Page 1

8PON Port GPON OLT Equipment
CLI User Manual
Version:V1.0
Page 2

Catalog
CATALOG ............................................................................................................................................ 2
THE CLI MANUAL CONVENTIONS .................................................................................................................. 7
Command Conventions .................................................................................................................... 7
Keyword Operation Conventions ...................................................................................................... 7
Symbol Conventions ......................................................................................................................... 7
Terms Conventions ........................................................................................................................... 8
Prompt .............................................................................................................................................. 8
1. CONFIGURATION MODE .......................................................................................................................... 9
1.1 enable ....................................................................................................................................... 11
1.2 config ........................................................................................................................................ 11
1.3 interface ................................................................................................................................... 11
1.4 dba-profile ................................................................................................................................ 12
1.5 ont-lineprofile ........................................................................................................................... 12
1.6 ont-srvprofile ............................................................................................................................ 12
1.7 multicast-vlan ........................................................................................................................... 12
1.8 exit ............................................................................................................................................ 13
2. EQUIPMENT UPGRADE .......................................................................................................................... 13
2.1 load........................................................................................................................................... 13
2.2 show version ............................................................................................................................. 14
2.3 show progress ........................................................................................................................... 14
3. EQUIPMENT MANAGEMENT ................................................................................................................... 15
3.1 reboot ....................................................................................................................................... 15
3.2 ip address ................................................................................................................................. 15
3.3 show interface mgmt................................................................................................................ 16
3.4 show interface vlanif ................................................................................................................ 16
3.5 show device info ....................................................................................................................... 17
4. OPERATION STATUS MONITOR ............................................................................................................... 17
4.1 show fan ................................................................................................................................... 17
4.2 show temperature .................................................................................................................... 18
4.3 show memory ........................................................................................................................... 18
4.4 show version ............................................................................................................................. 18
4.5 time .......................................................................................................................................... 19
4.6 show time ................................................................................................................................. 19
4.7 show uptime ............................................................................................................................. 19
5. CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................................ 20
5.1 backup ...................................................................................................................................... 20
5.2 load configuration .................................................................................................................... 20
5.3 show current-config .................................................................................................................. 21
5.4 save .......................................................................................................................................... 21
5.5 erase saved-config .................................................................................................................... 22
5.6 show saved-config .................................................................................................................... 22
6.ACCOUNT MANAGEMENT ...................................................................................................................... 23
Page 3

6.1 user add .................................................................................................................................... 23
6.2 user delete ................................................................................................................................ 23
6.3 user group ................................................................................................................................ 23
6.4 user password........................................................................................................................... 24
6.5 show user ................................................................................................................................. 24
7. PORT CONFIGURATION ......................................................................................................................... 24
7.1 shutdown .................................................................................................................................. 24
7.2 no shutdown ............................................................................................................................. 25
7.3 show port state ......................................................................................................................... 25
7.4 show port ddm-info .................................................................................................................. 27
7.5 show port vlan .......................................................................................................................... 27
7.6 auto-neg ................................................................................................................................... 28
7.7 duplex ....................................................................................................................................... 28
7.8 speed ........................................................................................................................................ 28
7.9 flow-control .............................................................................................................................. 28
7.10 mirror ..................................................................................................................................... 29
7.11 show mirror ............................................................................................................................ 29
7.12 mtu ......................................................................................................................................... 30
7.13 reset port statistic ................................................................................................................... 30
7.14 show port statistics ................................................................................................................. 30
7.15 show mac-address .................................................................................................................. 31
7.16 show location ......................................................................................................................... 32
7.17 mac-address limit port ........................................................................................................... 32
7.18 mac-address static .................................................................................................................. 33
7.19 mac-address timer .................................................................................................................. 33
7.20 mac-address learning ............................................................................................................. 34
7.21 mac-address black-hole .......................................................................................................... 34
7.22 mac-address flush................................................................................................................... 35
7.23 traffic-suppress ....................................................................................................................... 35
8. VLAN ............................................................................................................................................... 36
8.1 vlan ........................................................................................................................................... 36
8.2 show vlan ................................................................................................................................. 37
8.3 vlan mode ................................................................................................................................. 37
8.4 vlan access ................................................................................................................................ 38
8.5 vlan trunk ................................................................................................................................. 38
8.6 vlan hybrid ................................................................................................................................ 39
8.7 vlan native-vlan ........................................................................................................................ 39
8.8 show port vlan .......................................................................................................................... 39
8.9 interface vlanif .......................................................................................................................... 40
8.10 show interface vlanif .............................................................................................................. 40
9. MULTICAST MODULE ........................................................................................................................... 41
9.1 igmp-snooping.......................................................................................................................... 41
9.2 igmp-snooping fast-leave ......................................................................................................... 41
9.3 igmp-snooping host-aging-time ............................................................................................... 42
Page 4

9.4 igmp-snooping router-aging-time ............................................................................................ 42
9.5 igmp-snooping querier ............................................................................................................. 43
9.6 igmp-snooping querier interval ................................................................................................ 43
9.7 igmp-snooping querier max-response-time.............................................................................. 44
9.8 igmp-snooping querier source-ip .............................................................................................. 44
9.9 show igmp-snooping config ..................................................................................................... 44
9.10 show igmp-snooping group .................................................................................................... 45
9.11 multicast-vlan ......................................................................................................................... 46
9.12 show multicast-vlan ................................................................................................................ 46
9.13 port ......................................................................................................................................... 47
9.14 multicast-unknown ................................................................................................................. 47
10.RSTP ............................................................................................................................................... 47
10.1 spanning-tree ......................................................................................................................... 47
10.2 spanning-tree priority ............................................................................................................. 48
10.3 spanning-tree timer forward-delay ........................................................................................ 48
10.4 spanning-tree timer hello ....................................................................................................... 49
10.5 spanning-tree timer max-age ................................................................................................. 49
10.6 spanning-tree edged-port ....................................................................................................... 49
10.7 spanning-tree cost .................................................................................................................. 50
10.8 spanning-tree mcheck ............................................................................................................ 50
10.9 spanning-tree point-to-point .................................................................................................. 51
10.10 spanning-tree priority ........................................................................................................... 51
11.DBA PROFILE CONFIGURATION ............................................................................................................. 52
11.1 dba-profile .............................................................................................................................. 52
11.2 type......................................................................................................................................... 52
11.3 show dba-profile .................................................................................................................... 53
11.4 commit ................................................................................................................................... 54
12. ONT LINEPROFIEL CONFIGURATION ...................................................................................................... 54
12.1 ont-lineprofile ......................................................................................................................... 55
12.2 tcont ....................................................................................................................................... 55
12.3 gem add ................................................................................................................................. 56
12.4 gem delete .............................................................................................................................. 56
12.5 mapping-mode ....................................................................................................................... 56
12.6 gem mapping ......................................................................................................................... 57
12.7 show ont-lineprofile ................................................................................................................ 57
12.8 show ont-lineprofile current ................................................................................................... 58
13.ONT-SRVPROFILE CONFIGURATION ........................................................................................................ 58
13.1 ont-srvprofile .......................................................................................................................... 58
13.2 ont-port .................................................................................................................................. 59
13.3 port vlan ................................................................................................................................. 59
13.4 show ont-srvprofile ................................................................................................................. 60
13.5 show ont-srvprofile current .................................................................................................... 61
13.6 mac-learning .......................................................................................................................... 62
13.7 mac-aging .............................................................................................................................. 62
Page 5

13.8 commit ................................................................................................................................... 63
14.ONT MANAGEMENT .......................................................................................................................... 63
14.1 ont add ................................................................................................................................... 63
14.2 ont confirm ............................................................................................................................. 64
14.3 ont cancel ............................................................................................................................... 64
14.4 ont delete ............................................................................................................................... 65
14.5 ont description ........................................................................................................................ 65
14.6 ont autofind ............................................................................................................................ 66
14.7 ont active ................................................................................................................................ 66
14.8 ont deactive ............................................................................................................................ 66
14.9 ont modify .............................................................................................................................. 67
14.10 ont reboot ............................................................................................................................. 67
14.11 show ont info ........................................................................................................................ 68
14.12 show ont autofind ................................................................................................................ 70
14.13 show ont capability .............................................................................................................. 70
14.14 show ont config-capability ................................................................................................... 71
14.15 show ont optical-info ............................................................................................................ 71
14.16 show ont version .................................................................................................................. 72
15. LOG MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................................................ 72
15.1 loghost add ............................................................................................................................. 72
15.2 loghost delete ......................................................................................................................... 73
15.3 loghost activate ...................................................................................................................... 73
15.4 loghost deactivate .................................................................................................................. 74
15.5 show loghost list ..................................................................................................................... 74
15.6 syslog priority ......................................................................................................................... 74
15.7 show syslog priority severity................................................................................................... 75
15.8 backup log .............................................................................................................................. 75
15.9 terminal alarm-event severity ................................................................................................ 76
15.10 show terminal alarm-event severity ..................................................................................... 76
15.11 terminal debugging .............................................................................................................. 76
15.12 show terminal debugging ..................................................................................................... 77
16 DHCP-SNOOPING CONFIG...................................................................................................................... 77
16.1 dhcp-snooping arp-detect ...................................................................................................... 77
16.2 dhcp-snooping arp-reply-fast ................................................................................................. 78
16.3 dhcp-snooping bind-table clear .............................................................................................. 78
16.4 dhcp-snooping bind-table write-delay ................................................................................... 78
16.5 dhcp-snooping bind-table delete-time ................................................................................... 79
16.6 dhcp-snooping bind-table write-to-flash ................................................................................ 79
16.7 dhcp-snooping bind-table save-to-tftp ................................................................................... 79
16.8 show dhcp-snooping bind-table ............................................................................................. 80
16.9 dhcp-snooping binding ........................................................................................................... 80
16.10 dhcp-snooping chaddr-check ................................................................................................ 81
16.11 dhcp-snooping enable .......................................................................................................... 81
16.12 dhcp-snooping disable.......................................................................................................... 81
Page 6

16.13 dhcp-snooping limit-rate ...................................................................................................... 82
16.14 dhcp-snooping opton82 .................................................................................................... 82
16.15 dhcp-snooping option82 policy ............................................................................................ 82
16.16 (no) dhcp-snooping trust port .............................................................................................. 83
16.17 dhcp-snooping vlan ........................................................................................................ 83
16.18 show dhcp-snooping configuration ...................................................................................... 83
17 TRAFFIC PROFILE CONFIGURATION .......................................................................................................... 84
17.1 traffic-profile .......................................................................................................................... 84
17.2 modify .................................................................................................................................... 85
INCLUDING REMARKS ...................................................................................................................... 85
Page 7
The CLI manual conventions
Convention
Description
Boldface
The keywords of a command line are in boldface.
Italic
Command arguments are in italics.
[ ]
Items (keywords or arguments) in brackets [ ] are optional.
( x | y | ... )
Optional items are grouped in braces and separated by vertical
bars. One item is selected.
[ x | y | ... ]
Optional items are grouped in brackets and separated by
vertical bars. One item is selected or no item is selected.
<x-y>
One number from x to y can be selected
$
A line starting with the $ sign is comments.
Convention
Description
String with < >
It is key name. For example, <Enter>, <Tab>, <Backspace>, <a>,
<?> etc, it means to press the key button
<Key 1 + Key 2>
It means to press the key at same time. For example <
Ctrl+Alt+A> means to press “Ctrl”, “Alt”, “A” button together.
<Key 1 , Key 2>
It means to press the first button, then release, and presss the
second button. For example < Alt, F> means to press “Alt” first,
then release “Alt” buttion, and then press “A” button.
Command Conventions
The command conventions that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Keyword Operation Conventions
Symbol Conventions
The symbols that may be found in this document are defined as follows.:
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury
or broke the equipment. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards
involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing
accidents by making quick guide based on this guide.
Page 8

Indicates a hazard with a high level of risk, which if not avoided, it will result in death or
serious injury on human body.
Provides additional information to emphasize or supplement important points of the
main text.
Terms Conventions
OLT: It is the 8PON port Optical Line Terminal, included the switch and uplink port. PON: It
stand for PON protocol process module and PON port to connect with ONU side.
Prompt
CLI is case – sensitive.
Page 9

