Page 1
Chapter 24 Web Authentication
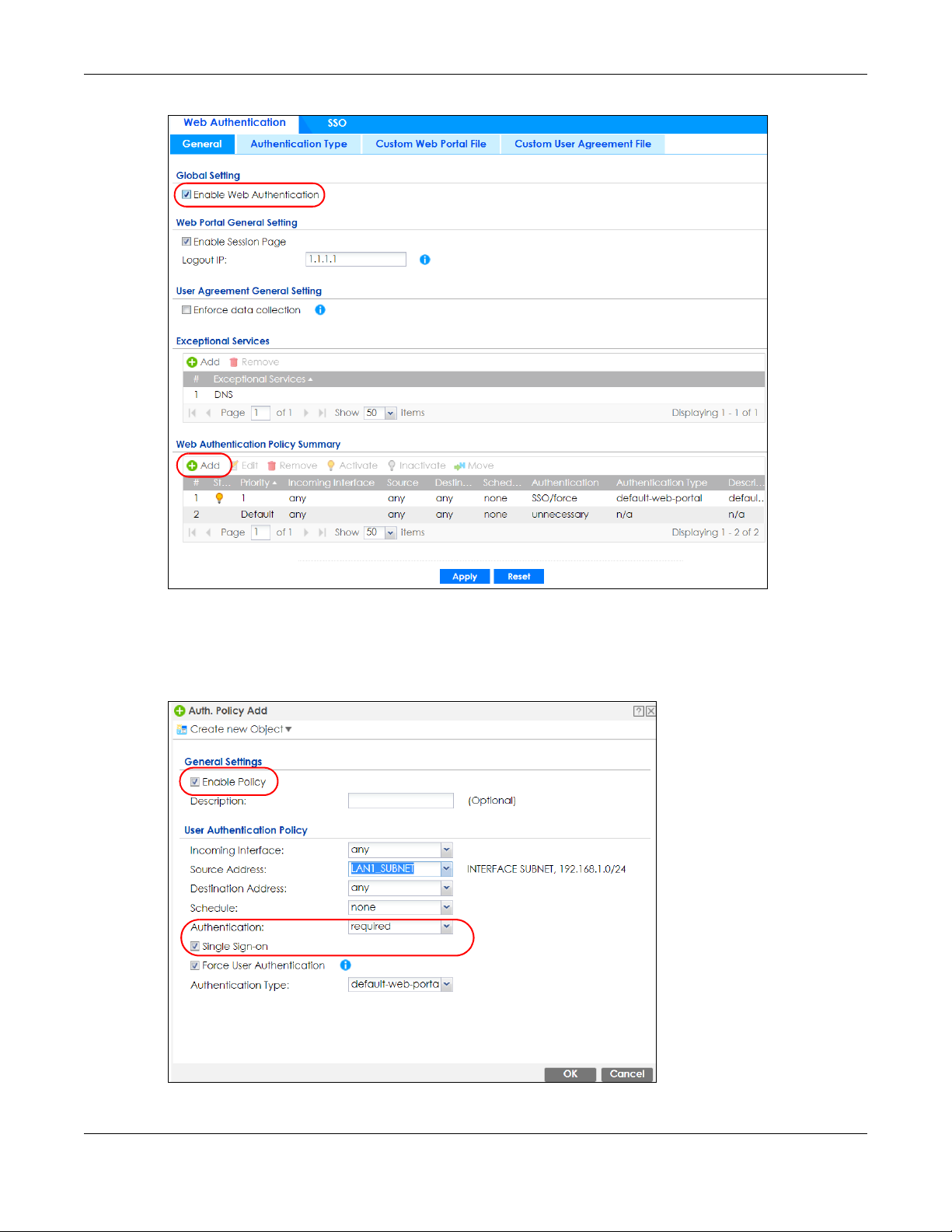
Make sure you select Enable Policy, Single Sign-On and choose required in Authentication.
Do NOT select any as the source address unless you want all incoming connections to be
authenticated!
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
481
Page 2
Chapter 24 Web Authentication
See Table 184 on page 462 and Table 185 on page 465 for more information on configuring these
screens.
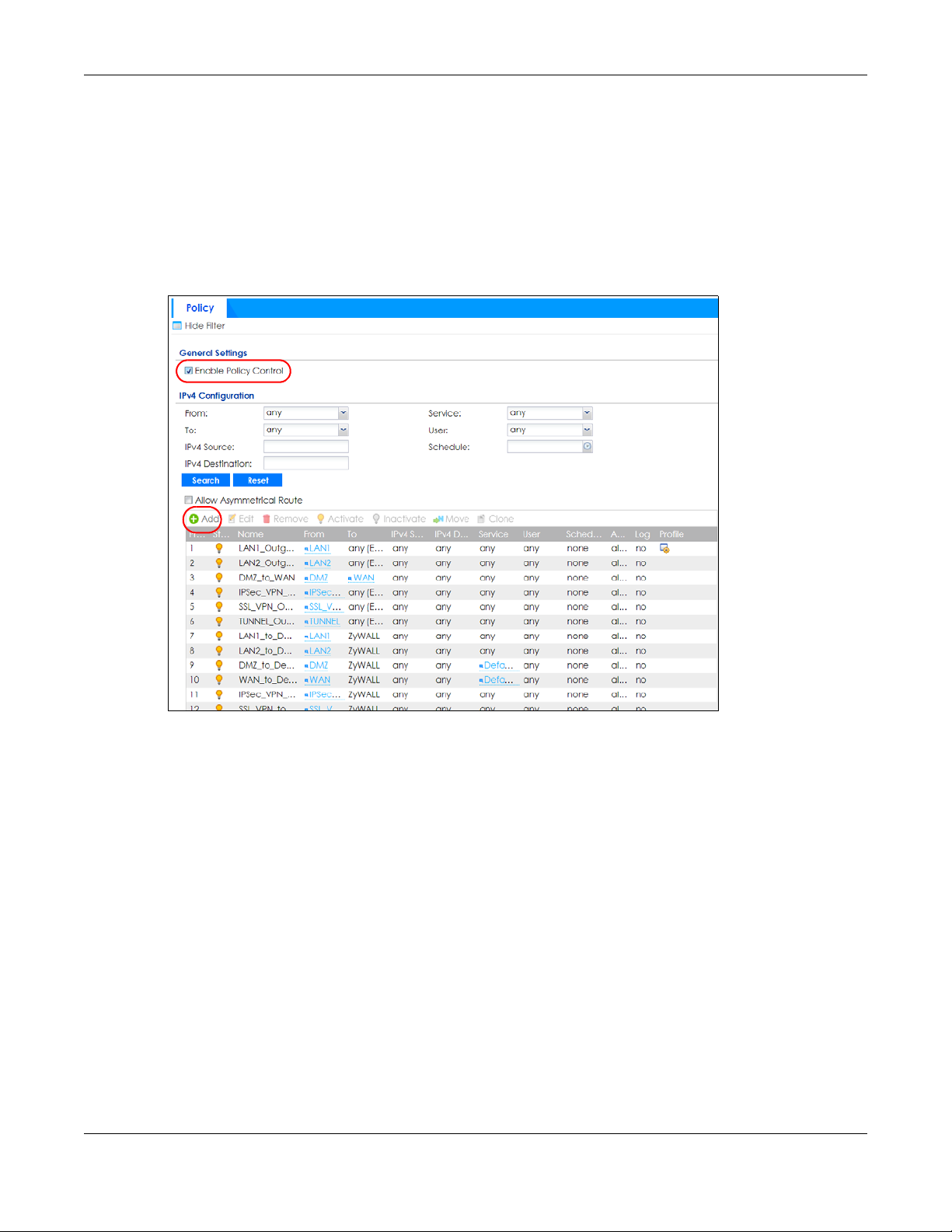
24.4.4 Create a Security Policy
Configure a Security Policy for SSO traffic source and destination direction in order to prevent the
security policy from blocking this traffic. Go to Configuration > Security Policy > Policy Control and add a
new policy if a default one does not cover the SSO web authentication traffic direction.
Configure the fields as shown in the following screen. Configure the source and destination addresses
according to the SSO web authentication traffic in your network.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
482
Page 3
Chapter 24 Web Authentication
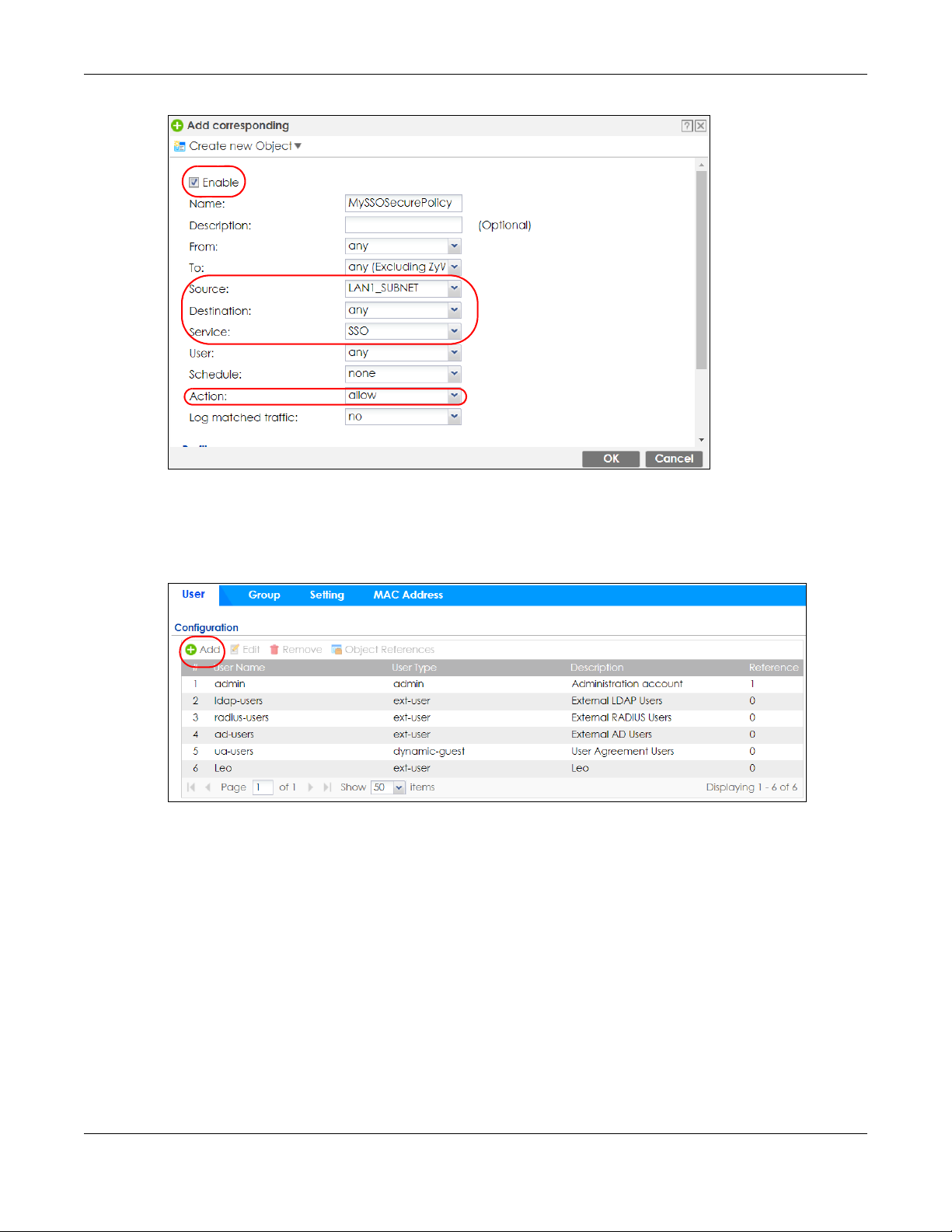
24.4.5 Configure User Information
Configure a User account of the ext-group-user type.
Configure Group Identifier to be the same as Group Membership on the SSO agent.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
483
Page 4
Chapter 24 Web Authentication
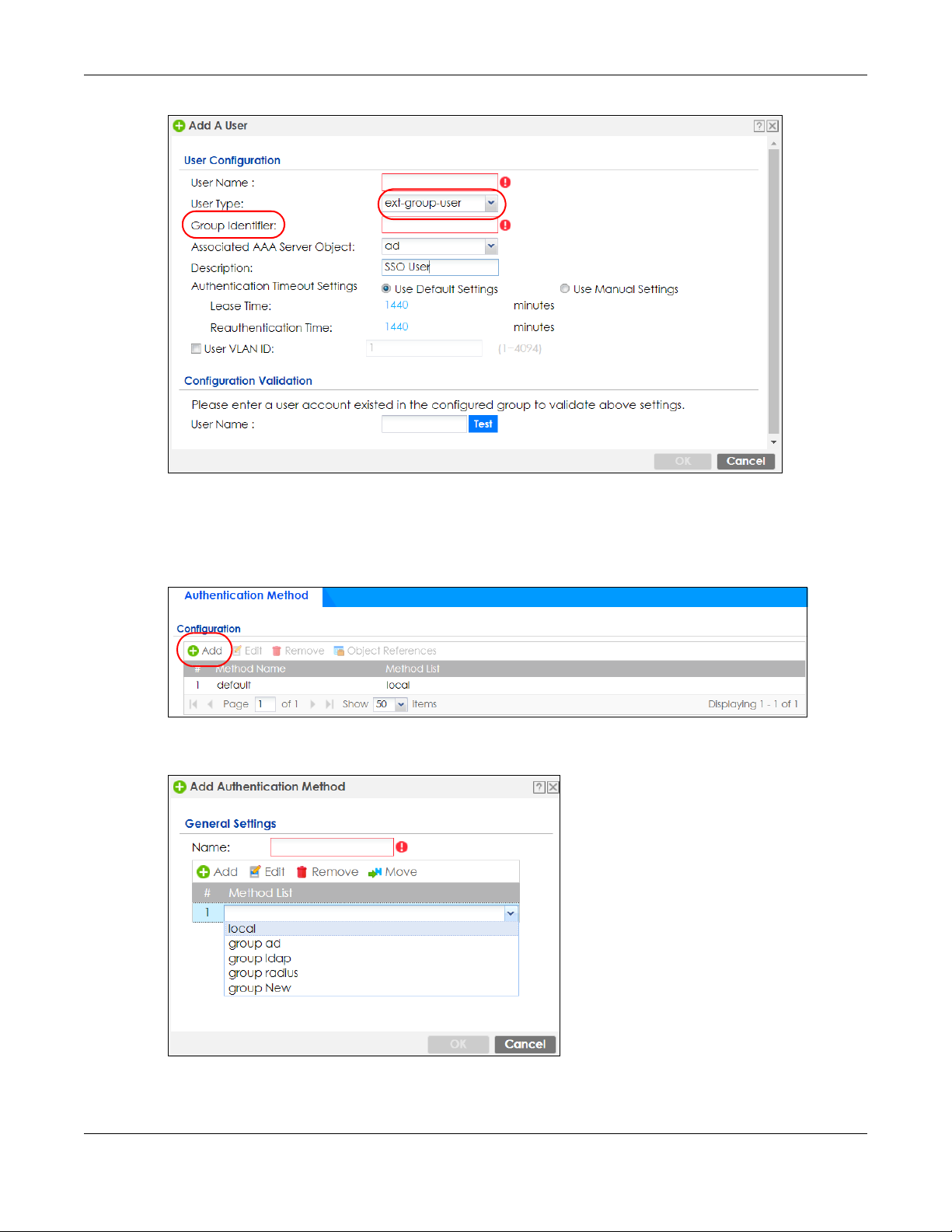
24.4.6 Configure an Authentication Method
Configure Active Directory (AD) for authentication with SSO.
Choose group ad as the authentication server for SSO.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
484
Page 5
Chapter 24 Web Authentication
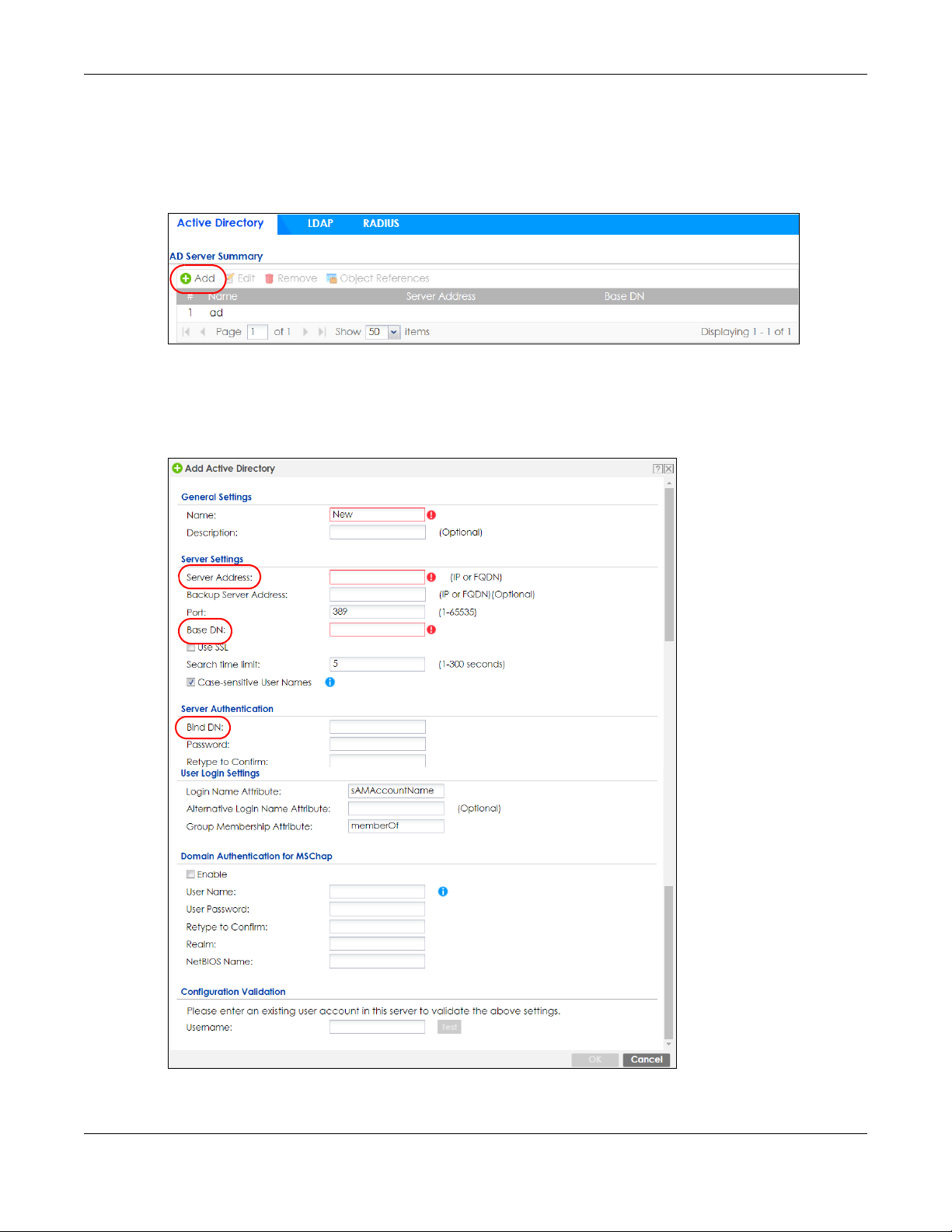
24.4.7 Configure Active Directory
You must configure an Active Directory (AD) server in AAA Setup to be the same as AD configured on
the SSO agent.
The default AD server port is 389. If you change this, make sure you make the same changes on the SSO.
Configure the Base DN exactly the same as on the Domain Controller and SSO. Bind DN is a user name
and password that allows the Zyxel Device to join the domain with administrative privileges. It is a
required field.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
485
Page 6
Chapter 24 Web Authentication
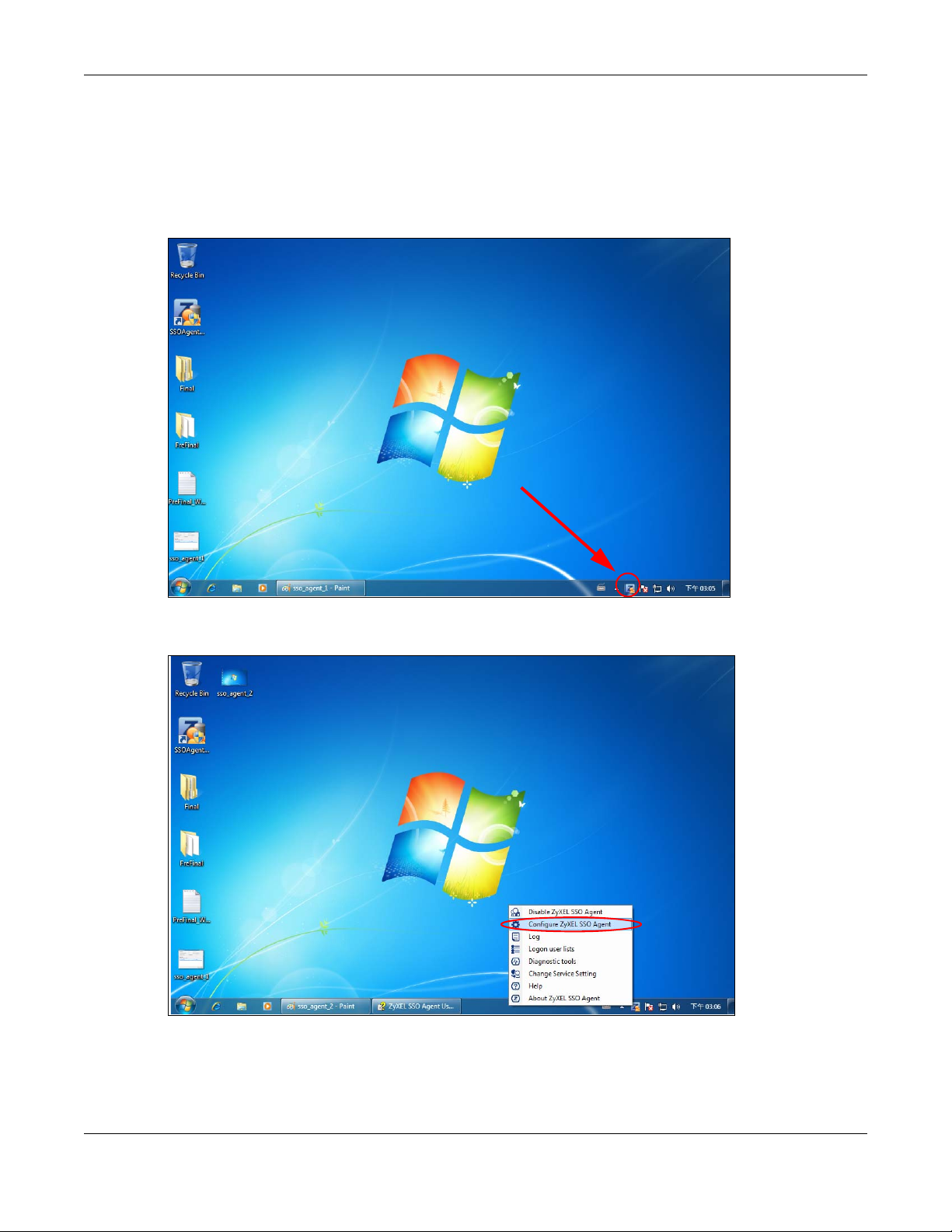
24.5 SSO Agent Configuration
This section shows what you have to do on the SSO agent in order to work with the Zyxel Device.
After you install the SSO agent, you will see an icon in the system tray (bottom right of the screen)
Right-click the SSO icon and select Configure Zyxel SSO Agent.
Configure the Agent Listening Port, AD server exactly as you have done on the Zyxel Device. Add the
Zyxel Device IP address as the Gateway. Make sure the Zyxel Device and SSO agent are able to
communicate with each other.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
486
Page 7
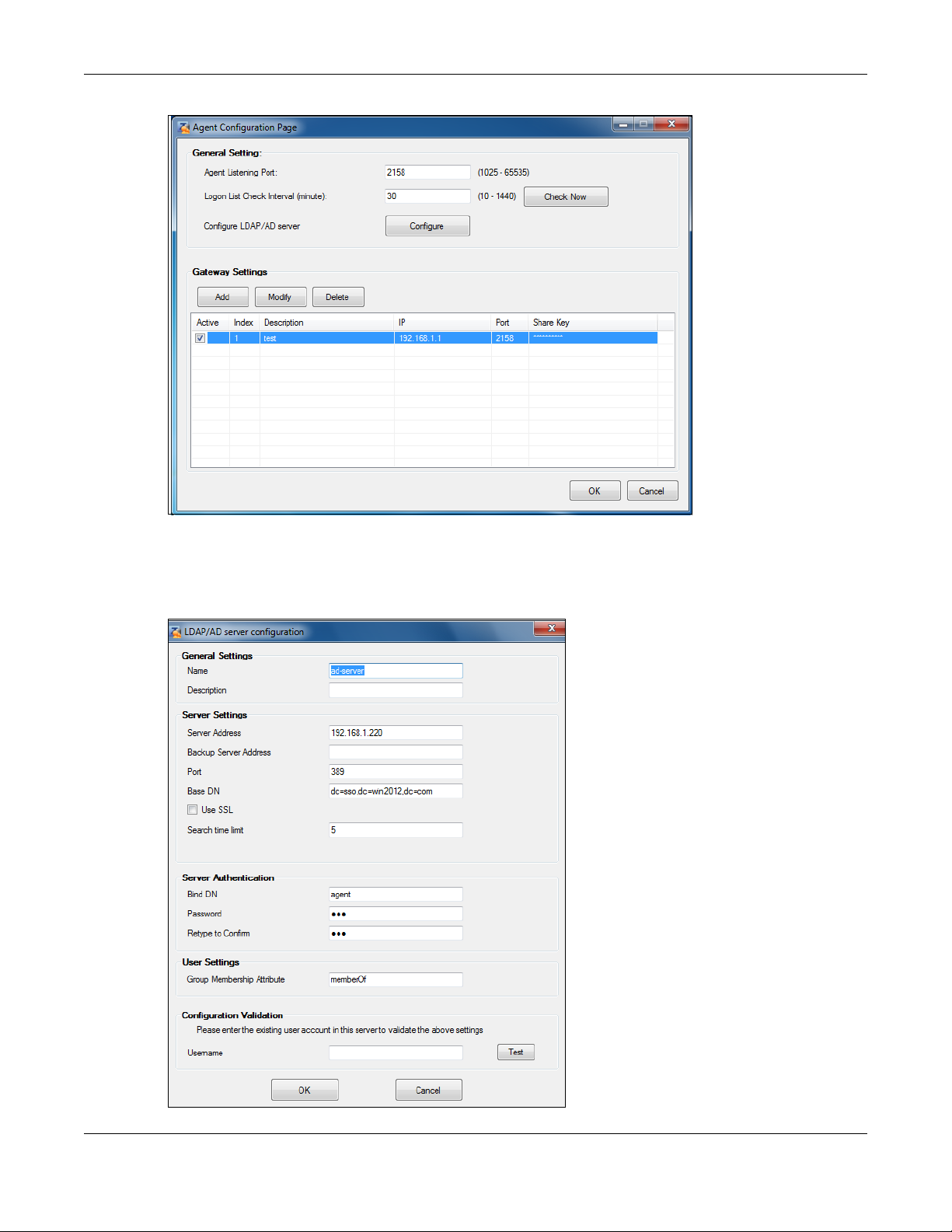
Chapter 24 Web Authentication
Configure the Server Address, Port, Base DN, Bind DN, Login Name Attribute and Group Membership for
the AD server settings exactly as you have done on the Zyxel Device. Group Membership is called Group
Identifier on the Zyxel Device.
LDAP/AD Server Configuration
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
487
Page 8
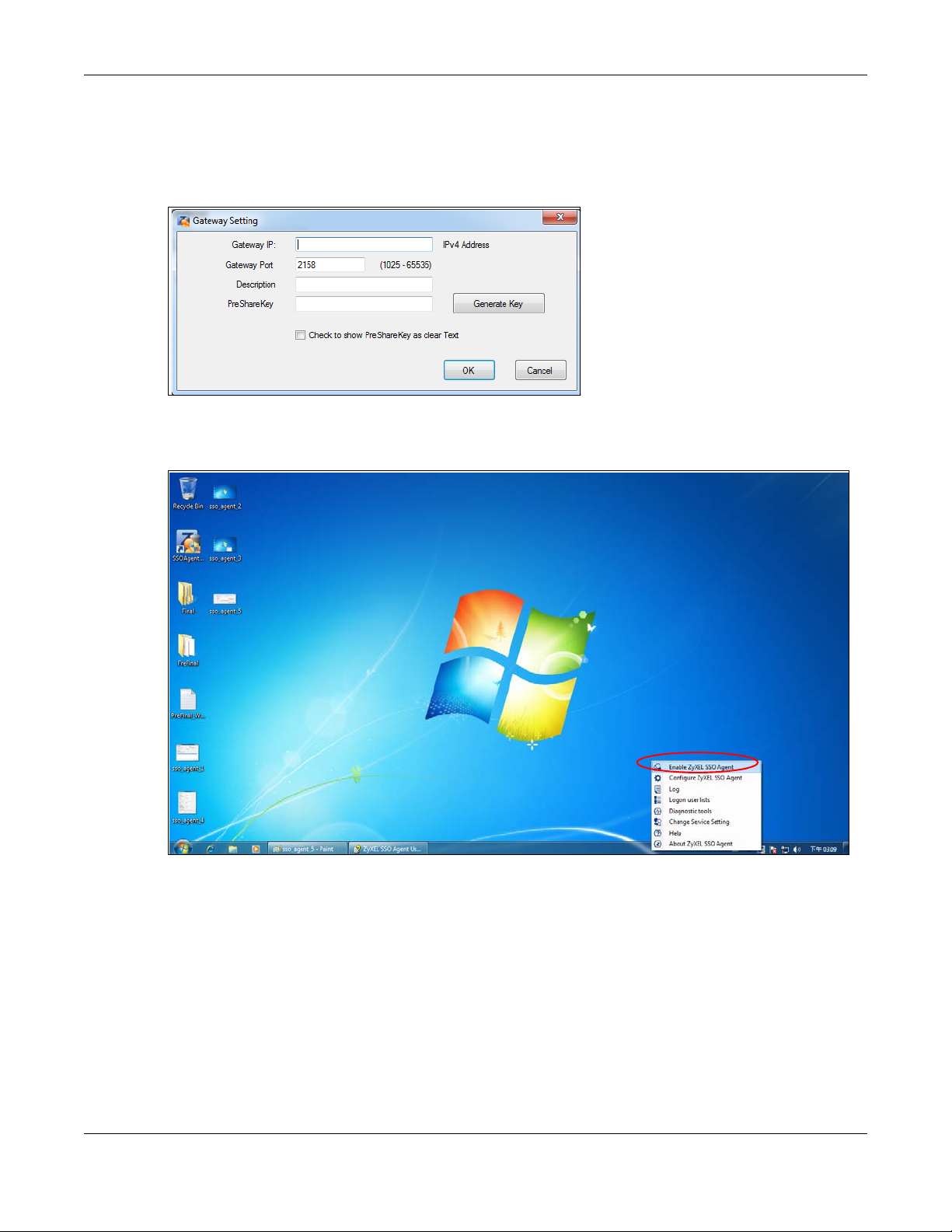
Chapter 24 Web Authentication
Configure the Gateway IP address, Gateway Port and PreShareKey exactly as you have done in the
Zyxel Device Configuration > Web Authentication > SSO screen. If you want to use Generate Key to have
the SSO create a random password, select Check to show PreShareKey as clear Text so as to see the
password, then copy and paste it to the Zyxel Device.
After all SSO agent configurations are done, right-click the SSO icon in the system tray and select Enable
Zyxel SSO Agent.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
488
Page 9
25.1 Overview
A security policy is a template of security settings that can be applied to specific traffic at specific times.
The policy can be applied:
• to a specific direction of travel of packets (from / to)
• to a specific source and destination address objects
• to a specific type of traffic (services)
• to a specific user or group of users
• at a specific schedule
The policy can be configured:
• to allow or deny traffic that matches the criteria above
• send a log or alert for traffic that matches the criteria above
• to apply the actions configured in the profiles (application patrol, content filter, IDP, anti-malware,
email security) to traffic that matches the criteria above
CHAPTER 25
Security Policy
Note: Security policies can be applied to both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic.
The security policies can also limit the number of user sessions.
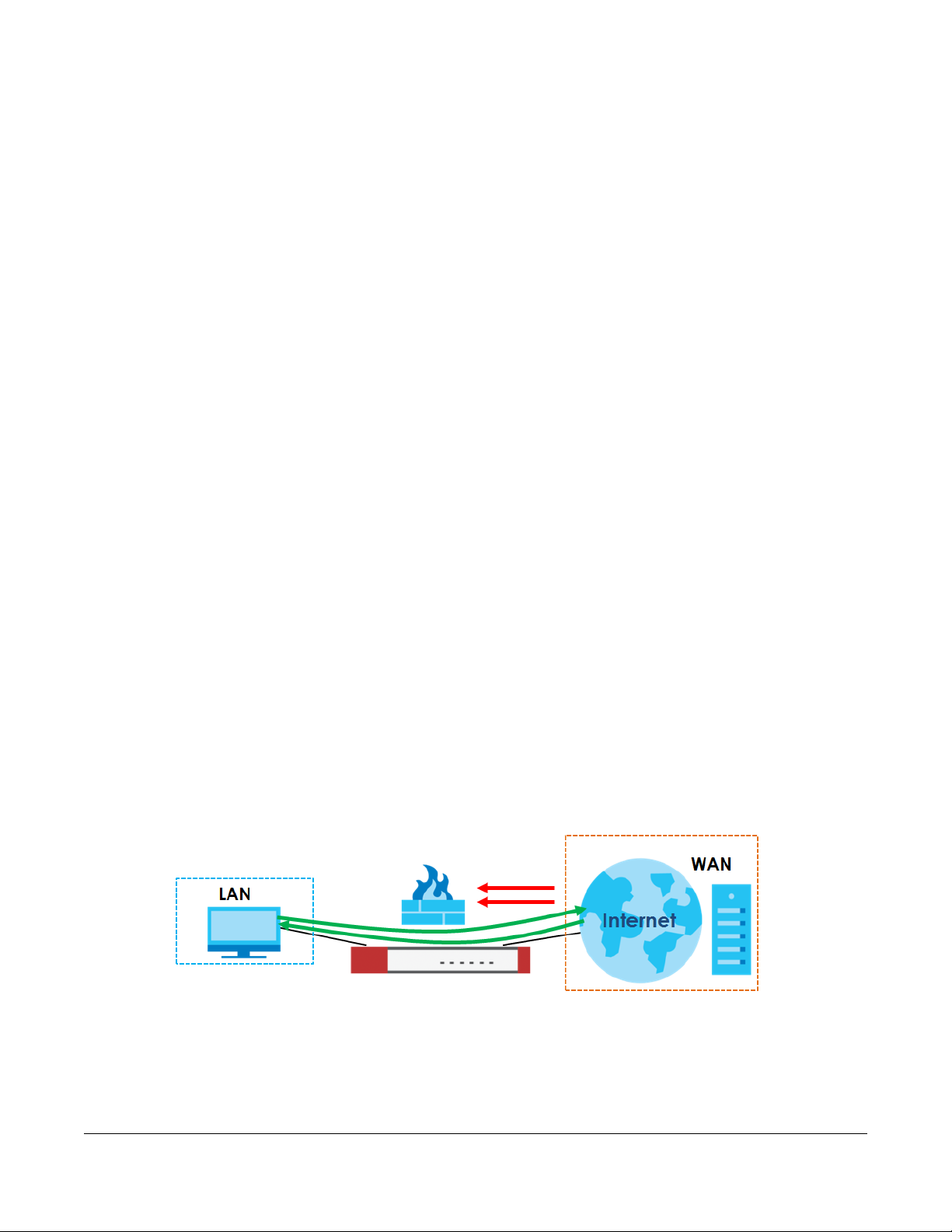
The following example shows the Zyxel Device’s default security policies behavior for a specific direction
of travel of packets. WAN to LAN traffic and how stateful inspection works. A LAN user can initiate a
Telnet session from within the LAN zone and the Zyxel Device allows the response. However, the Zyxel
Device blocks incoming Telnet traffic initiated from the WAN zone and destined for the LAN zone.
Figure 341 Default Directional Security Policy Example
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
489
Page 10
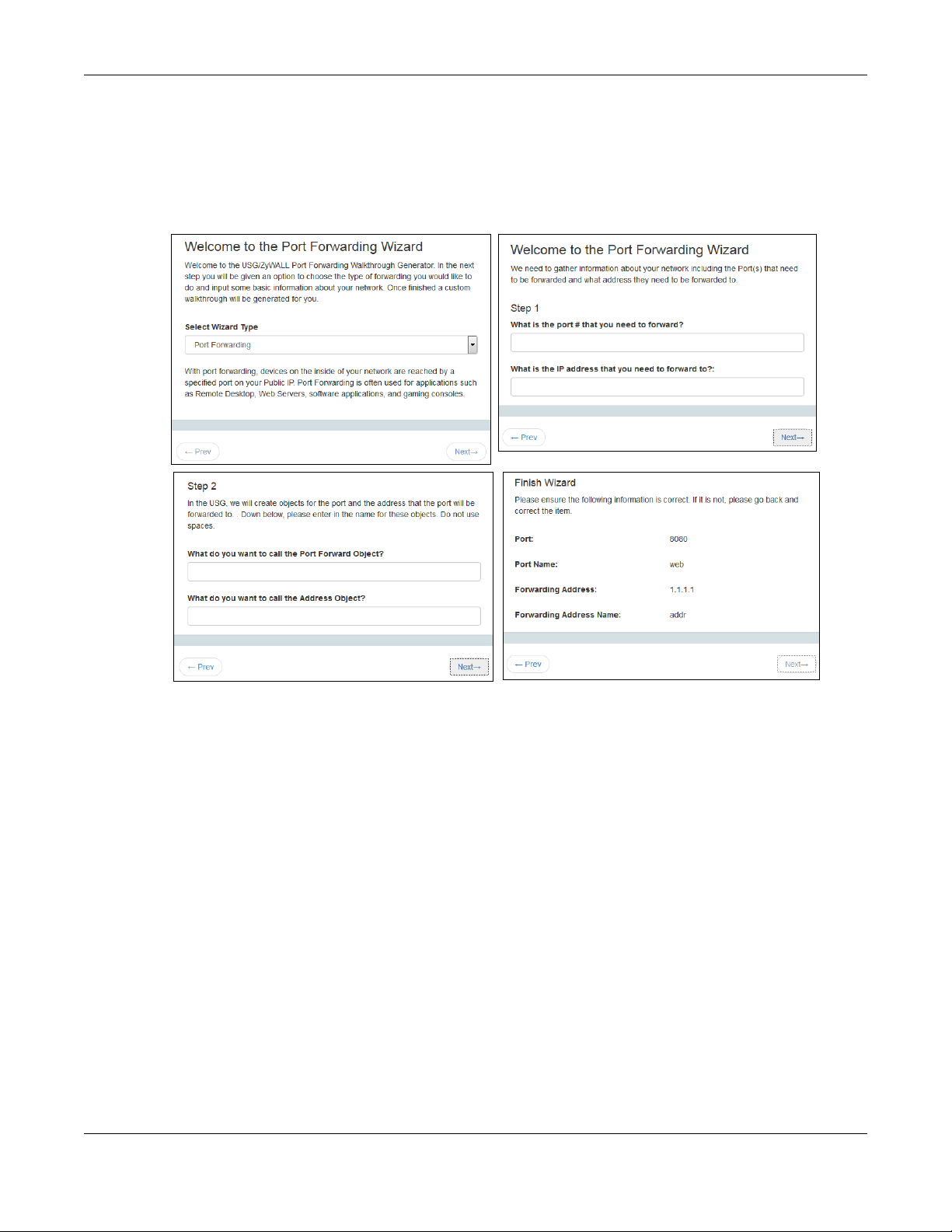
25.2 One Security
1
2
3
4
OneSecurity is a website with guidance on configuration walkthroughs, troubleshooting, and other
information. This is an example of a port forwarding configuration walkthrough.
Figure 342 Example of a Port Forwarding Configuration Walkthrough.
Chapter 25 Security Policy
This is an example of L2TP over IPSec VPN Troubleshooting troubleshooting.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
490
Page 11
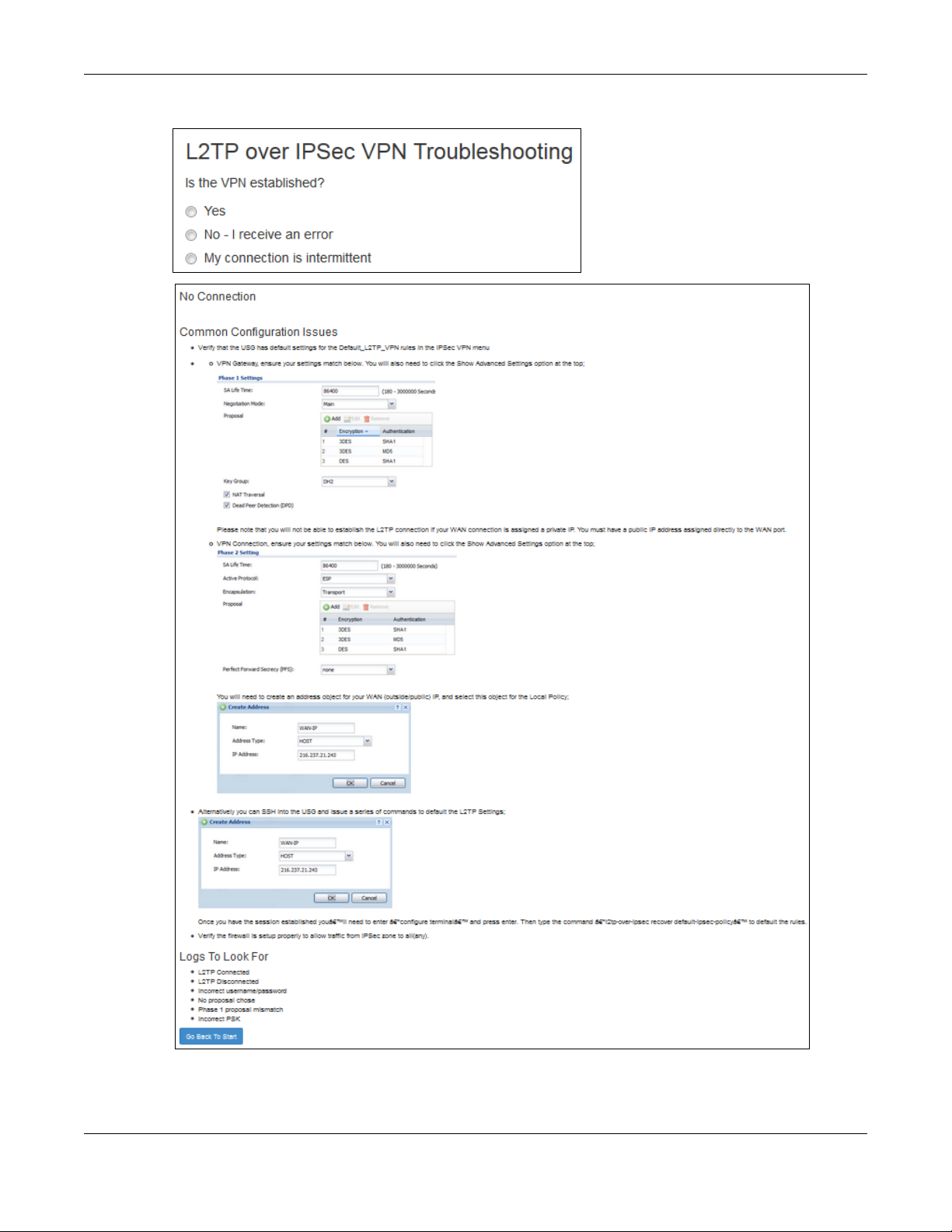
1
2
2
3
Chapter 25 Security Policy
Figure 343 Example of L2TP over IPSec Troubleshooting - 1
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
491
Page 12
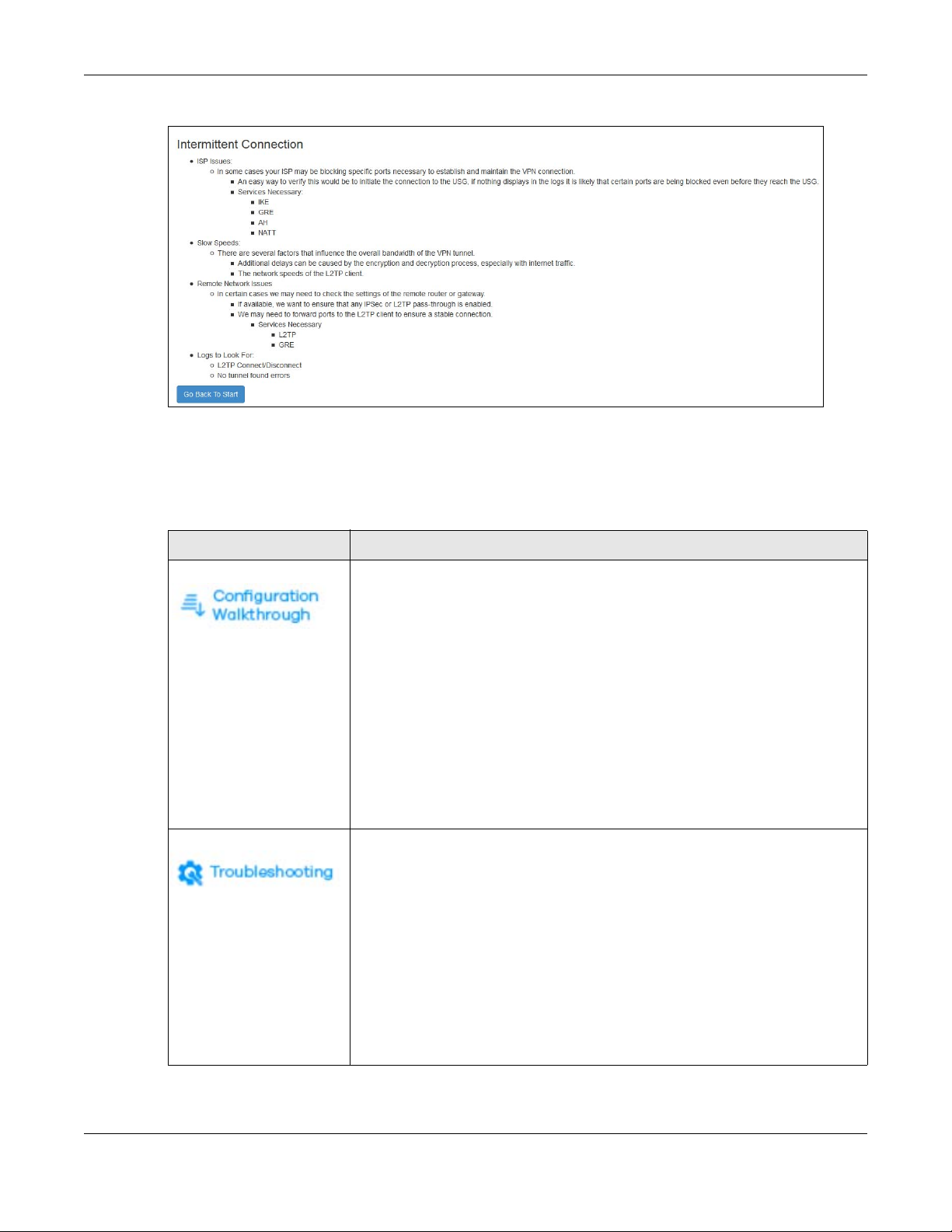
Chapter 25 Security Policy
3
Figure 344 Example of L2TP over IPSec Troubleshooting - 2
In the Zyxel Device, you will see icons that link to OneSecurity walkthroughs, troubleshooting and so on in
certain screens.
For example, at the time of writing, these are the OneSecurity icons you can see.
Table 191 OneSecurity Icons
ONESECURITY ICON SCREEN
Click this icon to go to a series of screens that guide you how to configure the
feature. Note that the walkthroughs do not perform the actual configuring, but just
show you how to do it.
• Device HA > General
• Licensing > Registration
• Network > NAT
• Network > Routing > Policy Route
• Security Service > App Patrol
• Security Service > Content Filter
• Security Service > IDP
• Security Service > Anti-Malware
• Security Service > Email Security
•VPN > IPSec VPN
•VPN > SSL VPN
•VPN > L2TP VPN
Click this icon to go to a series of screens that guide you how to fix problems with the
feature.
• Device HA > General
• Network > NAT
• Network > Routing > Policy Route
• Security Service > App Patrol
• Security Service > Content Filter
• Security Service > IDP
• Security Service > Anti-Malware
• Security Service > Email Security
•VPN > IPSec VPN
•VPN > SSL VPN
•VPN > L2TP VPN
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
492
Page 13
Chapter 25 Security Policy
Table 191 OneSecurity Icons (continued)
ONESECURITY ICON SCREEN
Click this icon for more information on Application Patrol, which identifies traffic that
passes through the Zyxel Device, so you can decide what to do with specific types
of traffic. Traffic not recognized by application patrol is ignored.
• Security Service > Application Patrol
Click this icon for more information on Content Filter, which controls access to
specific web sites or web content.
• Security Service > Content Filter
Click this icon for more information on IPSec and SSL VPN. Internet Protocol Security
(IPSec) VPN connects IPSec routers or remote users using IPSec client software. SSL
VPN allows users to use a web browser for secure remote user login without need of
a VPN router or VPN client software.
•VPN > IPSec VPN
•VPN > SSL VPN
Click this icon to download VPN client software.
•VPN > IPSec VPN
•VPN > SSL VPN
Click this icon for more information on the Wireless AP Controller which sets how the
Zyxel Device allows APs to connect to the wireless network.
• Wireless > AP Management > Mgnt. AP List
25.3 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• Use the Security Policy Control screens (Section 25.4 on page 495) to enable or disable policies,
asymmetrical routes, and manage and configure policies.
• Use the Anomaly Detection and Prevention (ADP) screens (Section 25.5 on page 501) to detect traffic
with protocol anomalies and take appropriate action.
• Use the Session Control screens (see Section 25.5 on page 501) to limit the number of concurrent NAT/
security policies traffic sessions a client can use.
25.3.1 What You Need to Know
Stateful Inspection
The Zyxel Device uses stateful inspection in its security policies. The Zyxel Device restricts access by
screening data packets against defined access rules. It also inspects sessions. For example, traffic from
one zone is not allowed unless it is initiated by a computer in another zone first.
Zones
A zone is a group of interfaces. Group the Zyxel Device’s interfaces into different zones based on your
needs. You can configure security policies for data passing between zones or even between interfaces.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
493
Page 14

