Yealink Sip IP User Manual

Table of Contents
iii


Table of Contents
iii
Table of Contents
Table of Contents ....................................................................... iii
Introduction ................................................................................. 1
Supported Phones.................................................................................................................. 1
Getting Started ............................................................................ 3
Obtaining Boot, Configuration and Resource Files ................................................................ 3
Boot Files ............................................................................................................................ 3
Configuration Files .............................................................................................................. 3
Resource Files .................................................................................................................... 4
Obtaining Template Files ..................................................................................................... 5
Obtaining Phone Information .................................................................................................. 5
Provisioning Yealink IP Phones .................................................. 7
Interoperating with Provisioning Server.................................................................................. 7
Auto Provisioning Process ...................................................................................................... 8
Old Mechanism – Without Boot Files .................................................................................. 8
New Mechanism – With Boot Files ..................................................................................... 9
Major Tasks for Auto Provisioning ........................................................................................ 11
An Instance of Auto Provision Configuration ........................................................................ 12
Managing Boot Files ................................................................. 15
Editing Common Boot File .................................................................................................... 15
Creating MAC-Oriented Boot File ......................................................................................... 17
Managing Configuration Files .................................................. 19
Editing Common CFG File ................................................................................................... 19
Editing MAC-Oriented CFG File ........................................................................................... 21
Creating a New CFG File ..................................................................................................... 23
Managing MAC-local CFG File ............................................................................................. 24
Encrypting Configuration Files ............................................................................................. 24
Managing Resource Files ......................................................... 25
Customizing Resource Files ................................................................................................. 25

Yealink IP Phones Auto Provisioning Guide
iv
Configuring a Provisioning Server ........................................... 27
Preparing a Root Directory ................................................................................................... 27
Configuring a TFTP Server................................................................................................... 28
Obtaining the Provisioning Server Address ............................ 31
Zero Touch ............................................................................................................................ 31
Plug and Play (PnP) Server ................................................................................................. 33
DHCP Options ...................................................................................................................... 34
Phone Flash ......................................................................................................................... 35
Configuring Wildcard of the Provisioning Server URL ......................................................... 36
Triggering the IP Phone to Perform Auto Provisioning .......... 39
Power On .............................................................................................................................. 39
Repeatedly ........................................................................................................................... 40
Weekly .................................................................................................................................. 41
Flexible Auto Provision ......................................................................................................... 42
Auto Provision Now .............................................................................................................. 43
Multi-mode Mixed ................................................................................................................. 44
SIP NOTIFY Message .......................................................................................................... 44
Auto Provisioning via Activation Code .................................................................................. 45
Downloading and Verifying Configurations ............................. 49
Downloading Boot, Configuration and Resource Files ......................................................... 49
Resolving and Updating Configurations ............................................................................... 49
Using MAC-local CFG File ................................................................................................... 50
Verifying Configurations........................................................................................................ 50
Troubleshooting ........................................................................ 53
Glossary ..................................................................................... 55
Appendix .................................................................................... 57
Configuring an FTP Server................................................................................................... 57
Preparing a Root Directory ............................................................................................... 57
Configuring an FTP Server ............................................................................................... 58
Configuring an HTTP Server ................................................................................................ 60
Preparing a Root Directory ............................................................................................... 60

Table of Contents
v
Configuring an HTTP Server ............................................................................................. 61

Yealink IP Phones Auto Provisioning Guide
vi
Introduction
1
Introduction
Yealink IP phones are full-featured telephones that can be plugged directly into an IP network
and can be used easily without manual configuration.
This guide provides instructions on how to provision Yealink IP phones with the minimum
settings required. Yealink IP phones support FTP, TFTP, HTTP, and HTTPS protocols for auto
provisioning and are configured by default to use the TFTP protocol.
Supported Phones
The purpose of this guide is to serve as a basic guide for provisioning Yealink IP phones.
The following table lists product names and available firmware versions for IP phones that use
auto provisioning process outlined in this guide.
Product Name
Boot File
(Available Firmware
Version)
Exclude Mode
(Available Firmware
Version)
VP59
Yes (83 or later)
Yes (83 or later)
SIP-T58A
Yes (80 or later)
Yes (83 or later)
SIP-T33P/T33G/T31P/T31G/T31/T30P/T30
Yes (85 or later)
Yes (85 or later)
SIP- T57W/T54W/T53W/T53
Yes (84 or later)
Yes (84 or later)
SIP-T48U/T46U/T43U/T42U
Yes (84 or later)
Yes (84 or later)
SIP-T48G/S
Yes (81 or later)
Yes (83 or later)
SIP-T46G/S
Yes (81 or later)
Yes (83 or later)
SIP-T42G/S
Yes (81 or later)
Yes (83 or later)
SIP-T41P/S
Yes (81 or later)
Yes (83 or later)
SIP-T40P/G
Yes (81 or later)
Yes (83 or later)
SIP-T29G
Yes (81 or later)
Yes (83 or later)
SIP-T27G
Yes (81 or later)
Yes (83 or later)
SIP-T23P/G
Yes (81 or later)
Yes (83 or later)
SIP-T21(P) E2
Yes (81 or later)
Yes (83 or later)
SIP-T19(P) E2
Yes (81 or later)
Yes (83 or later)
CP860
Yes (81 or later)
No
Yealink IP Phones Auto Provisioning Guide
2
Product Name
Boot File
(Available Firmware
Version)
Exclude Mode
(Available Firmware
Version)
CP960
Yes (80 or later)
Yes (83 or later)
CP920
Yes (81 or later)
No
W60P
Yes (81 or later)
No
W53P
Yes (83 or later)
No
CP930W-Base
Yes (83 or later)
No
W52P
W56P
Yes (81 or later)
No
We recommend that IP phones running the latest firmware should not be downgraded to an
earlier firmware version. The new firmware is compatible with old configuration parameters,
but not vice versa.

