Page 1
OfficeConnect®
ADSL Wireless 108Mbps 11g Firewall Router
User Guide
Model WL-553
3CRWDR200A-75
3CRWDR200B-75
http://www.3com.com/
Part No. 10015251 Rev. AB
Published August 2008
Page 2

3Com Corporation
350 Campus Drive
Marlborough, MA
USA 01752-3064
Copyright © 2008, 3Com Corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced
in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or
adaptation) without written permission from 3Com Corporation.
3Com Corporation reserves the right to revise this documentation and to make changes in content from time
to time without obligation on the part of 3Com Corporation to provide notification of such revision or change.
3Com Corporation provides this documentation without warranty, term, or condition of any kind, either
implied or expressed, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties, terms or conditions of
merchantability, satis34factory quality, and fitness for a particular purpose. 3Com may make improvements or
changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this documentation at any time.
If there is any software on removable media described in this documentation, it is furnished under a license
agreement included with the product as a separate document, in the hard copy documentation, or on the
removable media in a directory file named LICENSE.TXT or !LICENSE.TXT. If you are unable to locate a copy,
please contact 3Com and a copy will be provided to you.
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT LEGEND
If you are a United States government agency, then this documentation and the software described herein are
provided to you subject to the following:
All technical data and computer software are commercial in nature and developed solely at private expense.
Software is delivered as “Commercial Computer Software” as defined in DFARS 252.227-7014 (June 1995) or
as a “commercial item” as defined in FAR 2.101(a) and as such is provided with only such rights as are
provided in 3Com’s standard commercial license for the Software. Technical data is provided with limited rights
only as provided in DFAR 252.227-7015 (Nov 1995) or FAR 52.227-14 (June 1987), whichever is applicable.
You agree not to remove or deface any portion of any legend provided on any licensed program or
documentation contained in, or delivered to you in conjunction with, this User Guide.
Unless otherwise indicated, 3Com registered trademarks are registered in the United States and may or may
not be registered in other countries.
3Com, OfficeConnect and the 3Com logo are registered trademarks of 3Com Corporation.
Intel and Pentium are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows
NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Novell and NetWare are registered trademarks of
Novell, Inc. UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively
through X/Open Company, Ltd.
Netscape Navigator is a registered trademark of Netscape Communications.
JavaScript is a trademark of Sun Microsystems
Wi-Fi and the Wi-Fi logo are registered trademarks of the WI-Fi Alliance.
IEEE and 802 are trademarks of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are
associated.
ENVIRONMENTAL STATEMENT
It is the policy of 3Com Corporation to be environmentally-friendly in all operations. To uphold our policy, we
are committed to:
Establishing environmental performance standards that comply with national legislation and regulations.
Conserving energy, materials and natural resources in all operations.
Reducing the waste generated by all operations. Ensuring that all waste conforms to recognized environmental
standards. Maximizing the recyclable and reusable content of all products.
Ensuring that all products can be recycled, reused and disposed of safely.
Ensuring that all products are labelled according to recognized environmental standards.
Improving our environmental record on a continual basis.
End of Life Statement
3Com processes allow for the recovery, reclamation and safe disposal of all end-of-life electronic components.
Regulated Materials Statement
3Com products do not contain any hazardous or ozone-depleting material.
Environmental Statement about the Documentation
The documentation for this product is printed on paper that comes from sustainable, managed forests; it is
fully biodegradable and recyclable, and is completely chlorine-free. The varnish is environmentally-friendly, and
the inks are vegetable-based with a low heavy-metal content.
Page 3

CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Naming Convention 9
Conventions 9
Related Documentation 10
1 INTRODUCING THE ROUTER
OfficeConnect ADSL Wireless 108Mbps 11g Firewall Router 11
Firewall Router Advantages 13
Package Contents 13
Minimum System and Component Requirements 14
Front Panel 14
Rear Panel 16
2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
Introduction 19
Safety Information 19
Positioning the Router 19
Using the Rubber Feet 20
Stacking the Router 20
Wall Mounting 20
Before you Install your Router 21
Powering Up the Router 22
Connecting the Router 22
3 SETTING UP YOUR COMPUTERS
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically 25
Windows 2000 25
Windows Vista 27
Windows XP 27
Page 4

Windows 95/98/ME 27
Macintosh 28
Disabling PPPoE and PPTP Client Software 28
Disabling Web Proxy 29
4 RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
Accessing the Wizard 31
Welcome 33
Password 34
Time Zone 35
WAN Settings 36
LAN Settings 41
DHCP 41
Wireless Settings 42
Summary 44
5 ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Navigating Through the Router Configuration Pages 45
Main Menu 45
Option Tabs 46
Welcome Screen 46
Notice Board 46
Password 47
Wizard 48
LAN Settings 48
Unit Configuration 48
Static DHCP Assignment 50
DHCP Lease Table 51
Wireless Settings 51
Configuration 52
Encryption 54
WMM 57
Connection Control 59
Client List 61
Advanced Wireless Settings 61
WDS 64
Internet Settings 65
Page 5

Firewall 66
Virtual Servers 66
Special Applications 68
DMZ 69
SPI 70
PC Privileges 71
Schedule Rules 72
Content Filter 73
URL Filter 74
System Tools 76
Restart 77
Time Zone 78
Configuration 79
Upgrade 80
Advanced 81
Static Route 81
RIP 81
DDNS 82
Quality of Service 84
Proxy ARP 84
IPSec 85
Port Mapping 87
Management 88
Syslog 88
SNMP 89
UPnP 90
Trusted Station 91
Remote Management 92
Utility 92
Diagnostics 93
Device Info 94
Summary 95
WAN 95
Statistics 96
Route 97
ARP 97
Support/Feedback 98
Support/Feedback 98
Page 6

Support 98
Feedback 99
6 TROUBLESHOOTING
Basic Connection Checks 101
Browsing to the Router Configuration Screens 101
Connecting to the Internet 102
Forgotten Password and Reset to Factory Defaults 102
Wireless Networking 103
Power LED or Power Adapter OK LED Not Lit 105
Replacement Power Adapters 105
Alert LED 106
Recovering from Corrupted Software 106
Frequently Asked Questions 107
3Com Warranty and Support Services 108
A USING DISCOVERY
Running the Discovery Application 111
Windows Installation (95/98/2000/Me/NT/ XP) 111
B IP ADDRESSING
The Internet Protocol Suite 113
Managing the Router over the Network 113
IP Addresses and Subnet Masks 113
How does a Device Obtain an IP Address and Subnet Mask? 115
DHCP Addressing 115
Static Addressing 115
Auto-IP Addressing 115
C TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
ADSL Wireless 11g 108Mbps Firewall Router 117
Standards 118
System Requirements 119
Ethernet Performance 119
Wireless Performance 119
Page 7

Cable Specifications 119
D SAFETY INFORMATION
Important Safety Information 121
Wichtige Sicherheitshinweise 122
Consignes importantes de sécurité 123
E END USER SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT
GLOSSARY
INDEX
REGULATORY NOTICES
Regulatory Information 137
CAUTION: EXPOSURE TO RADIO FREQUENCY RADIATION. 137
US - Radio Frequency Requirements 138
USA-FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION (FCC) 138
MANUFACTURER’S DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY 139
CANADA – INDUSTR YCANADA (IC) 139
INDUSTRY CANADA (IC) EMISSIONS COMPLIANCE STATEMENT 140
DE CONFORMITÉ À LA RÉGLEMENTATION D’INDUSTRIE CANADA 140
SAFETY COMPLIANCE NOTICE 140
Page 8

Page 9
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
This guide describes how to install and configure the OfficeConnect ADSL
Wireless 108Mbps 11g Firewall Router (3CRWDR200A-75 and
3CRWDR200B-75).
This guide is intended for use by those responsible for installing and
setting up network equipment; consequently, it assumes a basic working
knowledge of LANs (Local Area Networks) and Internet Router systems.
If a release note is shipped with the OfficeConnect ADSL Wireless
108Mbps 11g Firewall Router and contains information that differs from
the information in this guide, follow the information in the release note.
Most user guides and release notes are available in Adobe Acrobat
Reader Portable Document Format (PDF) on the 3Com World Wide Web
site:
http://www.3com.com
Naming Convention Throughout this guide, the OfficeConnect ADSL Wireless 108Mbps 11g
Firewall Router is referred to as the “Router”.
Category 3 and Category 5 Twisted Pair Cables are referred to as Twisted
Pair Cables throughout this guide.
Conventions Ta bl e 1 and Tab l e 2 list conventions that are used throughout this guide.
Tab le 1 Notice Icons
Icon Notice Type Description
Information note Information that describes important features or
instructions.
Page 10
10 CHAPTER : ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Tab le 1 Notice Icons
Icon Notice Type Description
Caution Information that alerts you to potential loss of data or
potential damage to an application, system, or device.
Related
Documentation
Warning Information that alerts you to potential personal
injury.
Tab le 2 Text Conventions
Convention Description
The words “enter”
and “type”
When you see the word “enter” in this guide, you must type
something, and then press Return or Enter. Do not press
Return or Enter when an instruction simply says “type.”
Keyboard key names If you must press two or more keys simultaneously, the key
names are linked with a plus sign (+). Example:
Press Ctrl+Alt+Del
Words in italics Italics are used to:
■ Emphasize a point.
■ Denote a new term at the place where it is defined in the
text.
■ Identify menu names, menu commands, and software
button names. Examples:
From the Help menu, select Contents.
Click OK.
In addition to this guide, each Router document set includes one
Installation Guide. This guide contains the instructions you need to install
and configure your Router.
Page 11