Chapter 25 Security Policy
Default Directional Security Policy Behavior
Security Policies can be grouped based on the direction of travel of packets to which they apply. Here
is the The Zyxel Device has default Security Policy behavior for traffic going through the Zyxel Device in
various directions.
Table 192 Directional Security Policy Behavior
FROM ZONE TO ZONE BEHAVIOR
From any to Device DHCP traffic from any interface to the Zyxel Device is allowed.
From LAN1 to any (other than
the Zyxel Device)
From LAN2 to any (other than
the Zyxel Device)
From LAN1 to Device Traffic from the LAN1 to the Zyxel Device itself is allowed.
From LAN2 to Device Traffic from the LAN2 to the Zyxel Device itself is allowed.
From WAN to Device The default services listed in To-Device Policies are allowed from the WAN to the
From any to any Traffic that does not match any
Traffic from the LAN1 to any of the networks connected to the Zyxel Device is
allowed.
Traffic from the LAN2 to any of the networks connected to the Zyxel Device is
allowed.
Zyxel Device itself. All other WAN to Zyxel Device traffic is dropped.
Security policy is dropped. This includes traffic
from the WAN to any of the networks behind the Zyxel Device.
This also includes traffic to or from interfaces that are not assigned to a zone
(extra-zone traffic).
To-Device Policies
Policies with Device as the To Zone apply to traffic going to the Zyxel Device itself. By default:
• The Security Policy allows only LAN, or WAN computers to access or manage the Zyxel Device.
• The Zyxel Device allows DHCP traffic from any interface to the Zyxel Device.
• The Zyxel Device drops most packets from the WAN zone to the Zyxel Device itself and generates a
log except for AH, ESP, GRE, HTTPS, IKE, NATT.
When you configure a Security Policy rule for packets destined for the Zyxel Device itself, make sure it
does not conflict with your service control rule. The Zyxel Device checks the security policy before the
service control rules for traffic destined for the Zyxel Device.
A From Any To Device direction policy applies to traffic from an interface which is not in a zone.
Global Security Policies
Security Policies with from any and/or to any as the packet direction are called global Security Policies.
The global Security Policies are the only Security Policies that apply to an interface that is not included in
a zone. The from any policies apply to traffic coming from the interface and the to any policies apply to
traffic going to the interface.
Security Policy Rule Criteria
The Zyxel Device checks the schedule, user name (user’s login name on the Zyxel Device), source IP
address and object, destination IP address and object, IP protocol type of network traffic (service) and
Security Service profile criteria against the Security Policies (in the order you list them). When the traffic
matches a policy, the Zyxel Device takes the action specified in the policy.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
494
Page 15

