Page 1

PRECISION GPS+: HiPer GD & HiPer GGD
HiPer GD &
HiPer GGD
Operator’s Manual
Page 2

Page 3

POSITIONING SYSTEMS
HiPer® GD and HiPer GGD
Operator’s Manual
Part Number 7010-0626
Rev B
©Copyright Topcon Positioning Systems, Inc.
May, 2004
All contents in this manual are copyrighted by Topcon. All
rights reserved. The information contained herein may not be
used, accessed, copied, stored, displayed, sold, modified,
published, or distributed, or otherwise reproduced without
express written consent from Topcon.
Topcon only sells GPS products into Precision Markets.
Please go to www.topcongps.com for detailed market information.
Page 4

ECO#2231
Page 5

Table of Contents
Preface ............................................................... v
Terms and Conditions ................................................... v
Regulatory Information ................................................ viii
Manual Conventions ..................................................... x
Chapter 1
Introduction ....................................................... 1-1
Overview ....................................................................... 1-2
Principles of Operation ................................................. 1-3
GPS Overview ........................................................ 1-3
Calculating Positions ....................................... 1-4
GPS Positioning ............................................... 1-5
Conclusion ....................................................... 1-6
Receiver Overview .................. .... ..... .... .................. 1-6
Standard Package Contents ........................................... 1-8
Cables ..................................................................... 1-8
Power Supply/Charger ........................................... 1-9
Software ................................................................. 1-10
Literature ................................................................ 1-11
Getting Acquainted ....................................................... 1-12
Internal Components .............................................. 1-13
GPS+ Antenna ................................................. 1-13
Radio Modem .................................................. 1-13
Power Board ....... ..... .... ..... ............................... 1-14
GPS+ Receiver Board ...................................... 1-15
Battery ............................................................. 1-16
External Components ............................................. 1-16
Radome ............................................................ 1-16
Bottom Panel ................................................... 1-16
i
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
Page 6

Table of Contents
Front Panel ................................................. ..... . 1-17
Back Panel ....................................................... 1-19
Option Authorization File (OAF) ................................. 1-20
Chapter 2
Configuration .................................................... 2-1
Powering the Receiver .................................................. 2-2
Internal batteries ..................................................... 2-2
External Batteries ................................................... 2-3
Battery Charger ...................................................... 2-4
Turning On/Off the Receiver ................................. 2-4
Power Management ............................................... . 2-5
Charge Internal Batteries ................................. 2-9
Check Internal Battery Status .......................... 2-10
Connecting the Receiver and a Computer .................... 2-11
Receiver Configuration ................................................. 2-14
MINTER Configuration ................................................ 2-18
Radio Configuration ...................................................... 2-26
Configuring a UHF Radio Modem ......................... 2-26
Configuring a GSM Radio Modem ........................ 2-36
Collecting Almanacs ..................................................... 2-40
Chapter 3
Setup and Survey .............................................. 3-1
Receiver Setup .............................................................. 3-1
Step 1: Set up Receiver .......................................... 3-2
Step 2: Measure Antenna Height ............................ 3-2
Step 3: Collect Data ................................................ 3-5
External Antenna Setup .......................................... 3-5
Surveying with the Receiver ......................................... 3-9
Static Survey ........................................................... 3-9
Kinematic Survey ................................................... 3-12
Stop and Go Survey ......................................... 3-12
Kinematic Continuous .................................... . 3-14
ii
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Real-time Kinematic Survey .................................. 3-15
Setting up an RTK Base Station ...................... 3-15
Page 7

Table of Contents
Setting up an RTK Rover ................................ 3-20
Chapter 4
Operation ........................................................... 4-1
Using the MINTER ....................................................... 4-2
Power Key ................................... ..... .... .................. 4-2
Status LED ....... ..... .... ..... ........................................ 4-2
Reset Key ......... ..... .... ..... ........................................ 4-3
FN Key and Record LED ....................................... 4-3
Battery LED ........................................................... 4-7
Modem LED ........................................................... 4-7
Information Modes ................................................. 4-8
Normal ............................................................. 4-8
Extended Information Mode (EIM) ................. 4-8
Downloading Files to a Computer ................................ 4-10
Deleting Files ................................................................ 4-13
Checking an OAF ......................................................... 4-15
Loading OAFs .............................................................. 4-17
Managing Receiver Memory ........................................ 4-18
Clearing the NVRAM ................................................... 4-18
Using MINTER to Clear NVRAM ........................ 4-19
Using PC-CDU to Clear NVRAM ......................... 4-19
Changing Receiver Modes ............................................ 4-20
Sleep Mode ............................................................. 4-20
Zero Power Mode ................................................... 4-21
Checking Firmware Version ......................................... 4-21
Loading New Firmware ................................................ 4-23
Chapter 5
Troubleshooting ................................................ 5-1
Check This First ............................................................ 5-1
Power Problems ............................................................ 5-2
Receiver Problems ........................................................ 5-3
Obtaining Technical Support ........................................ 5-8
Phone ...................................................................... 5-9
E-mail ..................................................................... 5-9
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
iii
Page 8

Table of Contents
Website ................................................................... 5-9
Appendix A
Creating Scripts ................................................ A-1
Appendix B
Specifications .................................................... B-1
Receiver Specifications ................................................. B-1
Connector Specifications ...................... ........................ B-10
Power Connector .................................................... B-10
Serial C-RS232 Connector ..................................... B-11
Radio (Modem) RF Connector ............................... B-12
GPS External Antenna RF Connector .................... B-12
USB Connector ....................................................... B-13
EVENT and 1PPS Connectors (Optional) .............. B-13
Appendix C
Safety Warnings ................................................ C-1
General Warnings ......................................................... C-1
Internal Battery Pack Warnings .................................... C-2
Usage Warnings ............................................................ C-3
Appendix D
UHF Radio Usage .............................................. D-1
Appendix E
Warranty Terms ................................................. E-1
Index
iv
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 9

Preface
Thank you for purchasing this Topcon product. The materials
available in this Manual (the “Manual”) have been prepared by
Topcon Positioning Systems, Inc. (“TPS”) for owners of Topcon
products. It is designed to assist owners with the use of the Product
and its use is subject to these terms and conditions (the “Terms and
Conditions”).
NOTICE
Terms and Conditions
PROFESSIONAL USE – This product is designed to be used by a
professional. The user is required to be a professional surveyor or
have a good knowledge of surveying, in order to understand the
user and safety instructions, before operating, inspecting or
adjusting. Always wear required safety attire (safety shoes, hard
hat, etc.) when operating.
COPYRIGHT – All information contained in this Manual is the
intellectual property of, and copyrighted material of TPS. All rights
are reserved. You may not use, access, copy, store, display, create
derivative works of, sell, modify, publish, distribute, or allow any
third party access to, any graphics, content, information or data in
this Manual without TPS’ express written consent and may only use
such information for the care and operation of your HiPer GD or
HiPer GGD. The information and data in this Manual are a valuable
asset of TPS and are developed by the expenditure of considerable
NOTICE
Please read these Terms and Conditions carefully.
v
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
Page 10

Preface
work, time and money, and are the result of original selection,
coordination and arrangement by TPS.
TRADEMARKS – HiPer®, PG-A1™, Legacy-E™, LegAnt™,
Topcon® and Topcon Positioning Systems™ are trademarks or
registered trademarks of TPS. Windows® is a registered trademark
of Microsoft Corporation. Product and company names mentioned
herein may be trademarks of their respective owners.
DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTY
– EXCEPT FOR ANY
WARRANTIES IN AN APPENDIX OR A WARRANTY CARD
ACCOMPANYING THE PRODUCT, THIS MANU AL AND THE
HIPER GD OR HIPER GGD ARE PROVIDED “AS-IS.” THERE
ARE NO OTHER WARRANTIES. TPS DISCLAIMS ANY
IMPLIED W A RRANTY OF MERCHANT ABILITY OR FITNESS
FOR ANY PARTICULAR USE OR PURPOSE. TPS AND ITS
DISTRIBUTORS SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR TECHNICAL
OR EDITORIAL ERRORS OR OMISSIONS CONTAINED
HEREIN; NOR FOR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE FURNISHING,
PERFORMANCE OR USE OF THIS MATERIAL OR THE
RECEIVER. SUCH DISCLAIMED DAMAGES INCLUDE BUT
ARE NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF TIME, LOSS OR
DESTRUCTION OF DATA, LOSS OF PROFIT, SAVINGS OR
REVENUE, OR LOSS OF THE PRODUCT’S USE. IN
ADDITION TPS IS NOT RESPONSIBLE OR LIABLE FOR
DAMAGES OR COSTS INCURRED IN CONNECTION WITH
OBTAINING SUBSTITUTE PRODUCTS OR SOFTWARE,
CLAIMS BY OTHERS, INCONVENIENCE, OR ANY OTHER
COSTS. IN ANY EVENT, TPS SHALL HAVE NO LIABILITY
FOR DAMAGES OR OTHERWISE TO YOU OR ANY OTHER
PERSON OR ENTITY IN EXCESS OF THE PURCHASE PRICE
vi
FOR THE RECEIVER.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 11

Terms and Conditions
LICENSE AGREEMENT – Use of any computer programs or
software supplied by TPS or downloaded from a TPS website (the
“Software”) in connection with the HiPer GD or HiPer GGD
constitutes acceptance of these Terms and Conditions in this
Manual and an agreement to abide by these Terms and Conditions.
The user is granted a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable
license to use such Software under the terms stated herein and in
any case only with a single HiPer GD or HiPer GGD or single
computer. You may not assign or transfer the Software or this
license without the express written consent of TPS. This license is
effective until terminated. You may terminate the license at any
time by destroying the Software and Manual. TPS may terminate
the license if you fail to comply with any of the Terms or
Conditions. You agree to destroy the Software and manual upon
termination of your use of the HiPer GD or HiPer GGD. All
ownership, copyright and other intellectual property rights in and to
the Software belong to TPS. If these license terms are not
acceptable, return any unused software and manual.
CONFIDENTIALITY – This Manual, its contents and the
Software (collectively, the “Confidential Information”) are the
confidential and proprietary information of TPS. You agree to tr eat
TPS’ Confidential Information with a degree of care no less strin gent
that the degree of care you would use in safeguarding your o wn mo st
valuable trade secrets. Nothing in this paragraph shall restrict you
from disclosing Confidential Information to your employees as may
be necessary or appropriate to operate or care for the HiPer GD or
HiPer GGD. Such employees must also keep the Confidentiality
Information confidential. In the ev ent you b ecome le ga lly compelled
to disclose any of the Confidential Information, you shall give TPS
immediate notice so that it may seek a protective order or other
appropriate remedy .
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
vii
Page 12

Preface
WEBSITE; OTHER STATEMENTS – No statement contain ed at
the TPS website (or any other website) or in any other
advertisements or TPS literature or made by an employee or
independent contractor of TPS modifies these Terms and
Conditions (including the Software license, warranty and limitation
of liability).
SAFETY – Improper use of the HiPer GD or HiPer GGD can lead
to injury to persons or property and/or malfunction of the product.
The receiver should only be repaired by authorized TPS warranty
service centers. Users should review and heed the safety warnings
in Appendix C.
MISCELLANEOUS – The above Terms and Conditions may be
amended, modified, superseded, or canceled, at any time by TPS.
The above Terms and Conditions will be governed by, and
construed in accordance with, the laws of the State of California,
without reference to conflict of laws.
viii
Regulatory Information
The following sections provide information on this product’s
compliance with government regulations.
FCC Class B Compliance
These devices comply with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation
is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired ope r ation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the
limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the
FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 13

Regulatory Information
protection against harmful interference in residential
installations. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation.
If this equipment does cause interference to radio or television
equipment reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct
the interference by on or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Move the equipment away from the receiver.
• Plug the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is powered.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television
technician for additional suggestions.
CAUTION
CAUTION
Any changes or modifications to the equipment not
expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void your authority to operate such
equipment.
Canadian Emissions Labeling Requirements
This Class B digital apparatus meets all requirements of the
Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B respecte toutes les
exigences du Réglement sur le matériel brouilleur du Canada.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
ix
Page 14

