Dual Very Low Noise Precision
a
FEATURES
Very Low Noise 5 nV/
Excellent Input Offset Voltage 75 V Max
Low Offset Voltage Drift 1 V/ⴗC Max
Very High Gain 1500 V/mV Min
Outstanding CMR 106 dB Min
Slew Rate 2.4 V/s Typ
Gain Bandwidth Product 5 MHz Typ
Industry-Standard 8-Lead Dual Pinout
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The OP270 is a high performance, monolithic, dual operational
amplifier with exceptionally low voltage noise, 5 nV/÷Hz max at
1 kHz. It offers comparable performance to ADI’s industry
standard OP27.
The OP270 features an input offset voltage below 75 mV and an
offset drift under 1 mV/∞C, guaranteed over the full military tem-
perature range. Open-loop gain of the OP270 is over 1,500,000
into a 10 kW load, ensuring excellent gain accuracy and linearity,
even in high gain applications. Input bias current is under 20 nA,
which reduces errors due to signal source resistance. The OP270’s
CMR of over 106 dB and PSRR of less than 3.2 mV/V signifi-
cantly reduce errors due to ground noise and power supply
fluctuations. Power consumption of the dual OP270 is one-third
less than two OP27s, a significant advantage for power conscious
applications. The OP270 is unity-gain stable with a gain bandwidth
product of 5 MHz and a slew rate of 2.4 V/ms.
÷÷
÷Hz @ 1 kHz Max
÷÷
Operational Amplifier
OP270
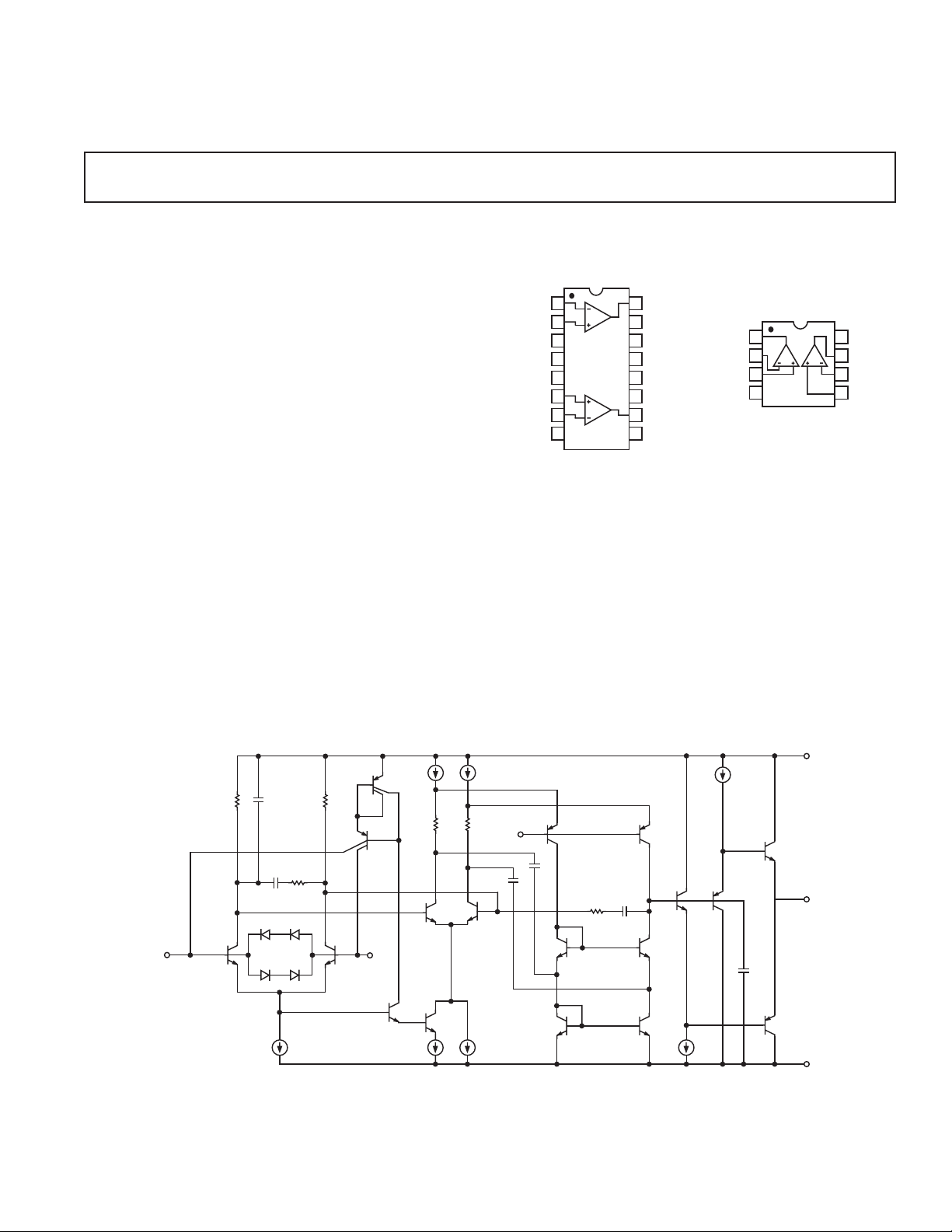
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
16-Lead SOIC
(S-Suffix)
1
–IN A
2
+IN A
3
NC
4
V–
5
NC
+IN B
6
–IN B
7
NC
8
NC = NO CONNECT
OP270
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
OUT A
NC
NC
V+
NC
NC
OUT B
NC
The OP270 offers excellent amplifier matching, which is important
for applications such as multiple gain blocks, low noise instrumentation amplifiers, dual buffers, and low noise active filters.
