Page 1

PROwatt™ 600
Inverter
Owner’s Guide
Page 2

PROwatt 600 Inverter
Owner’s Guide
Page 3

About Xantrex
Xantrex Technology Inc. is a world-leading supplier of advanced power
electronics and controls with products from 50 watt mobile units to 1 MW utilityscale systems for wind, solar, batteries, fuel cells, microturbines, and backup
power applications in both grid-connected and stand-alone systems. Xantrex
products include inverters, battery chargers, programmable power supplies, and
variable speed drives that convert, supply, control, clean, and distribute electrical
power.
Trademarks
PROwatt is a trademark of Xantrex International. Xantrex is a registered
trademark of Xantrex Technology Inc.
Other trademarks, registered trademarks, and product names are the property of
their respective owners and are used herein for identification purposes only.
Notice of Copyright
PROwatt 600 Owner’s Guide © January 2001 Xantrex International. All rights
reserved.
Disclaimer
While every precaution has been taken to ensure the accuracy of the contents of
this guide, Xantrex International assumes no responsibility for errors or
omissions. Note as well that specifications and product functionality may change
without notice.
Date and Revision
January 2001, Revision 1
Part Number
445-0115-01-01
Contact Information
Web: www.xantrex.com
Email: support.prowatt@xantrex.com
Phone: 1-800-670-0707
Fax: 1-800-994-7828
Page 4

About This Guide
Purpose
The PROwatt 600 Owner’s Guide contains information that
enables individuals to install, operate, and troubleshoot the
PROwatt 600 Inverter.
Scope
The guide provides safety guidelines, detailed information
for designing an installation, procedures for installing the
inverter, as well as operating and troubleshooting
information. It does not provide details about particular
brands of batteries. You need to consult individual battery
manufacturers for this information.
Audience
The guide is intended for anyone who needs to install and
operate the PROwatt™ 600 Inverter.
Page 5

About This Guide
Organization
This guide has four chapters and four appendixes.
Chapter 1, “Introduction”, outlines the main performance and
safety features of the PROwatt 600 Inverter. Reading this
chapter will give you a clear understanding of the inverter’s
capabilities.
Chapter 2, “Installation”, outlines the inverter’s main
physical features. This information will give you a good
orientation to the product before you install it. The chapter
then goes on to explain how to plan and complete an effective
installation.
Chapter 3, “Operation”, provides information about turning
on and operating the inverter. Details are provided about how
to read the front panel indicators to monitor the system. The
chapter also provides information about battery charging and
routine maintenance.
Chapter 4, “Troubleshooting”, explains how to identify and
solve problems that can occur with the inverter.
Appendix A, “Specifications”, provides the electrical and
physical specifications.
Appendix B, “Battery Types and Sizes”, provides
background information about battery types as well as
information that will allow you to calculate the size and
number of batteries your system requires.
Appendix C, “Alternators and Charging Systems”, describes
charging system components and explains how to design a
charging system for your installation.
Appendix D,“Product and System Information” , contains the
product’s warranty, explains how to return a product for
service, and describes how to prepare for a call to Xantrex
Customer Service.
iv
Page 6

Conventions Used
The following conventions are used in this guide.
WARNING
Warnings identify conditions that could result in
personal injury or loss of life and appear in this
form.
CAUTION
Cautions identify conditions or practices that could
result in damage to the PROwatt unit or to other
equipment.
About This Guide
Note
:
Notes describe additional information which may
add to your understanding of how to use the inverter.
Related Information
You can find more information about Xantrex
Technology Inc. as well as its products and services at
www.xantrex.com
v
Page 7

vi
Page 8
Important Safety Information
WARNING
Before installing and using your PROwatt
Inverter, read and save these safety instructions.
General Precautions
1. Before installing and using the inverter, read all
appropriate sections of this guide and any cautionary
markings on the inverter and the batteries.
2. Do not operate the inverter if it has received a sharp
blow, been dropped, or otherwise damaged. If the unit is
damaged, see “Warranty” on page 42 and “Return
Material Authorization Policy” on page 43.
3. Do not dismantle the inverter; it contains no user
serviceable parts. Attempting to service the unit yourself
could cause electrical shock or fire.
remain charged after all power is disconnected.
page 43 for instructions on obtaining service.
™
600
Internal capacitors
See
4. To reduce the risk of electrical shock, disconnect both
AC and DC power from the inverter before working on
any circuits connected to the inverter. Turning off the
front panel On/Off will not reduce this risk.
5. Protect the inverter from rain, snow, spray, and bilge
water.
6. To reduce the risk of overheating or fire, keep the
ventilation openings clear, and do not install the inverter
in a zero-clearance compartment.
vii
Page 9

Explosive Gas Precautions
Explosive Gas Precautions
1. Batteries generate explosive gases during normal
operation. Be sure you follow all relevant instructions
exactly before installing or using your inverter.
2. This equipment contains components which tend to
produce arcs or sparks. To prevent fire or explosion, do
not install the inverter in compartments containing
batteries or flammable materials or in locations that
require ignition-protected equipment. This includes any
space containing gasoline-powered machinery, fuel
tanks, as well as joints, fittings, or other connections
between components of the fuel system.
Precautions When Working With Batteries
1. Follow all instructions published by the battery
manufacturer and the manufacturer of the equipment in
which the battery is installed.
2. Make sure the area around the battery is well ventilated.
3. Never smoke or allow a spark or flame near the engine or
battery.
4. Use caution to reduce the risk of dropping a metal tool on
the battery. It could spark or short circuit the battery or
other electrical parts and could cause an explosion.
5. Remove metal items like rings, bracelets, and watches
when working with lead-acid batteries. These batteries
produce a short-circuit current high enough to weld a ring
or the like to metal, and thus cause a severe burn.
6. If you need to remove a battery, always remove the
positive terminal from the battery first. Make sure all
accessories are off so you don’t cause an arc.
viii
Page 10

Precautions For Using Rechargeable Appliances
Precautions For Using Rechargeable
Appliances
Most battery-operated equipment uses a separate charger or
transformer that is plugged into an AC receptacle and
produces a low voltage output. If the label on the AC adapter
or charger states that the adapter or charger produces a low
voltage AC or DC output (less than 30 volts), the PROwatt
can power this charger or adapter safely.
Some rechargers for small nickel-cadmium batteries can be
damaged if connected to the PROwatt 600 Inverter. Do not
use the following with the PROwatt 600 Inverter:
• Small battery-operated appliances like flashlights, razors,
and night lights that can be plugged directly into an AC
receptacle to recharge
• Chargers for battery packs used in hand power tools.
These chargers display a warning label stating that
dangerous voltages are present at the battery terminals
AC Wiring Warning
Do not connect the PROwatt 600 Inverter to AC distribution
wiring.
The PROwatt is designed to be connected directly to standard
electrical and electronic equipment. Do not connect it to
household or recreational vehicle AC distribution wiring. Do
not connect it to any AC load circuit in which the neutral
conductor is connected to ground (earth) or to the negative of
the DC (battery) source. Doing so will destroy the unit.
ix
Page 11

x
Page 12

Contents
General Precautions - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - vii
Explosive Gas Precautions - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - viii
Precautions When Working With Batteries - - - - - - - - - - - - - - viii
Precautions For Using Rechargeable Appliances - - - - - - - - - - - ix
AC Wiring Warning - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ix
1Introduction
Quality Power and Ease of Use - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2
Comprehensive Protection - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2
2 Installation
AC Wiring Warning - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4
Safety Instructions - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4
PROwatt 600 Materials- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4
Front Panel (AC End) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5
Back Panel (DC End) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5
Installation Tools and Materials - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6
Tools - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6
Materials - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6
Planning Your Installation- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 7
Calculating Battery Requirements - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 7
Choosing a Charging System - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 7
Choosing a Location - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 8
Mounting the Inverter- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 9
xi
Page 13

