
TSI
Number
030-500
Vehicle Management System
Vectro II From 1998
PV776-TSP144528

Foreword
The descriptions and service procedures contained in this manual are based on designs and methods studies carried out up to June 2001.
The products are under continuous development. Vehicles and components produced
after the above date may therefore have different specifications and repair methods.
When this is believed to have a significant bearing on this manual, supplementary service bulletins will be issued to cover the changes.
The new edition of this manual will update the changes.
In service procedures where the title incorporates an operation number, this is a refer-
ence to an S.R.T. (Standard Repair Time).
Service procedures which do not include an operation number in the title are for gen-
eral information and no reference is made to an S.R.T.
The following levels of observations, cautions and warnings are used in this Service
Documentation:
Note: Indicates a procedure, practice, or condition that must be followed in order to
have the vehicle or component function in the manner intended.
Caution: Indicates an unsafe practice where damage to the product could occur.
Warning: Indicates an unsafe practice where personal injury or severe damage to the
product could occur.
Danger: Indicates an unsafe practice where serious personal injury or death could oc-
cur.
Volvo Trucks North America, Inc.
Greensboro, NC USA
Order number: PV776-144528
© 2001 Volvo Trucks North America, Inc., Greensboro, NC USA
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in
retrieval system, or transmitted in any forms by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written
permission of Volvo Trucks North America, Inc.

Contents
General .................................................................................................... 7
Vehicle Management System ................................................................ 7
Engine Control System Glossary ........................................................ 8
Specifications ....................................................................................... 10
Description of Signals .......................................................................... 10
EECU (D7C) and Breakout Box Connected in Series Between
EECU and Wiring Harness ............................................................... 10
EECU, D7C, with Breakout Box Connected to Wiring Harness Only 13
EECU (D12B and D12C), Breakout Box Connected in Series Be-
tween EECU and Wiring Harness ..................................................... 16
EECU (D12B and D12C), Breakout Box Connected to Wiring
Harness Only ..................................................................................... 19
Pinouts ................................................................................................. 22
Engine Electronic Control Unit (EECU) ............................................ 22
Pinouts ................................................................................................. 26
Vehicle Electronic Control Unit(VECU) ............................................. 26
Schematic ............................................................................................ 28
D12B .................................................................................................. 28
Schematic ............................................................................................ 29
D12C ................................................................................................. 29
Schematic ............................................................................................ 30
D7C ................................................................................................... 30
Schematic ............................................................................................ 31
VECU ................................................................................................. 31
Tools ...................................................................................................... 33
Special Tools ....................................................................................... 33
Other Special Equipment .................................................................... 35
Design and Function ........................................................................... 37
Vehicle Management System .............................................................. 37
Strategy ............................................................................................. 37
Conventional Control Systems .......................................................... 37
Data Link System .............................................................................. 38
Data Links, Design and Function ...................................................... 39
Diagnostic Connector ........................................................................ 47
Communication Equipment ............................................................... 48
Instrument Cluster ............................................................................. 49
Vehicle Electronic Control Unit (VECU) ............................................ 50
Engine Electronic Control Unit .......................................................... 51
ABS Brake System ECU ................................................................... 63
SRS Airbag ECU ............................................................................... 64
Transmission ECU ............................................................................. 65
Breakout Boxes and Harnesses ........................................................ 66
VECU Overview ................................................................................ 67
VECU Functions ................................................................................ 68
Sensor Locations ............................................................................... 73
Control Unit Locations ....................................................................... 77
Fuses and Relays .............................................................................. 81
Troubleshooting ................................................................................... 85
Fault Code Troubleshooting ................................................................... 85
Message and Parameter Descriptions ................................................ 85
FMI Table ............................................................................................. 87
Reading/Clearing Fault Codes .......................................................... 88
1

Fault Tracing Strategy ....................................................................... 88
MID 128 EECU ...................................................................................... 92
MID 128 Fault Code Table .................................................................. 92
MID 128 PID 45 Preheater Status ...................................................... 96
Fault Codes ....................................................................................... 96
MID 128 PID 45 Preheater Status, Check .......................................... 97
MID 128 PID 49 ABS Control Status .................................................. 98
Fault Codes ....................................................................................... 98
MID 128 PID 49 ABS Control Status, Check ...................................... 99
MID 128 PID 84 Road Speed ........................................................... 100
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 100
MID 128 PID 84 Road Speed, Check ............................................... 101
MID 128 PID 85 Cruise Control Status ............................................. 102
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 102
MID 128 PID 85 Cruise Control Status, Check ................................ 103
MID 128 PID 91 Accelerator Pedal Position ..................................... 104
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 104
MID 128 PID 91 Accelerator Pedal Position, Check ......................... 105
MID 128 PID 94 Fuel Delivery Pressure ........................................... 106
D7C and D12C ................................................................................ 106
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 106
MID 128 PID 94 Fuel Delivery Pressure, Check .............................. 107
D7C and D12C ................................................................................ 107
MID 128 PID 100 Engine Oil Pressure ............................................. 110
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 110
MID 128 PID 100 Engine Oil Pressure, Check ................................. 111
MID 128 PID 102 Boost Pressure ..................................................... 114
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 114
MID 128 PID 102 Boost Pressure, Check ........................................ 115
MID 128 PID 105 Boost Air Temperature ......................................... 118
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 118
MID 128 PID 105 Boost Air Temperature, Check ............................. 119
MID 128 PID 107 Air Filter Differential Pressure .............................. 122
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 122
MID 128 PID 107 Air Filter Differential Pressure, Check .................. 124
MID 128 PID 108 Atmospheric Pressure .......................................... 125
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 125
MID 128 PID 110 Engine Coolant Temperature ............................... 126
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 126
MID 128 PID 110 Engine Coolant Temperature, Check ................... 127
MID 128 PID 111 Coolant Level ....................................................... 129
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 129
MID 128 PID 111 Coolant Level, Check ........................................... 130
MID 128 PID 158 Battery Voltage ..................................................... 131
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 131
MID 128 PID 158 Battery Voltage, Check ........................................ 132
MID 128 PID 172 Air Inlet Temperature ............................................ 133
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 133
MID 128 PID 172 Air Inlet Temperature, Check ............................... 134
MID 128 PID 174 Fuel Temperature ................................................. 136
D7C and D12C ................................................................................ 136
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 136
MID 128 PID 174 Fuel Temperature, Check ..................................... 137
D7C and D12C ................................................................................ 137
MID 128 PID 175 Engine Oil Temperature ....................................... 140
2

Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 140
MID 128 PID 175 Engine Oil Temperature, Check ........................... 141
MID 128 PID 228 Road Speed Sensor Calibration .......................... 144
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 144
MID 128 PID 228 Road Speed Sensor Calibration, Check .............. 145
MID 128 PPID 86 Engine Brake Torque Percent .............................. 146
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 146
MID 128 PPID 86 Engine Brake Torque Percent, Check ................. 147
MID 128 PPID 119 High Coolant Temperature ................................. 148
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 148
MID 128 PPID 119 High Coolant Temperature, Check .................... 149
MID 128 PPID 122 VCB Engine Compression Brake ...................... 151
D12B and D12C .............................................................................. 151
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 151
MID 128 PPID 122 VCB Engine Compression Brake, Check .......... 152
D12B and D12C .............................................................................. 152
MID 128 PPID 123 EPG 2 ................................................................ 153
D12B and D12C .............................................................................. 153
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 153
MID 128 PPID 123 EPG 2, Check .................................................... 154
D12B and D12C .............................................................................. 154
MID 128 PPID 124 EPG 1 ................................................................ 155
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 155
MID 128 PPID 124 EPG 1, Check .................................................... 156
MID 128 SID 1/2/3/4/5/6 Injector ..................................................... 157
D12B and D12C .............................................................................. 157
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 157
MID 128 SID 1/2/3/4/5/6 Injector, Check .......................................... 159
D12B and D12C .............................................................................. 159
MID 128 SID 17 Fuel Shutoff Valve .................................................. 161
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 161
MID 128 SID 17 Fuel Shutoff Valve, Check ...................................... 162
D7C only .......................................................................................... 162
MID 128 SID 20 Timing Sleeve ......................................................... 163
D7C only .......................................................................................... 163
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 163
MID 128 SID 20 Timing Sleeve, Check ............................................ 165
D7C only .......................................................................................... 165
MID 128 SID 21 Engine Position Timing Sensor .............................. 166
D12B and D12C .............................................................................. 166
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 166
MID 128 SID 21 Engine Position Timing Sensor, Check .................. 167
D12B and D12C .............................................................................. 167
MID 128 SID 21 Needle Lift Sensor ................................................. 168
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 168
MID 128 SID 21 Needle Lift Sensor, Check ..................................... 169
D7C only .......................................................................................... 169
MID 128 SID 22 Engine Speed Sensor ............................................ 170
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 170
MID 128 SID 22 Engine Speed Sensor, Check ................................ 171
MID 128 SID 23 Rack Actuator ......................................................... 172
D7C only .......................................................................................... 172
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 172
MID 128 SID 23 Rack Actuator, Check ............................................. 174
D7C only .......................................................................................... 174
3

MID 128 SID 24 Rack Position Sensor ............................................. 175
D7C only .......................................................................................... 175
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 175
MID 128 SID 24 Rack Position Sensor, Check ................................. 176
D7C only .......................................................................................... 176
MID 128 SID 33 Fan Control ............................................................. 177
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 177
MID 128 SID 33 Fan Control, Check ................................................ 178
MID 128 SID 64 Redundant Engine Speed Sensor ......................... 179
D7C only .......................................................................................... 179
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 179
MID 128 SID 64 Redundant Engine Speed Sensor, Check ............. 180
D7C only .......................................................................................... 180
MID 128 SID 70 Preheater Element 1 .............................................. 181
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 181
MID 128 SID 70 Preheater Element 1, Check .................................. 182
MID 128 SID 71 Preheater Element 2 .............................................. 183
D12B only ........................................................................................ 183
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 183
MID 128 SID 71 Preheater Element 2, Check .................................. 184
D12B ................................................................................................ 184
MID 128 SID 230 Idle Validation Switch 1 ........................................ 185
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 185
MID 128 SID 230 Idle Validation Switch 1, Check ............................ 186
MID 128 SID 231 SAE J1939 Control Link ....................................... 187
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 187
MID 128 SID 232 5 Volt DC Supply .................................................. 189
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 189
MID 128 SID 232 5 Volt DC Supply, Check ...................................... 190
MID 128 SID 240 Program Memory ................................................. 191
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 191
MID 128 SID 250 SAE J1587/1708 Information Link ....................... 192
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 192
MID 128 SID 253 Data Set Memory EEPROM ................................ 193
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 193
MID 128 SID 254 Engine Electronic Control Unit (EECU) ............... 194
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 194
MID 144 VECU .................................................................................... 196
MID 144 Fault Code Table ................................................................ 196
MID 144 PID 29 Second Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor ........... 198
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 198
MID 144 PID 29 Second Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor, Check 199
MID 144 PID 84 Road Speed ........................................................... 201
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 201
MID 144 PID 84 Road Speed, Check ............................................... 202
MID 144 PID 91 Accelerator Pedal Position ..................................... 204
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 204
MID 144 PID 91 Accelerator Pedal Position, Check ......................... 205
MID 144 PID 152 VECU, Number of Resets .................................... 207
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 207
MID 144 PPID 69 Idle Validation Switch ........................................... 208
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 208
MID 144 PPID 69 Idle Validation Switch, Check .............................. 209
MID 144 PPID 70 Pedal Switches, Supply ....................................... 211
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 211
4

MID 144 PPID 70 Pedal Switches, Supply, Check ........................... 212
MID 144 PPID 71 Cruise Control and Engine Brake, Supply Switch 215
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 215
MID 144 PPID 71 Cruise Control and Engine Brake, Supply
Switch, Check .................................................................................... 216
MID 144 PPID 72 Accelerator Pedal, Supply Sensors ..................... 220
Fault Codess ................................................................................... 220
MID 144 PPID 72 Accelerator Pedal, Supply Sensors, Check ......... 221
MID 144 PPID 73 Second Accelerator Pedal, Supply Sensors ........ 223
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 223
MID 144 PPID 73 Second Accelerator Pedal, Supply Sensors,
Check ................................................................................................. 224
MID 144 PPID 75 Range Inhibitor, Solenoid Valve Status ............... 226
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 226
MID 144 PPID 75 Range Inhibitor, Solenoid Valve Status, Check ... 227
MID 144 SID 230 Idle Validation Switch 1 ........................................ 229
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 229
MID 144 SID 230 Idle Validation Switch 1, Check ............................ 230
MID 144 SID 231 SAE J1939 Control Link ....................................... 232
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 232
MID 144 SID 231 SAE J1939 Control Link, Check .......................... 233
MID 144 SID 240 Program Memory ................................................. 234
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 234
MID 144 SID 243 Cruise Control Set Switch .................................... 235
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 235
MID 144 SID 243 Cruise Control Set Switch, Check ....................... 236
MID 144 SID 250 SAE J1587/1708 Information Link ....................... 238
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 238
MID 144 SID 250 SAE J1587/1708 Information Link, Check ........... 239
MID 144 SID 253 Data Set Memory EEPROM ................................ 240
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 240
MID 144 PSID 3 Idle Validation Switch 3 ......................................... 241
Fault Codes ..................................................................................... 241
MID 144 PSID 3 Idle Validation Switch 3, Check ............................. 242
Service Procedures ........................................................................... 245
Engine ECU, Replacement ................................................................ 245
Feedback
Operation Numbers
5

6
Group 28 General
General
Vehicle Management System
W2002520
This information covers the Vehicle Management System, which includes VECTRO II
electronics, the vehicle ECU, and other control systems used in the vehicle.
7

Group 28 General
Engine Control System Glossary
ATA
FMI (Failure Mode Identifier)
American Trucking Association
ATDC (After Top Dead Center)
The 180
top center (normal direction of rotation).
AC (Alternating Current)
An electrical current that alternates level and direction.
BTDC (Before Top Dead Center)
The 180
top center (normal direction of rotation).
INFO lamp
Light that warns the operator of an active diagnostic fault
code; also referred to as the diagnostic lamp.
Data link
An electrical connection for communication with other
microprocessor-based devices (such as powertrain control, trip recorders and maintenance systems) that are
compatible with the ATA and SAE standard.
Diagnostic fault code
These codes indicate an electronic system malfunction,
indicating a problem with the D12 electrical systems.
Diagnostic flash code
Codes flashed out in a series via the INFO lamp to indicate an active fault code.
DC (Direct Current)
An electrical current that flows in one direction only.
EEPROM (Electrical Erasable Programmable Read
Only Memory)
of crankshaft rotation after the piston reaches
of crankshaft rotation before the piston reaches
Numbers and names used to identify how a system or
part failed.
FMI Description
0 Data valid but above normal operating range
1
Data valid but below normal operating range
2
Data erratic, intermittent, or incorrect
3
Voltage above normal
4
Voltage below normal
5
Current below normal or open circuit
6
Current above normal or short circuit
7
Mechanical system not responding properly
8
Abnormal frequency, pulse rate or period
9
Abnormal update
10
11
12 Defective device or component
13
14/15
Abnormal rate of change
Failure mode not identifiable
Uncalibrated device or component
Reserved for future assignment
The contents of this type of memory may be electronically erased and new information programmed into the
device.
EECU (Engine Electronic Control Unit)
The computer that controls the power supplied to the engine electronics, monitors and governs engine functions.
EUI (Electronic Unit Injector)
An injector pump which is mechanically activated and
electronically controlled. It combines metering and injecting in a single unit.
Engine brake disable system
During the time ABS (anti-lock braking system) is active,
the engine brake is disabled.
8
Hz (Hertz)
Measure of frequency in cycles per second.
MID
Message Identification Description
Open circuit
Condition where an electrical wire or connector is broken, preventing signal or supply voltage from reaching its
intended destination.
Parameter
A programmable value that affects the characteristics or
behavior of the engine and/or vehicle.

