W49V002FA
256K × 8 CMOS FLASH MEMORY
WITH FWH INTERFACE
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The W49V002FA is a 2-megabit, 3.3-volt only CMOS flash memory organized as 256K × 8 bits. The
device can be programmed and erased in-system with a standard 3.3V power supply. A 12-volt VPP is
not required. The unique cell architecture of the W49V002FA results in fast program/erase operations
with extremely low current consumption. This device can operate at two modes, Programmer bus
interface mode and FWH bus interface mode. As in the Programmer interface mode, it acts like the
traditional flash but with a multiplexed address inputs. But in the FWH interface mode, this device
complies with the Intel FWH specification. The device can also be programmed and erased using
standard EPROM programmers.
FEATURES
• Single 3.3-volt operations:
− 3.3-volt Read
− 3.3-volt Erase
− 3.3-volt Program
• Fast program operation:
− Byte-by-byte programming: 50 µS (typ.)
• Fast erase operation: 150 mS (typ.)
• Fast read access time: Tkq 11 nS
• Endurance: 10K cycles (typ.)
• Twenty-year data retention
• Hardware data protection
− #TBL & #WP serve as hardware protection
• One 16K bytes Boot Block with lockout
protection
• Two 8K bytes Parameter Blocks
• Four main memory blocks (with 32K bytes, 64K
bytes, 64K bytes, 64K bytes each)
• Low power consumption
− Active current: 40 mA (typ. for FWH)
• Automatic program and erase timing with
internal VPP generation
• End of program or erase detection
− Toggle bit
− Data polling
• Latched address and data
• TTL compatible I/O
• Available packages: 32L PLCC, 32L STSOP
Publication Release Date: February 19, 2002
- 1 - Revision A2
W49V002FA
T
v
#WE(FWH4)
DQ3(FWH3)
DQ2(FWH2)
DQ1(FWH1)
DQ0(FWH0)
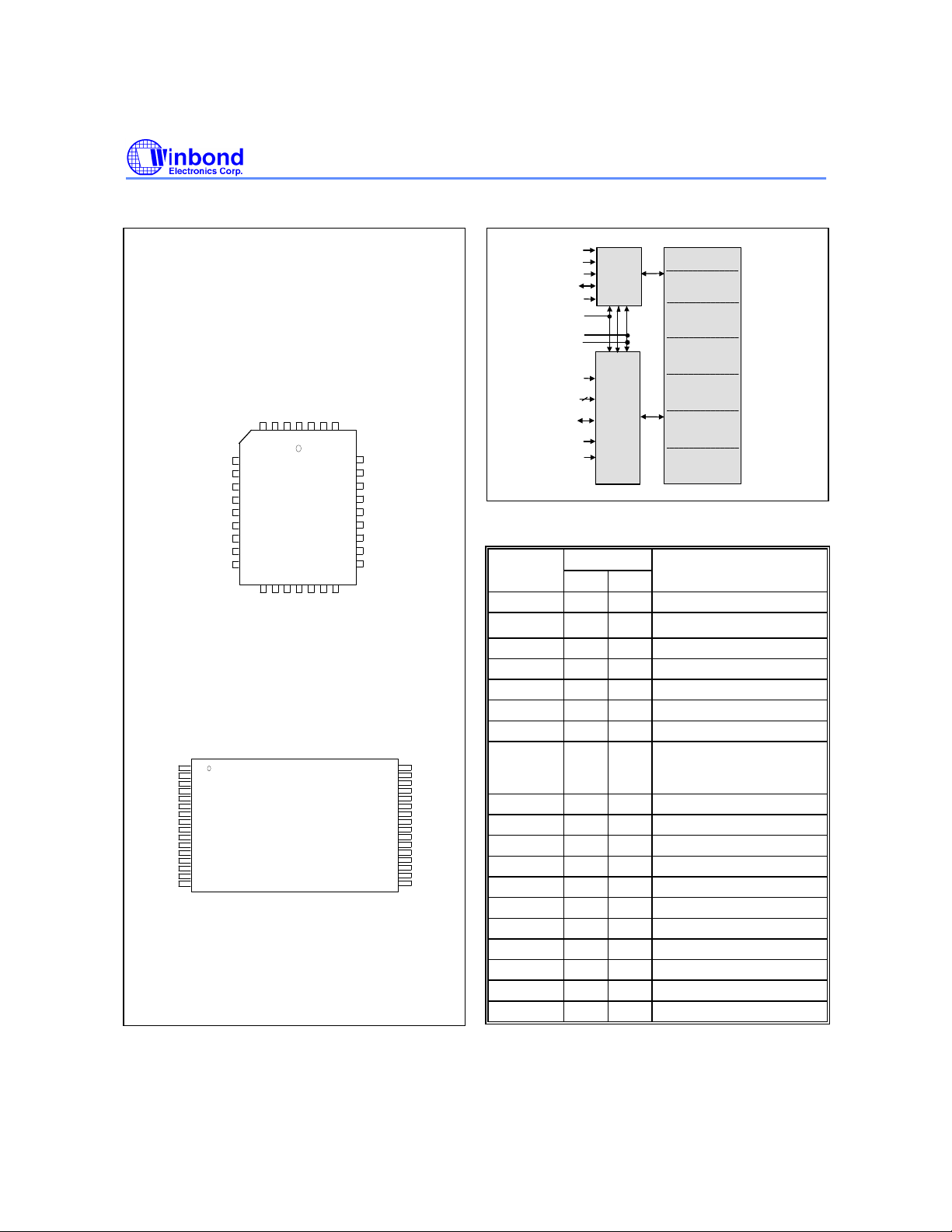
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
A
NC
NC
NC
GND
A10(FGPI4)
R/#C(CLK)
V
NC
#RESET
A9(FGPI3)
A8(FGPI2)
A7(FGPI1)
A6(FGPI0)
A5(#WP)
A4(#TBL)
IC
DD
A7(FGPI1)
A6(FGPI0)
A5(#WP)
A4(#TBL)
A3(ID3)
A2(ID2)
A1(ID1)
A0(ID0)
DQ0(FWH0)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
A
9
8
^
F
F
G
G
P
P
I
I
3
2
v
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
D
D
Q
Q
1
^
F
F
W
W
H
H
1
v
^
#
R
E
S
E
N
C
v
1
2
32L
PLCC
D
G
Q
N
2
3
D
^
^
F
W
H
2
3
v
v
32L
TSOP
R
#
C
^
C
V
L
D
K
D
v
1817161514
D
D
Q
Q
5
4
^
^
R
R
S
S
V
V
v
v
BLOCK DIAGRAM
#WP
#TBL
CLK
FWH[3:0]
FWH4
A
1
0
^
F
G
P
I
4
A[10:0]
DQ[7:0]
303132
29
IC
28
GND
NC
27
26
GND
25
VDD
24
#OE(#INIT)
23
#WE(FWH4)
22
NC
21
DQ7(RSV)
2019
D
Q
6
^
R
S
V
v
PIN DESCRIPTION
SYM. INTERFACE
IC * * Interface Mode Selection
#RESET * * Reset
#INIT * Initialize
Interface
IC
#RESET
#INIT