The OP270 conforms to the industry-standard 8-lead DIP pinout.
It is pin compatible with the MC1458, SE5532/A, RM4558, and
HA5102 dual op amps, and can be used to upgrade systems
using those devices.
For higher speed applications, the OP271, with a slew rate of
8V/ms, is recommended. For a quad op amp, see the OP470.
8-Lead PDIP (P-Suffix)
8-Lead CERDIP
(Z-Suffix)
OUT A
–IN A
+IN A
1
2
A
3
4
V–
OP270
8
V+
7
OUT B
B
6
–IN B
5
+IN B
SIMPLIFIED SCHEMATIC
(One of Two Amplifiers Is Shown)
–IN
+IN
REV. C
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective companies.
V+
BIAS
OUT
V–
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © 2003 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

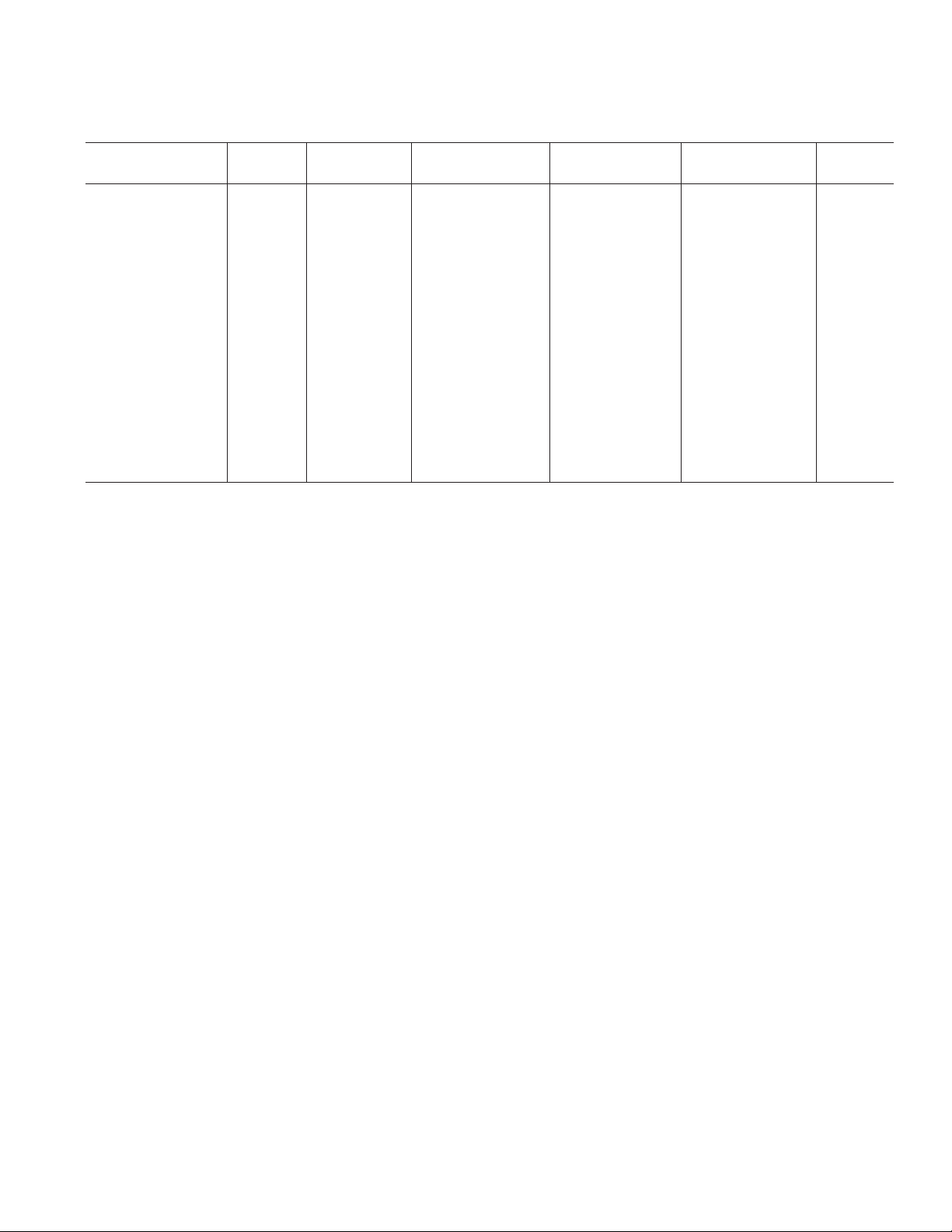
OP270–SPECIFICATIONS
(VS = ⴞ15 V, TA=25ⴗC, unless otherwise noted.)
OP270E OP270F OP270G
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Input Offset Voltage V
Input Offset Current l
Input Bias Current I
Input Noise Voltage e
OS
OS
B
p-p 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz 80 200 80 200 80 nV p-p
n
VCM=0 V 1 10 315 520nA
VCM=0 V 5 20 10 40 15 60 nA
10 75 20 150 50 250 mV
(Note 1)
Input Noise f
Voltage Density f
e
n
= 10 Hz 3.6 6.5 3.6 6.5 3.6 nV/
O
= 100 Hz 3.2 5.5 3.2 5.5 3.2 nV/
O
fO= 1 kHz 3.2 5.0 3.2 5.0 3.2 nV/
(Note 2)
Input Noise f
