Texas Instruments TMX320DM355ZCE270, TMS320DM355 Datasheet

www.ti.com
1 TMS320DM355 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
1.1 Features
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
encoder
• High-Performance Digital Media
System-on-Chip • External Memory Interfaces (EMIFs)
– 216- and 270-MHz ARM926EJ-S Clock Rate – DDR2 and mDDR SDRAM 16-bit wide EMIF
With 256 MByte Address Space (1.8-V I/O)
– Fully Software-Compatible With ARM9
– Asynchronous16-/8-bit Wide EMIF (AEMIF)
• ARM926EJ-S Core
• Flash Memory Interfaces
– Support for 32-Bit and 16-Bit (Thumb Mode)
– NAND (8-/16-bit Wide Data)
Instruction Sets
– OneNAND(16-bit Wide Data)
– DSP Instruction Extensions and Single
Cycle MAC
• Flash Card Interfaces
– ARM Jazelle Technology
– Two Multimedia Card (MMC) / Secure
– EmbeddedICE-RT Logic for Real-Time Digital (SD/SDIO)
Debug
– SmartMedia
• ARM9 Memory Architecture
• Enhanced Direct-Memory-Access (EDMA)
– 16K-Byte Instruction Cache Controller (64 Independent Channels)
– 8K-Byte Data Cache
• USB Port with Integrated 2.0 High-Speed PHY
that Supports
– 32K-Byte RAM
– USB 2.0 Full and High-Speed Device
– 8K-Byte ROM
– USB 2.0 Low, Full, and High-Speed Host
– Little Endian
• Three 64-Bit General-Purpose Timers (each
• Video Processing Subsystem
configurable as two 32-bit timers)
– Front End Provides:
• One 64-Bit Watch Dog Timer
• Hardware IPIPE for Real-Time Image
Processing • Three UARTs (One fast UART with RTS and
CTS Flow Control)
• CCD and CMOS Imager Interface
• Three Serial Port Interfaces (SPI) each with
• 14-Bit Parallel AFE (Analog Front End)
two Chip-Selects
Interface Up to 75MHz
• One Master/Slave Inter-Integrated Circuit
• Glueless Interface to Common Video
(I2C) Bus™
Decoders
• BT.601/BT.656 Digital YCbCr 4:2:2 • Two Audio Serial Port (ASP)
(8-/16-Bit) Interface
– I2S and TDM I2S
• Histogram Module
– AC97 Audio Codec Interface
• Resize Engine
– S/PDIF via Software
– Resize Images From 1/16x to 8x
– Standard Voice Codec Interface (AIC12)
– Separate Horizontal/Vertical Control
– SPI Protocol (Master Mode Only)
– Two Simultaneous Output Paths
• Four Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) Outputs
– Back End Provides:
• Four RTO (Real Time Out) Outputs
• Hardware On-Screen Display (OSD)
• Up to 104 General-Purpose I/O (GPIO) Pins
• Composite NTSC/PAL video encoder
(Multiplexed with Other Device Functions)
output
• On-Chip ARM ROM Bootloader (RBL) to Boot
• 8-/16-bit YCC and Up to 18-Bit RGB666
From NAND Flash, MMC/SD, or UART
Digital Output
• Configurable Power-Saving Modes
• BT.601/BT.656 Digital YCbCr 4:2:2
• Crystal or External Clock Input (typically
(8-/16-Bit) Interface
24MHz or 36MHz)
• Supports digital HDTV (720p/1080i)
• Flexible PLL Clock Generators
output for connection to external
• Debug Interface Support
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas
Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this document.
I2C-bus is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
Windows is a trademark of Microsoft.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
PRODUCT PREVIEW information concerns products in the
Copyright © 2007, Texas Instruments Incorporated
formative or design phase of development. Characteristic data and
other specifications are design goals. Texas Instruments reserves
the right to change or discontinue these products without notice.

www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
– IEEE-1149.1 (JTAG) • 337-Pin Ball Grid Array (BGA) Package
Boundary-Scan-Compatible (ZCE Suffix), 0.65-mm Ball Pitch
– ETB (Embedded Trace Buffer) with
• 90nm Process Technology
4K-Bytes Trace Buffer memory
• 3.3-V and 1.8-V I/O, 1.3-V Internal
– Device Revision ID Readable by ARM
2 TMS320DM355 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Submit Documentation Feedback

www.ti.com
1.2 Description
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
The DM355 is a highly integrated, programmable platform for digital still camera, digital photo frames, IP
security cameras, 4-channel digital video recorders, video door bell application, and other low cost
portable digital video applications. Designed to offer portable video designers and manufacturers the
ability to produce affordable portable digital video solutions with high picture quality, the DM355 combines
high performance, high quality, low power consumption at a very low price point. The DM355 also enables
seamless interface to most additional external devices required for a complete digital camera
implementation. The interface is flexible enough to support various types of CCD and CMOS sensors,
signal conditioning circuits, power management, DDR/mDDR memory, SRAM, NAND, shutter, Iris and
auto-focus motor controls, etc.
The processor core is an ARM926EJ-S RISC processor. The ARM926EJ-S is a 32-bit processor core that
performs 32-bit and 16-bit instructions and processes 32-bit, 16-bit, and 8-bit data. The core uses
pipelining so that all parts of the processor and memory system can operate continuously. The ARM core
incorporates:
• A coprocessor 15 (CP15) and protection module
• Data and program Memory Management Units (MMUs) with table look-aside buffers.
• Separate 16K-byte instruction and 8K-byte data caches. Both are four-way associative with virtual
index virtual tag (VIVT).
DM355 performance is enhanced by its MPEG/JPEG co-processor. The MPEG/JPEG co-processor
performs the computational operations required for image processing; JPEG compression and MPEG1,2,4
video and imaging standards.
The device has a Video Processing Subsystem (VPSS) with two configurable video/imaging peripherals:
• A Video Processing Front-End (VPFE)
• A Video Processing Back-End (VPBE)
The VPFE port provides an interface for CCD/CMOS imager modules and video decoders. The VPBE
provides hardware On Screen Display (OSD) support and composite NTSC/PAL and digital LCD output.
The DM355 peripheral set includes:
• An inter-integrated circuit (I2C) Bus interface
• Two audio serial ports (ASP)
• Three 64-bit general-purpose timers each configurable as two independent 32-bit timers
• A 64-bit watchdog timer
• Up to 104-pins of general-purpose input/output (GPIO) with programmable interrupt/event generation
modes, multiplexed with other peripherals
• Three UARTs with hardware handshaking support on one UART
• Three serial port Interfaces (SPI)
• Four pulse width modulator (PWM) peripherals
• Four real time out (RTO) outputs
• Two Multi-Media Card / Secure Digital (MMC/SD) interfaces
• A USB 2.0 full and high-speed device and host interface
• Two external memory interfaces:
– An asynchronous external memory interface (AEMIF) for slower memories/peripherals such as
NAND and OneNAND,
– A high speed synchronous memory interface for DDR2/mDDR.
For software development support the has a complete set of ARM development tools which include: C
compilers, assembly optimizers to simplify programming and scheduling, and a Windows™ debugger
interface for visibility into source code execution.
Submit Documentation Feedback TMS320DM355 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) 3
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
1.3 Functional Block Diagram
Peripherals
64bitDMA/DataBus
JTAG
24MHz 27MHz
(optional)
CCD/
CMOS
Module
DDR2/MDDR16
CLOCK
PLL
CLOCKctrl
PLLs
JTA
JTAG
I/F
Clocks
ARM
z )
ARM926EJ-S_Z8
I-
cach
e
16 K
B
l-cache
16KB
B
RA
M
32 K
B
RAM
32KB
B
D-
cach
e
8K
D-cache
8KB
RO
M
8 K
ROM
8KB
CCD
C
CCDC
3A
3A
DMA / Dataandconfigurationbus
DMA/Dataandconfigurationbus
DDR
MH
z )
DDR
controller
DL
DLL/
PHY
16bit
32bitConfigurationBus
IPIP
E
IPIPE
VPBE
Vide
o
Encod
er
Video
Encoder
10b
DAC
OS
D
OSD
er
c
ARM
ARMINTC
Enhanced
channels
3PCC /TC
(100 MHz
EnhancedDMA
64channels
Compositevideo
DigitalRGB/YUV
Nand /
Nand/SM/
Async/OneNand
(EMIF2.3)
USB 2.0
USB2.0PHY
Speaker
microphone
LD /
ASP (2x)
LD/CM
B
ufferLogic
VPSS
MMC/SD(x2)
SPII/F(x3)
UART (x3)
I2C
Timer/
WDT (x4-64)
GIO
PWM(x4)
RTO
VPFE
Enhanced
channels
3PCC /TC
(100 MHz
MPEG/JPEG
Co-processor
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
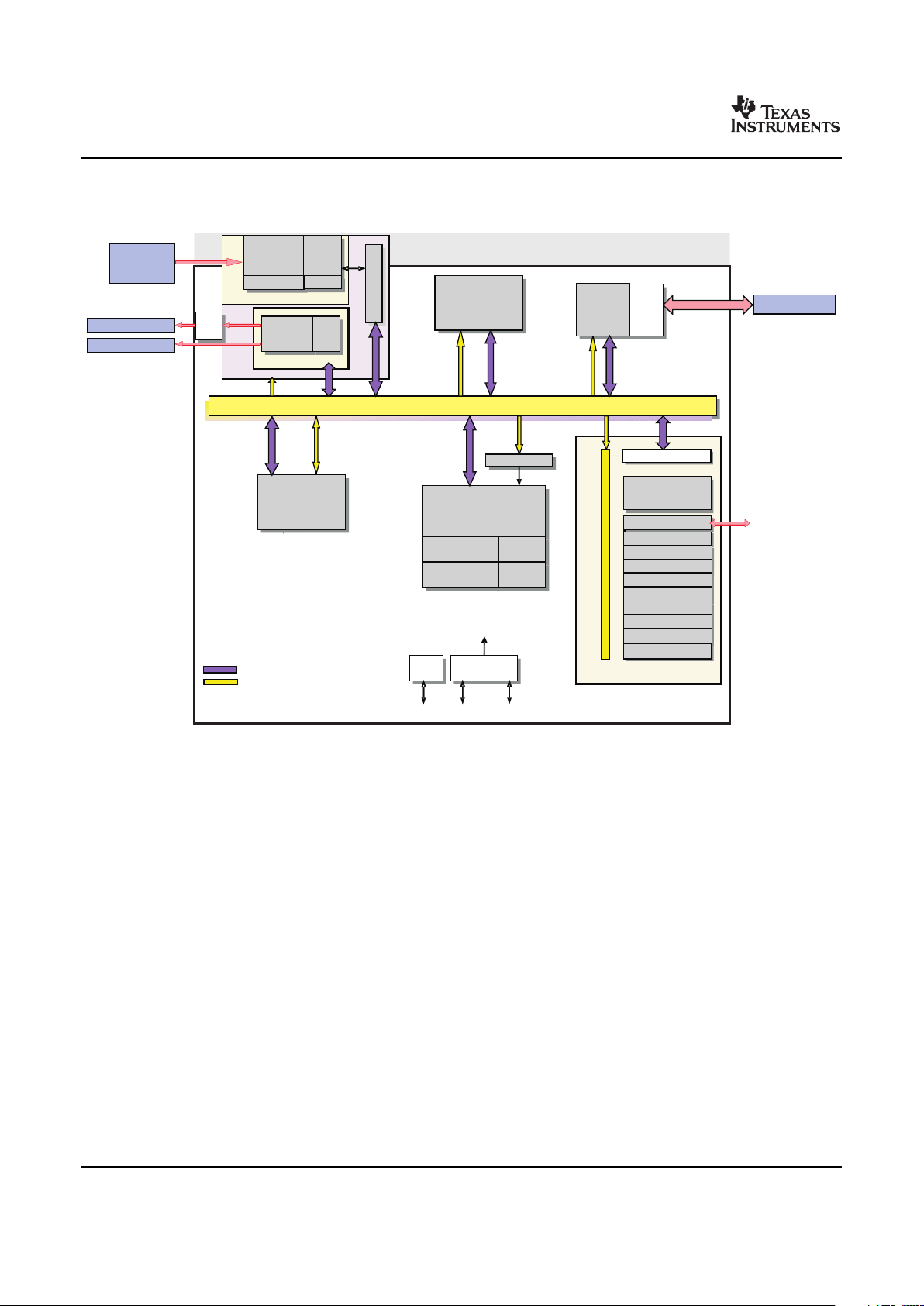
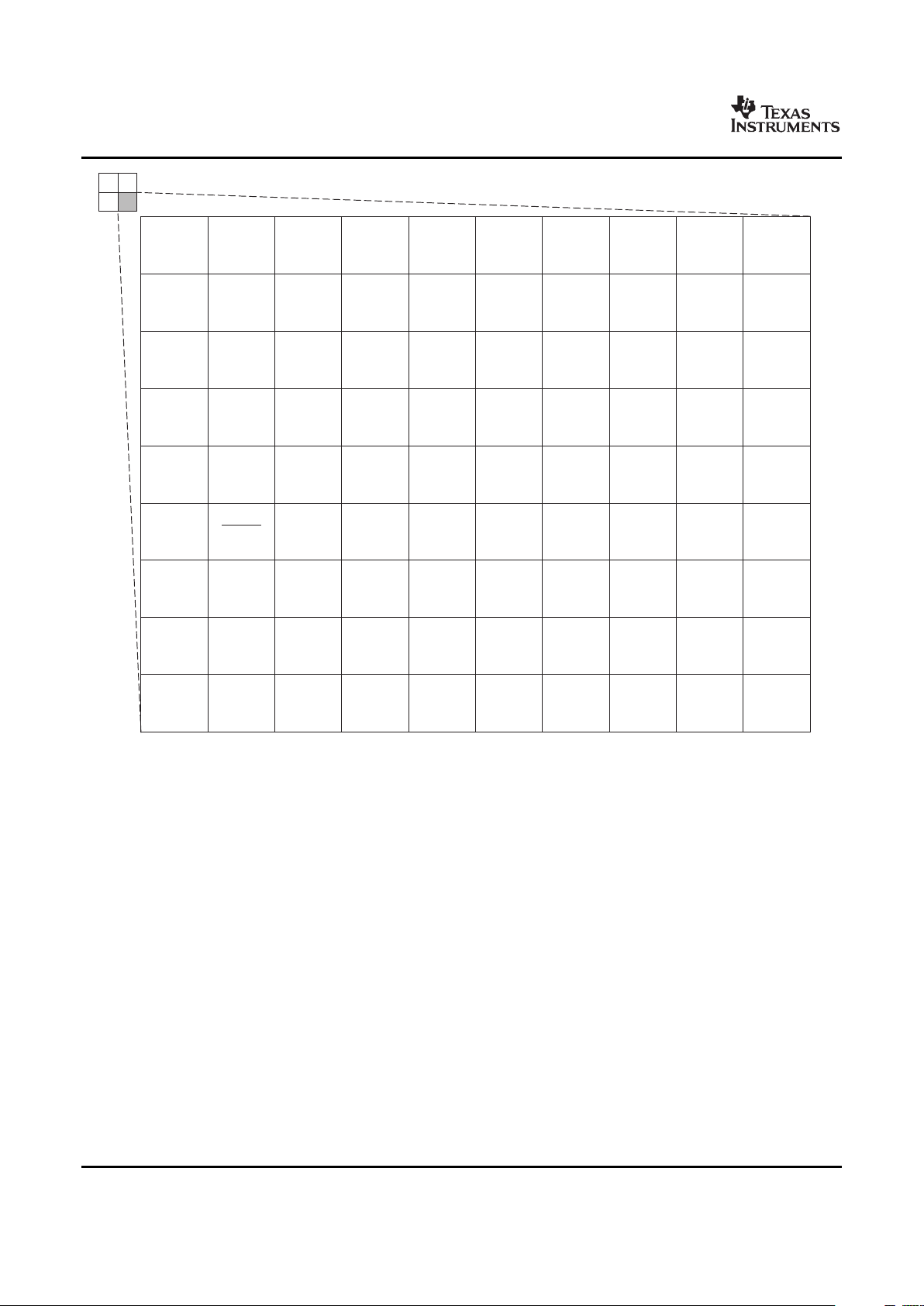
Figure 1-1 shows the functional block diagram of the DM355 device.