R/#C
Programmer
Interface
#OE
#WE
PGM FWH
BOOT BLOCK
16K BYTES
PARAMETER
BLOCK1
8K BYTES
PARAMETER
BLOCK2
8K BYTES
MAIN MEMORY
BLOCK1
32K BYTES
MAIN MEMORY
BLOCK2
64K BYTES
MAIN MEMORY
BLOCK3
64K BYTES
MAIN MEMORY
BLOCK4
64K BYTES
#TBL * Top Boot Block Lock
#WP * Write Protect
CLK * CLK Input
FGPI[4:0] * General Purpose Inputs
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
#OE(#INIT)
NC
DQ7(RSV)
DQ6(RSV)
DQ5(RSV)
DQ4(RSV)
GND
A0(ID0)
A1(ID1)
A2(ID2)
A3(ID3)
ID[3:0] * Identification Inputs They
Are Internal Pull Down to
VSS
FWH[3:0]
FWH4
* Address/Data Inputs
* FWH Cycle Initial
R/#C * Row/Column Select
A[10:0] * Address Inputs
DQ[7:0] * Data Inputs/Outputs
#OE * Output Enable
#WE * Write Enable
VDD * * Power Supply
GND * * Ground
RSV * * Reserved Pins
NC * * No Connection
3FFFF
3C000
3BFFF
3A000
39FFF
38000
37FFF
30000
2FFFF
20000
1FFFF
10000
0FFFF
00000
PIN NAME
- 2 -

W49V002FA
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Interface Mode Selection And Description
This device can be operated in two interface modes, one is Programmer interface mode, the other is
FWH interface mode. The IC pin of the device provides the control between these two interface
modes. These interface modes need to be configured before power up or return from #RESET. When
IC pin is set to high state, the device will be in the Programmer mode; while the IC pin is set to low
state (or leaved no connection), it will be in the FWH mode. In Programmer mode, this device just
behaves like traditional flash parts with 8 data lines. But the row and column address inputs are
multiplexed, which go through address inputs A[10:0]. For FWH mode, It complies with the FWH
Interface Specification. Through the FWH[3:0] to communicate with the system chipset .
Read (Write) Mode
In Programmer interface mode, the read (write) operation of the W49V002FA is controlled by #OE
(#WE). The #OE(#WE) is held low for the host to obtain(write) data from(to) the outputs(inputs). #OE
is the output control and is used to gate data from the output pins. The data bus is in high impedance
state when #OE is high. As for in the FWH interface mode, the read or write is determined by the "bit 0
& bit 1 of START CYCLE ". Refer to the FWH cycle definition for further details.
Reset Operation
The #RESET input pin can be used in some application. When #RESET pin is at high state, the device
is in normal operation mode. When #RESET pin is at low state, it will halt the device and all outputs will
be at high impedance state. As the high state re-asserted to the #RESET pin, the device will return to
read or standby mode, it depends on the control signals.