Group 28 General
PID
Parameter Identification code.
PTO (Power Takeoff)
Operated with the cruise control switches, this mode permits setting a constant engine rpm when the vehicle is
not moving.
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
A signal consisting of variable-width pulses at fixed intervals to vary; “TIME ON” versus versus “TIME OFF.”
RAM (Random Access Memory)
A memory that has stored information immediately available when addressed.
Reference voltage
A regulated voltage supplied by the EECU to a sensor,
which uses it to generate a signal voltage.
Password
A group of seven alphanumeric characters designed to
restrict access to level-2 parameters. The password is
automatically defaulted to seven empty spaces if customer has not specified password.
SID
Subsystem Identification code.
Signal
A voltage value used to transmit information typically
from a sensor to the EECU.
Supply voltage
A constant voltage that supplies electrical power to a
component. It may be generated by the EECU or supplied by the vehicle battery.
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
An electronic sensor that is connected to the accelerator
pedal and sends a Pulse Width Modulated signal to the
EECU.
Vehicle Specification Programming (VSP)
VSP consists of two levels of programming: engine configuration (level 1) and customer parameters (level 2).
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
An electromagnetic device that measures vehicle speed
from the rotation of gear teeth in the drivetrain of the vehicle.
SAE
Society of Automotive Engineers.
Short circuit
A connection of comparatively low resistance, accidentally or intentionally made between two points on a
circuit.
VEB (Volvo Engine Brake)
Consists of a compression brake (VCB) and an exhaust
pressure governor (EPG).
9
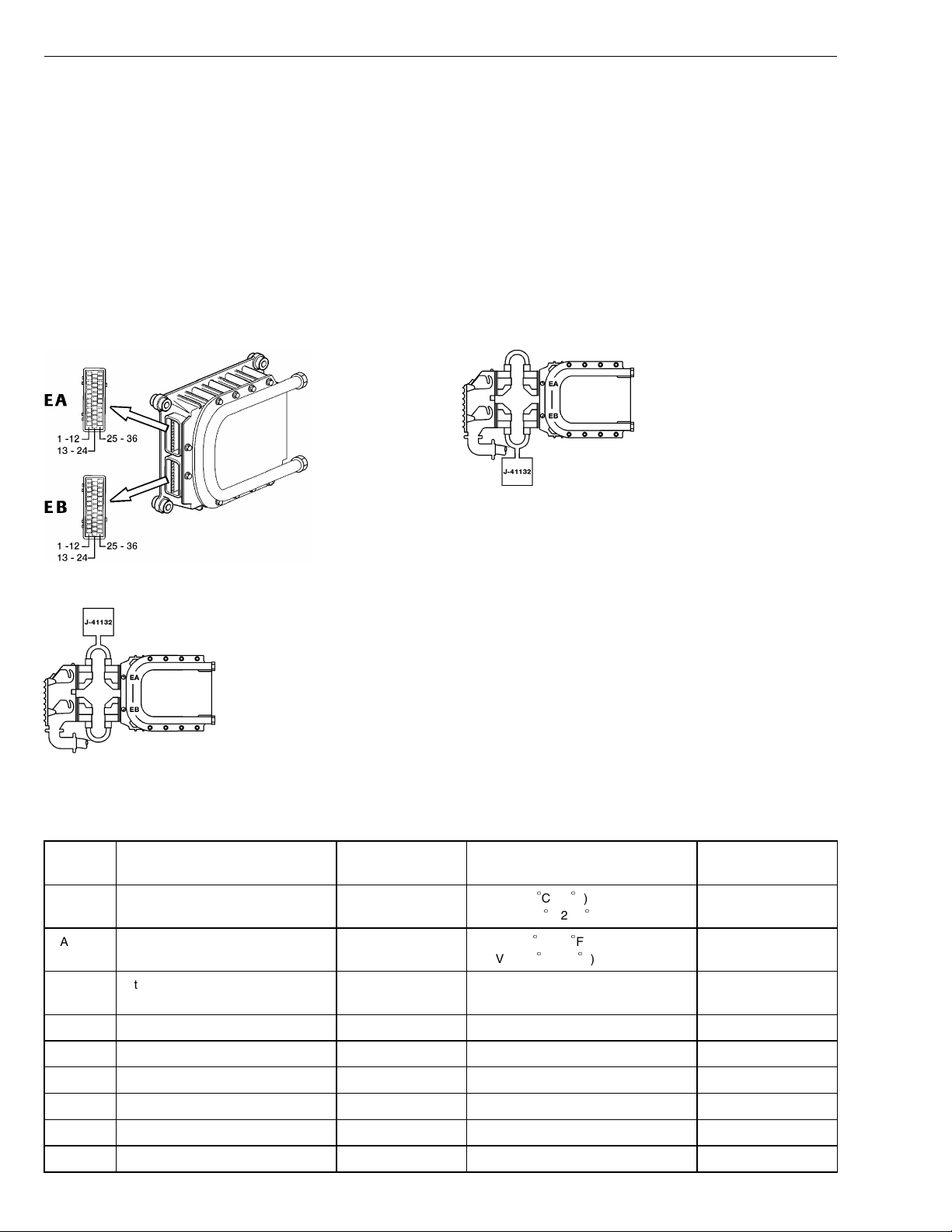
Group 28 Specifications
Specifications
Description of Signals
EECU (D7C) and Breakout Box Connected in Series Between EECU
and Wiring Harness
For the measurements below, the following applies:
Breakout box J-41132 connected between connec-
•
tor EA or EB and the EECU.
Jumper harness J–43233 connected between con-
•
nector EA or EB and the EECU.
The EECU connected.
•
Ignition key in ON position.
•
Engine not running.
•
Measuring voltage.
•
W2002710
Fig. 3: EECU voltage check, EB
W2003555
Fig. 1: EECU with pinouts
W2002712
Fig. 2: EECU voltage check, EA
B+ = battery voltage
Connection
EA1 Oil temperature sensor, signal EA1 - EA5 3.0 V (+20C/68F)
EA2 Intake manifold temperature sensor,
EA3 Intake manifold pressure sensor, sig-
EA4 Supply to sensors (5 V), + EA4 - EA5 4.8 - 5.15 V
Signal type Measuring points Ignition key in the ON position Other
C/212F)
C/104F)
signal
nal
0.4 V (+100
EA2 - EA5 2.6 V (+20C/68F)
1.6 V (+40
EA3 - EA5 1.1 V (sea level)
EA5 Signal ground to sensors, -
EA6 Not currently used
EA7 Redundant engine speed sensor, +
EA8 Rack drive PWM, +
EA9 Timing sleeve PWM, +
10
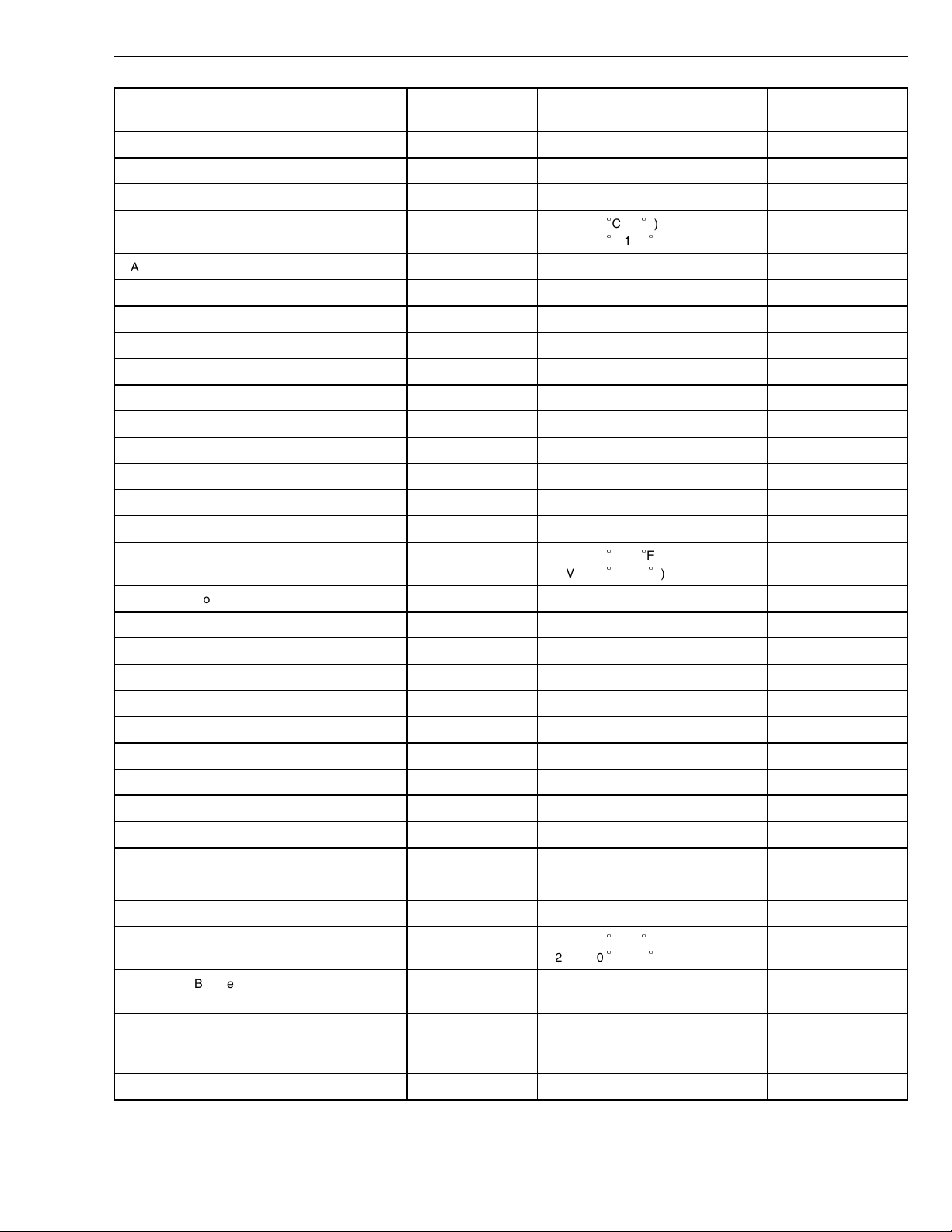
Group 28 Specifications
Connec-
Signal type Measuring points Ignition key in the ON position Other
tion
EA10
Rack drive PWM, -
EA11 Not currently used
EA12 Not currently used
EA13 Fuel temperature sensor, signal EA13 - EA5 3.0 V (+20
2.0 V (+40
C/68
C/104F)
F)
EA14 Oil pressure sensor, signal EA14 - EA5 0.5 V (for cold engines)
EA15 Needle lift sensor, +
EA16 Rack position sensor, search coil
EA17 Rack position sensor, common
EA18 Redundant engine speed sensor, -
EA19 Not currently used
EA20 Not currently used
EA21 Timing sleeve PWM, -
EA22 Not currently used
EA23 Not currently used
EA24 Not currently used
EA25 Coolant temperature sensor, signal EA25 - EA5 3.0 V (+20
0.6 V (+85
C/68F)
C/185F)
EA26 Not currently used
EA27 Fuel pressure sensor, signal EA27-EA5 ≈ 0.5V (for cold engines) D12 C
EA28 Needle lift sensor, -
EA29 Rack position sensor, reference coil
EA30 Engine speed sensor (crank), +
EA31 Engine speed sensor (crank), -
EA32 Not currently used
EA33 Not currently used
EA34 Not currently used
EA35 Not currently used
EA36 Not currently used
EB1 SAE J1939 A Communications link EB1/EB9 ≈2-5V
EB2 SAE J1939 B Communications link EB2/EB9 ≈0-3V
EB3 Ambient air temperature sensor, sig-
nal
EB3 - EB13 2.6 V (+20
1.2 V (+50
C/68F)
C/122F)
EB4 Buffered idle validation switch EB4 - EB9 < 4 V (idle)
> 8 V (off idle)
EB5 Pre-heat sense 1 EB5 - EB9 55 % of B+ (open)
0 V (closed)
EB6 Not currently used
Normally closed with
the ignition key in the
ON position.
11
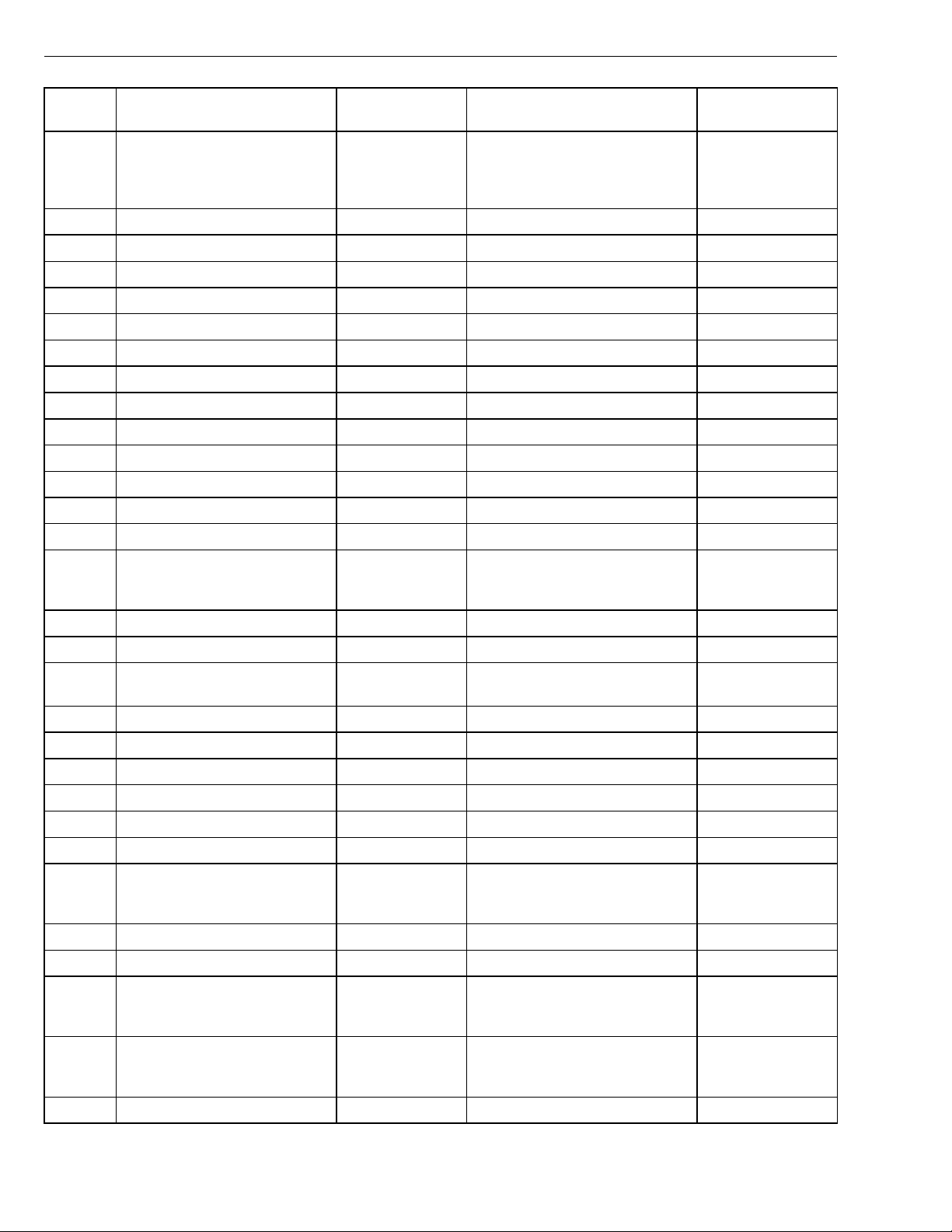
Group 28 Specifications
Connection
EB7
EB8 Signal ground to sensors, -
EB9 EECU ground, -
EB10 EECU ground, -
EB11 EECU B+ EB11 - EB9 B+
EB12 EECU B+ EB12 - EB10 B+
EB13 Ambient air temperature sensor
EB14 Not currently used
EB15 Not currently used
EB16 Not currently used
EB17 Air filter indicator sensor signal
EB18 Not currently used
EB19 Not currently used
EB20 Not currently used
EB21 Fan control (if equipped with on/off
Signal type Measuring points Ignition key in the ON position Other
Coolant level sensor, signal EB7 - EB8 80% B+ (open)
0 V (closed)
EB21 - EB9 B+ (fan on)
fan)
0 V (fan off)
Applies to WX and
VN. Normally open
with the ignition key in
the ON position.
Normally ON with the
ignition key in the ON
position.
EB22 Not currently used
EB23 Not currently used
EB24 EOL Enable EB24 - EB9 < 6 V or O/C (EOL Disable)
> 9.6 V (EOL Enable)
EB25 SAE J1587A/J1708A Information link EB25-EB9 ≈ 0-5V
EB26 SAE J1587B/J1708B Information link EB26-EB9 ≈ 0-5V
EB27 Not currently used
EB28 Not currently used
EB29 Not currently used
EB30 Not currently used
EB31 Pre-heating relay, Coil ground EB31 - EB9 B+ (pre-heat off)
0 V (pre-heat on)
EB32 Not currently used
EB33 Not currently used
EB34 Fuel shut-off valve EB34 - EB9 0 V (valve on)
> 1.0V (valve off)
EB35 EPG 1 EB35 - EB9 B+ (EPG off)
0 V (EPG on)
EB36 Not currently used
Normally ON with the
ignition key in the ON
position.
Normally ON with the
ignition key in the ON
position.
Normally OFF with