Figure 1-1. Functional Block Diagram
TMS320DM355 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)4 Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
Contents
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Case
1 TMS320DM355 Digital Media System-on-Chip
Temperature Range
(DMSoC) ................................................... 1
(Unless Otherwise Noted) .......................... 90
1.1 Features .............................................. 1
4.2 Recommended Operating Conditions ............... 91
1.2 Description ............................................ 3
4.3 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended
1.3 Functional Block Diagram ............................ 4
Ranges of Supply Voltage and Operating Case
2 Device Overview ......................................... 6
Temperature (Unless Otherwise Noted) ............ 92
2.1 Device Characteristics ................................ 6
5 Peripheral Information and Electrical
Specifications ........................................... 93
2.2 Memory Map Summary ............................... 7
5.1 Parameter Information Device-Specific Information 93
2.3 Pin Assignments ...................................... 9
5.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition
2.4 Pin Functions ........................................ 13
Behavior ............................................. 95
2.5 Pin List .............................................. 36
5.3 Power Supplies ...................................... 95
2.6 Device Support ...................................... 55
5.4 Reset ................................................ 97
3 Detailed Device Description .......................... 59
5.5 Oscillators and Clocks ............................... 98
3.1 ARM Subsystem Overview .......................... 59
5.6 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) ............. 103
3.2 ARM926EJ-S RISC CPU ............................ 60
5.7 External Memory Interface (EMIF) ................. 105
3.3 Memory Mapping .................................... 62
5.8 MMC/SD ........................................... 112
3.4 ARM Interrupt Controller (AINTC) ................... 63
5.9 Video Processing Sub-System (VPSS) Overview . 114
3.5 Device Clocking ..................................... 65
5.10 USB 2.0 ............................................ 127
3.6 PLL Controller (PLLC) ............................... 72
5.11 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
3.7 Power and Sleep Controller (PSC) .................. 76
(UART) ............................................. 129
3.8 System Control Module ............................. 76
5.12 Serial Port Interface (SPI) .......................... 131
3.9 Pin Multiplexing ...................................... 77
5.13 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) ....................... 134
3.10 Device Reset ........................................ 78
5.14 Audio Serial Port (ASP) ............................ 137
3.11 Default Device Configurations ....................... 79
5.15 Timer ............................................... 144
3.12 Device Boot Modes ................................. 82
5.16 Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) ..................... 145
3.13 Power Management ................................. 84
5.17 Real Time Out (RTO) .............................. 147
3.14 64-Bit Crossbar Architecture ........................ 86
5.18 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG ................................ 148
3.15 MPEG/JPEG Overview .............................. 89
6 Mechanical Data ....................................... 151
4 Device Operating Conditions ........................ 90
6.1 Thermal Data for ZCE ............................. 151
6.1.1 Packaging Information ............................. 151
Submit Documentation Feedback Contents 5
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
2 Device Overview
2.1 Device Characteristics
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
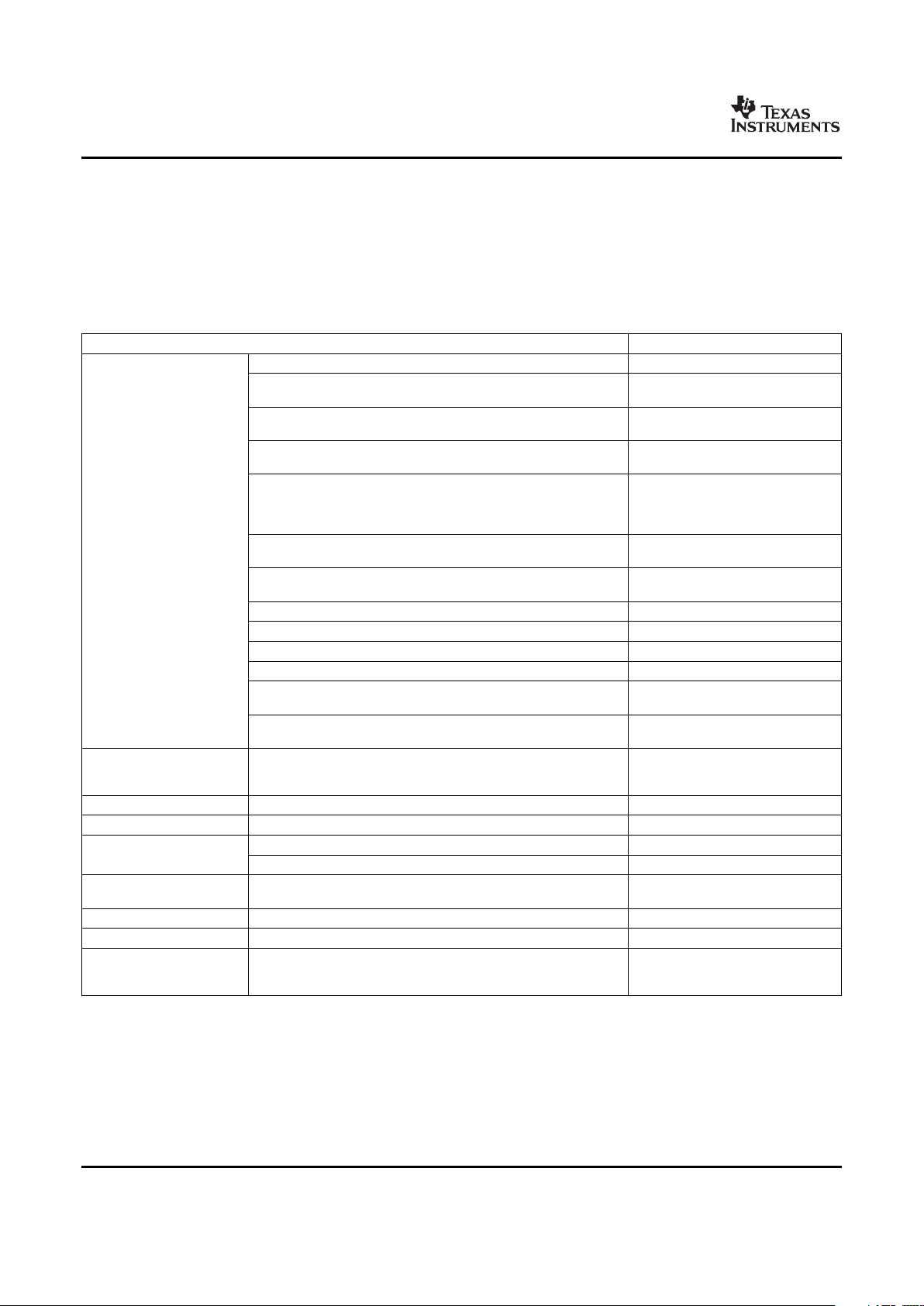
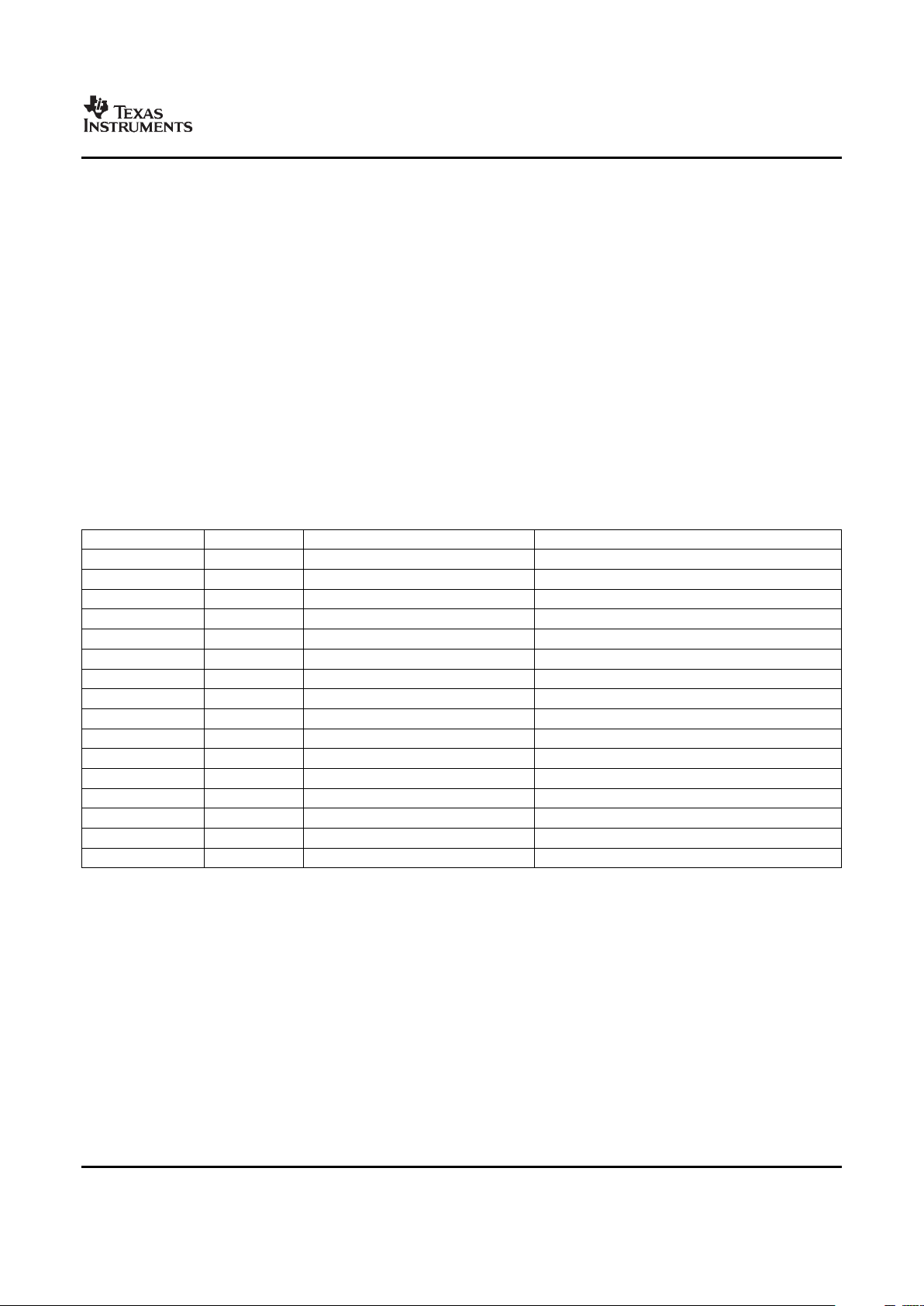
Table 2-1 provides an overview of the DMSoC. The table shows significant features of the device,
including the peripherals, capacity of on-chip RAM, ARM operating frequency, the package type with pin
count, etc.
