Page 1

Sports and Fast-pacedSports and Fast-paced
Sports and Fast-paced
Sports and Fast-pacedSports and Fast-paced
Event Photography with theEvent Photography with the
Event Photography with the
Event Photography with theEvent Photography with the
Olympus CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RSOlympus CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS
Olympus CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS
Olympus CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RSOlympus CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS
Page 2

Olympus America, Inc.
Two Corporate Drive
Melville, N.Y. 11747-3157
Copyright 2000 Olympus America Inc. are registered trade marks of Olympus Inc.
Page 3

ForewordForeword
Foreword
ForewordForeword
This technology paper is provided to illustrate the technical advances that enable fastpaced action and event photography with the Olympus’ CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS
and to demonstrate how these technical advances can benefit professional and serious
amateur digital photographers.
The CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS SLR (single lens reflex) is specifically targeted by
Olympus to professionals and serious amateur digital photographers and offers “best of
class” features such as a 10x aspherical optical zoom lens, (equivalent to a 380mm
lens), a innovative pre-capture image caching mode and 15 frames per second burst
capability. It also features image stabilization to steady the lens and a precision electronic viewfinder.
Up until now, most digital camera manufacturers have tried to produce digital cameras
that in many ways mimic traditional film cameras, especially with pro or prosumer digital
cameras. The introduction of the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS represents a unique circumstance in which Olympus has purposely pushed the technology envelope to provide
features that specifically address the critical needs of sports and fast-paced event digital
photographers, an industry first.
The E-100 ZOOM RS includes a bevy of “digital-specific” features that go well beyond
the capabilities of traditional professional quality film cameras. After all, why go digital if
you aren’t allowed to utilize the efficiencies of digital processes to their fullest extent?
We invite you to read further about the uniquely “digital-specific” features of the CAMEDIA
E-100 ZOOM RS SLR and how it allows fast-paced event and sports photography to be
even better.
John Knaur
Olympus America, Inc.
For More Information about the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS SLR go to:
http://e-100rs.olympus.com
For More Example Photographs for the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS go to:
http://www.camediagallery.com
1
Page 4
Digital Camera OverviewDigital Camera Overview
Digital Camera Overview
Digital Camera OverviewDigital Camera Overview
