Yealink Teams HD IP Phones Administrator Manual


Contents
Introduction.................................................................................................. 7
Related Documentations..................................................................................................................... 7
Typographic and Writing Conventions.................................................................................................7
Recommended References.................................................................................................................8
Summary of Changes......................................................................................................................... 8
Change for Guide Version 15.1................................................................................................8
Getting Started.............................................................................................9
Initialization Process Overview............................................................................................................9
Loading the ROM File.............................................................................................................. 9
Configuring the VLAN...............................................................................................................9
Querying the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server....................................... 9
Contacting the Provisioning Server........................................................................................ 10
Updating Firmware................................................................................................................. 10
Downloading the Resource Files............................................................................................10
Verifying Startup................................................................................................................................ 10
NET Probe Configuration....................................................................................................... 10
Teams Feature License.....................................................................................................................11
Importing License via the Web User Interface.......................................................................12
Importing License Configuration.............................................................................................12
| Contents | ii
Device Network.......................................................................................... 12
IPv4 and IPv6 Network Settings....................................................................................................... 13
IP Addressing Mode Configuration.........................................................................................13
IPv4 Configuration.................................................................................................................. 13
IPv6 Configuration.................................................................................................................. 16
DHCP Option for IPv4.......................................................................................................................19
Supported DHCP Option for IPv4.......................................................................................... 19
DHCP Option 160 and Option 161........................................................................................ 20
DHCP Option 66, Option 43 and Custom Option.................................................................. 20
DHCP Option 42 and Option 2.............................................................................................. 21
DHCP Option 12.....................................................................................................................21
DHCP Option 60.....................................................................................................................21
DHCP Option for IPv6.......................................................................................................................22
Supported DHCP Option for IPv6.......................................................................................... 22
VLAN..................................................................................................................................................22
LLDP Configuration.................................................................................................................23
CDP Configuration..................................................................................................................23
Manual VLAN Configuration...................................................................................................24
DHCP VLAN Configuration.....................................................................................................26
VLAN Change Configuration.................................................................................................. 27
Wi-Fi...................................................................................................................................................27
Wi-Fi Configuration................................................................................................................. 27
Internet Port and PC Port................................................................................................................. 30
Supported Transmission Methods.......................................................................................... 30
Internet Port and PC Port Configuration................................................................................30
802.1x Authentication........................................................................................................................ 31

| Contents | iii
802.1x Authentication Configuration.......................................................................................32
Proxy Server......................................................................................................................................33
Proxy Server Configuration.................................................................................................... 33
Device Provisioning...................................................................................37
Provisioning Points to Consider........................................................................................................ 37
Boot Files, Configuration Files, and Resource Files.........................................................................37
Boot Files................................................................................................................................37
Configuration Files..................................................................................................................40
Resource Files........................................................................................................................43
Files Download Process.........................................................................................................43
Provisioning Methods........................................................................................................................ 44
Provisioning Methods Priority.................................................................................................44
Manual Provisioning................................................................................................................45
Central Provisioning................................................................................................................48
Setting Up a Provisioning Server......................................................................................................50
Supported Provisioning Protocols.......................................................................................... 50
Supported Provisioning Server Discovery Methods............................................................... 51
Configuring a Provisioning Server..........................................................................................52
Provisioning Devices on the Microsoft Teams Admin Center...............53
Device Management..........................................................................................................................53
Editing Your Device Info......................................................................................................... 53
Customizing the Displayed Elements of Devices................................................................... 54
Viewing the Device Details.....................................................................................................54
Assigning Configuration Profile to Devices............................................................................ 54
Updating Device Software......................................................................................................54
Restarting Your Devices......................................................................................................... 55
Configuration Profiles Management.................................................................................................. 55
Creating a Configuration Profile............................................................................................. 55
Editing a Configuration Profile................................................................................................55
Remote Provisioning and Sign in from Teams Admin Center...........................................................56
Step 1: Add a Device MAC Address......................................................................................56
Step 2: Generate a Verification Code.................................................................................... 56
Step 3: Provisioning on the Device........................................................................................56
Step 4: Sign in Remotely....................................................................................................... 57
Firmware Upgrade..................................................................................... 57
Firmware for Each Device Model......................................................................................................57
Firmware Upgrade Configuration...................................................................................................... 58
Using CP960 Cascaded Mode.................................................................. 58
Guidelines for Configuring Cascaded Mode..................................................................................... 59
CP960 Cascaded Mode Configuration..............................................................................................60
Example: Configuring CP960 Cascaded Mode................................................................................ 61
Device Customization................................................................................61
Language........................................................................................................................................... 62
Language Display Configuration.............................................................................................62
Language Customization........................................................................................................ 63
Example: Setting a Custom Language for Device Display.....................................................67

| Contents | iv
Screen Saver.....................................................................................................................................67
Screensaver Configuration......................................................................................................68
Backlight.............................................................................................................................................70
Backlight Brightness and Time Configuration........................................................................ 71
Time and Date...................................................................................................................................71
Time Zone...............................................................................................................................72
NTP Settings...........................................................................................................................75
DST Settings...........................................................................................................................76
Time and Date Manual Configuration.................................................................................... 80
Time and Date Format Configuration.....................................................................................80
Tones..................................................................................................................................................81
Supported Tones.....................................................................................................................82
Tones Configuration................................................................................................................82
Volume............................................................................................................................................... 83
Volume Configuration..............................................................................................................83
Noise Suppression............................................................................................................................ 84
Noise Suppression Configuration...........................................................................................84