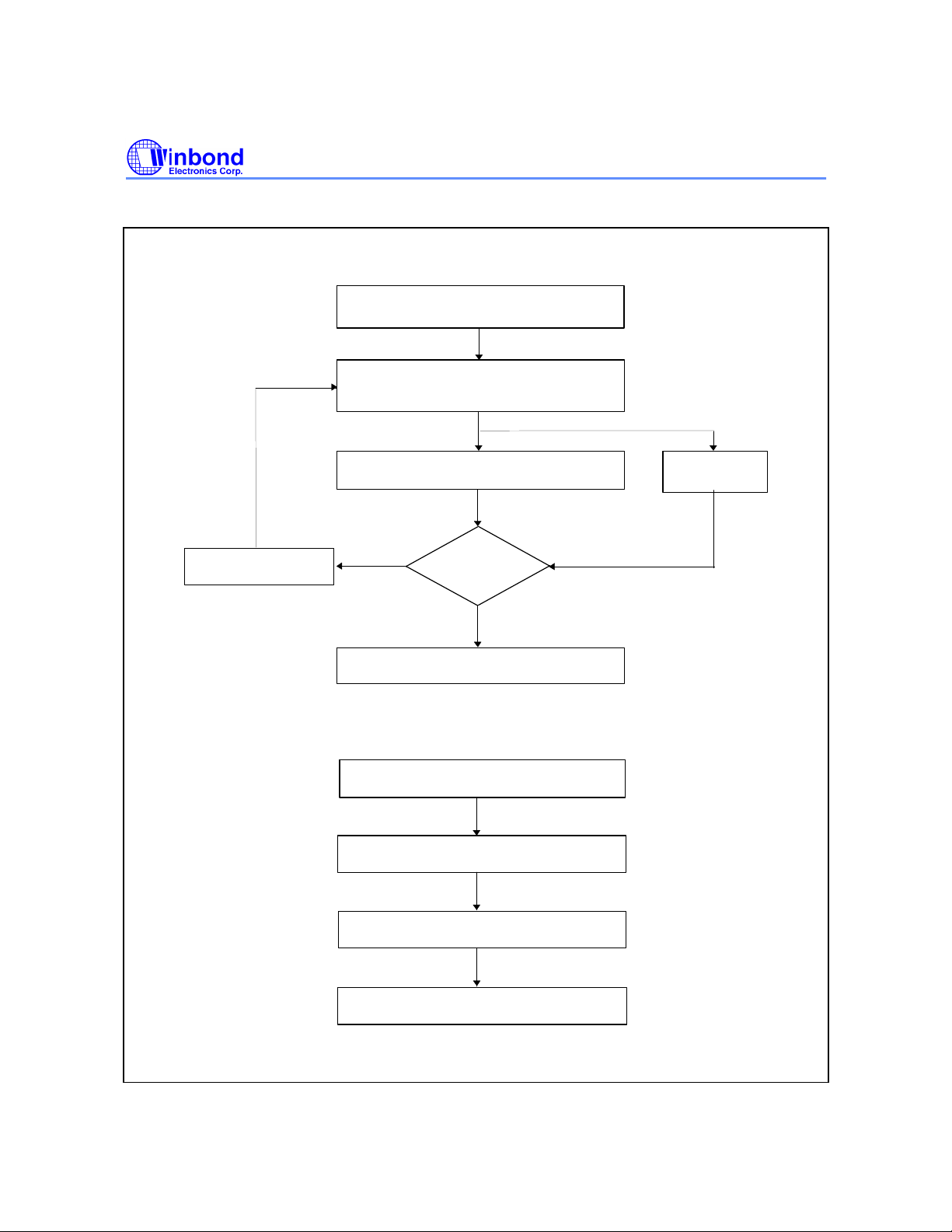
Chip Erase Operation
The chip-erase mode can be initiated by a six-byte command sequence. After the command loading
cycle, the device enters the internal chip erase mode, which is automatically timed and will be
completed within fast 150 mS (typical). The host system is not required to provide any control or timing
during this operation. If the boot block programming lockout is activated, only the data in the other
memory blocks will be erased to FF(hex) while the data in the boot block will not be erased (remains
as the same state before the chip erase operation). The entire memory array will be erased to FF(hex)
by the chip erase operation if the boot block programming lockout feature is not activated. The device
will automatically return to normal read mode after the erase operation completed. Data polling and/or
Toggle Bits can be used to detect end of erase cycle.
Sector Erase Operation
The seven sectors, one boot block and two parameter memory and four main blocks, can be erased
individually by initiating a six-byte command sequence. Sector address is latched on the falling #WE
edge of the sixth cycle, while the 30(hex) data input command is latched at the rising edge of #WE.
After the command loading cycle, the device enters the internal sector erase mode, which is
automatically timed and will be completed within fast 150 mS (typical). The host system is not required
to provide any control or timing during this operation. The device will automatically return to normal
read mode after the erase operation completed. Data polling and/or Toggle Bits can be used to detect
end of erase cycle.
