A
IF Receiver
FEATURES
Performance with NSR enabled
SNR: 75.2 dBFS in a 55 MHz band to 185 MHz at 250 MSPS
SNR: 72.8 dBFS in an 82 MHz band to 185 MHz at 250 MSPS
Performance with NSR disabled
SNR: 66.4 dBFS up to 185 MHz at 250 MSPS
SFDR: 87 dBc up to 185 MHz at 250 MSPS
Total power consumption: 358 mW at 250 MSPS
1.8 V supply voltages
LVDS (ANSI-644 levels) outputs
Integer 1-to-8 input clock divider (625 MHz maximum input)
Internal ADC voltage reference
Flexible analog input range
1.4 V p-p to 2.0 V p-p (1.75 V p-p nominal)
Differential analog inputs with 350 MHz bandwidth
Serial port control
Energy saving power-down modes
User-configurable, built-in self test (BIST) capability
APPLICATIONS
Communications
Diversity radio and smart antenna (MIMO) systems
Multimode digital receivers (3G)
WCDMA, LTE, CDMA2000
WiMAX, TD-SCDMA
I/Q demodulation systems
General-purpose software radios
VIN+
VIN–
VCM
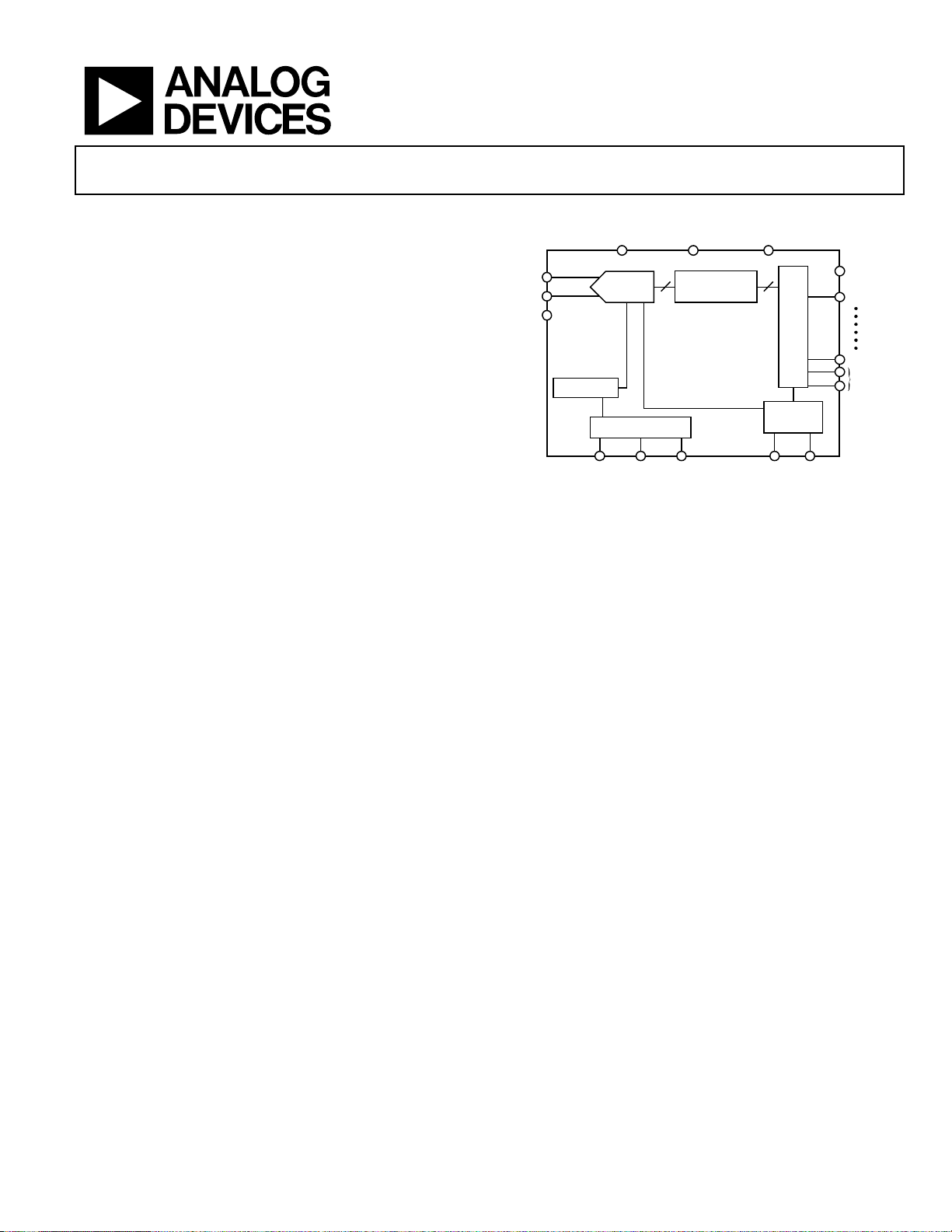
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
VDD
PIPELINE
ADC
REFERENCE
SERIAL PORT
SCLK SDIO CSB CLK+ CLK–
AGND DRVDD
NOISE SHAPING
REQUANTIZ ER
AD6672
Figure 1.