Contents
Connecting the Chassis Ground - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 9
Grounding Locations - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 10
Connecting DC Cables - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 10
Cabling Guidelines - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 10
Cabling Procedure- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 11
3Operation
Turning the Inverter On and Off- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 16
Operating Several Loads at Once - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 16
Turning the Inverter Off Between Charges- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 16
Reading the Front Panel Indicators - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 17
Green POWER LED - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 17
Red FAULT LED - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 17
Operating Limits - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 18
Power Output - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 18
Input Voltage - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 18
Inverter Loads- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 19
Problem Loads - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 19
Trouble Loads - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 19
Battery Charging Frequency - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 20
Routine Maintenance - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 20
4 Troubleshooting
Common Problems - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 22
Buzz in Audio Equipment - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 22
Television Reception - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 22
Troubleshooting Reference - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 23
A
Specifications
Electrical Performance - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 26
Physical - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 26
B
Battery Types and Sizes
Battery Types - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 28
xii
Page 14

Automotive Starting Batteries - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 28
Deep-Cycle Lead-Acid Batteries - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 29
Battery Size - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 29
Estimating Battery Requirements - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 31
Battery Sizing Example - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 32
Battery Sizing Worksheet - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 33
Two Batteries Connected In Parallel- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 34
Battery Tips - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 35
C
Alternators and Charging Systems
Charging System Requirements - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 38
Charging With an Engine Alternator - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 38
Using Your Vehicle’s Standard Engine Alternator - - - - - - - - - 38
Using an Alternator Controller - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 39
Contents
Using a High-Output Alternator - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 39
Charging From AC Power- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 39
Charging From Alternative Energy Sources - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 40
D
Product and System Information
Warranty - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 42
Return Material Authorization Policy - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 43
Return Material Procedure - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 43
Information About Your System - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 45
Index - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 47
xiii
Page 15

xiv
Page 16

1
Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of the
PROwatt™ 600 Inverter! As part of the
PROwatt Inverter family, the PROwatt 600
has been designed to give you quality power,
ease of use, and outstanding reliability.
Please take a few moments to read this
chapter to familiarize yourself with the
PROwatt 600’s main performance and
protection features.
Page 17

Quality Power and Ease of Use
Quality Power and Ease of Use
The PROwatt 600 Inverter is a professional-quality, midrange inverter designed to handle a variety of household and
commercial applications including large screen TVs, VCRs,
computer systems, bread makers, blenders, fans, and small
power tools.
Superior features and rugged durability have been combined
with extreme ease of use:
• The unit is compact, light weight, and easy to install.
• The easy-to-read indicators on the front panel.
• Low standby battery demand means you don’t have to
worry about draining your battery if you leave the
inverter on for a few days. When the inverter is on but is
not powering any loads, the draw on the battery is less
than 300mA.
Comprehensive Protection
The PROwatt 600 Inverter comes equipped with numerous
protection features to guarantee you safe and worry-free
operation:
Low battery alarm
discharged to 10.7V or lower.
Automatic low voltage shutdown feature
from becoming completely discharged if the battery voltage
drops below 10V.
High voltage shutdown feature
input voltage rises to 15V or more.
Over temperature shutdown feature
the temperature rises above an acceptable level.
Alerts you if the battery has become
Protects the inverter if the
Protects the battery
Turns the inverter off if
2
Page 18

2
Installation
Chapter 2 explains how to install the
PROwatt 600 Inverter.
Installing the PROwatt 600 is
straightforward. Here’s a summary of the
five main steps:
• Plan the installation.
• Choose a location.
• Mount the inverter.
• Connect the chassis ground.
• Connect the DC cables.
Remember: the better your planning, the
better the performance you will receive from
the PROwatt 600 Inverter.
3
Page 19
AC Wiring Warning
AC Wiring Warning
WARNING
Do not connect the PROwatt 600 Inverter to AC
distribution wiring.
The PROwatt is designed to be connected directly to standard
electrical and electronic equipment. Do not connect it to
household or recreational vehicle AC distribution wiring. Do
not connect it to any AC load circuit in which the neutral
conductor is connected to ground (earth) or to the negative of
the DC (battery) source. Doing so will destroy the unit.
Safety Instructions
Before you install the PROwatt 600:
• Review the “Important Safety Information” on page vii.
• Read and follow all Warnings and Cautions in this
chapter.
PROwatt 600 Materials
Your PROwatt 600 Inverter package includes:
• 1 PROwatt 600 Inverter
• 1 Owner’s Guide
If either of these items is missing or is unsatisfactory in any
way, please contact Xantrex Customer Service:
Phone:
Fax:
Email:
1-800-670-0707
1-800-994-7828
support.prowatt@xantrex.com
As soon as you unpack your inverter, be sure to record the
product information asked for on page 45. Then take a minute
to familiarize yourself with the front and back panel features.
4
Page 20
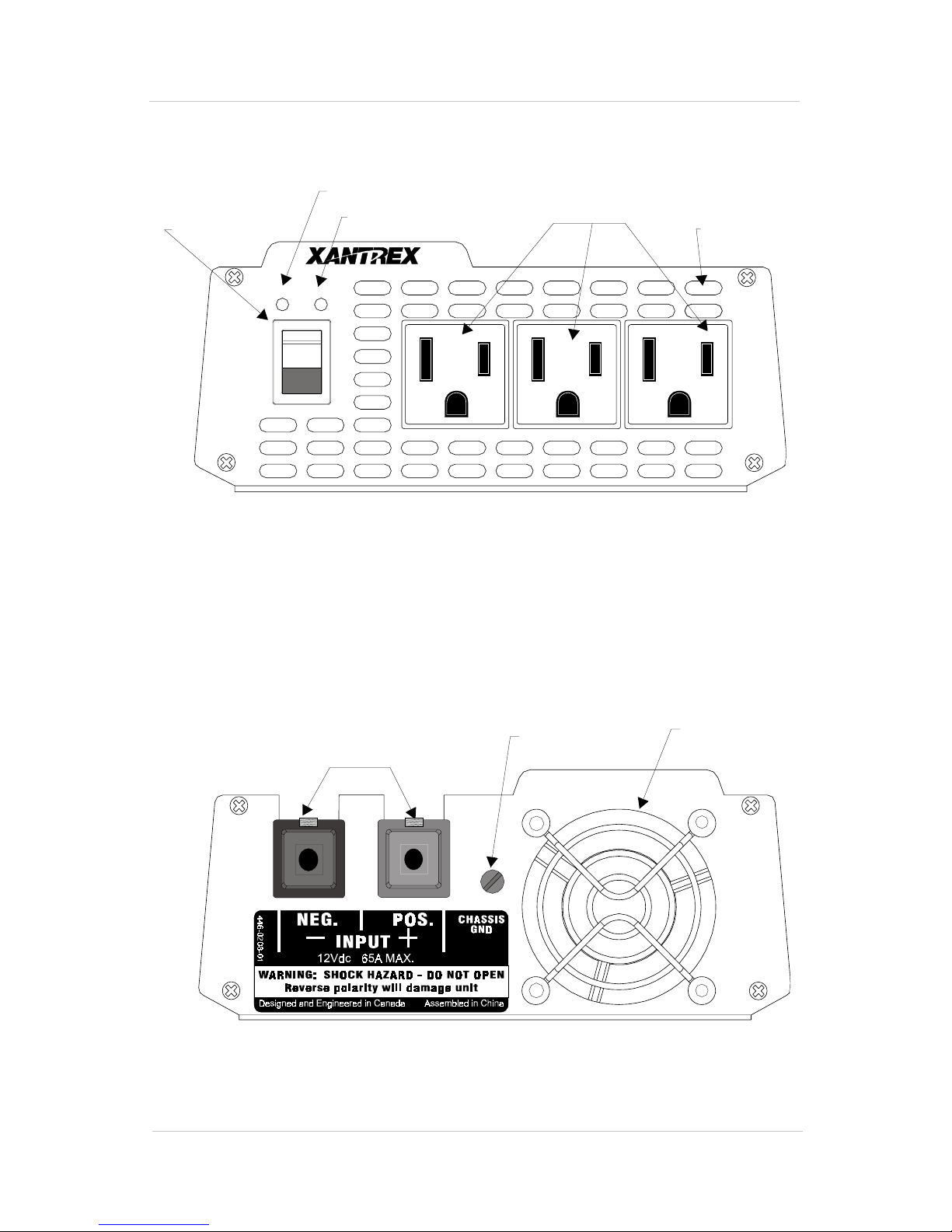
Front Panel (AC End)
Front Panel (AC End)
POWER LED
On/Off Switch
POWER
ON
OFF
FAULT LED
FAULT
Figure 1 Front Panel (AC End)
AC Power Receptacles
Ventilation
Openings
OUTPUT
115Vac
60Hz
Back Panel (DC End)
Negative and Positive
DC Cabling Terminals
Figure 2 Back Panel (DC End)
Chassis Ground
Screw
Ventilation
Openings
5
Page 21