the ignition key in the
ON position.
12
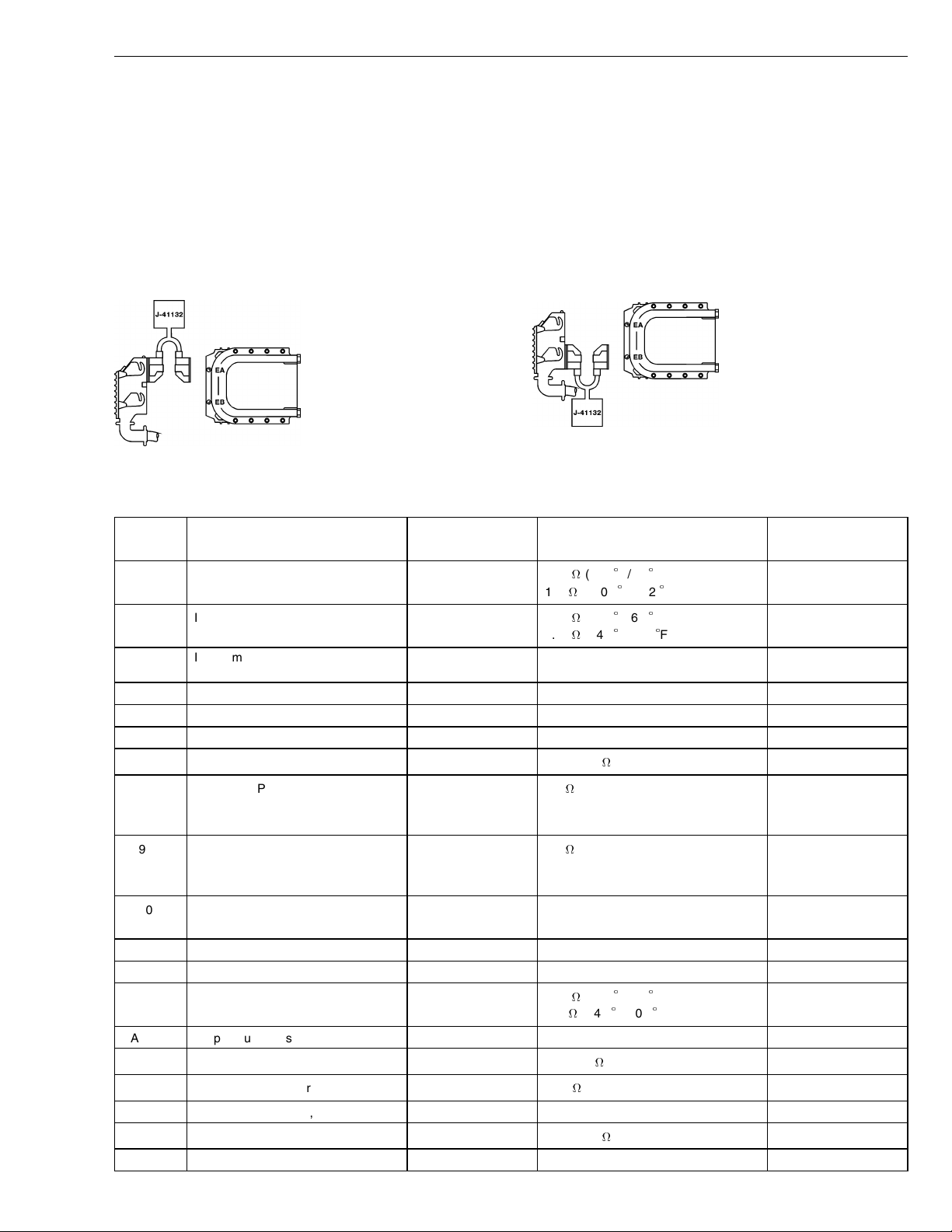
Group 28 Specifications
EECU, D7C, with Breakout Box Connected to Wiring Harness Only
For the measurements below, the following applies:
Breakout box J-41132 connected to connector EA or
•
EB.
The EECU is not connected.
•
Ignition key must be in the OFF position.
•
Measuring resistance.
•
W2002713
W2002711
Fig. 4: EECU harness checks, EA
Fig. 5: EECU harness checks, EB
Connection
EA1 Oil temperature sensor, signal EA1 / EA5 1.9 k(+20C/68F)
EA2 Intake manifold temperature sensor,
EA3
EA4 Sensor supply to (5 V), +
EA5 Sensors ground , -
EA6 Not currently used
EA7 Redundant engine speed sensor, + EA7 / EA18 775 - 945
EA8 Rack drive PWM, + EA8 / EA10
EA9 Timing sleeve PWM, + EA9 / EA21
EA10 Rack drive PWM, - EA10 / alternate
EA11 Not currently used
EA12 Not currently used
EA13 Fuel temperature sensor, signal EA13 / EA5 1.9 k(+20C/68F)
EA14 Oil pressure sensor, signal
EA15 Needle lift sensor, + EA15 / EA28 65 - 165
EA16 Rack position sensor, search coil EA16 / EA17 20.0
EA17 Rack position sensor, common
EA18 Redundant engine speed sensor, - EA18 / EA7 775 - 945
EA19 Not currently used
Signal type Measuring points Ignition key in the OFF position Other
(+100C/212
100
EA2 / EA5 6.2 k
signal
Intake manifold pressure sensor, signal
EA8 / alternate
ground
EA9 / alternate
ground
ground
(+20C/68F)
(+40
2.5 k
1.5
open circuit
1.5
open circuit
open circuit (see also EA8)
800
C/104F)
(+40C/104F)
F)
13
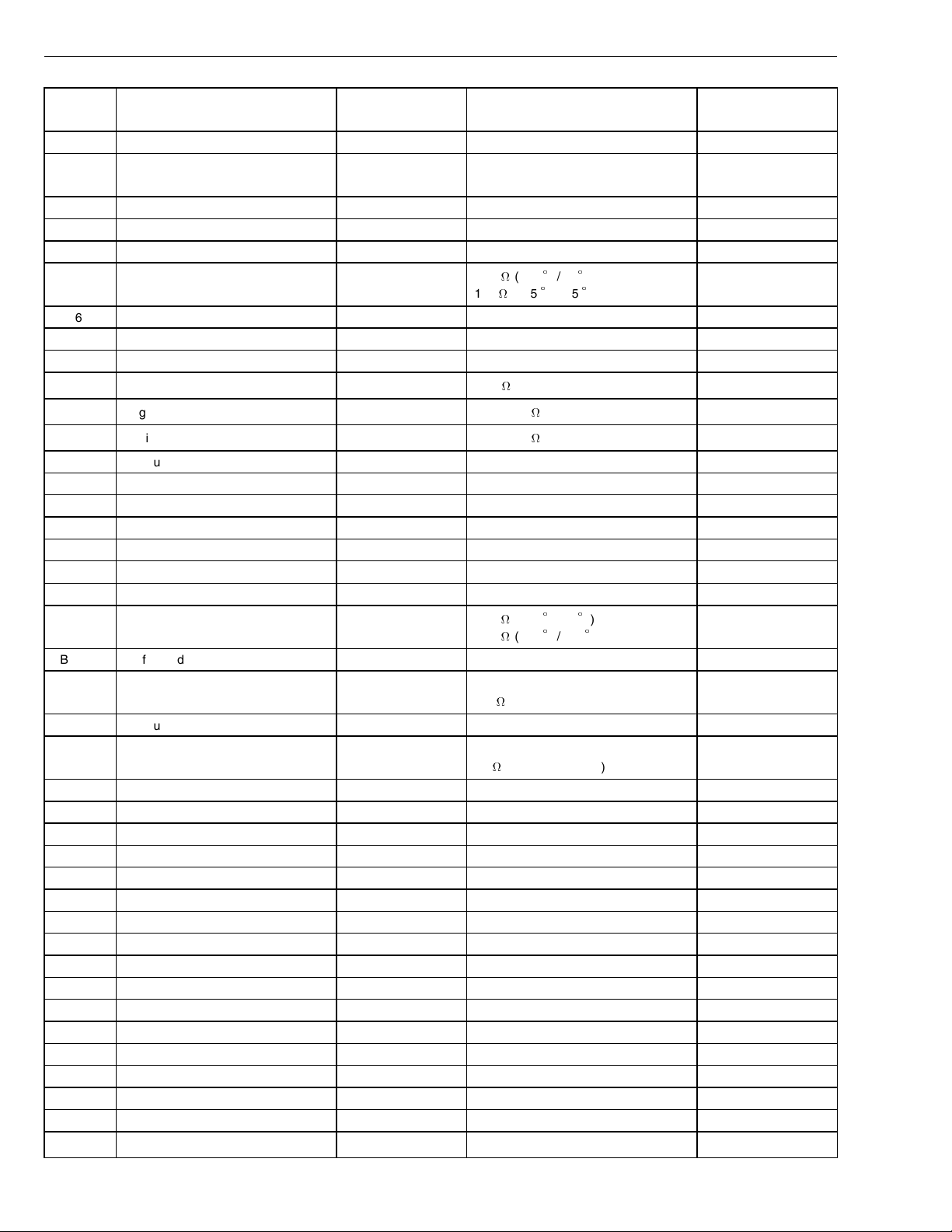
Group 28 Specifications
Connec-
Signal type Measuring points Ignition key in the OFF position Other
tion
EA20 Not currently used
EA21 Timing sleeve PWM, - EA21 / alternate
open circuit (see also EA9)
ground
EA22 Not currently used
EA23 Not currently used
EA24 Not currently used
EA25 Coolant temperature sensor, signal EA25 / EA5 1.9 k(+20
160
C/68
(+85C/185
F)
F)
EA26 Not currently used
EA27 Fuel pressure sensor D12 C
EA28 Needle lift sensor, -
EA29 Rack position sensor, reference coil EA29 / EA17 20.0
EA30 Engine speed sensor (crank), + EA30 / EA31 775 - 945
EA31 Engine speed sensor (crank), - EA31 / EA30 775 - 945
EA32 Not currently used
EA33 Not currently used
EA34 Not currently used
EA35 Not currently used
EA36 Not currently used
EB1 SAE J1939A Communications link
EB2 SAE J1939B Communications link
EB3 Ambient air temperature sensor, sig-
nal
EB3 / EB13 6.2 k
1.7 k
(+20C/68
(+50
C/122F)
F)
EB4 Buffered idle validation switch
EB5 Pre-heat sense 1 EB5 / EB9 open circuit (open)
(closed)
<5
EB6 Not currently used
EB7 Coolant level sensor, signal EB7 / EB8 open circuit (coolant level normal)
(coolant level low)
<1
Applies to WX and VN
EB8 Sensor ground
EB9 EECU ground, -
EB10 EECU ground, -
EB11 EECU, B+
EB12 EECU, B+
EB13 Ambient air temperature ground
EB14 Not currently used
EB15 Not currently used
EB16 Not currently used
EB17 Air filter indicator sensor signal
EB18 Not currently used
EB19 Not currently used
EB20 Not currently used
EB21 Not currently used
EB22 Not currently used
EB23 Not currently used
EB24 EOL Enable EB24/EB9 open circuit (open)
14
Group 28 Specifications
Connection
EB25 SAE J1587/J1708 A Information link
EB26 SAE J1587/J1708 B Information link
EB27 Not currently used
EB28 Not currently used
EB29 Not currently used
EB30 Not currently used
EB31 Pre-heating relay, coil ground
EB32 Not currently used
EB33 Not currently used
EB34 Fuel shut-off valve, include
EB35 EPG 1, -
EB36 Not currently used
Signal type Measuring points Ignition key in the OFF position Other
EB25 / (connection
A in 6 pin diagnostics connector)
EB25 / (connection
F in 9 pin diagnostics connector)
EB26 / (connection
B in the 6 pin diagnostics connector)
EB26 / (connection
G in the 9 pin diagnostics connector)
<1
<1
<1
<1
15
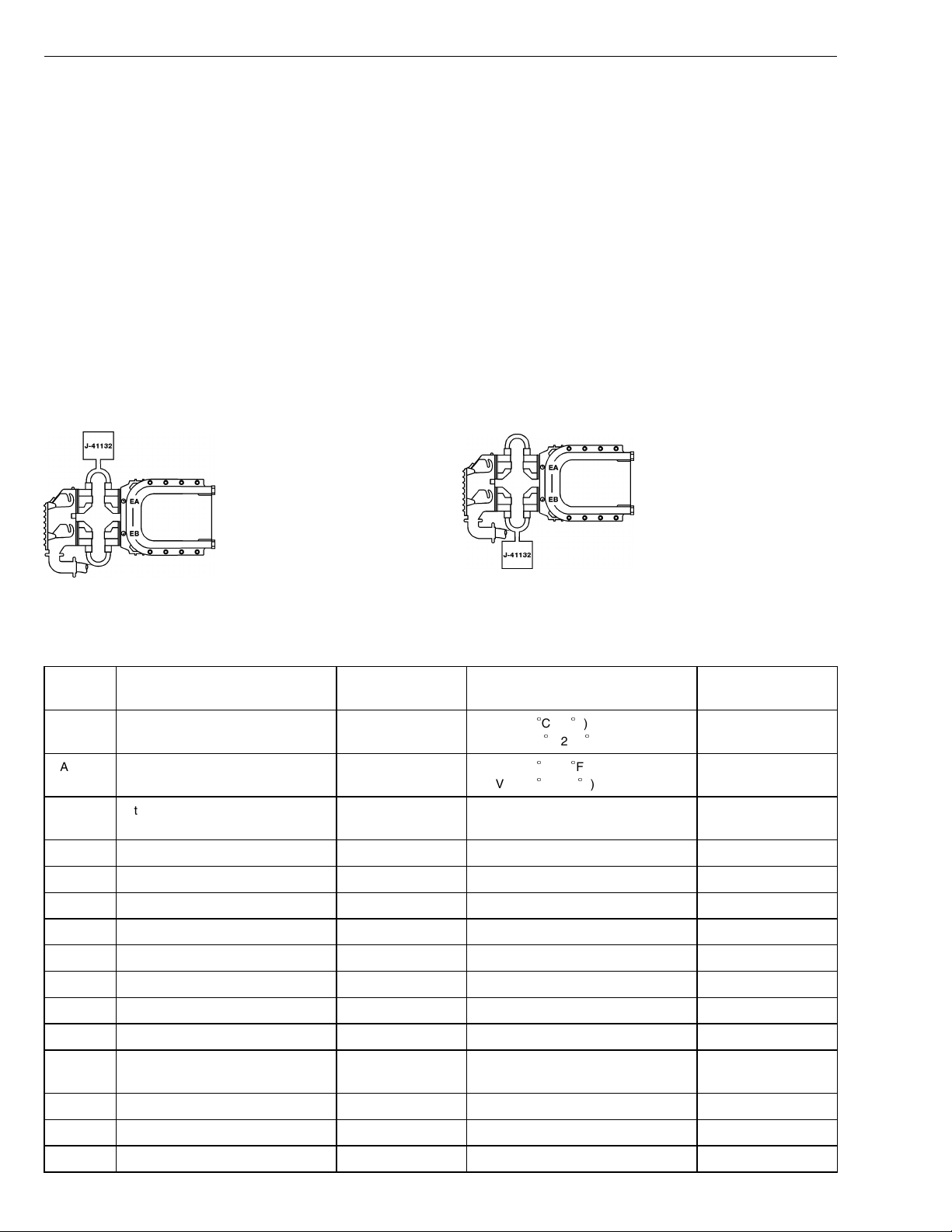
Group 28 Specifications
EECU (D12B and D12C), Breakout Box Connected in Series Between
EECU and Wiring Harness
For the measurements below, the following applies:
Breakout box J-41132 connected between connec-
•
tor EA or EB and the EECU.
Jumper harness J43233 connected between con-
•
nector EA or EB and the EECU.
The EECU connected.
•
Ignition key in ON position.
•
Engine not running.
•
Measuring voltage.
•
W2002712
Fig. 6: EECU voltage check, EA
Fig. 7: EECU voltage check, EB
W2002710
B+ = battery voltage
Connection
EA1 Oil temperature sensor, signal EA1 / EA5 3.0 V (+20C/68F)
EA2 Intake manifold temperature sensor,
EA3 Intake manifold pressure sensor, sig-
EA4 Sensor supply (5 V), + EA4 / EA5 4.8 - 5.15 V
EA5 Sensor ground
EA6 Not currently used
EA7 Engine position sensor (cam), +
EA8 Not currently used
EA9 Not currently used
EA10 Not currently used
EA11 Unit injector cylinder 1, -
EA12 Unit injector cylinder 1, 2, 3 (90
EA13 Fuel temperature sensor, signal D12 C
Signal type Measuring points Ignition key in the ON position Other
C/212F)
C/68F)
C/104
F)
signal
nal
Volt), +
0.4 V (+100
EA2 / EA5 2.6 V (+20
1.6 V (+40
EA3 / EA5 1.1 V (sea level)
EA14 Oil pressure sensor, signal EA14 / EA5 0.5 V (for cold engines)
EA15 Not currently used
16
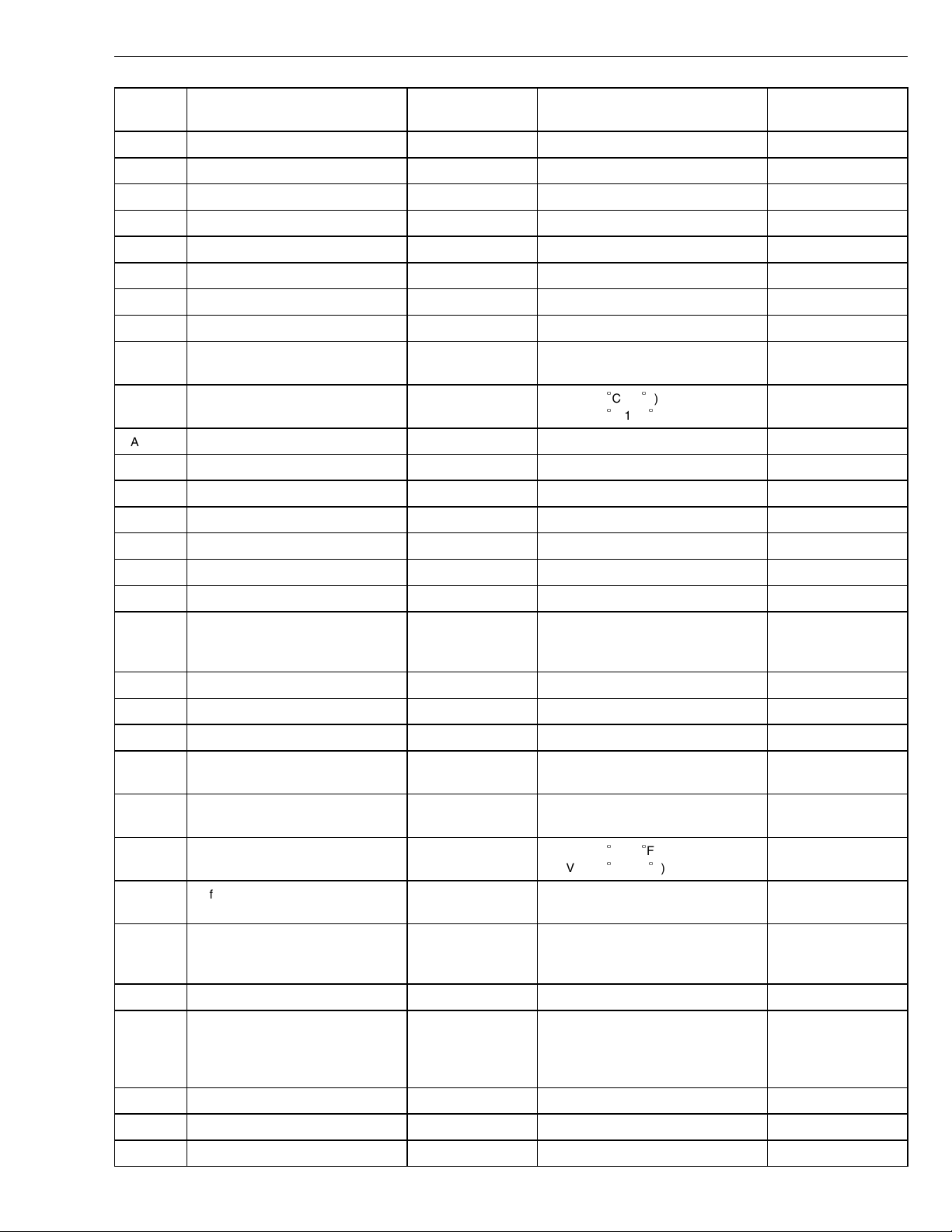
Group 28 Specifications
Connec-
Signal type Measuring points Ignition key in the ON position Other
tion
EA16
Not currently used
EA17 Not currently used
EA18 Engine position sensor (cam), -
EA19 Not currently used
EA20 Not currently used
EA21 Not currently used
EA22 Unit injector cylinder 2, -
EA23 Unit injector cylinder 3, -
EA24 Unit injector cylinder 4, 5, 6 (90
Volt), +
EA25 Coolant temperature sensor, signal EA25 / EA5 3.0 V (+20
0.6 V (+85
C/68
C/185
F)
F)
EA26 Not currently used
EA27 Fuel pressure sensor D12 C
EA28 Not currently used
EA29 Not currently used
EA30 Engine speed sensor (crank), +
EA31 Engine speed sensor (crank), -
EA32 Not currently used
EA33 VCB, - EA33 / alternate
ground
B+ (VCB off)
0 V (VCB on)
EA34 Unit injector cylinder 4, -
EA35 Unit injector cylinder 5, -
EA36 Unit injector cylinder 6, -
EB1 SAE J1939 Communications link,
