Analog Devices AD7243SQ-883B, AD7243BR, AD7243BQ, AD7243AR, AD7243AQ Datasheet
REV. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
a
LC2MOS
12-Bit Serial DACPORT
AD7243
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 617/329-4700 Fax: 617/326-8703
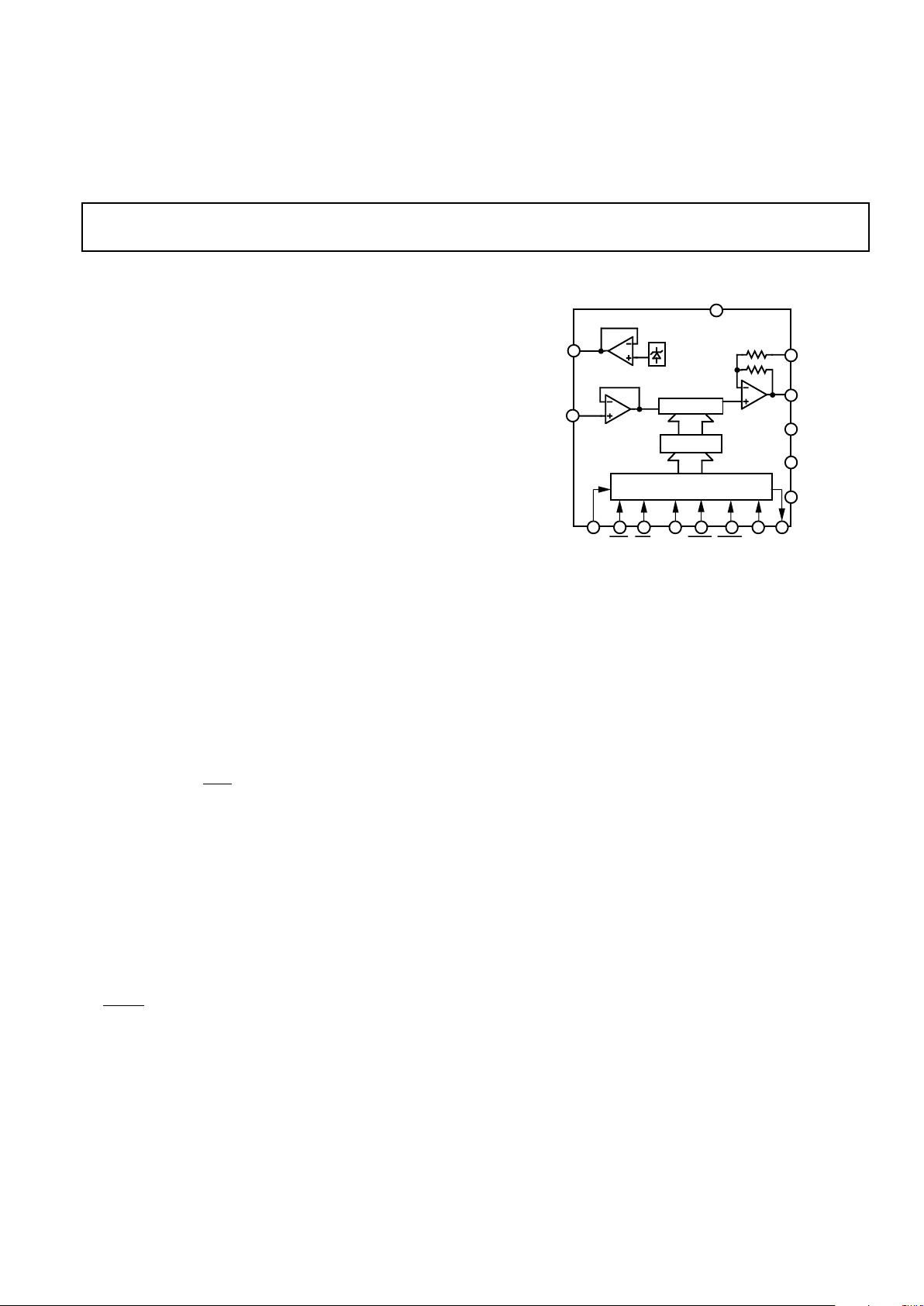
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
INPUT SHIFT REGISTER
DAC LATCH
12 - BIT DAC
12
12
AGND
DGND
REFOUT
REFIN
SDIN CLR SCLK
DCEN SDO
R
OFS
V
OUT
V
SS
V
DD
2R
2R
AD7243
BIN/
COMP
SYNC
LDAC
FEATURES
12-Bit CMOS DAC with
On-Chip Voltage Reference
Output Amplifier
3 Selectable Output Ranges
–5 V to +5 V, 0 V to +5 V, 0 V to +10 V
Serial Interface
300 kHz DAC Update Rate
Small Size: 16-Pin DIP or SOIC
Nonlinearity: 61/2 LSB T
MIN
to T
MAX
Low Power Dissipation: 100 mW typical
APPLICATIONS
Process Control
Industrial Automation
Digital Signal Processing Systems
Input/Output Ports
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7243 is a complete 12-bit, voltage output, digital-toanalog converter with output amplifier and Zener voltage reference on a monolithic CMOS chip. No external trims are
required to achieve full specified performance.