Preface
Community of Europe Compliance
We, Topcon Corporation, declare EC Conformity for the
following products:
Product Identification:
Brand: Topcon
Model/Type: HIPER GD, GNSS RECEIVER
HIPER GGD, GNSS RECEIVER
Model Number: 01-830401
01-040401
Manufacturer:
Name: Topcon Positioning Systems
Address: 5758 W. Las Positas Blvd., Pleasanton, CA 94588
Country: USA
Tel: 925-460-1300 Fax: 925-460-1336
Standards used:
IEC 60 950:1999 / EN 60 950:2000
EN300 339 V1.1.1 (1998-06)
Means of Conformity:
The product is in conformity with Standard EN 300 339
harmonized under Article 3(1)(b) of the R&TTE Council
Directive 1999/5/EC and Article 4 of the EMC Council
Directive 89/336/EEC based on test. CE Marking was
attached in 2002.
Manual Conventions
This manual uses the following conventions:
Example Description
x
FileExit Click the File menu and click Exit.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 15

Manual Conventions
Connection Indicates the name of a dialog box or screen.
Frequency Indicates a field on a dialog box or screen, or a tab
within a dialog box or screen.
Enter Press or click the button or key labeled Enter.
TIP
TIP
Supplementary information that can help you configure,
maintain, or set up a system.
NOTICE
NOTICE
Supplementary information that can have an affect on
system operation, system performance, measurements,
or personal safety.
CAUTION
CAUTION
Notification that an action has the potential to
adversely affect system operation, system
performance, data integrity, or personal health.
WARNING
WARNING
Notification that an action will result in system
damage, loss of data, loss of warranty, or personal
injury.
DANGER
DANGER
UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES SHOULD THIS ACTION BE
PERFORMED.
xi
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
Page 16

Preface
Notes:
xii
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 17

Chapter 1
Introduction
This chapter describes:
• The HiPer® GD and HiPer® GGD receivers (Figure 1-1)
• GPS/GLONASS and your receiver
• Common receiver functions
• Standard package contents and configurations
• Receiver components
• The Option Authorization File (OAF)
Figure 1-1. HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Receivers
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
1-1
Page 18

Introduction
Overview
Topcon Positioning System’s HiPer GD and HiPer GGD receivers
are dual-frequency, GPS+ receivers built to be the most advanced
and compact receiver for the surveying market. The HiPer GD and
HiPer GGD are multi-function, multi-purpose receivers intended
for precision markets. Precision markets means markets for
equipment, subsystems, components and software for surveying,
construction, commercial mapping, civil engineering, precision
agriculture and land-based construction and agriculture machine
control, photogrammetry mapping, hydrographic and any use
reasonably related to the foregoing.
The HiPer GD and HiPer GGD can receive and process both L1 and
L2 signals, improving the accuracy of your survey points and
positions. The GPS+ component of HiPer GD and HiPer GGD
receivers means you can access both the GPS (Global Positioning
System) satellites of the United States, and the GLONASS (Global
Navigation Satellite System) satellites of the Russian Federation,
increasing the number of satellites your receiver can detect, thus
improving the accuracy of your survey points, increasing
productivity, and reducing cost.
1-2
The dual-frequency and GPS+ features of the receiver combines to
provide the only real time kinematic (RTK) system accurate for
short and long baselines. Several other features, including multipath
mitigation and co-op tracking, provide under-canopy and lo w signal
strength reception. The receivers provide the functionality,
accuracy, availability, and integrity needed for fast and easy data
collection.
NOTICE
NOTICE
For more information on the difference between the HiPer
GD and HiPer GGD receivers, see Table 1-1, “HiPer GD
vs. HiPer GGD,” on page 12.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 19

Principles of Operation
Principles of Operation
Surveying with the right GPS receiver can provide users accurate
and precise positioning, a requirement for any surveying project.
This section gives an overview of GPS and receiver functions to
help you understand and apply GPS principles, allowing you to get
the most out of your receiver.
GPS Overview
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based, lineof-sight radio navigation system run by the United States
Department of Defense (DoD). This system offers a global, all
weather, 24-hour positioning, velocity, and time service to any
user equipped with a GPS tracking receiver, who is on or near
the Earth’s surface. The Global Navigation Satellite System
(GLONASS), is the Russian Federation Ministry of Defense
counterpart to GPS. At any one time, with a standard 15 degree
angle, up to 10 or 12 GPS satellites are visible from any point
on earth. When a receiver can also track GLONASS satellites,
between 10 and 16 satellites are visible.
For information on current GPS constellation status, visit the
U.S. Navel Observatory website (http://tycho.usno.navy.mil/)
or the U.S. Coast Guard Navigation Center website (http://
www.navcen.uscg.gov/).
Despite numerous technical differences in the implementation
of these systems, both GPS and GLONASS ha ve three essential
components:
• Space – GPS and GLONASS satellites orbiting
approximately 12,000 nautical miles above Earth and are
equipped with a clock and radio. These satellites broadcast
digital information (ephemerides, almanacs, time frequency
corrections, etc.).
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
1-3
Page 20

Introduction
• User – The community and military that use GPS/
GLONASS receivers and the corresponding satellites to
calculate positions.
• Control – Ground stations located around the Earth that
upload data, including clock corrections and new
ephemerides (satellite positions as a function of time), to
ensure the satellites transmit data properly.
Calculating Positions
Once the receiver locks on to a satellite, it starts recording
measurements and receiving the various digital information
(ephemeris, almanac, and so on) the satellites broadcast. To
calculate a position, receivers use the following basic
formula:
Velocity x Time = Distance
Where Velocity is the speed at which radio waves travel
(i.e., the speed of light) and Time is the difference between
the signal transmission time and signal reception time.
To calculate absolute 3-D positions—latitude, longitude,
altitude—the receiver must lock on to four satellites. In a
mixed GPS and GLONASS scenario, the receiver must
lock on to at least five satellites to obtain an absolute
position.
1-4
To provide fault tolerance using only GPS or only
GLONASS, the receiv er must lock onto a f ifth satellite. Six
satellites will provide fault tolerance in mixed scenarios.
Usually, the number of GPS and GLONASS satellites in
view does not exceed twenty (20).
Once locked on to a satellite, the receiver collects
ephemerides and almanacs, saving this information to its
NVRAM (Non-Volatile RAM).
• GPS and GLONASS satellites broadcast ephemeris
data cyclically, with a period of 30 seconds.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 21

Principles of Operation
• GPS satellites broadcast almanac data cyclically with a
period of 12.5 minutes; GLONASS satellites broadcast
almanac data cyclically with a period of 2.5 minutes.
GPS Positioning
Achieving quality position results requires the following
three elements:
• Accuracy – The accuracy of a position depends upon
the number, signal integrity, and placement (also
known as Dilution of Precision, or DOP) of satellites.
–Differential GPS (DGPS) strongly mitigates
atmospheric and orbital errors, and counteracts antispoofing signals the US Department of Defense
transmits with GPS signals.
–The more satellites in view , the stronger the signal, the
lower the DOP number, providing more accurate
positioning.
• Availability – The availability of satellites affects the
calculation of valid positions. The more visible
satellites available, the more valid and accurate the
position. Natural and man-made objects can block,
interrupt, and weaken signals, lowering the number of
available satellites.
• Integrity – Fault tolerance allows a position to have
greater integrity, increasing accuracy. Several factors
combine to provide fault tolerance, including:
–Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM)
detects faulty GPS and GLONASS satellites and
removes them from the position calculation.
–Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) creates
and transmits DGPS correction messages.
–Five or more visible satellites for only GPS or only
GLONASS; six or more satellites for mixed scenarios.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
1-5
Page 22

Introduction
–Current ephemerides and almanacs.
–Several algorithms to detect and correct faulty
information.
Conclusion
Surveyors can use Topcon GPS+ receivers to collect data
from a network of satellites and control stations to
triangulate precise points anywhere on Earth.
This overview simply outlines the basics of GPS and
GLONASS positioning. For more detailed information,
visit the TPS website (www.topconps.com/gpstutorial/).
Receiver Overview
When power is turned on and the receiver self-test completes,
the receiver’s 40 channels initialize and begin tracking visible
GPS and GLONASS satellites. Each of the receiver’s channels
can be used to track C/A-L1, P-L1, or P-L2 signals. The
number of channels available allows the receiver to track
simultaneously all visible GPS and GLONASS satellites at an y
time and location. The combination GPS and GLONASS
(GPS+) antenna receives the different signals for processing.
1-6
An internal or external GPS+ antenna equipped with an
optional low noise amplifier (LNA) and the receiver’s radio
frequency (RF) device are connected with a coaxial cable. The
wide-band signal received is down-converted, filtered,
digitized, and assigned to different channels. The receiver
processor controls the process of signal tracking.
Once the signal is locked in the channel, it is demodulated and
necessary signal parameters (carrier and code phases) are
measured. Also, broadcast navigation data are retrieved from
the navigation frame.
After the receiver locks on to four or more satellites, it is
possible to solve the so-called “absolute positioning problem”
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 23

Principles of Operation
and compute the receiver’s coordinates and time (in WGS-84).
All this information is stored in the receiver’s memory, which
can be downloaded later onto a computer and processed using a
post-processing software package. When the receiver is run in
RTK mode, raw data measurements can also be recorded into
the receiver’s internal memory. This allows the operator to
double check real-time results obtained in the field.
Depending on your options, capabilities of the receiver include:
• Co-Op Tracking
• Multipath reduction
• Wide area augmentation system (WAAS)
• Adjustable phase locked loop (PLL) and delay lock loop
(DLL) parameters
• Dual-frequency static, kinematic, real-time kinematic
(RTK), and differential GPS (DGPS) survey modes
• Auto data logging
• Setting different mask angles
• Setting different survey parameters
• Static or dynamic modes
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
1-7
Page 24

Introduction
Standard Package Contents
The receiver becomes a typical real-time kinematic (R TK) package
with a Legacy-E as the Base Station and the HiPer GD or HiPer
GGD as the Rover (also, refer to the re-packaging instruction card).
The contents of this package include:
• HiPer GD or HiPer GGD receiver
• Legacy-E GPS receiver
• PG-A1 precision micro-centered antenna
• UHF Base radio kit
•LitePole
• Tripod, tribrach, and adapter
• Topcon T o ols softw a re
• Cables and power supply/charger
•Literature
Cables
1-8
Standard cables (Figure 1-2 on page 1-9) include the following:
• Receiver-to-computer RS232 serial cable (p/n
14-008005-03) – used to connect the receiver’s serial port
and an external device (hand-held controller or computer)
• Receiver-to-SAE power cable (p/n 14-008016-03) – used to
connect the receiver’s power port and the power supply’s
SAE connector or the extension cable’s SAE connector
• Antenna cable (p/n 14-008012-01) – used to connect the
receiver and antenna
• SAE-to-SAE cable extension (p/n 14-008022-01) – used to
connect SAE connectors over longer distances
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 25

Standard Package Contents
• Alligator clips-to-SAE cable (p/n 14-008025-01) – used to
connect any 12-volt DC power source and the Receiver-toSAE power cable
• Power supply-to-outlet cable (p/n 14-008052-01 for U.S. or
14-008054-01 for E.U.) – used to connect the power
charger to a power outlet
• USB cable (p/n 14-008031-01) – for HiPer GGD only; used
to connect the receiver and an external device (hand-held
controller or computer) via the USB port
Serial
SAE-to-SAE extension
Receiver Pwr-to-SAE
USB
Figure 1-2. System Cables
Antenna
Alligator clip-to-SAE
Power Supply/Charger
The Power Supply/Charger unit (p/n 22-034101-01) is used to
charge the internal batteries when connected to a grounded
outlet; it can also be used as an external power source
(Figure 1-3 on page 1-10). This unit converts the alternating
current (AC) normally supplied from an electrical outlet to a
direct current (DC) used to charge the batteries and power the
receiver.
• input voltage – between 100 and 240 V AC
• frequency of input power – between 50 Hz and 60 Hz
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
1-9
Page 26