Current Density i
n
Large-Signal V
Voltage Gain A
VO
= 10 Hz 1.1 1.1 1.1 pA/
O
fO = 100 Hz 0.7 0.7 0.7 pA/
f
= 1 kHz 0.6 0.6 0.6 pA/
O
= ± 10 V
O
RL = 10 kW 1500 2300 1000 1700 750 1500 V/mV
R
=2 kW 750 1200 500 900 350 700 V/mV
L
Input Voltage Range IVR (Note3) ± 12 ±12.5 ± 12 ± 12.5 ± 12 ± 12.5 V
Output Voltage Swing V
O
RL≥ 2kW±12 ± 13.5 ± 12 ± 13.5 ± 12 ± 13.5 V
Common-Mode
Rejection CMR V
= ± 11 V 106 125 100 120 90 110 dB
CM
Power Supply
Rejection Ratio PSRR V
= ± 4.5 V 0.56 3.2 1.0 5.6 1.5 6 mV/V
S
to ± 18 V
Slew Rate SR 1.7 2.4 1.7 2.4 1.7 2.4 V/ms
Supply Current I
SY
No Load 4 6.5 4 6.5 4 6.5 mA
(All Amplifiers)
Gain Bandwidth GBP 5 5 5 MHz
Product
Channel Separation CS V
= ± 20 V p-p
O
= 10 Hz 125 175 125 175 175 dB
f
O
(Note 1)
Input Capacitance C
Input Resistance R
IN
IN
33 3pF
0.4 0.4 0.4 MW
Differential-Mode
Input Resistance R
INCM
20 20 20 GW
Common-Mode
Settling Time t
S
AV = +1, 10 V 5 5 5 ms
Step to 0.01%
NOTES
1. Guaranteed but not 100% tested.
2. Sample tested.
3. Guaranteed by CMR test.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
÷÷
÷Hz
÷÷
÷÷
÷Hz
÷÷
÷÷
÷Hz
÷÷
÷÷
÷Hz
÷÷
÷÷
÷Hz
÷÷
÷÷
÷Hz
÷÷
–2–
REV. C
SPECIFICATIONS
OP270
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Input Offset Voltage V
OS
(Vs = ⴞ15 V, –40∞C £ TA£ 85ⴗC, unless otherwise noted.)