The worldwide adoption of digital photography in the past
four years has simply been astounding and dwarfs the adop-
tion growth rate of other entrenched devices such as inkjet
printers and scanners. By 2002, consumer digital cameras
will surpass flatbed scanners in yearly adoption and this will
have taken just 7 years in comparison to 12 years for flatbed
scanners to reach this equivalent adoption rate. The world-
wide forecast now puts consumer digital camera shipments
at over 50 million units by 2005. It took PC’s over 14 years to
reach this level of penetration. By comparison, digital cam-
eras will reach this same penetration in 9 years.
In 1999 alone, worldwide consumer digital camera shipments,
excluding toy cameras exceeded 5.8 million units and repre-
sented over $2.9 billion in street valued revenue. In the U.S.,
unit shipments exceeded 2.5 million representing over $1.3
billion in street valued revenue with a projected five-year com-
pound average growth rate, (CAGR) out to 2005 of 39.8%. (All
sources: Imerge Consulting Group - 2000)
and color science, all working in tandem to provide users
sharper, more accurate images.
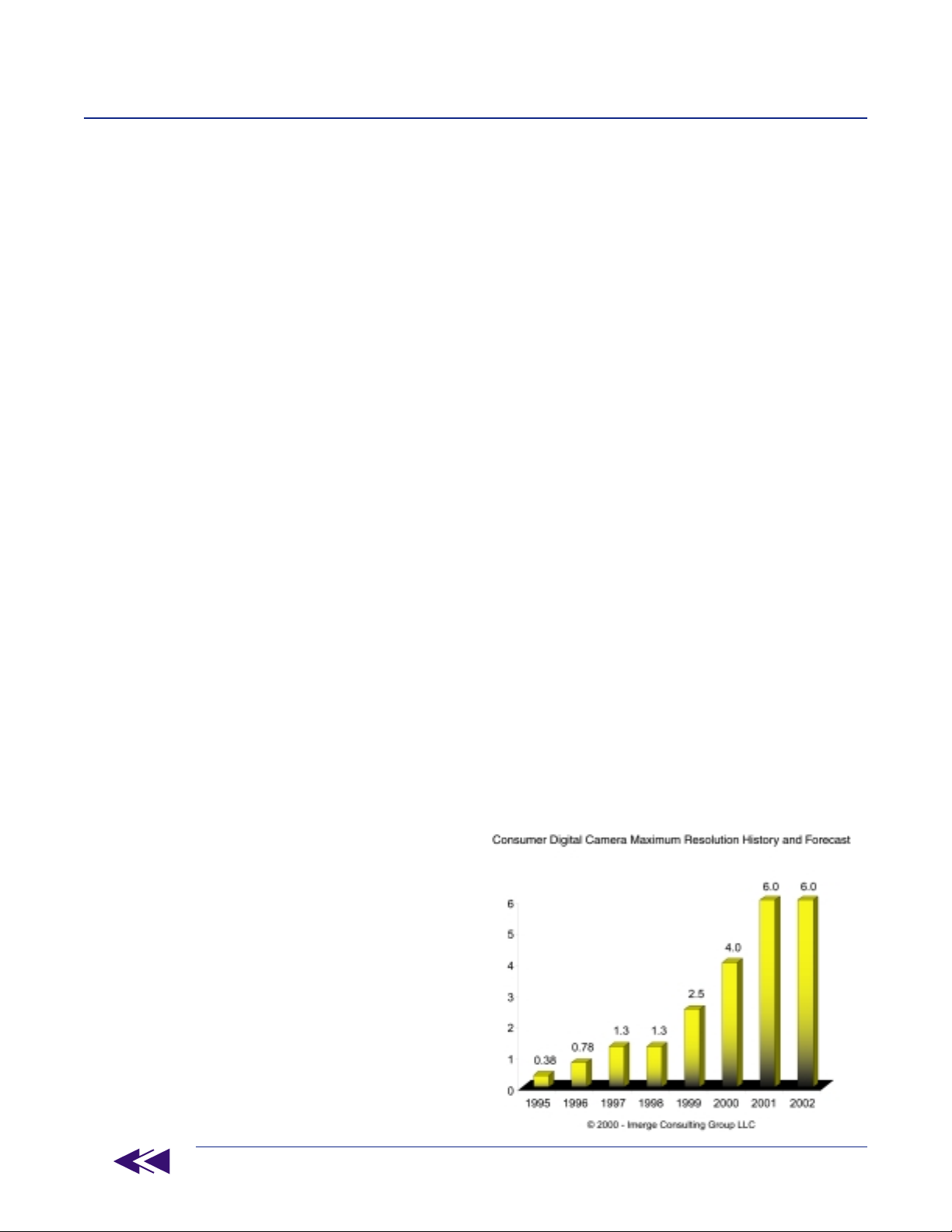
Olympus again led the third plateau of adoption with the intro-
duction of 1.3 mega-pixel resolution in a consumer digital
camera. This resolution would later become the industry
benchmark for representing “photo-quality”. Photo-quality
images are simply the equivalent in image quality to a con-
sumer film camera when output to a 4” x 6” print on photo-
grade paper. But resolution alone cannot provide photo-qual-
ity images. It is the resolution provided by the CCD sensor in
tandem to the camera’s internal opto-electronics and entire
optical path.
The Move to Digital Specific Attributes
Currently the state of digital camera development is entering
a new era driven by higher resolutions and advanced feature-
sets which move digital cameras beyond the capabilities of
film cameras by using “digital specific” attributes. In-fact, from
Plateaus of Adoption
Unit shipments and revenue only tell part of the dynamic story
of digital cameras. The adoption of digital cameras has oc-
curred in stages or plateaus, driven entirely upon technical
advances. The first plateau occurred with the introduction of a
viewable color LCD, providing instant gratification to consum-
ers in 1995.
With the second plateau of adoption in 1996, Olympus set
out to move digital cameras away from being just novelty
products for viewing images, to products people could actu-
ally benefit from, by providing the industry’s most regarded
“optical path”. The optical path is a combination of lens qual-
ity, internal opto-electronics, image processing (algorithms),
2
1995, (the first year consumer digital cameras were intro-
duced) until present, digital camera resolutions have in-
creased at a phenomenal average rate of 45.8%.
Page 5