Getting Started
3
Getting Started
This section provides instructions on how to get ready for auto provisioning. To begin the auto
provisioning, the following steps are required:
⚫ Obtaining Boot, Configuration and Resource Files
⚫ Obtaining Phone Information
Obtaining Boot, Configuration and Resource Files
Boot Files
The IP phone tries to download the boot file first, and then download the configuration files
referenced in the boot file during auto provisioning. You can select whether to use the boot file or
not according to your deployment scenario. If required, you need to obtain the template boot file
named as “y000000000000.boot” before auto provisioning.
You can use a boot file to specify which configuration files to be downloaded for specific phone
groups by phone model identity, and customize the download sequence of configuration files. It
is efficient for you to provision IP phones in different deployment scenarios, including all IP
phones, specific phone groups, or a single phone.
The configuration files referenced in the boot file are flexible: you can rearrange the
configuration parameters within the Yealink-supplied template configuration files or create your
own configuration files from configuration parameters you want. You can create and name as
many configuration files as you want and your own configuration files can contain any
combination of configuration parameters.
Configuration Files
Before provisioning, you also need to obtain template configuration files. There are two
configuration files both of which are CFG-formatted. We call these two files Common CFG file
and MAC-Oriented CFG file.
The configuration files contain parameters that affect the features of the phone. You can use the
configuration files to deploy and maintain a mass of Yealink IP phones automatically.
You can create and name as many configuration files as you want (for example, account.cfg,
sip.cfg, features.cfg) by using the template configuration files. The custom configuration files can
contain the configuration parameters of the same feature modules for all phones.
Yealink IP Phones Auto Provisioning Guide
4
Resource Files
When configuring some particular features, you may need to upload resource files to IP phones,
such as personalized AutoDST file, language package file, and local contact file. Resource files
are optional, but if the particular feature is being employed, these files are required.
Yealink supplies the following resource file templates:
Feature
Template File Name
DST
AutoDST.xml
Language Packs