Chapter 25 Security Policy
User Specific Security Policies
You can specify users or user groups in Security Policies. For example, to allow a specific user from any
computer to access a zone by logging in to the Zyxel Device, you can set up a policy based on the user
name only. If you also apply a schedule to the Security Policy, the user can only access the network at
the scheduled time. A user-aware Security Policy is activated whenever the user logs in to the Zyxel
Device and will be disabled after the user logs out of the Zyxel Device.
Session Limits
Accessing the Zyxel Device or network resources through the Zyxel Device requires a NAT session and
corresponding Security Policy session. Peer to peer applications, such as file sharing applications, may
use a large number of NAT sessions. A single client could use all of the available NAT sessions and
prevent others from connecting to or through the Zyxel Device. The Zyxel Device lets you limit the
number of concurrent NAT/Security Policy sessions a client can use.
25.4 The Security Policy Screen
Asymmetrical Routes
If an alternate gateway on the LAN has an IP address in the same subnet as the Zyxel Device’s LAN IP
address, return traffic may not go through the Zyxel Device. This is called an asymmetrical or “triangle”
route. This causes the Zyxel Device to reset the connection, as the connection has not been
acknowledged.
You can have the Zyxel Device permit the use of asymmetrical route topology on the network (not reset
the connection). However, allowing asymmetrical routes may let traffic from the WAN go directly to the
LAN without passing through the Zyxel Device. A better solution is to use virtual interfaces to put the Zyxel
Device and the backup gateway on separate subnets. Virtual interfaces allow you to partition your
network into logical sections over the same interface. See the chapter about interfaces for more
information.
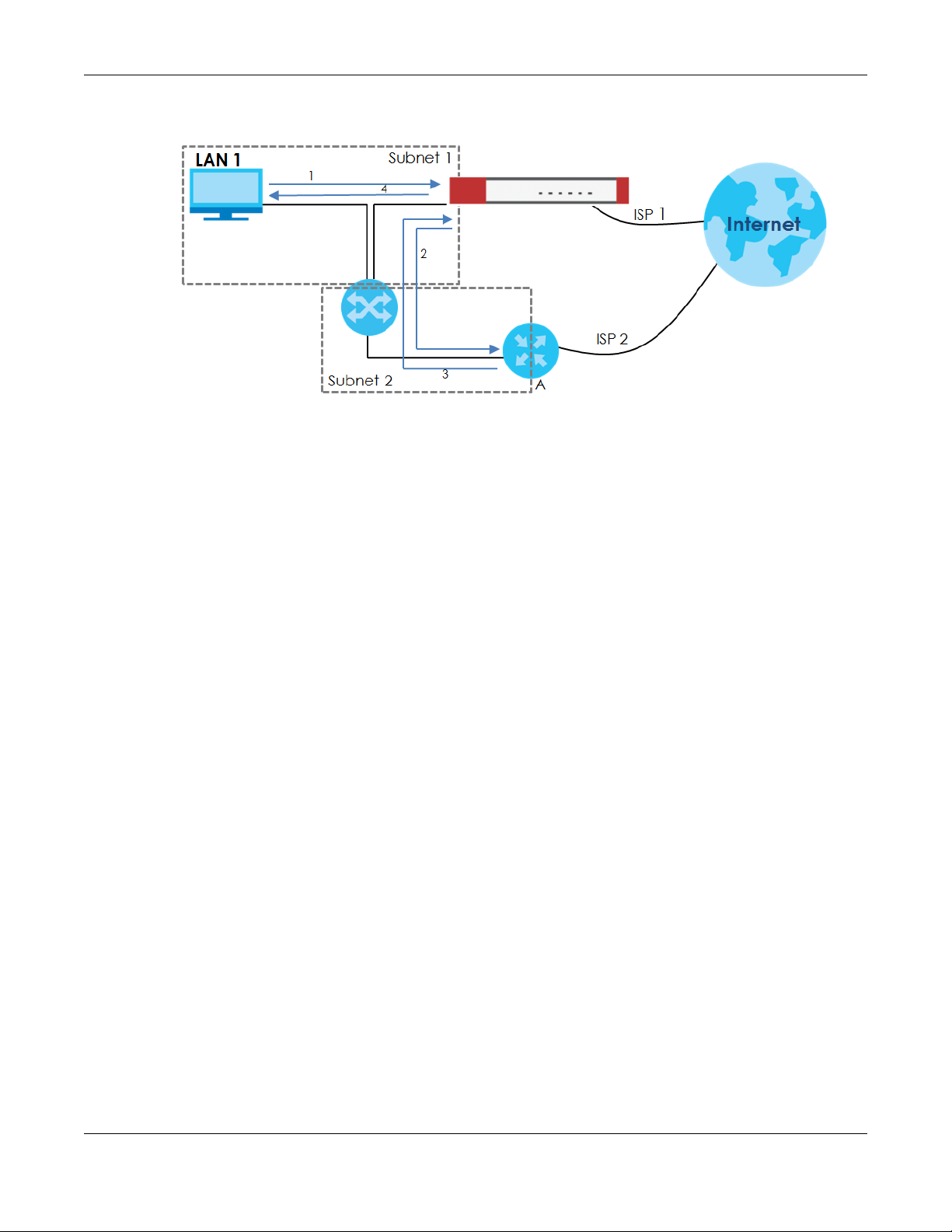
By putting LAN 1 and the alternate gateway (A in the figure) in different subnets, all returning network
traffic must pass through the Zyxel Device to the LAN. The following steps and figure describe such a
scenario.
1 A computer on the LAN1 initiates a connection by sending a SYN packet to a receiving server on the
WAN.
2 The Zyxel Device reroutes the packet to gateway A, which is in Subnet 2.
3 The reply from the WAN goes to the Zyxel Device.
4 The Zyxel Device then sends it to the computer on the LAN1 in Subnet 1.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
495
Page 16
Chapter 25 Security Policy
Figure 345 Using Virtual Interfaces to Avoid Asymmetrical Routes
25.4.1 Configuring the Security Policy Control Screen
Click Configuration > Security Policy > Policy Control to open the Security Policy screen. Use this screen
to enable or disable the Security Policy and asymmetrical routes, set a maximum number of sessions per
host, and display the configured Security Policies. Specify from which zone packets come and to which
zone packets travel to display only the policies specific to the selected direction. Note the following.
• Besides configuring the Security Policy, you also need to configure NAT rules to allow computers on
the WAN to access LAN devices.
• The Zyxel Device applies NAT (Destination NAT) settings before applying the Security Policies. So for
example, if you configure a NAT entry that sends WAN traffic to a LAN IP address, when you configure
a corresponding Security Policy to allow the traffic, you need to set the LAN IP address as the
destination.
• The ordering of your policies is very important as policies are applied in sequence.
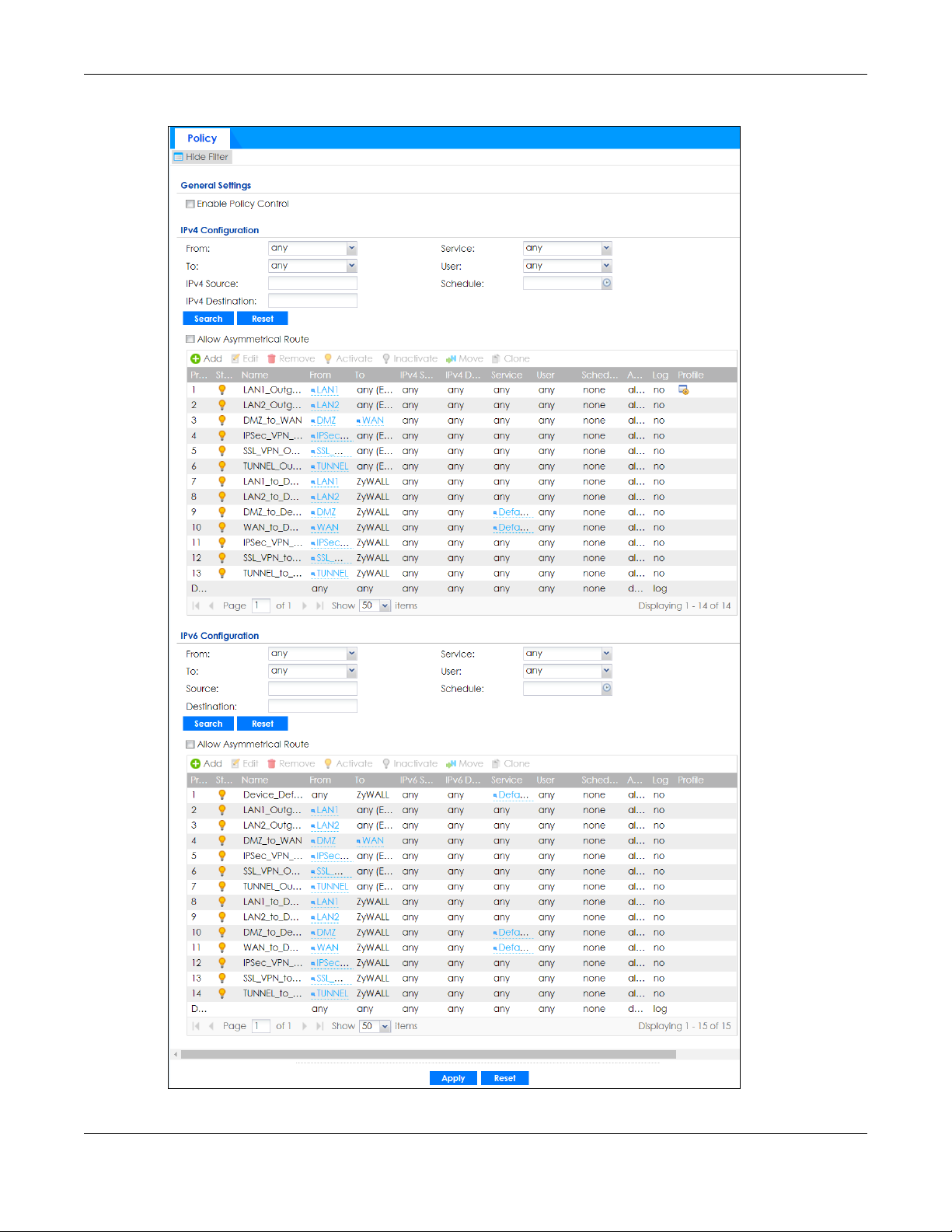
The following screen shows the Security Policy summary screen.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
496
Page 17
Chapter 25 Security Policy
Figure 346 Configuration > Security Policy > Policy Control
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
497
Page 18
Chapter 25 Security Policy
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 193 Configuration > Security Policy > Policy Control
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Show Filter/Hide
Filter
General Settings Enable or disable the Security Policy feature on the Zyxel Device.
Enable Policy
Control
IPv4 / IPv6
Configuration
From / To Select a zone to view all security policies from a particular zone and/or to a particular zone.
IPv4 / IPv6
Source
IPv4 / IPv6
Destination
Click Show Filter to display IPv4 and IPv6 (if enabled) security policy search filters.
Select this to activate Security Policy on the Zyxel Device to perform access control.
Use IPv4 / IPv6 search filters to find specific IPv4 and IPv6 (if enabled) security policies based on
direction, application, user, source, destination and/or schedule.
any means all zones.
Type an IPv4 or IPv6 IP address to view all security policies based on the IPv4 / IPv6 source
address object used.
• An IPv4 IP address is written as four integer blocks separated by periods. This is an example
IPv4 address: 172.16.6.7.
• An 128-bit IPv6 address is written as eight 16-bit hexadecimal blocks separated by colons
(:). This is an example IPv6 address: 2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000.
Type an IPv4 or IPv6 IP address to view all security policies based on the IPv4 / IPv6 destination
address object used.
• An IPv4 IP address is written as four integer blocks separated by periods. This is an example
IPv4 address: 172.16.6.7.
• An 128-bit IPv6 address is written as eight 16-bit hexadecimal blocks separated by colons
(:). This is an example IPv6 address: 2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000.
Service View all security policies based the service object used.
User View all security policies based on user or user group object used.
Schedule View all security policies based on the schedule object used.
IPv4/IPv6 Policy
Management
Allow
Asymmetrical
Route
Use the following items to manage IPv4 and IPv6 policies.
If an alternate gateway on the LAN has an IP address in the same subnet as the Zyxel Device’s
LAN IP address, return traffic may not go through the Zyxel Device. This is called an
asymmetrical or “triangle” route. This causes the Zyxel Device to reset the connection, as the
connection has not been acknowledged.
Select this check box to have the Zyxel Device permit the use of asymmetrical route topology
on the network (not reset the connection).
Note: Allowing asymmetrical routes may let traffic from the WAN go directly to the
LAN without passing through the Zyxel Device. A better solution is to use virtual
interfaces to put the Zyxel Device and the backup gateway on separate
subnets.
Add Click this to create a new entry. Select an entry and click Add to create a new entry after the
selected entry.
Edit Double-click an entry or select it and click Edit to open a screen where you can modify the
Remove To remove an entry, select it and click Remove. The Zyxel Device confirms you want to remove
Activate To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
entry’s settings.
it before doing so.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
498
Page 19

Chapter 25 Security Policy
Table 193 Configuration > Security Policy > Policy Control (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Move To change a policy’s position in the numbered list, select the policy and click Move to display a
field to type a number for where you want to put that policy and press [ENTER] to move the
policy to the number that you typed.
The ordering of your policies is important as they are applied in order of their numbering.
Clone Use Clone to create a new entry by modifying an existing one.
• Select an existing entry.
•Click Clone, type a number where the new entry should go and then press [ENTER].
• A configuration copy of the selected entry pops up. You must at least change the name as
duplicate entry names are not allowed.
The following read-only fields summarize the policies you have created that apply to traffic traveling in the
selected packet direction.
Priority This is the position of your Security Policy in the global policy list (including all through-Zyxel
Device and to-Zyxel Device policies). The ordering of your policies is important as policies are
applied in sequence. Default displays for the default Security Policy behavior that the Zyxel
Device performs on traffic that does not match any other Security Policy.
Status This icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the entry is inactive.
Name This is the name of the Security policy.
From / To This is the direction of travel of packets. Select from which zone the packets come and to
which zone they go.
Security Policies are grouped based on the direction of travel of packets to which they apply.
For example, from LAN to LAN means packets traveling from a computer or subnet on the LAN
to either another computer or subnet on the LAN.
From any displays all the Security Policies for traffic going to the selected To Zone.
To any displays all the Security Policies for traffic coming from the selected From Zone.
From any to any displays all of the Security Policies.
To ZyWALL policies are for traffic that is destined for the Zyxel Device and control which
computers can manage the Zyxel Device.
IPv4 / IPv6 Source This displays the IPv4 / IPv6 source address object, including geographic address and FQDN
IPv4 / IPv6
Destination
Service This displays the service object to which this Security Policy applies.
User This is the user name or user group name to which this Security Policy applies.
Schedule This field tells you the schedule object that the policy uses. none means the policy is active at all
Action This field displays whether the Security Policy silently discards packets without notification
Log Select whether to have the Zyxel Device generate a log (log), log and alert (log alert) or not
Profile This field shows you which Security Service profiles (application patrol, content filter, IDP, anti-
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
(group) objects, to which this Security Policy applies.
This displays the IPv4 / IPv6 destination address object, including geographic address and
FQDN (group) objects, to which this Security Policy applies.
times if enabled.
(deny), permits the passage of packets (allow) or drops packets with notification (reject)
(
no) when the policy is matched to the criteria listed above.
malware, email security) apply to this Security policy. Click an applied Security Service profile
icon to edit the profile directly.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
499
Page 20
Chapter 25 Security Policy
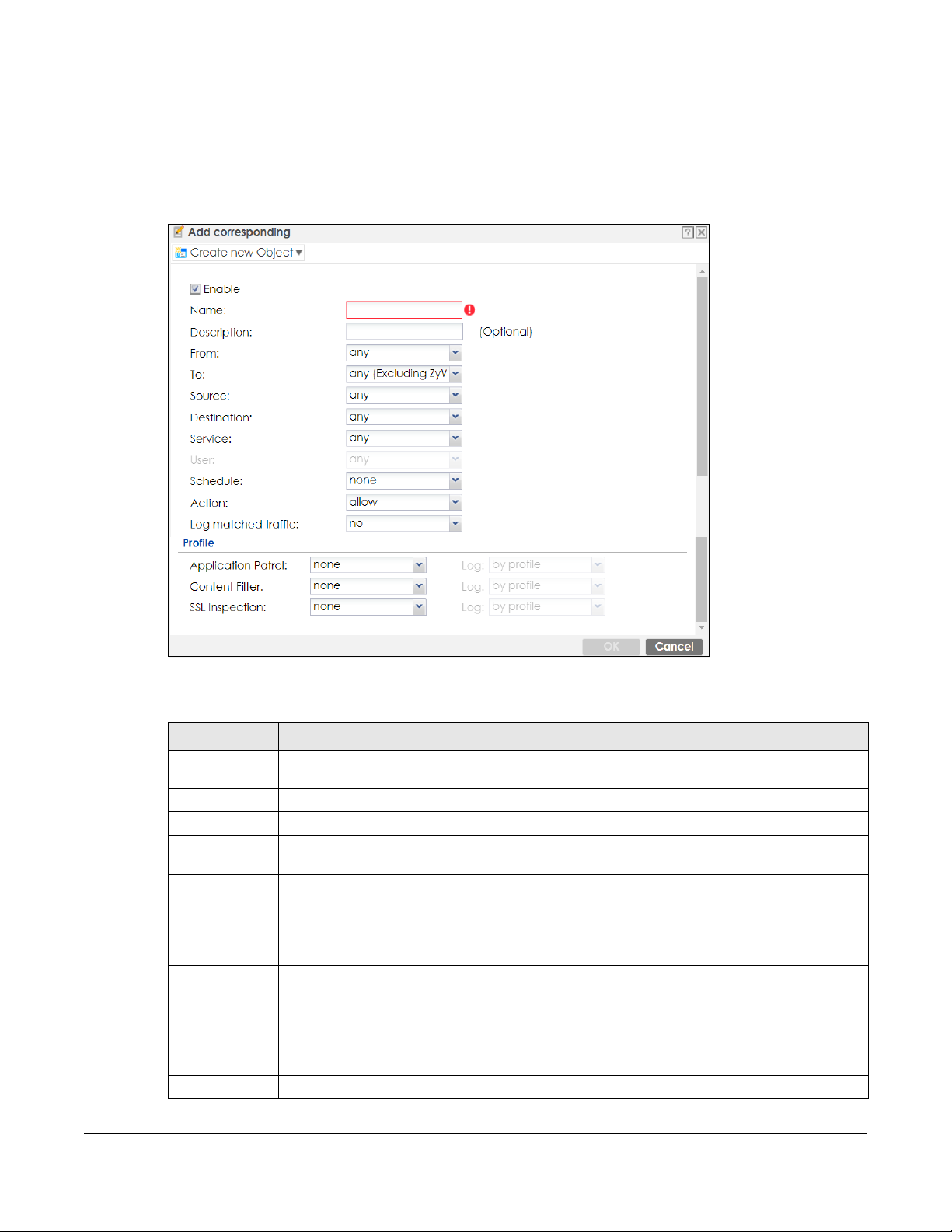
25.4.2 The Security Policy Control Add/Edit Screen
In the Security Policy Control screen, click the Edit or Add icon to display the Security Policy Edit or Add
screen.
Figure 347 Configuration > Security Policy > Policy Control > Add
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 194 Configuration > Security Policy > Policy Control > Add
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Create new
Object
Enable Select this check box to activate the Security policy.
Name Type a name to identify the policy
Description Enter a descriptive name of up to 60 printable ASCII characters for the Policy. Spaces are
From
To
Source Select an IPv4 / IPv6 address or address group object, including geographic address and FQDN
Destination Select an IPv4 / IPv6 address or address group, including geographic address and FQDN (group)
Service Select a service or service group from the drop-down list box.
Use to configure any new settings objects that you need to use in this screen.
allowed.
For through-Zyxel Device policies, select the direction of travel of packets to which the policy
applies.
any means all interfaces.
Device means packets destined for the Zyxel Device itself.
(group) objects, to apply the policy to traffic coming from it. Select any to apply the policy to all
traffic coming from IPv4 / IPv6 addresses.
objects, to apply the policy to traffic going to it. Select any to apply the policy to all traffic going
to IPv4 / IPv6 addresses.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
500
Page 21
Chapter 25 Security Policy
Table 194 Configuration > Security Policy > Policy Control > Add (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
User This field is not available when you are configuring a to-Zyxel Device policy.
Select a user name or user group to which to apply the policy. The Security Policy is activated
only when the specified user logs into the system and the policy will be disabled when the user
logs out.
Otherwise, select any and there is no need for user logging.
Note: If you specified a source IP address (group) instead of any in the field below, the
user’s IP address should be within the IP address range.
Schedule Select a schedule that defines when the policy applies. Otherwise, select none and the policy is
always effective.
Action Use the drop-down list box to select what the Security Policy is to do with packets that match this
policy.
Select deny to silently discard the packets without sending a TCP reset packet or an ICMP
destination-unreachable message to the sender.
Select reject to discard the packets and send a TCP reset packet or an ICMP destination-
unreachable message to the sender.
Select allow to permit the passage of the packets.
Log matched
traffic
Profile Use this section to apply anti- x profiles (created in the Configuration > Security Service screens)
Select whether to have the Zyxel Device generate a log (log), log and alert (log alert) or not (no)
when the policy is matched to the criteria listed above..
to traffic that matches the criteria above. You must have created a profile first; otherwise none
displays.
Use Log to generate a log (log), log and alert (log alert) or not (no) for all traffic that matches
criteria in the profile.
Application
Patrol
Content
Filter
SSL
Inspection
OK Click OK to save your customized settings and exit this screen.
Cancel Click Cancel to exit this screen without saving.
Select an Application Patrol profile from the list box; none displays if no profiles have been
created in the Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol screen.
Select a Content Filter profile from the list box; none displays if no profiles have been created in
the Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter screen.
Select an SSL Inspection profile from the list box; none displays if no profiles have been created in
the Configuration > Security Service > SSL Inspection screen.
25.5 Anomaly Detection and Prevention Overview
Anomaly Detection and Prevention (ADP) protects against anomalies based on violations of protocol
standards (RFCs – Requests for Comments) and abnormal flows such as port scans. This section
introduces ADP, anomaly profiles and applying an ADP profile to a traffic direction.
Traffic Anomalies
Traffic anomaly policies look for abnormal behavior or events such as port scanning, sweeping or
network flooding. They operate at OSI layer-2 and layer-3. Traffic anomaly policies may be updated
when you upload new firmware.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
501
Page 22
Chapter 25 Security Policy
Protocol Anomalies
Protocol anomalies are packets that do not comply with the relevant RFC (Request For Comments).
Protocol anomaly detection includes:
•TCP Decoder
• UDP Decoder
•ICMP Decoder
Protocol anomaly policies may be updated when you upload new firmware.
Note: First, create an ADP profile in the In the Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > Profile
screen.
Then, apply the profile to traffic originating from a specific zone in the Configuration >
Security Policy > ADP > General screen.
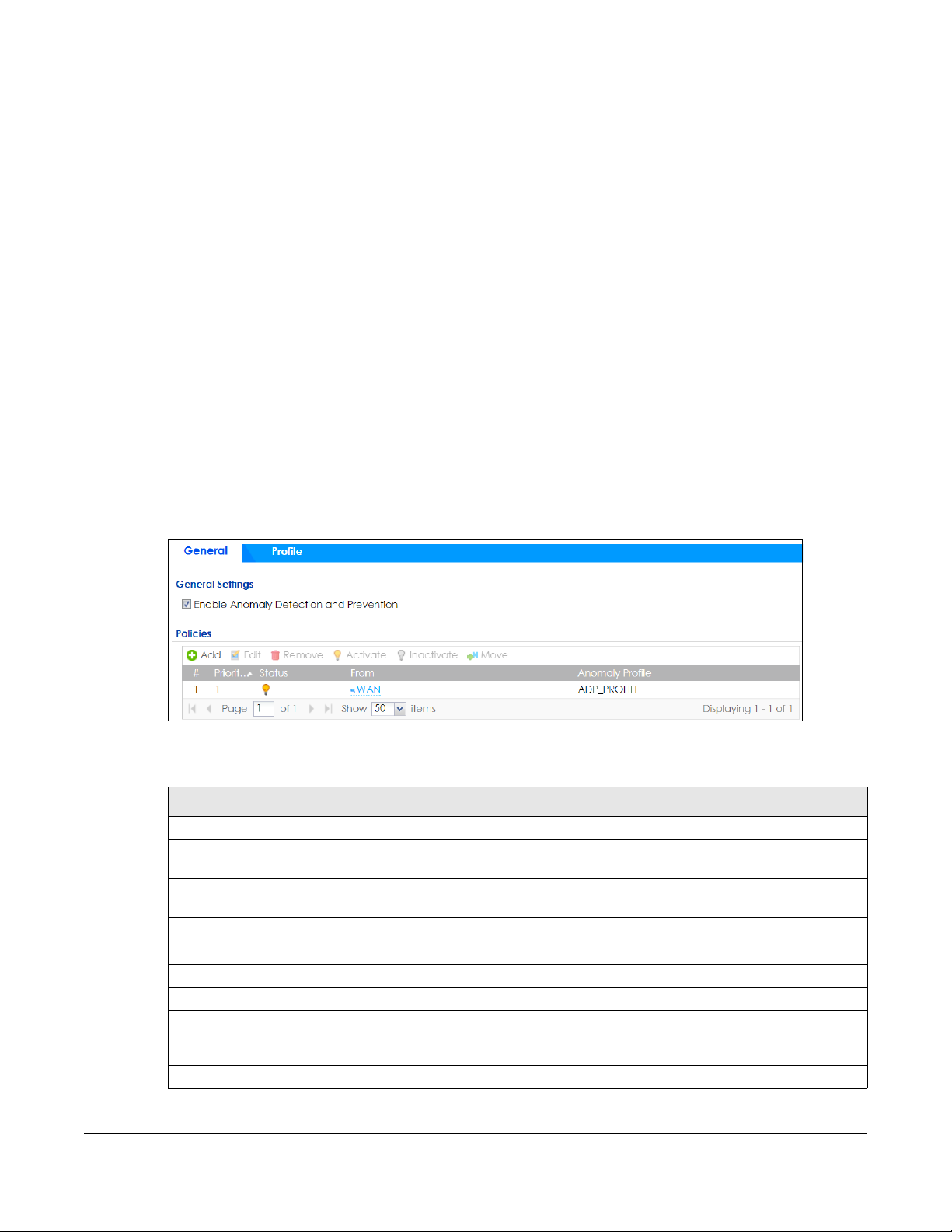
25.5.1 The Anomaly Detection and Prevention General Screen
Click Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > General to display the next screen.
Figure 348 Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > General
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 195 Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General Settings
Enable Anomaly Detection
and Prevention
Add Select an entry and click Add to append a new row beneath the one selected. ADP
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
Activate
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
Move To change an entry’s position in the numbered list, select it and click Move to display
#
Select this to enable traffic anomaly and protocol anomaly detection and
prevention.
policies are applied in order (Priority) shown in this screen
To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
a field to type a number for where you want to put that entry and press [ENTER] to
move the entry to the number that you typed.
This is the entry’s index number in the list.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
502
Page 23
Chapter 25 Security Policy
Table 195 Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Priority This is the rank in the list of anomaly profile policies. The list is applied in order of
priority.
Status The activate (light bulb) icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the
From This is the direction of travel of packets to which an anomaly profile is bound. Traffic
Anomaly Profile An anomaly profile is a set of anomaly policies with configured activation, log and
entry is inactive.
direction is defined by the zone the traffic is coming from.
Use the From field to specify the zone from which the traffic is coming. Select ZyWALL
to specify traffic coming from the Zyxel Device itself.
From LAN means packets traveling from a computer on one LAN subnet to a
computer on another subnet via the Zyxel Device’s LAN1 zone interfaces. The Zyxel
Device does not check packets traveling from a LAN computer to another LAN
computer on the same subnet.
From WAN means packets that come in from the WAN zone and the Zyxel Device
routes back out through the WAN zone.
Note: Depending on your network topology and traffic load, applying
every packet direction to an anomaly profile may affect the Zyxel
Device’s performance.
action settings. This field shows which anomaly profile is bound to which traffic
direction. Select an ADP profile to apply to the entry’s traffic direction. Configure the
ADP profiles in the ADP profile screens.
25.5.2 Creating New ADP Profiles
Create new ADP profiles in the Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > Profile screens.
When creating ADP profiles. you may find that certain policies are triggering too many false positives or
false negatives. A false positive is when valid traffic is flagged as an attack. A false negative is when
invalid traffic is wrongly allowed to pass through the Zyxel Device. As each network is different, false
positives and false negatives are common on initial ADP deployment.
To counter this, you could create a ‘monitor profile’ that creates logs, but all actions are disabled.
Observe the logs over time and try to eliminate the causes of the false alarms. When you’re satisfied that
they have been reduced to an acceptable level, you could then create an ‘in-line profile’ whereby you
configure appropriate actions to be taken when a packet matches a policy.
ADP profiles consist of traffic anomaly profiles and protocol anomaly profiles. To create a new profile,
select a base profile and then click OK to go to the profile details screen. Type a new profile name,
enable or disable individual policies and then edit the default log options and actions.
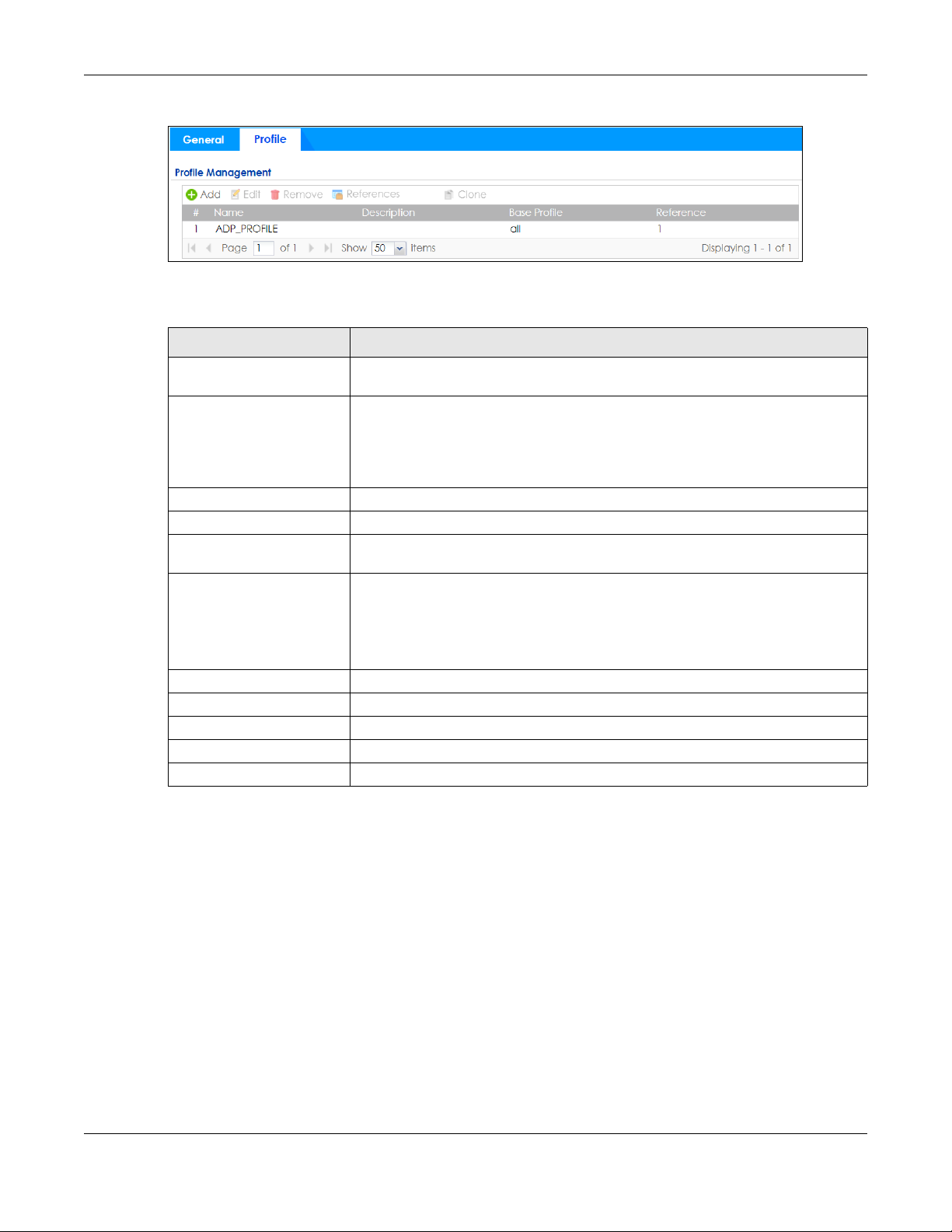
Click Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > Profile to view the following screen.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
503
Page 24
Chapter 25 Security Policy
Figure 349 Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > Profile
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 196 Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > Profile
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Profile Management Create ADP profiles here and then apply them in the Configuration > Security Policy
> ADP > Profile screen.
Add Click Add and first choose a none or all Base Profile.
• none base profile sets all ADP entries to have Log set to no and Action set to
none by default.
• all base profile sets all ADP entries to have Log set to log and Action set to block
by default.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
References Select an entry and click References to open a screen that shows which settings use
the entry. Click Refresh to update information on this screen.
Clone Use Clone to create a new entry by modifying an existing one.
• Select an existing entry.
•Click Clone.
• A configuration copy of the selected entry pops up. You must at least change
the name as duplicate entry names are not allowed.
#
Name This is the name of the profile you created.
Description This is the description of the profile you created.
Base Profile This is the name of the base profile used to create this profile.
Reference This is the number of object references used to create this profile.
This is the entry’s index number in the list.
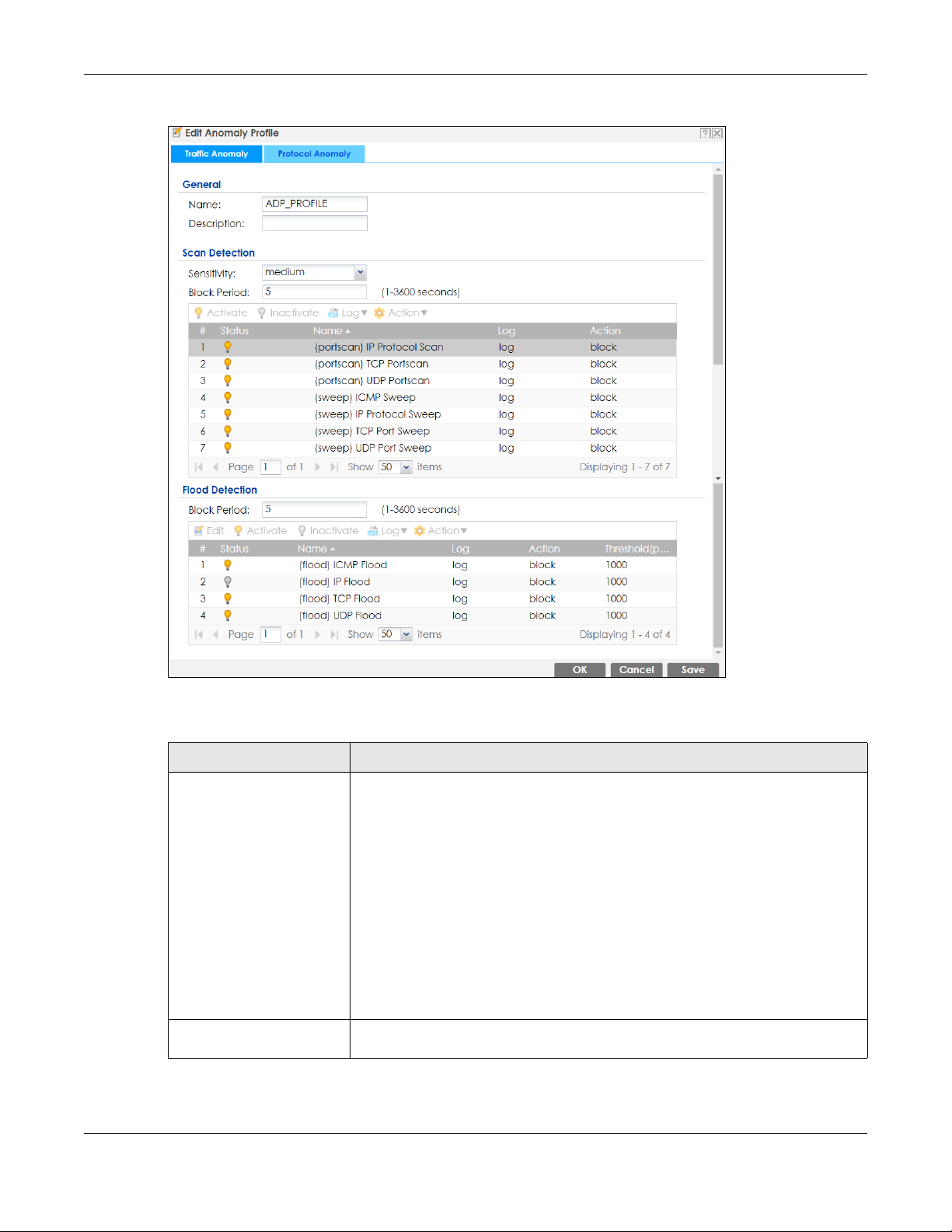
25.5.3 Traffic Anomaly Profiles
Traffic anomaly detection looks for abnormal behavior such as scan or flooding attempts. In the
Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > Profile screen, click the Edit or Add icon and choose a base
profile. Traffic Anomaly is the first tab in the profile.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
504
Page 25
Chapter 25 Security Policy
Figure 350 Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > Profile > Add-Traffic-Anomaly
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 197 Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > Profile > Add-Traffic-Anomaly
LABELS DESCRIPTION
Name A name is automatically generated that you can edit. The name must be the same
in the Traffic Anomaly and Protocol Anomaly screens for the same ADP profile. You
may use 1-31 alphanumeric characters, underscores(
character cannot be a number. This value is case-sensitive. These are valid, unique
profile names:
•MyProfile
• mYProfile
• Mymy12_3-4
These are invalid profile names:
•1mYProfile
•My Profile
• MyProfile?
• Whatalongprofilename123456789012
Description In addition to the name, type additional information to help you identify this ADP
profile.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
_), or dashes (-), but the first
505
Page 26
Chapter 25 Security Policy
Table 197 Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > Profile > Add-Traffic-Anomaly (continued)
LABELS DESCRIPTION
Scan/Flood Detection Scan detection, such as port scanning, tries to find attacks where an attacker scans
device(s) to determine what types of network protocols or services a device
supports.
Flood detection tries to find attacks that saturate a network with useless data, use up
all available bandwidth, and so aim to make communications in the network
impossible.
Sensitivity (Scan detection only.) Select a sensitivity level so as to reduce false positives in your
network. If you choose low sensitivity, then scan thresholds and sample times are set
low, so you will have fewer logs and false positives; however some traffic anomaly
attacks may not be detected.
If you choose high sensitivity, then scan thresholds and sample times are set high, so
most traffic anomaly attacks will be detected; however you will have more logs and
false positives.
Block Period Specify for how many seconds the Zyxel Device blocks all packets from being sent
Edit (Flood Detection
only)
Activate To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
Log To edit an item’s log option, select it and use the Log icon. Select whether to have
Action To edit what action the Zyxel Device takes when a packet matches a policy, select
to the victim (destination) of a detected anomaly attack. Flood Detection applies
blocking to the destination IP address and Scan Detection applies blocking to the
source IP address.
Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
the Zyxel Device generate a log (log), log and alert (log alert) or neither (no) when
traffic matches this anomaly policy.
the policy and use the Action icon.
none: The Zyxel Device takes no action when a packet matches the policy.
block: The Zyxel Device silently drops packets that matches the policy. Neither
sender nor receiver are notified.
#
Status The activate (light bulb) icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the
Name This is the name of the anomaly policy. Click the Name column heading to sort in
Log These are the log options. To edit this, select an item and use the Log icon.
Action This is the action the Zyxel Device should take when a packet matches a policy. To
Threshold (pkt/sec) (Flood detection only.) Select a suitable threshold level (the number of packets per
OK Click OK to save your settings to the Zyxel Device, complete the profile and return to
Cancel Click Cancel to return to the profile summary page without saving any changes.
Save Click Save to save the configuration to the Zyxel Device but remain in the same
This is the entry’s index number in the list.
entry is inactive.
ascending or descending order according to the protocol anomaly policy name.
edit this, select an item and use the Action icon.
second that match the flood detection criteria) for your network. If you choose a
low threshold, most traffic anomaly attacks will be detected, but you may have
more logs and false positives.
If you choose a high threshold, some traffic anomaly attacks may not be detected,
but you will have fewer logs and false positives.
the profile summary page.
page. You may then go to the another profile screen (tab) in order to complete the
profile. Click OK in the final profile screen to complete the profile.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
506
Page 27