Table 2-1. Characteristics of the Processor
HARDWARE FEATURES
DDR2 / mDDR Memory Controller DDR2 / mDDR (16-bit bus width)
Asynchronous (8/16-bit bus width)
Asynchronous EMIF (AEMIF)
RAM, Flash (NAND, OneNAND)
Two MMC/SD
Flash Card Interfaces
One SmartMedia/xD
64 independent DMA channels
EDMA
Eight EDMA channels
Three 64-Bit General Purpose (each
configurable as two separate 32-bit
Timers
timers)
Peripherals
One 64-Bit Watch Dog
Not all peripherals pins are
Three (one with RTS and CTS flow
available at the same time
UART
control)
(For more detail, see the
Device Configuration
Three (each supports two slave
SPI
section).
devices)
I2C One (Master/Slave)
Audio Serial Port [ASP] Two ASP
General-Purpose Input/Output Port Up to 104
Pulse width modulator (PWM) Four outputs
One Input (VPFE)
Configurable Video Ports
One Output (VPBE)
High, Full Speed Device
USB 2.0
High, Full, Low Speed Host
ARM
On-Chip CPU Memory Organization 16-KB I-cache, 8-KB D-cache, 32-KB
RAM, 8-KB ROM
JTAG BSDL_ID JTAGID register (address location: 0x01C4 0028) 0x0B73B01F
CPU Frequency (Maximum) MHz ARM 216 MNz and 270 Mhz
Core (V) 1.3 V
Voltage
I/O (V) 3.3 V, 1.8 V
Reference frequency options 24 MHz (typical), 36 MHz
PLL Options
Configurable PLL controller PLL bypass, programmable PLL
BGA Package 13 x 13 mm 337-Pin BGA (ZCE)
Process Technology 90 nm
Product Preview (PP),
Product Status
(1)
Advance Information (AI), PD
or Production Data (PD)
(1) PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date. Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Device Overview6 Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
2.2 Memory Map Summary
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
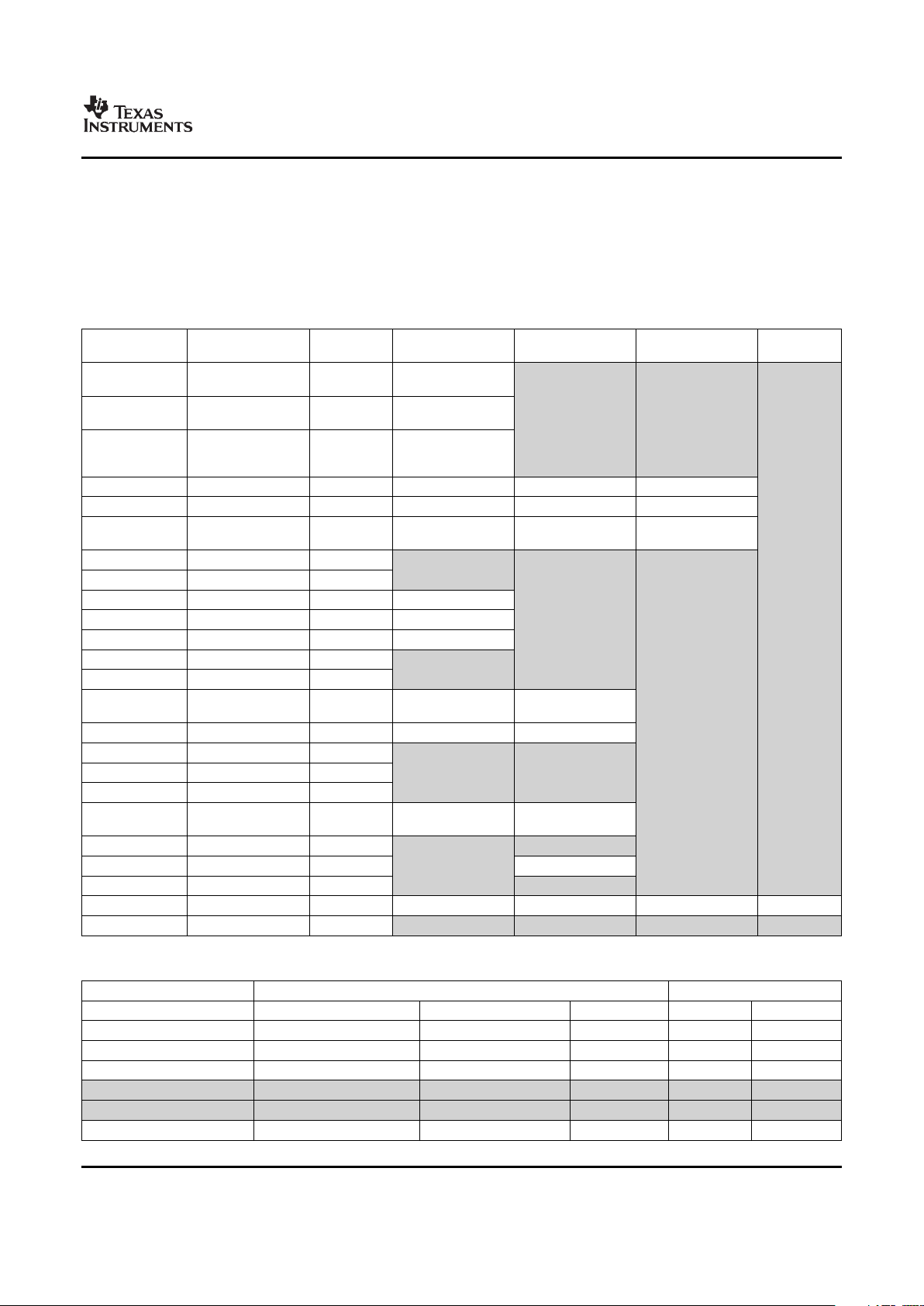
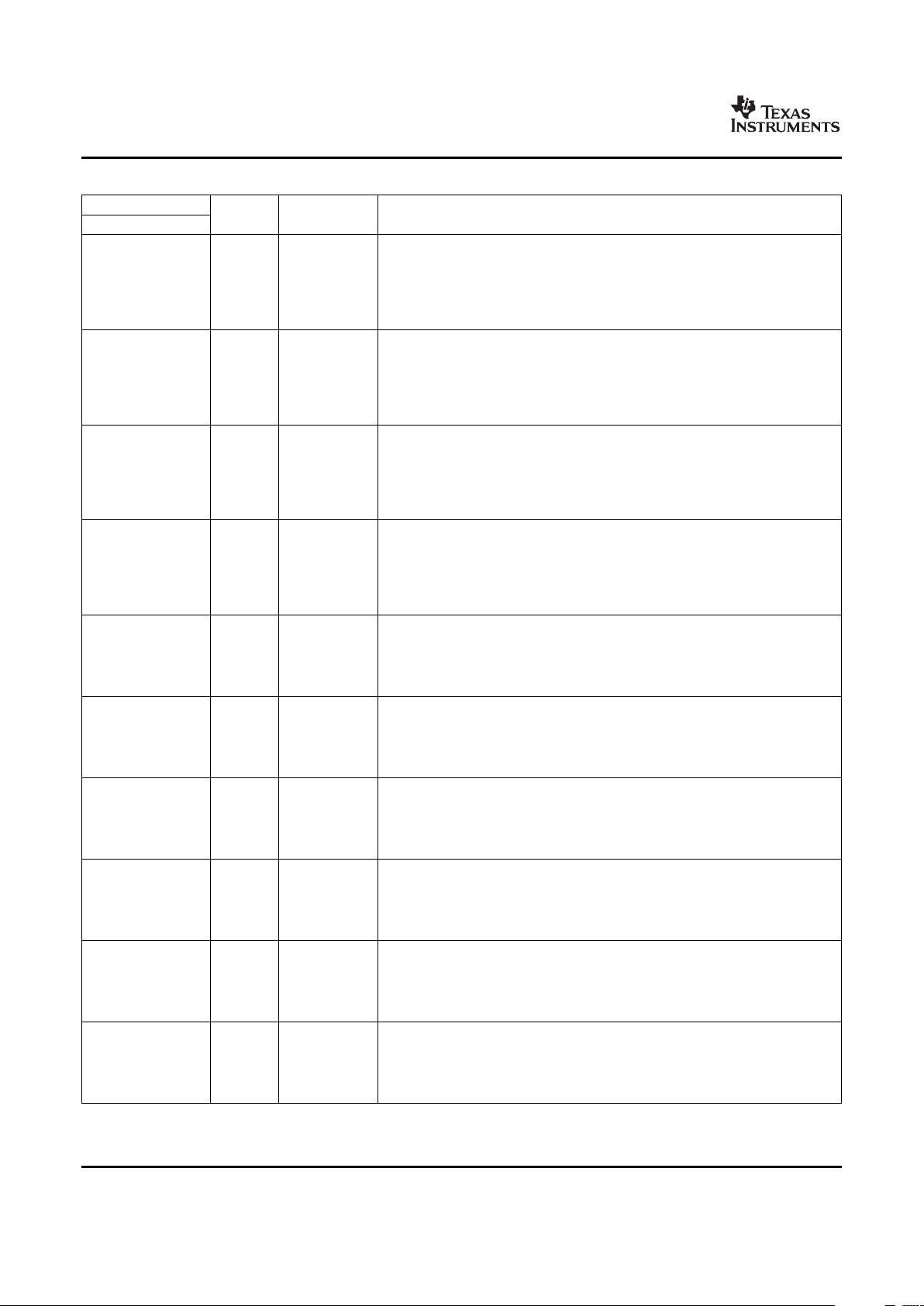
Table 2-3 shows the memory map address ranges of the device. Table 2-3 depicts the expanded map of
the Configuration Space (0x01C0 0000 through 0x01FF FFFF). The device has multiple on-chip memories
associated with its processor and various subsystems. To help simplify software development a unified
memory map is used where possible to maintain a consistent view of device resources across all bus
masters. The bus masters are the ARM, EDMA, USB, and VPSS.
Table 2-2. DM355 Memory Map
Start Address End Address Size (Bytes) ARM EDMA USB VPSS
Mem Map Mem Map Mem Map Mem Map
0x0000 0000 0x0000 3FFF 16K ARM RAM0
(Instruction)
0x0000 4000 0x0000 7FFF 16K ARM RAM1
Reserved Reserved
(Instruction)
0x0000 8000 0x0000 FFFF 32K ARM ROM
(Instruction)
- only 8K used
0x0001 0000 0x0001 3FFF 16K ARM RAM0 (Data) ARM RAM0 ARM RAM0
0x0001 4000 0x0001 7FFF 16K ARM RAM1 (Data) ARM RAM1 ARM RAM1
0x0001 8000 0x0001 FFFF 32K ARM ROM (Data) ARM ROM ARM ROM
- only 8K used
0x0002 0000 0x000F FFFF 896K Reserved
0x0010 0000 0x01BB FFFF 26M
0x01BC 0000 0x01BC 0FFF 4K ARM ETB Mem
0x01BC 1000 0x01BC 17FF 2K ARM ETB Reg Reserved
0x01BC 1800 0x01BC 18FF 256 ARM IceCrusher Reserved
0x01BC 1900 0x01BC FFFF 59136 Reserved
0x01BD 0000 0x01BF FFFF 192K
0x01C0 0000 0x01FF FFFF 4M CFG Bus CFG Bus
Reserved
Peripherals Peripherals
0x0200 0000 0x09FF FFFF 128M ASYNC EMIF (Data) ASYNC EMIF (Data)
0x0A00 0000 0x11EF FFFF 127M - 16K
0x11F0 0000 0x11F1 FFFF 128K Reserved Reserved
0x11F2 0000 0x1FFF FFFF 141M-64K
0x2000 0000 0x2000 7FFF 32K DDR EMIF Control DDR EMIF Control
Regs Regs
0x2000 8000 0x41FF FFFF 544M-32K Reserved
0x4200 0000 0x49FF FFFF 128M Reserved AEMIF - shadow
0x4A00 0000 0x7FFF FFFF 864M Reserved
0x8000 0000 0x8FFF FFFF 256M DDR EMIF DDR EMIF DDR EMIF DDR EMIF
0x9000 0000 0xFFFF FFFF 1792M Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
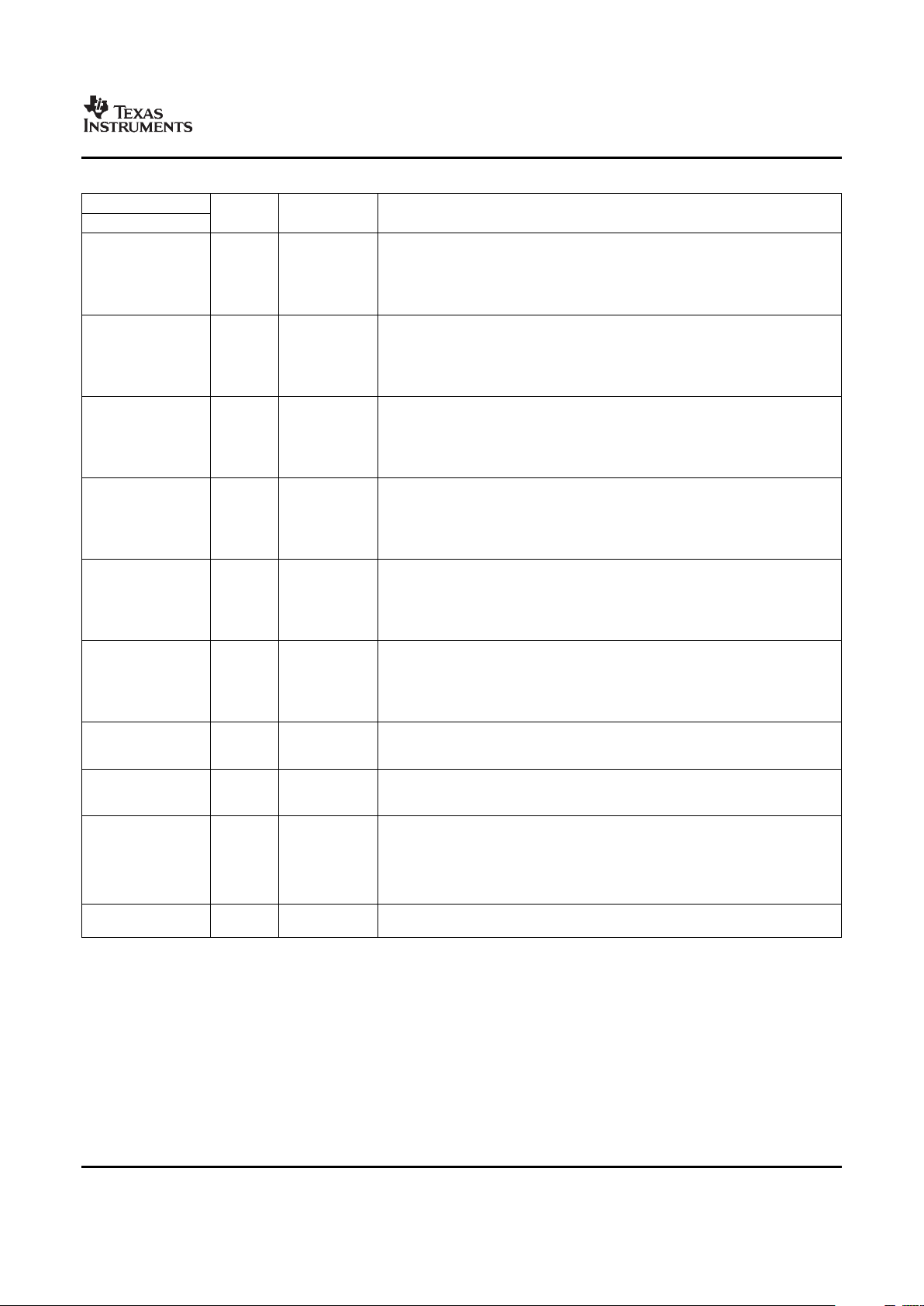
Table 2-3. DM355 ARM Configuration Bus Access to Peripherals
Address Accessibility
Region Start End Size ARM EDMA
EDMA CC 0x01C0 0000 0x01C0 FFFF 64K √ √
EDMA TC0 0x01C1 0000 0x01C1 03FF 1K √ √
EDMA TC1 0x01C1 0400 0x01C1 07FF 1K √ √