1. Configuration Mode
You can configure and manage the OLT with the CLI via a management network environment or
the console.
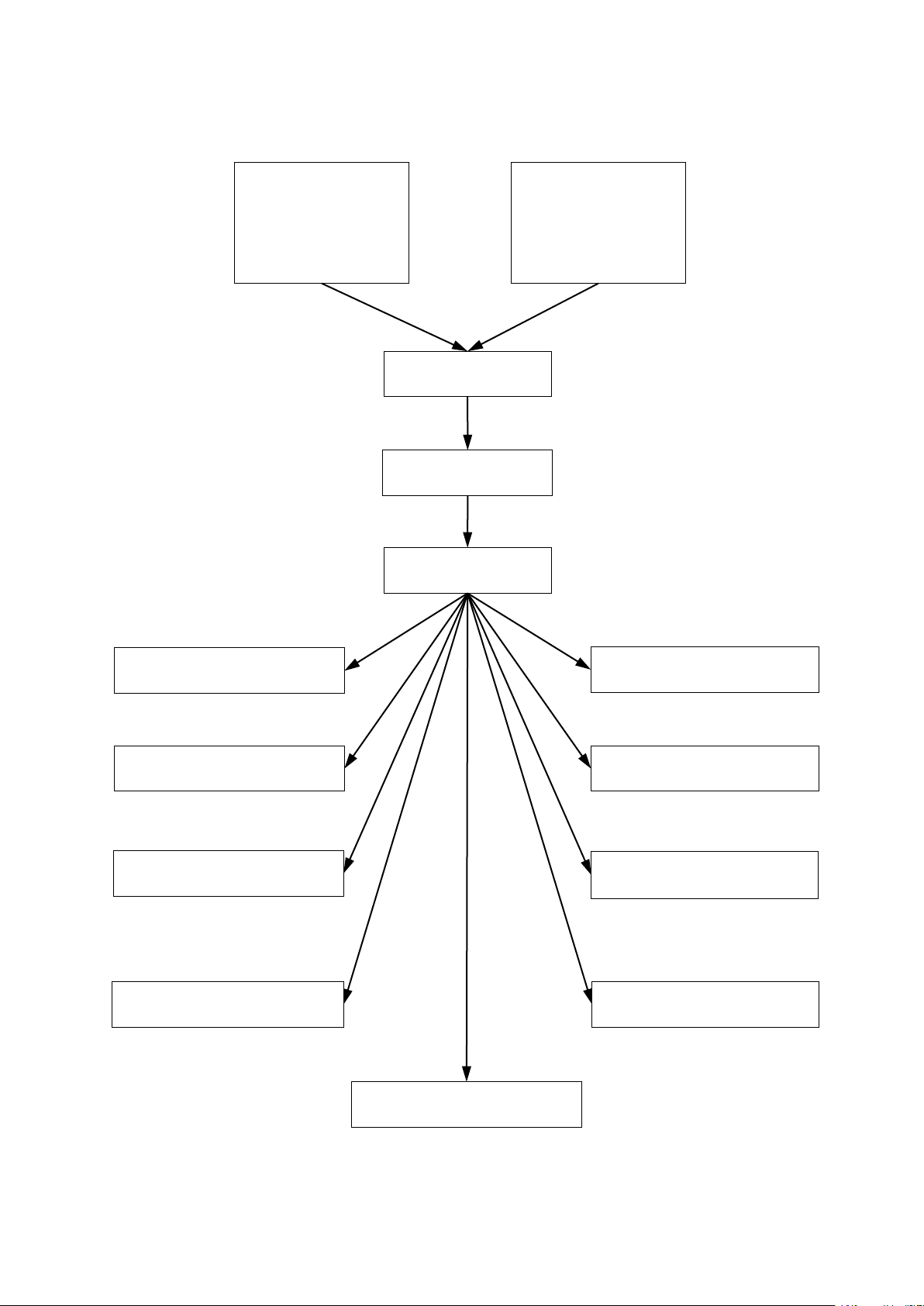
The The The CLI provides the following command modes:
User EXEC Mode, when you log in the OLT, the CLI will start with User ECEC Mode.
Ther are some basic command on this EXEC mode.
The system prompt as: OLT>
Privileged EXEC Mode, it called Enabble View Mode or Privileged EXEC Mode. You can enter
into privileged EXEC Mode with the enable comman.
The system prompt will changes from OLT> to OLT#
Configuration Mode, it called Configuration Mode or Global Configuration Mode. You can
enter in Configuration Mode with the conf terminal command.
The system prompt will changes from OLT# to : OLT(config)#
GE interface Mode, enter the interface ge command, the system prompt will be changed
from OLT(config)# to OLT(interface-ge)#
XGE interface Mode, enter the interface xge command, the system prompt will be
changed from OLT(config)# to OLT(interface-xge)#
GPON interface Mode, enter the interface gpon command, the system prompt will be
changed from OLT(config)# to OLT(interface-gpon)#
VLANIF interface Mode, enter the interface vlanif vlanID command, the system prompt
will be changed from OLT(config)# to OLT(interface-vlanif-20)#
(VLAN 20 is an example)
MGMT interface Mode, enter the interface mgmt command, the system prompt will be
changed from OLT(config)# to OLT(interface-mgmt)#
Dba-profile Mode, enter the dba-profile profile-id id command, the system prompt will be
changed from OLT(config)# to OLT(dba-profile-1)#
Lineprofile Mode, enter the ont-lineprofile profile-id id command, the system prompt
will be changed from OLT(config)# to OLT(ont-lineprofile-1)#
Srvprofile Mode, enter the ont-srvprofile profile-id id command, the system prompt will
be changed from OLT(config)# to OLT(ont-srvprofile-1)#
Multicast-vlan Mode, enter the multicast-vlan vlanid command, the system prompt will be
changed from OLT(config)# to OLT(multicast-vlan-100)#
(VLAN 100 is an example)
Page 10
Command Modes Overview
Connect
User name:
User password:
Serial interface
(Bits per second: 9600
Data bits: 8
Parity: none
Stop bits: 1
Flow control: none)
PuTTY
(telnet)
User EXEC mode
OLT>
enable
Privileged EXEC
mode
config
Dba-profile mode
OLT(dba-profile-1)#
dba-profile profile-id id
profile-id id:1-128
Gpon interface mode
OLT(interface-gpon)#
interface gpon
Mgmt interface mode
OLT(interface-mgmt)#
interface mgmt
Multicast vlan mode
OLT(multicast-vlan-100)#
multicast-vlan vlanid
vlanID:1-4094
Configuration mode
OLT(config)#
Ge interface mode
OLT(interface-ge)#
interface ge
Xge interface mode
OLT(interface-xge)#
interface xge
Vlanif interface mode
OLT(interface-vlanif-100)
interface vlanif vlanID
vlanID:1-4094
Lineprofile mode
OLT(ont-lineprofile-1)#
ont-lineprofile profile-id id
profile-id id:1-512
Srvprofile mode
OLT(ont-srvprofile-1)#
ont-srvprofile profile-id id
profile-id id:1-512
Page 11
1.1 enable
【Command】
enable
【View Mode】
User EXEC mode
【Parameter】
No
【Description】
From User EXEC mode to Privileged EXEC Mode
【Example】
OLT > enable
OLT #
【Command】
config
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode
【Parameter】
No
【Description】
From Privileged EXEC Mode to Configuration mode
【Example】
OLT # config
OLT (config)#
【Command】
interface ge
interface xge
interface gpon
interface vlanif vlanid
interface mgmt
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
Vlanid: VLAN ID. <U><1~4094>
【Description】
From Configuration mode to Interface Mode (Included XGE, GE, GPON,
VLAN If, Mgnt
【Example】
OLT(config)# interface ge
OLT(interface-ge)#
OLT(config)# interface xge
OLT(interface-xge)#
OLT(config)# interface gpon
OLT(interface-gpon)#
OLT(config)# interface vlanif 100
OLT(interface-vlanif-100)#
OLT(config)# interface mgmt
OLT(interface-mgmt)#
1.2 config
1.3 interface
Page 12
1.4 dba-profile
【Command】
dba-profile profile-id id
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
Id: Profile ID. <U><1~128>
【Description】
From Configuration mode to DBA Mode
【Example】
OLT(config)# dba-profile profile-id 1
OLT(dba-profile-1)#
【Command】
ont-lineprofile profile-id id
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
Id: Profile ID. <U><1~128>
【Description】
From Configuration mode to Ont-lineprofile Mode
【Example】
OLT(config)# ont-lineprofile profile-id 1
OLT(ont-lineprofile-1)#
【Command】
ont-srvprofile profile-id id
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
Id: Profile ID. <U><1~128>
【Description】
From Configuration mode to Ont-srvprofile Mode
【Example】
OLT(config)# ont-srvprofile profile-id 1
OLT(ont-srvprofile-1)#
【Command】
multicast-vlan vlanid
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
vlanID: <U><1~4094>
【Description】
From Configuration mode to multicast-vlan Mode
【Example】
OLT(config)# multicast-vlan 100
OLT(multicast-vlan-100)#
1.5 ont-lineprofile
1.6 ont-srvprofile
1.7 multicast-vlan
Page 13
1.8 exit
【Command】
exit
【View Mode】
Any Mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
Exit from current mode, return to up level mode
【Example】
OLT(multicast-vlan-100)# exit
OLT(config)#
【Command】
load packetfile ftp server-ip-address user-name user-password filename
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
【Parameter】
server-ip-address:ip address of the ftp Server
user-name:User Name of login ftp
user-password:Password of login ftp
filename:The filename to use for OLT upgrade
【Description】
The command is used for upgrade the OLT to new version, root account
is necessary.
【Example】
OLT Application Software Upgrade:
File name is 8pon port_FW_V1.0.2_150914_1603.img,ftp Server IP Address is 192.168.1.16,
ftp user name is amdin,password is admin. Reboot the OLT after the OLT display ‘upgrade
OK’.
OLT(config)# load packetfile ftp 192.168.1.16 admin admin 8pon port
_FW_V1.0.2_150914_1603.img
Broadcast message from root:
Upgrade is in process.
File [8pon port _FW_V1.0.2_150914_1603.img] download .......... OK
File [8pon port _FW_V1.0.2_150914_1603.img] upgrade .......... OK
OLT Kernel Software Upgrade:
Filename is 8pon port_Kernel_150914_1605.img,ftp Server IP Address is 192.168.1.16,ftp
2. Equipment upgrade
For the system enhancement and stability, new software may be released. Using this software,
OLT can be upgraded without any hardware change. You can simply upgrade your system
software with the provided functionality via CLI.
2.1 load
Page 14

User Name is amdin,password is admin. Reboot the OLT after the OLT display ‘upgrade OK’.
OLT(config)# load packetfile ftp 192.168.1.16 admin admin 8pon port_Kernel_150914
_1605.img
Broadcast message from root:
Upgrade is in process.
File [8pon port_Kernel_150914_1605.img] download ............. OK
File [8pon port_Kernel_150914_1605.img] upgrade ............. OK
【Command】
show version
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
The command is used for check information of the OLT hardware,
software and kernel.
【Example】
Show information of OLT
OLT(config)# show version
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Local Configuration Command
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
<cr> - Please press ENTER to execute command
OLT(config)# show version
Hardware version : V1.1
Firmware version : V1.0.2 (Oct 8 2015 13:35:52)
Kernel version : V539 (Mon Sep 14 16:05:47 CST 2015)
【Command】
show progress load
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
The command is used check the process of the OLT load, copy, and
backup.
【Example】
OLT(config)# show progress load
2.2 show version
2.3 show progress
Page 15

-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Transmit Protocal : FTP
FTP Server : 192.168.1.16
FTP User Name : admin
FTP Password : admin
Transmit FileName : config
Transmit Action : Put
Transmit Status : Success
Transmit Progress : 100%
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Load Operation : Null
Load FileName : config
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
reboot
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
To reboot the OLT, need root account for this operation.
【Example】
Reboot OLT
OLT# reboot
Please check whether data has saved, the unsaved data will lose if reboot syst
em. Are you sure to reboot system? (y/n)[n]:y
【Command】
ip address ip-addr ip-mask
no ip address
【View Mode】
Vlanif Mode,MGMT Mode
【Parameter】
ip-addr:IP Address
ip-mask:subnet mask
【Description】
ip address is used to configure the IP address and subnet mask of VLAN
interface, to let the realize the layer3 message transfer.
【Example】
3. Equipment management
3.1 reboot
3.2 ip address
Page 16
To configure an IP address 192.168.100.123 for VLAN 100 interface, subnet mask is
255.255.255.0。
OLT(interface-vlanif-100)# ip address 192.168.100.123 255.255.255.0
To configure an IP address 192.1.105.123 for outband management interface, subnet mask is
255.255.255.0。
OLT(interface-mgmt)# ip address 192.168.1.105 255.255.255.0
【Command】
show interface mgmt
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
It is used to check the outband management IP, MTU and MAC address.
【Example】
OLT(config)# show interface mgmt
Description : mgmt interface
The Maximum Transmit Unit is 1500 bytes
Internet Address is 192.168.1.105, netmask 255.255.255.0
Hardware address is XX:XX:XX:00:00:01
Receive 4340 packets, 4479715 bytes
Transmit 1539 packets, 101742 bytes
【Command】
show interface vlanif (all | vlan-id vlan-id)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
all: Show all VLAN interface informaion
vlan-id: Show the information of that VALN iD , from 1~4094
【Description】
It is used to check the VLAN interface information.
【Example】
Show vlanif 10 information
OLT(config)# show interface vlanif vlan-id 100
Description : vlan[100] management interface
The Maximum Transmit Unit is 1500 bytes
Internet Address is 192.168.100.123, netmask 255.255.255.0
Hardware address is XX:XX:XX:00:00:02
Recive 105 packets, 5292 bytes
3.3 show interface mgmt
3.4 show interface vlanif
Page 17
Transmit 35 packets, 1866 bytes
Show all vlanif interface information
OLT(config)# show interface vlanif all
Interface IP Address Netmask
vlanif[100] 192.168.100.123 255.255.255.0
vlanif[200] 192.168.101.123 255.255.255.0
【Command】
show device info
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
Check the information of the OLT
Device model
Device MAC address
Device serial-number
Device vendor name
【Example】
OLT(config)# show device info
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Device model : 8pon port
Device MAC address : XX:XX:XX:00:00:01
Device serial-number :
Device vendor name :
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
show fan
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
To show the status of the fan
3.5 show device info
4. Operation Status Monitor
4.1 show fan
Page 18
【Example】
OLT# show fan
---------------------------------------------
FAN[1] status: Normal (7207RPM)
FAN[2] status: Normal (7060RPM)
FAN[3] status: Normal (7265RPM)
FAN[4] status: Normal (7207RPM)
---------------------------------------------
4.2 show temperature
【Command】
show temperature
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
To display the temperature of device
【Example】
OLT(config)# show temperature
The temperature of the board: 36.5(C)
【Command】
show memory
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
To show the CPU load
【Example】
OLT# show memory
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total memory : 502MB
Free memory : 435MB
Used percent : 5%
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
show version
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
4.3 show memory
4.4 show version
Page 19