Smart Noise Block.............................................................................................................................84
Smart Noise Block Configuration........................................................................................... 84
Acoustic Shield.................................................................................................................................. 85
Acoustic Shield Configuration.................................................................................................85
Power Saving.....................................................................................................................................85
Power Saving Configuration................................................................................................... 85
Power LED Indicator..........................................................................................................................88
Power LED Indicator Configuration........................................................................................ 88
Bluetooth............................................................................................................................................89
Bluetooth Configuration.......................................................................................................... 89
Common Area Phone................................................................................ 90
Call Features.............................................................................................. 90
Call Queue.........................................................................................................................................90
Call Park and Retrieve......................................................................................................................91
Security Features.......................................................................................91
User and Administrator Identification................................................................................................ 91
User and Administrator Identification Configuration............................................................... 92
User Access Level Configuration........................................................................................... 93
Phone Lock........................................................................................................................................93
Phone Lock Configuration...................................................................................................... 94
Transport Layer Security (TLS).........................................................................................................94
Supported Cipher Suites........................................................................................................ 95
Supported Trusted and Server Certificates............................................................................95
TLS Configuration...................................................................................................................98
Encrypting Configuration Files........................................................................................................ 100
Configuration Files Encryption Tools.................................................................................... 100
Configuration Files Encryption and Decryption....................................................................100
Encryption and Decryption Configuration.............................................................................100
Example: Encrypting Configuration Files............................................................................. 102
Hybrid Mode............................................................................................. 103
Hybrid Mode Configuration..............................................................................................................104

| Contents | v
Paging Configuration....................................................................................................................... 105
SIP Account Registration Configuration..........................................................................................109
Account Codec Configuration..........................................................................................................111
Local Directory Configuration..........................................................................................................114
Device Management................................................................................ 115
Device Management Configuration................................................................................................. 115
Managing the USB Camera UVC30 Room.............................................115
Upgrading UVC30 Camera............................................................................................................. 116
Exporting Camera Log.................................................................................................................... 116
Troubleshooting Methods....................................................................... 116
Log Files.......................................................................................................................................... 116
Local Log.............................................................................................................................. 117
Syslog Log............................................................................................................................ 121
Packets Capture.............................................................................................................................. 124
Capturing the Packets via Web User Interface.................................................................... 124
Ethernet Software Capturing Configuration..........................................................................125
Analyzing Configuration Files..........................................................................................................126
Exporting BIN Files from the Device....................................................................................126
Importing BIN Files from the Device....................................................................................126
Exporting All the Diagnostic Files...................................................................................................127
Device Status...................................................................................................................................127
Viewing the Device Status....................................................................................................127
Resetting Device and Configuration................................................................................................128
Resetting the Device to Default Factory Settings.................................................................128
Resetting the Device to Custom Factory Settings................................................................128
Deleting the Custom Factory Settings Files.........................................................................129
Device Reboot................................................................................................................................. 129
Rebooting the Device via Phone User Interface.................................................................. 129
Rebooting the Device via Web User Interface..................................................................... 130
Capturing the Current Screen of the Phone................................................................................... 130
Enabling the Screen Capture via Phone User Interface...................................................... 130
Capturing the Current Screen of the Device via Web User Interface...................................130
Troubleshooting Solutions......................................................................131
IP Address Issues........................................................................................................................... 131
The device does not get an IP address...............................................................................131
IP Conflict............................................................................................................................. 131
Specific format in configuring IPv6 on Yealink devices........................................................ 132
Time and Date Issues.....................................................................................................................132
Display time and date incorrectly......................................................................................... 132
Display Issues..................................................................................................................................132
The device LCD screen blank..............................................................................................132
The device displays “Offline”................................................................................................ 132
Firmware and Upgrading Issues..................................................................................................... 133
Fail to upgrade the device firmware.....................................................................................133
The device does not update the configurations................................................................... 133
System Log Issues..........................................................................................................................133
Fail to export the system log from a provisioning server (FTP/TFTP server).......................133
Fail to export the system log from a syslog server.............................................................. 133

Password Issues..............................................................................................................................133
Restore the administrator password.....................................................................................134
Introduction
Yealink administrator guide provides general guidance on setting up device network, provisioning and
managing Teams devices. This guide is not intended for end users, but administrators.
Yealink MP58/MP58-WH/MP56/MP54/T58A/T56A/T55A/CP960/VP59 Microsoft Teams devices are the
collaborative devices with Microsoft. As an administrator, you can do the following with this guide:
• Manage the Teams devices with Microsoft Teams & Skype for Business Admin Center.
• Set up a provisioning server.
• Provision the device with features and settings.
• Troubleshoot, update, and maintain the devices.
The information detailed in this guide applies to the following Yealink devices running firmware:
• T58A/T56A/T55A Teams IP phones: 58.15.0.124 or later
• CP960 Teams IP phones: 73.15.0.117 or later
• VP59 Teams IP phones: 91.15.0.58 or later
• MP58/MP58-WH/MP56/MP54 Teams IP phones: 122.15.0.36 or later
| Introduction | 7
Read the Yealink Products Regulatory Notices guide for all regulatory and safety guidance.
• Related Documentations
• Typographic and Writing Conventions
• Recommended References
• Summary of Changes
Related Documentations
The following related documents are available:
• Quick Start Guides, describe how to assemble devices and configure the most basic features available
on the devices.
• User Guides, describe how to configure and use the basic and advanced features available on the
devices via the phone user interface or web user interface.
• Auto Provisioning Guide, describes how to provision the devices using the boot file and configuration
files.
The Auto Provisioning Guide is to serve as a basic guidance for provisioning Yealink Teams devices with
a provisioning server. If you are a novice, this guide is helpful for you.
For support or service, please contact your Yealink reseller or go to Yealink Technical Support online: http://
support.yealink.com/.
Typographic and Writing Conventions
Yealink documentations contain a few typographic conventions and writing conventions.
You need to know the following basic typographic conventions to distinguish the types of in-text information:

Convention Description
| Introduction | 8
Bold
Italics Used to emphasize text, to show the example values or inputs (format of examples:
You also need to know the following writing conventions to distinguish conditional information:
Convention Description
< > Indicates that you must enter specific information. For example, when you see
> Indicates that you need to select an item from a menu. For example, Settings
Highlights the web/phone user interface items such as menus, menu selections, soft
keys, or directory names when they are involved in a procedure or user action (for
example, select Settings > Device Settings.
Also used to emphasize text (for example, Important!).
http(s)://[IPv6address]).
<MAC>, enter your device’s 12-digit MAC address. If you see <deviceIPAddress>,
enter your device’s IP address.
> Device Settings indicates that you need to select Device Settings from the
Settings menu.
Recommended References
For more information on configuring and administering other Yealink products not included in this guide,
refer to the product support page at Yealink Technical Support.
To access the latest Release Notes or other guides for Yealink devices, refer to the Document Download
page for your device at Yealink Technical Support.
If you want to find Request for Comments (RFC) documents, type http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfcNNNN.txt (NNNN
is the RFC number) into the location field of your browser.
This guide mainly takes the T58A Teams phone as an example for reference. For more details on other
Teams devices, refer to Yealink Teamsdevice-specific user guide.
For other references, look for the hyperlink or web info throughout this administrator guide.
