Page 1

HPD 300 Watt Series
Programmable DC
Power Supply
HPD 15-20
HPD 30-10
HPD 60-5
Operating Manual
Page 2

Page 3

Operating Manual for
HPD Series
Programmable DC
Power Supply
Page 4

Limited
Warranty
What does this warranty cover and how long does it last?
This Limited Warranty is provided by Xantrex Technology, Inc. (“Xantrex”) and
covers defects in workmanship and materials in your HPD 300 Watt Series DC
Power Supply. This warranty lasts for a Warranty Period of 5 years from the date
of purchase at point of sale to you, the original end user customer.
What will Xantrex do?
Xantrex will, at its option, repair or replace the defective product free of charge,
provided that you notify Xantrex of the product defect within the Warranty Period,
and provided that Xantrex through inspection establishes the existence of such a
defect and that it is covered by this Limited Warranty.
Xantrex will, at its option, use new and/or reconditioned parts in performing
warranty repair and building replacement products. Xantrex reserves the right to use
parts or products of original or improved design in the repair or replacement. If
Xantrex repairs or replaces a product, its warranty continues for the remaining
portion of the original Warranty Period or 90 days from the date of the return
shipment to the customer, whichever is greater. All replaced products and all parts
removed from repaired products become the property of Xantrex.
Xantrex covers both parts and labor necessary to repair the product, and return
shipment to the customer via a Xantrex-selected non-expedited surface freight
within the contiguous United States and Canada. Alaska and Hawaii are excluded.
Contact Xantrex Customer Service for details on freight policy for return shipments
outside of the contiguous United States and Canada.
How do you get service?
If your product requires troubleshooting or warranty service, contact your merchant.
If you are unable to contact your merchant, or the merchant is unable to provide
service, contact Xantrex directly at:
Phone: 604 422 8595
Toll Free North America: 1 800 667 8422
Fax: 604 421 3056
Email: info@xantrex.com
ii Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 5

Direct returns may be performed according to the Xantrex Return Material
Authorization Policy described in your product manual. For some products, Xantrex
maintains a network of regional Authorized Service Centers. Call Xantrex or check
our website to see if your product can be repaired at one of these facilities.
In any warranty claim, dated proof of purchase must accompany the product and the
product must not have been disassembled or modified without prior written
authorization by Xantrex.
Proof of purchase may be in any one of the following forms:
• The dated purchase receipt from the original purchase of the product at point of
sale to the end user, or
• The dated dealer invoice or purchase receipt showing original equipment
manufacturer (OEM) status, or
• The dated invoice or purchase receipt showing the product exchanged under
warranty
What does this warranty not cover?
This Limited Warranty does not cover normal wear and tear of the product or costs
related to the removal, installation, or troubleshooting of the customer’s electrical
systems. This warranty does not apply to and Xantrex will not be responsible for any
defect in or damage to:
a. the product if it has been misused, neglected, improperly installed, physically
damaged or altered, either internally or externally, or damaged from improper
use or use in an unsuitable environment;
b. the product if it has been subjected to fire, water, generalized corrosion,
biological infestations, and high input voltage from lightning strikes;
c. the product if repairs have been done to it other than by Xantrex or its authorized
service centers (hereafter “ASCs”);
d. the product if it is used as a component part of a product expressly warranted by
another manufacturer;
e. the product if its original identification (trade-mark, serial number) markings
have been defaced, altered, or removed.
Release 1.2 iii
Page 6

Disclaimer Product
THIS LIMITED WARRANTY IS THE SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE WARRANTY PROVIDED
BY XANTREX IN CONNECTION WITH YOUR XANTREX PRODUCT AND IS, WHERE
PERMITTED BY LAW, IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, CONDITIONS,
GUARANTEES, REPRESENTATIONS, OBLIGATIONS AND LIABILITIES, EXPRESS
OR IMPLIED, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE IN CONNECTION WITH THE PRODUCT,
HOWEVER ARISING (WHETHER BY CONTRACT, TORT, NEGLIGENCE, PRINCIPLES
OF MANUFACTURER’S LIABILITY, OPERATION OF LAW, CONDUCT, STATEMENT
OR OTHERWISE), INCLUDING WITHOUT RESTRICTION ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY
OR CONDITION OF QUALITY, MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE TO THE EXTENT REQUIRED UNDER
APPLICABLE LAW TO APPLY TO THE PRODUCT SHALL BE LIMITED IN DURATION
TO THE PERIOD STIPULATED UNDER THIS LIMITED WARRANTY.
IN NO EVENT WILL XANTREX BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT,
INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, LOSSES, COSTS OR EXPENSES
HOWEVER ARISING WHETHER IN CONTRACT OR TORT INCLUDING WITHOUT
RESTRICTION ANY ECONOMIC LOSSES OF ANY KIND, ANY LOSS OR DAMAGE TO
PROPERTY, ANY PERSONAL INJURY, ANY DAMAGE OR INJURY ARISING FROM OR
AS A RESULT OF MISUSE OR ABUSE, OR THE INCORRECT INSTALLATION,
INTEGRATION OR OPERATION OF THE PRODUCT.
Exclusions If this product is a consumer product, federal law does not allow an exclusion of
implied warranties. To the extent you are entitled to implied warranties under federal
law, to the extent permitted by applicable law they are limited to the duration of this
Limited Warranty. Some states and provinces do not allow limitations or exclusions
on implied warranties or on the duration of an implied warranty or on the limitation
or exclusion of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitation(s) or
exclusion(s) may not apply to you. This Limited Warranty gives you specific legal
rights. You may have other rights which may vary from state to state or province to
province.
iv Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 7