EB1/EB9 ≈ 2-5V
can HI
EB2 SAE J1939 Communications link,
EB2/EB9 ≈ 0-3V
can LOW
EB3 Ambient air temperature sensor, sig-
nal
EB3 / EB13 2.6 V (+20
1.2 V (+50
C/68F)
C/122F)
EB4 Buffered idle validation switch EB4 / EB9 < 4 V (inactive)
> 8 V (active)
EB5 Pre-heat sense 1 (if equipped) EB5 / EB9 55% of B+ (open)
0 V (closed)
EB6 Not currently used
EB7 Coolant level sensor, signal EB7 / EB8 80% B+ (open)
0 V (closed)
Normally OFF with
the ignition key in the
ON position.
Normally closed with
the ignition key in the
ON position.
VN and VHD. Normally open with the
ignition key in the ON
position.
EB8 Sensor ground
EB9 EECU ground, -
EB10 EECU ground, -
17
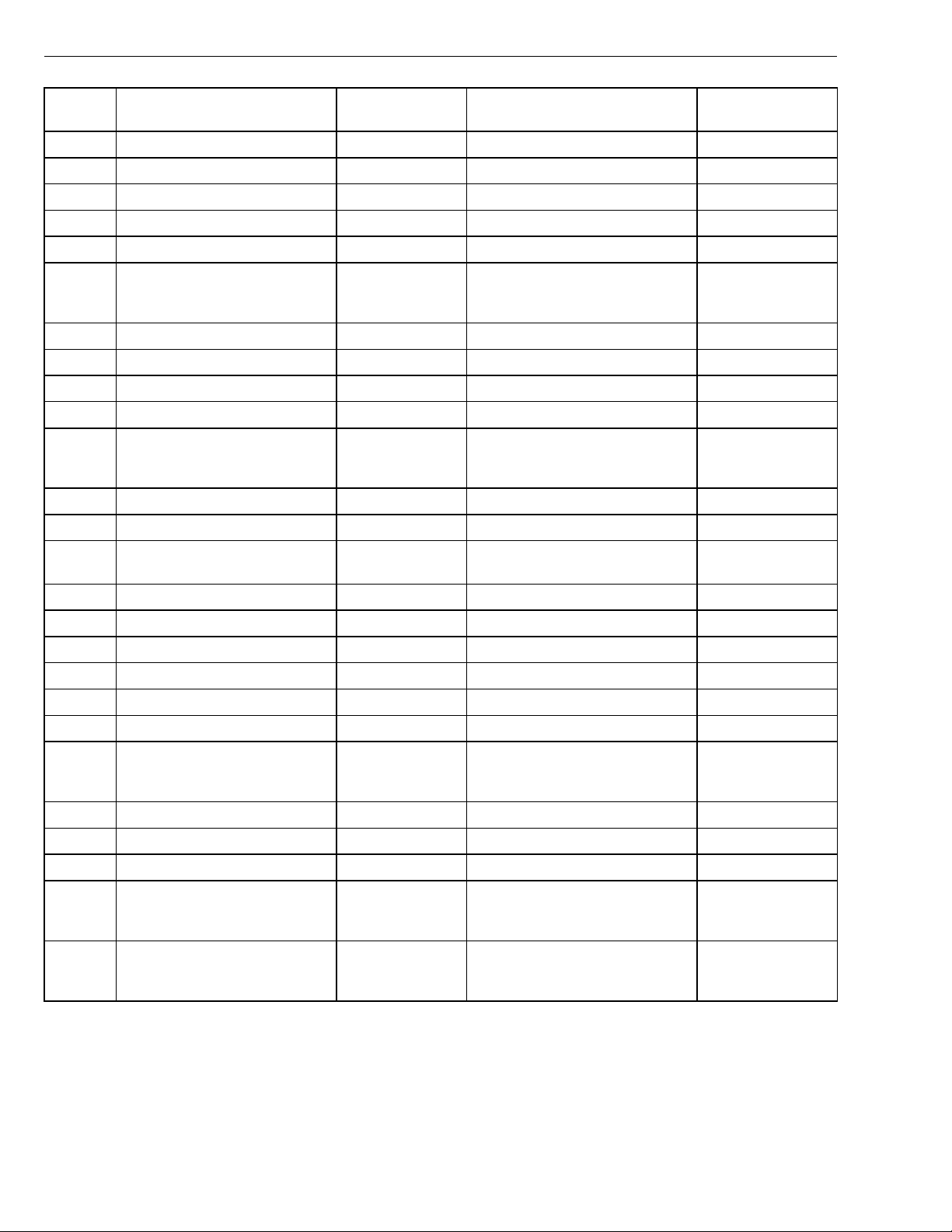
Group 28 Specifications
Connection
EB11
EB12 EECU B+ EB12 / EB10 B+
EB13 Ambient air temperature sensor
EB14 Not currently used
EB15 Not currently used
EB16 Pre-heat sensor 2 (if equipped) EB16 / EB9 55 % of B+ (open)
EB17 Air filter indicator sensor signal
EB18 Not currently used
EB19 Not currently used
EB20 Not currently used
EB21 Engine fan control (if equipped with
EB22 Not currently used
EB23 Not currently used
EB24 EOL Enable EB24 / EB9 < 6 V or O/C (EOL disable)
EB25 SAE J1587/J1708 + Information link
Signal type Measuring points Ignition key in the ON position Other
EECU B+ EB11 / EB9 B+
0 V (closed)
EB21 / EB9 B+ (fan on/solenoid inactive)
on/off fan), -
0 V (fan off/solenoid active)
> 9.6 V (EOL Enable)
Normally closed with
the ignition key in the
ON position.
Normally ON with the
ignition key in the ON
position.
EB26 SAE J1587/J1708 - Information link EB25/EB9 ≈ 0-5V
EB27 Not currently used EB26/EB9 ≈ 0-5V
EB28 Not currently used
EB29 Not currently used
EB30 Not currently used
EB31 Pre-heating relay coil ground (if
equipped)
EB32 Not currently used
EB33 Not currently used
EB34 Not currently used
EB35 EPG 1 EB35 / EB9 B+ (EPG off)
EB36 EPG 2 EB36 / EB9 B+ (EPG off)
EB31 / EB9 B+ (pre-heat off)
0 V (pre-heat on)
0 V (EPG on)
0 V (EPG on)
Normally OFF with
the ignition key in the
ON position.
Normally OFF with
the ignition key in the
ON position.
Normally OFF with
the ignition key in the
ON position.
18
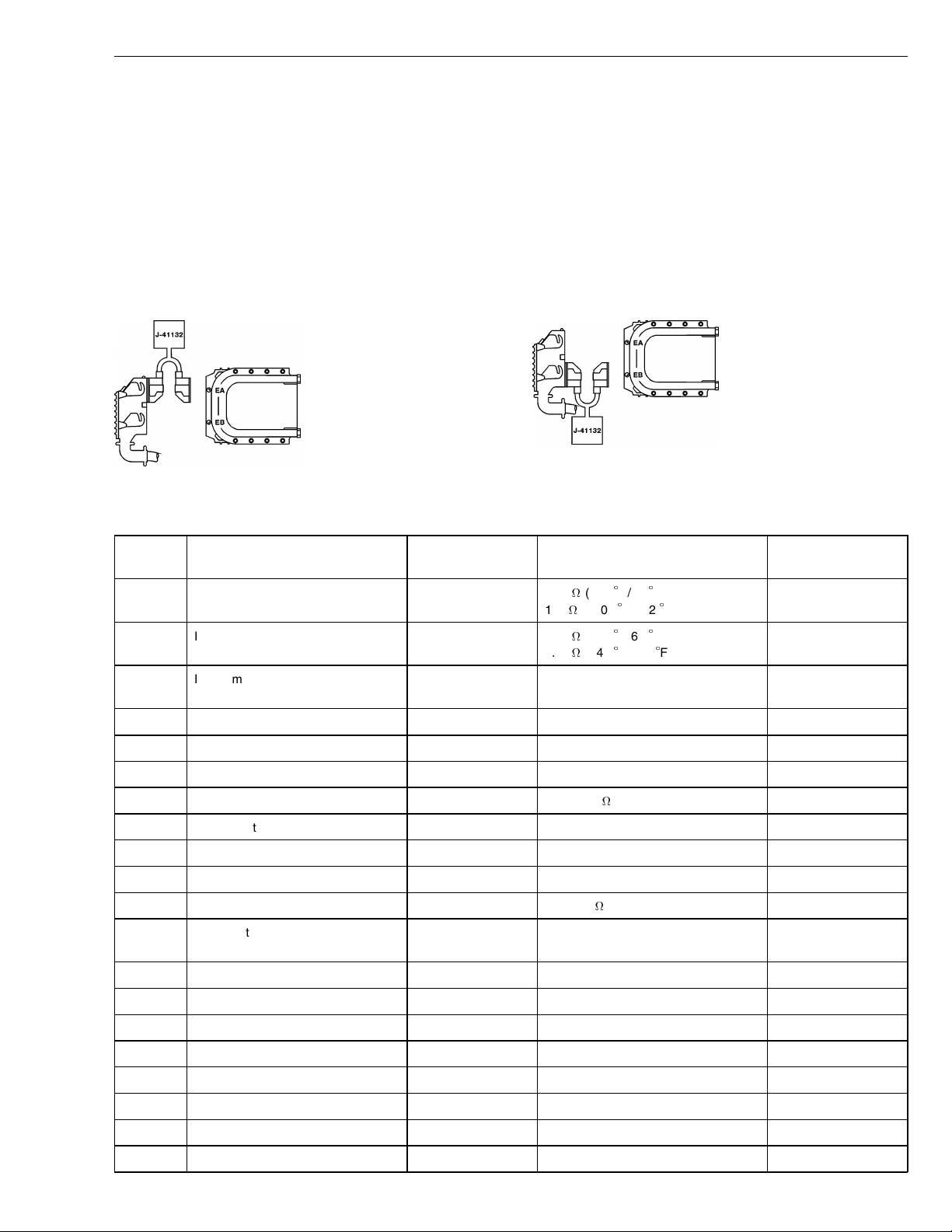
Group 28 Specifications
EECU (D12B and D12C), Breakout Box Connected to Wiring Harness
Only
For the measurements below, the following applies:
Breakout box J-41132 connected to connector EA or
•
EB.
The EECU not connected.
•
Ignition key must be in the OFF position.
•
Measuring resistance.
•
W2002713
W2002711
Fig. 8: EECU harness checks, EA
Fig. 9: EECU harness checks, EB
Connection
EA1 Oil temperature sensor, signal EA1 / EA5 1.9 k(+20C/68F)
EA2 Intake manifold temperature sensor,
EA3 Intake manifold pressure sensor, sig-
EA4 Sensor supply (5 V), +
EA5 Sensor ground
EA6 Not currently used
EA7 Engine position sensor (cam), + EA7 / EA18 775 - 945
EA8 Not currently used
EA9 Not currently used
EA10 Not currently used
EA11 Unit injector cylinder 1, - EA11 / EA12 1.5 - 2.0
EA12 Unit injector cylinder 1, 2, 3 (90
EA13 Fuel temperature sensor, signal D12 C
EA14 Oil pressure sensor, signal
EA15 Not currently used
Signal type Measuring points Ignition key in the OFF position Other
F)
F)
signal
nal
Volt), +
100
EA2 / EA5 6.2 k
2.5 k
see EA11, EA22 and EA23
(+100C/212
(+20C/68F)
(+40C/104
EA16 Not currently used
EA17 Not currently used
EA18 Engine position sensor (cam), - see EA7
EA19 Not currently used
EA20 Not currently used
19
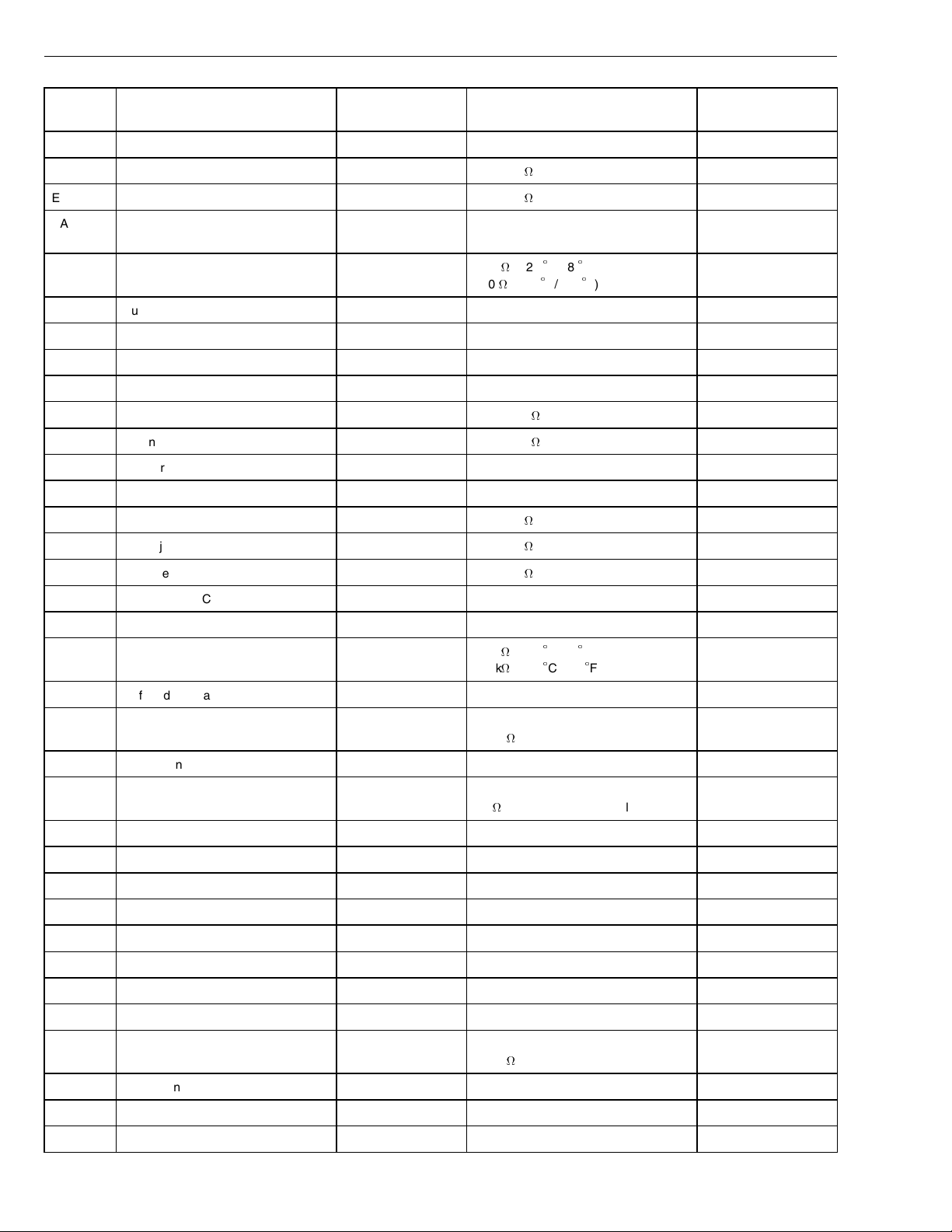
Group 28 Specifications
Connec-
Signal type Measuring points Ignition key in the OFF position Other
tion
EA21
EA22 Unit injector cylinder 2, - EA22 / EA12 1.5 - 2.0
EA23 Unit injector cylinder 3, - EA23 / EA12 1.5 - 2.0
EA24 Unit injector cylinder 4, 5, 6 (90
Not currently used
see EA34, EA35, and EA36
Volt), +
EA25 Coolant temperature sensor, signal EA25 / EA5 1.9 k
160
C/68
(+20
(+85C/185
F)
F)
EA26 Fuel pressure sensor, signal D12 C
EA27 Not currently used
EA28 Not currently used
EA29 Not currently used
EA30 Engine speed sensor (crank), + EA30 / EA31 775 - 945
EA31 Engine speed sensor (crank), - EA31 / EA30 775 - 945
EA32 Not currently used
EA33 VCB, -
EA34 Unit injector cylinder 4, - EA34 / EA24 1.5 - 2.0
EA35 Unit injector cylinder 5, - EA35 / EA24 1.5 - 2.0
EA36 Unit injector cylinder 6, - EA36 / EA24 1.5 - 2.0
EB1 SAE J1939 + Communications link
EB2 SAE J1939 - Communications link
EB3 Ambient air temperature sensor, sig-
nal
EB3 / EB13 6.2 k
1.7 k
(+20C/68
(+50
C/122F)
F)
EB4 Buffered idle validation switch
EB5 Pre-heat sense 1 (if equipped) EB5 / EB9 open circuit (open)
(closed)
< 5.0
EB6 Not currently used
EB7 Coolant level sensor, signal EB7 / EB8 open circuit (coolant level normal)
; closed (coolant level low)
<1
EB8 Sensors ground
EB9 EECU ground, -
EB10 EECU ground, -
EB11 EECU B+
EB12 EECU B+
EB13 Ambient air temperature sensor
EB14 Not currently used
EB15 Not currently used
EB16 Pre-heat sensor 2 (if equipped) EB16 / EB9 open circuit (open)
(closed)
< 5.0
EB17 Air filter indicator sensor signal
Applies to WX , VN
and VHD
EB18 Not currently used
EB19 Not currently used
20
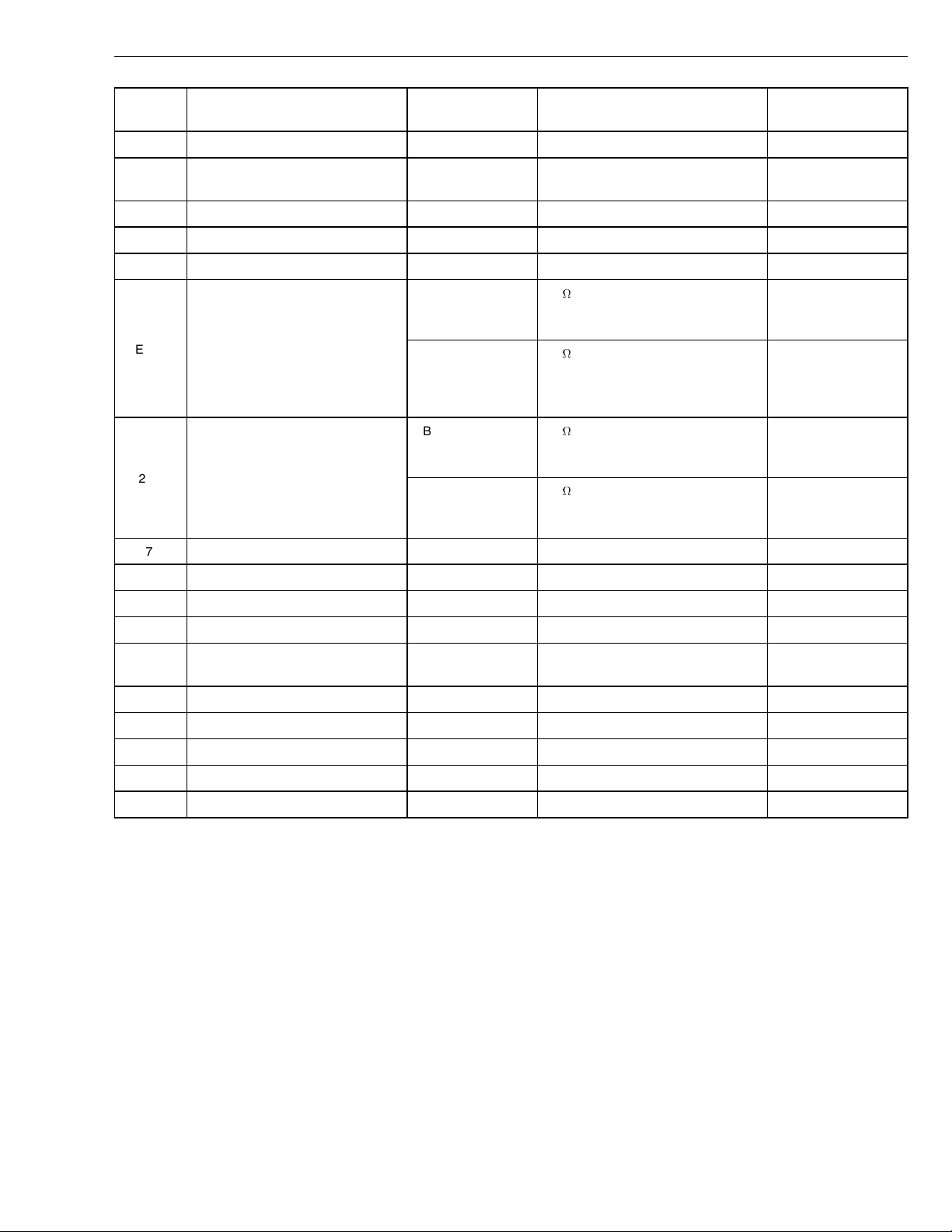
Group 28 Specifications
Connection
EB20
EB21 Engine fan control (if equipped with
EB22 Not currently used
EB23 Not currently used
EB24 EOL Enable EB24/EB9 Open circuit(open)
EB25 SAE J1587/J1708 A Information link
EB26 SAE J1587/J1708 B Information link
EB27 Not currently used
EB28 Not currently used
Signal type Measuring points Ignition key in the OFF position Other
Not currently used
on/off fan)
EB25 / (connection
A in the 6 pin diagnostics connector)
EB25 / DCA (connection F in the 9
pin diagnostics connector)
EB26 / (connection
B in the 6 pin diagnostics connector)
EB26 / (connection
G in the 9 pin diagnostics connector)
<1
<1
<1
<1
EB29 Not currently used
EB30 Not currently used
EB31 Preheating relay coil ground (if
equipped)
EB32 Not currently used
EB33 Not currently used
EB34 Not currently used
EB35 EPG 1, -
EB36 EPG 2, -
21
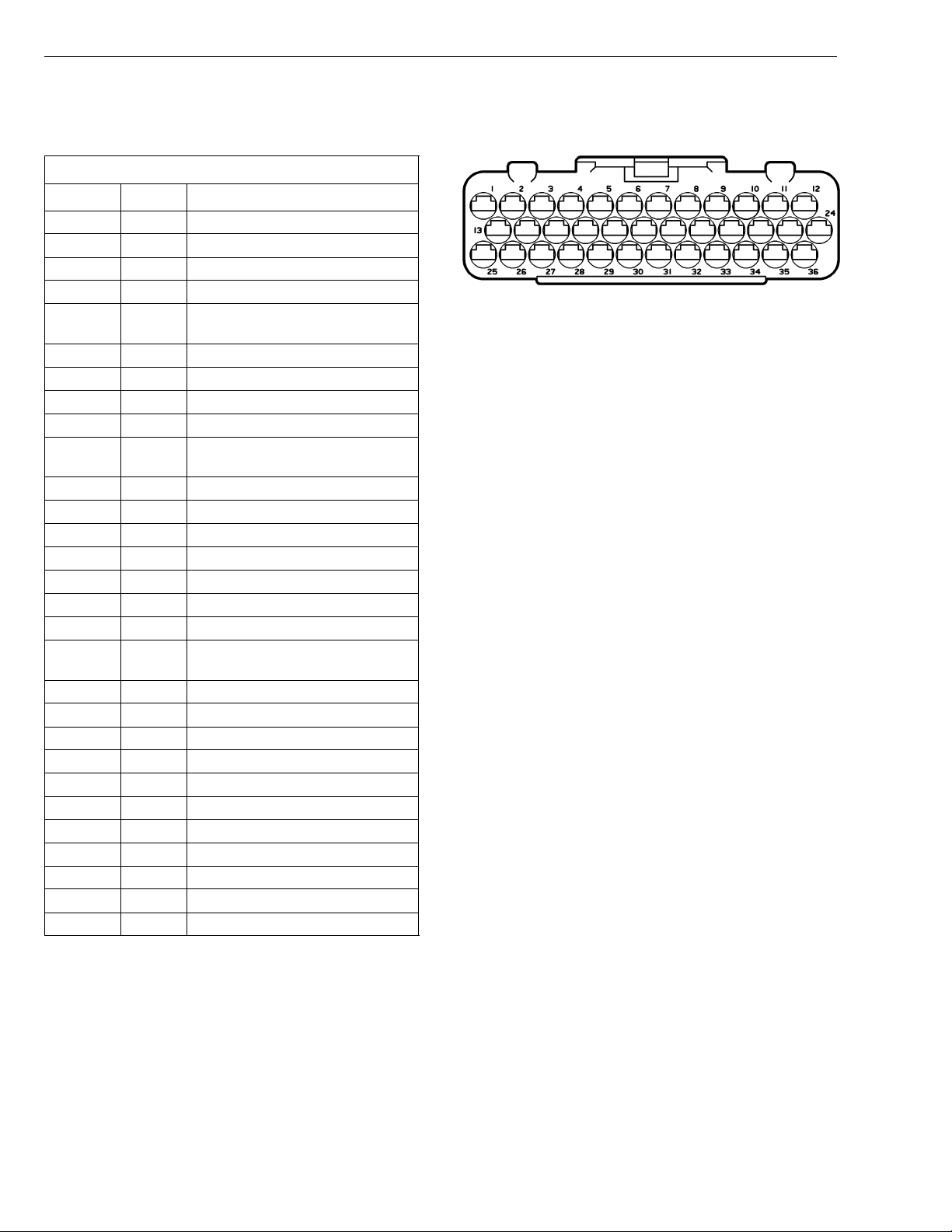