For example,
000.GUI.English.lang
1.English_note.xml
1.English.js
Replace Rule
dialplan.xml
Dial-now
dialnow.xml
Softkey Layout
(not applicable to
CP960/W52P/W53P/W5
6P/W60P/CP930W-Base
phones)
CallFailed.xml
CallIn.xml
Connecting.xml
Dialing.xml (not applicable to
VP59/T58A/T57W/T48U/T48G/T48S phones)
RingBack.xml
Talking.xml
Directory
favorite_setting.xml
Super Search in dialing
super_search.xml
Local Contact File
contact.xml
Remote XML Phone
Book
Department.xml
Menu.xml
Screen Saver
(not applicable to
VP59/T58A/CP960/W52
P/W53P/W56P/W60P/C
P930W-Base phones)
CustomScreenSaver.xml
Firmware
X.83.0.XX.rom
For example,
44.83.0.10.rom

Getting Started
5
Obtaining Template Files
You can ask the distributor or Yealink FAE for template files. You can also obtain them online:
http://support.yealink.com/documentFront/forwardToDocumentFrontDisplayPage.
To download template boot, configuration and resource files:
1. Go to Yealink Document Download page and select the desired phone model.
2. Download and extract the combined template files to your local system.
For example, the following illustration shows the template files available for SIP-T23G IP
phones running firmware version 82.
3. Open the folder you extracted and identify the files you want to edit.
Obtaining Phone Information
Before provisioning, you also need the IP phone information. For example, MAC address and
the SIP account information of the IP phone.
MAC Address: The unique 12-digit serial number of the IP phone. You can obtain it from the bar
code on the back of the IP phone.
SIP Account Information: This may include SIP credentials such as user name, password and
IP address of the SIP server. Ask your system administrator for SIP account information.

Yealink IP Phones Auto Provisioning Guide
6
Provisioning Yealink IP Phones
7
Provisioning Yealink IP Phones
This section provides instructions on how IP phones interoperate with provisioning server for
auto provisioning, and shows you the auto provisioning process and the four major tasks to
provision the phones. It will help users who are not familiar with auto provisioning to understand
this process more easily and quickly.
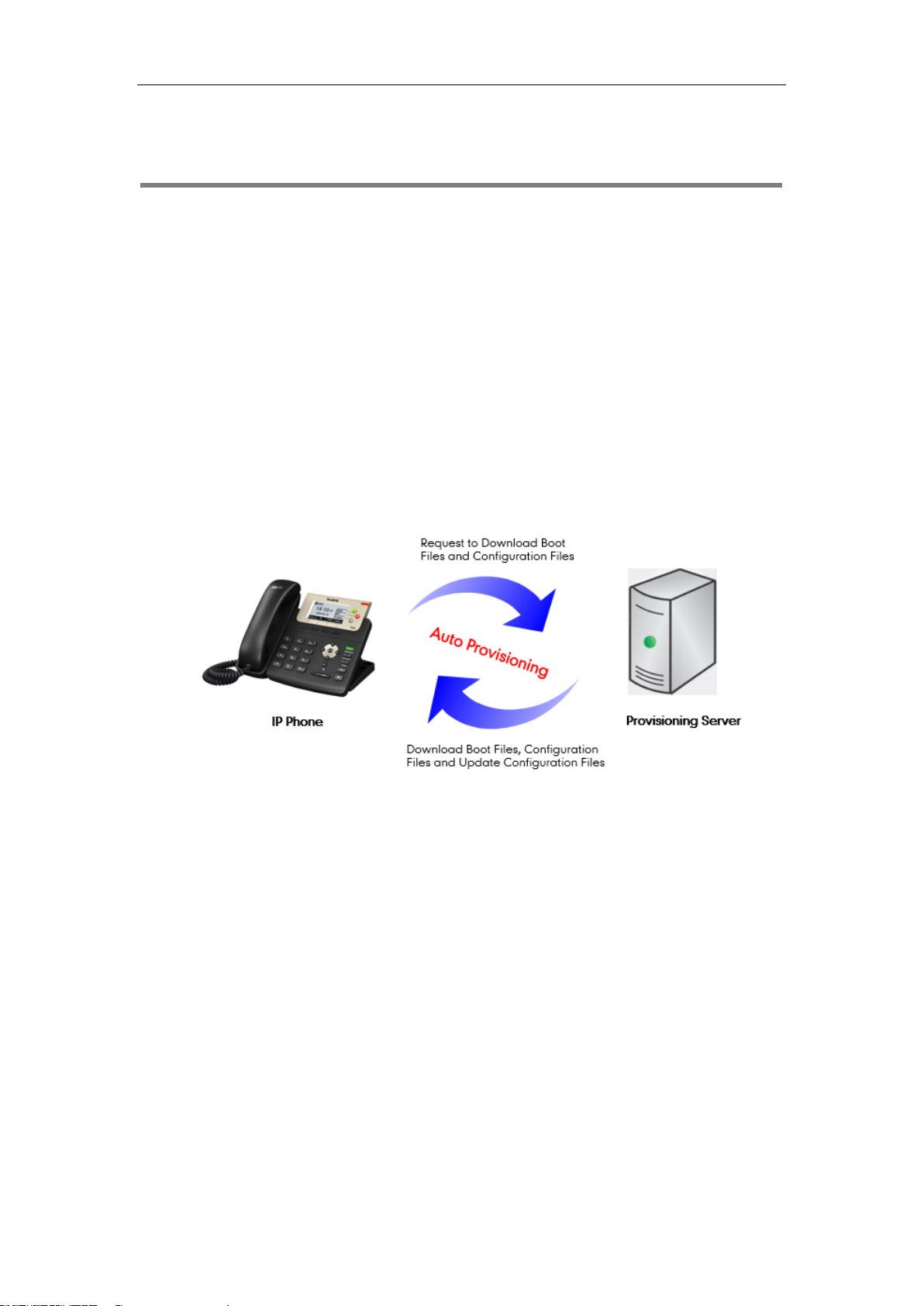
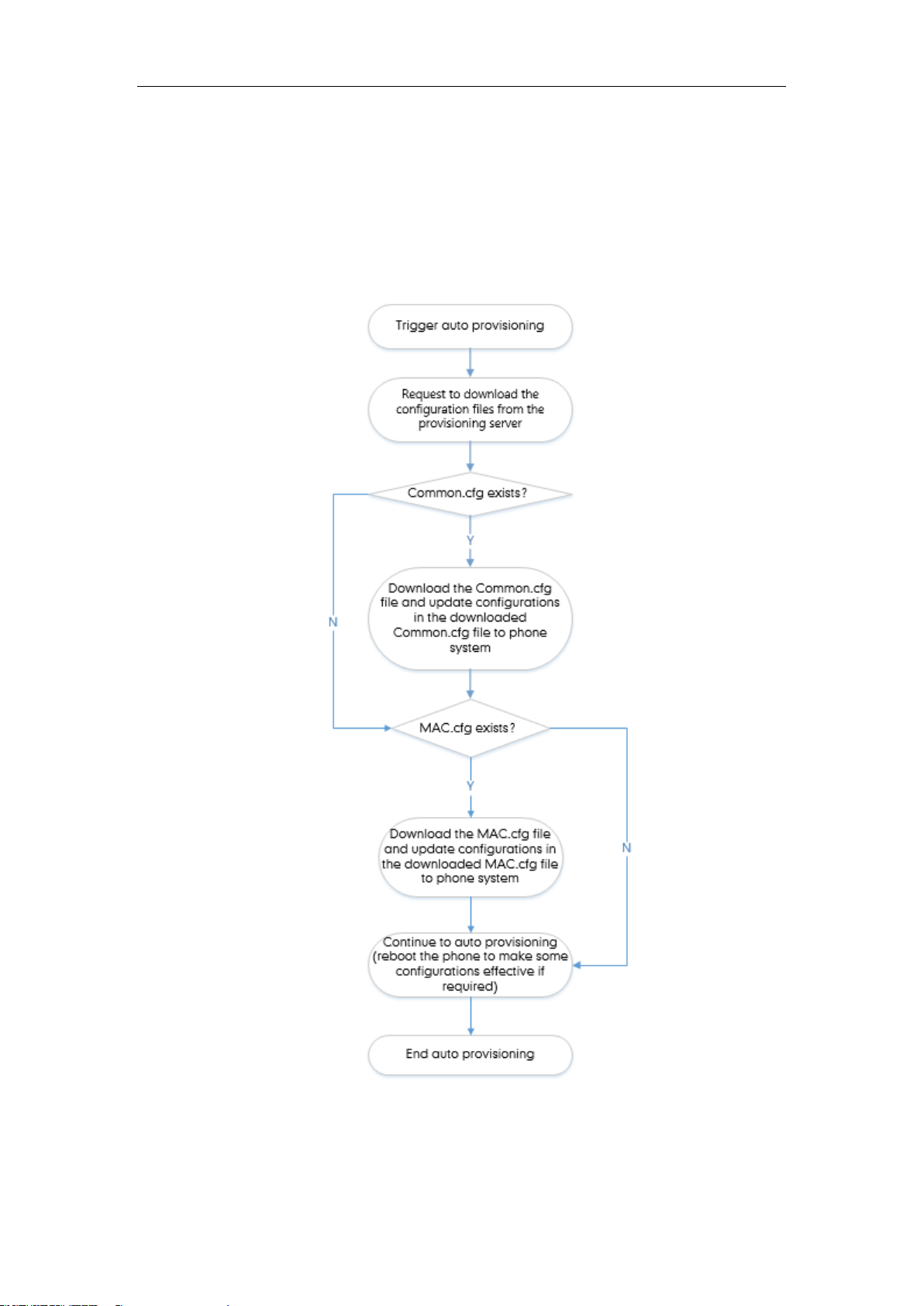
Interoperating with Provisioning Server
When IP phones are triggered to perform auto provisioning, they will request to download the
boot files and configuration files from the provisioning server. During the auto provisioning, the
IP phone will download and update configuration files to the phone flash.