1
INTRODUCING THE ROUTER
Welcome to the world of networking with 3Com®. In the modern
business environment, communication and sharing information is crucial.
Computer networks have proved to be one of the fastest modes of
communication but, until recently, only large businesses could afford the
networking advantage. The OfficeConnect® product range from 3Com
has changed all this, bringing networks to the small office.
The products that compose the OfficeConnect range give you, the small
office user, the same power, flexibility, and protection that has been
available only to large corporations. Now, you can network the
computers in your office, connect them all to a single Internet outlet, and
harness the combined power of all of your computers.
OfficeConnect ADSL Wireless 108Mbps 11g Firewall Router
The OfficeConnect ADSL Wireless 108Mbps 11g Firewall Router is
designed to provide a cost-effective means of sharing a single broadband
Internet connection amongst several wired and wireless computers. The
Router also provides protection in the form of an electronic “firewall”,
preventing anyone outside of your network from seeing your files or
damaging your computers.
features such as scheduled internet access policies, web content filter, and
intrusion detections.
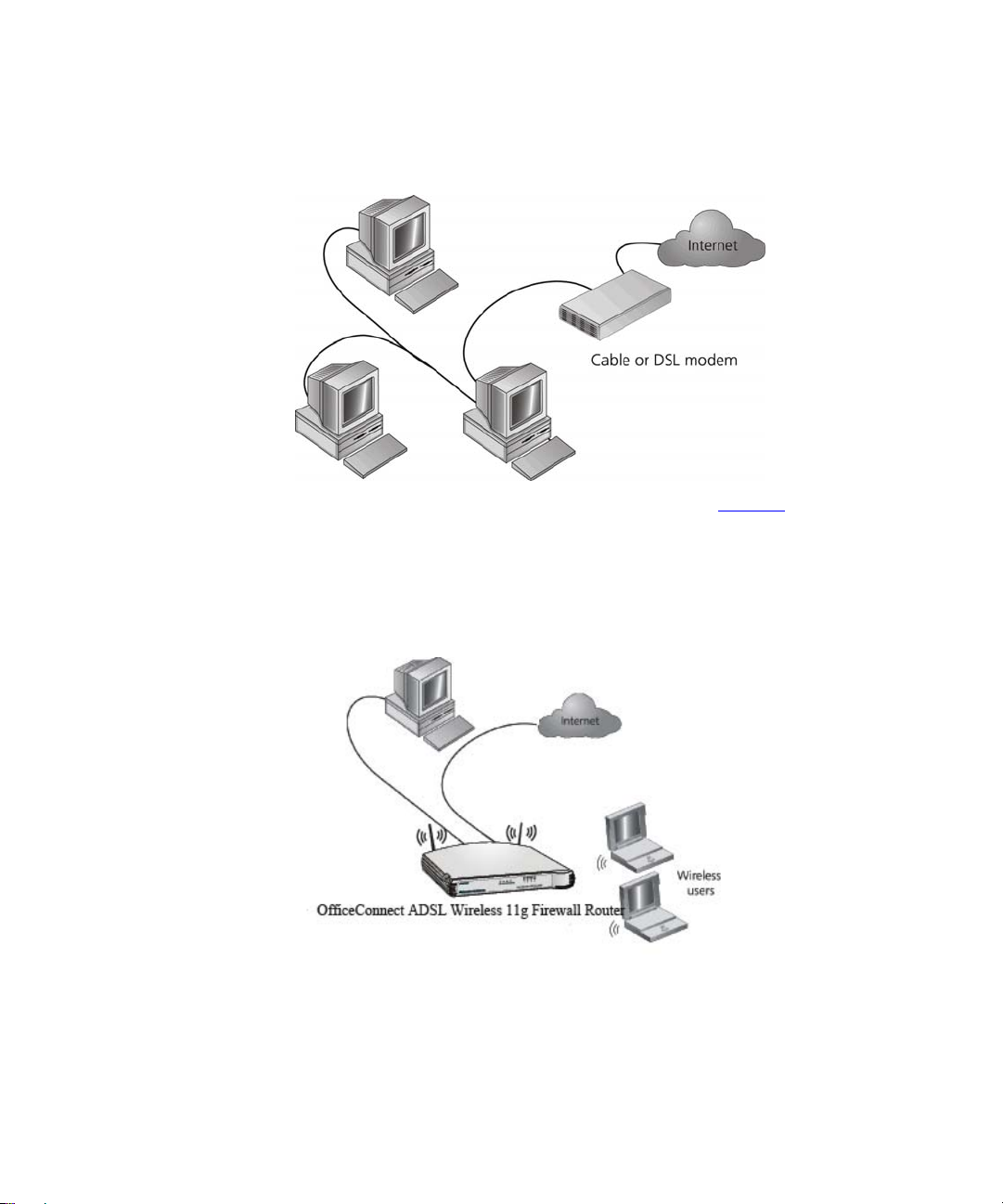
Figure 1 shows an example network without a Router. In this network,
only one computer is connected to the Internet. This computer must
always be powered on for the other computers on the network to access
the Internet.
The Router also gives you many administrative
Page 12
12 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING THE ROUTER
Figure 1 Example Network Without a Firewall Router
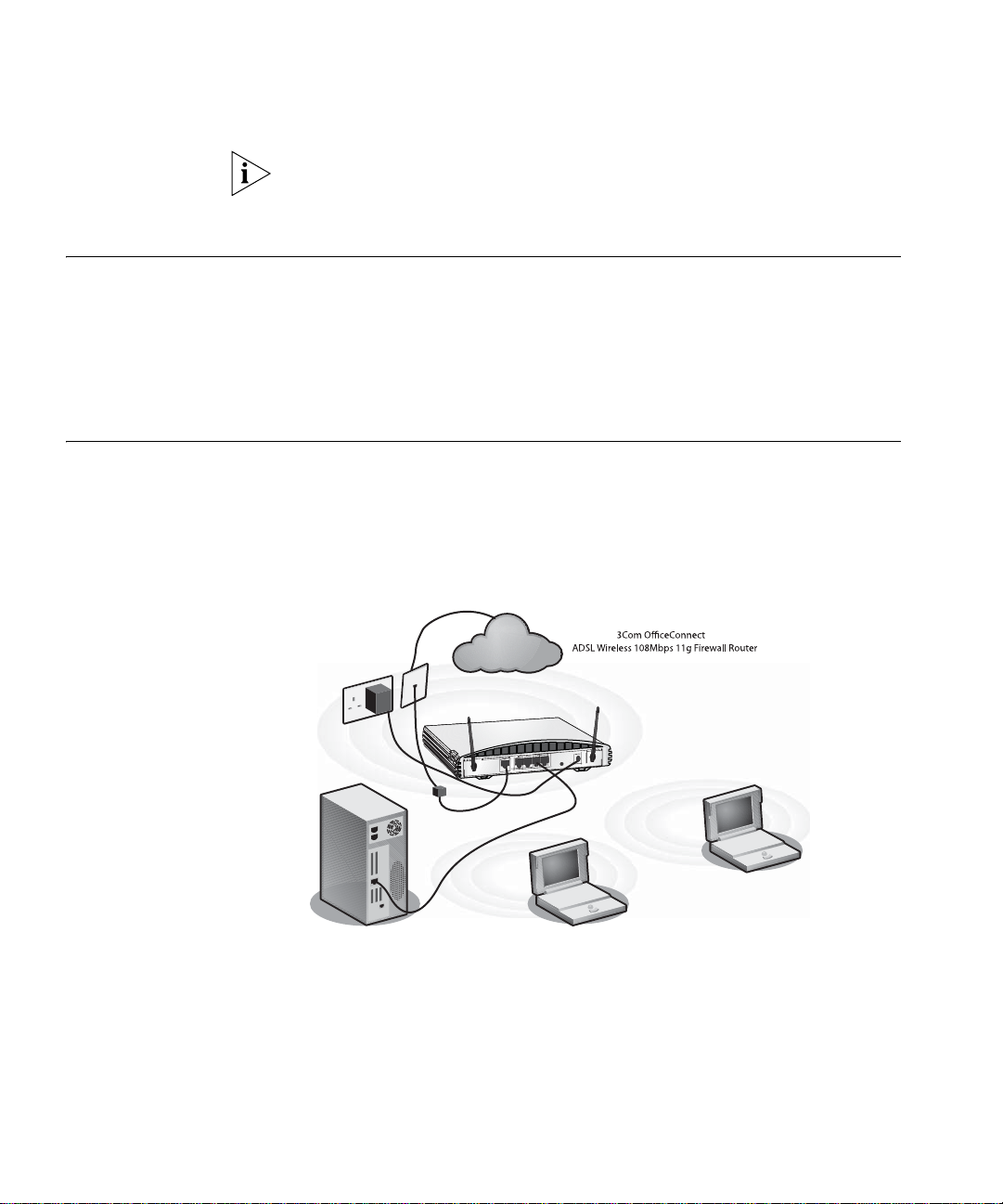
When you use the Firewall Router in your network (Figure 2), it becomes
your connection to the Internet. Connections can be made directly to the
Router, or to an OfficeConnect Switch or Hub, expanding the number of
computers you can have in your network.
Figure 2 Example Network Using a ADSL Wireless 108Mbps 11g Firewall Router
Page 13

Firewall Router Advantages 13
Firewall Router Advantages
The advantages of the Firewall ADSL Wireless 108Mbps 11g Firewall
Router include:
■ Shared Internet connection for both wired and wireless computers
■ High speed 802.11g wireless networking
■ No need for a dedicated, “always on” computer serving as your
Internet connection
■ Cross-platform operation for compatibility with Windows, Unix and
Macintosh computers
■ Easy-to-use, Web-based setup and configuration
■ Provides centralization of all network address settings (DHCP)
■ Acts as a Virtual server to enable remote access to Web, FTP, and other
services on your network
■ Security — Firewall protection against Internet hacker attacks and
encryption to protect wireless network traffic
■ Filtered access of inappropriate Web sites using the built-in URL filter
■ Internet Access Policy, to schedule your Internet Acccess rules with
options in keywords and applications blocking
■ Wireless Multimedia, to maximize the quality of your internet service
with traffic prioritization
Package Contents The Router kit includes the following items:
■ One OfficeConnect ADSL Wireless 108Mbps 11g Firewall Router
■ One power adapter for use with the Router
■ Four rubber feet
■ One RJ 11 cable (typically a telephone cable) if your model is
3CRWDR200A-75
■ One RJ 45 cable (typically an Ethernet cable) if your model is
3CRWDR200B-75
■ One CD-ROM containing the Router Discovery program and this User
Guide
■ Installation Guide
■ One Support and Safety Information Sheet
Page 14

14 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING THE ROUTER
■ One Warranty Flyer
If any of these items are missing or damaged, please contact your retailer.
Minimum System and Component Requirements
Your Router requires that the computer(s) and components in your
network be configured with at least the following:
■ A computer with an operating system that supports TCP/IP
networking protocols (for example Windows 95/98/NT/Me/2000/XP,
Unix, Mac OS 8.5 or higher).
■ An Ethernet 10Mbps or 10/100/1000 Mbps NIC for each computer to
be connected to the four-port switch on your Router.
■ An 802.11b or 802.11g wireless NIC.
■ An active ADSL subscription and connection.
■ A Web browser that supports JavaScript, such as Netscape 4.7 or
higher, Internet Explorer 5.0 or higher, or Mozilla 1.2.1 or higher.
Front Panel The front panel of the Router contains a series of indicator lights (LEDs)
that help describe the status of various networking and connection
operations.
Figure 3 Router — Front Panel
3CRWDR200A-75
ADSL Wireless 108Mbps 11g Firewall Router
Alert Power
WLAN
Sync
DSL
Data
DSL
On= 10M/100M, Flash = Activity
1 Alert LED
Orange
Indicates a number of different conditions, as described below.
Off — The Router is operating normally.
Flashing quickly — Indicates one of the following conditions:
Page 15