Installation Tools and Materials
Installation Tools and Materials
Tools
❐
Wire stripper
❐
Slot head screwdriver
❐
Wrench(es) for DC terminals
❐
Drill
Materials
❐
4 corrosion-resistant fasteners sized #10 or larger for
mounting the inverter
❐
Copper DC cable sized appropriately for your installation
❐
Lugs and terminals for the DC cables as well as
appropriate tools (e.g. crimping tool). (You may find it
convenient to have the crimp connectors attached by the
company that sells you the cable.)
❐
DC fuse(s) Bussman ANL-80 or a Gould type A3T80
Class T fuse with fuse holder
❐
Appropriately sized copper cable for the chassis ground
❐
Battery isolator
❐
Alternator controller*
❐
High-output alternator*
* Consult Appendix B and Appendix C to determine whether
you need these components.
6
Page 22

Planning Your Installation
Before doing anything else, you need to determine how you
will be using your PROwatt 600 and on the basis of that,
design a power system that will give the best performance.
The more thorough your planning, the better your power
needs will be met. In particular, you need to:
• Calculate your battery requirements
• Choose an effective charging system
Calculating Battery Requirements
Battery type and size strongly affect performance of the
PROwatt 600. Therefore, you must identify the type of loads
your inverter will be powering. Once you know how much
power you will be using, you can determine how much
battery capacity you need. Xantrex recommends that you
purchase as much battery capacity as possible.
Planning Your Installation
Consult Appendix B “Battery Types and Sizes” on page 27
for a detailed explanation of how to determine the appropriate
number and size of batteries for your installation.
CAUTION
The PROwatt 600 must only be connected to a
battery that has a nominal output of 12 volts. It will
not operate when connected to a 6 volt battery and
will be damaged if connected to a 24 volt battery.
Choosing a Charging System
Your charging system must be appropriate for your inverter
installation. This will ensure that power is available when
you need it and that your batteries remain in top condition.
Inadequate charging will degrade system performance, and
the wrong type of charger will reduce battery life.
Consult Appendix C “Alternators and Charging Systems” on
page 37 for information that will explain how to design an
effective charging system.
7
Page 23

Choosing a Location
Choosing a Location
WARNING
The PROwatt 600 contains components that tend to
produce arcs or sparks. To prevent fire or explosion,
do not install the PROwatt in compartments
containing batteries or flammable materials or in
locations that require ignition-protected equipment.
WARNING
To reduce the risk of fire, do not cover or obstruct the
ventilation openings. Do not install the PROwatt 600
in a zero-clearance compartment. Overheating may
result.
The PROwatt 600 Inverter should only be installed in a
location that meets these requirements:
Dry
Cool
Ven ti lat ed
Safe
Close to
battery
Protected
from battery
gases
Do not allow water or other liquids to drop or splash
on the PROwatt 600.
Ambient air temperature should be between 32º F
and 105º F (0º C and 40º C)—the cooler the better
within this range.
Leave at least 2 inches (5 cm) clearance around the
PROwatt 600 for air flow. Ensure that ventilation
openings at the front and rear are not obstructed.
Do not install the inverter in the same compartment
as batteries or in any compartment capable of storing
flammable liquids like gasoline.
DC cables must be shorter than 4 feet (1.2 m) each.
Longer AC wires are preferable to longer DC wires.
Do not mount the inverter where it will be exposed to
battery gases. These are very corrosive, and
prolonged exposure will damage the inverter.
8
Page 24

Mounting the Inverter
To mount the PROwatt 600 Inverter:
1. Turn off the inverter’s On/Off switch.
2. Select an appropriate mounting location and orientation.
The PROwatt must be oriented in one of these two ways:
• Horizontally on a vertical surface. (The ventilation
openings must not point up or down.)
• On or under a horizontal surface
3. Mark the positions of the four mounting screws, and
pilot-drill the mounting holes.
4. Fasten the inverter using corrosion-resistant hardware
sized #10 or larger.
Mounting the Inverter
Connecting the Chassis Ground
WARNING: Electrical Shock Hazard
Never operate the PROwatt 600 without
connecting the chassis to ground. Electrical shock
hazard could result.
This inverter does not provide isolation between
the DC and AC circuits. Therefore the AC line and
neutral are both “hot” relative to battery negative.
The ground pins of the AC output receptacles are
connected to the battery negative as is the chassis
of the inverter.
The PROwatt 600 has a screw terminal labeled
GND
used to connect the inverter’s chassis to the ground. To
connect the chassis to ground, follow the guidelines below.
on the rear panel as shown in Figure 1. This is to be
CHASSIS
9
Page 25

