Page 1

TL-SL2210/TL-SL2218/TL-SL2428/TL-SL2452
Smart Switch
REV1.1.0
1910010971
Page 2

COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS
Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a registered trademark of
TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Other brands and product names are trademarks or
registered trademarks of their respective holders.
No part of the specifications may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any
derivative such as translation, transformation, or adaptation without permission from TP-LINK
TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Copyright © 2014 TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights
reserved.
http://www.tp-link.com
I
Page 3

CONTENTS
Preface .............................................................................................................. 1
Chapter 1 Using the CLI ....................................................................................... 3
1.1 Accessing the CLI..............................................................................................................3
1.2 CLI Command Modes........................................................................................................4
1.3 Security Levels ..................................................................................................................7
1.4 Conventions ......................................................................................................................7
1.4.1 Format Conventions ................................................................................................7
1.4.2 Special Characters ..................................................................................................8
1.4.3 Parameter Format ...................................................................................................8
Chapter 2 User Interface ...................................................................................... 9
enable......................................................................................................................................9
enable p
disable ...................................................................................................................................
configure................................................................................................................................10
exit......................................................................................................................................... 1
end ........................................................................................................................................ 1
assword .....................................................................................................................9
10
1
1
Chapter 3 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Commands ........................................................ 12
vlan........................................................................................................................................12
interface vlan .........................................................................................................................
name .....................................................................................................................................
switchport gener
switchport pvid.......................................................................................................................14
show vlan summary............................................................................................................... 14
show vlan brief ......................................................................................................................15
show vlan ..............................................................................................................................15
show interface switchport ......................................................................................................16
al allowed vlan.............................................................................................13
12
13
Chapter 4 Voice VLAN Commands.................................................................... 17
voice vlan ..............................................................................................................................17
voice vlan aging time............................................................................................................. 17
voice vlan priority................................................................................................................... 18
voice vlan mac-address.........................................................................................................18
switchport voice vlan mode ...................................................................................................19
switchport voice vlan security ................................................................................................20
II
Page 4

show voice vlan .....................................................................................................................20
show voice vlan oui ...............................................................................................................21
show voice vlan switchport .................................................................................................... 21
Chapter 5 Etherchannel Commands ................................................................. 23
channel-group .......................................................................................................................23
port-channel load-balance .....................................................................................................24
lacp system-priority ...............................................................................................................24
lacp port-priority.....................................................................................................................25
show etherchannel ................................................................................................................25
show etherchannel load-balance...........................................................................................26
show lacp ..............................................................................................................................26
show lacp sys-id ....................................................................................................................27
Chapter 6 User Management Commands ......................................................... 28
user name .............................................................................................................................28
user access-control ip-based.................................................................................................29
user access-control mac-based.............................................................................................29
user access-control port-based ............................................................................................. 30
user max-number ..................................................................................................................31
user idle-timeout....................................................................................................................31
show user account-list...........................................................................................................32
show user configuration.........................................................................................................32
Chapter 7 System Log Commands.................................................................... 34
logging buffer.........................................................................................................................34
logging file flash.....................................................................................................................34
logging file flash (for TL-SL2452) ..........................................................................................35
logging file flash frequency ....................................................................................................36
logging file flash level ............................................................................................................36
clear logging ..........................................................................................................................37
logging host index .................................................................................................................38
show logging local-config ......................................................................................................38
show logging loghost............................................................................................................. 39
show logging buffer ...............................................................................................................39
show logging flash.................................................................................................................40
Chapter 8 SSH Commands................................................................................. 41
ip ssh server ..........................................................................................................................41
III
Page 5

ip ssh version ........................................................................................................................41
ip ssh timeout ........................................................................................................................ 42
ip ssh max-client....................................................................................................................42
ip ssh download.....................................................................................................................43
show ip ssh............................................................................................................................43
Chapter 9 SSL Commands ................................................................................. 45
ip http secure-server..............................................................................................................45
ip http secure-server download certificate .............................................................................45
ip http secure-server download key.......................................................................................46
show ip http secure-server ....................................................................................................47
Chapter 10 MAC Address Commands................................................................. 48
mac address-table static........................................................................................................48
mac address-table aging-time ............................................................................................... 49
mac address-table filtering ....................................................................................................49
mac address-table max-mac-count .......................................................................................50
show mac address-table address..........................................................................................51
show mac address-table aging-time......................................................................................51
show mac address-table max-mac-count interface ............................................................... 52
show mac address-table interface.........................................................................................52
show mac address-table mac-num........................................................................................ 53
show mac address-table mac................................................................................................53
show mac address-table vlan ................................................................................................54
Chapter 11 System Commands ........................................................................... 55
system-time manual ..............................................................................................................55
system-time ntp .....................................................................................................................55
system-time dst predefined ...................................................................................................57
system-time dst date .............................................................................................................58
system-time dst recurring ...................................................................................................... 59
hostname...............................................................................................................................60
location ..................................................................................................................................
cont
act-info............................................................................................................................61
ip management-vlan .............................................................................................................. 61
ip address..............................................................................................................................62
ip address-alloc dhcp ............................................................................................................62
ip address-alloc bootp ...........................................................................................................63
reset ......................................................................................................................................
IV
60
63
Page 6

reboot ....................................................................................................................................64
copy running-config startup-config ........................................................................................64
copy startup-config tftp ..........................................................................................................65
copy tftp startup-config ..........................................................................................................65
firmware upgrade ..................................................................................................................66
ping .......................................................................................................................................
tracert ....................................................................................................................................67
loopback interface .................................................................................................................
show system-info...................................................................................................................68
show running-config ..............................................................................................................69
show system-time..................................................................................................................69
show system-time dst............................................................................................................69
show system-time ntp............................................................................................................ 70
show cable-diagnostics interface...........................................................................................70
66
68
Chapter 12 Ethernet Configuration Commands ................................................. 72
interface fastEthernet ............................................................................................................72
interface range fastEthernet .................................................................................................. 72
interface gigabitEthernet........................................................................................................73
interface range gigabitEthernet .............................................................................................73
description ............................................................................................................................. 74
shutdown ...............................................................................................................................74
flow-control ............................................................................................................................75
media-type.............................................................................................................................76
duplex....................................................................................................................................
speed.....................................................................................................................................77
storm-control broadcast.........................................................................................................
storm-control multicast ..........................................................................................................78
storm-control unicast .............................................................................................................79
bandwidth ..............................................................................................................................79
clear counters........................................................................................................................80
show interface status............................................................................................................. 80
show interface counters.........................................................................................................81
show interface description ..................................................................................................... 81
show interface flowcontrol .....................................................................................................82
show interface configuration..................................................................................................82
show storm-control ................................................................................................................83
76
77
show bandwidth..................................................................................................................... 83
V
Page 7

Chapter 13 QoS Commands................................................................................. 85
qos ........................................................................................................................................85
qos cos..................................................................................................................................85
qos dscp................................................................................................................................86
qos queue cos-map...............................................................................................................
qos queue dscp-map.............................................................................................................87
qos queue mode.................................................................................................................... 88
show qos interface ................................................................................................................89
show qos cos-map ................................................................................................................90
show qos dscp-map ..............................................................................................................90
show qos queue mode ..........................................................................................................91
show qos status.....................................................................................................................91
87
Chapter 14 Port Mirror Commands ..................................................................... 92
monitor session destination interface ....................................................................................92
monitor session source interface...........................................................................................93
show monitor session............................................................................................................94
Chapter 15 Port Isolation Commands ................................................................. 95
port isolation ..........................................................................................................................95
show port isolation interface .................................................................................................. 95
Chapter 16 Loopback Detection Commands...................................................... 97
loopback-detection(global) ....................................................................................................97
loopback-detection interval....................................................................................................97
loopback-detection recovery-time.......................................................................................... 98
loopback-detection(interface) ................................................................................................98
loopback-detection config......................................................................................................99
loopback-detection recover ...................................................................................................99
show loopback-detection global ..........................................................................................100
show loopback-detection interface ......................................................................................100
Chapter 17 ACL Commands................................................................................102
access-list create.................................................................................................................102
mac access-list....................................................................................................................102
access-list standard............................................................................................................. 103
access-list extended............................................................................................................ 104
rule ......................................................................................................................................
access-li
st policy name........................................................................................................105
VI
105
Page 8

access-list policy action.......................................................................................................106
access-list bind(interface)....................................................................................................107
access-list bind(vlan) ........................................................................................................... 107
show access-list .................................................................................................................. 108
show access-list policy ........................................................................................................108
show access-list bind ..........................................................................................................109
Chapter 18 DHCP Filtering Commands..............................................................110
ip dhcp filtering .................................................................................................................... 110
ip dhcp filtering trust ............................................................................................................110
show ip dhcp filtering........................................................................................................... 111
show ip dhcp filtering interface ............................................................................................ 111
Chapter 19 MSTP Commands.............................................................................112
spanning-tree(global)........................................................................................................... 112
spanning-tree(interface) ......................................................................................................112
spanning-tree common-config ............................................................................................. 113
spanning-tree mode............................................................................................................. 114
spanning-tree mst configuration .......................................................................................... 115
instance ............................................................................................................................... 11
name ................................................................................................................................... 1
revision ................................................................................................................................11
spanning-tree mst instance ................................................................................................. 117
spanning-tree mst................................................................................................................ 117
spanning-tree priority........................................................................................................... 118
spanning-tree tc-defend....................................................................................................... 119
spanning-tree timer.............................................................................................................. 119
spanning-tree hold-count.....................................................................................................120
spanning-tree max-hops......................................................................................................121
spanning-tree bpdufilter.......................................................................................................121
spanning-tree bpduguard ....................................................................................................122
5
16
6
spanning-tree guard loop.....................................................................................................122
spanning-tree guard root ..................................................................................................... 123
spanning-tree guard tc.........................................................................................................123
spanning-tree mcheck .........................................................................................................124
show spanning-tree active...................................................................................................125
show spanning-tree bridge .................................................................................................. 125
show spanning-tree interface ..............................................................................................125
VII
Page 9

show spanning-tree interface-security................................................................................. 126
show spanning-tree mst ......................................................................................................127
Chapter 20 IGMP Commands..............................................................................128
ip igmp snooping(global) .....................................................................................................128
ip igmp snooping(interface) ................................................................................................. 128
ip igmp snooping immediate-leave ......................................................................................129
ip igmp snooping drop-unknown.......................................................................................... 129
ip igmp snooping vlan-config ...............................................................................................130
ip igmp snooping multi-vlan-config ......................................................................................131
ip igmp snooping filter add-id...............................................................................................132
ip igmp snooping filter(global)..............................................................................................133
ip igmp snooping filter(interface) .........................................................................................133
ip igmp snooping filter maxgroup......................................................................................... 134
ip igmp snooping filter mode................................................................................................134
show ip igmp snooping........................................................................................................ 135
show ip igmp snooping interface ......................................................................................... 135
show ip igmp snooping vlan ................................................................................................136
show ip igmp snooping multi-vlan........................................................................................ 137
show ip igmp snooping groups ............................................................................................137
show ip igmp snooping filter ................................................................................................ 138
Chapter 21 SNMP Commands.............................................................................139
snmp-server ........................................................................................................................139
snmp-server view ................................................................................................................139
snmp-server group ..............................................................................................................140
snmp-server user ................................................................................................................141
snmp-server community ......................................................................................................143
snmp-server host................................................................................................................. 143
snmp-server engineID .........................................................................................................145
snmp-server traps snmp...................................................................................................... 145
snmp-server traps link-status...............................................................................................146
snmp-server traps................................................................................................................147
snmp-server traps mac........................................................................................................ 148
snmp-server traps vlan........................................................................................................ 148
rmon history.........................................................................................................................149
rmon event ..........................................................................................................................150
rmon alarm .......................................................................................................................... 151
VIII
Page 10

show snmp-server ...............................................................................................................152
show snmp-server view .......................................................................................................153
show snmp-server group .....................................................................................................153
show snmp-server user ....................................................................................................... 154
show snmp-server community.............................................................................................154
show snmp-server host .......................................................................................................154
show snmp-server engineID................................................................................................155
show rmon history ...............................................................................................................155
show rmon event .................................................................................................................155
show rmon alarm.................................................................................................................156
IX
Page 11

Preface
This Guide is intended for network administrator to provide referenced information about CLI
(Command Line Interface). The device mentioned in this Guide stands for
TL-SL2210/TL-SL2218/TL-SL2428/TL-SL2452 Smart Switch.
The four devices of TL-SL2210, TL-SL2218, TL-SL2428 and TL-SL2452 are sharing this User
Guide. For simplicity, we will take TL-SL2428 for example throughout the configuration chapters.
TL-SL2210, TL-SL2218, TL-SL2428 and TL-SL2452 just differ in the number of LED indicators
and ports and all figures in this guide are of TL-SL2428.
Overview of this Guide
Chapter 1: Using the CLI
Provide information about how to use the CLI, CLI Command Modes, Security Levels and some
Conventions.
Chapter 2: User Interface
Provide information about the commands used to switch between five CLI Command Modes.
Chapter 3: IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring IEEE 802.1Q VLAN.
Chapter 4: Voice VLAN Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring Voice VLAN.
Chapter 5: EtherChannel Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring LAG (Link Aggregation Group) and
Aggregation Control Protocol)..
(Link
LACP
Chapter 6: User Manage Commands
Provide information about the commands used for user management.
Chapter 7: S
Provide information about the commands used for configuring system log.
Chapter 8: SSH Commands
ystem Log Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring and managing SSH (Security
Shell).
Chapter 9: SSL Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring and managing SSL (Secure
Sockets Layer).
1
Page 12