Publication Release Date: February 19, 2002
- 3 - Revision A2

W49V002FA
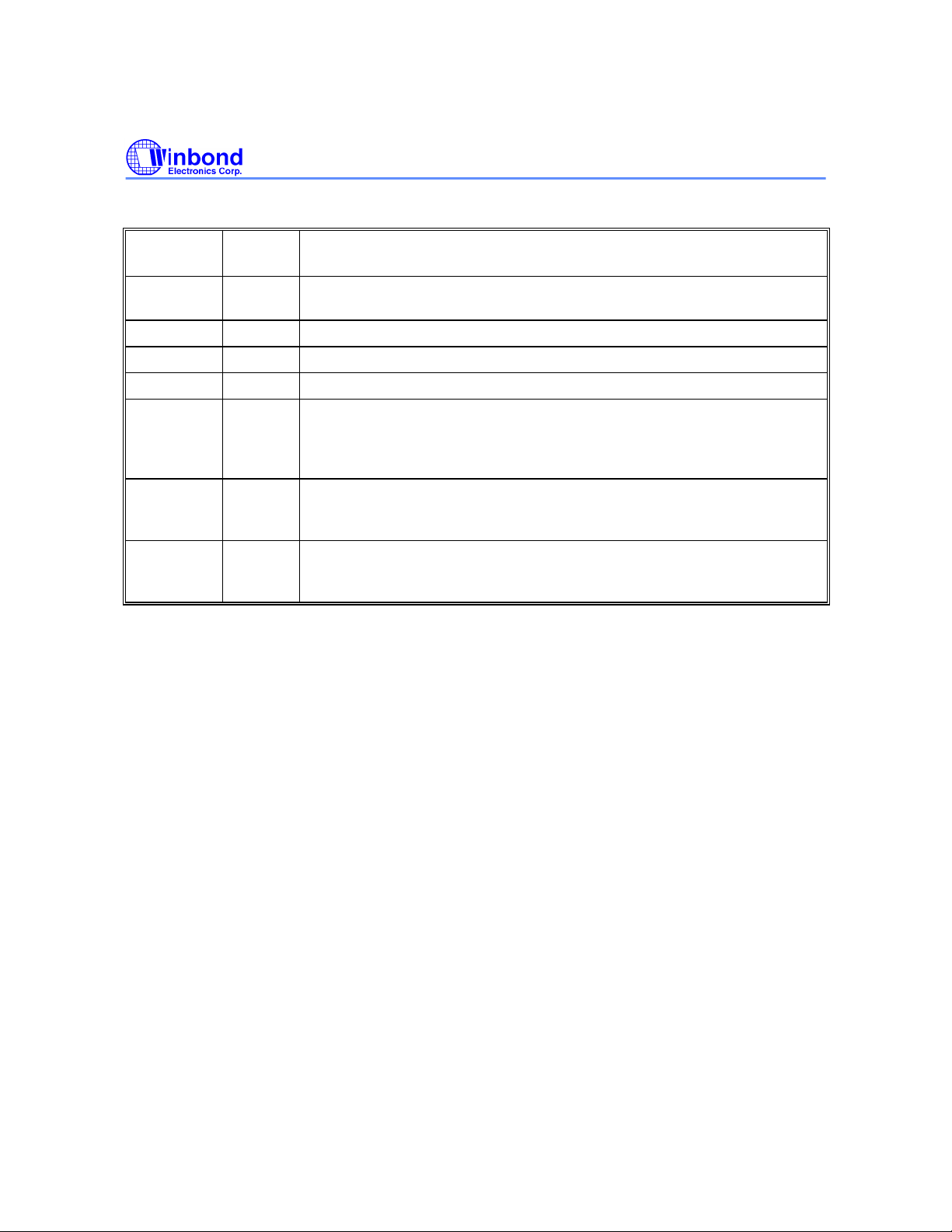
Program Operation
The W49V002FA is programmed on a byte-by-byte basis. Program operation can only change logical
data "1" to logical data "0." The erase operation, which changed entire data in main memory and/or
boot block from "0" to "1", is needed before programming.
The program operation is initiated by a 4-byte command cycle (see Command Codes for Byte
Programming). The device will internally enter the program operation immediately after the byteprogram command is entered. The internal program timer will automatically time-out (100 µS max. TBP) once it is completed and then return to normal read mode. Data polling and/or Toggle Bits can be
used to detect end of program cycle.
Boot Block Operation and Hardware Protection at Initial- #TBL & #WP
There are two alternatives to set the boot block. One is software command sequences method; the
other is hardware method. 16K-byte in the top location of this device can be locked as boot block,
which can be used to store boot codes. It is located in the last 16K bytes of the memory with the
address range from 3C000(hex) to 3FFFF(hex).
Please see Command Codes for Boot Block Lockout Enable for the specific code. Once this feature is
set, the data for the designated block cannot be erased or programmed (programming lockout), other
memory locations can be changed by the regular programming method.
Besides the software method, there is a hardware method to protect the top boot block and other
sectors. Before program/erase to this device, set the #TBL pin to low state and then the top boot block
will not be programmed/erased. When enabling hardware top boot block, #TBL being low state, it will
override the software method setting. That is, if #TBL is at low state, then top boot block cannot be
programmed/erased no matter how the software boot block lock setting.
Another pin, #WP, will protect the whole chip if this pin is set to low state before program/erase. The
enable of this pin will override the #TBL setting. That is, the top boot block cannot be
programmed/erased if this pin is set to low no matter how the #TBL or software boot block lock setting.
Hardware Data Protection
The integrity of the data stored in the W49V002FA is also hardware protected in the following ways:
(1) Noise/Glitch Protection: A #WE pulse of less than 15 nS in duration will not initiate a write cycle.
(2) VDD Power Up/Down Detection: The programming and read operation are inhibited when VDD is
less than 1.5V typical.
(3) Write Inhibit Mode: Forcing #OE low or #WE high will inhibit the write operation. This prevents
inadvertent writes during power-up or power-down periods.
(4) VDD power-on delay: When VDD has reached its sense level, the device will automatically time-out 5
mS before any write (erase/program) operation.