Information WITHOUT LIMITING THE GENERALITY OF THE FOREGOING, UNLESS
SPECIFICALLY AGREED TO BY IT IN WRITING, XANTREX
a. MAKES NO WARRANTY AS TO THE ACCURACY, SUFFICIENCY OR SUITABILITY
OF ANY TECHNICAL OR OTHER INFORMATION PROVIDED IN MANUALS OR
OTHER DOCUMENTATION PROVIDED BY IT IN CONNECTION WITH THE
PRODUCT; AND
b. ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY FOR LOSSES, DAMAGES,
COSTS OR EXPENSES, WHETHER SPECIAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT,
CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL, WHICH MIGHT ARISE OUT OF THE USE OF
SUCH INFORMATION.
THE USE OF ANY SUCH INFORMATION WILL BE ENTIRELY AT THE USER’S RISK.
WARNING:
Limitations
on Use
Please refer to your product user manual for limitations on uses of the product.
Specifically, please note that this power supply is not intended for use in connection
with life support systems and Xantrex makes no warranty or representation in
connection with any use of the product for such purposes.
Xantrex Technology, Inc.
8999 Nelson Way
Burnaby, British Columbia
Canada V5A 4B5
Information
About Your
Power
Supply
Please record the following information when you first open your Power Supply
package:
Model Number ______________________________________________
Serial Number ______________________________________________
Purchased From ______________________________________________
Purchase Date ______________________________________________
Release Release 1.2 (2003-04)
Copyright © 2002 Xantrex Technology Inc. All rights reserved.
Printed in Canada
Release 1.2 v
Page 8
Warnings
!
!
!
and
Cautions
Power
Supply
Safety
Warnings and cautions are defined and formatted in this manual as shown below.
WARNING
Describes a potential hazard which could result in injury or death, or, a procedure
which, if not performed correctly, could result in injury or death.
CAUTION
Describes a procedure which, if not performed correctly, could result in damage
to data, equipment, or systems.
WARNING—High Energy and High Voltage
Exercise caution when using and calibrating a power supply. High energy levels
can be stored at the output voltage terminals on a power supply in normal
operation. In addition, potentially lethal voltages exist in the power circuit and on
the output and sense connectors of a power supply with a rated output greater
than 40 V. Filter capacitors store potentially dangerous energy for some time after
power is removed.
CAUTION
Operate the power supply in an environment free of flammable gases or fumes. To
ensure that the power supply’s safety features are not compromised, use the
power supply as specified in this manual and do not substitute parts or make any
unauthorized modifications. Contact the service technician for service and repair
help. Repairs must be made by experienced service technicians only.
CAUTION
For Use as a Battery Charger
When you are using any of these power supplies for battery charging applications,
it is essential to provide an appropriately sized fuse or circuit breaker in series
between the power supply output and the battery.
Installation of a protector (fuse or DC circuit breaker) rated for about 115% of the
maximum current rating of the power supply and designed specifically to interrupt
the DC voltage of the battery, will provide adequate reverse polarity current
protection. Where several power supplies are in parallel, it is best to fuse each one,
rather than one large fuse for all.
vi Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 9

About This Manual
This Operating Manual contains operating instructions for the HPD Series of high
performance, switching, laboratory power supplies, available in several voltage
models at 300 watts. It provides information on features and specifications,
installation procedures, and basic functions testing, as well as operating procedures
for using both standard and multiple supply configurations.
Who Should Use This Manual
This manual is designed for the user who is familiar with basic electrical theory,
especially as applied to the operation of power supplies. This implies a recognition
of Constant Voltage and Constant Current operating modes and the control of input
and output power, as well as the observance of safe techniques while calibrating,
making supply connections, and/or making any changes in configuration.
Main Sections
Section 1 Features and Specifications Describes the power supply, lists its
features, and provides tables of specifications.
Section 2 Installation Reviews safety and inspection procedures, and provides
procedures for basic setup. Also includes directions for testing basic functions.
Section 3 Load Operation and Sensing Provides procedures for connecting
the load, grounding, and remote sensing.
Section 4 Operation Describes standard operation (Constant Voltage and
Constant Current), and series, parallel, and split supply operation.
Manual Revisions
The current release of this manual is listed below. Updates may be issued as an
addendum.
Release 1.2 (2003-04)
Release 1.2 vii
Page 10
About This Manual
Power Supply Safety Markings
Alternating Current Off (Supply)
Earth (Ground) Terminal Caution (Hot Surface)
Protective Conductor Terminal Caution (Check manual for
additional information.)
On (Supply)
viii Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 11

Contents
About This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Section 1.
Features and
Specifications
Section 2.
Installation
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Options and Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Front Panel Controls. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Rear Panel Connectors and Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Additional Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Input Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Environmental Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Mechanical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Chassis Dimensions and Weight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Single Output Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Dual Output Unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Basic Setup Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Initial Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Periodic Cleaning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Returning Power Supplies to the Manufacturer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Return Material Authorization Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Packaging for Shipping or Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Rack Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Location and Ventilation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
AC Input Power Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
AC Input Cord . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Functional Tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Power-on Check. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Voltage Mode Operation Check. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Current Mode Operation Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Section 3.
Load
Connection
and Sensing
Release 1.2 ix
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Load Connection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Load Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Making Load Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Connecting Multiple Loads. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Grounding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Local Sensing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Output Jumpers for Local Sensing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Remote Sensing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Page 12

Contents
Section 4. Operation
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Operating Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Constant Voltage Mode Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Constant Current Mode Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Setting the Current Limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Setting the Supply to Operate in CI Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Automatic Mode Crossover. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Constant Power Loads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Using Multiple Supplies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Connecting Multiple Supplies in Series (Voltage Mode Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Connecting Multiple Supplies in Parallel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Split Supply Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
x
Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 13