Chapter 10: MAC Address Commands
Provide information about the commands used for Address configuration.
Chapter 11: System Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the System information and System
IP, reboot and reset the switch, upgrade the switch system and other operations.
Chapter 12: Ethernet Configuration Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the Bandwidth Control, Negotiation
Mode, and Storm Control for Ethernet ports.
Chapter 13: QoS Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the QoS function.
Chapter 14: Port Mirror Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the Port Mirror function.
Chapter 15: Port Isolation Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the Port Isolation function.
Chapter 16: Loopback Detection Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the Loopback Detection function.
Chapter 17: ACL Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the ACL (Access Control List).
Chapter 18: DHCP Filtering Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the DHCP Filtering function.
Chapter 19: MSTP Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the MSTP (Multiple Spanning Tree
Protocol).
Chapter 20: IGMP Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the IGMP Snooping (Internet Group
Management Protocol Snooping).
Chapter 21: SNMP Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the SNMP (Simple Network
Management Protocol) functions.
2
Page 13
Chapter 1 Using the CLI
1.1 Accessing the CLI
You can log on to the switch and access the CLI by logging on to the switch remotely by a Telnet
through an Ethernet port. To log on to the switch by a Telnet connection, please take the following
steps:
1. Make sure the switch and the PC are in the same LAN.
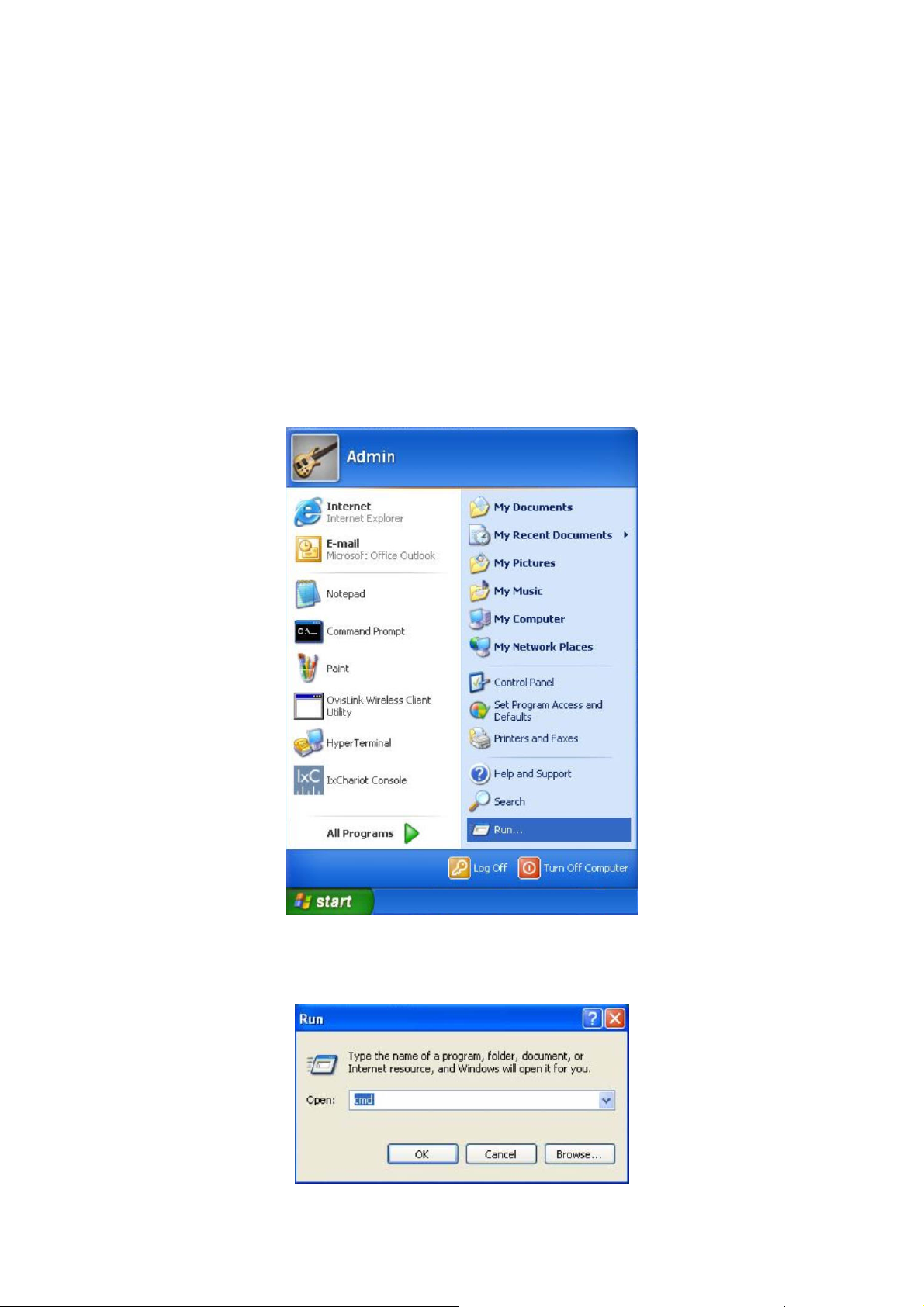
2. Click Start → Run to open the Run window.
Figure 1-1 Open the Run window
3. Type cmd in the prompt Run window as Figure 1-2 and click OK.
Figure 1-2 Run Window
3
Page 14
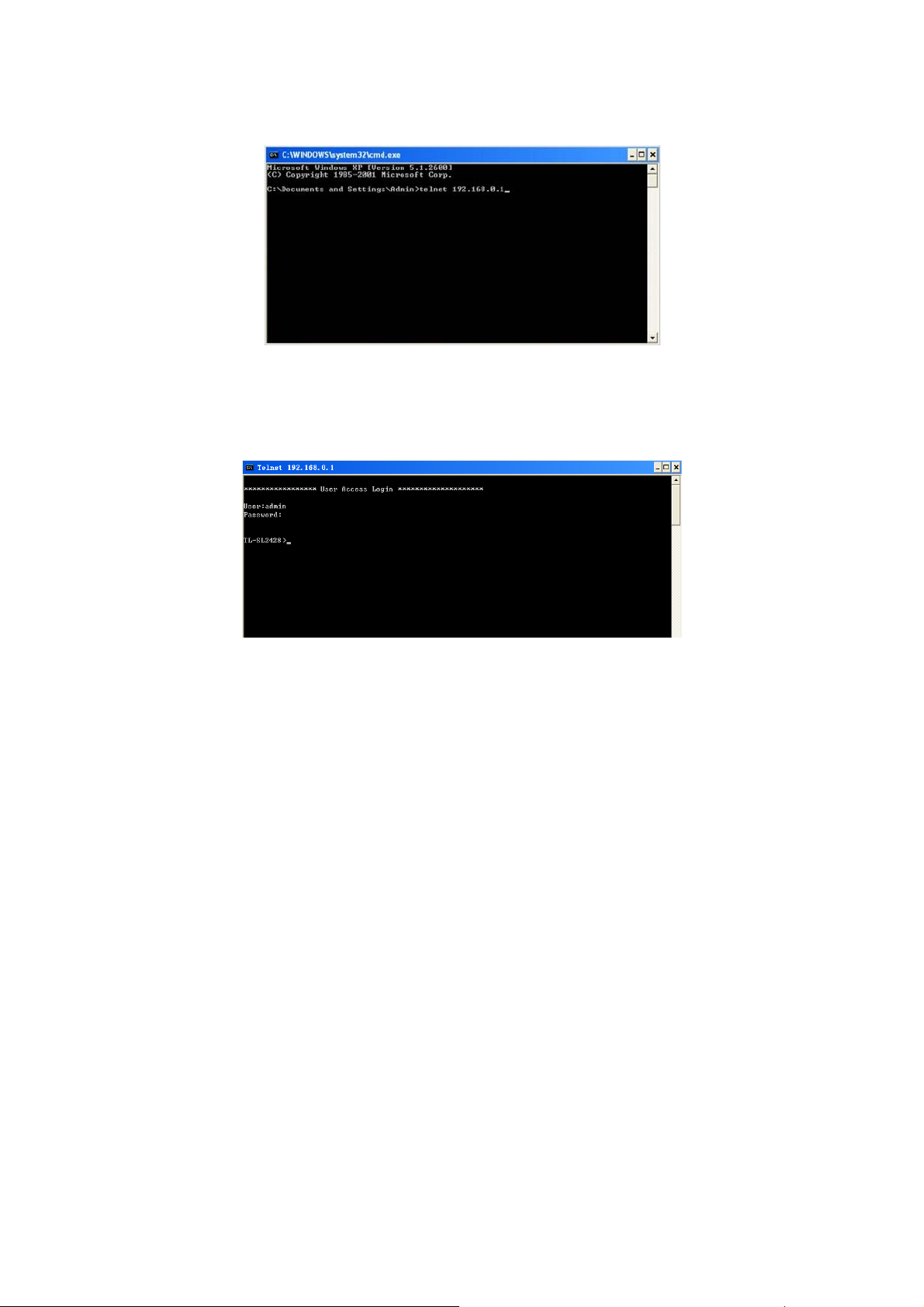
4. Type telnet 192.168.0.1 in the command prompt shown as Figure 1-3, and press the Enter
button.
Figure 1-3 Connecting to the Switch
5. Type the User name and Password (the factory default value for both of them is admin) and
press the Enter button, then you can use the CLI now, which is shown as Figure1-4.
Figure 1-4 Log in the Switch
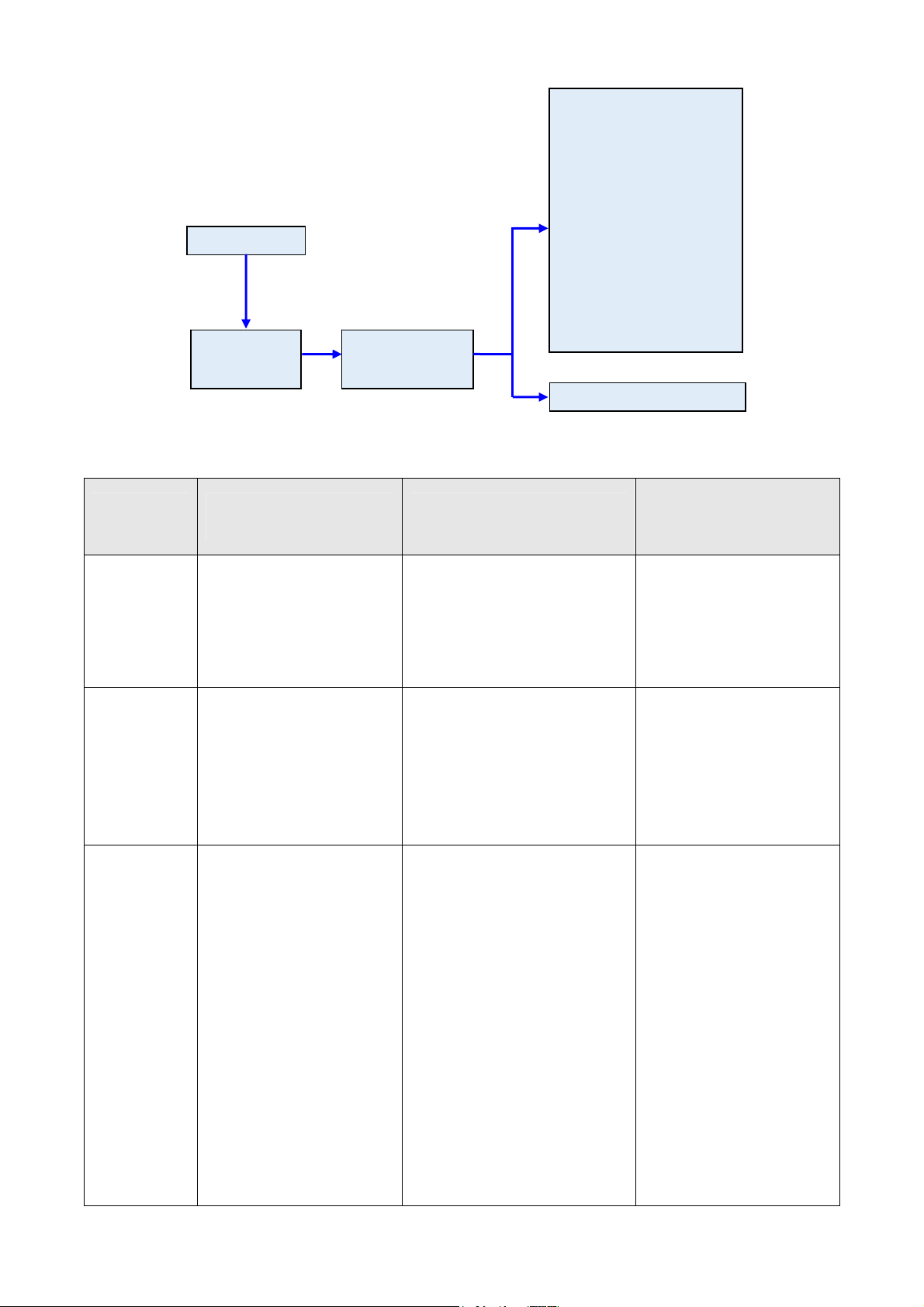
1.2 CLI Command Modes
The CLI is divided into different command modes: User EXEC Mode, Privileged EXEC Mode,
Global Configuration Mode, Interface Configuration Mode and VLAN Configuration Mode.
Interface Configuration Mode can also be divided into Interface fastEthernet, Interface
gigabitEthernet, Interface link-aggregation and some other modes, which is shown as the following
diagram.
4
Page 15
g
Interface Configuration Mode
Interface fastEthernet
Interface gigabitEthernet
Interface link-aggregation
Interface range fastEthernet
User EXEC Mode
Interface range gigabitEthernet
password
Privileged EXEC
Mode
Global Configuration
Mode
Interface range link-aggregation
Interface vlan
……
VLAN Confi
uration Mode
The following table gives detailed information about the Accessing path, Prompt of each mode and
how to exit the current mode and access the next mode.
Logout or Access the
Mode Accessing Path Prompt
next mode
User EXEC
Mode
Privileged
EXEC Mode
Primary mode once it is
connected with the switch.
Use the enable command to
enter this mode from User
EXEC mode.
TL-SL2428>
TL-SL2428#
Use the exit command to
disconnect the switch.
Use the enable command to
access Privileged EXEC
mode.
Enter the disable or the exit
command to return to User
EXEC mode.
Enter the configure
command to access Global
Configuration mode.
Global
Configuration
Mode
Use the configure command
to enter this mode from
Privileged EXEC mode.
TL-SL2428 (config)#
5
Use the exit or the end
command or press Ctrl+Z to
return to Privileged EXEC
mode.
Use the interface
fastEthernet/
gigabitEthernet port or
interface range
fastEthernet/gigabitEthernet
port-list command to access
interface Configuration mode.
Use the vlan vlan-list to
access VLAN Configuration
mode.
Page 16
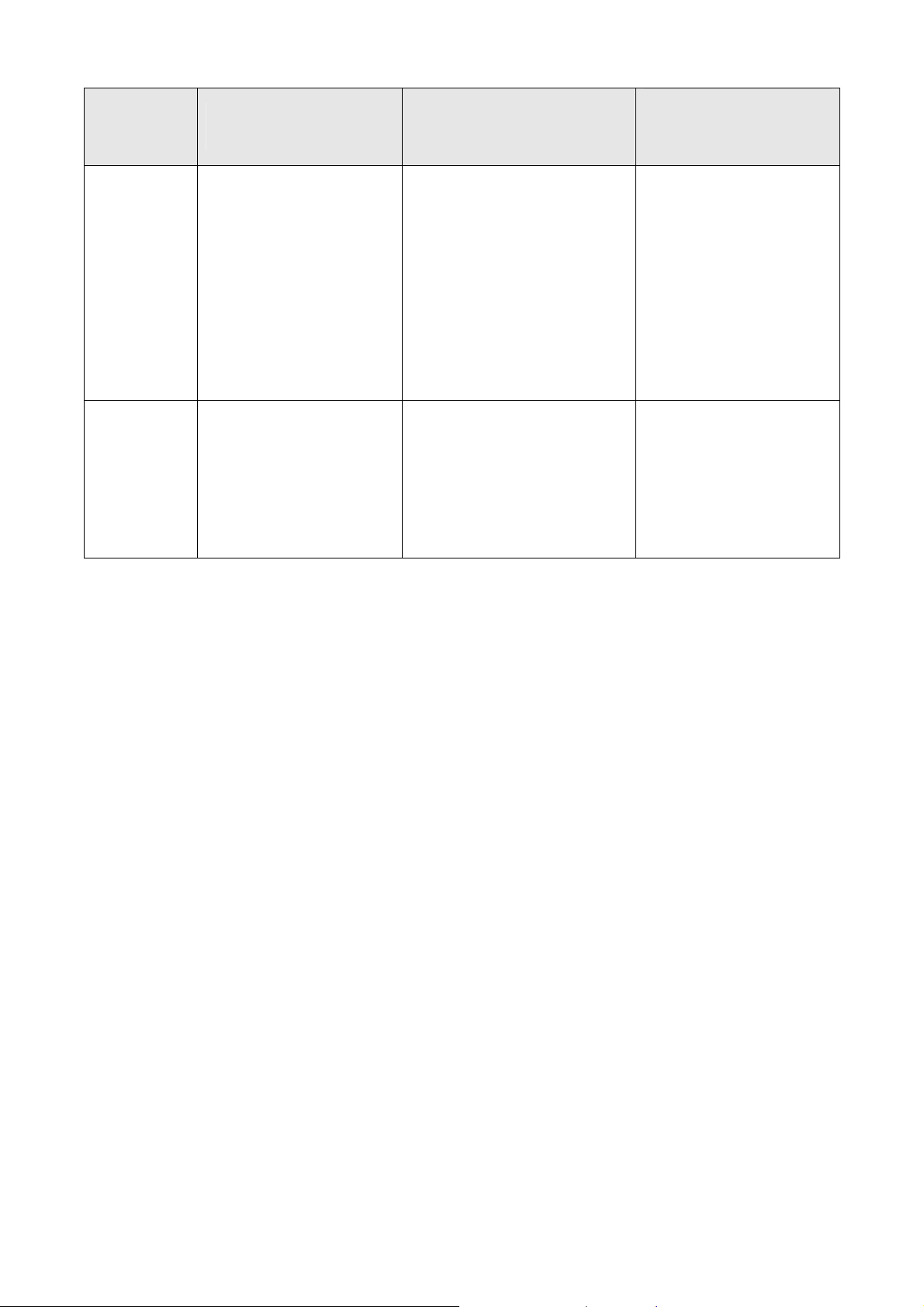
Mode Accessing Path Prompt
Use the interface
fastEthernet/gigabitEthernet
Interface
Configuration
Mode
VLAN
Configuration
port or interface range
fastEthernet/
gigabitEthernet port-list
command to enter this mode
from Global Configuration
mode.
Use the vlan vlan-list
command to enter this mode
from Global Configuration
mode.
TL-SL2428 (config-if)#
TL-SL2428(config-if-range)#
TL-SL2428 (config-vlan)#
Mode
or
Logout or Access the
next mode
Use the end command or
press Ctrl+Z to return to
Privileged EXEC mode.
Enter the exit command or the
# command to return to Global
Configuration mode.
A port number must be
specified in the interface
command.
Use the end command or
press Ctrl+Z to return to
Privileged EXEC mode.
Enter the exit command or the
# command to return to Global
configuration mode.
Note:
1. The user is automatically in User EXEC Mode after the connection between the PC and the
switch is established by a telnet connection.
2. Each command mode has its own set of specific commands. To configure some commands,
you should access the corresponding command mode firstly.
Global Configuration Mode: In this mode, global commands are provided, such as the
Spanning Tree, Schedule Mode and so on.
Interface Configuration Mode: In this mode, users can configure one or several ports,
different ports corresponds to different commands
a). Interface fastEthernet/gigabitEthernet: Configure parameters for a Fast/Gigabit
Ethernet port, such as Duplex-mode, flow control status.
b). Interface range fastEthernet/gigabitEthernet: The commands contained are the
same as that of the Interface fastEthernet/gigabitEthernet. Configure parameters for
several Ethernet ports.
c). Interface link-aggregation: Configure parameters for a link-aggregation, such as
broadcast storm.
d). Interface range link-aggregation: Configure parameters for multi-trunks.
e). Interface vlan: Configure parameters for the vlan-port.
6
Page 17