AD6672
1114
AND LVDS DRIVE RS
DATA MULITIPLEXER
1-TO-8
CLOCK
DIVIDER
DCO±
0/D0±
D9±/D10±
OR±
09997-001
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD6672 is an 11-bit intermediate receiver with sampling
speeds of up to 250 MSPS. The AD6672 is designed to support
communications applications, where low cost, small size, wide
bandwidth, and versatility are desired.
The ADC core features a multistage, differential pipelined
architecture with integrated output error correction logic. The
ADC features wide bandwidth inputs supporting a variety of
user-selectable input ranges. An integrated voltage reference
eases design considerations. A duty cycle stabilizer is provided
to compensate for variations in the ADC clock duty cycle,
allowing the converters to maintain excellent performance.
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
The ADC core output is connected internally to a noise shaping
requantizer (NSR) block. The device supports two output modes
that are selectable via the serial port interface (SPI). With the
NSR feature enabled, the outputs of the ADCs are processed such
that the AD6672 supports enhanced SNR performance within a
limited region of the Nyquist bandwidth while maintaining an
11-bit output resolution. The NSR block is programmed to provide
a bandwidth of up to 33% of the sample clock. For example, with
a sample clock rate of 250 MSPS, the AD6672 can achieve up to
73.6 dBFS SNR for an 82 MHz bandwidth at 185 MHz f
With the NSR block disabled, the ADC data is provided directly
to the output with an output resolution of 11 bits. The AD6672
can achieve up to 66.6 dBFS SNR for the entire Nyquist bandwidth
when operated in this mode.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
.
IN

AD6672
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Product Highlights ........................................................................... 3
Specifications..................................................................................... 4
ADC DC Specifications ............................................................... 4
ADC AC Specifications ............................................................... 5
Digital Specifications ................................................................... 7
Switching Specifications.............................................................. 8
Timing Specifications .................................................................. 9
Absolute Maximum Ratings.......................................................... 10
Thermal Characteristics ............................................................10
ESD Caution................................................................................ 10
Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions ......................... 11
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 12
Equivalent Circuits......................................................................... 15
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 16
ADC Architecture ......................................................................16
Analog Input Considerations.................................................... 16
Voltage Reference....................................................................... 18
Clock Input Considerations...................................................... 18
Power Dissipation and Standby Mode .................................... 19
Digital Outputs........................................................................... 20
ADC Overrange (OR)................................................................ 20
Noise Shaping Requantizer ........................................................... 21
22% BW NSR Mode (55 MHz BW at 250 MSPS)..................... 21
33% BW NSR Mode (>82 MHz BW at 250 MSPS) ............... 21
Serial Port Interface (SPI).............................................................. 23
Configuration Using the SPI..................................................... 23
Hardware Interface..................................................................... 23
SPI Accessible Features.............................................................. 24
Memory Map .................................................................................. 25
Reading the Memory Map Register Table............................... 25
Memory Map Register Table..................................................... 26
Memory Map Register Description ......................................... 28
Applications Information.............................................................. 29
Design Guidelines ...................................................................... 29
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 30
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 30
REVISION HISTORY
7/11—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 32

AD6672
When the NSR block is disabled, the ADC data is provided directly
to the output at a resolution of 11 bits. This allows the AD6672
to be used in telecommunication applications, such as a digital
predistortion observation path, where wider bandwidths are
required.
After digital signal processing, multiplexed output data is
routed into one 11-bit output port such that the maximum
data rate is 500 Mbps (DDR). This output is LVDS and
supports ANSI-644 levels.
The AD6672 receiver digitizes a wide spectrum of IF frequencies.
This IF sampling architecture greatly reduces component cost
and complexity compared with traditional analog techniques or
less integrated digital methods.
Flexible power-down options allow significant power savings.
Programming for device setup and control is accomplished
using a 3-wire, SPI-compatible serial interface with numerous
modes to support board level system testing.
The AD6672 is available in a 32-lead, RoHS-compliant LFCSP
and is specified over the industrial temperature range of −40°C
to +85°C. This product is protected by a U.S. patent.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. Integrated 11-bit, 250 MSPS ADC with a noise shaping
requantizer option.