The output amplifier is capable of developing +10 V across a
2 kΩ load. The output voltage ranges with single supply operation are 0 V to +5 V or 0 V to +10 V, while an additional bipolar ±5 V output range is available with dual supplies. The ranges
are selected using the internal gain resistor.
The data format is natural binary in both unipolar ranges, while
either offset binary or 2s complement format may be selected in
the bipolar range. A
CLR function is provided which sets the
output to 0 V in both unipolar ranges and in the 2s complement
bipolar range, while with offset binary data format, the output is
set to –REFIN. This function is useful as a power-on reset as it
allows the output to be set to a known voltage level.
The AD7243 features a fast versatile serial interface which
allows easy connection to both microcomputers and 16-bit digital signal processors with serial ports. The serial data may be applied at rates up to 5 MHz allowing a DAC update rate of
300 kHz. A serial data output capability is also provided which
allows daisy chaining in multi-DAC systems. This feature allows
any number of DACs to be used in a system with a simple
4-wire interface. All DACs may be updated simultaneously using
LDAC.
DACPORT is a registered trademark of Analog Devices, Inc.
The AD7243 is fabricated on Linear Compatible CMOS
(LC
2
MOS), an advanced, mixed technology process. It is pack-
aged in 16-pin DIP and 16-pin SOIC packages.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. Complete 12-Bit DACPORT
The AD7243 is a complete, voltage output, 12-bit DAC on
a single chip. The single chip design is inherently more
reliable than multichip designs.
2. Single or Dual Supply Operation.
3. Minimum 3-wire interface to most DSP processors.
4. DAC Update Rate–300 kHz.
5. Serial Data Output allows easy daisy-chaining in multiple
DAC systems.
AD7243–SPECIFICA TIONS
Parameter A
2
B
2
S
2
Units Test Conditions/Comments
STATIC PERFORMANCE
Resolution 12 12 12 Bits
Relative Accuracy
3
±1 ±1/2 ±1 LSB max
Differential Nonlinearity
3
±0.9 ± 0.9 ±0.9 LSB max Guaranteed Monotonic
Unipolar Offset Error
3
±4 ±4 ±5 LSB max VSS = 0 V or –12 V to –15 V1; DAC Latch
Contents All 0s
Bipolar Zero Error
3
±5 ±5 ±6 LSB max VSS = –12 V to –15 V1; DAC Latch Contents All 0s
Full-Scale Error
3, 4
±6 ±6 ±7 LSB max
Full-Scale Temperature Coefficient ±5 ±5 ±5 ppm of FSR/
°C typ
REFERENCE OUTPUT
REFOUT 4.95/5.05 4.95/5.05 4.95/5.05 V min/V max
Reference Temperature Coefficient ±25 ±25 ±30 ppm/°C typ
Reference Load Change
(∆REFOUT VS. IL) –1 –1 –1 mV max Reference Load Current (IL) Change (0–100 µA)
REFERENCE INPUT
Reference Input Range, REFIN 4.95/5.05 4.95/5.05 4.95/5.05 V min/V max 5 V ±1% for Specified Performance
Input Current 5 5 5 µA max
DIGITAL INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
INH
2.4 2.4 2.4 V min
Input Low Voltage, V
INL
0.8 0.8 0.8 V max
Input Current, I
IN
±1 ±1 ±1 µA max VIN = 0 V to V
DD
Input Capacitance
5
8 8 8 pF max
DIGITAL OUTPUT
Serial Data Out (SDO)
Output Low Voltage, V
OL
0.4 0.4 0.4 V max I
SINK
= 1.0 mA
Output High Voltage, V
OH
4.0 4.0 4.0 V min I
SOURCE
= 400 µA
ANALOG OUTPUT
Output Range Resistor, R
OFS
15/30 15/30 15/30 kΩ min/max
Output Voltage Ranges
6
+5, +10 +5, +10 +5, +10 V Single Supply; VSS = 0 V
Output Voltage Ranges
6
+5, +10, ±5 +5, +10, ±5 +5, +10, ±5 V Dual Supply; VSS = –12 V to –15 V
DC Output Impedance 0.5 0.5 0.5 Ω typ
AC CHARACTERISTICS
5
Voltage Output Settling-Time Settling Time to Within ±1/2 LSB of Final Value
Positive Full-Scale Change 10 10 12 µs max Typically 3 µs
Negative Full-Scale Change 10 10 10 µs max Typically 5 µs; V
SS
= –12 V to –15 V
1
Negative Full-Scale Change 10 10 10 µs typ VSS = 0 V
Digital-to-Analog Glitch Impulse
3
30 30 30 nV secs typ DAC Latch Contents Toggled Between All 0s
