Allied Telesis AT-IE300-12GP Service Manual

IE300 Series
Industrial Ethernet Switches
AT-IE300-12GT
AT-IE300-12GP
Installation Guide
613-002041 Rev. B

Copyright © 2016 Allied Telesis, Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior written permission from Allied Telesis, Inc.
Allied Telesis and the Allied Telesis logo are trademarks of Allied Telesis, Incorporated. All other product names, company names,
logos or other designations mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Allied Telesis, Inc. reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior
written notice. The information provided herein is subject to change without notice. In no event shall Allied Telesis, Inc. be liable for
any incidental, special, indirect, or consequential damages whatsoever, including but not limited to lost profits, arising out of or related
to this manual or the information contained herein, even if Allied Telesis, Inc. has been advised of, known, or should have known, the
possibility of such damages.
Electrical Safety and Emissions Standards
This product meets the following standards:
U.S. Federal Communications Commission
Interference Statement
This device complies with part 15 of the FC C R ules. Operation is subject to the followi ng tw o co nd i ti on s :
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the
FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmfu l interference in a controlled
environment, such as a cabinet, hut or telecom closet. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The Federal Communications Commission warns that changes or modifications of the unit not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment and any assurances of safety
or performance, and could result in violation of part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Industry Canada
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
This equipment complies with radio frequency exposure limits set forth by Industry Canada for a controlled environment.
Cet éuipement est conforme aux limites d'exposition aux radiofréuences déinies par Industrie Canada pour un
environnement contré.
European Union Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous Substances
(RoHS) in Electrical and Electronic Equipment
This Allied Telesis RoHS-compliant product conforms to the European Union Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous
Substances (RoHS) in Electrical and Electronic Equipment. Allied Telesis ensures RoHS conformance by requiring
supplier Declarations of Conformity, monito ri n g incomin g materials, and maintaining manufacturing process controls.
The regulatory approvals of the product are listed here:
Safety
UL/IEC/EN 60950-1
UL/IEC/EN 60950-22
CAN/CSA-22.2: 60950-1
CAN/CSA-22.2: 60950-22
3

EMC
CE, FCC Part 15 Class A
EN55032 (CISPR32) Class A
EN61000-3-2
EN61000-3-3
EN55024
EN61000-4-2
EN61000-4-3
EN61000-4-4
EN61000-4-5
EN61000-4-6
EN61000-4-8
EN61000-4-11
2004/108/EC EMC Directive
2006/95/EC Low Voltage Directive
Shock
EN60068-2-27
EN60068-2-31
IE300 Series Installation Guide
Vibration
EN60068-2-6
Allied Telesis approved SFP modules
EN60825-1
EN60825-2
UL/IEC/EN60950-1
FDA CDRH accession registration
Warning: In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in
which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Laser Safety EN60825
4

IE300 Series Installation Guide
Translated Safety Statements
Important: The indicates that a translation of the safety statement is available in a PDF
document titled “Translated Safety Statements” on our web site at
http://www.alliedtelesis.com/support.
5

6

Contents
Preface ...............................................................................................................................................................................13
Safety Symbols Used in this Document...............................................................................................................................14
Contacting Allied Telesis .....................................................................................................................................................15
Chapter 1: Overview ........................................................................................................................................................ 17
Hardware Components........................................................................................................................................................18
Features ..............................................................................................................................................................................21
Twisted Pair Ports........................................................................................................................................................21
Power Over Ethernet....................................................................................................................................................21
SFP Slots .....................................................................................................................................................................21
LEDs.............................................................................................................................................................................22
Alarm Connectors.........................................................................................................................................................22
MAC Address Tables .................................................................................. ........................... ......................................22
Management Software .................................................................................................................................................22
Management Methods..................................................................................................................................................22
Installation Options.......................................................................................................................................................22
Additional Features ........................................... .................................... ... .......................... ..........................................22
10/100/1000Base-T Twisted Pair Ports...............................................................................................................................24
Connector Type.............................................. .................................... ..........................................................................24
Speed...........................................................................................................................................................................24
Duplex Mode................................................................................................................................................................24
Maximum Distance.......................................................................................................................................................24
Cable Requirements.....................................................................................................................................................24
Automatic MDIX Detection ...........................................................................................................................................25
Port Pinouts........................................... ..................................... ..................................................................................25
Power over Ethernet............................................................................................................................................................26
PoE Versions................................................................................................................................................................26
Ethernet Cabling for PoE devices ................................................................................................................................26
Powered Device Classes for PoE and PoE+................................................................................................................27
Power Delivery with Alternatives A and B....................................................................................................................28
PoE Budget..................................................................................................................................................................30
Port Prioritization..........................................................................................................................................................30
SFP Slots.............................................................................................................................................................................32
Console Port........................................................................................................................................................................33
USB Port..............................................................................................................................................................................34
Reset Button........................................................................................................................................................................34
Ground Screw......................................................................................................................................................................35
PWR 1 and PWR 2 DC Power Connectors............................................ ... ..................................... .. ... ................................35
Alarm In Connector..............................................................................................................................................................36
Alarm Out Connector...........................................................................................................................................................39
DIN Rail Bracket......................................... .. ..................................... ... ...............................................................................40
Screw Holes for Wall Brackets............................................................................................................................................40
LEDs....................................................................................................................................................................................41
Status LEDs .................................................................................................................................................................41
Twisted Pair Port LEDs................................................................................................................................................42
SFP Slot LEDs .............................................................................................................................................................44
PoE Status LEDs..........................................................................................................................................................45
Power Supplies....................................................................................................................................................................48
Optional Drip Guard.............................................................................................................................................................49
7