2. Operation from a single 1.8 V supply and a separate digital
output driver supply accommodating LVDS outputs.
3. On-chip 1-to-8 integer clock divider function to support a
wide range of clocking.
4. Noise shaping requantizer function allows attaining improved
SNR within a reduced frequency band. With NSR enabled,
the AD6672 supports up to 82 MHz at 250 MSPS.
5. Standard serial port interface (SPI) that supports various
product features and functions, such as data formatting
(offset binary, twos complement, or gray coding), enabling
the clock DCS, power-down, test modes, and voltage
reference mode.
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 32
AD6672
SPECIFICATIONS
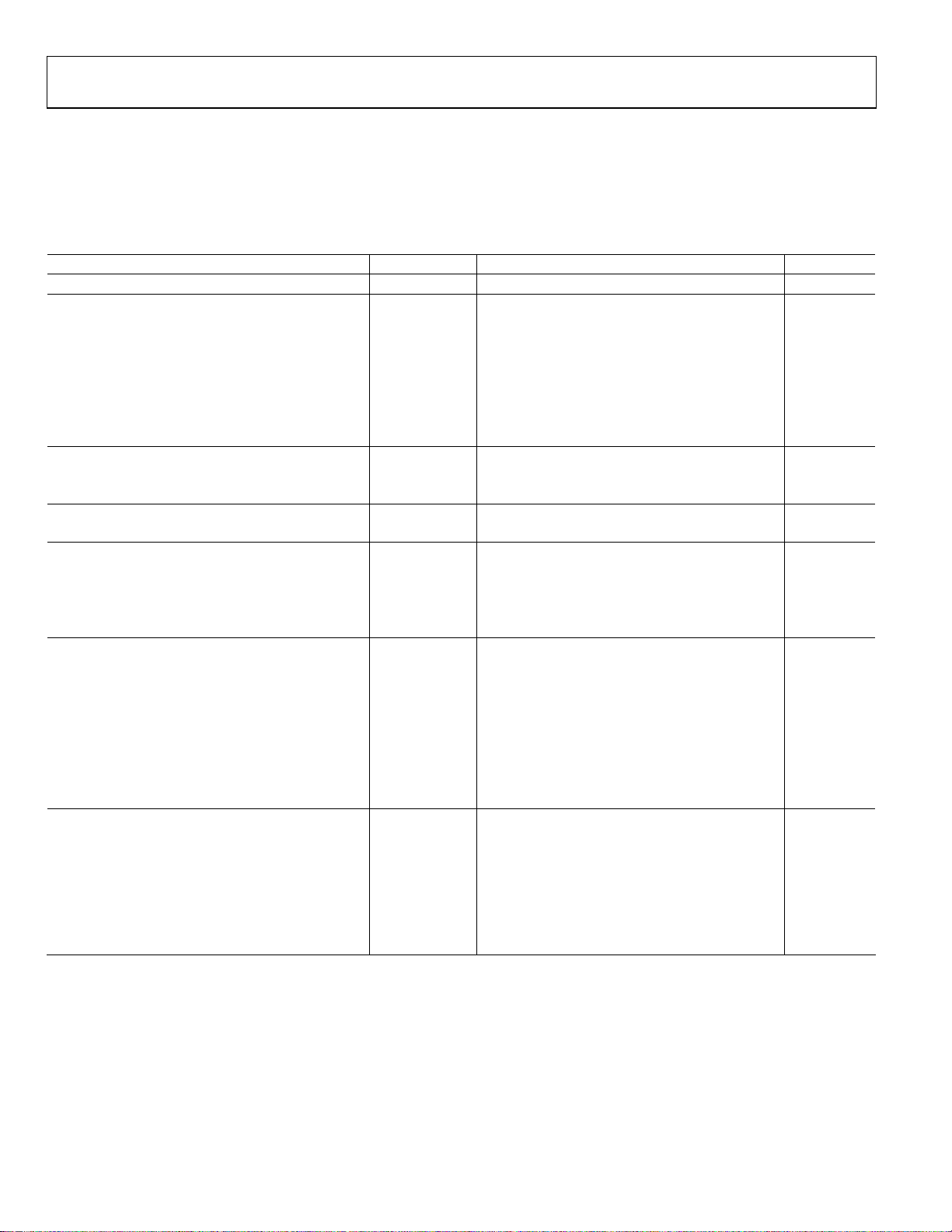
ADC DC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 1.8 V, maximum sample rate, VIN = −1.0 dBFS differential input, 1.75 V p-p full-scale input range,
DCS enabled, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Temperature Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION Full 11 Bits
ACCURACY
No Missing Codes Full Guaranteed
Offset Error Full ±11 mV
Gain Error Full +3/−6.5 % FSR
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) Full ±0.2 LSB
25°C ±0.1 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)1 Full ±0.3 LSB
25°C ±0.12 LSB
TEMPERATURE DRIFT
Offset Error Full ±7 ppm/°C
Gain Error Full ±85 ppm/°C
INPUT-REFERRED NOISE
VREF = 1.0 V 25°C 0.65 LSB rms
ANALOG INPUT
Input Span Full 1.75 V p-p
Input Capacitance2 Full 5 pF
Input Resistance Full 20 kΩ
Input Common-Mode Voltage Full 0.9 V
POWER SUPPLIES
Supply Voltage
AVDD Full 1.7 1.8 1.9 V
DRVDD Full 1.7 1.8 1.9 V
Supply Current
1
I
Full 136 145 mA
AVDD
1
I
(NSR Disabled) Full 63 68 mA
DRVDD
1
I
(NSR Enabled, 22% Bandwidth Mode) Full 89 mA