Group 28 Specifications
Pinouts
Engine Electronic Control Unit (EECU)
VOLVO D12B/D12C EECU/EA Connector
Cavity Color Description
1
2 BL/W BOOST TEMPERATURE
3 GR BOOST PRESSURE
4 GN/W BOOST & OIL PRESSURE COMMON (+)
5 BN/W PRESSURE & TEMP. SENSOR COMMON
6 NOT USED
7 Y ENGINE POSITION SENSOR, CAM (+)
8-10 NOT USED
11 W INJECTOR, CYL 1 (-)
12 W CYL 1, CYL 2, CYL 3 INJECTOR COM-
13 GN FUEL TEMPERATURE (D12C)
14 BN OIL PRESSURE
15-17 NOT USED
18 BN/W ENGINE POSITION SENSOR, CAM (-)
19-21 NOT USED
22 W INJECTOR, CYL 2 (-)
23 W INJECTOR, CYL 3 (-)
24 W CYL 4, CYL 5, CYL 6 INJECTOR COM-
25 Y/W COOLANT TEMPERATURE
26 NOT USED
27 BN FUEL PRESSURE (D12C)
28-29 NOT USED
30 BL/SB ENGINE SPEED SENSOR, CRANK (+)
31 BL/R ENGINE SPEED SENSOR, CRANK (-)
32 NOT USED
33 GN/W VCB SOLENOID VALVE RETURN
34 W INJECTOR, CYL 4 (-)
35 W INJECTOR, CYL 5 (-)
36 W INJECTOR, CYL 6 (-)
GN OIL TEMPERATURE
W3000945
(-)
MON, 90 Volt (+)
MON, 90 Volt (+)
Wire Colors:
22
BL BLUE R RED
BN BROWN SB SOLID BLACK
GN GREEN VO VIOLET
GR GRAY W WHITE
OR ORANGE Y YELLOW
P PINK
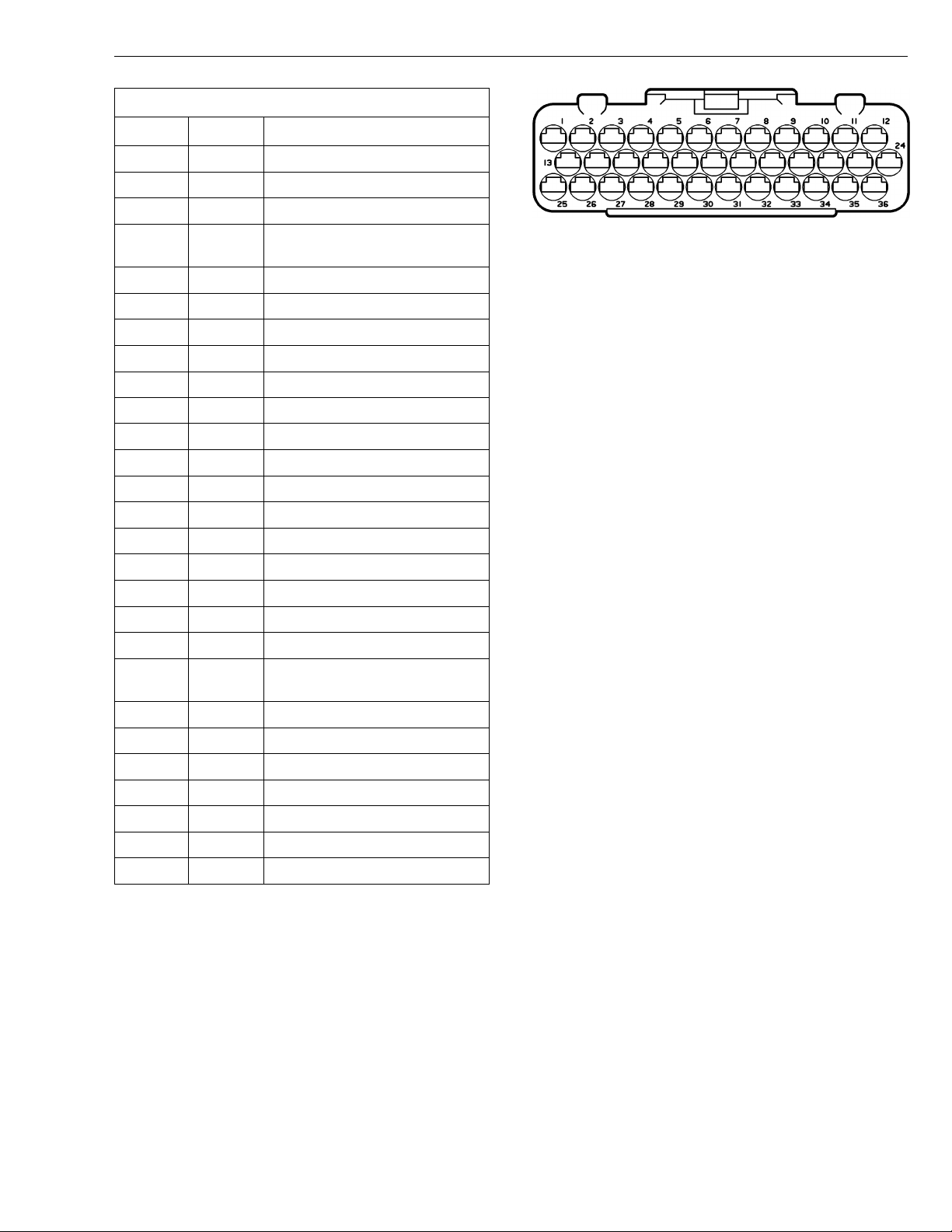
Group 28 Specifications
VOLVO D12B/D12C EECU/EB Connector
Cavity Color Description
1
2 GN DATA LINK J1939 CAN LO
3 BL/Y AMBIENT AIR TEMPERATURE
4 P BUFFERED IDLE VALIDATION
5 R PREHEAT SENSE 1
6 NOT USED
7 BL/SB COOLANT LEVEL WARNING
8 GR/W AIR FILTER, COOL LVL COMMON
9 W GROUND (-)
10 W GROUND (-)
11 R/SB POWER SUPPLY (+)
12 R/SB POWER SUPPLY (+)
13 V0/W AMBIENT AIR TEMP COMMON (-)
14-15 NOT USED
16 R/W PREHEAT SENSE 2
17 BL/R AIR FILTER INDICATOR
18-20 NOT USED
21 GR/R COOLING FAN CONTROL (-)
22-23 NOT USED
24 Y/SB FACTORY PROGRAMMING (NOT
25 GR DATA LINK J1708/1587 (+)
26 OR DATA LINK J1708/1587 (-)
27-30 NOT USED
31 BL/R PREHEAT RELAY(Coil Ground)
32-34 NOT USED
35 GR/SB EPG1 CONTROL
36 GR/W EPG2 CONTROL
Y DATA LINK J1939 CAN HI
W3000945
SWITCH
USED)
Wire Colors:
BL BLUE R RED
BN BROWN SB SOLID BLACK
GN GREEN VO VIOLET
GR GRAY W WHITE
OR ORANGE Y YELLOW
P PINK
23
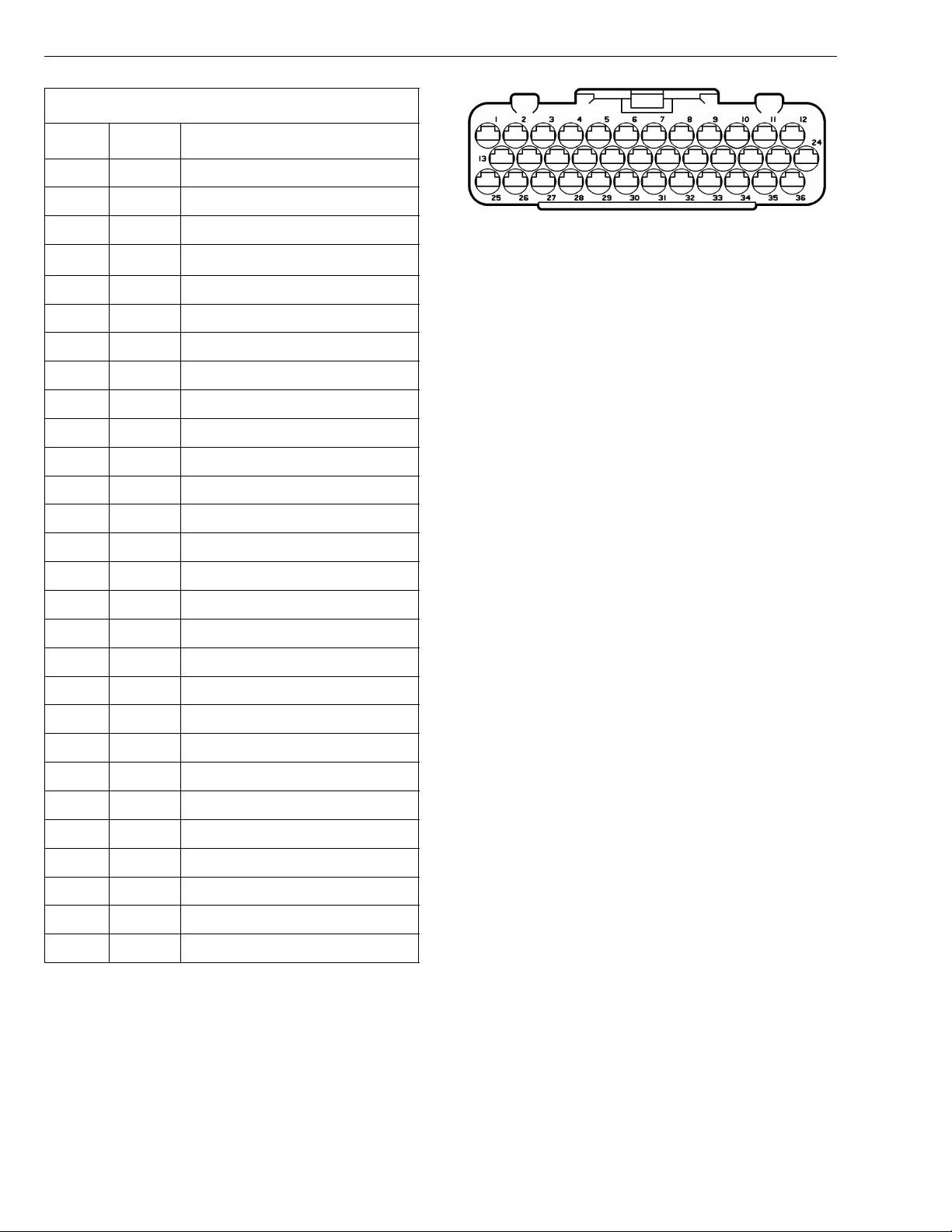
Group 28 Specifications
VOLVO D7C EECU/EA Connector
Cavity Color Description
1
GN OIL TEMPERATURE
2 BL/W BOOST TEMPERATURE
3 GR BOOST PRESSURE
4 GN/W
5 BN/W
BOOST, OIL & FUEL PRESSURE COMMON (+)
PRESSURE & TEMP. SENSOR COMMON
6 NOT USED
7 Y
REDUNDANT ENGINE SPEED SENSOR (+)
8 Y/R RACK DRIVE, PWM (+)
9 Y/SB TIMING SLEEVE, PWM
10 GN/BN RACK DRIVE, PWM (-)
11-12 NOT USED
13 GN/BN FUEL TEMPERATURE
14 BN OIL PRESSURE
15 GR/SB NEEDLE LIFT SENSOR(+)
16 BL/R
RACK POSITION SENSOR, SEARCH COIL
17 Y/GR RACK POSITION SENSOR, COMMON
18 BN/W
REDUNDANT ENGINE SPEED SENSOR (-)
W3000945
19-20 NOT USED
21 OR TIMING SLEEVE, PWM (-)
22-24 NOT USED
25 Y/W COOLANT TEMPERATURE
26 NOT USED
27 BN FUEL PRESSURE
28 GR/R NEEDLE LIFT SENSOR (-)
29 Y/W
RACK POSITION SENSOR, REFERENCE COIL
30 BL/SB ENGINE SPEED SENSOR, CRANK(+)
31 BL/R ENGINE SPEED SENSOR, CRANK(-)
32-36 NOT USED
Wire Colors:
BL BLUE R RED
BN BROWN SB SOLID BLACK
GN GREEN VO VIOLET
GR GRAY W WHITE
OR ORANGE Y YELLOW
P PINK
24
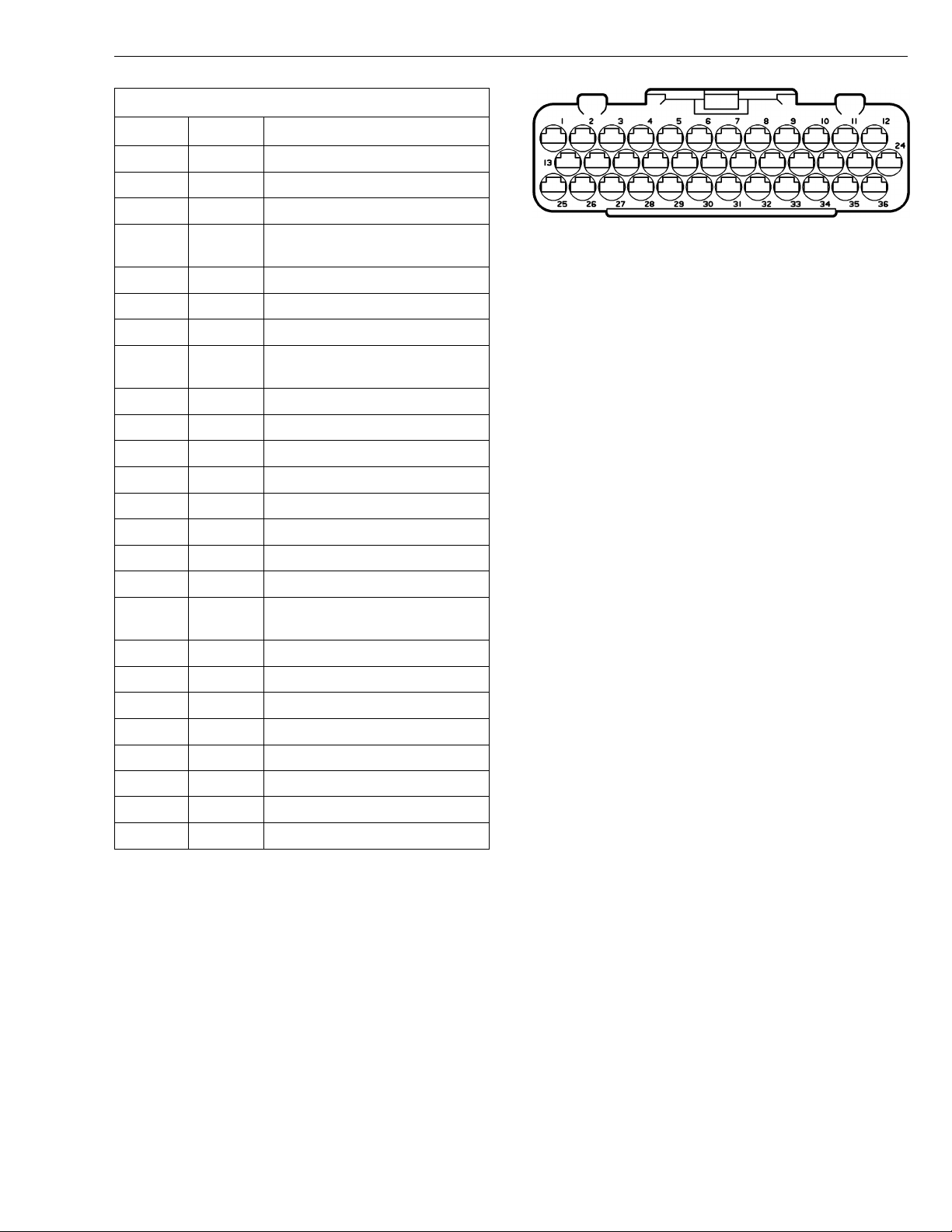
Group 28 Specifications
VOLVO D7C EECU/EB Connector
Cavity Color Description
1
2 GN DATA LINK J1939 CAN LO
3 BL/Y AMBIENT AIR TEMPERATURE
4 P BUFFERED IDLE VALIDATION
5 R PREHEAT SENSE 1
6 NOT USED
7 BL/SB COOLANT LEVEL WARNING
8 GR/W AIR FILTER, COOL LEVEL COM-
9 W GROUND (-)
10 W GROUND (-)
11 R/SB POWER SUPPLY (+)
12 R/SB POWER SUPPLY (+)
13 V0/W AMBIENT AIR TEMP COMMON (-)
14-16 NOT USED
17 BL/R AIR FILTER INDICATOR
18-23 NOT USED
24 Y/SB FACTORY PROGRAMMING (NOT
25 GR DATA LINK J1708/1587 (+)
26 OR DATA LINK J1708/1587 (-)
27-30 NOT USED
31 BL/R PREHEAT RELAY, CONTROL
32-33 NOT USED
34 Y/BN FUEL SHUTOFF VALVE CONTROL
35 GR EPG1
36 NOT USED
Y DATA LINK J1939 CAN HI
W3000945
SWITCH
MON (-)
USED)
Wire Colors:
BL BLUE R RED
BN BROWN SB SOLID BLACK
GN GREEN VO VIOLET
GR GRAY W WHITE
OR ORANGE Y YELLOW
P PINK
25
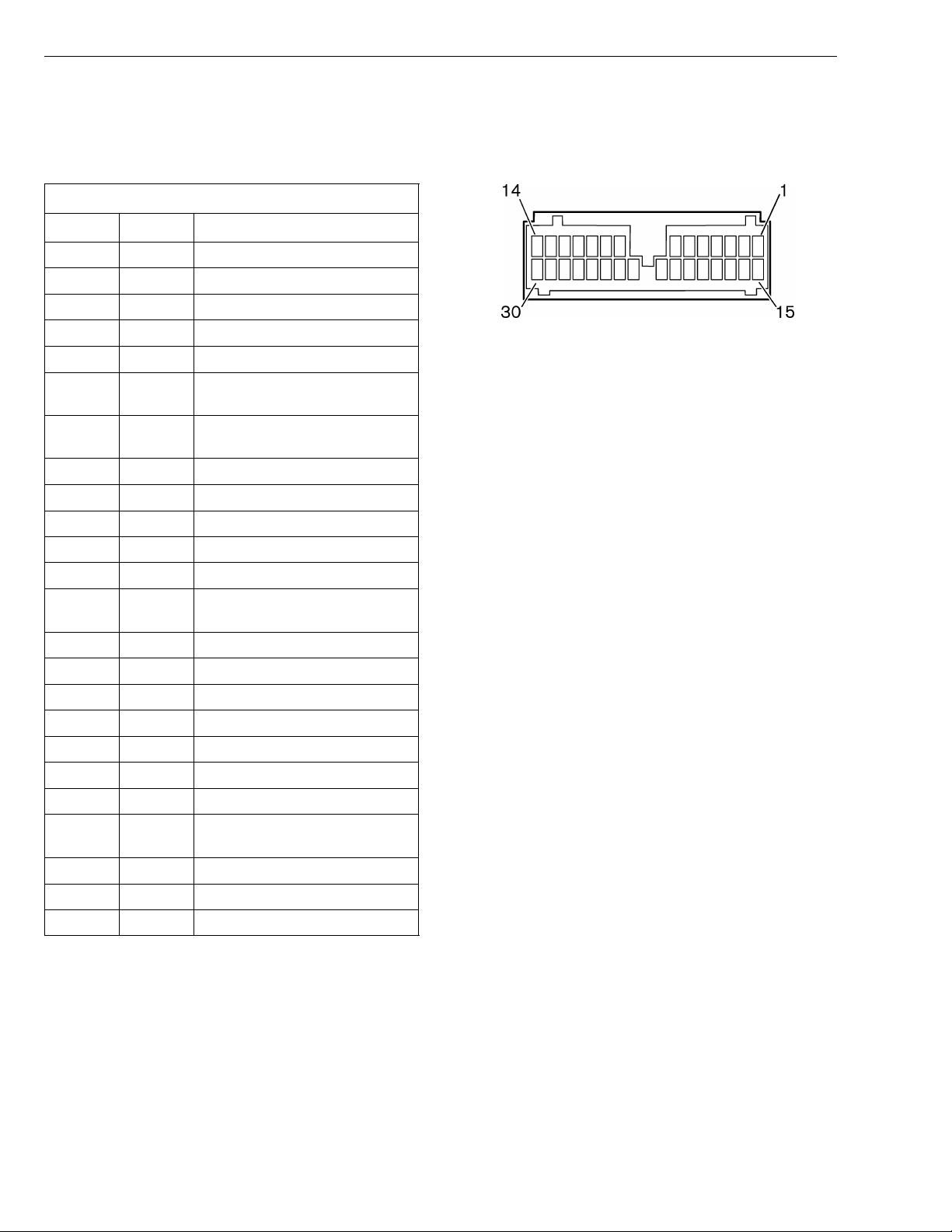
Group 28 Specifications
Pinouts
Vehicle Electronic Control Unit(VECU)
Vehicle ECU Connector A-(GREEN)
Cavity Circuit Description
1
2 563A CC/PTO SWITCH SET(+) INPUT
3 562A CC/PTO SWITCH ON INPUT
4 NOT USED
5 567B SERVICE BRAKE SWITCH INPUT
6 284-A 12V STARTER CONTROL SOLE-
7 245 ENGINE PREHEAT CIRCUIT PRO-
8 571 CLUTCH SWITCH INPUT
9 385-A PARK CONTROL WIPER MOTOR
10 388 INTERMITTENT WIPER INPUT
11 387-C SWITCH TO WASHER MOTOR
12 0XE ELECTRONIC GROUND
13 18V ELECTRONIC ENGINE SWITCHED
14 196V IGNITION SWITCH DR FEED
15-18 NOT USED
19 300D MANUAL FAN SWITCH INPUT
20 629 ENGINE BRAKE MEDIUM FEED
21 628 ENGINE BRAKE LOW FEED
22 NOT USED
23 555 IDLE VALIDATION INPUT
24 682 HIGH REFRIGERANT PRESSURE
25-28 NOT USED
29 573 PTO SWITCH ON INPUT
30 565A CC/PTO SWITCH RESUME INPUT
564A CC/PTO SWITCH SET(-) INPUT
W3002689
NOID FEED
TECTION FEED
BATTERY FEED
SWITCH FEED
26
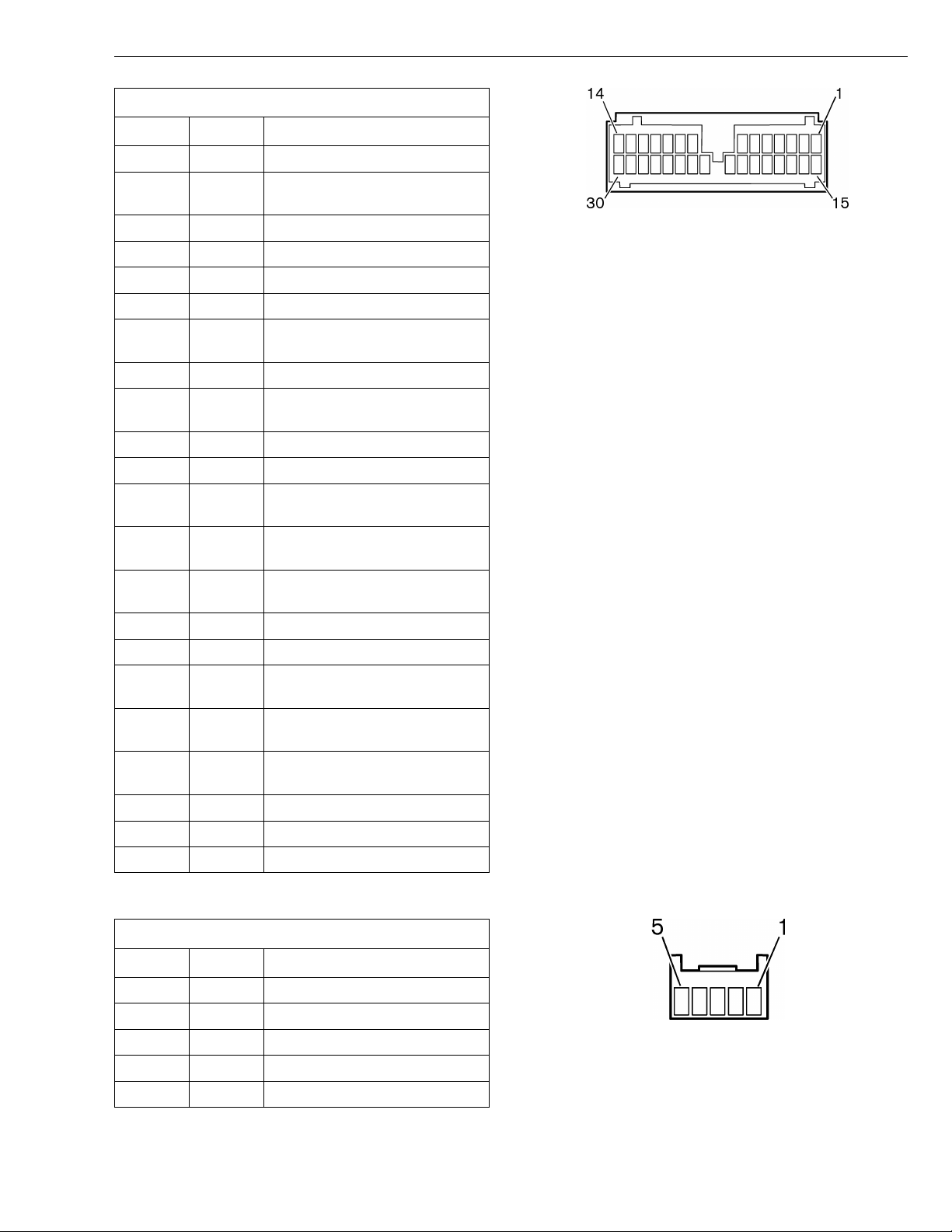
Group 28 Specifications
Vehicle ECU Connector B-(BLUE)
Cavity Circuit Description
1
2 312A TRANSMISSION AREA INHIBITOR
3-4 NOT USED
5 597 ECU COMMON 12V OUTPUT
6 550 VEHICLE SPEED INPUT
7 NOT USED
8 553 THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR IN-
9 NOT USED
10 552 THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
11 581 PARKING BRAKE SWITCH INPUT
12-14 NOT USED
15 583 POWER CONTROL FROM ENGINE
16 389B INTERMITTENT WIPER RELAY
17 555A IDLE VALIDATION FROM ENGINE
18 312C RANGE INHIBITOR VALVE RETURN
19 558 ECU COMMON +12V OUTPUT
20 551 VEHICLE SPEED RETURN FROM
21 317B TRANSMISSION LOW RANGE INDI-
22 554 THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR RE-
23-26 NOT USED
27 567A SERVICE BRAKE SWITCH INPUT
28-30 NOT USED
NOT USED
VALVE RETURN
W3002689
PUT
SUPPLY
ECU
COIL RETURN
ECU
ECU
CATOR SIGNAL
TURN
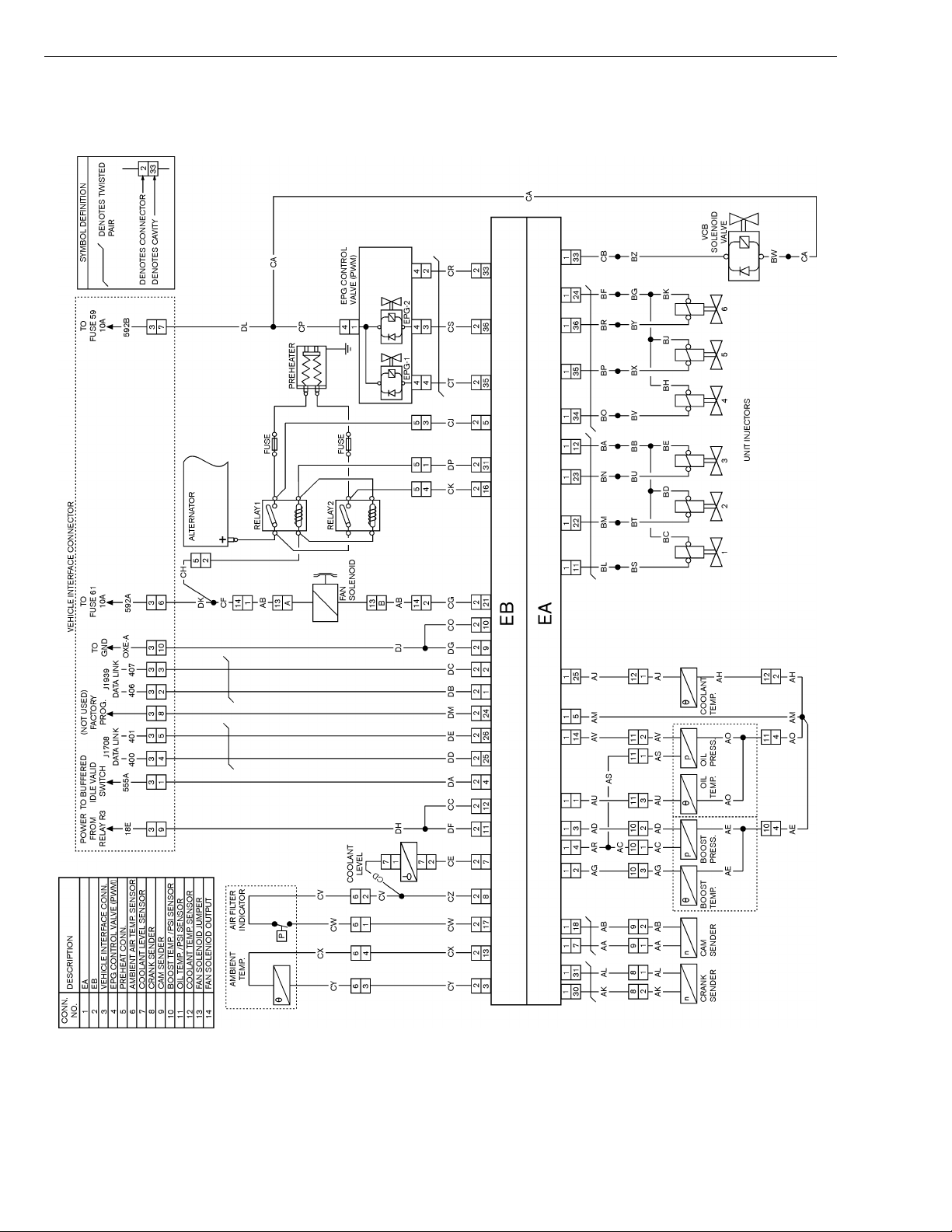
Vehicle ECU Connector C-(GREEN)
Cavity Circuit Description
1 401-D DATA LINK J1708 (-)
2 400-D DATA LINK J1708 (+)
3 408-B DATA LINK J1939 SHIELD
4 406-B DATA LINK J1939 CAN HI
5 407-B DATA LINK J1939 CAN LOW
W3002690
27
Group 28 Specifications
Schematic
D12B
28
W2002827

