1
PRELIMINARY
Z86C60/65
CP96Z8X0400
FEATURES
ROM RAM* Speed 28-pin
Part (KB) (Bytes) I/O (MHz) DIP
Z86C60 16 256 22 1 6 X
Z86C65 32 256 22 1 6 X
■ Low EMI Mode Option
■ Auto Latches
■ Two Programmable 8-Bit Counter/Timers Each with 6-
Bit Programmable Prescaler
■ Three Vectored, Priority Interrupts from Three Different
Sources
■ On-Chip Oscillator that Accepts a Crystal Ceramic
Resonator, LC, or External Clock Source
■ ROM Mask Options:
– ROM Protect
– RAM Protect
*General-Purpose
■ 28-Pin DIP Package
■ 3.0V to 5.5V Operating Range
■ Low-Power Consumption: 200 mW
■ Fast Instruction Pointer: 0.75 µs @ 16 MHz
■ Two Standby Modes: STOP and HALT
P
RELIMINARY
C
USTOMER PROCUREMENT SPECIFICATION
Z86C60/65
CMOS Z8
®
32K ROM MICROCONTROLLER
The Z86C60/65 microcontrollers introduce a new level of
sophistication to single-chip architecture. The Z86C65 is a
member of the Z8 single-chip microcontroller family with
32 Kbytes of ROM and 256 bytes of RAM. The Z86C60 is
identical, except that it only has 16 Kbytes of ROM.
The Z86C60/65 are housed in a 28-pin DIP package, and
manufactured in CMOS technology. The Z86C96 ROMless
Z8 will support the Z86C60/65.
Zilog’s CMOS microcontroller offers fast execution, more
efficient use of memory, more sophisticated interrupts,
input/output bit manipulation capabilities, and easy hardware/software system expansion along with low cost and
low power consumption.
The Z86C60/65 architecture is characterized by Zilog’s
8-bit microcontroller core. The device offers a flexible I/O
scheme, an efficient register and address space structure,
multiplexed capabilities between address/data, I/O, and a
number of ancillary features that are useful in many industrial and advanced scientific applications.
For applications which demand powerful I/O capabilities,
the Z86C60/65 fulfills this with 22 pins dedicated to input
and output. These lines are grouped into four ports. Each
port is configurable under software control to provide
timing, status signals, serial or parallel I/O with or without
handshake, and an address/data bus for interfacing external memory.
There are three basic address spaces available to support
this wide range of configurations: Program Memory, Data
Memory, and 236 General-Purpose Registers.
To unburden the program from coping with the real-time
problems such as counting/timing and serial data communication, the Z86C60/65 offers two on-chip counter/timers
with a large number of user selectable modes.
Notes:
All Signals with a preceding front slash, "/", are active Low, e.g.,
B//W (WORD is active Low); /B/W (BYTE is active Low, only).
Power connections follow conventional descriptions below:
Connection Circuit Device
Power V
CC
V
DD
Ground GND V
SS
CP96Z8X0400 (5/96)
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2
PRELIMINARY
Z86C60/65
CP96Z8X0400
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
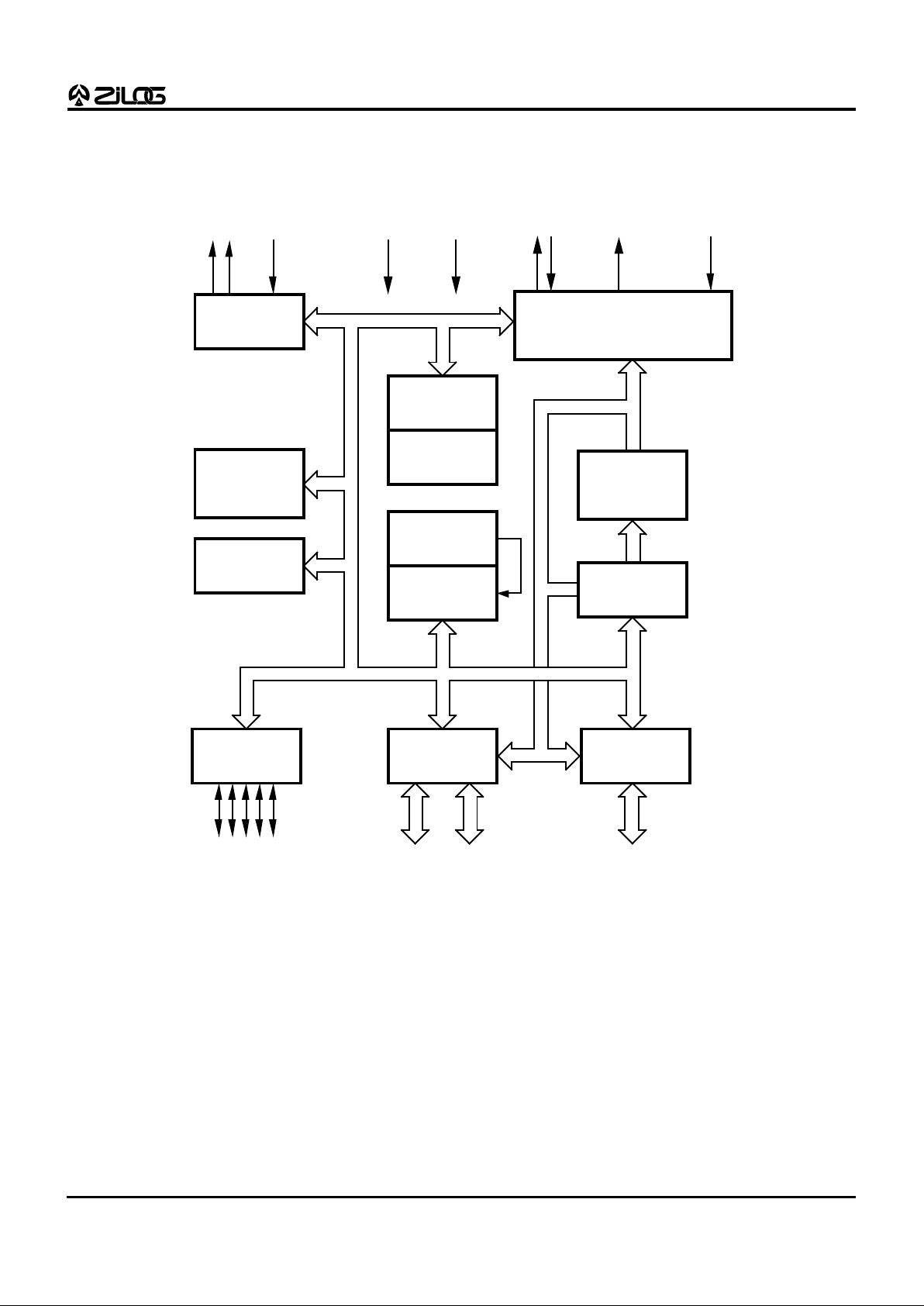
Figure 1. Z86C60/65 Functional Block Diagram
Port 3
Counter/
Timers
(2)
Interrupt
Control
Port 2
I/O
(Bit Programmable)
ALU
FLAGS
Register
Pointer
Register File
Machine T iming and
Instruction Control
Prg. Memory
Program
Counter
Vcc GND
XTAL
24
Port 0
Output Input
Address or I/O
(Nibble Programmable)
Port 1
8
Address/Data or I/O
(Byte Programmable)
/DS /RESET