Summary of Changes
• Change for Guide Version 15.1
Change for Guide Version 15.1
The following sections are new for this version:
• NET Probe Configuration
• Noise Suppression
• Smart Noise Block
• Acoustic Shield
• Remote Provisioning and Sign in from Teams Admin Center
Major updates have occurred to the following sections:
• Proxy Server Configuration

• User and Administrator Identification
• User and Administrator Identification Configuration
• Hybrid Mode Configuration
• TLS Configuration
• Using CP960 Cascaded Mode
• Provisioning Devices on the Microsoft Teams Admin Center
Getting Started
This chapter provides basic initialization instructions for Teams devices.
• Initialization Process Overview
• Verifying Startup
• Teams Feature License
Initialization Process Overview
| Getting Started | 9
The initialization process of the device is responsible for network connectivity and operation of the device
in your local network. Once you connect your device to the network and to an electrical supply, the device
begins its initialization process.
• Loading the ROM File
• Configuring the VLAN
• Querying the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server
• Contacting the Provisioning Server
• Updating Firmware
• Downloading the Resource Files
Loading the ROM File
The ROM file resides in the flash memory of the device. The device comes from the factory with a ROM file
preloaded. During initialization, the device runs a bootstrap loader that loads and executes the ROM file.
Configuring the VLAN
If you connect the device to a switch, the switch notifies the device of the VLAN information defined on the
switch (if using LLDP or CDP). The device can then proceed with the DHCP request for its network settings
(if using DHCP).
Querying the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server
The device is capable of querying a DHCP server.
After network connectivity is established, the device can obtain the following network parameters from the
DHCP server during initialization:
• IP Address
• Subnet Mask
• Default Gateway
• Primary DNS
• Secondary DNS
By default, the devices obtain these parameters from a DHCPv4. You can configure network parameters of
the device manually if any of them are not supplied by the DHCP server.
Contacting the Provisioning Server
If you configure the device to obtain configurations from the provisioning server, it will be connected to the
provisioning server, and then download the boot file and configuration file(s) during startup. The device
will be able to resolve and update configurations written in the configuration file(s). If the device does not
obtain configurations from the provisioning server, the device will use the configurations stored in the flash
memory.
Updating Firmware
If you define the access URL of firmware in the configuration file, the device will download firmware from
the provisioning server. If the MD5 value of the downloaded firmware file differs from the one stored in the
flash memory, the device will perform a firmware update.
You can manually upgrade the firmware if the device does not download firmware from the provisioning
server.
| Getting Started | 10
Downloading the Resource Files
In addition to the configuration file(s), the device may require resource files before it provides service.
These resource files are optional, but if you deploy some particular features, these files are required.
Verifying Startup
After connected to the power and network, the devices begin the initialization process:
1. The power LED indicators of MP58/MP58-WH/MP56/MP54/T58A/T56A/T55A/VP59 glow red.
The mute touch key LED indicators of CP960 glow red.
2. The message “Initializing… Please wait” (or “Initializing…”) appears on the LCD screen when the
devices start up.
3. The devices enter the language selection interface.
• NET Probe Configuration
NET Probe Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to detect network.
Parameter static.net.capportal.http.url <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
It configures the HTTP URL that detect the network connectivity.
Example:
http://domain/generate_204, domain is a complete domain name, such as www.g.cn.
Permitted Values String within 512 characters
Default http://www.g.cn/generate_204
Parameter static.net.capportal.https.url <y0000000000xx>.cfg
| Getting Started | 11
Description
Permitted Values String within 512 characters
Default http://www.g.cn/generate_204
Parameter static.net.capportal.fallback.url <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted Values String within 512 characters
Default http://www.g.cn/generate_204
It configures the HTPPS URL that detect network connectivity.
Example:
https://domain/generate_204, domain is a complete domain name, such as www.g.cn.
It configures the reserved http URL that detect network connectivity.
Example:
http://domain/generate_204, domain is a complete domain name, such as www.g.cn.
Note: It can be set differently from "static.net.capportal.http.url".
Teams Feature License
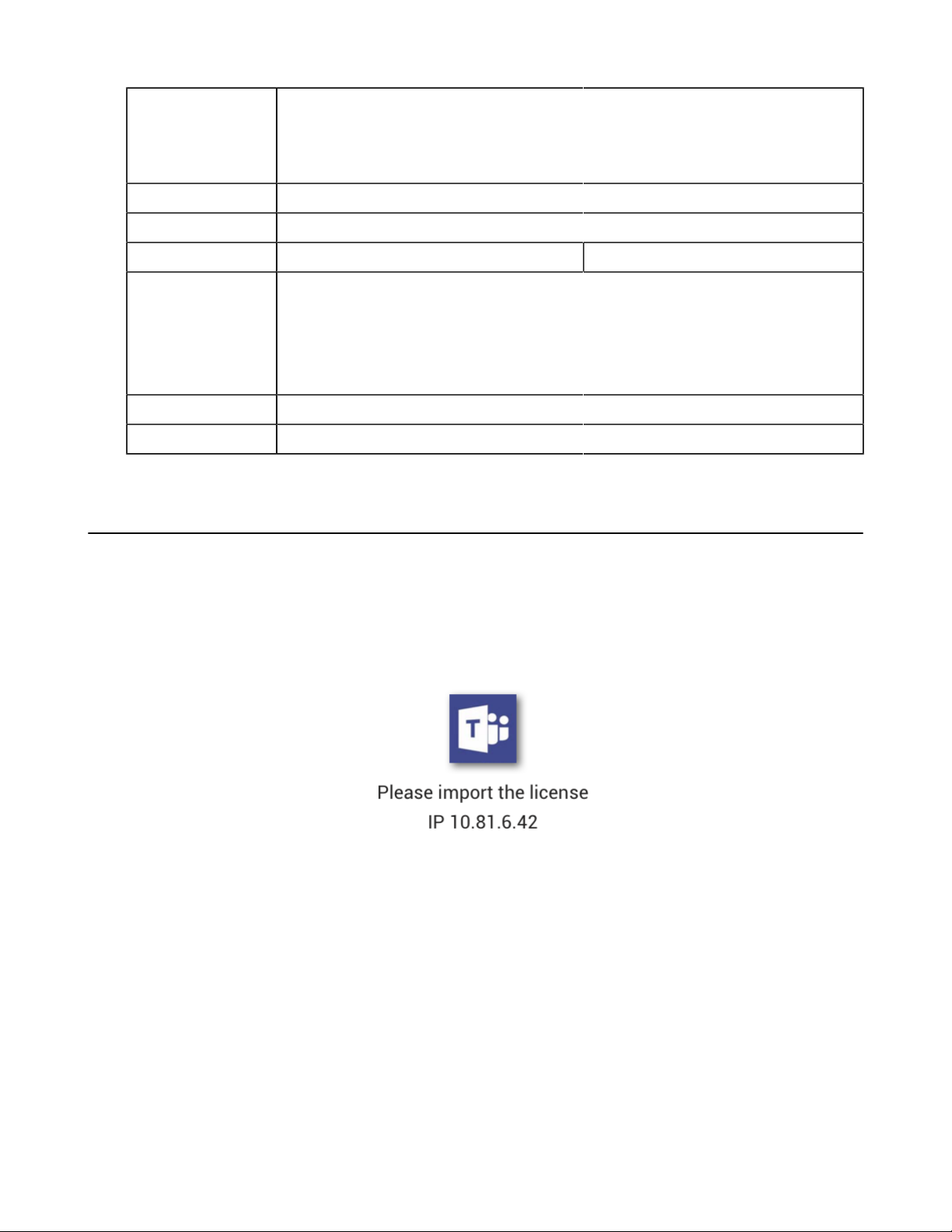
Yealink offers MP58/MP58-WH/MP56/MP54/T58A/T56A/T55A/CP960/VP59 devices configured for use
with Microsoft Teams. By default, the device has a built-in Teams feature license, which allows users to use
Yealink devices with Teams features directly. If the device has not imported a license yet, the screen will be
shown as below:
You need to upload the license to use the device normally.