Group 28 Specifications
Schematic
D12C
W2003348
29

Group 28 Specifications
Schematic
D7C
30
W2002826

Group 28 Specifications
Schematic
VECU
W3003497
31

32

Group 28 Tools
Tools
Special Tools
The following special tools are required for work with the D12 electronic control system. The 3917916 VOLVO breakout kit, along with its components, is available from
Volvo Truck. When requesting tools, provide the appropriate part number. Part numbers beginning with ”J” are available from Kent-Moore.
See list on next page for information about the tools in the picture.
W2003598
33

Group 28 Tools
9998534 4–pin breakout harness
J-39200 digital multimeter
J-43147 2–pin breakout harness
9998482 Guage for inspection of control unit con-
nector
J-41132 36–pin breakout box
J-42472 2–pin breakout harness
J-43233 36–pin jumper
J-38748 7–pin fuel injection pump breakout box
9809687 AC/DC power supply for PC
toll.(optional)
9809678 12 Pin DIN Connector cable-alternative
programming cable for EECU
9809685 Power extension cable —used together
w/9808635.
J-43234 Adapter(Kent Moore).
9998551/J-
60 Pin Breakout Box/Overlay.
43340
34

Group 28 Tools
Other Special Equipment
The following hardware is used to operate VCADS Pro. The tools can be ordered from
Volvo quoting the specified part number.
VCADS Pro tools for diagnostics is for vehicles built from 1998 and later. For diagnostics on vehicles built prior to 1998, use Pro-Link 9000 (J-38500) with Volvo Application
Cartridge J-38500–2000.
See list on next page for information about the tools in the picture.
W2003597
35

Group 28 Tools
1 PC tool -package.
2 Didgipass password generator, model 300 or 500.
3 Laser printer; HP 1100A (To be purchased from a local supplier. Not supplied by
Volvo.)
9998574 Laser printer labels. Used when printing labels for the engine electronic control
unit (EECU).
9998555 Communication interface unit; for connection between the PC tool and the vehi-
cle’s diagnostic connector.
9812331 Extension Cable; for communication, 22 yards (optional)
J-43999 6 Pin Diagnostic adapter; for vehicles prior to 1999
J-43939 9 Pin Diagnostic adapter; for vehicles built from January 1999.
9998496 Pressure Guage
9998489 Oscilloscope interface
9998554 Oscilloscope Cable-BNC connector cable to banana jack (optional)
9998553 Oscilloscope Cable-25 pin parallel cable (optional)
9998617 Programming Kit (see below)
9808635 Programming Unit
9808560 Cable for direct
connection to the Engine ECU
9808561
9808562 Cable for direct
9808563 Cable for power supply
Note: There are three ways of connecting the power cable; 1) To radio power supply, 2) Directly to battery with battery.
3) To cigar lighter.
Cable for direct
connection to the Vehicle ECU
connection to the Intstrument Cluster
36

Group 28 Design and Function
Design and Function
Vehicle Management System
Strategy
The vehicle management system is designed to incorporate the entire vehicle system and instantly receive
real-time data from key vehicle components.
Uniform interfaces between the control systems.
•
Standard adaptations to the vehicle’s functions.
•
Stand-alone diagnostics for the vehicle’s main elec-
•
tronic components.
Vehicle
Communication
Equipment
Transmission
SRS
⇔
⇔
Production
Owner
Conventional Control Systems
In principle, a conventional control system is constructed
so that one or several of the vehicle’s components have
their own control units that receive signals from different
sensors. Each control unit serves its own component and
sends signals to other control units via electrical wires.
An example of this is the engine control unit that receives signals from different sensors on the engine, as
well as from other control units on the vehicle. The accelerator pedal position, the clutch pedal position, the
speed signal, engaged power take-off etc., are sent to
the engine electronic control unit (EECU) via wires from
different sensors and contacts.
Brakes
Engine
Instrument Cluster ⇔
Expansion capability
⇔
⇔
Driver
Body Builder
Service
The system must have one or more communication
ports, to which tools can be connected for programming
as well as for reading information and any fault codes.
In the future, the vehicle’s sub-components will require
several specific control units and the vehicle electronics
will therefore become even more complex. In the long
run this will limit the ability of conventional control systems to fulfill their tasks.
T3008752
37

Group 28 Design and Function
Data Link System
Volvo’s vehicle electronics are constructed on the principle that all communications between the control units in
the system are accomplished via two data links:
the J1939 Control Data Link
•
and the J1587/1708 Information Data Link
•
The vehicle’s main components have their own control
units that are connected to one or both links in order to
be able to communicate with each other.
Here is how the system works on a vehicle equipped
with a Volvo engine: when the driver wants to increase
the vehicle’s speed, a signal is sent from the accelerator
position sensor to the vehicle electronic control unit
(VECU). The signal is then transferred via the data link
to the engine electronic control unit (EECU).
The EECU communicates with its own sensors to verify
that the conditions exist to permit increased acceleration.
If the conditions are met, it carries out the VECU’s request.
The EECU communicates with the other control units via
the data links, either by requesting or by receiving direct
information that all prerequisites are met in order to be
able to carry out the request.
If an error should occur in any of the systems, a signal is
sent out on the J1587/1708 information data link, which
makes it possible to read the information, either on the
driver’s instrument cluster, or via a PC or diagnostic tool
(i.e. Pro-Link, VCADS or VCADS Pro) connected to the
diagnostic connector.
J1587
/1708
A
B
J1939
C
D
The data link system provides an extremely flexible solution with great potential for expansion.
CAUTION
No modifications or connections should be made to
wires 406 (yellow), 407 (green) or 408 (shielded).
These wires carry the high-speed communications between the electronic systems in the vehicle. Any
modification, connection to, or damage to these
wires can result in the failure of the vehicle’s electronic systems.
38

Group 28 Design and Function
Data Links, Design and Function
Data links are one way of transferring information between various components. In conventional systems,
analog signals have mostly been used.
Analog signals mean that different voltage levels represent different values. A simplified example of analog
signals could be:
1 volt = 10
2 volts = 20
3 volts = 30
Data links use digital communication. This means that
the voltage only varies between two different values, either “high” or “low”. By combining these high and low
signals various values can be described.
The diagram shows an oscilloscope image where the
voltage of the data link is measured. As can be seen
from the diagram, a large part of the time the link is
“silent” but at times a number of fast pulses are sent. A
group of pulses is called a message.
C
C
C
W3003960
The enlarged portion of the diagram shows that each
message consists of a combination of high and low voltage levels.
The following sections describe what type of information
this message contains.
W3003957
39

Group 28 Design and Function
Messages and Information Content
Different voltage levels are represented by the different
numbers in the binary number system. The binary number system has only two numbers, one and zero.
The ones are normally represented by a high voltage
and the zeros by a low voltage.
Each binary number is called a “bit”. This message consists of four groups of binary numbers. Each group of
eight bits makes up a “byte”, a decimal number from 0–
W3003956
255 with information, as well as a start bit and a stop bit.
The purpose of the start and stop bits is to function as
markers for where that group of data begins and ends.
In the diagram above only the start and stop bits are labeled. The other information is shaded.
Example
The diagram shows the information content in the four
different parts of the message. The start and stop bits
are shaded since they do not contain any information.
The box in the diagram shows the different binary and
decimal values which comprise the message.
Note: The information is sent over the data link with the
“least” bit first in the binary numbers. The normal way to
notate binary numbers is shown in the box in the
diagram.
W3003958
40

Group 28 Design and Function
Message 144–091–000–240 in this example, has the following meaning:
A MID 144 — The message comes from the Vehicle ECU.
B PID 091 — The message states the accelerator pedal position percentage.
C Data 000 — The accelerator pedal is in the completely released position.
000 is a data component, which in this case states how much the accelerator pedal has been
pressed down. The value can vary between 000 for a completely released pedal and 255 for a completely pressed down accelerator pedal.
D Check 240 — The checksum is used as a check that the message is reasonable.
W2003293
41

Group 28 Design and Function
Diagnostic Message Description
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and the American Trucking Association
(ATA) have developed a standardized list of diagnostic messages, or fault codes. These
diagnostic messages are used to communicate information about problems detected
by an electronic control unit’s (ECU’s) self-diagnostic program. In addition to the
industry-standard SAE codes, Volvo has developed a list of diagnostic messages that
are unique to Volvo applications. Generally, diagnostic messages and their descriptions
are listed in the service manual for each respective ECU and in the user manual for diagnostic tools.
MID MID is an acronym for Message Identification Description. MIDs are SAE stan-
dardized codes used to identify individual electronic control units.
PID PID is an acronym for Parameter Identification Description. PIDs are SAE stan-
dardized codes used to identify parameters or values.
PPID PPID is an acronym for Proprietary Parameter Identification Description. PPIDs
are Volvo’s unique codes used to identify parameters or values.
SID SID is an acronym for Subsystem Identification Description. SIDs are SAE stan-
dardized codes used to identify components.
PSID PSID is an acronym for Proprietary Subsystem Identification Description. PSIDs
are Volvo’s unique codes used to identify components.
FMI FMI is an acronym for Failure Mode Identifier. FMIs are SAE standardized codes
used to identify a type of failure.
42

Group 28 Design and Function
Data Link Communication
General
Communication between the different ECUs takes place
via the two data links: the J1939 control data link and
the J1587/1708 information data link.
The diagram shows how the control units, the diagnostic
connector, and the instrument cluster are connected in
principle.
The instrument cluster, the engine ECU and the diagnostic connector are always included in the system.
The system may include other control units, depending
on the vehicle type, engine type and optional equipment.
Diagnos-
tic
connector
Communication
Equipment
(Expansion
capability)
Instrument Cluster
MIDs 234 & 140
SRS ECU
MID 232
Engine ECU
MID 128
Vehicle ECU
MID 144
Terminating
Resistor
SAE J1587
/1708
Transmission ECU
MID 130
Control unit
(Expansion
capability)
ABS ECU
MID 136
SAE J1939
Terminating
Resistor
43

Group 28 Design and Function
SAE J1939 Control Data Link
The system’s control signals are sent via this link.
The J1939 link is very fast, operating at 250,000 bits per
second. This operating speed allows the system to function more effectively and adapt quickly to changing
conditions and vehicle requirements.
The link complies with SAE standards, and consists of
three twisted wires: a green wire (407), a yellow wire
(406) and in early deisgns a shield wire (408–optional).
The twisted wire set (40 turns per meter) is used to protect the link from electrical interference.
CAUTION
No modifications or connections should be made to
wires 406 (yellow), 407 (green) or 408 (shielded).
These wires carry the high-speed communications between the electronic systems in the vehicle. Any
modification, connection to, or damage to these
wires can result in the failure of the vehicle’s electronic systems.
44

Group 28 Design and Function
Terminating Resistor
Communication
Equipment
(Expansion
capability)
Instrument Cluster
W3002905
Terminating resistors are wired into each end of the
J1939 data link. One is located near the ABS ECU and
the other near the engine ECU. On Volvo engines, the
terminating resistor at the engine ECU end is located inside the EECU.
If you measure 120 ohm (+/- 10 ohm) between circuits
406 and 407, then there is only one terminatig resistor.
Check to determine which is missing and reconnect it.
Note: With Volvo engines, one terminating resistor is
within the engine ECU. The other is poitioned at the end
of the J1939 network, typically at the ABS ECU. The one
within the ECU is not accessible and should not be at
fault.
If you measure less than 60 ohm, only two terminating
resistors are used in a vehicle. Never install three in one
truck. If more than two terminating resistors exist in the
J1939 circuit, damage to the ECU electronics can occur
over time. You can easily check to see if you have two
resistors by measuring the resistance between circuits
406 and 407 with the ignition OFF. The correct resis-
tance is 60
.
Diagnostic
connector
SAE J1587
/1708
MIDs 234 & 140
SRS ECU
MID 232
Engine ECU
MID 128
Vehicle ECU
MID 144
Transmission ECU
MID 130
Terminating
Resistor
SAE J1939
The purpose of these resistors is to prevent data link
signal reflections. They must remain connected for the
system to function properly.
Control unit
(Expansion
capability)
ABS ECU
MID 136
Terminating
Resistor
45

Group 28 Design and Function
SAE J1587/1708 Information Data Link
Information and diagnostic signals are sent via this
link. The link also functions as a “backup” should the
J1939 control data link fail to function for any reason.
SAE J1708 is a standard that specifies hardware and a
databus speed of 9600 bits per second. SAE J1587 is a
protocol that provides a standard method for exchanging
information between microprocessors.
The J1587 link consists of two wires (400 and 401) that
are twisted around each other approx. 30 turns per meter. The twisted-pair wires are to protect the link against
electrical interference.
CAUTION
If a circuit must be added to the electrical system, and
will carry high currents or frequencies, route it in a location AWAY from wires 400 and 401 to prevent
mutual inductance from interfering with data link functions.
CAUTION
Wires 400 and 401 MUST NOT be cut or spliced for
any connections. These wires are used for the transmission of data for diagnostic messages and gauges.
Modifying this circuit can cause these functions to fail.
Diagnostic
connector
SAE J1587
/1708
Communication
Equipment
(Expansion
capability)
Instrument Cluster
MIDs 234 & 140
SRS ECU
MID 232
Engine ECU
MID 128
Vehicle ECU
MID 144
Transmission ECU
MID 130
Terminating
Resistor
SAE J1939
SAE J1922 Data Link
For a short period of time some vehicles were produced
which used the J1922 data link. The J1922 data link was
developed as an interim standard until the J1939 control
data link was established. The J1922 link operates on
J1708 defined hardware and is used like a control link
for communication between engine, transmission and
ABS ECUs.
The J1922 link consists of two wires (404 and 405) that
are twisted around each other approx. 30 turns per meter. The twisted-pair wires are to protect the link against
electrical interference.
Control unit
(Expansion
capability)
ABS ECU
MID 136
Terminating
Resistor
46

Group 28 Design and Function
Diagnostic Connector
Communication
Equipment
(Expansion
capability)
Instrument Cluster
MIDs 234 & 140
SRS ECU
MID 232
W8001310
The diagnostic connector is a round Deutsch connector
located in the driver’s side kick panel. The diagnostic
connector is connected to the J1587/1708 information
link and gives the system a way to communicate with an
external PC or diagnostic tool.
With a PC or diagnostic tool connected, fault codes can
be read from all the control units. This is important in
fault tracing to carry out basic checks of all the vital
parts of the vehicle’s electronics.
Some programming can also be done via the diagnostic
connector.
The standard diagnostic connector is a 6–pin Deutsch. A
newer 9–pin Deutsch version has been introduced on
certain vehicle/engine variants. The new 9–pin connector
connects to both the J1939 and J1587/1708 data links.
Diagnostic
connector
SAE J1587
/1708
Engine ECU
MID 128
Vehicle ECU
MID 144
Transmission ECU
MID 130
Control unit
(Expansion
capability)
ABS ECU
MID 136
Terminating
Resistor
SAE J1939
Terminating
Resistor
47

Group 28 Design and Function
Communication Equipment
Communication
Equipment
(Expansion
capability)
Instrument Cluster
MIDs 234 & 140
SRS ECU
W2003295
Pro-Driver Display
MID 232
Various manufacturers offer communication equipment
designed to allow drivers to keep log book records electronically, maintain communication with the home office,
monitor and record vehicle operations, and many other
functions. Currently these communication devices are
connected to the J1587/1708 Information Data Link.
Newer and more sophisticated versions of these devices
may also connect to the J1939 Control Data Link. Note:
No provisions have currently been made to add communication equipment to the J1939 link in aftermarket
adaptations.
CAUTION
No modifications or connections should be made to
wires 406 (yellow), 407 (green) or 408 (shielded).
These wires carry the high-speed communications between the electronic systems in the vehicle. Any
modification, connection to, or damage to these
wires can result in the failure of the vehicle’s electronic systems.
Provisions are made for adding aftermarket communication devices to the J1587/1708 link via connectors in the
wiring harness.
Diagnostic
connector
SAE J1587
/1708
Engine ECU
MID 128
Vehicle ECU
MID 144
Transmission ECU
MID 130
Control unit
(Expansion
capability)
ABS ECU
MID 136
Terminating
Resistor
SAE J1939
Terminating
Resistor
Some of the communication devices currently used in
Volvo trucks include Road Relay, Pro-Driver, Qualcomm
and Highway Master.
48

Group 28 Design and Function
Instrument Cluster
W3003621
The instrument cluster used on Volvo vehicles uses both
data link signals and hardwired sensors depending on
the vehicle/engine variant and instrument configuration.
A graphic display screen is integrated into the instrument
cluster to provide additional features and vehicle system
information not available from other gauges. Diagnostic
codes can also be retrieved and displayed. The instrument cluster is connected to the J1587/1708 information
data link.
For information about the instrumentation that communicates via the data link, refer to service manuals in group
38:
Communication
Equipment
(Expansion
capability)
Instrument Cluster
MIDs 234 & 140
Model: See Publication:
WG/AC/WC/WI from
1994; WX with elec-
Data Link Instrumentation,
PV776–381–620SM
tronic engines from
5.96
WX Kysor Mini-Cluster, PV776–
TSP108262
VN from 1.98–2.99 Instrumentation, PV776–
TSP106805/1
VN from 3.99 ADN
VHD
Instrumentation, PV776–
TSP139790
Diagnostic
connector
SAE J1587
/1708
SRS ECU
MID 232
Engine ECU
MID 128
Vehicle ECU
MID 144
Transmission ECU
MID 130
Control unit
(Expansion
capability)
ABS ECU
MID 136
Terminating
Resistor
SAE J1939
Terminating
Resistor
49

Group 28 Design and Function
Vehicle Electronic Control Unit (VECU)
W2002673
The vehicle electronic control unit (VECU) is part of the
integrated vehicle electronics. The VECU is located in the
cab, but its specific mounting location varies by model.
The main function of the VECU is to collect data from
different cab control units and then to pass this data to
other ECUs in the system (primarily to the engine ECU).
Communication
Equipment
(Expansion
capability)
For detailed information about the VECU see Vehicle
Electronic Control Unit, MID 144, Volvo service publication number PV776–300–610.
The VECU is only used in vehicles equipped with
Volvo engines.
Diagnostic
connector
SAE J1587
/1708
Instrument Cluster
MIDs 234 & 140
SRS ECU
MID 232
Engine ECU
MID 128
Vehicle ECU
MID 144
Transmission ECU
MID 130
Terminating
Resistor
SAE J1939
50
Control unit
(Expansion
capability)
ABS ECU
MID 136
Terminating
Resistor

Group 28 Design and Function
Engine Electronic Control Unit
W2003294
Irrespective of engine variant, the engine electronic control unit (EECU) performs the same basic functions in
the system: control of engine operation. The EECU receives signals from various sensors and the data links.
Based on these signals and the parameters programmed
into the EECU, the EECU calculates the proper injection
angle and fuel quantity to satisfy the requested operating
requirements.
The EECU is connected to both the J1939 control data
link and the J1587/1708 information data link.
Communication
Equipment
(Expansion
capability)
Instrument Cluster
MIDs 234 & 140
Note: Early production model EECUs may use only the
J1587/1708 data link, or the J1587/1708 and the J1922
data links.
For detailed information about EECUs see the service
literature for that particular engine.
Diagnostic
connector
SAE J1587
/1708
SRS ECU
MID 232
Engine ECU
MID 128
Vehicle ECU
MID 144
Transmission ECU
MID 130
Control unit
(Expansion
capability)
Terminating
Resistor
SAE J1939
ABS ECU
MID 136
Terminating
Resistor
51

Group 28 Design and Function
EECU
The EECU is an electronic control unit that monitors certain operational parameters of the Volvo engine from the
SAE J1587 Data Link and appropriate sensors.
W2003076
52

Group 28 Design and Function
ON/OFF Engine Cooling Fan
The EECU receives the input from the engine coolant
temperature sensor to turn on the cooling fan at 115
F). The fan will remain engaged until the engine
(202
coolant drops to 90
The ON/OFF cooling fan can also be engaged by the
EECU if it receives a signal from the air conditioning systems APADS module. When the A/C system pressure
reaches 20.5 bar (300 psi) the APADS module will send
a signal to the EECU to engage the cooling fan. The on
time of the cooling fan is controlled by the APADS module.
If the EECU does not receive any coolant temperature
data, the fan is engaged for a minimum of 30 seconds.
The fan will stay engaged until valid coolant temperature
data is received and the coolant temperature drops below 90
C (195
F).
C (195
F).
C
Converting Engine Oil Pressure Signal
The EECU takes an analog signal from a pressure transducer and broadcasts the signal on the SAE J1587 data
link.
Engine Information and Warning Lamp-On Dash
Engine Oil Pressure
•
The EECU will make the
icon in the display light up if the oil pressure is < 41
± 3 kPa (6 ± 1.2 psi). Also a warning signal sounds
if the engine is running.
Engine Coolant Level
•
The EECU will make the
(solid) if the low coolant level sensor detects a low
coolant level condition. The low coolant level condition is active only after 5 seconds of a constant
signal from the low level sensor.
Engine Coolant Temperature
•
The EECU will make the
nate and gauge LED illuminate, plus the icon in the
display if a high coolant temperature from the engine ECU is received.
Engine Oil Temperature
•
If the Engine oil temperature becomes too high an
information message is shown automatically with
the text HIGH. At the same time the yellow
lamp under the display lights up. The engine may
also derate, if it is set up to do so in the engine
ECU programming. The temperature which activates
this warning varies for different engines. This
temperature is set in the engine ECU. For Volvo engines, it is 275
F (135C).
1
STOP lamp light and the
1
STOP lamp light stay on
1
STOP lamp light illumi-
1
INFO
Note: If the engine is running and the stop lamp comes
on you will get a buzzer or warning signal.
53