Vlan Configuration Mode: In this mode, users can create a VLAN and add a specified
port to the VLAN.
3. Some commands are global, that means they can be performed in all modes:
show: display all information of switch, for example: statistic information, port information,
VLAN information.
history: Display the commands history.
1.3 Security Levels
This switch’s security is divided into two levels: User level and Admin level.
User level only allows users to do some simple operations in User EXEC Mode; Admin level
allows you to monitor, configure and manage the switch in Privileged EXEC Mode, Global
Configuration Mode, Interface Configuration Mode and VLAN Configuration Mode.
Users get the privilege to the User level once logging in by Telnet. However, Guest users are
restricted to access the CLI.
Users can enter Privileged EXEC mode from User EXEC mode by using the enable command. In
default case, no password is needed. In Global Configuration Mode, you can configure password
for Admin level by enable password command. Once password is configured, you are required to
enter it to access Privileged EXEC mode.
1.4 Conventions
1.4.1 Format Conventions
The following conventions are used in this Guide:
Items in square brackets [ ] are optional
Items in braces { } are required
Alternative items are grouped in braces and separated by vertical bars. For example: speed
{10 | 100 | 1000 }
Bold indicates an unalterable keyword. For example: show logging
Normal Font indicates a constant (several options are enumerated and only one can be
selected). For example: mode {dynamic | static | permanent}
Italic Font indicates a variable (an actual value must be assigned). For example: bridge
aging-time aging-time
7
Page 18

1.4.2 Special Characters
You should pay attentions to the description below if the variable is a character string:
These six characters ” < > , \ & can not be input.
If a blank is contained in a character string, single or double quotation marks should be used,
for example ’hello world’, ”hello world”, and the words in the quotation marks will be identified
as a string. Otherwise, the words will be identified as several strings.
1.4.3 Parameter Format
Some parameters must be entered in special formats which are shown as follows:
MAC address must be enter in the format of xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
One or several values can be typed for a port-list or a vlan-list using comma to separate. Use
a hyphen to designate a range of values, for instance, 1,3-5,7 indicates choosing 1,3,4,5,7.
8
Page 19

Chapter 2 User Interface
enable
Description
The enable command is used to access Privileged EXEC Mode from User
EXEC Mode.
Syntax
enable
Command Mode
User EXEC Mode
Example
If you have set the password to access Privileged EXEC Mode from User EXEC
Mode:
TL-SL2428>enable
Enter password:
TL-SL2428#
enable password
Description
The enable password command is used to set the password for users to
access Privileged EXEC Mode from User EXEC Mode. To return to the default
configuration, please use no enable password command.
Syntax
enable password password [secret {simple | cipher} ]
no enable password
Parameter
password —— super password,which can contains 16 characters at most,
composing digits, English letters and underdashes only. By default, it is empty.
simple | cipher —— The way of displaying p
default, it is “simple”. This function is not supported by TL-SL2210.
assword in configuration file. By
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
9
Page 20

Example
disable
Description
Syntax
Command Mode
Set the super password as admin to access Privileged EXEC Mode from User
EXEC Mode:
TL-SL2428(config)# enable password admin
The disable command is used to return to User EXEC Mode from Privileged
EXEC Mode.
disable
Privileged EXEC Mode
Example
configure
Description
Syntax
Command Mode
Example
Return to User EXEC Mode from Privileged EXEC Mode:
TL-SL2428# disable
TL-SL2428>
The configure command is used to access Global Configuration Mode from
Privileged EXEC Mode.
configure
Privileged EXEC Mode
Access Global Configuration Mode from Privileged EXEC Mode:
TL-SL2428# configure
TL-SL2428(config)#
10
Page 21

exit
Description
The exit command is used to return to the previous Mode from the current
Mode.
Syntax
exit
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Return to Global Configuration Mode from Interface Configuration Mode, and
then return to Privileged EXEC Mode:
TL-SL2428(config-if)# exit
TL-SL2428(config)#exit
TL-SL2428#
end
Description
The end command is used to return to Privileged EXEC Mode.
Syntax
end
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Return to Privileged EXEC Mode from Interface Configuration Mode:
TL-SL2428(config-if)#end
TL-SL2428#
11
Page 22

Chapter 3 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Commands
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) technology is developed for the switch to divide the LAN into
multiple logical LANs flexibly. Hosts in the same VLAN can communicate with each other,
regardless of their physical locations. VLAN can enhance performance by conserving bandwidth,
and improve security by limiting traffic to specific domains.
vlan
Description
The vlan command is used to create IEEE 802.1Q VLAN and enter VLAN
Configuration Mode. To delete the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN, please use no vlan
command.
Syntax
vlan vlan-list
no vlan vlan-list
Parameter
vlan-list —— Specify IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID list, ranging from 2 to 4094, in the
format of 2-3, 5. It is multi-optional.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Create VLAN 2-10 and VLAN 100:
TL-SL2428(config)# vlan 2-10,100
Delete VLAN 2:
TL-SL2428(config)# no vlan 2
interface vlan
Description
The interface vlan command is used to create VLAN Interface and enter
Interface VLAN Mode. To delete VLAN Interface, please use no interface vlan
command.
Syntax
interface vlan vlan-id
no interface vlan vlan-id
12
Page 23

Parameter
Command Mode
Example
name
Description
Syntax
vlan-id —— Specify IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID, ranging from 1 to 4094.
Global Configuration Mode
Create VLAN Interface 2:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface vlan 2
The name command is used to assign a description to a VLAN. To clear the
description, please use no name command.
name descript
no name
Parameter
descript ——String to describe the VLAN, which contains 16 characters at most.
Command Mode
VLAN Configuration Mode(VLAN)
Example
Specify the name of VLAN 2 as “group1”:
TL-SL2428(config)# vlan 2
TL-SL2428(config-vlan)# name group1
switchport general allowed vlan
Description
Syntax
The switchport general allowed vlan command is used to add the desired
General port to IEEE 802.1Q VLAN and specify the port’s type. To delete the
corresponding VLAN(s), please use no switchport general allowed vlan
command.
switchport general allowed vlan vlan-list { tagged | untagged }
no switchport general allowed vlan vlan-list
13
Page 24
Parameter
vlan-list —— Specify IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID list, ranging from 2 to 4094, in the
format of 2-3, 5. It is multi-optional.
tagged | untagged —— Egress rule,untagged or tagged. Tagged: All packets
forwarded by the port are tagged. The packets contain VLAN information.
Untagged: Packets forwarded by the port are untagged.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Add port 4 it to VLAN 2 and configure the type of port 4 as tagged:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/4
TL-SL2428(config-if)# switchport general allowed vlan 2 tagged
switchport pvid
Description
The switchport pvid command is used to configure the PVID for the switch
ports.
Syntax
switchport pvid vlan-id
Parameter
vlan-id —— VLAN ID, ranging from 1 to 4094.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Specify the PVID of port 2 as 2:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/2
TL-SL2428(config-if)# switchport pvid 2
show vlan summary
Description
The show vlan summary command is used to display the summarized
information of IEEE 802.1Q VLAN.
14
Page 25