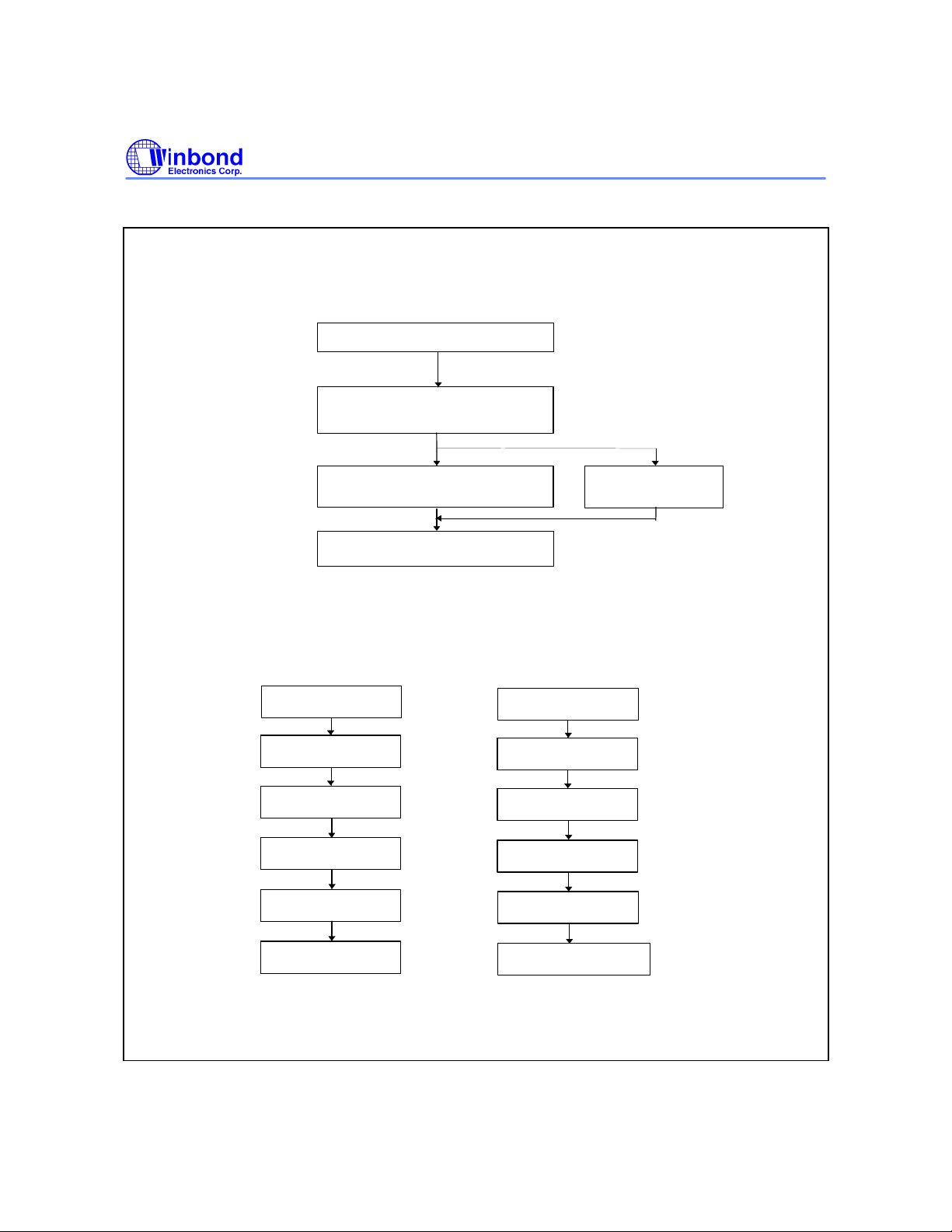
Data Polling (DQ7)- Write Status Detection
The W49V002FA includes a data polling feature to indicate the end of a program or erase cycle.
When the W49V002FA is in the internal program or erase cycle, any attempts to read DQ7 of the last
byte loaded will receive the complement of the true data. Once the program or erase cycle is
completed, DQ7 will show the true data. Note that DQ7 will show logical "0" during the erase cycle, and
when erase cycle has been completed it becomes logical "1" or true data.
- 4 -
W49V002FA
Toggle Bit (DQ6)- Write Status Detection
In addition to data polling, the W49V002FA provides another method for determining the end of a
program cycle. During the internal program or erase cycle, any consecutive attempts to read DQ6 will
produce alternating 0's and 1's. When the program or erase cycle is completed, this toggling between
0's and 1's will stop. The device is then ready for the next operation.