Contents
Chapter 2: Beginning the Installation ............................................................................................................................51
Reviewing Safety Precautions............................................................................................................................................ 52
Safety Precautions When Working with Electricity............................................................................................................. 56
Reviewing Site Requirements ............................................................................................................................................. 57
Verifying the Package Contents.......................................................................................................................................... 59
Chapter 3: Installing the Switch .....................................................................................................................................63
Installing the Switch on a DIN Rail...................................................................................................................................... 64
Installing the Switch on a Wooden Wall.............................................................................................................................. 67
Tools and Material.......................................................................................................................................................68
Installing the Plywood Base.........................................................................................................................................68
Installing the Switch on the Plywood Base .................................................................................................................. 69
Installing the Switch on a Concrete Wall............................................................................................................................. 71
Chapter 4: Cabling the Ports ..........................................................................................................................................75
Cabling the Twisted Pair Ports............................................................................................................................................ 76
Installing SFP Transceivers................................................................................................................................................ 78
Chapter 5: Powering On the Switch ...............................................................................................................................83
Connecting the Grounding Wire.......................................................................................................................................... 84
Wiring the ALM IN and ALM OUT Connectors................................................................................................................... 87
Preparing the DC Power Cables.........................................................................................................................................92
Powering On the Switch......................................................................................................................................................96
Verifying Switch Operations....................................................................................................
Monitoring the Initialization Process................................................................................................................................... 98
Starting a Local Management Session............................................................................................................................. 100
Verifying the AT-IE300-12GP Switch................................................................................................................................ 102
Verifying the PoE Budget .......................................................................................................................................... 102
Configuring Alternatives A and B...............................................................................................................................103
Configuring the Provisioned PoE Budget .................................................................................................................. 104
Installing the Optional Drip Guard.....................................................................................................................................107
..................................... 97
Chapter 6: Troubleshooting ..........................................................................................................................................109
PWR 1 and PWR 2 LEDs ..................................................................................................... ............................................ 110
Twisted Pair Ports.............................................. .. ... .......................................................... ................................................ 111
SFP Slots.......................................................................................................................................................................... 113
Power Over Ethernet........................................................................................................................................................ 114
Appendix A: Technical Specifications .........................................................................................................................117
Physical Specifications .....................................................................................................................................................118
Environmental Specifications............................................................................................................................................ 120
Power Specifications......................................................................................................................................................... 121
Certifications..................................................................................................................................................................... 122
RJ-45 Twisted Pair Port Pinouts.......................................................................................................................................123
RJ-45 Style Serial Console Port Pinouts.......................................................................................................................... 125
PWR 1 and PWR 2 DC Power Connectors ............................. ... ... ....................................... ............................................ 126
8