Syntax
show vlan summary
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the summarized information of IEEE 802.1Q VLAN:
TL-SL2428(config)# show vlan summary
show vlan brief
Description
The show vlan brief command is used to display the brief information of IEEE
802.1Q VLAN.
Syntax
Command Mode
Example
show vlan
Description
Syntax
show vlan brief
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Display the brief information of IEEE 802.1Q VLAN:
TL-SL2428(config)# show vlan brief
The show vlan command is used to display the information of IEEE 802.1Q
VLAN .
show vlan [vlan-list]
Parameter
vlan-list —— VLAN ID, ranging from 1 to 4094. By default , display all the
information of IEEE 802.1Q VLAN.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
15
Page 26

Example
Display the information of vlan 5:
TL-SL2428(config)# show vlan 5
show interface switchport
Description
The show interface switchport command is used to display the IEEE 802.1Q
VLAN configuration information of the specified port or all ports.
Syntax
show interface switchport [port]
Parameter
port —— The port number. By default, display the VLAN configuration
information of all ports.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the VLAN configuration information of all ports:
TL-SL2428(config)# show interface switchport
16
Page 27

Chapter 4 Voice VLAN Commands
Voice VLANs are configured specially for voice data stream. By configuring Voice VLANs and
adding the ports with voice devices attached to voice VLANs, you can perform QoS-related
configuration for voice data, ensuring the transmission priority of voice data stream and voice
quality.
voice vlan
Description
The voice vlan command is used to enable Voice VLAN function. To disable
Voice VLAN function, please use no voice vlan command.
Syntax
voice vlan vlan-id
no voice vlan
Parameter
vlan-id —— Specify IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID, ranging from 2 to 4094.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Enable the Voice VLAN function for VLAN 10:
TL-SL2428(config)#voice vlan 10
voice vlan aging time
Description
Syntax
The voice vlan aging time command is used to set the aging time for a voice
VLAN. To restore to the default aging time for the Voice VLAN, please use no
voice vlan aging time command.
voice vlan aging time time
no voice vlan aging time
17
Page 28

Parameter
time —— Aging time (in minutes) to be set for the Voice VLAN. It ranges from 1
to 43200 and the default value is 1440.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Set the aging time for the Voice VLAN as 1 minute:
TL-SL2428(config)#voice vlan aging time 1
voice vlan priority
Description
The voice vlan priority command is used to configure the priority for the Voice
VLAN. To restore to the default priority, please use no voice vlan priority
command.
Syntax
voice vlan priority pri
no voice vlan priority
Parameter
pri —— Priority, ranging from 0 to 7, and the default value is 6.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure the priority of the Voice VLAN as 5:
TL-SL2428(config)#voice vlan priority 5
voice vlan mac-address
18
Page 29

Description
The voice vlan mac-address command is used to create Voice VLAN OUI. To
delete the specified Voice VLAN OUI, please use no voice vlan mac-address
command.
Syntax
voice vlan mac-address mac-addr mask mask [description descript]
no voice vlan mac-address mac-addr
Parameter
mac-addr —— The OUI address of the voice device, in the format of
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX.
mask —— The OUI address mask of the voice device, in the format of
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX.
descript —— Give a description to the OUI for identification which contains 16
characters at most.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Create a Voice VLAN OUI described as “TP-Phone” with the OUI address
00:11:11:11:11:11 and the mask address FF:FF:FF:00:00:00:
TL-SL2428(config)#voice vlan mac-address 00:11:11:11:11:11 mask
FF:FF:FF:00:00:00 description TP- Phone
switchport voice vlan mode
Description
The switchport voice vlan mode command is used to configure the Voice
VLAN mode for the Ethernet port.
Syntax
switchport voice vlan mode { manual | auto }
Parameter
manual | auto —— Port mode.
19
Page 30

Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Configure the Fast Ethernet port 3 to operate in the auto voice VLAN mode:
TL-SL2428(config)#interface fastEthernet 1/0/3
TL-SL2428(config-if)#switchport voice vlan mode auto
switchport voice vlan security
Description
The switchport voice vlan security command is used to enable the Voice
VLAN security feature. To disable the Voice VLAN security feature, please use
no switchport voice vlan security command.
Syntax
switchport voice vlan security
no switchport voice vlan security
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Enable the Fast Ethernet port 3 for Voice VLAN security feature:
TL-SL2428(config)#interface fastEthernet 1/0/3
TL-SL2428(config-if)#switchport voice vlan security
show voice vlan
Description
The show voice vlan command is used to display the global configuration
information of Voice VLAN.
Syntax
show voice vlan
20
Page 31

Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the configuration information of Voice VLAN globally:
TL-SL2428(config)#show voice vlan
show voice vlan oui
Description
The show voice vlan oui command is used to display the configuration
information of Voice VLAN OUI.
Syntax
show voice vlan oui
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the configuration information of Voice VLAN OUI:
TL-SL2428(config)#show voice vlan oui
show voice vlan switchport
Description
The show voice vlan switchport command is used to display the configuration
information of all the ports or one specified port in the Voice VLAN.
Syntax
show voice vlan switchport [fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet port]
Parameter
port ——The Fast/Gigabit Ethernet port number selected to display the
configuration information.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
21
Page 32

Example
Display the configuration information of Fast Ethernet port 1 in the Voice VLAN:
TL-SL2428(config)#show voice vlan switchport fastEthernet 1/0/1
Display the configuration information of all the ports in the Voice VLAN:
TL-SL2428(config)#show voice vlan switchport
22
Page 33

Chapter 5 Etherchannel Commands
Etherchannel Commands are used to configure LAG and LACP function.
LAG (Link Aggregation Group) is to combine a number of ports together to make a single
high-bandwidth data path, which can highly extend the bandwidth. The bandwidth of the LAG is
the sum of bandwidth of its member port.
LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) is defined in IEEE802.3ad and enables the dynamic link
aggregation and disaggregation by exchanging LACP packets with its partner. The switch can
dynamically group similarly configured ports into a single logical link, which will highly extend the
bandwidth and flexibly balance the load.
channel-group
Description
The channel-group command is used to add a port to the EtherChannel Group
and configure its mode. To delete the port from the EtherChannel Group, please
use no channel-group command.
Syntax
channel-group num mode { on | active | passive }
no channel-group
Parameter
num —— The number of the EtherChannel Group, ranging from 1 to 6.
on —— Enable the static LAG.
active —— Enable the active LACP mode.
passive —— Enable the passive LACP mode.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Add ports 2-4 to EtherChannel Group 1 and enable the static LAG:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface range fastEthernet 1/0/2-4
TL-SL2428(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode on
23
Page 34

port-channel load-balance
Description
The port-channel load-balance command is used to configure the Aggregate
Arithmetic for LAG. To return to the default configurations, please use no
port-channel load-balance command.
Syntax
port-channel load-balance { src-dst-mac | src-dst-ip }
no port-channel load-balance
Parameter
src-dst-mac —— The source and destination MAC address. When this option
is selected, the Aggregate Arithmetic will be based on the source and
destination MAC addresses of the packets. The Aggregate Arithmetic for LAG is
“src-dst-mac” by default.
src-dst-ip—— The sour
selected, the Aggregate Arithmetic will be based on the source and destination
IP addresses of the packets.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure the Aggregate Arithmetic for LAG as “src-dst-mac”:
TL-SL2428(config)# port-channel load-balance src-dst-mac
lacp system-priority
Description
The lacp system-priority command is used to configure the LACP system
priority globally. To return to the default configurations, please use no lacp
system-priority command.
ce and destination IP
address. When this option is
Syntax
lacp system-priority pri
no lacp system-priority
Parameter
pri —— The system priority, ranging from 0 to 65535. It is 32768 by default.
24
Page 35

Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure the LACP system priority as 1024 globally:
TL-SL2428(config)# lacp system-priority 1024
lacp port-priority
Description
The lacp port-priority command is used to configure the LACP port priority for
specified ports. To return to the default configurations, please use no lacp
port-priority command.
Syntax
lacp port-priority pri
no lacp port-priority
Parameter
pri —— The port priority, ranging from 0 to 65535. It is 32768 by default.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Configure the LACP port priority as 1024 for ports 1-3:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface range fastEthernet 1/0/1-3
TL-SL2428(config-if-range)# lacp port-priority 1024
Configure the LACP port priority as 2048 for port 4:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/4
TL-SL2428(config-if)# lacp port-priority 2048
show etherchannel
Description
The show etherchannel command is used to display the EtherChannel
information.
25
Page 36

Syntax
show etherchannel [ channel-group-num ] { detail | summary }
Parameter
channel-group-num —— The EtherChannel Group number, ranging from 1 to 6.
By default, it is empty, and will display the information of all EtherChannel
Groups.
detail —— The detailed information of EtherChannel.
summary —— The EtherChannel information in summary.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the detailed information of EtherChannel Group 1:
TL-SL2428(config)# show etherchannel 1 detail
show etherchannel load-balance
Description
The show etherchannel load-balance command is used to display the
Aggregate Arithmetic of LAG.
Syntax
show etherchannel load-balance
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the Aggregate Arithmetic of LAG:
TL-SL2428(config)# show etherchannel load-balance
show lacp
Description
The show lacp command is used to display the LACP information for a
specified EtherChannel Group.
Syntax
show lacp [ channel-group-num ] { internal | neighbor }
26
Page 37

Parameter
channel-group-num —— The EtherChannel Group number, ranging from 1 to 6.
By default, it is empty, and will display the information of all LACP groups.
internal —— The internal LACP information.
neighbor —— The neighbor LACP information.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the internal LACP information of EtherChannel Group 1:
TL-SL2428(config)# show lacp 1 internal
show lacp sys-id
Description
The show lacp sys-id command is used to display the LACP system priority
globally.
Syntax
show lacp sys-id
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the LACP system priority:
TL-SL2428(config)# show lacp sys-id
27
Page 38

Chapter 6 User Management Commands
User Management Commands are used to configure the user name and password for users to log
on to the Web management page with a certain access level so as to protect the settings of the
switch from being randomly changed.
user name
Description
The user name command is used to add a new user or modify the existed
user’s information. To delete the existed users, please use no user name
command.
Syntax
user name user-name password password [ type { guest | admin }] [ status
{ disable | enable}] [secret {simple | cipher}]
no user name user-name
Parameter
user-name ——Type a name for users' login, which contains 16 characters at
most, composing digits, English letters and underlines only.
ssword ——Type a password for users' login, which contains 16 characters at
pa
most, composing digits, English letters and underlines only.
guest | admin ——
settings without the right to
modify and view all the settings of diff
disable | enable ——Enable/disable the user. The new added user is enabled by
default.
simple | cipher —— The way of displaying password in configuration file. By
default, it is “simple”. This function is not supported by TL-SL2210.
Access level. Guest means that you ca
edit and modify. Admin means that you can edit,
erent functions. It is “admin” by default.
n only view the
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Add and enable a new admin user named tplink, of which the password is
password:
28
Page 39

TL-SL2428(config)# user name tplink password password type admin status
enable
user access-control ip-based
Description
The user access-control ip-based command is used to limit the IP-range of
the users for login. Only the users within the IP-range you set here are allowed
to login. To cancel the user access limit, please use no user acce
command.
Syntax
user access-control ip-based ip-addr ip-mask
no user access-control
Parameter
ip-addr —— The source IP address. Only the users within the IP-range you set
here are allowed for login.
ip-mask ——The subnet mask of the IP address.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Enable the access-control of the user whose IP address is 192.168.0.148:
ss-con
trol
TL-SL2428(config)# user access-control ip-based 192.168.0.148
255.255.255.255
user access-control mac-based
Description
The user access-control mac-based command is used to limit the MAC
address of the users for login. Only the user with this MAC address you set here
is allowed to login. To cancel the user access limit, please use no user
ss-
acce
Syntax
user access-control mac-based mac-addr
control command.
29
Page 40

no user access-control
Parameter
mac-addr —— The source MAC address. Only the user with this MAC address
is allowed to login.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure that only the user whose MAC address is 00:00:13:0A:00:01 is
allowed to login:
TL-SL2428(config)# user access-control mac-based 00:00:13:0A:00:01
user access-control port-based
Description
The user access-control port-based command is used to limit the ports for
Only the users connected to these ports you set here are allowed to login.
login.
To cancel the user access limit, please use no user access-control command.
Syntax
user access-control port-based interface { fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet
port | range fastEthernet port-list | range gigabitEthernet port-list }
no user access-control
Parameter
port —— The Ethernet port number.
port-list ——The list group of Ethernet ports, in the format of 1/0/1-4. You can
appoint 5 ports at most.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure that only the users connected to ports 2-6 are allowed to login:
TL-SL2428(config)# user access-control port-based interface range
fastEthernet 1/0/2-6
30
Page 41

user max-number
Description
The user max-number command is used to configure the number of the users
logging on at the same time. To cancel the limit to the numbers of the users
logging in, please use no user max-number command.
Syntax
user max-number admin-num guest-num
no user max-number
Parameter
admin-num —— The maximum number of the users logging on as Admin,
ranging from 1 to 16. The total number of Admin and Guest should be less than
16.
guest-num —— The maximum number of the users logging on as Guest,
rangin
g
from 0 to 15.The total number of Admin and Guest should be less than
16.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure the number of the users as Admin and Guest logging on as 5 and 3:
TL-SL2428(config)# user max-num 5 3
user idle-timeout
Description
The user idle-timeout command is used to configure the timeout time of the
switch. To restore to the default timeout time, please use no user idle-timeout
Syntax
command.
user idle-timeout minutes
no user idle-timeout
31
Page 42