Introduction
• output voltage – 12 V DC@2.5 A (30 W)
Figure 1-3. Power Supply/Charger
Software
Standard receiver software includes:
• PC-CDU – controller software that can run on a
Windows-based computer. Please refer to the PC-CDU
User’s Manual for detailed information on this software.
• GPS radio configuration software – software for
configuring the radio; such as, PDLCONF from Pacific
Crest and TopSURV from Topcon.
1-10
• Topcon Tools – Topcon’s post-processing software.
Software and software information are also available on the
Topcon website (www.topcongps.com/software/index.html or
http://www.topcongps.com/software/3rdparty.html).
The following software will also be useful for operating, caring
for and using your receiver, and may be required for some
applications.
• FLoader – Topcon’s firmware loader; available on the
Topcon website.
• PDLCONF from Pacific Crest – radio configuration
program included with Base station package; firmware
upgrades available from the Pacific Crest website
(www.paccrst.com/download/upgrade.htm).
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 27

Standard Package Contents
• T opSURV – T opcon’s field data collection software; among
many other functions, can be used to configure the radio/
modem.
• Survey Pro GPS – optional third-party software for data
collection and display; contact your TPS dealer.
• Carlson SurvCE – optional third-party software for data
collection; contact your TPS dealer.
Literature
Receiver literature includes:
• One year warranty card
• HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
• Functional specifications
• Packaging instruction card
Manuals and other product information are also available on the
Topcon website.
• www.topcongps.com/support/manuals.html
• www.topcongps.com/hardware/index.html (then click on
the appropriate product)
The following manuals will also be useful for operating and
caring for your receiver . These are also av ailable on the Topcon
website (www.topcongps.com/support/manuals.html).
• PC-CDU User’s Manual
• FLoader User’s Manual
• MINTER User’s Manual
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
1-11
Page 28
Introduction
Getting Acquainted
The HiPer GD/HiPer GGD receiver is 159mm wide, 172mm deep,
88mm high, weighs 1.65kg, and is a versatile receiver that can be
configured in several different ways, depending on the usage and
function of the receiver at the jobsite. The casing allocates space for
two nonremova b l e, on-board Li-Ion batteries and two Euro cards.
One of those cards is the GPS+ receiver and the other is used for
communications (modem, spread spectrum, GSM, or DGPS).
The HiPer GD/HiPer GGD has standard interior receiver
components and two end panels for user interface, communication,
and power supply.
Table 1-1 shows the differences of certain components and options
between the HiPer GD and HiPer GGD receivers. For receiver
specifications, see Appendix B. See also T a ble 1-2 on page 1-15 for
detailed receiver board comparisons.
Table 1-1. HiPer GD vs. HiPer GGD
Components and Options HiPer GD HiPer GGD
User interface 4-light MINTER 4-light MINTER
Ports Serial A, B, C, D,
PWR
Receiver board Euro-80 Euro-112
GPS L1, L1/L2 L1, L1/L2
GLONASS L1 L1, L1/L2
Memory Standard: 0 MB
Optional: 1 MB up to
512 MB
Battery life with radio ON ~16 hours ~12 hours
Battery life with radio OFF ~18 hours ~14 hours
Serial A, B, C, D,
USB, PWR
Standard: 0 MB
Optional: 1 MB up to
1 GB
1-12
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 29

Getting Acquainted
Internal Components
Features inside the receiver casing are described in the
following sections.
GPS+ Antenna
An internal, micro-strip antenna capable of receiving GPS
L1/L2 and GLONASS L1/L2 signals.
Radio Modem
The receiver incorporates an internal modem for receiving
data from a Base station. The Base station’s modem
transmits the carrier phase and code measurements along
with the reference station information (i.e., location and
description) to the Rover’s modem.
Your receiver may be equipped with one of the following
communication boards (howev er , your receiver may also be
configured without a radio modem):
• UHF modem – a Pacific Crest PDL (Positioning Data
Link) modem; either a 450–470 MHz or 430–450
MHz; receiving only.
• GSM – dual-band, dual-user cell phone frequency
modem (Europe and Japan: 900/1800 MHz; USA and
Canada: 900/1900 MHz).
NOTICE
NOTICE
To comply with RF exposure requirements, maintain at
least 20cm between the user and the GSM radio modem.
The Base station operator is responsible for complying with
local regulations for radio operation. In the US, the FCC
regulates the use of radio transmitters, requiring a license.
Broadcasting without a license can result in severe
penalties including the confiscation of your radio and
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
1-13
Page 30

Introduction
GPS+ equipment. Please call TPS Customer Support if you
need advice on obtaining the proper license in the USA.
The internal radio modem comes with a number of preset
frequencies programmed at TPS.
WARNING
WARNING
The use of these preset frequencies without a license
is illegal. Contact your local authorities (the FCC in
the US) to use these preset frequencies.
Once the FCC, or your local authority, issues the proper
licenses, your TPS dealer will program your PDL radios
(Base and Rover) to enable communications.
Complete information regarding your radio system can also
be found in your radio modem documentation.
Power Board
The internal power board manages receiver power and
battery charging, and is connected to the receiver board and
the batteries. The power board receives power from the
internal batteries, even when the receiver is turned of f. This
feature allows the internal batteries to charge, regardless of
the receiver’s status (on or off). To prevent the batteries
from discharging when the receiver is stored, put the
receiver in Zero Power Mode (see “Zero Power Mode” on
page 4-21 for more information). The batteries will not
charge in this mode.
1-14
The power board’ s processor and firmware are independent
of the receiver card. To ensure firmware compatibility, the
GPS receiver board and power board must be loaded with
firmware from the same package.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 31

GPS+ Receiver Board
The receiver is supplied with one of the following receiver
boards:
• Euro-80 card for HiPer GD receivers
• Euro-112 card for HiPer GGD receivers
Depending on the purchased options, these cards are
capable of processing the following signals:
• GPS L1 or GPS L1/L2
• GPS/GLONASS L1 or GPS/GLONASS L1/L2
Table 1-2 lists the options available for these cards.
Table 1-2. Euro Card Options for HiPer GD and HiPer GGD
Euro Card Model Available Options
Euro-80 GG (HE_GG) G: GPS L1
GG: GPS/GLONASS L1
Euro-80 GD (HE_GD) G: GPS L1
GD: GPS L1/L2
Getting Acquainted
Euro-112 (HE_GGD) G: GPS L1
GD: GPS L1/L2
GG: GPS/GLONASS L1
GGD: GPS/GLONASS L1/L2
A WAAS-enabled TPS receiver allows simultaneous
tracking of two WAAS satellites. Each of the WAAS
satellites is allocated its own channel.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
1-15
Page 32

Introduction
Battery
The receiver is equipped with two nonremovable, on-board,
rechargeable Lithium-Ion battery packs connected to the
receiver’s power board. Each one of these Lithium-Ion
battery packs is 7.4 V and 3 Ah, giving you a total po wer of
7.4 V, nominal, and 6 Ah when fully charged.
With a full charge, the internal batteries should power both
the GPS+ receiver and the radio modem for at least 16
working hours for the HiPer GD or 12 hours for the HiPer
GGD. If the internal radio modem is turned off, and with
fully charged on-board batteries, the GPS+ receiver should
run at least 18 hours for the HiPer GD or 14 hours for the
HiPer GGD.
The Li-Ion batteries used in the receiver sh ou ld run at no
less than 98% capacity after 500 charging cycles. These
batteries do not need to be drained before recharging.
A battery charger (AC adapter) is included with the
standard package. See Appendix B for technical
specifications on the battery.
1-16
External Components
The HiPer GD/HiPer GGD casing include panels for antenna
attachment, a user interface, a power port, and ports for
configuration.
Radome
Location of GPS/GLONASS internal antenna.
Bottom Panel
• Receiver serial number
• Receiver part number
• Antenna Reference Point (ARP)
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 33

Getting Acquainted
Front Panel
Figure 1-4 and Figure 1-5 on page 1-18 show front panel
components for the HiPer GD and HiPer GGD.
Figure 1-4. HiPer GD Front Panel
• MINTER – The Minimum INTERface for the HiPer
GD and HiPer GGD receivers. The MINTER consists
of two keys and four, three-color LEDs. See “Using the
MINTER” on page 4-2 for descriptions and usages of
the MINTER components.
• Reset – This key performs a hard reset for both the
receiver board and the power board. Once this key is
pressed, the controllers governing the receiver and
power boards reboot and the device restarts.
This key can be used to leave Zero Power Mode or if
the receiver does not respond to commands. See “Using
the MINTER” on page 4-2 for more information on the
Reset key.
• Four serial ports:
–Port A used for communication between the receiver
and a controller or any other external device.
–Port B used for an optional third serial port.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
1-17
Page 34

Introduction
–Port C used internally to connect the modem and
receiver boards.
–Port D used for communication between the receiver
and an external device.
Figure 1-5. HiPer GGD Front Panel
• USB – Only available on the HiPer GGD receiv er; used
for high-speed data transfer and communication
between the receiver and an external device.
1-18
• PWR – The power input port to which an external
power source (+6 to +28 V DC) is connected and where
the unit is charged.
• Slant height measure mark (SHMM)
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 35

Getting Acquainted
Back Panel
Figure 1-6 shows back panel components for the HiPer GD
and HiPer GGD receivers; components are the same for
both receivers.
Figure 1-6. HiPer GGD and HiPer GD Back Panels
• Modem – modem antenna connector.
• Event (optional) – The BNC event marker connector;
provides event input synchronized with a specified
reference time.
• 1PPS (optional) – The BNC connector for 1 pulse-per-
second (1PPS); generates 1PPS signals with
programmable reference time, period, and offset;
synchronized to a specified reference time.
• Modem antenna connector – Modem antenna
connector used for internal modem RF connection.
This is a BNC female connector for Pacific Crest PDL
(UHF) modems, or a TNC female connector for GSM
modems.
• Slant height measure mark (SHMM)
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
1-19
Page 36

Introduction
Option Authorization File (OAF)
Topcon Positioning Systems issues an Option Authorization File
(OAF) to enable the specific options that customers purchase. An
Option Authorization File allows customers to customize and
configure the receiver according to particular needs, thus only
purchasing those options needed.
Typically, all receivers ship with a temporary OAF that allows the
receiver to be used for a predetermined period of time. When the
receiver is purchased, a new OAF activates desired, purchased
options permanently. Receiver options remain intact when clearing
the NVRAM or resetting the receiver.
The OAF enables the following kinds of functions. For a complete
list of available options and details, visit the TPS website
(www.topcongps.com/tech/index) or consult your TPS dealer.
• Type of signal (standard L1; optional L2)
• Memory (standard 0MB; for HiPer GD, optional 1MB up to
512MB; for HiPer GGD, optional 1MB up to 1 GB)
1-20
• Update rate standard 1Hz (optional 5, 10, or 20Hz)
• RTK at 1Hz, 5Hz, 10Hz, and 20Hz
• R TCM/CMR Inpu t/Outp ut
•Event marker
• Co-Op tracking
• Advanced multipath reduction
• Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS)
• Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM)
• 1 PPS (Pulse-Per-Second; a timing signal)
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 37

Chapter 2
Configuration
This chapter describes:
• Receiver’s power supply
• Connecting the receiver and a computer
• Configuring the receiver
• Minimum INTERface (MINTER) configuration
• Radio configuration
• Collecting almanacs
Before you can use your receiver, you need to:
1. Charge the batteries. See “Powering the Receiver” on page 2-2.
2. Configure the various parts of your receiver. See:
• “Connecting the Receiver and a Computer” on page 2-11,
• “Receiver Configuration” on page 2-14,
• “MINTER Configuration” on page 2-18, and
• “Radio Configuration” on page 2-26 (if applicable).
3. Collect an almanac. See “Collecting Almanacs” on page 2-40.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-1
Page 38

