Page 1
3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
Monochord U8431216
Instruction sheet
02/08 ALF
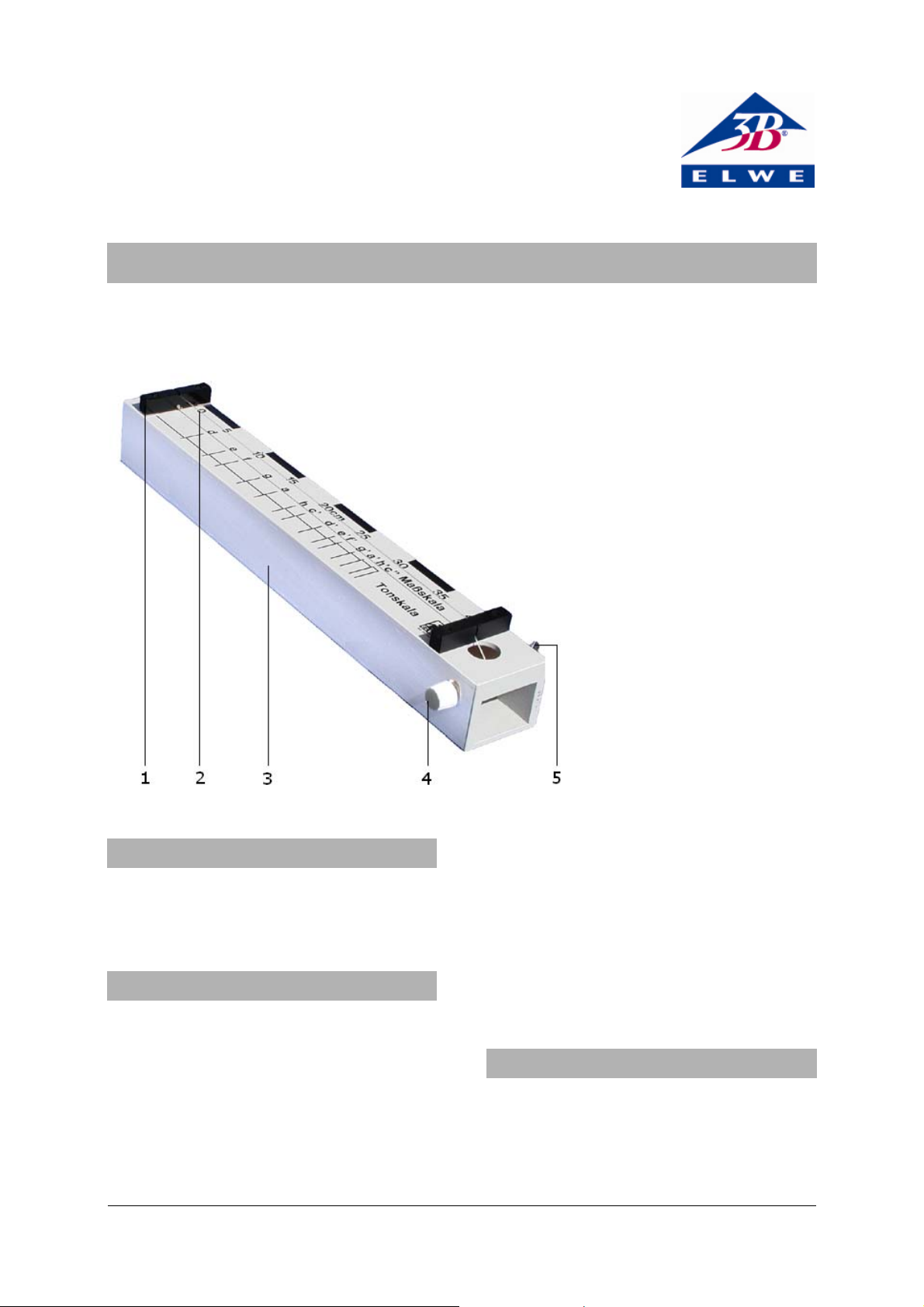
1 Fixed bridge
2 String
3 Resonator
4 Knurled screw
(tuning peg)
5 Wing screw
1. Safety instructions
Be careful not to apply too much tension to the
string. The string might snap and cause injury.
• Do not bend over the resonator while using the
monochord.
2. Description
The monochord is used to demonstrate the relation
between the pitch of vibrating strings and their
tension, thickness and length.
The monochord consists of a wooden box open on
both ends, upon which a steel or nylon string is
held tight at one end. The tension of the string can
be adjusted at the other end by means of a knurled
screw that is used as the tuning peg. The length of
the string can be varied by moving a bridge. One
scale for measuring length and a musical scale are
printed on the resonator box.
2.1 Scope of delivery
1 Resonator
1 Bridge
1 Steel string (B string)
1 Nylon string (B string)
1 Dynamometer
3. Technical data
Resonator box: 490 x 70 x 60 mm3
Scale length: 600 mm
Scale divisions: in cm
Weight: 0.6 kg approx.