The following figure shows how the IP phone interoperates with the provisioning server:
Yealink IP Phones Auto Provisioning Guide
8
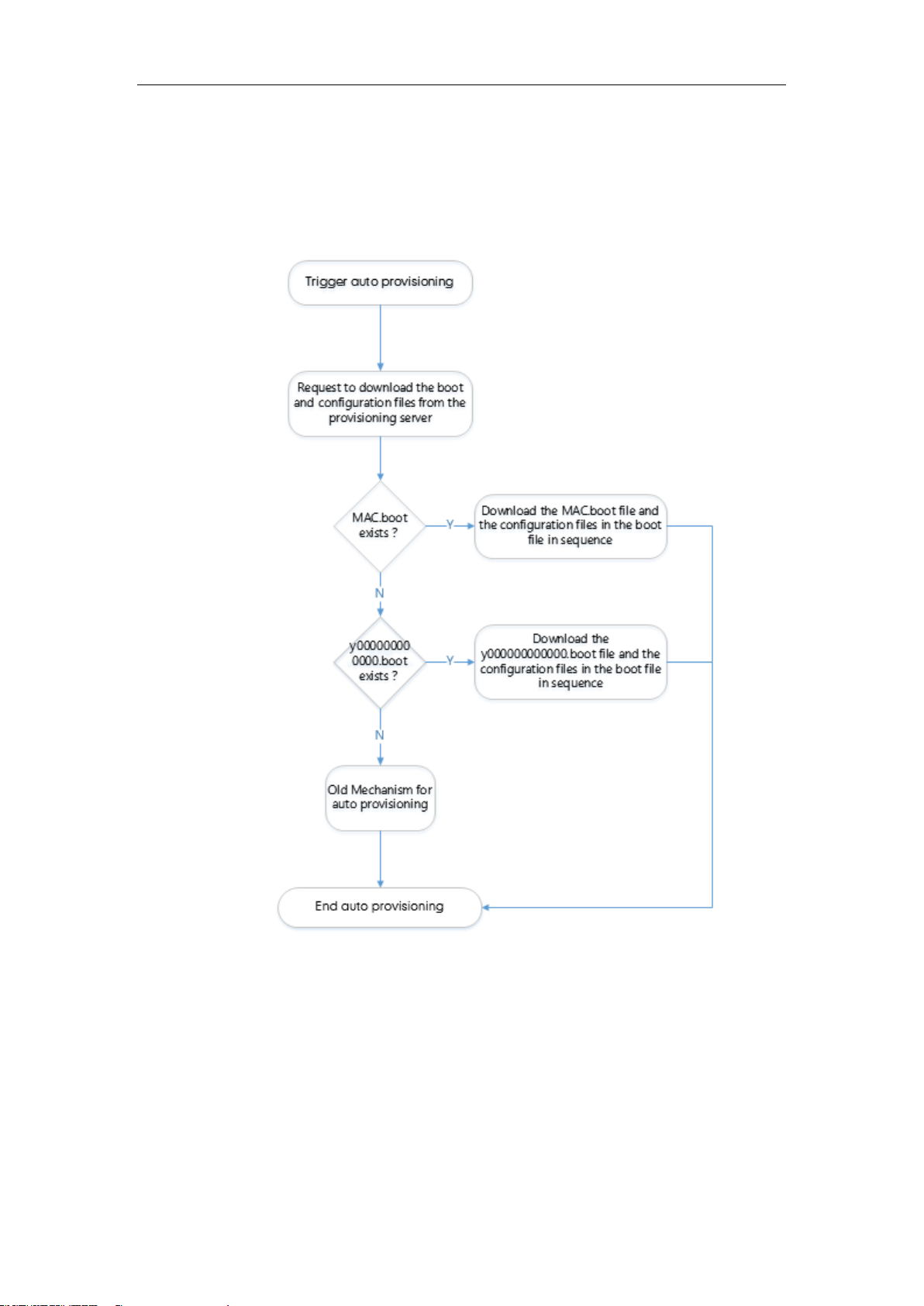
Auto Provisioning Process
Old Mechanism – Without Boot Files
The following flowchart shows how Yealink IP phones perform auto provisioning when using
configuration files only:
Provisioning Yealink IP Phones
9
New Mechanism – With Boot Files
The following figure shows auto provisioning flowcharts for Yealink IP phones when using boot files:
Scenario A – Do Not Support Exclude Mode
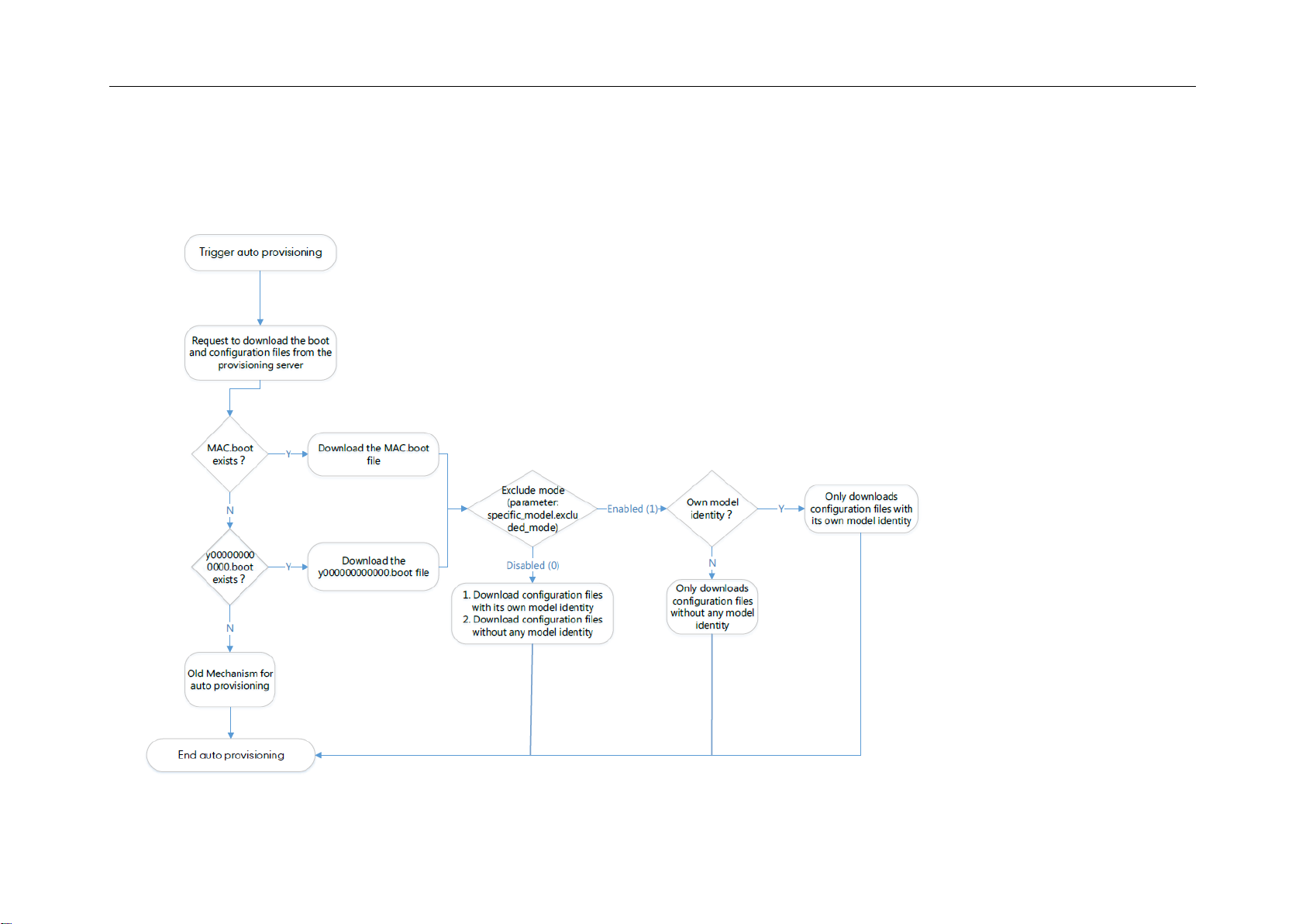
Yealink IP Phones Auto Provisioning Guide
10
Scenario B – Support Exclude Mode
This scenario is only applicable to IP phones (except W52P/W56P IP phones) running firmware version 83 or later.