Section 1. Features and Specifications
Introduction
The HPD Series of DC power supplies provides highly stable, variable output
voltage and current for a broad range of development and system requirements.
These units employ high frequency switching regulator technology to achieve high
power density and small package size, as well as a linear post-regulator circuit for
low output noise and fast response. A wide variety of options is available, including
both analog and IEEE-488 controlled programming, to make this series the first
choice in flexible power system design.
Table 1.1 300 Watt Series Models
Model Output Voltage Output Current
15–20 0–15 V 0–20 A
30–10 0–30 V 0–10 A
60–5 0–60 V 0–5 A
Features
• High frequency switching technology allows high power density, providing
increased power output in a small, light, package.
• The power supply delivers simultaneous digital displays for both voltage and
current, and bar graph displays for monitoring transient changes, which gives the
user the benefit of continuous, up-to-date information.
• Ten-turn voltage control permits high resolution setting of the output voltage.
• Current limit is fully adjustable from zero to the rated output with a single turn
control.
• The automatic crossover system allows the power supply to automatically
switch operating modes into current or voltage mode.
• Impedance-switched remote sensing lets operators display the voltage at the load
with no switch ambiguity.
• Multiple units can be connected in parallel or series to produce greater diversity.
• Short-circuit-proof power outlets give greater operating safety.
• These power supplies (available in single and dual outputs) can be combined
with one or more 60 watt series power supplies to create mixed units that are
ideal for high precision applications.
Release 1.2 11
Page 14
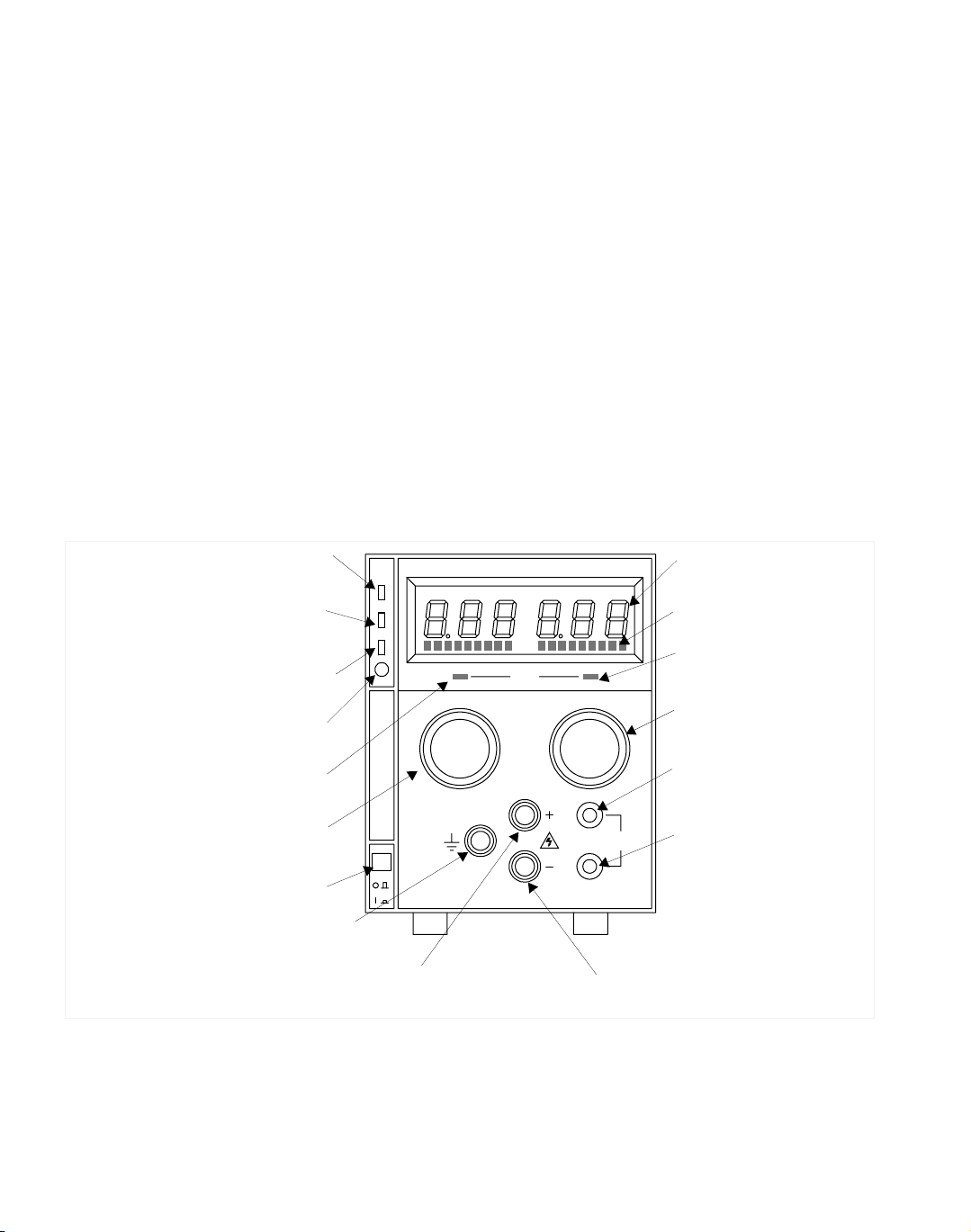
Section 1. Features and Specifications
Options and Accessories
Options and Accessories
• Internal Analog Programming (APG) interface for analog signal control of
voltage and current, overvoltage protection (OVP), master/slave output tracking,
and remote ON/OFF.
• Internal RS-232 interface for serial instrument programming using RS-232
protocol.
• Internal GPIB interface for complete remote digital programming. IEEE-488
standard.
• Optional 200–250 Vac input (Option AC200). Standard is 115 Vac. Optional AC
input cords for use in different countries.
• Ten-turn current potentiometer (Option M11). Rack mount kit (Option RM).
• Locking voltage and/or current adjust knobs (Option M13A).
Front Panel Controls
Figure 1.1 shows the controls, LEDs, and meters located on the unit’s front panel.
Remote Programming LED (PGM)
(For units with APG installed.
See also Figure 1.2).
Shutdown LED (S/D)
(For units with APG installed.)
OVP Shutdown (OVP)
(For units with APG installed.)
OVP Adjust Potentiometer (OVP ADJ)
(For units with APG installed.)
Voltage Mode
Indicator (Green LED)
Voltage Control Knob
(10-turn standard)
AC Power Switch
Safety Ground
Binding Post (Green)
Positive (+) Output Binding Post (Red)
Figure 1.1 Front Panel Controls
REGULATED DC POWER SUPPLY
P
G
M
S
/
D
O
V
P
OVP
ADJ
VOLTAGE CURRENT
POWER
MODE
Digital Display of DC Output
(Volts, Amperes)
Analog Bar Graph Display
Current Limit Mode
Indicator (Red LED)
Current Limit Adjust Knob
(1-turn standard)
Positive (+) Sense
Connection
(Banana Jack)
SENSE
Return (−) Sense
Connection
(Banana Jack)
Return (−) Output Binding
Post (Black)
12 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 15

Section 1. Features and Specifications
Rear Panel Connectors and Outputs
Figure 1.2 shows the programming interface indicators for units that have a digital
programming interface installed.
Remote Programming LED (REM)
OVP Shutdown (OVP)
Figure 1.2 Remote Programming Interface Indicators
Rear Panel Connectors and Outputs
Figure 1.3 shows the connectors and outputs available at the rear panel. (Figure 1.3
shows the 15 V or 30 V low voltage model.)
Output Block for
High Voltage (60 V) Model
Shutdown LED (SRQ)
OVP Adjust Potentiometer (OVP ADJ)
Blank Subplate
(Replaced if a programming
option is installed.)
Output Barrier Strip
AC Input Connector
Figure 1.3 Rear Panel
Note
The power supply is shipped with jumpers for local sensing of the output voltage. See
“Local Sensing” on page 29.
Release 1.2 13
Page 16