DRVDD
1
I
(NSR Enabled, 33% Bandwidth Mode) Full 99 mA
DRVDD
POWER CONSUMPTION
Sine Wave Input (DRVDD = 1.8 V, NSR Disabled) Full 358 385 mW
Sine Wave Input (DRVDD = 1.8 V, NSR Enabled,
22% Bandwidth Mode) Full 405
Sine Wave Input (DRVDD = 1.8 V, NSR Enabled,
33% Bandwidth Mode) Full 423
Standby Power3 Full 50 mW
Power-Down Power Full 5 mW
1
Measured with a low input frequency, full-scale sine wave, with approximately 5 pF loading on each output bit.
2
Input capacitance refers to the effective capacitance between one differential input pin and AGND. See for the equivalent analog input structure. Figure 18
3
Standby power is measured with a dc input, the CLK pin inactive (set to AVDD or AGND).
mW
mW
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 32
AD6672
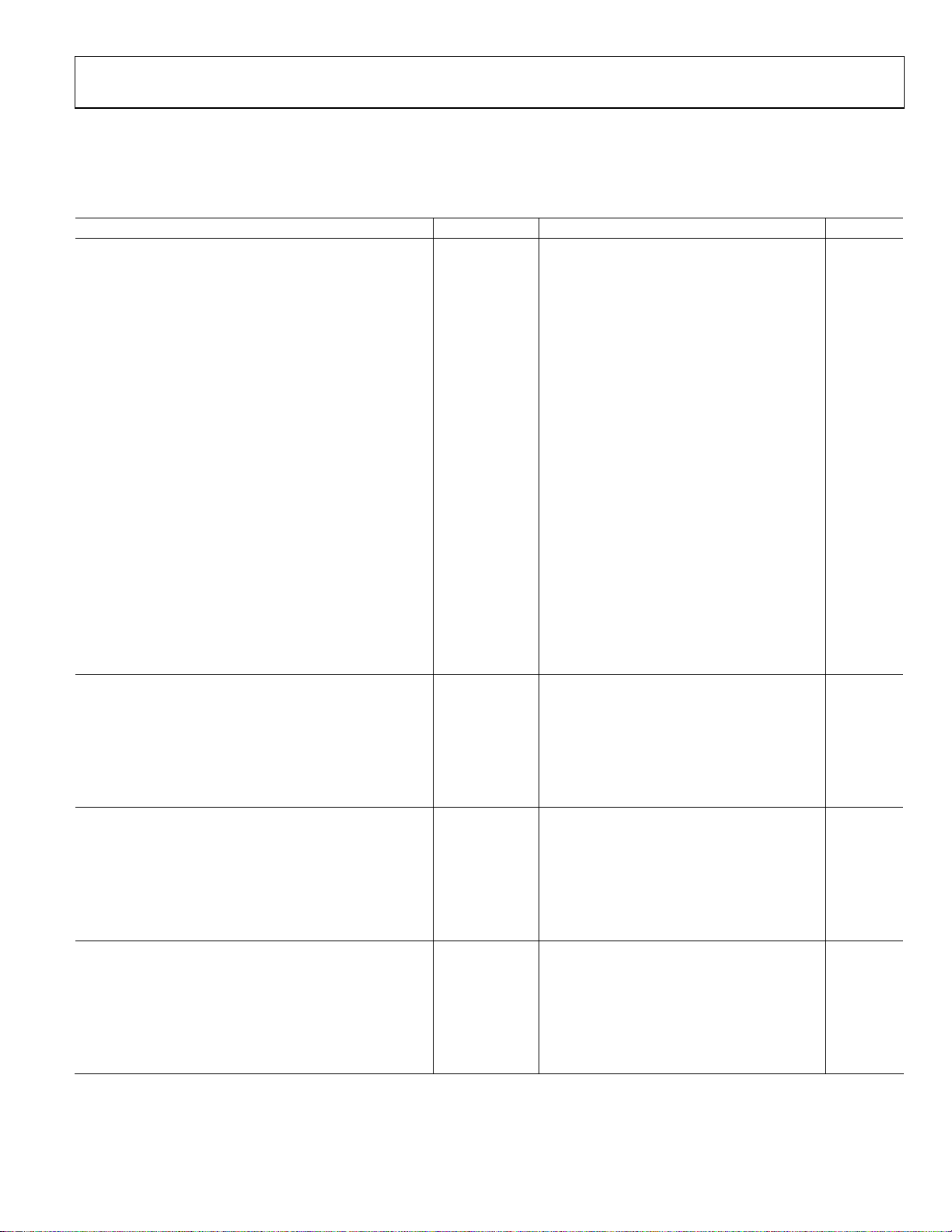
ADC AC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 1.8 V, maximum sample rate, VIN = −1.0 dBFS differential input, 1.75 V p-p full-scale input range, unless
otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter1 Temperature Min Typ Max Unit
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE-RATIO (SNR)
NSR Disabled
fIN = 30 MHz 25°C 66.6 dBFS
fIN = 90 MHz 25°C 66.6 dBFS
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C 66.5 dBFS
fIN = 185 MHz 25°C 66.4 dBFS
Full 65.4 dBFS
fIN = 220 MHz 25°C 66.3 dBFS
NSR Enabled
22% Bandwidth Mode
fIN = 30 MHz 25°C 75.8 dBFS
fIN = 90 MHz 25°C 75.7 dBFS
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C 75.6 dBFS
fIN = 185 MHz 25°C 75.2 dBFS
Full 72.2 dBFS
fIN = 220 MHz 25°C 74.8 dBFS
33% Bandwidth Mode
fIN = 30 MHz 25°C 73.4 dBFS
fIN = 90 MHz 25°C 73.3 dBFS
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C 73.2 dBFS
fIN = 185 MHz 25°C 72.8 dBFS
Full 69.2 dBFS