Connecting DC Cables
Grounding Locations
The chassis ground terminal must be connected to a
grounding point, which varies depending on where you
install the PROwatt 600. Follow the guidelines that
correspond to your type of installation.
Vehicle
Connect the
CHASSIS GND
chassis using 8 AWG copper wire (preferably with green/
yellow insulation).
Marine
Connect the
CHASSIS GND
grounding bus or the engine’s negative bus using 6 AWG
copper wire that has insulation rated at 90º C.
Fixed Location
CHASSIS GND
(residential, for example). Connect the
screw to your system’s DC grounding point
using 6 AWG wire. The system’s grounding point will
usually be the AC service entrance grounding point or a
separate ground rod. For a solar PV (photovoltaic)
installation, this is usually the same ground rod used to
ground the PV array.
Connecting DC Cables
screw to the vehicle’s
screw to the boat’s DC
Proper cables and wiring are essential to effective operation
of the PROwatt 600. Because the PROwatt 600 has a low
voltage, high current input, low-resistance wiring between
the battery and the inverter is essential to deliver the
maximum amount of usable energy to your load.
Cabling Guidelines
Deviating from these guidelines will cause excessive voltage
drop or melting of the cable and/or connectors. The inverter
may also shut down or fail to operate some loads.
• Make sure each cable between the inverter and the
battery is no longer than 4 feet (1.2 m).
• Use 4 AWG copper (90º C insulation rating).
10
Page 26

• Do not use aluminum. It has about 1/3 more resistance
than copper cable of the same size, and it is difficult to
make good, low-resistance connections to aluminum.
Cabling Procedure
Follow the procedure given below and consult Figure 3 and
Figure 4 for details that are specific to your installation.
ISO L AT OR
GROUND TO
VEHICLE
CHASSIS
Connecting DC Cables
FROM ALTERNATO R
OR CHARGER
TO DC
LOADS
PROwatt
FUSE O R
CIRCUIT
BREAKER
GROUND TO
VEHICLE
CHASSIS
600
DEEP-CYCLE
FUSE OR
CIRCUIT
BREAKER
AUXILIARY
BATTERY
Figure 3 Installation for Normal Loads
VEHICLE
STARTING
BATTERY
TO VEHICLE
GROUND TO
VEHICLE
CHASSIS
11
Page 27

Connecting DC Cables
FRO M A LTE RNATOR
OR CHARGER
IS OLATO R
TO DC
LOADS
FUSE OR
CIRCUIT
BREA KER
PROwatt
DEEP-CYCLE
DEEP-CYCLE
FUSE OR
CIRCUIT
BREAKER
AUXILIARY
BATTERY
AUXILIARY
BATTERY
GROUND TO
VEHICLE
CHASSIS
600
GROUND TO
VEHICLE
CHASSIS
VEHICLE
STARTING
BATTERY
TO VEHICLE
GROUND TO
VEHICLE
CHASSIS
Figure 4 Installation for Heavy Loads
Cabling Procedure
To connect the DC cables:
1. Cut the cables to the correct length.
2. Strip the appropriate amount of insulation from one end
of each cable and attach the connectors that will join the
cables to the battery, battery isolator switch, or fuse
block. The connectors you use must create a permanent,
low-resistance connection.
12
Page 28

Connecting DC Cables
If you are using crimp connectors, use the tool
recommended by the terminal manufacturer. Make sure
no stray wires protrude from the terminal. (You can also
have the crimp connectors attached by the company that
sells you the cable.)
3. Strip about 1/2 inch (1.25cm) from the ends of the cables
that will be connected to the inverter.
4. Install a fuse and fuse holder in the cable that will be used
for the positive side of the DC circuit. The fuse must be
as close to the battery as possible, must be rated for DC
circuits, rated 80A max, and have a short-circuit interrupt
rating that exceeds the short-circuit current available
from the battery.
Xantrex recommends a Bussman ANL-80 fuse or a
Gould type A3T80 Class T fuse, or equivalent for
installations requiring a “code fuse”.
5. Insert the stripped ends of the cables into the cabling
terminals on the rear of the inverter and tighten the
screws securely. The red terminal is positive (+); the
black terminal is negative (–). See Figure 2.
6. Attach the connector on the negative cable to the
negative battery terminal. Make a secure connection.
Loose connectors cause excessive voltage drop and may
cause overheated wires and melted insulation.
CAUTION: Reverse Polarity
Power connections to the PROwatt 600 must be
positive to positive and negative to negative.
A reverse polarity connection (positive to negative)
will blow a fuse in the inverter and may cause
permanent damage. Your warranty does not cover
damage caused by a reverse polarity connection.
13
Page 29

Connecting DC Cables
7. Before proceeding, make sure that the cable you have just
installed connects the negative terminal of the inverter to
the negative terminal of the battery.
8. Connect the cable from the positive (red) terminal of the
PROwatt 600 to the positive terminal of the battery.
This is the last cable connection. A spark is normal when
you make it.
9. If you have installed a battery selector switch, use it to
select one of the batteries.
WARNING: Explosion or Fire
Do not complete the next step if flammable fumes
are present. Explosion or fire may result.
Thoroughly ventilate the battery compartment
before making this connection.
10. Turn on the inverter’s On/Off switch.
11. Check the inverter’s front panel. The
should be on. If it is not, or if the
POWER
FAULT
indicator is on,
check your battery and the connections to the inverter.
indicator
14
Page 30

3
Operation
Chapter 3
PROwatt 600 Inverter efficiently.
Specifically, this chapter:
• Explains how to turn the inverter on
• Describes operating limits
• Provides information about routine
maintenance
• Discusses optimal battery charging
frequency
tells you how to operate the
15
Page 31

Turning the Inverter On and Off
Turning the Inverter On and Off
The On/Off switch on the front panel turns the control circuit
in the PROwatt 600 on and off.
To turn the inverter on or off:
• Turn the On/Off switch or off.
CAUTION
The inverter’s On/Off switch does not disconnect
power from the PROwatt.
When the switch is Off, the inverter draws no current from
the battery.
Operating Several Loads at Once
If you are going to operate several loads from the
PROwatt 600, turn them on separately after you have turned
the inverter on. This will ensure that the inverter does not
have to deliver the starting current for all the loads at once.
Turning the Inverter Off Between Charges
When the switch is on but no power is being supplied to a
load, the inverter draws less than 300 mA from the battery.
This is a low current draw. It would take more than a week to
discharge a 100 Ah battery at this current, so you don’t have
to worry about excessive drain on your battery if you leave
the inverter switched on for a few days.
If you are not planning to recharge your battery within a week
or so, turn the inverter off.
16
Page 32

Reading the Front Panel Indicators
Reading the Front Panel Indicators
Green POWER LED
The
POWER
power and the inverter is switched On.
Red FAULT LED
The
FAULT
Condition Cause / Action
Over Temperature
Shutdown
LED is on when the inverter is connected to DC
LED comes on for one of the following reasons:
The PROwatt 600 has overheated and shut
down. The inverter may have overheated
because it was operated at power levels
above its 600W continuous output rating or
because it was installed in a location that
does not allow it to dissipate heat properly.
Turn the inverter off and then back on after
it has cooled down.
Note:
any loads, and leave the switch on to keep
the fan running.
To cool the inverter quickly, remove
Overload Shutdown A severe overload has caused the
PROwatt 600 to shut down.
Turn it off for 4–5 seconds, correct the fault
condition, and turn it back on. Do not turn
the inverter on again unless you have
corrected the fault condition (removed the
load or unplugged it).
Low Voltage
Shutdown
High Voltage
Shutdown
The supply voltage (battery) has dropped
below 10 V.
The supply voltage (battery) has exceeded
15 V.
See “Troubleshooting Reference” on page 23 for further
details about the
FAULT
LED.
17
Page 33