As digital cameras move well above the “photo-quality” bench-
cameras that are produced to meet the specific needs of
mark, resolutions are a driving attribute but not the principal
driver for adoption. Rather it is these aforementioned “digital
specific” attributes that will compel consumers and profes-
sionals to purchase digital cameras over film cameras.
Olympus again is among the first to recognize this shift and
has begun a new phase of design and development of digital
New 10x Optical Zoom LensNew 10x Optical Zoom Lens
New 10x Optical Zoom Lens
New 10x Optical Zoom LensNew 10x Optical Zoom Lens
with Image Stabilizationwith Image Stabilization
with Image Stabilization
with Image Stabilizationwith Image Stabilization
The CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS’s optical lens and image
stabilization is designed to be digitally specific for action,
sports and fast-paced event photography. The new 10x
photographers using “digital specific” processes. One of
these categories among professional and prosumers is ac-
tion, sports and fast-paced event photography. As you will
see by reading further, the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS and its
unique capabilities specifically address the needs of this
category of photographers like no other digital camera on the
market, at any price point.
create compactions of foreground to background and con-
trol selective depth-of-field that would be otherwise impos-
sible with shorter focal length lenses.
optical zoom, which is a 6.4-70mm in digital lens terms,
(equivalent to 35mm-380mm in traditional 35mm film pho-
tography) is one of the industry’s first 10x zoom lens in an
affordably priced digital camera. The CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM
RS’s back-saving weight is just over 1-1/3 lb. compared to
a professional film camera and lens assembly of equiva-
lent focal length weighing in at about 25 lb.
Expanded Focal Length Means More
Creativity, Greater Control
This extension of the focal length out to an equivalent 380mm
allows digital photographers to compose images that were
impossible in the past. In many circumstances, a sports
photographer cannot be right next to the subject matter.
This new expanded focal length lens allows the photogra-
pher to pull the subject into range, shoot tighter images,
Walter Urie, a southern California commercial photogra-
pher for 20 years recently used the CAMEDIA E-100
ZOOM RS for a series of on-location shoots in Moab, Utah.
Walter specializes in annual report and advertising pho-
tography on-location and has used a number of digital and
film cameras for his work. Walter’s award winning images
have been featured in Communications Arts Magazine and
he currently teaches photography at Orange Coast Col-
lege. He has worked with Mercedes Benz, Isuzu, 3Com
and many others.
Walter Urie talks about his experiences with the CAMEDIA
E-100 ZOOM RS on location, “This camera and lens com-
bination allowed me to compose images that would other-
wise have been impossible. I’ve never used a still camera
with this kind of zoom range. It was incredibly useful. It
3
Page 6

Pre-capture ModePre-capture Mode
Pre-capture Mode
Pre-capture ModePre-capture Mode
zoomed very smoothly and fluidly. One of the difficulties I’ve
encountered when using other digital cameras is the short
focal length zoom lens allows you to have tremendous
depth-of-field. Conversely, if you want or need a selective
depth-of-field, it’s difficult to get that with other digital cam-
eras. With this lens’ ability to zoom out so far, selective
focusing becomes easy.”
Image Stabilization - Sharper Images at
Slower Shutter Speeds
Walter continues, “another situation I had was at a flat-
track motorcycle race at dusk. Light levels were low and I
was forced to shoot without a tripod. I was able to handhold
the camera at full zoom with the on-board image stabiliza-
tion while panning and got sharp, crisp images. This would
have been impossible to do with a 35mm film camera. The
The pre-capture ability on the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS is
exclusively an Olympus technology and is one attribute that
truly sets this digital camera apart from any others. Like many
other features, it was designed with action, sports and fast-
paced event photography in mind.
Previous Work-around
An inherent attribute of any digital camera is the slight time
lag from when the shutter button is depressed and the time
the image is actually captured. One method digital photogra-
phers have used to counter this is to try and anticipate when
the precise moment of capture will occur and start depress-
ing the shutter button well before the moment of intended
capture. This has been a hit-and-miss proposition for nearly
all photographers.
lens would be far too heavy at this focal length to handhold.
With image stabilization you can shoot at slower shutter
speeds to compensate for low light and still produce a
sharp image.”
The CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS’s “pre-capture” capabilities
alleviate the need for this clumsy technique and completely
removes the anxiety of missing “the critical moment” for digi-
tal photographers.
Caching to a 9 Mb Buffer
The “pre-capture” process begins by holding down the shut-
ter button halfway, (see the diagram entitled CAMEDIA E-100
Panning in low light
using the CAMEDIA
E-100 ZOOM RS’s
image stabalization
© 2000 Walter Urie
4
Page 7