For the Teams feature license and device version, you need to pay attention to the following points
• Any Open SIP build upgrades to Teams build will be required to apply and import the license.
• Any Teams upgrades to Skype for Business will not need to be required additional license. And vice
versa.
• Any Teams will not be allowed to downgrade to the Open SIP from this release. If Teams phones are
under temporary license (for demo testing purpose) and want to get back to Open SIP, please contact
Yealink support team for technical support for an unlock license.
• Once upgraded to the latest Teams, it will not be allowed to downgrade to the previous Teams version.
For information about purchasing a Teams feature license, contact your reseller or sales representative.
Note: If the device running the Skype for Business firmware has been imported a Skype for
Business feature license, you do not need to import the license after you upgrade to the Teams
firmware.
• Importing License via the Web User Interface
• Importing License Configuration
Related information
Firmware Upgrade
Importing License via the Web User Interface
If the device has not imported a license or the license is expired, you need to import the license manually.
Procedure
1. On your web user interface, go to Security > License.
2. In the Load License File (or Upload License File) block, click the white box to select the license from
your local system.
3. Click Upload.
| Device Network | 12
Importing License Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to import license.
Parameter lync_license_dat.url
Description
Permitted
Values
Default Blank
Web UI Security > License
[1]
If you change this parameter, the device will reboot to make the change take effect.
It configures the access URL of the Teams feature license.
Example:
lync_license_dat.url = http://192.168.1.20/License_$MAC.dat
The devices will replace the characters “$MAC” with their MAC addresses during
auto provisioning. For example, the MAC address of one T58A Teams device is
00156543EC97. When performing auto provisioning, the device will request to
download the License_00156543ec97.dat file from the provisioning server address
“http://192.168.1.20”.
String within 99 characters
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Device Network
Yealink Teams devices operate on an Ethernet local area network (LAN). You can configure the local
area network to accommodate many network designs, which varies by organizations and Yealink Teams
devices.
• IPv4 and IPv6 Network Settings
• DHCP Option for IPv4
• DHCP Option for IPv6
• VLAN
• Wi-Fi
• Internet Port and PC Port
• 802.1x Authentication
• Proxy Server
IPv4 and IPv6 Network Settings
Teams devices support IPv4 addressing mode, IPv6 addressing mode, as well as an IPv4&IPv6 dual-stack
addressing mode. After connected to the wired network, the devices can obtain the IPv4 or IPv6 network
settings from a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server if your network supports it. To make
it easier to manage IP settings, we recommend using automated DHCP which is possible to eliminate
repetitive manual data entry. You can also configure IPv4 or IPv6 network settings manually.
Note: Teams devices comply with the DHCPv4 specifications documented in RFC 2131, and
DHCPv6 specifications documented in RFC 3315.
• IP Addressing Mode Configuration
• IPv4 Configuration
• IPv6 Configuration
| Device Network | 13
IP Addressing Mode Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to configure IP addressing mode.
Parameter static.network.ip_address_mode
Description It configures the IP addressing mode.
Permitted
Values
Default 0
Web UI Network > Basic > Internet Port > Mode(IPv4/IPv6)
Phone UI
[1]
If you change this parameter, the device will reboot to make the change take effect.
0-IPv4
1-IPv6
2-IPv4 & IPv6
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN Port >
IP Mode
[1]
IPv4 Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure IPv4.
Parameter static.network.internet_port.type
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
<MAC>.cfg
Description It configures the Internet port type for IPv4.
Note: It works only if “static.network.ip_address_mode” is set to 0 (IPv4) or 2 (IPv4 &
IPv6).
| Device Network | 14
Permitted Values
0-DHCP
2-Static IP
Default 0
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Configuration Type
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv4 Type
Parameter static.network.internet_port.ip
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Description It configures the IPv4 address.
Note: It works only if “static.network.ip_address_mode” is set to 0 (IPv4) or 2 (IPv4 &
IPv6), and "static.network.internet_port.type" is set to 2 (Static IP).
Permitted Values IPv4 Address
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Configuration Type(Static IP) > IP Address
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv4 Type(Static IP) > IP Address
Parameter static.network.internet_port.mask
Description
It configures the IPv4 subnet mask.
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Note: It works only if “static.network.ip_address_mode” is set to 0 (IPv4) or 2 (IPv4 &
IPv6), and "static.network.internet_port.type" is set to 2 (Static IP).
Permitted Values Subnet Mask
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Configuration Type(Static IP) > Subnet Mask
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv4 Type(Static IP) > Subnet Mask
Parameter static.network.internet_port.gateway
Description
It configures the IPv4 default gateway.
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Note: It works only if “static.network.ip_address_mode” is set to 0 (IPv4) or 2 (IPv4 &
IPv6), and "static.network.internet_port.type" is set to 2 (Static IP).