Provisioning Yealink IP Phones
11
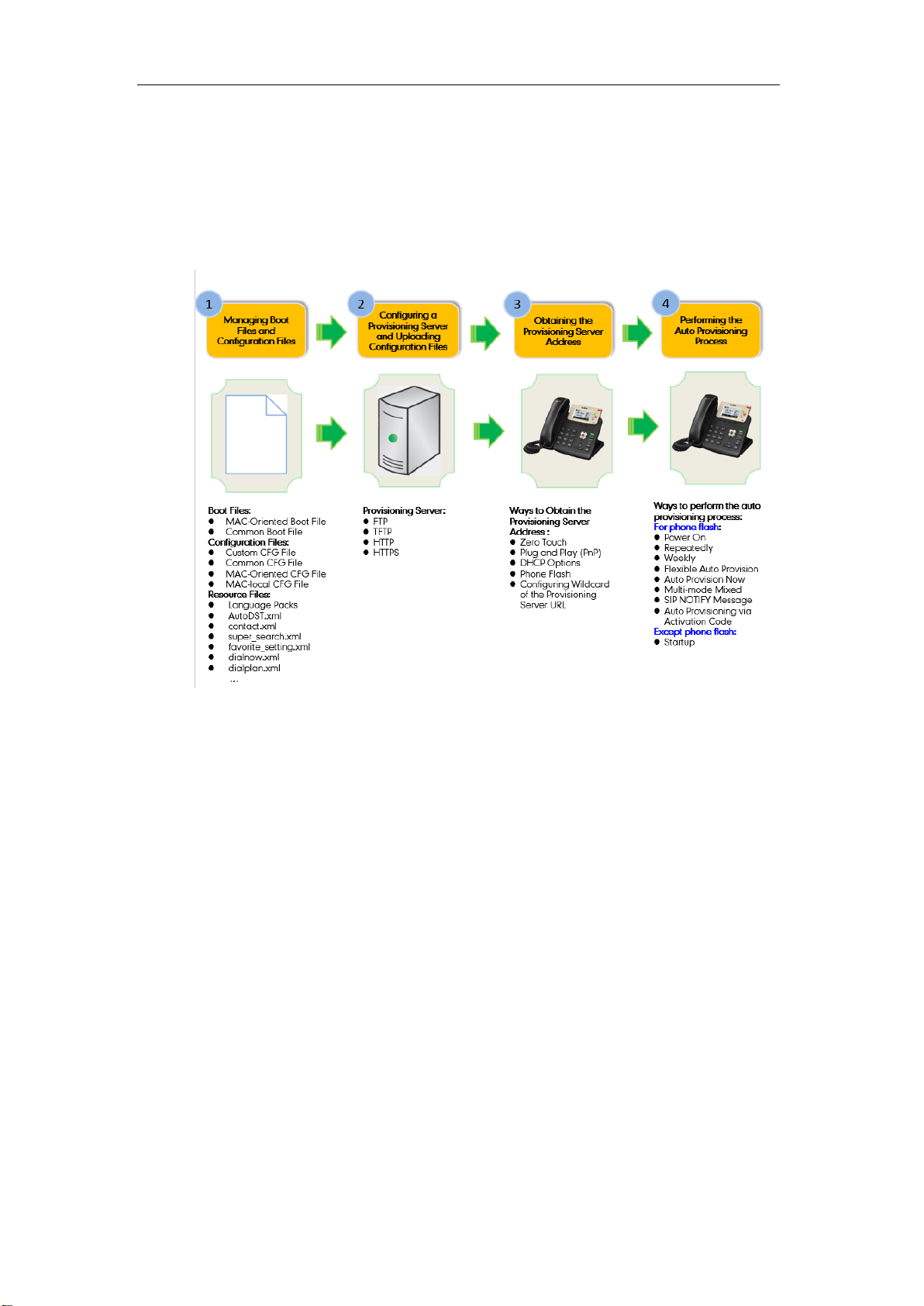
Major Tasks for Auto Provisioning
You need to complete four major tasks to provision Yealink IP phones.
The following figure shows an overview of four major provisioning tasks:
For more information on how to manage boot files, refer to Managing Boot Files.
For more information on how to manage configuration files, refer to Managing Configuration
Files.
For more information on how to manage resource files, refer to Managing Resource Files.
For more information on how to configure a provisioning server, refer to Configuring a
Provisioning Server.