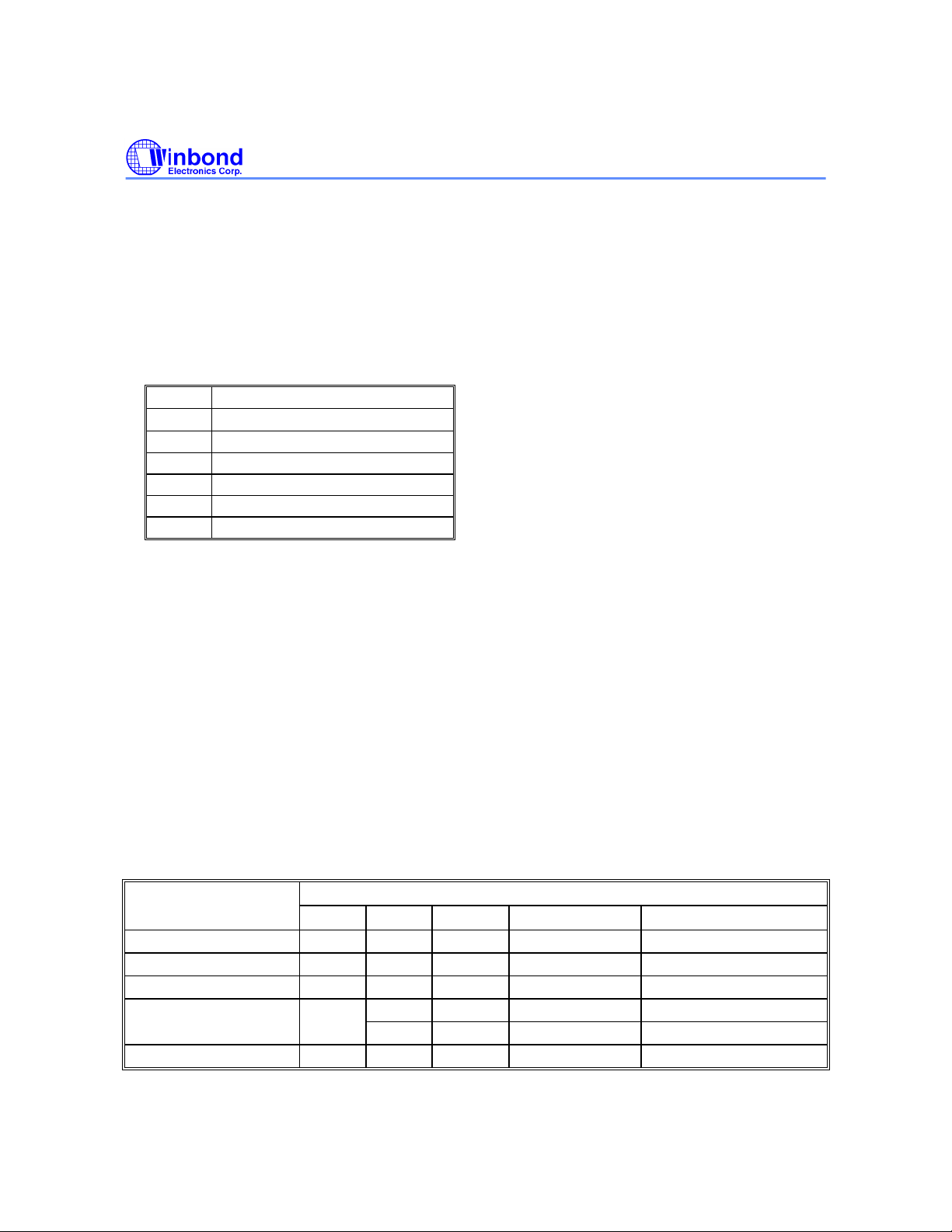
General Purpose Inputs Register
This register reads the FGPI[4:0] pins on the W49V002FA.This is a pass-through register which can
read via memory address FFBC0100(hex). Since it is pass-through register, there is no default value.
BIT FUNCTION
7 − 5
Product Identification
Reserved
4 Read FGPI4 pin status
3 Read FGPI3 pin status
2 Read FGPI2 pin status
1 Read FGPI1 pin status
0 Read FGPI0 pin status
The product ID operation outputs the manufacturer code and device code. Programming equipment
automatically matches the device with its proper erase and programming algorithms.
The manufacturer and device codes can be accessed by software operation. In the software access
mode, a six-byte (or JEDEC 3-byte) command sequence can be used to access the product ID for
programmer interface mode. A read from address 0000(hex) outputs the manufacturer code, DA(hex).
A read from address 0001(hex) outputs the device code, 32(hex).” The product ID operation can be
terminated by a three-byte command sequence or an alternate one-byte command sequence (see
Command Definition table).
As for FWH interface mode, a read from FFBC, 0000(hex) can output the manufacturer code,
DA(hex). A read from FFBC, 0001(hex) can output the device code 32(hex).
TABLE OF OPERATING MODES
Operating Mode Selection - Programmer Mode
(VHH = 12V ± 5%)
MODE PINS
Read VIL VIH VIH AIN Dout
Write VIH VIL VIH AIN Din
Standby X X VIL X High Z
Write Inhibit VIL X VIH X High Z/DOUT
X VIH VIH X High Z/DOUT
Output Disable VIH X VIH X High Z
#OE #WE #RESET
ADDRESS DQ.