【Parameter】
None
【Description】
To show the version of hardware and software
【Example】
OLT(config)# show version
Hardware version : V1.1
Firmware version : V1.0.2 (Oct 8 2015 13:35:52)
Kernel version : V539 (Mon Sep 14 16:05:47 CST 2015)
【Command】
time time
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
time:System time, format:YYYY/MM/DD-HH:MM:SS
【Description】
To set system time and date.
【Example】
OLT(config)# time 2015/10/10-17:12:00
【Command】
show time
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
To show system time and date.
【Example】
OLT(config)# show time
Sat Jan 1 08:28:31 2000
【Command】
show uptime
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
4.5 time
4.6 show time
4.7 show uptime
Page 20

【Description】
To show system boot time and how long it have run
【Example】
OLT(config)# show uptime
System up time : 0 day 0 hour 55 minute 14 second
System boot time : Fri Oct 9 23:13:07 2015
【Command】
backup configuration ftp server-ip-address user-name user-password
filename
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
【Parameter】
server-ip-address:ip address of ftp server
user-name:ftp user name
user-password:ftp password
filename: A name for your backup file
【Description】
To back up the OLT configuration in a file
【Example】
File name is config, ftp Server IP is 192.168.1.16, ftp username is amdin, password is admin。
OLT(config)# backup configuration ftp 192.168.1.16 admin admin config
Start backup configuration files
The backup is successful
【Command】
load configuration ftp server-ip-address user-name user-password
filename
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
server-ip-address:ip address of ftp server
user-name:ftp user name
user-password:ftp password
filename: The file name of the configuration you want load to the OLT
【Description】
To load the configuration file to the OLT
【Example】
Configuration file name is ‘config’, ftp Server IP is 192.168.1.16, ftp username is amdin,
password is admin。
5. Configuration Management
5.1 backup
5.2 load configuration
Page 21

OLT(config)# load configuration ftp 192.168.1.16 admin admin config
The new configuration file will overwrite the old one
Are you sure to load new
configuration file? (y/n)[n]:y
Broadcast message from root:
Start loading configuration
The loading is successful
Note: The configuration file will take effect after reboot
【Command】
show current-config
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
To check the running configuration.
When you do some configuration, you can use this command to check if
the command have come into operation.
【Example】
【Command】
save
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
To save the current configuration.
【Example】
OLT(config)# save
Save configuration starting ...
The percentage of saved data is: 0%
The percentage of saved data is: 14%
The percentage of saved data is: 28%
The percentage of saved data is: 42%
The percentage of saved data is: 57%
The percentage of saved data is: 71%
The percentage of saved data is: 85%
The percentage of saved data is: 100%
Save configuration completed!
5.3 show current-config
5.4 save
Page 22

5.5 erase saved-config
【Command】
erase saved-config
【View Mode】
Privileged EXEC Mode, Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
To erase the configuration file, the OLT will beboot after the
configuration be delete.
【Example】
OLT# erase saved-config
This command will clear the active board data that has been saved
Please rememb
er to backup the system configuration data
Are you sure to continue? (y/n)[n]: y
Successfully restored factory configuration!
【Command】
show saved-config
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
To check the saved configuration.
【Example】
OLT(config)# show saved-config
#Saving user: root
#Saving time: 2000-01-01 05:33:19+0000
# No DBA profile configurations
# No line profile configurations
# No service profile configurations
# No ONT authenticated
interface mgmt
ip address 192.168.1.105 255.255.255.0
exit
5.6 show saved-config
Page 23
6.Account Management
【Command】
user add name group
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
name:User name for a new user
group:The group of the new user, there are root、admin and guest for
choice.
【Description】
The command is used to creates a system account. There are root、
admin and guest level for choice.
Root: Full right.
Admin: Right except reboot and upgrade.
Guest: Only check the configuration and do configuration back up.
【Example】
Create a new guest account, user name is admin, password is admin
OLT(config)# user add admin guest
Enter new password for user admin:
Confirm new password for user admin:
【Command】
user delete name
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
name:User name will be delete
【Description】
The command is used to delete a system account. The root account
can’t be deleted.
【Example】
To delete an exist account named admin.
OLT(config)# user delete admin
【Command】
user group name group
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
Name: The account need to change group.
6.1 user add
6.2 user delete
6.3 user group
Page 24

group:The group for that account
【Description】
The command is used to change the account to another group.
【Example】
Change xxxxxx accout to admin group.
OLT(config)# user group XXXXX admin
【Command】
user password name
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
Name: The accounat need to change password.
【Description】
The command is used to change the account password
【Example】
Change account admin password to admin
OLT(config)# user password admin
Enter new password for user admin:
Confirm new password for user admin:
【Command】
show user
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
The command is used to show all account
【Example】
OLT(config)# show user
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
User Group
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
root root
admin admin
admin admin
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
6.4 user password
6.5 show user
7. Port Configuration
7.1 shutdown
Page 25

【Command】
shutdown port-list
【View Mode】
GE Mode, GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-list:The port number that you want to configure.
【Description】
The command is used to shut down the specified port
【Example】
Shut down the ge1 port
OLT(interface-ge)# shutdown 1
【Command】
no shutdown port-list
【View Mode】
GE Mode, GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-list: The port number that you want to configure.
【Description】
The command is used to open the specified port
【Example】
Enable the ge1 port
OLT(interface-ge)# no shutdown 1
【Command】
show port state all
show port state port-id
【View Mode】
GE Mode, GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:Specified port number
【Description】
The command is used to show port information of the specified port.
【Example】
Check the information of the OLT ge1
OLT(interface-ge)# show port state 1
ge1 information summary :
current port state : enable
current link state : DOWN
The Maximum Transmit Unit is 1500
Link speed is autonegotiation(1000 MBps)
link duplex is autonegotiation(FULL)
Flow-control is supported
broadcasts stormcontrol 0(pps)
7.2 no shutdown
7.3 show port state
Page 26

multicasts stormcontrol 0(pps)
unicasts stormcontrol 0(pps)
native-vlan is 300
Port link-type: Access
Tagged VLAN ID : none
Untagged VLAN ID :
300,
statistics from last clean(maybe the statistics would overflow):
Input(total):0 bytes
Input:unicast 0, broadcasts 0, multicasts 0, errors 0
Output(total):0 bytes
Output:unicast 0, broadcasts 0, multicasts 0, errors 0
Check the all GE port
OLT(interface-ge)# show port state all
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port Optic Pvid Auto Speed Dup Flow Learn Enable Link Mtu
Status Nego /Mbps lex Ctrl
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
ge1 normal 100 enable 1000 full off enable enable on 1500
ge2 normal 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
ge3 normal 1 enable 1000 full off enable enable on 1500
ge4 absence 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
ge5 absence 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
ge6 absence 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
ge7 absence 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
ge8 absence 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
ge9 - 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
ge10 - 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
ge11 - 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
ge12 - 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
ge13 - 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
ge14 - 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
ge15 - 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
ge16 - 1 enable 1000 full on enable enable off 1500
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 27

7.4 show port ddm-info
【Command】
show port ddm-info port-id
【View Mode】
GPON Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:Specified port number
【Description】
The command is used to show Digital Diagnostic Monitoring of specified
PON port. You can use the command to get the PON module
information of temperature, voltge, bias-current, Tx power, Rx power.
【Example】
Check the information of PON1
OLT(interface-gpon)# show port ddm-info 1
Temperature(C) : 44.6
Supply Voltage(V) : 3.36
TX Bias current(mA) : 13
TX power(dBm) : 5.29
RX power(dBm) : -40.00
【Command】
show port vlan port-id
【View Mode】
GE Mode, GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:Specified port number
【Description】
The command is used to show VLAN information.
【Example】
Check VLAN configuration of ge1
OLT(interface-ge)# show port vlan 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port: ge1 Native-Vlan: 1 Mode: Access
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tagged-Vlan:
-
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Untagged-Vlan:
1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
7.5 show port vlan
Page 28

7.6 auto-neg
【Command】
auto-neg port-list switch
【View Mode】
GE Mode
【Parameter】
port-list:The port list that want to configure
switch: To enable or disable the port status of Auto-Negotiation
【Description】
To enable or disable the port status of Auto-Negotiation.
【Example】
OLT(interface-ge)# auto-neg 1 enable
【Command】
duplex port-list duplex
【View Mode】
GE Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-list:The port list that want to configure
duplex: Half-duplex or full-duplex
【Description】
To enable or disable the port half Ethernet operates in either
half-duplex or full mode
【Example】
OLT(interface-ge)# duplex 1 full
【Command】
speed port-list speed
【View Mode】
GE Mode
【Parameter】
port-list:The port list that want to configure
speed: Sets the transmit rate, 10/100/1000 Mbps.
【Description】
To set the transmit rate of an Ethernet port
【Example】
Set ge1 port transmit rate to 100Mbit/s
OLT(interface-ge)# speed 1 100
【Command】
flow-control port-list
no flow-control port-list
7.7 duplex
7.8 speed
7.9 flow-control
Page 29

【View Mode】
GE Mode, GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-list:The port list that want to configure
【Description】
To enable or disable flow control on specified port
【Example】
OLT(interface-gpon)# flow-control 1
【Command】
mirror src-port src-port dst-port (ge|xge) port-id direction
no mirror src-port src-port direction
【View Mode】
GE Mode, GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
src-port:Here is the designates mirrored port, it is source port number
port-id:port-id here is the monitor port number
direction: ingress/ egress / all , it is to configure what direction traffic
need to monitor.
Ingress: Copy the ingress traffic of src-port to the dst-port .
Egress: Copy the egress traffic of src-port to the dst-port .
All: Copy the ingress traffic of src-port to the dst-port .
【Description】
Port mirroring is the function of monitoring a designated port. Here,
one port to monitor is called mirrored (src-port). Traffic transmitted
from mirrored port are copied and sent to monitor port (dst-port) so
that user can monitor network traffic.
【Example】
Copy the ingress traffic of ge1 to the ge2
OLT(interface-ge)# mirror src-port 1 dst-port ge 2 ingress
【Command】
show mirror
【View Mode】
GE Mode, GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
Shows a configured port mirroring
【Example】
To display a configured port mirroring on GE Mode
OLT(interface-ge)# show mirror
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Admin : Enable
7.10 mirror
7.11 show mirror
Page 30

Destnation Port : ge2
Source Ingress Ports : ge1
Source Egress Ports : ge5
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
mtu port-list mtu-value
no mtu port-list
【View Mode】
GE Mode, GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-list :To configure mtu on specified port
mtu-value:mtu value is 328~16356
【Description】
MTU is the largest packet size that can be sent over a network.
Command mtu is to set the MTU size, the default is 1500.
Command no mtu is to set the MTU size to default size.
【Example】
Set ge1 port mtu size to 2000
OLT(interface-ge)# mtu 1 2000
【Command】
reset port statistic port-id
【View Mode】
GE Mode, GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-id :The specified port you want to clean the history statistic
information
【Description】
The command is used to clean the history statistic information
【Example】
Clean the history statistic information of ge1
OLT(interface-ge)# reset port statistic 1
【Command】
show port statistics port-id
【View Mode】
GE Mode, GPON Mode, XGE Mode
7.12 mtu
7.13 reset port statistic
7.14 show port statistics
Page 31
【Parameter】
port-id :The specified port you want to check statistic information
【Description】
It is to show traffic statistics of the port. It is useful for the
troubleshooting. Total(bytes) is the total traffic , Uncast(pkts) is unicast
traffic, Bcast(pkts) is the brocast traffic, Mcast(pkts) is multicast traffic,
Err(pkts) is the error traffic.
【Example】
Check the statics information of port ge9
OLT(interface-ge)# show port statistics 9
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Direction Total Uncast Bcast Mcast Err
(bytes) (pkts) (pkts) (pkts) (pkts)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
RX 320734 454 2215 1212 0
TX 35232 456 0 0 0
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
show mac-address all
show mac-address black-hole
show mac-address dynamic
show mac-address port ge port-id
show mac-address port xge port-id
show mac-address port gpon port-id
show mac-address static
show mac-address timer
show mac-address vlan vlan-id
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
all:To check all the MAC information in the MAC table
black-hole:To check the black-hole MAC information in the MAC table
dynamic:To check the dymamic MAC information in the MAC table
port port-id :To check the MAC information at specified port in the
MAC table
static:To check the static MAC information in the MAC table
timer:To check ageing time of the MAC
vlan vlan-id:To check the MAC information of specified vlan id.
【Description】
To show the MAC table
【Example】
To check the MAC information at ge1 port
OLT(config)# show mac-address port ge 1
7.15 show mac-address
Page 32