Section 1. Features and Specifications
Electrical Specifications
Electrical Specifications
Specifications are warranted over a temperature range of 0 to 30 °C with default
local sensing. Above 30 °C, the output voltage needs to be derated linearly to zero at
70 °C. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Table 1.2 Electrical Specifications for 15 V to 60 V Models
Models 15–20 30–10 60–5
Output Ratings:
Output Voltage
Output Current
Output Power
Line Regulation:
Voltage (0.01% of Vmax + 2 mV)
Current (0.01% of Imax + 1 mA)
Load Regulation:
Voltage (0.01% of Vmax + 2 mV)
Current (0.01% of Imax + 1 mA)
Meter Accuracy:
Voltage (1% of Vmax + 1 count)
Current (1% of Imax + 1 count)
Output Noise and Ripple
(20 Hz-20 MHz):
Voltage (p-p)
Voltage (rms)
Current (rms)
Drift (60 minutes):
Voltage (0.02% of Vmax)
Current (0.03% of Imax)
Drift (8 hours):
Voltage (0.02% of Vmax)
Current (0.08% of Imax)
Temperature Coefficient
Voltage (0.015% of Vmax/°C)
Current (0.02% of Imax/°C)
1. For input voltage variation over the AC input voltage range, with constant rated load.
2. For 0 to 100% load variation, with constant nominal line voltage.
3. Current mode noise is measured from 10% to 100% of rated output voltage, full current.
4. Maximum drift over 60 minutes with constant line, load, and temperature, after 60-minute
warm-up.
5. Maximum drift over 8 hours with constant line, load, and temperature, after 60-minute
warm-up.
6. Change in output per °C change in ambient temperature, with constant line and load.
1
2
3
4
5
0–15 V
0–20 A
300 W
3.5 mV
4mA
3.5 mV
4mA
250 mV
300 mA
100 mV
5mV
20 mA
3mV
6mA
3mV
16 mA
6
2.25 mV
4mA
0–30 V
0–10 A
300 W
5mV
3mA
5mV
3mA
400 mV
200 mA
100 mV
5mV
10 mA
6mV
3mA
6mV
8mA
4.5 mV
2mA
0–60 V
0–5A
300 W
8mV
2.5 mA
8mV
2.5 mA
700 mV
60 mA
100 mV
5mV
5mA
12 mV
1.5 mA
12 mV
4mA
9mV
1mA
14 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 17

Additional Electrical Specifications
Section 1. Features and Specifications
Additional Electrical Specifications
Voltage Mode Transient Response
(Time for the output voltage to
recover to ±50 mV band for 50%
load change in the range of 25% to
100% of the rated load.)
Time delay from power on until
output stable
Input Conditions
Rated AC Input Voltage 120 Vac standard; 230/240 Vac AC200 option
Maximum AC Input Power 625 VA
Operational AC Input Voltage Range Single Unit: 104
AC 200 Option Single Unit: 200
Maximum Input Current (per unit) at
nominal power line impedances
Input Frequency Range 47
<500 µs
1.5 s maximum
–127 Vac at 6 Arms
Dual Unit: 104
Dual Unit: 200
–127 Vac at 12 Arms
–250 Vac at 3 Arms
–250 Vac at 6 Arms
6 A maximum at 104 Vac
–63 Hz
Release 1.2 15
Page 18

Section 1. Features and Specifications
Electrical Characteristics
Electrical Characteristics
Switching Frequency 100 kHz (nominal)
Output Hold-up Time ≥25 ms at nominal line
Maximum Voltage Differential from
output to safety ground
Insulation Resistance Input to chassis: >120 MΩ
Isolation Voltage
(Output not to exceed ±400 Vdc from
chassis potential.)
Maximum Remote Sense Line Drop
Compensation.
deducted from the supply’s maximum
output voltage.)
(Line drop must be
Environmental Specifications
Operating Ambient Temperature 0 to 30 °C with default local sensing. Above
Storage Temperature Range –55° to 85 °C
Humidity Range 0 to 80% RH non-condensing
Operating Altitude Up to 6,500 feet (2000 m)
Storage Altitude Up to 50,000 feet (15 000 m)
±400 Vdc
Output to chassis: >120 MΩ
Input to output: 1350 Vac
0.5 V/line
30 °C, derate output linearly to 0 at 70 °C.
Installation Category Intended for use in installation category
(overvoltage category) II (IEC 1010-1 standard)
Pollution Degree Category 2 (IEC 1010-1 standard)
16 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 19

Mechanical Specifications
Section 1. Features and Specifications
Mechanical Specifications
Front Panel Voltage and Current
Control
10-turn voltage and 1-turn current
potentiometers (10-turn current control
optional)
Front Panel Voltage Control
0.02% of maximum voltage
Resolution
Front Panel AC Input Power Switch Push ON/push OFF switch
Front Panel Voltage and Current
Meters
Independent 3-digit green numeric LED
display and analog bar graph displays for
current and voltage. For meter accuracy, see
Table 1.2.
AC Input Connector Type IEC 320 Connector, appropriate power cord for
destination country.
Front Panel Output Connector Three binding posts: positive (+),
negative (–), and ground.
Rear Panel Output and Sense
Connector
Four terminal barrier strips. The 60 V unit is
shipped with a 4-terminal output block.
Chassis Ground Front panel binding post and power cord safety
ground.
Cooling Convection cooled. Air enters the unit from the
bottom and lower sides and exits from the
upper sides and top.
Mounting Optional rack for mounting several units in a
standard rack. Can be combined with 60 watt
Approvals
series units. See
CSA certified to UL 1012, and CSA C22.2 No.
“Rack Mounting” on page 22.
107.1
FCC Part 15B and Industry Canada Class A
CE Marked for Low Voltage Directive and
EMC Directive (Class A emissions)
Release 1.2 17
Page 20