1
Page 2
4. Operation
Additionally required:
Tuning forks
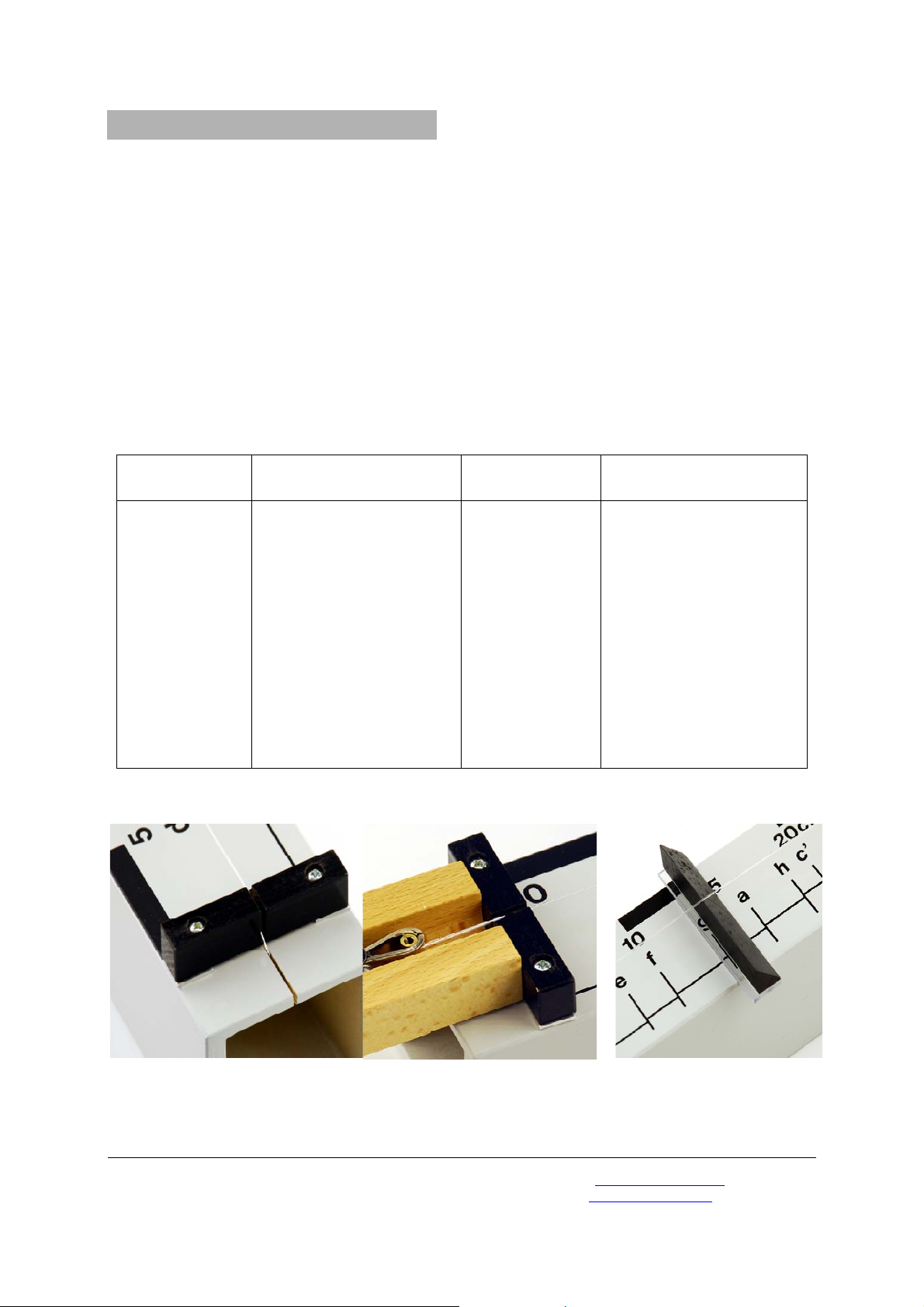
• Fit the string onto the monochord. To do this,
fit the string into the slot at the left-hand end
of the instrument by means of the small metal
ring and push the free end through the peg
fig. 1).
(
• While tightening the peg, tune the string with
the help of a tuning fork. Fix the peg with the
wing screw.
• Make the string vibrate either by plucking it or
bowing it.
• Adjust the desired string length by carefully
shifting the bridge and take the reading off the
length scale (fig. 3).
• In order to change the tension on the string,
slightly loosen the wing screw and set the
string tension with the help of the knurled
screw. Subsequently tighten the wing screw.
• In order to determine the tension of the string,
attach the dynamometer to the monochord
and insert the end of the string into the slot of
the dynamometer (fig. 2).
The following relations between the string lengths result in a major scale:
Notation of notes Frequency ratios
Intervals Ratios of string lengths
Key note : higher note
C : C
C : D
C : E
C : F
C : G
C : A
C : H
C : C`
C : G`
C : C``
C : E``
C : G``
1 : 1
8 : 9
4 : 5
3 : 4
2 : 3
3 : 5
8 : 15
1 : 2
1 : 3
1 : 4
1 : 5
1 : 6
Prime
Second
Major third
Fourth
Fifth
Major sixth
Major seventh
Octave
Key tone : higher tone
1 : 1
9 : 8
5 : 4
4 : 3
3 : 2
5 : 3
15 : 8
2 : 1
3 : 1
4 : 1
5 : 1
6 : 1
Fig 1
Fig. 2
Elwe Didactic GmbH • Steinfelsstr. 6 • 08248 Klingenthal • Germany • www.elwedidactic.com
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Germany • www.3bscientific.com
Subject to technical amendments
© Copyright 2008 3B Scientific GmbH
Fig. 3
 Loading...
Loading...