Publication Release Date: February 19, 2002
- 5 - Revision A2
W49V002FA
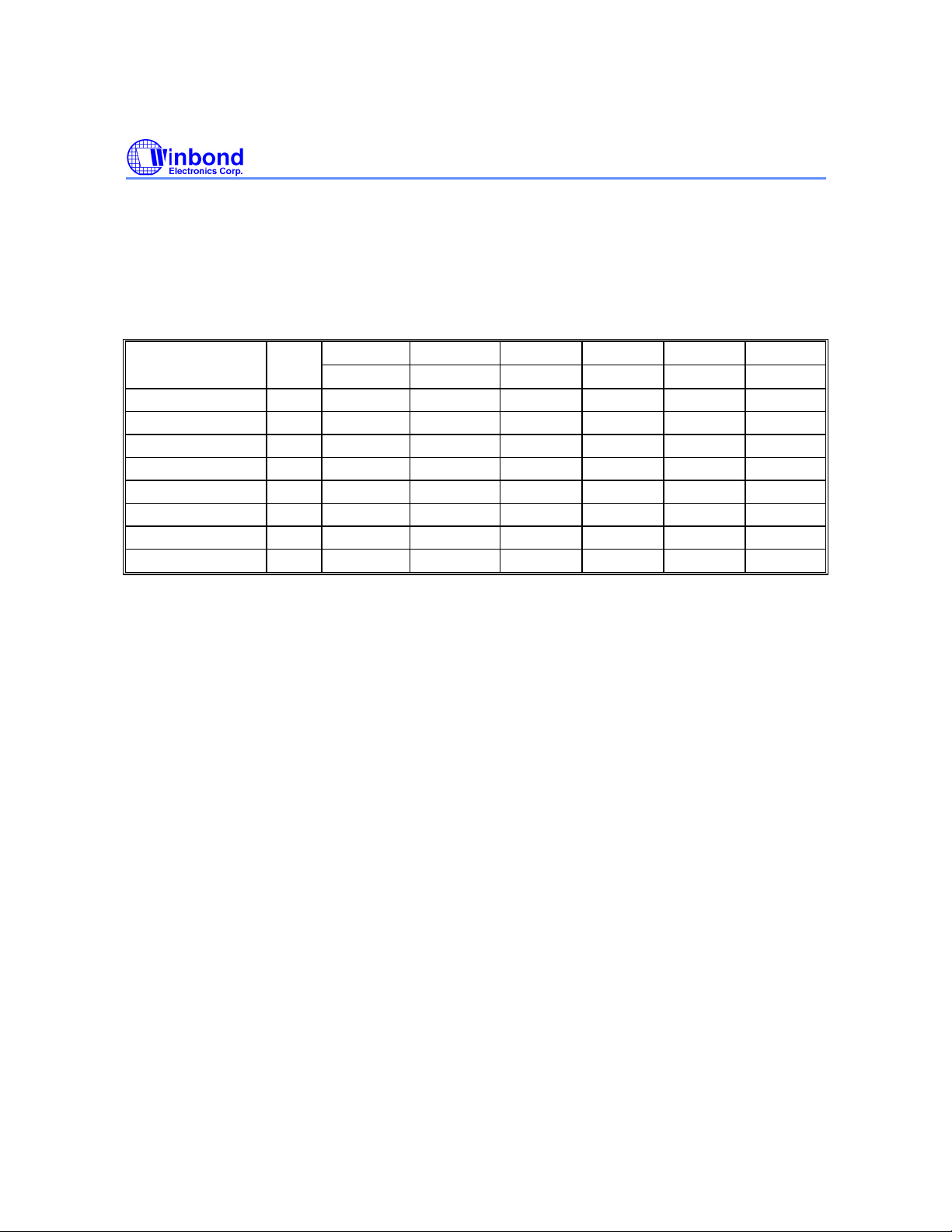
Operating Mode Selection - FWH Mode
Operation modes in FWH interface mode are determined by "START Cycle" when it is selected. When
it is not selected, its outputs (FWH[3:0]) will be disable. Please reference to the "FWH Cycle
Definition".
TABLE OF COMMAND DEFINITION
COMMAND NO. OF 1ST CYCLE 2ND CYCLE 3RD CYCLE 4TH CYCLE 5TH CYCLE 6TH CYCLE
DESCRIPTION Cycles
Read 1 AIN D
Chip Erase 6 5555 AA 2AAA 55 5555 80 5555 AA 2AAA 55 5555 10
Sector Erase 6 5555 AA 2AAA 55 5555 80 5555 AA 2AAA 55 SA 30
Byte Program 4 5555 AA 2AAA 55 5555 A0 AIN D
Boot Block Lockout 6 5555 AA 2AAA 55 5555 80 5555 AA 2AAA 55 5555 40
Product ID Entry 3 5555 AA 2AAA 55 5555 90
Product ID Exit
Product ID Exit
(1)
3 5555 AA 2AAA 55 5555 F0
(1)
1 XXXX F0
Addr. Data Addr. Data Addr. Data Addr. Data Addr. Data Addr. Data
OUT
IN
Notes:
1. The cycle means the write command cycle not the FWH clock cycle.
2. The Column Address / Row Address are mapped to the Low / High order Internal Address. i.e. Column Address
A[10:0] are mapped to the internal A[10:0], Row Address A[6:0] are mapped to the internal A[17:11]
3. Address Format: A14−A0 (Hex); Data Format: DQ7-DQ0 (Hex)
4. Either one of the two Product ID Exit commands can be used.
5. SA: Sector Address
SA = 3C000h to 3FFFFh for Boot Block
SA = 3A000h to 3BFFFh for Parameter Block1
SA = 38000h to 39FFFh for Parameter Block2
SA = 30000h to 37FFFh for Main Memory Block1
SA = 2XXXXh for Main Memory Block2
SA = 1XXXXh for Main Memory Block3
SA = 0XXXXh for Main Memory Block4
- 6 -
FWH CYCLE DEFINITION
Data Phase for Memory Cycle. The data transfer least significant nibble first
W49V002FA
FIELD NO. OF
CLOCKS
START 1 "1101b" indicates FWH Memory Read cycle; while "1110b" indicates FWH
Memory Write cycle.
IDSEL 1 This one clock field indicates which FWH component is being selected.
MSIZE 1 Memory Size. There is always show “0000b” for single byte access.
TAR 2 Turned Around Time
ADDR 7 Address Phase for Memory Cycle. FWH supports the 28 bits address
protocol. The addresses transfer most significant nibble first and least
significant nibble last. (i.e. Address[27:24] on FWH[3:0] first , and
Address[3:0] on FWH[3:0] last.)
SYNC N Synchronous to add wait state. "0000b" means Ready, "0101b" means
Short Wait, "0110b" means Long Wait, "1001b" for DMA only, "1010b"
means error, and other values are reserved.
DATA 2
and most significant nibble last. (i.e. DQ[3:0] on FWH[3:0] first , then
DQ[7:4] on FWH[3:0] last.)