OP270E OP270F OP270G
25 150 45 275 100 400 mV
Average Input
Offset Voltage Drift TCV
Input Offset Current I
Input Bias Voltage I
OS
OS
B
Large-Signal V
Voltage Gain A
VO
VCM=0 V 1.5 30 5 40 15 50 nA
VCM=0 V 6 60 15 70 19 80 nA
= ± 10 V
O
RL = 10 kW 1000 1800 600 1400 400 1250 V/mV
=2 kW 500 900 300 700 225 670 V/mV
R
L
0.2 1 0.4 2 0.7 3 mV/∞C
Input Voltage Range* IVR ± 12 ± 12.5 ± 12 ± 12.5 ± 12 ± 12.5 V
Output Voltage Swing V
O
RL≥ 2kW±12 ± 13.5 ± 12 ± 13.5 ± 12 ± 13.5 V
Common-Mode
Rejection CMR V
= ± 11 V 100 120 94 115 90 100 dB
CM
Power Supply
Rejection Ratio PSRR V
= ± 4.5 V 0.7 5.6 1.8 10 2.0 1.5 mV/V
S
to ± 18 V
Supply Current I
SY
No Load 4.4 7.2 4.4 7.2 4.4 7.2 mA
(All Amplifiers)
* Guaranteed by CMR test.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
REV. C
–3–
OP270
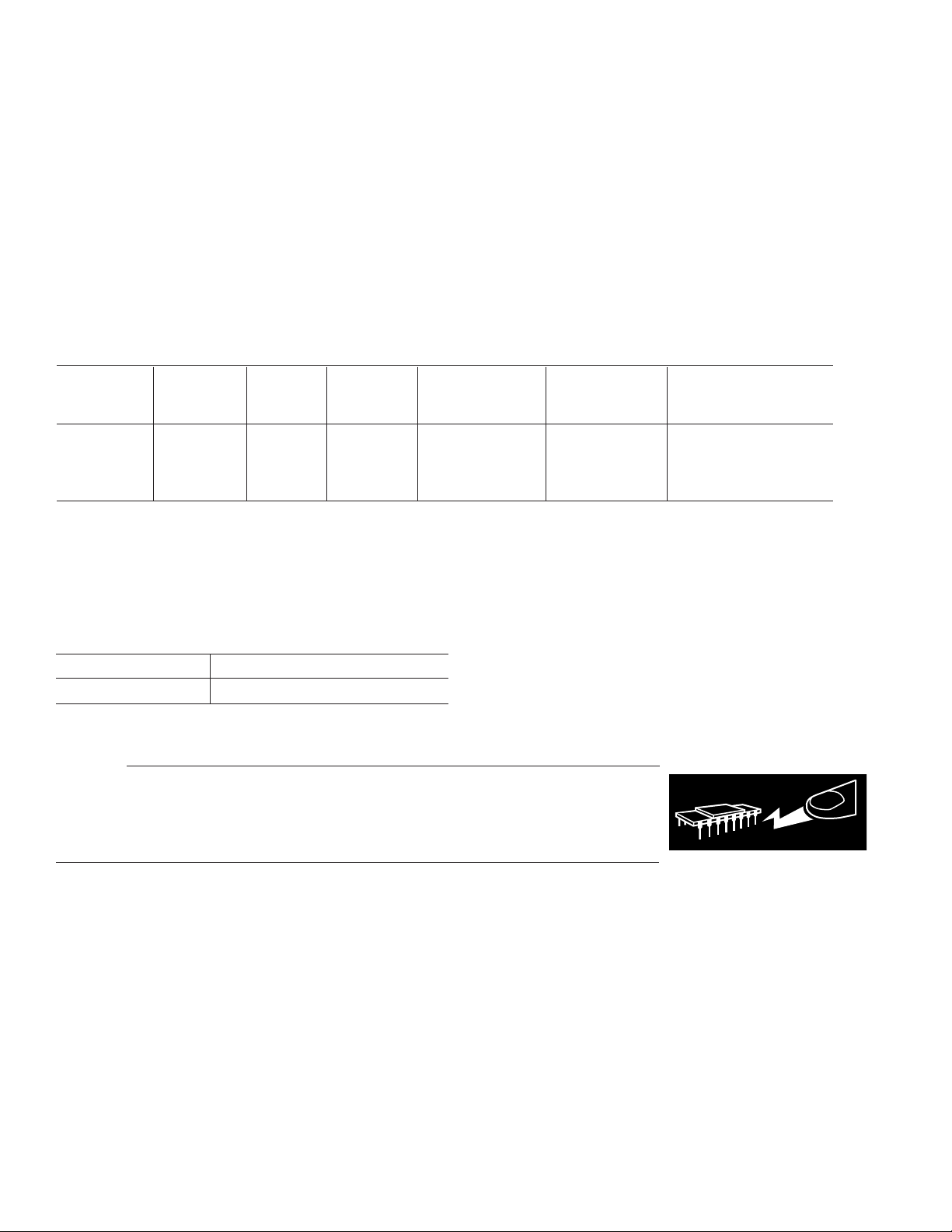
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ± 18 V
Differential Input Voltage
Differential Input Current
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ± 1.0 V
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ± 25 mA
Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Supply Voltage
Output Short-Circuit Duration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Continuous
Storage Temperature Range
P, S, Z Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering, 60 sec) . . . . . . . . 300°C
Junction Temperature (T
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
J
1
Operating Temperature Range