ZOOM RS Sequential Image Cache) when you think the criti-
pre-capture and capture altogether. This guarantees that you
cal moment you want to capture is near. Five sequential im-
ages are then cached in the on-board 9 Mb buffer, and are
rolled over as long as the shutter button remains halfway
depressed.
In the pre-capture mode, the sixth image overwrites the num-
ber one image, number seven overwrites the number two
pre-captured image and so-on until the shutter button is ei-
ther depressed fully, moving the camera into the sequential
“capture” mode or the shutter button is released stopping the
CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS Sequential Image Cache
Shutter
Button
Released
Shutter
Button 1/2
Depressed
will not suffer from missed opportunities due to shutter lag
and allows you to capture the precise moment you need.
Walter Urie comments, “going back to the motorcycle races I
shoot with the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS, I wanted to catch
the riders, which were going very, very fast at an exact spot on
the curve using a panning technique. I was following the ac-
tion and as the riders entered the designated area, I started
to depress the shutter button halfway down. Out of 100 pans,
I was able to capture accurately and with precision 95 pans.”
Shutter
Button Fully
Depressed
Shutter
Button
Released
Auto focus
actived
After shutter button is 1/2 depressed, pre-capture
operation starts, records data in the memory buffer
and overwrites the oldest images
P1 P1 P1 P1 P1 P6
P2 P2 P2 P2 P2 1
P3 P3 P3 P3 P3 2
After shutter button is fully depressed,
image data stored into buffer until the
buffer is full.
P6 P6 P6 P6 5
1 1 1 1
2 2 2
P4 P4 P4 P4 P4 3 3 3
P5 P5 P5 P5 P5 4 4
Pre-capture Mode Capture Mode
Total memory allocation Image captured instantaneously Images cached
Auto focus
actived
Data is read
from buffer and
recorded on
Memory Card
5
Page 8

15 Frames per Second Frame15 Frames per Second Frame
15 Frames per Second Frame
15 Frames per Second Frame15 Frames per Second Frame
Rate Capable CaptureRate Capable Capture
Rate Capable Capture
Rate Capable CaptureRate Capable Capture
Just 5 years ago, if you had a professional film camera that
could provide 7-8 frames per second with a motor drive, you
had a top of the line camera. The CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS
provides more than double that frame rate as part of its digital
specific design attributes. This allows the user to capture subtle-
ties in photo illustration, for example capturing a golf swing.
According to pro shooter Walter Urie, “when you’re photo-
graphing action, this camera gives you the opportunity to cap-
ture the exact moment I wanted and capture the action every
single time.”
Capturing a golf swing at15
FPS with the CAMEDIA E-100
ZOOM RS © 2000 Walter Urie
6
Page 9