DESCRIPTION
Publication Release Date: February 19, 2002
- 7 - Revision A2
Embedded Programming Algorithm
Write Program Command Sequence
W49V002FA
Start
(see below)
Increment Address
Program Command Sequence (Address/Command):
#Data Polling/ Toggle bit
No
Last Address
?
Programming Completed
5555H/AAH
2AAAH/55H
Yes
Pause T
BP
5555H/A0H
Program Address/Program Data
- 8 -
Embedded Erase Algorithm
W49V002FA
Start
Write Erase Command Sequence
(see below)
#Data Polling or Toggle
Successfully Completed
Erasure Completed
Chip Erase Command Sequence
(Address/Command):
5555H/AAH
2AAAH/55H
5555H/80H
5555H/AAH
Individual Sector Erase
Command Sequence
(Address/Command):
5555H/AAH
2AAAH/55H
5555H/80H
5555H/AAH
Pause
TEC/T
SEC
2AAAH/55H
5555H/10H
2AAAH/55H
Sector Address/30H
Publication Release Date: February 19, 2002
- 9 - Revision A2
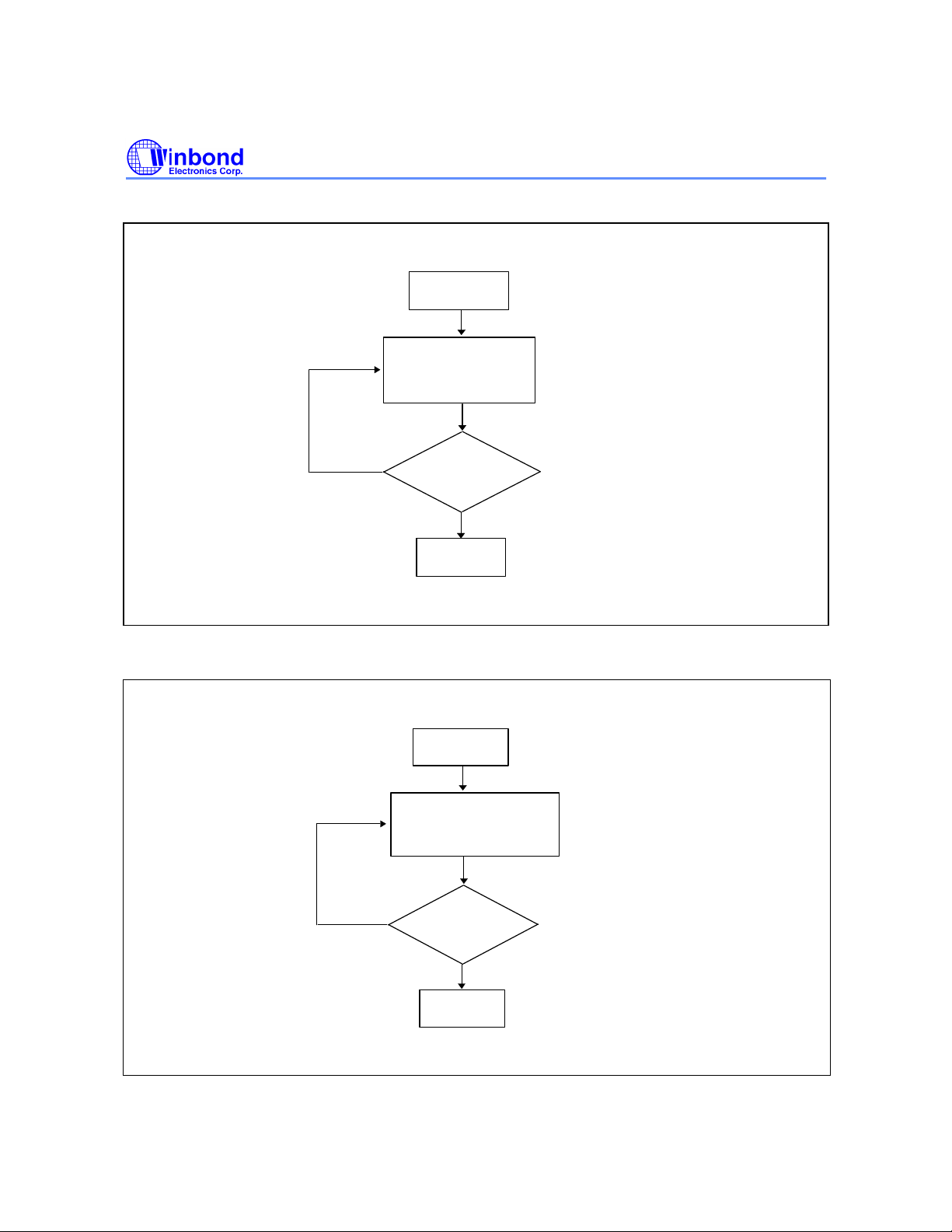
Embedded #Data Polling Algorithm
Read Byte
(DQ0 - DQ7)
Address = VA
W49V002FA
Start
VA = Byte address for programming
= Any of the sector addresses within
the sector being erased during sector
erase operation
= Valid address equals any sector group
address during chip erase
No
Embedded Toggle Bit Algorithm
DQ7 = Data
?
Yes
Pass
Start
Read Byte
(DQ0 - DQ7)
Address = Don't Care
Yes
DQ6 = Toggle
?
No
Pass
- 10 -
 Loading...
Loading...