Parameter
minutes ——The timeout time, ranging from 5 to 30 in minutes. By default, the
value is 10.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure the timeout time of the switch as 15 minutes:
TL-SL2428(config)# user idle-timeout 15
show user account-list
Description
The show user account-list command is used to display the information of the
current users.
Syntax
show user account-list
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the information of the current users:
TL-SL2428(config)# show user account-list
show user configuration
Description
The show user configuration command is used to display the security
configuration information of the users, including access-control, max-number
and the idle-timeout, etc.
Syntax
show user configuration
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
32
Page 43

Example
Display the security configuration information of the users:
TL-SL2428(config)# show user configuration
33
Page 44

Chapter 7 System Log Commands
The log information will record the settings and operation of the switch respectively for you to
monitor operation status and diagnose malfunction.
logging buffer
Description
The logging buffer command is used to configure the severity level and the
status of the configuration input to the log buffer. To disable the logging buffer
function, please use no logging
information saved in the
saved to two different positions, log buffer and log file. The log buffer indicates
the RAM for saving system log and the information in the log buffer can be got
by show logging buffer
Syntax
logging buffer level
no logging buffer
Parameter
level —— Severity level of the log information output to each channel. There are
8 severity levels marked with values 0-7. The smaller value has the higher priority.
Only the log with the same or smaller severity level value will be output. By default,
it is 7 indicating that all the log information will be saved in the log buffer.
Command Mode
buffer command. Local Log is the log
switch. It has two output channels, that is, it can be
command. It will be lost when the switch is restarted.
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Set the severity level as 6:
TL-SL2428(config)# logging buffer 6
logging file flash
Description
The logging file flash command is used to configure the level and the status of
the log file input. To disable the logging file flash funtion, please use no logging
34
Page 45

file flash command. The log file indicates the flash sector for saving system log.
The information in the log
be got by the show logging flash
TL-SL2452.
Syntax
logging file flash level
no logging file flash
Parameter
level —— Severity level of the log information output to each channel. There
are 8 severity levels marked with values 0-7. The smaller value has the higher
priority. Only the log with the same or smaller severity level value will be output.
By default, it is 2 indicating that the log information marked with 0~2 will be
saved in the log buffer.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
file will not be lost after the switch is restarted and can
command. This command does not apply to
Example
Enable the log file function and set the severity as 7:
TL-SL2428(config)# logging file flash 7
logging file flash (for TL-SL2452)
Description
The logging file flash command is used to store the log messages in a flie in
the flash on the switch. To disable the log file flash function, please use no
logging file flash command. The log file flash indicates the flash sector for
saving system log. The information in the log file of
the switch is restarted and can be got by the show logging flash
This command only applies to TL-SL2452.
Syntax
the flash will not be lost after
command.
logging file flash
no logging file flash
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
35
Page 46

Example
Enable the log file flash function:
TL-SL2452(config)#logging file flash
logging file flash frequency
Description
The logging file flash frequency command is used to specify the frequency to
synchronize the system log file in the log buffer to the flash. To resume the
default synchronizing frequency, please use the no logging file flash
frequency command. This command only applies to TL-SL2452.
Syntax
logging file flash frequency { periodic periodic | immediate }
no logging file flash frequency
Parameter
periodic —— The frequency to synchronize the system log file in the log buffer
to the flash, ranging from 1 to 48 hours. By default, the synchronization process
takes place every 24 hours.
immediate —— The system log file in the buffer will be synchronized to the
flash immediately. This option will reduce the life of the flash and is not
recommended.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Specify the log file synchronization frequency as 10 hours:
TL-SL2452(config)#logging file flash frequency 10
logging file flash level
Description
The logging file flash level command is used to specify the system log
message severity level. Messages will a severity level equal to or higher than
this value will be stored to the flash. To restore to the default level, please use
36
Page 47
no logging file flash level command. This command only applies to
TL-SL2452.
Syntax
logging file flash level level
no logging file flash level
Parameter
level —— Severity level of the log message. There are 8 severity levels marked
with values 0-7. The smaller value has the higher priority. Only the log with the
same or smaller severity level value will be saved to the flash. By default, it is 2
indicating that the log message marked with 0~2 will be saved in the log flash.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Save the log messages with their severities equal or higher than 7 to the flash :
TL-SL2452(config)#logging file flash level 7
clear logging
Description
The clear logging command is used to clear the information in the log buffer
and log file.
Syntax
clear logging [ buffer | flash ]
Parameter
buffer | flash —The output channels: buffer and flash. Clear the information of
the two channels, by default.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Clear the information in the log file:
TL-SL2428(config)# clear logging buffer
37
Page 48

logging host index
Description
The logging host index command is used to configure the Log Host. To clear
the configuration of the specified Log Host, please use no logging host index
command. Log Host is to receive the system log from other devices. You can
remotely monitor the settings and operation status of other devices through the
log host.
Syntax
logging host index idx host-ip level
no logging host index idx
Parameter
idx —— The index of the log host. The switch supports 4 log hosts at most.
host-ip —— The IP for the log host.
level —— The severity level of the log information
are 8 severity levels marked with values 0-7. The smaller value has the higher
priority. Only the log with the same or smaller severity level value will be sent to
the corresponding log host. By default, it is 6 indicating that the log information
marked with 0~6 will be sent to the log host.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Enable log host 2 and set its IP address as 192.168.0.148, the level 5:
TL-SL2428(config)# logging host index 2 192.168.0.148 5
show logging local-config
sent to each log host.
There
Description
The show logging local-config command is used to display the configuration
of the Local Log including the log buffer and the log file.
Syntax
show logging local-config
38
Page 49

Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the configuration of the Local Log:
TL-SL2428(config)# show logging local-config
show logging loghost
Description
The show logging loghost command is used to display the configuration of the
log host.
Syntax
show logging loghost [ index ]
Parameter
index ——The index of the log host whose configuration will be displayed,
ranging from 1 to 4. Display the configuration of all the log hosts by default.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the configuration of the log host 2:
TL-SL2428(config)# show logging loghost 2
show logging buffer
Description
The show logging buffer command is used to display the log information in the
log buffer according to the severity level.
Syntax
show logging buffer [ level level ]
39
Page 50

Parameter
level —— Severity level. There are 8 severity levels marked with values 0-7.
The information of levels with priority not lower than the select level will display.
Display all the log information in the log buffer by default.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the log information from level 0 to level 5 in the log buffer:
TL-SL2428(config)# show logging buffer level 5
show logging flash
Description
The show logging flash command is used to display the log information in the
log file according to the severity level.
Syntax
show logging flash [ level level ]
Parameter
level —— Severity level. There are 8 severity levels marked with values 0-7.
The information of levels with priority not lower than the select level will display.
Display all the log information in the log file by default.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the log information with the level marked 0~3 in the log file:
TL-SL2428(config)# show logging flash level 3
40
Page 51

Chapter 8 SSH Commands
SSH (Security Shell) can provide the unsecured remote management with security and powerful
authentication to ensure the security of the management information.
ip ssh server
Description
The ip ssh server command is used to enable SSH function. To disable the
SSH function, please use no ip ssh server command.
Syntax
ip ssh server
no ip ssh server
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Enable the SSH function:
TL-SL2428(config)# ip ssh server
ip ssh version
Description
The ip ssh version command is used to enable the SSH protocol version. To
disable the protocol version, please use no ip ssh version command.
Syntax
ip ssh version { v1 | v2 }
no ip ssh version { v1 | v2 }
Parameter
v1 | v2 —— The SSH protocol version to be enabled. They represent SSH v1
and SSH v2 respectively.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
41
Page 52

Example
Enable SSH v2:
TL-SL2428(config)# ip ssh version v2
ip ssh timeout
Description
The ip ssh timeout command is used to specify the idle-timeout time of SSH.
To restore to the factory defaults, please use ip ssh timeout command.
Syntax
ip ssh timeout value
no ip ssh timeout
Parameter
value —— The Idle-timeout time. During this period, the system will automatically
release the connection if there is no operation from the client. By default, this
value is 120. For TL-SL2210, it ranges from 1 to 999 in seconds; and for
TL-SL2218/ TL-SL2428/ TL-SL2452, it ranges from 1 to 120 in seconds.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Specify the idle-timeout time of SSH as 100 seconds:
TL-SL2428(config)# ip ssh timeout 100
ip ssh max-client
Description
The ip ssh max-client command is used to specify the maximum number of the
connections to the SSH server. To return to the default configuration, please use
no ip ssh max-client command.
Syntax
ip ssh max-client num
no ip ssh max-client
Parameter
num —— The maximum number of the connections to the SSH server. It
ranges from 1 to 5. By default, this value is 5.
42
Page 53

Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Specify the maximum number of the connections to the SSH server as 3:
TL-SL2428(config)# ip ssh max-client 3
ip ssh download
Description
The ip ssh download command is used to download the SSH key file from
TFTP server.
Syntax
ip ssh download { v1 | v2 } key-file ip-address ip-addr
Parameter
v1 | v2 —— Select the type of SSH key to download, v1 represents SSH-1, v2
represents SSH-2.
key-file —— The name of the key-file which is selected to download. The
length of the name ranges from 1 to 25 characters. The key length of the
downloaded file must be in the range of 256 to 3072 bits.
ip-addr —— The IP address of the TFTP server.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Download a SSH-1 type key file named ssh-key from TFTP server with the IP
address 192.168.0.148:
TL-SL2428(config)# ip ssh download v1 ssh-key ip-address 192.168.0.148
show ip ssh
Description
The show ip ssh command is used to display the global configuration of SSH.
Syntax
show ip ssh
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
43
Page 54
Example
Display the global configuration of SSH:
TL-SL2428(config)# show ip ssh
44
Page 55

Chapter 9 SSL Commands
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer), a security protocol, is to provide a secure connection for the
application layer protocol(e.g. HTTP) based on TCP. Adopting asymmetrical encryption technology,
SSL uses key pair to encrypt/decrypt information. A key pair refers to a public key (contained in the
certificate) and its corresponding private key. By default the switch has a certificate (self-signed
certificate) and a corresponding private key. The certificate/key download function enables the
user to replace the default key pair.
ip http secure-server
Description
The ip http secure-server command is used to enable the SSL function
globally on the switch. To disable the SSL function, please use no ip http
secure-server command. Only the SSL function is enabled, a secure HTTPS
connection can be established.
Syntax
ip http secure-server
no ip http secure-server
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Enable the SSL function:
TL-SL2428(config)# ip http secure-server
ip http secure-server download certificate
Description
Syntax
The ip http secure-server download certificate command is used to
download a certificate to the switch from TFTP server.
ip http secure-server download certificate ssl-cert ip-address ip-addr
45
Page 56

Parameter
ssl-cert —— The name of the SSL certificate which is selected to download to
the switch. The length of the name ranges from 1 to 25 characters. The
certificate must be BASE64 encoded.
ip-addr —— The IP address of the TFTP server.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Download a SSL certificate named ssl-cert from TFTP server with the IP
address of 192.168.0.146:
TL-SL2428(config)# ip http secure-server download certificate ssl-cert
ip-address 192.168.0.146
ip http secure-server download key
Description
The ip http secure-server download key command is used to download a
SSL key to the switch from TFTP server.
Syntax
ip http secure-server download key ssl-key ip-address ip-addr
Parameter
ssl-key —— The name of the SSL key which is selected to download to the
switch. The length of the name ranges from 1 to 25 characters. The key must be
BASE64 encoded.
ip-addr —— The IP address of the TFTP server.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Download a SSL key named ssl-key from TFTP server with the IP address of
192.168.0.146:
TL-SL2428(config)# ip http secure-server download key ssl-key ip-address
192.168.0.146
46
Page 57

show ip http secure-server
Description
The show ip http secure-server command is used to display the global
configuration of SSL.
Syntax
show ip http secure-server
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the global configuration of SSL:
TL-SL2428(config)# show ip http secure-server
47
Page 58