and All 1s
Digital Feedthrough
3
10 10 10 nV secs typ LDAC = High
POWER REQUIREMENTS
VDD Range +10.8/+16.5 +11.4/+15.75 +11.4/+15.75 V min/V max For Specified Performance Unless Otherwise Stated
V
SS
Range (Dual Supplies) –10.8/–16.5 –11.4/–15.75 –11.4/–15.75 V min/V max For Specified Performance Unless Otherwise Stated
I
DD
10 10 12 mA max Output Unloaded; Typically 7 mA
ISS (Dual Supplies) 4 4 4 mA max Output Unloaded; Typically 2 mA
NOTES
1
Power Supply Tolerance A Version: ±10%; B, S Versions: ±5%.
2
Temperature ranges are as follows: A, B Versions: –40°C to +85 °C; S Version: –55 °C to +125 °C.
3
See terminology.
4
Measured with respect to REFIN and includes unipolar/bipolar offset error.
5
Sample tested @ +25°C to ensure compliance.
6
0 V to +10 V output range is available only with VDD ≥ +14.25 V.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
(VDD = +12 V to +15 V,1 VSS = 0 V or –12 V to –15 V,1 AGND = DGND = O V, REFIN = +5 V,
RL = 2 kV, CL = 100 pF to AGND. All Specifications T
MIN
to T
MAX
unless otherwise noted.)
–2–
REV. 0

REV. 0
–3–
AD7243
Limit at +258C Limit at T
MIN
, T
MAX
Parameter (All Versions) (All Versions) Units Conditions/Comments
t
1
3
200 200 ns min SCLK Cycle Time
t
2
50 50 ns min SYNC to SCLK Falling Edge Setup Time
t
3
120 190 ns min SYNC to SCLK Hold Time
t
4
10 10 ns min Data Setup Time
t
5
100 100 ns min Data Hold Time
t
6
0 0 ns min SYNC High to LDAC Low
t
7
50 50 ns min LDAC Pulse Width
t
8
0 0 ns min LDAC High to SYNC Low
t
9
75 75 ns min CLR Pulse Width
t
10
4
120 180 ns max SCLK Falling Edge to SDO Valid
NOTES
1
Sample tested at +25°C to ensure compliance. All input signals are specified with tr = tf = 5 ns (10% to 90% of 5 V) and timed from a voltage level of 1.6 V.
2
See Figures 7 & 8.
3
SCLK mark/space ratio range is 40/60 to 60/40.
4
SDO load capacitance is no greater than 50 pF.
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Relative Accuracy Package Option
1
AD7243AN –40°C to +85°C ±1 LSB N-16
AD7243BN –40°C to +85°C ±1/2 LSB N-16
AD7243AR –40°C to +85°C ±1 LSB R-16
AD7243BR –40°C to +85°C ±1/2 LSB R-16
AD7243AQ –40°C to +85°C ±1 LSB Q-16
AD7243BQ –40°C to +85°C ±1/2 LSB Q-16
AD7243SQ
2
–55°C to +125°C ±1 LSB Q-16
NOTES
1
N = Plastic DIP; R = SOIC; Q = Cerdip.
2
Available to /883B processing only. Contact your local sales office for military data sheet.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
1
(TA = +25°C unless otherwise noted)
VDD to AGND, DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +17 V
V
SS
to AGND, DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +0.3 V to –17 V
AGND to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to V
DD
+ 0.3 V
V
OUT
2
to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –6 V to VDD + 0.3 V
REFOUT to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0 V to V
DD
REFIN to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V
Digital Inputs to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to V
DD
+ 0.3 V
SDO to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to V
DD
+ 0.3 V
Operating Temperature Range
Industrial (A, B Versions) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Extended (S Version) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –55°C to +125°C
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
1, 2
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD7243 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 secs) . . . . . . . . . . . +300°C
Power Dissipation (Any Package) to +75°C . . . . . . . . 450 mW
Derates above +75°C by . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 mW/°C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the
operational sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. Only
one Absolute Maximum Rating may be applied at any time.