The Benefits of the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS’sThe Benefits of the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS’s
The Benefits of the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS’s
The Benefits of the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS’sThe Benefits of the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS’s
Progressive Scan CCDProgressive Scan CCD
Progressive Scan CCD
Progressive Scan CCDProgressive Scan CCD
Most consumer and professional digital cameras are not
designed to be “digital specific” like the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM
RS is for action and sports event photography. The majority of
digital cameras have a maximum shutter speed of 1/500th of
a second due to their incorporation of an interlaced CCD
sensor. The CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS incorporates a pro-
gressive scan CCD with 1/10,000th of a second capability.
Why does this matter? An interlaced CCD digital camera has
a fast enough shutter speed for most typical applications, but
falls short if you are trying to capture lateral movement in
sports or event photography.
A progressive scan CCD refers to a very simple and
intuitive operation of the sensor when all lines are output in
ascending order. In order to accomplish this progression, a
digital camera must not have a frame store within the CCD
sensor, or have a frame transfer CCD or a full-frame, interline
and you want to stop the action with your digital camera with-
out causing blurring. Or the situation could be college or pro-
fessional football, or your local children’s soccer game. Un-
less the action is coming straight to you, the chances that
blurring will occur when following fast action are great.
Ask any professional NFL football photographer and they will
tell you that they would prefer to shoot at higher shutter speeds
than 1/500th of a second, light permitting. At 1/500th of a sec-
ond there is a risk that some of their images that show lateral
motion will be blurred and unusable.
In summation, cameras with a full frame shutter, such as
the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS are designated as “progres-
sive scan” cameras and have the ability to capture moving
objects with full horizontal and vertical resolution. This allows
them to capture at much higher shutter speeds than stan-
transfer CCD.
The full-frame interline transfer CCD sensor incorporated in
the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS with an interlined frame store
has the same resolution as the sensor area. Simpler inter-
laced cameras with a standard interline transfer CCDs have
frame stores with only half the vertical resolution.
The line scan order is really not the most relevant issue.
Whether a digital camera is able to capture a moving object
with full resolution, is. There is no mechanical shutter in a
CCD sensor and so the term “progressive scan” has been
used instead of the term “full frame shutter”. Let’s concen-
trate on what this means in an actual shooting situation.
Imagine that you are about to photograph an event where
there are World-class athletes running laterally in front of you
dard interlaced CCD digital cameras, which can only capture
moving objects with half the vertical resolution (but full
horizontal resolution).
The CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS allows the user to capture the
fastest action possible without blurring, even shooting 200-
MPH race cars while panning.
7
Page 10

The Importance of Match-The Importance of Match-
The Importance of Match-
The Importance of Match-The Importance of Matching Lens to CCDing Lens to CCD
ing Lens to CCD
ing Lens to CCDing Lens to CCD
More than 200 years ago, Newton showed that white light
was composed of multiple wavelengths, (RGB) which are
now called photons. These waves of light pass through a
lens on a camera and are supposed to be “imaged” at the
same point, onto film emulsion for example. When the pho-
tons are not imaged properly onto the film plane, chromatic
aberration occurs and is most commonly caused by using
single lens construction. Incorporating two lenses made of
different materials can solve chromatic aberration with film
camera lenses. The net effect of chromatic aberration is un-
intended color artifacts such as halos and wild colors.
The marriage between lens and CCD is critical to delivering
the best possible images. Post imaging processing can only
do so much to help a poor image. Remember the old axiom,
garbage in - garbage out.
causes a digital form of chromatic aberration. Film emulsion
layers are designed to read light from an oblique angle and
the fall-off from the lens. Olympus found that in order to get
the best possible images from a digital camera, the light
coming into a CCD must be straight on.
The CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS Lens
Elements and Interaction with the CCD
Lens Elements
Film
Emulsion
Layers
The same holds true for uncorrected lenses made for digital
cameras and the net effect it causes are unwanted artifacts,
noise and a degraded image. Unbeknownst to many in the
industry, digital camera lenses require different construction
than film camera lenses. If a manufacturer, (and some do)
tries to place a lens designed for a film camera onto a digital
camera, the net effect is chromatic aberration and only a small
portion of the lens will actually throw light onto the CCD. This
gross under-utilization also causes a loss in edge-to-edge
sharpness that could be delivered to the CCD.
The digital camera lens construction of the CAMEDIA E-100
ZOOM RS contains a concave element that forces photons
coming through the lens into a straight-ahead alignment to
the 28 MHz high-speed progressive scan CCD. All CCD sen-
sors are very picky about how light is delivered to them and
they don’t like oblique angles of light hitting them, which
Lens Elements
CCD¤
Sensor
Light - Photons
8
Page 11