Chapter 25 Security Policy
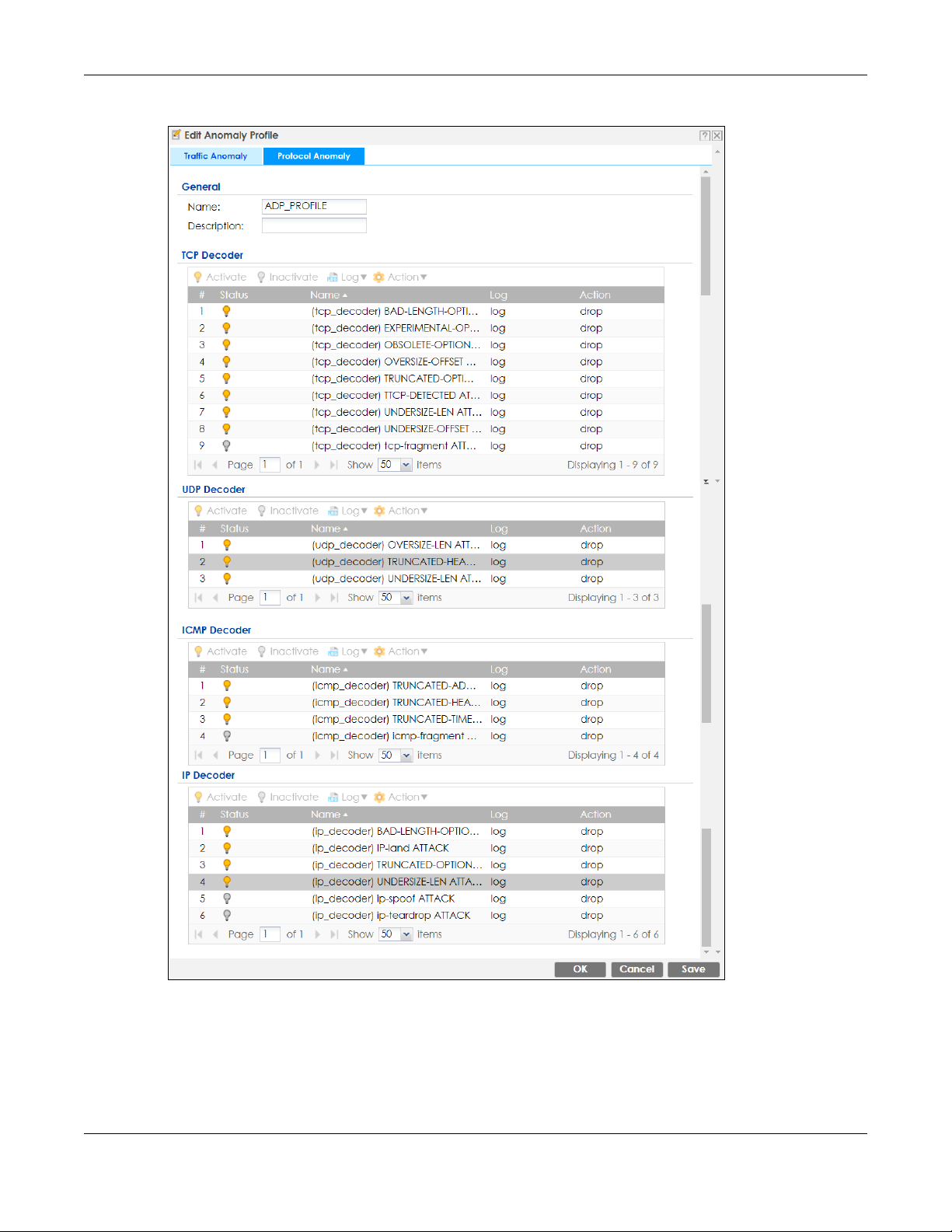
25.5.4 Protocol Anomaly Profiles
Protocol anomalies are packets that do not comply with the relevant RFC (Request For Comments).
Protocol anomaly detection includes:
•TCP Decoder
• UDP Decoder
•ICMP Decoder
• IP Decoder
Teardrop
When an IP packet is larger than the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) configured in the Zyxel Device, it
is fragmented using the TCP or ICMP protocol.
A Teardrop attack falsifies the offset which defines the size of the fragment and the original packet. A
series of IP fragments with overlapping offset fields can cause some systems to crash, hang, or reboot
when fragment reassembling is attempted at the destination.
IP Spoofing
IP Spoofing is used to gain unauthorized access to network devices by modifying packet headers so
that it appears that the packets originate from a host within a trusted network.
• In an IP Spoof from the WAN, the source address appears to be in the same subnet as a Zyxel Device
LAN interface.
• In an IP Spoof from a LAN interface, the source address appears to be in a different subnet from that
Zyxel Device LAN interface.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
507
Page 28
Chapter 25 Security Policy
Figure 351 Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > Profile > Add-Protocol-Anomaly
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
508
Page 29
Chapter 25 Security Policy
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 198 Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > Profile > Add-Protocol-Anomaly
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name A name is automatically generated that you can edit. The name must be the same
in the Traffic Anomaly and Protocol Anomaly screens for the same ADP profile. You
may use 1-31 alphanumeric characters, underscores(
character cannot be a number. This value is case-sensitive. These are valid, unique
profile names:
•MyProfile
• mYProfile
• Mymy12_3-4
• These are invalid profile names:
•1mYProfile
•My Profile
• MyProfile?
• Whatalongprofilename123456789012
Description In addition to the name, type additional information to help you identify this ADP
TCP Decoder/UDP
Decoder/ICMP Decoder/IP
Decoder
Activate To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
Log To edit an item’s log option, select it and use the Log icon. Select whether to have
Action To edit what action the Zyxel Device takes when a packet matches a policy, select
profile.
Perform the following actions for each type of encoder.
the Zyxel Device generate a log (log), log and alert (log alert) or neither (no) when
traffic matches this anomaly policy.
the policy and use the Action icon.
original setting: Select this action to return each rule in a service group to its
previously saved configuration.
none: Select this action to have the Zyxel Device take no action when a packet
matches a policy.
drop: Select this action to have the Zyxel Device silently drop a packet that matches
a policy. Neither sender nor receiver are notified.
reject-sender: Select this action to have the Zyxel Device send a reset to the sender
when a packet matches the policy. If it is a TCP attack packet, the Zyxel Device will
send a packet with a ‘RST’ flag. If it is an ICMP or UDP attack packet, the Zyxel
Device will send an ICMP unreachable packet.
_), or dashes (-), but the first
reject-receiver: Select this action to have the Zyxel Device send a reset to the
receiver when a packet matches the policy. If it is a TCP attack packet, the Zyxel
Device will send a packet with an a ‘RST’ flag. If it is an ICMP or UDP attack packet,
the Zyxel Device will do nothing.
reject-both: Select this action to have the Zyxel Device send a reset to both the
sender and receiver when a packet matches the policy. If it is a TCP attack packet,
the Zyxel Device will send a packet with a ‘RST’ flag to the receiver and sender. If it is
an ICMP or UDP attack packet, the Zyxel Device will send an ICMP unreachable
packet.
# This is the entry’s index number in the list.
Status The activate (light bulb) icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the
Name This is the name of the anomaly policy. Click the Name column heading to sort in
entry is inactive.
ascending or descending order according to the protocol anomaly policy name.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
509
Page 30
Chapter 25 Security Policy
Table 198 Configuration > Security Policy > ADP > Profile > Add-Protocol-Anomaly
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Log These are the log options. To edit this, select an item and use the Log icon.
Action This is the action the Zyxel Device should take when a packet matches a policy. To
edit this, select an item and use the Action icon.
OK Click OK to save your settings to the Zyxel Device, complete the profile and return to
Cancel Click Cancel to return to the profile summary page without saving any changes.
Save Click Save to save the configuration to the Zyxel Device but remain in the same
the profile summary page.
page. You may then go to the another profile screen (tab) in order to complete the
profile. Click OK in the final profile screen to complete the profile.
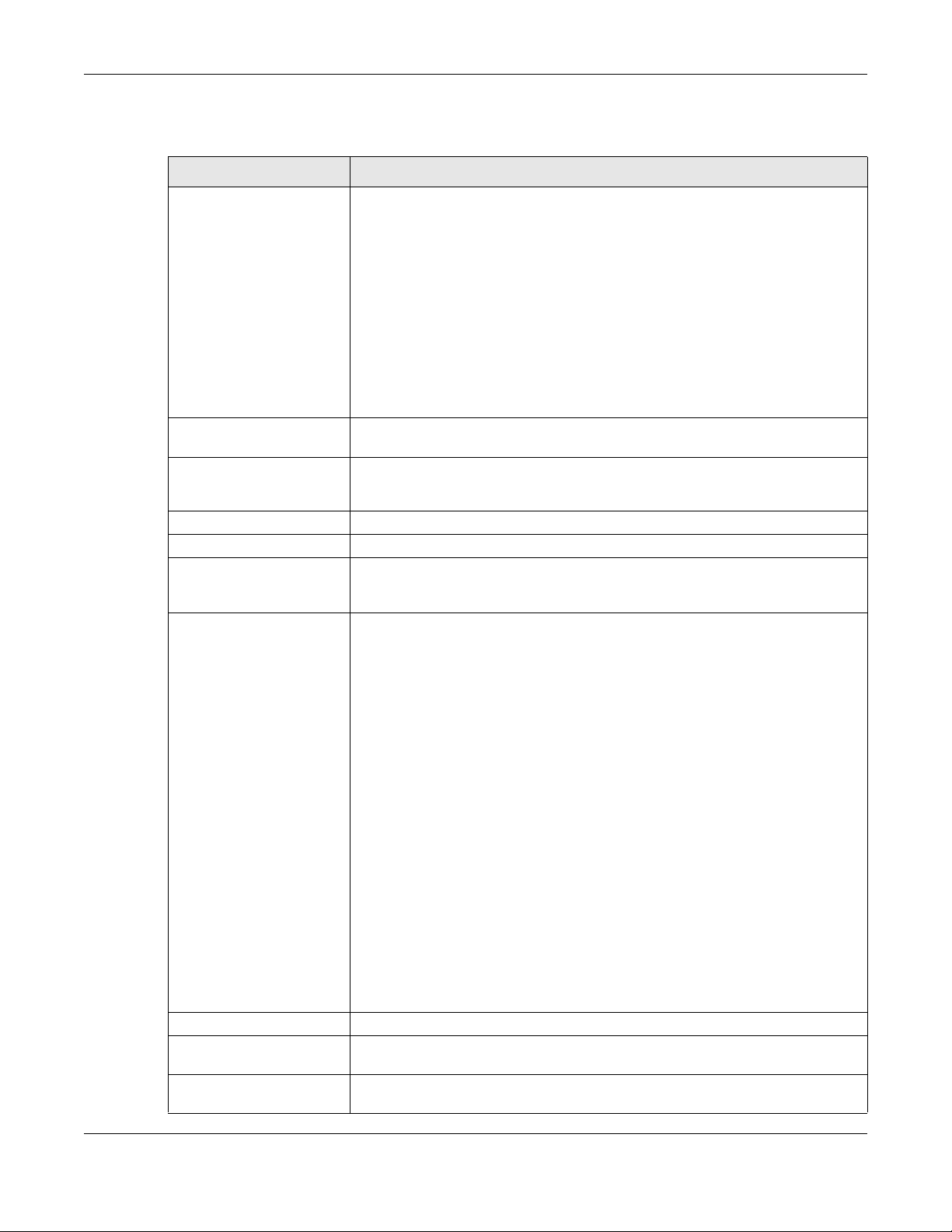
25.6 The Session Control Screen
Click Configuration > Security Policy > Session Control to display the Security Policy Session Control
screen. Use this screen to limit the number of concurrent NAT/Security Policy sessions a client can use.
You can apply a default limit for all users and individual limits for specific users, addresses, or both. The
individual limit takes priority if you apply both.
Figure 352 Configuration > Security Policy > Session Control
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
510
Page 31

Chapter 25 Security Policy
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 199 Configuration > Security Policy > Session Control
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General Settings
UDP Session Time
Out
Session Limit
Settings
Enable Session
limit
IPv4 / IPv6
Configuration
Default
Session per
Host
Add Click this to create a new entry. Select an entry and click Add to create a new entry after the
Edit Double-click an entry or select it and click Edit to open a screen where you can modify the
Remove To remove an entry, select it and click Remove. The Zyxel Device confirms you want to remove
Activate To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
Move To change a rule’s position in the numbered list, select the rule and click Move to display a field
# This field is a sequential value showing the number of the profile. The profile order is not
Status This icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the entry is inactive.
# This is the index number of a session limit rule. It is not associated with a specific rule.
User This is the user name or user group name to which this session limit rule applies.
IPv4 / IPv6 Address This is the IPv4 / IPv6 address object, including geographic address (group) objects to which
Description This is the information configured to help you identify the rule.
Limit This is how many concurrent sessions this user or address is allowed to have.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
Set how many seconds the Zyxel Device will allow a UDP session to remain idle (without UDP
traffic) before closing it.
Select this check box to control the number of concurrent sessions hosts can have.
This table lists the rules for limiting the number of concurrent sessions hosts can have.
This field is configurable only when you enable session limit.
Use this field to set a common limit to the number of concurrent NAT/Security Policy sessions
each client computer can have.
If only a few clients use peer to peer applications, you can raise this number to improve their
performance. With heavy peer to peer application use, lower this number to ensure no single
client uses too many of the available NAT sessions.
Create rules below to apply other limits for specific users or addresses.
selected entry.
entry’s settings.
it before doing so.
to type a number for where you want to put that rule and press [ENTER] to move the rule to the
number that you typed.
The ordering of your rules is important as they are applied in order of their numbering.
important.
this session limit rule applies.
25.6.1 The Session Control Add/Edit Screen
Click Configuration > Security Policy > Session Contr ol and the Add or Edit icon to display the Add or Edit
screen. Use this screen to configure rules that define a session limit for specific users or addresses.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
511
Page 32