Figures
Figure 1: Front Panel of the AT-IE300-12GT Switch............................................................................................................18
Figure 2: Front Panel of the AT-IE300-12GP Switch............................................................................................................19
Figure 3: Top Panel..............................................................................................................................................................19
Figure 4: Back Panel Features.............................................................................................................................................20
Figure 5: Example 1 of the Alarm In (ALM IN) Connector....................................................................................................37
Figure 6: Example 2 of the Alarm In (ALM IN) Connector....................................................................................................38
Figure 7: Example of the Alarm Out Port..............................................................................................................................40
Figure 8: Twisted Pair Port LEDs on the AT-IE300-12GT Switch........................................................................................42
Figure 9: Twisted Pair Ports on the AT-IE300-12GP Switch................................................................................................43
Figure 10: Optional Drip Guard.............................................................................................................................................49
Figure 11: Pre-installed Components on the Front Panel.....................................................................................................59
Figure 12: Pre-installed Components on the Top Panel.......................................................................................................60
Figure 13: Pre-installed Component on the Back Panel.......................................................................................................61
Figure 14: Components in the Accessory Kit........................................................................................................................62
Figure 15: Orientation of the Switch on a DIN Rail...............................................................................................................64
Figure 16: Installing the Switch on a DIN Rail - 1 .................................................................................................................65
Figure 17: Installing the Switch on a DIN Rail - 2 .................................................................................................................65
Figure 18: Verifying the DIN Rail Installation........................................................................................................................66
Figure 19: Switch on the Wall with a Plywood Base.............................................................................................................67
Figure 20: Steps to Installing the Switch with a Plywood Base ............................................................................................68
Figure 21: Installing the Wall Brackets on the Switch...........................................................................................................69
Figure 22: Attaching the Switch to the Plywood Base..........................................................................................................70
Figure 23: Marking the Locations of the Bracket Holes on a Concrete Wall .................................... ...................
Figure 24: Installing the Switch on a Concrete Wall.............................................................................................................73
Figure 25: Removing the Dust Plug from an SFP Slot .........................................................................................................79
Figure 26: Installing an SFP Transceiver..............................................................................................................................79
Figure 27: Removing the Dust Cover from an SFP Transceiver ..........................................................................................80
Figure 28: Verifying the Position of the SFP Handle ............................................................................................................80
Figure 29: Connecting a Fiber Optic Cable to an SFP Transceiver......................................................................................81
Figure 30: Stripping the Grounding Wire..............................................................................................................................84
Figure 31: Loosening the Grounding Screw.........................................................................................................................85
Figure 32: Wrapping the Grounding Wire Around the Grounding Screw..............................................................................85
Figure 33: Securing the Grounding Wire to the Switch.........................................................................................................86
Figure 34: Polarity Legend for the Alarm Connectors...........................................................................................................88
Figure 35: Stripping an Alarm Wire.......................................................................................................................................88
Figure 36: Wrapping the Wire Strands.................................................................................................................................89
Figure 37: Removing an Alarm Connector ...........................................................................................................................89
Figure 38: Loosening the Wire Retaining Screws on an Alarm Connector............................................. ... ...........................89
Figure 39: Inserting the Wires into the DC Cable Connector................................................................................................90
Figure 40: Inserting the DC Connector into the Alarm Connector........................................................................................91
Figure 41: Pin Signals Legends for the PWR 1 and PWR 2 Connectors .............................................................................92
Figure 42: Stripping a Power Cable Wire.............................................................................................................................93
Figure 43: Removing the PWR 1 - PWR 2 Cable Connector ...............................................................................................93
Figure 44: Loosening the Wire Retaining Screws on the PWR 1 - PWR 2 Cable Connector...............................................94
Figure 45: Inserting the Wires into the PWR 1 - PWR 2 Cable Connector...........................................................................94
Figure 46: Verifying the Wire Installation..............................................................................................................................95
Figure 47: Connecting the Power Cable to the PWR 1 - PWR 2 Connector ........................................................................96
Figure 48: Initialization Messages........................................................................................................................................98
Figure 49: Initialization Messages (Continued).....................................................................................................................99
.................72
9

Figures
Figure 50: Installing the Optional Drip Guard......................................................................................................................107
Figure 51: Securing the Drip Guard....................................................................................................................................108
Figure 52: RJ-45 Port Pin Layout (Front View)...................................................................................................................123
Figure 53: Console Port Pin Layout (Front View) ...............................................................................................................125
10

Tables
Table 1: Twisted Pair Cable for the AT-IE300-12GT Switch ...............................................................................................25
Table 2: Maximum Power Levels .........................................................................................................................................26
Table 3: Twisted Pair Cable for Powered Devices on the AT-IE300-12GP Switch .............................................................27
Table 4: PoE and PoE+ Powered Device Classes ..............................................................................................................27
Table 5: Maximum Installation Site Temperatures Versus SFP Temperature Ratings .......................................................32
Table 6: Status LEDs ...........................................................................................................................................................41
Table 7: Twisted Pair Port LEDs on the AT-IE300-12GT Switch .........................................................................................43
Table 8: Twisted Pair Port LEDs on the AT-IE300-12GP Switch ........................................................................................44
Table 9: SFP Slot LED ........................................................................................................................................................44
Table 10: PoE Status LEDs .................................................................................................................................................45
Table 11: Ground Resistivity Recommendations .................................................................................................................58
Table 12: Product Dimensions ...........................................................................................................................................118
Table 13: Product Weights ................................................................................................................................................118
Table 14: Ventilation Requirements for Cabinet Installation ..............................................................................................118
Table 15: Minimum Cabinet Dimensions ...........................................................................................................................119
Table 16: Environmental Specifications .............................................................................................................................120
Table 17: Ingress Protection ..............................................................................................................................................120
Table 18: Maximum Power Consumptions ........................................................................................................................121
Table 19: Input Power Specifications ................................................................................................................................121
Table 20: Heat Dissipation (British Thermal Units/Hour) ...................................................................................................121
Table 21: Regulatory Approvals ........................................................................................................................................122
Table 22: Pin Signals for 10 and 100 Mbps .......................................................................................................................123
Table 23: Pin Signals for 1000 Mbps .................................................................................................................................123
Table 24: RJ-45 Style Console Port Pin Signals ...............................................................................................................125
Table 25: PWR 1 and PWR 2 DC Connector Pin Signals on the AT-IE300-12GT Switch ................................................126
Table 26: PWR 1 and PWR 2 DC Connector Pin Signals on the AT-IE300-12GP Switch ........................................... .. ...126
11