fIN = 220 MHz 25°C 72.4 dBFS
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO AND DISTORTION (SINAD)
fIN = 30 MHz 25°C 65.7 dBFS
fIN = 90 MHz 25°C 65.7 dBFS
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C 65.6 dBFS
fIN = 185 MHz 25°C 65.3 dBFS
Full 64.4 dBFS
fIN = 220 MHz 25°C 65.2 dBFS
WORST SECOND OR THIRD HARMONIC
fIN = 30 MHz 25°C −88 dBc
fIN = 90 MHz 25°C −88 dBc
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C −89 dBc
fIN = 185 MHz 25°C −87 dBc
Full −80 dBc
fIN = 220 MHz 25°C −88 dBc
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE (SFDR)
fIN = 30 MHz 25°C 88 dBc
fIN = 90 MHz 25°C 88 dBc
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C 89
fIN = 185 MHz 25°C 87 dBc
Full 80 dBc
fIN = 220 MHz 25°C 88 dBc
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 32
AD6672
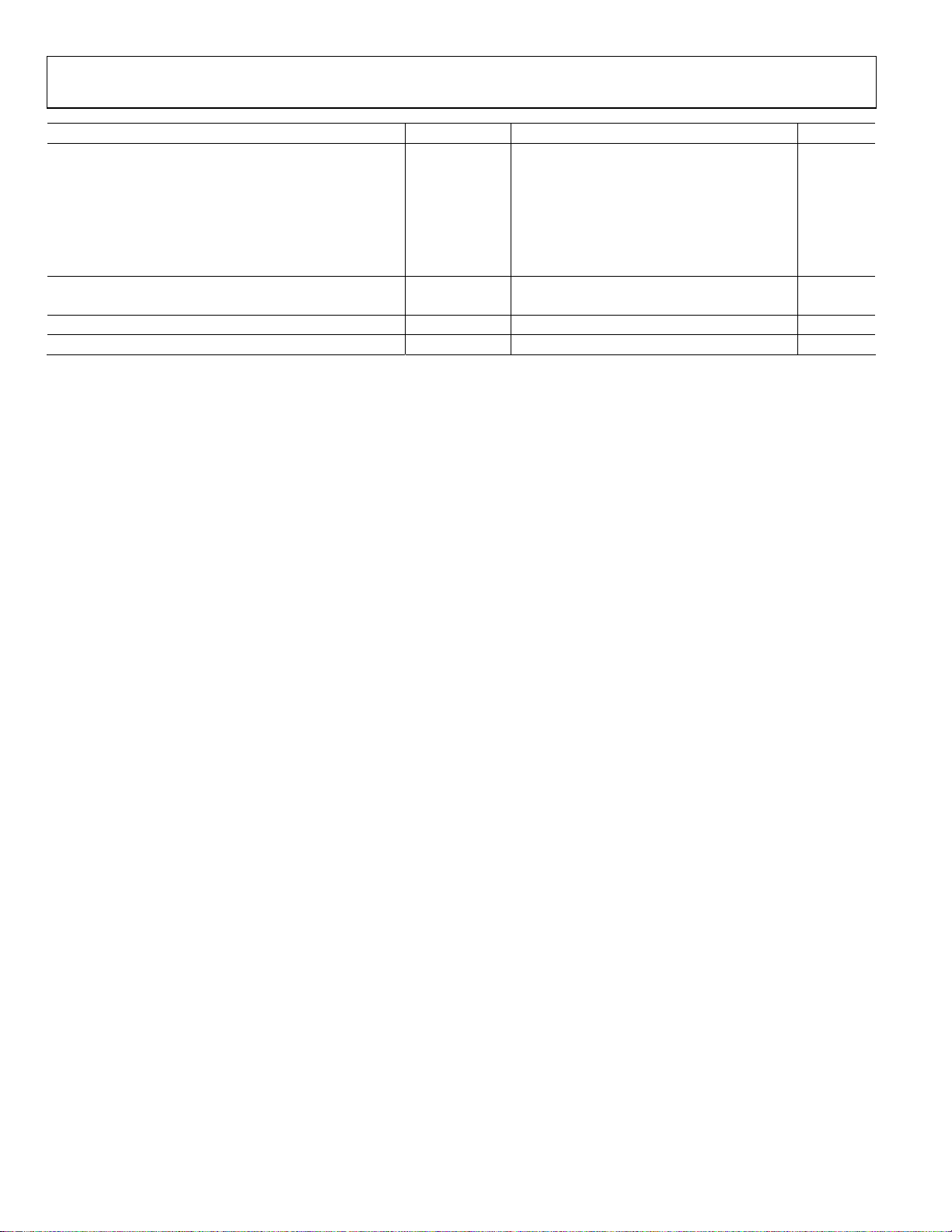
Parameter1 Temperature Min Typ Max Unit
WORST OTHER (HARMONIC OR SPUR)
fIN = 30 MHz 25°C −96 dBc
fIN = 90 MHz 25°C −97 dBc
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C −97 dBc
fIN = 185 MHz 25°C −98 dBc
Full −81 dBc
fIN = 220 MHz 25°C −97 dBc
TWO-TONE SFDR
fIN = 184.12 MHz, 187.12 MHz (−7 dBFS) 25°C 88 dBc
FULL POWER BANDWIDTH2 25°C 350 MHz
NOISE BANDWIDTH3 25°C 1000 MHz
1
See the AN-835 Application Note, Understanding High Speed ADC Testing and Evaluation, for a complete set of definitions.
2
Full power bandwidth is the bandwidth of operation where typical ADC performance can be achieved.
3
Noise bandwidth is the −3 dB bandwidth for the ADC inputs across which noise may enter the ADC and is not attenuated internally.
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 32
AD6672
DIGITAL SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 1.8 V, maximum sample rate, VIN = −1.0 dBFS differential input, 1.0 V internal reference,