Configuration
Powering the Receiver
You can power the receiver using the internal batteries, an external
battery, or the battery charger.
Internal batteries
With a full charge, the recei ver’ s internal batteries should power
both the GPS receiver and the radio modem for not less than 16
working hours for the HiPer GD or 12 hours for the HiPer
GGD. If the internal radio modem is turned off, and with fully
charged on-board batteries, the receiver should run at least 18
hours for the HiPer GD or 14 hours for the HiPer GGD.
1. To charge the internal batteries:
• Plug the receiver-to-SAE power cable into the
receiver’s power input port.
• Connect the receiver-to-SAE power cable and the
power supply-to-outlet cable to the AC adapter.
• Plug the power supply-to-outlet cable into an available
outlet.
2-2
CAUTION
CAUTION
Use a grounded wall outlet or grounded surge
protector while charging.
2. Press the Reset key on the receiver. This will ensure that
the receiver is in Normal mode for charging. The receiver
will not charge in Zero Power Mode (see “Zero Power
Mode” on page 4-21 for more information).
3. Leave ov ernight. A nine-h our charge will charge the
batteries about 90%. A ten-hour charge will fully charge
the receiver. The internal batteries cannot be overcharged.
The speed of the charge depends on the Power and Charger
settings on the PC-CDU Receiver Configuration screen, and
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 39

Powering the Receiver
whether the receiver is turned off or on. See “Power
Management” on page 2-5 fo r more information.
The Li-Ion batteries used in the receiv er shou ld run at no less
than 98% capacity after 500 charging cycles. These batteries do
not need to be drained before recharging.
External Batteries
In addition to the internal batteries, you can use your receiver
with external batteries. The use of external batteries allo ws you
to continue using the receiver in case the internal batteries are
discharged. To use external batteries, you must have:
• a 12 V, 2.3 A*h battery
• a 2.3 A*h battery clip-to-SAE cable
• an SAE-to-Power Plug cable
When the receiver uses external batteries, make sure that the
charger mode is set to Off. Otherwise, the e xternal batteries will
also charge the internal batteries, causing operation time to
decrease. See “Power Management” on page 2-5 for more
information on setting the charger mode.
1. Connect the SAE ends of the battery clip-to-SAE and the
SAE-to-power plug cables.
2. Plug the power cable into the receiver’s power port.
3. Attach the battery clip to the battery.
A single external 12 V, 2.3 A*h battery should run the receiver
for about 7 hours and the receiver and modem for 5 hours.
TIP
TIP
Use an SAE-to-SAE extension cable and an Alligator
clip-to-SAE cable, and power the receiver directly from a
battery, such as the battery used to power the Base
radio, or other similar battery.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-3
Page 40

Configuration
Battery Charger
The same charger used to charge the internal batteries can be
used as an external power supply for the receiver. The charger
is provided with the receiver package.
1. Connect the receiver-to-SAE cable to the receiver’s power
port.
2. Connect the SAE end of the cable to the battery charger.
3. Plug the battery charger’s power cable into the AC adapter.
4. Plug the power cable into an available, grounded outlet.
The power input for your battery charger should be AC
between 90 and 264 V 1A (110 V AC) and between 47 Hz
and 63 Hz. The battery charger outputs DC 12 V 2.5 A
(30 W).
Turning On/Off the Receiver
T o turn On the receiv er, press the green power k ey for about 0.5
seconds and release it.
2-4
NOTICE
NOTICE
If the receiver does not turn on, it may be in Zero Power
Mode. See “Zero Power Mode” on page 4-21 for more
information.
T o turn Of f the recei ver , press and hold the green power key for
one to four seconds (until both the STAT and the REC LEDs
turn off). This delay (about 1 second) will prevent the receiver
from being turned off by mistake.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 41

Powering the Receiver
Power Management
You can use Topcon’s PC-CDU software to manage your
receiver’s power. The complete description of PC-CDU
exceeds the scope of this manual, but can be found in the
PC-CDU User’s Manual. The latest copy of this software and
the manual can be downloaded from the TPS website.
Use the following procedure to access the tab controlling the
power settings of the receiver.
1. Connect your receiver and computer. See “Connecting the
Receiver and a Computer” on page 2-11 for this procedure.
2. Once connected, click ConfigurationReceiver
(Figure 2-1).
Figure 2-1. Configure Receiver
3. Select the Power Mode drop-down list to set the desired
power source (Figure 2-2 on page 2-6). Current Mode
displays the current power source.
• Auto – receiver automatically selects the power source
• Mix – receiver automatically detects and consumes
power from the source with the largest voltage
• Battery A – receiver consumes power from battery A
• Battery B – receiver consumes power from battery B
• External – receiver uses an external power supply
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-5
Page 42

Configuration
Figure 2-2. Select Power Mode
4. Select the Charger Mode drop-down list to set the desired
charger mode (Figure 2-3). Current Mode displays the
charging battery: a, b, or none (off).
• Off – receiver will not charge batteries
• Charge A – receiver charges only battery A
• Charge B – receiver charges only battery B
2-6
• Auto – receiver automatically detects and charges both
batteries
Figure 2-3. Select Charger Mode
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 43

Powering the Receiver
5. Select the Power output modes, Ports drop-down list to set
power output on the serial ports (Figure 2-4).
• On – the power board will deli ver v oltage on pin one of
all serial port connectors when the receiver is turned
on. If the receiver is turned off, there will not be any
power on the ports.
• Off – the power will be absent even if the receiver is
turned on
• Always – the power board will deliver voltage on pin
one of all serial port connectors even if the receiver is
turned off
Figure 2-4. Select Power Output Modes – Ports
6. Select the Power output modes, Slots drop-down list to set
power output on internal slots (Figure 2-5 on page 2-8).
• On – all slots are powered if the receiver is turned on
• Off – internal slots will not be powered even if the
receiver is turned on
• Always – internal slots will be powered even if the
receiver is turned off
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-7
Page 44

Configuration
Figure 2-5. Select Power Output Modes – Slots
7. View the Voltages information (Figure 2-6).
• External – displays the external power supply’s voltage
• On Board – displays the voltage drawn by the receiver
board
• Battery A – displays the voltage of battery A
2-8
• Battery B – displays the voltage of battery B
• Charger – displays the charger’s output voltage during
battery charging
Figure 2-6. View Voltages Information
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 45

Powering the Receiver
8. Select and check each of the Turn on/off Slots check boxes
to enable the corresponding internal slots (Figure 2-7).
9. Select and check the Enable Low P ower Mode check box to
put the receiver’s processor into low power consumption
mode (Figure 2-7).
Figure 2-7. Enable and Apply Power Settings
10. Click Apply.
Charge Internal Batteries
Use one of the following conditions for maximum battery
charge speed.
• The receiver is turned off. Power Mode and Charger
Mode are set to Auto. See “Power Management” on
page 2-5 for setting these parameters.
• The receiver is turned on. Power Mode is set to
External and Charger Mode is set to Auto.
1. To charge the internal batteries:
• Plug the receiver-to-SAE power cable into the
receiver’s power input port.
• Connect the receiver-to-SAE power cable and the
power supply-to-outlet cable to the AC adapter.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-9
Page 46

Configuration
2. Press the Reset key on the receiver. This will ensure
3. Leave overnight. A nine-hour charge will charge the
4. When finished charging, set Power Mode to Auto.
• Plug the power supply-to-outlet cable into an
available outlet.
that the receiver is in Normal mode for charging. The
receiver will not charge in Zero Po wer Mode (see “Zero
Power Mode” on page 4-21 for more information).
batteries about 90%. A ten-hour charge will fully
charge the receiver. The internal batteries cannot be
overcharged.
2-10
NOTICE
NOTICE
If you remove a power supply cable before setting Power
Mode to Auto, the receiver will be turned off. To turn it on,
you will need to connect an external power supply once
again.
Check Internal Battery Status
To check the status of the internal batteries:
1. View the BATT LED for battery status. See “Battery
LED” on page 4-7 for more information on this LED.
• A green light indicates greater than 85% charge.
• An orange light indicates an intermediate charge.
• A red light indicates less than 15% charge.
2. Do one of the following:
• Click on ConfigurationReceiver to view battery
voltages on the Receiver Configuration screen.
• Click on HelpAbout to view battery voltages on
the About PC-CDU screen.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 47

Connecting the Receiver and a Computer
Connecting the Receiver and a
Computer
To configure, manage files, or maintain the receiver, you need to
connect the receiver and a computer, and start PC-CDU.
• For HiPer GD or HiPer GGD – use an RS232 cable.
• For HiPer GGD – use a USB cable and a computer with the
TPS USB driver installed (available at
http://www.topcongps.com/software/updates.html).
PC-CDU is a Personal Computer-Control Display Unit software
used to manage the various functions of your receiver. The full
range of PC-CDU configuration and function is outside the scope of
this manual. For more information on any of the procedures in this
section or on PC-CDU, refer to the PC-CDU User’s Manual
available on the TPS website.
Once you have established a connection between the receiver and
the computer, you will be able to:
• Configure the receiver and its components
• Send commands to the receiver
• Download files from the receiver’s memory
• Load OAFs and configuration files to the receiver
• Use FLoader to load new firmware to the receiver
1. Connect the computer and receiver:
• For HiPer GD or HiPer GGD – using the RS232 cable,
connect the serial port of your computer (usually COM1) to
the receiver’s serial port A.
• For HiPer GGD – using the USB cable, connect the USB
port on the receiver to a USB port on the computer (make
sure the computer has the TPS USB driver installed).
2. Press the power buttons on the receiver and computer to turn
them on.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-11
Page 48

Configuration
3. Start PC-CDU on your computer. The PC-CDU main screen
displays (Figure 2-8).
Figure 2-8. PC-CDU Main Screen
Notice that the lower-left hand corner shows the receiver status as
“Disconnected”.
4. Click FileConnect (Figure 2-9).
2-12
Figure 2-9. Connect to Receiver
5. On the Connection Parameters dialog box, select the following
parameters and click Connect (Figure 2-10 on page 2-13):
•Set the Connection mode (Direct).
• Set the port for your computer (typically COM1) from the
Port drop-down list.
• Set the communication rate between the receiver and the
computer (usually 115200) from the Baud rate drop-down
list.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 49

Connecting the Receiver and a Computer
Figure 2-10. Connection Parameters
Once a PC-CDU connection with the receiver has been established,
the current communications settings—such as, port name, baud rate
(if applicable), and flow control (if applicable)—display in the
lower-left corner of the main window of PC-CDU. A timer begins
to count up in the lower-right corner as well (Figure 2-11).
Figure 2-11. PC-CDU Connection Established
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-13
Page 50

Configuration
Receiver Configuration
PC-CDU is Topcon’s receiver configuration software, used to
configure the various parts of the receiver. An y settings made using
PC-CDU will be saved in the receiver’s memory, and will be
reflected when you use the MINTER. The full range of PC-CDU
configuration and function is outside the scope of this manual.
TIP
TIP
Refer to the PC-CDU User’s Manual to manage all
possible receiver configurations.
The following configur ation is recommended for the most common
applications. However, you can select configuration parameters as
needed for your particular jobsite. Also, available parameters may
differ for the HiPer GD and HiPer GGD receivers.
2-14
NOTICE
NOTICE
Click Apply after making any configuration change,
otherwise the receiver will not accept the change.
1. Connect your receiver and computer. See “Connecting the
Receiver and a Computer” on page 2-11 for this procedure.
2. Once connected, click ConfigurationReceiver
(Figure 2-12).
Figure 2-12. Configure Receiver
The Receiver Configuration dialog box displays.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 51

Receiver Configuration
3. Click the MINTER tab, configure the following settings, and
click Apply (Figure 2-13).
•Set the Recording interval in seconds.
•Set the Elevation mask for Log file in degrees.
•Enter the File name prefix. Use the last three digits of the
receiver serial number. The receiver’s serial number and
part number can be found on the bottom panel of the
receiver.
Figure 2-13. Receiver Configuration – MINTER Tab
If your jobsite is in an area that has obstructions (buildings, trees,
etc.), and/or the antenna location is near reflective objects,
configure the receiver to reduce errors from these sources.
WARNING
WARNING
Do not make other changes without consulting the
PC-CDU User’s Manual.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-15
Page 52

Configuration
4. Click the Advanced tab on the Receiver Configuration screen
(Figure 2-14).
Figure 2-14. Receiver Configuration – Advanced Tab
5. Click the Multipath Reduction tab, enable the following boxes,
and click Apply (Figure 2-15).
• Code multipath reduction
2-16
• Carrier multipath reduction
Figure 2-15. Advanced Configuration – Multipath Reduction
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 53