Tables
12

Preface
This guide contains the hardware installation instructions for the IE300
Series of industrial managed switches. The preface contains the following
sections:
“Safety Symbols Used in this Document” on page 14
“Contacting Allied Telesis” on page 15
13

Preface
Note
Caution
Warning
Warning
Warning
Safety Symbols Used in this Document
This document uses the following conventions.
Notes provide additional information.
Cautions inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in equipment damage or loss of data.
Warnings inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in bodily injury.
Laser warnings inform you that an eye or skin hazard exists due to
the presence of a Class 1 laser device.
Warnings inform you of hot surfaces.
14

Contacting Allied Telesis
If you need assistance with this product, you may contact Allied Telesis
technical support by going to the Support & Services section of the Allied
Telesis web site at www.alliedtelesis.com/support. You can find links for
the following services on this page:
24/7 Online Support — Enter our interactive support center to
search for answers to your product questions in our knowledge
database, to check support tickets, to learn about RMAs, and to
contact Allied Telesis technical experts.
USA and EMEA phone support — Select the phone number that
best fits your location and customer type.
Hardware warranty information — Learn about Allied Telesis
warranties and register your product online.
Replacement Services — Submit a Return Merchandise
Authorization (RMA) request via our interactive support center.
IE300 Series Installation Guide
Documentation — View the most recent installation and user
guides, software release notes, white papers, and data sheets for
your products.
Software Downloads — Download the latest software releases for
your managed products.
For sales or corporate information, go to www.alliedtelesis.com/
purchase and select your region.
15