Chapter 25 Security Policy
Figure 353 Configuration > Security Policy > Session Control > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 200 Configuration > Security Policy > Session Control > Add / Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Create new
Object
Enable Rule Select this check box to turn on this session limit rule.
Description Enter information to help you identify this rule. Use up to 60 printable ASCII characters. Spaces
User Select a user name or user group to which to apply the rule. The rule is activated only when the
Use to configure new settings for User or Address objects that you need to use in this
screen.Click on the down arrow to see the menu.
are allowed.
specified user logs into the system and the rule will be disabled when the user logs out.
Otherwise, select any and there is no need for user logging.
Note: If you specified an IP address (or address group) instead of any in the field
below, the user’s IP address should be within the IP address range.
Address Select the IPv4 source address or address group, including geographic address (group)
object, to which this rule applies. Select any to apply the rule to all IPv4 source addresses.
IPv6 Address Select the IPv6 source address or address group, including geographic address (group)
object, to which this rule applies. Select any to apply the rule to all IPv6 source addresses.
Session Limit per
Host
OK Click OK to save your customized settings and exit this screen.
Cancel Click Cancel to exit this screen without saving.
Use this field to set a limit to the number of concurrent NAT/Security Policy sessions this rule’s
users or addresses can have.
For this rule’s users and addresses, this setting overrides the Default Session per Host setting in
the general Security Policy Session Control screen.
25.7 Security Policy Example Applications
Suppose you decide to block LAN users from using IRC (Internet Relay Chat) through the Internet. To do
this, you would configure a LAN to WAN Security Policy that blocks IRC traffic from any source IP address
from going to any destination address. You do not need to specify a schedule since you need the
Security Policy to always be in effect. The following figure shows the results of this policy.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
512
Page 33

Chapter 25 Security Policy
Figure 354 Blocking All LAN to WAN IRC Traffic Example
Your Security Policy would have the following settings.
Table 201 Blocking All LAN to WAN IRC Traffic Example
# USER SOURCE DESTINATION SCHEDULE SERVICE ACTION
1 Any Any Any Any IRC Deny
2 Any Any Any Any Any Allow
• The first row blocks LAN access to the IRC service on the WAN.
• The second row is the Security Policy’s default policy that allows all LAN1 to WAN traffic.
The Zyxel Device applies the security policies in order. So for this example, when the Zyxel Device
receives traffic from the LAN, it checks it against the first policy. If the traffic matches (if it is IRC traffic)
the security policy takes the action in the policy (drop) and stops checking the subsequent security
policies. Any traffic that does not match the first security policy will match the second security policy
and the Zyxel Device forwards it.
Now suppose you need to let the CEO use IRC. You configure a LAN1 to WAN security policy that allows
IRC traffic from the IP address of the CEO’s computer. You can also configure a LAN to WAN policy that
allows IRC traffic from any computer through which the CEO logs into the Zyxel Device with his/her user
name. In order to make sure that the CEO’s computer always uses the same IP address, make sure it
either:
• Has a static IP address,
or
• You configure a static DHCP entry for it so the Zyxel Device always assigns it the same IP address.
Now you configure a LAN1 to WAN security policy that allows IRC traffic from the IP address of the CEO’s
computer (172.16.1.7 for example) to go to any destination address. You do not need to specify a
schedule since you want the security policy to always be in effect. The following figure shows the results
of your two custom policies.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
513
Page 34

Chapter 25 Security Policy
Figure 355 Limited LAN to WAN IRC Traffic Example
Your security policy would have the following configuration.
Table 202 Limited LAN1 to WAN IRC Traffic Example 1
# USER SOURCE DESTINATION SCHEDULE SERVICE ACTION
1 Any 172.16.1.7 Any Any IRC Allow
2 Any Any Any Any IRC Deny
3 Any Any Any Any Any Allow
• The first row allows the LAN1 computer at IP address 172.16.1.7 to access the IRC service on the WAN.
• The second row blocks LAN1 access to the IRC service on the WAN.
• The third row is the default policy of allowing all traffic from the LAN1 to go to the WAN.
Alternatively, you configure a LAN1 to WAN policy with the CEO’s user name (say CEO) to allow IRC
traffic from any source IP address to go to any destination address.
Your Security Policy would have the following settings.
Table 203 Limited LAN1 to WAN IRC Traffic Example 2
# USER SOURCE DESTINATION SCHEDULE SERVICE ACTION
1 CEO Any Any Any IRC Allow
2 Any Any Any Any IRC Deny
3 Any Any Any Any Any Allow
• The first row allows any LAN1 computer to access the IRC service on the WAN by logging into the Zyxel
Device with the CEO’s user name.
• The second row blocks LAN1 access to the IRC service on the WAN.
• The third row is the default policy of allowing allows all traffic from the LAN1 to go to the WAN.
The policy for the CEO must come before the policy that blocks all LAN1 to WAN IRC traffic. If the policy
that blocks all LAN1 to WAN IRC traffic came first, the CEO’s IRC traffic would match that policy and the
Zyxel Device would drop it and not check any other security policies.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
514
Page 35

Application Patrol
26.1 Overview
Application patrol provides a convenient way to manage the use of various applications on the
network. It manages general protocols (for example, HTTP and FTP) and instant messenger (IM), peer-topeer (P2P), Voice over IP (VoIP), and streaming (RSTP) applications. You can even control the use of a
particular application’s individual features (like text messaging, voice, video conferencing, and file
transfers).
26.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• Use the App Patrol summary screen (see Section 26.2 on page 516) to manage the application patrol
profiles. You can also view license registration and signature information.
• Use the App Patrol Add/Edit screens (see Section 26.2.2 on page 520 & Section 26.2.3 on page 521) to
set actions for application categories and for specific applications within the category.
CHAPTER 26
26.1.2 What You Need to Know
If you want to use a service, make sure both the Security Policy and application patrol allow the
service’s packets to go through the Zyxel Device.
Note: The Zyxel Device checks secure policies before it checks application patrol rules for
traffic going through the Zyxel Device.
Application patrol examines every TCP and UDP connection passing through the Zyxel Device and
identifies what application is using the connection. Then, you can specify whether or not the Zyxel
Device continues to route the connection. Traffic not recognized by the application patrol signatures is
ignored.
Application Profiles & Policies
An application patrol profile is a group of categories of application patrol signatures. For each profile,
you can specify the default action the Zyxel Device takes once a packet matches a signature (forward,
drop, or reject a service’s connections and/or create a log alert).
Use policies to link profiles to traffic flows based on criteria such as source zone, destination zone, source
address, destination address, schedule, user.
Classification of Applications
There are two ways the Zyxel Device can identify the application. The first is called auto. The Zyxel
Device looks at the IP payload (OSI level-7 inspection) and attempts to match it with known patterns for
specific applications. Usually, this occurs at the beginning of a connection, when the payload is more
consistent across connections, and the Zyxel Device examines several packets to make sure the match
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
515
Page 36

Chapter 26 Application Patrol
is correct. Before confirmation, packets are forwarded by App Patrol with no action taken. The number
of packets inspected before confirmation varies by signature.
Note: The Zyxel Device allows the first eight packets to go through the security policy,
regardless of the application patrol policy for the application. The Zyxel Device
examines these first eight packets to identify the application.
The second approach is called service ports. The Zyxel Device uses only OSI level-4 information, such as
ports, to identify what application is using the connection. This approach is available in case the Zyxel
Device identifies a lot of “false positives” for a particular application.
Custom Ports for SIP and the SIP ALG
Configuring application patrol to use custom port numbers for SIP traffic also configures the SIP ALG to
use the same port numbers for SIP traffic. Likewise, configuring the SIP ALG to use custom port numbers
for SIP traffic also configures application patrol to use the same port numbers for SIP traffic.
26.2 Application Patrol Profile
Use the application patrol screens to customize action and log settings for a group of application patrol
signatures. You then link a profile to a policy. Use this screen to create an application patrol profile, and
view signature information. It also lists the registration status and details about the signature set the Zyxel
Device is using.
Note: You must register for the AppPatrol signature service (at least the trial) before you can
use it.
A profile is an application object(s) or application group(s) that has customized action and log settings.
Click Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol to open the following screen.
Click the Application Patrol icon for more information on the Zyxel Device’s security features.
Figure 356 Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
516
Page 37

Chapter 26 Application Patrol
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 204 Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Add Click this to create a new entry. Select an entry and click Add to create a new entry after the
Edit Double-click an entry or select it and click Edit to open a screen where you can modify the
Remove Select an entry and click Remove to delete the selected entry.
References Select an entry and click References to open a screen that shows which settings use the entry.
# This field is a sequential value showing the number of the profile. The profile order is not
Name This displays the name of the profile created.
Description This displays the description of the App Patrol Profile.
Scan Option This field displays the scan options from the App Patrol profile.
Reference This displays the number of times an object reference is used in a profile.
Action Click this icon to apply the entry to a security policy.
Signature
Information
Current Version This field displays the App Patrol signature set version number. This number gets larger as the set
Signature
Number
Released Date This field displays the date and time the set was released.
Update
Signatures
selected entry.
entry’s settings.
Click Refresh to update information on this screen.
important.
Go to the Configuration > Security Policy > Policy Control screen to check the result.
The following fields display information on the current signature set that the Zyxel Device is
using.
is enhanced.
This field displays the number of IDP signatures in this set. This number usually gets larger as the
set is enhanced. Older signatures and rules may be removed if they are no longer applicable
or have been supplanted by newer ones.
Click this link to go to the screen you can use to download signatures from the update server.
26.2.1 Apply to a Security Policy
Click the icon in the Action field of an existing application patrol file to apply the profile to a security
policy.
Go to the Configuration > Security Policy > Policy Control screen to check the result.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
517
Page 38

Chapter 26 Application Patrol
Figure 357 Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol > Action
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 205 Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol > Action
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Show Filter/Hide
Filter
IPv4 / IPv6
Configuration
From / To Select a zone to view all security policies from a particular zone and/or to a particular zone.
Click Show Filter to display IPv4 and IPv6 (if enabled) security policy search filters.
Use IPv4 / IPv6 search filters to find specific IPv4 and IPv6 (if enabled) security policies based on
direction, application, user, source, destination and/or schedule.
any means all zones.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
518
Page 39

Chapter 26 Application Patrol
Table 205 Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol > Action
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IPv4 / IPv6
Source
IPv4 / IPv6
Destination
Service View all security policies based the service object used.
User View all security policies based on user or user group object used.
Schedule View all security policies based on the schedule object used.
Priority This is the position of your Security Policy in the global policy list (including all through-Zyxel
Status This icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the entry is inactive.
Name This is the name of the Security policy.
From / To This is the direction of travel of packets. Select from which zone the packets come and to
Type an IPv4 or IPv6 IP address to view all security policies based on the IPv4 / IPv6 source
address object used.
• An IPv4 IP address is written as four integer blocks separated by periods. This is an example
IPv4 address: 172.16.6.7.
• An 128-bit IPv6 address is written as eight 16-bit hexadecimal blocks separated by colons
(:). This is an example IPv6 address: 2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000.
Type an IPv4 or IPv6 IP address to view all security policies based on the IPv4 / IPv6 destination
address object used.
• An IPv4 IP address is written as four integer blocks separated by periods. This is an example
IPv4 address: 172.16.6.7.
• An 128-bit IPv6 address is written as eight 16-bit hexadecimal blocks separated by colons
(:). This is an example IPv6 address: 2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000.
Device and to-Zyxel Device policies). The ordering of your policies is important as policies are
applied in sequence. Default displays for the default Security Policy behavior that the Zyxel
Device performs on traffic that does not match any other Security Policy.
which zone they go.
Security Policies are grouped based on the direction of travel of packets to which they apply.
For example, from LAN to LAN means packets traveling from a computer or subnet on the LAN
to either another computer or subnet on the LAN.
From any displays all the Security Policies for traffic going to the selected To Zone.
To any displays all the Security Policies for traffic coming from the selected From Zone.
From any to any displays all of the Security Policies.
To ZyWALL policies are for traffic that is destined for the Zyxel Device and control which
computers can manage the Zyxel Device.
IPv4 / IPv6 Source This displays the IPv4 / IPv6 source address object, including geographic address and FQDN
(group) objects, to which this Security Policy applies.
IPv4 / IPv6
Destination
Service This displays the service object to which this Security Policy applies.
User This is the user name or user group name to which this Security Policy applies.
Schedule This field tells you the schedule object that the policy uses. none means the policy is active at all
Action This field displays whether the Security Policy silently discards packets without notification
Log Select whether to have the Zyxel Device generate a log (log), log and alert (
Profile This field shows you which Security Service profiles (application patrol, content filter, IDP, anti-
OK Click OK to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Cancel Click Cancel to exit this screen without saving.
This displays the IPv4 / IPv6 destination address object, including geographic address and
FQDN (group) objects, to which this Security Policy applies.
times if enabled.
(deny), permits the passage of packets (allow) or drops packets with notification (reject)
log alert) or not
(no) when the policy is matched to the criteria listed above.
malware, email security) apply to this Security policy. Click an applied Security Service profile
icon to edit the profile directly.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
519
Page 40

Chapter 26 Application Patrol
26.2.2 The Application Patrol Profile Add/Edit Screen - My Application
Use this screen to configure profile settings. Click Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol > Add/
Edit, then click My Application to open the following screen.
Figure 358 Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol > Add/Edit > My Application
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 206 Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol > Add/Edit > My Application
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General Settings
Name Type the name of the profile. You may use 1-31 alphanumeric characters, underscores(
or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a number. This value is case-sensitive. These
are valid, unique profile names:
•MyProfile
•mYProfile
•Mymy12_3-4
These are invalid profile names:
• 1mYProfile
• My Profile
• MyProfile?
• Whatalongprofilename123456789012
Description Type a description for the profile rule to help identify the purpose of rule. You may use 1-31
alphanumeric characters, underscores (
a number. This value is case-sensitive. This field is optional.
Total Category(s) This field displays the total number of the selected category(ies) in the Query Result screen.
Total Application(s) This field displays the total number of the selected applications in the Query Result screen.
Remove Select an entry and click Remove to delete the selected entry.
_), or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be
_),
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
520
Page 41

Chapter 26 Application Patrol
Table 206 Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol > Add/Edit (continued)> My Application
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Log Select whether to have the Zyxel Device generate a log (log), log and alert (log alert) or
neither (no) by default when traffic matches a signature in this category.
Action Select the default action for all signatures in this category.
forward - the Zyxel Device routes packets that matches these signatures.
drop - the Zyxel Device silently drops packets that matches these signatures without
notification.
reject - the Zyxel Device drops packets that matches these signatures and sends
notification.
# This field is a sequential value showing the number of the profile. The profile order is not
important.
Application This field displays the application name of the policy.
Category This field displays the category type of the application.
Tag This field displays the tag information of the application.
Action Select the default action for all signatures in this category.
forward - the Zyxel Device routes packets that matches these signatures.
drop - the Zyxel Device silently drops packets that matches these signatures without
notification.
reject - the Zyxel Device drops packets that matches these signatures and sends
notification.
Log Select whether to have the Zyxel Device generate a log (log), log and alert (log alert) or
Save & Exit A profile consists of separate category editing screens. If you want to configure just one
Cancel Click Cancel to return to the profile summary page without saving any changes.
Save If you want to configure more than one category for a profile, click Save to save your
neither (no) by default when traffic matches a signature in this category.
category for a profile, click OK to save your settings to the Zyxel Device, complete the
profile and return to the profile summary page.
settings to the Zyxel Device without leaving this page.
26.2.3 The Application Patrol Profile Add/Edit Screen - Query Result
Click Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol > Add, then click Query Result to search for certain
applications within a specific category, and the selected applications will be added to My Application
screen. You can also click an existing profile, click Edit (or double-click it), then click Query Result to
open the following screen.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
521
Page 42

Chapter 26 Application Patrol
Figure 359 Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol > Add/Edit > Query Result
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 207 Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol > Add/Edit > Query Result
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General Settings
Name Type the name of the profile. You may use 1-31 alphanumeric characters, underscores(_),
or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a number. This value is case-sensitive. These
are valid, unique profile names:
•MyProfile
•mYProfile
•Mymy12_3-4
These are invalid profile names:
• 1mYProfile
• My Profile
• MyProfile?
• Whatalongprofilename123456789012
Description Type a description for the profile rule to help identify the purpose of rule. You may use 1-31
alphanumeric characters, underscores (
a number. This value is case-sensitive. This field is optional.
Search Application(s)
By Name
Search Application(s)
By Category
Filter by Tags Add or delete a tag(s) to display or not display an application(s).
# This field is a sequential value showing the number of the profile. The profile order is not
Application This field displays the application name of the policy.
Category This field displays the category type of the application.
Enter a name to search for relevant applications.
Select a category(ies) below to search for relevant applications.
important.
_), or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
522
Page 43

Chapter 26 Application Patrol
Table 207 Configuration > Security Service > App Patrol > Add/Edit (continued)> Query Result
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Tag This field displays the tag information of the policy.
Action Select the default action for all signatures in this category.
forward - the Zyxel Device routes packets that matches these signatures.
drop - the Zyxel Device silently drops packets that matches these signatures without
notification.
reject - the Zyxel Device drops packets that matches these signatures and sends
notification.
Log Select whether to have the Zyxel Device generate a log (log), log and alert (log alert) or
Add to My
Application
Reset Click this button to reset the fields to default settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to return to the profile summary page without saving any changes.
neither (no) by default when traffic matches a signature in this category.
Select an application(s) to show in the My Application profile screen.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
523
Page 44

27.1 Overview
Use the content filtering feature to control access to specific web sites or web content.
27.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• Use the Filter Profile screens (Section 27.2 on page 526) to set up content filtering profiles.
• Use the Trusted Web Sites screens (Section 27.3 on page 539) to create a common list of good
(allowed) web site addresses.
• Use the Forbidden Web Sites screens (Section 27.4 on page 540) to create a common list of bad
(blocked) web site addresses.
27.1.2 What You Need to Know
CHAPTER 27
Content Filter
Content Filtering
Content filtering allows you to block certain web features, such as cookies, and/or block access to
specific web sites. It can also block access to specific categories of web site content. You can create
different content filter policies for different addresses, schedules, users or groups and content filter
profiles. For example, you can configure one policy that blocks John Doe’s access to arts and
entertainment web pages during the workday and another policy that lets him access them after work.
Content Filtering Policies
A content filtering policy allows you to do the following.
• Use schedule objects to define when to apply a content filter profile.
• Use address and/or user/group objects to define to whose web access to apply the content filter
profile.
• Apply a content filter profile that you have custom-tailored.
Content Filtering Profiles
A content filtering profile conveniently stores your custom settings for the following features.
• Category-based Blocking
The Zyxel Device can block access to particular categories of web site content, such as pornography
or racial intolerance.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
524
Page 45

Chapter 27 Content Filter
• Restrict Web Features
The Zyxel Device can disable web proxies and block web features such as ActiveX controls, Java
applets and cookies.
• Customize Web Site Access
You can specify URLs to which the Zyxel Device blocks access. You can alternatively block access to
all URLs except ones that you specify. You can also have the Zyxel Device block access to URLs that
contain particular keywords.
Content Filtering Configuration Guidelines
When the Zyxel Device receives an HTTP request, the content filter searches for a policy that matches
the source address and time (schedule). The content filter checks the policies in order (based on the
policy numbers). When a matching policy is found, the content filter allows or blocks the request
depending on the settings of the filtering profile specified by the policy. Some requests may not match
any policy. The Zyxel Device allows the request if the default policy is not set to block. The Zyxel Device
blocks the request if the default policy is set to block.
External Web Filtering Service
When you register for and enable the external web filtering service, your Zyxel Device accesses an
external database that has millions of web sites categorized based on content. You can have the Zyxel
Device block, block and/or log access to web sites based on these categories.
HTTPS Domain Filter
HTTPS Domain Filter works with the Content Filter category feature to identify HTTPS traffic and take
appropriate action. SSL Inspection identifies HTTPS traffic for all Security Service traffic and has higher
priority than HTTPS Domain Filter. HTTPS Domain Filter only identifies keywords in the domain name of an
URL and matches it to a category. For example, if the keyword is 'picture' and the URL is http://
www.google.com/picture/index.htm, then HTTPS Domain Filter cannot identify 'picture' because that
keyword in not in the domain name 'www.google.com'. However, SSL Inspection can identify 'picture' in
the URL http://www.google.com/picture/index.htm.
Keyword Blocking URL Checking
The Zyxel Device checks the URL’s domain name (or IP address) and file path separately when
performing keyword blocking.
The URL’s domain name or IP address is the characters that come before the first slash in the URL. For
example, with the URL www.zyxel.com.tw/news/pressroom.php
www.zyxel.com.tw
The file path is the characters that come after the first slash in the URL. For example, with the URL
www.zyxel.com.tw/news/pressroom.php
Since the Zyxel Device checks the URL’s domain name (or IP address) and file path separately, it will not
find items that go across the two. For example, with the URL www.zyxel.com.tw/news/pressroom.php
the Zyxel Device would find “tw” in the domain name (www.zyxel.com.tw)
the file path (news/pressroom.php
.
, the file path is news/pressroom.php.
) but it would not find “tw/news”.
, the domain name is
,
. It would also find “news” in
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
525
Page 46

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Finding Out More
•See Section 27.5 on page 541 for content filtering background/technical information.
27.1.3 Before You Begin
• You must configure an address object, a schedule object and a filtering profile before you can set up
a content security policy.
• You must have Content Filtering license in order to use the function.subscribe to use the external
database content filtering (see the Licensing > Registration screens).
27.2 Content Filter Profile Screen
Click Configuration > Security Service> Content Filter > Profile to open the Content Filter Profile screen.
Use this screen to enable content filtering, view and order your list of content filter policies, create a
denial of access message or specify a redirect URL and check your external web filtering service
registration status.
Click the Content Filter icon for more information on the Zyxel Device’s security features.
Figure 360 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Profile
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
526
Page 47

Chapter 27 Content Filter
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 208 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Profile
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General Settings
Enable HTTPS Domain Filter
for HTTPS traffic
Drop connection when
HTTPS connection with SSL
V3 or previous version
Content Filter Category
Service Timeout
Denied Access Message Enter a message to be displayed when content filter blocks access to a web page.
Redirect URL Enter the URL of the web page to which you want to send users when their web
Profile Management
Add Click Add to create a new content filter rule.
Edit Click Edit to make changes to a content filter rule.
Remove Click Remove the delete a content filter rule.
References Select an entry and click References to open a screen that shows which settings use
# This column lists the index numbers of the content filter profile.
Name This column lists the names of the content filter profile rule.
Description This column lists the description of the content filter profile rule.
Reference This displays the number of times an Object Reference is used in a rule.
Action Click this icon to apply the content filter profile with a security policy.
Select this check box to have the Zyxel Device block HTTPS web pages using the
cloud category service.
In an HTTPS connection, the Zyxel Device can extract the Server Name Indication
(SNI) from a client request, check if it matches a category in the cloud content filter
and then take appropriate action. The keyword match is for the domain name only.
Select this check box to have the Zyxel Device block HTTPS web pages using SSL V3 or
a previous version.
Specify the allowable time period in seconds for accessing the external web filtering
service’s server.
Use up to 127 characters (0-9a-zA-Z;/?:@&=+$\.-_!~*'()%,”). For example, “Access to
this web page is not allowed. Please contact the network administrator”.
It is also possible to leave this field blank if you have a URL specified in the Redirect URL
field. In this case if the content filter blocks access to a web page, the Zyxel Device
just opens the web page you specified without showing a denied access message.
access is blocked by content filter. The web page you specify here opens in a new
frame below the denied access message.
Use “http://” or “https://” followed by up to 262 characters (0-9a-zA-Z;/?:@&=+$\._!~*'()%). For example, http://192.168.1.17/blocked access.
the entry. Click Refresh to update information on this screen.
Go to the Configuration > Security Policy > Policy Control screen to check the result.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
27.2.1 Apply to a Security Policy
Click the icon in the Action field to apply the entry to a security policy.
Go to the Configuration > Security Policy > Policy Control screen to check the result.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
527
Page 48

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Figure 361 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Action
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 209 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Action
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Show Filter/Hide
Filter
IPv4 / IPv6
Configuration
From / To Select a zone to view all security policies from a particular zone and/or to a particular zone.
Click Show Filter to display IPv4 and IPv6 (if enabled) security policy search filters.
Use IPv4 / IPv6 search filters to find specific IPv4 and IPv6 (if enabled) security policies based on
direction, application, user, source, destination and/or schedule.
any means all zones.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
528
Page 49

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Table 209 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Action
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IPv4 / IPv6
Source
IPv4 / IPv6
Destination
Service View all security policies based the service object used.
User View all security policies based on user or user group object used.
Schedule View all security policies based on the schedule object used.
Priority This is the position of your Security Policy in the global policy list (including all through-Zyxel
Status This icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the entry is inactive.
Name This is the name of the Security policy.
From / To This is the direction of travel of packets. Select from which zone the packets come and to
Type an IPv4 or IPv6 IP address to view all security policies based on the IPv4 / IPv6 source
address object used.
• An IPv4 IP address is written as four integer blocks separated by periods. This is an example
IPv4 address: 172.16.6.7.
• An 128-bit IPv6 address is written as eight 16-bit hexadecimal blocks separated by colons
(:). This is an example IPv6 address: 2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000.
Type an IPv4 or IPv6 IP address to view all security policies based on the IPv4 / IPv6 destination
address object used.
• An IPv4 IP address is written as four integer blocks separated by periods. This is an example
IPv4 address: 172.16.6.7.
• An 128-bit IPv6 address is written as eight 16-bit hexadecimal blocks separated by colons
(:). This is an example IPv6 address: 2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000.
Device and to-Zyxel Device policies). The ordering of your policies is important as policies are
applied in sequence. Default displays for the default Security Policy behavior that the Zyxel
Device performs on traffic that does not match any other Security Policy.
which zone they go.
Security Policies are grouped based on the direction of travel of packets to which they apply.
For example, from LAN to LAN means packets traveling from a computer or subnet on the LAN
to either another computer or subnet on the LAN.
From any displays all the Security Policies for traffic going to the selected To Zone.
To any displays all the Security Policies for traffic coming from the selected From Zone.
From any to any displays all of the Security Policies.
To ZyWALL policies are for traffic that is destined for the Zyxel Device and control which
computers can manage the Zyxel Device.
IPv4 / IPv6 Source This displays the IPv4 / IPv6 source address object, including geographic address and FQDN
(group) objects, to which this Security Policy applies.
IPv4 / IPv6
Destination
Service This displays the service object to which this Security Policy applies.
User This is the user name or user group name to which this Security Policy applies.
Schedule This field tells you the schedule object that the policy uses. none means the policy is active at all
Action This field displays whether the Security Policy silently discards packets without notification
Log Select whether to have the Zyxel Device generate a log (log), log and alert (
Profile This field shows you which Security Service profiles (application patrol, content filter, IDP, anti-
OK Click OK to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Cancel Click Cancel to exit this screen without saving.
This displays the IPv4 / IPv6 destination address object, including geographic address and
FQDN (group) objects, to which this Security Policy applies.
times if enabled.
(deny), permits the passage of packets (allow) or drops packets with notification (reject)
log alert) or not
(no) when the policy is matched to the criteria listed above.
malware, email security) apply to this Security policy. Click an applied Security Service profile
icon to edit the profile directly.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
529
Page 50