Permitted Values IPv4 Address
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Configuration Type(Static IP) > Default
Gateway
| Device Network | 15
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv4 Type(Static IP) > Default Gateway
Parameter static.network.static_dns_enable
Description
It triggers the static DNS feature to on or off.
[1]
Note: It works only if “static.network.internet_port.type” is set to 0 (DHCP).
Permitted Values
0-Off, the device will use the IPv4 DNS obtained from DHCP.
1-On, the device will use manually configured static IPv4 DNS.
Default 0
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Static DNS
Parameter static.network.primary_dns
Description
It configures the primary IPv4 DNS server.
[1]
Note: It works only if “static.network.ip_address_mode” is set to 0 (IPv4)
or 2 (IPv4 & IPv6). In DHCP environment, you also need to make sure
“static.network.static_dns_enable" is set to 1 (On).
Permitted Values IPv4 Address
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<MAC>.cfg
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Configuration Type(Static IP) > Primary DNS
Or Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Configuration Type(DHCP) > Static
DNS(Enable) > Primary DNS
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv4 Type(Static IP) > Pri.DNS
Or > Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv4 Type(DHCP) > IPv4 Static DNS(Enable) > Pri.DNS
Parameter static.network.secondary_dns
Description
It configures the secondary IPv4 DNS server.
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Note: It works only if “static.network.ip_address_mode” is set to 0 (IPv4)
or 2 (IPv4 & IPv6). In DHCP environment, you also need to make sure
“static.network.static_dns_enable" is set to 1 (On).
Permitted Values IPv4 Address
Default Blank
| Device Network | 16
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Configuration Type(Static IP) > Secondary DNS
Or Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Configuration Type(DHCP) > Static
DNS(Enable) > Secondary DNS
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv4 Type(Static IP) > Sec.DNS
Or > Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv4 Type(DHCP) > IPv4 Static DNS(Enable) > Sec.DNS
[1]
If you change this parameter, the device will reboot to make the change take effect.
IPv6 Configuration
If you configure the network settings on the device for an IPv6 network, you can set up an IP address for
the device by using SLAAC (ICMPv6), DHCPv6, or by manually entering an IP address. Ensure that your
network environment supports IPv6. Contact your ISP for more information.
When you enable both SLAAC and DHCPv6 on the device, the server can specify the device to obtain the
IPv6 address and other network settings either from SLAAC or from DHCPv6, if the SLAAC server is not
working, the device will try to obtain the IPv6 address and other network settings via DHCPv6.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure IPv6.
Parameter static.network.ipv6_internet_port.type
Description
It configures the Internet port type for IPv6.
Note: It works only if “static.network.ip_address_mode” is set to 1 (IPv6) or 2 (IPv4
& IPv6).
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Permitted Values
0-DHCP
1-Static IP
Default 0
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv6 Config > Configuration Type
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv6 Type
Parameter static.network.ipv6_internet_port.ip
Description
It configures the IPv6 address.
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Note: It works only if “static.network.ip_address_mode” is set to 1 (IPv6) or 2 ( IPv4
& IPv6), and "static.network.ipv6_internet_port.type" is set to 1 (Static IP).
Permitted Values IPv6 Address
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv6 Config > Configuration Type(Static IP) > IP Address

| Device Network | 17
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv6 Type(Static IP) > IP Address
Parameter static.network.ipv6_prefix
Description
It configures the IPv6 prefix.
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Note: It works only if “static.network.ip_address_mode” is set to 1 (IPv6) or 2 ( IPv4
& IPv6), and "static.network.ipv6_internet_port.type" is set to 1 (Static IP).
Permitted Values Integer from 0 to 128
Default 64
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv6 Config > Configuration Type(Static IP) > IPv6
Prefix(0~128)
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv6 Type(Static IP) > IPv6 IP Prefix(0~128)
Parameter static.network.ipv6_internet_port.gateway
Description
It configures the IPv6 default gateway.
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Note: It works only if “static.network.ip_address_mode” is set to 1 (IPv6) or 2 ( IPv4
& IPv6), and "static.network.ipv6_internet_port.type" is set to 1 (Static IP).
Permitted Values IPv6 Address
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv6 Config > Configuration Type(Static IP) > Default
Gateway
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv6 Type(Static IP) > Default Gateway
Parameter static.network.ipv6_static_dns_enable
Description
It triggers the static IPv6 DNS feature to on or off.
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Note: It works only if “static.network.ipv6_internet_port.type” is set to 0 (DHCP).
Permitted Values
0-Off, the device will use the IPv6 DNS obtained from DHCP.
1-On, the device will use manually configured static IPv6 DNS.
Default 0
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv6 Config > IPv6 Static DNS (or Static IPv6 DNS)
Parameter static.network.ipv6_primary_dns
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
| Device Network | 18
Description
It configures the primary IPv6 DNS server.
Note: It works only if “static.network.ip_address_mode" is set to 1 (IPv6)
or 2 (IPv4 & IPv6). In DHCP environment, you also need to make sure
“static.network.ipv6_static_dns_enable" is set to 1 (On).
Permitted Values IPv6 Address
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv6 Config > Configuration Type(Static IP) > Primary DNS
Or Network > Basic > IPv6 Config > Configuration Type(DHCP) > Static
DNS(Enable) > Primary DNS
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv6 Type(Static IP) > Pri.DNS
Or > Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) >
WAN Port > IPv6 Type(DHCP) > IPv6 Static DNS(Enable) > Pri.DNS
Parameter static.network.ipv6_secondary_dns
Description
It configures the secondary IPv6 DNS server.
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Note: It works only if “static.network.ip_address_mode" is set to 1 (IPv6)
or 2 (IPv4 & IPv6). In DHCP environment, you also need to make sure
“static.network.ipv6_static_dns_enable" is set to 1 (On).
Permitted Values IPv6 Address
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv6 Config > Configuration Type(Static IP) > Secondary
DNS
Or Network > Basic > IPv6 Config > Configuration Type(DHCP) > Static
DNS(Enable) > Secondary DNS
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > WAN
Port > IPv6 Type(Static IP) > Sec.DNS
Or > Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) >
WAN Port > IPv6 Type(DHCP) > IPv6 Static DNS(Enable) > Sec.DNS
Parameter static.network.ipv6_icmp_v6.enable
Description
It enables or disables the phone to obtain IPv6 network settings via SLAAC
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
(Stateless Address Autoconfiguration).
Note: It works only if “static.network.ipv6_internet_port.type” is set to 0 (DHCP).