Preface
16

Chapter 1
Overview
This chapter describes the hardware features of the IE300 Series of
managed industrial switches. The sections in the chapter are listed here:
“Hardware Components” on page 18
“Features” on page 21
“10/100/1000Base-T Twisted Pair Ports” on page 24
“Power over Ethernet” on page 26
“SFP Slots” on page 32
“Console Port” on page 33
“USB Port” on page 34
“Reset Button” on page 34
“Ground Screw” on page 35
“PWR 1 and PWR 2 DC Power Connectors” on page 35
“Alarm In Connector” on page 36
“Alarm Out Connector” on page 39
“DIN Rail Bracket” on page 40
“Screw Holes for Wall Brackets” on page 40
“LEDs” on page 41
“Power Supplies” on page 48
“Optional Drip Guard” on page 49
17
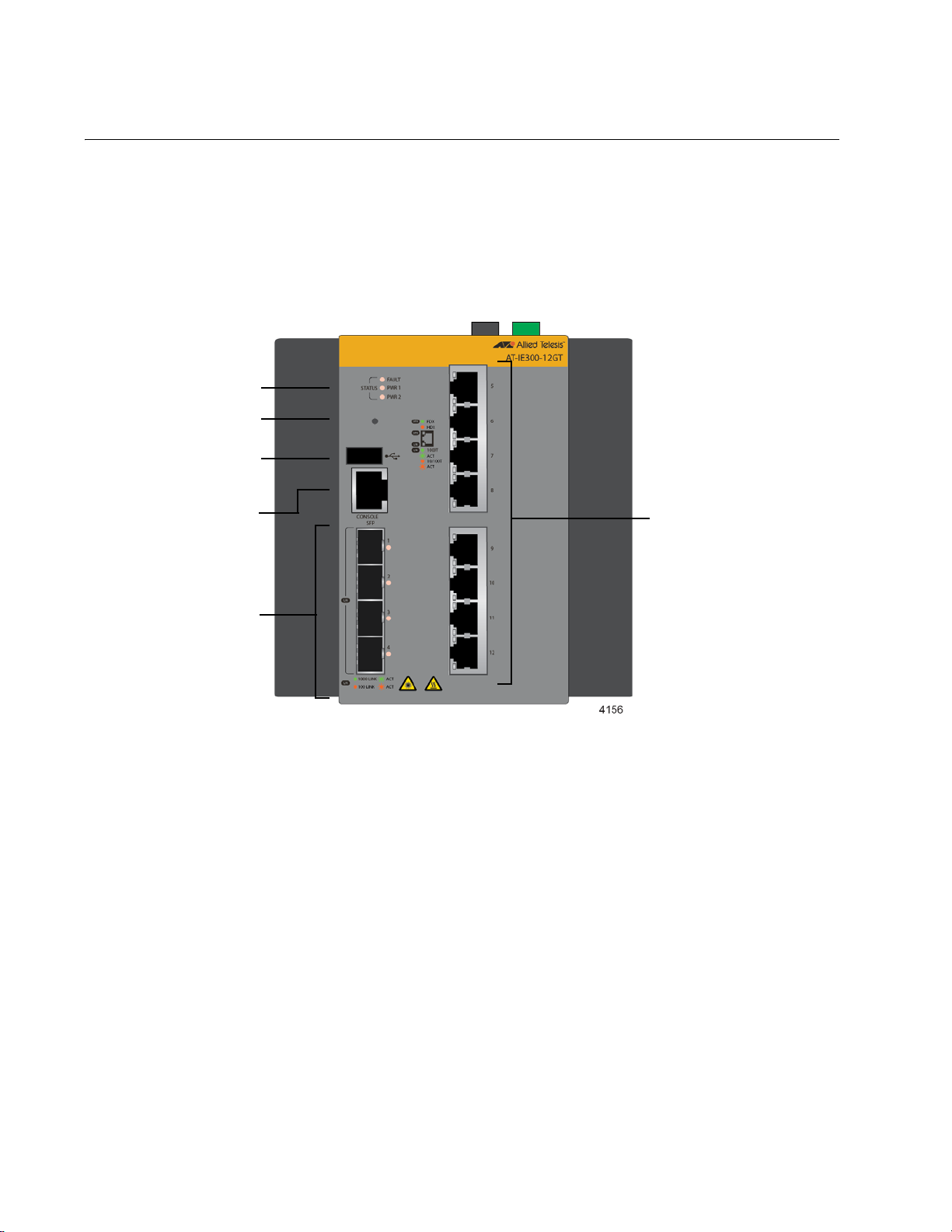
Chapter 1: Overview
10/100/1000Base-T
twisted pair ports
Slots for
100/1000Base-FX
SFP transceivers
Console
management
port
USB port
Status LEDs
Reset button
Hardware Components
The switches in the IE300 Series are listed here:
AT-IE300-12GT
AT-IE300-12GP
The front panel of the AT-IE300-12GT Switch is shown in Figure 1.
18
Figure 1. Front Panel of the AT-IE300-12GT Switch
The front panel of the AT-IE300-12GP Switch is shown in Figure 2 on
page 19.

IE300 Series Installation Guide
10/100/1000Base-T
twisted pair ports
with PoE and PoE+
Slots for
100/1000Base-FX
SFP transceivers
Console
management
port
10/100/1000Base-T
twisted pair ports
with PoE, PoE+, and
Hi-PoE
PoE status LEDs
USB port
Status LEDs
Reset button
PWR 2 DC
power connector
PWR 1 DC
power connector
Alarm In
connector
Alarm Out
connector
Grounding screw
Figure 2. Front Panel of the AT-IE300-12GP Switch
Figure 3 identifies the components on the top panel.
Figure 3. Top Panel
19

Chapter 1: Overview
Screw holes for
wall bracket
DIN rail
bracket
Screw holes for
wall bracket
Figure 4 on page 20 identifies the components on the back panel.
Figure 4. Back Panel Features
20

Features
IE300 Series Installation Guide
Here are the basic features of the switches.
Twisted Pair
Ports
Power Over
Ethernet
Here are the basic features of the 10/100/1000 Mbps twisted pair ports:
8 ports per switch
10Base-T, 100Base-TX, and 1000Base-T compliant
IEEE 802.3u Auto-Negotiation compliant
Auto-MDI/MDIX
100 meters (328 feet) maximum operating distance
IEEE 802.3x flow control in 10/100Base-TX full-duplex mode
IEEE 802.3x backpressure in 10/100Base-TX half-duplex mode
IEEE 802.3ab 1000Base-T
Jumbo frames up to 9KB
RJ-45 connectors
Ports 5 to 12 on the AT-IE300-12GP Switch have these Power over
Ethernet features:
Ports 5 to 8 support PoE (15 watts) and PoE+ (30 watts)
Ports 9 to 12 support PoE, PoE+, and Hi-PoE (60 watts)
Powered device classes 0 to 4
Maximum PoE budget of 240 watts with one or two power supplies
Port prioritization
Alternative A wiring for PoE or PoE+ devices
Combined Alternatives A and B wiring for Hi-PoE devices
SFP Slots The four SFP slots support the following types of transceivers:
100Base-FX transceivers
1000Base-SX/LX transceivers
Single-port Bi-directional (BiDi) 1000Base-LX transceivers
1000Base-ZX transceivers
1000Base-T twisted pair transceivers
SFP transceivers must be purchased separately. Refer to the product
datasheet for a list of supported transceivers.
21