Front Panel 15
■ The Router has just been started up and is running a self-test routine,
or
■ The administrator has invoked the Reset to Factory Defaults
command, or
■ The system software is in the process of being upgraded
In each of these cases, wait until the Router has completed the current
operation and the alert LED is Off.
Flashing slowly — The Router has completed the Reset to Factory
Defaults process, and is waiting for you to reset the unit. To do this,
remove power, wait 10 seconds and then re-apply power. The Router will
then enter the start-up sequence and resume normal operation.
On for 2 seconds, and then off — The Router has detected and prevented
a hacker from attacking your network from the Internet.
Continuously on — A fault has been detected with your Router during
the start-up process. Refer to Chapter 6
“Troubleshooting”.
2 Power LED
Green
Indicates that the Router is powered on.
3 Wireless LAN (WLAN) Status LED
Yellow
If the LED is on it indicates that wireless networking is enabled. If the LED
is flashing, data is being transmitted or received. If the LED is off, the
Wireless LAN has been disabled in the Router, or there is a problem. Refer
to Chapter 6
“Troubleshooting”.
4 Four LAN Status LEDs
Green (100 Mbps link) / yellow (10 Mbps link)
If the LED is on, the link between the port and the next piece of network
equipment is OK. If the LED is flashing, the link is OK and data is being
transmitted or received. If the LED is off, nothing is connected, the
connected device is switched off, or there is a problem with the
connection (refer to Chapter 6
“Troubleshooting”). The port will
automatically adjust to the correct speed and duplex.
5 Sync DSL Status LED
Page 16
16 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING THE ROUTER
The LED lights up and stays on when the connection between ADSL
service and the Router is OK. If the LED is off, nothing is connected or
there is a problem (refer to Chapter 6
“Troubleshooting”).
6 Data DSL Status LED
If the LED is flashing, the link is OK and data is being transmitted or
received over the internet.
has failed on a PPPoE or PPPoA ADSL connection
The Sync DSL LED and Data DSL LED are excellent diagnostic indicators.
If interpreted correctly they can give a reliable indication of the cause of an
ADSL connection failure.
If the LED is off this can also indicate the login
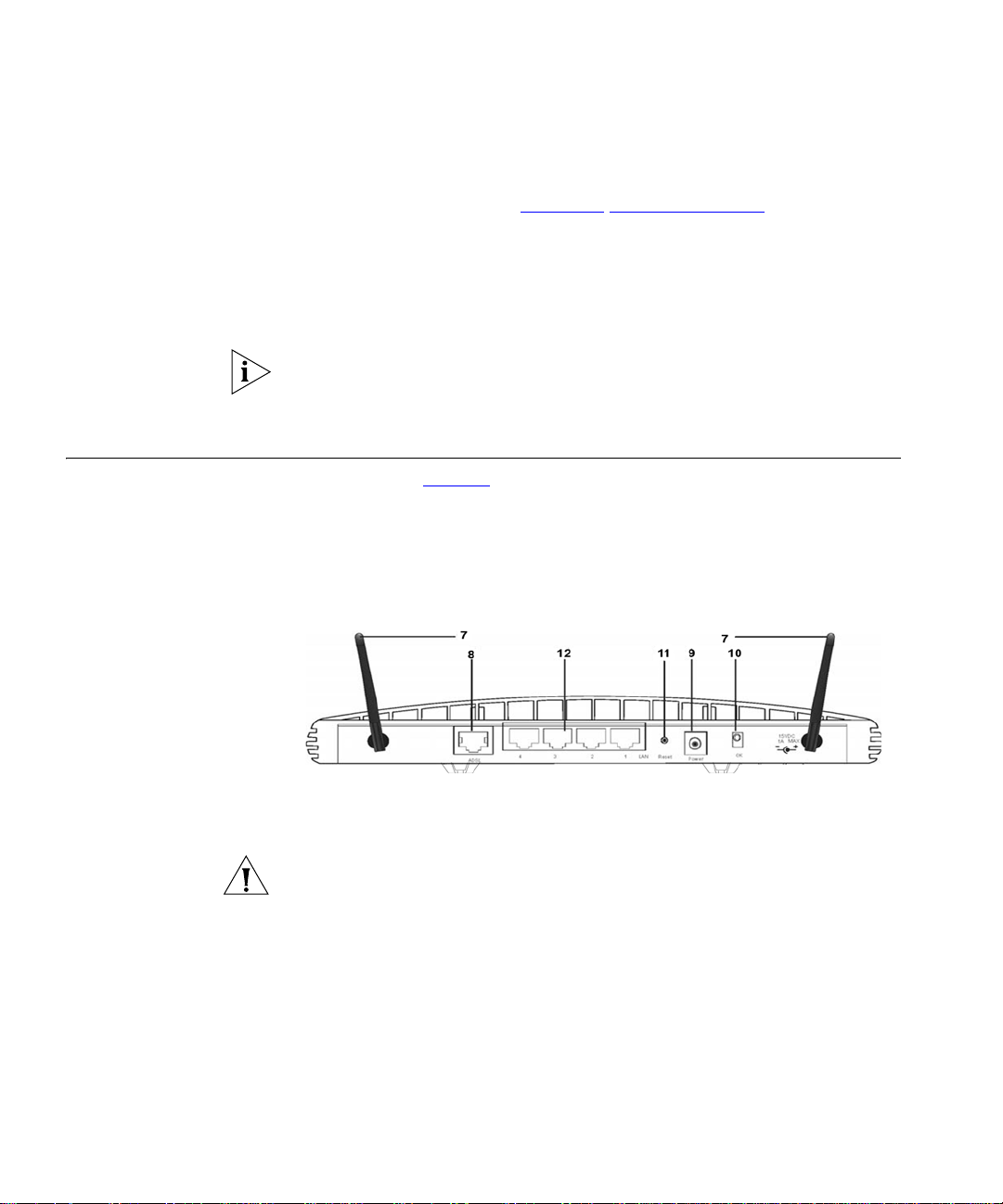
Rear Panel The rear panel (Figure 4) of the Router contains four LAN ports, one
Ethernet ADSL port, a power adapter OK LED, and a power adapter
socket.
Figure 4 Router - Rear Panel
7 Wireless Antennae
The antennae on the product should be placed in a ‘V’ position when
initially installed.
CAUTION: Do not force the antennae beyond their mechanical stops.
Rotating the antennae further may cause damage.
8 ADSL Port
Using the RJ11 cable provided, connect your Router to the telephone
socket via a splitter.
or
Using the RJ45 cable provided, connect your Router to the telephone
socket via a splitter.
9 Power Adapter Socket
Page 17

Rear Panel 17
Only use the power adapter supplied with this Router. Do not use any
other adapter.
10 Power Adapter OK LED
Green
Indicates that the power adapter is supplying power to the Router. If the
LED is off, there may be a problem with the power adapter or adapter
cable.
11 Reset Button
Press this button to reset your Router to factory default.
12 Four 10/100 LAN ports
Using suitable RJ-45 cable, you can connect your Router to a computer,
or to any other piece of equipment that has an Ethernet connection (for
example, a hub or a switch). The LAN ports will automatically set
themselves to MDI or MDIX depending on the device to which they are
connected and the type of cable used.
Page 18

18 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING THE ROUTER
Page 19
HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2
Introduction This chapter will guide you through a basic installation of the Router,
including:
■ Connecting the Router to the Internet.
■ Connecting the Router to your network.
■ Setting up your computers for networking with the Router.
Safety Information
Positioning the Router
WARNING: Please read the “
before you start.
VORSICHT: Bitte lesen Sie den Abschnitt “
sorgfältig durch, bevor Sie das Gerät einschalten.
AVERTISSEMENT: Veuillez lire attentivement la section “
importantes de sécurité” avant de mettre en route.
You should place the Router in a location that:
■ is conveniently located for connection to the telephone socket that
will be used to connect to the Internet.
■ is centrally located to the wireless computers that will connect to the
Router. A suitable location might be on top of a high shelf or similar
furniture to optimize wireless connections to computers in both
horizontal and vertical directions, allowing wider coverage.
■ allows convenient connection to the computers that will be connected
to the four LAN ports on the rear panel, if desired.
■ allows easy viewing of the front panel LED indicator lights, and access
to the rear panel connectors, if necessary.
Safety Information” section in Appendix D
Wichtige Sicherheitshinweise”
Consignes
Page 20
20 CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE INSTALLATION
When positioning your Router, ensure:
■ It is out of direct sunlight and away from sources of heat.
■ Cabling is away from power lines, fluorescent lighting fixtures, and
sources of electrical noise such as radios, transmitters and broadband
amplifiers.
■ Water or moisture cannot enter the case of the unit.
■ Air flow around the unit and through the vents in the side of the case
is not restricted. 3Com recommends you provide a minimum of
25 mm (1 in.) clearance.
Using the Rubber
Feet
Use the four self-adhesive rubber feet to prevent your Router from
moving around on your desk or when stacking with other flat top
OfficeConnect units. Only stick the feet to the marked areas at each
corner of the underside of your Router.
Stacking the Router If you are stacking your Router with other OfficeConnect units, install the
Router at the top of the stack. Refer to the documentation supplied with
your other OfficeConnect unit for details on using the stacking clip.
A stacking clip is not supplied with the Router. Use the stacking clip
supplied with another stackable OfficeConnect unit.
Wall Mounting There are two slots on the underside of the Router that can be used for
wall mounting.
When wall mounting the unit, ensure that it is within reach of the power
Do not install the Router more than 200 cm above the ground.
outlet.
You will need two suitable screws to wall mount the unit. To do this:
1 Ensure that the wall you use is smooth, flat, dry and sturdy and make two
screw holes which are 150 mm (5.9 in.) apart.
2 Fix the screws into the wall, leaving their heads 3 mm (0.12 in.) clear of
the wall surface.
3 Remove any connections to the unit and locate it over the screw heads.
When in line, gently push the unit on to the wall and move it downwards
to secure.
Page 21
Before you Install your Router 21
When making connections, be careful not to push the unit up and off the
wall.
CAUTION: Only wall mount single units, do not wall mount stacked
units.
Before you Install your Router
Before you install and configure your Router, you need the following
additional information. If you do not have this information, contact your
Internet Service Provider (ISP). Space is provided below for you to record
this information.
If you have a DSL connection and your ISP allocates IP information
dynamically over PPPoE, (or PPPoA, which is in common use in the UK),
you need a User Name and Password:
PPPoE User Name : ______________________
PPPoE Password : ______________________
PPPoE Service Name : ______________________
You only need a PPPoE Service Name if your ISP requires one. Do not
enter anything if your ISP does not require this information.
You should leave the Authentication Method as its default: Auto if your
ISP does not specify this parameter.
If your ISP allocates fixed or static IP information, you need the following
information:
IP Address : ____.____.____.____
Subnet Mask : ____.____.____.____
Default Router address : ____.____.____.____
DNS address : ____.____.____.____
Page 22
22 CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE INSTALLATION
If your ISP allocates IP information dynamically over a protocol other than
PPPoE, you do not need any further information. This configuration is
typical of cable connections.
Powering Up the Router
Connecting the Router
To power up the Router:
1 Plug the power adapter into the power adapter socket located on the
back panel of the Router.
2 Plug the power adapter into a standard electrical wall socket.
The first step for installing your Router is to physically connect it to an
RJ11or RJ45 cable, as appropriate, with the splitter and then connect the
Router to a computer in order to be able to access the Internet. See
Figure 5:
Figure 5 Connecting the Router
Qpxfs!
Tvqqmz!Voju
Joufsofu
O
P
N
A
L
1
2
L
S
D
/
e
l
b
a
C
K
O
R
E
W
Xjsfmftt!
Vtfst
To use your Router to connect to the Internet through an DSL connection:
1 Insert one end of the supplied telephone (RJ-11) cable into the ADSL port
on the rear panel of the Router. Check that the DSL Sync status LED lights
on the Router.
2 Connect your computer to one of the four LAN ports on the Router using
a Category 5 twisted pair cable. Check that the corresponding LAN status
LED on the Router lights.
Page 23

Connecting the Router 23
You have now completed the hardware installation of your Router. Next
you need to set up your computers so that they can make use of the
Router to communicate with the Internet.
3Com recommends that you perform the initial Router configuration
from a computer that is directly connected to one of the LAN ports.
If you configure the Router from a wireless computer, note that you may
lose contact with the Router if you change the wireless configuration.
To communicate wirelessly with your Router, your wireless NIC should be
set as follows:
■ Encryption — none
■ Service Area Name/SSID — 3Com
■ Channel — 11
Page 24