Permitted Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 1
Web UI Network > Advanced > ICMPv6 Status > Active
[1]
If you change this parameter, the device will reboot to make the change take effect.
DHCP Option for IPv4
The Teams device can obtain IPv4-related parameters in an IPv4 network via the DHCP option.
Note: For more information on DHCP options, refer to RFC 2131 or RFC 2132.
• Supported DHCP Option for IPv4
• DHCP Option 160 and Option 161
• DHCP Option 66, Option 43 and Custom Option
• DHCP Option 42 and Option 2
• DHCP Option 12
• DHCP Option 60
Supported DHCP Option for IPv4
The following table lists common DHCP options for IPv4 supported by the devices.
Parameter DHCP Option Description
Subnet Mask 1 Specify the client’s subnet mask.
| Device Network | 19
Time Offset 2 Specify the offset of the client's subnet in
seconds from Coordinated
Universal Time (UTC).
Router 3 Specify a list of IP addresses for routers on the
client’s subnet.
Time Server 4 Specify a list of time servers available to the
client.
Domain Name Server 6 Specify a list of domain name servers available
to the client.
Log Server 7 Specify a list of MIT-LCS UDP servers available
to the client.
Host Name 12 Specify the name of the client.
Domain Server 15 Specify the domain name that the client should
use when resolving hostnames via DNS.
Broadcast Address 28 Specify the broadcast address in use on the
client's subnet.
Network Time Protocol
Servers
Vendor-Specific
Information
42 Specify a list of NTP servers available to the
client by IP address.
43 Identify the vendor-specific information.
Vendor Class Identifier 60 Identify the vendor type.
TFTP Server Name 66 Identify a TFTP server when the 'sname' field
in the DHCP header has been used for DHCP
options.
DHCP Option 160 and Option 161
Yealink Teams devices support obtaining the provisioning server address by detecting DHCP custom
option during startup.
If DHCP Option 66 is not available, you can use custom option (160 or 161) with the URL or IP address
of the provisioning server. The device will automatically detect the option 160 or 161 for obtaining the
provisioning server address.
To use DHCP option 160 or option 161, make sure the DHCP Active feature is enabled and the custom
option is configured.
• DHCP Option 160 and Option 161 Configuration
DHCP Option 160 and Option 161 Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure DHCP option 160 or 161.
Parameter static.auto_provision.dhcp_option.enable
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
| Device Network | 20
Description
Permitted
It triggers the DHCP Option feature to on or off.
0-Off
Values
1-On
Default 1
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > DHCP Active
Parameter static.auto_provision.dhcp_option.list_user_options
Description
It configures the custom DHCP option for requesting provisioning server address.
[1]
Multiple DHCP options are separated by commas.
Note: It works only if “static.auto_provision.dhcp_option.enable” is set to 1 (On).
Permitted
Integer from 128 to 254
Values
Default 160,161
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Custom Option
[1]
If you change this parameter, the device will reboot to make the change take effect.
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
DHCP Option 66, Option 43 and Custom Option
During the startup, the device will automatically detect the custom option, option 66, or option 43 for
obtaining the provisioning server address. The priority of obtaining the provisioning server address is as
follows: custom option > option 66 (identify the TFTP server) > option 43.
The Teams device can obtain the Auto Configuration Server (ACS) address by detecting option 43 during
startup.
To obtain the server address via DHCP option, make sure you have configured the DHCP option on the
device. The option must be in accordance with the one defined in the DHCP server.
Note: If you fail to configure the DHCP options for discovering the provisioning server on the DHCP
server, an alternate method of automatically discovering the provisioning server address is required.
One possibility is that connecting to the secondary DHCP server that responds to DHCP INFORM
queries with a requested provisioning server address. For more information, refer to RFC 3925.
If a single alternate DHCP server responds, this is functionally equivalent to the scenario where
the primary DHCP server responds with a valid provisioning server address. If no DHCP server
responds, the INFORM query process will retry and until the time is out.
DHCP Option 42 and Option 2
Yealink Teams devices can use the NTP server address offered by DHCP.
DHCP option 42 is used to specify a list of NTP servers available to the client by IP address. NTP servers
should be listed in order of preference.
DHCP option 2 is used to specify the offset of the client’s subnet in seconds from Coordinated Universal
Time (UTC).
Related information
NTP Settings
DHCP Option 12
You can specify a hostname for the device when using DHCP. The DHCP client uses option 12 to send a
predefined hostname to the DHCP registration server. The name may or may not be qualified with the local
domain name (based on RFC 2132). See RFC 1035 for character restrictions.
| Device Network | 21
• DHCP Option 12 Hostname Configuration
DHCP Option 12 Hostname Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to configure DHCP option 12 hostname.
Parameter static.network.dhcp_host_name
Description It configures the DHCP option 12 hostname on the device.
Permitted
Values
Default For T58A: SIP-T58
[1]
If you change this parameter, the device will reboot to make the change take effect.
String within 99 characters
For T56A: SIP-T56A
For CP960: SIP-CP960
For T55A: SIP-T55A
For VP59: VP59
For MP54: MP54
For MP56: MP56
For MP58/MP58-WH: MP58
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
DHCP Option 60
DHCP option 60 is used to identify the vendor and functionality of a DHCP client. You can set the format for
option 60. The default vendor class ID is “yealink”.
• DHCP Option 60 Configuration
DHCP Option 60 Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to configure DHCP option 60.

| Device Network | 22
Parameter static.auto_provision.dhcp_option.option60_value
Description
Permitted Values String within 99 characters
Default yealink
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > DHCP Option Value
[1]
If you change this parameter, the device will reboot to make the change take effect.
It configures the value (vendor name of the device) of DHCP option 60.
[1]
DHCP Option for IPv6
The Teams device can obtain IPv6-related parameters in an IPv6 network via the DHCP option.
• Supported DHCP Option for IPv6
Supported DHCP Option for IPv6
The following table lists common DHCP options for IPv6 supported by Yealink Teams devices.
Parameters DHCP Option Description
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
DNS Server 23 Specify a list of DNS servers available
to the client.
DNS Domain Search List 24 Specify a domain search list to a client.
SNTP Server 31 Specify a list of Simple Network Time
Protocol (SNTP) servers available to the
client.
Information Refresh Time 32 Specify an upper bound for how long
a client should wait before refreshing
information retrieved from DHCPv6.