Chapter 1: Overview
LEDs The switches have the following LEDs:
Link/activity and duplex mode LEDs for the twisted pair ports on
the AT-IE300-12GT Switch.
Link/activity and PoE status LEDs for the twisted pair ports on the
AT-IE300-12GP Switch.
Link/activity LEDs for the SFP ports.
Fault and power supply status LEDs
PoE LEDs on the AT-IE300-12GP Switch
Alarm
Connectors
MAC Address
Tables
Management
Software
Management
Methods
The switches have two alarm connectors:
Alarm In connector for an external sensor, such as a motion
detector or door relay, to monitor the wiring closet or cabinet.
Alarm Out connector for an external alert device, such as a buzzer
or LED, to indicate switch alarms.
Here are the basic features of the MAC address tables:
Storage capacity of 16,000 MAC address entries
Automatic learning and aging
The switches support the following management software and interfaces:
AlliedWare Plus management software, version 5.4.6 or later
Command line interface
Web browser interface
You can manage the switches in the following ways:
Local management through the Console port
22
Installation
Options
Additional
Features
Remote Telnet or secure shell management
Remote HTTP or HTTPS web browser management
SNMPv1, v2c, or v3
The switches support the following installation options:
DIN rail installation (compatible with DIN 35x7.5mm rail)
Concrete or wood wall
Here are additional features:
Slot for USB flash memory
Reset button

Two DC power supply connectors
Extended environmental range
IP30-compliant without optional drip guard
IP31-compliant with optional drip guard
RJ-45 style Console port for local management
IE300 Series Installation Guide
23

Chapter 1: Overview
Note
Note
10/100/1000Base-T Twisted Pair Ports
This section describes the twisted pair ports.
Connector Type The twisted-pair ports have 8-pin RJ-45 connectors. The ports use four
pins at 10 or 100 Mbps and all eight pins at 1000 Mbps. The pin
assignments are listed in Table 22 on page 123 and Table 23 on
page 123.
Speed The ports can operate at 10, 100, or 1000 Mbps. The switch can set the
speeds automatically with Auto-Negotiation, the default setting, or you can
manually set the speeds with the AlliedWare Plus operating system.
Twisted-pair ports must be set to Auto-Negotiation to operate at
1000 Mbps. You cannot manually set twisted-pair ports to 1000
Mbps.
Duplex Mode The twisted-pair ports can operate in either half- or full-duplex mo de a t 10
or 100 Mbps. Ports operating at 1000 Mbps can only operate in full-dup lex
mode. The twisted-pair ports are IEEE 802.3u Auto-Negotiation compliant.
The switch can set the duplex modes automatically or you can disable
Auto-Negotiation and set the duplex modes manually.
Speed and duplex mode settings can be set independently of each other
on the ports. For example, the speed of a port can be configured manually
while its duplex mode is established through Auto-Negotiation.
Switch ports connected to 10 or 100 Mbps end nodes that do not
support Auto-Negotiation should not use Auto-Negotiation to set
their speed and duplex mode settings, because duplex mode
mismatches might occur. You should disable Auto-Negotiation and
set the speed and duplex mode settings manually with the
AlliedWare Plus operating system.
Maximum
The ports have a maximum operating distance of 100 meters (328 feet).
Distance
Requirements
24
Cable
The cable requirements for the ports on the AT-IE300-12GT Switch are
listed in Table 1.

IE300 Series Installation Guide
Table 1. Twisted Pair Cable for the AT-IE300-12GT Switch
Cable Type 10Mbps 100Mbps 1000Mbps
Automatic MDIX
Detection
Standard TIA/EIA 568-Bcompliant Category 3 shielded
or unshielded cabling with 100
ohm impedance and a
frequency of 16 MHz.
Standard TIA/EIA 568-Acompliant Category 5 or TIA/
EIA 568-B-compliant Enhanced
Category 5 (Cat 5e) shielded or
unshielded cabling with 100
ohm impedance and a
frequency of 100 MHz.
Standard TIA/EIA 568-Bcompliant Category 6 or 6a
shielded cabling.
The 10/100/1000 Mbps twisted-pair ports are IEEE 802.3ab compliant,
with automatic MDIX detection at 10 or 100 Mbps. (Automatic MDIX
detection does not apply to 1000 Mbps.) This feature automatically
configures the ports to MDI or MDI-X depending on the wiring
configurations of the end nodes.
Yes Yes No
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Switch ports connected to network devices that do not support automatic
MDIX detection default to MDIX.
You may disable automatic MDIX detection on the individual ports and
configure the MDI/MDI-X settings manually.
Port Pinouts Refer to Table 22 on page 123 for the pinouts of the twisted-pair ports at
10 or 100 Mbps and to Table 23 on page 123 for the port pinouts at 1000
Mbps.
25