3
PRELIMINARY
Z86C60/65
CP96Z8X0400
Z86C60/65 28-Pin DIP Pin Identification
Pin # Symbol Function Direction
1VCCPower Supply Input
2 XTAL2 Crystal, Oscillator Clock Output
3 XTAL1 Crystal, Oscillator Clock Input
4 /RESET Reset Input
5 /DS Data Strobe Output
6 P 3 5 Port 3, Pin 5 Output
7 GND Ground Input
8-13 P05-P00 Port 0, Pins 0,1,2,3,4,5 In/Output
14-21 P17-P10 Port 1, Pins 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7In/Output
22-26 P25-P21 Port 2, Pins 1,2,3,4,5 In/Output
2 7 P 3 1 Port 3, Pin 1 Input
2 8 P 3 6 Port 3, Pin 6 Output
PIN DESCRIPTION
Figure 2. Z86C60/65 28-Pin DIP
Pin Assignments
1
2
9
3
4
5
6
7
8
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
P36
P31
P16
P25
P24
P23
P22
P21
P17
VCC
XTAL2
RESET
/DS
P35
GND
P00
19
18
17
16
1514
10
11
12
13
XTAL1
P03
P04
P05
P10
P15
P14
P13
P12
P11
P01
P02

4
PRELIMINARY
Z86C60/65
CP96Z8X0400
STANDARD TEST CONDITIONS
The characteristics listed below apply for standard test
conditions as noted. All voltages are referenced to GND.
Positive current flows into the referenced pin (Test Load).
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Symbol Description Min Max Units
V
CC
Supply Voltage* –0.3 +7.0 V
T
STG
Storage Temp –65 +150 C
T
A
Oper Ambient Temp † †
Notes:
* Voltages on all pins with respect to GND.
† See ordering information
Stresses greater than those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; operation of the device at
any condition above those indicated in the operational
sections of these specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for an extended period may affect device reliability.
Figure 3. Test Load Diagram
From Output
Under Test
150 pF
I