Group 28 Design and Function
Electronic Unit Injectors
The engine has six unit injectors, one for each cylinder.
Each Electronic Unit Injector, or EUI, is a combination
of injection pump and injector, but operates at a considerably higher pressure than a standard injector.
Each unit injector is mounted vertically in the cylinder
head at each cylinder, centered between the four valves.
The compressive force for the unit injector is developed
by a lobe on the overhead camshaft. It is then transferred by a rocker arm to the injector.
The injection angle and the amount of fuel to be injected
into the cylinder is determined by the EECU, which
transmits signals to the electromagnetically controlled
fuel valve in the unit injector valve housing.
Make sure to turn the ignition key off before working
on the electronic unit injectors. This eliminates the
possibility of electric shock which may result in personal injury or death.
Calculating Fuel Quantities
The EECU calculates the quantity of fuel to be injected
into a cylinder. This calculation provides the period of
time during which the fuel valve is closed (when the fuel
valve is closed, fuel is injected into the cylinder). Factors
that determine how much fuel to inject into a cylinder are:
Requested fuel amount
•
Limitation of fuel amount
•
Flywheel
There are 54 notches cut into the flywheel; these are
read by the speed sensor for the flywheel. With the help
of these notches, the EECU can set the correct injection
angle and calculate the time which gives the correct fuel
amount.
The notches are divided into three groups, with 18
notches in each group. There is a flat area between
each group of notches equivalent to 18
18 notches is equivalent to 120
third of a full turn. The area between each notch equals
on the flywheel.
6
.Aflat area and
on the flywheel, or a
T2006998
Electronic unit injector
54
T2007019
Flywheel

Group 28 Design and Function
Cam Sensor Wheel
The cam sensor wheel has six teeth (one tooth for each
unit injector) evenly spaced at 60
an extra tooth, placed 15
cylinder number 1.
The EECU uses these teeth to determine which injector
is in line for injection. In other words, each tooth (teeth
1–6) represents the start of a cylinder operating phase
(does not apply to the extra tooth).
center-to-center, plus
before the tooth that indicates
T2007099
Cam sensor wheel
Flywheel and Cam Sensor Wheel
The ratio between the flywheel and cam sensor is 2:1.
This means that when the flywheel has rotated two
turns, the cam sensor wheel has rotated one turn or
when the flywheel has rotated 30
wheel has rotated 15
and so on.
, the cam sensor
55

Group 28 Design and Function
Injector Operational Phases
The operational phase of the number 1 cylinder is given
in the following example. Fuel is injected at 7
dead center (BTDC) (the injection angle may vary between 18
BTDC and 6
after top dead center).
The cam sensor reacts to the extra tooth on the cam
sensor wheel. This informs the control unit that the next
tooth in turn (tooth 1) indicates the number 1 cylinder.
The cam sensor wheel detects tooth 1 and the flywheel
sensor reaches a flat area on the flywheel at the same
time.
At this point, the piston is on its way upward in the cylinder and no fuel is injected into the cylinder.
before top
T2007100
Locating number 1 cylinder
A top dead center (TDC)
The sensor detects the first notch after a flat area on the
flywheel. Using the engine speed calculation, the EECU
can determine:
When to begin injecting fuel into the number 1 cylin-
•
der. This gives selected injection angle (7
BTDC in
the example).
When to stop injecting fuel into the number 1 cylin-
•
der. This gives the selected fuel amount.
Engine speed calculated
A top dead center (TDC)
Calculating injection angle
A TDC
B 7
C ATDC (injection stops)
BTDC (injection begins)
T2007101
T2007102
56

Group 28 Design and Function
From the first notch after a flat area, the EECU advances the angle from which it is to begin injecting fuel
into the cylinder and on to the angle where it is to stop
injecting fuel into the cylinder. If the calculated angles do
not agree with the notches on the flywheel, the EECU
measures the time between the last notches to rectify
the angles.
Because the EECU must calculate the engine speed
during 120
der occurs one step ahead at all times. In other words,
during the operational phase for one cylinder, the EECU
calculates engine speed for the next cylinder and so on.
This procedure is repeated for the next cylinder in the
same manner as described for the number 1 cylinder.
Note: Note that the calculation of the injection angle and
fuel amount takes place continuously, regardless of the
operational phase of the cylinders.
, the engine speed calculation for each cylin-
Cylinder Balancing
The EECU can provide each cylinder with a different
quantity of fuel to make the engine run more smoothly at
idling speeds. At higher speeds, there are no problems
with smooth running and all cylinders receive the same
amount of fuel. If the variation in fuel quantity between
different cylinders is too great during cylinder balancing,
the EUI, which deviates most, triggers a fault code from
31 to 36. This indicates that there must be a fault in the
cylinder in question.
For cylinder balancing to take place, the following conditions must be satisfied:
Idling speed must be below 650 rpm.
•
Fuel requirement must be below a specific rating.
•
Idling adjustment function must not be active.
•
PTO not active.
•
Cruise control mode not active.
•
Accelerator pedal in idling position.
•
Coolant temperature must be above 50
•
Vehicle must be at a standstill.
•
No fault codes in existence.
•
C (122
F).
57

Group 28 Design and Function
Other Functions
The EECU guides the EUIs based on the following ”control functions.”
Smoke limitation — To prevent injecting too much fuel
into the cylinder, the EECU checks:
Boost pressure
•
Engine speed
•
Boost air temperature
•
PTO engine speed — The engine can be kept at a con-
stant rpm level that is at least 100 rpm greater than low
idle and less than high idle.
Cruise control — The engine can be set to maintain a
constant speed between 48 km/h (30 mph) and 140
km/h (87 mph). For the cruise control mode to function,
the following conditions must be satisfied:
Cruise control in ON position.
•
Brake pedal must not be depressed.
•
Clutch pedal must not be depressed.
•
Speed limitation — The EECU can be programmed to
limit the maximum speed up to 140 km/h (87 mph). A
fault on the sensor signal and/or a faulty cable to the
EECU generates a fault code.
Differentiated speed limitation — This mode is avail-
able as an option. It limits the speed to various levels
depending on the gear selected. In other words, each
gear has a maximum speed.
58

Group 28 Design and Function
Engine protection — To a certain extent, the EECU can
also protect the engine by:
Reducing engine speed at low coolant temperatures
•
(cold engine cranking): When coolant temperature is
lower than 50
during a specific time to 1000 rpm immediately after
starting. At –20
16 seconds, and above 50
C (122
C(–4
F), engine speed is limited
F) and lower, this period is
C (122
F) the period is
0 second. This function allows oil pressure to build
up before engine speeds become too high.
W2000768
Engine speed during cold cranking
Reducing engine output at high coolant tempera-
•
tures (during engine operation): Should coolant
temperature exceed 102
C (216
F), the maximum
fuel provision is reduced by a certain percentage of
its original rating and the coolant temperature warning lamp lights up. If the coolant temperature
becomes excessively high, the engine will gradually
reduce power to 50%. When coolant temperature
has dropped below 100
C (212
F), maximum fuel
provision is permitted again and the coolant temperature warning lamp goes out.
The safety signal is an optional system that enables the
EECU too switch off the engine. The EECU can be programmed to provide three levels of engine protection:
No engine protection (fire engine)
•
Engine protection
•
Extended engine protection
•
W2000769
Engine speed during operation
59

Group 28 Design and Function
Idle shutdown — This function is available as an option.
It switches off the engine after it has run at idling speed
for a specific time. This time can be set to between 1
and 40 minutes. The engine will be switched off if the following conditions are met:
Vehicle speed is 0.
•
Parking brake is applied.
•
Engine running at idle speed.
•
Coolant temperature is above 45
•
Cold starts, idling — Idling speed is automatically
boosted to heat the engine more quickly from a cold start
when coolant temperature is below a specific level. When
this mode is activated, idling speed is boosted to 650
rpm. When coolant temperature has reached 30
F), idling speed drops steadily to its normal level which
is reached at a coolant temperature of 45
C (113
C (113
F).
C (86
F).
60

Group 28 Design and Function
Starting the engine
Before any fuel can be injected into the cylinders, the
EECU must have had a sufficient amount of time to
carry out the first calculations on injection angles and
fuel quantities. This time is equivalent to two engine revolutions.
VEB (VOLVO engine brake)
The VEB consists of an exhaust brake and a compression brake. The EECU activates the VEB when the
following conditions are satisfied:
Accelerator pedal at idling position (fuel injection
•
must not occur).
Engine speed must exceed 1200 rpm.
•
Clutch pedal must not be depressed.
•
Boost pressure must be lower than 152 kPa (22 psi)
•
(overpressure).
PTO not activated.
•
Vehicle speed is greater than 3.2 km/h (2 mph).
•
ABS not activated.
•
Engine coolant temperature is greater than 40 ± 2
•
C (104 ± 5
Engine oil temperature is greater then 55
•
F).
The VEB may be activated when the cruise control is in
use. For this to take place, the following condition must
be satisfied:
Vehicle road speed must exceed the set speed of
•
the cruise control by between 5 and 30 km/h (4 and
20 mph), depending on what level has been programmed into the EECU.
F).
C (130
61

Group 28 Design and Function
Idle Speed Adjustment
Note: This service information should be considered
supplemental to the Engine Control information for base
D12 B and C engine.
The idle speed is adjusted on the VN vehicles at the turn
signal stalk. The idle speed can be adjusted between
500 RPM and 650 RPM.
Prerequisites to adjusting idle speed:
Accelerator pedal not depressed.
•
Engine temperature above 45
•
Vehicle is stationary / Parking brake set.
•
Idle speed adjustment
1 Cruise control in the ON position.
2 Depress the brake pedal and continue to hold it dur-
ing the entire adjustment procedure.
3 Move the ON/OFF switch to the RESUME position
and hold for four seconds. Release the switch; the
engine speed will drop to approximately 500 RPM.
4 The idle speed can be adjusted with the SET
switch. Each time the SET switch is pressed, the
idle speed will increase approximately 10 RPM.
5 Move the ON/OFF switch to the RESUME position
and the idle speed will decrease approximately 10
RPM each time.
6 Hold in the SET switch and move the ON/OFF
switch to the RESUME position and hold them in
position for four seconds. Release the switches
7 Release the brake pedal and the new idle speed is
set. If an error was made during the adjustment procedure, the default idle speed will be maintained.
C (113
F).
1 A-Set
2 B-Resume, On/Off
62
T3014326

Group 28 Design and Function
ABS Brake System ECU
W5000669
The ABS ECU continuously monitors wheel speed and
helps to control braking in exterme situations. It also
helps prevent wheel spin in vehicles equipped with traction control systems (ATC or TCS).
The ABS ECU is connected to the J1939 control data
link and the J1587/1708 information data link.
Communication
Equipment
(Expansion
capability)
Note: Early production model ABS ECUs may be connected to the J1587/1708 and J1922 data link or have
no data link connection at all.
For detailed information about ABS systems see the appropriate service literature for the type of ABS system
used on the vehicle.
Diagnostic
connector
SAE J1587
/1708
Instrument Cluster
MIDs 234 & 140
SRS ECU
MID 232
Engine ECU
MID 128
Vehicle ECU
MID 144
Transmission ECU
MID 130
Terminating
Resistor
SAE J1939
Control unit
(Expansion
capability)
ABS ECU
MID 136
Terminating
Resistor
63

Group 28 Design and Function
SRS Airbag ECU
T8006850
The Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ECU senses
frontal collisions with two rapid deceleration sensors.
The SRS ECU will deploy the airbag module in the
steering wheel if a collision of sufficient force and duration is detected.
The SRS ECU is connected to the J1587/1708 information data link. For detailed information about the SRS
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS), VNL, VNM,
see
Volvo service publication number PV776–TSP21771/1.
Note: The SRS system is not available on all models.
Communication
Equipment
(Expansion
capability)
Instrument Cluster
MIDs 234 & 140
Diagnostic
connector
SAE J1587
/1708
SRS ECU
MID 232
Engine ECU
MID 128
Vehicle ECU
MID 144
Transmission ECU
MID 130
Control unit
(Expansion
capability)
ABS ECU
MID 136
Terminating
Resistor
SAE J1939
Terminating
Resistor
64

Group 28 Design and Function
Transmission ECU
The transmission electronic control unit (ECU) receives
signals directly from switches and sensors and via the
data links. Based on those inputs, the transmission ECU
controls transmission operation via solenoid valves and
switches. The transmission ECU also supplies system
status and diagnostic information.
The transmission ECU is connected to both the J1939
control data link and the J1587/1708 information data
link.
Note: Early production model transmission ECUs may
be connected to the J1587/1708 and J1922 data links.
For detailed information about transmission ECUs see
the service literature for that particular transmission.
Diagnostic
connector
W4001493
Communication
Equipment
(Expansion
capability)
Instrument Cluster
MIDs 234 & 140
SRS ECU
MID 232
Engine ECU
MID 128
Vehicle ECU
MID 144
Terminating
Resistor
SAE J1587
/1708
Transmission ECU
MID 130
Control unit
(Expansion
capability)
ABS ECU
MID 136
SAE J1939
Terminating
Resistor
65

Group 28 Design and Function
Breakout Boxes and Harnesses
The harness adapters are used to gain access to the
EECU, the VECU, the throttle pedal and certain other
sensors on the engine, while the circuit is intact. This allows the technician and vehicle to take measurements
on functional circuits.
Example:
The 36-pin breakout box allows the technician to
measure resistance and voltage on the EECU’s EA connector (which covers the engine mounted components)
and the EB connector (which covers the remaining components involved).
CAUTION
Check that the proper cable and connector location is
observed and used while connectin to the ECU.
Ohterwise, damage to the ECU or tool will occur.
66
W2002712
W2002710

Group 28 Design and Function
VECU Overview
The Vehicle Electronic Control Unit (VECU) receives
inputs and generates output signals for functions associated with cab devices. It also converts information into
digital data to be broadcast over the J1587/1708 Information Link and the J1939 Control Link.
Note: The VECU may also be referred to as the “Cab
Controller” on the graphics display of the VN series dash
and in some Volvo publications.
VECU Programming
Each VECU is programmed with specific vehicle
performance characteristics corresponding to customerordered options for that particular vehicle. This dataset is
stored in the VECU memory, making the VECU unique
to each vehicle.
For this reason, it is not possible to “swap” a suspected
faulty VECU with one from another vehicle without reprogramming the replacement VECU.
Replacement VECUs are programmed using the VCADS
Pro tool. Programming is based on the particular dataset
that matches the vehicle; datasets are stored in the
Volvo Data Administration (VDA) database. Authorized
technicians can update and/or alter software datasets,
change customer parameters, and perform campaigns.
W0001632
For more information about the proper operation of the
VCADS Pro tool and VECU programming, please refer
to Information on VCADS Pro in Group O. This manual
is also available as a pdf file within VCADS Pro tool located under Help.
Note: Customer parameter changes are not stored in
the VDA database. Therefore, after a replacement VECU
is programmed for the vehicle, it will have to be customized to include those customer alterations.
67

Group 28 Design and Function
VECU Functions
The following functions are monitored or controlled by
the VECU. Only the functions needed for each specific
vehicle/engine application are wired and programmed
into the VECU.
Accelerator Pedal
The accelerator pedal signals travel first to the VECU
and are transferred to the Engine Electronic Control Unit
(EECU) via the J1939 Control Link.
If there is a fault in the J1939 Control Link, the accelerator pedal signal travels to the EECU via the J587/1708
Information Link. The vehicle can also be driven in the
“limp home” mode is there is a fault in both links. In this
situation, the idle validation switch is used to determine
when the accelerator pedal is pressed; then, the VECU
sends a buffered idle validation switch signal (via hard
wire) to the EECU.
Second Accelerator Pedal
If the vehicle is equipped with a second accelerator
pedal, the second accelerator pedal signals travel first to
the VECU and are transferred to the Engine Electronic
Control Unit (EECU) via the J1939 Control Link.
A road speed limit may be programmed into the VECU
to limit vehicle speed when the second accelerator pedal
is being used. Second accelerator pedal road speed limit
can be programmed using the VCADS Pro tool.
Speedometer
The speed signal comes from a sensor on the transmission or as a digital signal, if an electronically-controlled
transmission (Allison) is used. The VECU then sends the
vehicle speed signal on both the J1939 Control Link and
J1587/1708 Information Link. The signal on the J1939
Control Link is used to control vehicle operation. The
signal on the J1587/1708 Information Link is collected by
the instrument cluster and is displayed on the
speedometer.
Cruise Control
The VECU receives signals from the cruise control
switch and sends signals to the EECU via the J1939
Control Link. Cruise control parameters can be programmed with the VCADS Pro too.
68

Group 28 Design and Function
Power Take-Off (PTO)
PTO functions are controlled by the VECU through the
cruise control switch. Basic or optional PTO parameters
can be programmed with the VCADS Pro tool.
Ignition Switch
Ignition switch positions are recognized by the VECU,
which transfers the ignition switch position information to
the EECU.
Idle Shut-Down
Timed engine shut-off can be controlled by the VECU as
a customer option. Idle shut-down time can be programmed with the VCADS Pro tool.
Engine Brake
The control for the engine brake (including the exhaust
pressure governor [EPG] and compression brake [VCB],
if installed) are monitored by the VECU. At the request
of the ABS ECU, the VECU can de-activate the engine
brake.
Windshield Wipers
Windshield wiper function on the VN and VHD (with
Volvo engine) is controlled by the VECU using signals
received from the wiper switch.
Calibration Number
The calibration number (K factor) is a measurement of
“Drivetrain Constant Pulses per Mile” and is used by the
VECU to determine vehicle speed and distance traveled.
The calibration number is calculated by multiplying “tire
revolutions per mile” x “rear axle ratio” x “number of
teeth on the transmission output shaft chopper wheel.”
The calibration number is programmed into the VECU
using the VCADS Pro tool.
69

Group 28 Design and Function
Optional Engine Speed Limit
Optional engine speed limit is the maximum speed at
which the engine can be operated with the vehicle at
zero road speed and the PTO mode engaged. Optional
engine speed limit parameters can be programmed with
the VCADS Pro tool.
Optional Vehicle Speed Limit
Optional vehicle speed limit allows for an optional switch
to limit vehicle speed. Typically, this switch is operated
on the vehicle by someone other than the driver, such as
a garbage collector who rides on the back of the vehicle.
Optional vehicle speed limit parameters can be programmed with the VCADS Pro tool.
Note: Basic vehicle speed limit is set by the EECU.
Shut-Down Request
Optional engine shut-down request is made via a remote
mounted switch (the ignition switch is the basic engine
shut-down request). After the VECU receives the shutdown request, the request is sent to the EECU via the
J1939 Control Link. Shut-down request is enabled using
the VCADS Pro tool.
Note: The engine shut-down request function should not
be considered or used as an emergency shut-down.
Torque Limit
Torque limit 1 and 2 are used to limit drive line torque.
Torque limit parameters can be programmed with the
VCADS Pro tool.
Engine Fan Request
The VECU receives the request for engine fan operation
from either a manual switch or a high pressure A/C refrigerant switch. The VECU then transfers the request to
the EECU via the J1939 Control Link.
Brake/Clutch Status Switches
The VECU recognizes the position of the brake, clutch,
and parking brake. Various VECU functions (i.e. cruise
control or PTO) operate only when these switches are in
the proper position.
70

Group 28 Design and Function
Safety Warnings/Cautions
Always wear approved eye protection.
•
To avoid personal injury and damage to the vehicle,
•
always refer to and follow the vehicle manufacturer’s
WARNINGS, CAUTIONS, and service procedures.
Unless otherwise directed, turn the ignition switch
•
OFF before disconnecting or connecting any electrical components.
Read and understand the manual provided with the
•
tool before operating your Pro-Link
VGHT recommends an assistant drive the vehicle
•
while you use the Pro-Link
Never leave the vehicle unattended while testing.
•
®
9000.
®
9000.
71

Group 28 Design and Function
VCADS Pro
From the VCADS Pro Main Menu, VCADS Pro Test, Calibration, Programming and Job Cards are started. In
addition, a number of settings can be done, i.e. the selection of language. Ensure your “language” is selected
to get the right tests for your country’s vehicle variant.
Do one of the following to start an application:
Select the application in the menu Select applica-
•
tion. When highlighted press “Enter”.
Click the program’s function button in the toolbar;
•
test (1), calibration (2), programming (3) and job
card (4).
Double click the desired program in the function tree.
•
The following can be performed in the Administrative
functions
Language selection
•
Selection of screen saver and screen saver delay.
•
Selection of background image.
•
Selection of default application.
•
T0009469
Update the system. Get a new program version of
•
VCADS Pro from Volvo via connection to the central
systems.
User administration. Select the user to change the
•
password for. This function requires authorization
and is not available to all users.
General adminstration. Selection of communication
•
method, vehicle/machine type and activation/deactivation of the simulator is possible.
72

Group 28 Design and Function
Sensor Locations
VN/VHD Sensors and Switches
Inside cab
1 Throttle position sensor
2 Microswitch(service brake)
3 Engine/Exhaust Brake
4 VECU
5 Pressure Switch-Parking and Service Brake
6 ON/OFF—Resume Switch
7 Resume Switch
8 Diagnostic connector
W2003551
73

Group 28 Design and Function
D7C
1 EECU connector EA/EB
2 EPG solenoid
3 Boost pressure/temperature sensor
4 Oil pressure/temperature sensor
5 Engine timing (crank) sensor
6 Engine electronic control unit (EECU)
1 Needle lift sensor (at injector #1)
2 Coolant temperature sensor
3 Redundant engine speed sensor (1); Fuel pres-
sure/temperature sensor (2); Fuel shut-off valve (3);
7–pin connector (4), includes rack drive, rack position sensor, and timing sleeve
W2002748
74
W2002749