Chapter 27 Content Filter
27.2.2 Content Filter Add Profile Category Service
Click Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Profile > Add or Edit to open the Add Filter Profile
screen.
Figure 362 Content Filter > Profile > Add Filter Profile > Category Service
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
530
Page 51

Chapter 27 Content Filter
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 210 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Profile > Add > Category Service
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name Enter a descriptive name for this content filtering profile name. You may use 1-31
Description Enter a description for the content filtering profile rule to help identify the purpose
Enable SafeSearch SafeSearch is a search engine that can automatically filter sexually explicit videos
Enable Content Filter
Category Service
Log all web pages Select this to record attempts to access web pages when:
alphanumeric characters, underscores(
cannot be a number. This value is case-sensitive.
of rule. You may use 1-31 alphanumeric characters, underscores(
but the first character cannot be a number. This value is case-sensitive.
This field is optional.
and images from the search result without overloading the Zyxel Device. It does
this by adding a parameter in the search URL:
https://www.google.com.tw/?gws_rd=ssl#q=porn&safe=active.
Supported search engines at the time of writing are:
Yahoo, Google, MSN Live Bing, Yandex
Enable external database content filtering to have the Zyxel Device check an
external database to find to which category a requested web page belongs. The
Zyxel Device then blocks or forwards access to the web page depending on the
configuration of the rest of this page.
_), or dashes (-), but the first character
_), or dashes (-),
Action for Managed Web
Pages
Action for Unrated Web
Pages
• They match the other categories that you select below.
• They are not categorized.
• The external content filtering database is unavailable.
Select Pass to allow users to access web pages that match the other categories
that you select below.
Select Block to prevent users from accessing web pages that match the other
categories that you select below. When external database content filtering
blocks access to a web page, it displays the denied access message that you
configured in the Content Filter General screen along with the category of the
blocked web page.
Select Log to record attempts to access web pages that match the other
categories that you select below.
Select Pass to allow users to access web pages that the external web filtering
service has not categorized.
Select Block to prevent users from accessing web pages that the external web
filtering service has not categorized. When the external database content filtering
blocks access to a web page, it displays the denied access message that you
configured in the Content Filter General screen along with the category of the
blocked web page.
Select Warn to display a warning message before allowing users to access web
pages that the external web filtering service has not categorized.
Select Log to record attempts to access web pages that are not categorized.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
531
Page 52

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Table 210 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Profile > Add > Category Service
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Action When Category
Server Is Unavailable
Select Categories
Select All Categories Select this check box to restrict access to all site categories listed below.
Clear All Categories Select this check box to clear the selected categories below.
Managed Categories These are categories of web pages based on their content. Select categories in
Test Web Site Category
URL to test You can check which category a web page belongs to. Enter a web site URL in
If you think the category is
incorrect
Test Against Content Filter
Category Server
OK Click OK to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Cancel Click Cancel to exit this screen without saving your changes.
Select Pass to allow users to access any requested web page if the external
content filtering database is unavailable.
Select Block to block access to any requested web page if the external content
filtering database is unavailable.
Select Warn to display a warning message before allowing users to access any
requested web page if the external content filtering database is unavailable.
The following are possible causes for the external content filtering server not being
available:
• There is no response from the external content filtering server within the time
period specified in the Content Filter Server Unavailable Timeout field.
• The Zyxel Device is not able to resolve the domain name of the external
content filtering database.
• There is an error response from the external content filtering database. This can
be caused by an expired content filtering registration (External content
filtering’s license key is invalid”).
Select Log to record attempts to access web pages that occur when the external
content filtering database is unavailable.
this section to control access to specific types of Internet content.
You must have the Category Service content filtering license to filter these
categories. See the next table for category details.
the text box.
When the content filter is active, you should see the web page’s category. The
query fails if the content filter is not active.
Content Filtering can query a category by full URL string (for example, http://
www.google.com/picture/index.htm), but HTTPS Domain Filter can only query a
category by domain name ('www.google.com'), so the category may be
different in the query result. URL to test displays both results in the test.
Click this link to see the category recorded in the Zyxel Device’s content filtering
database for the web page you specified (if the database has an entry for it).
Click this button to see the category recorded in the external content filter server’s
database for the web page you specified.
The following table describes the managed categories.
Table 211 Managed Category Descriptions
CATEGORY DESCRIPTION
Advertisements & Pop-Ups Sites that provide advertising graphics or other ad content files such as banners
and pop-ups. For example, pagead2.googlesyndication.com,
ad.yieldmanager.com.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
532
Page 53

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Table 211 Managed Category Descriptions (continued)
Alcohol & Tobacco Sites that promote or sell alcohol- or tobacco-related products or services. For
example, www.drinks.com.tw, www.p9.com.tw, beer.ttl.com.tw.
Arts Sites with artistic content or relating to artistic institutions such as theaters,
museums, galleries, dance companies, photography, and digital graphic
resources. For example, www.npm.gov.tw, www.nmh.gov.tw.
Business Sites that provide business related information such as corporate Web sites.
Information, services, or products that help businesses of all sizes to do their day-today commercial activities. For example, www.kinkos.com,
www.proctorgamble.com, www.bbb.org.
Transportation Sites that provide information about motor vehicles such as cars, motorcycles,
boats, trucks, RVs and the like. Includes manufacturer sites, dealerships, review
sites, pricing,, online purchase sites, enthusiasts clubs, etc. For example,
www.toyota.com.tw, www.ford.com.tw, www.sym.com.tw.
Chat Sites that enable web-based exchange of real time messages through chat
services or chat rooms. For example, me.sohu.com, blufiles.storage.live.com.
Forums & Newsgroups Sites for sharing information in the form of newsgroups, forums, bulletin boards. For
example, ck101.com, my.xuite.net, ptt.cc.
Computers & Technology Sites that contain information about computers, software, hardware, IT, peripheral
Criminal Activity Sites that offer advice on how to commit illegal or criminal activities, or to avoid
Dating & Personals Sites that promote networking for interpersonal relationships such as dating and
Download Sites Sites that contain downloadable software, whether shareware, freeware, or for a
Education Sites sponsored by educational institutions and schools of all types including
Entertainment Sites related to television, movies, music and video (including video on demand),
Finance Sites related to banking, finance, payment or investment, including banks,
Gambling Sites that offer or are related to online gambling, lottery, casinos and betting
Games Sites relating to computer or other games, information about game producers, or
Government Sites run by governmental organizations, departments, or agencies, including
and computer services, such as product reviews, discussions, and IT news. For
example, www.informationsecurity.com.tw, blog.ithome.com.tw.
detection. These can include how to commit murder, build bombs, pick locks, etc.
Also includes sites with information about illegal manipulation of electronic
devices, hacking, fraud and illegal distribution of software. For example,
www.hackbase.com, jia.hackbase.com, ad.adver.com.tw.
marriage. Includes sites for match-making, online dating, spousal introduction. For
example, www.i-part.com.tw, www.imatchi.com.
charge. Includes peer-to-peer sites. For example, www.hotdl.com,
toget.pchome.com.tw, www.azroo.com.
distance education. Includes general educational and reference materials such
as dictionaries, encyclopedias, online courses, teaching aids and discussion
guides. For example, www.tfam.museum, www.lksf.org, www.1980.org.tw.
such as program guides, celebrity sites, and entertainment news. For example,
www.ctitv.com.tw, www.hboasia.com, www.startv.com.tw.
brokerages, online stock trading, stock quotes, fund management, insurance
companies, credit unions, credit card companies, and so on. For example,
www.concords.com.tw, www.polaris.com.tw, www.bochk.com.
agencies involving chance. For example, www.taiwanlottery.com.tw, www.iwin.com.tw, www.hkjc.com.
how to obtain cheat codes. Game-related publication sites. For example,
www.gamer.com.tw, www.wowtaiwan.com.tw, tw.lineage.gamania.com.
police departments, fire departments, customs bureaus, emergency services, civil
defense, counter-terrorism organizations, military and hospitals. For example,
www.ey.gov.tw, www.whitehouse.gov, www.npa.gov.tw.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
533
Page 54

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Table 211 Managed Category Descriptions (continued)
Hate & Intolerance Sites that promote a supremacist political agenda, encouraging oppression of
people or groups of people based on their race, religion, gender, age, disability,
sexual orientation or nationality. For example, www.racist-jokes.com, aryannations.org, whitepower.com.
Health & Medicine Sites containing information pertaining to health, healthcare services, fitness and
well-being, including information about medical equipment, hospitals, drugstores,
nursing, medicine, procedures, prescription medications, etc. For example,
www.lksf.org, www.ohayo.com.tw.
Illegal Drugs Sites with information on the purchase, manufacture, and use of illegal or
recreational drugs and their paraphernalia, and misuse of prescription drugs and
other compounds For example, www.cannabis.net, www.amphetamines.com.
Job Search Sites containing job listings, career information, assistance with job searches (such
Streaming Media &
Downloads
News Sites covering news and current events such as newspapers, newswire services,
Non-profits & NGOs Sites devoted to clubs, communities, unions, and non-profit organizations. Many of
Nudity Sites that contain full or partial nudity that are not necessarily overtly sexual in
Personal Sites Sites about or hosted by personal individuals, including those hosted on
Politics Sites that promote political parties or political advocacy, or provide information
Pornography/Sexually Explicit Sites that contain explicit sexual content. Includes adult products such as sex toys,
Real Estate Sites relating to commercial or residential real estate services, including renting,
Religion Sites that deal with faith, human spirituality or religious beliefs, including sites of
Restaurants & Dining Sites that list, review, promote or advertise food, dining or catering services.
Search Engines & Portals Sites enabling the searching of the Web, newsgroups, images, directories, and
Shopping Sites for online shopping, catalogs, online ordering, auctions, classified ads.
as resume writing, interviewing tips, etc.), employment agencies or head hunters.
For example, www.104.com.tw, www.1111.com.tw, www.yes123.com.tw.
Sites that deliver streaming content, such as Internet radio, Internet TV or MP3 and
live or archived media download sites. Includes fan sites, or official sites run by
musicians, bands, or record labels. For example, www.youtube.com,
pfp.sina.com.cn, my.xunlei.com.
personalized news services, broadcasting sites, and magazines. For example,
www.tvbs.com.tw?Awww.ebc.net.tw?Awww.iset.com.tw.
these groups exist for educational or charitable purposes. For example,
www.tzuchi.org.tw, web.redcross.org.tw, www.lksf.org.
intent. Includes sites that advertise or sell lingerie, intimate apparel, or swim wear.
For example, www.easyshop.com.tw, www.faster-swim.com.tw,
image.baidu.com.
commercial sites. For example, blog.yam.com, www.wretch.cc, blog.xuite.net.
about political parties, interest groups, elections, legislation or lobbying. Also
includes sites that offer legal information and advice. For example,
www.kmt.org.tw, www.dpp.org.tw, cpc.people.com.cn.
CD-ROMs, and videos, adult services such as videoconferencing, escort services,
and strip clubs, erotic stories and textual descriptions of sexual acts. For example,
www.dvd888.com, www.18center.com, blog.sina.com.tw.
purchasing, selling or financing homes, offices, etc. For example,
www.sinyi.com.tw, www.yungching.com.tw, house.focus.cn.
churches, synagogues, mosques and other houses of worship. For example,
www.fgs.org.tw, www.twtaoism.net, www.fhl.net.
Includes sites for recipes, cooking instruction and tips, food products, and wine
advisors. For example, www.jogoya.com.tw, www.dintaifung.com.tw,
www2.pizzahut.com.tw.
other online content. Includes portal and directory sites such as white/yellow
pages. For example, tw.yahoo.com, www.pchome.com.tw, www.google.com.tw.
Excludes shopping for products and services exclusively covered by another
category such as health & medicine. For example, shopping.pchome.com.tw,
buy.yahoo.com.tw, www.tkec.com.tw.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
534
Page 55

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Table 211 Managed Category Descriptions (continued)
Social Networking Sites that enable social networking for online communities of various topics, for
friendship, dating, or professional reasons. For example, www.facebook.com,
www.flickr.com, www.groups.google.com.
Sports Sites relating to sports teams, fan clubs, scores and sports news. Relates to all
Translators Sites that translate Web pages or phrases from one language to another. These
Travel Sites that provide travel and tourism information or online booking of travel
Violence Sites that contain images or text depicting or advocating physical assault against
Weapons Sites that depict, sell, review or describe guns and weapons, including for sport. For
Web-based Email Sites that enable users to send and receive email through a web-accessible email
General Sites that do not clearly fall into other categories, for example, blank Web pages.
Leisure & Recreation Sites relating to recreational activities and hobbies including zoos, public
Cults Sites relating to non-traditional religious practice typically known as "cults," that is,
Fashion & Beauty Sites concerning fashion, jewelry, glamour, beauty, modeling, cosmetics or related
Greeting cards Sites that allow people to send and receive greeting cards and postcards. For
Hacking Sites that promote or give advice about how to gain unauthorized access to
Illegal Software Sites that illegally distribute software or copyrighted materials such as movies or
Image Sharing Sites that host digital photographs and images, online photo albums and digital
Information Security Sites that provide legitimate information about data protection, including newly
Instant Messaging Sites that enable logging in to instant messaging services such as ICQ, AOL Instant
sports, whether professional or recreational. For example, www.yankees.com,
www.nba.com, mlb.mlb.com.
sites may be used to attempt to bypass a filtering system. For example,
translate.google.com.tw, www.smartlinkcorp.com, translation.paralink.com.
services such as airlines, accommodations, car rentals. Includes regional or city
information sites. For example, www.startravel.com.tw, taipei.grand.hyatt.com.tw,
www.car-plus.com.tw.
humans, animals, or institutions. Sites of a particularly gruesome nature such as
shocking depictions of blood or wounds, or cruel animal treatment. For example,
crimescene.com, deathnet.com, michiganmilitia.com.
example, www.ak-47.net, warfare.ru.
account. For example, mail.163.com, mail.google.com, mail.yahoo.com.tw.
For example, bs.serving-sys.com, simg.sinajs.cn, i0.itc.cn.
recreation centers, pools, amusement parks, and hobbies such as gardening,
literature, arts & crafts, home improvement, home d?cor, family, etc. For example,
tpbg.tfri.gov.tw, tw.fashion.yahoo.com, www.relaxtimes.com.tw.
considered to be false, unorthodox, extremist, or coercive, with members often
living under the direction of a charismatic leader. For example,
www.churchofsatan.com, www.ccya.org.tw.
products or services. Includes product reviews, comparisons, and general
consumer information. For example, women.sohu.com,
baodian.women.sohu.com.
example, www.e-card.com.tw, card.ivy.net.tw.
proprietary computer systems, for the purpose of stealing information,
perpetrating fraud, creating viruses, or committing other illegal activity related to
theft of digital information. For example, www.hackbase.com,
www.chinahacker.com.
music, software cracks, illicit serial numbers, illegal license key generators. For
example, www.zhaokey.com.cn, www.tiansha.net.
photo exchanges. For example, photo.pchome.com.tw, photo.xuite.net,
photobucket.com.
discovered vulnerabilities and how to block them. For example,
www.informationsecurity.com.tw, www.itis.tw.
Messenger, IRC, MSN, Jabber, Yahoo Messenger, and the like. For example,
www.meebo.com, www.aim.com, www. ebuddy.com.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
535
Page 56

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Table 211 Managed Category Descriptions (continued)
Peer-to-Peer Sites that enable direct exchange of files between users without dependence on
a central server. For example, www.eyny.com.
Private IP Addresses Sites that are private IP addresses as defined in RFC 1918, that is, hosts that do not
require access to hosts in other enterprises (or require just limited access) and
whose IP address may be ambiguous between enterprises but are well defined
within a certain enterprise. For example, 172.21.20.123, 192.168.35.62.
School Cheating Sites that promote unethical practices such as cheating or plagiarism by providing
test answers, written essays, research papers, or term papers. For example,
www.zydk788.com, www.huafengksw.com.
Sex Education Sites relating to sex education, including subjects such as respect for partner,
abortion, gay and lesbian lifestyle, contraceptives, sexually transmitted diseases,
and pregnancy. For example, apps.rockyou.com, www.howmama.com.tw,
www.mombaby.com.tw.
Tasteless Sites with offensive or tasteless content such as bathroom humor or profanity. For
example, comedycentral.com, dilbert.com.
Child Abuse Images Sites that portray or discuss children in sexual or other abusive acts. For example,
a.uuzhijia.info.
Unknown Unknown For example, www.669.com.tw, www.appleballoon.com.tw,
www.uimco.com.tw.
27.2.3 Content Filter Add Filter Profile Custom Service
Click Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Filter Profile > Add or Edit > Custom Service to
open the Custom Service screen. You can create a list of good (allowed) web site addresses and a list
of bad (blocked) web site addresses. You can also block web sites based on whether the web site’s
address contains a keyword. Use this screen to add or remove specific sites or keywords from the filter
list.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
536
Page 57

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Figure 363 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Filter Profile > Custom Service
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 212 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Profile > Custom Service
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name Enter a descriptive name for this content filtering profile name. You may use 1-31
alphanumeric characters, underscores(
cannot be a number. This value is case-sensitive.
Description Enter a description for the content filtering profile rule to help identify the
purpose of rule. You may use 1-31 alphanumeric characters, underscores(
dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a number. This value is casesensitive.
This field is optional.
Enable Custom Service Select this check box to allow trusted web sites and block forbidden web sites.
Allow Web traffic for trusted web
sites only
Content filter list customization may be enabled and disabled without reentering these site names.
When this box is selected, the Zyxel Device blocks Web access to sites that are
not on the Trusted Web Sites list. If they are chosen carefully, this is the most
effective way to block objectionable material.
_), or dashes (-), but the first character
_), or
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
537
Page 58

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Table 212 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Profile > Custom Service (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Check Common Trusted/
Forbidden List
Restricted Web Features Select the check box(es) to restrict a feature. Select the check box(es) to
Block
ActiveX
Java Java is a programming language and development environment for building
Cookies Cookies are files stored on a computer’s hard drive. Some web servers use them
Web Proxy A server that acts as an intermediary between a user and the Internet to
Allow Java/ActiveX/Cookies/
Web proxy to trusted web sites
Trusted Web Sites These are sites that you want to allow access to, regardless of their content
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
# This displays the index number of the trusted web sites.
Trusted Web Site This column displays the trusted web sites already added.
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
# This displays the index number of the forbidden web sites.
Select this check box to check the common trusted and forbidden web sites
lists. See Section 27.3 on page 539 and Section 27.4 on page 540 for information
on configuring these lists.
restrict a feature.
• When you download a page containing ActiveX or Java, that part of the
web page will be blocked with an X.
• When you download a page coming from a Web Proxy, the whole web
page will be blocked.
• When you download a page containing cookies, the cookies will be
removed, but the page will not be blocked.
ActiveX is a tool for building dynamic and active web pages and distributed
object applications. When you visit an ActiveX web site, ActiveX controls are
downloaded to your browser, where they remain in case you visit the site again.
downloadable Web components or Internet and intranet business applications
of all kinds.
to track usage and provide service based on ID.
provide security, administrative control, and caching service. When a proxy
server is located on the WAN it is possible for LAN users to circumvent content
filtering by pointing to this proxy server.
When this box is selected, the Zyxel Device will permit Java, ActiveX and
Cookies from sites on the Trusted Web Sites list to the LAN. In certain cases, it
may be desirable to allow Java, ActiveX or Cookies from sites that are known
and trusted.
rating, can be allowed by adding them to this list.
Enter host names such as www.good-site.com into this text field. Do not enter
the complete URL of the site – that is, do not include “http://”. All subdomains
are allowed. For example, entering “*zyxel.com” also allows “www.zyxel.com”,
“partner.zyxel.com”, “press.zyxel.com”, and so on. You can also enter just a top
level domain. For example, enter “*.com” to allow all .com domains.
Use up to 127 characters (0-9a-z-). The casing does not matter. “*” can be used
as a wildcard to match any string. The entry must contain at least one “.” or it
will be invalid.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
538
Page 59

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Table 212 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Profile > Custom Service (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Forbidden Web Sites This list displays the forbidden web sites already added.
Enter host names such as www.bad-site.com into this text field. Do not enter the
complete URL of the site – that is, do not include “http://”. All subdomains are
also blocked. For example, entering “*bad-site.com” also blocks “www.badsite.com”, “partner.bad-site.com”, “press.bad-site.com”, and do on. You can
also enter just a top level domain. For example, enter “*.com” to block all .com
domains.
Use up to 127 characters (0-9a-z-). The casing does not matter. “*” can be used
as a wildcard to match any string. The entry must contain at least one “.” or it
will be invalid.
Blocked URL Keywords This section allows you to block Web sites with URLs that contain certain
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
# This displays the index number of the blocked URL keywords.
Blocked URL Keywords This list displays the keywords already added.
keywords in the domain name or IP address.
Enter a keyword or a numerical IP address to block. You can also enter a
numerical IP address.
Use up to 127 case-insensitive characters (0-9a-zA-Z;/?:@&=+$\.-_!~*()%). “*”
can be used as a wildcard to match any string. Use “|*” to indicate a single
wildcard character.
For example enter *Bad_Site* to block access to any web page that includes
the exact phrase Bad_Site. This does not block access to web pages that only
include part of the phrase (such as Bad for example).
OK Click OK to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Cancel Click Cancel to exit this screen without saving your changes.
27.3 Content Filter Trusted Web Sites Screen
Click Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Trusted Web Sites to open the Trusted Web Sites
screen. You can create a common list of good (allowed) web site addresses. When you configure Filter
Profiles, you can select the option to check the Common Trusted Web Sites list. Use this screen to add or
remove specific sites from the filter list.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
539
Page 60

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Figure 364 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Trusted Web Sites
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 213 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Trusted Web Sites
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Common Trusted Web Sites These are sites that you want to allow access to, regardless of their content
rating, can be allowed by adding them to this list.
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
# This displays the index number of the trusted web sites.
Trusted Web Site This column displays the trusted web sites already added.
Enter host names such as www.good-site.com into this text field. Do not enter
the complete URL of the site – that is, do not include “http://”. All subdomains
are allowed. For example, entering “zyxel.com” also allows “www.zyxel.com”,
“partner.zyxel.com”, “press.zyxel.com”, and so on. You can also enter just a top
level domain. For example, enter .com to allow all .com domains.
Use up to 127 characters (0-9a-z-). The casing does not matter.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
27.4 Content Filter Forbidden Web Sites Screen
Click Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Forbidden Web Sites to open the Forbidden Web
Sites screen. You can create a common list of bad (blocked) web site addresses. When you configure
Filter Profiles, you can select the option to check the Common Forbidden Web Sites list. Use this screen to
add or remove specific sites from the filter list.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
540
Page 61

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Figure 365 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Forbidden Web Sites
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 214 Configuration > Security Service > Content Filter > Forbidden Web Sites
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Forbidden Web Site List Sites that you want to block access to, regardless of their content rating, can be
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
# This displays the index number of the forbidden web sites.
Forbidden Web Sites This list displays the forbidden web sites already added.
allowed by adding them to this list.
Enter host names such as www.bad-site.com into this text field. Do not enter the
complete URL of the site – that is, do not include “http://”. All subdomains are
also blocked. For example, entering “bad-site.com” also blocks “www.badsite.com”, “partner.bad-site.com”, “press.bad-site.com”, and do on. You can
also enter just a top level domain. For example, enter .com to block all .com
domains.
Use up to 127 characters (0-9a-z-). The casing does not matter.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Cancel Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
27.5 Content Filter Technical Reference
This section provides content filtering background information.
External Content Filter Server Lookup Procedure
The content filter lookup process is described below.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
541
Page 62

Chapter 27 Content Filter
Figure 366 Content Filter Lookup Procedure
1 A computer behind the Zyxel Device tries to access a web site.
2 The Zyxel Device looks up the web site in its cache. If an attempt to access the web site was made in the
past, a record of that web site’s category will be in the Zyxel Device’s cache. The Zyxel Device blocks,
blocks and logs or just logs the request based on your configuration.
3 Use the Content Filter Cache screen to configure how long a web site address remains in the cache as
well as view those web site addresses. All of the web site address records are also cleared from the local
cache when the Zyxel Device restarts.
4 If the Zyxel Device has no record of the web site, it queries the external content filter database and
simultaneously sends the request to the web server.
5 The external content filter server sends the category information back to the Zyxel Device, which then
blocks and/or logs access to the web site based on the settings in the content filter profile. The web
site’s address and category are then stored in the Zyxel Device’s content filter cache.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
542
Page 63

28.1 Overview
Use the Zyxel Device’s anti-malware feature to protect your connected network from malware
(malicious software) infection, such as computer virus, worms, and spyware. The Zyxel Device checks
traffic going in both directions for signature matches. In the following figure, the Zyxel Device checks
traffic coming from the WAN zone (which includes two interfaces) to the LAN zone.
Figure 367 Zyxel Device Anti-Malware Example
CHAPTER 28
Anti-Malware
The anti-malware matches a file with those in a malware database. This is done as files go through the
Zyxel Device.
Virus, Worm, and Spyware
A computer virus is a type of malicious software designed to corrupt and/or alter the operation of other
legitimate programs. A worm is a self-replicating virus that resides in active memory and duplicates itself.
The effect of a virus attack varies from doing so little damage that you are unaware your computer is
infected to wiping out the entire contents of a hard drive to rendering your computer inoperable.
Spyware infiltrate your device and secretly gathers information about you, such as your network activity,
passwords, bank details, and so on.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
543
Page 64