Receiver Configuration
6. Click the Loop Management tab, enable the following boxes,
and click Apply (Figure 2-16).
• Enable Co-Op tracking
• Static Mode (used for static receivers only, disable if using
the receiver as a Rover)
Figure 2-16. Advanced Configuration – Loop Management
7. Click OK to close the Receiver Configuration screen.
8. Click FileDisconnect, then FileExit to quit PC-CDU.
NOTICE
NOTICE
Disconnecting the receiver from the computer before
exiting will eliminate any possible conflict in the
management of your serial ports.
Once the receiver is configured, the configuration will remain until
you change it either using PC-CDU or clearing the NVRAM.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-17
Page 54

Configuration
MINTER Configuration
The Minimum INTERface (MINTER) consists of two keys (Power
and FN) and up to four LEDs (STAT, REC, BATT, and RX) that
control and display the receiver’s operation (Figure 2-17 on
page 2-19).
The MINTER performs numerous functions:
• Turn the receiver on/off, put it in Sleep or Zero power mode.
• Turn data recording on or off (FN key).
• Change the receiver’s information mode.
• Show the number of GPS (green) and GLONASS (orange)
satellites being tracked (STAT LED).
• Show data recording status (REC LED).
• Show each time data records to internal memory (REC LED).
• Show the status of post-processing mode (static or dynamic)
when performing a Post-Processing Kinematic survey with the
help of FN key (REC LED).
2-18
• Show the status (high charge, intermediate charge, or low
charge) of the battery (BATT LED).
• Show the power source for the receiver (BATT LED).
• Show the modem’s status and if it receives signals (RX LED).
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 55

MINTER Configuration
Figure 2-17. HiPer GGD and HiPer GD MINTERs
You use PC-CDU to configure MINTER settings. Refer to the
PC-CDU User’s Manual for all possible MINTER configurations.
1. Connect your receiver and computer. See “Connecting the
Receiver and a Computer” on page 2-11 for this procedure.
2. On the Connection Parameters dialog box, enable RTS/CTS
handshaking (Figure 2-18).
Figure 2-18. Connection Parameters – RTS/CTS Handshaking
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-19
Page 56

Configuration
3. Click ConfigurationReceiver (Figure 2-19).
Figure 2-19. Configure Receiver
4. Click the MINTER tab, set the following parameters and click
Apply (Figure 2-20). See the following pages for descriptions
of these parameters.
• Recording interval on page 2-21
• Elevation mask for log file on page 2-21
• File name prefix on page 2-21
• Always append to the file on page 2-21
• Files Creation mode on page 2-22
• Automatic File Rotation Mode (AFRM) on page 2-22
• FN key mode on page 2-23
2-20
• Initial data collection dynamic mode on page 2-24
• Data recording auto-start on page 2-24
Figure 2-20. Receiver Configuration – MINTER Tab
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 57

MINTER Configuration
Recording Interval parameter
This parameter specifies the message output interval into the
log file when the MINTER FN key (pressed for 1–5 seconds)
activates data logging. This setting is used not only when
logging a single log file, but also when logging recei ver data in
AFRM mode. Values are 1–86400 seconds.
The default value is one second.
Elevation Mask for Log File parameter
This parameter specifies the minimum elevation angle for the
satellites whose data will be put in the receiver files logged
when pressing FN.
The default value is five degrees.
File Name Prefix parameter
This parameter specifies what prefix will be added to the names
of the receiver files created when pressing FN. The prefix can
be up to 20 characters long.
The default value is log.
Log file names have the following structure:
<prefix><month><day><sequential alphabet letter>
The file name depends on both the file creation time (month
and day) and additional letter suffixes to avoid confusion
between files created on the same day.
Always Append to the File parameter
If you want the new recei ver data to be appended to an existing
log file, enter the desired filename in this parameter. The setting
can be up to 20 characters long.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-21
Page 58

Configuration
Files Creation Mode parameter
This parameter has two possible operation modes:
• Log file – If the log file radio button has been selected,
pressing the FN key will result in closing the current log
file. If data logging is off, pressing FN will open a new log
file.
• AFRM – If AFRM radio button has been selected, pressing
FN will enable this mode. If AFRM has been enabled,
pressing FN will disable this mode.
Automatic File Rotation Mode (AFRM) parameters
TPS receivers are capable of automatically rotating log files.
During a “file rotation” event, the receiver closes the current
file and opens a new one according to a user-defined schedule.
The Period and Phase parameters specify this schedule. File
rotation launches the moment the receiver time module Period
is equal to Phase. More precisely, a new log file opens
immediately before the scheduled epoch causing data tagged
with this epoch to be recorded to the new log file.
2-22
When opening a new log file, the receiver enables the default
set of messages outputted with the default output period. Both
the default set of messages and the default output period are
programmable.
• Period – specifies the time duration of each log file created in
AFRM mode.
Values are 60 to 86400 seconds. The default value is 3600
seconds.
• Phase – specifies the “phase” (constant time shift) of creating
multiple log files in AFRM mode.
Values are 0 to 86400 seconds. The default value is zero
seconds.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 59

MINTER Configuration
• Files (total) – a counter that specifies how many multiple log
files must be created in AFRM until this mode automatically
turns off. This counter decrements on every file rotation until it
value becomes zero, then file rotation automatically stops. The
counter initializes with AFRM.
Note that a log file opens immediately after turning AFRM on.
This startup file is not considered a file rotation event; the
AFRM counter will not decrement.
Values are 0 to [2
31
-1]. The default value is 0 (zero). Zero
means that an unlimited number of log files will be created.
NOTICE
NOTICE
The receiver’s memory holds up to 512 files.
• Files (remain) – specifies the number of files left for the
receiver to create in AFRM.
31
Values are 0 to [2
-1]. The default value is zero.
• Automatically remove old files – when no free memory is
available to log data, automatically remo ves the earliest log f ile.
If this parameter is enabled, your receiver will erase the file
with the earliest file creation time/date. AFRM must be enabled
to use this FIFO (First-In, First-Out) feature.
The default value is off (disabled).
FN Key Mode parameter
You use these two radio buttons to program how the receiver
will react when pressing the FN key.
• LED blink mode switch – pressing FN will toggle between the
MINTER’s normal/extended information modes and start/stop
data recording of Static survey.
– FN pressed less than 1 second: changes the information mode
(Normal or Extended Information (EI) Modes).
2-23
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
Page 60

Configuration
– FN pressed from 1 to 5 seconds: starts or stops recording
(Static post-processing mode).
• Occupation mode switch – pressing FN (less than one second)
will insert into the corresponding log file a message indicating
that the survey type has been changed from static to kinematic,
or vice versa. If the REC LED blinks green, the current mode is
dynamic, if it blinks orange, the current mode is static. For
more details, see Table 4-1 on page 4-5, and refer to the
MINTER User’s Manual and PC-CDU User’s Manual.
Initial Data Collection Dynamic Mode parameter
These radio buttons specify the starting occupation type
descriptor inserted at the beginning of receiver files logged.
You select Static or Kinematic to specify that the corresponding
log file will start with a static (STOP) or kinematic (GO,
Trajectory) occupation, respectively.
Data Recording Auto-start parameter
These radio buttons allow you to program your receiver’s
behavior in the event of a power failure.
2-24
Table 2-1 on page 2-25 gives the different scenarios available
and the results after power is restored to the receiver . “Specif ied
file” refers to the file name entered in the Al ways ap pend to f ile
parameter.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 61

MINTER Configuration
Table 2-1. Data Recording Parameter Behavior
Before Power
Failure
1
Receiver data
logged to file
specified.
2
Receiver data
logged to
default file.
3
File specified;
receiver data
logging not
started.
4
No file
specified;
receiver data
logging off.
Enabled Radio Button Results
Off On Always
Data logging will
not resume when
power is restored.
Data logging will
not resume when
power is restored.
No file will open
with this name.
Data logging will
not start when
power is restored.
Data logging will
not start when
power is restored.
Receiver will
resume data
logging to the
same file when
power is restored.
A new log file
will open when
power is restored
and data will log
to this file.
No file will open
with this name.
Data logging will
not start when
power is restored.
Data logging will
not start when
power is restored.
Receiver will
resume data
logging to the
same file when
power is restored.
A new log file
will open when
power is restored
and data will log
to this file.
A log file with
this name will
open and data
logging will start
after power is
restored.
A log file with a
default name will
open and data
logging will start
after power is
restored.
Also, if Always is enabled, the receiver will automatically start
logging data (to a newly created or an existing file) in the
following three cases:
• After pressing the MINTER power key.
• After resetting the receiver (with PC-CDU or the Reset
key).
• After taking the receiver out of Sleep Mode.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-25
Page 62

Configuration
Radio Configuration
The internal radio in your receiver and the Base radio can be
configured differently depending on your needs and working
conditions. The software program required to configure the radio
modem differs depending on your receiver’s configuration, and
allows you to:
• access the internal modem
• configure the modem
• check or change the modem configuration
The following sections provide basic radio configuration
information for UHF and GSM radio modems.
2-26
NOTICE
NOTICE
Your receiver may be configured without a radio modem.
If this is the case, please skip to “Collecting Almanacs”
on page 2-40.
Configuring a UHF Radio Modem
To access your PDL UHF radio modem, you create a daisy
chain between the receiver serial port (A or D) and the radio
modem (Port C) using PC-CDU. You then activate the PDL
configuration program on your PC and proceed with the radio
configuration.
1. Connect your receiver and computer. See “Connecting the
Receiver and a Computer” on page 2-11 for this procedure.
2. On the Connection Parameters dialog box, select a 38400
baud rate and turn off the RTS/CTS handshaking parameter
(if needed).
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 63

Radio Configuration
3. Once connected, click on FileManual Mode
(Figure 2-21) to open the Manual Mode dialog box.
Figure 2-21. Enter Manual Mode
4. T o create a daisy chain between the recei ver’s port (A or D)
and the PDL modem, type each of the following
commands, pressing Enter (or clicking Send command)
after each command.
%%set,dev/ser/c/rate,38400
%%set,dev/ser/c/echo,/cur/term
%%set,dev/ser/c/imode,echo
%%set,cur/term/eoff,QUIT
%%set,cur/term/echo,/dev/null
%%set,cur/term/imode,echo
%%set,cur/term/echo,/dev/ser/c
The Manual Mode screen displays RE002%% in response
to each of these commands. When finished, you should
have seven responses (Figure 2-22 on page 2-28).
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-27
Page 64

Configuration
Figure 2-22. Manual Mode – Command Responses
TIP
TIP
Save this set of commands to a script file and load this
file later to the receiver with a single operation. To create
a script file, see Appendix A.
2-28
5. Click Disconnect (Figure 2-22).
6. Run the PDL Radio Configuration Program (pdlconf.exe)
from Pacific Crest (Figure 2-23 on page 2-29).
Make sure you have the latest version (2.40 or higher).
Upgrades for this software are available on the Pacif ic Crest
website (www.paccrst.com/download/upgrade.htm).
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 65

Radio Configuration
Figure 2-23. PDL Radio Configuration Main Screen
7. Click the Pacific Crest logo in the upper left corner of the
main screen and click Select Serial Port (Figure 2-24).
Figure 2-24. PDL Top Left Corner Icon Menu and Select Serial Port
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-29
Page 66

Configuration
8. Select the computer serial port used to connect the receiver
and computer, and click OK (Figure 2-25).
Figure 2-25. Select Serial Port
If unsure about the location of the modem, click Locate
Modem to have PDLCONF automatically locate the
modem. This process may take several minutes. When
finished, click OK on the confirmation (Figure 2-26).
Figure 2-26. Automatically Locate Modem
2-30
9. Click the Pacific Crest logo in the upper left corner of the
main screen and click Set Capture MethodSoft Break
(Figure 2-27).
Figure 2-27. PDL Top Left Corner Icon Menu and Set Capture Method
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 67