VLAN
The purpose of VLAN configurations on the device is to insert a tag with VLAN information to the packets
generated by the device. When VLAN is properly configured for the ports (Internet port and PC port) on the
device, the device will tag all packets from these ports with the VLAN ID. The switch receives and forwards
the tagged packets to the corresponding VLAN according to the VLAN ID in the tag, as described in IEEE
Std 802.3.
VLAN on devices allows simultaneous access to a regular PC. This feature allows a PC to be daisy
chained to a device and the connection for both PC and phone to be trunked through the same physical
Ethernet cable.
In addition to manual configuration, the device also supports the automatic discovery of VLAN via LLDP,
CDP, or DHCP. The assignment takes effect in this order: assignment via LLDP/CDP, manual configuration,
then assignment via DHCP.
• LLDP Configuration
• CDP Configuration
• Manual VLAN Configuration
• DHCP VLAN Configuration
• VLAN Change Configuration
LLDP Configuration
LLDP (Linker Layer Discovery Protocol) is a vendor-neutral Link Layer protocol, which allows devices to
receive and/or transmit device-related information from/to directly connected devices on the network that
are also using the protocol, and store the information about other devices.
When the LLDP feature is enabled on the devices, the devices periodically advertise their information
to the directly connected LLDP-enabled switch. The devices can also receive LLDP packets from the
connected switch. When the application type is “voice”, the devices decide whether to update the VLAN
configurations obtained from the LLDP packets. When the VLAN configurations on the devices are different
from the ones sent by the switch, the devices perform an update and reboot. This allows the devices to
plug into any switch, obtain their VLAN IDs, and then start communications with the call control.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure LLDP.
Parameter static.network.lldp.enable
Description It enables or disables the LLDP feature on the device.
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
| Device Network | 23
Permitted Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled, the device will attempt to determine its VLAN ID through LLDP.
Default 1
Web UI Network > Advanced > LLDP > Active
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > LLDP
> LLDP Status
Parameter static.network.lldp.packet_interval
Description
It configures the interval (in seconds) that how often the device sends the LLDP
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
request.
Note: It works only if “static.network.lldp.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted Values Integer from 1 to 3600
Default 60
Web UI Network > Advanced > LLDP > Packet Interval(1-3600s)
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > LLDP
> LLDP Interval
[1]
If you change this parameter, the device will reboot to make the change take effect.
CDP Configuration
CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol) allows devices to receive and/or transmit device-related information from/
to directly connected devices on the network that are also using the protocol, and store the information
about other devices.
If the CDP feature is enabled on the devices, the devices will periodically advertise their information to the
directly connected CDP-enabled switch. The devices can also receive CDP packets from the connected
switch. If the VLAN configurations on the devices are different from the ones sent by the switch, the devices
| Device Network | 24
will perform an update and reboot. This allows you to connect the devices into any switch, obtain their
VLAN IDs, and then start communications with the call control.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure CDP.
Parameter static.network.cdp.enable
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It enables or disables the CDP feature.
Permitted Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled, the phone will attempt to determine its VLAN ID through CDP.
Default 1
Web UI Network > Advanced > CDP > Active
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > CDP
> CDP Status
Parameter static.network.cdp.packet_interval
Description
It configures the interval (in seconds) at which the phone sends the CDP request.
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Note: It works only if “static.network.cdp.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted Values Integer from 1 to 3600
Default 60
Web UI Network > Advanced > CDP > CDP Interval (1~3600s)
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > CDP
> CDP Interval
[1]
If you change this parameter, the device will reboot to make the change take effect.
Manual VLAN Configuration
VLAN is disabled on the devices by default. You can configure VLAN for the Internet port and PC port
manually. Before configuring VLAN on the device, you need to obtain the VLAN ID from your network
administrator.
The PC port is not applicable to CP960, and you can only configure VLAN for the Internet port manually.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure VLAN manually.
Parameter static.network.vlan.internet_port_enable
Description It enables or disables the VLAN for the Internet port.
Permitted Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
Web UI Network > Advanced > VLAN > WAN Port > Active
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
| Device Network | 25
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > VLAN
> WAN Port
Parameter static.network.vlan.internet_port_vid
Description
It configures the VLAN ID for the Internet port.
[1]
Note: It works only if “static.network.vlan.internet_port_enable” is set to 1
(Enabled).
Permitted Values Integer from 1 to 4094
Default 1
Web UI Network > Advanced > VLAN > WAN Port > VID
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > VLAN
> WAN Port > VID
Parameter static.network.vlan.internet_port_priority
Description
It configures the VLAN priority for the Internet port.
[1]
7 is the highest priority, 0 is the lowest priority.
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Note: It works only if “static.network.vlan.internet_port_enable” is set to 1
(Enabled).
Permitted Values Integer from 0 to 7
Default 1
Web UI Network > Advanced > VLAN > WAN Port > Priority
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > VLAN
> WAN Port > Priority
Parameter static.network.vlan.pc_port_enable
Description
It enables or disables the VLAN for the PC port.
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Note: It works only if “static.network.pc_port.enable” is set to 1 (Auto Negotiation).
Permitted Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
Supported Devices All devices except CP960
Web UI Network > Advanced > VLAN > PC Port > Active
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > VLAN
> PC Port
Parameter static.network.vlan.pc_port_vid
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
| Device Network | 26
Description
It configures the VLAN ID for the PC port.
Note: It works only if “static.network.pc_port.enable” is set to 1 (Auto Negotiation)
and “static.network.vlan.pc_port_enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted Values Integer from 1 to 4094
Default 1
Supported Devices All devices except CP960
Web UI Network > Advanced > VLAN > PC Port > VID
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > VLAN
> PC Port > VID
Parameter static.network.vlan.pc_port_priority
Description
It configures the VLAN priority for the PC port.
[1]
7 is the highest priority, 0 is the lowest priority.
Note: It works only if “static.network.pc_port.enable” is set to 1 (Auto Negotiation)
and “static.network.vlan.pc_port_enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted Values Integer from 1 to 7
Default 0
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Supported Devices All devices except CP960
Web UI Network > Advanced > VLAN > PC Port > Priority
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > VLAN
> PC Port > Priority
[1]
If you change this parameter, the device will reboot to make the change take effect.
DHCP VLAN Configuration
Yealink Teams devices support VLAN discovery via DHCP. When the VLAN discovery method is set to
DHCP, the device will examine the DHCP option for a valid VLAN ID. The predefined option 132 is used to
supply the VLAN ID by default. You can customize the DHCP option used to request the VLAN ID.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure DHCP VLAN discovery.