For more information on how to obtain the provisioning server address, refer to Obtaining the
Provisioning Server Address.
For more information on how to perform auto provisioning, refer to Triggering the IP Phone to
Perform Auto Provisioning.
If you are not familiar with auto provisioning on Yealink IP phones, you can refer to An Instance
of Auto Provision Configuration.
Yealink IP Phones Auto Provisioning Guide
12
An Instance of Auto Provision Configuration
This section shows an instance of auto provision configuration.
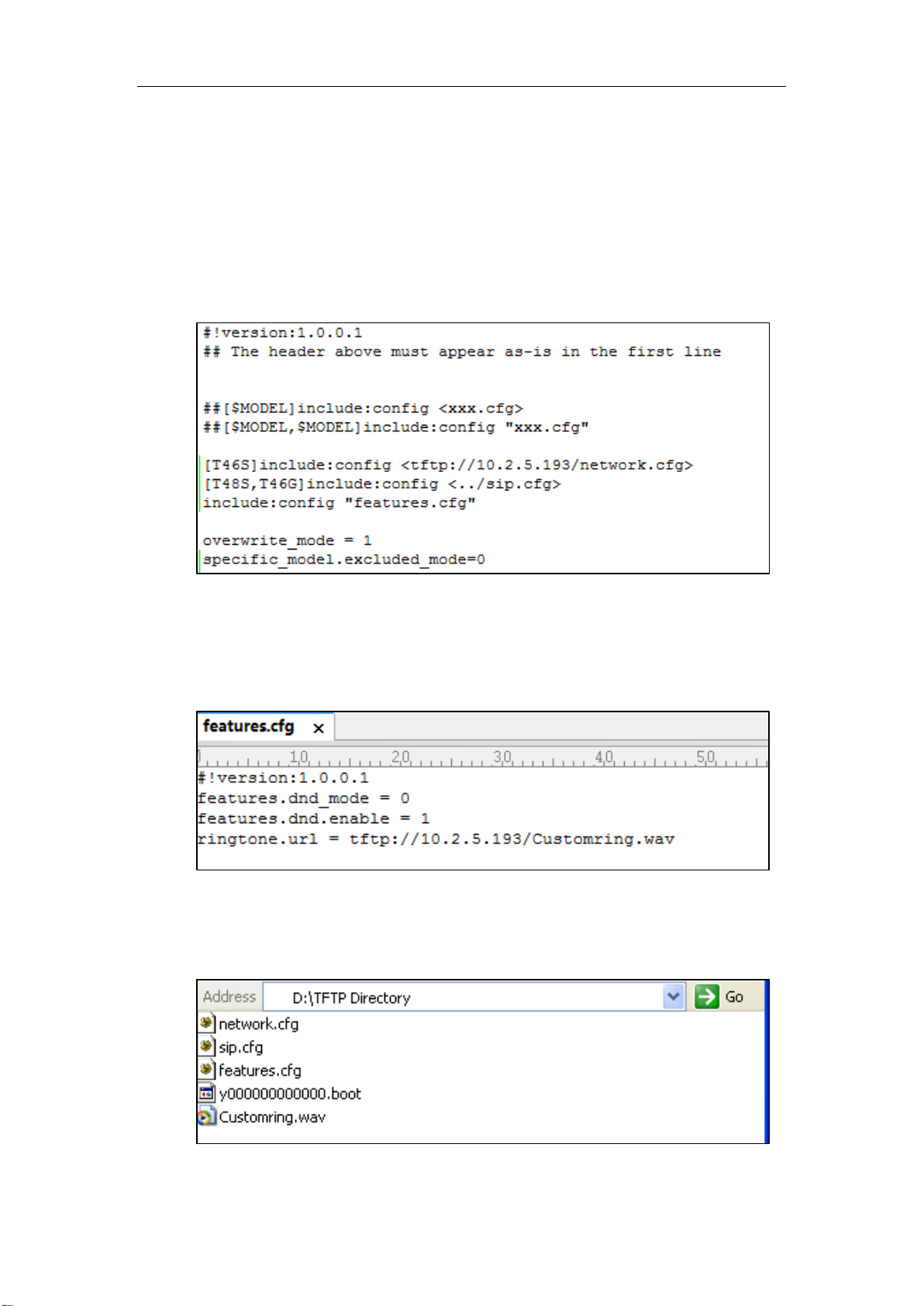
1. Manage boot files.
Specify the desired URL (for example, tftp://10.2.5.193/network.cfg) of the configuration
files in the boot file (for example, y000000000000.boot). For more information, refer to
Managing Boot Files.
2. Manage configuration files.
Add/Edit the desired configuration parameters in the CFG file (for example, features.cfg)
you want the IP phone to download. For more information on how to manage configuration
files, refer to Managing Configuration Files.