Radio Configuration
10. Click Load to connect to the radio (Figure 2-28).
Figure 2-28. Click Load
11. On the Identification tab, type Owner information
(Figure 2-29).
The Identification screen supplies current information
concerning firmware v ersion, serial number , frequ ency, and
power of the radio modem.
Figure 2-29. PDL Identification Tab
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-31
Page 68

Configuration
12. Click the Radio Link tab (Figure 2-30) and set the
following parameters according to the selected link rate as
shown in Table 2-2.
Table 2-2. Radio Link Parameters
Link Rate
Controls
9600 19200
Manual enable enable
Channel TX RX set channel and frequency
as desired
Modulation T ype GMSK 4-Level-FSK
Digisquelch High High
Forward Error
Correction
Scrambling enable enable
Local Address 0 0
disable enable
set channel and frequency
as desired
2-32
Figure 2-30. PDL Radio Link Tab
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 69
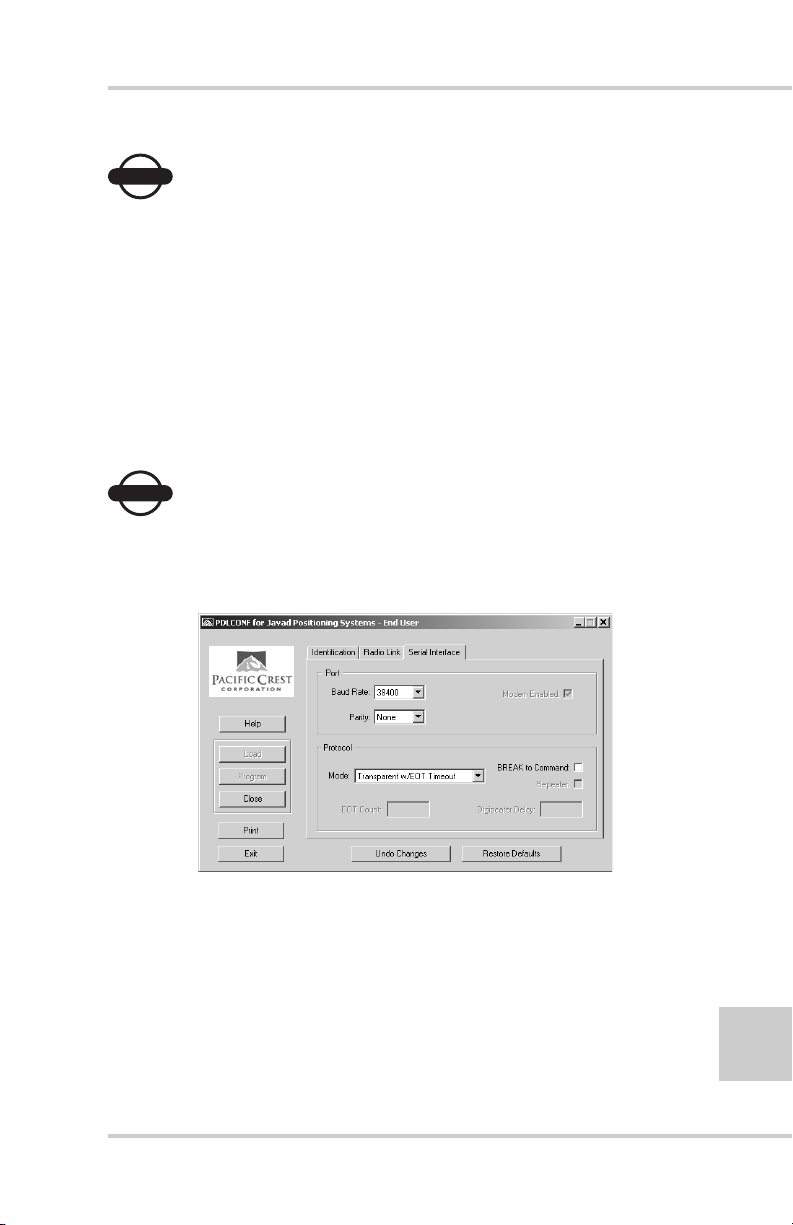
Radio Configuration
NOTICE
NOTICE
The Base and internal receiver (Rover) PDL radios must
be configured with the same Channels, Radio Link
characteristics (except Digisquelch) and Serial Interface
parameters.
13. Click the Serial Interface tab and set the following
parameters (Figure 2-31):
• Baud Rate – 38400
• Parity – None
NOTICE
NOTICE
Parity should always be set to None.
• Mode – Transparent w/EOT Timeout
Figure 2-31. PDL Serial Interface Tab
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-33
Page 70

Configuration
14. If you made changes, click Program on the left of the
screen to save them to the modem’s memory (Figure 2-32).
Figure 2-32. PDL – Click Program
15. Click Close and then Exit to quit the program
(Figure 2-33).
2-34
Figure 2-33. Click Close then Exit
16. Open PC-CDU.
17. Click FileConnect.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 71

Radio Configuration
18. On the Connection Parameters screen, select a baud rate of
38400 and enable the Manual mode only check box
(Figure 2-34), then click Connect.
Figure 2-34. Connection Parameters – Manual Mode Only
19. On the Manual Mode screen, type the following
commands, pressing Enter (or clicking Send command)
after each command. When finished, you should have five
responses (Figure 2-35 on pa ge 2-36).
QUIT
%%set,cur/term/imode,cmd
%%set,dev/ser/c/echo,/dev/null
%%set,dev/ser/c/imode,cmd
%%set,dev/ser/c/rate,38400
%%set,cur/term/rate,115200
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-35
Page 72

Configuration
Figure 2-35. Manual Mode Command Responses
20. Click Disconnect (Figure 2-35). Continue with other
configuration or operation functions as needed.
Configuring a GSM Radio Modem
2-36
NOTICE
NOTICE
To comply with RF exposure requirements, maintain at
least 20cm between the user and the GSM radio modem.
To access your GSM radio modem, you will need to use
Topcon’s FC-1000 external controller and TopSURV™. Refer
to the TopSURV Reference Manual or the TopSURV User’s
Manual for more detailed configuration information.
NOTICE
NOTICE
Configuration parameters are similar regardless of the
software used for configuring a GSM modem.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 73

Radio Configuration
Unlike the UHF radio modems and PDLCONF, TopSURV
automatically connects the receiver and modem boards for
configuration purposes. When you configure radios, you
configure the Base and Rover radios separately.
1. Using the RS232 cable, connect your external controller
(FC-1000) to the receiver’s serial port A.
2. Press the power buttons on the receiver and external
controller to turn them on, and start TopSURV.
3. Click JobConfigSurvey to open the Select Survey
Config dialog box (Figure 2-36).
Figure 2-36. Select a Survey Configuration
4. From the GPS+ Config drop-down list, select My RTK, or
the name of your GPS+ survey configuration, and click the
“...” (continue) button (Figure 2-36).
TIP
TIP
If this is a new configuration, refer to the TopSURV User’s
Manual for the procedure to configure a new survey.
Otherwise, continue below to configure your radio.
5. Press Next to navigate to the Base Radio or Rover Radio
configuration screen, usually a couple dialog box es beyond
the Select Survey Config dialog box.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-37
Page 74

Configuration
6. On the radio configuration dialog box, select the
appropriate GSM radio modem and set the following
parameters (Figure 2-37):
• Port – C for internal radio modems or D for external
radio modems
• Parity – None
• Data – 8
• Baud – 9600
• Stop – 1
2-38
Figure 2-37. Base or Rover Radio Configuration
7. Press Configure GSM to display the appropriate Cell
Phone parameters dialog box, and enter the following
parameters for either the Base or Rover (Figure 2-38).
• For the Base radio – if the GSM modem does not
require a PIN, leave this field blank.
The Base radio is the Slave, only receiving calls from
Rover stations, so no phone number to call is required.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 75

Radio Configuration
• For the Rover radio – if the GSM modem does not
require a PIN, leave this field blank.
The Rover radio is the Master , sending calls to the Base
station. The Base station’s phon e numb er is req uired ,
so have it available to input at this time, or select the
correct number from the Phone number list (if
available).
Then press Add to save the phone number to the list, or
press Delete to remove unwanted phone numbers from
the list.
Figure 2-38. Set Base or Rover Cell Phone Parameters
8. Press OK to return to the radio configuration screen.
Continue with other configuration or operation functions as
needed.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
2-39
Page 76

Configuration
Collecting Almanacs
Each satellite broadcasts a message (almanac) which gives the
approximate orbit for itself and all other satellites. If the receiver
has an almanac, you can considerably reduce the time needed to
search for and lock on to satellite signals.
The receiver regularly updates the almanac and stores the most
recent almanac in its Non-Volatile Random Access Memory
(NVRAM).
1. Set up the receiver (connect the external antenna if needed) in a
location with a clear view of the sky.
2. Turn on the receiver. Wait for about 15 minutes while the
receiver collects almanac data from satellites.
2-40
NOTICE
NOTICE
If 15 minutes have passed and the receiver does not lock
on to satellites, you may need to clear the NVRAM. See
“Clearing the NVRAM” on page 4-18 for this procedure.
You will need to collect or update the almanac:
• If the receiver has been off for a long time.
• If the last known receiver position, stored in the NVRAM, is
different from the present position by several hundred
kilometers.
• After loading a new OAF.
• After loading new firmware.
• After clearing the NVRAM.
• Before surveying.
The collection and/or update of an almanac can take as long as 15
minutes.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 77

Chapter 3
Setup and Survey
This chapter describes:
• Receiver setup
• RTK Base station setup
• RTK Rover setup
• Basic surveying with the HiPer GD or HiPer GGD receiver
Your receiver can be used with either the internal antenna or an
external antenna (with optional base station kit and optional internal
radio card).
Receiver Setup
To set up the receiver, you must:
1. Configure the receiver as shown in Chapter 2.
2. Set up your Base or Rover station. See “Step 1: Set up
Receiver” on page 3-2
3. Measure the antenna height. See “Step 2: Measure Antenna
Height” on page 3-2 for internal antennas, or see “External
Antenna Setup” on page 3-5 for external antennas.
4. Begin collecting data. See “Step 3: Collect Data” on page 3-5.
All receivers include an internal, micro-strip antenna. This antenna
is able to capture L1/L2 signals from GPS and GLONASS
satellites.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
3-1
Page 78

Setup and Survey
Step 1: Set up Receiver
This section assumes you have already configured your receiv er
using PC-CDU.
1. Place the receiver on the appropriate tripod or bipod.
2. Center the receiver over the point at which data will be
collected. For most applications, this should be at a location
with a clear view of the sky.
3. If using the receiver as a Base station, connect the external
radio to the receiver.
Step 2: Measure Antenna Height
The location of the antenna relative to the point being measured
is very important for both surveys in which the elevation of the
points is important and in surveys for horizontal location only.
Horizontal surveys are often larger in area than can reliably fit
on a flat plane, therefore the antenna adjustment must be done
in three dimensions and then projected onto a two dimensional
plane.
3-2
The receiver calculates the coordinates of the antenna’s phase
center. To determine the coordinates of the station marker, the
user must specify the following:
• Measured height of the antenna above the station marker
• Method of measuring the antenna height
• Model of the antenna used
Antennas have two types of measurements:
• Vertical – measured from the marker to the antenna
reference point (ARP) located on the bottom of the receiver
at the base of the mounting threads.
• Slant – measured from the marker to the lower edge of the
antenna slant height measure mark (SHMM) located on
both end panels of the receiver.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 79

Receiver Setup
1. Measure the antenna height above the point or marker (see
“External Antenna Setup” on page 3-5 for external antenna
measurements and setup).
Figure 3-1 illustrates the antenna offsets. (See Figure 1-4
on page 1-17 and Figure 1-6 on page 1-19 for the exact
SHMM location.)
Figure 3-1. HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Antenna Offsets
• SHMM to ARP vertical offset = 30.5mm
• SHMM to ARP horizontal offset = 76.3mm
Table 3-1 gives the offset values for the receivers.
Table 3-1. Antenna Offset Values for HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Options
To L1 Phase Center To L2 Phase Center
Up 106.0mm 101.2mm
Table 3-2 gives the offset values for GD, L1 receivers.
Table 3-2. Antenna Offset Values for HiPer GD, L1 Options
To L1 Phase Center
Up 106.0mm
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
3-3
Page 80