Chapter 10 MAC Address Commands
MAC address configuration can improve the network security by configuring the Port Security and
maintaining the address information by managing the Address Table.
mac address-table static
Description
The mac address-table static command is used to add the static MAC address
entry. To remove the corresponding entry, please use no mac address-table
static command. The static address can be added or removed manually,
independent of the aging time. In the stable networks, the static MAC address
entries can facilitate the switch to reduce broadcast packets and enhance the
efficiency of packets forwarding remarkably.
Syntax
mac address-table static mac mac-addr vid vid interface { fastEthernet port |
gigabitEthernet port }
no mac address-table static { mac mac-addr | vid vid | mac mac-addr vid vid |
interface { fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet port } }
Parameter
mac-addr ——The MAC address of the entry you desire to add.
vid —— The VLAN ID number of your desired entry. It ranges from 1 to 4094.
port —— The Ethernet port number of your desired entry.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Add a static Mac address entry to bind the MAC address 00:02:58:4f:6c:23,
VLAN1 and port 1 together:
TL-SL2428(config)# mac address-table static mac 00:02:58:4f:6c:23 vid 1
interface fastEthernet 1/0/1
48
Page 59

mac address-table aging-time
Description
The mac address-table aging-time command is used to configure aging time
for the dynamic address. To return to the default configuration, please use no
mac address-table aging-time command.
Syntax
mac address-table aging-time aging-time
no mac address-table aging-time
Parameter
aging-time —— The aging time for the dynamic address. The value of it can be
0 or ranges from 10 to 630 seconds. When 0 is entered, the Auto Aging function
is disabled. It is 300 by default.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure the aging time as 500 seconds:
TL-SL2428(config)# mac address-table aging-time 500
mac address-table filtering
Description
The mac address-table filtering command is used to add the filtering address
entry. To delete the corresponding entry, please use no mac address-table
filtering command. The filtering address function is to forbid the undesired
package to be forwarded. The filtering address can be added or removed
manually, independent of the aging time.
Syntax
mac address-table filtering mac mac-addr vid vid
no mac address-table filtering {[ mac mac-addr ] [ vid vid ]}
Parameter
mac-addr —— The MAC address to be filtered.
vid —— The corresponding VLAN ID of the MAC address. It ranges from 1 to
4094.
49
Page 60

Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Add a filtering address entry of which VLAN ID is 1 and MAC address is
00:1e:4b:04:01:5d:
TL-SL2428(config)# mac address-table filtering mac 00:1e:4b:04:01:5d vid 1
mac address-table max-mac-count
Description
The mac address-table max-mac-count command is used to configure the
Port Security. To return to the default configurations, please use no mac
address-table max-mac-count command. Port Security is to protect the switch
from the malicious MAC address attack by limiting the maximum number of the
MAC addresses that can be learned on the port. The port with Port Security
feature enabled will learned the MAC address dynamically. When the learned
MAC address number reaches the maximum, the port will stop learning.
Therefore, the other devices with the MAC address unlearned can not access to
the network via this port.
Syntax
mac address-table max-mac-count {[ max-number num ] [ mode { dynamic |
static | permanent }] [ status { disable | enable }]}
no mac address-table max-mac-count
Parameter
num —— The maximum number of MAC addresses that can be learned on the
port. It ranges from 0 to 64. By default this value is 64.
dynamic | static | permanent —— Learn mode for MAC addresses. There are
three modes, including Dynamic mode, Static mode and Permanent mode.
When Dynamic mode is selected, the learned MAC address will be deleted
automatically after the aging time. When Static mode is selected, the learned
MAC address will be out of the influence of the aging time and can only be
deleted manually. The learned entries will be cleared after the switch is rebooted.
When permanent mode is selected, the learned MAC address will be out of the
influence of the aging time and can only be deleted manually too. However, the
learned entries will be saved even the switch is rebooted.
status —— Enable or disable the Port Security function for a specified port. By
default, this function is disabled.
50
Page 61

Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Enable Port Security function for port 1, select Static mode as the learn mode,
and specify the maximum number of MAC addresses that can be learned on
this port as 30:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/1
TL-SL2428(config-if)# mac address-table max-mac-count max-number 30
mode static status enable
show mac address-table address
Description
The show mac address-table address command is used to display the
information of all address entries.
Syntax
show mac address-table address { dynamic | static | drop | all }
Parameter
dynamic | static | drop | all —— The type of your desired entry
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the information of all address entries:
TL-SL2428(config)# show mac address-table address all
show mac address-table aging-time
Description
The show mac address-table aging-time command is used to display the
Aging Time of the MAC address.
Syntax
show mac address-table aging-time
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
51
Page 62

Example
Display the Aging Time of the MAC address:
TL-SL2428(config)# show mac address-table aging-time
show mac address-table max-mac-count interface
Description
The show mac address-table max-mac-count interface command is used to
display the security configuration of all Fast/Ethernet ports or the specified port.
Syntax
show mac address-table max-mac-count interface { fastEthernet [port] |
gigabitEthernet [port] }
Parameter
port —— The Fast/Gigabit Ethernet port number.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the security configuration of all Gigabit Ethernet ports:
TL-SL2428(config)# show mac address-table max-mac-count interface
gigabitEthernet
Display the security configuration of port 1:
TL-SL2428(config)# show mac address-table max-mac-count interface
fastEthernet 1/0/1
show mac address-table interface
Description
The show mac address-table interface command is used to display the
address configuration of the specified port.
Syntax
show mac address-table interface { fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet
port }
Parameter
port —— The Ethernet port number.
52
Page 63

Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the address configuration of port 1:
TL-SL2428(config)# show mac address-table interface fastEthernet 1/0/1
show mac address-table mac-num
Description
The show mac address-table mac-num command is used to display the total
amount of MAC address table.
Syntax
show mac address-table mac-num
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the total amount of MAC address table:
TL-SL2428(config)# show mac address-table mac-num
show mac address-table mac
Description
The show mac address-table mac command is used to display the information
of the specified MAC address.
Syntax
show mac address-table mac mac-addr
Parameter
mac-addr ——The specified MAC address.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the information of the MAC address 00:00:00:23:00:00:
TL-SL2428(config)#show mac address-table mac 00:00:00:23:00:00
53
Page 64

show mac address-table vlan
Description
The show mac address-table vlan command is used to display the MAC
address configuration of the specified vlan.
Syntax
show mac address-table vlan vid
Parameter
vid ——The specified VLAN id.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the MAC address configuration of vlan 1:
TL-SL2428(config)# show mac address-table vlan 1
54
Page 65

Chapter 11 System Commands
System Commands can be used to configure the System information and System IP, reboot and
reset the switch, upgrade the switch system and other operations.
system-time manual
Description
The system-time manual command is used to configure the system time
manually.
Syntax
system-time manual time
Parameter
time —— Set the date and time manually, MM/DD/YYYY-HH:MM:SS
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure the system mode as manual, and the time is 12/20/2010 17:30:35
TL-SL2428(config)# system-time manual 12/20/2010-17:30:35
system-time ntp
Description
The system-time ntp command is used to configure the time zone and the IP
address for the NTP Server. The switch will get UTC automatically if it has
connected to a NTP Server.
Syntax
system-time ntp { timezone } { ntp-server } { backup-ntp-server }
{ fetching-rate }
Parameter
timezone —— Your local time-zone, and it ranges from UTC-12:00 to
UTC+13:00.
The detailed information that each time-zone means are displayed as follow:
UTC-12:00 —— TimeZone for International Date Line West.
UTC-11:00 —— TimeZone for Coordinated Universal Time-11.
UTC-10:00 —— TimeZone for Hawaii.
55
Page 66

UTC-09:00 —— TimeZone for Alaska.
UTC-08:00 —— TimeZone for Pacific Time(US Canada).
UTC-07:00 —— TimeZone for Mountain Time(US Canada).
UTC-06:00 —— TimeZone for Central Time(US Canada).
UTC-05:00 —— TimeZone for Eastern Time(US Canada).
UTC-04:30 —— TimeZone for Caracas.
UTC-04:00 —— TimeZone for Atlantic Time(Canada).
UTC-03:30 —— TimeZone for Newfoundland.
UTC-03:00 —— TimeZone for Buenos Aires, Salvador, Brasilia.
UTC-02:00 —— TimeZone for Mid-Atlantic.
UTC-01:00 —— TimeZone for Azores, Cape Verde Is.
UTC —— TimeZone for Dublin, Edinburgh, Lisbon, London.
UTC+01:00 —— TimeZone for Amsterdam, Berlin, Bern, Rome, Stockholm,
Vienna.
UTC+02:00 —— TimeZone for Cairo, Athens, Bucharest, Amman, Beirut,
Jerusalem.
UTC+03:00 —— TimeZone for Kuwait, Riyadh, Baghdad.
UTC+03:30 —— TimeZone for Tehran.
UTC+04:00 —— TimeZone for Moscow, St.Petersburg, Volgograd, Tbilisi, Port
Louis.
UTC+04:30 —— TimeZone for Kabul.
UTC+05:00 —— TimeZone for Islamabad, Karachi, Tashkent.
UTC+05:30 —— TimeZone for Chennai, Kolkata, Mumbai, New Delhi.
UTC+05:45 —— TimeZone for Kathmandu.
UTC+06:00 —— TimeZone for Dhaka,Astana, Ekaterinburg.
UTC+06:30 —— TimeZone for Yangon (Rangoon).
UTC+07:00 —— TimeZone for Novosibrisk, Bangkok, Hanoi, Jakarta.
UTC+08:00 —— TimeZone for Beijing, Chongqing, Hong Kong, Urumqi,
Singapore.
UTC+09:00 —— TimeZone for Seoul, Irkutsk, Osaka, Sapporo, Tokyo.
UTC+09:30 —— TimeZone for Darwin, Adelaide.
UTC+10:00 —— TimeZone for Canberra, Melbourne, Sydney, Brisbane.
UTC+11:00 —— TimeZone for Solomon Is., New Caledonia, Vladivostok.
UTC+12:00 —— TimeZone for Fiji, Magadan, Auckland, Welington.
UTC+13:00
ntp-server
——
TimeZone for Nuku'alofa, Samoa.
—— The IP address for the Primary NTP Server.
backup-ntp-server —— The IP address for the Secondary NTP Server.
fetching-rate —— S
pecify the rate fetching time from NTP server.
56
Page 67

Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure the system time mode as NTP, the time zone is UTC-12:00, the
primary NTP server is 133.100.9.2 and the secondary NTP server is
139.78.100.163, the fetching-rate is 11 hours:
TL-SL2428(config)# system-time ntp UTC-12:00 133.100.9.2 139.79.100.163
11
system-time dst predefined
Description
The system-time dst predefined command is used to select a daylight saving
time configuration from the predefined mode. The configuration can be used
recurrently. To disable DST function, please use no system-time dst
command.
Syntax
system-time dst predefined {USA | Australia | Europe| New-Zealand}
no system-time dst
Parameter
USA | Australia | Europe | New-Zealand —— The mode of daylight saving time.
There are 4 options which are USA, Australia, Europe and New-Zealand
respectively. The default value is Europe.
Following ar
USA: Secon
Australia: First Sunday in October, 02:00 ~ First Sunday in April, 03:00.
Europe: Last Sunday in March, 01:00 ~ Last Sunday in October, 01:00.
New Zealand: Last Sunday in September, 02:00 ~ First Sunday in April, 03:00.
e the time ranges of each option:
d Sunday in March, 02:00 ~ First Sunday in November, 02:00.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure the daylight saving time as USA standard:
TL-SL2428(config)#system-time dst predefined USA
57
Page 68

system-time dst date
Description
The system-time dst date command is used to configure the one-off daylight
saving time. The start date is in the current year by default. The time range of
the daylight saving time must shorter than one year
spanning years. To disable DST function, please use no s
command.
Syntax
system-time dst date {smonth} {sday} {stime} {emonth} {eday} {etime} [offset]
no system-time dst
Parameter
smonth ——The start month of the daylight saving time. There are 12 values
showing as follows: Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, Dec.
sday —— The start day of the daylight saving time, ranging from 1 to 31. Here
you should show special attention to February and the differences between a
solar month and a lunar month.
stime —— The start moment of the daylight saving time, HH:MM.
emonth —— The end month of the daylight saving time. There are 12 values
, but you can configure it
y
stem-time dst
showing as follows: Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, Dec.
eday —— The end day of the daylight saving time, ranging from q to 31. Here
you should show special attention to February and the differences between a
solar month and a lunar month.
etime —— The end moment of the daylight saving time, HH:MM.
offset —— The number of minutes to add during the daylight saving time. The
value ranges from 1 to 1440 and the default value is 60 minutes. It is optional.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure the daylight saving time from zero clock, Apr 1st to zero clock Oct 1st
and the offset is 30 minutes:
TL-SL2428(config)# system-time dst date Apr 1 00:00 Oct 1 00:00 30
58
Page 69

system-time dst recurring
Description
The system-time dst recurring command is used to configure the recurring
daylight saving time. It can be configured spanning years. To disable DST
function, please use no sy
Syntax
system-time dst recurring {sweek} {sday} {smonth} {stime} {eweek} {eday}
{emonth} {etime} [offset]
no system-time dst
Parameter
sweek——The start week of the daylight saving time. There are 5 values
showing as follows: first, second, third, fourth, last.
sday —— The start day of the daylight saving time. There are 7 values
showing as follows: Sun, Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat.
smonth —— The start month of the daylight saving time. There are 12 values
showing as follows: Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, Dec.
stime —— The start moment of the daylight saving time, HH:MM.
eweek ——The end week of the daylight saving time. There are 5 values
stem-time dst command.
showing as follows: first, second, third, fourth, last.
eday —— The end day of the daylight saving time. There are 5 values showing
as follows: Sun, Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat.
emonth —— The end month of the daylight saving time. There are 12 values
showing as following: Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov,
Dec.
etime —— The end moment of the daylight saving time, HH:MM.
offset —— The number of minutes to add during the daylight saving time. It is
60 minutes by default.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure the daylight saving time from 2:00am, the first Sunday of May to
2:00am, the last Sunday of Oct and the offset is 45 minutes:
59
Page 70

hostname
Description
Syntax
Parameter
TL-SL2428(config)# system-time dst recurring first Sun May 02:00 last Sun
Oct 02:00 45
The hostname command is used to configure the system name. To clear the
system name information, please use no hostname command.
hostname hostname
no hostname
hostname —— System Name. The length of the name ranges from 1 to 32
Command Mode
Example
location
Description
Syntax
characters. By default, it is the device name, for example “TL-SL2428”.
Global Configuration Mode
Configure the system name as TPLINK:
TL-SL2428(config)# hostname TPLINK
The location command is used to configure the system location. To clear the
system location information, please use no location command.
location location
no location
Parameter
location —— Device Location. It consists of 32 characters at most. It is
“SHENZHEN” by default.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
60
Page 71