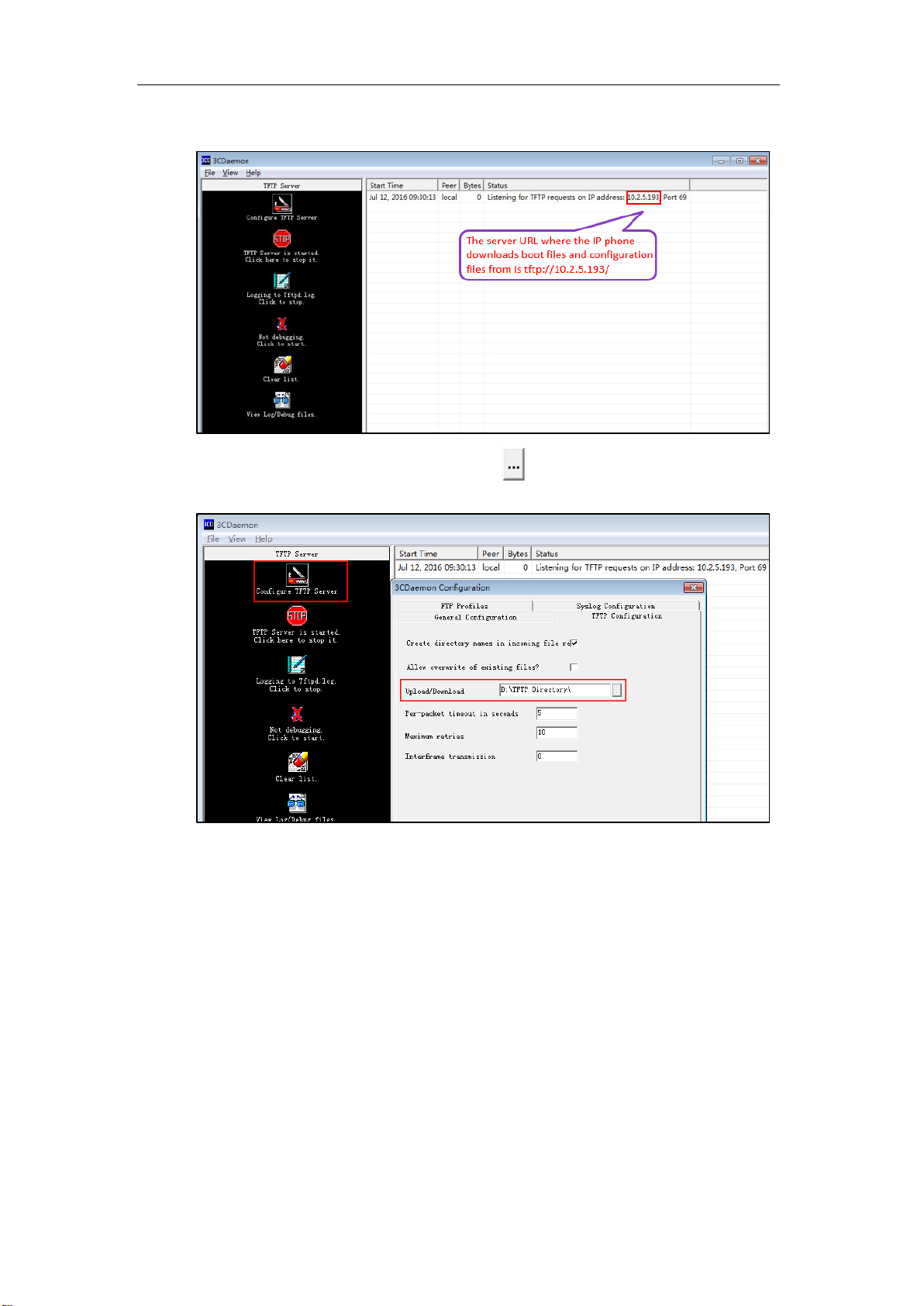
3. Configure the TFTP server.
1) Place boot files, configuration files and resource files to TFTP root directory (for
example, D:\TFTP Directory).
Provisioning Yealink IP Phones
13
2) Start the TFTP server. The IP address of the TFTP server is shown as below:
3) Select Configure TFTP Server. Click the button to locate the TFTP root directory
in your local system.
For more information on how to configure a provisioning server, refer to Configuring a
Provisioning Server.
Yealink IP Phones Auto Provisioning Guide
14
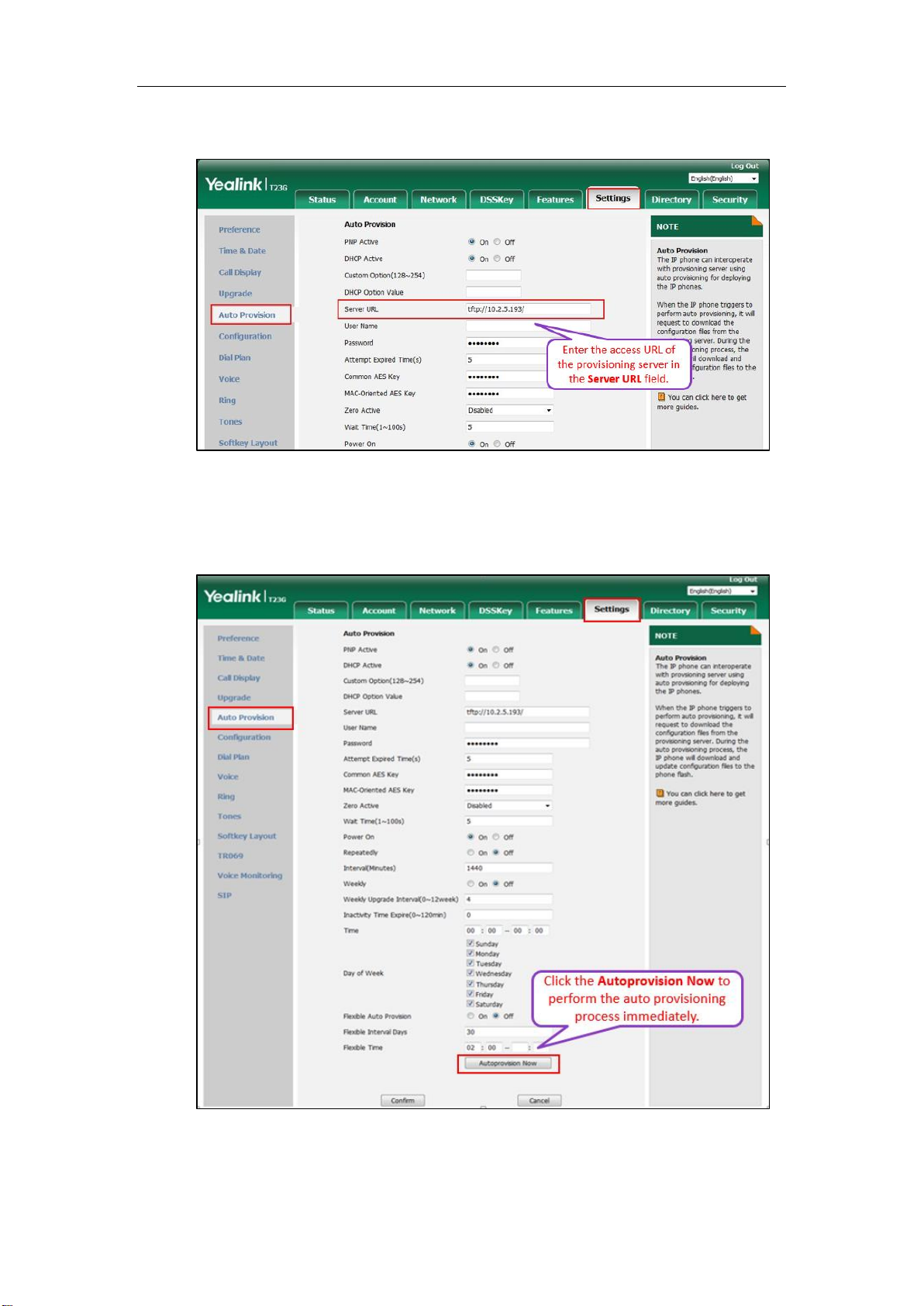
4. Configure the provisioning server address on the IP phone.
For more information on how to obtain the provisioning server address, refer to Obtaining
the Provisioning Server Address.