Reserved 0x01C1 8800 0x01C1 9FFF 6K √ √
Reserved 0x01C1 A000 0x01C1 FFFF 24K √ √
UART0 0x01C2 0000 0x01C2 03FF 1K √ √
Submit Documentation Feedback Device Overview 7
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-3. DM355 ARM Configuration Bus Access to Peripherals (continued)
Address Accessibility
UART1 0x01C2 0400 0x01C2 07FF 1K √ √
Timer4/5 0x01C2 0800 0x01C2 0BFF 1K √ √
Real-time out 0x01C2 0C00 0x01C2 0FFF 1K √ √
I2C 0x01C2 1000 0x01C2 13FF 1K √ √
Timer0/1 0x01C2 1400 0x01C2 17FF 1K √ √
Timer2/3 0x01C2 1800 0x01C2 1BFF 1K √ √
WatchDog Timer 0x01C2 1C00 0x01C2 1FFF 1K √ √
PWM0 0x01C2 2000 0x01C2 23FF 1K √ √
PWM1 0x01C2 2400 0x01C2 27FF 1K √ √
PWM2 0x01C2 2800 0x01C2 2BFF 1K √ √
PWM3 0x01C2 2C00 0x01C2 2FFF 1K √ √
System Module 0x01C4 0000 0x01C4 07FF 2K √ √
PLL Controller 0 0x01C4 0800 0x01C4 0BFF 1K √ √
PLL Controller 1 0x01C4 0C00 0x01C4 0FFF 1K √ √
Power/Sleep Controller 0x01C4 1000 0x01C4 1FFF 4K √ √
ARM Interrupt Controller 0x01C4 8000 0x01C4 83FF 1K √ √
USB OTG 2.0 Regs / RAM 0x01C6 4000 0x01C6 5FFF 8K √ √
SPI0 0x01C6 6000 0x01C6 67FF 2K √ √
SPI1 0x01C6 6800 0x01C6 6FFF 2K √ √
GPIO 0x01C6 7000 0x01C6 77FF 2K √ √
SPI2 0x01C6 7800 0x01C6 FFFF 2K √ √
VPSS Subsystem 0x01C7 0000 0x01C7 FFFF 64K √ √
VPSS Clock Control 0x01C7 0000 0x01C7 007F 128 √ √
Hardware 3A 0x01C7 0080 0x01C7 00FF 128 √ √
Image Pipe (IPIPE) Interface 0x01C7 0100 0x01C7 01FF 256 √ √
On Screen Display 0x01C7 0200 0x01C7 02FF 256 √ √
High Speed Serial IF 0x01C7 0300 0x01C7 03FF 256 √ √
Video Encoder 0x01C7 0400 0x01C7 05FF 512 √ √
CCD Controller 0x01C7 0600 0x01C7 07FF 256 √ √
VPSS Buffer Logic 0x01C7 0800 0x01C7 08FF 256 √ √
CFA Multiply Mask / Lens 0x01C7 0900 0x01C7 09FF 256 √ √
Distortion
Image Pipe (IPIPE) 0x01C7 1000 0x01C7 3FFF 12K √ √
Reserved 0x01CC 0000 0x01CD FFFF 128K √ √
Reserved 0x01CD 0000 0x01CD 007F 128 √ √
Reserved 0x01CD 0380 0x01CD 03FF 128 √ √
Reserved 0x01CD F400 0x01CD F4FF 256 √ √
Sequencer 0x01CD FF00 0x01CD FFFF 256 √ √
Multimedia / SD 1 0x01E0 0000 0x01E0 1FFF 8K √ √
ASP0 0x01E0 2000 0x01E0 3FFF 8K √ √
ASP1 0x01E0 4000 0x01E0 5FFF 8K √ √
UART2 0x01E0 6000 0x01E0 63FF 1K √ √
Reserved 0x01E0 6400 0x01E0 FFFF 39K √ √
ASYNC EMIF Control 0x01E1 0000 0x01E1 0FFF 4K √ √
Multimedia / SD 0 0x01E1 1000 0x01E1 FFFF 60K √ √
Reserved 0x01E2 0000 0x01FF FFFF 1792K √ √
ASYNC EMIF Data (CE0) 0x0200 0000 0x03FF FFFF 32M √ √
Device Overview8 Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
2.3 Pin Assignments
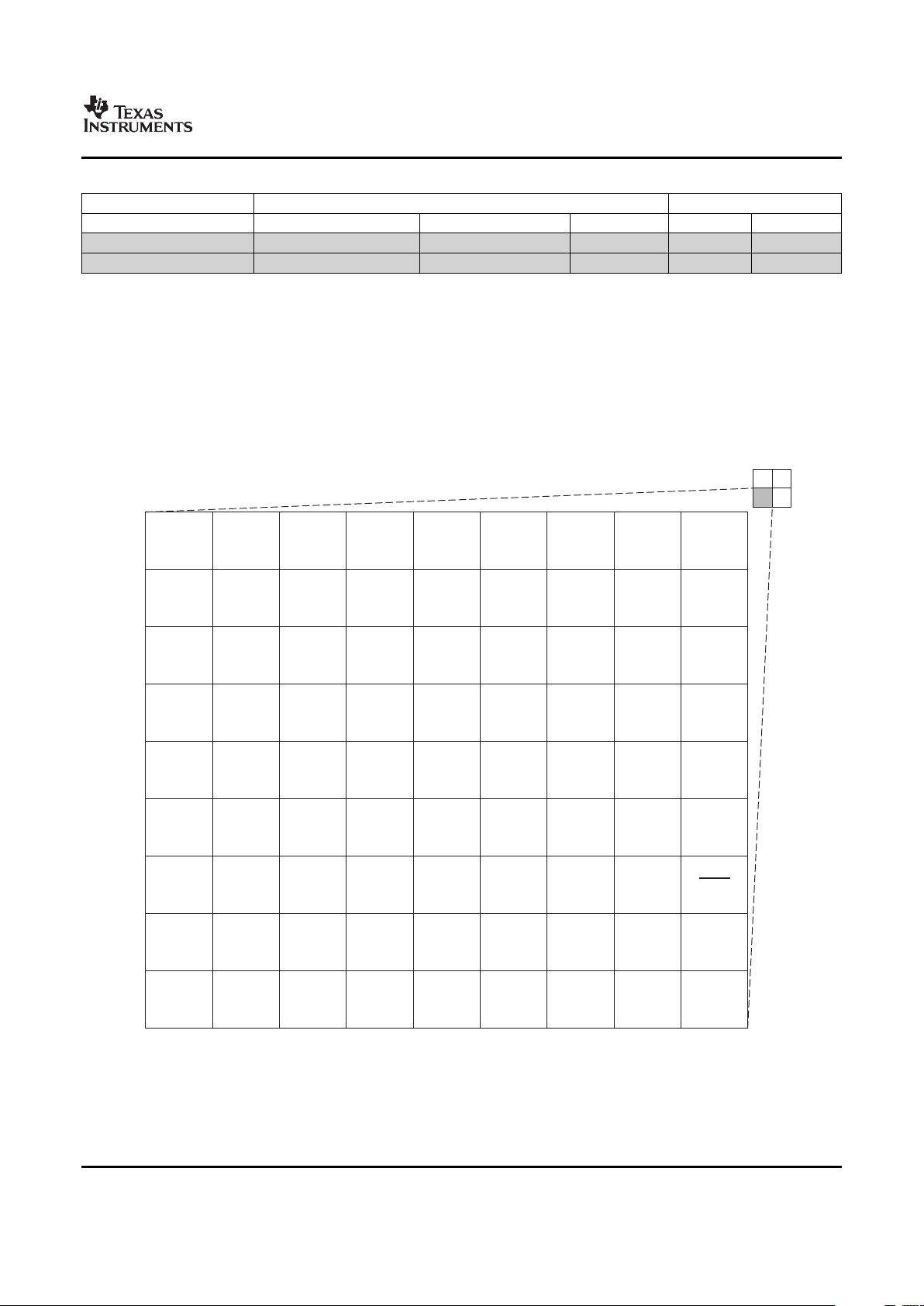
2.3.1 Pin Map (Bottom View)
9
J
8
VSSA_
PLL2
7
VDDA3P3
USB
6
5
4
31
H
G
VDDA1P2
_USB
V
SS
F
E
D
CIN2
C
B
A
VREF
CIN3CIN0DP
VDDA_
PLL2
V
SS
VVALIDFIELDVCLK
V
SS
V
SS
VDDSHV
V
DD
VSYNCEXTCLKVFB
VDDSHVVDDSHV4VDDSHV4VDDSHV4HSYNCCOUT0COUT1TVOUT
TDOEMU0EMU1
VSS_USB
USB_
VBUS
COUT2COUT3IOUT
TDITMS
VSS_USB
USB_IDCOUT4
V
SS
TRSTVSSREFUSB_R1
VDDD1P2
USB
USB_DRV
VBUS
V
DD
YOUT7COUT5
MXO1
V
SS
VSS_USBVDDA_
USB_PLL
V
SS
YOUT5YOUT4YOUT0
MXI1
V
SS
USB_DPUSB_DM
V
SS
YOUT6YOUT2
V
DD
V
DD
2
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
IBIAS
V
SS
COUT6
COUT7
YOUT3
YOUT1
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-3. DM355 ARM Configuration Bus Access to Peripherals (continued)
Address Accessibility
ASYNC EMIF Data (CE1) 0x0400 0000 0x05FF FFFF 32M √ √
Reserved 0x0A00 0000 0x0BFF FFFF 32M √ √
Reserved 0x0C00 0000 0x0FFF FFFF 64M √ √
Extensive use of pin multiplexing is used to accommodate the largest number of peripheral functions in
the smallest possible package. Pin multiplexing is controlled using a combination of hardware
configuration at device reset and software programmable register settings.
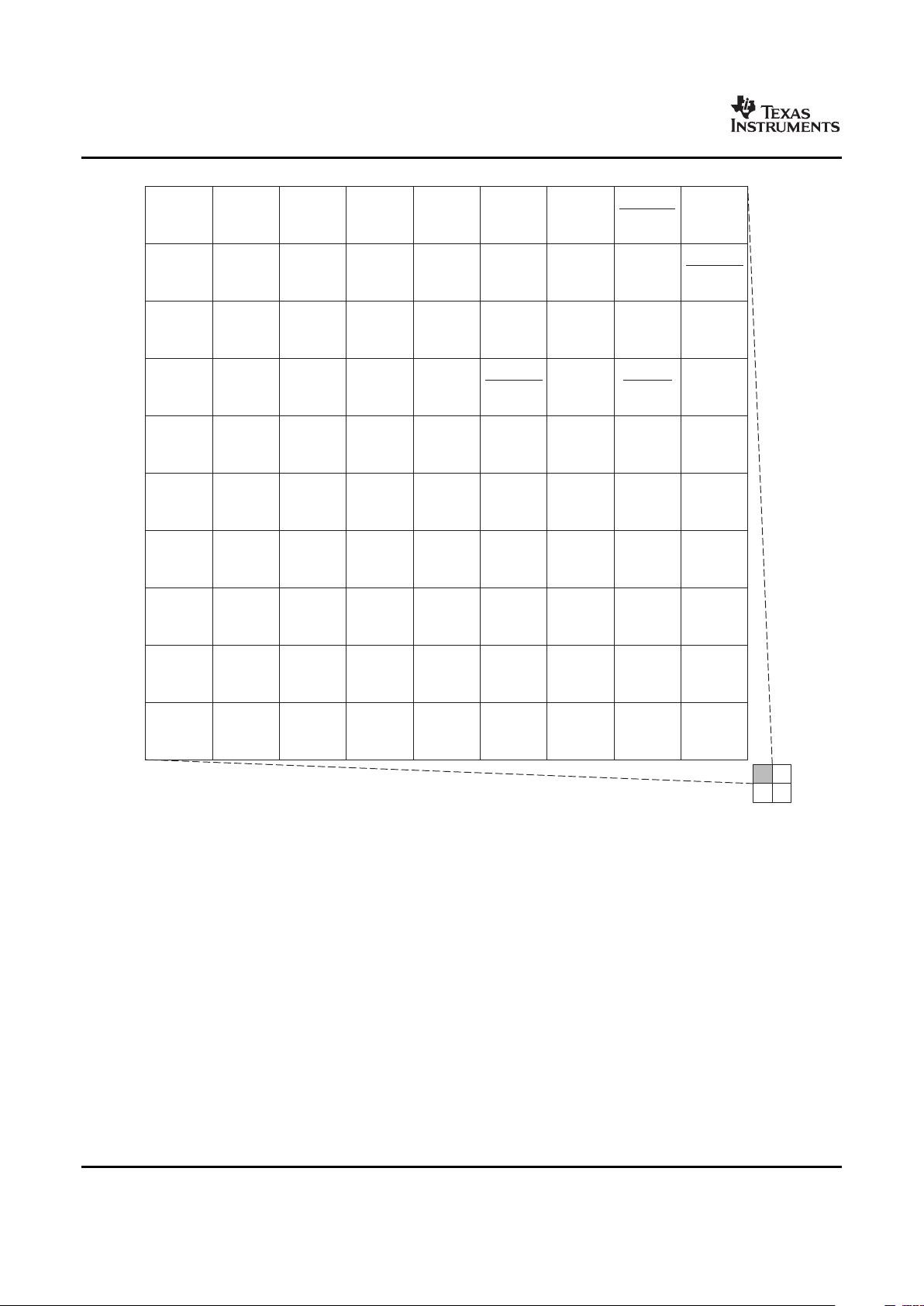
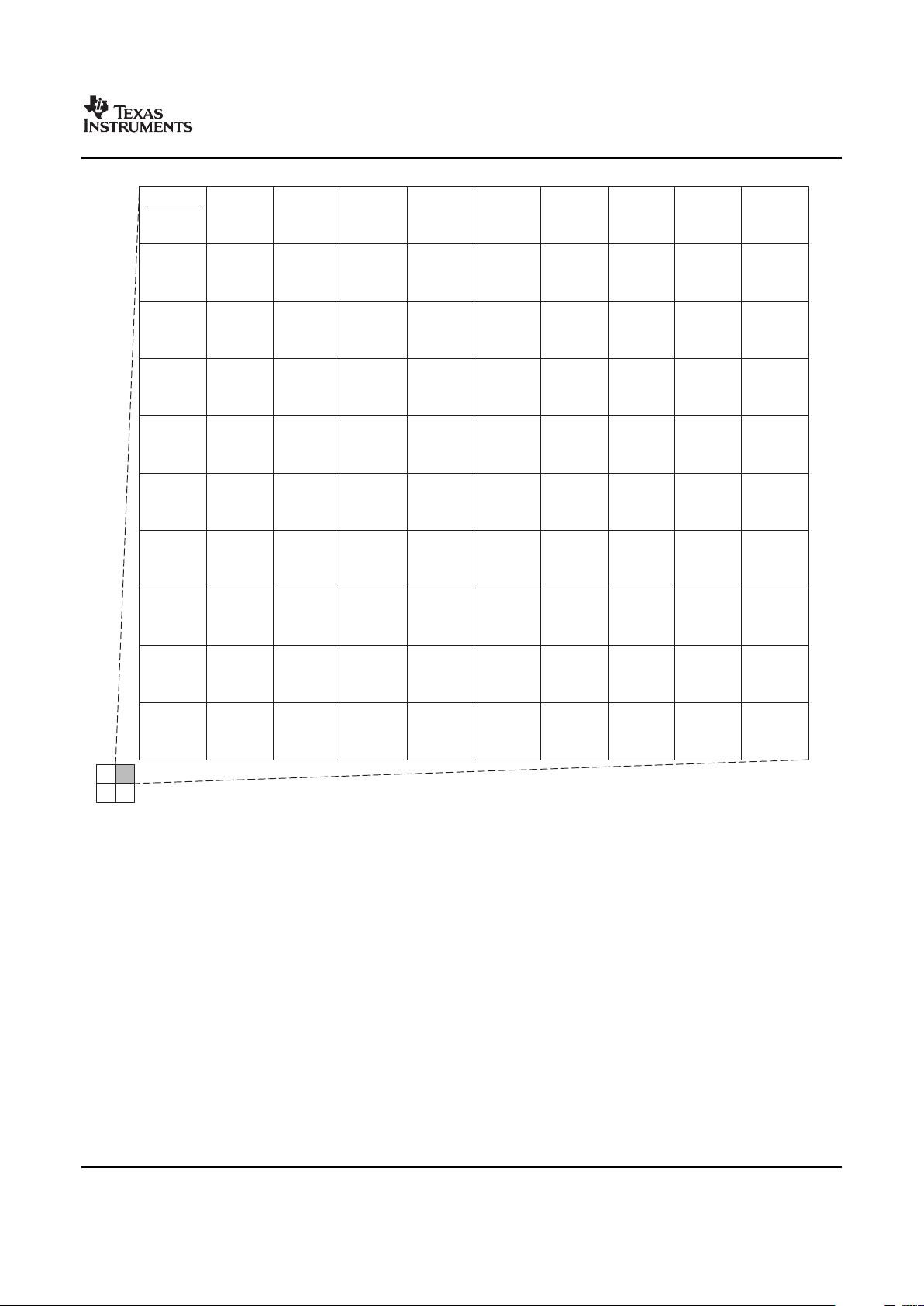
Figure 2-1 through Figure 2-4 show the pin assignments in four quadrants (A, B, C, and D). Note that
micro-vias are not required. Contact your TI representative for routing recommendations.