DCS enabled, unless otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter Temperature Min Typ Max Unit
DIFFERENTIAL CLOCK INPUTS (CLK+, CLK−)
Logic Compliance CMOS/LVDS/LVPECL
Internal Common-Mode Bias Full 0.9 V
Differential Input Voltage Full 0.3 3.6 V p-p
Input Voltage Range Full AGND AVDD V
Input Common-Mode Range Full 0.9 1.4 V
High Level Input Current Full 10 +22 µA
Low Level Input Current Full −22 −10 µA
Input Capacitance Full
4
Input Resistance Full 12 15 18 kΩ
LOGIC INPUT (CSB)1
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.22 2.1 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.6 V
High Level Input Current Full 50 71 µA
Low Level Input Current Full −5 +5 µA
Input Resistance Full 26 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 2 pF
LOGIC INPUT (SCLK)2
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.22 2.1 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.6 V
High Level Input Current Full 45 70 µA
Low Level Input Current Full −5 +5 µA
Input Resistance Full 26 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 2 pF
LOGIC INPUTS (SDIO)1
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.22 2.1 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.6 V
High Level Input Current Full 45 70 µA
Low Level Input Current Full −5 +5 µA
Input Resistance Full 26 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 5 pF
DIGITAL OUTPUTS (OR+, OR−)
LVDS Data and OR Outputs
Differential Output Voltage (VOD), ANSI Mode Full 250 350 450 mV
Output Offset Voltage (VOS), ANSI Mode Full 1.15 1.25 1.35 V
Differential Output Voltage (VOD), Reduced Swing Mode Full 150 200 280 mV
Output Offset Voltage (VOS), Reduced Swing Mode Full 1.15 1.25 1.35 V
1
Pull-up.