24 CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE INSTALLATION
Page 25
3
SETTING UP YOUR COMPUTERS
The Router has the ability to dynamically allocate network addresses to
the computers on your network, using DHCP. However, your computers
need to be configured correctly for this to take place. To change the
configuration of your computers to allow this, follow the instructions in
this chapter. If your computers are configured with fixed or static
addresses and you do not wish to change this, then you should use the
Discovery program on the Router CD-ROM to detect and configure your
Router. Refer to Appendix A
program.
for information on using the Discovery
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically
Windows 2000 If you are using a Windows 2000-based computer, use the following
Refer to the section below that relates to your operating system for
details on how to obtain an IP address automatically.
procedure to change your TCP/IP settings:
1 From the Windows Start Menu, select Settings > Control Panel.
2 Double click on Network and Dial-Up Connections.
3 Double click on Local Area Connection.
4 Click on Properties.
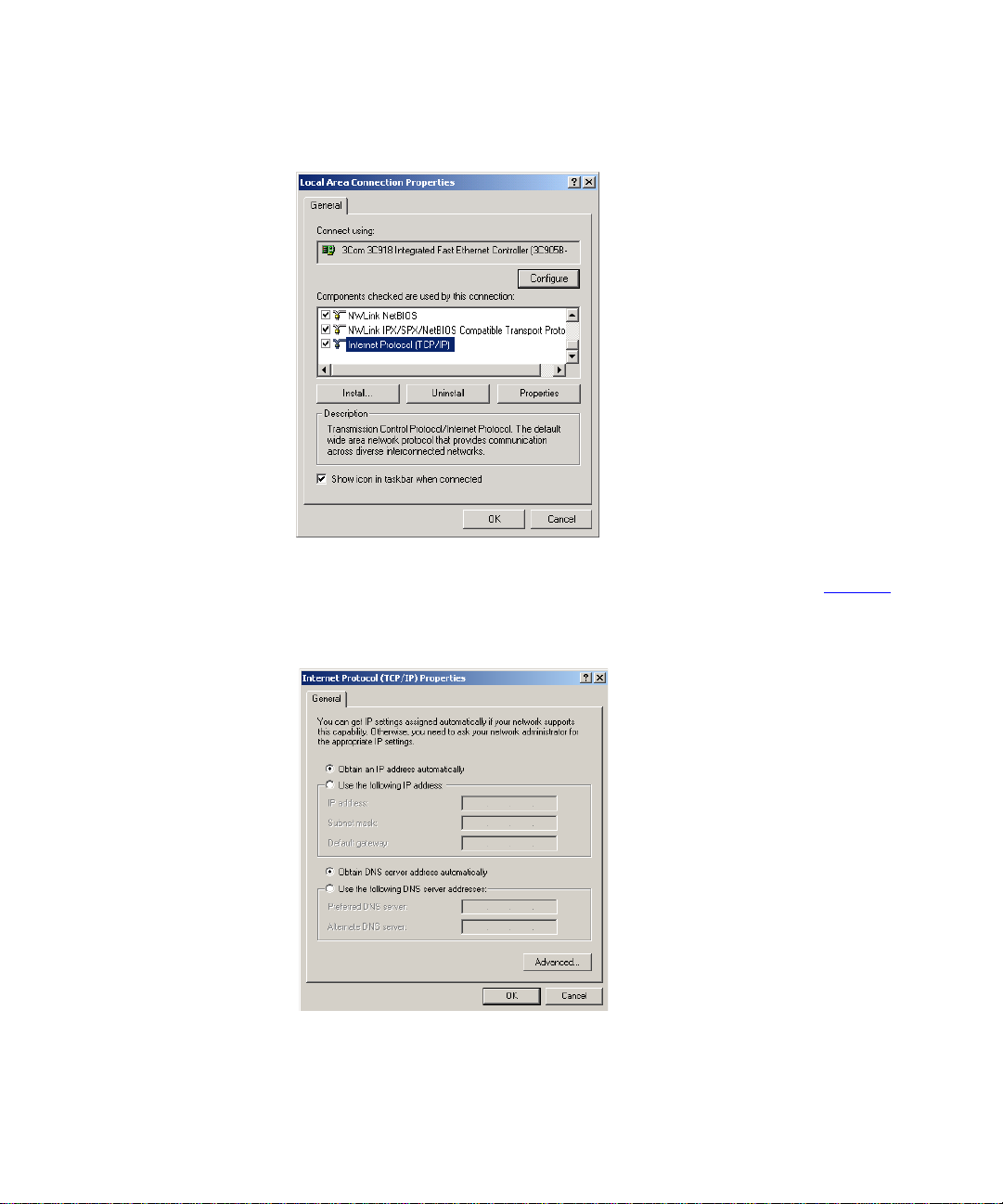
5 A screen similar to Figure 6
TCP/IP and click on Properties.
should be displayed. Select Internet Protocol
Page 26
26 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP YOUR COMPUTERS
Figure 6 Local Area Properties Screen
6 Ensure that the options Obtain an IP Address automatically, and Obtain
DNS server address automatically are both selected as shown in Figure 7
Click OK.
.
Figure 7 Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties Screen
7 Restart your computer.
Page 27

Obtaining an IP Address Automatically 27
Windows Vista If you are using a Windows Vista computer, use the following procedure
to change your TCP/IP settings:
1 From the Windows start menu, select Network.
2 Select Network Center option from the top menu.
3 Select Manage Networks from the left panel.
4 Double click on the Local Area Connection icon. A screen titled Local
Area Connection Status will appear.
5 Click on Details and bring up the Local Area Connection Properties tab.
6 Select Internet Protocol TCP/IP and click on Properties.
7 Ensure that the options Obtain an IP Address automatically, and Obtain
DNS servers automatically are both selected. Click OK.
Windows XP If you are using a Windows XP computer, use the following procedure to
change your TCP/IP settings:
1 From the Windows Start menu, select Control Panel.
2 Click on Netmwork and Internet Connections.
3 Click on the Network Connections icon.
4 Double click on LAN or High Speed Connection icon. A screen titled Local
Area Connection Status will appear.
5 Select Internet Protocol TCP/IP and click on Properties.
6 Ensure that the options Obtain an IP Address automatically, and Obtain
DNS servers automatically are both selected. Click OK.
7 Restart your computer.
Windows 95/98/ME If you are using a Windows 95/98/ME computer, use the following
procedure to change your TCP/IP settings:
1 From the Windows Start Menu, select Settings > Control Panel.
2 Double click on Network. Select the TCP/IP item for your network card
and click on Properties.
3 In the TCP/IP dialog, select the IP Address tab, and ensure that Obtain IP
address automatically is selected. Click OK
.
Page 28
28 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP YOUR COMPUTERS
Macintosh If you are using a Macintosh computer, use the following procedure to
change your TCP/IP settings:
1 From the desktop, select Apple Menu, Control Panels, and TCP/IP.
2 In the TCP/IP control panel, set Connect Via: to “Ethernet”.
3 In the TCP/IP control panel, set Configure: to “Using DHCP Server.”
4 Close the TCP/IP dialog box, and save your changes.
5 Restart your computer.
Disabling PPPoE and PPTP Client Software
If you have PPPoE or PPTP client software installed on your computer, you
will need to disable it. To do this:
1 From the Windows Start menu, select Settings > Control Panel.
2 Double click on Internet Options.
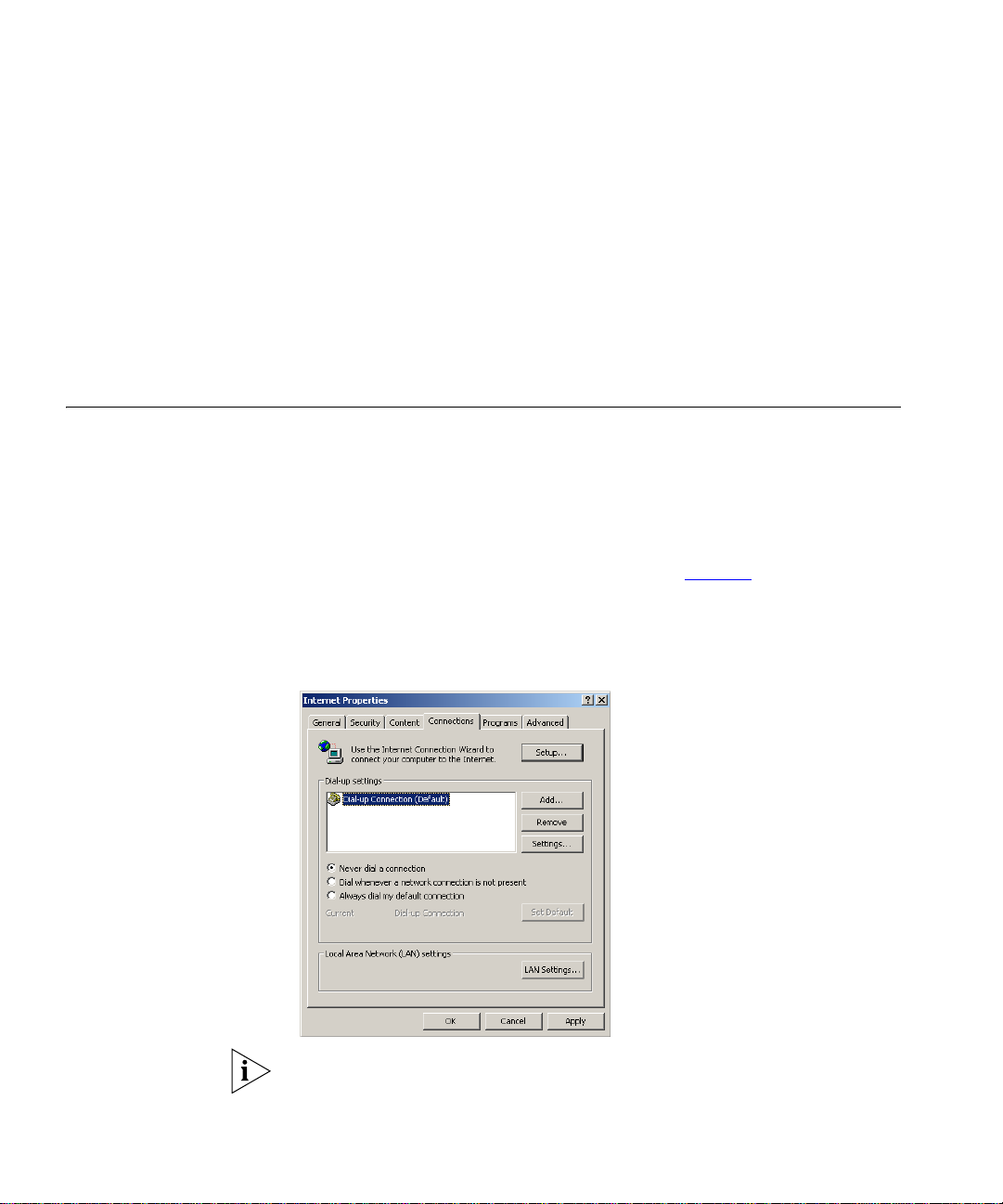
3 Select the Connections Tab. A screen similar to Figure 8
displayed.
4 Select the Never Dial a Connection option.
Figure 8 Internet Properties Screen
should be
You may wish to remove the PPPoE client software from your computer
to free resources, as it is not required for use with the Router.
Page 29

Disabling Web Proxy 29
Disabling Web Proxy
Ensure that you do not have a web proxy enabled on your computer.
Go to the Control Panel and click on Internet Options. Select the
Connections tab and click LAN Settings at the bottom. Make sure that
the Use Proxy Server option is unchecked.
Page 30

30 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP YOUR COMPUTERS
Page 31

4
RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
Accessing the Wizard
The Router setup program is Web-based, which means that it is accessed
through your Web browser (Netscape Navigator 4.7 or higher, Internet
Explorer 5.0 or higher, or Mozilla 1.2.1 or higher).
To use the Setup Wizard:
1 Ensure that you have at least one computer connected to the Router.
Refer to Chapter 2
2 Launch your Web browser on the computer.
3 Enter the following URL in the location or address field of your browser:
http://192.168.1.1. The Login screen displays.
Figure 9 Web Browser Location Field (Factory Default)
4 To log in as an administrator, enter the password (the default setting is
admin) in the System Password field and click Log in .
for details on how to do this.
Page 32

32 CHAPTER 4: RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
Figure 10 Router Login Screen
5 If the password is correct, the Country Selection screen will appear. Select
the country you wish to configure the Router for, then click Apply.
If you purchased your Router in the United States, you do not see this
screen, as it is automatically set.
Figure 11 Country Selection Screen
Page 33

Accessing the Wizard 33
6 When you have selected a country either:
■ The Welcome screen will appear (Figure 12). Select the Wizard
tab and click Wizard.
or
■ If your Router has not been configured before, the Wizard will
launch automatically (refer to Figure 13
).
7 Click Next.
8 You will be guided step-by-step through a basic setup procedure.
Welcome
Figure 12 Welcome Screen
Page 34

34 CHAPTER 4: RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
Figure 13 Wizard Screen
Password Figure 14 Change Administration Password Screen
When the Change Administration Password screen appears, type the Old
Password, then a new password in both the New Password and Confirm
Password boxes.
Page 35

Accessing the Wizard 35
3Com recommends entering a new password when setting up the Router
for the first time. The Router is shipped from the factory with a default
password, admin.
1. Password is case sensitive.
2. Write the new password down and keep it in a safe place, so that you
can change your settings in the future.
Click Next to display the Time Zone setup screen.
Time Zone
Figure 15 Time Zone Screen
Select your time zone from the pull-down menu, check the daylight
savings option if required, and then click Next.
The Daylight Savings option advances the system clock by one hour. It
does not cause the system clock to be updated for daylight savings time
automatically.
Page 36

36 CHAPTER 4: RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
WAN Settings Figure 16 Internet Settings Screen
This Internet Addressing Mode window allows you to set up the Router
for the type of Internet connection you have. Before setting up your
Internet connection mode, have the account information from your ISP
ready.
Select an Internet Addressing mode from the following:
■ PPPoE
■ PPPoA
■ Dynamic/Fix IP in 1483 Bridge Mode
■ IP over ATM
■ Bridging
Page 37