OP270E, OP270F, OP270G . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
The OP270’s inputs are protected by back-to-back diodes. Current limiting
resistors are not used, in order to achieve low noise performance. If differential
voltage exceeds +10 V, the input current should be limited to ±25 mA.
ORDERING GUIDE
TA = +25°C
Max θ
V
OS
JC
θJA* Temperature Package Package
Model (V) (°C/W) (°C/W) Range Description Option
OP270EZ 75 12 134 XIND 8-Lead CERDIP Q-8 (Z-Suffix)
OP270FZ 150 12 134 XIND 8-Lead CERDIP Q-8 (Z-Suffix)
OP270GP 250 37 96 XIND 8-Lead PDIP N-8 (P-Suffix)
OP270GS 250 27 92 XIND 16-Lead SOIC RW-16 (S-Suffix)
*θJA is specified for worst-case mounting conditions, i.e., θJA is specified for device
in socket for CERDIP and PDIP packages; θJA is specified for device soldered to
printed circuit board for SOIC package.
For military processed devices, please refer to the Standard
Microcircuit Drawing (SMD) available at
www.dscc.dla.mil/programs/milspec/default.asp.
SMD Part Number ADI Equivalent
5962-8872101PA OP270AZMDA
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
the OP270 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices
subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
–4–
REV. C
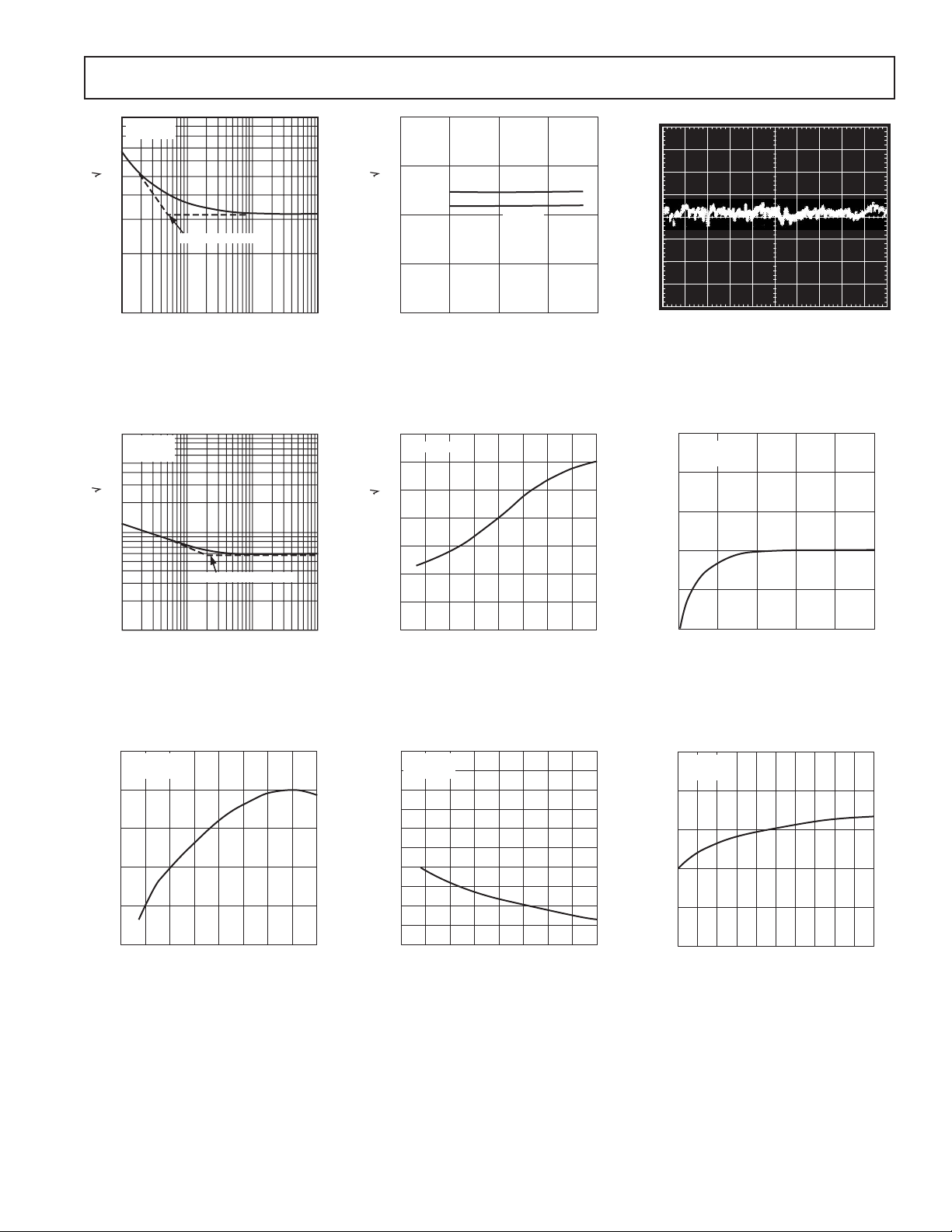
COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE (V)
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (nA)
7
–12.5
2
4
3
6
TA = 25ⴗC
V
S
= ⴞ15V
5
–10.0
–7.5
–5.0
–2.5
0.0
2.5