Figure 2-1. Pin Map [Quadrant A]
Submit Documentation Feedback Device Overview 9
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
W
9
DDR_CLK
8
DDR_CLK
7654
DDR_A5
32
DDR_A2
1
V
DDR_A7DDR_A4DDR_A0
U
V
SS
T
PCLK
R
P
N
M
L
K
DDR_A11DDR_A9DDR_A8
V
SS
DDR_CASDDR_
BA[2]
DDR_A12DDR_A10DDR_A1
V
SS
DDR_
BA[0]
DDR_
BA[1]
DDR_A13DDR_A6
DDR_A3
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
DDR_ZNDDR_CSDDR_RAS
V
SS
V
SS
MXO2
V
DDS
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
CAM_WEN_
FIELD
CAM_VDYIN3
V
SS
MXI2
V
DDS
VDDSHV3VDDSHV3VDDSHV3
YIN0YIN2YIN4YIN1MX2GND
V
SS
V
SS
V
DD
CAM_HDCIN7LVIREF
V
SS
V
DDS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
YIN5YIN6CIN5
VDDA18V
_CCP2
SN
V
SS
VSS_DACVDDA18V
_DAC
VDDSHV1
YIN7CIN4CIN1
V
SS
SP
V
SS
VDDSHV2
V
DD
CIN6
V
SS
VSSA_
CCP2
DN
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Figure 2-2. Pin Map [Quadrant B]
Device Overview10 Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
V
DD
19
W
18
DDR_
GATE0
17
DDR_
DQ15
16
DDR_
DQ13
15
DDR_
DQ11
14
DDR_
DQ10
13
DDR_DQ7
12
DDR_DQ5
11
DDR_DQ1
10
DDR_WE
EM_A13
V
V
SS
DDR_
GATE1
DDR_
DQ14
DDR_
DQS[1]
DDR_DQ9DDR_DQ6
DDR_
DQS[0]
DDR_DQ0DDR_CKE
EM_A12
U
UART0_
RXD
V
SS
DDR_
DQ12
DDR_
DQM[1]
V
SS
DDR_DQ8DDR_DQ4DDR_DQ2DDR_
VREF
EM_A8
T
UART0_
TXD
V
DD
V
SS
V
DDS
DDR_
DQM[0]
DDR_DQ3
EM_A5
R
EM_A10
UART1_
TXD
EM_A11
UART1_
RXD
I2C_SCLI2C_SDA
V
DDS
DDR_
VSSDLL
DDR_
VDDDLL
EM_BA1
P
EM_A6
EM_A9EM_A7EM_A4
V
DDS
V
DDS
V
DDS
V
DDS
V
DDS
EM_BA0
N
EM_A3EM_A1EM_A2
V
SS
VDDSHVVDDSHV
EM_D14
M
EM_D15
V
SS
EM_A0EM_D13
V
SS
VDDSHVVDDSHVVDDSHVVDDSHV
EM_D10
L
EM_D12EM_D11EM_D8EM_D4
V
SS
V
SS
VDDSHV
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
V
SS
EM_D7
K
EM_D9EM_D6VDDSHV
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Figure 2-3. Pin Map [Quadrant C]
Submit Documentation Feedback Device Overview 11
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
19181716151413121110
EM_D5
J
EM_D2
H
EM_CE1
G
F
E
D
C
VDDSHV
B
A
EM_D3EM_D1EM_CE0EM_WE
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
EM_D0
V
DD
EM_ADV
ASP0_
DX
V
SS
V
DD
VSS_PLL
1
V
SS
V
DD
EM_WAIT
ASP0_
FSX
GIO3
VDDA_
PLL1
V
DD
EM_OE
ASP0_
CLKX
ASP0_
CLKR
ASP0_
FSR
GIO2VDDSHVVDDSHVVDDSHVVDDSHVVDDSHV
EM_CLK
ASP0_
DR
ASP1_
FSR
ASP1_
FSX
V
SS
GIO1
SPI1_
SDENA
SPI1_SDORTCKTCK
ASP1_
CLKX
ASP1_
CLKR
ASP1_
CLKS
GIO5
SD0_
DATA1
CLKOUT1RESET
ASP1_
DR
ASP1_
DX
GIO7GIO0
MMCSD1_
CLK
MMCSD0_
CMD
SPI1_
SCLK
SPI0_
SCLK
CLKOUT3MX1GND
V
DD
V
SS
GIO6
MMCSD1_
DATA0
MMCSD1_
DATA3
MMCSD1_
DATA2
GIO4
MMCSD1_
CMD
MMCSD1_
DATA1
MMCSD0_
CLK
MMCSD0_
DATA0
MMCSD0_
DATA3
MMCSD0_
DATA2
SPI1_SDI
SPI0_
SDENA
SPI0_SDI
SPI0_SDO
CLKOUT2
V
SS
V
DD
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Figure 2-4. Pin Map [Quadrant D]
12 Device Overview Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
2.4 Pin Functions
2.4.1 Image Data Input - Video Processing Front End
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
The pin functions tables (Table 2-4 through Table 2-22 ) identify the external signal names, the associated
pin (ball) numbers along with the mechanical package designator, the pin type, whether the pin has any
internal pullup or pulldown resistors, and a functional pin description. For more detailed information on
device configuration, peripheral selection, multiplexed/shared pins, and debugging considerations, see
Section 3 . For the list of all pin in chronological order see Section 2.5
The CCD Controller module in the Video Processing Front End has an external signal interface for image
data input. It supports YUV (YC) inputs as well as Bayer RGB and complementary input signals (I.e.,
image data input).
The definition of the CCD controller data input signals depend on the input mode selected.
• In 16-bit YCbCr mode, the Cb and Cr signals are multiplexed on the Cl signals and the order is
configurable (i.e., Cb first or Cr first).
• In 8-bit YCbCr mode, the Y, Cb, and Cr signals are multiplexed and not only is the order selectable,
but also the half of the bus used.
Table 2-4. CCD Controller Signals for Each Input Mode
PIN NAME CCD 16-BIT YCbCr 8-BIT YCbCr
Cl7 Cb7,Cr7 Y7,Cb7,Cr7
Cl6 Cb6,Cr6 Y6,Cb6,Cr6
Cl5 CCD13 Cb5,Cr5 Y5,Cb5,Cr5
Cl4 CCD12 Cb4,Cr4 Y4,Cb4,Cr4
Cl3 CCD11 Cb3,Cr3 Y3,Cb3,Cr3
Cl2 CCD10 Cb2,Cr2 Y2,Cb2,Cr2
Cl1 CCD9 Cb1,Cr1 Y1,Cb1,Cr1
Cl0 CCD8 Cb0,Cr0 Y0,Cb0,Cr0
Yl7 CCD7 Y7 Y7,Cb7,Cr7
Yl6 CCD6 Y6 Y6,Cb6,Cr6
Yl5 CCD5 Y5 Y5,Cb5,Cr5
Yl4 CCD4 Y4 Y4,Cb4,Cr4
Yl3 CCD3 Y3 Y3,Cb3,Cr3
Yl2 CCD2 Y2 Y2,Cb2,Cr2
Yl1 CCD1 Y1 Y1,Cb1,Cr1
Yl0 CCD0 Y0 Y0,Cb0,Cr0
Submit Documentation Feedback Device Overview 13
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-5. CCD Controller/Video Input Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): NOT USED
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/SR[07]
CIN7/
PD
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO101/ N3 I/O/Z
V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[07]
SPI2_SCLK
SPI: SPI2 Clock
GIO: GIO[101]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): NOT USED
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/SR[06]
CIN6/
PD
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO100/ K5 I/O/Z
V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[06]
SPI2_SDO
SPI: SPI2 Data Out
GIO: GIO[100]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[13]
CIN5/ • YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/SR[05]
GIO099/ PD
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
M3 I/O/Z
SPI2_SDEN V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[05]
A[0]
SPI: SPI2 Chip Select
GIO: GIO[099]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[12]
CIN4/ • YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/SR[04]
GIO098/ PD
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
L4 I/O/Z
SPI2_SDEN V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[04]
A[1]
SPI: SPI2 Data In
GIO: GIO[098]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[11]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/SR[03]
CIN3/ PD
J4 I/O/Z
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO097/ V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[03]
GIO: GIO[097]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[10]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/SR[02]
CIN2/ PD
J5 I/O/Z
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO096/ V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[02]
GIO: GIO[097]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[09]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/SR[01]
CIN1/ PD
L3 I/O/Z
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO095/ V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[01]
GIO: GIO[095]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[08]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: CB/SR[00]
CIN0/ PD
J3 I/O/Z
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO094/ V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[00]
GIO: GIO[094]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[07]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[07]
YIN7/ PD
L5 I/O/Z
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO093 V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[07]
GIO: GIO[093]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[06]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[06]
YIN6/ PD
M4 I/O/Z
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO092 V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[06]
GIO: GIO[092]
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) PD = internal pull-down, PU = internal pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 k Ω resistor should be used.)
(3) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
Device Overview14 Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
2.4.2 Image Data Output - Video Processing Back End (VPBE)
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-5. CCD Controller/Video Input Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[05]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[05]
YIN5/ PD
M5 I/O/Z
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO091 V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[05]
GIO: GIO[091]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[04]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[04]
YIN4/ PD
P3 I/O/Z
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO090 V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[04]
GIO: GIO[090]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[03]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[03]
YIN3/ PD
R3 I/O/Z
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO089 V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[03]
GIO: GIO[089]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[02]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[02]
YIN2/ PD
P4 I/O/Z
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO088 V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[02]
GIO: GIO[088]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[01]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[01]
YIN1/ PD
P2 I/O/Z
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO087 V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[01]
GIO: GIO[087]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): Raw[00]
• YCC 16-bit: Time multiplexed between chroma: Y[00]
YIN0/ PD
P5 I/O/Z
• YCC 8-bit (which allows for two simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time
GIO086 V
DD_VIN
multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[00]
GIO: GIO[086]
Horizontal synchronization signal that can be either an input (slave mode) or an
CAM_HD/ PD
N5 I/O/Z output (master mode). Tells the CCDC when a new line starts.
GIO085 V
DD_VIN
GIO: GIO[085]
Vertical synchronization signal that can be either an input (slave mode) or an output
CAM_VD PD
R4 I/O/Z (master mode). Tells the CCDC when a new frame starts.