Setup and Survey
The actual point to which surveying with GPS/GLONASS
measures is called the Phase Center of the antenna. This is
analogous to the point at which a distance meter measures
in a prism. A user must enter the prism offset to
compensate for this point not being at a physical surface of
the prism. In the case of a GPS/GLONASS antenna, the
offset is entered depending on the type of measurement
taken. For vertical, the offset is simply added to the
measured vertical height to produce a “true” v ertical height.
For slant height, the vertical height must first be calculated
using the radius of the antenna, then the offset can be
added. The offsets are not the same number because of the
difference in location between the slant measuring point
and the vertical measuring point.
2. Record the receiver serial number, antenna height, point
name, and start time in the field notes.
3. Press the power key and release it to turn the receiver on.
The STAT (status) light (LED) will blink red at first.
4. Once the receiver has locked on to one or more satellites,
the STAT light will blink green for GPS satellites, orange
for GLONASS satellites, and a short red blink indicating it
has not solved a position. Four or more satellites provide
optimal positioning.
5. Once the short red blink is gone, the receiver has a position
and surveying can begin. You should wait for green and
orange lights before beginning data collection. This ensures
that the receiver has the correct date and time, and is locked
on to enough satellites to ensure good quality data.
3-4
The process of locking on to satellites normally takes less
than one minute. In a new area, under heavy tree canopy, or
after resetting the receiver, it may take several minutes.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 81

Receiver Setup
Step 3: Collect Data
1. To begin collecting data, press and hold the FN (function)
key for more than one second and less than five seconds.
2. Release the FN key when the REC (recording) LED light
turns green. This indicates that a file has opened and data
collection has started. The REC LED blinks each time data
is saved to the internal memory.
TIP
TIP
You can use PC-CDU to configure data logging. See
“MINTER Configuration” on page 2-18 or refer to the PC-
CDU User’s Manual for more information.
3. When finished, press and hold the FN key until the REC
LED light goes out.
4. Press and hold the power key until all lights go out, then
release.
External Antenna Setup
The receiver can also be used with an external antenna. Follow
the steps below to connect an external antenna to the receiver
and measure its offset.
1. Attach the antenna to a tripod or bipod and center it over
the point at which data will be collected.
2. Measure the antenna height. Antennas have two types of
measurements:
• Vertical – measured from the marker to the antenna
reference point (ARP) located on the bottom of the
antenna at the base of the mounting threads.
• Slant – measured from the marker to the lower edge of
the antenna’s slant height measure mark (SHMM).
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
3-5
Page 82

Setup and Survey
LegAnt-2 antenna offsets are shown in Figure 3-2;
PG-A1 antenna offsets are shown in Figure 3-3 on
page 3-7. Offset measurements for these antennas are given
in Table 3-3 on page 3-7.
3-6
Figure 3-2. LegAnt-2 Antenna Offset Measurements
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 83
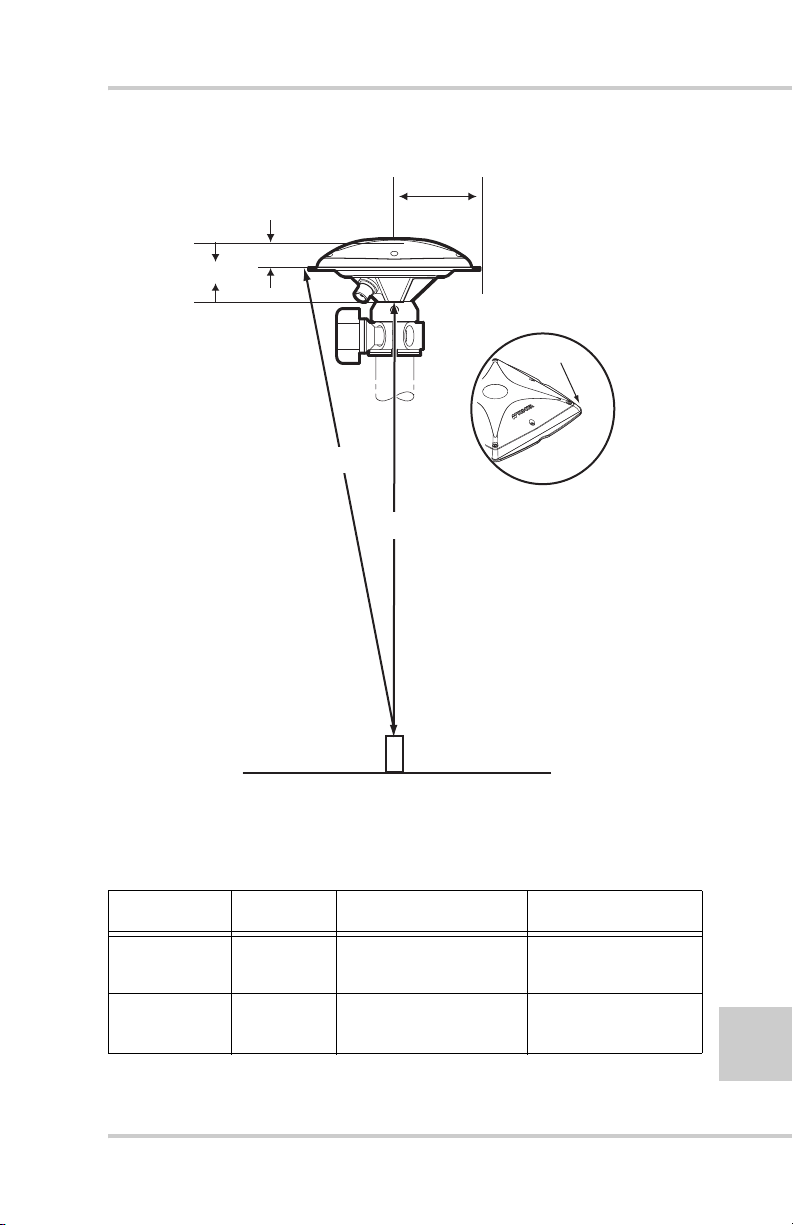
Phase Center
A
Receiver Setup
Radius
C
SHMM
Slant Height
Measurement Point
Vertical Height
Marker
Figure 3-3. PG-A1 Antenna Offset Measurements
Table 3-3. Antenna Offset Measurements
Antenna Radius A, Vertical Offset C, Slant Offset
LegAnt-2 122mm
0.399 ft
PG-A1 89.7mm
0.294ft
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
54mm (L1)
0.176 ft (L1)
54.3mm (L1)
60.5mm (L2)
21mm (L1)
0.069 ft (L1)
26.8mm (L1)
33.0mm (L2)
3-7
Page 84

Setup and Survey
3. Record the receiver serial number, antenna height, point
name, and start time in the field notes.
4. Attach the flexible RF cable from the external antenna to
the antenna connector on the back panel of the receiver.
5. Turn on the receiver and continue with step 3 on page 3-4.
The receiver antenna default is set to Auto, allowing the
receiver to detect automatically the available antenna (whether
internal or external). If you have changed this setting, or the
receiver does not detect the external antenna, use the procedure
below to set the External Antenna detection option.
1. Connect your receiver and computer. See “Connecting the
Receiver and a Computer” on page 2-11 for this procedure.
2. Click ConfigurationReceiver (Figure 3-4).
Figure 3-4. Configure Receiver
3-8
3. On the General tab, select the External Antenna option and
click Apply (Figure 3-5).
Figure 3-5. Select External Antenna Option
4. Click FileDisconnect, then FileExit to quit PC-CDU.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 85

Surveying with the Receiver
Surveying with the Receiver
The receiver can be used to perform static, kinematic, or real-time
kinematic (RTK) surveying.
Static Survey
Static surveying is the classic survey method, well suited for all
kinds of baselines (short, medium, long). At least two receiver
antennas, plumbed over the survey marks, simultaneously
collect raw data at each end of a baseline during a certain
period of time. These two receivers track four or more common
satellites, have the same data logging rate (5–30 seconds), and
the same elevation mask angles. The length of the observation
sessions can vary from a few minutes to several hours. The
optimal observation session length depends on the surveyor’s
experience as well as the following factors:
• The length of the baseline measured
• The number of satellites in view
• The satellite geometry (DOP)
• The antenna’s location
• The ionospheric activity level
• The types of receivers used
• The accuracy requirements
• The necessity of resolving carrier phase ambiguities
Generally , single-frequency receivers are used for baselines
whose lengths do not exceed 15 kilometers (9.32 miles). For
baselines 15 kilometers or greater, use dual-frequency
receivers.
Dual-frequency receivers have two major benefits. First, dualfrequency receivers can estimate and remove almost all
ionospheric effect from the code and carrier phase
measurements, providing much greater accuracy than single-
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
3-9
Page 86

Setup and Survey
frequency receivers over long baselines or during ionospheric
storms. Secondly, dual frequency receivers need far less
observation time to reach the desired accuracy requirement.
After the survey completes, data the receivers collect can be
downloaded onto a computer and processed using postprocessing software (for example, Pinnacle).
The procedure that follows describes the steps the operator
should take to perform a Static Survey using MINTER.
1. Connect your receiver and computer. See “Connecting the
Receiver and a Computer” on page 2-11 for this procedure.
2. Open PC-CDU, click ConfigurationReceiver
MINTER and specify the following parameters, then
click Apply (Figure 3-6):
• Recording interval – 15 seconds
• Elevation mask angle – 15 de grees
• File name prefix – last 3 digits of receiver serial number
• LED blink mode switch – enable to start and stop static
data recording using the FN key
3-10
Figure 3-6. Enable MINTER and Recording Parameters
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 87

Surveying with the Receiver
3. Click the Advanced tab and then the Multipath tab, set the
following parameters, then click Apply (Figure 3-7):
• Code multipath reduction – enable
• Carrier multipath reduction – enable
Figure 3-7. Enable Multipath Parameters
4. Click the Loop Management tab and set the following
parameters, then click Apply (Figure 3-8 on page 3-11):
• Enable Co-Op tracking – enable
• Static mode – enable
Figure 3-8. Set Tracking and Mode Parameters
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
3-11
Page 88

Setup and Survey
5. Set up each antenna and receiver as described in “Receiver
Setup” on page 3-1.
6. Begin your survey.
Kinematic Survey
You can use the kinematic survey method for either a Stop and
go survey or a Kinematic continuous (trajectory) survey.
Stop and Go Survey
The stationary receiver (Base station) is set up at a known
point such as a survey monument, or an unknown point.
The receiver continually tracks satellites and logs raw data
into its memory. The ro v er recei v er is set up at an unknown
point and collects data in static mode for 2 to 10 minutes.
When finished, assign the Rover to kinematic status and
move to the next survey point. At this point, and each
subsequent point, the receiver is changed to static mode to
collect data. So, while moving, the Rover is in kinematic
mode, and while collecting data, the Rover is in static
mode.
3-12
1. Using PC-CDU, configure and set up the Base as
described in “Static Survey” on page 3-9.
2. Using PC-CDU, click ConfigurationReceiver
MINTER, and configure the Rover with the
following parameters, then click Apply (Figure 3-9 on
page 3-13):
• FN key mode, Occupation mode switch – enable
• Initial data collection dynamic mode, Static – enable
See Table 4-1 on page 4-5 for FN key functions and
REC LED statuses.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 89

Surveying with the Receiver
Figure 3-9. Rover MINTER Configuration
NOTICE
NOTICE
Both Base and Rover receivers must collect data from
common satellites at a common data recording rate and
with identical elevation mask angles.
3. Set up the Ro ver at an unkno wn poin t and press power.
Allow the Rover to collect static data for two to ten
minutes. The REC LED will be orange.
4. Check the STAT light for satellites tracked.
5. When finished, press the FN key for less than a second
to assign the Rover to kinematic.
TIP
TIP
If the REC LED blinks green, the current mode is
dynamic, if it blinks orange, the current mode is static.
3-13
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
Page 90