2
Pull-down.
pF
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 32
AD6672
SWITCHING SPECIFICATIONS
Table 4.
Parameter Temperature Min Typ Max Unit
CLOCK INPUT PARAMETERS
Input Clock Rate Full 625 MHz
Conversion Rate1 Full 40 250 MSPS
CLK Period—Divide-by-1 Mode (t
CLK Pulse Width High (tCH)
Divide-by-1 Mode, DCS Enabled Full 1.8 2.0 2.2 ns
Divide-by-1 Mode, DCS Disabled Full 1.9 2.0 2.1 ns
Divide-by-2 Mode Through Divide-by-8 Mode Full 0.8 ns
Aperture Delay (tA) Full 1.0 ns
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter, tJ) Full 0.1 ps rms
DATA OUTPUT PARAMETERS
Data Propagation Delay (tPD) Full 4.1 4.7 5.2 ns
DCO Propagation Delay (t
DCO-to-Data Skew (t
DCO
) Full 0.3 0.5 0.7 ns
SKEW
Pipeline Delay (Latency)—NSR Disabled Full 10 Cycles
Pipeline Delay (Latency)—NSR Enabled Full 13 Cycles
Wake-Up Time (from Standby) Full 10 µs
Wake-Up Time (from Power-Down) Full 100 µs
Out-of-Range Recovery Time Full 3 Cycles
1
Conversion rate is the clock rate after the divider.
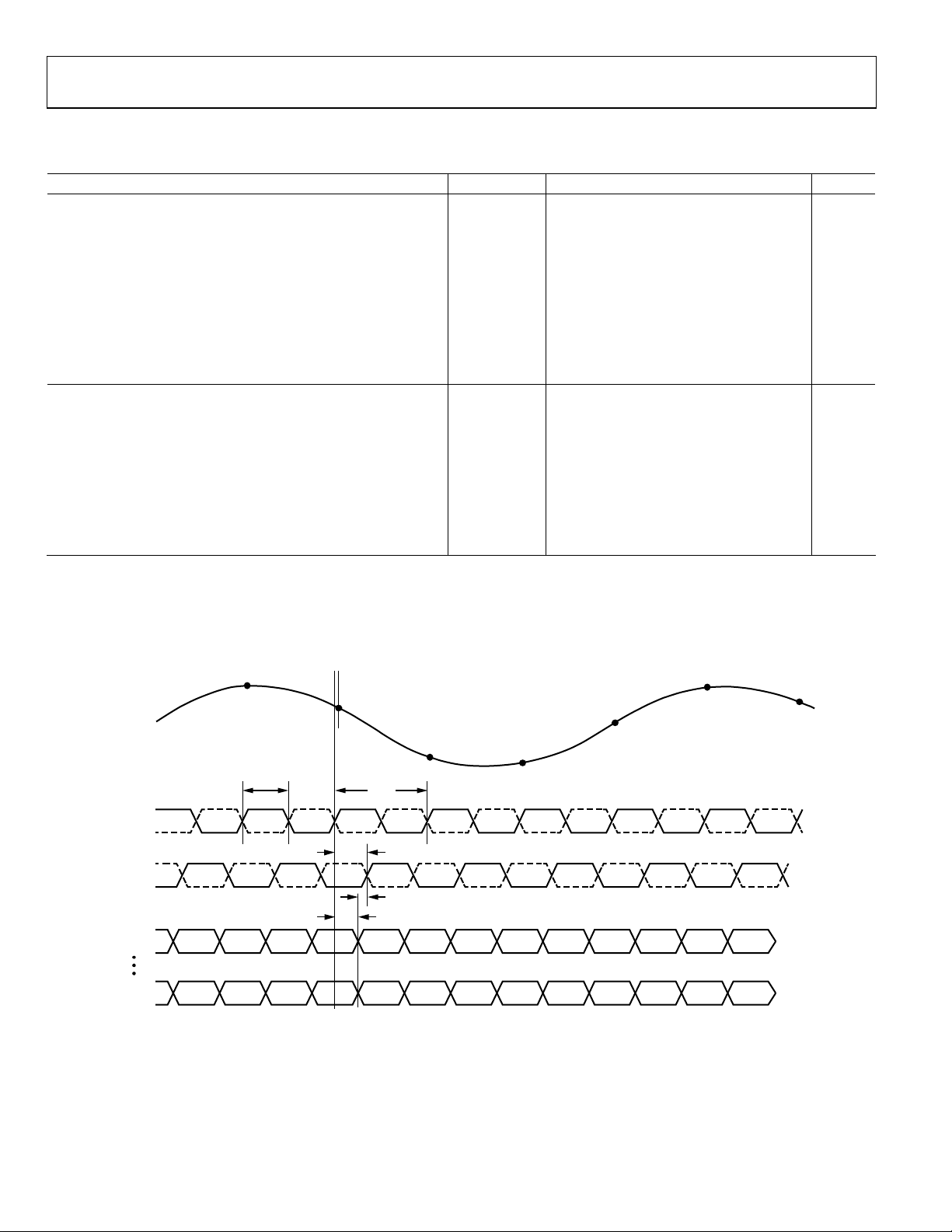
Timing Diagram
VIN
) Full 4 ns
CLK
) Full 4.7 5.3 5.8 ns
t
N – 1
A
N
N + 3
N + 4
N + 5
CLK+
CLK–
DCO–
DCO+
ODD/EVEN
0/D0±
(LSB)
D9±/D10±
(MSB)
N + 1
t
CH
t
CLK
t
DCO
t
PD
N – 10D0N – 10
D9
N – 10
t
SKEW
0
N – 9D0N – 90N – 8D0N – 80N – 7
D10
N – 10D9N – 9
0
N + 2
D10
N – 9D9N – 8
D10
N – 8D9N – 7
D0
N – 7
D10
N – 7D9N – 6
0
N – 6
09997-002
Figure 2. LVDS Data Output Timing
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 32

AD6672
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
Table 5.
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
SPI TIMING REQUIREMENTS See Figure 42 for the SPI timing diagram
tDS Setup time between the data and the rising edge of SCLK 2 ns
tDH Hold time between the data and the rising edge of SCLK 2 ns
t
Period of the SCLK 40 ns
CLK
tS Setup time between CSB and SCLK 2 ns
tH Hold time between CSB and SCLK 2 ns
t
Minimum period that SCLK should be in a logic high state 10 ns
HIGH
t
Minimum period that SCLK should be in a logic low state 10 ns
LOW
t
EN_SDIO
t
DIS_SDIO
Time required for the SDIO pin to switch from an input to an output
relative to the SCLK falling edge (not shown in Figure 42)