GIO084 V
DD_VIN
GIO: GIO[084]
Write enable input signal is used by external device (AFE/TG) to gate the DDR
output of the CCDC module. Alternately, the field identification input signal is used
CAM_WEN
PD by external device (AFE/TG) to indicate which of two frames is input to the CCDC
_FIELD\ R5 I/O/Z
V
DD_VIN
module for sensors with interlaced output. CCDC handles 1- or 2-field sensors in
GIO083
hardware.
GIO: GIO[083]
PCLK/ PD Pixel clock input (strobe for lines C17 through Y10)
T3 I/O/Z
GIO082 V
DD_VIN
GIO: GIO[0082]
The Video Encoder/Digital LCD interface module in the video processing back end has an external signal
interface for digital image data output as described in Table 2-7 and Table 2-8 .
The digital image data output signals support multiple functions / interfaces, depending on the display
mode selected. The following table describes these modes. Parallel RGB mode with more than RGB565
signals requires enabling pin multiplexing to support (i.e., for RGB666 mode).
Submit Documentation Feedback Device Overview 15
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-6. Signals for VPBE Display Modes
PIN NAME YCC16 YCC8/ PRGB SRGB
REC656
HSYNC HSYNC HSYNC HSYNC HSYNC
GIO073
VSYNC VSYNC VSYNC VSYNC VSYNC
GIO072
LCD_OE As needed As needed As needed As needed
GIO071
FIELD As needed As needed As needed As needed
GIO070
R2
PWM3C
EXTCLK As needed As needed As needed As needed
GIO069
B2
PWM3D
VCLK VCLK VCLK VCLK VCLK
GIO068
YOUT7 Y7 Y7,Cb7,Cr7 R7 Data7
YOUT6 Y6 Y6,Cb6,Cr6 R6 Data6
YOUT5 Y5 Y5,Cb5,Cr5 R5 Data5
YOUT4 Y4 Y4,Cb4,Cr4 R4 Data4
YOUT3 Y3 Y3,Cb3,Cr3 R3 Data3
YOUT2 Y2 Y2,Cb2,Cr2 G7 Data2
YOUT1 Y1 Y1,Cb1,Cr1 G6 Data1
YOUT0 Y0 Y0,Cb0,Cr0 G5 Data0
COUT7 C7 LCD_AC G4 LCD_AC
GIO081
PWM0
COUT6 C6 LCD_OE G3 LCD_OE
GIO080
PWM1
COUT5 C5 BRIGHT G2 BRIGHT
GIO079
PWM2A
RTO0
COUT4 C4 PWM B7 PWM
GIO078
PWM2B
RTO1
COUT3 C3 CSYNC B6 CSYNC
GIO077
PWM2C
RTO2
COUT2 C2 - B5 GIO076
PWM2D
RTO3
COUT1 C1 - B4 GIO075
PWM3A
COUT0 C0 - B3 GIO074
PWM3B
Device Overview16 Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-7. Digital Video Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
(4)
NAME NO.
YOUT7-R7 C2 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
YOUT6-R6 A4 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
YOUT5-R5 B4 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
YOUT4-R4 B3 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
YOUT3-R3 B2 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
YOUT2-G7 A3 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
YOUT1-G6 A2 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
YOUT0-G5 B1 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
COUT7G4/GIO081 C2 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[081] PWM0
/PWM0
COUT6-G3
/GIO080 D2 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[080] PWM1
/PWM1
COUT5-G2
/ GIO079 /
C1 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[079] PWM2A RTO0
PWM2A /
RTO0
COUT4-B7 /
GIO078 /
D3 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[078] PWM2B RTO1
PWM2B /
RTO1
COUT3-B6 /
GIO077 /
E3 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[077] PWM2C RTO2
PWM2C /
RTO2
COUT2-B5 /
GIO076 /
E4 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[076] PWM2D RTO3
PWM2D /
RTO3
COUT1-B4 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
GIO075 / F3 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
GIO: GIO[075]
PWM3A PWM3A
COUT0-B3 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function
GIO074 / F4 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
GIO: GIO[074]
PWM3B PWM3B
HSYNC / PD Video Encoder: Horizontal Sync
F5 I/O/Z
GIO073 V
DD_VOUT
GIO: GIO[073]
VSYNC / PD Video Encoder: Vertical Sync
G5 I/O/Z
GIO072 V
DD_VOUT
GIO: GIO[072]
FIELD / Video Encoder: Field identifier for interlaced display formats
GIO070 / GIO: GIO[070]
H4 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
R2 / Digital Video Out: R2
PWM3C PWM3C
Video Encoder: External clock input, used if clock rates > 27 MHz are needed, e.g.
EXTCLK /
74.25 MHz for HDTV digital output
GIO069 / PD
G3 I/O/Z GIO: GIO[069]
B2 / V
DD_VOUT
Digital Video Out: B2
PWM3D
PWM3D
VCLK / Video Encoder: Video Output Clock
H3 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
GIO068 GIO: GIO[068]
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 k Ω resistor should be used.)
(4) To reduce EMI and reflections, depending on the trace length, approximately 22 Ω to 50 Ω damping resistors are recommend on the
following outputs placed near the DM355: YOUT(0-7),COUT(0-7), HSYNC,VSYNC,LCD_OE,FIELD,EXTCLK,VCLK. The trace lengths
should be minimized.
Submit Documentation Feedback Device Overview 17
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
2.4.3 Asynchronous External Memory Interface (AEMIF)
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-8. Analog Video Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
Video DAC: Reference voltage output (0.45V, 0.1uF to GND). When the DAC is not
VREF J7 A I/O/Z
used, the VREF signal should be connected to VSS.
Video DAC: Pre video buffer DAC output (1000 ohm to VFB). When the DAC is not
IOUT E1 A I/O/Z
used, the IOUT signal should be connected to VSS.
Video DAC: External resistor (2550 Ohms to GND) connection for current bias
IBIAS F2 A I/O/Z configuration. When the DAC is not used, the IBIAS signal should be connected to
VSS.
Video DAC: Pre video buffer DAC output (1000 Ohms to IOUT, 1070 Ohms to
VFB G1 A I/O/Z
TVOUT). When the DAC is not used, the VFB signal should be connected to VSS.
Video DAC: Analog Composite NTSC/PAL output (SeeFigure 5-31 andFigure 5-32 for
TVOUT F1 A I/O/Z V circuit connection). When the DAC is not used, the TVOUT signal should be left as a
No Connect or connected to VSS.
Video DAC: Analog 1.8V power. When the DAC is not used, the V
DDA18_DAC
signal
V
DDA18_DAC
L7 PWR
should be connected to VSS.
Video DAC: Analog 1.8V ground. When the DAC is not used, the V
SSA_DAC
signal
V
SSA_DAC
L8 GND
should be connected to VSS.
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal. Specifies the operating I/O supply
voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(2) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 k Ω resistor should be used.)
The Asynchronous External Memory Interface (AEMIF) signals support AEMIF, NAND, and OneNAND.
Table 2-9. Asynchronous EMIF/NAND/OneNAND Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[13]
EM_A13/
PD GIO: GIO[67]
GIO067/ V19 I/O/Z
V
DD
System: BTSEL[1:0] sampled at power-on-reset to determine boot method. Used
BTSEL[1]
to drive boot status LED signal (active low) in ROM boot modes.
EM_A12/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[12]
PD
GIO066/ U19 I/O/Z GIO: GIO[66]
V
DD
BTSEL[0] System: BTSEL[1:0] sampled at power-on-reset to determine boot method.
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[11]
EM_A11/
PU GIO: GIO[65]
GIO065/ R16 I/O/Z
V
DD
AECFG[3:0] sampled at power-on-reset to AECFG configuration. AECFG[3] sets
AECFG[3]
default for PinMux2_EM_D15_8: AEMIF default bus width (16 or 8 bits)
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[10]
EM_A10/ GIO: GIO[64]
PU
GIO064/ R18 I/O/Z AECFG[3:0] sampled at power-on-reset to AECFG configuration. AECFG[2:1]
V
DD
AECFG[2] sets default for PinMux2_EM_BA0: AEMIF EM_BA0 definition (EM_BA0,
EM_A14, GIO[054], rsvd)
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[09]
EM_A09/ GIO: GIO[63]
PD
GIO063/ P17 I/O/Z AECFG[3:0] sampled at power-on-reset to AECFG configuration. AECFG[2:1]
V
DD
AECFG[1] sets default for PinMux2_EM_BA0: AEMIF EM_BA0 definition (EM_BA0,
EM_A14, GIO[054], rsvd)
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[08]
GIO: GIO[62]
EM_A08/
PD
AECFG[0] sets default for:
GIO062/ T19 I/O/Z
V
DD
AECFG[0] • PinMux2_EM_A0_BA1: AEMIF address width (OneNAND or NAND)
• PinMux2_EM_A13_3: AEMIF address width (OneNAND or NAND)
EM_A07/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[07]
P16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO061 GIO: GIO[61]
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 k Ω resistor should be used.)
Device Overview18 Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-9. Asynchronous EMIF/NAND/OneNAND Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
EM_A06/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[06]
P18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO060 GIO: GIO[60]
EM_A05/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[05]
R19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO059 GIO: GIO[59]
EM_A04/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[04]
P15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO058 GIO: GIO[58]
EM_A03/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[03]
N18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO057 GIO: GIO[57]
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[02]
EM_A02/ N15 I/O/Z V
DD
NAND/SM/xD: CLE - Command latch enable output
Async EMIF: Address bus bit[01]
EM_A01/ N17 I/O/Z V
DD
NAND/SM/xD: ALE - Address latch enable output
EM_A00/ Async EMIF: Address bus bit[00]
M16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO056 GIO: GIO[56]
Async EMIF: Bank address 1 signal - 16-bit address:
EM_BA1/ • In 16-bit mode, lowest address bit.
P19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO055
• In 8-bit mode, second lowest address bit.
GIO: GIO[055]
Async EMIF: Bank address 0 signal - 8-bit address:
EM_BA0/
• In 8-bit mode, lowest address bit. or can be used as an extra address line
GIO054 T19 I/O/Z V
DD
(bit14) when using 16-bit memories.
EM_A14
GIO: GIO[054]
EM_D15/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 15
M18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO053 GIO: GIO[053]
EM_D14/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 14
M19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO052 GIO: GIO[052]
EM_D13/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 13
M15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO051 GIO: GIO[051]
EM_D12/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 12
L18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO050 GIO: GIO[050]
EM_D11/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 11
L17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO049 GIO: GIO[049]
EM_D10/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 10
L19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO048 GIO: GIO[048]
EM_D09/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 09
K18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO047 GIO: GIO[047]
EM_D08/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 08
L16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO046 GIO: GIO[046]
EM_D07/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 07
K19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO045 GIO: GIO[045]
EM_D06/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 06
K17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO044 GIO: GIO[044]
EM_D05/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 05
J19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO043 GIO: GIO[043]
EM_D04/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 04
L15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO042 GIO: GIO[042]
EM_D03/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 03
J18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO041 GIO: GIO[041]
EM_D02/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 02
H19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO040 GIO: GIO[040]
EM_D01/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 01
J17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO039 GIO: GIO[039]
EM_D00/ Async EMIF: Data bus bit 00
H18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO038 GIO: GIO[038]
Submit Documentation Feedback Device Overview 19
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
2.4.4 DDR Memory Interface
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-9. Asynchronous EMIF/NAND/OneNAND Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
Async EMIF: Lowest numbered chip select. Can be programmed to be used for
EM_CE0/ standard asynchronous memories (example: flash), OneNAND, or NAND
J16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO037 memory. Used for the default boot and ROM boot modes.
GIO: GIO[037]
Async EMIF: Second chip select. Can be programmed to be used for standard
EM_CE1/
G19 I/O/Z V
DD
asynchronous memories(example: flash), OneNAND, or NAND memory.
GIO036
GIO: GIO[036]
Async EMIF: Write Enable
EM_WE/
J15 I/O/Z V
DD
NAND/SM/xD: WE (Write Enable) output
GIO035
GIO: GIO[035]
Async EMIF: Output Enable
EM_OE/
F19 I/O/Z V
DD
NAND/SM/xD: RE (Read Enable) output
GIO034
GIO: GIO[034]
Async EMIF: Async WAIT
EM_WAIT/
G18 I/O/Z V
DD
NAND/SM/xD: RDY/ BSY input
GIO033
GIO: GIO[033]
EM_AVD/ OneNAND: Address valid detect for OneNAND interface
H16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO032 GIO: GIO[032]
EM_CLK/ OneNAND: Clock for OneNAND flash interface
E19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO031 GIO: GIO[031]
The DDR EMIF supports DDR2 and mobile DDR.
Table 2-10. DDR Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
DDR_CLK W9 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Clock
DDR_CLK W8 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Complementary Data Clock
DDR_RAS T6 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Row Address Strobe
DDR_CAS V9 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Column Address Strobe
DDR_ WE W10 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Write Enable
DDR_ CS T8 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Chip Select
DDR_CKE V10 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Clock Enable
DDR_DQM[
Data mask outputs:
U15 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
1]
• DQM0 - For DDR_DQ[7:0]
DDR_DQM[
T12 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
• DQM1 - For DDR_DQ[15:8]
0]
DDR_DQS[ Data strobe input/outputs for each byte of the 16-bit data bus used to
V15 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
1] synchronize the data transfers. Output to DDR when writing and inputs when
reading.
DDR_DQS[
• DQS1 - For DDR_DQ[15:8]
V12 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
0]
• DQS0 - For DDR_DQ[7:0]
DDR_BA[2] V8 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
Bank select outputs. Two are required for 1Gb DDR2 memories.
DDR_BA[1] U7 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
Bank select outputs. Two are required for 1Gb DDR2 memories.
DDR_BA[0] U8 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
Bank select outputs. Two are required for 1Gb DDR2 memories.
DDR_A13 U6 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 13
DDR_A12 V7 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 12
DDR_A11 W7 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 11
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 k Ω resistor should be used.)