Section 1. Features and Specifications
Chassis Dimensions and Weight
Chassis Dimensions and Weight
Single Output
Unit
Dual Output
Unit
Height 5.25 in.
Width 4.25 in.
Depth 11.7 in.
Weight 7.7 lb.
Height 5.25 in.
Width
132 mm
109 mm
297 mm
3.5 kg
132 mm
8.5 in.
216 mm
Depth 11.7 in.
297 mm
Weig ht
14.2 lb.
6.5 kg
18 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 21

Section 2. Installation
Introduction
This section provides recommendations and procedures for inspecting, installing,
and testing the power supply.
Basic Setup Procedure
Table 2.1 Basic Setup Procedure
Step# Description Action Reference
1 Inspection Perform an initial physical
inspection of the supply.
2 Installation Install the supply and
ensure adequate ventilation.
3 Test Perform functional tests for
voltage mode operation,
current mode operation, and
front panel controls.
“Initial Inspection” on page 19
“Location and Ventilation” on
page 22
“Functional Tests” on page 24
Initial Inspection
Verify that the power supply was shipped with an IEC power cord set appropriate to
the destination country, two 2-position terminal block jumpers, and an operating
manual. When you first receive your unit, perform a quick physical check.
1. Inspect the unit for scratches and cracks, broken switches, connectors, terminals,
and missing accessories.
2. Have a service technician check the unit if you suspect internal damage.
If the unit is damaged, save all packing materials and notify the carrier immediately.
See instructions in “Packaging for Shipping or Storage” on page 21.
Periodic
Cleaning
Release 1.2 19
No routine servicing of the power supply is required except for periodic cleaning.
Whenever a unit is removed from operation, clean the outside surfaces with a weak
solution of soap and water. If required, use low-pressure compressed air to blow dust
from in and around components on the printed circuit boards.
Page 22

Section 2. Installation
Returning Power Supplies to the Manufacturer
Returning Power Supplies to the Manufacturer
Return
Material
Authorization
Policy
Before returning a product directly to Xantrex you must obtain a Return Material
Authorization (RMA) number and the correct factory “Ship To” address. Products
must also be shipped prepaid. Product shipments will be refused and returned at your
expense if they are unauthorized, returned without an RMA number clearly marked
on the outside of the shipping box, if they are shipped collect, or if they are shipped
to the wrong location.
When you contact Xantrex to obtain service, please have your operating manual
ready for reference and be prepared to supply:
• The serial number of your product
• Information about the installation and use of the unit
• Information about the failure and/or reason for the return
• A copy of your dated proof of purchase
When you ship:
1. Package the unit safely following the procedures on page 21, preferably using
the original box and packing materials. Please ensure that your product is
shipped fully insured in the original packaging or equivalent. This warranty will
not apply where the product is damaged due to improper packaging.
2. Include the following:
• The RMA number supplied by Xantrex Technology Inc clearly marked on
the outside of the box.
• A return address where the unit can be shipped. Post office boxes are not
acceptable.
• A contact telephone number where you can be reached during work hours
• A brief description of the problem
Ship the unit prepaid to the address provided by your Xantrex customer service
representative.
If you are returning a product from outside of the USA or Canada:
In addition to the above, you MUST include return freight funds and are fully
responsible for all documents, duties, tariffs, and deposits.
If you are returning a product to a Xantrex Authorized Service Center (ASC):
A Xantrex return material authorization (RMA) number is not required. However,
you must contact the ASC prior to returning the product or presenting the unit to
verify any return procedures that may apply to that particular facility.
20 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 23

Section 2. Installation
Returning Power Supplies to the Manufacturer
Packaging for
Shipping or
Storage
Follow these instructions to prepare the unit for shipping or storage.
1. When returning the unit or sending it to the service center, attach a tag to the unit
stating its model number (available from the front panel label) and its serial
number (available from the rear panel label). Give the date of purchase and an
invoice number, if you have it, as well as a brief description of the problem.
2. For storage or shipping, repack the power supply in its original container. If the
original container is not available, seal the unit in a plastic bag and then pack it
in a 200 lb. (90 kg) test, corrugated cardboard carton large enough to allow 2
inches (5 cm) of cushioning material to surround the unit. Use a material such as
foam slabs or chips.
3. Label the carton as shown in Figure 2.1.
4. If shipping, mark the address of the service center and your return address on the
carton.
5. If storing, stack no more than eight cartons high. Check the storage temperature
range and storage altitude specification in “Environmental Specifications” on
page 16.
POWER SUPPLY
Model Number: _______________________
Serial Number: _______________________
FRAGILE — ELECTRONIC EQUIPMENT
Figure 2.1 Shipping or Storage Carton Label
Release 1.2 21
Page 24

Section 2. Installation
Rack Mounting
Rack Mounting
Use the power supply in benchtop or in rack-mounted applications.
WARNING
Ensure that any mounting screws do not protrude more than 1/8 in. (3.0 mm) into the
bottom of the unit.
The power is supply is designed to fill one quarter of a standard 19 in. (483 mm)
equipment rack.
Dual and quad configurations can be combined with 60 watt series models for
custom applications. Contact the manufacturer about the rack mount kit (Option
RM).
Location and Ventilation
Whether you place the power supply in a rack or on a bench, allow cooling air to
reach the ventilation inlets on the bottom and sides of the unit. Ensure that
rack-mounted supplies have 1 U (1.75 in./44.5 mm) above and below units. Any
ventilation space around the supply will further lower internal operating
temperatures.
See “Environmental Specifications” on page 16, for the operating altitude
specification and the operating ambient temperature range measured at the unit case.
22 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 25

AC Input Power Connection
!
WARNING
There is a potential shock hazard if the power supply chassis and cover are not
connected to an electrical ground via the safety ground in the AC input connector.
Ensure that the power supply is connected to a grounded AC outlet with the
recommended AC input connector configured for the available line voltage as
described in this section.
CAUTION
When the power switch is turned on, the output voltage or current previously set is
applied to loads.
The AC input connector is a standard IEC 320 male connector located on the power
supply’s rear panel.
Table 2.2 Operational AC Input Voltage Ranges and Frequency
AC Voltage Range Frequency
104–127 Vac 1
200–250 Vac 1
φ (standard) 47–63 Hz
φ (AC200 option) 47–63 Hz
Section 2. Installation
AC Input Power Connection
AC Input
Cord
WARNING
The AC input cord is the disconnect device for the power supply. The plug must
be readily identifiable by and accessible to the operator. The input cord must be
no longer than 9.85 feet (3 m).
The AC input cord that we provide is appropriate to the destination country. If you
require a special cord, call us.
Release 1.2 23
Page 26