DualSlot Media CapabilityDualSlot Media Capability
DualSlot Media Capability
DualSlot Media CapabilityDualSlot Media Capability
Voice Annotation CapabilityVoice Annotation Capability
Voice Annotation Capability
Voice Annotation CapabilityVoice Annotation Capability
with QuickTime™with QuickTime™
with QuickTime™
with QuickTime™with QuickTime™
File CaptureFile Capture
File Capture
File CaptureFile Capture
The dual slot media capability on the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS
is an exclusively unique Olympus feature that allows the user to
simultaneously write to either a 2M, 4M, 8M, 16M, 32M, and 64M
SmartMedia NAND flash card or a Type I or Type II CompactFlash
card. Or, you can opt to use one type of media at a time. This
capability allows the user more flexibility in their choice of flash
media and allows the camera to be “media agnostic”.
Often professional photographers on the move need to have the
ability to quickly jot down a subject’s name or a notation of where
the image was shot for publication. In the “good ol days”, pros had
to carry a notepad and pencil in their breast pockets ready for
taking quick notes of who, what and where. Again, the digital-
specific features allow the user to annotate an image with useful
information. Why have new-world capture technology with old-
world notations.
New Accurate ElectronicNew Accurate Electronic
New Accurate Electronic
New Accurate ElectronicNew Accurate Electronic
LCD ViewfinderLCD Viewfinder
LCD Viewfinder
LCD ViewfinderLCD Viewfinder
The CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS solves this problem by allowing
up to 5 seconds of voice annotation per image and saves it as a
QuickTime™ audio file so the user has a digital notation to go
with the image file.
Viewfinders on most digital cameras use TTL (through the lens)
viewing and because some digital camera lenses are slightly
over-sized compared to the size of the CCD, give an inaccurate
view of the area that is actually being captured. This misrepresen-
tation on a professional level can mean the difference between
having an acceptable image or not. This is especially true with
professional photographers
since many pros choose to strategically place important elements
of composition on the outer fringes of the image to keep overzeal-
ous picture editors from cropping their images too much.
The new EVF (Electronic Viewfinder) on the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM
RS represents the area being captured with 100% accuracy since
it is reading directly from the CCD, not through the lens. What you
see really is what you get.
9
Page 12

The Criticality of NeutralThe Criticality of Neutral
The Criticality of Neutral
The Criticality of NeutralThe Criticality of Neutral
Color ManagementColor Management
Color Management
Color ManagementColor Management
One of the benefits of pre-selecting a black and white mode
is to let the camera do the work to discard the unnecessary
The CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS’s color management system
allows the user to capture with “neutral color” that is truer to
the intended values of the original subject. The camera’s
post processing provides advanced algorithms that keeps
the image from being too warm on the Kelvin scale or too
cool, (3200º K represents tungsten light, 5500º K represents
high noon daylight). Often adjusting an image in either direc-
tion causes unwanted noise, which often effects image qual-
ity. With Olympus’s Neutral Color Management, you can color
correct the image in either direction without negatively effect-
ing the image quality.
Shooting with Color orShooting with Color or
Shooting with Color or
Shooting with Color orShooting with Color or
Black and White PresetBlack and White Preset
Black and White Preset
Black and White PresetBlack and White Preset
Previously, digital photojournalists and sports photographers
haven’t had the option to preset the mode they wished to
color data before saving to the camera’s storage media. Sec-
ondly, after-capture converting takes up valuable time, a PC
and an image editing application, which could mean the dif-
ference in a missed deadline. Lastly, wouldn’t it be better to
check the black and white image in comparison with real life
values while its there in front of you rather than “visioning”
what it should have looked like afterward?
Photographer Walter Urie adds, “I specialize in black and
white photography and I’m very picky. I was extremely im-
pressed in the way this camera translated color to black and
white tonal values.”
90º Image Rotation in Play-90º Image Rotation in Play-
90º Image Rotation in Play-
90º Image Rotation in Play-90º Image Rotation in Playbackback
back
backback
Shooting in a vertical format is an absolute necessity for pro-
shoot in, i.e. black and white or RGB color. The E-100 RS
solves this problem, in-camera. In many cases, digital pho-
tographers are forced to shoot in color and later convert im-
ages to black and white. There are a few reasons why this is
not acceptable to most professionals. First, color images
take up much more storage on the camera’s memory card(s)
than black and white images, which could mean the differ-
ence between having enough storage or not on a shoot.
10
fessional and prosumer photographers. The problem is, most
digital cameras don’t rotate the images on playback for you to
see them properly and users are forced to accomplish this
basic task on a PC with image editing software. Not any-
more! Again, Olympus overcame this problem with a “digital
specific” feature on the CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS that al-
lows you to rotate your images 90º on playback, so there’s no
need to use a PC or editing software.
Page 13