Operating Limits
Operating Limits
Power Output
The PROwatt 600 Inverter will deliver 600W or 5A
continuously. This wattage rating applies to resistive loads
such as incandescent lights while the current rating applies to
reactive loads such as motors.
Input Voltage
The input voltage limits are shown in the following table.
Operating
Condition Voltage Range Comment
Normal 10 V–15 V
Peak Performance 12 V–14 V
Low Voltage Alarm At or below 10.7 V The audible low battery alarm sounds
Low Voltage Shut
Down
High Voltage Shut
Down
FAULT
and
Less than 10 V The inverter shuts down to protect the
battery from being over-discharged.
It will not restart unless the input
voltage exceeds 10 V and the unit is
manually reset. You manually reset
the unit by turning it off for 4–5
seconds and then turning it back on.
At or above 15 V The inverter shuts down to protect
itself from excessive input voltage.
FAULT
The
Note:
incorporates over-voltage protection,
it can still be damaged if input
voltage exceeds 16 V.
indicator comes on.
indicator comes on.
Although the PROwatt 600
18
The unit will not restart unless the
input voltage is less than 15 V and the
unit is manually reset. You manually
reset the unit by turning it off for 4–5
seconds and then turning it back on.
Page 34

Inverter Loads
The PROwatt 600 will operate most AC loads within its
power rating (600 watts / 5 amps). However, some appliances
and equipment may be difficult to operate, and other
appliances may actually be damaged if you try to operate
them with the PROwatt 600. Please read “Problem Loads”
and “Trouble Loads” carefully.
Problem Loads
Som e indu ction m otors used in freezers, pum ps, an d other
motor-operated equipm ent need high surge currents to start.
The PROwatt 600 may not be able to start some of these
m otors even though their rated current draw is w ithin the
PR O w att’s lim its. The P R O w att 600 w ill norm ally start
single-phase induction motors rated at 1/4 horsepower or less.
Inverter Loads
Trouble Loads
Some appliances, including the types listed below, may be
damaged if they are connected to the PROwatt 600:
• Electronics that modulate RF (radio frequency) signals
on the AC line will not work and may be damaged.
• Speed controllers found in some fans, kitchen appliances,
and other loads may be damaged.
• Some rechargers for small nickel-cadmium batteries can
be damaged if connected to the PROwatt 600. See
“Precautions For Using Rechargeable Appliances” on
page ix for further details.
CAUTION
Some equipment may be damaged by the
PROwatt 600’s quasi-square wave output.
If you are unsure about powering any device with the
PROwatt 600, contact the manufacturer of the device.
19
Page 35

Battery Charging Frequency
Battery Charging Frequency
When possible, recharge your batteries when they are about
50% discharged or earlier. This will give you a much longer
battery cycle life than recharging when the batteries are
almost completely discharged.
Routine Maintenance
Minimal maintenance is required to keep your PROwatt 600
operating properly. Periodically you should:
• Clean the exterior of the unit with a damp cloth to
prevent the accumulation of dust and dirt
• Tighten the screws on the DC input terminals
20
Page 36

4
Troubleshooting
Chapter 4
most problems that can occur with the
PROwatt 600 Inverter.
If a problem occurs, please review this
chapter before contacting Xantrex Customer
Service.
If you cannot solve a problem and need to
contact Xantrex, record the information that
is asked for in
System” on page 4545
Customer Service Representatives give you
better service.
will help you identify the source of
“Information About Your
. This will help our
21
Page 37

Common Problems
Common Problems
WARNING
Do not dismantle the PROwatt 600 Inverter. It does
not contain any user-serviceable parts. Attempting
to service the unit yourself could result in an
electrical shock or burn.
Buzz in Audio Equipment
Some inexpensive stereo systems emit a buzzing noise from
their loudspeakers when operated from the PROwatt 600.
This occurs because the power supply in the audio system
does not adequately filter the modified sine wave produced
by the PROwatt. The only solution is to use a sound system
that has a higher quality power supply.
Television Reception
When the PROwatt 600 is operating, it can interfere with
television reception on some channels. If interference occurs,
try the following:
1. Make sure the chassis ground screw on the rear of the
PROwatt is solidly connected to the ground system of
your vehicle, boat, or home.
2. Make sure that the television antenna provides an
adequate (“snow-free”) signal and that you are using
good quality cable between the antenna and the
television.
3. Keep the cables between the battery and the PROwatt as
short as possible and twist them together with two to
three twists per foot. (This minimizes radiated
interference from the cables.)
4. Move the television as far away from the PROwatt as
possible.
5. Do not operate high power loads with the PROwatt while
the television is on.
22
Page 38

Troubleshooting Reference
Troubleshooting Reference
Problem Possible Cause Solution
Low output voltage
(96 Vac–104 Vac)
Load runs for a few
seconds and then
FAULT
indicator lights.
No output voltage, alarm
sounding, and
FAULT
indicator on.
No output voltage;
neither indicator on.
You are using a
voltmeter that cannot
Use a true RMS reading
voltmeter.
accurately read the
RMS voltage of a
modified sine wave.
Overload Reduce the load.
Low input voltage Recharge battery; check
connections and cable.
The inverter is off.
No power to the
inverter.
Inverter fuse open.
Turn the inverter on.
Check wiring to inverter.
Have a qualified technician
check and replace the fuse
if necessary.
Reverse DC polarity.
Have a service technician
check and replace the fuse,
making sure to observe
correct polarity.
No output voltage and
FAULT
indicator is on.
Low battery alarm stays
on; load ran for short
time.
No output voltage;
FAULT
indicator on;
load exceeds 600 W/5 A
output. Unit hot to touch.
No output voltage and
FAULT
indicator is on.
High input voltage. Make sure the PROwatt is
connected to a 12 V battery.
Check voltage regulation of
the charging system.
Poor DC wiring; poor
battery condition.
Use proper cable and make
solid connections. Install a
new battery.
Thermal shutdown. Allow the unit to cool off.
Reduce the load if
continuous operation is
required.
Improve ventilation. Make
sure ventilation openings
are not obstructed. Reduce
ambient temperature.
Short circuit.
Check AC wiring for short
circuit.
Very high power load.
Remove the load.
23
Page 39

24
Page 40

A
Specifications
Appendix A contains electrical and physical
specifications for the PROwatt 600 Inverter.
25
Page 41

Electrical Performance
Electrical Performance
Output power at 20º C ambient
and 12 Vdc input:
• Continuous power
• Surge power
Output voltage 115 Vac RMS ±10%
Output waveform Modified sine wave (quasi-
Output frequency 60 Hz ±4 Hz
Input voltage 10 Vdc–15 Vdc
Low battery alarm Audible, 10.7 V
Low battery shutdown 10 V
600 W
1200 W
square wave)
High battery shutdown 15 V
Optimum efficiency 90%
No load current draw ≤0.3 A
Physical
Length 11” (28 cm)
Width 6.25” (16 cm)
Height 2.5” (6.5 cm)
Weight 4.1lb. (2 kg)
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
26
Page 42

B
Battery Types
and Sizes
The batteries you use strongly affect the
performance of the PROwatt 600 Inverter. It
is important to connect the inverter to the
correct size and type of battery.
The information in Appendix B will help
you select, connect, and maintain batteries
that are most appropriate for your
application.
27
Page 43