Example
Configure the system location as SHENZHEN:
TL-SL2428(config)# location SHENSHEN
contact-info
Description
The contact-info command is used to configure the system contact information.
To clear the system contact information, please use no contact-info command.
Syntax
contact-info contact_info
no contact-info
Parameter
contact_info —— Contact Information. It consists of 32 characters at most. It is
“www.tp-link.com” by default.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Configure the system contact information as www.tp-link.com:
TL-SL2428(config)# contact-info www.tp-link.com
ip management-vlan
Description
The ip management-vlan command is used to configure the IP management
VLAN,
Syntax
through which you can log on to the switch.
ip management-vlan vlan-id
Parameter
vlan-id —— VLAN ID, ranging from 1 to 4094.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Set the VLAN 6 as IP management VLAN:
61
Page 72

TL-SL2428(config)# ip management-vlan 6
ip address
Description
The ip address command is used to configure the system IP address, Subnet
Mask and Default Gateway. To restore to the factory defaults, please use no ip
address command. This command should be configured in the Interface
Configuration Mode of the management VLAN.
Syntax
ip address {ip-addr} {ip-mask} [gateway]
no ip address
Parameter
ip-addr —— The system IP of the switch. The default system IP is 192.168.0.1.
ip-mask —— The Subnet Mask of the switch. The default Subnet Mask is
255.255.255.0.
gateway —— The Default Gateway of the switch. By default, it is empty.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface vlan)
Example
Configure the system IP as 192.168.0.69 and the Subnet Mask as
255.255.255.0 when the management VLAN of the switch is VLAN1:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface vlan 1
TL-SL2428(config-if)# ip address 192.168.0.69 255.255.255.0
ip address-alloc dhcp
Description
Syntax
The ip address-alloc dhcp command is used to enable the DHCP Client
function. When this function is enabled, the switch will obtain IP from DHCP
server. This command should be configured in the Interface Configuration Mode
of the management VLAN.
ip address-alloc dhcp
62
Page 73

Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface vlan)
Example
Enable the DHCP Client function when the management VLAN of the switch is
VLAN1:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface vlan 1
TL-SL2428(config-if)# ip address-alloc dhcp
ip address-alloc bootp
Description
The ip address-alloc bootp command is used to enable the BOOTP Protocol.
When the BOOTP Protocol is enabled, the switch will obtain IP address from
BOOTP Server. This command should be configured in the Interface
reset
Configuration Mode of the management VLAN.
Syntax
ip address-alloc bootp
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface vlan)
Example
Enable the BOOTP Protocol to obtain IP address from BOOTP Server when the
management VLAN of the switch is VLAN1:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface vlan 1
TL-SL2428(config-if)# ip address-alloc bootp
Description
The reset command is used to reset the switch’s software. After resetting, all
configuration of the switch will restore to the factory defaults and your current
settings will be lost.
Syntax
reset
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode
63
Page 74

Example
Reset the software of the switch:
reboot
Description
Syntax
Command Mode
TL-SL2428# reset
The reboot command is used to reboot the switch. To avoid damage, please
don’t turn off the device while rebooting.
reboot
Privileged EXEC Mode
Example
Reboot the switch:
TL-SL2428# reboot
copy running-config startup-config
Description
The copy running-config startup-config command is used to save the current
settings.
Syntax
copy running-config startup-config
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode
Example
Save current settings:
TL-SL2428# copy running-config startup-config
64
Page 75

copy startup-config tftp
Description
The copy startup-config tftp command is used to backup the configuration file
to TFTP server.
Syntax
copy startup-config tftp ip-address ip-addr filename name
Parameter
ip-addr —— IP address of the TFTP server.
name —— Specify the name for the configuration file which would be backup.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode
Example
Backup the configuration files to TFTP server with the IP 192.168.0.148 and
name this file config:
TL-SL2428# copy startup-config tftp ip-address 192.168.0.148 filename
config
copy tftp startup-config
Description
The copy tftp startup-config command is used to download the configuration
file to the switch from TFTP server.
Syntax
copy tftp startup-config ip-address ip-addr filename name
Parameter
ip-addr —— IP address of the TFTP server.
name —— Specify the name for the configuration file which would be downloaded.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode
Example
Download the configuration file named as config to the switch from TFTP server
with the IP 192.168.0.148:
65
Page 76

TL-SL2428# copy tftp startup-config ip-address 192.168.0.148 filename
config
firmware upgrade
Description
The firmware upgrade command is used to upgrade the switch system file via
the TFTP server.
Syntax
firmware upgrade ip-address ip-addr filename name
Parameter
ip-addr —— IP address of the TFTP server.
name —— Specify the name for the firmware file.
ping
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode
Example
Upgrade the switch system file named as firmware.bin via the TFTP server with
the IP address 192.168.0.148:
TL-SL2428# firmware upgrade ip-address 192.168.0.148 filename
firmware.bin
Description
The ping command is used to test the connectivity between the switch and one
node of the network.
Syntax
ping {ip_addr} [-n count] [-l count] [-i count]
Parameter
ip_addr —— The IP address of the destination node for ping test.
count (-n) —— The amount of times to send test data during Ping testing. It
ranges from 1 to 10. By default, this value is 4.
count (-l) —— The size of the sending data during ping testing. It ranges from 1
to 1024 bytes. By default, this value is 64.
66
Page 77

Command Mode
Example
tracert
count (-i) —— The interval to send ICMP request packets. It ranges from 100
to 1000 milliseconds. By default, this value is 1000.
User EXEC Mode and Privileged EXEC Mode
To test the connectivity between the switch and the network device with the IP
192.168.0.131, please specify the count (-l) as 512 bytes and count (-i) as 1000
milliseconds. If there is not any response after 8 times’ Ping test, the connection
between the switch and the network device is failed to establish:
TL-SL2428# ping 192.168.0.131 –n 8 –l 512
Description
The tracert command is used to test the connectivity of the gateways during its
journey from the source to destination of the test data.
Syntax
tracert {ip-addr} [maxHops]
Parameter
ip-addr —— The IP address of the destination device.
maxHops —— The maximum number of the route hops the test data can pass
though. It ranges from 1 to 30. By default, this value is 4.
Command Mode
User EXEC Mode and Privileged EXEC Mode
Example
Test the connectivity between the switch and the network device with the IP
192.168.0.131. If the destination device has not been found after 20 maxHops,
the connection between the switch and the destination device is failed to
establish:
TL-SL2428# tracert 192.168.0.131 20
67
Page 78

loopback interface
Description
The loopback interface command is used to test whether the port is available
or not.
Syntax
loopback interface { fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet port } { internal |
external }
Parameter
port —— The Fast/Gigabit Ethernet port number.
internal | external —— Loopback Type. There are two options: “internal” and
“external”.
Command Mode
User EXEC Mode and Privileged EXEC Mode
Example
Do an internal-type loopback test for Gigabit Ethernet port 27:
TL-SL2428# loopback interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/27 internal
Do an external-type loopback test for Gigabit Ethernet port 27:
TL-SL2428# loopback interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/27 external
show system-info
Description
The show system-info command is used to display System Description,
Device Name, Device Location, System Contact, Hardware Version, Firmware
Version, System Time, Run Time and so on.
Syntax
show system-info
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the system information:
TL-SL2428# show system-info
68
Page 79

show running-config
Description
The show running-config command is used to display the current operating
configuration of the system or a specified port.
Syntax
show running-config [ interface { fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet port } ]
Parameter
port —— The Fast/Gigabit Ethernet port number.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the system information:
TL-SL2428# show running-config
show system-time
Description
The show system-time command is used to display the time information of the
switch.
Syntax
show system-time
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the time information of the switch
TL-SL2428# show system-time
show system-time dst
Description
The show system-time dst command is used to display the DST time
information of the switch.
Syntax
show system-time dst
69
Page 80

Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the DST time information of the switch
TL-SL2428# show system-time dst
show system-time ntp
Description
The show system-time ntp command is used to display the NTP mode
configuration information.
Syntax
show system-time ntp
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the NTP mode configuration information of the switch:
TL-SL2428# show system-time ntp
show cable-diagnostics interface
Description
The show cable-diagnostics interface command is used to display the cable
diagnostics of the connected Ethernet Port., which facilitates you to check the
connection status of the cable connected to the switch, locate and diagnose the
trouble spot of the network.
Syntax
show cable-diagnostics interface { fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet port }
Parameter
port —— The number of the port which is selected for Cable test.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
70
Page 81
Example
Show the cable-diagnostics of port 3:
TL-SL2428# show cable-diagnostics interface fastEthernet 1/0/3
71
Page 82

Chapter 12 Ethernet Configuration Commands
Ethernet Configuration Commands can be used to configure the Bandwidth Control, Negotiation
Mode and Storm Control for Ethernet ports.
interface fastEthernet
Description
The interface fastEthernet command is used to enter the interface
fastEthernet Configuration Mode and configure the corresponding Fast Ethernet
port.
Syntax
interface fastEthernet port
Parameter
port —— The Fast/Gigabit Ethernet port number.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
To enter the Interface fastEthernet Configuration Mode and configure Fast
Ethernet port 2:
TL-SL2428(config)#interface fastEthernet 1/0/2
interface range fastEthernet
Description
The interface range fastEthernet command is used to enter the interface
range fastEthernet Configuration Mode and configure multiple Fast Ethernet
ports at the same time.
Syntax
interface range fastEthernet port-list
Parameter
port-list —— The list of Fast Ethernet ports.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
72
Page 83

User Guidelines
Command in the Interface Range fastEthernet Mode is executed
independently on all ports in the range. It does not effect the execution on the
other ports at all if the command results in an error on one port.
Example
To enter the Interface Range fastEthernet Configuration Mode, and configure
ports 1, 2, 3, 6, 7 and 9 at the same time by adding them to one port-list:
TL-SL2428(config)#interface range fastEthernet 1/0/1-3,1/0/6-7,1/0/9
interface gigabitEthernet
Description
The interface gigabitEthernet command is used to enter the interface
gigabitEthernet Configuration Mode and configure the corresponding Gigabit
Ethernet port.
Syntax
interface gigabitEthernet port
Parameter
port —— The Fast/Gigabit Ethernet port number.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
To enter the Interface gigabitEthernet Configuration Mode and configure Gigabit
Ethernet port 27:
TL-SL2428(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/27
interface range gigabitEthernet
Description
The interface range gigabitEthernet command is used to enter the interface
range gigabitEthernet Configuration Mode and configure multiple Gigabit
Ethernet ports at the same time.
Syntax
interface range gigabitEthernet port-list
73
Page 84

Parameter
port-list —— The list of Gigabit Ethernet ports.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
User Guidelines
Command in the Interface Range gigabitEthernet Mode is executed
independently on all ports in the range. It does not effect the execution on the
other ports at all if the command results in an error on one port.
Example
To enter the Interface Range gigabitEthernet Configuration Mode, and configure
Gigabit Ethernet ports 27 and 28 at the same time by adding them to one
port-list:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface range gigabitEthernet 1/0/27-28
description
Description
The description command is used to add a description to the Ethernet port. To
clear the description of the corresponding port, please use no description
command.
Syntax
description string
no description
Parameter
string —— Content of a port description, ranging from 1 to 16 characters.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode ((interface fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet)
Example
Add a description Port #5 to port 5:
shutdown
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/5
TL-SL2428(config-if)# description Port#5
74
Page 85

Description
The shutdown command is used to disable an Ethernet port. To enable this port
again, please use no shutdown command.
Syntax
shutdown
no shutdown
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Disable port 3:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/3
TL-SL2428(config-if)# shutdown
flow-control
Description
The flow-control command is used to enable the flow-control function for a port.
To disable the flow-control function for this corresponding port, please use no
flow-control command. With the flow-control function enabled, the Ingress
Rate and Egress Rate can be synchronized to avoid packet loss in the network.
Syntax
flow-control
no flow-control
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Enable the flow-control function for port 3:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/3
TL-SL2428(config-if)# flow-control
75
Page 86

media-type
Description
The media-type command is used to configure the media type of Combo port.
For a Combo port, the media type should be configured before you set its speed
and mode. This command does not apply to TL-SL2210/TL-SL2452 since
TL-SL2210/TL-SL2452 has no Combo port.
Syntax
media-type { rj45 | sfp }
Parameter
rj45 | sfp —— Media type.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
Example
duplex
Description
Syntax
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Configure the media type of Combo port 27T as “SFP”:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/27
TL-SL2428 (config-if)# media-type sfp
The duplex command is used to configure the Duplex Mode for an Ethernet
port. To return to the default configuration, please use no duplex command.
duplex { full | half }
no duplex
Parameter
full | half —— The duplex mode of the Ethernet port. There are two options:
full-duplex mode (default) and half-duplex mode.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Configure the Duplex Mode as full-duplex for port 3:
76
Page 87

speed
Description
Syntax
Parameter
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/3
TL-SL2428(config-if)# duplex full
The speed command is used to configure the Speed Mode for an Ethernet port.
To return to the default configuration, please use no speed command.
speed { 10 | 100 | 1000 | auto }
no speed
10 | 100 | 1000 | auto —— The speed mode of the Ethernet port. There are
four options: 10Mbps, 100Mbps, 1000Mbps and Auto negotiation mode
(default).
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Configure the Speed Mode as 100Mbps for port 3:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/3
TL-SL2428(config-if)# speed 100
storm-control broadcast
Description
The storm-control broadcast command is used to enable the broadcast
control function. To disable the broadcast control function, please use no
storm-control broadcast command. Broadcast control function allows the
switch to filter broadcast in the network. If the transmission rate of the broadcast
Syntax
packets exceeds the set bandwidth, the packets will be automatically discarded
to avoid network broadcast storm.
storm-control broadcast [rate rate]
no storm-control broadcast
77
Page 88