Chapter 28 Anti-Malware
Hash Value
A hash function is an algorithm that maps data of arbitrary size to data of fixed size. The value returned
by a hash function is a hash value. Hash values can be used to identify the contents of a file. During an
anti-malware file scan, the hash value of a file is matched with signatures. At the time of writing, MD5
(Message Digest 5) is supported. MD5 is a hash algorithm used to authenticate packet data.
Local Signature Databases
The Zyxel Device downloads the signature(s) after it is registered and the anti-malware license is
activated at myZyxel. A signature is a unique string of bits, or binary pattern, of a malware. A signature
acts as a fingerprint that can be used to detect and identify specific malware. The Zyxel Device
downloads the following signatures:
• Anti-malware signature
• Threat Intelligence Machine Learning
These signatures are periodically updated if you have a valid license. See Section 28.2 on page 548 for
how the Zyxel Device updates these signatures for the anti-malware license.
Cloud Query
Another method of malware protection is through cloud query. This process is illustrated in the next
figure. If Cloud Query is enabled, the Zyxel Device queries the Defend Center database by sending the
file’s hash value (A) and receiving the scan results (B) through the Defend Center (DC).
Figure 368 Cloud Query
Anti-Malware Licensing
Having extensive, up-to-date signatures with the most common malware is critical to making the antimalware service work effectively. Section 7.2 on page 189 shows licensing information for the different
signature databases that can be used by the Zyxel Device.
After the anti-malware license expires, you need to purchase an iCard to update your local signature
database and use cloud query. Extend your license in the Registration > Service screen.
Anti-Malware Scan Process
Before going through the Anti-Malware scan, the Zyxel Device first identifies the packets sent by the
following four major protocols with corresponding standard ports:
• FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
544
Page 65

Chapter 28 Anti-Malware
• HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol)
• SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
• POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3)
The Zyxel Device records the order of packets in TCP connection-oriented sessions to check for
matching malware signatures. The order of non-setup packets such as SYN, ACK and FIN is ignored.
Anti-Malware Scanning Procedure:
1 The Zyxel Device checks every packet of the file for matches with the local signature databases.
If a malware pattern signature is matched, the actions you specify for identified malware will be
applied. If Destroy infected file is enabled, the file will be modified. Logs/alerts will be sent according to
your settings.
Note: The receiver is not notified if a file is modified by the Zyxel Device. If the file cannot be
used, the receiver should contact the Zyxel Device administrator to confirm if the Zyxel
Device modified the file by checking the logs.
2 If no match is found with the local databases, the Zyxel Device uses Cloud Query to forward the file’s
hash value to Defend Center.
3 Defend Center checks its database for malware signature matches and sends the results back to the
Zyxel Device.
If a malware signature is matched, the actions you specify for identified malware will be applied. If
Destroy infected file is enabled, the file will be modified. Logs/alerts will be sent according to your
settings.
The next figure shows a flow chart detailing the anti-malware scan.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
545
Page 66

Chapter 28 Anti-Malware
Figure 369 Anti-Malware flowchart
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
546
Page 67

Chapter 28 Anti-Malware
Cloud Query Supported File Types
At the time of writing, the following file types are supported by Cloud Query:
• 7z Archive (7z) • AVI Video (avi) • BMP Image (bmp) • BZ2 Archive (bz2)
• Executables (exe) • Macromedia Flash
Data (swf)
• JPG Image (jpg) • MOV Video (mov) • MP3 Audio (mp3) • MPG Video (mpg)
• MS Office
Document (doc...)
• RM Video (rm) • RTF Document (rtf) • TIFF Image (tif) • WAV Audio (wav)
• ZIP Archive (zip)
•PDF Document
(pdf)
• GIF Image (gif) • GZ Archive (gz)
• PNG Image (png) • RAR Archive (rar)
Notes About the Zyxel Device Anti-Malware
The following lists important notes about the Zyxel Device’s anti-malware feature:
1 Zyxel’s anti-malware feature can detect polymorphic malware (see Section 28.6 on page 554).
2 When malware is detected, a log is created or an alert message is sent to the administrator depending
on your log settings.
3 Changes to the Zyxel Device’s anti-malware settings only affect new sessions, not sessions that already
existed before you applied the changed settings.
4 Enabling Cloud Query may affect file transfer speeds.
5 The Zyxel Device does not scan the following file/traffic types:
• Simultaneous downloads of a file using multiple connections. For example, when you use FlashGet
to download sections of a file simultaneously.
• Encrypted traffic. This could be password-protected files or VPN traffic where the Zyxel Device is not
the endpoint (pass-through VPN traffic).
• Traffic through custom (non-standard) ports. The Zyxel Device scans whatever port number is
specified for FTP in the ALG screen.
• All compressed files within a compressed file. Note that a single file can still be decompressed and
scanned if you select Enable file decompression (ZIP and RAR).
• Traffic compressed or encoded using a method the Zyxel Device does not support.
Finding Out More
•See Section 28.6 on page 554 for anti-malware background information.
28.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• Use the Anti-Malware screen (Section 28.2 on page 548) to turn anti-malware on or off, and check
the anti-malware signature status. In addition, you can set up anti-malware black (blocked) and
white (allowed) lists of malware patterns.
• Use the Signature screen (Section 28.5 on page 553) to search for particular signatures and get more
information about them.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
547
Page 68

Chapter 28 Anti-Malware
28.2 Anti-Malware Screen
Click Configuration > Security Service > Anti-Malware to display the configuration screen as shown next.
Click the Anti-Malware icon for more information on the Zyxel Device’s security features.
Note: The threat intelligence machine learning (TIML) feature is not available if the gold
security pack is expired. Neither will the Zyxel Device update the TIML signatures, nor will
it scan the TIML signatures that were downloaded when you used the gold security
pack.
See Subscription Services Available on page 186 for more information on the
subscription services for the two types of security packs.
Note: If “Destroy infected file” is disabled and “log” is set to “no”, the Zyxel Device will still
perform the scan but will not do anything else. It is recommended to enable at least
one of the two functions.
If “Destroy infected file” is disabled, any malicious file found can still be
executed by the end user after it is forwarded. The administrator would
have to inform the user if there is an infected file.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
548
Page 69

Chapter 28 Anti-Malware
Figure 370 Configuration > Security Service > Anti-Malware
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
549
Page 70
Chapter 28 Anti-Malware
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 215 Configuration > Security Service > Anti-Malware
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General Setting
Enable Select this checkbox to activate the anti-malware feature to protect your connected
Scan and detect
EICAR test virus
Enable Cloud Query Select this check box to enable the cloud query service. This improves the effectiveness of
Available File Types File types that can be checked by the Zyxel Device through cloud query are listed here.
Applied File Types File types that go through the cloud query process are listed here. If you don’t want a file
Destroy infected file When you select this check box, if a malware signature is matched, the Zyxel Device
Log These are the log options:
Check White List Select this check box to have the Zyxel Device not perform the anti-malware check on files
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
Activate To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
Status The activate (light bulb) icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the entry is
# This is the entry’s index number in the list.
File Pattern This is the file name pattern. If a file’s name matches this pattern, the Zyxel Device does not
Check Black List Select this check box to log and delete files with names that match the black list patterns.
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
network from infection and the installation of malicious software.
Selecting this checkbox also activates the threat intelligence machine learning (TIML)
feature. TIML signatures come from the sandboxing inspection results and helps the Zyxel
Device block possible malicious or suspicious files.
Select this option to have the Zyxel Device check for the EICAR test file and treat it in the
same way as a real malware file. The EICAR test file is a standardized test file for signature
based anti-malware scanners. When the scanner detects the EICAR file, it responds in the
same way as if it found a real malware. Besides straightforward detection, the EICAR file
can also be compressed to test whether the anti-malware software can detect it in a
compressed file. The test string consists of the following human-readable ASCII characters.
X5O!P%@AP[4\PZX54(P^)7CC)7}$EICAR-STANDARD-ANTIVIRUS-TEST-FILE!$H+H*
malware detection, but can affect file transfer speeds as it needs to send information to the
cloud.
Note that the files on this list are currently bypassed. To use the cloud query feature on a
specific file type, click this file type and then click the right arrow button.
See available file types in Section 28.1 on page 543.
type to be checked, click this file type and then click the left arrow button.
overwrites the infected portion of the file with zeros before being forwarded to the user. The
uninfected portion of the file will pass through unmodified.
• no: Do not create a log when a packet matches a signature(s).
• log: Create a log on the Zyxel Device when a packet matches a signature(s).
• log alert: An alert is an emailed log for more serious events that may need more
immediate attention. Select this option to have the Zyxel Device send an alert when a
packet matches a signature(s).
with names that match the white list patterns.
inactive.
check the file for malware.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
550
Page 71

Chapter 28 Anti-Malware
Table 215 Configuration > Security Service > Anti-Malware (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Activate To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
Status The activate (light bulb) icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the entry is
inactive.
# This is the entry’s index number in the list.
File Pattern This is the file name pattern. If a file’s name that matches this pattern, the Zyxel Device logs
and then destroys the file.
File decompression
Enable file
decompression (ZIP
and RAR)
Select this check box to have the Zyxel Device scan a compressed file (the file does not
need to have a “zip” or “rar” file extension). The Zyxel Device first decompresses the file and
then scans the contents for malware.
Note: The Zyxel Device decompresses a compressed file once. The Zyxel Device
does NOT decompress any file(s) within a compressed file.
Destroy
compressed files
that could not
be
decompressed
When you select this check box, the Zyxel Device deletes compressed files that use
password encryption.
Select this check box to have the Zyxel Device delete any compressed files that it cannot
decompress. The Zyxel Device cannot decompress password protected files or a file within
another compressed file. There are also limits to the number of compressed files that the
Zyxel Device can concurrently decompress.
Note: The Zyxel Device’s firmware package cannot go through the Zyxel Device
with this check box enabled. The Zyxel Device classifies the firmware
package as a file that cannot be decompressed and then deletes it. Clear
this check box when you download a firmware package from the Zyxel
website. It’s OK to upload a firmware package to the Zyxel Device with the
check box selected.
Signature
Information
Current Version This field displays the signature set version number currently used by the Zyxel Device. This
Released Date This field displays the date and time the set was released.
Update
Signatures
Apply Click Apply to save your changes.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
The following fields display information on the current signature set that the Zyxel Device is
using.
number gets larger as the set is enhanced.
Click this link to go to the screen you can use to download signatures from the update
server.
28.3 The Black List Screen
A black list allows you to specify the file or encryption pattern that you want to block. False positives
occur when a non-infected file matches a malware signature.
Enter a file or encryption pattern that would cause the Zyxel Device to log and then destroy this file.
Click Configuration > Security Service > Anti-Malware > Black/White List > Black List to display the
following screen. Use Add to put a new entry in the list or Edit to change an existing one or Remove to
delete an existing entry.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
551
Page 72

Chapter 28 Anti-Malware
Figure 371 Configuration > Security Service > Anti-Malware > Black/White List > Black List
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 216 Configuration > Security Service > Anti-Malware > Black/White List > Black List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Check Black List Select this check box to log and delete files with names or encryption algorithm (MD5 Hash)
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
Activate To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
# This is the entry’s index number in the list.
Status The activate (light bulb) icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the entry is
Type This field displays the type (MD5 Hash or File Pattern) used to distinguish whether a file should
Value This field displays the file or encryption pattern of the entry.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
that match the black list patterns.
inactive.
be blocked.
Select the type (MD5 Hash or File Pattern) that you want to use to distinguish whether a file
should be blocked.
Enter the file or encryption pattern for this entry.
28.4 The White List Screen
A white list allows you to specify the file or encryption pattern to allow in order to avoid false positives.
False positives occur when a non-infected file matches a malware signature.
Enter a file or encryption pattern that would cause the Zyxel Device to allow this file.
Click Configuration > Security Service > Anti-Malware > Black/White List > White List to display the
following screen. Use Add to put a new entry in the list or Edit to change an existing one or Remove to
delete an existing entry.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
552
Page 73

Chapter 28 Anti-Malware
Figure 372 Configuration > Security Service > Anti-Malware > Black/White List > White List
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 217 Configuration > Security Service > Anti-Malware > Black/White List > White List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Check White List Select this check box to have the Zyxel Device not perform the anti-malware check on files
with names or algorithm (MD5 Hash) that match the white list patterns.
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
Activate To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
# This is the entry’s index number in the list.
Status The activate (light bulb) icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the entry is
Type This field displays the type (MD5 Hash or File Pattern) used to distinguish whether a file should
Value This field displays the file or encryption pattern of the entry.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
inactive.
be allowed.
Select the type (MD5 Hash or File Pattern) that you want to use to distinguish whether a file
should be allowed.
Enter the file or encryption pattern for this entry.
28.5 Anti-Malware Signature Searching
Click Configuration > Security Service > Anti-Malware > Signature to display this screen. Use this screen
to locate signatures and display details about them.
If your web browser opens a warning screen about a script making the web browser run slowly and the
computer unresponsive, just click No to continue. Click a column’s heading cell to sort the table entries
by that column’s criteria. Click the heading cell again to reverse the sort order.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
553
Page 74

Chapter 28 Anti-Malware
Figure 373 Configuration > Security Service > Anti-Malware > Signature
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 218 Configuration > Security Service > Anti-Malware > Signature
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Signatures Search Enter the name, part of the name or keyword of the signature(s) you want to find and click
Query all signatures
and export
Query Result
# This is the entry’s index number in the list.
Name This is the name of the anti-malware signature. Click the Name column heading to sort your
Search. This search is not case-sensitive and accepts numerical strings.
Click Export to have the Zyxel Device save all of the anti-malware signatures to your
computer in a .txt file.
search results in ascending or descending order according to the signature name.
Click a signature’s name to see details about the malware.
28.6 Anti-Malware Technical Reference
Types of Malware
The following table describes some of the common malware.
Table 219 Common Malware Types
TYPE DESCRIPTION
File Infector This is a small program that embeds itself in a legitimate program. A file infector is able to
copy and attach itself to other programs that are executed on an infected computer.
Boot Sector Virus This type of virus infects the area of a hard drive that a computer reads and executes
Macro Virus Macro viruses or Macros are small programs that are created to perform repetitive actions.
Email Virus Email viruses are malicious programs that spread through email.
Polymorphic Virus A polymorphic virus (also known as a mutation virus) tries to evade detection by changing
during startup. The virus causes computer crashes and to some extend renders the infected
computer inoperable.
Macros run automatically when a file to which they are attached is opened. Macros
spread more rapidly than other types of viruses as data files are often shared on a network.
a portion of its code structure after each execution or self replication. This makes it harder
for an anti-malware scanner to detect or intercept it.
A polymorphic virus can also belong to any of the virus types discussed above.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
554
Page 75

Chapter 28 Anti-Malware
Malware Infection and Prevention
The following describes a simple life cycle of malware.
1 A computer gets a copy of malware from a source such as the Internet, email, file sharing or any
removable storage media. The malware is harmless until the execution of an infected program.
2 The malware spreads to other files and programs on the computer.
3 The infected files are unintentionally sent to another computer thus starting the spread of the malware.
4 Once the malware is spread through the network, the number of infected networked computers can
grow exponentially.
Types of Anti-Malware Scanner
The section describes two types of anti-malware scanner: host-based and network-based.
A host-based anti-malware (HAM) scanner is often software installed on computers and/or servers in the
network. It inspects files for malware patterns as they are moved in and out of the hard drive. However,
host-based anti-malware scanners cannot eliminate all malware for a number of reasons:
• HAM scanners are slow in stopping malware threats through real-time traffic (such as from the
Internet).
• HAM scanners may reduce computing performance as they also share the resources (such as CPU
time) on the computer for file inspection.
• You have to update the malware signatures and/or perform malware scans on all computers in the
network regularly.
A network-based anti-malware (NAM) scanner is often deployed as a dedicated security device (such
as your Zyxel Device) on the network edge. NAM scanners inspect real-time data traffic (such as email
messages or web) that tends to bypass HAM scanners. The following lists some of the benefits of NAM
scanners.
• NAM scanners stop malware threats at the network edge before they enter or exit a network.
• NAM scanners reduce computing loading on computers as the read-time data traffic inspection is
done on a dedicated security device.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
555
Page 76

29.1 Overview
Use the Reputation Filter screens to configure settings for IP reputation and botnet filtering.
29.1.1 What You Need to Know
IP Reputation
IP reputation checks the reputation of an IP address from a database. An IP address with bad
reputation associates with suspicious activities, such as spam, virus, and/or phishing. The Zyxel Device will
respond when there are packets coming from an IPv4 address with bad reputation.
Botnet Filtering
CHAPTER 29
Reputation Filter
A botnet is a network consisting of computers that are infected with malware and remotely controlled.
The infected computers will contact and wait for instructions from a command and control (C&C)
server(s). An attacker can control the botnet by setting up a C&C server and sending commands to the
infected computers. Alternatively, a peer-to-peer network approach is used. The infected computer
scans and communicates with the peer devices in the same botnet to share commands or malware
sent by the C&C server.
29.1.2 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• Use the IP Reputation screen (Section 29.2 on page 556) to enable IP reputation and specify what
action the Zyxel Device takes when any IP address with bad reputation is detected.
• Use the Botnet Filter screen (Section 29.3 on page 561) to enable botnet filtering and specify what
action the Zyxel Device takes when any suspicious activity is detected.
29.2 IP Reputation Screen
When you register for and enable the IP reputation service, your Zyxel Device downloads signature files
that identifies reputation of IPv4 addresses. You can have the Zyxel Device forward, block, and/or log
packets from IPv4 addresses based on these signatures and categories.
Use this screen to enable IP reputation and specify the action the Zyxel Device takes when it detects a
suspicious activity or a connection attempt to or from an IPv4 address with bad reputation.
Click Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > IP Reputation > General to display the
configuration screen as shown next.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
556
Page 77

Chapter 29 Reputation Filter
Figure 374 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > IP Reputation > General
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 220 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > IP Reputation > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Blocking
Enable Select this option to turn on IP blocking on the Zyxel Device. Otherwise, deselect it.
Action Set what action the Zyxel Device takes when packets come from an IPv4 address with bad
reputation.
forward: Select this action to have the Zyxel Device allow the packet to go through.
block: Select this action to have the Zyxel Device deny the packets and send a TCP RST to
both the sender and receiver when a packet comes from an IPv4 address with bad
reputation.
Threat Level
Threshold
Select the threshold threat level to which the Zyxel Device will take action (high, medium
and above, Low and above).
The threat level is determined by the IP reputation engine. It grades IPv4 addresses.
• high: An IPv4 address that scores 0 to 20 points.
• medium and above: An IPv4 address that scores 0-60 points.
• Low and above: An IPv4 address that scores 0-80 pointgs.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
557
Page 78

Chapter 29 Reputation Filter
Table 220 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > IP Reputation > General (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Log These are the log options:
no: Do not create a log when the packet comes from an IPv4 address with bad reputation.
log: Create a log on the Zyxel Device when the packet comes from an IPv4 address with
bad reputation.
log alert: An alert is an emailed log for more serious events that may need more immediate
attention. Select this option to have the Zyxel Device send an alert when the packet comes
from an IPv4 address with bad reputation.
Types of Cyber
Threats Coming From
The Internet
Anonymous
Proxies
Denial of Service Sites that issue Denial of Service (DoS) attacks, such as DoS, DDoS, SYN flood, and
Select the categories of packets that come from the Internet and are known to pose a
security threat to users or their computers. Otherwise, deselect it.
Sites and proxies that act as an intermediary for surfing to other websites in an anonymous
fashion, whether to circumvent Web filtering or for other reasons. For example, blog.go2.tw,
anonymizer.com, www.qu365.com.
anomalous traffic detection.
DoS attacks can flood your Internet connection with invalid packets and connection
requests, using so much bandwidth and so many resources that Internet access becomes
unavailable. The goal of DoS attacks is not to steal information, but to disable a device or
network on the Internet.
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is one in which multiple compromised systems
attack a single target, thereby causing denial of service for users of the targeted system.
SYN flood is an attack that attackers flood SYN packets to a server in TCP handshakes, and
not respond with ACK packets on purpose. This keeps the server waiting for attackers’
responses to establish TCP connections, and make the server unavailable.
Anomalous traffic detection could be malicious activities, such as malware outbreaks or
hacking attempts.
Exploits Sites that distribute exploits or exploit kits to infect website visitors’ devices. Exploits include
shellcode, root kits, worms, or viruses that download additional malware to infect devices.
An exploit kit consists of different exploits.
Negative
Reputation
Scanners Sites that run unauthorized system vulnerabilities scan to look for vulnerabilities in website
Spam Sources Sites that have been promoted through spam techniques. For example,
TOR Proxies Sites that act as the exit nodes in a Tor (The Onion Router) network.
Sites that have bad reputation and associate with suspicious activities, such as spam, virus,
and/or phishing.
visitors’ devices.
img.tongji.linezing.com, banner.chinesegamer.net.
Tor is a service that keep users anonymous in the Internet and make users’ Internet activities
untraceable. Tor hides user’s real IP addresses by encrypting data and transmitting the
encrypted data in a chain of selected nodes acting as intermediaries. Each node can only
decrypt the data sent from the node before it. The first node that receives the encrypted
data is called the entry node. The last node is the last intermediary that the encrypted data
will go through before it arrives at the destination.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
558
Page 79

Chapter 29 Reputation Filter
Table 220 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > IP Reputation > General (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Web Attacks Sites that launch web attacks, such as SQL injection, cross site scripting, iframe injection,
and brute force attack.
SQL injection (SQLI) is an attack that attackers insert malicious SQL (Structured Query
Language) code into a web application database query. Attackers can then access, add,
modify, or delete data in users’ databases.
Cross site scripting (XSS) is an attack that attackers injects malicious scripts to websites or
web applications in the form of HTML or JavaScript code. The scripts execute when users
visit the infected web page or perform the infected web applications. XSS will cause failures
to encrypt traffic, cookie stealing, identity impersonation, and phishing.
Iframe injection is an attack that attackers injects malicious iframe (inline frame) tags to
websites. The malicious iframe tag downloads malware to the devices of the infected
websites’ visitors, and steal users’ sensitive information. An iframe tag is an HTML tag that is
used to embed contents from another source in a website, but attackers misuse this feature.
Brute force attack is an attack that attackers attempt to gain access to websites or device
via a succession of different passwords.
Types of Cyber
Threats Coming From
The Internet And
Local Networks
Botnets Sites that use bots (zombies) including command-and-control (C&C) servers.
Phishing Sites that are used for deceptive or fraudulent purposes (e.g. phishing), such as stealing
Test IP Threat Category
IP to test Enter an IPv4 address of a website, and click the Query button to check if the website
Signature
Information
Select the categories of packets that come from the Internet and local network. The
categories of packets are known to pose a security threat to users or their computers.
Otherwise, deselect it.
financial or other user account information. These sites are most often designed to appear
as legitimate sites in order to mislead users into entering their credentials. For example,
optimizedby.rmxads.com, 218.1.71.226/.../e3b.
associates with suspicious activities that could pose a security threat to users or their
computers.
The Zyxel Device comes with signatures for IP reputation. These signatures are continually
updated as new malware evolves. New signatures can be downloaded to the Zyxel Device
periodically if you have subscribed for the IP reputation signatures service.
You need to create an account at myZyxel, register your Zyxel Device and then subscribe
for IP reputation service in order to be able to download new signatures from myZyxel (see
the Registration screens).
The following fields display information on the current signature set that the Zyxel Device is
using.
Current Version This field displays the signature set version number currently used by the Zyxel Device. This
number gets larger as new signatures are added.
Signature Number This field displays the number of signatures in this set.
Released Date This field displays the date and time the set was released.
Update Signatures Click this to go to the Configuration > Licensing > Signature Update screen to check for new
Apply Click Apply to save your changes.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
signatures at myZyxel. You can schedule or immediately download signatures.
29.2.1 IP Reputation White List Screen
Use this screen to create white list entries. The Zyxel Device will allow the incoming and outgoing packets
from the listed IPv4 addresses.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
559
Page 80

Chapter 29 Reputation Filter
You can add up to 256 entries in the IP reputation white list.
Figure 375 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > IP Reputation > White List
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 221 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > IP Reputation > White List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
White List
Check White List Select this check box and the Zyxel Device will allow the incoming packets that come
from the listed IPv4 addresses.
Note: Enable IP blocking in the Configuration > Security Service > Reputation
Filter > IP Reputation > General screen for the white list to take effect.
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
Activate To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
# This is the entry’s index number in the list.
Status The activate (light bulb) icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the entry is
inactive.
IPv4 Address This field displays the IPv4 address of this entry.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
29.2.2 IP Reputation Black List Screen
Use this screen to create black list entries. The Zyxel Device will block the incoming and outgoing
packets from the listed IPv4 addresses.
You can add up to 256 entries in the IP reputation black list.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
560
Page 81

Chapter 29 Reputation Filter
Figure 376 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > IP Reputation > Black List
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 222 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > IP Reputation > Black List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Black List
Check Black List Select this check box and the Zyxel Device will block the incoming packets that come
from the listed IPv4 addresses.
Note: Enable IP blocking in the Configuration > Security Service > Reputation
Filter > IP Reputation > General screen for the black list to take effect.
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
Activate To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
# This is the entry’s index number in the list.
Status The activate (light bulb) icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the entry is
inactive.
IPv4 Address This field displays the IPv4 address of this entry.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
29.3 Botnet Filter Screen
The Zyxel Device’s botnet filtering service allows you to detect and block connection attempts to or
from the C&C server or known botnet IP addresses.
When you register for and enable the botnet filtering service, your Zyxel Device downloads signature
files that contain known botnet domain names and IP addresses. The Zyxel Device will also access an
external database that has millions of web sites categorized based on content. You can have the Zyxel
Device allow, block, block and/or log access to web sites or hosts based on these signatures and
categories.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
561
Page 82

Chapter 29 Reputation Filter
Use this screen to enable botnet filtering and specify the action the Zyxel Device takes when it detects a
suspicious activity or a connection attempt to or from a botnet C&C server.
Click the Botnet Filter icon for more information on the Zyxel Device’s security features.
Click Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > Botnet Filter to display the configuration
screen as shown next.
Figure 377 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > Botnet Filter > General
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 223 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > Botnet Filter > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
URL Blocking
Enable Select this option to turn on URL blocking on the Zyxel Device.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
562
Page 83

Chapter 29 Reputation Filter
Table 223 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > Botnet Filter > General (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Action Set what action the Zyxel Device takes when it detects a connection attempt to or from the
web pages of the specified categories.
block: Select this action to have the Zyxel Device block access to the web pages that
match the categories that you select above.
warn: Select this action to have the Zyxel Device display a warning message to the access
requesters for the web pages before allowing users to access web pages that match the
categories that you select above.
pass: Select this action to have the Zyxel Device allow access to the web pages that match
the categories that you select above.
Log These are the log options:
no: Do not create a log when it detects a connection attempt to or from the web pages of
the specified categories.
log: Create a log on the Zyxel Device when it detects a connection attempt to or from the
web pages of the specified categories.
Message to display when a site is blocked
Denied Access
Message
Enter a message to be displayed when the botnet filter blocks access to a web page. Use
up to 127 characters (0-9a-zA-Z;/?:@&=+$\.-_!~*'()%,”). For example, “Access to this web
page is not allowed. Please contact the network administrator”.
It is also possible to leave this field blank if you have a URL specified in the Redirect URL field.
In this case if the botnet filter blocks access to a web page, the Zyxel Device just opens the
web page you specified without showing a denied access message.
Redirect URL Enter the URL of the web page to which you want to send users when their web access is
blocked by the botnet filter. The web page you specify here opens in a new frame below
the denied access message.
Use “http://” or “https://” followed by up to 262 characters (0-9a-zA-Z;/?:@&=+$\.-_!~*'()%).
For example, http://192.168.1.17/blocked access.
Managed
Categories
Anonymizers Sites and proxies that act as an intermediary for surfing to other Web sites in an anonymous
Botnet C&C Sites that use bots (zombies) including command-and-control (C&C) servers.
Compromised Sites that have been compromised by someone other than the site owner in order to install
Malware Sites that install unwanted software on a user's computer with the intent to enable third-
Phishing & Fraud Sites that are used for deceptive or fraudulent purposes (e.g. phishing), such as stealing
Spam Sites Sites that have been promoted through spam techniques. For example,
Select the categories of web pages that are known to pose a security threat to users or their
computers. Otherwise, deselect it.
fashion, whether to circumvent Web filtering or for other reasons. For example, blog.go2.tw,
anonymizer.com, www.qu365.com.
malicious programs without the user's knowledge. Includes sites that may be vulnerable to a
particular high-risk attack. For example, www.wokoo.net, movie.sx.zj.cn.
party monitoring or make system changes without the user's consent. For example,
www.tqlkg.com, aladel.net.
financial or other user account information. These sites are most often designed to appear
as legitimate sites in order to mislead users into entering their credentials. For example,
optimizedby.rmxads.com, 218.1.71.226/.../e3b.
img.tongji.linezing.com, banner.chinesegamer.net.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
563
Page 84