Chapter 1: Overview
Power over Ethernet
Ports 5 to 12 on the AT-IE300-12GP Switch support Power over Ethernet
(PoE). With PoE, the switch can supply electrical power to network
devices over the same twisted pair cables that carry network traffic. The
feature can simplify network installation and maintenance because it
allows you to use the switch as a central power source for other network
devices.
Devices that receive their power over Ethernet cables are called powered
devices (PD). Examples of PDs include wireless access points, IP
telephones, web cams, and even other Ethernet switches. A PD
connected to a port on the switch receives both network traffic and power
over the same twisted-pair cable.
PoE Versions The AT-IE300-12GP Switch supports the following versions of Power over
Ethernet:
PoE (IEEE 802.3af)
Ethernet Cabling
for PoE devices
PoE+ (802.3at)
Hi-PoE (802.3bt)
Table 2 lists the switch ports that support PoE and the maximum power
levels.
Table 2. Maximum Power Levels
Maximum
PoE Version Switch Ports
PoE 5 to 12 15.4W 12.95W
PoE+ 5 to 12 30.0W 25.9W
Hi-PoE 9 to 12 60.0W 51.8W
The cable requirements for the twisted pair ports on the AT-IE300-12GP
Switch for powered devices are given in Table 3 on page 27. For cable
requirements for ports connected to non-PoE devices, refer to Table 1 on
page 25.
Power Output
at Switch Port
Maximum
Power at PD
26

IE300 Series Installation Guide
Table 3. Twisted Pair Cable for Powered Devices on the AT-IE300-12GP
Switch
10Mbps 100Mbps 1000Mbps
Cable Type
Standard TIA/EIA 568B-compliant Category 3
shielded or unshielded
cabling with 100 ohm
impedance and a
frequency of 16 MHz.
Standard TIA/EIA 568A-compliant Category 5
shielded or unshielded
cabling with 100 ohm
impedance and a
frequency of 100 MHz.
Standard TIA/EIA 568B-compliant Enhanced
Category 5 (Cat 5e)
shielded or unshielded
cabling with 100 ohm
impedance and a
frequency of 100 MHz.
PoE+
PoE
No No No No No No
Yes No Yes No No No
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
or Hi-
PoE
PoE
PoE+
or Hi-
PoE
PoE
PoE+
or Hi-
PoE
Powered Device
Classes for PoE
and PoE+
Standard TIA/EIA 568B-compliant Category 6
or 6a shielded cabling.
The PoE and PoE+ standards define five powered device classes. The
classes are defined by the power requirements of the powered devices.
The classes are shown in Table 4 on page 27. The AT-IE300-12GP
Switch supports all five classes.
Table 4. PoE and PoE+ Powered Device Classes
Class Usage
0 Default 15.4W .044W to
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Maximum
Power Output
at the Switch
Port
PD Power
Range
12.95W
27

Chapter 1: Overview
Table 4. PoE and PoE+ Powered Device Classes (Continued)
Maximum
Class Usage
1 Optional 4.0W 0.44W to 3.84W
2 Optional 7.0W 3.84W to 6.49W
3 Optional 15.4W 6.49W to
4 Optional 30.0W 12.95W to
Power Output
at the Switch
Port
PD Power
Range
12.95W
25.9W
Power Delivery
with Alternatives
A and B
The PoE standards define two methods for delivering power over twisted
pair cables from power sources such as the Ethernet switch to powered
devices. The methods, called Alternatives A and B, identify the wire
strands that carry the electrical power over the Ethernet cables to the
powered devices from the power source, which in this case is the IE300
Series switch.
Twisted pair cabling usually has eight strands. For 10Base-T and
100Base-TX devices, the wire strands connected to pins 1, 2, 3, and 6
carry the network traffic while the strands connected to pins 4, 5, 7, and 8
are unused. 1000Base-T devices use all eight strands to carry network
traffic.
For PoE and PoE+ devices, power is delivered over four of the eight
strands. In Alternative A, power is delivered on strands 1, 2, 3, and 6,
which are the same strands that carry the 10/100Base-TX network traffic.
In Alternative B, power is delivered on strands 4, 5, 7, and 8. These are
the unused strands.
For Hi-PoE devices, power is delivered on all eight strands in Ethernet
cabling.
The AT-IE300-12GP Switch supports PoE and PoE+ powered devices
that comply with the IEEE 802.3af and 802.3at standards. The standards
require that powered devices support both Alternatives A and B. However,
legacy PDs that are non-standard or were manufactured before the
completion of the standards might support only one method.
28
The AT-IE300-12GP Switch supports Alternatives A and B on the twisted
pair ports as follows:
Port 5 to 8 - Alternative A only
Ports 9 to 12 - Alternative A, Alternative B, or both