Parameter
rate —— Specify the bandwidth for receiving broadcast packets on the port.
The packet traffic exceeding the bandwidth will be discarded. By default, the
value is “128K”.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Enable the broadcast control function for port 5:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/5
TL-SL2428(config-if)# storm-control broadcast
storm-control multicast
Description
The storm-control multicast command is used to enable the multicast control
function. To disable the multicast control function, please use no storm-control
multicast command. Multicast control function allows the switch to filter
multicast in the network. If the transmission rate of the multicast packets
exceeds the set bandwidth, the packets will be automatically discarded to avoid
network broadcast storm.
Syntax
storm-control multicast [rate rate]
no storm-control multicast
Parameter
rate —— Select the bandwidth for receiving multicast packets on the port. The
packet traffic exceeding the bandwidth will be discarded. By default, the value is
“128K”.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Enable the multicast control function for port 5:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/5
TL-SL2428(config-if)# storm-control multicast
78
Page 89

storm-control unicast
Description
The storm-control unicast command is used to enable the unicast control
function. To disable the unicast control function, please use no storm-control
unicast command. Unicast control function allows the switch to filter UL frame
in the network. If the transmission rate of the UL frames exceeds the set
bandwidth, the packets will be automatically discarded to avoid network
broadcast storm.
Syntax
storm-control unicast [rate rate]
no storm-control unicast
Parameter
rate —— Select the bandwidth for receiving UL-Frame on the port. The packet
traffic exceeding the bandwidth will be discarded. By default, the value is
“128K”.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Enable the unicast control function for port 5:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/5
TL-SL2428(config-if)# storm-control unicast
bandwidth
Description
The bandwidth command is used to configure the bandwidth limit for an
Syntax
Ethernet port. To disable the bandwidth limit, please use no bandwidth
command.
bandwidth {[ ingress ingress-rate ] [ egress egress-rate ]}
no bandwidth { all | ingress | egress }
79
Page 90

Parameter
ingress-rate —— Specify the bandwidth for receiving packets. Range:
1-1024000 for the gigaport.
egress-rate —— Specify the bandwidth for sending packets. Range:
1-1024000 for the gigaport.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
Example
Configure the ingress-rate as 5120Kbps and egress-rate as 1024Kbps for port
5:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/5
TL-SL2428(config-if)# bandwidth ingress 5120 egress 1024
clear counters
Description
The clear counters command is used to clear the statistic information of all the
Ethernet ports.
Syntax
clear counters
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Clear the statistic information of all ports
TL-SL2428(config)# clear counters
show interface status
Description
The show interface status command is used to display the connective-status
of an Ethernet port.
Syntax
show interface [fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet port] status
80
Page 91

Parameter
port —— The Ethernet port number.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the connective-status of all ports:
TL-SL2428(config)# show interface status
Display the connective-status of port 1:
TL-SL2428(config)# show interface fastEthernet 1/0/1 status
show interface counters
Description
The show interface counters command is used to display the statistic
information of all ports or an Ethernet port.
Syntax
show interface [fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet port] counters
Parameter
port —— The Ethernet port number.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the statistic information of all Ethernet ports:
TL-SL2428(config)# show interface counters
Display the statistic information of port 2:
TL-SL2428(config)# show interface fastEthernet 1/0/2 counters
show interface description
Description
The show interface description command is used to display the description of
all ports or an Ethernet port.
Syntax
show interface [fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet port] description
81
Page 92

Parameter
port —— The Ethernet port number.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the description of all Ethernet ports:
TL-SL2428(config)# show interface description
Display the description of port 2:
TL-SL2428(config)# show interface fastEthernet 1/0/2 description
show interface flowcontrol
Description
The show interface flowcontrol command is used to display the flow-control
information of an Ethernet port.
Syntax
show interface [fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet port] flowcontrol
Parameter
port —— The Ethernet port number.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the flow-control information of all Ethernet ports:
TL-SL2428# show interface flowcontrol
Display the flow-control information of port 2:
TL-SL2428# show interface fastEthernet 1/0/2 flowcontrol
show interface configuration
Description
The show interface configuration command is used to display the
configurations of all ports or an Ethernet port, including Port-status, Flow Control,
Negotiation Mode and Port-description.
Syntax
show interface [fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet port] configuration
82
Page 93

Parameter
port —— The Ethernet port number.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the configurations of all Ethernet ports:
TL-SL2428(config)# show interface configuration
Display the configurations of port 2:
TL-SL2428(config)# show interface fastEthernet 1/0/2 configuration
show storm-control
Description
The show storm-control command is used to display the storm-control
information of Ethernet ports.
Syntax
show storm-control [ interface { fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet port |
range fastEthernet port-list | range gigabitEthernet port-list }]
Parameter
port —— The Ethernet port number.
port-list —— The list of Ethernet ports.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the storm-control information of port 4, 5, 6, and 7:
TL-SL2428(config)# show storm-control interface range fastEthernet
1/0/4-7
show bandwidth
Description
The show bandwidth command is used to display the bandwidth-limit
information of Ethernet ports.
83
Page 94

Syntax
show bandwidth [interface { fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet port | range
fastEthernet port-list | range gigabitEthernet port-list }]
Parameter
port
——
The Ethernet port number.
port-list —— The list of the Ethernet ports.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the bandwidth-limit information of port 4:
TL-SL2428(config)# show bandwidth interface fastEthernet 1/0/4
84
Page 95

Chapter 13 QoS Commands
QoS (Quality of Service) function is used to optimize the network performance. It provides you with
network service experience of a better quality.
qos
Description
The qos command is used to configure the prority based on port. To return to
the default configuration, please use no qos command.
Syntax
qos tc-id
no qos
Parameter
tc-id —— The priority of port. It ranges from 0 to 3, which represent TC 0 -TC 3
respectively. By default, the priority is TC 0.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface fastEthernet / interface range
fastEthernet / interface gigabitEthernet / interface range gigabitEthernet)
User Guidelines
Port priority is one property of the port. When the port priority is specified, the
data will be classified into the egress queue based on the tc-id value of the
ingress port.
Example
Configure the priority of port 5 as 3:
TL-SL2428(config)# interface fastEthernet 1/0/5
TL-SL2428(config-if)# qos 3
qos cos
Description
The qos cos command is used to enable the mapping relation between
IEEE802.1P Priority and TC egress queue. To disable the mapping relation,
please use no qos cos command.
85
Page 96

Syntax
qos cos
no qos cos
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
User Guidelines
IEEE 802.1P gives the Pri field in IEEE 802.1Q tag a recommended definition.
When the mapping relation between IEEE 802.1P Priority and TC egress queue
is enabled, the data will be classified into the egress queue based on this
mapping relation.
Example
Enable the mapping relation between IEEE 802.1P Priority and egress queue:
TL-SL2428(config)# qos cos
qos dscp
Description
Syntax
Command Mode
User Guidelines
The qos dscp command is used to enable the mapping relation between DSCP
Priority and TC egress queue. To disable the mapping relation, please use no
qos dscp command.
qos dscp
no qos dscp
Global Configuration Mode
DSCP (DiffServ Code Point) is a new definition to IP ToS field given by IEEE.
DSCP priorities are mapped to the corresponding TC egress queue. IP
datagram will be classified into the egress queue based on the
mapping relation
between
Example
Enable the mapping relation between DSCP Priority and TC egress queue:
TL-SL2428(config)# qos dscp
DSCP priority and TC egress queue.
86
Page 97

qos queue cos-map
Description
The qos queue cos-map command is used to configure the mapping relation
between IEEE 802.1P priority tag/IEEE 802.1Q tag and the TC egress queue.
To return to the default configuration, please use no qos queue cos-map
command. When 802.1P Priority is enabled, the packets with 802.1Q tag are
mapped to different priority levels based on 802.1P priority mode. The untagged
packets are mapped based on port priority mode.
Syntax
qos queue cos-map { tag/cos-id } { tc-id }
no qos queue cos-map
Parameter
tag/cos-id —— The 8 priority levels defined by IEEE 802.1P or the priority level
the packets with tag are mapped to, which ranges from 0 to 7.
tc-id —— The egress queue the packets with tag are mapped to. It ranges from
0 to 3, which represents TC0, TC1, TC2 and TC3 respectively.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
User Guidelines
1. By default, the mapping relation between tag/cos and the egress queue is:
0-TC1, 1-TC0, 2-TC0, 3-TC1, 4-TC2, 5-TC2, 6-TC3, 7-TC3
2. Among the priority levels TC0-TC3, the bigger value, the higher
priority.
Example
Map tag 5 to TC 2.:
TL-SL2428(config)# qos queue cos-map 5 2
qos queue dscp-map
Description
The qos queue dscp-map command is used to configure the mapping relation
between DSCP Priority and the TC egress queue. To return to the default
configuration, please use no qos queue dscp-map command. DSCP (DiffServ
Code Point) is a new definition to IP ToS field given by IEEE. This field is used to
divide IP datagram into 64 priorities. When DSCP Priority is enabled, IP
87
Page 98

datagram are mapped to different priority levels based on DSCP priority mode;
non-IP datagram with IEEE 802.1Q tag are mapped to different priority levels
based on IEEE 802.1P priority mode if IEEE 802.1P Priority is enabled; the
untagged non-IP datagram are mapped based on port priority mode.
Syntax
qos queue dscp-map { dscp-list } { tc-id }
no qos queue dscp-map
Parameter
dscp-list —— List of DSCP value. One or several DSCP values can be typed
using comma to separate. Use a hyphen to designate a range of values, for
instance, 1,4-7,11 indicates choosing 1,4,5,6,7,11. The DSCP value ranges
from 0 to 63.
tc-id —— The priority level the packets with tag are mapped to, which ranges
from tc 0 to tc 3.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
User Guidelines
By default, the mapping relation between tag and the egress queue is:
(0-15)-TC 0, (16-31)-TC 1, (32-47)-TC 2, (48-63)-TC 3.
Example
Map DSCP values 10-12 to TC 2:
TL-SL2428(config)# qos queue dscp-map 10-12 2
qos queue mode
Description
The qos queue mode command is used to configure the Schedule Mode. To
return to the default configuration, please use no qos queue mode command.
When the network is congested, the problem that many packets compete for
Syntax
resources must be solved, usually in the way of queue scheduling. The switch
will control the forwarding sequence of the packets according to the priority
queues and scheduling algorithms you set. On this switch, the priority levels are
labeled as TC0, TC1… TC3.
qos queue mode { sp | wrr | sp+wrr | equ }
no qos queue mode
88
Page 99

Parameter
sp —— Strict-Priority Mode. In this mode, the queue with higher priority will
occupy the whole bandwidth. Packets in the queue with lower priority are sent
only when the queue with higher priority is empty.
wrr —— Weight Round Robin Mode. In this mode, packets in all the queues
are sent in order based on the weight value for each queue. The weight value
ratio of TC0, TC1, TC2 and TC3 is 1:2:4:8.
sp+wrr —— Strict-Priority + Weight Round Robin Mode. In this mode, the
switch provides two scheduling groups, SP group and WRR group. Queues in
SP group and WRR group are scheduled strictly based on Strict-Priority mode
while the queues inside WRR group follow the WRR mode. In SP + WRR mode,
TC3 is the SP group; TC0, TC1 and TC2 belong to the WRR group and the
weight value ratio of TC0, TC1 and TC2 is 1:2:4. In this way, when scheduling
queues, the switch allows TC3 to occupy the whole bandwidth following the SP
mode and the TC0, TC1 and TC2 in the WRR group will take up the bandwidth
according to their ratio 1:2:4.
equ —— Equal-Mode. In this mode, all the queues occupy the bandwidth
equally. The weight value ratio of all the queues is 1:1:1:1.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Example
Specify the Schedule Mode as Weight Round Robin Mode:
TL-SL2428(config)# qos queue mode wrr
show qos interface
Description
The show qos interface command is used to display the configuration of QoS
based on port priority.
Syntax
show qos interface [ fastEthernet port | gigabitEthernet port | range
fastEthernet port-list | range gigabitEthernet port-list ]
Parameter
port —— The Ethernet port number.
port-list —— The list of Ethernet ports.
89
Page 100

Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the configuration of QoS for port 5:
TL-SL2428# show qos interface fastEthernet 1/0/5
Display the configuration of QoS for ports 1-4:
TL-SL2428# show qos interface range fastEthernet 1/0/1-4
show qos cos-map
Description
The show qos cos-map command is used to display the configuration of IEEE
802.1P priority and the mapping relation between IEEE 802.1P priority and tc-id.
Syntax
show qos cos-map
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the configuration of IEEE 802.1P priority and the mapping relation
between IEEE 802.1P priority and tc-id:
TL-SL2428# show qos cos-map
show qos dscp-map
Description
The show qos dscp-map command is used to display the configuration of
DSCP Priority.
Syntax
show qos dscp-map
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Example
Display the configuration of DSCP Priority:
TL-SL2428# show qos dscp-map
90
 Loading...
Loading...