Setup and Survey
6. Move the Rover to the next location (survey point), and
press the FN key for less than a second to collect the
data in static mode for two to ten minutes.
7. Repeat steps five and six until all points have been
surveyed. The occupation time for the points depends
on the same factors as for the static survey method.
8. When finished, press the FN key for one to five
seconds to stop logging data. Turn off the Rover if
needed.
This method of GPS survey allows the operator to reduce
the point occupation time, thus permitting field crews to
survey many more points compared to the other methods
available.
Kinematic Continuous
Kinematic continuous surveying, also known as trajectory
surveying, allows the Rover to move without having to
stand still, record data, move to another point, and repeat
the procedure.
3-14
If the surveyor knows the coordinates of the starting point,
the rover will not need to be initialized. The determination
of ambiguity parameters is carried out while the rover is
moving and is called “on the fly ambiguity resolution.”
Furthermore, if loss of lock occurs (such as, an obstruction
that prevents a clear view of the sky), the receiver will be
re-initialized on the fly.
After the survey completes, raw data collected by the
receivers are downloaded onto a computer and processed
using post-processing software (for example, Topcon
Tools).
1. Using PC-CDU, configure and set up the Base as
described in “Static Survey” on page 3-9.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 91

Surveying with the Receiver
2. Using PC-CDU, click ConfigurationReceiver
MINTER, and configure the Rover with the
following parameters, then click Apply (Figure 3-9 on
page 3-13):
• FN key mode, Occupation mode switch – enable
• Initial data collection dynamic mode,
Kinematic – enable
3. Set up the Rover at a starting point with unknown
coordinates and press the power key. Pause for several
minutes while the receiver compiles an almanac.
4. Check the STAT light for satellites tracked.
5. Press the FN key for one to four seconds to begin
logging data in kinematic mode (the antenna status is
kinematic).
6. Move the Rover receiver along the selected trajectory.
7. Once the Rover receiver reaches the end point of the
trajectory, pause for several minutes.
8. When finished, press the FN key to stop logging data
and turn off the Rover.
Real-time Kinematic Survey
Real-time kinematic (R TK) is a differential GPS process where
information, such as differential corrections, is transmitted in
real-time from a Base station to one or more Rover stations.
Setting up an RTK Base Station
To configure an RTK Base station using PC-CDU, take the
following steps:
1. Set up the Base station receiver’s antenna as described
in “Receiver Setup” on page 3-1.
2. Connect an external modem to port C for a Legacy-E
receiver or port D for the HiPer receiver.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
3-15
Page 92

Setup and Survey
3. Set up hardware as shown in Figure 3-10. This setup
shows a Legacy-E Base station setup.
3-16
Figure 3-10. Legacy-E with PG-A1 Antenna Base Station Setup
NOTICE
NOTICE
Connect the radio antenna before switching the modem
to the transmitting mode.
4. Press the power key on the receiver.
5. Check the STAT light for tracked satellites.
6. Connect your receiver and computer. See “Connecting
the Receiver and a Computer” on page 2-11 for this
procedure.
7. Using PC-CDU click ConfigurationReceiver.
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 93
Surveying with the Receiver
8. Click the Set all parameters to defaults button located
at the bottom of the Receiver Configuration screen
(Figure 3-11).
Figure 3-11. Set All Parameters to Defaults
9. On the Receiver Configuration screen, select the
MINTER tab. Specify desired settings. Refer to the
PC-CDU User’s Manual for more information.
10. Select the Positioning tab and set the Position Masks,
Elevation mask parameter to 15 (Figure 3-12).
Figure 3-12. Receiver Configuration (HiPer GGD) – Positioning
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
3-17
Page 94

Setup and Survey
11. Select the Base tab and set the following parameters
(Figure 3-13):
• GPS/GLO at one time – enable
• Antenna position under Reference Geodetic
Coordinates – enter Lat, Lon, and Alt v alues. Do one
of the following:
–If known, type in the values.
–Click Get from receiver.
–Enable Aver aged and enter the Averaged Span in
seconds, then click Apply. Click ToolsReset
receiver and wait until the specified interval (span)
completes. Examine the Base coordinates on the
Base tab, they should correspond to the coordinates
obtained from the average. Click Refresh if the
coordinates are zeros.
3-18
NOTICE
NOTICE
The reference geodetic coordinates you specify on this
tab relate to the antenna L1 phase center.
Figure 3-13. Base Tab Configuration (HiPer GGD)
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 95

Surveying with the Receiver
12. Select the Ports tab and set the following port
parameters (Figure 3-14). Use serial port C for internal
PDL or GSM modems.
• Output drop-down list – select type and format of
differential corrections.
• Period (sec) – enter interval at which receiver will
generate differential corrections.
• Baud rate drop-down list – select a baud rate (i.e., the
rate at which differential messages will be
transmitted from receiver to modem).
TIP
TIP
For Pacific Crest PDL (UHF) modems, use a 38400 baud
rate.
Figure 3-14. Base Configuration – Ports
13. Click Apply. The receiver begins sending data to the
selected port.
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
3-19
Page 96

Setup and Survey
If using a Pacific Crest PDL (UHF) external modem, follo w
these steps to configure this modem:
NOTICE
NOTICE
Connect the radio antenna before switching the modem
to the transmitting mode.
14. When finished with the previous steps, press the power
button on the external modem.
15. Select the radio transmission power using the Low/
High toggle on the rear panel of the modem. When in
High, the AMP PWR LED will be on.
16. Use the Channel button to set the frequency channel.
Check that the modem transmits the corrections (the
TX LED will blink red each time data transmits).
For more details on the settings available for configuring
the Base station, refer to the PC-CDU User’ s Manu al .
Setting up an RTK Rover
Use the following steps to set up an RTK Rover station.
You should already have programmed the modem.
Figure 3-15 on page 3-21 shows the hardware setup for a
Rover station with an external controller.
3-20
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 97

Surveying with the Receiver
Figure 3-15. Rover Station Setup
1. Set up the Rov er station recei ver’s antenna as described
in “Receiver Setup” on page 3-1.
2. Connect your receiver and computer. See “Connecting
the Receiver and a Computer” on page 2-11 for this
procedure.
3. Click ConfigurationReceiv er.
4. Select the Positioning tab and set the Position Masks,
Elevation mask (degrees) parameter to 15 (Figure 3-12
on page 3-17).
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
3-21
Page 98
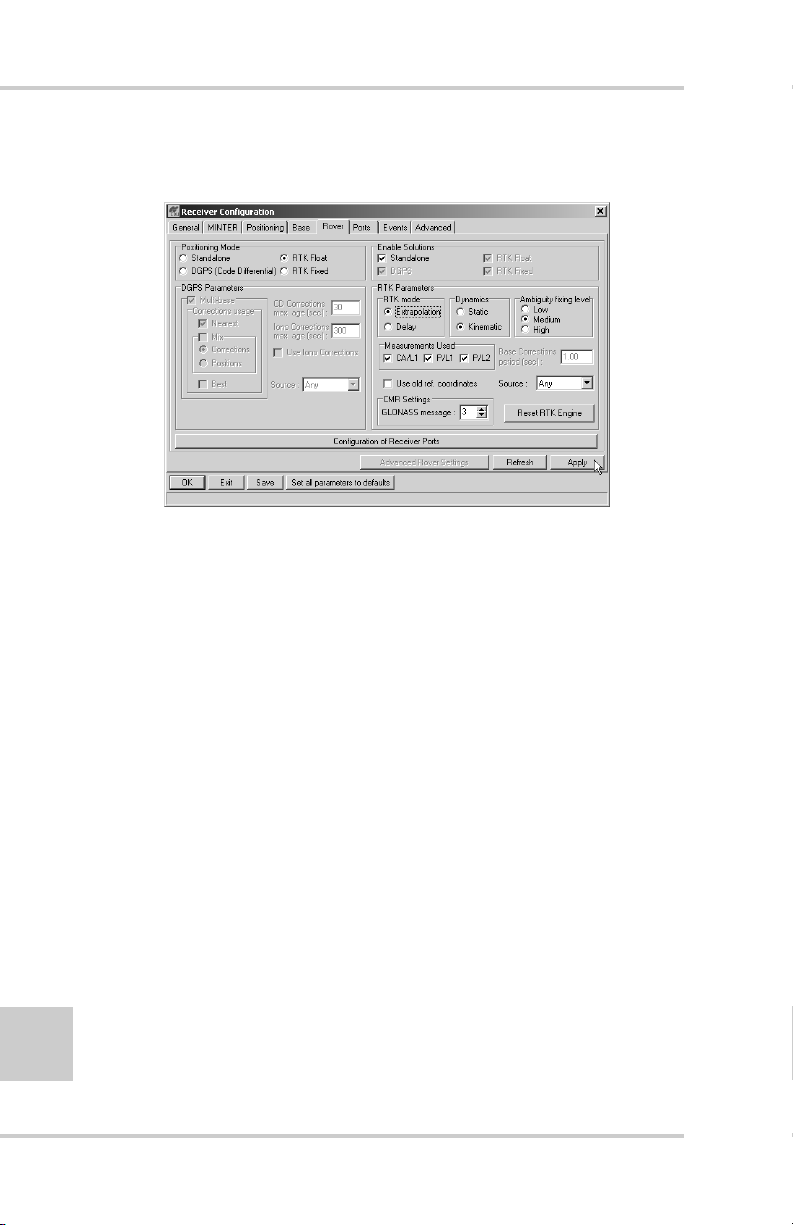
Setup and Survey
5. Select the Rover tab and set the desired Positioning
Mode (Figure 3-16).
If you selected RTK Float or RTK Fixed, adjust the
following RTK Parameters settings:
• Select Extrapolation or Delay.
Figure 3-16. Rover Tab Configuration
3-22
–Extrapolation is for low-latency, high frequency
output (>= 5 Hz) RTK applications. The rover will
extrapolate the base station’s carrier phase
measurement corrections when computing the rover's
current RTK position.
–Delay is for 1 Hz high precision RTK applications.
The Rover R TK engine will compute either a delayed
RTK position (for the epoch to which the newly
received RTCM/CMR message corresponds) or the
current stand-alone position (while waiting for new
RTCM/CMR messages coming from the base).
• Select the antenna status during RTK, either Static or
Kinematic.
• Specify the Ambiguity fixing level (not applicable to
RTK Float). The Ambiguity fixing le vel radio b u ttons
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
Page 99

Surveying with the Receiver
govern the process of the RTK engine, fixing integer
ambiguities. The RTK engine uses the ambiguity fix
indicator when making decisions whether or not to
fix ambiguities. Low, Medium, and High correspond
to the indicator's 95%, 99.5% and 99.9% states,
respectively. The higher the specified confidence
level, the longer the integer ambiguity search time
6. Select the Ports tab and set the following parameters
for Serial C (Figure 3-17 on page 3-23):
• Input drop-down list – select desired differential
correction format.
• Period (sec) – leave as is.
• Baud rate drop-down list – select a baud rate (i.e., the
rate at which differential messages will be received
from the modem).
TIP
TIP
For Pacific Crest PDL (UHF) modems, use a 38400 baud
rate.
Figure 3-17. Rover Configuration – Ports
P/N 7010-0626 www.topconpositioning.com
3-23
Page 100

Setup and Survey
7. Click Apply.
8. Click OK to close the Receiver Configuration screen.
9. On the main screen (Figure 3-18), check the LQ field to
ensure the receiver obtains differential corrections.
Usually , the recei ver wil l start to output the coordinates
of the antenna’s phase center along with the solution
type within 10–30 seconds.
3-24
Figure 3-18. PC-CDU Main Screen for GPS and GPS/GLONASS Options
The geodetic coordinates displayed on the Geo tab are
always computed in WGS84 and have four solution types.
• Standalone – where receiver computes 3D coordinates
in autonomous mode without using differential
corrections.
• Code differential – where the Rover receiver computes
the current relative coordinate in differential mode
using only pseudo ranges.
• RTK float – where the Rover receiver computes the
current relative coordinates in differential mode using
both pseudo ranges and phases; however, with a float
Topcon HiPer GD and HiPer GGD Operator’s Manual
 Loading...
Loading...