SummationSummation
Summation
SummationSummation
After reading about all the “digital specific” attributes that this innovative digital camera has to
offer we hope that you now understand their practical applications and benefits for on-location
sports, action and fast-paced event photography. The CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS has many
other attributes not mentioned but the areas where this camera is specifically differentiated
from other digital cameras include the 10x optical zoom lens with image stabilization, pre-
capture modes, 15 frames per second frame rate capture capabilities, the fast progressive
scan CCD, matching lens to CCD for accuracy, the dual slot media capability, the accurate
electronic LCD viewfinder, Olympus’ neutral color management, voice annotation capabilities,
the black and white presets, and 90 degrees of rotation in playback capabilities.
Hopefully you also have an understanding of the positioning of this digital camera in the
marketplace as a whole. To quote professional photographer Walter Urie, “there is no doubt
that this camera was designed specifically for action, sports and events and is even easy
enough for parents to use. It provides all the tools anyone would need for this type of application
and be successful at it. It had everything I needed to be successful in my location photography”.
No digital camera is complete without quality print output. The CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS
is designed to produce professional-quality prints on the new Olympus P-400 dye sublimation
A4 printer. All you do is plug your media card in and you can use the printer’s controls to
crop and print.
Ron Tussy
Principal Imaging Analyst
Imerge Consulting Group LLC
Olympus P-400 dye sublimation A4 printer
11
Page 14

<< Specifications of the E-100 SLR <<
Model name Olympus CAMEDIA E-100 ZOOM RS Digital Camera
Product Type Digital EVF SLR Camera with 4.5cm/1.8inch color TFT LCD monitor
Memory 3V (3.3V) SmartMedia (SSFDC) Card (4M,8M,16M 32M and 64MB)
One 8 MB card including Panorama function is supplied with camera
CompactFlash Type II flash memory. Micro-Drive not recommended
Recording system Still image ; JPEG (DCF: “Design rule for Camera File system”),
TIFF (non-compress), DPOF support
10 Bit A>D Converter
QuickTime™ JPEG Motion VGA and 1/8 VGA
Number of 4: TIFF 1368 X 1024
storable pictures with 28: SHQ JPEG 1368 X 1024
8MB SmartMedia card 84: HQ JPEG 1368 X 1024
96: SQ1 1280 X 960 68: SQ2 1280 X 960
152: SQ1 1024 X 768 104: SQ2 1024 X 768
328: SQ1 640x480 264: SQ2 640 X 480
16 sec. 30 fps Motion JPEG 640 X480
32 sec. 15 fps Motion JPEG 640 X 480
32sec. 30 fps Motion JPEG 160 X 120
64 sec. 15 fps Motion JPEG 160 X 120
Image pickup element 1/2 inch CCD solid-state images pickup 1.51 Million Pixel (effective 1.4 Megapixel Image)
RGB Progressive Scan : 28MHz (High Speed CCD)
White balance iESP full-auto TTL,
Preset Manual (Daylight, Cloudy, Florescent and Tungsten)
“One Touch” Manual
Lens Olympus lens 6.8– 70 mm 2.8-3.5, Glass Aspherical Zoom Lens
(Equivalent to 35 - 380 mm lens on 35 mm camera)
Image Stabilized System with 2.7x Digital Super Telephoto
Optional 0.8x B-28 Wide-Angle or 1.7x B-300 Telephoto: [E series lenses can also be used].
Filter Size 49mm (To attach accessory lens an filters) 49>55mm Step up needed for thick filters
Photometric system Digital-“ESP” Multi-Pattern metering system, Center-weighted Spot meter and,
(8 area memorized) multi-spot metering
Exposure control S-Program mode with Portrait, Landscape, Sports, Night Scene and Custom setup modes
Programmed auto exposure, Aperture priority, Shutter priority
+/- 2Ev by 1/3EV steps exposure compensation
Auto Bracketing: select-able from 1/3EV, 2/3 EV and 1EV; 3 or 5 images
Aperture priority: Wide ; F2.8 – 8.0, Tele ; 3.8 – 8.0, 1/3EV steps
Shutter priority: 2 - 1/10000 sec. (Electrical CCD and mechanical shutter), 1/3EV steps
Manual exposure: shutter speed, 16 sec. –1/1000 sec.
ISO Auto, user selectable, 100, 200, 400 equivalent ISO
Focusing iESP TTL or spot system autofocus (contrast detection system) with focusing illuminator.
Focusing range: 24”/0.6 m–¥ (infinity) wide-angle, 79”/2m–¥ (infinity)
Telephoto: 4.3”/0.1m- 24” wide-angle macro, 79”/1m-79”/2m telephoto macro- stepless
(iESP off in rapid shooting mode.)
Manual focus (manual focus setting by gauge) with focusing range: 24”/0.6 m–¥ (infinity):240 steps
12
Page 15