IE300 Series Installation Guide
Note
Here are the default settings for Alternatives A and B on the switch:
For ports 5 to 8 the default setting for Alternative A is enabled.
For ports 9 to 12 the default settings are enabled for Alternative A
and disabled for Alternative B.
Here are guidelines to enabling or disabling Alternatives A and B on the
switch ports for different types of powered devices:
PoE or PoE+ devices that comply with the IEEE 802.3af and
802.3at standards and support both Alternatives A and B can be
connected to any of the twisted pair ports. Since Alternative A is
enabled by default on all the twisted pair ports, no extra steps are
required to support these devices.
PoE or PoE+ devices that do not comply with the standards and
only support Alternative A can also be connected to any of the
twisted pair ports. Again, no extra steps are required to support
these devices because Alternative A is enabled by default on all
the twisted pair ports.
PoE or PoE+ devices that do not comply with the standards and
only support Alternative B must be connected to ports 9 to 12. You
must disable Alternative A and enable Alternative B on ports
connected to these devices. The command in the AlliedWare Plus
operating system for disabling Alternative A is shown here:
NO POWER-INLINE PAIR DATA ENABLE
The command for enabling Alternative B is shown here:
POWER-INLINE PAIR SPARE ENABLE
The commands are located in the Port Interface mode.
Hi-PoE devices must be connected to ports 9 to 12. Ports
connected to Hi-PoE devices must use both Alternatives A and B
because Hi-PoE devices require power on all eight strands in
Ethernet cabling. The switch only supports Hi-PoE devices that
also support both Alternatives A and B, and that receive power on
all eight strands. Since Alternative A is enabled by default, you do
not have to enable it on ports connected to Hi-PoE devices.
However, you do have to enable Alternative B, using the above
POWER-INLINE command.
To be compatible with Hi-PoE on the switch, 10-Base-T and
100Base-T devices must have transformers with center taps on pair
4 and 5 and pair 7 and 8 to extract power from center taps. Devices
without the transformers and center taps will not work with the
switch.
29

Chapter 1: Overview
PoE Budget The AT-IE300-12GP Switch has a PoE budget. This is the total wattage
Non-PoE devices can be connected to any of the twisted pair ports
on the switch. Ports connected to network nodes that are not PDs
(that is, devices that receive power from another power source)
function as regular Ethernet ports, without PoE. The PoE feature
remains enabled on the ports but no power is delivered to the
devices.
the switch has available for the powered devices on its ports. The
maximum possible budget is 240W. The PoE budget can never be more
than that, but it can be less, depending on the DC power supply.
The number of powered devices the switch can support at one time will
depend on the switch’s PoE budget and the wattage requirements of the
powered devices. As long as the total wattage requirements of the
powered devices is less than the budget of the switch, the switch can
supply power to all the devices. If the total wattage requirements exceed
the PoE budget, the switch will deny power to one or more devices using a
mechanism referred to as port prioritization.
Port
Prioritization
To determine whether the wattage requirements of the PoE devices you
plan to connect to the switch exceed its budget, refer to their
documentation for their power requirements and add the requirements
together. The switch should be able to power all the devices
simultaneously as long as the total is below its PoE budget. If the total
exceeds the available power budget, you should consider reducing the
number of PoE devices so that all the devices receive power. Otherwise,
the switch powers a subset of the devices, based on port prioritization.
The switch can handle different power requirements on different ports.
This enables you to connect different classes of PoE equipment to the
ports on the switch.
If the power requirements of the powered devices exceed the switch’s
power budget, the switch denies power to some ports based on a system
called port prioritization. You may use this mechanism to ensure that
powered devices critical to the operations of your network are given
preferential treatment by the switch in the distribution of power should the
demands of the devices exceed the available capacity.
There are three priority levels:
Critical
30
High
Low
Ports set to the Critical level, the highest priority level, are guaranteed
power before any of the ports assigned to the other two priority levels.
Ports assigned to the other priority levels receive power only if all the
 Loading...
Loading...