PPPoE Mode
Figure 17 PPPoE Screen
Accessing the Wizard 37
To setup the Router for use with a PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) connection,
use the following procedure:
1 Enter your PPP user name in the PPPoE User Name text box.
2 Enter your PPP password in the PPPoE Password text box.
3 Enter your PPP over Ethernet service name in the PPPoE Service Name text
box.
Do not enter anything in this box if your ISP does not require a service
name.
4 Select Dial on Demand if you want the the internet connection dropped
when there is no activities with the Internet. Enter an idle time from the
Maximum Idle Time drop down list. This is the amount of time without
Internet activity that you want to allow before the Router ends the PPPoE
session.
5 Manual IP Address/DNS Server configuration: Enter the IP Address that
you would like to be assigned to the router’s WAN interface if you have
required one from your ISP. And enter the DNS Server’s IP Address if it is
given by your ISP(optional).
6 Check all of your settings, and then click Next.
Page 38

38 CHAPTER 4: RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
PPPoA Mode
Figure 18 The PPPoA Screen
To setup the Router for use with a PPPoA connection:
1 Enter your PPP over ATM user name in the PPP User Name text box.
2 Enter your PPP over ATM password in the PPP Password text box.
3 Select Dial on Demand if you want the internet connection dropped
when there is no activities with the Internet. Enter an idle time from the
Maximum Idle Time drop down list. This is the amount of time without
Internet activity that you want to allow before the Router ends the PPPoE
session.
4 Manual IP Address/DNS Server configuration: Enter the IP Address that
you would like to be assigned to the router’s WAN interface if you have
required one from your ISP. And enter the DNS Server’s IP Address if it is
given by your ISP(optional).
5 Check all of your settings, and then click Next.
VPI/VCI: VPI (Virtual Path Identifier) and VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier)
define an ATM PVC(Permanent Virtual Circuit). Please obtain these values
from your ISP.
Page 39

Accessing the Wizard 39
Dynamic/Fixed IP in 1483 Bridge Mode
Figure 19 The Dynamic/Fixed IP in Bridge Mode
To setup the Router for use with a Dynamic/Fixed IP in 1483 Bridge
Mode connection, use the following procedure:
1 Manual IP Address Configuration: You may enter the router’s WAN IP
address and subnet mask here if your ISP has given you a static IP
Address.
2 Manual Default Gateway Configuration: Enter the gateway’s IP address or
select the WAN interface to use to connect to it.
3 Manual DNS Server Configuration:
Your ISP may provide you with primary and secondary DNS addresses. If
they have been provided, enter the addresses in the appropriate text
boxes. If not, leave 0.0.0.0 in the boxes.
4 Check all of your settings, and then click Next.
Page 40

40 CHAPTER 4: RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
IP over ATM Mode(IPoA)
Figure 20 The IP over ATM Screen
To set up the Router for use with an IPoA mode, use the following
procedure:
1 WAN IP Address: Enter the IP Address given by your ISP.
2 WAN Subnet Mask: Enter the subnet mask given by your ISP.
3 Manual Default Gateway Configuration: Select this option to enter the
WAN interface’s IP Address if you are given with this information by your
ISP or select a WAN interface to use to connect to it.
4 Manual DNS configuration: Enter the DNS server’s address from the ISP if
it is required. (this is optional).
Page 41

Accessing the Wizard 41
Bridging Mode
Figure 21 Bridging Mode Screen
With bridging the router simply acts like a modem. The router passes
traffic through to another device, usually a computer or a router, which
handles authentication with the ISP.
LAN Settings
DHCP The Router contains a Dynamic Host Configuration (DHCP) server that
Figure 22 LAN IP Address Screen
This screen displays a suggested LAN IP address and subnet mask of the
Router. It also allows you to change the IP address and subnet mask.
can automatically configure the TCP/IP settings of every computer on
your network.
Page 42

42 CHAPTER 4: RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
Figure 23 DHCP Server Setup Screen
To activate the DHCP Server option, select Enable the DHCP server with
the following settings: and specify the IP pool range. The largest available
continuous IP pool will be automatically entered; if this is not appropriate,
make your required changes. To disable DHCP, select Do not enable the
DHCP server. Click Next when you have finished.
Wireless Settings
Figure 24 Wireless Configuration Screen
This screen displays the Channel and Service Area Name. It also allows
you to change these settings. There are a maximum of 14 channels, the
number available to you is dependent on the country you reside in.
Selecting Clear Channel Select from the Channel drop-down list allows
Page 43

Accessing the Wizard 43
the Router to automatically select an available channel when first
powered on.
The Service Area Name default for 3Com products is “3Com”. Up to 32
(case sensitive) characters can be entered for the Service Area Name.
3Com strongly recommends that you change the SSID to something
other than the default.
Click Next when you have finished.
If you are configuring the Router from a wireless computer any changes
you make to the wireless configuration will result in communication
between the Router and your computer being lost. This is why 3Com
strongly recommends that you configure the Router from a wired
computer.
It is very important that you set up your wireless clients to use the same
Service Area Name or SSID as the one you use on this screen. If your
clients use a different Service Area Name then they will not be able to
communicate with the Router.
The choice of channel is less important as Clients will generally search all
of the available channels. You should however make a note of the
channel you select as this may be useful if you experience problems with
your clients.
Page 44

44 CHAPTER 4: RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
Summary Figure 25 Configuration Summary Screen
When you complete the Setup Wizard, a configuration summary will
display. 3Com recommends that you verify the configuration information
of the Router and then print this page for your records. Click Finish and
the router will reboot now.
If you have made changes to the LAN Settings or wireless configuration
options, you may need to reconfigure the computer you are using in
order to make contact with the Router again.
Your Router is now configured and ready for use.
For information on improving your Wireless network security see
“Wireless Settings”
on page 51.
See Chapter 5 for a detailed description of the Router configuration
screens.
Page 45

5
ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Navigating Through the Router Configuration Pages
Main Menu At the left side of all screens is a main menu, as shown in Figure 26
This chapter describes all the screens available through the Router
configuration pages, and is provided as a reference. To get to the
configuration pages, browse to the Router by entering the URL in the
location bar of your browser. The default URL is http://192.168.1.1 but if
you changed the Router LAN IP address during initial configuration, use
the new IP address instead. When you have browsed to the Router, log in
using your system password (default admin).
on
page 46
appear in the main part of the screen.
■ Welcome — displays the firmware version of the Router, allows you to
■ LAN Settings — allows you to configure IP address and subnet mask
■ Wireless Settings — enables /disables access from wireless computers,
. When you click on a topic from the main menu, that page will
change your password, and launch the Wizard
information, set up DHCP server parameters, and display the DHCP
client list.
configures WPA/WPA2 or WEP encryption, provides facilities for
improving the security of the wireless network, setup WMM
parameters, Wireless mode selection, Mac Access Control and
Advanced Wireless Settings.
■ Internet Settings — sets up Internet addressing modes.
■ Firewall — allows configuration of the Router’s firewall features:
Virtual Servers, Special Applications, Content Filtering, URL Filtering,
Internet Access Policy, and SPI options.
■ System Tools — allows the administrator to perform maintenance
activities on the Router.
Page 46

46 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
■ Advanced — allows you to monitor and configure the Router’s
advanced features, including Static Route, RIP, DDNS, IPSec, Proxy ARP,
Port Mapping and QoS(Quality of Service).
■ Management — displays the current status and activity logs of the
Router, SNMP enable/disable, and remote management control.
■ Device Info — Providing the configuration summary and statistics on
your LAN/WAN/ATM/ADSL connection.
■ Support/Feedback — contains a comprehensive online help system
and allows you to provide 3Com with feedback on your Router.
Option Tabs Each corresponding menu page may also provide sub-sections which are
accessed through the use of tabs (see Figure 26
sub-section, simply click on the required tab.
Getting Help
On every screen, a Help button is available which provides access to the
context-sensitive online help system. Click Help for further assistance and
guidance relating to the current screen.
for example). To access a
Welcome Screen The Welcome section allows you to view the Notice board and to change
your Password. You can also gain access to the Configuration Wizard.
Notice Board Figure 26 Notice Board Screen
Page 47

Welcome Screen 47
The Notice Board is used to display firmware version and configuration
warning messages. For example, you would be warned if you had
disabled wireless networking or wireless encryption.
Password
Figure 27 Password Screen
Changing the Administration Password
You can change the password to prevent unauthorized access to the
Administration System. To do this:
1 Enter the current password in the Old Password field
2 Enter the new password in the New Password field
3 Enter the new password again in the Confirm Password field
4 Click Apply to apply the new password
The password is case sensitive.
f you have forgotten your password you need to reset the Router.
Page 48

48 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Wizard Figure 28 Wizard Screen
Click WIZARD... to launch the configuration wizard. Refer to Chapter 4
for information on how to run the wizard.
LAN Settings The LAN Settings menu provides the following options:
Unit Configuration
Figure 29 Unit Configuration Screen
Page 49

LAN Settings 49
This screen allows you to change the IP address and subnet mask.
1 IP Address: Enter the IP Address for the router.
2 Subnet Mask: Enter the Subnet Mask for the router.
3 Enable DHCP server on the LAN: Check this box to enable the DHCP
service on the router(enabled by default).
The Firewall Router contains a Dynamic Host Configuration (DHCP) server
that can automatically configure the TCP/IP settings of every computer on
your network.
4 Select Enable the DHCP server with the following settings: Enter the start
and end IP Address of your DHCP range. Enter the leased time in hours to
specify the frequency for DHCP assignment.
Check all of your settings and
click Save, then click Apply.
Auto IP Range: Click this to automatically allocate valid hosts in this
network, ie, Class C. And there is 253(254-1 for the router) available
addresses in the network.
5 3Com NBX Call Processor: If you have 3Com NBX Call Processor, enter its
IP Address here.
6 Enable DHCP Server Relay: Check this box to make the device act as a
DHCP relaying agent. Thus, it forwards DHCP requests to your existing
DHCP server instead. Please enter your DHCP server’s IP Address in the
fields.
Page 50

50 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Static DHCP
Assignment
Figure 30 Static DHCP Assignment Screen
To assign a LAN client with a static IP Address, please do the following:
1 Enter the IP Address that you would like to lease and the client MAC
address in the fields appropriately.
The MAC Address must be entered as 6 hexadecimal pairs, for example
12-34-56-78-90-ab.
Click Apply to apply your changes. The device will now reboot.
Page 51

DHCP Lease Table Figure 31 DHCP Lease Table Screen
Wireless Settings 51
The DHCP Lease table screen list the client’s name, MAC Address, IP
Address and Expiration time which reflects the value specified in DHCP
server setting in “
Unit Configuration”on this chapter.
Wireless Settings The Wireless Settings menu provides options described in the following
sections.
To improve the security of your wireless network, 3Com recommends
that you:
1. Change the SSID from its default value
2. Enable Encryption
3. Enable Connection Control
Page 52

52 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Configuration Figure 32 Configuration Screen
Enable Wireless Networking
Use this check box to enable or disable the wireless section of your LAN.
When disabled, no wireless PCs can gain access to either the Internet or
other PCs on your Wired or Wireless LAN through this Router.
Country Domain
Please select your country from the drop-down list.
Wireless Mode
You may choose from the menu to let your wireless network to operate in
a 802.11b, 802.11g, SuperG, or Mixed 11b/11g which is the default.
Channel Selection
Select a number from the drop-down list to specify which Channel the
Router will transmit and receive on. If another access point or Router
nearby is using the same Channel as you, there will be a reduction in the
performance of your network. If this seems to be the case, you should
select a different channel number. Usually the Wireless computers will
scan to find the correct channel, but if they don't you must configure
them to use the same Channel number as the Router.
Page 53