Section 2. Installation
Functional Tests
Functional Tests
These functional test procedures include power-on and front panel function checks
as well as voltage and current mode operation checks.
Power-on
Check
Voltage Mode
Operation
Check
Current Mode
Operation
Check
1. Ensure that the front panel power switch is in the extended (OFF) position and
the voltage and current controls are in their fully counter-clockwise positions.
2. Ensure that the AC line voltage is within operating range.
3. Plug the line cord into a grounded AC outlet.
4. Push the power switch to turn on the power supply.
After a short power-on delay, the display and the red current mode LED lights. The
meter reading remains at zero.
For more about standard operations, see Section 4, “Operation”.
1. Ensure that the front panel voltage and current control are turned fully
counter-clockwise.
2. Set the power switch to ON.
3. Rotate the current control one half-turn clockwise. Slowly rotate the voltage
control clockwise and observe the digital meter. Minimum control range should
be from zero to maximum rated output. Observe the bar graph meter to see that
it tracks as the voltage rises. Verify that the voltage mode indicator light is ON.
4. Set the power switch to OFF.
1. Ensure that the front panel power switch is set to OFF.
2. Rotate the voltage and current controls fully counter-clockwise.
3. Rotate the voltage control one half-turn clockwise.
4. Connect a short circuit across the output terminals. Use leads of sufficient
current carrying capacity.
5. Set the power switch to ON.
6. Rotate the current control slowly clockwise. The control range should be from
zero to the maximum rated output. Also check that the current bar graph meter
follows the rise in current and that the current mode indicator light is ON.
7. Set the power switch to OFF.
24 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 27

Section 3. Load Connection and Sensing
!
Introduction
This section covers single and multiple load connection, constant voltage and
constant current operating modes, and alternate power supply configurations such as
series and parallel connections.
Load Connection
WARNING
There is a potential shock hazard at the load when using a power supply with an
output greater than 40 V. Take appropriate precautions to protect personnel against
accidental contact with hazardous voltages. Also ensure that the insulation rating of
the load wiring and circuitry is greater than or equal to the maximum voltages to
ground being applied.
CAUTION
When making load connections, be sure to observe correct polarity or the power
supply may be damaged.
You can obtain reliable performance from your power supply if you take certain
basic precautions when making load connections.
To obtain a stable, low noise output, pay attention to the following:
1. consider the conductor ratings, the system grounding techniques and the way
that you make AC input, DC output, and remote sensing connections
2. use a conductor size that satisfies the current rating requirements
3. to overcome impedance and coupling effects, we recommend larger gauge wire
and shorter leads.
4. where positive load transients such as back EMF (electromotive force) from a
motor may occur, connect a transorb or a varistor across the output to protect the
power supply.
Release 1.2 25
Page 28

Section 3. Load Connection and Sensing
Load Connection
Load Wiring To select wiring for connecting the load to the power supply, consider the following
factors:
• Insulation rating of the wire
• Current carrying capacity of the wire
• Maximum load wiring length for operation with sense lines
• Noise and impedance effects of the load lines
Insulation Rating Use load wiring with a minimum insulation rating at least
equivalent to the maximum output voltage of the power supply. If the output is offset
from ground, the insulation must be rated at least for the sum of the supply’s
maximum output and the offset.
Current Carrying Capacity As a minimum, load wiring must have a current
capacity greater than the output current rating of the power supply. This ensures that
the wiring will not be damaged even if the load is shorted. See Tab l e 3.1 for the
maximum current rating, based on 450 A/cm
2
, for various gauges of wire rated for
105 °C operation. Operating at the maximum current rating results in a temperature
rise of approximately 30 °C for a wire operating in free air. Where load wiring must
operate in areas with elevated ambient temperatures or is bundled with other wiring,
use larger gauges or wiring rated for higher temperatures.
Table 3.1 Current Carrying Capacity for Load Wiring
Wire Size
(AWG)
20 2.5 6 61
18 4 4 97
16 6 2 155
14 10 1 192
12 16 1/0 247
10 21 2/0 303
836
Maximum Current
(A)
Wire Size
(AWG)
Maximum Current
(A)
26 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 29

Section 3. Load Connection and Sensing
Load Connection
Load Wiring Length for Operation With Sense Lines For applications using
remote sensing, you must limit the voltage drop across each load line. See Figure 3.1
for some maximum allowable lengths for a given load current and wire size. We
recommend that you use the larger load wiring to ensure a smaller voltage drop
(0.1 V typical maximum), although units can compensate for up to 0.5 V drop in
1
each line
.)
Figure 3.1 Maximum Wire Length for 100 mV Line Drop
Noise and Impedance Effects To minimize noise pickup or radiation, use
shielded pair wiring of the shortest possible length for load wires. Connect the shield
to the chassis via the front panel binding post or a rear panel mounting screw. Where
shielding is impossible or impractical, simply twisting the wires together will offer
some noise immunity.
1. Any losses in the load cables must be deducted from the maximum output
voltage of the supply. For example, a 15 V supply with a 1 V loss in the load
cables can supply a maximum of 14 V regulated at the load.
Release 1.2 27
Page 30

Section 3. Load Connection and Sensing
Load Connection
Making Load Connections
Connections at the Front Panel Binding Posts
To make connections at the front panel, connect load wires using stripped wire
(0.6 in./15 mm), spade lugs, or banana plugs to the output binding posts.
For binding posts locations, see Figure 1.1, “Front Panel Controls”.
Connections at the Rear Panel Terminals
Low Voltage Models
appropriate gauge wire
To make load connections to low voltage models, attach an
1
following the steps below:
1. Strip load wires 0.75 in. (19 mm). An alternative is to attach tongue lugs (#6
stud) to the load wires, following the manufacturer’s instructions
.
2. Using a flat-bladed or #2 Phillips screwdriver, loosen the positive (+) and
negative (−) output terminal screws on the output barrier strip. See Figure 3.2,
“Output Barrier Strip With Jumpers Installed”.
3. Wrap stripped wire around the appropriate terminal screw. Tighten the screw.
High Voltage Models To make load connections to high voltage models, attach
an appropriate gauge wire
1
(maximum #12 wire) following the steps below:
1. Strip load wires 0.6 in. (15 mm).
2. Using a 1/8 in. (4 mm) flat-bladed screwdriver, loosen the terminal screws on the
output terminal block. Insert wires into the output terminals (−, +) from the
bottom of the block. See Figure 3.3, “Output Terminal Block With Jumpers
Installed”.
3. Tighten the terminal screws.
Connecting
Multiple
Loads
Proper connection of distributed loads is an important aspect of power supply use. A
common mistake is to connect leads from the power supply to one load and then from
that load to other loads. In this parallel power distribution method, the voltage at each
load depends on the current drawn by the other loads, and DC ground loops develop.
Except for low current applications, we recommend that you do not use this method.
1. See Table 3.1, “Current Carrying Capacity for Load Wiring,” on page 26 for the
correct wire gauge.
28 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 31