-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total: 1
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
MAC VLAN Port MAC-Type
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
XX:XX:XX:00:1B:24 1 ge1 static
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
To check the static MAC information in the MAC table
OLT(config)# show mac-address static
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total: 2
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
MAC VLAN Port MAC-Type
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
XX:XX:XX:00:E2:3B 100 ge1 static
XX:XX:XX:48:97:0A 100 ge1 static
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
show location mac-address
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
mac-address:MAC address
【Description】
To locate the port of the specified MAC
【Example】
To display the port information of the MAC 3C:97:0E:FD:0C:69
OLT(config)# show location 3C:97:0E:FD:0C:69
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
MAC VLAN Port MAC-Type
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
3C:97:0E:FD:0C:69 100 ge9 dynamic
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
7.16 show location
7.17 mac-address limit port
Page 33

【Command】
mac-address limit port ge port-list count
mac-address limit port gpon port-list count
mac-address limit port xge port-list count
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
port-list:The port you want to set
count:The number of MAC
【Description】
Limits the number of MAC address, if the MAC address over the limit
then discard it.
【Example】
Limits the max MAC on the ge1 port to the 100
OLT(config)# mac-address limit port ge 1 100
【Command】
mac-address static port (ge | gpon | xge) port-id vlan vlanid
mac-address
no mac-address static port (ge | gpon | xge) port-id vlan vlanid
mac-address
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
port-list:The port you want to set。
vlan-id:The corresponding vlan id of the static MAC
mac-address:static MAC address
【Description】
To set a static address to the specified port and VLAN
【Example】
Set xx:xx:xx:00:12:9c at OLT ge1 poet, vlanis 100
OLT(config)# mac-address static port ge 1 vlan 100 xx:xx:xx:00:12:9c
【Command】
mac-address timer aging-time
mac-address timer no-aging
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
aging-time
:
Specifies MAC aging time, the range is from 10 to
1000000S
【Description】
It is used to manage the aging time of the MAC table. The aging timer is
used by the OLT to delete inactive dynamic MAC addresses from the
7.18 mac-address static
7.19 mac-address timer
Page 34

MAC address table, to prevent the table from becoming full of inactive
addresses. An address is considered inactive if no packets are sent to or
received from the corresponding node for the duration of the timer.
no-aging:Set to no aging time Setting the aging timer to none disables
the timer. No dynamic MAC addresses are aged out, and the table stops
learning new addresses after reaching its maximum capacity.
【Example】
This example shows how to set the aging time for entries in the MAC address table to 60
seconds
OLT(config)# mac-address timer 60
【Command】
mac-address learning port ge port-list switch
mac-address learning port gpon port-list switch
mac-address learning port xge port-list switch
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
port-list: Interface to set mac-address learning
switch: enable or disable MAC address learning
【Description】
To enable or disable MAC address learning on an interface.
【Example】
This example shows how to enable MAC address learning on OLT ge1
OLT(config)# mac-address learning port ge 1 enable
【Command】
mac-address black-hole vlan-id mac-address
no mac-address black-hole vlan-id mac-address
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
vlan-id:The vlan id of the black-hole MAC
mac-address:Black-hole MAC address
【Description】
To set a black-hole MAC address table, if the source MAC or destination
MAC address of packet matched with the black-hole MAC address, the
7.20 mac-address learning
7.21 mac-address black-hole
Page 35

OLT will discard the packet.
【Example】
Add a black-hole MAC address item, black-hole MAC is xx:xx:xx:a5:39:a2, the VLAN is 50
OLT(config)# mac-address black-hole 50 xx:xx:xx:a5:39:a2
【Command】
mac-address flush all
mac-address flush black-hole
mac-address flush dynamic
mac-address flush port ge port-id type
mac-address flush port gpon port-id type
mac-address flush port xge port-id type
mac-address flush static
mac-address flush vlan vlan-id type
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
port-id:To set the specified port of MAC flush
type:MAC address type
vlan-id:To clean the MAC address of the specified vlan id
【Description】
It is used to clean the all mac address or specified type mac address
【Example】
To clean all dynamic MAC address at ge1 port
OLT(config)# mac-address flush port ge 1 dynamic
【Command】
traffic-suppress port-id broadcast (kbps| pps) value
traffic-suppress port-id multicast (kbps| pps) value
traffic-suppress port-id unicast (kbps| pps) value
no traffic-suppress port-id (unicast | multicast | broadcast) (kbps|
pps) value
【View Mode】
GE Mode, GPON Mode, Xge Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:Specified port to enable traffic suppress 。
broadcast: To control the broadcast traffic
multicast:To control the multicast traffic
7.22 mac-address flush
7.23 traffic-suppress
Page 36

unicast:To control the unicast traffic
kbps value: Specifies the maximum number of ingress packets per
second of the designated type the port will forward. The range is 1 to
1000000, unit is kbps.
pps value: Specifies the maximum number of ingress packets per second
of the designated type the port will forward. The range is 1 to 1488100,
unit is pps.
【Description】
Allows you to monitor the levels of the incoming broadcast, multicast,
and unicast traffic. The traffic storm control circuitry monitors packets
that pass from a Layer 2 interface. The circuitry determines if the packet
is unicast or broadcast, tracks the current count of packets within the
1-second interval, and filters out subsequent packets when a threshold
is reached to avoid the netwok blocking.
no traffic-suppress is use to shut down this function.
【Example】
To set the ge1 port broadcast threshold to 1024kbps
OLT(interface-ge)# traffic-suppress 1 broadcast kbps 1024
To control the ge1 multicast traffic to 2048bps
OLT(interface-ge)# traffic-suppress 1 multicast kbps 2048
To control the ge1 unknow unicast traffic to 10240kbps
OLT(interface-ge)# traffic-suppress 1 unicast kbps 10240
【Command】
vlan vlan-list
no vlan vlan-list
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
vlan-list: Creat VLAN, specify a VID number, which has a range of 1 to
4094.
【Description】
vlan command is used to creates one new VLAN or a group of VLAN
【Example】
Creats vlan 100
8. VLAN
8.1 vlan
Page 37

OLT(config)# vlan 100
Creats vlan 200-220
OLT(config)# vlan 200-220
【Command】
show vlan all
show vlan vlan-id
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
all:Specifies all the VLANs on the OLT to display
vlan-id:Specifies the VID of the VLAN you want to display
【Description】
To display all exist VLAN or one specified VLAN information, such as port
and tagged/untagged
【Example】
Displays vlan 100 information
OLT(config)# show vlan 100
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
VLAN Tagged-Ports Untagged-Ports
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
100 p1-p8 xge1
【Command】
vlan mode port-list mode
【View Mode】
GE Mode,GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-list:Specifies port to set VLAN mode
mode:vlan mod, there are access、hybrid、trunk model.
【Description】
access mode: Only untagged traffic will enter the port and be added the
native vlan, other traffic will discard. Remove any VLAN information
from the frame before it is sent out.
Trunk mode: Trunk port receive packet and judge whether there is VLAN
information belong the VLAN table of the port, if it is forward, if not
belong to discard it. The trunk port to send packet, it comparison of
VLAN information with VLAN table, if it is directly transmit, if not equal
to discard it.
Hybrid Mode: receive packet and judge whether there is VLAN
information belong the VLAN table of the port, if it is forward, if not
8.2 show vlan
8.3 vlan mode
Page 38

belon to discard it. The hybrid port to send packet, it can set tagged or
untagged. if untag is the stripping VLAN information, send, if tag is
directly send.
【Example】
Set the OLT ge1 to trunk mode
OLT(interface-ge)# vlan mode 1 trunk
【Command】
vlan access port-list vlan-id
【View Mode】
GE Mode,GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-list:Specifies port to set VLAN
vlan-id:Specifies VLAN ID
【Description】
To add access vlan at specified port, the vlan should have created
before, and the poer is on access mode.
【Example】
To add VLAN 100 at ge1 port
OLT(interface-ge)# vlan access 1 100
【Command】
vlan trunk port-list allowed vlan-list
no vlan trunk port-list allowed vlan-list
【View Mode】
GE Mode,GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-list:Specifies port to set VLAN
vlan-id:Specifies VLAN ID
【Description】
To add trunk vlan at specified port, the vlan should have created before,
and the port is on trunk mode.
【Example】
Add trunk vlan 100,200,300 to ge1
OLT(interface-ge)# vlan trunk 1 allowed 100,200,300
ge1 : trunk allowed vlan:
Fail: 0, Success: 3
8.4 vlan access
8.5 vlan trunk
Page 39

8.6 vlan hybrid
【Command】
vlan hybrid port-list (tagged | untagged) vlan-list
no vlan hybrid port-list (tagged | untagged) vlan-list
【View Mode】
GE Mode,GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-list:Specifies port to set VLAN
vlan-list:Specifies VLAN ID list
tagged | untagged –To set the port send packet with tag or without tag.
【Description】
To add hybrid vlan at specified port, the vlan should have created
before, and the port is on hybrid mode.
【Example】
To add ge1 hybrid vlan 100 in tagged and vlan1000 in untagged at ge1 port.
OLT(interface-ge)# vlan hybrid 1 tagged 100
ge1 : hybrid add tag vlan:
Fail: 0, Success: 1
OLT(interface-ge)# vlan hybrid 1 untagged 1000
ge1 : hybrid add untag vlan:
Fail: 0, Success: 1
【Command】
vlan native-vlan port-list vlan-id
【View Mode】
GE Mode,GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-list:Specifies port to set VLAN
vlan-id:Specifies VLAN ID
【Description】
To add native vlan at specified port, the packet ingress will add the
native vlan, for the exgress packed, if the vlan information equal the
native vlan id it will strip the tag, if not, the packet will discard.
【Example】
To set the ge1 port in native vlan 100
OLT(interface-ge)# vlan native-vlan 1 100
【Command】
show port vlan port-id
【View Mode】
GE Mode,GPON Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:Specifies port to set VLAN
8.7 vlan native-vlan
8.8 show port vlan
Page 40

【Description】
To show the port vlan information
【Example】
OLT(interface-ge)# show port vlan 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port: ge1 Native-Vlan: 100 Mode: Hybrid
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tagged-Vlan:
-
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Untagged-Vlan:
1,100,1000
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
interface vlanif vlan-id
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
vlan-id:VLAN ID, specifies a VLAN
【Description】
To create VLANIF interface and enter the VLANIF Mode. You can set the
IP address to this virtual level 3 interface.
【Example】
When you have created a VLAN 100, you can create a VLANIF interface for vlan 100, and
enter the interface to configure it.
OLT(config)# interface vlanif 100
OLT(interface-vlanif-100)#
【Command】
show interface vlanif (all | vlan-id vlan-id)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
vlan-id:VLAN ID, specifies a VLAN
【Description】
To check VLANIF interface information.
【Example】
Displays vlanif interface information of vlan 100
OLT(config)# show interface vlanif vlan-id 100
Description : vlan[100] management interface
The Maximum Transmit Unit is 1500 bytes
8.9 interface vlanif
8.10 show interface vlanif
Page 41

Internet Address is 192.168.100.123, netmask 255.255.255.0
Hardware address is XX:XX:XX:00:00:02
Recive 105 packets, 5292 bytes
Transmit 35 packets, 1866 bytes
Display all information of the vlanif
OLT(config)# show interface vlanif all
Interface IP Address Netmask
vlanif[100] 192.168.100.123 255.255.255.0
vlanif[200] 192.168.101.123 255.255.255.0
【Command】
igmp-snooping enable
igmp-snooping disable
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
enable:To enable the OLT’s igmp-snooping function
disable:To disable the OLT’s igmp-snooping function
【Description】
IGMP Snooping(Internet Group Management Protocol Snooping. IGMP
snooping allows the OLT to control the flow of multicast packets from its
ports. It enables the OLT to forward packets of multicast groups to only
ports that have host nodes that want to join the multicast groups.
【Example】
Enables igmp-snooping
OLT(config)# igmp-snooping enable
【Command】
igmp-snooping fast-leave switch
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
switch:igmp-snooping fast leave function on or off, on means enable,
off means disable.
【Description】
on:To enable igmp-snooping fast leave function. When ONT received a
9. Multicast Module
9.1 igmp-snooping
9.2 igmp-snooping fast-leave
Page 42
IGMP leave message, it will update the multicast forwarding entry table
immediately. It do not have query process. If you want set a leave
latency as 0, you can enable it.
off: To disable igmp-snooping fast leave function. ONT will sent
group-specific query message upon receipt message from a host. If ONT
do not receive the report from host, ONT judge the host offline and
update the multicast forwarding table.
【Example】
To enable OLTigmp-snooping fast-leave
OLT(config)# igmp-snooping fast-leave on
【Command】
igmp-snooping host-aging-time time
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
time
:
To specify the aging time for multicast group member
【Description】
Use the igmp-snooping host-aging-time command to configure the port
aging time of the multicast group members.
This command is used to set the aging time of the multicast group
member so that the refresh frequency can be controlled. When the
group members change frequently, the aging time should be
comparatively short, and vice versa.
【Example】
Set the aging time to 300 seconds.
OLT(config)# igmp-snooping host-aging-time 300
【Command】
igmp-snooping router-aging-time time
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
time
:
To specify the aging time for multicast router port
【Description】
Use the igmp-snooping router-aging-time command to configure the
port aging time of the multicast group router.
This command is used to set the aging time of the multicast group
router. When the OLT do not receiver IGMP General Query packet or
PIM Hello packet of some port, the port will delete them form the table.
9.3 igmp-snooping host-aging-time
9.4 igmp-snooping router-aging-time
Page 43