Group 28 Design and Function
D12B
1 Boost pressure/temperature sensor
2 Coolant temperature sensor
3 Oil pressure/temperature sensor
4 Engine timing (crank) sensor
5 Engine electronic control unit (EECU)
6 EECU connector EA/EB
7 Engine position (cam) sensor
1 Compression brake, VCB (under valve cover)
2 EPG control (PWM box)
W2002745
W2002746
75

Group 28 Design and Function
D12C
W2003550
Fig. 10: Engine electronic control unit (EECU) sensor locations D12C
Several engine sensors send signals to the EECU. They
are:
1 Cam Sensor (timing gears)—This sensor deter-
mines which cylinder is in line for injection. It detects
the camshaft’s position via a pole wheel bolted to
the camshaft drive gear.
2 Oil Pressure/temperature sensor (cylinder
block)—This combined sensor monitors oil pressure
and oil temperature.
3 Fuel Pressure/Temperature Sensor — Monitors
the fuel pressure and fuel temperature
4 Crank Sensor (flywheel housing) — This sensor
detects the crank-shafts’s position and speed, via
teeth in the flywheel. Detects Engine RPM’s.
5 Coolant Temperature Sensor (cylinder head)—
This sensor monitors coolant temperature.
6 Intake Manifold Pressure (intake manifold)—This
is a combined sensor that monitors both the intake
manifold air pressure and temperature.
76

Group 28 Design and Function
Control Unit Locations
VN/VHD: Cab and Engine Compartment
The diagram shows the normal location of the different
control units on a VN vehicle equipped with a Volvo engine.
Control units may vary slightly in location, depending on
vehicle and component type (variant). The locations are
virtually the same on a VHD vehicle.
1 Vehicle electronic control unit (VECU)
2 Instrument cluster
3 ABS control unit; crossmember located toward rear
of cab
W3003955
4 SRS control unit
5 Engine electronic control unit (EECU)
77

Group 28 Design and Function
WG/AC: Cab and Engine Compartment
The diagram shows the normal location of the different
control units on WG and AC vehicles.
Control units may vary slightly in location, depending on
vehicle type (variant).
1 ABS control unit, on right side frame rail
2 Instrument cluster
78
W3003963
3 Vehicle electronic control unit (VECU)
4 Engine electronic control unit (EECU)

Group 28 Design and Function
WX/WXLL: Cab and Engine Compartment
The diagram shows the normal location of the different
control units on a WX or WXLL vehicle.
Control units may vary slightly in location, depending on
vehicle type (variant).
1 Vehicle electronic control unit (VECU), location in
WX narrow cab only
2 Instrument cluster
3 Engine electronic control unit (EECU)
4 Transmission ECU, under driver’s seat
W3003961
5 ABS control unit, right side engine tunnel
6 VECU, WX and WXLL, right side engine tunnel
7 ABS control unit, location in WX narrow cab only
79

Group 28 Design and Function
WXR: Cab and Engine Compartment
The diagram shows the normal location of the different
control units on a WXR vehicle.
Control units may vary slightly in location, depending on
vehicle type (variant).
1 Engine electronic control unit (EECU)
2 Instrument cluster
3 ABS control unit
80
W3003962
4 Transmission ECU
5 Vehicle electronic control unit (VECU) — on left side
of cab, below center dash panel

Group 28 Design and Function
Fuses and Relays
W8000923
The VN/VHD vehicles have easy access to the TEC
panel. Fuses and relays are easily identified by referring
to the decals inside the TEC covers.
W3004398
81

Group 28 Design and Function
VN
Note: Refer to the decal inside the TEC cover for vehi-
cle’s exact fuse descriptions and ratings.
82
W3002729
Fig. 11: Fuse and Relay Positions (in the top TEC panel, VN)
B1–1 through B1–6 Ignition Expansion Blocks
B2–2 through B2–4 Battery Expansion Blocks
PR1 Accessory Power Relay
PR2, PR3 Igntion Power Relays
One Accessory an two Ignition Power relays are used to transfer the heavy current load coming from the battery
to the Ignition/Accessory circuits. These relays are located on the TEC tray for easy access and replacement.

Group 28 Design and Function
VHD
Note: Refer to the decal inside the TEC cover for vehi-
cle’s exact fuse descriptions and ratings.
Fig. 12: Fuse and Relay Positions (in the top TEC panel, VHD)
B1–1 through B1–6 Battery and Ignition Expansion Block
PR1 Accessory Power Relay
PR2, PR3, PR4, R24 Ignition Power Relays
One Accessory and four ignition Power relays are used to transfer the heavy current load coming from the
battery to the Ignition/Accessory circuits. These relays are located on the TEC tray for easy access and replacement. PR4 is used in the VHD bodybuilder applications
W3004362
83

84

Group 28 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Fault Code Troubleshooting
Message and Parameter Descriptions
MID’s
(message ID’s)
128 EECU (Engine Electronic Control Unit)
232 SRS (Supplemental Restraint System)
136 ABS (Antilock Braking System
140 Instrument Cluster Center Module
234 Instrument Cluster Left Module
144 VECU (Vehicle Electronic Control Unit)
130 TECU (Transmission Electronic Control Unit)
PID’s
(Parameter ID’s)
84 Road Speed
91 % Accelerator Pedal
100 Engine Oil Pressure
102 Boost Pressure
105 Air Inlet Temperature
Description
Description
110 Engine Coolant Temperature
111 Coolant Level
173 Pyrometer
175 Engin Oil Temperature
190 Engine Speed
85

Group 28 Troubleshooting
PPID’s
(Proprietary Parameter
ID’s)
69 Buffered idle switch
70 Pedal switches, supply
71 Cruise control and retarder, supply switch
72 Accelerator pedal and retarder, supply sensors
73 Accelerator control 2 and primary tank, supply sensors
75 Range inhibitor, status solenoid valve
77 Compressor, status solenoid valve
78 Interval wiper, status relay
79 Area inhibitor, status solenoid valve
86 Engine brake torque percent
109 EOG3 drive stage failure
121 MTE (Engine compsressor control output) failure
122 VCB Engine compression brake
123 EPG2 Start and Warmhold
Description
124 EPG1 Engine brake
125 EOL Enable failure
195 Proprietary Diagnostic Data Request Clear Count
196 Proprietary Diagnostic Data/Count Clear Response
86

Group 28 Troubleshooting
FMI Table
SAE Standard
FMI value SAE Text
0 Data Valid, but above normal operating range.
1 Data Valid, but under normal operating range.
2 Intermittent or incorrect data.
3 Abnormally high voltage.
4 Abnormally low voltage.
5 Abnormally low current or open circuit.
6 Abnormally high current or chort circuit.
7 Mechanical system no repsonse
8 Abnormal frequency or Pulse Width
9 Abnormal update rate
10 Abnormal change rate
11 Failure unkown
12 Bad device
13 Out of calibration
14 Special instruction (see Note)
Note: The special instruction FMI 14 is broadcast when the airbag has stored crash data.
Engine-specific for Injectors
FMI value Explanation
2 Short circuit to battery voltage, unit injector high side.
3 Short circuit to battery voltage, unit injector low side.
4 Short circuit to ground, unit injector high or low side.
5 Open circuit in the unit injector circuit.
Engine-specific for Injection Pump
FMI value Explanation
2 Short circuit to battery voltage, injection pump high side.
3 Short circuit to battery voltage, injection pump low side.
4 Short circuit to ground, injection pump high or low side.
5 Open circuit in the unit injection pump circuit.
6 Short circuit to ground, injection pump high side.
8 Injection pump current too high for long period of time.
87

Group 28 Troubleshooting
Reading/Clearing Fault Codes
Fault codes can be read and cleared using the VCADS
Pro tool or the Pro-Link tool with Volvo application cartridge. See the appropriate service information for details
on reading and clearing fault codes using VCADS Pro or
Pro-Link tools.
On VN-series vehicles, fault codes also can be accessed,
read, and cleared via the instrument cluster graphic display. Clearing fault codes is password protected. For
information, see “Instrumentation VN, from 3/99 and
VHD,” Volvo Service Publication PV776–TSP139790.”
The Data Link Instrument cluster used WX-series vehicles can access and read a limited number of fault
codes. However, it does not have the ability to clear fault
codes. For more information, see “Data Link Instrumentation,” Volvo Service Publication PV776–381–620SM.
Fault Tracing Strategy
CAUTION
Check that the proper cable and connector location is
observed and used while connecting to the ECU. Failure to do so may result in permanent damage to the
ECU or the tool.
Generally, the fault tracing strategy employed in this section follows a set sequence in which measurements are
taken at specific points in the vehicle wiring. The three
basic elements in this strategy are:
1 Vehicle Electronic Control Unit (VECU)
2 The actual component being tested (varies with
each fault code)
W3003493
3 Wiring between VECU and the component being
tested
The following information describes the three test strategies:
“Measurement at the Component’s Connector, to
•
the VECU” page 90
“Check of Component” page 90
•
“Check of the Subsystem” page 91
•
88

Group 28 Troubleshooting
Measurement at the Component’s Connector, to the VECU
In this procedure, the component is disconnected and
measurements are made at specific pin locations on the
wiring harness end of the connector. Measurements
usually involve supply, ground, and signal wire connections through the wiring harness and VECU.
Breakout boxes or harnesses may be used to assist in
taking measurements. Measurements outside “expected
values” may indicate faults in the wiring or in the VECU
itself
W3003494
Check of Component
In this procedure, the component is disconnected and
measurements are made at specific pin locations on the
component wiring harness or directly to the component.
The component is usually a sensor or switch; it is identified at the beginning of each check.
Breakout boxes or harnesses may be used to assist in
taking measurements. Measurements outside “expected
values” may indicate faults in the component or in the
wiring to the component.
W3003495
89

Group 28 Troubleshooting
Check of the Subsystem
In this procedure, the VECU is disconnected, a breakout
box is connected between the VECU and wiring harness,
and measurements are made at specific pin locations on
the breakout box. This check is made to measure the
voltage that is present at the VECU with the circuit intact.
Measurements outside “expected values” may indicate
faults in the component, wiring, or VECU.
Tests Using the VCADS Pro Tool
®
The VCADS Pro tool is a Windows95
that is used to program, test, and read information from
the VECU and EECU.
A number of “real time” tests can be performed by connecting the VCADS Pro tool to the vehicle’s diagnostic
connector. If a test in the VCADS Pro tool may be of
benefit when troubleshooting a specific fault code, that
test will be referenced in the section titled, “Appropriate
tests in the VCADS Pro tool.”
Note: Not all tests will apply to all vehicle variants. When
starting VCADS Pro, menu selections for various vehicles and engines are entered. Only those tests that
apply will be available for selection.
For information about the proper operation of the
VCADS Pro tool, please refer to VCADS Pro Service Information in group 0.
-based PC tool
W0001632
90

Group 28 Troubleshooting
MID 128 EECU
MID 128 Fault Code Table
MID:Message Identification Description.
SID:Subsystem Identification Description.
PID:Parameter Identification Description.
Error code Component/Function FMI Section
MID 128-PID 45 Preheater Status 3, 4, 5 “MID 128 PID 45 Pre-
MID 128-PID 49 ABS Control Status 9 “MID 128 PID 49 ABS
MID 128-PID 84 Road speed 9, 11 “MID 128 PID 84 Road
MID 128-PID 85 Cruise Control Status 9 “MID 128 PID 85
MID 128-PID 91 Accelerator Pedal Position 9, 11 “MID 128 PID 91 Accel-
MID 128-PID 94 Fuel Delivery Pressure (D7C
and D12C only)
MID 128-PID 100 Engine Oil Pressure 1, 3, 4 “MID 128 PID 100 En-
MID 128–PID 102 Boost Pressure 3, 4 “MID 128 PID 102
FMI:Failure Mode Identifier.
heater Status” page 96
Control Status” page 98
Speed” page 100
Cruise Control Status”
page 102
erator Pedal Position”
page 104
1, 3, 4 “MID 128 PID 94 Fuel
Delivery Pressure” page
106
gine Oil Pressure” page
110
Boost Pressure” page
114
MID 128–PID 105 Boost Air Temperature 3, 4 “MID 128 PID 105
Boost Air Temperature”
page 118
MID 128–PID 107 Air Filter Differential Pressure 0, 3, 4, 5 “MID 128 PID 107 Air
Filter Differential Pressure” page 122
MID 128–PID 108 Atmospheric Pressure 3, 4 “MID 128 PID 108 At-
mospheric Pressure”
page 125
MID 128–PID 110 Engine Coolant Temperature 0, 3 ,4 “MID 128 PID 110
Engine Coolant Temperature” page 126
MID 128–PID 111 Coolant level 1 “MID 128 PID 111
Coolant Level” page 129
MID 128–PID 158 Battery Voltage 3 “MID 128 PID 158 Bat-
tery Voltage” page 131
MID 128–PID 172 Air Inlet Temperature 3, 4 “MID 128 PID 172 Air
Inlet Temperature” page
133
MID 128–PID 174 Fuel Temperature (D7C and
D12C only)
3, 4 “MID 128 PID 174 Fuel
Temperature” page 136
91

Group 28 Troubleshooting
Error code
Component/Function FMI Section
MID 128–PID 175 Engine Oil Temperature 0, 3, 4 “MID 128 PID 175 En-
gine Oil Temperature”
page 140
MID 128–PID 228 Road Speed Sensor Calibra-
tion
11 “MID 128 PID 228
Road Speed Sensor
Calibration” page 144
MID 128–PPID 86 Engine Brake Torque Percent 9 “MID 128 PPID 86 En-
gine Brake Torque
Percent” page 146
MID 128–PPID 119 High Coolant Temperature 0 “MID 128 PPID 119
High Coolant Temperature” page 148
MID 128–PPID 122 VCB Engine Compression
Brake (D12B adn D12C only)
3, 4, 5 “MID 128 PPID 122
VCB Engine Compression Brake” page 151
MID 128–PPID 123 EPG 2 (D12B adn D12C only) 3, 4, 5 “MID 128 PPID 123
EPG 2” page 153
MID 128–PPID 124 EPG 1 3, 4, 5 “MID 128 PPID 124
EPG 1” page 155
MID 128–SID 1-6 Injector (D12B and D12C only) 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 11 “MID 128 SID
1/2/3/4/5/6 Injector ”
page 157
MID 128–SID 17 Fuel Shutoff Valve (D7C only) 3, 4, 5 “MID 128 SID 17 Fuel
Shutoff Valve” page 161
MID 128–SID 20 Timing Sleeve (D7C only) 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 11 “MID 128 SID 20 Tim-
ing Sleeve” page 163
MID 128–SID 21 Engine Position Timing Sen-
sor (D12B and D12C)
3, 8 “MID 128 SID 21 En-
gine Position Timing
Sensor” page 166
MID 128–SID 21 Needle Lift Sensor (D7C only) 2 “MID 128 SID 21 Nee-
dle Lift Sensor” page
168
MID 128–SID 22 Engine Speed Sensor 2, 3, 8 “MID 128 SID 22 En-
gine Speed Sensor”
page 170
MID 128–SID 23 Rack Actuator (D7C only) 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 11 “MID 128 SID 23 Rack
Actuator” page 172
MID 128–SID 24 Rack Position Sensor (D7C
only)
2, 13 “MID 128 SID 24 Rack
Position Sensor” page
175
MID 128–SID 33 Fan Control 3, 4, 5 “MID 128 SID 33 Fan
Control” page 177
MID 128–SID 64 Redundant Engine Speed
Sensor (D7C only)
3, 8 “MID 128 SID 64 Re-
dundant Engine Speed
Sensor” page 179
MID 128–SID 70 Preheater Element 1 3, 4, 5 “MID 128 SID 70 Pre-
heater Element 1” page
181
92

Group 28 Troubleshooting
Error code
MID 128–SID 71 Preheater Element 2 (D12B
Component/Function FMI Section
3, 4, 5 “MID 128 SID 71 Pre-
only)
heater Element 2” page
183
MID 128–SID 230 Idle Validation Switch 1 3, 4 “MID 128 SID 230 Idle
Validation Switch 1”
page 185
MID 128–SID 231 SAE J1939 Control Link 2, 9, 11, 12 “MID 128 SID 231 SAE
J1939 Control Link”
page 187
MID 128–SID 232 5 Volt DC Supply 3, 4 “MID 128 SID 232 5 Volt
DC Supply” page 189
MID 128–SID 240 Program Memory 2, 12 “MID 128 SID 240 Pro-
gram Memory” page 191
MID 128–SID 250 SAE J1587/1708 Information
Link
12 “MID 128 SID 250 SAE
J1587/1708 Information
Link” page 192
MID 128–SID 253 Data Set Memory EEPROM 2, 12 “MID 128 SID 253 Data
Set Memory EEPROM”
page 193
MID 128–SID 254 Engine Electronic Control Unit
(EECU)
2, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13 “MID 128 SID 254 En-
gine Electronic Control
Unit (EECU)” page 194
93

Group 28 Troubleshooting
94

Group 28 Troubleshooting
MID 128 PID 45 Preheater Status
The preheat relay is provided battery voltage at all times through the supply wire. If the
EECU requests preheat operation (based on engine temperature), the control wire will
be grounded through the EECU. Preheating is standard on the D7C engine with one
preheat relay/element. Preheating is optional on the D12B engine with two preheat relays/elements.
Fault Codes
FMI 3
Short circuit to battery voltage.
Conditions for fault code:
Output activated.
•
Short circuit to battery voltage on EB31.
•
Possible cause:
Short circuit to battery voltage on wire between pre-
•
heating relay and EECU.
Short circuit in the preheating relay.
•
Reaction from the EECU:
Fault code is set.
•
Yellow lamp is requested.
•
The EECU switches off the output.
•
Noticeable external symptom:
Yellow lamp lights up.
•
The preheating relay is not activated.
•
White smoke for cold start.
•
Difficult to start in extreme cold.
•
FMI 4
Short circuit to ground.
Conditions for fault code:
Output switched off.
•
Short circuit to ground on EB31.
•
Possible cause:
Short circuit to ground on wire between preheating
•
relay and EECU.
Reaction from the EECU:
Fault code is set.
•
Yellow lamp is requested.
•
Noticeable external symptom:
Yellow lamp lights up.
•
The intake air is warm since the preheating relay is
•
on all the time.
High current consumption.
•
FMI 5:
Break
Conditions for fault code:
Output switched off.
•
Open circuit.
•
Possible cause:
Blown fuse to the supply for preheating relay.
•
Open circuit in wire between EECU and preheating
•
relay.
Open circuit in the preheating relay.
•
Open circuit in supply wire to preheating relay.
•
Reaction from the EECU:
Fault code is set.
•
Yellow lamp is requested.
•
The EECU switches off the output.
•
Noticeable external symptom:
Yellow lamp lights up.
•
The preheating relay is not activated.
•
White smoke for cold start.
•
Difficult to start in extreme cold.
•
95

Group 28 Troubleshooting
MID 128 PID 45 Preheater Status, Check
Special tools: J-43233, J-39200, J-41132
NOTE!
Check all the particular connectors for loose connections, switch resistance, and oxidation.
For detailed circuit information, refer to “VNL, VNM Electrical Schematics,” Group 37.
Measurement at the component’s
connector, to the EECU
1
Note: Check the component to verify
that each of the following values is
correct. Incorrect values can cause
this component to fail.
2
Disconnect the control wire (D7C:
small blue/red wire; D12B: small solid
black wire) at the preheat relay.
Control wire:
3
Ignition key must be in the OFF position.
Measuring
points
Control wire / alternate ground
Optimal value
180 k
J-39200
Check of component
Preheating relay
1
Disconnect the control and supply
wires to the preheat relay.
Ignition key must be in the OFF position.
Note: Each relay must be checked independently.
Measuring
points
Control and supply terminals on
the preheat relay
Optimal value
8.5
Check of Subsystem
Control of the preheating relay
1
Ignition key must be in the ON position.
Connect breakout box J-41132 in series between connector EB and the
EECU. Connect jumper harness J43233 in series between connector EA
and the EECU.
Note: Test with “Preheat ON” can only
be performed if the EECU requested
preheat.
Measuring
points
Optimal value
J-39200
J-41132
J-43233
J-39200
Supply wire:
4
Measure the voltage at the supply wire
(D7C: small solid black wire; D12B:
small blue/red wire) using voltmeter J-
39200.
Ignition key must be in the ON position.
Measuring
points
Supply wire / alternate ground
96
Optimal value
B+
J-39200
EB31 / EB9 B+ (preheat off)
EB31 / EB9 0 V (preheat on)
Ground term
EB31 with a
jumper wire
preheat relay
clicks on

Group 28 Troubleshooting
MID 128 PID 49 ABS Control Status
Applies only to vehicles with ABS.
Fault Codes
FMI 9
Status message from the ABS control unit is not available (SAE J1587 message).
Conditions for fault code:
PID 49 — the message is unavailable or is not be-
•
ing updated regularly.
Possible cause:
Error in the information link (SAE J1587).
•
Error from the ABS control unit.
•
Reaction from the EECU:
Fault code is set.
•
Yellow lamp is requested.
•
Noticeable external symptom:
Yellow lamp lights up.
•
97

Group 28 Troubleshooting
MID 128 PID 49 ABS Control
Status, Check
Special tools: J-43233, J-39200, J-41132
NOTE!
Check all the particular connectors for loose connections
as well as for switch resistance and oxidation.
For detailed circuit information, refer to “VNL, VNM Electrical Schematics,” Group 37.
Also check if the ABS system has any active fault codes.
This fault code could be due to the fact that there is a
fault in the ABS system.
Check of Subsystem
Check of the SAE J1587 Information link
1
Ignition key must be in the OFF position.
Connect breakout box J-41132 in series between connector EB and the
EECU.
2
Connect jumper harness J-43233 in
series between connector EA and the
EECU.
Measuring
points
EB25 / DCA
(connection A in
diagnostics connector)
EB26 / DCB
(connection B in
diagnostics connector)
Optimal value
<1
<1
J-41132
J-43233
J-39200
98
 Loading...
Loading...