2
The outputs may be shorted to voltages in this range provided the power dissipation
of the package is not exceeded. Short circuit current is typically 80 mA.
(VDD = +10.8 V to +16.5 V, VSS = 0 V or –10.8 V to –16.5 V, AGND = DGND = 0 V,
RL = 2 kV, CL = 100 pF. All Specifications T
MIN
to T
MAX
unless otherwise noted.)
AD7243
–4–
REV. 0
AD7243 PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION (DIP & SOIC PIN NUMBERS)
Pin Mnemonic Description
1 REFIN Voltage Reference Input. It is internally buffered before being applied to the DAC. The nominal reference
voltage for specified operation of the AD7243 is 5 V.
2 REFOUT Voltage Reference Output. The internal 5 V analog reference is provided at this pin. To operate the part using
its internal reference, REFOUT should be connected to REFIN.
3
CLR Clear, Logic Input. Taking this input low sets V
OUT
to 0 V in both unipolar ranges and the 2s complement
bipolar range and to –REFIN in the offset binary bipolar range.
4
BIN/COMP Logic Input. This input selects the data format to be either binary or 2s complement. In both unipolar ranges,
natural binary format is selected by connecting this input to a Logic “0.” In the bipolar configuration, offset
binary format is selected with a Logic “0” while a Logic “1” selects 2s complement format.
5 SCLK Serial Clock, Logic Input. Data is clocked into the input register on each falling SCLK edge.
6 SDIN Serial Data In, Logic Input. The 16-bit serial data word is applied to this input.
7
SYNC Data Synchronization Pulse, Logic Input. Taking this input low initializes the internal logic in readiness for a
new data word.
8 DGND Digital Ground. Ground reference for all digital circuitry.
9
LDAC Load DAC, Logic Input. Updates the DAC output. The DAC output is updated on the falling edge of this
signal or alternatively if this line is permanently low, an automatic update mode is selected whereby the DAC
is updated on the 16th falling SCLK pulse.
10 DCEN Daisy-Chain Enable, Logic Input. Connect this pin high if a daisy-chain interface is being used, otherwise
this pin must be connected low.
11 SDO Serial Data Out, Logic Output. With DCEN at Logic “1” this output is enabled, and the serial data in the
input shift register is clocked out on each falling SCLK edge.
12 AGND Analog Ground. Ground reference for all analog circuitry.
13 R
OFS
Output Offset Resistor for the amplifier. It is connected to V
OUT
for the +5 V range, to AGND for the +10 V
range and to REFIN for the –5 V to +5 V range.
14 V
OUT
Analog Output Voltage. This is the buffer amplifier output voltage. Three different output voltage ranges can
be chosen: 0 V to +5 V, 0 to +10 V and –5 V to +5 V.
15 V
SS
Negative Power Supply (used for the output amplifier only, may be connected to 0 V for single supply
operation or to –12 V to –15 V for dual supplies).
16 V
DD
Positive Power Supply (+12 V to +15 V).
TERMINOLOGY
Bipolar Zero Error
Bipolar Zero Error is the voltage measured at V
OUT
when the
DAC is configured for bipolar output and loaded with all 0s (2s
Complement Coding) or with 1000 0000 0000 (Offset Binary
Coding). It is due to a combination of offset errors in the DAC,
amplifier and mismatch between the internal gain resistors
around the amplifier.
Full-Scale Error
Full-Scale Error is a measure of the output error when the amplifier output is at full scale (for the bipolar output range full
scale is either positive or negative full scale). It is measured with
respect to the reference input voltage and includes the offset
errors.
Digital-to-Analog Glitch Impulse
This is the voltage spike that appears at V
OUT
when the digital
code in the DAC latch changes, before the output settles to its
final value. The energy in the glitch is specified in nV secs, and
is measured for an all codes change from 0000 0000 0000 to
1111 1111 1111.
Digital Feedthrough
This is a measure of the voltage spike that appears on V
OUT
as a
result of feedthrough from the digital inputs on the AD7243. It
is measured with
LDAC held high.
Relative Accuracy (Linearity)
Relative Accuracy, or endpoint linearity, is a measure of the
maximum deviation of the DAC transfer function from a
straight line passing through the endpoints of the transfer function. It is measured after allowing for zero and full-scale errors
and is expressed in LSBs or as a percentage of full-scale reading.