【Example】
Set the multicast router port aging time to 300 seconds.
OLT(config)# igmp-snooping router-aging-time 300
【Command】
igmp-snooping querier enable
igmp-snooping querier disable
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
enable:To active igmp snooping querier
disable:To deactivate igmp snooping querier
【Description】
Multicast routers are an essential part of IP multicasting. They send out
queries to the network nodes to determine group memberships, route
the multicast packets across networks, and maintain lists of the
multicast groups and the ports where group members are located.
IGMP snooping querier can be used in place of multicast routers in
situations where IP multicasting is restricted to a single LAN, without
the need for routing. This feature enables the OLT to mimic a multicast
router by sending out general IGMP queries to the host nodes.
【Example】
OLT(config)# igmp-snooping querier enable
【Command】
igmp-snooping querier interval time
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
interval time:Specifies an IGMP snooping query interval in the unit of
second
【Description】
The IGMP snooping querier periodically sends General Query messages
to trigger memebership report messages from a host that wants to
receiver IP multicast traffic.
【Example】
Set the igmp snooping query interval time to 60 second
OLT(config)# igmp-snooping querier interval 60
9.5 igmp-snooping querier
9.6 igmp-snooping querier interval
Page 44

9.7 igmp-snooping querier max-response-time
【Command】
igmp-snooping querier max-response-time time
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
max-response-time time:Specifices a maximum response time
【Description】
Membership query messages include the maximum response time field.
This field specifes the maximum time allowed before sending a
responding report. The maximum query response time allows a router
to quickly detect that there are no more hosts interested in receiving
multicast traffic. To get the network to converge faster, use the
command and set a low response time value, so that the clients will
respond immediately with a report as a response to the IGMP Querie.
【Example】
Set the igmp snooping query response time to 10 second
OLT(config)# igmp-snooping querier max-response-time 10
【Command】
igmp-snooping querier source-ip source_ip
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
source_ip:Specified an IP address as the source IP address to be carried
in the IGMP queries sent by the device
【Description】
Use the igmp-snooping general-query source-ip ip-address command to
specify an IP address as the source IP address of IGMP queries. When a
level 2 device received the IGMP Query message from souce ip 0.0.0.0 ,
it will not set it to a dynamic router port, that will influence the creating
multicast forwarding table and cause the traffic blocking. If an IP
address is assigned to a VLAN, which has IGMP querier enabled on it,
then the IGMP Snooping querier uses the VLAN’s IP address as the
Source IP Address in IGMP queries, it will avoid the 0.0.0.0 issue.
【Example】
To configure the igmp snooping querier ip to 192.168.1.1
OLT(config)# igmp-snooping querier source-ip 192.168.1.1
【Command】
show igmp-snooping config
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
9.8 igmp-snooping querier source-ip
9.9 show igmp-snooping config
Page 45

【Parameter】
None
【Description】
To display the igmp snooping information, include igmp snooping status,
fast leave status, aging time, igmp snooping querier status, response
time, interval time and source ip
【Example】
Check the igmp snooping configuration.
OLT(config)# show igmp-snooping config
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Snooping switch : Disable
Fast leave : Off
Host aging time(s) : 260
Router aging time(s) : 130
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Query switch : Enable
Max response time(s) : 10
Query interval(s) : 60
Source ip of the query : 192.168.1.1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
show igmp-snooping group (all | ip-address ip-address | static | vlan
vlan-id)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
all : all multicast group information
ip-address ip-address: Specifies a multicast source by its IP address.
static:
vlan vlan-id: Specifies a multicast VLAN
【Description】
To display the multicast group information
【Example】
Check OLT multicast group information
OLT(config)# show igmp-snooping group all
Total Groups:2
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Index:1
IP address:224.2.2.2
Mac address:xx:xx:xx:02:02:02
vlan :100
RouterPort: NONE
MemberPort: ge13
9.10 show igmp-snooping group
Page 46

Index:2
IP address:239.255.255.250
Mac address:xx:xx:xx:7f:ff:fa
vlan :100
RouterPort: NONE
MemberPort: ge13
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
multicast-vlan vlan-id
no multicast-vlan vlan-id
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
vlan vlan-id: Specifies a multicast VLAN, before you use a VLAN ID for
multicast vlan you should creat that VLAN first.
【Description】
Use multicast-vlan to configure a multicast VLAN and enter multicast
VLAN view mode. The multicast Vlan is one of the application of VLAN,
you can configure the multicast parameter under this mode.
【Example】
Configures VLAN 100 as a multicast VLAN and enter its view
OLT(config)# multicast-vlan 100
OLT(multicast-vlan-100)#
【Command】
show multicast-vlan (all | vlan-id vlan-id)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
vlan vlan-id: Specifies a multicast VLAN
all:To show information of all multicast VLAN
【Description】
Use the command to display information about multicast VLAN.
【Example】
9.11 multicast-vlan
9.12 show multicast-vlan
Page 47

【Command】
port (ge | gpon | xge)port-id
no port (ge | gpon | xge)port-id
【View Mode】
Multicast-vlan Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:Specified port to be added to the multicast VLAN
【Description】
Uses the command to add the OLT port to the specified multicast VLAN.
no port is used for delete port from multicast vlan
【Example】
Adds ge1 port to multicast vlan100
OLT(multicast-vlan-100)# port ge 1
【Command】
multicast-unknown policy (discard | transparent)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
discard:dropping unknown multicast data
transparent:transparent unknown multicast data。
【Description】
Uses the command to control unknow , if the multicast data is useful
unknow traffic then set transparent, if not set discard.
【Example】
Configure the unknow multicast data transparent
OLT(config)# multicast-unknown policy transparent
【Command】
spanning-tree (enable | disable)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
enable:Active the STP protocol
disable:Deactive the STP protocol
9.13 port
9.14 multicast-unknown
10.RSTP
10.1 spanning-tree
Page 48

【Description】
The command is used to active/deactive global STP, only when STP have
enabled you can configure the stp function
【Example】
Active the STP function
OLT(config)# spanning-tree enable
【Command】
spanning-tree priority priority
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
Priority: Specifies a priority number for the switch. The range is 0 to
61440, in increments of 4096, more small number gets more hight
priority.
【Description】
Use this command to assign the switch a priority number. The device
that has the lowest priority number in the spanning tree can becomes
the root bridge. If two or more devices have the same priority value, the
device with the numerically lowest MAC address becomes the root
bridge. The range is 0 to 61,440, in increments of 4,096. The priority
value can be set only in increments of 4,096.
【Example】
This example sets the priority value of the OLT to 4096
OLT(config)# spanning-tree priority 4096
【Command】
spanning-tree timer forward-delay time
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
time:forward Delay in second, <4~30>
【Description】
Use this command to set the forward delay value. The forward delay
sets the time (in seconds) to control how fast a port changes its
spanning tree state when moving towards the forwarding state. This
value determines the maximum time taken to transition from discarding
to learning and from learning to forwarding. The range is 4 to 30
second.
【Example】
Sets OLT forward-delay time to 20 second
OLT(config)# spanning-tree timer forward-delay 20
10.2 spanning-tree priority
10.3 spanning-tree timer forward-delay
Page 49

【Command】
spanning-tree timer hello time
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
time:hello time interval in second, range 1 to 2 second
【Description】
Use this command to set the hello-time. This sets the time in seconds
between the transmission of switch spanning tree configuration
information.
【Example】
Sets OLT hello time to 1 second
OLT(config)# spanning-tree timer hello 1
【Command】
spanning-tree timer max-age time
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
time: <6-40> The maximum time, in seconds.
【Description】
Use this command to set the max-age. This sets the maximum age, in
seconds, that dynamic spanning tree configuration information is stored
in the switch before it is discarded. Range is 6 to 40 second.
【Example】
Max-age is the maximum time in seconds for which a message is considered valid.
Configure this value sufficiently high, so that a frame generated by the root bridge can be
propagated to the leaf nodes without exceeding the max-age.Sets OLT hello time to 1 S
The forward delay, max-age, and hello time parameters should be set according to the
following formulae, as specified in IEEE Standard 802.1d:
2 x (forward delay - 1.0 seconds) >= max-age
max-age >= 2 x (hello time + 1.0 seconds)
Example is to set the max-age to 6 second.
OLT(config)# spanning-tree timer max-age 6
【Command】
spanning-tree edged-port port-id switch
10.4 spanning-tree timer hello
10.5 spanning-tree timer max-age
10.6 spanning-tree edged-port
Page 50

【View Mode】
GE Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:Specifies the port id
switch:To configure the port as a edged-port or not. Value:enable、
disable。
【Description】
Use this command to set a port as an edge-port.
Use this command on a switch port connected to a LAN that has no
other bridges attached. If a BPDU is received on the port that indicates
that another bridge is connected to the LAN, then the port is no longer
treated as an edge port.
【Example】
Sets ge 1 as a edged-port
OLT(interface-ge)# spanning-tree edged-port 1 enable
【Command】
spanning-tree cost port-id cost
【View Mode】
GE Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:Specifies the port id
cost:More lower the path cost value, more good of the network
connection. Range is 1 to 200000000。
【Description】
Use this command to set the cost of a path for the specified port. This
value then combines with others along the path to the root bridge in
order to determine the total cost path value from the particular port, to
the root bridge. The lower the numeric value, the higher the priority of
the path. This applies when the port is the root port.
【Example】
Sets ge 1 port path-cost to 500
OLT(interface-ge)# spanning-tree cost 1 500
【Command】
spanning-tree mcheck port-id switch
【View Mode】
GE Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:Specifies the port id
10.7 spanning-tree cost
10.8 spanning-tree mcheck
Page 51

switch: value is enable、disable, to active or deactive the mcheck
【Description】
Use this command to set the port to run mcheck operation. If the port
connect with the STP device, the port will move to STP compatible
mode.
【Example】
To active the mcheck mode of the ge1 port
OLT(interface-ge)# spanning-tree mcheck 1 enable
【Command】
spanning-tree point-to-point port-id mode
【View Mode】
GE Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:Specifies the port id
mode:Sets the mode of RSTP, value is true, false, auto
【Description】
Use this command to set the specified port is a point to point link or
not.
【Example】
Set1 ge 1 port point-to-point to true
OLT(interface-ge)# spanning-tree point-to-point 1 true
【Command】
spanning-tree priority port-id priority
【View Mode】
GE Mode, XGE Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:Specifies the port id
priority:<0-240>, in increments of 16. The port priority, which will be
rounded down to a multiple of 16.
【Description】
Use this command to set the port priority for specified port. A lower
priority value indicates a greater likelihood of the port becoming part of
the active topology.
【Example】
Configure ge1 port the port priority to 16
OLT(interface-ge)# spanning-tree priority 1 16
10.9 spanning-tree point-to-point
10.10 spanning-tree priority
Page 52
11.DBA Profile Configuration
【Command】
dba-profile (profile-id profile-id | profile-name profile-name)
no dba-profile (profile-id profile-id | profile-name profile-name)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
profile-id profile-id:Id for the DBA profile, the system will automatically
assigned a id to the profile with name “dba-profile_x” if you do not give
a id, “x” is the sequence number as id.
【Description】
Use this command to creat DBA(Dynamic Bandwidth Assignment)
profile. OLT uses the DBA for the upstream bandwidth allocation.
There are some default profiles. If the default profile can not meet
business requirement, you can creat a DBA profile based on your
business.
If you need to delete a DBA profile , use no dba-profile command.
【Example】
To creat a DBA profile with ID 10 at default name rule
OLT(config)# dba-profile profile-id 10
【Command】
type1 fix fix
type2 assure assure
type3 assure assure max max
type4 max max
type5 fix fix assure assure max max
【View Mode】
dba-profile Mode
【Parameter】
The system supports five DBA profile types, namely, type1 (fixed
bandwidth), type2 (assured bandwidth), type3 (assured
bandwidth+maximum bandwidth), type4 (maximum bandwidth), and
type5 (fixed bandwidth+assured bandwidth+maximum bandwidth).
type1 This fixed bandwidth is provisioned for the specified ONU or
business, the bandwidth is occupied fully even no business in use, the
bandwith can not use by other ONU. It suit for hight priority and
services sensitive to delay business, such as TDM and VOIP. 。
type2 This assured bandwidth is guaranteed bandwidth type to assure
the ONU can get bandwidth it need. When the ONU do not need using
such more bandwitdth it will release and use by other ONU business. It
is dynamic allocation. It mainly used for video services and data serves
11.1 dba-profile
11.2 type
Page 53

of higher priorities.
type3 This is combination of assured bandwidth and maximum
bandwidth. Users are allowed to preempt the bandwidth on condition
that the users' assured bandwidth is guaranteed. However, the total
bandwidth cannot exceed the maximum bandwidth. It mainly used for
Voip and IPTV business.
type4 This is maximum bandwidth type and mainly used for data
service, such as Internet and service of low priority. It have not
bandwidth guarantee but it has eligibility in best effort bandwidth
sharing.
type5 This is mixed type. It reserved fix bandwidth to monopolize it. It
also assured bandwidth and maximum bandwidth.
fix fix It is the fix bandwidth. It is provisioned for user. Other user can
not use them.
assure assure It is guranted bandwidth.
max max It is maximum bandwidth
The maximum bandwidth value should be same or more than the sum
of a fixed bandwidth and assured bandwidth value.
Maximumu BW>= fixed B/W + assured B/W
【Description】
Use the command to create a DBA profile. The OLT dynamically allocates
bandwidth to uplink interfaces of ONUs according to the parameters in
the DBA profile. By configuring a DBA profile, you can set the bandwidth
allocation mode and bandwidth parameters uniformly. The ONT reports
the status of the queues associated with the service scheduler to the
OLT. Based on the bandwidth demand, the OLT Dynamic Bandwidth
Allocation (DBA) engine allocates upstream transmit opportunities to
the service scheduler, resulting in one or more ONT upstream queues
with the opportunity to send data up the PON.
【Example】
To set dba profile 10 as the type 5 , fixed bandwidth 5Mbit/s, assured bandwidth 10Mbit/s,
manimum bandwidth 30Mbit/s
OLT(dba-profile-10)# type5 fix 5120 assure 10240 max 30720
【Command】
show dba-profile (all | profile-id profile-id | profile-name profile-name)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
all:Displays all the DBA profile information
profile-id profile-id:To display the DBA profile of specified ID
11.3 show dba-profile
Page 54

profile-name profile-name:To display the specified DBA profile
【Description】
Uses the command to check the DBA profile information
【Example】
Displays all DBA profile
OLT(config)# show dba-profile all
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Profile Profile Type Fix Assure Max Bind
ID Name (kbps) (kbps) (kbps) times
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
10 dba-profile_10 5 2048 2048 10240 0
20 dba-profile_20 2 0 128 0 0
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total: 2
Displays DBA profile of ID 10
OLT(config)# show dba-profile profile-id 10
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Profile ID : 10
Profile Name : dba-profile_10
Type : 5
Fix(kbps) : 2048
Assure(kbps) : 2048
Max(kbps) : 10240
Bind Times : 0
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
show dba-profile (all | profile-id profile-id | profile-name profile-name)
【View Mode】
dba-profile Mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
Uses the command to apply the DBA profile
【Example】
To apply the current DBA profile
OLT(dba-profile-10)# commit
11.4 commit
12. ONT Lineprofiel Configuration
Page 55