Parameter static.network.vlan.dhcp_enable
Description It enables or disables the DHCP VLAN discovery feature on the device.
Permitted Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled.
Default 1
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Web UI Network > Advanced > DHCP VLAN > Active
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > DHCP
VLAN
| Device Network | 27
Parameter static.network.vlan.dhcp_option
Description
It configures the DHCP option from which the device obtains the VLAN settings.
[1]
You can configure at most five DHCP options and separate them by commas.
Permitted Values Integer from 1 to 255
Default 132
Web UI Network > Advanced > DHCP VLAN > Option(1-255)
Phone UI
> Settings > Device Settings > Network (default password: admin) > DHCP
VLAN > Option
[1]
If you change this parameter, the device will reboot to make the change take effect.
VLAN Change Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to configure the VLAN change.
Parameter static.network.vlan.vlan_change.enable
Description
It enables or disables the device to obtain VLAN ID using lower preference of VLAN
assignment method or to close the VLAN feature when the device cannot obtain VLAN ID
using the current VLAN assignment method.
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
The priority of each method is LLDP/CDP > Manual > DHCP VLAN.
Permitted Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled, the device will attempt to use the lower priority method when failing to obtain
the VLAN ID using a higher priority method. If all the methods are attempted, the device will
disable the VLAN feature.
Default 0
[1]
If you change this parameter, the device will reboot to make the change take effect.
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi feature enables you to connect the devices to the organization’s wireless network.
Note: For T56A/T55A/MP54, make sure the Wi-Fi USB Dongle WF50 is connected to the device.
• Wi-Fi Configuration
Wi-Fi Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure the Wi-Fi.
Parameter static.wifi.function.enable
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It enables or disables the Wi-Fi feature.
Permitted Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 1
Parameter static.wifi.enable <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It activates or deactivates the Wi-Fi mode.
Note: It works only if “static.wifi.function.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
| Device Network | 28
Permitted Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
Web UI Network > Wi-Fi > Wi-Fi Active (or Wi-Fi)
Phone UI
Parameter static.wifi.X.label
> Settings > Device Settings > Wi-Fi > Wi-Fi
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the profile name of a specific wireless network.
Note: It works only if "static.wifi.function.enable" and "static.wifi.enable" are set to
1 (Enabled).
Permitted Values String within 32 characters
Default Blank
Parameter static.wifi.X.ssid
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the SSID of a specific wireless network.
SSID is a unique identifier for accessing wireless access points.
Note: It works only if "static.wifi.function.enable" and "static.wifi.enable" are set to
1 (Enabled).
Permitted Values String within 32 characters
Default Blank
Parameter static.wifi.X.priority
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the priority for a specific wireless network.
5 is the highest priority, 1 is the lowest priority.
Note: It works only if "static.wifi.function.enable" and "static.wifi.enable" are set to
1 (Enabled).
Permitted Values Integer from 1 to 5
Default 1
Parameter static.wifi.X.security_mode
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the security mode of a specific wireless network.
Note: It works only if "static.wifi.function.enable" and "static.wifi.enable" are set to
1 (Enabled).
Permitted Values NONE, WEP, WPA/WPA2 PSK, 802.1x EAP
Default NONE
| Device Network | 29
Parameter static.wifi.X.cipher_type
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the encryption type of a specific wireless network.
If "static.wifi.X.security_mode" is set to NONE, the permitted value of this
parameter is NONE.
If "static.wifi.X.security_mode" is set to 802.1x EAP, the permitted values of this
parameter are PEAP, TLS, TTLS, or PWD.
Note: It works only if "static.wifi.function.enable" and "static.wifi.enable" are set to
1 (Enabled).
Permitted Values NONE, PEAP, TLS, TTLS, PWD
Default NONE
Parameter static.wifi.X.password
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the password of a specific wireless network.
Note: It works only if "static.wifi.function.enable" and "static.wifi.enable" are set to
1 (Enabled).
Permitted Values String within 64 characters
Default Blank
Parameter static.wifi.X.eap_type
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the EAP authentication mode of a specific wireless network.
Note: It works only if "static.wifi.function.enable" and "static.wifi.enable" are set to
1 (Enabled).
Permitted Values TTLS, PEAP or TLS
Default Blank
Parameter static.wifi.X.eap_user_name
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the EAP authentication username of a specific wireless network.
Note: It works only if "static.wifi.function.enable" and "static.wifi.enable" are set to
1 (Enabled).
Permitted Values String within 64 characters
Default Blank
Parameter static.wifi.X.eap_password
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the EAP authentication password of a specific wireless network.
Note: It works only if "static.wifi.function.enable" and "static.wifi.enable" are set to
1 (Enabled).
Permitted Values String within 64 characters
Default Blank
[1]
If you change this parameter, the device will reboot to make the change take effect.
[2]
X is the Wi-Fi ID. X=1-5.
Internet Port and PC Port
Yealink Teams devices support two Ethernet ports: Internet port and PC port. You can enable or disable
the PC port on the devices.
The PC port is not applicable to CP960 devices.
• Supported Transmission Methods
• Internet Port and PC Port Configuration
Supported Transmission Methods
Three optional methods of transmission configuration for the device Internet port and PC port:
• Auto Negotiation
• Half-duplex (transmit in 10Mbps or 100Mbps)
• Full-duplex (transmit in 10Mbps, 100Mbps or 1000Mbps (not applicable to CP960))
Auto negotiation is configured for both Internet and PC ports on the device by default.
Internet Port and PC Port Configuration
| Device Network | 30
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure the Internet port and PC port.
Parameter static.network.pc_port.enable
Description It enables or disables the PC port.
Permitted Values
Default 1
Supported Devices All devices except CP960
Web UI Network > PC Port > PC Port Active
Phone UI
Parameter static.network.internet_port.speed_duplex
Description It configures the transmission method of the Internet port.
Permitted Values
0-Disabled
1-Auto Negotiation
> Settings > Device Settings > Network(default password: admin) > PC
Port
Note: You can set the transmission speed to 1000Mbps/Auto Negotiation to
transmit in 1000Mbps if the phone is connected to the switch which supports
Gigabit Ethernet. We recommend that you do not change this parameter.
0-Auto Negotiation
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Default 0
1-Full Duplex 10Mbps
2-Full Duplex 100Mbps
3-Half Duplex 10Mbps
4-Half Duplex 100Mbps
5-Full Duplex 1000Mbps (not applicable to CP960)
 Loading...
Loading...