Chapter 29 Reputation Filter
Table 223 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > Botnet Filter > General (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Signature
Information
Current Version This field displays the signature set version number currently used by the Zyxel Device. This
Signature Number This field displays the number of signatures in this set.
Released Date This field displays the date and time the set was released.
Update Signatures Click this to go to the Configuration > Licensing > Signature Update screen to check for new
Apply Click Apply to save your changes.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
The Zyxel Device comes with signatures for the botnet filter. These signatures are continually
updated as new malware evolves. New signatures can be downloaded to the Zyxel Device
periodically if you have subscribed for the botnet filter signatures service.
You need to create an account at myZyxel, register your Zyxel Device and then subscribe
for botnet filter service in order to be able to download new signatures from myZyxel (see
the Registration screens).
The following fields display information on the current signature set that the Zyxel Device is
using.
number gets larger as new signatures are added.
signatures at myZyxel. You can schedule or immediately download signatures.
29.3.1 Botnet Filter White List Screen
Use this screen to create white list entries. The Zyxel Device will allow the incoming packets from the
listed IPv4 addresses and URLs.
Figure 378 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > Botnet Filter > White List
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 224 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > Botnet Filter > White List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
White List
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
# This is the entry’s index number in the list.
White List This field displays the URL of this entry.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
564
Page 85

Chapter 29 Reputation Filter
29.3.2 Botnet Filter Black List Screen
Use this screen to create black list entries. The Zyxel Device will block the incoming packets from the
listed IPv4 addresses and URLs.
Figure 379 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > Botnet Filter > Black List
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 225 Configuration > Security Service > Reputation Filter > Botnet Filter > Black List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Black List
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
# This is the entry’s index number in the list.
Black List This field displays the URL of this entry.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Zyxel Device.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
565
Page 86

30.1 Overview
This chapter introduces packet inspection IDP (Intrusion, Detection and Prevention), custom signatures,
and updating signatures. An IDP system can detect malicious or suspicious packets and respond
instantaneously. IDP on the Zyxel Device protects against network-based intrusions.
30.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• Use the Security Service > IDP screen (Section 30.2 on page 566) to view registration and signature
information.
• Use the Security Service > IDP > Custom Signature > Add screens (Section 30.3 on page 572) to create
a new custom signature, edit an existing signature, delete existing signatures or save signatures to
your computer.
CHAPTER 30
IDP
30.1.2 What You Need To Know
Packet Inspection Signatures
A signature is a pattern of malicious or suspicious packet activity. You can specify an action to be taken
if the system matches a stream of data to a malicious signature. You can change the action in the
profile screens. Packet inspection examine OSI (Open System Interconnection) layer-4 to layer-7 packet
contents for malicious data. Generally, packet inspection signatures are created for known attacks
while anomaly detection looks for abnormal behavior.
Applying Your IDP Configuration
Changes to the Zyxel Device’s IDP settings affect new sessions, but not the sessions that already existed
before you applied the new settings.
30.1.3 Before You Begin
• Register for a trial IDP subscription in the Registration screen. This gives you access to free signature
updates. This is important as new signatures are created as new attacks evolve. When the trial
subscription expires, purchase and enter a license key using the same screens to continue the
subscription.
30.2 The IDP Screen
An IDP profile is a set of packet inspection signatures.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
566
Page 87

Chapter 30 IDP
Click Configuration > Security Service > IDP to open this screen. Use this screen to view registration and
signature information.
Note: You must register in order to update packet inspection signatures. See the Registration
screens.
If you try to enable IDP when the IDP service has not yet been registered, a warning screen displays and
IDP is not enabled.
Click the IDP icon for more information on the Zyxel Device’s security features.
Figure 380 Configuration > Security Service > IDP
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
567
Page 88

Chapter 30 IDP
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 226 Configuration > Security Service > IDP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General Settings
Enable Select this check box to activate the IDP feature which detects and prevents malicious
Query Signatures
Name Type the name or part of the name of the signature(s) you want to find.
Signature ID Type the ID or part of the ID of the signature(s) you want to find.
Search all custom
signatures
Severity Search for signatures by severity level(s). Hold down the [Ctrl] key if you want to make
Classification Type Search for signatures by attack type(s) (see Table 227 on page 569). Attack types are
Platform Search for signatures created to prevent intrusions targeting specific operating
Service Search for signatures by IDP service group(s). See Table 227 on page 569 for group
Action Search for signatures by the response the Zyxel Device takes when a packet matches a
Activation Search for activated and/or inactivated signatures here.
Log Search for signatures by log option here.
Query Result The results are displayed in a table showing the SID, Name, Severity, Classification Type,
Custom Signature Rules Use this part of the screen to create, edit, delete or export (save to your computer)
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
Export To save an entry or entries as a file on your computer, select them and click Export. Click
or suspicious packets and responds instantaneously.
Select this check box to include signatures you created or imported in the Custom
Signatures screen in the search. You can search for specific signatures by name or ID. If
the name and ID fields are left blank, then all signatures are searched according to the
criteria you select.
multiple selections.
These are the severities as defined in the Zyxel Device. The number in brackets is the
number you use if using commands.
Severe (5): These denote attacks that try to run arbitrary code or gain system privileges.
High (4): These denote known serious vulnerabilities or attacks that are probably not
false alarms.
Medium (3): These denote medium threats, access control attacks or attacks that could
be false alarms.
Low (2): These denote mild threats or attacks that could be false alarms.
Very-Low (1): These denote possible attacks caused by traffic such as Ping, trace route,
ICMP queries etc.
known as policy types in the group view screen. Hold down the [Ctrl] key if you want to
make multiple selections.
system(s). Hold down the [Ctrl] key if you want to make multiple selections.
details. Hold down the [Ctrl] key if you want to make multiple selections.
signature.Hold down the [Ctrl] key if you want to make multiple selections.
Platform, Service, Log, and Action criteria as selected in the search. Click the SID column
header to sort search results by signature ID.
custom signatures.
Save in the file download dialog box and then select a location and name for the file.
Custom signatures must end with the ‘rules’ file name extension, for example,
MySig.rules.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
568
Page 89

Chapter 30 IDP
Table 226 Configuration > Security Service > IDP (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the entry’s index number in the list.
SID SID is the signature ID that uniquely identifies a signature. Click the SID header to sort
signatures in ascending or descending order. It is automatically created when you click
the Add icon to create a new signature. You can edit the ID, but it cannot already exist
and it must be in the 9000000 to 9999999 range.
Name This is the name of your custom signature. Duplicate names can exist, but it is advisable
to use unique signature names that give some hint as to intent of the signature and the
type of attack it is supposed to prevent.
Customer Signature Rule
Importing
Use this part of the screen to import custom signatures (previously saved to your
computer) to the Zyxel Device.
Note: The name of the complete custom signature file on the Zyxel Device is
‘custom.rules’. If you import a file named ‘custom.rules’, then all custom
signatures on the Zyxel Device are overwritten with the new file. If this is
not your intention, make sure that the files you import are not named
‘custom.rules’.
File Path Type the file path and name of the custom signature file you want to import in the text
box (or click Browse to find it on your computer) and then click Importing to transfer the
file to the Zyxel Device.
New signatures then display in the Zyxel Device IDP > Custom Signatures screen.
Signature Information The following fields display information on the current signature set that the Zyxel Device
is using.
Current Version This field displays the IDP signature set version number. This number gets larger as the set
is enhanced.
Signature Number This field displays the number of IDP signatures in this set. This number usually gets larger
Released Date This field displays the date and time the set was released.
Update Signatures Click this link to go to the screen you can use to download signatures from the update
as the set is enhanced. Older signatures and rules may be removed if they are no longer
applicable or have been supplanted by newer ones.
server.
Policy Types
This table describes Policy Types as categorized in the Zyxel Device.
Table 227 Policy Types
POLICY TYPE DESCRIPTION
Access Control Access control refers to procedures and controls that limit or detect access. Access
control attacks try to bypass validation checks in order to access network resources such
as servers, directories, and files.
Any Any attack includes all other kinds of attacks that are not specified in the policy such as
Backdoor/Trojan Horse A backdoor (also called a trapdoor) is hidden software or a hardware mechanism that
password, spoof, hijack, phishing, and close-in.
can be triggered to gain access to a program, online service or an entire computer
system. A Trojan horse is a harmful program that is hidden inside apparently harmless
programs or data.
Although a virus, a worm and a Trojan are different types of attacks, they can be
blended into one attack. For example, W32/Blaster and W32/Sasser are blended attacks
that feature a combination of a worm and a Trojan.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
569
Page 90

Chapter 30 IDP
Table 227 Policy Types (continued)
POLICY TYPE DESCRIPTION
BotNet A Botnet is a number of Internet computers that have been set up to forward
transmissions including spam or viruses to other computers on the Internet though their
owners are unaware of it. It is also a collection of Internet-connected programs
communicating with other similar programs in order to perform tasks and participate in
distributed Denial-Of-Service attacks.
Buffer Overflow A buffer overflow occurs when a program or process tries to store more data in a buffer
(temporary data storage area) than it was intended to hold. The excess information can
overflow into adjacent buffers, corrupting or overwriting the valid data held in them.
Intruders could run codes in the overflow buffer region to obtain control of the system,
install a backdoor or use the victim to launch attacks on other devices.
DoS/DDoS The goal of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks is not to steal information, but to disable a
device or network on the Internet.
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is one in which multiple compromised
systems attack a single target, thereby causing denial of service for users of the targeted
system.
Instant Messenger IM (Instant Messenger) refers to chat applications. Chat is real-time, text-based
Mail A Mail or email bombing attack involves sending several thousand identical messages to
Misc Miscellaneous attacks takes advantage of vulnerable computer networks and web
P2P Peer-to-peer (P2P) is where computing devices link directly to each other and can
Scan A scan describes the action of searching a network for an exposed service. An attack
SPAM Spam is unsolicited “junk” email sent to large numbers of people to promote products or
Stream Media A Stream Media attack occurs when a malicious network node downloads an
Tunnel A Tunneling attack involves sending IPv6 traffic over IPv4, slipping viruses, worms and
communication between two or more users via networks-connected computers. After
you enter a chat (or chat room), any room member can type a message that will
appear on the monitors of all the other participants.
an electronic mailbox in order to overflow it, making it unusable.
servers by forcing cache servers or web browsers into disclosing user-specific information
that might be sensitive and confidential. The most common type of Misc. attacks are
HTTP Response Smuggling, HTTP Response Splitting and JSON Hijacking.
directly initiate communication with each other; they do not need an intermediary. A
device can be both the client and the server. In the Zyxel Device, P2P refers to peer-topeer applications such as e-Mule, e-Donkey, BitTorrent, iMesh, etc.
may then occur once a vulnerability has been found. Scans occur on several network
levels.
A network scan occurs at layer-3. For example, an attacker looks for network devices
such as a router or server running in an IP network.
A scan on a protocol is commonly referred to as a layer-4 scan. For example, once an
attacker has found a live end system, he looks for open ports.
A scan on a service is commonly referred to a layer-7 scan. For example, once an
attacker has found an open port, say port 80 on a server, he determines that it is a HTTP
service run by some web server application. He then uses a web vulnerability scanner (for
example, Nikto) to look for documented vulnerabilities.
services.
overwhelming amount of media stream data that could potentially exhaust the entire
system. This method allows users to send small requests messages that result in the
streaming of large media objects, providing an opportunity for malicious users to exhaust
resources in the system with little effort expended on their part.
spyware through the network using secret tunnels. This method infiltrates standard
security measures through IPv6 tunnels, passing through IPv4 undetected. An external
signal then triggers the malware to spring to life and wreak havoc from inside the
network.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
570
Page 91

Chapter 30 IDP
Table 227 Policy Types (continued)
POLICY TYPE DESCRIPTION
Virus/Worm A computer virus is a small program designed to corrupt and/or alter the operation of
other legitimate programs. A worm is a program that is designed to copy itself from one
computer to another on a network. A worm’s uncontrolled replication consumes system
resources, thus slowing or stopping other tasks.
Web Attack Web attacks refer to attacks on web servers such as IIS (Internet Information Services).
IDP Service Groups
An IDP service group is a set of related packet inspection signatures.
Table 228 IDP Service Groups
WEB_PHP WEB_MISC WEB_IIS WEB_FRONTPAGE
WEB_CGI WEB_ATTACKS TFTP TELNET
SQL SNMP SMTP RSERVICES
RPC POP3 POP2 P2P
ORACLE NNTP NETBIOS MYSQL
MISC_EXPLOIT MISC_DDOS MISC_BACKDOOR MISC
IMAP IM ICMP FTP
FINGER DNS n/a
30.2.1 Query Example
This example shows a search with these criteria:
•Severity: Severe
• Classification Type: Misc
• Platform: Windows
•Service: Any
•Actions: Any
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
571
Page 92

Figure 381 Query Example Search
Chapter 30 IDP
30.3 IDP Custom Signatures
Create custom signatures for new attacks or attacks peculiar to your network. Custom signatures can
also be saved to/from your computer so as to share with others.
You need some knowledge of packet headers and attack types to create your own custom signatures.
IP Packet Header
These are the fields in an Internet Protocol (IP) version 4 packet header.
Figure 382 IP v4 Packet Headers
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
572
Page 93

Chapter 30 IDP
The header fields are discussed in the following table.
Table 229 IP v4 Packet Headers
HEADER DESCRIPTION
Version The value 4 indicates IP version 4.
IHL IP Header Length is the number of 32 bit words forming the total length of the header
Type of Service The Type of Service, (also known as Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP)) is
Total Length This is the size of the datagram in bytes. It is the combined length of the header and
Identification This is a 16-bit number, which together with the source address, uniquely identifies this
Flags Flags are used to control whether routers are allowed to fragment a packet and to
Fragment Offset This is a byte count from the start of the original sent packet.
Time To Live This is a counter that decrements every time it passes through a router. When it
Protocol The protocol indicates the type of transport packet being carried, for example, 1 =
Header Checksum This is used to detect processing errors introduced into the packet inside a router or
Source IP Address This is the IP address of the original sender of the packet.
Destination IP Address This is the IP address of the final destination of the packet.
Options IP options is a variable-length list of IP options for a datagram that define IP Security
Padding Padding is used as a filler to ensure that the IP packet is a multiple of 32 bits.
(usually five).
usually set to 0, but may indicate particular quality of service needs from the network.
the data.
packet. It is used during reassembly of fragmented datagrams.
indicate the parts of a packet to the receiver.
reaches zero, the datagram is discarded. It is used to prevent accidental routing
loops.
ICMP; 2= IGMP; 6 = TCP; 17= UDP.
bridge where the packet is not protected by a link layer cyclic redundancy check.
Packets with an invalid checksum are discarded by all nodes in an IP network.
Option, IP Stream Identifier, (security and handling restrictions for the military), Record
Route (have each router record its IP address), Loose Source Routing (specifies a list of
IP addresses that must be traversed by the datagram), Strict Source Routing (specifies
a list of IP addresses that must ONLY be traversed by the datagram), Timestamp (have
each router record its IP address and time), End of IP List and No IP Options.
Select Configuration > Security Service. The Custom Signature Rules section shows a summary of all
custom signatures created. Click the SID or Name heading to sort. Click the Add icon to create a new
signature or click the Edit icon to edit an existing signature. You can also delete custom signatures here
or save them to your computer.
Note: The Zyxel Device checks all signatures and continues searching even after a match is
found. If two or more rules have conflicting actions for the same packet, then the Zyxel
Device applies the more restrictive action (reject-both, reject-receiver or reject-sender,
drop, none in this order). If a packet matches a rule for reject-receiver and it also
matches a rule for reject-sender, then the Zyxel Device will reject-both.
30.3.1 Add / Edit Custom Signatures
Click the Add icon to create a new signature or click the Edit icon to edit an existing signature in the
screen as shown in Figure 380 on page 567.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
573
Page 94

Chapter 30 IDP
A packet must match all items you configure in this screen before it matches the signature. The more
specific your signature (including packet contents), then the fewer false positives the signature will
trigger.
Try to write signatures that target a vulnerability, for example a certain type of traffic on certain
operating systems, instead of a specific exploit.
Figure 383 Configuration > Security Service > IDP > Custom Signatures > Add/Edit
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
574
Page 95

Chapter 30 IDP
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 230 Configuration > Security Service > IDP > Custom Signatures > Add/Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name Type the name of this custom signature. You may use 1-31 alphanumeric characters,
Signature ID A signature ID is automatically created when you click the Add icon to create a new
Information Use the following fields to set general information about the signature as denoted below.
Severity The severity level denotes how serious the intrusion is. Categorize the seriousness of the
Platform Some intrusions target specific operating systems only. Select the operating systems that
Classification Type Categorize the attack type here. See Table 227 on page 569 as a reference.
Frequency Recurring packets of the same type may indicate an attack. Use the following field to
Threshold Select Threshold and then type how many packets (that meet the criteria in this
Header Options
Network Protocol Configure signatures for IP version 4.
Type Of Service Type of service in an IP header is used to specify levels of speed and/or reliability. Some
Identification The identification field in a datagram uniquely identifies the datagram. If a datagram is
Fragmentation A fragmentation flag identifies whether the IP datagram should be fragmented, not
Fragment Offset When an IP datagram is fragmented, it is reassembled at the final destination. The
Time to Live Time to Live is a counter that decrements every time it passes through a router. When it
underscores(
case-sensitive.
Duplicate names can exist but it is advisable to use unique signature names that give
some hint as to intent of the signature and the type of attack it is supposed to prevent.
Refer to (but do not copy) the packet inspection signature names for hints on creating a
naming convention.
signature. You can edit the ID to create a new one (in the 9000000 to 9999999 range),
but you cannot use one that already exists. You may want to do that if you want to order
custom signatures by SID.
intrusion here.
the intrusion targets, that is, the operating systems you want to protect from this intrusion.
SGI refers to Silicon Graphics Incorporated, who manufactures multi-user Unix
workstations that run the IRIX operating system (SGI's version of UNIX). A router is an
example of a network device.
indicate how many packets per how many seconds constitute an intrusion
signature) per how many seconds constitute an intrusion.
intrusions use an invalid Type Of Service number. Select the check box, then select Equal
or Not-Equal and then type in a number.
fragmented, it contains a value that identifies the datagram to which the fragment
belongs. Some intrusions use an invalid Identification number. Select the check box and
then type in the invalid number that the intrusion uses.
fragmented or is a reserved bit. Some intrusions can be identified by this flag. Select the
check box and then select the flag that the intrusion uses.
fragmentation offset identifies where the fragment belongs in a set of fragments. Some
intrusions use an invalid Fragment Offset number. Select the check box, select Equal,
Smaller or Greater and then type in a number
reaches zero, the datagram is discarded. Usually it’s used to set an upper limit on the
number of routers a datagram can pass through. Some intrusions can be identified by
the number in this field. Select the check box, select Equal, Smaller or Greater and then
type in a number.
_), or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a number. This value is
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
575
Page 96

Chapter 30 IDP
Table 230 Configuration > Security Service > IDP > Custom Signatures > Add/Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Options IP options is a variable-length list of IP options for a datagram that define IP Security
Option, IP Stream Identifier, (security and handling restrictions for the military), Record
Route (have each router record its IP address), Loose Source Routing (specifies a list of IP
addresses that must be traversed by the datagram), Strict Source Routing (specifies a list
of IP addresses that must ONLY be traversed by the datagram), Timestamp (have each
router record its IP address and time), End of IP List and No IP Options. IP Options can help
identify some intrusions. Select the check box, then select an item from the list box that
the intrusion uses
Same IP Select the check box for the signature to check for packets that have the same source
and destination IP addresses.
Transport Protocol The following fields vary depending on whether you choose TCP, UDP or ICMP.
Transport Protocol: TCP
Port Select the check box and then enter the source and destination TCP port numbers that
Flow The selected keyword sets the criteria as to which traffic is matched. You can match
will trigger this signature.
traffic based on direction or whether the connection is established or not. You can also
specify whether you want to match signatures per packet or in a stream of packets.
Established: Match established connections.
Stateless: Match packets that are not part of an established connection.
To Client: Match packets that flow from server to client..
To Server: Match packets that flow from client to server.
From Client: Match packets that flow from client to server.
From Servers: Match packets that flow from server to client.
No Stream: Match packets that have not been reassembled by the stream engine. It will
not match packets that have been reassembled.
Only Stream: Match packets that have been reassembled.
Flags Select what TCP flag bits the signature should check.
Sequence Number Use this field to check for a specific TCP sequence number.
Ack Number Use this field to check for a specific TCP acknowledgment number.
Window Size Use this field to check for a specific TCP window size.
Transport Protocol: UDP
Port Select the check box and then enter the source and destination UDP port numbers that
will trigger this signature.
Transport Protocol:
ICMP
Type Use this field to check for a specific ICMP type value.
Code Use this field to check for a specific ICMP code value.
ID Use this field to check for a specific ICMP ID value. This is useful for covert channel
Sequence Number Use this field to check for a specific ICMP sequence number. This is useful for covert
Payload Options The longer a payload option is, the more exact the match, the faster the signature
programs that use static ICMP fields when they communicate.
channel programs that use static ICMP fields when they communicate.
processing. Therefore, if possible, it is recommended to have at least one payload option
in your signature.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
576
Page 97

Chapter 30 IDP
Table 230 Configuration > Security Service > IDP > Custom Signatures > Add/Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Payload Size This field may be used to check for abnormally sized packets or for detecting buffer
overflows
Select the check box, then select Equal, Smaller or Greater and then type the payload
size.
Stream rebuilt packets are not checked regardless of the size of the payload.
Add Click this to create a new entry.
Edit Select an entry and click this to be able to modify it.
Remove Select an entry and click this to delete it.
# This is the entry’s index number in the list.
Offset This field specifies where to start searching for a pattern within a packet. For example, an
offset of 5 would start looking for the specified pattern after the first five bytes of the
payload.
Content Type the content that the signature should search for in the packet payload.
Hexadecimal code entered between pipes is converted to ASCII. For example, you
could represent the ampersand as either & or |26| (26 is the hexadecimal code for the
ampersand).
Case-insensitive Select Yes if content casing does NOT matter.
Decode as URI A Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) is a string of characters for identifying an abstract or
physical resource (RFC 2396). A resource can be anything that has identity, for example,
an electronic document, an image, a service (“today's weather report for Taiwan”), a
collection of other resources. An identifier is an object that can act as a reference to
something that has identity. Example URIs are:
ftp://ftp.is.co.za/rfc/rfc1808.txt; ftp scheme for File Transfer Protocol services
http://www.math.uio.no/faq/compression-faq/part1.html; http scheme for Hypertext
Transfer Protocol services
mailto:mduerst@ifi.unizh.ch; mailto scheme for electronic mail addresses
.
telnet://melvyl.ucop.edu/; telnet scheme for interactive services via the TELNET Protocol
Select Yes for the signature to search for normalized URI fields. This means that if you are
writing signatures that includes normalized content, such as %2 for directory traversals,
these signatures will not be triggered because the content is normalized out of the URI
buffer.
For example, the URI:
/scripts/..%c0%af../winnt/system32/cmd.exe?/c+ver
will get normalized into:
/winnt/system32/cmd.exe?/c+ver
OK Click this button to save your changes to the Zyxel Device and return to the summary
screen.
Cancel Click this button to return to the summary screen without saving any changes.
30.3.2 Custom Signature Example
Before creating a custom signature, you must first clearly understand the vulnerability.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
577
Page 98

30.3.2.1 Understand the Vulnerability
Check the Zyxel Device logs when the attack occurs. Use web sites such as Google or Security Focus to
get as much information about the attack as you can. The more specific your signature, the less chance
it will cause false positives.
As an example, say you want to check if your router is being overloaded with DNS queries so you create
a signature to detect DNS query traffic.
30.3.2.2 Analyze Packets
Use the packet capture screen and a packet analyzer (also known as a network or protocol analyzer)
such as Wireshark or Ethereal to investigate some more.
Figure 384 DNS Query Packet Details
Chapter 30 IDP
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
578
Page 99

Chapter 30 IDP
From the details about DNS query you see that the protocol is UDP and the port is 53. The type of DNS
packet is standard query and the Flag is 0x0100 with an offset of 2. Therefore enter |010| as the first
pattern.
The final custom signature should look like as shown in the following figure.
Figure 385 Example Custom Signature
30.3.3 Applying Custom Signatures
After you create your custom signature, it becomes available in an IDP profile (Configuration > Security
Service > IDP > Profile > Edit screen). Custom signatures have an SID from 9000000 to 9999999.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
579
Page 100

Chapter 30 IDP
Search for, then activate the signature, configure what action to take when a packet matches it and if
it should generate a log or alert in a profile. Then bind the profile to a zone.
30.3.4 Verifying Custom Signatures
Configure the signature to create a log when traffic matches the signature. (You may also want to
configure an alert if it is for a serious attack and needs immediate attention.) After you apply the
signature to a zone, you can see if it works by checking the logs (Monitor > Log).
The Priority column shows warn for signatures that are configured to generate a log only. It shows critical
for signatures that are configured to generate a log and alert. All IDP signatures come under the IDP
category. The Note column displays ACCESS FORWARD when no action is configured for the signature. It
displays ACCESS DENIED if you configure the signature action to drop the packet. The destination port is
the service port (53 for DNS in this case) that the attack tries to exploit.
Figure 386 Custom Signature Log
30.4 The White List Screen
Use this screen to view the IDP white list. The Zyxel Device will exclude the incoming packets of the listed
signature(s), and these packets won’t be intercepted and will be passed through uninspected.
Click Configuration > Security Service > IDP > White List to display the following screen. Use Add to put a
new item in the list or Edit to change an existing one or Remove to delete an existing entry.
ZyWALL ATP Series User’s Guide
580
 Loading...
Loading...