Battery Types
Battery Types
Automotive Starting Batteries
Purpose
The lead-acid battery you are most familiar with is probably
the starting battery in your automobile. An automotive
starting battery is designed to deliver a large amount of
current for a short period of time (so it can start your engine).
Only a small portion of the battery’s capacity is used to start
the engine, and it is quickly recharged by the running engine.
This type of battery is not designed for repeated cycles where
the battery is almost completely discharged and then
recharged. If it is used in this kind of deep discharge service,
it will wear out rapidly.
Light Loads
If your installation uses relatively low power loads (that is,
power consumption of 300 W or less) and relatively short
operating times before recharging (one hour or less), you can
connect the PROwatt 600 directly to the vehicle starting
battery. See Figure 5.
28
GROUND TO
VEHICLE
CHAS SIS
VEHICLE
STARTING
BATTERY
FROM
ALTERNATOR
PROwatt
GROUND TO
VEHICLE
CHAS SIS
600
FUSE OR
CIRCUIT
BREA KER
Figure 5 Battery Connection for Light Loads
Page 44

Deep-Cycle Lead-Acid Batteries
Purpose
Deep-cycle lead-acid batteries are designed for deep
discharge service where they will be repeatedly discharged
and recharged. They are marketed for use in recreational
vehicles, boats, and electric golf carts—so you may see them
referred to as RV batteries, marine batteries, or golf cart
batteries.
Average and Heavier Loads
For most applications of the PROwatt 600 Inverter, Xantrex
recommends that you use one or more deep-cycle batteries
that are separated from the vehicle’s starting battery by a
battery isolator.
A battery isolator is a solid-state electronic circuit that allows
equipment to be operated from an auxiliary battery without
danger of discharging the vehicle’s starting battery. During
vehicle operation, the battery isolator automatically directs
the charge from the alternator to the battery requiring the
charge. Figure 6 shows a battery isolator.
Battery Size
Battery isolators are available at marine and RV dealers and
most auto parts stores.
Battery Size
CAUTION
The PROwatt 600 must only be connected to
batteries with a nominal output voltage of 12 volts.
The PROwatt 600 will not operate from a 6 volt
battery and will be damaged if connected to a 24
volt battery.
Importance of Battery Size
Battery size or capacity is as important as the battery type
you use.
29
Page 45

Battery Size
Battery Capacity Standards
A number of different standards are used to rate battery
energy storage capacity. Automotive and marine starting
batteries are normally rated in cranking amps. This is not a
relevant rating for continuous loads like an inverter. Deepcycle batteries use a more suitable rating system, either
“amp-hours” (“Ah”) or “reserve capacity” in minutes.
Battery Reserve Capacity
Battery reserve capacity is a
measure of how long a battery can deliver a certain amount of
current—usually 25 amps. For example, a battery with a
reserve capacity of 180 minutes can deliver 25 amps for 180
minutes before it is completely discharged.
Amp-hour (Ah) Capacity
Amp-hour capacity is a measure
of how many amps a battery can deliver for a specified length
of time—usually 20 hours. For example, a typical marine or
RV battery rated for 100Ah can deliver 5 amps for 20 hours
(5 A x 20 hours = 100 Ah).
Actual Battery Capacity
Actual battery capacity decreases
as discharge current increases. A battery rated at 100Ah
which can deliver 5 A for 20 hours may deliver 20 A for only
4 hours, resulting in an actual capacity of 80 Ah. For this
reason, it is difficult to compare rated Ah capacity with
battery reserve capacity. For example, a battery with a reserve
capacity of 180 minutes has the following calculated Ah
capacity:
180 minutes
However its actual Ah rating will be closer to 100 because it
is rated at the discharge current required to get 20 hours of
operation (about 5 A).
To calculate the battery capacity you require, read
“Estimating Battery Requirements” on page 31 and “Battery
Sizing Example” on page 32, and then complete the “Battery
Sizing Worksheet” on page 33.
30
60 = 3 hours x 25 A = 75 Ah
÷
Page 46

Estimating Battery Requirements
Estimating Battery Requirements
To determine the battery capacity you require:
1. Determine how many watts are consumed by each
appliance that you will be operating from the
PROwatt 600. You can normally find this on a label on
the product. If only the current draw is given, multiply it
by 115 to get the power consumption in watts.
2. Estimate how many hours each appliance will be
operating each day.
3. Calculate the daily watt-hours needed for each appliance.
4. Add the total number of watt-hours needed for all the
appliances and multiply it by the number of days between
charges.
5. Divide the total watt-hours of AC load between charges
by 10. This gives the battery Ah used between charges.
6. Double the total Ah used between charges to get the
recommended battery size in Ah.
See the battery sizing example that follows.
31
Page 47

Battery Sizing Example
Battery Sizing Example
This example illustrates a typical calculation, assuming an
opportunity to charge the batteries every three days.
Daily watt-hours
needed for this
(A) Power
Appliance
TV & VCR 115 W 3 hours 345 Wh
Sewing machine 150 W 1 hour 150 Wh
Bread maker 600 W 1 1/2 hour 900 Wh
Blender 300 W 15 min = 1/4 hour 75 Wh
Consumption
Total Daily watt-hours of AC load 1470 Wh
(B) Operating
Time per Day
appliance
(= A x B)
x Number of Days between charges 3
= Total watt-hours of AC load between charges 4410 Wh
Battery Ah used between charges (divide by 10) 441 Ah
Recommended Battery Bank Size in Ah (multiply by 2) 882 Ah
This example illustrates how quickly your battery needs can
escalate. To reduce the required battery size, you can
conserve energy by eliminating or reducing the use of some
loads or re-charge more frequently.
When sizing your battery, resist the temptation to skip the last
step of this calculation (multiplying by 2). More capacity is
better since you will have more reserve capacity, be better
able to handle large loads and surge loads, and your battery
won't be discharged as deeply. Battery life is directly
dependent on how deeply the battery is discharged. The
deeper the discharge, the shorter the battery life.
32
Page 48

Battery Sizing Worksheet
Use the following worksheet to calculate your battery needs.
To ensure sufficient battery capacity, be generous when
estimating the operating time per day for each of the loads
you will run.
(A)
Appliance
Power
Consumption
Operating Time
per day
W hours Wh
W hours Wh
W hours Wh
(B)
Battery Sizing Worksheet
Daily watt-
hours needed
for this
appliance
(= A x B)
W hours Wh
W hours Wh
W hours Wh
W hours Wh
W hours Wh
Total Daily watt-hours of AC load Wh
x Number of Days between charges
= Total watt-hours of AC load between charges Wh
Battery Ah used between charges (divide by 10) Ah
Recommended Battery Bank Size in Ah (multiply by 2) Ah
As your power requirements increase, you may need to use
more than one battery to obtain sufficient capacity. Read
“Two Batteries Connected In Parallel” to determine whether
two batteries are appropriate for the applications you intend
to power.
33
Page 49