12.1 ont-lineprofile
【Command】
ont-lineprofile (profile-id profile-id | profile-name profile-name)
no ont-lineprofile (profile-id profile-id | profile-name profile-name)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
profile-id: Creates or enter for a specified GPON ONT line profile, ID is
the unique identify number of the line profile. If no assigned the ID ,the
system will automatically assigned an id to the profile
profile-name:A name for the GPON ONT line profile.
【Description】
A line profile describes binding between the T-CONT and the DBA
profile, the QoS mode of the service flow, and mapping between the
GEM port and the ONU-side service.
This command is to create the ONT line profile.
【Example】
To creat the GPON ONT line profile with ID 10.
OLT(config)# ont-lineprofile profile-id 10
OLT(ont-lineprofile-10)#
【Command】
tcont tcont-list ( dba-profile-id dba-profile-id | dba-profile-name
dba-profile-name)
no tcont tcont-list
【View Mode】
lineprofile Mode
【Parameter】
tcont-list:T-CONT list, support “,” and “-”
dba-profile-id:DBA profile ID。
dba-profile-name:DBA profile name
【Description】
In the line profile mode, bind T-CONT 4 to DBA profile. A T-CONT is
bound to a DBA profile for dynamic bandwidth allocation, improving
upstream bandwidth utilization.
undo tcont command is used to delete the T-CONT
【Example】
Creats tcont1 under line profile 10 and bind with DBA profile 10
OLT(ont-lineprofile-10)# tcont 1 dba-profile-id 10
12.2 tcont
Page 56

12.3 gem add
【Command】
gem add gem-id tcont tcont-id
【View Mode】
lineprofile Mode
【Parameter】
gem-id:GEM ID
tcont-id:tcont ID
【Description】
Use the command to configure the GEM port and TCONT bound, creat
GEM port.
【Example】
To creat the gem 1 in line profile 10 and bind with tcont 1
OLT(ont-lineprofile-10)# gem add 1 tcont 1
【Command】
gem add gem-id tcont tcont-id
【View Mode】
lineprofile Mode
【Parameter】
gem-id:GEM ID
【Description】
Use the command to delete the GEM
【Example】
To delete GEM 1 of line profile 10
OLT(ont-lineprofile-10)# gem delete 1
【Command】
mapping-mode (priority | vlan | vlan-priority)
【View Mode】
lineprofile Mode
【Parameter】
priority:To use 802.1p priority mapping mode
vlan:To use VLAN mapping mode
vlan-priority:To use vlan+802.1p maping mode
【Description】
Uses the command to configure the mapping mode of the ONT line
profile. It configure the mapping mode from the GEM port to ONU-side
service. VLAN is default mapping mode.
【Example】
To configure line profile 10 with vlan mapping mode
12.4 gem delete
12.5 mapping-mode
Page 57

OLT(ont-lineprofile-10)# mapping-mode vlan
【Command】
gem mapping gem-id mapping-id [vlan-id vlan-id | priority priority]
no gem mapping gem-id mapping-id
【View Mode】
lineprofile Mode
【Parameter】
gem-id:GEM ID
mapping-id:mapping ID
vlan-id:vlan ID
priority:To configure a priority with the gem-id
【Description】
The command is used to map the GEM port and ont side service. The
service flow of user VLAN will map to GEM port in the ONT line profile
【Example】
To configure the gem 1、mapping 1、vlan 100 mapping
OLT(ont-lineprofile-10)# gem mapping 1 1 vlan-id 100
【Command】
show ont-lineprofile (all | profile-id profile-id | profile-name
profile-name)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
all:Displays all the line profile information
profile-id profile-id:To display the line profile of specified ID
profile-name profile-name:To display the specified line profile
【Description】
The command is used to display the line profile information.
【Example】
Displays the all line profile
OLT(config)# show ont-lineprofile all
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Profile-ID Profile-name Binding times
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
10 dba-profile_10 0
100 dba-profile_100 0
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total: 2
12.6 gem mapping
12.7 show ont-lineprofile
Page 58

【Command】
show ont-lineprofile current
【View Mode】
lineprofile Mode
【Parameter】
【Description】
Show not issued by the line template information
【Example】
Show not issued by the line template 10 configuration information
OLT(ont-lineprofile-10)# show ont-lineprofile current
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Profile-ID : 10
Profile-name : dba-profile_10
Binding times : 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Mapping mode : VLAN
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
<T-CONT 1> DBA-Profile ID : 10
<Gem ID 1>
Mapping-ID VLAN Priority
1 100 -
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
ont-srvprofile (profile-id profile-id | profile-name profile-name)
no ont-srvprofile (profile-id profile-id | profile-name profile-name)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
profile-id profile-id : Id for the service profile, the system will
automatically assigned a id to the profile with name “srv-profile_x” if
you do not give a id, “x” is the sequence number as id.
【Description】
Use this command to creat service profile. A service profile provides the
service configuration channel for the ONT that is managed by using
optical network terminal managemnt and control interface (OMCI). You
12.8 show ont-lineprofile current
13.ONT-srvprofile configuration
13.1 ont-srvprofile
Page 59

can configure the capability set of ONT port to adaptive. Then the
system automatically adapts to the ONT according to the actual
capability of the online ONT.
【Example】
Creats the service profile 10 for the ONT
OLT(config)# ont-srvprofile profile-id 10
OLT(ont-srvprofile-10)#
【Command】
ont-port (eth eth | pots pots)
【View Mode】
srvprofile Mode
【Parameter】
eth eth:The number of the Ethernet port on ONT
pots pots:The number of the voice port on ONT
【Description】
Uses the command to configure the capacity of the ONT.
【Example】
To configure the ONT service profile 10, the ONT have 4 eth ports and 1 telephone POTS
OLT(ont-srvprofile-10)# ont-port eth 4 pots 1
【Command】
port vlan eth port-list native-vlan vlan-id
port vlan eth port-list q-in-q vlan-id user-vlan vlan-id
port vlan eth port-list translation vlan-id user-vlan vlan-id
port vlan eth port-list transparent
port vlan eth port-list vlan vlan-id
no port vlan eth port-list vlan vlan-id
【View Mode】
srvprofile Mode
【Parameter】
eth port-list:The list of ONT port that need to configure a VLAN. It is
useful for batch configuration.
native-vlan vlan-id: native vlan of the ONT port。
q-in-q vlan-id user-vlan vlan-id:q-in-q vlan-id is the outer vlan,
user-vlan vlan-id is the inner vlan.
translation vlan-id user-vlan vlan-id:user-vlan vlan-id is user side vlan
vlan vlan-id:To add the ONT port to specified VLAN
13.2 ont-port
13.3 port vlan
Page 60

【Description】
Uses the port vlan command to configure the port vlan of the ONT uni
port in GPON ONT service profile, assigned the port to specified VLAN.
The no port vlan command is used to delete the port vlan of the ONT
service profile.
【Example】
Adds eth1 to vlan 10 in ONT srvprofile 10
OLT(ont-srvprofile-10)# port vlan eth 1 vlan 10
In ONT srvprofile 10, to set ONT uni port 2 to QinQ vlan 100, the user vlan is 10
OLT(ont-srvprofile-10)# port vlan eth 2 q-in-q 100 user-vlan 10
In ONT srvprofile 10, to set ONT uni port 2 working as transparent
OLT(ont-srvprofile-10)# port vlan eth 2 transparent
In ONT srvprofile 10, to set ONT uni port 1 working as VLAN translation , the vlan 100 will
translate to user vlan 200
OLT(ont-srvprofile-10)# port vlan eth 1 translation 100 user-vlan 200
【Command】
show ont-srvprofile (all | profile-id profile-id | profile-name
profile-name)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
all:To display all GPON ONT srv-profile information, include profile ID,
name, and number of bound times.
profile-id profile-id:To display the specified ID srv-profile
profile-name profile-name:To display the specified name srv-profile
【Description】
To check the ONT srv-profile information
【Example】
Displays all ONT srv-profile
OLT(config)# show ont-srvprofile all
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Profile-ID Profile-name Binding times
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
10 srvprofile_10 0
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total: 1
Display srv-profile of ID 10
13.4 show ont-srvprofile
Page 61

OLT(config)# show ont-srvprofile profile-id 10
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Profile-ID : 10
Profile-name : srvprofile_10
Binding times : 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port-type Port-number
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ETH 4
POTS 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
MAC learning switch : Enable
MAC aging time(s) : 300
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port Port Service-type Index Native S-VLAN S-PRI C-VLAN C-PRI ENCAP S-PRI
type ID VLAN
POLICY
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ETH 1 Translation 1 1 100 - 200 - - -
ETH 2 Transparent - - - - - - - -
ETH 3 Transparent - - - - - - - -
ETH 4 Transparent - - - - - - - -
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
show ont-srvprofile current
【View Mode】
Srvprofile Mode
【Parameter】
【Description】
To check the ont srv-profile that is applyed
【Example】
OLT(ont-srvprofile-10)# show ont-srvprofile current
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Profile-ID : 10
Profile-name : srvprofile_10
Binding times : 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port-type Port-number
13.5 show ont-srvprofile current
Page 62

---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ETH 4
POTS 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
MAC learning switch : Enable
MAC aging time(s) : 300
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port Port Service-type Index Native S-VLAN S-PRI C-VLAN C-PRI ENCAP S-PRI
type ID VLAN
POLICY
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ETH 1 Translation 1 1 100 - 200 - - -
ETH 2 Transparent - - - - - - - -
ETH 3 Transparent - - - - - - - -
ETH 4 Transparent - - - - - - - -
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
mac-learning switch
【View Mode】
Srvprofile Mode
【Parameter】
【Description】
mac-learning switch
MAC Address lerarning active or deactive.
MAC addresses learning let the ONT automatically add the MAC of client
device to the MAC table and dropped from it when they are not in use.
If address was not accessed during a specified interval called “MAC
aging-time”, its registered MAC address will be deleted from the table.
If you deactive MAC address learning, the ONT will not learning the
MAC address dymanic.
【Example】
Uses the command to active or deactive the MAC address learning.
To active the MAC address learning in srvprofile 10.
OLT(ont-srvprofile-10)# mac-learning enable
【Command】
mac-aging (aging-time | no-aging)
【View Mode】
Srvprofile Mode
13.6 mac-learning
13.7 mac-aging
Page 63

【Parameter】
mac-aging aging-time:aging time in seconds (default value is 300 s),
range is from 10 to 1000000s
mac-aging no-aging:No limit of aging time
【Description】
Sets the maximum amount of time a dynamically "learned".
MAC address remains in the MAC table.
【Example】
Sets the maximum amount of time to 200 second
OLT(ont-srvprofile-10)# mac-aging 200
【Command】
commit
【View Mode】
Srvprofile Mode
【Parameter】
【Description】
Uses the command to submit the configuration of the srvprofile. The
configuration will come into operation after this command.
【Example】
OLT(ont-srvprofile-10)# commit
【Command】
ont add port-id ont-id sn-auth sn-value ont-lineprofile-id
ont-lineprofile-id ont-srvprofile-id ont-srvprofile-id
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:To add the ONT on the specified GPON Port.
ont-id: To specified an identify number to ONT
sn-auth sn-value:To assign SN as an authentication security method of
ONT
ont-lineprofile-id ont-lineprofile-id:To assign the ONT line profile
ont-srvprofile-id ont-srvprofile-id:To assign the ONT srv profile
13.8 commit
14.ONT Management
14.1 ont add
Page 64