5
PRELIMINARY
Z86C60/65
CP96Z8X0400
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Z86C60/65
TA = 0°C Typical
to +70°C at
Sym Parameter Min Max 25°C Units Conditions
VCCOperating Voltage 4.5 5.5 V [3]
Max Input Voltage 7 V [3] IIN < 250 µA
V
CH
Clock Input High Voltage 0.85 VCCV
CC
+ 0.3 V Driven by External Clock Generator
V
CL
Clock Input Low Voltage V
SS
– 0.3 0.8 V Driven by External Clock Generator
V
IH
Input High Voltage 2 V
CC
+ 0.3 V
V
IL
Input Low Voltage V
SS
– 0.3 0.2 V
CC
V
V
OH
Output High Voltage 2.4 V
CC
VI
OH
= –2.0 mA
V
OH
Output High Voltage V
CC
– 100 mV V IOH = –100 µA
V
OH
Output High Voltage (Low EMI) 2.4 V IOH = –0.5 mA
V
OL
Output Low Voltage 0.4 V IOL = +5.0 mA [2]
V
OL
Output Low Voltage (Low EMI) 0.4 V IOL = +2.0 mA [2]
V
RH
Reset Input High Voltage 0.85 VCCV
CC
+ 0.3 V
V
Rl
Reset Input Low Voltage –0.3 0.2 V
CC
V
I
IL
Input Leakage –2 2 µ AV
IN
= 0 V, V
CC
I
OL
Output Leakage –2 2 µAV
IN
= 0 V, V
CC
I
IR
Reset Input Current –180 µAV
RL
= 0 V
I
CC
Supply Current (Standard Mode) 35 24 m A [1] @ 16 MHz
I
CC
Supply Current (Low EMI) 6.0 4.0 m A @ 4 MHz
I
CC1
Standby Current (Standard Mode) 15 4.5 m A [1] HALT Mode VIN = 0 V, V
CC
@ 16 MHz
I
CC1
Standby Current (Low EMI) 1.6 0.8 m A @ 4 MHz
I
CC2
Standby Current 10 5 µ A [1] STOP Mode VIN = 0 V, V
CC
I
ALL
Auto Latch Low Current –14 +14 5 µ AV
CC
= 5.0V
Notes:
[1] All inputs driven to either 0V or VCC, outputs floating.
[2] VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V
[3] /Reset pin must be a maximum of VCC + 0.3V.

6
PRELIMINARY
Z86C60/65
CP96Z8X0400
Clock
1
3
4
8
2
2 3
TIN
IRQN
6
5
7
7
9
Figure 4. Additional Timing
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Additional Timing Table
Z86C60/65 (Standard Mode Only)
TA = 0°C
to +70°C
16 MHz
No Symbol Parameter Min Max Units Notes
1 TpC Input Clock Period 62.5 DC ns [1]
2 TrC,TfC Clock Input Rise & Fall Times 1 0 n s [1]
3 TwC Input Clock Width 31 n s [1]
4 TwTinL Timer Input Low Width 7 5 n s [2 ]
5 TwTinH Timer Input High Width 5 TpC n s [2]
6 TpTin Timer Input Period 8 TpC ns [2]
7 TrTin,TfTin Timer Input Rise and Fall Times 100 n s [2]
8 a TwIL Interrupt Request Input Low Times 70 ns [2,4]
8 b TwIL Interrupt Request Input Low Times 5 TpC ns [2,5]
9 TwIH Interrupt Request Input High Times 5 TpC ns [2,3]
Notes:
[1] Clock timing references use 0.85VCC for a logic 1 and 0.8V for a logic 0.
[2] Timing references use 2.0V for a logic 1 and 0.8V for a logic 0.
[3] Interrupt references request through Port 3.
[4] Interrupt request through Port 3 (P33-P31).
[5] Interrupt request through Port 30.
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Additional Timing Diagram

7
PRELIMINARY
Z86C60/65
CP96Z8X0400
© 1996 by Zilog, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document
may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means
without the prior written consent of Zilog, Inc. The information in
this document is subject to change without notice. Devices sold
by Zilog, Inc. are covered by warranty and patent indemnification
provisions appearing in Zilog, Inc. Terms and Conditions of Sale
only. Zilog, Inc. makes no warranty, express, statutory, implied or
by description, regarding the information set forth herein or
regarding the freedom of the described devices from intellectual
property infringement. Zilog, Inc. makes no warranty of merchantability or fitness for any purpose. Zilog, Inc. shall not be
responsible for any errors that may appear in this document.
Zilog, Inc. makes no commitment to update or keep current the
information contained in this document.
Zilog’s products are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems unless a specific written
agreement pertaining to such intended use is executed between
the customer and Zilog prior to use. Life support devices or
systems are those which are intended for surgical implantation
into the body, or which sustains life whose failure to perform,
when properly used in accordance with instructions for use
provided in the labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in
significant injury to the user.
Zilog, Inc. 210 East Hacienda Ave.
Campbell, CA 95008-6600
Telephone (408) 370-8000
FAX 408 370-8056
Internet: http://www.zilog.com
formance with some aspects of the CPS may be found,
either by Zilog or its customers in the course of further
application and characterization work. In addition, Zilog
cautions that delivery may be uncertain at times, due to
start-up yield issues.
Pre-Characterization Product:
The product represented by this CPS is newly introduced
and Zilog has not completed the full characterization of the
product. The CPS states what Zilog knows about this
product at this time, but additional features or non-con-
 Loading...
Loading...