±14 ±18
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – Volts
Figure 6. Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
–3–
 Loading...
Loading...