Device Overview20 Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-10. DDR Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
DDR_A10 V6 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 10
DDR_A09 W6 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 09
DDR_A08 W5 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 08
DDR_A07 V5 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 07
DDR_A06 U5 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 06
DDR_A05 W4 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 05
DDR_A04 V4 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 04
DDR_A03 W3 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 03
DDR_A02 W2 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 02
DDR_A01 V3 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 01
DDR_A00 V2 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Address Bus bit 00
DDR_DQ15 W17 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 15
DDR_DQ14 V16 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 14
DDR_DQ13 W16 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 13
DDR_DQ12 U16 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 12
DDR_DQ11 W15 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 11
DDR_DQ10 W14 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 10
DDR_DQ09 V14 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 09
DDR_DQ08 U13 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 08
DDR_DQ07 W13 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 07
DDR_DQ06 V13 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 06
DDR_DQ05 W12 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 05
DDR_DQ04 U12 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 04
DDR_DQ03 T11 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 03
DDR_DQ02 U11 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 02
DDR_DQ01 W11 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 01
DDR_DQ00 V11 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR Data Bus bit 00
DDR_GATE DDR: Loopback signal for external DQS gating. Route to DDR and back to
W18 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
0 DDR_GATE0 with same constraints as used for DDR clock and data.
DDR_GATE DDR: Loopback signal for external DQS gating. Route to DDR and back to
V17 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
1 DDR_GATE0 with same constraints as used for DDR clock and data.
DDR: Voltage input for the SSTL_18 I/O buffers. Note even in the case of mDDR
DDR_VREF U10 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
an external resistor divider connected to this pin is necessary.
DDR_VSSD
R11 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR: Ground for the DDR DLL
LL
DDR_VDDD
R10 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
DDR: Power (3.3 V) for the DDR DLL
LL
DDR: Reference output for drive strength calibration of N and P channel outputs.
DDR_ZN T9 I/O/Z V
DD_DDR
Tie to ground via 50 ohm resistor @ 0.5% tolerance.
Submit Documentation Feedback Device Overview 21
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
2.4.5 GPIO
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
The General Purpose I/O signals provide generic I/O to external devices. Most of the GIO signals are
multiplexed with other functions.
Table 2-11. GPIO Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
GIO: GIO[000] Active low during MMC/SD boot (can be used as MMC/SD power
GIO000 C16 I/O/Z V
DD
control).
Can be used as external clock input for Timer 3.
GIO001 E14 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[001] Can be used as external clock input for Timer 3.
GIO002 F15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[002] Can be used as external clock input for Timer 3.
GIO003 G15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[003] Can be used as external clock input for Timer 3.
GIO004 B17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[004]
GIO005 D15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[005]
GIO006 B18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[006]
GIO007 /
GIO: GIO[007]
SPI0_SDE C17 I/O/Z V
DD
SPI0: Chip Select 1
NA[1]
SPI1_SD
SPI1: Data Out
O / B11 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[008]
GIO008
SPI1_SDI
/ GIO009 /
A12 I/O/Z V
DD
SPI1: Data In -OR- SPI1: Chip Select 1 GIO: GIO[009]
SPI1_SDE
NA[1]
SPI1_SCL
SPI1: Clock GIO:
K / C12 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO[010]
GIO010
SPI1_SDE
SPI1: Chip Select 0
NA[0] / B12 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[011]
GIO011
UART1_T
UART1: Transmit Data
XD / R17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[012]
GIO012
UART1_R
UART1: Receive Data
XD / R15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[013]
GIO013
I2C_SCL / I2C: Serial Clock GIO:
R14 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO014 GIO[014]
I2C_SDA / I2C: Serial Data
R13 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO015 GIO: GIO[015]
CLKOUT3 CLKOUT: Output Clock 3
C11 I/O/Z V
DD
/ GIO016 GIO: GIO[016]
CLKOUT2 CLKOUT: Output Clock 2
A11 I/O/Z V
DD
/ GIO017 GIO: GIO[017]
CLKOUT1 CLKOUT: Output Clock 1
D12 I/O/Z V
DD
/ GIO018 GIO: GIO[018]
MMCSD1
_DATA0 / MMCSD1: DATA0
GIO019 / A18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[019]
UART2_T UART2: Transmit Data
XD
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 k Ω resistor should be used.)
Device Overview22 Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-11. GPIO Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
MMCSD1
_DATA1 / MMCSD1: DATA1
GIO020 / B15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[020]
UART2_R UART2: Receive Data
XD
MMCSD1
_DATA2 / MMCSD1: DATA2
GIO021 / A16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[021]
UART2_C UART2: CTS
TS
MMCSD1
_DATA3 / MMCSD1: DATA3
GIO022 / B16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[022]
UART2_R UART2: RTS
TS
MMCSD1
MMCSD1: Command
_CMD / A17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[023]
GIO023
MMCSD1
MMCSD1: Clock
_CLK / C15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[024]
GIO024
ASP0_FS
ASP0: Receive Frame Synch
R / F16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[025]
GIO025
ASP0_CL
ASP0: Receive Clock
KR / F17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[026]
GIO026
ASP0_DR ASP0: Receive Data
E18 I/O/Z V
DD
/ GIO027 GIO: GIO[027]
ASP0_FS
ASP0: Transmit Frame Synch
X / G17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[028]
GIO028
ASP0_CL
ASP0: Transmit Clock
KX / F18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[029]
GIO029
ASP0_DX ASP0: Transmit Data
H15 I/O/Z V
DD
/ GIO030 GIO: GIO[030]
EM_CLK /
E19 I/O/Z V
DD
OneNAND: Clock signal for OneNAND flash interface GIO: GIO[031]
GIO031
EM_AVD / PD OneNAND: Address Valid Detect for OneNAND interface
H16 I/O/Z
GIO032 V
DD
GIO: GIO[032]
EM_WAIT PU Async EMIF: Async WAIT NAND/SM/xD: RDY/_BSY input
G18 I/O/Z
/ GIO033 V
DD
GIO: GIO[033]
Async EMIF: Output Enable
EM_OE /
F19 I/O/Z V
DD
NAND/SM/xD: RE (Read Enable) output
GIO034
GIO: GIO[034]
Async EMIF: Write Enable
EM_WE /
J15 I/O/Z V
DD
NAND/SM/xD: WE (Write Enable) output
GIO035
GIO: GIO[035]
Async EMIF: Second Chip Select., Can be programmed to be used for standard
EM_CE1 /
G19 I/O/Z V
DD
asynchronous memories (example: flash), OneNand or NAND memory.
GIO036
GIO: GIO[036]
Async EMIF: Lowest numbered Chip Select. Can be programmed to be used for
EM_CE0 / standard asynchronous memories (example: flash), OneNand or NAND memory.
J16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO037 Used for the default boot and ROM boot modes.
GIO: GIO[037]
EM_D00 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[00]
H18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO038 GIO: GIO[038]
Submit Documentation Feedback Device Overview 23
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-11. GPIO Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
EM_D01 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[01]
J17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO039 GIO: GIO[039]
EM_D02 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[02]
H19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO040 GIO: GIO[040]
EM_D03 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[03]
J18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO041 GIO: GIO[041]
EM_D04 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[04]
L15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO042 GIO: GIO[042]
EM_D05 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[05]
J19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO043 GIO: GIO[043]
EM_D06 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[06]
K17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO044 GIO: GIO[044]
EM_D07 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[07]
K19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO045 GIO: GIO[045]
EM_D08 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[08]
L16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO046 GIO: GIO[046]
EM_D09 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[09]
K18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO047 GIO: GIO[047]
EM_D10 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[10]
ML19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO048 GIO: GIO[048]
EM_D11 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[11]
L17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO049 GIO: GIO[049]
EM_D12 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[12]
L18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO050 GIO: GIO[050]
EM_D13 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[13]
M15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO051 GIO: GIO[051]
EM_D14 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[14]
M19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO052 GIO: GIO[052]
EM_D15 / Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[15]
M18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO053 GIO: GIO[053]
Async EMIF: Bank Address 0 signal = 8-bit address. In 8-bit mode, lowest
EM_BA0 /
address bit. Or, can be used as an extra Address line (bit[14] when using 16-bit
GIO054 / T19 I/O/Z V
DD
memories.
EM_A14
GIO: GIO[054]
Async EMIF: Bank Address 1 signal = 16-bit address. In 16-bit mode, lowest
EM_BA1 /
P19 I/O/Z V
DD
address bit. In 8-bit mode, second lowest address bit
GIO055
GIO: GIO[055]
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[00] Note that the EM_A0 is always a 32-bit
EM_A00 /
M16 I/O/Z V
DD
address
GIO056
GIO: GIO[056]
EM_A03 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[03]
N18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO057 GIO: GIO[057]
EM_A04 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[04]
P15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO058 GIO: GIO[058]
EM_A05 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[05]
R19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO059 GIO: GIO[059]
EM_A06 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[06]
P18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO060 GIO: GIO[060]
EM_A07 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[07]
P16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO061 GIO: GIO[061] - Used by ROM Bootloader to provide progress status via LED
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[08]
EM_A08 /
GIO: GIO[062] AECFG[0] sets default for - PinMux2.EM_A0_BA1: AEMIF
GIO062 / T19 I/O/Z V
DD
Address Width (OneNAND or NAND) - PinMux2.EM_A13_3: AEMIF Address
AECFG[0]
Width (OneNAND or NAND)
Device Overview24 Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-11. GPIO Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[09]
EM_A09 /
GIO: GIO[063] System: AECFG[3:0] sampled at Power-on-Reset to set AEMIF
GIO063 / P17 I/O/Z V
DD
Configuration AECFG[2:1] sets default for PinMux2.EM_BA0: AEMIF EM_BA0
AECFG[1]
Definition (EM_BA0, EM_A14, GIO[054], rsvd)
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[10]
EM_A10 /
GIO: GIO[064] System: AECFG[3:0] sampled at Power-on-Reset to set AEMIF
GIO064 / R18 I/O/Z V
DD
Configuration AECFG[2:1] sets default for PinMux2.EM_BA0: AEMIF EM_BA0
AECFG[2]
Definition (EM_BA0, EM_A14, GIO[054], rsvd)
EM_A03 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[03]
N18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO057 GIO: GIO[057]
EM_A04 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[04]
P15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO058 GIO: GIO[058]
EM_A05 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[05]
R19 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO059 GIO: GIO[059]
EM_A06 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[06]
P18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO060 GIO: GIO[060]
EM_A07 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[07]
P16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO061 GIO: GIO[061] - Used by ROM Bootloader to provide progress status via LED
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[08]
EM_A08 /
PU GIO: GIO[062] AECFG[0] sets default for - PinMux2.EM_A0_BA1: AEMIF
GIO062 / T19 I/O/Z
V
DD
Address Width (OneNAND or NAND) - PinMux2.EM_A13_3: AEMIF Address
AECFG[0]
Width (OneNAND or NAND)
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[09]
EM_A09 /
PD GIO: GIO[063] System: AECFG[3:0] sampled at Power-on-Reset to set AEMIF
GIO063 / P17 I/O/Z
V
DD
Configuration AECFG[2:1] sets default for PinMux2.EM_BA0: AEMIF EM_BA0
AECFG[1]
Definition (EM_BA0, EM_A14, GIO[054], rsvd)
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[10]
EM_A10 /
PU GIO: GIO[064] System: AECFG[3:0] sampled at Power-on-Reset to set AEMIF
GIO064 / R18 I/O/Z
V
DD
Configuration AECFG[2:1] sets default for PinMux2.EM_BA0: AEMIF EM_BA0
AECFG[2]
Definition (EM_BA0, EM_A14, GIO[054], rsvd)
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[11]
EM_A11 /
PU GIO: GIO[065] System: AECFG[3:0] sampled at Power-on-Reset to set AEMIF
GIO065 / R16 I/O/Z
V
DD
Configuration AECFG[3] sets default for PinMux2.EM_D15_8: AEMIF Default
AECFG[3]
Bus Width (16 or 8 bits)
EM_A12 / Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[12]
PD
GIO066 / U19 I/O/Z GIO: GIO[066] System: BTSEL[1:0] sampled at Power-on-Reset to determine
V
DD
BTSEL[0] Boot method
Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[13]
EM_A13 /
PD GIO: GIO[067] System: BTSEL[1:0] sampled at Power-on-Reset to determine
GIO067 / V19 I/O/Z
V
DD
Boot method Used to drive Boot Status LED signal (active low) in ROM boot
BTSEL[1]
modes
VCLK / Video Encoder: Video Output Clock
H3 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
GIO068 GIO: GIO[068]
EXTCLK /
Video Encoder: External clock input, used if clock rates > 27 MHz are needed,
GIO069 / PD
G3 I/O/Z e.g. 74.25 MHz for HDTV digital output
B2 / V
DD_VOUT
GIO: GIO[069] Digital Video Out: B2 PWM3D
PWM3D
FIELD /
GIO070 / Video Encoder: Field identifier for interlaced display formats
H4 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
R2 / GIO: GIO[070] Digital Video Out: R2 PWM3C
PWM3C
VSYNC / PD Video Encoder: Vertical Sync
G5 I/O/Z
GIO072 V
DD_VOUT
GIO: GIO[072]
HSYNC / PD Video Encoder: Horizontal Sync
F5 I/O/Z
GIO073 V
DD_VOUT
GIO: GIO[073]
COUT0-
B3 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[074]
F4 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
GIO074 / PWM3B
PWM3B
Submit Documentation Feedback Device Overview 25
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-11. GPIO Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
COUT1B4 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[075]
F3 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
GIO075 / PWM3A
PWM3A
COUT2B5 /
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[076] PWM2D
GIO076 / E4 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
RTO3
PWM2D /
RTO3
COUT3B6 /
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[077] PWM2C
GIO077 / E3 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
RTO2
PWM2C /
RTO2
COUT4B7 /
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[078] PWM2B
GIO078 / D3 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
RTO1
PWM2B /
RTO1
COUT5G2 /
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[079] PWM2A
GIO079 / C1 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
RTO0
PWM2A /
RTO0
COUT6G3 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[080]
D2 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
GIO080 / PWM1
PWM1
COUT7G4 / Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function GIO: GIO[081]
C2 I/O/Z V
DD_VOUT
GIO081 / PWM0
PWM0
PCLK / PD
T3 I/O/Z Pixel clock input (strobe for lines CI7 through YI0) GIO: GIO[082]
GIO082 V
DD_VIN
Write enable input signal is used by external device (AFE/TG) to gate the DDR
CAM_WE output of the CCDC module. Alternately, the field identification input signal is
PD
N_FIELD / R5 I/O/Z used by external device (AFE/TG) to indicate the which of two frames is input to
V
DD_VIN
GIO083 the CCDC module for sensors with interlaced output. CCDC handles 1- or 2-field
sensors in hardware. GIO: GIO[083]
Vertical synchronization signal that can be either an input (slave mode) or an
CAM_VD / PD
R4 I/O/Z output (master mode). Tells the CCDC when a new frame starts.