Two Batteries Connected In Parallel
Two Batteries Connected In Parallel
Two identical batteries can be connected positive (+) to
positive (+) and negative (–) to negative (–) in a parallel
system. A parallel system doubles capacity and maintains the
voltage of a single battery. Figure 6 shows two batteries
connected in parallel.
CAUTION
Do not make a parallel connection between
batteries made by different manufacturers,
different types of batteries, or batteries that have
different Ah ratings. Decreased battery life and
improper charging will result.
Do not connect an old battery to a new one.
TO DC
LOADS
FUSE OR
CIRCUIT
BREAKE R
PROwatt
DEEP-CYCLE
AUXILIARY
DEEP-CYCLE
AUXILIARY
FUSE OR
CIRCUIT
BREAKER
BATTERY
BATTERY
GROUND TO
VEHICLE
CHASSIS
600
IS OL ATO R
GROUND TO
VEHICLE
CHASSIS
FROM ALTERN ATOR
OR CHARGER
VEHICLE
STARTING
BATTERY
TO VEH ICLE
GROUND TO
VEHICLE
CHASSIS
Figure 6 Two Batteries Connected in Parallel
34
Page 50

Battery Tips
Battery Tips
WARNING
Review “Precautions When Working With
Batteries” on page viii before you work with the
batteries in your system.
Explosive/Corrosive Gases
Lead-acid batteries may emit
hydrogen, oxygen, and sulfuric acid fumes when recharging.
To reduce the risk of explosion:
• Vent the battery compartment to prevent the
accumulation of gases.
• Do not install electronic or electrical equipment in the
battery compartment.
• Do not smoke or use an open flame when working
around batteries.
Temperature Sensitivity
The capacity of lead-acid batteries
is temperature sensitive. Battery capacity is rated at 77º F
(25º C). At 0º F (–20º C), the Ah capacity is about half the
rated capacity. Temperature should be considered when you
design your system.
Low Temperatures
If extremely low temperatures are
expected where the inverter is going to be located, you should
consider a heated equipment room. If the system is located in
an unheated space, an insulated battery enclosure is
recommended.
High Temperatures
from high temperatures. These can be caused by high
ambient temperatures, solar heating of the battery enclosure,
or heat released by a nearby engine or generator. High battery
temperature results in short battery life and should be avoided
by ventilating the enclosure and reducing the external heat
source by shading and insulation.
The batteries should also be protected
35
Page 51

Battery Tips
Discharged Batteries
Do not leave batteries in a discharged
state for more than a day or two. They will undergo a
chemical process (sulfation) that can permanently damage the
battery. As well, batteries self-discharge over a period of
three to six months, so they should be recharged periodically
even if they are not being used.
Electrolyte Level
If your batteries are not the “maintenancefree” type, check the electrolyte level at least once a month.
Excessive fluid loss is a sign of overcharging. Replenish the
electrolyte using distilled water only.
Battery Connections
Connections to battery posts must be
made with permanent connectors that provide a reliable, lowresistance connection. Do not use alligator clips. Clean the
connections regularly and prevent corrosion by using a
protective spray coating or vaseline.
Battery State of Charge
You can measure battery state of
charge with a hydrometer or, more easily, with a voltmeter.
Use a digital voltmeter than can display tenths or hundredths
of a volt when measuring 10 to 30 volts. Make your
measurements when the battery has not been charged or
discharged for several hours. For a deep-cycle battery at
77º F (25º C), use the following table:
36
Battery Voltage State of Charge
12.7–13.0 100%
12.5–12.6 80%
12.3–12.4 60%
12.1–12.2 40%
11.9–12.0 20%
Page 52

C
Alternators and
Charging
Systems
A good charging system is important for the
health of your batteries. Poor recharging
methods can quickly damage them.
Appendix C provides guidelines for
recharging batteries from an alternator, from
AC power, and from alternate energy
sources.
37
Page 53

Charging System Requirements
Charging System Requirements
Your charging system should be capable of delivering a
charging current equal to 10–25% of the amp-hour capacity
of your battery. For example, if you have a 200 Ah battery,
the charging system should be able to deliver 50 amps. The
charging system must also be able to charge each 12 volt
battery up to approximately 14.4 V and then drop back to a
“float” voltage of 13.5–14 V (or shut off).
CAUTION
Never operate the PROwatt 600 directly from an
alternator. To work properly the PROwatt must be
connected to a battery or a well-regulated, highcurrent DC power supply.
Charging With an Engine Alternator
The following information will let you determine whether
your vehicle’s standard alternator will be adequate by itself,
whether you should install an alternator controller, or whether
you need a high-output alternator.
Using Your Vehicle’s Standard Engine Alternator
A typical engine alternator (12 volts) may not be able to meet
these requirements if your system uses large capacity
batteries. Alternators are typically rated for the current they
can deliver when they are cold. In use, alternators heat up,
and their output current capability drops by as much as 25%.
Therefore, standard alternators with ratings of 40–105 A will
only deliver a maximum of 30–80 A in actual use and will
deliver even less as battery voltage rises. Many alternators
cannot produce more than 13.6 V when they are hot. As a
result, a standard alternator may not be able to charge a large
battery quickly and completely.
Two solutions are to install an alternator controller or to
install a high-output alternator.
38
Page 54

Using an Alternator Controller
If your regular alternator is inadequate by itself, you can
install an alternator controller that will bypass the voltage
regulator and boost the alternator’s output voltage during
charging. This will increase the alternator’s charging rate at
higher battery voltages and ensure more rapid and complete
charging. Alternator controllers are available from marine
product dealers.
Using a High-Output Alternator
Heavy-duty alternators rated from 100–140A can replace
standard alternators and produce the higher current and
voltage required to charge multiple battery systems. They are
available from RV and marine dealers as well as auto parts
suppliers.
Charging From AC Power
Charging From AC Power
When recharging from AC power, use a good quality marine
battery charger or RV converter that meets the requirements
outlined in “Charging System Requirements” on page 38. For
information about battery chargers manufactured by Xantrex,
see the Xantrex web site at
Do not use chargers intended for occasional recharging of
automotive starting batteries. These chargers are not intended
for continuous use.
www.xantrex.com
39
Page 55

Charging From Alternative Energy Sources
Charging From Alternative Energy Sources
Your batteries can also be recharged from alternative energy
sources such as solar panels, wind, or hydro systems. Make
sure you use the appropriate battery charge controller for
your particular energy source.
CAUTION
Never operate the PROwatt 600 Inverter directly from
an energy source such as a solar panel. The PROw att
must be connected to a battery or a well-regulated, highcurrent DC power supply to work properly.
40
Page 56

D
Product and
System
Information
Appendix D contains the warranty for your
PROwatt 600 Inverter as well as instructions
for returning the product for servicing.
Appendix D also has a place where you can
record information about your system in case
you need to contact Customer Service.
41
Page 57

Warranty
Warranty
What does this warranty cover?
Xantrex manufactures its
products from parts and components that are new or
equivalent to new, in accordance with industry-standard
practices. This warranty covers any defects in workmanship
or materials.
How long does the coverage last?
This warranty lasts for
twelve months from the date of purchase. Implied warranties
of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose are
limited to twelve months from the date of purchase. Some
jurisdictions do not allow limitations on how long an implied
warranty lasts, so the above limitation may not apply to you.
What does this warranty not cover?
This warranty will not
apply where the product has been misused, neglected,
improperly installed, physically damaged or altered, either
internally or externally, or damaged from improper use or use
in an unsuitable environment. Xantrex does not warrant
uninterrupted operation of its products. Xantrex shall not be
liable for damages, whether direct, incidental, special, or
consequential, or economic loss even though caused by the
negligence or fault of Xantrex. Some jurisdictions do not
allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or
consequential damages, so the above limitation or exclusion
may not apply to you.
What will Xantrex do?
replace the defective product free of charge. Xantrex will, at
its own option, use new and/or reconditioned parts made by
various manufacturers in performing warranty repair and
building replacement products. If Xantrex repairs or replaces
a product, its warranty term is not extended. Xantrex owns all
parts removed from repaired products.
How do you get service?
proof of purchase must be provided and the product must not
be disassembled or modified without prior authorization by
Xantrex. If your product requires warranty service, please
return it to the place of purchase along with a copy of your
42
Xantrex will, at its option, repair or
To qualify for the warranty, dated
Page 58