AF Illuminator Standard mode: 24”/0.6m-10’/3m (Can be turned off)
working range User selectable on/off controls
Viewfinder EVF (Electronic Viewfinder) SLR viewfinder 100% accurate image view,
(Full Information/Mode AV,SV/Spot/CW/ESP/+/-/AF/Flash/Buffer)
.55” Color LCD EVF (Low Battery Drain)
LCD monitor 4.5cm/1.8inch wider angle color TFT LCD monitor with 113,500 pixels
(made from Low-temperature poly-silicon), 100% accurate image view
Flash modes Built-in Flash : Auto-Flash (low-& back-light), Read-Eye Reducing Flash, Off, Fill-in
External terminal: Off, Auto, Forced activation
Slow Synchronization (First-Curtain Synchronization effect, Second-Curtain Synchronization effect)
External terminal 5 pin TTL connector for FL-40 or PC sync, Optional Bracket and cable needed
Flash working range Wide; approx. 30”/0.8 – 18’/5.6m, telephoto; approximately. 8”/0.2 –9’/2.8m ( ISO 100)
Battery charging time Less than 6 sec. (at normal temperature with new battery) for flash
Sequence mode SHQ JPEG (1368 X 1024) 15/7.5/5/3 frames per sec. up to 10 frames
HQ JPEG (1368 X 1024) 15/7.5/5/3 frames per sec. up to 16 frames
SQ1/SQ2 (1280 X 960) 15/7.5/5/3 frames per sec. up to 21/7 frames
SQ1/SQ2 JPEG (1024 X 768) 15/7.5/5/3 frames per sec. up to 27/17 frames
SQ1/SQ2 JPEG (640 X 480) 15/7.5/5/3 frames per sec. up to 47/123 frames
less than 1.2 second shot to shot at all times (unlimited quantity)
Pre-Capture Begins capturing image before shutter release: User adjustable from 1-5 photos
Cancel Shot Recording Cancels recording to Memory Card Preparing camera to immediately start shooting.
Selftimer / 12 second delay / 2 sec. after optional remote controller operation
remote controller E-10 Remote Cable (Bulb won’t work)
Setting memorization Possible
Outer Connector DC input terminal, Data input/output USB interface (Storage Class)
Audio/Video Output terminal ( NTSC), external flash terminal for FL-40 (5-pinn TTL) or
PC sync with optional cables and bracket.
Operating environment Operation : 32F/0C – 104F/40C, 30 – 90 % Humidity
Storage : -4F/-20C – 140F/60C, 10 – 90% Humidity
Power Supply 4 x AA Ni-MH batteries and charger included/ 2 x Lithium battery CR-V3 (LB-01);
Optional 7AU-AC adapter / 4 x AA Lithium batteries /Use only high capacity AA Alkaline batteries
(Manganese batteries cannot be used.)
Date/Time/Calendar Simultaneous recording onto image data.
Automatic calendar Up to year 2030
system
Dimensions 4.25”/10.8cm (W) x 3.25”/8.25cm (H) x 5.6”/14.23cm (D) (excluding projections)
Weight 21.8oz/603g (without batteries and SmartMedia Card)
All products indicated by trademark symbols are trademarket and/or registered by their respective companies. Specifications and equiptment
are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer. © 2000 - Olympus America, Inc.
13
Page 16

www.olympusamerica.com
or
http://e-100rs.com
 Loading...
Loading...