GIO084 V
DD_VIN
GIO: GIO[084]
Horizontal synchronization signal that can be either an input (slave mode) or an
CAM_HD / PD
N5 I/O/Z output (master mode). Tells the CCDC when a new line starts.
GIO085 V
DD_VIN
GIO: GIO[085]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[00] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
between luma: Y[00] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
YIN0 / PD
P5 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel.
GIO086 V
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[00]
GIO: GIO[086]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[01] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
between luma: Y[01] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
YIN1 / PD
P2 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel.
GIO087 V
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[01]
GIO: GIO[087]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[02] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
between luma: Y[02] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
YIN2 / PD
P4 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel.
GIO088 V
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[02]
GIO: GIO[088]
Device Overview26 Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-11. GPIO Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[03] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
between luma: Y[03] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
YIN3 / PD
R3 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel.
GIO089 V
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[03]
GIO: GIO[089]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[04] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
between luma: Y[04] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
YIN4 / PD
P3 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel.
GIO090 V
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[04]
GIO: GIO[090]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[05] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
between luma: Y[05] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
YIN5 / PD
M5 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel.
GIO091 V
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[05]
GIO: GIO[091]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[06] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
between luma: Y[06] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
YIN6 / PD
M4 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel.
GIO092 V
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[06]
GIO: GIO[092]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[07] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
between luma: Y[07] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder
YIN7 / PD
L5 I/O/Z inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel.
GIO093 V
DD_VIN
Y/CB/CR[07]
GIO: GIO[093]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[08] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
between chroma: CB/CR[00] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
CIN0 / PD
J3 I/O/Z decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper
GIO094 V
DD_VIN
channel. Y/CB/CR[00]
GIO: GIO[094]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[09] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
between chroma: CB/CR[01] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
CIN1 / PD
L3 I/O/Z decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper
GIO095 V
DD_VIN
channel. Y/CB/CR[01]
GIO: GIO[095]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[10] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
between chroma: CB/CR[02] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
CIN2 / PD
J5 I/O/Z decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper
GIO096 V
DD_VIN
channel. Y/CB/CR[02]
GIO: GIO[096]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[11] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
between chroma: CB/CR[03] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
CIN3 / PD
J4 I/O/Z decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper
GIO097 V
DD_VIN
channel. Y/CB/CR[03]
GIO: GIO[097]
CIN4 /
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[12] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
GIO098 /
between chroma: CB/CR[04] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
SPI2_SDI PD
L4 I/O/Z decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper
/ V
DD_VIN
channel. Y/CB/CR[04] SPI: SPI2 Data In
SPI2_SDE
GIO: GIO[098]
NA[1]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): raw[13] YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed
CIN5 /
between chroma: CB/CR[05] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous
GIO099 / PD
M3 I/O/Z decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper
SPI2_SDE V
DD_VIN
channel. Y/CB/CR[05] SPI: SPI2 Chip Select
NA[0]
GIO: GIO[99]
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): NOT USED YCC 16-bit: time
CIN6 /
multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[06] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2
GIO100 / PD
K5 I/O/Z simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of
SPI2_SD V
DD_VIN
the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[06] SPI: SPI2 Data Out
O
GIO: GIO[100]
Submit Documentation Feedback Device Overview 27
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
2.4.6 Multi-Media Card/Secure Digital (MMC/SD) Interfaces
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-11. GPIO Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
Standard CCD Analog Front End (AFE): NOT USED YCC 16-bit: time
CIN7 /
multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[07] YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2
GIO101 / PD
N3 I/O/Z simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of
SPI2_SCL V
DD_VIN
the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[07] SPI: SPI2 Clock
K
GIO: GIO[101]
SPI0_SDI SPI0: Data In
A12 I/O/Z V
DD
/ GIO102 GIO: GIO[102]
SPI0_SDE
SPI0: Chip Select 0
NA[0] / B12 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[103]
GIO103
The DM355 includes two Multi-Media Card/Secure Digital card interfaces that are compatible with the
MMC/SD and SDIO protocol.
Table 2-12. MMC/SD Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
MMCSD0_
A15 I/O/Z V
DD
MMCSD0: Clock
CLK/
MMCSD0_
C14 I/O/Z V
DD
MMCSD0: Command
CMD/
MMCSD0_
B14 I/O/Z V
DD
MMCSD0: DATA0
DATA0/
MMCSD0_
D14 I/O/Z V
DD
MMCSD0: DATA1
DATA1/
MMCSD0_
B13 I/O/Z V
DD
MMCSD0: DATA2
DATA2/
MMCSD0_
A14 I/O/Z V
DD
MMCSD0: DATA3
DATA3/
MMCSD1_
MMCSD1: Clock
CLK/ C15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[024]
GIO024
MMCSD1_
MMCSD1: Command
CMD/ A17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[023]
GIO023
MMCSD1_
DATA0/ MMCSD1: DATA0
GIO019/ A18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[019]
UART2_T UART2: Transmit data
XD
MMCSD1_
DATA1/ MMCSD1: DATA1
GIO020/ B15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[020]
UART2_R UART2: Receive data
XD
MMCSD1_
DATA2/ MMCSD1: DATA2
GIO021/ A16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[021]
UART2_C UART2: CTS
TS
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 k Ω resistor should be used.)
Device Overview28 Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
2.4.7 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Interface
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
Table 2-12. MMC/SD Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
MMCSD1_
DATA3/ MMCSD1: DATA3
GIO022/ B16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[022]
UART2_R UART2: RTS
TS
The Universal Serial Bus (USB) interface supports the USB2.0 High-Speed protocol and includes dual-role
Host/Slave support. However, no charge pump is included.
NOTE
OTG supplies are not supported. Please ignore all references to OTG in this document.
Table 2-13. USB Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
USB D+ (differential signal pair).
USB_DP A7 A I/O/Z V
DDA33_USB
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
SS_USB
.
USB D- (differential signal pair).
USB_DM A6 A I/O/Z V
DDA33_USB
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
SS_USB
.
USB reference current output
Connect to VSS_USB_REF via 10K ohm , 1% resistor placed as close to the
USB_R1 C7 A I/O/Z
device as possible.
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
SS_USB
.
USB operating mode identification pin
For Device mode operation only, pull up this pin to VDD with a 1.5K ohm resistor.
For Host mode operation only, pull down this pin to ground (VSS) with a 1.5K
USB_ID D5 A I/O/Z V
DDA33_USB
ohm resistor.
If using an OTG or mini-USB connector, this pin will be set properly via the
cable/connector configuration.
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
SS_USB
.
For host or device mode operation, tie the VBUS/USB power signal to the USB
connector.
USB_VBUS E5 A I/O/Z V
DD
When used in OTG mode operation, tie VBUS to the external charge pump and
to the VBUS signal on the USB connector.
When the USB is not used, tie VBUS to Vss_USB.
Digital output to control external 5 V supply
USB_DRVVBUS C5 O/Z V
DD
When USB is not used, this signal should be left as a No Connect.
USB Ground Reference
V
SS_USB_REF
C8 GND V
DD
Connect directly to ground and to USB_R1 via 10K ohm, 1% resistor placed as
close to the device as possible
Analog 3.3 V power USBPHY
V
DDA3P3_USB
J8 PWR V
DD
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
SS_USB
.
Common mode 3.3 V power for USB PHY
V
DDACM3P3_USB
B6 PWR V
DD
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
SS_USB
.
Analog 1.2 V power for USB PHY
V
DDA1P2_USB
H7 PWR V
DD
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
SS_USB
.
Digital 1.2 V power for USB PHY
V
DDD1P2_USB
C6 PWR V
DD
When USB is not used, this signal should be connected to V
SS_USB
.
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 k Ω resistor should be used.)
Submit Documentation Feedback Device Overview 29
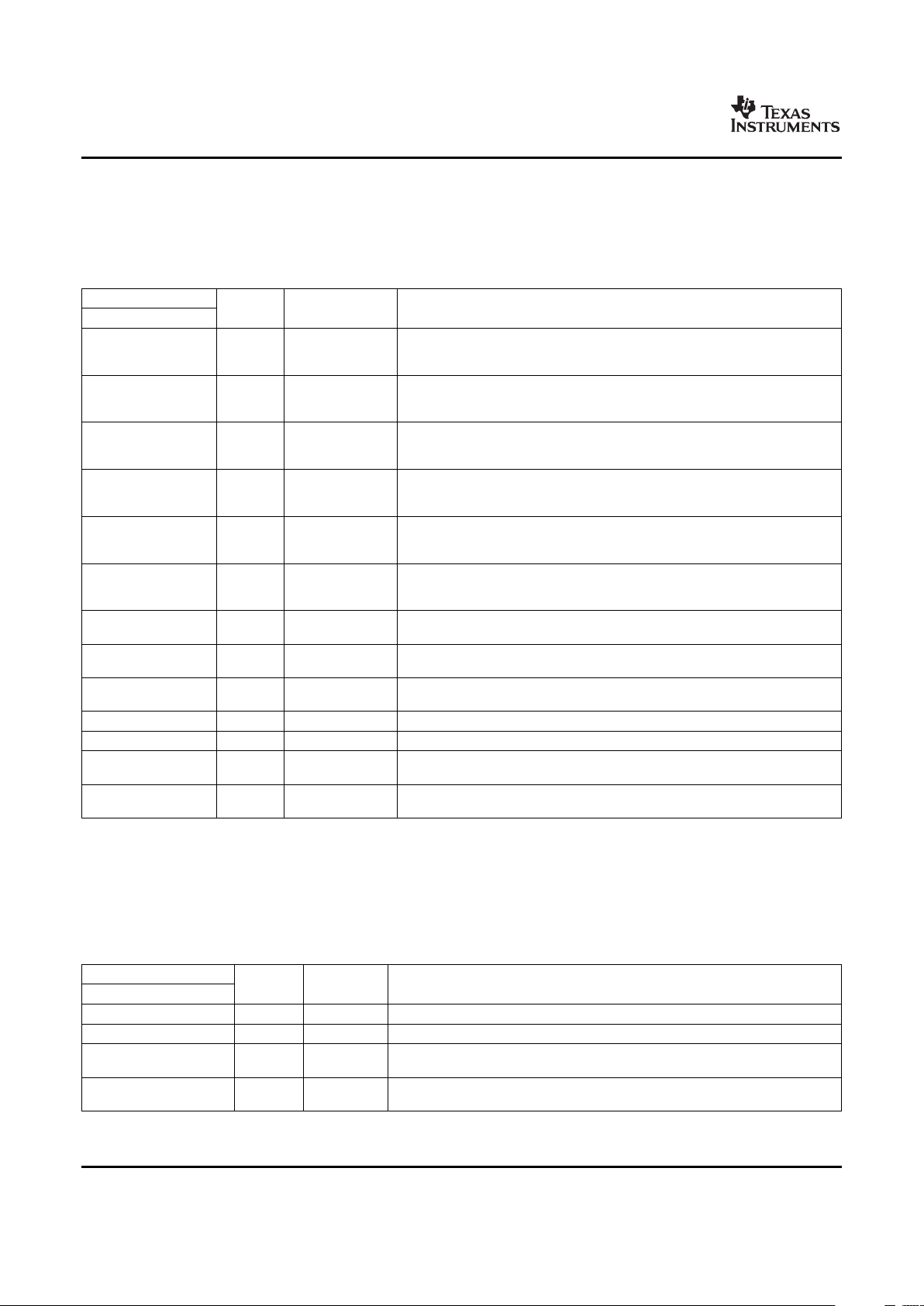
www.ti.com
PRODUCT PREVIEW
2.4.8 Audio Interfaces
2.4.9 UART Interface
TMS320DM355
Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
SPRS463 – SEPTEMBER 2007
The DM355 includes two Audio Serial Ports (ASP ports), which are backward compatible with other TI
ASP serial ports and provide I2S audio interface. One interface is multiplexed with GIO signals.
Table 2-14. ASP Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
ASP0_CL
ASP0: Receive Clock
KR/ F17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[026]
GIO26
ASP0_CL
ASP0: Transmit Clock
KX / F18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[029]
GIO029
ASP0_DR
ASP0: Receive DataF
/ E18 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[027]
GIO027
ASP0_DX
ASP0: Transmit Data
/ H15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[030]
GIO030
ASP0_FS
ASP0: Receive Frame Synch
R / F16 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO: GIO[025]
GIO025
ASP0_FS
X / G17 I/O/Z V
DD
ASP0: Transmit Frame SynchGIO: GIO[028]
GIO028
ASP1_CL
D18 I/O/Z V
DD
ASP1: Receive Clock
KR
ASP1_CL
D17 I/Z V
DD
ASP1: Master Clock
KS
ASP1_CL
D19 I/O/Z V
DD
ASP1: Transmit Clock
KX
ASP1_DR C19 I/O/Z V
DD
ASP1: Receive Data
ASP1_DX C18 I/O/Z V
DD
ASP1: Transmit Data
ASP1_FS
E17 I/O/Z V
DD
ASP1: Receive Frame Synch
R
ASP1_FS
E16 I/O/Z V
DD
ASP1: Transmit Frame Sync
X
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 k Ω resistor should be used.)
The includes three UART ports. These ports are multiplexed with GIO and other signals.
Table 2-15. UART Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
TYPE
(1)
OTHER
(2) (3)
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
UART0_RXD U18 I V
DD
UART0: Receive data. Used for UART boot mode
UART0_TXD T18 O V
DD
UART0: Transmit data. Used for UART boot mode
UART1_RXD UART1: Receive data.
R15 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO013 GIO: GIO013
UART1_TXD UART1: Transmit data.
R17 I/O/Z V
DD
GIO012 GIO: GIO012
(1) I = Input, O = Output, Z = High impedance, S = Supply voltage, GND = Ground, A = Analog signal.
(2) Specifies the operating I/O supply voltage for each signal. See Section 5.3 , Power Supplies for more detail.
(3) PD = pull-down, PU = pull-up. (To pull up a signal to the opposite supply rail, a 1 k Ω resistor should be used.)
Device Overview30 Submit Documentation Feedback
 Loading...
Loading...