Wireless Settings 53
Choose the
Auto
option to automatically choose the clearest channel. The
Router will check for the clearest channel whenever it is rebooted,
powered up, and when the Clear Channel Select option is first applied.
Valid channels are country dependent. See “Regulatory Notices”
page 137
for a list of channels approved by each country.
on
Service Area Name/SSID
This allows you to name your Wireless network. The Service Area
Name/SSID field will accept any alphanumeric string and has a maximum
length of 32 characters. Your Wireless computers must be configured
with exactly the same name or you will not establish a connection. The
Service Area Name may also be referred to as “ESSID” depending on your
networking vendor. By default the Router uses the name “3Com”. 3Com
recommends that you change the default name.
In order that your wireless computers can connect to the Router, you
must:
■ Use Infrastructure Mode, not Ad hoc Mode.
■ Have the same Service Area Name as the Router.
■ Have the same Channel number as the Router.
■ Use the same encryption type and keys as the Router.
■ Ensure that the PC is not included in the denied Wireless PCs list if
Connection Control is enabled. See page 59
.
Enable Broadcast SSID
Disable this feature after you have installed your wireless network to
improve the security of your network. When the check box is checked,
the Router will broadcast the Service Area Name/SSID of your wireless
network, which reduces the security of your Router as it allows any
wireless client to see your wireless LAN.
If you have a wireless client that can detect all the available SSIDs in your
area, your client will not list the Router SSID unless this feature is enabled.
The clients will still be able to connect, provided that they are supplied
with the SSID.
3Com recommends that you install your wireless network with this
feature enabled and then disable it once you have set up the Router and
wireless clients.
Page 54

54 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Profile Support for NICs
You may save your wireless settings here by clicking Save Profile. Please
choose Save to Disk option when a dialog box opens. Thus, you may save
your wireless settings to an external file and later on use this file to import
the settings with supported 3Com Wireless Network Cards.
Encryption When setting up wireless networks, it is important to remember that with
encryption disabled, anyone with a Wireless PC can eavesdrop on your
network. 3Com recommends that you get the network working with
encryption disabled first and then enable it as the last step. This will
simplify setting up your network.
The Router supports the following types of encryption:
■ WPA/WPA2/Mixed WPA WPA2 — Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a
subset of the IEEE 802.11i standard. Both WPA and WPA2 use
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), Message Integrity Check (MIC)
and IEEE 802.11x. In addition to TKIP, WPA2 also uses Advanced
Encryption Standard (AES). The mixed mode will let you choose the
encryption mechanism interchangeably with either TKIP or AES.
■ WEP — Wireless Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a 64 bit or 128 bit
encryption method with user configurable fixed keys.
■ WPA+Radius/WPA2+Radius/Mixed WPA WPA2 +Radius features using
of a RADIUS server with the pre-shared key authentication method.
(This should only be used when a RADIUS server is connected to the
Router).
WPA and WPA2 provides a higher level of security, provided by its longer
key and dynamic changes made to the key over time. 3Com recommends
that you use WPA with any clients which support it.
If you enable encryption on the Router, you must reconfigure your
wireless PCs to use exactly the same Encryption Type and Keys otherwise
the devices will not understand each other.
The encryption methods used by the Router secure data transmitted
through wireless communications between the Router and its wireless
clients. Enabling encryption has no security effect on data transmitted
through wired (Ethernet) connections or through your connections to the
Internet.
Page 55

Wireless Settings 55
WEP
To enable WEP, select WEP from the Encryption Type.
Figure 33 Encryption — WEP
1 Please choose from 64 bits or 128 bits for the Encryption Strength.
2 Enter the Passphrase which can be up to 31 characters long and may
contain any alphanumeric characters in the field.
3 Click on Generate to generate 4 hex keys automatically. Virtually all
manufacturers support this scheme. Hexadecimal numbers are formed
from 0-9 and A-F. In 64 bit WEP, the passphrase will generate 4 different
However, in 128 bit WEP, this method only generates 1 key which is
keys.
replicated for all 4 keys.
4 Manually assign each key. If you selected 64 bits encryption, enter 10 HEX
characters (0-F) for each key. If you selected 128 bits encryption,enter 26
HEX characters (0-F) for each key.
If you encounter any difficulty when you enable WEP ensure that you
check that each key on your wireless computer is exactly the same as each
key on your Router. In other words, Key number 1 on the Wireless computer
must have the same Hex number as Key number 1 on the Router, Key 2 on
the Wireless computer must match Key 2 on the Router and so on.
5 Current WEP Key: Select a key to be the active key. You can change the
selected key periodically to increase the security of your network.
Page 56

56 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Click Save to save the setting.
WPA
To enable WPA, select WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK from the Encryption
Ty pe .
Figure 34 Encryption — WPA
1 Select either TKIP or AES as the Encryption Method.
2 Enter a passphrase between 8 to 63 characters long for the Pre-Shared
Key.
3 Enter the desired key renewal time in seconds for WPA Group Rekey
Interval.
Click Save to save the setting.
WPA with RADIUS
If you are using a RADIUS server in your network for authentication, you
may choose WPA or WPA2+ Radius from the Encryption Type.
Page 57

Wireless Settings 57
Figure 35 Encryption — WAP/WPA2 with RADIUS
1 Select Encryption Method from the drop-down box.
2 Enter the frequency for Group Rekey Interval in seconds..
3 Enter the RADIUS Server IP address.
4 Enter the RADIUS Port number.
5 Enter your RADIUS KEY here.
Click Save to save the setting.
WMM You can enable Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) support to help improve the
Quality of Service (QoS) for your wireless traffic.3Com recommends that
you leave the settings unchanged if you are not sure with your
configuration. Changing the values may lead to unexpected blockages of
traffic on your wireless LAN, and the blockages might be difficult to
diagnose.
WMM provides prioritized media access and is based on the Enhanced
Distributed Channel (EDCA) method. The WMM screen gives two
separate menus to set up the parameters; one is for Access Point and the
other one is for Wireless Stations.
Page 58

58 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Figure 36 WMM Screen
Typically, voice and video traffic types are delay-sensitive, but are tolerant
of some frame losses.On the other hand, data traffic type is
delay-tolerable, but requires loss-free transmission. So you may adjust
theses parameters with regard to the characteristics of these types of
data to better manage your network flow.
AC (Access Category): It uses 4 different ACs, from high to low:
VO:Voice, VI: Video, BE:Best Effort, BK: Background
AIFS (Arbitrary Interframe Space): An Interframe Space for different
Access Category
TXOP (Transmission Opportunity): WMM (Wireless Multimedia)
Transmission Opportunity: defined by IEEE 802.11e, the TXOP is the
interval of time when a particular STA (station) has the right to initiate
transmissions.
ACM (Admission Mandatory): Advertised in the EDCA parameter set
element to indicate the admission control is required for each of the ACs.
EDCA AP Paramenters:
Theses values of AIFS, CWmin, and CWmax are announced by the AP via
beacon frames. The AP can adapt these parameters dynamically
depending on the network conditions. Basically, the smaller AIFS and
CWmin, the shorter the channel access delay for the corresponding
Page 59

Wireless Settings 59
priority, and hence the more capacity share for a given traffic
condition.However, the probability of collisions increases when operating
with smaller CWmin. These parameters can be used in order to
differentiate the channel access among different priority traffic.
EDCA STA Parameters:
Each station maintains a Contention Window (CW), which is used to
select the random back off counter.The BC is determined as a random
integer drawn from a uniform distribution over the interval (0, CW).The
CW size is initially assigned CWmin, and increases when a transmission
fails, i.e., the transmitted data frame has not been acknowledged.After
any unsuccessful transmission attempt, another back off timer is
performed, with an upper bound of CWmax.This reduces the collision
probability in case there are multiple stations attempting to access the
channel.
CW min: should be smaller for delay-sensitive data
CW max: should be smaller for delay-sensitive data
AIFSN: should be smaller for delay-sensitive data
TXOPLimit: These will allow multiple MAC frames consecutively as
long as the whole transmission time does not exceed the TXOP limit.So
keep it larger for delay-sensitive data.
ACM: Admission Mandatory; could be turned on to mandatory
execution of the contention control.
Connection Control You can restrict certain wireless clients from accessing the router by
specifying their MAC address and enabling access restriction.
Page 60

60 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Figure 37 Connection Control Screen
To specify that only certain wireless computers can connect to the Router,
select allow/deny, and then enter the MAC addresses of the wireless
clients. You may enter a maximum of 64 PCs in the list.
Click Save to save your existing configurations or Cancel to discard all
changes.
Page 61

Client List Figure 38 Client List Screen
The Wireless Client List provides details on the devices that are connected
to the Wireless LAN. The list is only created when Wireless Networking is
enabled. For each device that is connected to the Wireless LAN, the MAC
address and Connection Speed of that device is displayed. As you
connect more devices to the Wireless LAN, the client list will grow to a
maximum of 64 (the maximum number of wireless devices that the
Router can support).
Wireless Settings 61
Advanced Wireless
Settings
The router provides some advanced wireless functionalities to let the
users better manage their wireless network.
Page 62

62 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Figure 39 Advanced Wireless Settings Screen
Authentication Type The default is set to Auto (Default), allows
either Open System or Shared Key authentication to be used. With Open
System authentication, the sender and the recipient do NOT use a WEP
key for authentication. With Shared Key authentication, the sender and
recipient use a WEP key for authentication.
Basic Rate The Basic Rate setting is not actually one rate of
transmission but a series of rates at which the Router can transmit. The
Router will advertise its Basic Rate to the other wireless devices in your
network, so they know which rates will be used. The Router will also
advertise that it will automatically select the best rate for transmission.
The default setting is Default, when the Router can transmit at all
standard wireless rates (1-2Mbps, 5.5Mbps, 11Mbps, 18Mbps, and
24Mbps). Other options are 1-2Mbps, for use with older wireless
technology, and All, when the Router can transmit at all wireless rates.
The Basic Rate is not the actual rate of data transmission. If you want to
specify the Router's rate of data transmission, configure the Transmission
Rate setting.
Transmission Rate The rate of data transmission should be set
depending on the speed of your wireless network. You can select from a
range of transmission speeds, or you can select Auto (Default) to have the
Router automatically use the fastest possible data rate and enable the
Page 63

Wireless Settings 63
Auto-Fallback feature. Auto-Fallback will negotiate the best possible
connection speed between the Router and a wireless client. The default
value is Auto (Default).
Transmission Power (Transmit Power Control) The greater the
transmission power used, the larger the area a wireless network covers.
To minimize the likelihood of eavesdropping by unauthorized wireless
users, do not use more transmission power than necessary to cover the
range needed by your wireless network. Try using the Router at different
levels of transmission power, and determine how much power is needed
to reach the wireless client, such as a PC or access point, that is farthest
from the Router. Then select the appropriate level, Full (Default), Half,
Quarter, Eighth, or Min, from the drop-down menu. The default is Full
(Default).
CTS Protection Mode CTS (Clear-To-Send) Protection Mode should be
set to Auto (Default). The Router will automatically use CTS Protection
Mode when your Wireless-G products are experiencing severe problems
and are not able to transmit to the Router in an environment with heavy
802.11b traffic. This function boosts the Router's ability to catch all
Wireless-G transmissions but will severely decrease performance. If you
do not want to use CTS Protection Mode at all, select Disabled.
XR Mode The Extended Range mode can be enabled to further extend
the wireless coverage to eliminate dead spots or corners in your office.
Frame Burst Mode Enabling this option should provide your network
with greater performance, depending on the manufacturer of your
wireless products. If you are not sure how to use this option, keep the
default, Enabled.
Beacon Interval The default value is 100. The Beacon Interval value
indicates the frequency interval of the beacon. A beacon is a packet
broadcast by the Router to synchronize the wireless network.
DTIM Interval This value indicates the interval of the Delivery Traffic
Indication Message (DTIM). A DTIM field is a countdown field informing
clients of the next window for listening to broadcast and multicast
messages. When the Router has buffered broadcast or multicast
messages for associated clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM
Interval value. Its clients hear the beacons and awaken to receive the
broadcast and multicast messages. The default value is 1.
Page 64