【Description】
Uses the command to add ONT and configure it. It mainly used for
offline ONT, the configuration is saved in the srv-profiel, when the ONT
online, the configuration will assign to the ONT.
【Example】
To add an ONT under GPON OLT PON port 1, ONT ID is 2, use SN for authorization, SN is
DB25B34BB8D5, binding with line profile 10 and svr-profiel 10
OLT(interface-gpon)# ont add 1 2 sn-auth DB25B34BB8D5 ont-lineprofile-id 10 ontsrvprofile-id 10
【Command】
ont confirm port-id sn-auth sn-value ont-lineprofile-id ont-lineprofile-id
ont-srvprofile-id ont-srvprofile-id
ont confirm port-id all sn-auth ont-lineprofile-id ont-lineprofile-id
ont-srvprofile-id ont-srvprofile-id
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:The PON port number of the ONT that you want to confirm
all:To confirm the all ONT that be found automatic under specified PON
port in batch
sn-auth sn-value:To use SN as authorization key
ont-lineprofile-id ont-lineprofile-id:To asign the ONT line profile ID
ont-srvprofile-id ont-srvprofile-id:To assign the ONT srvprofile ID
【Description】
Whe the OLT enable the auto discovery function of the ONT, the OLT can
get the information of the ONT. Use the ont confirm command to
confirm the auto-discovered ONT.
【Example】
To confirm all the auto discovered ONT of OLT PON 1, and bind the line profile 10 and
srvprofile 10
OLT(interface-gpon)# ont confirm 1 all sn-auth ont-lineprofile-id 10 ont-srvprofile
ile-id 10
Number of ONTs that can be added: 2, success: 2
【Command】
ont cancel port-id (all | sn sn-value)
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:The PON port number of the ONT that you want to cancel
14.2 ont confirm
14.3 ont cancel
Page 65

all:To cancel all ONT that be found automatic under specified PON port
in batch
sn sn-value:The SN of the ONT that you want to cancel
【Description】
Use the ont confirm command to cancel the auto-discovered ONT.
【Example】
To cancel the auto-discover ONT of PON port 1
OLT(interface-gpon)# ont cancel 1 all
【Command】
ont delete port-id (all | ont-id)
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:The PON port number of the ONT that you want to delete
all:To delete all ONT that be found automatic under specified PON port
in batch
sn sn-value:The SN of the ONT that you want to delete
【Description】
Use the ont confirm command to delete the auto-discovered ONT.
【Example】
To delete the ONT with ID 2 of PON port 1
OLT(interface-gpon)# ont delete 1 2
To delete all ONT under PON port 1
OLT(interface-gpon)# ont delete 1 all
This command will delete all the ONT in port. Are you sure to execute this co
mmand? (y/n)[n]:y
Number of ONTs that can be delete: 1, success: 1
【Command】
ont description port-id ont-id describe-value
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:The PON port number of the ONT that you want to add
description.
ont-id: The identify number of the ONT you want to add description.
describe-value:ONT describe information
【Description】
Use the command to add description of ONT, it is useful for ONT
management.
14.4 ont delete
14.5 ont description
Page 66

【Example】
To add description “admin” to the ONT ID 1 under PON Port 1
OLT(interface-gpon)# ont description 1 1 admin
【Command】
ont autofind port-id switch
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:The PON port number of the ONT that you want to active auto
discover ONT function.
switch: ONT auto-discover enable or disable
【Description】
Use the command to enable/disable the auto-discover ONT function.
【Example】
To enable auto-discover ONT function on PON port 1
OLT(interface-gpon)# ont autofind 1 enable
【Command】
ont active port-id (all | ont-id)
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:The PON port number of the ONT that you want to active.
all: To active all the ONT of specified PON port
ont-id:To active the specified ONT
【Description】
Use the command to active the ONT.
【Example】
To active ONT 1 under PON port 1
OLT(interface-gpon)# ont activate 1 1
To active all ONT of PON port 1。
OLT(interface-gpon)# ont activate 1 all
Number of ONTs that can be activated: 1, success: 1
【Command】
ont deactive port-id (all | ont-id)
14.6 ont autofind
14.7 ont active
14.8 ont deactive
Page 67

【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:The PON port number of the ONT that you want to deactive.
all: To deactive all the ONT of specified PON port
ont-id:To deactive the specified ONT
【Description】
Use the command to deactive the ONT.
【Example】
To deactive ONT 1 under PON port 1
OLT(interface-gpon)# ont deactivate 1 1
To deactive all ONT of PON port 1。
OLT(interface-gpon)# ont deactivate 1 all
Number of ONTs that can be deactivated: 1, success: 1
【Command】
ont modify port-id ont-id ont-lineprofile-id ont-lineprofile-id
ont-srvprofile-id ont-srvprofile-id
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:The PON port number of the ONT that you want to modify.
ont-id:To modify the specified ONT
ont-lineprofile-id: The line profile you want to used on this ONT
ont-srvprofile-id:The srv profile you want to used on this ONT
【Description】
Use the command to bind with new line profile and srv-profile on ONT.
【Example】
To change the ONT 1 under PON port 2 srv-profile to srv profile 200
OLT(interface-gpon)# ont modify 2 1 ont-srvprofile-id 200
【Command】
ont reboot port-id (all | ont-id)
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:The PON port number of the ONT that you want to reboot.
all : to reboot all the ont of specified PON port
ont-id:To reboot the specified ONT
【Description】
Use the command to reboot ONT.
【Example】
14.9 ont modify
14.10 ont reboot
Page 68

To reboot the ONT 1 under PON port 2.
OLT(interface-gpon)# ont reboot 2 1
14.11 show ont info
【Command】
show ont info port-id (ont-id | all)
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id:The PON port number of the ONT that you want to display.
all : to display all the ont of specified PON port
ont-id:To display the specified ONT
【Description】
Use the command to diplay the ONT information below:
Port:The PON port that the ONT connected
ONT ID: The ID of the specified ONT
SN: SN of the ONT
Control flag:(active or deactive)
active:ONT is in active status, the ONT can permit online or
offline after active.
deactive:ONT is in deactive status, use active command to
active the ONT.
Run state:ONT operation status, “online” or “offline” status.
Config state:Configuration status, it shows if the configuration
download to ONT success, “initial”、 “failed”、“Success”.
initial:The configuration in download processing
failed:Failed of download configuration
Success:Successed getting configuration.
【Example】
To display all ont information of PON port 1
OLT(interface-gpon)# show ont info 2 all
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port ONT SN Control Run Config Match
ID flag state state state
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
2 1 HWTC568DA228 Active Online Success Match
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total: 1, online 1
To display information of ONT 1 under PON port 1
OLT(interface-gpon)# show ont info 1 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
PORT-ID : 1
ONT-ID : 1
Page 69

Control flag : Active
Run state : Online
Config state : Success
Match state : Mismatch
ONT distance(m) : 271331472
SN : HWTC56A96228 (4857544356A96228)
Description :
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Line profile ID : 20
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Profile-ID : 20
Profile-name : dba-profile_20
Binding times : 1
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Mapping mode : VLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Service profile ID : 10
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Profile-ID : 10
Profile-name : srvprofile_10
Binding times : 1
Press any key to continue (Q to quit)
[01/01/00 01:01:01]: Pon 1 onu C000 is not regist.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port-type Port-number
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ETH 0
POTS 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
MAC learning switch : Enable
MAC aging time(s) : 300
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 70

14.12 show ont autofind
【Command】
show ont autofind port-id (all | sn sn-value)
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id: The PON port number you want to check ONT
sn sn-value:To check ONT by specified SN
all: To checkall auto-discover ONT at specified PON port
【Description】
To check information of auto-discover ONT. You can use the command
to check the ONT SN, password when you add ONT on OLT.
【Example】
To display all information of auto-discover ONT on PON1 port
OLT(interface-gpon)# show ont autofind 1 all
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Index SN Password Autofind-Time
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
2 HWTC17D81536 - 2000-01-01 02:44:58
3 DB25B34BB8D5 1234567890 2000-01-01 02:44:58
4 HWTC56A8E428 - 2000-01-01 02:43:28
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total: 3
【Command】
show ont capability port-id ont-id
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id: The PON port number you want to check ONT capacity
ont-id: The ID of ONT you want to check capacity
【Description】
To check capacity information of ONT, such as UNI port type and
quantity.
【Example】
To check capacity of ONT 1 on PON port 1
OLT(interface-gpon)# show ont capability 1 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
ONT-ID : 1
Equipment ID : MA5671
Number of uplink PON ports : 1
Number of POTS ports : 0
Number of ETH ports : 4 (GE:4, FE:0)
Number of GEM ports : 32
14.13 show ont capability
Page 71

Number of Traffic Schedulers : 32
Number of T-CONTs : 8
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
show ont config-capability port-id ont-id
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id: The PON port number you want to check ONT capacity
ont-id: The ID of ONT you want to check capacity
【Description】
To check user configure capacity information of ONT, such as UNI port
type and quantity.
【Example】
To check user configure capacity of ONT 1 on PON port 1
OLT(interface-gpon)# show ont config-capability 1 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
ONT-ID : 1
Equipment ID : MA5671
Number of uplink PON ports : 1
Number of POTS ports : 0
Number of ETH ports : 4
Number of GEM ports : 1
Number of Traffic Schedulers : 1
Number of T-CONTs : 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
show ont optical-info port-id ont-id
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id: The PON port number you want to check ONT optical
information
ont-id: The ID of ONT you want to check optical information
【Description】
To check optical information of ONT
【Example】
14.14 show ont config-capability
14.15 show ont optical-info
Page 72

To check optical informaion of ONT 1 on PON port 1
OLT(interface-gpon)# show ont optical-info 1 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Voltage(V) : 3.26
Tx optical power(dBm) : 2.1400
Rx optical power(dBm) : -9.7280
Laser bias current(uA) : 25000.00
Temperature(C) : 39.00
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
show ont version port-id ont-id
【View Mode】
Gpon Mode
【Parameter】
port-id: The PON port number you want to check ONT version
ont-id: The ID of ONT you want to check version
【Description】
To check version of ONT
【Example】
To check version of ONT 1 on PON port 1
OLT(interface-gpon)# show ont version 1 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port : 1
ONT-ID : 1
Vendor-ID : HWTC
ONT Version : CE4.A
Product-ID : 206
Equipment-ID : MA5671
Main Software Version : V8R313C00S102
Standby Software Version : V8R313C00S102
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
14.16 show ont version
15. log management
15.1 loghost add
Page 73

【Command】
loghost add ip-addr host-name
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
ip-addr:IP address of syslog server
host-name:Hostname of syslog server
【Description】
Syslog is a logging feature that gives administrators a way to centrally
log and analyze configuration events and system error messages.Uses
the command to add a syslog server to save log information.
【Example】
Add syslog server, IP address is 192.168.1.223, named log.
OLT(config)# loghost add 192.168.1.223 log
Successfully add syslog host!
【Command】
loghost delete (ip-addr ip-addr host-name host-name)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
ip-addr:IP address of syslog server
host-name:Hostname of syslog server
【Description】
To delete a syslog server
【Example】
To delet a syslog server
OLT(config)# loghost delete ip-addr 192.168.1.223
Successfully delete syslog host!
【Command】
loghost activate (ip-addr ip-addr host-name host-name)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
ip-addr:IP address of syslog server
host-name:Hostname of syslog server
【Description】
To active a syslog server
【Example】
To active syslog server 192.168.1.223
OLT(config)# loghost activate ip-addr 192.168.1.223
Successfully activate syslog host!
15.2 loghost delete
15.3 loghost activate
Page 74

【Command】
loghost activate (ip-addr ip-addr host-name host-name)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
ip-addr:IP address of syslog server
host-name:Hostname of syslog server
【Description】
To deactive a syslog server
【Example】
To deactive syslog server 192.168.1.223
OLT(config)# loghost activate ip-addr 192.168.1.223
Successfully deactivate syslog host!
【Command】
show loghost list
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
No
【Description】
To check syslog server configuration informaion
【Example】
To check all syslog server infromaiton
OLT(config)# show loghost list
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
IP address Host name Terminal state
192.168.1.223 log inactive
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
【Command】
syslog priority severity
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
severity: Level of syslog output
15.4 loghost deactivate
15.5 show loghost list
15.6 syslog priority
Page 75

Level 5:critical informaion
Level 4:error information or more serious
Level 3:warning information or more serious
Level 2:notice information or more serious
Level 1:debug information or more serious
【Description】
To configure syslog messages depending on severity level. The output
takes place regardless of a priority which part of system has
generated the message
【Example】
To configure the syslog priority serverity to notice。
OLT(config)# syslog priority notice
【Command】
show syslog priority severity
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
【Description】
To check the syslog output level
【Example】
To check the syslog level
OLT(config)# show syslog priority severity
Syslog priority severity: notice
【Command】
backup log ftp server-ip-address user-name user-password filename
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
server-ip-address:IP address of ftp server
user-name:ftp user name
user-password:ftp password
filename:File to save the log
【Description】
Uses the command to save the log in the ftp server
【Example】
To save log in ftp server, ftp server ip is 192.168.1.223, user name: admin, password: admin,
the name of file is log
15.7 show syslog priority severity
15.8 backup log
Page 76

OLT(config)# backup log ftp 192.168.1.223 admin admin logback
Start backup log files
The backup is successful
【Command】
terminal alarm-event severity severity
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
severity: Level of syslog output
Level 5:critical informaion
Level 4:error information or more serious
Level 3:warning information or more serious
Level 2:notice information or more serious
Level 1:debug information or more serious
【Description】
Uses the command to set the display level of syslog, only the specified
level or more serious level will display on terminal.
【Example】
To set syslog temainal display level to notice
OLT(config)# terminal alarm-event severity notice
【Command】
show terminal alarm-event severity
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
Uses the command to check the terminal display level of syslog
【Example】
To check the terminal display level of syslog
OLT(config)# show terminal alarm-event severity
Terminal alarm-event priority severity: notice
【Command】
terminal debugging
no terminal debugging
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
15.9 terminal alarm-event severity
15.10 show terminal alarm-event severity
15.11 terminal debugging
Page 77