5.0
7.5
10.0
12.5
Typical Performance Characteristics–
OP270
10
TA = 25ⴗC
9
VS = ⴞ15V
8
7
6
5
4
3
1/f CORNER = 5Hz
10 100 1k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
VOLTA G E NOISE (nV/ Hz)
2
1
1
TPC 1. Voltage Noise Density
vs. Frequency
10
TA = 25ⴗC
= ⴞ15V
V
S
1.0
CURRENT NOISE (pA/ Hz)
0.1
10 100 10k
1/f CORNER = 200Hz
1k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
TPC 4. Current Noise Density
vs. Frequency
5
T
= 25ⴗC
A
4
AT 10Hz
3
2
VOLTA G E NOISE (nV/ Hz)
1
0 ⴞ5 ⴞ15 ⴞ20
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
AT 1kHz
ⴞ10
TPC 2. Voltage Noise Density
vs. Supply Voltage
40
VS = ⴞ15V
30
20
10
0
–10
VOLTA G E NOISE (nV/ Hz)
–20
–30
–50 –25 0 25 50 75 100 125
–75
TEMPERATURE (ⴗC)
TPC 5. Input Offset Voltage vs.
Temperature
0.1Hz TO 10Hz NOISE
NOISE VOLTAGE (100nV/DIV)
TA = 25ⴗC
= ⴞ15V
V
S
TIME (1sec/DIV)
TPC 3. 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz Input
Voltage Noise
5
TA = 25ⴗC
= ⴞ15V
V
S
4
3
2
1
CHANGE IN OFFSET VOLTAGE (A)
0
12345
0
TIME (Minutes)
TPC 6. Warm-Up Offset Voltage
Drift
7
6
5
4
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (nA)
3
2
–75
TPC 7. Input Bias Current vs.
Temperature
REV. C
VS = ⴞ15V
= 0V
V
CM
–50 0 50 100 125
–25 25 75
TEMPERATURE (ⴗC)
5
VS = ⴞ15V
= 0V
V
CM
4
3
2
1
INPUT OFFSET CURRENT (nA)
0
–75
–50 0 50 100 125
–25 25 75
TEMPERATURE (ⴗC)
TPC 8. Input Offset Current vs.
Temperature
–5–
TPC 9. Input Bias Current vs.
Common-Mode Voltage
 Loading...
Loading...