64 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Fragmentation Threshold This value specifies the maximum size for
a packet before data is fragmented into multiple packets. If you
experience a high packet error rate, you may slightly increase the
Fragmentation Threshold. Setting the Fragmentation Threshold too low
may result in poor network performance. Only minor reduction of the
default value is recommended. In most cases, it should remain at its
default value of 2346.
RTS Threshold Should you encounter inconsistent data flow, only
minor reduction of the default value, 2347, is recommended. If a
network packet is smaller than the preset RTS threshold size, the RTS/CTS
mechanism will not be enabled. The Router sends Request to Send (RTS)
frames to a particular receiving station and negotiates the sending of a
data frame. After receiving an RTS, the wireless station responds with a
Clear to Send frame to acknowledge the right to begin transmission. The
RTS Threshold value should remain at its default value of 2346.
Do not alter these parameters unless you understand the implications.
WDS WDS (Wireless Distribution System) is comprised of a bridging and/or a
repeater mode. The Router supports the Wireless Distribution System
(WDS) repeater mode. WDS repeating enables one or more Access Points
to rebroadcast received signals to extend range and reach, though this
can affect the overall throughput of data.
Page 65

Internet Settings 65
Figure 40 WDS Screen
To setup a WDS, make sure that the following conditions are met for all
of the linked APs:
1 Both AP's WDS should be enabled.
2 APs are configured with the same Channel, SSID and Encryptions.
3 Each AP should have a different IP Address.
Internet Settings Before you can configure the Router, you need to know the IP
information allocation method used by your ISP. There are five different
ways that ISPs can allocate IP information, as described below:
1 PPPoA (PPP over ATM)
The ISP provides the IP addressing information for you to enter manually.
To configure the Router you will need to know the following:
■ User name
■ Password
■ Authentication Method
Page 66

66 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
2 PPPoE
PPP over Ethernet, provides routing for multiple PCs, this mode is often
used for the DSL connection. To configure this function correctly, you should
obtain the information from your ISP.
3 Dynamic/Fixed IP in 1483 Bridge Mode
In this mode of connection, your ADSL router simply acts like a modem
but can also carry multiple upper-layer protocols such as IP, IPX, and
NetBIOS. Please consult your ISP for the necessary configuration
information.
4 IPoA (IP over ATM)
It is a technique which transmits IP packets over the ATM network. Please
consult your ISP for the necessary configuration information.
5 Bridging Mode
In this mode, your ADSL router simply acts like a modem when
connecting to the internet. Thus, you may have seperate DSL connections
behind via a computer or router. Enter the following parameters in the
configuration:
VPI: Virtual Path Identifier(from 0 to 255), which is assigned by your ISP.
VCI: Virtual Channel Identifier(from 32 to 65535), which is assigned by
your ISP.
Encapsulation Mode: Select from either VC or LLC.
Firewall On the main frame of the Firewall setup screen is a menu with eight tabs:
Virtual Servers, Special Applications, DMZ, SPI, PC Privileges, Schedule
Rules, Content Filter, and URL Filter.
Virtual Servers Selecting the Firewall option on the main menu displays the Virtual
Servers setup screen.
Page 67

Figure 41 Virtual Servers Screen
Firewall 67
Virtual Server
Activating and configuring a virtual server allows one or more of the
computers on your network to function as a public server. For example,
one of your computers could be configured as an FTP server, allowing
others outside of your office network to download files of your choosing.
Or, if you have created a Web site, you can configure one of your
computers as a Web server, so that others can view your Web site.
To configure a virtual server:
1 Select an application from the drop-down menu or fill in the blank fields
to specify your own application.
2 The port(s) that will be used will be shown for a common application or
you may enter the port numbers required for that service if it is not
pre-defined.
3 Enter the last digit of the LAN server IP address.
4 Click Apply to apply the changes.
The port numbers are specified using a comma-separated list, with dash
to denote port number ranges. So for example, entering 2, 3, 5-7 would
cause ports 2, 3, 5, 6, and 7 to be activated.
Page 68

68 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Special Applications Figure 42 Special Applications Screen
Some software applications require special or multiple connections to the
Internet and these would normally be blocked by the firewall. For
example Internet Telephony or Video conferences require multiple
connections.
So that these special applications can work properly and are not blocked,
the firewall needs to be told about them. In each instance there will be a
trigger port and incoming port(s), where traffic on the trigger port tells
the firewall to open the incoming ports.
Each defined Special Application only supports a single computer user,
and up to32 Special Applications can be defined. Any incoming ports
opened by a Special Application trigger will be closed after five minutes
of inactivity.
To configure special applications:
1 Click Add to open the Special Applications screen.
2 Select an application from the drop-down menu or enter the application
name.
3 Enter the Triggered port and the forwarded range in the text boxes.
4 Select the Enabled box to make it activated.
Page 69

Firewall 69
5 Click Apply to save the configuration and apply the changes.
The Router will automatically allow FTP and NetMeeting sessions. You do
not need to configure these as Special Applications.
Only one computer on your network can use the special application at
any one time.
DMZ
Figure 43 DMZ Screen
DMZ (De-Militarized Zone) Host is a computer without the protection of
the firewall. This feature allows a single computer to be exposed to
unrestricted 2-way communication from outside of your network. This
feature should be used only if the Virtual Server or Special Applications
options do not provide the level of access needed for certain applications.
Single DMZ
To configure one of your computers as a DMZ host, enter the IP address
of the computer in the DMZ Host IP Address, and then click Save/Apply.
Multiple DMZ
You may enable the multiple DMZ function if you have more than one
registered public IP assigned to your server. Please enter the Public IP
Page 70

70 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Address and the corresponding LAN IP Address in the fields and click Add
to add the Entry. Click Apply/Reboot to apply your settings.
SPI Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) inspects, and if required blocks packets at
the application layer. SPI also maintains TCP and UDP session information,
including timeouts and the number of active sessions, and provides the
ability to detect and prevent certain types of network attacks such as DoS
attacks.
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks are aimed at devices and networks with a
connection to the Internet. The goal is not to steal information, but to
disable a device or network so users no longer have access to network
resources.
To configure SPI information on your Router:
1 Select Firewall from the main menu, then select the SPI tab to display the
SPI screen:
Figure 44 SPI Screen
Intrusion Detection: Check on the box to enable the Stateful Packet
Inspection (SPI), Hacker Pattern detection and Denial of Services(DoS)
features to further guard your networks from internet attacks.
Page 71

Firewall 71
Email Alert:: Use this feature if you want the router to send you an email
if a DoS attack has attempted.
Connection Policy: These settings determine the timeouts between the
router’s recognizing and blocking DoS attempts before allowing
legitimate traffic using these protocols to be permitted.
Do not adjust these settings unless you are confident in your reconfigured
settings.
ALG: Check this box if you use a SIP phone with the router.
PC Privileges
Figure 45 PC Privileges Screen
Select PC Privileges to display the PC Privilege setup screen.
Access from the local network to the Internet can be controlled on a
computer-by-computer basis. In the default configuration the Router will
allow all connected computers unlimited access to the Internet.
PC Privileges allows you to assign different access rights for different
computers on your network.
Page 72

72 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
To use access control for the computers:
1 Enter the PC’s description and the range of the ip addresses.
2 Select to bypass the URL or Content Filter if you would like the clients to
bypass the rules.(Please refer to the URL or Content Filter tab)
3 Please select to block specific services or protocols.
4 You may also block additional ports by listing the port range in the User
Defined Blocked Ports.
5 To apply a time schedule to the rule, set up a schedule rule on the
Scheduled Rules tab, and then select the named rule in the pull-down list.
6 Click Save to save the settings or Cancel to discard them.
To assign different access rights for different computers, click Add PC at
the PC Privileges screen. You can create up to 10 policies.
Schedule Rules You can also schedule when PCs can access the Internet. By default, all
PCs can access the internet all day, every day. The Schedule Rules work in
conjuction with the PC Privileges so you can schedule when PCs can
access the Internet.
To add the schedule:
Page 73

Figure 46 The Schedule Rules Screen
1 Click Add Rule at the Schedule Rules screen.
Firewall 73
2 Enter the Schedule name and give a brief description.
3 Check the appropriate check box for each day you want to block access,
and enter the times for each day in 24-hour clock format.
Content Filter You can subscribe to the 3Com Content Filter Service, which enables you
to block or allow the URLs of a number of pre-defined categories.
The Router comes with a 14-day free trial of the 3Com Content Filter
Service. To activate the 14-day free trial of the service, you must first
register your Router at
www.3com.com. To continue using the service after
the trial period, you must purchase the full 3Com Content Filter Service
(3CSBCFS).
URL filtering rules supersede content filtering rules. If the 3Com Content
Filter is blocking certain Web sites that you want to allow, you can add
these sites to URL Filter’s allow list.
Page 74

74 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
To activate Content Filtering:
1 Select Firewall from the main menu, then select the Content Filter tab.
The Content Filter screen displays.
Figure 47 Content Filter Screen
2 Make sure the Enable Content Filter check box is checked.
3 Select the Content Filter Server that you require from the drop-down list.
If you select custom entry, enter the server IP address in the text box.
4 Select the Server Timeout value in milliseconds. The default is 3000
milliseconds (3 seconds).
5 Select Allow or Deny for each displayed category, as required.
Click Save To Save The Changes and Apply to apply The Settings.
URL Filter Select the URL Filter tab to set the websites that you want your clients to
be able or not able to access.
Page 75

Figure 48 The URL Filter Screen
To enable the URL Filtering, please do the following:
Firewall 75
1 Check the Enable URL Filtering Function box to enable the URL
filtering.
2 Enter the URL or key words of the URL in the text field for your desired
website.
To filter a specific site, enter the URL for that site. For example, to stop
your users from browsing a site called www.badsite.com, enter
www.badsite.com or badsite.com in one of the fields.
If badsite.com has multiple sub-domains, such as this.badsite.com and
that.badsite.com then you can either:
■ Block them individually by entering this.badsite.com in one field
and that.badsite.com in another.
■ or
■ Block them by entering the keyword badsite.com into one of the
fields. This will block all URLs containing the string badsite.com. As
well as blocking this.badsite.com and that.badsite.com, the
keyword badsite.com would block searches that mentioned
badsite.com in their domain name, for example
www.notabadsite.com.
Page 76

76 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
To filter a generic keyword enter it into one of the fields. You should
exercise caution when choosing a keyword as many keywords are
contained within other words. For example, filtering the word sex would
filter the following example URLs:
■ www.sussex.com
■ www.thisexample.com
You can filter up to 30 keywords and URLs.
3 Please select from the mode to whether allow or deny the URL.Since URL
Filter supersedes Content Filter, you may list your allowed URL here.
The Router filters all traffic from domains that have been blocked using
the URL filter. If you need to access an external mail server, FTP server or
other named device outside your network, you must list it in one of the
allow fields.
Computers that should not be subject to URL filtering can be excluded by
listing them as the full access PC's IP Addresses in the Filter Policy Tab.
System Tools The main frame of the System Tools screen includes four administration
items: Restart, Time Zone, Configuration, and Upgrade .
Page 77

Restart Figure 49 Restart Screen
If your Router is not operating correctly, you can choose to restart the
Router by selecting Restart the Router, simulating the effect of power
cycling the unit. No configuration information will be lost but the log files
will be erased. This function may be of use if you are experiencing
problems and you wish to re-establish your Internet connection. Any
network users who are currently accessing the Internet will have their
access interrupted whilst the restart takes place, and they may need to
reboot their computers when the restart has completed and the Router is
operational again.
System Tools 77
Page 78

78 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Time Zone Figure 50 Time Zone Screen
Choose the time zone that is closest to your actual location. The time
zone setting is used by the system clock when displaying the correct time
in the log files.
If you use Daylight saving tick the Enable Day Light savings box, and then
click Save.
The Router reads the correct time from NTP servers on the Internet and
sets its system clock accordingly. The Daylight Savings option merely
advances the system clock by one hour. It does not cause the system
clock to be updated for daylight savings time automatically.
Page 79