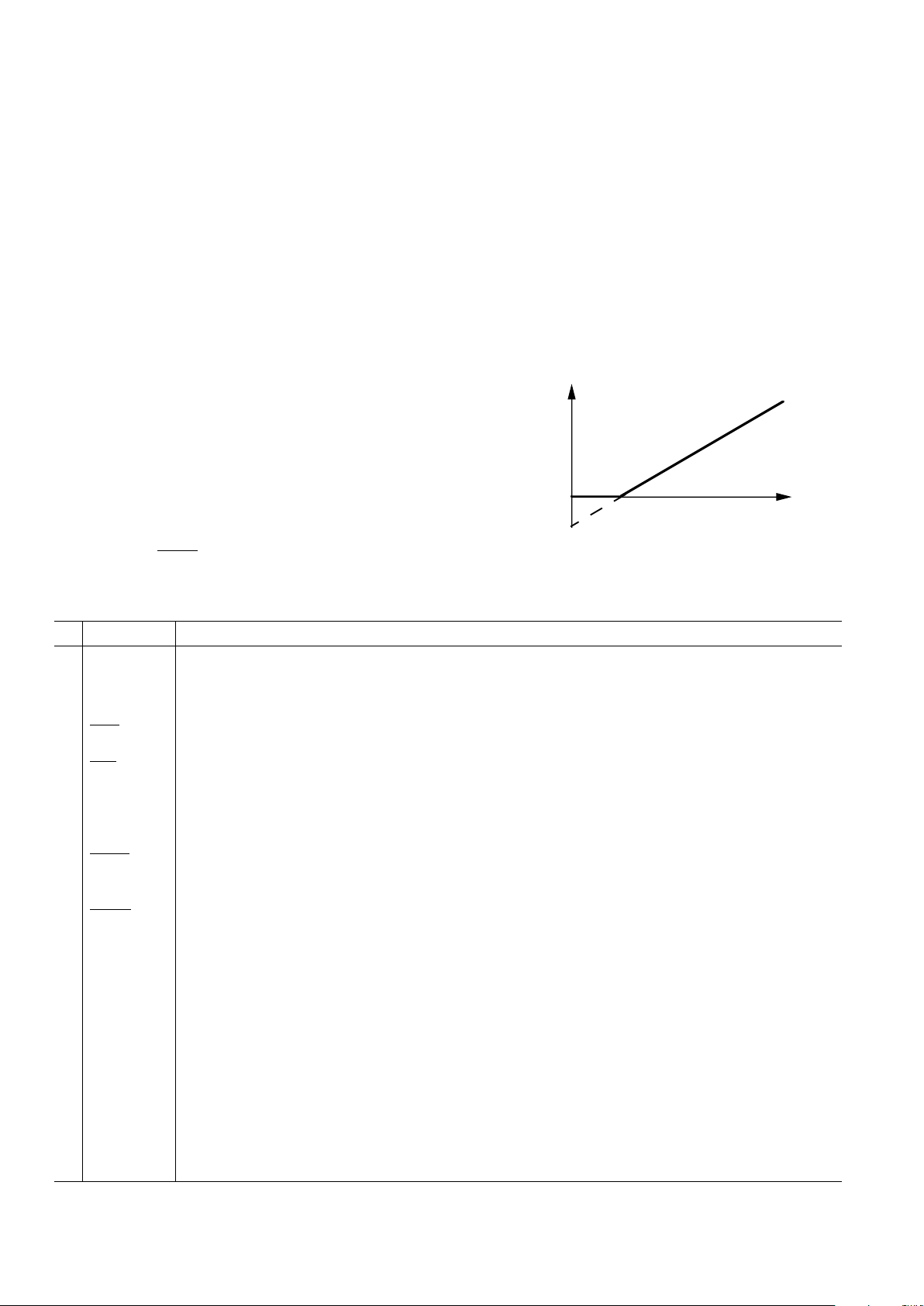
Single Supply Linearity and Gain Error
The output amplifier on the AD7243 can have true negative offsets even when the part is operated from a single +15 V supply.
However, because the negative supply rail (V
SS
) is 0 V, the output cannot actually go negative. Instead, when the output offset
voltage is negative, the output voltage sits at 0 V, resulting in the
transfer function shown in Figure 1.
OUTPUT
VOLTAGE
NEGATIVE
OFFSET
DAC CODE
0V
{
Figure 1. Effect of Negative Offset (Single Supply)
 Loading...
Loading...