【Parameter】
None
【Description】
Uses the command to output the debugging information on terminal. It
is useful for troubleshooting.
【Example】
To enable dsplaying the debug message on terminal.
OLT(config)# terminal debugging
Current terminal debugging is on
【Command】
show terminal debugging
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
Uses the command to check the terminal debugging status on or off.
【Example】
To check the terminal debugging status
OLT(config)# show terminal debugging
Current terminal debugging is ON.
【Command】
dhcp-snooping arp-detect enable
dhcp-snooping arp-detect disable
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
dhcp-snooping arp-detect enable: When enabled, system will check
legality of the user who sends ARP message according to DHCP
snooping so as to avoid ARP attacks
dhcp-snooping arp-detect disable: Disable ARP detection function
【Example】
Enable ARP detection function:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping arp-detect enable
15.12 show terminal debugging
16 dhcp-snooping configuration
16.1 dhcp-snooping arp-detect
Page 78

16.2 dhcp-snooping arp-reply-fast
【Command】
Enable ARP fast reply function:
dhcp-snooping arp-reply-fast enable
Disable ARP fast reply function:
dhcp-snooping arp-reply-fast disable
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
dhcp-snooping arp-reply-fast enable: When enabled, system will
choose to make fast ARP reply according to DHCP snooping table, when
this function is enable, system will snoop ARP message, if system can
find relative records of the ARP message in DHCP snooping table,
system will fast reply the ARP request instead of broadcasting the
message to uplink network so that ARP broadcasting message will be
reduced
dhcp-snooping arp-reply-fast disable: Disable ARP fast reply function
【Example】
enable ARP fast reply function:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping arp-reply-fast enable
【Command】
Delete entries of DHCP snooping binding list according to type:
dhcp-snooping bind-table clear (all | static | dynamic |
ip-address|vlan)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
all:Delete all entries in snooping binding list
static: Delete static entries in snooping binding list
dynamic: Delete dynamic entries in snooping binding list
ip-address: Delete entries with specified IP in snooping binding list
Vlan:Delete snooping entries in specified VLAN
【Description】
Delete entries of snooping binding list
【Example】
Delete all entries of snooping binding list:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping bind-table clear all
【Command】
dhcp-snooping bind-table write-delay time
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
16.3 dhcp-snooping bind-table clear
16.4 dhcp-snooping bind-table write-delay
Page 79

【Parameter】
time: Write delay time
【Description】
Configure delay time of writing into flash for DHCP snooping binding
table. When DHCP snooping binding table is changed, system will wait
for the configurated time then write the table entries into flash
【Example】
Configure that DHCP snooping binding table will be updated after 4 seconds when the table is
changed:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping bind-table wtite-delay 4
【Command】
dhcp-snooping bind-table delete-time time
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
time:Delete time of dynamic entries
【Description】
Configure delete time of dynamic entries in DHCP snooping binding
table. Dynamic entries will be deleted after the delete-time when lease
time is over instead of being deleted right away in the end of lease time.
【Example】
Configure that dynamic entries will be deleted after 240 seconds when lease time is over:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping bind-table delete-time 240
【Command】
dhcp-snooping bind-table write-to-flash
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
Write DHCP snooping binding table into flash manually
【Example】
Write DHCP snooping binding list into flash manually:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping bind-table write-to-flash
【Command】
dhcp-snooping bind-table save-to-tftp ip
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
ip: IP address of TFTP server which binding entries will be saved to
【Description】
Write DHCP snooping binding table into flash manually and upload the
table to TFTP server:
【Example】
16.5 dhcp-snooping bind-table delete-time
16.6 dhcp-snooping bind-table write-to-flash
16.7 dhcp-snooping bind-table save-to-tftp
Page 80

Write DHCP snooping binding list into flash manually and upload the list to TFTP server with
IP address 192.168.1.1:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping bind-table save-to-tftp 192.168.1.1
16.8 show dhcp-snooping bind-table
【Command】
show dhcp-snooping bind-table (all | static | dynamic | ip | vlan)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
all:view all entries in snooping binding table
static: view static entries in snooping binding table
dynamic: view dynamic entries in snooping binding table
ip-address: view entries with specified IP in snooping binding table
Vlan:view snooping entries in specified VLAN
【Description】
View entries of DHCP snooping binding table
【Example】
View all information of DHCP snooping binding table:
OLT(config)# show dhcp-snooping bind-table all
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
database entries count: 5 database entries delete time: 300(s)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
MacAddress IpAddress Vlan Port Lease(s) Type Status
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
00:50:BA:50:73:27 192.168.12.5 1 ge13 594 Dynamic Valid
00:50:BA:50:73:26 192.168.12.4 1 ge13 594 Dynamic Valid
00:50:BA:50:73:25 192.168.12.3 1 ge13 594 Dynamic Valid
20:89:84:2A:1A:91 192.168.12.2 1 ge13 541 Dynamic Valid
00:0F:1F:C5:10:08 192.168.1.101 100 ge10 - Static Valid
【Command】
dhcp-snooping binding mac ip vlan port (ge | EPON| xge | lag )port-id
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
mac:MAC address of static binding entry
ip: IP address of static binding entry
vlan: VLAN of static binding entry
port-id: Port ID of static binding entry
【Description】
dhcp-snooping binding: Binding policy configuration based on request
message
【Example】
Add one static binding entry with MAC address 00:0f:1f:c5:10:08, IP address 192.168.1.101,
VLAN 100 and port ge10:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping binding mac 00:0f:1f:c5:10:08 ip 192.168.1.101 vlan100 port
16.9 dhcp-snooping binding
Page 81

ge 10
16.10 dhcp-snooping chaddr-check
【Command】
dhcp-snooping chaddr-check enable
dhcp-snooping chaddr-check disable
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
port-list: Add specified port list
【Description】
dhcp-snooping chaddr-check enable: When enabled, system will
check whether the MAC address of DHCP request message from untrust
port is the same as CHADDR field, snoop the message if it is the same,
discard the message if not
dhcp-snooping chaddr-check disable: Disable MAC address detection
of untrust port
【Example】
Disable MAC address detection of untrust port:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping chaddr-check disable
【Command】
dhcp-snooping enable
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
dhcp-snooping enable: When enabled, trust/untrust port function, MAC
address detection function, rate limit function of DHCP message from
untrust port, port recovery function, option82 function, ARP dynamic
monitoring function and ARP quick response function will be enabled
【Example】
Enable DHCP-SNOOPING function:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping enable
【Command】
dhcp-snooping disable
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
Disable DHCP-SNOOPING function: When disabled, trust/untrust port
function, MAC address detection function, rate limit function of DHCP
message from untrust port, port recovery function, option82 function,
ARP dynamic monitoring function and ARP quick response function will
be disabled
【Example】
16.11 dhcp-snooping enable
16.12 dhcp-snooping disable
Page 82

Disable DHCP-SNOOPING function:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping disable
16.13 dhcp-snooping limit-rate
【Command】
dhcp-snooping limit-rate rate port (ge | gon|xge | lag)port-list
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
rate: Limit the rate of DHCP request message
port-list: Port that needs to be configure
【Description】
Configure receiving rate of DHCP request message from untrust port,
message over the limit-rate will be discarded. Rate limit of trust port can
be configure but will not take effect.
【Example】
Limit the receiving rate of DHCP message from port GE6 and GE9 as 20pps, rate limit for port
xGE1 as 100pps and rate limit for port gpon 2-8 as 50pps:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping limit-rate 20 port ge 6,9
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping limit-rate 100 port xge 1
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping limit-rate 100 port gpon 2-8
【Command】
dhcp-snooping opton82 enable
dhcp-snooping opton82 disable
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
When enabled, system will add Option82 information in DHCP request
message from untrust port and strip the Option82 information of DHCP
reponse message from trust port
【Example】
Enabel DHCP option82 function:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping option82 enable
【Command】
dhcp-snooping option82 policy (keep|drop|replace)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
keep: Forward DHCP message with Option82 field without changing
drop: Discard DHCP message with Option82 field
replace: Replace Option82 field in DHCP message then forward the
message
【Description】
dhcp-snooping option82 policy: Opton82 forwarding policy
configuration based request message
16.14 dhcp-snooping opton82
16.15 dhcp-snooping option82 policy
Page 83

【Example】
Configurete DHCP forwarding policy as the original forwarding policy:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping option82 policy keep
16.16 (no) dhcp-snooping trust port
【Command】
dhcp-snooping trust port (ge | xge | EPON| lag) port-list
no dhcp-snooping trust port (ge | xge| EPON | lag )port-list
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
port-list: Add specified port list
【Description】
dhcp-snooping trust port : Configure trust ge port, which can receive all
DHCP messages
no dhcp-snooping trust port: Configure untrust port, which can not
receive DHCP response message
【Example】
Configure port GE10, GE12, xGE1 and gpon3-5 as tust port, GE1-GE5, xGE2, gpon2, gpon 5 as
untrust prot:
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping trust port ge 10,12
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping trust port xge 1
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping trust port gpon 3-5
OLT(config)# no dhcp_snooping trust port ge 1-5
OLT(config)# no dhcp_snooping trust port xge 2
OLT(config)# no dhcp_snooping trust port gpon 2,5
【Command】
dhcp-snooping vlan vlan-list
no dhcp-snooping vlan vlan-list
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
vlan-list: Add specified VLAN list
【Description】
dhcp-snooping vlan: Add specified snooping VLAN, DHCP message in
the snooping VLAN range will be snooped, and DHCP message out of
the snooping VLAN range will be forwarded without changing any
thing.
no dhcp-snooping vlanvlan-list: Delete specified snooping VLAN
【Example】
Add snooping VLAN 100, 200, 300
OLT(config)# dhcp-snooping vlan 100,200-300
【Command】
show dhcp-snooping configuration
16.17 (no)dhcp-snooping vlan
16.18 show dhcp-snooping configuration
Page 84

【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
None
【Description】
View dhcp-snooping configuration
【Example】
View dhcp-snooping configuration:
OLT(config)# show dhcp-snooping configuration
17 Traffic profile configuration
【Command】
traffic-profile (profile-id profile-id | profile-name profile-name|cir
cir|pir pir|cbs cbs|pbs pbs)
no traffic-profile (profile-id profile-id | profile-name profile-name)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
Profile-id:
show the traffic profile id, which can be used later when you need to
bind the traffic profile.
Profile-name:
Show the traffic profile name, which can be modified when you need to
bind the traffic profile.
Cir:
To show and modify the guaranteed bandwidth, the effect of bandwidth
is to ensure that the traffic rate can reach its guaranteed bandwidth when
the traffic is congested. The default minimum configuration is 64kbps,
and the unit is kpbs.
Pir:
The maximum bandwidth is shown and modified, and the maximum
bandwidth is only a limited effect. The limit of the traffic can not exceed
its maximum bandwidth. The default minimum configuration is
128kbps, and the unit is kpbs.
Cbs:
Show and modify the guarantee burst length, that is the instantaneous
ability to pass the promise burst traffic, the default minimum
configuration is 2000bytes, the unit is byte.
Pbs:
Show and modify peak burst length, peak burst size, the default
minimum configuration is 2000bytes, the unit is byte.
【Description】
The traffic profile on GPON OLT is mainly applied to the ONU port for
the port speed limit. Applying to an ACL for speed limits for a particular
message.
【Example】
17.1 traffic-profile
Page 85

Create a traffic profile,profile ID is 123,profile name is test,cir is 10240,pir is 409600,cbs is
20000,pbs is 20001
OLT(config)# traffic-profile profile-id 123 profile-name test cir 10240 pir 409600 cbs 20000
pbs 20001
17.2 modify
【Command】
traffic-profile (modify|profile-id profile-id | profile-name
profile-name|cir cir|pir pir|cbs cbs|pbs pbs)
【View Mode】
Configuration mode
【Parameter】
Profile-id:
show the traffic profile id, which can be used later when you need to
bind the traffic profile.
Profile-name:
Show the traffic profile name, which can be modified when you need to
bind the traffic profile.
Cir:
To show and modify the guaranteed bandwidth, the effect of bandwidth
is to ensure that the traffic rate can reach its guaranteed bandwidth when
the traffic is congested. The default minimum configuration is 64kbps,
and the unit is kpbs.
Pir:
The maximum bandwidth is shown and modified, and the maximum
bandwidth is only a limited effect. The limit of the traffic can not exceed
its maximum bandwidth. The default minimum configuration is
128kbps, and the unit is kpbs.
Cbs:
Show and modify the guarantee burst length, that is the instantaneous
ability to pass the promise burst traffic, the default minimum
configuration is 2000bytes, the unit is byte.
Pbs:
Show and modify peak burst length, peak burst size, the default
minimum configuration is 2000bytes, the unit is byte.
【Description】
Modify the traffic profile information,include profile
name,cir,pir,cbs,and pbs information.
【Example】
Modify traffic profile 123 name to test1
OLT(config)# traffic-profile modify profile-id 123 profile-name test1
Including Remarks
Thanks to the use our company Products!
Page 86

 Loading...
Loading...