5. Trigger the IP phone to perform auto provisioning.
For more information on how to trigger the phone to perform auto provisioning, refer to
Triggering the IP Phone to Perform Auto Provisioning.
Managing Boot Files
15
Managing Boot Files
Yealink IP phones can download CFG files referenced in the boot files. Before provisioning, you
may need to edit and customize your boot files.
Yealink supports the following two types of boot files:
⚫ MAC-Oriented boot file (for example, 00156574b150.boot)
⚫ Common boot file (y000000000000.boot)
You can edit the template boot file directly or create a new boot file as required. Open each boot
file with a text editor such as Notepad++.
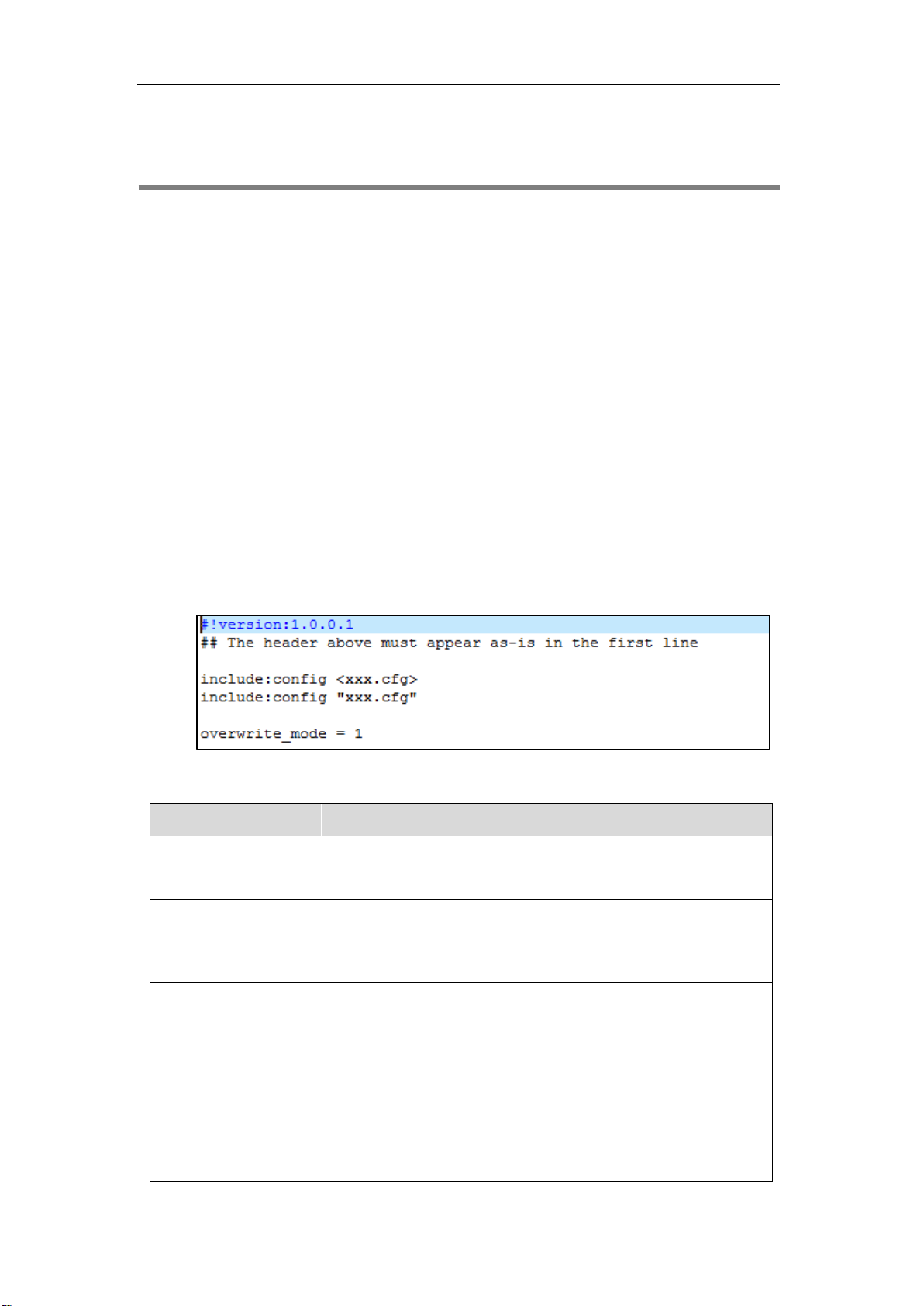
Editing Common Boot File
The common boot file is effective for all phones. It uses a fixed name “y000000000000.boot” as
the file name.
The following figure shows the contents of the common boot file:
The following table lists guidelines you need to know when editing the boot file:
Item
Guidelines
#!version:1.0.0.1
It must be placed in the first line.
Do not edit and delete.
## The header above
must appear as-is in the
first line
The line beginning with “#” is considered to be a comment.
You can use “#” to make any comment in the boot file.
include:config <xxx.cfg>
include:config "xxx.cfg"
1) Each “include” statement can specify a URL where a
configuration file is stored. The configuration file format must be
*.cfg.
2) The URL in <> or “” supports the following two forms:
⚫ Relative URL (relative to the boot file):
For example, sip.cfg, HTTP Directory/sip.cfg
⚫ Absolute URL:
 Loading...
Loading...