Return Material Authorization Policy
dated proof of purchase. If you are unable to contact your
merchant, or the merchant is unable to provide service,
contact Xantrex directly at:
Phone:
Fax:
Email:
1-800-670-0707
1-800-994-7828
support.prowatt@xantrex.com
Return Material Authorization Policy
You must obtain a Return Material Authorization (RMA)
number from Xantrex before returning a product directly to
Xantrex. Products returned without an RMA number or
shipped collect will be refused. When you contact Xantrex to
obtain service, be prepared to supply the serial number of
your product and its date of purchase as well as information
about the installation and use of the unit. Record this
information in “Information About Your System” on page 45
of this guide.
Return Material Procedure
If you are returning a product from the USA or Canada,
follow this procedure:
1. Obtain an RMA number and a shipping address from
Xantrex.
2. Package the unit safely, preferably using the original box
and packing materials. Include the following:
• The RMA number
• A copy of your dated proof of purchase
• A return address where the repaired unit can be shipped
• A contact telephone number
• A brief description of the problem
3. Ship the unit freight prepaid to the address provided in
step 1. Collect shipments will be refused.
43
Page 59

Return Material Procedure
How do other laws apply?
This warranty gives you specific
legal rights, and you may also have other rights which vary
from jurisdiction to jurisdiction.
For our Canadian customers:
When used herein “implied
warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular
purpose” includes all warranties and conditions, express or
implied, statutory or otherwise, including without limitation
implied warranties and conditions of merchantability and
fitness for a particular purpose.
44
Page 60

Information About Your System
Information About Your System
As soon as you open your PROwatt 600 Inverter package,
record the following information and be sure to keep your
proof of purchase.
❐
Model Number
(on top of unit)
❐
Serial Number
(on bottom of unit)
❐
Purchased From
❐
Purchase Date
If you need to contact Customer Service, please record the
following details before calling. This information will help
our representatives give you better service.
________________________
________________________
________________________
________________________
❐
Type of installation (e.g.
RV, boat, home)
❐
Length of time inverter has
been installed
❐
Battery size
❐
Battery type (e.g. flooded,
sealed gel cell, AGM)
❐
DC wiring size and length
❐
Alarm sounding?
❐
Description of indicators
❐
Appliances operating when
problem occurred
❐
Description of problem
__________________________________________________
__________________________
__________________________
__________________________
__________________________
__________________________
__________________________
__________________________
__________________________
__________________________
__________________________________________________
45
Page 61

46
Page 62

Index
A
AC wiring, warning about ix, 4
alarm, low battery
alternator controller
described
installing
alternator, high-output
amp-hour (Ah) capacity
appliances
battery-operated
blender
bread maker
possible damage to
power consumption
rechargeable
TV
audio equipment, buzz in
39
2
2
39
2
ix
2, 18,
ix
23
6
39
6,
30
19
33
22
B
batteries
amp-hour capacity
and temperature extremes
automotive starting
charging frequency
connecting 2 in parallel
connections for low power loads
deep-cycle lead-acid
30
28,
20
29
30
34
35
28
depth of discharge
discharged
electrolyte level
explosive gases
golf cart
marine
nickel-cadmium
parallel connection illustrated
reserve capacity
routine maintenance
RV
29
temperature sensitivity
battery chargers
recommended types
battery connections
battery isolator
component
using
battery packs
battery reserve capacity
battery selector switch
battery size
estimating example
estimating requirements
estimating worksheet
battery state of charge
blender
bread maker
29
2
29
29
2
36
6
ix
viii
36
ix
30
36
32
20
39
14
32
36
30
33
35
7, 29,
34
31
47
Page 63

Index
C
cables. See DC cables.
charging
from AC power
from alternative energy sources
with engine alternator
charging frequency for batteries
charging system requirements
charging systems, designing
CHASSIS GND
chassis ground
for fixed location
for marine installation
for vehicles
guidelines for connecting
computer systems
Customer Service
email
fax number
phone number
preparing to call
4,
43
10
4,
9
43
4,
39
2
45
10
43
38
10
7,
9
38
38
20
40
F
FAULT indicator 14, 17, 23
freezers
fuses
installing
make and size
replacing
19
13
23
6
G
gases
battery, venting
explosive
ground. See chassis ground.
viii, 14, 35
8
H
high voltage shutdown 2
high-output alternator
described
installing
mention
39
39
6
D
DC cables
correct polarity
fuses in
guidelines for selecting
procedure for connecting
recommended size and length
depth of discharge (DOD)
13
13
E
electrolyte level 36
explosive gases
48
viii, 14, 35
10
32
11
10
I
indicators
FAULT
how to read
POWER
input voltage
installation
materials
overview of steps
planning
tools
inverter
input voltage
loads
manual reset
14, 17,
14,
6
19
18
6
7
17
17
18
18
23
3
Page 64

Index
mounting location 8, 9
mounting orientation
operating several loads
power output
problem loads
proof of purchase
serial number
trouble loads
turning off
turning on
16
16
18
43
19
19
42
L
loads
average and heavy
light
28
operating several at once
possible damage to
problem
reactive
resistive
trouble
low battery alarm
low voltage shutdown
18
19
19
18
2, 18,
29
19
16
23
5
23
2
illustrated
9
16
using
output voltage low
over temperature shutdown
overload
P
polarity, maintaining correct 13, 23
16
POWER indicator
power output
power tools
product information, recording
proof of purchase
pumps
19
18
2
14,
42,
17
45
4
R
reserve capacity 30
Return Material Authorization number
43
returning products
23
2
how to package
policy
procedure
43
43
43
M
manual reset 18
motors
mounting orientation
18
induction
19
N
nickel-cadmium batteries ix
O
On/Off switch
S
safety information vii, 4
serial number
9
servicing
no user-serviceable parts
shutdown
high voltage
low voltage
over temperature
specifications
electrical
physical
26
26
43
2
vii, 22
2
2
49
Page 65

Index
starting batteries 30
state of charge
36
T
television reception 22
televisions
temperature
ideal ambient temperature
over temperature shutdown
troubleshooting
buzz in audio equipment
common problems
reference table
television reception
2
21
22
23
22
V
22
8
17
VCR 2
ventilation
ventilation openings
8,
35
vii, 8, 9, 23
W
warranty
and damage caused by reverse
polarity
obtaining service
period of coverage
terms and conditions
wiring. See DC cables.
13
42
42
42
X
Xantrex
email
fax number
phone number
4,
43
4,
43
4,
43
50
Page 66

PROwatt™ 600
Inverter
Made in China445-0115-01-01
Tel: 1-800-670-0707
Fax: 1-800-994-7828
Email: support.prowatt@xanrex.com
Web: www.xantrex.com
 Loading...
Loading...