Configuration Figure 51 Configuration Screen
Select the Configuration tab to display the Configuration screen.
System Tools 79
Backup Configuration
Click BACKUP to save the current Router configuration. You will be
prompted to download and save a file to disk.
Restore Configuration Data
If you want to reinstate the configuration settings previously saved to a
file, press Browse to locate the backup file on your computer, and then
click RESTORE to copy the data into the Router's memory.
The password will remain unchanged.
Reset to Factory Default
If you want to reset the settings on your Router to those that were loaded
at the factory, click RESET. You will lose all your configuration changes.
The Router LAN IP address will revert to 192.168.1.1, and the DHCP
server on the LAN will be enabled. You may need to reconfigure and
restart your computer to re-establish communication with the Router.
Page 80

80 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Upgrade Figure 52 Upgrade Screen
The Upgrade facility allows you to install on the Router any new releases
of system software that 3Com may make available. To install new
software, you first need to download the software from the 3Com
support web site to a folder on your computer. Once you have done this,
select Browse to tell your web browser where this file is on your
computer, and then click Apply. The file will be copied to the Router, and
once this has completed, the Router will restart. Although the upgrade
process has been designed to preserve your configuration settings, it is
recommended that you make a backup of the configuration beforehand,
in case the upgrade process fails for any reason (for example, the
connection between the computer and the Router is lost while the new
software is being copied to the Router).
The upgrade procedure can take up to four minutes, and is complete
when the Alert LED has stopped flashing and is permanently off. Make
sure that you do not interrupt power to the Router during the upgrade
procedure; if you do, the software may be corrupted and the Router may
not start up properly afterwards. If the Alert LED comes on continuously
after a failed upgrade, refer to Chapter 6
, “Troubleshooting”.
Page 81

Advanced 81
Advanced Selecting Advanced from the main menu displays the following seven
tabs in your Web browser window: Static Route, RIP, DDNS, Quality of
Service, ProxyARP, Port Mapping, and IPSec.
Static Route The Router supports static route functionality. Select the Static Route tab
to display the screen.
Figure 53 Static Route screen
Please enter the following values in the box respectively to specify a static
route:
■ Network Address — the network address of the route. If network
address and subnet mask are both set to 0.0.0.0, this is the default
route.
■ Subnet Mask — the subnet mask of the route. If network address and
subnet mask are both set to 0.0.0.0, this is the default route.
■ Gateway — the gateway used to route data to the network specified
by the network address.
■ The network interface associated with the IP address.
RIP The Router supports the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). RIP allows
you to set up routing information on one RIP enabled device, and have
Page 82

82 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
that routing information replicated to all RIP enabled devices on the
network. LAN and WAN interfaces can be configured independently of
each other.
Select the RIP tab to display the screen.
Figure 54 RIP screen
Setting Up RIP
Check the Enable RIP Mode check box if you want the Router to start
routing via RIP.
1 Select either 1 (for RIPv1) or 2 (for RIPv2) from the Version drop-down list.
2 Select from either Passive or Active in the Operation drop-down list. If you
select Active, the Router transmits RIP update information to other RIP
enabled devices. If you select Passive, the Router only receives RIP update
messages.
3 Check to Enable the process.
DDNS Dynamic Domain Name Server (DDNS) enables you to map a static
domain name to a dynamic IP address. The Router supports five DDNS
providers, TZO.com, DYNDNS.org, Zoneedit, NO-IP, DtDns. Before you
can set up DDNS, you must obtain an account, password and static
domain name from your DDNS provider. DDNS is disabled by default.
Page 83

Advanced 83
To set up DDNS:
1 Select Advanced from the main menu, then select the DDNS tab. The
DDNS screen displays.
Figure 55 DDNS screen
2 Select a DDNS Service provider from the drop-down list. This can be
TZO.com, DynDNS.org, DtDns, NOIP or Zoneedit.com.
TZO.com
If you select TZO.com:
1 In the Domain Name text box, enter the domain name.
2 In the Username/E-mail text box, enter the account name.
3 In the Key text box, enter the account password.
4 In the Refresh Time box, enter how often you want the service to
automatically refresh, in days. The default is three days.
5 Click Apply to make this service active.
DynDNS.org/DtDns.com/Zoneedit.com
If you select DYNDNS.org, DtDns, or Zoneedit.com:
1 In the Host Name text box, enter the host name.
2 In the Username text box, enter the account name.
Page 84

84 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
3 In the Password text box, enter the account password.
4 Click add to add your DDNS.
NOIP.com
1 In the Host Name text box, enter the host name.
2 In the E-mail text box, enter the account name.
3 In the Password text box, enter the account password.
4 Click save to save the changes and Apply to make this service active.
Quality of Service
Figure 56 QoS Screen
This screen lists the QoS classifiers or policy. A classifier groups upstream
traffic into data flows according to specific criteria such as the source
addresses, destination addresses, source ports or destination ports. The
policy also assigns a specific Priority queue, DSCP mark or ToS value.
Please enter your settings into the fields provided.
Please do not alter any settings unless you are an experienced network
administrator.
Proxy ARP Proxy ARP is a variation of Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), in which an
intermediate device (in this case, the Router) sends an ARP response on
behalf of an end node to the requesting host. Proxy ARP can help
Page 85

Advanced 85
decrease bandwidth consumption on slow-speed WAN links and allows a
site to use a single IP address for two physical networks.
To use proxy ARP, you must have a range of static IP addresses assigned
by your ISP.
Figure 57 The Proxy ARP Screen
To configure Proxy ARP:
1 On the menu, click Advanced.
2 Click the Proxy ARP tab.
3 Select the Enable Proxy ARP check box.
4 Enter the static IP addresses that your ISP has given to you.
5 Click Save to save your changes.
IPSec Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a standards-based VPN that offers
flexible solutions for secure data communications across a public network
like the Internet. The Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a popular
technology used for communications between two networking sites
without the expense of leased site-to-site lines.
Page 86

86 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Figure 58 The IPSec Screen
Below is a description of the basic configuration parameters:
IPSec Connection Name: Please enter a name to define your
connection.
Remote IPSec Gateway Address: This is the static WAN IP address or
URL of the remote IPSec router.
Tunnel Access from Local IP Addresses: Select if you want to create a
tunnel access for a single computer or a subnet.
IP Address/Subnetmask for VPN: If you choose a single computer from
the above, please enter the local computer’s IP Address; otherwise, enter
a subnet and the corresponding subnetmask in the field provided.
Tunnel Access from Remote IP Addresses: Select if you want to create
a tunnel access with the remote site for a single computer or a subnet.
IP Address/Subnetmask for VPN: If you choose a single computer from
the above, please enter the remote computer’s IP Address; otherwise,
enter a subnet and the corresponding subnetmask in the field provided.
Page 87

Advanced 87
Key Exchange Method: Select IKE or Manual from the drop-down list
box. Manual is useful for troubleshooting when you have problems using
IKE key management.
Pre-Shared Key: Type your pre-shared key in this field. Enter 8 to 31
case-sensitive ASCII characters. Both routers which would build a VPN
tunnel must use the same pre-shared key.
Port Mapping Port Mapping supports multiple ports to PVC and bridging groups. Each
group will perform as an independent network. To support this feature,
you must create mapping groups with appropriate LAN and WAN
interfaces using the Add button. The Remove button will remove the
grouping and add the ungrouped interfaces to the Default group.
Figure 59 The Port Mapping Screen
To create a new mapping group:
Enter the Group name and select interfaces from the available interface
list and add it to the grouped interface list using the arrow buttons to
create the required mapping of the ports. The group name must be
unique. A maximum 16 entries can be configured.
Click Apply to make the changes effective immediately.
Page 88

88 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Do not alter any settings unless you are an experienced network
administrator.
Management The management Screen lets you administer your routers with features
such as System Log, SNMP, UPnP, Trust Station, Remote Management,
and Utility.
Syslog If you have a syslog server on the network, you can configure the Router
Point to send the device logs to the server.
You may need to configure the syslog server to accept logs from the
Router.
Page 89

Figure 60 The System Log Screen
To view the current logs:
Management 89
1 Click the View Log button.
To enable the system log:
1 Check Enable System Log box.
2 Select the drop-down menu for a list of available types of logging
activities.
3 Select the Display Level for a list of available types of logging display.
Select Select on the Mode for logging mode: Local, Remote, or Both. For
the remote logging, enter the remote server’s IP address and Port number
for receiving the logs.
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is the protocol used for
exchanging management information between network devices.
Page 90

90 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Figure 61 The SNMP Screen
Click Enable/Disable to enable/disable the agent.
To Configure the SNMP:
1 Type the Read Community, which is the password for the incoming Get
and GetNext requests from the management station.
2 Type the Set Community, which is the password for incoming Set requests
from the management station
.
3 Type the System Name for the program.
4 Type the System Location for the program.
5 Type the System Contact for the Contact person’s name.
6 Type the IP Address of the station/device for sending your SNMP traps
to.
7 Click Apply.
UPnP Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is a distributed, open networking standard
that uses TCP/IP for simple peer-to-peer network connectivity between
devices. UPnP compatible devices can dynamically join a network and
learn about other devices on the network. UPnP hardware will be shown
in the Network Connections folder in Windows XP.
Page 91

Figure 62 The UPnP Screen
Check UPnP Enabled to activate UPnP.
Management 91
Trusted Station
Figure 63 The Trusted Station Screen
The Trusted Station Screen lets you add/remove the MAC address of the
stations which can access the web administration.
Page 92

92 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Remote Management It is possible to administer the Router remotely. Select one of the
following options for remote administration:
Figure 64 The Remote Management Screen
■ Disable Remote Administration — This option is set as default.
■ Enable administration from a single Internet Host — Only the
specified Host IP Address can manage the Router. Any other users will
be rejected.
■ Enable administration from a whole subnet — This option allows a
number of users within the specified Host Network Address and
Subnet Mask to administer the Router.
■ Enable administration from any Internet Host — This option allows
any host to access the administration pages.
To remotely administer your Router, enter http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8000
in the location bar of the browser running on the remote computer,
where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the Internet IP address of the Router. You may
then login using the administration password.
Your Internet IP address can be found at the bottom of the screen.
Utility The utility screen will let you execute some commands to test your
internet connections.
Page 93

Figure 65 The Utility Screen
To use the utility:
Diagnostics 93
1 Select commands that you would like to run from the menu.
2 Enter the IP Address or Domain Name in the field provided.
3 Click Start to start executing the command.
4 The results will be shown on the screen below.
Diagnostics The Diagnostics Screen lets you diagnose your DSL connection to the
internet and your wired and wireless LAN networkings. Click on the Test
button to start testing.
Page 94

94 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Figure 66 The Diagnostics Screen
Device Info The Device Info Settings menu provides the following options:
Page 95

Summary Figure 67 The Summary Screen
The Summary screen is used to display the information of your LAN
status.
Device Info 95
WAN Figure 68 The WAN Screen
The WAN Status Screen is used to display the information of your DSL
Connection Status.
Page 96

96 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Statistics Figure 69 The Statistics Screen
The Statistics Screen is used to display the information of your
LAN/WAN/ATM/ADSL Connection Statistics. Click on the button for each
connection device for more detailed information.
Page 97

Route Figure 70 The Route Screen
The Route Screen is used to display the routing status/information.
Device Info 97
ARP
Figure 71 The ARP Screen
The ARP screen is used to display the ARP status.
Page 98

98 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Support/Feedback Selecting Support/Feedback from the main menu displays the Status,
Logs, Routing Table, and Syslog screens in your Web browser window.
Support/Feedback Selecting Support/Feedback from the main menu displays the Support
and Feedback screens.
Support Figure 72 Support Screen
Selecting the Support option on the main menu displays the support links
screen, which contains a list of Internet links that provide information and
support concerning the Route.
Page 99

Feedback Figure 73 Feedback Screen
Selecting the Feedback option displays the Feedback screen and allows
you to provide feedback to 3Com on the operation of your Router. This
screen should not be used to obtain technical support.
Support/Feedback 99
Page 100

100 CHAPTER 5: ROUTER CONFIGURATION
 Loading...
Loading...