Grounding
Local Sensing
Section 3. Load Connection and Sensing
Grounding
Make proper ground connections to avoid developing paths between separate ground
points. To avoid ground loops, there must be only one ground return point in a power
system. If the load itself is not grounded, ground the positive or negative output to
the supply’s chassis using a rear panel screw or the front panel ground binding post.
Output voltage can be sensed from both the rear panel and the front panel output
connectors. Default local sensing regulates the voltage at the power supply output
terminal. Use remote sensing (see “Remote Sensing” on page 31) when the voltage
needs to be regulated at the load rather than at the power supply output terminals.
Without sense line connections, the supply regulates the voltage at the output
terminals of the power supply. For improved local sensing, connect jumpers between
the sense terminals and the output terminals. See Figure 3.2 and Figure 3.3.
See Figure 1.1, “Front Panel Controls”, and Figure 1.3, “Rear Panel”, for sense
terminal locations on the front and rear panels.
Output
Jumpers for
Local
Sensing
WARNING
Disconnect the AC input before installing or removing jumpers.
Low Voltage Models Two barrier strip jumpers are shipped unattached with 15 V
and 30 V models. If your application requires precisely regulated output voltage at
the rear output terminals, install the jumpers as noted below.
1. Use a flat-bladed or #2 Phillips screwdriver to loosen the four terminal screws at
the output barrier strip.
2. Slide the jumpers under the screws.
3. Tighten the screws to the barrier strip. See Figure 3.2.
Release 1.2 29
Page 32

Section 3. Load Connection and Sensing
Local Sensing
Negative Output
Te r m i n al ( −)
Negative Remote
Sense Line (−SNS)
Positive Output
Ter m in a l (+)
Positive Remote
Sense Line (+SNS)
Jumper
Figure 3.2 Output Barrier Strip With Jumpers Installed
High Voltage Models Two wire jumpers are shipped unattached with 60 V
models. If your application requires precisely regulated output voltage at the rear
output terminals, install the jumpers by inserting the jumper wires into the jumper
terminals as shown. See Figure 3.3.
Wire
Jumper
Figure 3.3 Output Terminal Block With Jumpers Installed
30 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 33

Remote Sensing
!
!
!
Section 3. Load Connection and Sensing
Remote Sensing
WARNING
There is a potential shock hazard at the sense points when using a power supply
with a rated output greater than 40 V. Ensure that connections at the load end are
shielded to prevent contact with hazardous voltages.
CAUTION
Operation of the supply in remote sense mode without the assured connection of
the load wires and remote sense wires to the load may damage the power
supply.
CAUTION
Ground the sense line shield in one place only. Locations include the power
supply’s return output connection at the load, the power supply’s return output at
the negative output terminal, or the power supply’s ground binding post on the
front panel.
Remote sensing permits you to relocate the regulation point of the power supply
from the output terminals to the load or other distribution point terminals.
The power supply provides sense connections beside the output terminals at the front
and rear panels. Use 22-24 AWG twisted, shielded pair wiring to make sense
connections.
With the remote sense leads in place, the supply regulates for the displayed voltage
at the point where the sense lines are connected to the output leads (provided the sum
of these lead losses does not exceed 0.5 V). With the sense lines disconnected, the
supply regulates the voltage at the output terminals. Remote sensing is not required
for constant current mode of operation, where the supply is regulating the output
current.
Note
Do not operate the supply with sense lines connected to the load without also connecting
the normal load power leads to the output terminals.
Always use shielded pair wiring for sense lines to minimize noise effects. (See
“Grounding” on page 29.)
CAUTION
Do not reverse positive (+) and negative (−) lead connections.
Release 1.2 31
Page 34

Section 3. Load Connection and Sensing
Remote Sensing
32 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 35

Section 4. Operation
Introduction
Once you have installed the power supply and have connected both the AC input
power and the load as covered in Section 2, “Installation”, the power supply is ready
to operate.
• “Operating Modes”, below, offers a brief explanation of Constant Voltage and
Constant Current Mode operation.
• “Connecting Multiple Supplies in Series (Voltage Mode Only)” on page 36,
covers using multiple supplies.
Operating Modes
Your power supply has two basic operating modes: Constant Voltage Mode and
Constant Current Mode. The mode in which the power supply operates at any given
time depends on the combination of:
• Output voltage setting V
• Output current limit setting I
• Resistance or impedance of the attached load R
SET
SET
L
Figure 4.1 represents the relationships between these variables.
Output
Voltage
V SET
O
O
Constant Voltage
Mode Region
Constant Current
Mode Region
I SET
Figure 4.1 Relationship Between Operating Mode Variables
Note
The control circuits have been designed to allow you to set output voltage and current
up to 5% over the model-rated maximum values. The power supply will operate within
these extended ranges, but we cannot guarantee full performance to specification.
Release 1.2 33
RL > V
Crossover Point
Output
Current
SET
I
SET
V
R
L
SET
=
I
SET
R
V
L
SET
<
I
SET
Where:
= Load Resistance
R
L
= Output Voltage Setting
V
SET
= Output Current Setting
I
SET
Page 36