Time required for the SDIO pin to switch from an output to an input
relative to the SCLK rising edge (not shown in Figure 42)
10 ns
10 ns
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 32
AD6672
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 6.
Parameter Rating
Electrical
AVDD to AGND −0.3 V to +2.0 V
DRVDD to AGND −0.3 V to +2.0 V
VIN+, VIN− to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
CLK+, CLK− to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
VCM to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
CSB to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
SCLK to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
SDIO to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
0/D0−, 0/D0 + Through D9−/D10−,
−0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
D9+/D10+ to AGND
OR+/OR− to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
DCO+, DCO− to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
Environmental
Operating Temperature Range
−40°C to +85°C
(Ambient)
Maximum Junction Temperature
150°C
Under Bias
Storage Temperature Range
−65°C to +125°C
(Ambient)
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
The exposed paddle must be soldered to the ground plane for the
LFCSP package. Soldering the exposed paddle to the customer
board increases the reliability of the solder joints, maximizing
the thermal capability of the package.
Table 7. Thermal Resistance
Airflow
Package
Typ e
32-Lead LFCSP
5 mm × 5 mm
(CP-32-12)
1
Per JEDEC 51-7, plus JEDEC 25-5 2S2P test board.
2
Per JEDEC JESD51-2 (still air) or JEDEC JESD51-6 (moving air).
3
Per MIL-Std 883, Method 1012.1.
4
Per JEDEC JESD51-8 (still air).
Veloc ity
(m/sec) θ
1, 2
JA
1, 3
θ
JC
1, 4
θ
Unit
JB
0 37.1 3.1 20.7 °C/W
1.0 32.4 °C/W
2.0 29.1 °C/W
Typical θJA is specified for a 4-layer PCB with a solid ground
plane. As shown in Ta b le 7 , airflow increases heat dissipation,
which reduces θ
. In addition, metal in direct contact with the
JA
package leads from metal traces—through holes, ground, and
power planes—reduces the θ
.
JA
ESD CAUTION
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 32
 Loading...
Loading...