Section 4. Operation
Operating Modes
Constant
Voltage Mode
Operation
Constant
Current Mode
Operation
Setting the
Current Limit
The power supply will operate in constant voltage (CV) mode whenever the load
current I
In CV, the power supply maintains the output voltage at the selected value (V
while the load current I
is less than the current limit setting I
L
varies with the load requirements.
L
or: IL < I
SET
(Note: IL = V
SET
SET
/ RL).
)
SET
To use the power supply in CV mode, either set the current limit to maximum by
turning the current control to its extreme clockwise position, or take the precaution
of setting a desired maximum current, and then set the voltage control to the desired
voltage.
The power supply will operate in constant current (CI) mode whenever the load
resistance is low enough that at V
current limit setting I
SET
.
In CI mode, the power supply maintains the output current at the selected value (I
the load current would be greater than the
SET
V
SET
-------------
>
I
R
SET
L
SET
while the output voltage varies with the load requirements.
Set the Current Limit by following the steps below:
1. Connect a shorting lead across the output terminals.
2. Turn the voltage control a half-turn clockwise.
3. Set the desired maximum current limit by turning the current control slowly
clockwise to the desired level.
)
4. Disconnect the shorting lead from the output terminals. The power supply will
now automatically switch into current limiting mode (current regulation) as
soon as the preset current level is reached.
Setting the
Supply to
Operate in CI
Mode
To operate the supply in CI mode:
1. Set the current limit as described above.
2. Set the voltage control fully clockwise or to the compliance voltage of the circuit.
As soon as the supply starts operating in current mode, the red current mode
LED will turn on.
34 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 37

Section 4. Operation
Operating Modes
Automatic
Mode
Crossover
Constant
Power Loads
The automatic crossover system allows the power supply to automatically switch
operating modes in response to changing load requirements. For example, if the load
current attempts to increase above the setting of the current adjust control, the unit
switches automatically from CV to CI mode. If you lower the load requirements, the
supply automatically returns to CV mode.
When powering constant power loads such as switch mode regulators, it is preferable
to run in constant voltage mode, with the current limit set to supply ample current.
Operating near the CV/CI transition point can cause operation to become unstable.
Release 1.2 35
Page 38

Section 4. Operation
!
Using Multiple Supplies
Using Multiple Supplies
Connecting
Multiple
Supplies in
Series
(Voltage
Mode Only)
You can operate two or more power supplies with outputs connected in series or in
parallel to obtain increased load voltage or current. A split supply configuration
allows you to obtain two positive outputs or a positive and a negative output.
CAUTION
The maximum allowable voltage in series operation is 400 Vdc.
As described below, you can connect power supplies in series to obtain a single
output supply with higher output voltage. Connect the negative (–) terminal of one
supply to the positive (+) terminal of the next supply.
The total voltage available is the sum of the maximum voltages of each supply (add
voltmeter readings). The maximum current available to the load is equal to the
current of the lowest rated supply in the series. See Figure 4.2 for a representation of
series operation.
Figure 4.2 Series Operation With and Without OVP
Note
You do not need to use remote sensing for series operation. If you choose to use it,
refer to
Diodes CR1 and CR2 protect sense circuits during transient events such as
momentary current limit events which may cause supply outputs to collapse. Use
general purpose 1A rectifiers, such as IN1004 or equivalent.
36 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
“Remote Sensing” on page 31 and connect as shown in Figure 4.2.
Page 39

Connecting
!
!
Multiple
Supplies in
Parallel
Section 4. Operation
Using Multiple Supplies
CAUTION
For parallel operation with OVP-equipped supplies, set all OVP trip points higher
than the maximum output voltage. To prevent the internal OVP fuse from blowing
during OVP trip events, add external blocking diodes as illustrated in
Use diodes rated to handle the maximum current for the supply.
CAUTION
The configuration shown in Figure 4.3 is for use with local sense only. Do not
attempt to use remote sensing with the diodes as shown. Damage to the sense
circuits may occur.
Figure 4.3.
As described below, you can connect power supplies in parallel to obtain a single
output supply with a higher output current limit. Set all the outputs to the same
voltage before connecting the positive (+) and negative (−) terminals in parallel.
The total current available is the sum of the maximum currents of each supply. The
maximum voltage available at the load is equal to the voltage of the lowest rated
supply. When you connect two supplies in parallel, the supply with the higher
voltage setting is in the current limiting mode, while the other supply controls the
output voltage.
Figure 4.3 Parallel Operation With OVP-Equipped Units (local sensing only)
Release 1.2 37
Page 40

Section 4. Operation
Using Multiple Supplies
Split Supply
Operation
Split supply operation uses two power supplies to obtain two positive voltages with
a common ground, or to obtain a positive-negative supply.
Two Positive Voltages To obtain two positive voltages, join the negative output
terminals of both supplies in a common connection as shown in Figure 4.4. The
positive output terminals provide the required voltages with respect to the common
connection.
Postive Sense
Positive Output
Terminal
Negative Output
Terminal
Return Sense
Power Supply 1
Postive Sense
Positive Output
Terminal
Negative Output
Terminal
Return Sense
Power Supply 2
Load Lines
Use the largest gauge and
shortest length possible
Positive Load
Terminal #1
Postive Load
Terminal #2
Negative Load
Terminal
Load
Figure 4.4 Split Supply Operation of Multiple Supplies (two positive voltages)
Positive-Negative Supply To obtain a positive-negative supply, connect the
negative output terminal of one supply to the positive terminal of the second supply
as shown in Figure 4.5. The positive output terminal of the first supply now provides
a positive voltage relative to the common connection. The negative output terminal
of the second supply provides the negative voltage. The current limits can be set
independently of each other. The maximum current available in split operation is
equal to the rated output of the supplies.
38 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 41

Section 4. Operation
Using Multiple Supplies
Postive Sense
Positive Output
Terminal
Negative Output
Terminal
Return Sense
Power Supply 1
Postive Sense
Positive Output
Terminal
Negative Output
Terminal
Return Sense
Load Lines
Use the largest gauge and
shortest length possible
Positive Load
Terminal
Common Load
Terminal
Negative Load
Terminal
Load
Power Supply 2
Figure 4.5 Split Supply Operation of Multiple Supplies (positive-negative supply)
Note
The optional Analog Programming (APG) Interface has a Master/Slave Tracking
feature which will allow one-knob control of both supplies in a split supply configuration.
Release 1.2 39
Page 42

Section 4. Operation
Using Multiple Supplies
40 Operating Manual for HPD Series Power Supply
Page 43

Page 44

Xantrex Technology Inc.
8999 Nelson Way
Burnaby, British Columbia
Canada V5A 4B5
604 422 8595 Tel
604 421 3056 Fax
800 667 8422 Toll Free North America
prg.info@xantrex.com
www.xantrex.com
TM-30OP-01XN
PRINTED IN CANADA
 Loading...
Loading...